- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs

Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.
Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

Angelique O'Rourke
13 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
Believe it or not, creating a business plan for a nonprofit organization is not that different from planning for a traditional business.
Nonprofits sometimes shy away from using the words “business planning,” preferring to use terms like “strategic plan” or “operating plan.” But, the fact is that preparing a plan for a for-profit business and a nonprofit organization are actually pretty similar processes. Both types of organizations need to create forecasts for revenue and plan how they’re going to spend the money they bring in. They also need to manage their cash and ensure that they can stay solvent to accomplish their goals.
In this guide, I’ll explain how to create a plan for your organization that will impress your board of directors, facilitate fundraising, and ensures that you deliver on your mission.
- Why does a nonprofit need a business plan?
Good business planning is about setting goals, getting everyone on the same page, tracking performance metrics, and improving over time. Even when your goal isn’t to increase profits, you still need to be able to run a fiscally healthy organization.
Business planning creates an opportunity to examine the heart of your mission , the financing you’ll need to bring that mission to fruition, and your plan to sustain your operations into the future.
Nonprofits are also responsible for meeting regularly with a board of directors and reporting on your organization’s finances is a critical part of that meeting. As part of your regular financial review with the board, you can compare your actual results to your financial forecast in your business plan. Are you meeting fundraising goals and keeping spending on track? Is the financial position of the organization where you wanted it to be?
In addition to internal use, a solid business plan can help you court major donors who will be interested in having a deeper understanding of how your organization works and your fiscal health and accountability. And you’ll definitely need a formal business plan if you intend to seek outside funding for capital expenses—it’s required by lenders.
Creating a business plan for your organization is a great way to get your management team or board to connect over your vision, goals, and trajectory. Even just going through the planning process with your colleagues will help you take a step back and get some high-level perspective .
- A nonprofit business plan outline
Keep in mind that developing a business plan is an ongoing process. It isn’t about just writing a physical document that is static, but a continually evolving strategy and action plan as your organization progresses over time. It’s essential that you run regular plan review meetings to track your progress against your plan. For most nonprofits, this will coincide with regular reports and meetings with the board of directors.
A nonprofit business plan will include many of the same sections of a standard business plan outline . If you’d like to start simple, you can download our free business plan template as a Word document, and adjust it according to the nonprofit plan outline below.
Executive summary
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That’s because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan – the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization.
Write it as though you might share with a prospective donor, or someone unfamiliar with your organization: avoid internal jargon or acronyms, and write it so that someone who has never heard of you would understand what you’re doing.
Your executive summary should provide a very brief overview of your organization’s mission. It should describe who you serve, how you provide the services that you offer, and how you fundraise.
If you are putting together a plan to share with potential donors, you should include an overview of what you are asking for and how you intend to use the funds raised.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Opportunity
Start this section of your nonprofit plan by describing the problem that you are solving for your clients or your community at large. Then say how your organization solves the problem.
A great way to present your opportunity is with a positioning statement . Here’s a formula you can use to define your positioning:
For [target market description] who [target market need], [this product] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [key competition], it [most important distinguishing feature].
And here’s an example of a positioning statement using the formula:
For children, ages five to 12 (target market) who are struggling with reading (their need), Tutors Changing Lives (your organization or program name) helps them get up to grade-level reading through a once a week class (your solution).
Unlike the school district’s general after-school homework lab (your state-funded competition), our program specifically helps children learn to read within six months (how you’re different).
Your organization is special or you wouldn’t spend so much time devoted to it. Layout some of the nuts and bolts about what makes it great in this opening section of your business plan. Your nonprofit probably changes lives, changes your community, or maybe even changes the world. Explain how it does this.
This is where you really go into detail about the programs you’re offering. You’ll want to describe how many people you serve and how you serve them.
Target audience
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be used to define your target market . For nonprofit organizations, it’s basically the same thing but framed as who you’re serving with your organization. Who benefits from your services?
Not all organizations have clients that they serve directly, so you might exclude this section if that’s the case. For example, an environmental preservation organization might have a goal of acquiring land to preserve natural habitats. The organization isn’t directly serving individual groups of people and is instead trying to benefit the environment as a whole.
Similar organizations
Everyone has competition —nonprofits, too. You’re competing with other nonprofits for donor attention and support, and you’re competing with other organizations serving your target population. Even if your program is the only one in your area providing a specific service, you still have competition.
Think about what your prospective clients were doing about their problem (the one your organization is solving) before you came on this scene. If you’re running an after-school tutoring organization, you might be competing with after school sports programs for clients. Even though your organizations have fundamentally different missions.
For many nonprofit organizations, competing for funding is an important issue. You’ll want to use this section of your plan to explain who donors would choose your organization instead of similar organizations for their donations.
Future services and programs
If you’re running a regional nonprofit, do you want to be national in five years? If you’re currently serving children ages two to four, do you want to expand to ages five to 12? Use this section to talk about your long-term goals.
Just like a traditional business, you’ll benefit by laying out a long-term plan. Not only does it help guide your nonprofit, but it also provides a roadmap for the board as well as potential investors.
Promotion and outreach strategies
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be about marketing and sales strategies. For nonprofits, you’re going to talk about how you’re going to reach your target client population.
You’ll probably do some combination of:
- Advertising: print and direct mail, television, radio, and so on.
- Public relations: press releases, activities to promote brand awareness, and so on.
- Digital marketing: website, email, blog, social media, and so on.
Similar to the “target audience” section above, you may remove this section if you don’t promote your organization to clients and others who use your services.
Costs and fees
Instead of including a pricing section, a nonprofit business plan should include a costs or fees section.
Talk about how your program is funded, and whether the costs your clients pay are the same for everyone, or based on income level, or something else. If your clients pay less for your service than it costs to run the program, how will you make up the difference?
If you don’t charge for your services and programs, you can state that here or remove this section.
Fundraising sources
Fundraising is critical for most nonprofit organizations. This portion of your business plan will detail who your key fundraising sources are.
Similar to understanding who your target audience for your services is, you’ll also want to know who your target market is for fundraising. Who are your supporters? What kind of person donates to your organization? Creating a “donor persona” could be a useful exercise to help you reflect on this subject and streamline your fundraising approach.
You’ll also want to define different tiers of prospective donors and how you plan on connecting with them. You’re probably going to include information about your annual giving program (usually lower-tier donors) and your major gifts program (folks who give larger amounts).
If you’re a private school, for example, you might think of your main target market as alumni who graduated during a certain year, at a certain income level. If you’re building a bequest program to build your endowment, your target market might be a specific population with interest in your cause who is at retirement age.
Do some research. The key here is not to report your target donors as everyone in a 3,000-mile radius with a wallet. The more specific you can be about your prospective donors —their demographics, income level, and interests, the more targeted (and less costly) your outreach can be.
Fundraising activities
How will you reach your donors with your message? Use this section of your business plan to explain how you will market your organization to potential donors and generate revenue.
You might use a combination of direct mail, advertising, and fundraising events. Detail the key activities and programs that you’ll use to reach your donors and raise money.
Strategic alliances and partnerships
Use this section to talk about how you’ll work with other organizations. Maybe you need to use a room in the local public library to run your program for the first year. Maybe your organization provides mental health counselors in local schools, so you partner with your school district.
In some instances, you might also be relying on public health programs like Medicaid to fund your program costs. Mention all those strategic partnerships here, especially if your program would have trouble existing without the partnership.
Milestones and metrics
Without milestones and metrics for your nonprofit, it will be more difficult to execute on your mission. Milestones and metrics are guideposts along the way that are indicators that your program is working and that your organization is healthy.
They might include elements of your fundraising goals—like monthly or quarterly donation goals, or it might be more about your participation metrics. Since most nonprofits working with foundations for grants do complex reporting on some of these, don’t feel like you have to re-write every single goal and metric for your organization here. Think about your bigger goals, and if you need to, include more information in your business plan’s appendix.
If you’re revisiting your plan on a monthly basis, and we recommend that you do, the items here might speak directly to the questions you know your board will ask in your monthly trustee meeting. The point is to avoid surprises by having eyes on your organization’s performance. Having these goals, and being able to change course if you’re not meeting them, will help your organization avoid falling into a budget deficit.
Key assumptions and risks
Your nonprofit exists to serve a particular population or cause. Before you designed your key programs or services, you probably did some research to validate that there’s a need for what you’re offering.
But you probably are also taking some calculated risks. In this section, talk about the unknowns for your organization. If you name them, you can address them.
For example, if you think there’s a need for a children’s literacy program, maybe you surveyed teachers or parents in your area to verify the need. But because you haven’t launched the program yet, one of your unknowns might be whether the kids will actually show up.
Management team and company
Who is going to be involved and what are their duties? What do these individuals bring to the table?
Include both the management team of the day-to-day aspects of your nonprofit as well as board members and mention those who may overlap between the two roles. Highlight their qualifications: titles, degrees, relevant past accomplishments, and designated responsibilities should be included in this section. It adds a personal touch to mention team members who are especially qualified because they’re close to the cause or have special first-hand experience with or knowledge of the population you’re serving.
There are probably some amazing, dedicated people with stellar qualifications on your team—this is the place to feature them (and don’t forget to include yourself!).
Financial plan
The financial plan is essential to any organization that’s seeking funding, but also incredibly useful internally to keep track of what you’ve done so far financially and where you’d like to see the organization go in the future.
The financial section of your business plan should include a long-term budget and cash flow statement with a three to five-year forecast. This will allow you to see that the organization has its basic financial needs covered. Any nonprofit has its standard level of funding required to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will consistently maintain at least that much in the coffers.
From that point, it’s all about future planning: If you exceed your fundraising goals, what will be done with the surplus? What will you do if you don’t meet your fundraising goals? Are you accounting for appropriate amounts going to payroll and administrative costs over time? Thinking through a forecast of your financial plan over the next several years will help ensure that your organization is sustainable.
Money management skills are just as important in a nonprofit as they are in a for-profit business. Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public is ranking the credibility of charities based on what percentage of donations makes it to the programs and services. As a nonprofit, people are interested in the details of how money is being dispersed within organizations, with this information often being posted online on sites like Charity Navigator, so the public can make informed decisions about donating.
Potential contributors will do their research—so make sure you do too. No matter who your donors are, they will want to know they can trust your organization with their money. A robust financial plan is a solid foundation for reference that your nonprofit is on the right track.
- Business planning is ongoing
It’s important to remember that a business plan doesn’t have to be set in stone. It acts as a roadmap, something that you can come back to as a guide, then revise and edit to suit your purpose at a given time.
I recommend that you review your financial plan once a month to see if your organization is on track, and then revise your plan as necessary .
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Angelique is a skilled writer, editor, and social media specialist, as well as an actor and model with a demonstrated history of theater, film, commercial and print work.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
Differences Between Single-Use and Standing Plans Explained

14 Min. Read
How to Write a Five-Year Business Plan

11 Min. Read
Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
- Nonprofit & Community
Nonprofit Business Plan

2. Organization Overview
Depending on the organization’s details, you must add various organizational overview elements. Still, every organization should include some foundational elements like its name, purpose, operations, legal structure, location, and history.
Organization Description:
Provide all the basic information about your nonprofit in this section like
- Name & Type of Your Organization: Describe the name and type of your nonprofit organization. For instance, you may operate one of these types of nonprofit organizations:
- Educational organizations
- Charitable organizations
- Healthcare organizations
- Religious organizations
- Location of your nonprofit and why you selected that place.
Mission & Vision:
Organization history:.
If you’re an established nonprofit, you can provide information about your organization’s history, like when it was founded and how it evolved. If you can, add some personality and intriguing details, especially if you got any achievements or recognitions till now for your incredible community services.
Future goals:
It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and your vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals with the nonprofit; they can be specific targets depending on your ultimate vision.
This section should provide an in-depth understanding of the nonprofit organization. Also, the business overview section should be engaging and precise.
3. Products, Programs, and Services
The products, programs, and services section of a nonprofit business plan should describe specific products, programs, and services that will offer to its beneficiaries. Your nonprofit may or may not have all products, programs, and services to offer.
So, write this section depending on your organization’s offerings:
In a nutshell, your products, programs, and services section should describe how your nonprofit meets needs and positively impacts the community. Use solid examples and numbers to back your claims.
Some additional tips for writing the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Use a variety of sources to gather data, including industry reports, market research studies, and surveys.
- Be specific and provide detailed information wherever possible.
- Include charts and graphs to help illustrate your key points.
- Keep your target audience in mind while writing the business plan
4. Market Analysis
Market analysis provides a clear understanding of the market your nonprofit will run along with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. Your market analysis should contain the following essential components:
Target Market:
Market size and growth potential:, competitive analysis:, market trends:.
- For example, It may be necessary for a nonprofit focused on environmental conservation to adapt its messaging to reflect the growing demand for sustainable products and practices.
Regulatory Environment:
Some additional tips for writing the market analysis section of your nonprofit business plan:
- Use various sources to gather data, including industry reports, market research studies, and surveys.
- Keep your target audience in mind while writing the business plan.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Building awareness, promoting engagement, and generating revenue should be the focus of your business plan’s “Sales and marketing strategies” section. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
Unique Value Proposition (UVP):
Marketing mix:, marketing channels:, fundraising strategies:.
- Identify fundraising strategies that align with the nonprofit’s mission, vision, and values.
Donor Retention:
In short, a nonprofit business plan’s sales and marketing strategies section should describe how your organization can reach, engage, and retain your target market and generate sustainable revenue.
Be specific, realistic, and data-driven in your approach, and be prepared to adjust your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
When writing the operations plan section, it’s essential to consider the various aspects of your organization’s processes and procedures involved in operating a nonprofit. Here are the components to include in an operations plan:
Staffing & Training:
Operational process:.
- Your operations must also include details on monitoring and evaluating programs and their impact on the community.
Quality Control:
Facilities and equipment:, technology & information system:.
By including these key elements in your operations plan section, you can create a comprehensive plan that outlines how you will run your nonprofit organization.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of the nonprofit organization’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
Founders/CEO:
Key managers:.
- It should include the owners, senior management, other department managers, and people involved in the organizational operations, along with their education and professional background.
Organizational structure:
Compensation plan:.
Overall, the management team section of your business plan should mention key personnel involved in successfully running your organizational operations.
So, highlight your organization’s key personnel and demonstrate why you have the right team to execute your organization’s mission.
8. Financial Plan
When writing the financial plan section of a business plan, it’s important to provide a comprehensive overview of your financial projections and goals for the first few years of your organization.
Revenue Streams:
Fundraising goals:, financial ratios:, risk analysis:.
Remember to be realistic with your financial projections and provide supporting evidence for your estimates.
9. Appendix
Include any additional information supporting your plan’s main content when writing the appendix section. This may include financial statements, market research data, legal documents, and other relevant information.
- Include a table of contents for the appendix section to make it easy for readers to find specific information.
- Include financial statements such as income, balance sheets, and cash flow statements . These should be up-to-date and show your financial projections for at least the first three years of your business.
- Provide market research data, such as statistics on the industry’s size, consumer demographics, and trends in the industry.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Provide any additional documentation related to your business plans, such as marketing materials, product brochures, and operational procedures.
- Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your nonprofit organization should only include relevant and essential information supporting your plan’s main content.
Download a sample nonprofit organization business plan
Need help writing a business plan for your nonprofit? Here you go; download our free nonprofit organization business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your nonprofit organization. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
You may explore our other nonprofit and community business plan examples before you start writing
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.

Write your business plan with Upmetrics
A business plan app like Upmetrics is the best way to draft your business plan. This incredible tool comes with step-by-step instructions and 400+ customizable sample business plans to help you get started.
So, whether starting a nonprofit organization or planning to grow an existing one, Upmetrics is the tool you need to create a business plan.
Related Posts
Charity Business Plan
Community Center Business Plan
What are the Elements of an Operations Plan
How to Make an Appendix Section of Business Plan
400+ Free Business Plan Template
Youth Mentoring Program Business Plan
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a nonprofit business plan.
Business plans outline the organization’s goals, strategies, and tactics for achieving its mission. Nonprofit business plans serve as a roadmap for staff, lenders, and other shareholders, helping them make informed decisions, measure progress, and remain focused on the organization’s mission.
How to get funding for your nonprofit business?
Fundraising for a nonprofit can be challenging, but a few strategies and a strategic approach can help you achieve your goal.
Here are some of the most common ways to get funding for your nonprofit:
- Individual Donations: Individual donations are among key revenue streams for any nonprofit. It includes both one-time payments as well as recurring assistance.
- Grants: Many foundations and government agencies offer grants to nonprofit organizations that meet specific criteria.
- Corporate Sponsorships: A nonprofit can approach corporations that align with its values and mission to gain sponsorships for charity events, programs, or projects.
- Crowdfunding: The process of supporting a business or organization by getting many people to invest in your nonprofit organization, usually online.
Where to find business plan writers for your nonprofit business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and idea better than you, so we recommend you write your nonprofit business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your nonprofit business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any nonprofit business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .


Charity Business Plan Template

What is a Charity Business Plan?
A charity business plan outlines the goals, projects, and initiatives of a non-profit organization or social enterprise. It serves as a roadmap for the organization's activities, and helps to ensure that the organization is working towards achieving its objectives in an effective and efficient manner. The charity business plan template provides a structure for outlining the organization's mission and goals, as well as the strategies, projects, and KPIs that can be used to achieve them.
What's included in this Charity Business Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Charity Business Plan template for?
The charity business plan template is designed for non-profit organizations and social enterprises that want to develop a business plan that outlines their mission, goals, and strategies. The template provides an organized and systematic way to create a business plan that takes into consideration the organization's resources, goals, and objectives. It is designed to help organizations create an effective and efficient business plan that can be used to track their progress and ensure that they are on the right path towards achieving their mission.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
Focus areas are the broad topics that the organization is focusing on. Examples of focus areas may include increasing outreach, improving efficiency, or increasing impact. Each focus area should have several objectives and projects that are related to that focus area.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the goals that the organization wants to achieve within a particular focus area. These objectives should be specific, measurable, and achievable. Examples of objectives may include reaching new donors, engaging existing donors, or automating data entry.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs, or key performance indicators, are measurable targets that are used to track progress towards an organization's objectives. Examples of KPIs may include increasing website visits, increasing email response rate, or decreasing time to process donations.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects are the actions that are taken to achieve the organization's objectives and KPIs. Examples of projects may include creating a digital marketing campaign, implementing email strategies, or automating data entry.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade Strategy Execution Platform provides a comprehensive suite of tools and resources to help organizations develop and implement a successful business plan. It offers features such as goal setting, project tracking, real-time reporting, and automated notifications, which can help organizations see faster results from their strategy.

3 Sample Nonprofit Business Plans For Inspiration
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here
Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan.
- Example #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
- Example #2 – Church of the Sacred Heart – a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO
- Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
Executive summary.
Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization that seeks to provide opportunities for students who might otherwise not have access to the arts and humanities. We believe all students should have the opportunity to discover and develop their interests and talents, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. We offer completely free after-school programming in music production, digital photography, creative writing, and leadership development to 12-18-year-olds at risk of dropping out of high school.
Our organization has been active for over five years and has run highly successful programs at two schools in the city of Chicago. We have been awarded an active grant from a local foundation for this coming year, but we will need to cover all costs on our own after that point. Nonprofit administrators have seen a lot of turnovers, leaving the organization without a sustainable plan for reaching its goals.
Organization Overview
The Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization with a mission to provide opportunities for development and self-expression to students who might otherwise not have access. Audiences include at-risk, low-income students from elementary through high school in the Chicago area.
Our programs are built around creative learning with two goals: firstly, creating a space for learning and growth; secondly, encouraging students to share their work with the world.
KAOFP runs three different programs in partnership with closely related nonprofit organizations, providing after-school programming for elementary, middle, and high school-aged children. Programs take place twice a week at different schools around Chicago. While each program is unique in its goals and activities, all programs focus on creative development in the arts and humanities.
Products, Programs, and Services
The three programs offered by KAOFP are Leadership Development (LD), Creative Writing (CW), and Music Production (MP). Students learn in small groups led by skilled instructors. All activities are designed to encourage student engagement, creativity, expression, and community building. Instructors encourage students to share their work with the world through presentations on- and off-site.
Leadership Development (LD)
The Leadership Development program is designed to provide leadership opportunities for high school students who might not otherwise have access to these experiences. Students learn about facilitation, collaboration, communication, and organizational skills as they plan and run projects of their own design. The program’s goal is to provide a structured environment that encourages students to become more confident and comfortable being leaders in their schools, communities, and future careers.
Creative Writing (CW)
Students learn how to use writing creatively as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In small groups led by skilled instructors, students write poetry, short stories, and essays of their own design. They also learn about the publishing industry, read each others’ work, and share their writing with the community.
Music Production (MP)
Students learn how to use digital media as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In weekly sessions led by skilled instructors, students explore music production through computer software and recording equipment. Students produce their own music and write about their experiences in weekly journals. Industry professionals in the community often volunteer to lead special workshops and seminars.
Industry Analysis
The youth arts and humanities field is extremely competitive. There are many different types of nonprofit organizations doing similar work, but few credible providers with long-term commitments to their communities. KAOFP’s greatest strengths and competitive advantages are our stable and qualified staff, a strong foundation of funding and community support, and a diverse set of programs.
Our biggest competitors include national non-profits with large budgets for advertising and marketing as well as commercial programs that offer music lessons and creative writing courses which may be more cost-effective than our programs. We feel that by focusing on specific areas of creative expression, KAOFP can better serve its communities and differentiate itself from other nonprofit organizations effectively.
Customer Analysis
KAOFP serves elementary, middle, and high school-aged students with programs that include both after-school and summer programming.
Our focus is on low-income neighborhoods with a high population of at-risk youth. In these areas, KAOFP fills a void in the education system by providing opportunities for creative expression and leadership development to students who would not otherwise have access to these resources.
The demographics of our current students are as follows:
- 91% African-American/Black
- 6% Hispanic/Latino
- 5% Multiracial
- 3.9% Low Income
- 4.9% Not Identified
Our main target is low-income African American and Latino youth in Chicago Public Schools. We would like to expand our outreach to include other communities in need of creative enrichment opportunities.
Marketing Plan
KAOFP’s marketing program is designed to support student, parent, and staff recruitment by promoting the organization’s goals and programs. Our main target audience consists of parents seeking after-school enrichment opportunities for their children that emphasize creativity and the arts.
To reach this audience, we advertise in public schools as well as on social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter. We intend to begin marketing online through a company-sponsored blog, which will feature regular updates about KAOFP events and activities. We also intend to use word of mouth as a form of marketing.
Strategic partnerships with local schools and community centers will provide us with additional exposure as well as additional resources to secure funding.
Operations Plan
KAOFP’s day-to-day operation is structured around its programs on Tuesdays from 4 pm to 8 pm.
Administrative offices are located in the same space as each program, allowing instructors to closely monitor their students and provide support as needed. The administrative offices serve the essential function of fundraising, communications, record-keeping, and volunteer coordination. KAOFP’s Board of Directors meets bi-monthly to provide further leadership, guidance, and oversight to our board members and volunteers.
Customer service is conducted by phone and email during our regular business hours of Monday – Friday 9 am to 12 pm. We are not open on weekends or holidays.
Management Team
KAOFP’s organizational structure includes a Board of Directors, an Executive Director, and Program Directors. The Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization, while the Executive Director manages day-to-day operations. The Program Directors oversee each of KAOFP’s programs.
KAOFP has a small but dedicated staff that is committed to our students and our mission. Our team has a wide range of experience in the arts, education, and nonprofit sector.
Executive Director
The Executive Director is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP. This includes supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Our Executive Director, Susie Brown, has been with KAOFP since its inception in 2010. She has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and an M.F.A. in Creative Writing from Columbia College Chicago. Susie is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP, including supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Program Directors
Each of KAOFP’s programs is overseen by a Program Director. The Program Directors are responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Art Program Director
The Art Program Director, Rachel Smith, has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Music Program Director
The Music Program Director, John Jones, has a B.A. in Music Education from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Theatre Program Director
The Theatre Program Director, Jane Doe, has a B.A. in Theatre Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Board of Directors
KAOFP’s Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization. The Board consists of community leaders, educators, artists, and parents. Board members serve three-year terms and can be renewed for one additional term.
Financial Plan
KAOFP’s annual operating budget is approximately $60,000 per year, with an additional one-time cost of about $10,000 for the purchase of equipment and materials. The agency makes very efficient use of its resources by maintaining low overhead costs. Our biggest expense is instructor salaries, which are approximately 75% of total expenses.
Pro Forma Income Statement
Pro forma balance sheet, pro forma cash flow statement, nonprofit business plan example #2 – church of the sacred heart – a nonprofit church based in st. louis, mo.
The Church of Sacred Heart is a nonprofit organization located in St. Louis, Missouri that provides educational opportunities for low-income families. We provide the best quality of education for young children with tuition rates significantly lower than public schools. It has been voted Best Catholic Elementary School by the St Louis Post Dispatch for four years running, and it has maintained consistently high ratings of 4.5 out of 5 stars on Google Reviews since its opening in 1914.
The Church of Sacred Heart strives to build strong relationships with our community by making an impact locally but not forgetting that we operate on global principles. As such, our school commits 10% of its profits to charitable organizations throughout the world every year, while also conducting fundraisers throughout the year to keep tuition rates affordable.
We are currently transitioning from a safe, high-quality learning environment to an even more attractive facility with state-of-the-art technology and modern materials that will appeal to young students and their families. New facilities, such as additional classrooms and teachers’ lounges would allow us not only to accommodate new students but also attract current families by having more places within the school where they can spend time between classes.
By taking full advantage of available opportunities to invest in our teachers, students, and facilities, we will be able to achieve steady revenue growth at 4% per year until 20XX.
The Church of Sacred Heart provides a safe learning environment with an emphasis on strong academics and a nurturing environment that meets the needs of its young students and their families. Investing in new facilities will allow us to provide even better care for our children as we continue to grow as a school.
Mission Statement: “We will strive diligently to create a safe, respectful environment where students are encouraged and inspired to learn through faith.”
Vision Statement: “Sacred Heart believes education gives every child the opportunity to achieve their full potential.”
The Church of the Sacred Heart was built in 1914 and is located in the Old North St. Louis neighborhood, an area with a high concentration of poverty, crime, unemployment, and abandoned buildings.
The church houses the only Catholic school for low-income families in the north city; together they formed Sacred Heart’s educational center (SCE). SCE has strived to provide academic excellence to children from low-income families by providing a small, nurturing environment as well as high academic standards.
The facility is in need of renovations and new equipment to continue its mission.
The Church of the Sacred Heart is a small nonprofit organization that provides a variety of educational and community services.
The services provided by Sacred Heart represent a $5 billion industry, with nonprofit organizations accounting for $258.8 billion of that total.
The health care and social assistance sector is the largest among nonprofits, representing 32 percent of revenues, followed by educational services (18 percent), and human and other social service providers (16 percent).
The key customers for the Church of the Sacred Heart are families in need of affordable education. The number of students in the school has increased from 500 when it opened in 1914 to 1,100 at its peak during 20XX-20XX but has since declined due to various reasons.
The children at Sacred Heart are from low-income families and 91 percent qualify for free or reduced lunches. Most parents work or have a family member who works full-time, while others don’t work due to child care restraints. The number of children enrolled in Sacred Heart is stable at 1,075 students because there is a lack of affordable alternatives to Catholic education in the area.
SCE offers K-5th grade students a unique learning experience in small groups with individualized instruction.
Sacred Heart has an established brand and is well known for its high standards of academic excellence, which include a 100 percent graduation rate.
Sacred Heart attracts prospective students through promotional materials such as weekly bulletins, mailers to homes that are located in the area served, and local churches.
Parents and guardians of children enrolled in Sacred Heart are mainly referrals from current families, word-of-mouth, and parishioners who learn about the school by attending Mass at Sacred Heart.
The Church of Sacred Heart does not currently advertise; however, it is one of the few Catholic schools that serve low-income families in St. Louis, MO, and therefore uses word of mouth to attract new students to its school.
The Church of Sacred Heart has an established brand awareness within the target audience despite not having direct marketing plans or materials.
The operations section for the Church of the Sacred Heart consists of expanding its after-school program as well as revamping its facility to meet the growing demand for affordable educational services.
Sacred Heart is located in an area where more than one-third of children live below the poverty line, which helps Sacred Heart stand out among other schools that are more upscale. Expansion into after-school programs will allow it to capture a larger market share by providing additional services to its target audience.
In order to expand, Sacred Heart will have to hire additional personnel as well as invest in new equipment and supplies for both the school and the after-school program.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial plan includes a fundraising plan that would help renovate the building as well as acquire new equipment and supplies for the school.
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, Catholic elementary schools across all grade levels spend an average of $6,910 per pupil on operating expenses. A fundraising initiative would help Sacred Heart acquire additional revenue while expanding its services to low-income families in St Louis, MO.
Financial Overview
The Church of the Sacred Heart expects to generate revenues of about $1.2 million in fiscal year 20XX, representing a growth rate of 2 percent from its 20XX revenue level. For 20XX, the church expects revenues to decrease by 4 percent due to a decline in enrollment and the lack of new students. The Church of Sacred Heart has experienced steady revenue growth since its opening in 1914.
- Revenue stream 1: Tuition – 22%
- Revenue stream 2: Investment income – 1%
Despite being located in a poverty-stricken area, the Church of Sacred Heart has a stable revenue growth at 4 percent per year. Therefore, Sacred Heart should be able to attain its 20XX revenue goal of $1.2 million by investing in new facilities and increasing tuition fees for students enrolled in its after-school program.
Income Statement f or the fiscal year ending December 31, 20XX
Revenue: $1.2 million
Total Expenses: $910,000
Net Income Before Taxes: $302,000
Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 20XX
Cash and Cash Equivalents: $25,000
Receivables: $335,000
Property and Equipment: $1.2 million
Intangible Assets: $0
Total Assets: $1.5 million
Balance Statement
The board of directors has approved the 20XX fiscal year budget for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, which is estimated at $1.3 million in revenues and $920,000 in expenditures.
Cash Flow Statement f or the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 20XX
Operating Activities: Income Before Taxes -$302,000
Investing Activities: New equipment and supplies -$100,000
Financing Activities: Fundraising campaign $200,000
Net Change in Cash: $25,000
According to the 20XX fiscal year financial statements for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, it expects its investments to decrease by 4 percent and expects to generate $1.3 million in revenues. Its total assets are valued at $1.5 million, which consists of equipment and property worth approximately 1.2 million dollars.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial statements demonstrate its long-term potential for strong revenue growth due to its steady market share held with low-income families in St. Louis, MO.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization that aims to provide low-income single-parent families with affordable housing. The management team has a strong background in the social service industry and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, Finally Home’s CEO has a background in real estate development, which will help the organization as they begin developing its operations.
Finally Home’s mission is to reinvent affordable housing for low-income single-parent families and make it more sustainable and accessible. They will accomplish this by buying homes from families and renting them out at an affordable price. Finally Home expects its model of affordable housing to become more sustainable and accessible than any other model currently available on the market today. Finally Home’s competitive advantage over similar organizations is that it will purchase land and buildings from which to build affordable housing. This gives them a greater amount of ownership over their communities and the properties in which the homes are located, as well as freedom when financing these projects.
Finally Home plans on accomplishing this by buying real estate in areas with high concentrations of low-income families who are ready to become homeowners. These homes will be used as affordable housing units until they are purchased by Finally Home’s target demographic, at which point the organizations will begin renting them out at a base rate of 30% of the family’s monthly household income.
Finally Home plans on financing its operations through both private donations and contributions from foundations, corporations, and government organizations.
Finally Home’s management team has strong backgrounds in the social service industry, with deep ties to families that will be prepared to take advantage of Finally Home’s affordable housing opportunities. The CEO of Finally Home also brings extensive real estate development experience to the organization, an asset that will be especially helpful as Finally Home begins its operations.
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization, incorporated in the State of California, whose mission is to help homeless families by providing them with housing and support services. The centerpiece of our program, which will be replicated nationwide if successful, is an apartment complex that offers supportive living for single parents and their children.
The apartments are fully furnished, and all utilities are paid.
All the single parents have jobs, but they don’t earn enough to pay market-rate rent while still paying for other necessities such as food and transportation.
The organization was founded in 20XX by Henry Cisneros, a former U.S. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development who served under President Bill Clinton. Cisneros is the chairman of Finally Home’s board of directors, which includes leaders with experience in banking, nonprofit management, and housing professions.
The core values are family unity, compassion for the poor, and respect for our clients. They are the values that guide our employees and volunteers at Finally Home from start to finish.
According to the United States Conference of Mayors’ Task Force on Hunger and Homelessness 20XX Report, “Hunger & Homelessness Survey: A Status Report on Hunger & Homelessness in America’s Cities,” almost half (48%) of all homeless people are members of families with children. Of this number, over one quarter (26%) are under the age of 18.
In 20XX, there were 9.5 million poor adults living in poverty in a family with children and no spouse present. The majority of these families (63%) have only one earner, while 44% have zero earners because the person is not old enough or does not work for other reasons.
The total number of people in poverty in 20XX was 46.5 million, the largest number since Census began publishing these statistics 52 years ago.
Finally Home’s goal is to help single parents escape this cycle of poverty through providing affordable housing and case management services to support them long term.
Unique Market Position
Finally Home creates unique value for its potential customers by creating housing where it does not yet exist.
By helping single parents escape poverty and become self-sufficient, Finally Home will drive demand among low-income families nationwide who are experiencing homelessness. The high level of need among this demographic is significant nationwide. However, there are no other organizations with the same market position as Finally Home.
Finally Home’s target customers are low-income families who are experiencing homelessness in the Los Angeles area. The organization will actively seek out these families through national networks of other social service providers to whom they refer their clients regularly.
Finally Home expects to have a waiting list of families that are interested in the program before they even open their doors.
This customer analysis is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
Industry Capacity
This information is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
There is a growing demand for low-income single-parent housing nationwide, yet there is no one organization currently providing these services on a national level like Finally Home.
Thus, Finally Home has a competitive advantage and market niche here because it will be the only nonprofit organization of its kind in the country.
Finally Home’s marketing strategies will focus on attracting potential customers through national networks of other social service providers. They will advertise to their referral sources using materials developed by the organization. Finally Home will also advertise its services online, targeting low-income families using Google AdWords.
Finally Home will be reinventing affordable housing to make it more accessible and sustainable for low-income single parents. In this new model, Finally Home will own the land and buildings on which its housing units are built, as well as the properties in which they are located.
When a family is ready to move into an affordable housing unit, Finally Home will buy the home they currently live in. This way, families can take advantage of homeownership services like property tax assistance and financial literacy courses that help them manage their newfound wealth.
Finally Home has already partnered with local real estate agents to identify properties for purchase. The organization expects this to result in homes that are at least 30% cheaper than market value.
Finally Home will finance its operational plan through the use of private contributions and donations from public and private foundations, as well as corporate sponsorships.
Finally Home’s management team consists of:
- Veronica Jones, CEO, and Founder
- Mark MacDonald, COO
- Scott Bader, CFO
Management Summary
The management team has a strong history of social service advocacy and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, the organization’s CEO has a background in real estate development that will be helpful as Finally Home begins operations.
- Year 1: Operation startup costs to launch first five houses ($621,865)
- Year 2: Deliver on market offer and complete first capital raise ($4,753,000)
- Year 3: Deliver on market offer and complete $5 million capital raise ($7,950,000)
- Year 4+: Continue to grow market share with a national network of social services providers ($15,350,000).
This nonprofit business plan will serve as an effective road map for Finally Home in its efforts to create a new model for affordable housing.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example PDF
Download our non-profit business plan pdf here. This is a free nonprofit business plan example to help you get started on your own nonprofit plan.
How to Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your nonprofit business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Nonprofit Business Planning Articles
- Non-Profit Business Plan
- How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
- 10 Tips to Make Your Nonprofit’s Business Plan Stand Out
- How to Write a Mission Statement for Your Nonprofit Organization
- Strategic Planning for a Nonprofit Organization
- How to Write a Marketing Plan for Your Nonprofit Business
- 4 Top Funding Sources for a Nonprofit Organization
- What is a Nonprofit Organization?
- 20 Nonprofit Organization Ideas For Your Community

Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Charity organizations play a crucial role in making the world a better place. But to truly make an impact, they need a solid roadmap. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations comes in.
This template is specifically designed to help charity leaders and managers:
- Clearly define their organization's mission, goals, and strategies
- Secure funding and establish key partnerships by presenting a comprehensive plan
- Guide their day-to-day operations towards maximizing social impact
Whether you're a non-profit veteran or just starting out, this template will provide the structure and guidance you need to create a powerful business plan that sets your charity up for success. So let's get started and make a difference together!
Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations Benefits
A business plan template for charity organizations offers a range of benefits to help leaders and managers effectively navigate the complex world of fundraising and social impact. Some of the key benefits include:
- Streamlining the planning process by providing a structured framework to outline the organization's mission, vision, and goals
- Enhancing credibility and professionalism when presenting the organization to potential donors, partners, and stakeholders
- Guiding strategic decision-making by identifying key priorities, target demographics, and sustainable funding models
- Facilitating effective communication and alignment among team members, board members, and volunteers
- Increasing the likelihood of securing funding and partnerships by demonstrating a clear roadmap and measurable outcomes.
Main Elements of Charity Organizations Business Plan Template
ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations is designed to help charity organization leaders and managers create a comprehensive and impactful business plan. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add important information to your business plan such as Reference, Approved, and Section, making it easy to organize and reference key details.
- Custom Views: Explore different perspectives of your business plan, including Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, to easily navigate and focus on specific areas of your plan.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations, you can streamline the process of creating a comprehensive and effective business plan to guide your organization's success in maximizing social impact.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations
If you're a charity organization looking to create a business plan, follow these six steps to make the most of the Business Plan Template in ClickUp:
1. Define your mission and vision
Start by clearly defining the mission and vision of your charity organization. What is the purpose of your organization? What impact do you hope to make in the world? This will serve as the foundation for your business plan and guide all of your future decisions.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to articulate your mission and vision statements.

2. Identify your target audience and beneficiaries
Next, identify the specific audience or beneficiaries that your charity organization aims to serve. Who are the individuals or communities that will benefit from your work? Understanding your target audience will help you tailor your programs and services to meet their needs.
Create tasks in ClickUp to list and categorize your target audience and beneficiaries.
3. Outline your programs and services
Now it's time to outline the specific programs and services that your charity organization will offer. What initiatives will you undertake to fulfill your mission? This could include fundraising events, community outreach programs, educational workshops, or any other activities that align with your goals.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to define and track your programs and services.
4. Develop a fundraising and financial strategy
Every charity organization needs a solid fundraising and financial strategy to support its operations. Determine the different fundraising methods you'll use, such as grants, donations, sponsorships, or partnerships. Additionally, create a budget and financial plan that outlines your expected income and expenses.
Utilize the Goals feature in ClickUp to set financial targets and track your progress.
5. Establish a marketing and communication plan
To raise awareness about your charity organization and attract supporters, you'll need a well-defined marketing and communication plan. Consider the various channels and strategies you'll use to reach your target audience, such as social media, email campaigns, press releases, or partnerships with influencers or media outlets.
Use the Calendar view in ClickUp to schedule and manage your marketing and communication activities.
6. Set goals, milestones, and measures of success
Finally, set specific goals, milestones, and measures of success for your charity organization. What do you hope to achieve in the short term and long term? Break down your goals into actionable steps and establish deadlines to keep yourself accountable.
Create Milestones in ClickUp to track your progress and celebrate your achievements.
By following these steps and utilizing the Business Plan Template in ClickUp, your charity organization will be well-equipped to create a comprehensive and effective business plan.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations
Charity organization leaders and managers can use the Business Plan Template for Charity Organizations in ClickUp to create a comprehensive plan that aligns with their mission and goals, and helps them secure funding and partnerships.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a powerful business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your plan into different sections, such as mission, goals, strategies, and financials
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- The Timeline View will give you a visual representation of your plan's milestones and deadlines
- The Business Plan View will provide a comprehensive overview of your plan, allowing you to easily navigate and make updates
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide step-by-step instructions on how to use the template and create an effective business plan
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and track key details
- Collaborate with team members to gather input, make revisions, and ensure everyone is aligned with the plan's objectives
- Monitor and analyze your plan's progress and performance to make informed decisions and drive social impact.
- Business Plan Template for Network Engineers
- Business Plan Template for Talent Acquisition
- Business Plan Template for Transportation Companies
- Business Plan Template for Voiceover Artists
- Business Plan Template for Sports Team
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
How to write a business plan for a small charity
Table of Contents
Description of charity
Explaining the audience, swot analysis, opportunities, financial projection, manage your finances for achieving objectives with countingup.
Typical businesses use a plan to secure funding by sharing it as a proposal to investors or forming part of an application to the bank for a loan. For a charity, though, there might be other uses to putting together a business plan . These may include the ability to set out a direction for your organisation or look for sizable donations, which may require you to share a plan.
This guide will make sure that you can get on with reaching your social objectives by showing you how to write a business plan for a charity. It includes:
For a social enterprise (charity), the business’ objectives are different from usual companies. Typical companies may aim to create wealth for the owner, for example. But, according to the UK Government , to be legally considered a charity, your organisation must have a charitable purpose. So the first thing to include in your business plan should be these aims.
If you can make it clear what the objectives of your business are, it provides a greater incentive for people to donate. It might also be helpful to explain why it’s the purpose you chose. With an objective, you should also describe how the organisation plans to help it. For example, if your charity aims to help blind people, they may look to fund guide dogs to be provided for them.
The other key element of your description of your charity should be how you plan to fund it. You may sell products, provide services or ask for donations. There may be other charities helping a similar cause, so you should also describe what makes you unique that will make people want to donate.
Charities rely on funding to fulfil their objectives. Without it, you may struggle to help those you would like to. As a result, running the organisation requires some business thinking. For example, identifying a target audience most likely to donate or pay for products/services shows that you are more likely to reach your goals.
To find your audience, you may have to carry out market research . Speak directly to those affected by the issue you aim to solve and those interested in helping your charity. You can gather information through surveys and interviews to find out as much as possible about your market. Another way to do this is by looking at similar charities’ focus and who they target.
It may be helpful for you to put together a customer profile (sometimes called customer avatar) to use your findings from your market research productively. By having a hypothetical person to think about, you can find insights for where you should be marketing to them and why they would donate.
A customer profile could include:
Putting these details together helps you describe how you plan to market your charity.
For more information on how to market your small business, see: How to Market Your Small Business Effectively: 9 Top Tips
It is essential to understand where the current position of your charity is to help you plan for the future. To think about all aspects of your business, you can do a SWOT analysis . This technique focuses on your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Your organisation’s strengths should provide the reasons that your charity is likely to achieve its goals. For example, you could mention the quotes and information of those who would benefit you in your marketing.
There are likely some weaknesses your charity may have. Identifying them lets you talk about how you will get over them. For example, if you lack experience in financial management, mention that you plan to use an app like Countingup to make it easier.
If you show that there are opportunities your organisation can take advantage of, it might give more confidence to someone willing to donate. For example, if a sports event is coming up later this year that relates to your cause, maybe you could partner with them.
Like any business, there may be potential threats to your charity. But by mentioning them, you can also say how you plan to avoid them. For example, if you sell donated things and you run out, mention your plans to make other things to sell.
Even though the primary purpose of the business is not to make a profit for the owners, it’s still essential that the charity covers its costs and makes enough to fund its social activities. So, it could be helpful to provide your business plan with some calculations to reassure those looking to donate towards your organisation that it will go towards a successful venture.
A sales forecast estimates the sales you expect. Multiply your planned prices for products, services or typical donation amounts by the number of customers you expect. Put this to a timescale of a month, quarter or year. You can refer to your projections in later stages and compare your performance.
This section may also be helpful for you to detail what the business would be hoping to use donations for specifically. For example, you may pay a marketing agency for a social media campaign if someone provides significant assistance. If you have a smaller donation, though, that may reach your particular objective.
It is important for your financial projection to be accurate and for you to monitor whether your business is sticking to your expectations. That’s why thousands of business owners use the Countingup app to make their financial admin easier.
Countingup is the business current account with built-in accounting software that allows you to manage all your financial data in one place. With features like automatic expense categorisation, you can see exactly where your costs are going in your charity. To make sure that you can fulfil the objectives of your organisation, cash flow insights let you receive reports about your finances. You can confidently keep on top of your business finances wherever you are.
You can also share your bookkeeping with your accountant instantly without worrying about duplication errors, data lags or inaccuracies. Seamless, simple, and straightforward!
Start your three-month free trial today. Find out more here .

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Bookkeeping and accounting tips for hairdressers.
As a self-employed hairdresser or salon owner, bookkeeping and accounting can be hard
What expenses can you claim as a childminder?
Being a childminder can be a great way to earn extra income or
How to get more clients as a freelance makeup artist
Whether you’re a professional makeup artist, a bridal makeup artist or a student
How to start a supported living business
Starting a supported living business is a challenging, but incredibly rewarding, way to
How To Start A Vending Machine Business In The UK
Starting a business is a great way to become your own boss and
How to start a dog daycare business
If you think dogs are a treat to be around, you’re not alone.
How to start a babysitting business
If you love spending time with children and offer to babysit for family,
How to start a cat sitting business
Did you know that 24% of the UK population own a cat? That’s
Money laundering regulations for estate agents
In December 2020, the government issued the National risk assessment of money laundering
How to become a freelance bookkeeper
If you enjoy balancing books and organising business finances, becoming a freelance bookkeeper
How to sell jewellery designs to companies
Do you enjoy creating unique jewellery designs? If so, you might want to
How to become a self-employed labourer
Do you enjoy working with your hands and like the idea of being
CHARITY BUSINESS PLAN: The Ultimate Guide To Writing A Non-Profit Business Plan
- by Kenechukwu Muoghalu
- August 14, 2023
- No comments
- 7 minute read

Table of Contents Hide
What is a charity business plan , why do i need a charity business plan, #1. executive summary, #2. present your opportunity, #3. target audience, #4. strategic plan objective, #5. your products and services, #6. operational plan, #7. marketing plan, #8. financial plan, #9. management team and board, #10. appendix, charity business plan template checklist, how many pages should my charity business plan be, how do i start a non-profit with no money, do not let your charity business plan miss out, charity business plan faqs, can i make money owning a charity business, how do charity owners make money, how do i start a small charity.
A lot of charity organizations do not like the idea of having a business plan. This is because they think that creating a business plan for their charity organization is a waste of time. But wait! What makes you think so? Isn’t a charity organization a form of business? Be it a profit or nonprofit, it makes no difference. Learn to accept that it is still in the business genre. This is why we have created an example of what a UK template checklist looks like, just to guide you while writing your charity business plan.
There are lots of benefits to having a business plan for your charity organization. This article will furtherly cover those grounds. Shall we!
A charity business plan isn’t just a document of many pages. When you define it like that, it is said to reduce its actual value. A charitable business plan details the products and services your nonprofit organization provides. A charity business plan also contains the people on your team, the community you work for, your financials, goals, and how to attain those goals. Now, this right here can count as a definition.
Don’t make the mistake of starting that excellent idea of yours without having a charity business plan on standby. Even those dreams and ideas can turn useless if you cannot formulate, execute, and implement a plan that can help you achieve them.
Creating a nonprofit business plan doesn’t have to be long and bulky. Even a short business plan can serve its purpose more than a long one. All it needs to contain is the necessary information about your organization and you are good to go.
Heaven yes! You do need a charity business plan. Having a charity business plan will save you tons of pitfalls. A charity business plan can help you create forecasts for revenue and also help you plan how to utilize any money that comes in. You would have a clear guide on all the activities your organization goes through. You can even measure your growth and denote where changes are needed for more growth.
When you talk about good business planning, you talk about setting goals , carrying your team along, tracking performance, and improving. Every business needs these essentials to grow, no matter the nature of the business. Even if you are not interested in whatever profits the organization will yield due to your large heart, you still need to run a healthy organization. Whichever angle you come from, you can’t run from it.
Read Also: How To Register A Business: Detailed Guide To Business Registration In The Uk
For example, when you run a charity business, you need to always report and plan with the board of directors. Most of the time, the financial status of the organization is mostly what is being discussed. This is where your charity business plan comes in. It can help you compare your actual results to your financial forecasts. It can guide the amount of spending you do while keeping your financial position in check.
Moreover, keeping a charity business plan can also help attract sponsors, donors, or even lenders who want to understand how your organization works and help you achieve your goals.
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Non-profit Business Plan
To create a charitable business plan, you will need to either follow some examples, which can also be accessed in a PDF, or follow these outlines. These outlines should be in check while creating a business plan for your charity organization. Nothing should be left out. This ultimate guide includes:
This is the general overview of the whole business plan. It is usually the first section to read and the last to write. While in this section, avoid jargon and write as though an external eye is going to access it. It should be easily accessible and easy to read. Go ahead to briefly state the overview of your mission. Include the services you provide and how you fundraise.
A great way to do this is by using a positioning statement . In this section, describe the problems people face and how your organization can solve them. It can be giving tutors to kids or providing food to a large number of people. Explain how your organization is different from other, and state what you do to help the community and saves lives.
If you have a specific target audience that your organization caters to, then specify it in this section. State who benefits from the services you render. You should also note that it is possible not to have a particular target market. This means that your product is utilized by all.
In your strategic plan objective , mention those plans and visions you want to observe next in your organization. With those improvements and a project plan, you are ready to take. For example, you feed 300 people per year, but then you are planning on making it 500 this particular year. It can even be about your organization. You can choose to grow from a regional nonprofit to a national nonprofit organization. Talk about those long-term goals in this section and work towards getting them done.
Just like the name implies, you will need to define the products and services you offer. Talk about how you will raise money and serve your community. Detail every item and avoid keeping it general. In this section, you will need to include even the smallest detail that you think no one would notice.
How will your charity organization operate? What are the legal structures, organizational structures, location, and inventory? What about the management team? How would they operate? You will need to answer these questions in this section.
When writing your charity business plan, our marketing strategy is an important factor because you will need to promote your organization. You will need to make it known, and let people know the services you offer and what your charity organization is all about. While at this, you can indirectly attract sponsors or donors that love what you do and will help in any way.
This section will have information on your financial details. You will include all your current funding, expenses, liabilities, revenue, and assets. Add statistics and make it more professional. Add graphs to make it more comprehensive. This section is also the most crucial to loaners and donors. Add expected expenses as well, salaries, utility bills, website hosting, insurance, subscriptions, and anyone expenses that the organization will be running.
List the individuals that will be present in your organization. Clearly, they have different duties and responsibilities. Both your day-to-day team and your board members should not be left out. Feature those capable workers that always put the organization first before any other thing. Indicate their qualifications and degree, and don’t forget to also mention how good you are too.
In this section, you will be free to include anything extra that you wish to. Any special feature that you think shouldn’t be exempted from your charity business plan? It can be the bios of your board members and any other details you feel are relevant for the section. When you follow all these, there shouldn’t be a reason why you will not have a successful charity organization.
To help you get started with your UK charity organization, we have created a business plan example template. This charity business plan template can also be utilized in other locations apart from the UK. So we urge you to explore. Don’t fret. Let’s take a look at our charity business plan example template. They include:
- Define your goals and milestones.
- Understand your team and other stakeholders.
- Assess your financing model.
- Identify your risks and manage them.
- Attract investment and volunteers.
- Research and discover new opportunities.
- Kink your plan.
You can have from seven to thirty pages in your business plan. It must not be made too long before it can serve its purpose in your organization. Just keep it clear and concise for anyone to scale through without difficulty. But why bother when we have an already composed charity business plan that is highly convertible. All you need to do is to get a copy here and start your journey to success.
The best action to take is to approach potential investors or donors for help. While doing this, you will need to explain the nature of your organization and whatever idea you have for its growth. Even with no cash at hand, you can still make this work.
Meanwhile ,
Our main priority is to boost your charity organization and to give you an opportunity that is rare to find.
Have you tried creating a plan and it seems tough? Do you have questions that you don’t have an answer to even after multiple trials? Stop trying!
Your plea has been heard and that is why we will be giving you a uniquely designed charity business plan. A plan that multiple charity organizations have tested and confirmed its productivity. You won’t have to stress more because it is simplified and easy for anyone to access. Take your charity organization to another level now!
Nonprofit organizations have proven to be created out of passion and enthusiasm. But passion without a proper business plan will render your zeal powerless. Imagine being patriotic, going to war without a weapon. How would you win? Just because it is labeled “nonprofit” doesn’t mean that you should operate it like any other business out there. Make a difference with your charity business plan.
A non-profit organization doesn’t earn a taxable profit. But that does not mean that the people that run it can’t receive a taxable salary. The founder can ensure that its workers earn a living, while still running a charity organization.
Charity businesses can earn money through regular activities like using volunteers, hosting fundraising events, sponsoring occasions, selling products, or even running adverts that can bring in donations.
Starting a charity business can be hectic but there are some steps to follow to make it a better experience. Start by defining your mission, picking a name, registering the business, opening a website, raising some cash and staying lean. Don’t forget to also own a Charity Business plan, which you can create using a UK template.
Starting a charity business can be hectic but there are some steps to follow to make it a better experience. Start by defining your mission, picking a name, registering the business, opening a website, raising some cash and staying lean. Don't forget to also own a Charity Business plan, which you can create using a UK template.
Related Articles
- CHILD PROTECTION PLAN: Initiation & Purpose of Section 47
- DIRECT DEBIT GUARANTEE | Detailed Explanation & Guide To The Processes
- BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION APPRENTICESHIP: Definitions, Duration and Levels
- Mortgage Guide: Best Guide For First Timer Buyers In 2023
Kenechukwu Muoghalu
Kenny, an accomplished business writer with a decade of experience, excels in translating intricate industry insights into engaging articles. Her passion revolves around distilling the latest trends, offering actionable advice, and nurturing a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape. With a proven track record of delivering insightful content, Kenny is dedicated to empowering her readers with the knowledge needed to thrive in the dynamic and ever-evolving world of business.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
BRITISH SENIOR LIFE INSURANCE REVIEWS (UPDATED)
Probate house sale: definitive guide to probate house sale.
All Formats
Table of Contents
5 steps for preparing a charity business plan, 9+ charity business plan templates in pdf | word, 1. charity fund business plan template, 2. charity commission business plan template, 3. charity organisation business plan template, 4. charity non-profit business plan template, 5. charity business plan template in pdf, 6. charity business plan in doc, 7. business plan for charities, 8. charity startup business plan format, 9. simple charity business plan template, 10. formal charity organisation business plan, charity templates.
A business plan is a crucial document that is required for several purposes. Charity organizations too produce such documents while starting a new venture, to secure fundings and also for expansion projects and more. The document provides elaborate details on the goals and objectives of the organization or a project as well as the budget plan and the estimated outcomes of the undertaking. We have prepared our professional plan templates to help you make such important documents conveniently.

Step 1: Provide the Executive Summary
Step 2: give an introduction to the organization, step 3: define your market and operational plans, step 4: provide summary of your finances, step 5: understand the risks.

More in Charity Templates
Simple volunteer charity flyer template, creative fundraising invitation template, red nose day fb post, red nose day website banner, red nose day cartoon background, red nose day design background, red nose day banner background, red nose day image background, red nose day photo background.
- 10+ Charity Assessment Templates in DOC | PDF
- 5+ Charity Disaster Recovery Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Charity Trustee Application Form Templates in PDF | Word
- 3+ Charity Cheque Templates in PDF
- 6+ Charity Bag Packing Templates in PDF
- 5+ Charity Employment Contract Templates in PDF
- 10+ Charity Job Description Templates in PDF | DOC
- 3+ Charity Project Plan Templates in PDF
- 9+ Charity Invoice Templates in Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel | Word | Numbers | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Charity Whistleblowing Policy Templates in DOC | PDF
- 11+ Charity Volunteer Agreement Templates in PDF
- 10+ Charity Direct Debit Form Templates in PDF
- 10+ Charity Walk Registration Form Templates in PDF | Word
- 11+ Charity Risk Assessment Templates in DOC | PDF
- 5+ Charity Request Letter Templates in PDF | DOC
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
Not registered for a My SCVO account?
Sign up below to create a My SCVO account. It's best to use a work email address in your own name if you can. Fill in your details and we'll send you a link to verify your email address. You'll then have the option to create an individual account or link your account to an organisation. If your organisation is an SCVO member or supporter, you'll gain immediate access to exclusive content and benefits. Privacy notice
Already have an account? Sign in
Complete the form below to receive a link to change your password
This website uses cookies for anonymised analytics and for account authentication. See our privacy and cookies policies for more information.
- Support & learning
- Events & training
- The Gathering
- Charity Awards
- Funding Scotland
The Scottish Council for Voluntary Organisations is the membership organisation for Scotland's charities, voluntary organisations and social enterprises. Charity registered in Scotland SC003558 . Registered office Mansfield Traquair Centre, 15 Mansfield Place, Edinburgh EH3 6BB.
- Support & learning
- Running your organisation
- Business planning
- Writing a business plan
While the language of business can seem at odds with the aims of voluntary organisations, you still need to plan for the future to get things done, and to account to your members, to funders and to the public as you carry out your activities.
Business planning in uncertain times
Your plan may need to be revised more often in response to the current cost of living crisis. By taking the time to try and identify future risks (such as an increase in costs or a reduction of funds) and some potential ways to address these, your organisation may be better equipped to adapt and respond quickly to lower the risks.
- to clarify and meet your aims and objectives
- to spot potential risks and problems
- to set out your goals
- to measure your progress, keep on track, manage performance
- to ensure you do not accumulate losses
- to ensure you comply with legislation and regulations
- to plan your approach and monitor your activities over time
- to raise money for the organisation or specific projects. It can be shown to other people who might provide or lend money, eg funders, public bodies, the bank.
You can also use your plan to introduce new groups of people to your organisation, such as volunteers or funders.
If you decide to apply to be a charity then the Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator will want to see a copy of a business plan, organisational plan or grant application, or any other documents detailing your organisation’s intended activities.
What should our business plan say?
A business plan is a clear and documented account of the activities you have decided to undertake over a given period of time, and the cost of making them happen. It should cover objectives and strategies, and enable the organisation to deliver more effectively. Business plans are as individual as the groups that develop them, but some common elements include:
- the history and background of your organisation and current activities
- future activities – what you are going to do and why?
- when and how you are going to do it?
- where will the money come from? When and how it will be spent?
- how will you assess the potential risks to your project?
- how will you keep track of your progress and spending? How will you monitor and review?
- how will you know if the plan is working? How will you evaluate?
Remember who you are writing the plan for: your management committee, your staff, members, clients. You should be honest and realistic when setting out your aims and objectives and how you intend to deliver them.
The information supplied in the ‘public version’ of a Business Plan may be slightly different to the version you will use for yourself. You should consider the information you supply to any third party carefully.
Who should be involved in the planning process?
Depending on the size of the organisation, it is useful to involve a number – or all – key players in the development of the plan to varying degrees. In voluntary organisations it is quite common to consult with clients, service users or members, as well as staff and/or the management committee.
Useful resources
- MyGov.scot - Writing a business plan Step by step guide to preparing a business plan.
- Forth sector development A business planning guide to developing a social enterprise.
- SCVO Business Planning webinar A look at new, more agile, ways of writing a business plan
- Risk analysis & management
- Monitoring, evaluation and review
- Mergers & collaborations
Information service
SCVO's information service is an online knowledge bank and enquiry service delivered by experts.
We provide:
- Information
- Free resources
- Guidance for charities and voluntary organisations in Scotland
- Support to set up and run a voluntary organisation
Find out more
- Sample Charity
FREE 12+ Charity Business Plan Samples in MS Word | PDF | Google Docs | Pages

With more than one million charities in the United States, one can expect a close competition, if there is any. Depending on the category your charity falls under, you can be unique and remain on the top of your game. To do that, you need to innovate to keep up with the industry and grow. But even a striving charity can experience plight on its journey, often heading downhill. Despite that, you can establish a charity business plan to lead the organization to its goals. With a business plan, you can set your expectations and maneuver a process in achieving it. Find out more about a business plan and how it affects charity projects with this article. Continue reading below.
Charity Business Plan
Free 12+ charity business plan samples, 1. charity fundraising plan template, 2. charity development plan template, 3. charity business plan template, 4. voluntary business strategic plan, 5. voluntary & charities business plan, 6. charity startup business plan, 7. non profit business plan template, 8. sample charity business plan, 9. executive charity business plan, 10. non-profit business plan format, 11. voluntary organisation business plan, 12. sample charity commission business plan, 13. charity trust business plan template, what is a business plan, a breakthrough: lean business plan, charity business plan: why is it important, does planning make a start-up successful, how to craft an effective charity business plan, what should a non-profit business plan contain, does a charity need a business plan, can i accept donations without being non-profit.

- Google Docs
Size: A4 & US

Size: 74 KB

Size: 453 KB

Size: 32 KB
Size: 13 KB

Size: 27 KB

Size: 804 KB

Size: 473 KB

Size: 438 KB
Size: 390 KB

Size: 852 KB

Size: 551 KB
The simplest way to define a business plan is to compare it with a guideline. It is a detailed plan that outlines goals and how to achieve these goals. Even if you have written down ideas on a piece of paper with some tasks you need to do, you have written a basic business plan . At its core, a business plan is a plan for the business operations, and how you are going to make it work.
Documenting your business ideas can take a lot of work. Often, it takes more writing and thinking. Thus, we recommend creating a lean business plan unless you are required to pass a formal business plan. Why? Aside from it is shorter than a usual business plan, it easier to create, and it includes pitch, strategy, tactics, business, schedule, budget, and committees. With this, companies can perform on their ideas fast and frequently. By writing a lean business plan , you can quickly sort useful things from what is not.
Essentially, you can only execute sample ideas right after a business plan is completed. That said, preparing a business plan is the smartest decision that an organization can make so that it can size up in terms of growth. With a charity business plan, you can set out the parts that the organizations should cover. Since it describes the charity and its undertakings, it can help in setting more goals, plans, finances, and risks that the organization might encounter.
According to a report posted by Harvard Business Review, based on research, a business plan makes a small business start-up more likely to become successful. In the report, it found out that a business person who writes a formal business plan has a 16% chance to achieve his goal compared to a non-planning entrepreneur. Furthermore, business start-ups that aim to gain high-growth are 7% more likely to write a plan. On top of that, entrepreneurs who are seeking external financial support are 19% more likely to commit to writing a business plan .
Successful organizations did not have it all until they come up with a plan. As an organization, a charity should give its administrator a reason to establish a strategic plan before it gets worse. Whether you are just a starting charity or a seasoned organization, you might consider the following steps beneficial for writing a charity business plan.
1. Keep It Simple and Straightforward
Along with charity membership forms , charity profiles , charity fundraising letters , and sponsorship forms , a charity business plan is a document made for a professional reader. That said, wordy sentences and jargon might be complex to some of your audiences. As much as you want to make your plan to sound good, you cannot put its content at risk by using hifalutin words. Rather, pay more attention to keeping it concise and straightforward. Though you can use infographics as visual elements, keep them to a minimum.
2. Be As Logical As Possible
When writing a business, clear your head, and do not be biased in making decisions. It’s important to remind yourself that the business plan can make a series of effects on your other plans, which involve marketing and other related areas. If you fail to foresee its impact to the organization, you might forget to anticipate the circumstances that could make or break the charity profile .
3. Write a Realistic Plan
Your ambitions are great guideposts, but limits exist for a reason. Being too positive can cause negative effects in most situations, as it locks your focus on your goals but not on the process of achieving it. Knowing this, take the time to create a roadmap or plot a schedule that will keep you on track. Whatever goals you have set for the charity, make sure you can execute them. Or you will waste your time believing your goals are doable.
4. Support Your Claims with Facts
Making a convincing business plan means incorporating facts from articles, statistics, research papers, and other references. All these will add credibility to the charity business plan. However, many references make it hard to choose a source. With this, verify the information, so you can use it to back up your claims. If you do not support your plan with relevant details, it is unlikely to become successful. You can even gather information from an existing charity business plan if there is any.
A basic business plan contains the following: an executive summary , problem, solutions, market analysis, target supporters, target clients, competition, and promotions for funding strategy.
Yes, a charity needs a business plan for its undertaking. Without a plan, the organization could not outline goals and how to achieve those goals.
State laws define whether an organization can accept donations or not. If your state allows donations for a non-profit organization, then you can accept charitable funds from donors.
A business plan is a forwarding tool for a charity. With no plans, an organization cannot implement growth, as it cannot execute its ideas. If you want your charity to be successful, start building a plan now.
Related Posts
Free 10+ charity data protection policy samples & templates in ..., free 17+ sample hr plan templates in ms word pdf, free 40+ sample proposal templates in ms word pages ..., free 10+ market research plan samples & templates in ms word ..., free 18+ event proposal letters samples in pdf ms word ..., sample supplier evaluation, free 12+ sample event sponsorship letter templates in pdf ..., sample restaurant budget, free 10+ charity volunteer policy samples & templates in ms ..., free 10+ charity grant application samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ charity volunteer application form samples & templates ..., free 9+ monthly business budget samples in pdf ms word | excel, free 14+ event marketing plan templates in pdf ms word, fundraising proposal template, free 10+ charity fundraising letter samples & templates in ms ..., free 10+ charity profile samples & templates in ms word pdf, sample non profit budget template, free 10+ sample donation sheet templates in google docs ..., free 3+ charity project budget samples & templates in pdf.
- Museums, libraries and archives
- Good Practice Guidance
Business plan good practice guidance
By reading this guidance you'll get help with how to develop a business plan, including basic headings and prompts on how to review your plan as it develops. It also includes a list of further resources and a glossary of terms to do with business planning.
Please note: if you already have a business plan, you don’t need to produce a new one.
Writing your plan
Before producing your business plan, consider:
- if you need expertise in areas such as market analysis, taxation or legal matters
- who will be involved in writing the plan, including staff and trustees
- the timelines for the business plan to be approved
The headings below give a basic framework for developing a business plan, but every organisation is different so you may want to use different headings or additional content that better explains how your organisation works:
- executive summary
- about the organisation
- governance and management structures
- market appraisal and current approach
- financial appraisal
- risk register
- monitoring and evaluating the organisation
- organisational impact assessment
- contact details for the organisation
Once you have a draft it’s a good idea to review it to assess its strengths and weaknesses, tackle any gaps and ensure it’s as clear, concise and logical as possible.
Your business plan will be a document you refer back to continually and update in the general course of running your organisation, so ask yourself:
- Does your business plan present a strategy for achieving your aims and your mission?
- Does your business plan align with our Heritage 2033 investment principles ?
Executive summary
Your plan should start with a concise overview (no more than two pages) highlighting the most important information in the document, including:
- an overview of your organisation including your mission statement and what you want to achieve
- the organisation’s key aims for the period of the plan (usually 3–5 years)
- key elements of your strategy including how you will assure the longer-term financial future of the organisation
- the main risks facing your organisation and how you plan to manage these in the short, medium and long term
- an explanation of how your organisation is resilient enough to meet challenges: likely including financial information, how you will ensure governance and management structures are fit for purpose, and the monitoring and evaluation processes you have in place
- any additional key information
Review this section by asking:
- Is it a well-structured summary highlighting key points from the plan?
- If someone with no prior knowledge of your organisation read this summary on its own, would it make sense?
About the organisation
This should provide information on the structure, objectives and activities of your organisation, including:
- when and why it was started
- its purpose, aims and key successes
- the key areas of activity, products and/or services that you deliver, how they are distinctive and how will they be developed over the course of the plan
- details of the targets you have set for each area of activity
- Legal status, eg: unincorporated association or trust, or incorporated by Act of Parliament, Royal Charter, as a company limited by shares/guarantee, (Scottish) Charitable Incorporated Organisation or Industrial and Provident Society. Indicate whether it is a Community Interest Company or is registered or recognised as a charity.
- whether it has a membership of individuals, and if so the number of members
- the names of any other entities with which it has a formal association (eg: any bodies with which there are funding agreements or that have the right to nominate multiple board members)
- Whether it is a partnership of different organisations with a shared interest, identifying the other organisations/stakeholders you will be working with, the basis of the arrangement and whether it is formal or informal. Summarise any partnership agreements.
- the number and roles of paid staff (in total and full-time equivalents) and explain the tasks they perform within the organisation
- the role of volunteers (give estimates of the number of regular volunteers, the tasks they do within the organisation and the total number of hours they work on each task every year)
- describe how you fund your organisation’s activities, noting any sources that account for a particularly large proportion of your income and, if these come from a funding body, when this funding will be subject to review
- Have you accurately described your organisation’s purpose and main areas of activity and how you are distinctive?
- Do you highlight key successes?
- Is it clear what services or products you offer and how you intend to develop them?
- Have you set clear targets?
- Is the structure of your organisation clearly set out in a way that is easy to understand?
- Have you included key information about your legal set up and how you staff and fund core activities?
Governance and management structures
This should explain your organisation’s management structure, decision-making processes, lines of communication and reporting. It can include simple organograms/network diagrams to show your governance, management and staffing structures.
Governance summary
This should provide an overview of the governance in place within your organisation to ensure that business plans and strategies are approved and monitored.
Describe the size and composition of the governing body (eg: council, board of trustees, board of directors) and, where appropriate, arrangements in place for succession planning and board development training. List the roles covered by your senior management team.
You should explain the make-up of your board. This includes how the board provides a diversity of perspective and skills. You should also explain their engagement with the organisation, particularly in relation to:
- business planning, pricing policies and marketing strategies
- financial management and administration
- fundraising
- approving potential projects and maintaining oversight
- commissioning advisers and consultants
Summarise the functions of any sub-groups, describing their membership, roles and responsibilities, and specifying any delegated powers they are authorised to use. Indicate how frequently such groups meet.
Management structure
You should include simple organigrams or network diagrams. These should show each job title. There’s no need to include individuals’ names.
Show how many post-holders are employed in each position and whether they are full-time, part-time or volunteers.

An accompanying schedule should list each role, summarising its purpose and function, and the name of the post-holder (so we can see if there are vacancies in key roles).
You should provide information on your recruitment policies for core staff. If you use external advisors regularly, you should give details of their company and role and how they relate to the positions on the organogram.
If volunteers are a key part of your organisation, you should explain:
- the roles volunteers play in the organisation, including the types of responsibilities they have
- how many volunteers the organisation works with
- the number of volunteer hours
- the role within your organisation responsible for managing volunteering and how this is monitored
- Have you covered how your organisation is managed and governed in a clear way? Is there any information missing?
- Have you included the main challenges you face in running your business?
- Is it clear what skills and experience are needed going forward? Have you included information on how you develop skills within the organisation?
- Have you included plans for developing your structure and processes in the future?
This should include a more detailed overview of the aims of your organisation for the period of the plan and how they relate to your overall mission, setting out the key activities you will undertake to achieve them.
Include any projects you plan to take on, demonstrating how they will work together to achieve your organisation’s aims. You should include information on the impact additional projects will have on your organisation and how you plan to deal with those impacts.
Include dates and a timetable for reviewing and updating your strategy.
Market appraisal and current approach
A market appraisal looks at your offer within the context of the marketplace. You should assess your market, your competition and your marketing strategy. Market analysis should be proportionate to the scope and size of your organisation.
Describe your current market:
- Is the profile of your heritage attraction or place of local or national interest? Is it well known?
- Is it valued by a wide cross-section of the public or a more limited special-interest group?
- How many customers have you had each year over the past 10 years?
- What are the demographics of your current customers and visitors – their age, gender, income, education, and occupation? What proportion are family groups/schools?
- Where do they live – very locally, from the surrounding region, from the UK or overseas?
- What proportion of customer contacts are repeats?
Show you know your market:
- On a national or regional basis, is your market growing, falling or stable?
- How does this relate to your organisation’s experience?
- Are there any national socio-economic trends or policies that will have an impact on your market?
- How might foreseeable political, economic, social and/or technological changes affect your market?
Consider your potential/target audience:
- Who are the people most likely to access your service?
- Are they single or repeat customers?
- What are their needs, behaviours, tastes and preferences?
- What has research shown you so far?
Review the competition
All organisations have competition of some sort. Find out what organisations are in competition with yours. Look at how they price their activities, their business strategy, strengths and weaknesses.
Develop a competitive strategy for your organisation
Do a ‘SWOT’ analysis looking at the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats to your organisation.
Use evidence-based information and remember to include internal and external factors. Describe what is unique and special to your organisation and include the disadvantages you have.
Outline your marketing strategy
A marketing strategy is how you will reach new audiences. It will likely be based on evidence from:
- data you have collected, over as long a period of time as is achievable
- national data, for example, the Taking Part survey (in England), national tourism surveys, national and local authority statistics
- existing market research
- market research commissioned to estimate potential markets and the potential popularity of the business with your target market
- reviewing operations that are similar to those you propose in your own area and further afield, using annual accounts available online from the Charity Commission (England) or Companies House
Your marketing strategy should clearly set out:
- people: who your target audiences are, including the size of these audiences
- product: what you’re offering people
- price: your pricing strategy and the rationale behind it
- promotion: the communication channels and messages you will use to reach your target audiences
Financial appraisal
This should include a general financial assessment of your organisation, an overview of your total financial need to support your day-to-day operations and details of your financial model, including your main sources of funding.
Provide supporting documents in an appendix at the end of your business plan, detailing:
- a forecast income and expenditure account
- a cashflow forecast showing the expected monthly cashflow
- statements of assumptions underlying the forecasts
Detail the assumptions made in your calculations. An assumption is anything you are relying on to make forecasts. For example, the average number of visitors you are expecting based on the previous year, or any unknown costs of materials. Make sure you also include details of any reserves.
You may want to undertake a sensitivity analysis to show what your finances would look like if your projections fall short by various amounts, for example between 5% and 20%. What would the risk to your operation be if either of these scenarios were to occur and what action might you need to take?
- Have you described how your organisation operates financially in a way that is easy to understand?
- Have you included an overview of your total financial needs, what your main sources of funding are and how your main activities contribute to achieving this?
- Have you included an expected cashflow forecast and income and expenditure forecast?
Risk register
A risk assessment identifies your organisation’s internal weaknesses and external threats. A risk register, usually set out as a table, lists all the identified risks prioritised in order of importance.
For each risk, outline:
- the nature of the risk, eg: technical, market, financial, economic, management, legal
- a description of the risk
- the probability of the risk happening: low, medium, high or as a percentage
- the effect the risk could have, eg: on cost, time, performance
- the level of effect: low, medium, high, or as a percentage
- how you would prepare for and lessen the risk’s effect
- Have you listed the key potential problems that your organisation faces?
- On reflection, are they your main risks or can the list be reduced?
- Have the risks been properly calculated?
- Do you need to do any further thinking about how risks will be mitigated?
- Are there any alternative courses of action that have not been considered?
Monitoring and evaluating your organisation
In this section you should set out your plans for monitoring and evaluating your organisation's performance and impact to ensure you are meeting your aims and achieving your mission.
You will need to gather different kinds of information at various stages, starting at the earliest opportunity by benchmarking where you are to start with. You should set a series of milestones, financial targets and performance targets to track these.
Evaluation should be carried out regularly using the monitoring information. You should summarise your planned approach and include details of milestones. Your approach should show when you anticipate evaluating your achievements and specify the scope of the evaluation and whether your organisation plans to bring in any expertise to help you assess the extent to which you are meeting your aims.
- Have you included details of the changes you want your organisation to make? How does this link to your mission and aims?
- Have you set out how you intend to monitor progress? Will you need any external advice?
- Have you detailed what success looks like? How will you know if you have achieved your targets?
- Do you have a plan for linking your findings into future decision-making? How do you report back to your board of trustees?
Organisational impact assessment
Within your application we want to see how your proposed project will impact your organisation and its finances and continue to deliver against our investment principles for a period of five years from the end of the project, including:
How will any additional costs created by the project continue to be funded?
These can include additional staffing and housekeeping costs, business rates, maintenance obligations arising from implementing management and maintenance plans (and, if applicable, conservation plans ). Document these additional costs in a table.
Where the project is expected to lead to reduced expenditure (for example, reduced energy expenditure, productivity gains due to improved technology), include the costs of the savings in the table to give the planned net additional cost or saving.
What additional volunteer input will be required?
Tell us about additional numbers of hours to be worked and the number of additional hours required. Indicate where these volunteers come from and the impact on your volunteer management and training arrangements.
Are there any changes in governance or management that could affect the project?
Tell us about any relevant changes to board composition or committee structure, or variation in individual duties or responsibilities. If the structure will be different during different phases of your project, provide separate diagrams to explain the arrangements. Outline any other material change in how the organisation will be managed as a consequence of the project.
Provide the following financial projections:
A statement of unrestricted funds, or of income and expenditure where the organisation is a local authority, university or other large organisation and the scale of the project is immaterial to the organisation's total financial circumstances. Where the organisation has a trading subsidiary, its projections should be consolidated with those of its parent. Include:
- the organisation's balance sheet
- the assumptions on which the financial projections are based
- a sensitivity analysis
In carrying out this impact assessment you should:
- Use the market appraisal you have carried out in your overall business planning to give details of your market size and the income generated. The assumptions should clearly show the basis on which the numbers have been calculated.
- demonstrate that the general trend will be for the organisation to generate annual surpluses on its unrestricted funds
- Base your assessment on your latest completed financial year if you have been in existence for that length of time (or the current year budget). Use this as a starting point for your projections so you can clearly assess the net impact on your financial position from the incremental, on-going income and expenditure caused by the project you are proposing.
- Include in the sensitivity analysis the income items that are most critical to the organisation's success, are most uncertain or contain the greatest risk. By adjusting these by percentages between 5% and 20%, depending on their nature and risk, it is possible to see the impact on the reported surplus.
Contact details for your organisation
At the end of your business plan, include:
- head office address
- telephone number
- email address
If you need to include additional information to support your plan, for example, evidence or reports you have commissioned, external advice, financial information or visuals which support the plan, add these as appendices.
When you have completed the plan, review your appendices to make sure you haven’t missed any relevant detail. Check whether you have included information in the main business plan that should be listed in the appendix instead.
Additional resources
- Sample business plans for various industries.
- Business planning guidance for arts and cultural organisations commissioned by Arts Council England for the arts and cultural sector.
- The Sustainable Sun tool : 10 steps towards financial sustainability from the National Council for Voluntary Organisations.
- An introduction to benchmarking , developed by The Audience Agency.
- How to build a measurement and evaluation framework , developed by New Philanthropy Capital.
- Impact and evaluation resources from the Small Charities Coalition
- DIY toolkit on how to invent, adopt or adapt ideas that can deliver better results, created by Nesta, the UK’s innovation agency. It includes a template for SWOT analysis .
- Various business planning resources from the Scottish Council for Voluntary Organisations.
- Various resources to help you run your organisation from the Wales Council for Voluntary Action.
- Resources and templates relating to business planning , including a template for developing a cashflow, from the Small Charities Programme.
Glossary of terms to do with business planning
Aims: a broad statement of intent.
Asset : an item of value owned and controlled by the organisation that has a useful life longer than a single accounting period.
Budget : a plan for future activity expressed in terms of incoming and outgoing resources.
Cashflow : the pattern of an organisation’s income and expenditure. Having surplus cash in hand after being able to meet all debts on the day they are due is a ‘positive’ cashflow, not having cash to meet debts as they fall due is a ‘negative’ cashflow.
Forecast : a financial projection, based on performance to date, of where the organisation expects to be at the end of the current financial period. Revised forecasts are often prepared throughout the financial year.
Impact: the intended or unintended sustainable changes brought about by an initiative, project, programme or organisation.
Mission : the overall guiding direction of the organisation, which usually states your purpose, refers to what your organisation does, who it does it for and what is unique or different about what you do.
Objectives : achievements set out for a business to aim for, often within a certain timeframe. These should be ‘SMART’, ie: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-based. They underpin planning and strategic activities and serve as the basis for performance monitoring and evaluation.
Trustee: a person who has independent control over, and legal responsibility for, an organisation’s (especially a charity’s) management and administration. Find out more about trustees on the Government’s website .
Sensitivity analysis: tests different scenarios to see how they will affect your bottom line, for example by increasing and decreasing your financial projections by between 5% and 20%.
Unrestricted funds: money that can be spent on any activity that furthers the organisation’s purpose.

Charity Business Plan

Various people lead different lives. That said, individuals consequently end up setting varying career goals . Some of them, such as people like you, find their calling in helping others. Most people who like supporting a cause start a charity. If you are here because you are planning to start one, or probably because you are finding ways to keep your nonprofit organization up and running, continue reading this article and learn how to devise a charity business plan.
10+ Charity Business Plan Examples
1. executive summary charity business plan.

Size: 187 KB
2. Starting Non Profit Charity Business Plan

Size: 96 KB
3. Business Plan for Non Profit Organisation
Size: 602 KB
4. Charity Business Continuity Plan
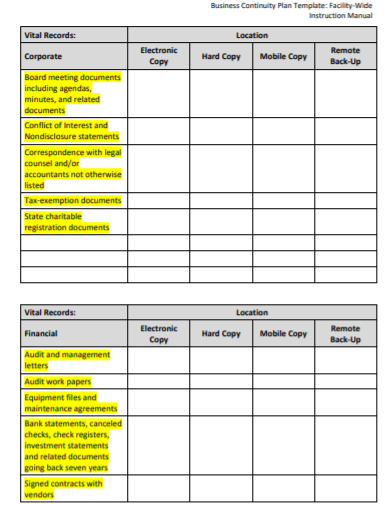
Size: 373 KB
5. Charity Business Plan for Orphans

Size: 70 KB
6. Charity Project Business Plan Template

Size: 394 KB
7. Small Business Charity Non Profit Plan
Size: 43 KB
8. Charity Business Plan Example
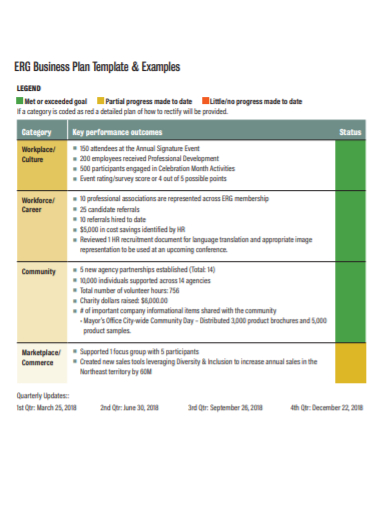
Size: 38 KB
9. Community Charity Shop Business Plan

10. Charity Commission Business Plan

Size: 12 MB
11. NGO Charity Business Plan Template

Size: 32 KB
What Is a Charity Business Plan?
A charity business plan is a document that provides a detailed description of the nonprofit organization. It also includes an outline of the business marketing strategy and techniques to secure volunteers and sponsors of the charity’s cause. In addition, it involves conducting a nonprofit analysis and other essential elements considering the influential factors in setting an organization.
How to Generate a Charity Business Plan?
A charity is different from a profit organization in how it handles its income and expenses. As a figurehead, you need to think as a businessman would. That said, you need to strategize and plan on how to secure business opportunities and how to handle various circumstances. Help more people by making your charity a success.
1. Conduct a Nonprofit SWOT Analysis
To know how your charity is operating and how you can better it, you must conduct a nonprofit SWOT analysis . This method will help you understand the standing of your nonprofit organization. Also, it will lead you to discover the strength of your organization and the weak areas that you need to improve. In addition, it will also uncover opportunities and help you detect the possible threats that will put your nonprofit business at risk.
2. Set Your Organizational Goals
The next step is to strengthen your organization’s cause by setting your goals. Goal-setting is a crucial step for all business ventures, may it be a profit or nonprofit. It is because your organizational goals will set the direction for all the upcoming plans and strategies. In addition, it will also strengthen your cause and help you come up with strategic methods to achieve your aim.
3. Devise a Nonprofit Marketing Plan
Now that you have your target, the next step in generating your charity business plan is to devise a nonprofit marketing plan . One way to secure and retain your foundation is to find people who would love to support your cause. To do that, you need to develop nonprofit marketing strategies . This action will boost the people’s awareness and persuade them to sponsor and volunteer for your organization.
4. Detail Your Nonprofit Budget
Another essential element to consider is your nonprofit budget . To gain more knowledge regarding your budget, you should conduct a financial analysis. To do this, you need to take note of your charity’s expenses and income. Take out essential paperwork that you might need in calculating for your budget plan . Remember to label each item on your budget sheet in detail to avoid confusion.
What are the best ways to raise funds for your charity?
There are numerous ways of fundraising for a charity. One of the best methods is to conduct fun and unique fundraising events. You can do all sorts of things for your event, such as bake sales, charity auctions, crowdfunding marathons, and boosting your online presence to ask for online donations. All of these are effective methods you can incorporate into your nonprofit fundraising plan .
What is a charity proposal?
A charity proposal is a document that will communicate your organization’s mission and vision, as well as your cause, to the potential prospects. This proposal letter will present your strategies and plans to secure sponsors and financial donations from charity volunteers. Writing this form is one method to raise funds for your charity. There are available business proposal templates online to make the process of composing this document easier.
What are some examples of impressive charity goals?
One example of a charity goal would be to increase staffing. Just like other businesses, nonprofit organizations need employees that will render their services. The more quality employees you have, the more people you can help. Another one is to gain more sponsors and volunteers. Most of the budget of charities comes from the donations of people who support a similar cause.
When doing business, a professional must not only look in one direction. Instead, you must do a complete three-sixty and look at all the possibilities for your organization. This statement applies to all business ventures, including nonprofits such as a charity. One way to do that is to evaluate the ins and outs of your business while devising a business plan. Generate a charity business plan as early as now to attain your goals.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
 (1).png)
How to Write a Charity Business Plan in 5 Easy Steps
Read Time: 3 Minutes
Posted: 16 Dec 2020
16 Dec 2020
Starting up your own charity or non-profit organisation can be extremely rewarding, but it’s important to set up a strong foundation before you even think about diving into fundraising. Planning ahead is the best way to ensure you’re having the biggest impact on your cause.
Although not run like a business in the traditional sense, charities definitely benefit from having a sound business plan – plus, it’ll make it easier to launch your charity and secure funding in the long run. Here’s exactly how to write your charity business plan in 5 easy steps.
Why Do Charities Need a Business Plan?
Ultimately, a business plan is an important document for a charity because it sets out your goals and the strategies you’ll be using to achieve these goals. Like a business makes a business plan to ensure it will be profitable, a charity makes a business plan to ensure it can benefit those it sets out to benefit.
Step 1: Say Who You Are
The first two sections of your business plan are your executive summary and charity description. In the executive summary, you’ll need to outline:
- Your personal details
- Your charity idea
- Your mission, goals and aims
- The type of organisation you’d like to set up
You’ll then go into more detail in your charity description, where you can talk about where your charity idea came from and why you believe it’s important to raise funds for this untapped cause.
You’ll also need to think about where you’ll be based and the advantages and disadvantages of this location.
Describe what you hope to achieve in the first, second and third years of your charity running, showing both ambition for your organisation but also that you know what is realistic to be able to achieve.
You may also want to brush on some of your unique selling points (USPs), explaining why your charity is necessary in the current climate and what makes you stand out from similar charities who may be raising awareness and funds for similar or the same cause.
Step 2: Understanding Your Market
It’s important to show that you’ve completed the necessary market research to understand how feasible your goals actually are. As well as knowing that there’s a community or group of people who would benefit from the funds raised for your charity, you also need to know that people will be willing to donate to you to create those funds in the first place.
Use polls or ask people face-to-face about their opinion on your cause, asking how much or how often (if at all) they’d be willing to donate to support you.
Furthermore, it’s important to know who else is raising awareness or funds for the same or a similar cause – in the business world, these would be known as your competitors. Check out what they’re doing and how you could do it better or target a more niche demographic of donors. It’s also great to look at other kinds of successful charities, who may not necessarily be supporting the same cause as you, for inspiration as to what works and what doesn’t.
We recommend completing a SWOT analysis as part of your market research. This helps you to identify yours and your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, giving a well-rounded view on where exactly you’d sit in the current market.
Step 3: Day-to-Day Operations
Next, you’ll need to get into the specifics of the day-to-day running of your charity. For this section, you should outline:
- Any resources you’ll need to run your charity
- Suppliers and other organisations you’ll work with
- Premises of your charity
- Equipment you’ll use
- Your process for taking payments from donors
- Any legal requirements like licenses you’ll need, e.g. for preparing food
- Any insurance you have or will need
You’ll also need to write a small biography for each person who is important to the running of your charity, including their role and their experience showing why they’re perfect for the role. Important people include the management team and any trustees. If this is set to change in the immediate future, make sure to include an overview of any planned changes to your management structure.
Finally, using your SWOT analysis, write down any skills gaps you have in your team and how you plan to fill these gaps.
Step 4: Social Impact
Whereas a regular business would need to see a financial return, a charity also needs to show a social impact. This is the difference you make for the communities and people you work with, and one of the most important parts of your charity business plan.
As well as saying what kind of impact you want to achieve for your chosen cause, you’ll also need to state what you’re going to measure to prove this impact and how you’re going to measure it. And, not forgetting, how you’ll use your learnings to keep adapting your processes.
Another important question to ask yourself for this section is: how are people going to find out about your charity? Luckily, we’ve come up with 20 budget-friendly charity marketing ideas to help give you some inspiration!
Step 5: Finances
In this section, you’ll need to outline your costs and expenditure. As great as your charity idea is, it’s nothing without a well-thought-out financial forecast.
You’ll need to include:
- Predicted costs and expenditure (using research to back this up)
- Main source of income (donors, trustees etc. and what you’d expect them to give)
- Pricing strategy if you plan on selling products or services to fund your charity
- Cash flow forecasts
- Costs table
By preparing for all eventualities with your business plan, you’re turning your charity idea into a reality - and that’s something you should be really proud of. We hope this guide has given you plenty of information to include in your business plan, and you can always view our 10-step checklist for writing a business plan for more information on this.

About the Author
Related posts.

Dirty Secrets: British Workers Reveal Gross Office Habits

Employee Spotlight: Laura Mucklow

How a Short Run Perfect Bound Book Is Made
Iso certified.
Bluetree Print Limited T/A has been certified to ISO 9001:2015 & ISO 14001:2015 for the following scope:
ISO 9001:2015: The production and supply of digitally, lithographically and nanographically printed products on paper, board and plastic substrates at the Manvers sites.
ISO 14001:2015: The production and supply of digitally, lithographically and nanographically printed products on paper, board and plastic substrates at the Manvers sites.
Certification is subject to periodic surveillance and re-assessment. For further information regarding the validity of the certification please Contact us for Certification Help. Call our helpful team today!
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
It's time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can't wait

Quil Lawrence

Matt and Helen Perry at their home in Yulee, Fla. Michelle Bruzzese for NPR hide caption
Matt and Helen Perry at their home in Yulee, Fla.
When Matt and Helen Perry first met in 2010, he had been a U.S. Marine long enough to form two strong opinions. He didn't like the U.S. Army, and he didn't like officers — which he told her on their first date.
"And I was, you know, an Army medical officer," Helen recalls.
They got married anyhow, and Matt went on the last of his four combat deployments while Helen worked at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center outside Washington, D.C. Her worst fear — that she'd see Matt come in on a medevac — never came to pass. She did start to worry though, about the military medical system that was treating troops and their families. In 2013 the Perrys were stationed at Fort Stewart, Ga.

U.S. Marine Sgt. Matt Perry on deployment in Djibouti, 2012 Matt and Helen Perry hide caption
"They were looking at closing Winn Army Medical Community Medical Hospital," says Perry.
Winn Hospital cares for tens of thousands of troops and more than twice that many family members and military retirees living near Fort Stewart. But the Pentagon was abuzz with plans to cut military medical costs, especially on families and retirees, by outsourcing them to local private health care — much to the chagrin of local providers, Helen Perry recalls.
"I vividly remember them putting out an article in the newspaper that was like ... 'We cannot absorb your obstetrical care. We can't absorb your inpatient care. We do not have the resources to absorb the amount of care that you would then be pushing out into the community,'" says Perry.
Obstetrics may not spring to mind when people think about military medicine, but troops get to have families. With the Pentagon pushing them off base to find care, the military hospitals lost the patient base they needed to justify keeping specialty clinicians. It didn't make sense to Perry.
"I was saying, well, why don't we just get the services? Why don't we get cardiology? We had it at one time, why did we lose it? Oh, well, we weren't seeing enough patients," she says.
The business end of cost-cutting
To Perry it looked like a death spiral — downsizing to the point where the military hospital is no longer viable . She even suspected some of the hospitals were attempting to avoid closure by keeping hold of patients they couldn't actually treat, to keep up numbers and justify staying open. When Perry asked questions, as a critical care nurse and junior officer, no one wanted to hear it.
"It's like, 'Lt. Perry, that's beyond you. Do your job. Stay quiet,'" she says.
She wasn't wrong though. She was just on the business end of a decades-long realignment, where the four branches of the military combined their medical services under one health agency and tried to cut costs. This year the Department of Defense has finally admitted that it's not going as planned.
"All these challenges and changes have created and affected our ability to generate and sustain a medically ready force and a ready medical force," says Dr. David Smith, deputy assistant secretary of Defense for health.

Army Capt. and critical care nurse Helen Perry at the Combat Support Hospital in Fort Eisenhower, Ga., in 2018. Matt and Helen Perry hide caption
Army Capt. and critical care nurse Helen Perry at the Combat Support Hospital in Fort Eisenhower, Ga., in 2018.
Smith is talking about two of the three missions of military health. A "medically ready force" means keeping the country's army in good health. A "ready medical force" means training up enough doctors and nurses to keep that army healthy and treat the wounds of war. There's a third part though: taking care of all the military family members who get dragged across the country every time a service member gets ordered to a new base.
The Pentagon has been trying to outsource the less war-related parts, says John Whitley, former acting secretary of the Army.
"We don't want to go back to the days of ... not having the trauma surgeons, the emergency medicine physicians, the critical care physicians we need, and instead having a force of pediatricians and obstetricians and family practice docs," he told NPR.
Of course, troops might not agree that keeping their families healthy is a lower priority.
"As if it doesn't matter to the war fighter whether or not their family members can access quality care," says Karen Ruedisueli with the Military Officers Association of America.

National Security
The self-proclaimed 'bipolar general' is waging war on the stigma of mental illness.
"If they're hearing from the family back home that they're struggling to get medical care, they can't focus on the mission," she says.
"And then my husband started having seizures"
Americans join the military for patriotic, but also practical, reasons and the quality of health care affects recruiting. In recent years, surveys show that health care is a growing concern for active duty families and also retirees as Helen and Matt Perry soon discovered.
"I stayed for two years at Fort Stewart, and I was seeing the results of families not having good access to care. And then my husband started having seizures," she says.
Matt's seizures hit in July of 2014, six years after a series of blast injuries in Afghanistan had left him with a traumatic brain injury.
"We knew he had a TBI. He got blown up three times in Afghanistan in 2008, like big booms. And we knew things were a little bit harder to learn for him after that. He was a little bit more forgetful. I mean, he had all of the classic sort of early TBI stuff that we see from, from most of our guys who've been blown up, but we just didn't know how bad it was," she says.
His first seizure lasted several minutes and he stopped breathing. A few hours later, he seized again and Helen took him to the nearest emergency room.
"He woke up in the ICU. He didn't know me, didn't know his name, didn't know anything," she says.
"We were not at a military facility. So they kept asking me like, did he ever have infantile seizures as a child? I would say, he got blown up really bad. And they would say, you know, all those explosions you see on television, that's not really how it happens," she says.
Matt's debilitating injuries sent the Perrys on a painful odyssey of seeking care within the military, trying to get Helen's Army superiors to assign her near the Marine base where Matt could get treated, and finally getting Matt the right medical discharge and the benefits he'd earned. Helen eventually left active duty and became his full-time caregiver.
"That's where we started to kind of find out all of the challenges with Tricare," she says.
Tricare is the military health care program for troops, families and retirees - which used to mean just going to almost any doctor and Tricare paid for it. In recent years the cost to military families has shot up , and millions of troops rely on Medicaid in addition to Tricare. And as the Perrys discovered, it's gotten harder to find doctors who accept it. They moved to Daytona Beach for a nursing job Helen landed, but it didn't work for Matt's care, or Helen's, or their newly arrived baby boy in 2021.

"We could not find anyone to accept Tricare, period. I work in health care so I knew all the people, so I was calling around trying to find a primary care provider," says Helen.
But the answer was consistent.
" 'Sorry, we don't take Tricare.' 'Sorry, we're not open to new patients.' We couldn't find a pediatrician for our son. Same thing — 'Sorry, we don't take Tricare,' " she says.
Not only is there a nationwide shortage of health care professionals after that pandemic, but, like Medicaid, Tricare reimburses at a lower rate than private health insurance. Helen says doctors told her they just couldn't afford to take Tricare patients. And she was hearing the same thing from other military caregivers nationwide.
"I got onto our little online forum, and I said, is anybody else having problems finding providers accepting Tricare?"
The replies came in a tidal wave.
"Can't find anybody to take us, we're commuting two hours, we're commuting five hours," she says.
The Perrys moved to the Jacksonville area in large part because that's where they found providers. In the meantime though, Helen was making lists of military communities where people can't find care, including many bases located in federally designated health care shortage areas.
NPR contacted a dozen families with similar complaints. Notably, the majority declined to be interviewed on the record, out of concern they'd get in trouble with their command. They told the same stories: They can't get care on base, and they can't find Tricare appointments in town. A Pentagon Inspector General Report echoed their complaints.
"Well, you can't get care at the military, so now you're gonna get care through Tricare. When they both fail, which is what they're currently doing, where are service members expected to go?" says Helen Perry.

The answer to veterans homelessness could be one of LA's most expensive neighborhoods
Pentagon about-face on private care.
David Smith, the deputy assistant secretary of Defense, says the Pentagon has realized the private sector doesn't have any extra capacity to lean on, and after a decade of pushing private care, the Pentagon will now do the opposite.
"We're having difficulties with access across the system. And so what we've concluded is bringing more into our system will actually have the best benefit. I think that's part of the epiphany," he told NPR.
That epiphany took the form of a recent DOD internal memo titled " Stabilizing and Improving the Military Health System ." The memo looks back at a decade's worth of downsizing and outsourcing and concludes, "This has resulted in increasing overall health care costs for the Department and missing readiness opportunities for the Force."
The memo calls on the Military Health System to grow and attract more patients back on to base for their health care. Smith says the Pentagon will train or hire more doctors and nurses to re-fill its clinics. The memo directs the Pentagon to review all medical staffing levels by June 30th. It may be the start of another long and monumental attempt to change military health care.
New memories
Helen Perry is glad to hear a fix is coming, but she hasn't seen any sign of that memo in action yet. Matt is making new memories with their son and now a baby daughter. He's seems at peace with the memories that he's lost.
"Stuff from way, way back there, that's kind of wiped clean. That hard drive's gone," he says.

Helen and Matt Perry at Helen's promotion to captain in July 2015, at San Antonio Military Medical Center, Texas. Matt and Helen Perry hide caption
Helen and Matt Perry at Helen's promotion to captain in July 2015, at San Antonio Military Medical Center, Texas.
That's a blessing in one way. Matt doesn't remember his time at war, so he doesn't have PTSD. When he gets frustrated, he calls one of his Marine battle-buddies. They remember.
"When I get a lot of anxiety or I just need to get away, I talk to them. I used to see a ... therapist. And that was OK, but they don't understand what I went through. Once I started talking to my buddies, man, that is the best therapy you can have right there. And it's free," says Matt.
Matt knows his biggest champion is Helen. Now retired from the reserves, she does aid work in conflict zones, like Ukraine, as a critical care nurse. Still, Matt worries that he's holding her back.
"There's a lot of stuff I wish was different. Like I know she wanted to become a doctor. I know she wants to do a lot more humanitarian work, but ... there's always that worry that something happens to me while she's gone," he says.
They juggle their two young kids between them, but being Matt's caregiver can be a full-time job. That, along with having been an Army nurse and a Tricare patient gives Helen some expertise she thinks the Pentagon and Congress might lack.
"I can speak to it from an active duty officer, from a reserve officer ... I can speak to it as a medical provider currently working in the health care system, and as a caregiver. I can speak to it from every angle, and I want to know that they know because I don't think that they do. Because I think if they did, they would be doing different things," she says.
Recently, Matt's condition has gotten unstable again. That means they are looking, again, for a new medical team that accepts Tricare.
- Health Care

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fill Out A Business Plan In Minutes. Easy To Use, Save, & Print. Try Free Today! Create, Download, & Print A Business Plan - Simple Platform - Try Free Today!
Fill In Professional Business Plan Templates. Download & Print Instantly- 100% Free! Answer Easy Questions & Create In Minutes - Save To PDF & Word - Jumpstart Your Business!
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a charity business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of charity company that you documented in your company overview.
This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization's background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more. Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program.
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit's mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising. Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit's operating environment. What if the sources of income that ...
Step 3: Outline. Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets). An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end.
Writing a charity business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and ...
confidential page 4 2. organization overview 2.1 organization background 2.2 mission statement and vision statement 2.3 opportunity
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE DISCLAIMER Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for reference only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accura cy, reliability,
Updated January 09, 2023. A non-profit business plan is a written roadmap for a non-profit organization. It serves to communicate the core purpose, funding needs, and action plan of the organization. Non-profit business plans typically describe in detail the organization's mission and values, administrative structure, staffing, industry analysis, revenue and donations, key milestones, and ...
Executive summary. The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That's because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan - the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization. Write it as though you might ...
3. Products, Programs, and Services. The products, programs, and services section of a nonprofit business plan should describe specific products, programs, and services that will offer to its beneficiaries. Your nonprofit may or may not have all products, programs, and services to offer. So, write this section depending on your organization's ...
The charity business plan template is designed for non-profit organizations and social enterprises that want to develop a business plan that outlines their mission, goals, and strategies. The template provides an organized and systematic way to create a business plan that takes into consideration the organization's resources, goals, and objectives.
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here. Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan. Example #1 - Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) - a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL. Example #2 - Church of the Sacred Heart - a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO.
A business plan template for charity organizations offers a range of benefits to help leaders and managers effectively navigate the complex world of fundraising and social impact. Some of the key benefits include: Streamlining the planning process by providing a structured framework to outline the organization's mission, vision, and goals.
A sales forecast estimates the sales you expect. Multiply your planned prices for products, services or typical donation amounts by the number of customers you expect. Put this to a timescale of a month, quarter or year. You can refer to your projections in later stages and compare your performance.
The best business plans aren't long and complex; they explain only the most important information - what you want to achieve, how you will get there and the things you need to do along the way. It's best to tackle a business plan in small chunks. The Prince's Trust Business Plan Pack can help. This is The Business Plan divided into ...
A charity business plan isn't just a document of many pages. When you define it like that, it is said to reduce its actual value. A charitable business plan details the products and services your nonprofit organization provides. A charity business plan also contains the people on your team, the community you work for, your financials, goals ...
Charity Business Plan Template in PDF. culturalevolution.org. Details. File Format. PDF; Size: 483.9 KB Download Now. Creating a business plan can easily turn into a tedious task, especially if prepared from scratch. We are sure having a useful sample of the same can make the task much easier as you will have something to refer to at all times ...
A business plan is a clear and documented account of the activities you have decided to undertake over a given period of time, and the cost of making them happen. It should cover objectives and strategies, and enable the organisation to deliver more effectively. Business plans are as individual as the groups that develop them, but some common ...
With a business plan, you can set your expectations and maneuver a process in achieving it. Find out more about a business plan and how it affects charity projects with this article. Continue reading below. FREE 12+ Charity Business Plan Samples 1. Charity Fundraising Plan Template
Business plan good practice guidance. 29/01/2024. A business plan is a document describing the key financial and organisational aspects of your business. It focuses on the overall organisation, not specific activities, and is a required as part of your funding application. By reading this guidance you'll get help with how to develop a business ...
3. Devise a Nonprofit Marketing Plan. Now that you have your target, the next step in generating your charity business plan is to devise a nonprofit marketing plan. One way to secure and retain your foundation is to find people who would love to support your cause. To do that, you need to develop nonprofit marketing strategies.
Step 1: Say Who You Are. The first two sections of your business plan are your executive summary and charity description. In the executive summary, you'll need to outline: Your personal details. Your charity idea. Your mission, goals and aims. The type of organisation you'd like to set up.
hsr.ca.gov
2024 Draft Business Plan. Required by PUC Section 185033. Every two years (even years) 2022 Business Plan. Included limited updates to forecasts at the time. COVID impacted release date of final 2020 Business Plan to 2021, so the 2022 updates were more limited. 2023 Program Update Report (PUR)
In 2006 a 15-year plan set national targets to raise research-and-development ... According to Jie Mao of the University of International Business and Economics in Beijing and his co-authors ...
The memo calls on the Military Health System to grow and attract more patients back on to base for their health care. Smith says the Pentagon will train or hire more doctors and nurses to re-fill ...