
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


6.1: Introduction
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 8987

- Terri Russ@Saint Mary’s College
- Millersville University via Public Speaking Project
Chapter Objectives
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- Understand and explain the importance of critical thinking
- Identify the core skills associated with critical thinking
- Demonstrate the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning
- Construct a logically sound and well-reasoned argument
- Avoid the various fallacies that can arise through the misuse of logic
- Apply chapter concepts in final questions and activities
As we meander through our daily routines, we are surrounded by numerous messages and people trying to get our attention and convince us to do something. We sign into our e-mail accounts and are bombarded with sales pitches to help us get rich quick or promise to fix all of our embarrassing physical problems. We drive to school and see billboards touting tantalizing restaurants or pitching local political candidates. We converse with our friends and family about current events like the crazy car thief who tried to avoid the police by driving down train tracks right into an oncoming train. Throughout all of these exchanges, we must constantly strive to make sense of the messages and determine which are true and which are not true, which are probable and which are improbable, which are intended and which are unintended. When we do this we practice critical thinking . We evaluate the arguments presented and determine if their logic is sound or if they rely on fallacies to build their case. In this chapter you will learn how to use critical thinking in all areas of your life, including preparing and presenting speeches. You will also learn how to construct a logical argument that avoids the pitfalls of fallacious thinking.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Hughes RG, editor. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008 Apr.

Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses.
Chapter 6 clinical reasoning, decisionmaking, and action: thinking critically and clinically.
Patricia Benner ; Ronda G. Hughes ; Molly Sutphen .
Affiliations
This chapter examines multiple thinking strategies that are needed for high-quality clinical practice. Clinical reasoning and judgment are examined in relation to other modes of thinking used by clinical nurses in providing quality health care to patients that avoids adverse events and patient harm. The clinician’s ability to provide safe, high-quality care can be dependent upon their ability to reason, think, and judge, which can be limited by lack of experience. The expert performance of nurses is dependent upon continual learning and evaluation of performance.
- Critical Thinking
Nursing education has emphasized critical thinking as an essential nursing skill for more than 50 years. 1 The definitions of critical thinking have evolved over the years. There are several key definitions for critical thinking to consider. The American Philosophical Association (APA) defined critical thinking as purposeful, self-regulatory judgment that uses cognitive tools such as interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, and explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations on which judgment is based. 2 A more expansive general definition of critical thinking is
. . . in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking. It presupposes assent to rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem solving abilities and a commitment to overcome our native egocentrism and sociocentrism. Every clinician must develop rigorous habits of critical thinking, but they cannot escape completely the situatedness and structures of the clinical traditions and practices in which they must make decisions and act quickly in specific clinical situations. 3
There are three key definitions for nursing, which differ slightly. Bittner and Tobin defined critical thinking as being “influenced by knowledge and experience, using strategies such as reflective thinking as a part of learning to identify the issues and opportunities, and holistically synthesize the information in nursing practice” 4 (p. 268). Scheffer and Rubenfeld 5 expanded on the APA definition for nurses through a consensus process, resulting in the following definition:
Critical thinking in nursing is an essential component of professional accountability and quality nursing care. Critical thinkers in nursing exhibit these habits of the mind: confidence, contextual perspective, creativity, flexibility, inquisitiveness, intellectual integrity, intuition, openmindedness, perseverance, and reflection. Critical thinkers in nursing practice the cognitive skills of analyzing, applying standards, discriminating, information seeking, logical reasoning, predicting, and transforming knowledge 6 (Scheffer & Rubenfeld, p. 357).
The National League for Nursing Accreditation Commission (NLNAC) defined critical thinking as:
the deliberate nonlinear process of collecting, interpreting, analyzing, drawing conclusions about, presenting, and evaluating information that is both factually and belief based. This is demonstrated in nursing by clinical judgment, which includes ethical, diagnostic, and therapeutic dimensions and research 7 (p. 8).
These concepts are furthered by the American Association of Colleges of Nurses’ definition of critical thinking in their Essentials of Baccalaureate Nursing :
Critical thinking underlies independent and interdependent decision making. Critical thinking includes questioning, analysis, synthesis, interpretation, inference, inductive and deductive reasoning, intuition, application, and creativity 8 (p. 9).
Course work or ethical experiences should provide the graduate with the knowledge and skills to:
- Use nursing and other appropriate theories and models, and an appropriate ethical framework;
- Apply research-based knowledge from nursing and the sciences as the basis for practice;
- Use clinical judgment and decision-making skills;
- Engage in self-reflective and collegial dialogue about professional practice;
- Evaluate nursing care outcomes through the acquisition of data and the questioning of inconsistencies, allowing for the revision of actions and goals;
- Engage in creative problem solving 8 (p. 10).
Taken together, these definitions of critical thinking set forth the scope and key elements of thought processes involved in providing clinical care. Exactly how critical thinking is defined will influence how it is taught and to what standard of care nurses will be held accountable.
Professional and regulatory bodies in nursing education have required that critical thinking be central to all nursing curricula, but they have not adequately distinguished critical reflection from ethical, clinical, or even creative thinking for decisionmaking or actions required by the clinician. Other essential modes of thought such as clinical reasoning, evaluation of evidence, creative thinking, or the application of well-established standards of practice—all distinct from critical reflection—have been subsumed under the rubric of critical thinking. In the nursing education literature, clinical reasoning and judgment are often conflated with critical thinking. The accrediting bodies and nursing scholars have included decisionmaking and action-oriented, practical, ethical, and clinical reasoning in the rubric of critical reflection and thinking. One might say that this harmless semantic confusion is corrected by actual practices, except that students need to understand the distinctions between critical reflection and clinical reasoning, and they need to learn to discern when each is better suited, just as students need to also engage in applying standards, evidence-based practices, and creative thinking.
The growing body of research, patient acuity, and complexity of care demand higher-order thinking skills. Critical thinking involves the application of knowledge and experience to identify patient problems and to direct clinical judgments and actions that result in positive patient outcomes. These skills can be cultivated by educators who display the virtues of critical thinking, including independence of thought, intellectual curiosity, courage, humility, empathy, integrity, perseverance, and fair-mindedness. 9
The process of critical thinking is stimulated by integrating the essential knowledge, experiences, and clinical reasoning that support professional practice. The emerging paradigm for clinical thinking and cognition is that it is social and dialogical rather than monological and individual. 10–12 Clinicians pool their wisdom and multiple perspectives, yet some clinical knowledge can be demonstrated only in the situation (e.g., how to suction an extremely fragile patient whose oxygen saturations sink too low). Early warnings of problematic situations are made possible by clinicians comparing their observations to that of other providers. Clinicians form practice communities that create styles of practice, including ways of doing things, communication styles and mechanisms, and shared expectations about performance and expertise of team members.
By holding up critical thinking as a large umbrella for different modes of thinking, students can easily misconstrue the logic and purposes of different modes of thinking. Clinicians and scientists alike need multiple thinking strategies, such as critical thinking, clinical judgment, diagnostic reasoning, deliberative rationality, scientific reasoning, dialogue, argument, creative thinking, and so on. In particular, clinicians need forethought and an ongoing grasp of a patient’s health status and care needs trajectory, which requires an assessment of their own clarity and understanding of the situation at hand, critical reflection, critical reasoning, and clinical judgment.
Critical Reflection, Critical Reasoning, and Judgment
Critical reflection requires that the thinker examine the underlying assumptions and radically question or doubt the validity of arguments, assertions, and even facts of the case. Critical reflective skills are essential for clinicians; however, these skills are not sufficient for the clinician who must decide how to act in particular situations and avoid patient injury. For example, in everyday practice, clinicians cannot afford to critically reflect on the well-established tenets of “normal” or “typical” human circulatory systems when trying to figure out a particular patient’s alterations from that typical, well-grounded understanding that has existed since Harvey’s work in 1628. 13 Yet critical reflection can generate new scientifically based ideas. For example, there is a lack of adequate research on the differences between women’s and men’s circulatory systems and the typical pathophysiology related to heart attacks. Available research is based upon multiple, taken-for-granted starting points about the general nature of the circulatory system. As such, critical reflection may not provide what is needed for a clinician to act in a situation. This idea can be considered reasonable since critical reflective thinking is not sufficient for good clinical reasoning and judgment. The clinician’s development of skillful critical reflection depends upon being taught what to pay attention to, and thus gaining a sense of salience that informs the powers of perceptual grasp. The powers of noticing or perceptual grasp depend upon noticing what is salient and the capacity to respond to the situation.
Critical reflection is a crucial professional skill, but it is not the only reasoning skill or logic clinicians require. The ability to think critically uses reflection, induction, deduction, analysis, challenging assumptions, and evaluation of data and information to guide decisionmaking. 9 , 14 , 15 Critical reasoning is a process whereby knowledge and experience are applied in considering multiple possibilities to achieve the desired goals, 16 while considering the patient’s situation. 14 It is a process where both inductive and deductive cognitive skills are used. 17 Sometimes clinical reasoning is presented as a form of evaluating scientific knowledge, sometimes even as a form of scientific reasoning. Critical thinking is inherent in making sound clinical reasoning. 18
An essential point of tension and confusion exists in practice traditions such as nursing and medicine when clinical reasoning and critical reflection become entangled, because the clinician must have some established bases that are not questioned when engaging in clinical decisions and actions, such as standing orders. The clinician must act in the particular situation and time with the best clinical and scientific knowledge available. The clinician cannot afford to indulge in either ritualistic unexamined knowledge or diagnostic or therapeutic nihilism caused by radical doubt, as in critical reflection, because they must find an intelligent and effective way to think and act in particular clinical situations. Critical reflection skills are essential to assist practitioners to rethink outmoded or even wrong-headed approaches to health care, health promotion, and prevention of illness and complications, especially when new evidence is available. Breakdowns in practice, high failure rates in particular therapies, new diseases, new scientific discoveries, and societal changes call for critical reflection about past assumptions and no-longer-tenable beliefs.
Clinical reasoning stands out as a situated, practice-based form of reasoning that requires a background of scientific and technological research-based knowledge about general cases, more so than any particular instance. It also requires practical ability to discern the relevance of the evidence behind general scientific and technical knowledge and how it applies to a particular patient. In dong so, the clinician considers the patient’s particular clinical trajectory, their concerns and preferences, and their particular vulnerabilities (e.g., having multiple comorbidities) and sensitivities to care interventions (e.g., known drug allergies, other conflicting comorbid conditions, incompatible therapies, and past responses to therapies) when forming clinical decisions or conclusions.
Situated in a practice setting, clinical reasoning occurs within social relationships or situations involving patient, family, community, and a team of health care providers. The expert clinician situates themselves within a nexus of relationships, with concerns that are bounded by the situation. Expert clinical reasoning is socially engaged with the relationships and concerns of those who are affected by the caregiving situation, and when certain circumstances are present, the adverse event. Halpern 19 has called excellent clinical ethical reasoning “emotional reasoning” in that the clinicians have emotional access to the patient/family concerns and their understanding of the particular care needs. Expert clinicians also seek an optimal perceptual grasp, one based on understanding and as undistorted as possible, based on an attuned emotional engagement and expert clinical knowledge. 19 , 20
Clergy educators 21 and nursing and medical educators have begun to recognize the wisdom of broadening their narrow vision of rationality beyond simple rational calculation (exemplified by cost-benefit analysis) to reconsider the need for character development—including emotional engagement, perception, habits of thought, and skill acquisition—as essential to the development of expert clinical reasoning, judgment, and action. 10 , 22–24 Practitioners of engineering, law, medicine, and nursing, like the clergy, have to develop a place to stand in their discipline’s tradition of knowledge and science in order to recognize and evaluate salient evidence in the moment. Diagnostic confusion and disciplinary nihilism are both threats to the clinician’s ability to act in particular situations. However, the practice and practitioners will not be self-improving and vital if they cannot engage in critical reflection on what is not of value, what is outmoded, and what does not work. As evidence evolves and expands, so too must clinical thought.
Clinical judgment requires clinical reasoning across time about the particular, and because of the relevance of this immediate historical unfolding, clinical reasoning can be very different from the scientific reasoning used to formulate, conduct, and assess clinical experiments. While scientific reasoning is also socially embedded in a nexus of social relationships and concerns, the goal of detached, critical objectivity used to conduct scientific experiments minimizes the interactive influence of the research on the experiment once it has begun. Scientific research in the natural and clinical sciences typically uses formal criteria to develop “yes” and “no” judgments at prespecified times. The scientist is always situated in past and immediate scientific history, preferring to evaluate static and predetermined points in time (e.g., snapshot reasoning), in contrast to a clinician who must always reason about transitions over time. 25 , 26
Techne and Phronesis
Distinctions between the mere scientific making of things and practice was first explored by Aristotle as distinctions between techne and phronesis. 27 Learning to be a good practitioner requires developing the requisite moral imagination for good practice. If, for example, patients exercise their rights and refuse treatments, practitioners are required to have the moral imagination to understand the probable basis for the patient’s refusal. For example, was the refusal based upon catastrophic thinking, unrealistic fears, misunderstanding, or even clinical depression?
Techne, as defined by Aristotle, encompasses the notion of formation of character and habitus 28 as embodied beings. In Aristotle’s terms, techne refers to the making of things or producing outcomes. 11 Joseph Dunne defines techne as “the activity of producing outcomes,” and it “is governed by a means-ends rationality where the maker or producer governs the thing or outcomes produced or made through gaining mastery over the means of producing the outcomes, to the point of being able to separate means and ends” 11 (p. 54). While some aspects of medical and nursing practice fall into the category of techne, much of nursing and medical practice falls outside means-ends rationality and must be governed by concern for doing good or what is best for the patient in particular circumstances, where being in a relationship and discerning particular human concerns at stake guide action.
Phronesis, in contrast to techne, includes reasoning about the particular, across time, through changes or transitions in the patient’s and/or the clinician’s understanding. As noted by Dunne, phronesis is “characterized at least as much by a perceptiveness with regard to concrete particulars as by a knowledge of universal principles” 11 (p. 273). This type of practical reasoning often takes the form of puzzle solving or the evaluation of immediate past “hot” history of the patient’s situation. Such a particular clinical situation is necessarily particular, even though many commonalities and similarities with other disease syndromes can be recognized through signs and symptoms and laboratory tests. 11 , 29 , 30 Pointing to knowledge embedded in a practice makes no claim for infallibility or “correctness.” Individual practitioners can be mistaken in their judgments because practices such as medicine and nursing are inherently underdetermined. 31
While phronetic knowledge must remain open to correction and improvement, real events, and consequences, it cannot consistently transcend the institutional setting’s capacities and supports for good practice. Phronesis is also dependent on ongoing experiential learning of the practitioner, where knowledge is refined, corrected, or refuted. The Western tradition, with the notable exception of Aristotle, valued knowledge that could be made universal and devalued practical know-how and experiential learning. Descartes codified this preference for formal logic and rational calculation.
Aristotle recognized that when knowledge is underdetermined, changeable, and particular, it cannot be turned into the universal or standardized. It must be perceived, discerned, and judged, all of which require experiential learning. In nursing and medicine, perceptual acuity in physical assessment and clinical judgment (i.e., reasoning across time about changes in the particular patient or the clinician’s understanding of the patient’s condition) fall into the Greek Aristotelian category of phronesis. Dewey 32 sought to rescue knowledge gained by practical activity in the world. He identified three flaws in the understanding of experience in Greek philosophy: (1) empirical knowing is the opposite of experience with science; (2) practice is reduced to techne or the application of rational thought or technique; and (3) action and skilled know-how are considered temporary and capricious as compared to reason, which the Greeks considered as ultimate reality.
In practice, nursing and medicine require both techne and phronesis. The clinician standardizes and routinizes what can be standardized and routinized, as exemplified by standardized blood pressure measurements, diagnoses, and even charting about the patient’s condition and treatment. 27 Procedural and scientific knowledge can often be formalized and standardized (e.g., practice guidelines), or at least made explicit and certain in practice, except for the necessary timing and adjustments made for particular patients. 11 , 22
Rational calculations available to techne—population trends and statistics, algorithms—are created as decision support structures and can improve accuracy when used as a stance of inquiry in making clinical judgments about particular patients. Aggregated evidence from clinical trials and ongoing working knowledge of pathophysiology, biochemistry, and genomics are essential. In addition, the skills of phronesis (clinical judgment that reasons across time, taking into account the transitions of the particular patient/family/community and transitions in the clinician’s understanding of the clinical situation) will be required for nursing, medicine, or any helping profession.
Thinking Critically
Being able to think critically enables nurses to meet the needs of patients within their context and considering their preferences; meet the needs of patients within the context of uncertainty; consider alternatives, resulting in higher-quality care; 33 and think reflectively, rather than simply accepting statements and performing tasks without significant understanding and evaluation. 34 Skillful practitioners can think critically because they have the following cognitive skills: information seeking, discriminating, analyzing, transforming knowledge, predicating, applying standards, and logical reasoning. 5 One’s ability to think critically can be affected by age, length of education (e.g., an associate vs. a baccalaureate decree in nursing), and completion of philosophy or logic subjects. 35–37 The skillful practitioner can think critically because of having the following characteristics: motivation, perseverance, fair-mindedness, and deliberate and careful attention to thinking. 5 , 9
Thinking critically implies that one has a knowledge base from which to reason and the ability to analyze and evaluate evidence. 38 Knowledge can be manifest by the logic and rational implications of decisionmaking. Clinical decisionmaking is particularly influenced by interpersonal relationships with colleagues, 39 patient conditions, availability of resources, 40 knowledge, and experience. 41 Of these, experience has been shown to enhance nurses’ abilities to make quick decisions 42 and fewer decision errors, 43 support the identification of salient cues, and foster the recognition and action on patterns of information. 44 , 45
Clinicians must develop the character and relational skills that enable them to perceive and understand their patient’s needs and concerns. This requires accurate interpretation of patient data that is relevant to the specific patient and situation. In nursing, this formation of moral agency focuses on learning to be responsible in particular ways demanded by the practice, and to pay attention and intelligently discern changes in patients’ concerns and/or clinical condition that require action on the part of the nurse or other health care workers to avert potential compromises to quality care.
Formation of the clinician’s character, skills, and habits are developed in schools and particular practice communities within a larger practice tradition. As Dunne notes,
A practice is not just a surface on which one can display instant virtuosity. It grounds one in a tradition that has been formed through an elaborate development and that exists at any juncture only in the dispositions (slowly and perhaps painfully acquired) of its recognized practitioners. The question may of course be asked whether there are any such practices in the contemporary world, whether the wholesale encroachment of Technique has not obliterated them—and whether this is not the whole point of MacIntyre’s recipe of withdrawal, as well as of the post-modern story of dispossession 11 (p. 378).
Clearly Dunne is engaging in critical reflection about the conditions for developing character, skills, and habits for skillful and ethical comportment of practitioners, as well as to act as moral agents for patients so that they and their families receive safe, effective, and compassionate care.
Professional socialization or professional values, while necessary, do not adequately address character and skill formation that transform the way the practitioner exists in his or her world, what the practitioner is capable of noticing and responding to, based upon well-established patterns of emotional responses, skills, dispositions to act, and the skills to respond, decide, and act. 46 The need for character and skill formation of the clinician is what makes a practice stand out from a mere technical, repetitious manufacturing process. 11 , 30 , 47
In nursing and medicine, many have questioned whether current health care institutions are designed to promote or hinder enlightened, compassionate practice, or whether they have deteriorated into commercial institutional models that focus primarily on efficiency and profit. MacIntyre points out the links between the ongoing development and improvement of practice traditions and the institutions that house them:
Lack of justice, lack of truthfulness, lack of courage, lack of the relevant intellectual virtues—these corrupt traditions, just as they do those institutions and practices which derive their life from the traditions of which they are the contemporary embodiments. To recognize this is of course also to recognize the existence of an additional virtue, one whose importance is perhaps most obvious when it is least present, the virtue of having an adequate sense of the traditions to which one belongs or which confront one. This virtue is not to be confused with any form of conservative antiquarianism; I am not praising those who choose the conventional conservative role of laudator temporis acti. It is rather the case that an adequate sense of tradition manifests itself in a grasp of those future possibilities which the past has made available to the present. Living traditions, just because they continue a not-yet-completed narrative, confront a future whose determinate and determinable character, so far as it possesses any, derives from the past 30 (p. 207).
It would be impossible to capture all the situated and distributed knowledge outside of actual practice situations and particular patients. Simulations are powerful as teaching tools to enable nurses’ ability to think critically because they give students the opportunity to practice in a simplified environment. However, students can be limited in their inability to convey underdetermined situations where much of the information is based on perceptions of many aspects of the patient and changes that have occurred over time. Simulations cannot have the sub-cultures formed in practice settings that set the social mood of trust, distrust, competency, limited resources, or other forms of situated possibilities.
One of the hallmark studies in nursing providing keen insight into understanding the influence of experience was a qualitative study of adult, pediatric, and neonatal intensive care unit (ICU) nurses, where the nurses were clustered into advanced beginner, intermediate, and expert level of practice categories. The advanced beginner (having up to 6 months of work experience) used procedures and protocols to determine which clinical actions were needed. When confronted with a complex patient situation, the advanced beginner felt their practice was unsafe because of a knowledge deficit or because of a knowledge application confusion. The transition from advanced beginners to competent practitioners began when they first had experience with actual clinical situations and could benefit from the knowledge gained from the mistakes of their colleagues. Competent nurses continuously questioned what they saw and heard, feeling an obligation to know more about clinical situations. In doing do, they moved from only using care plans and following the physicians’ orders to analyzing and interpreting patient situations. Beyond that, the proficient nurse acknowledged the changing relevance of clinical situations requiring action beyond what was planned or anticipated. The proficient nurse learned to acknowledge the changing needs of patient care and situation, and could organize interventions “by the situation as it unfolds rather than by preset goals 48 (p. 24). Both competent and proficient nurses (that is, intermediate level of practice) had at least two years of ICU experience. 48 Finally, the expert nurse had a more fully developed grasp of a clinical situation, a sense of confidence in what is known about the situation, and could differentiate the precise clinical problem in little time. 48
Expertise is acquired through professional experience and is indicative of a nurse who has moved beyond mere proficiency. As Gadamer 29 points out, experience involves a turning around of preconceived notions, preunderstandings, and extends or adds nuances to understanding. Dewey 49 notes that experience requires a prepared “creature” and an enriched environment. The opportunity to reflect and narrate one’s experiential learning can clarify, extend, or even refute experiential learning.
Experiential learning requires time and nurturing, but time alone does not ensure experiential learning. Aristotle linked experiential learning to the development of character and moral sensitivities of a person learning a practice. 50 New nurses/new graduates have limited work experience and must experience continuing learning until they have reached an acceptable level of performance. 51 After that, further improvements are not predictable, and years of experience are an inadequate predictor of expertise. 52
The most effective knower and developer of practical knowledge creates an ongoing dialogue and connection between lessons of the day and experiential learning over time. Gadamer, in a late life interview, highlighted the open-endedness and ongoing nature of experiential learning in the following interview response:
Being experienced does not mean that one now knows something once and for all and becomes rigid in this knowledge; rather, one becomes more open to new experiences. A person who is experienced is undogmatic. Experience has the effect of freeing one to be open to new experience … In our experience we bring nothing to a close; we are constantly learning new things from our experience … this I call the interminability of all experience 32 (p. 403).
Practical endeavor, supported by scientific knowledge, requires experiential learning, the development of skilled know-how, and perceptual acuity in order to make the scientific knowledge relevant to the situation. Clinical perceptual and skilled know-how helps the practitioner discern when particular scientific findings might be relevant. 53
Often experience and knowledge, confirmed by experimentation, are treated as oppositions, an either-or choice. However, in practice it is readily acknowledged that experiential knowledge fuels scientific investigation, and scientific investigation fuels further experiential learning. Experiential learning from particular clinical cases can help the clinician recognize future similar cases and fuel new scientific questions and study. For example, less experienced nurses—and it could be argued experienced as well—can use nursing diagnoses practice guidelines as part of their professional advancement. Guidelines are used to reflect their interpretation of patients’ needs, responses, and situation, 54 a process that requires critical thinking and decisionmaking. 55 , 56 Using guidelines also reflects one’s problem identification and problem-solving abilities. 56 Conversely, the ability to proficiently conduct a series of tasks without nursing diagnoses is the hallmark of expertise. 39 , 57
Experience precedes expertise. As expertise develops from experience and gaining knowledge and transitions to the proficiency stage, the nurses’ thinking moves from steps and procedures (i.e., task-oriented care) toward “chunks” or patterns 39 (i.e., patient-specific care). In doing so, the nurse thinks reflectively, rather than merely accepting statements and performing procedures without significant understanding and evaluation. 34 Expert nurses do not rely on rules and logical thought processes in problem-solving and decisionmaking. 39 Instead, they use abstract principles, can see the situation as a complex whole, perceive situations comprehensively, and can be fully involved in the situation. 48 Expert nurses can perform high-level care without conscious awareness of the knowledge they are using, 39 , 58 and they are able to provide that care with flexibility and speed. Through a combination of knowledge and skills gained from a range of theoretical and experiential sources, expert nurses also provide holistic care. 39 Thus, the best care comes from the combination of theoretical, tacit, and experiential knowledge. 59 , 60
Experts are thought to eventually develop the ability to intuitively know what to do and to quickly recognize critical aspects of the situation. 22 Some have proposed that expert nurses provide high-quality patient care, 61 , 62 but that is not consistently documented—particularly in consideration of patient outcomes—and a full understanding between the differential impact of care rendered by an “expert” nurse is not fully understood. In fact, several studies have found that length of professional experience is often unrelated and even negatively related to performance measures and outcomes. 63 , 64
In a review of the literature on expertise in nursing, Ericsson and colleagues 65 found that focusing on challenging, less-frequent situations would reveal individual performance differences on tasks that require speed and flexibility, such as that experienced during a code or an adverse event. Superior performance was associated with extensive training and immediate feedback about outcomes, which can be obtained through continual training, simulation, and processes such as root-cause analysis following an adverse event. Therefore, efforts to improve performance benefited from continual monitoring, planning, and retrospective evaluation. Even then, the nurse’s ability to perform as an expert is dependent upon their ability to use intuition or insights gained through interactions with patients. 39
Intuition and Perception
Intuition is the instant understanding of knowledge without evidence of sensible thought. 66 According to Young, 67 intuition in clinical practice is a process whereby the nurse recognizes something about a patient that is difficult to verbalize. Intuition is characterized by factual knowledge, “immediate possession of knowledge, and knowledge independent of the linear reasoning process” 68 (p. 23). When intuition is used, one filters information initially triggered by the imagination, leading to the integration of all knowledge and information to problem solve. 69 Clinicians use their interactions with patients and intuition, drawing on tacit or experiential knowledge, 70 , 71 to apply the correct knowledge to make the correct decisions to address patient needs. Yet there is a “conflated belief in the nurses’ ability to know what is best for the patient” 72 (p. 251) because the nurses’ and patients’ identification of the patients’ needs can vary. 73
A review of research and rhetoric involving intuition by King and Appleton 62 found that all nurses, including students, used intuition (i.e., gut feelings). They found evidence, predominately in critical care units, that intuition was triggered in response to knowledge and as a trigger for action and/or reflection with a direct bearing on the analytical process involved in patient care. The challenge for nurses was that rigid adherence to checklists, guidelines, and standardized documentation, 62 ignored the benefits of intuition. This view was furthered by Rew and Barrow 68 , 74 in their reviews of the literature, where they found that intuition was imperative to complex decisionmaking, 68 difficult to measure and assess in a quantitative manner, and was not linked to physiologic measures. 74
Intuition is a way of explaining professional expertise. 75 Expert nurses rely on their intuitive judgment that has been developed over time. 39 , 76 Intuition is an informal, nonanalytically based, unstructured, deliberate calculation that facilitates problem solving, 77 a process of arriving at salient conclusions based on relatively small amounts of knowledge and/or information. 78 Experts can have rapid insight into a situation by using intuition to recognize patterns and similarities, achieve commonsense understanding, and sense the salient information combined with deliberative rationality. 10 Intuitive recognition of similarities and commonalities between patients are often the first diagnostic clue or early warning, which must then be followed up with critical evaluation of evidence among the competing conditions. This situation calls for intuitive judgment that can distinguish “expert human judgment from the decisions” made by a novice 79 (p. 23).
Shaw 80 equates intuition with direct perception. Direct perception is dependent upon being able to detect complex patterns and relationships that one has learned through experience are important. Recognizing these patterns and relationships generally occurs rapidly and is complex, making it difficult to articulate or describe. Perceptual skills, like those of the expert nurse, are essential to recognizing current and changing clinical conditions. Perception requires attentiveness and the development of a sense of what is salient. Often in nursing and medicine, means and ends are fused, as is the case for a “good enough” birth experience and a peaceful death.
- Applying Practice Evidence
Research continues to find that using evidence-based guidelines in practice, informed through research evidence, improves patients’ outcomes. 81–83 Research-based guidelines are intended to provide guidance for specific areas of health care delivery. 84 The clinician—both the novice and expert—is expected to use the best available evidence for the most efficacious therapies and interventions in particular instances, to ensure the highest-quality care, especially when deviations from the evidence-based norm may heighten risks to patient safety. Otherwise, if nursing and medicine were exact sciences, or consisted only of techne, then a 1:1 relationship could be established between results of aggregated evidence-based research and the best path for all patients.
Evaluating Evidence
Before research should be used in practice, it must be evaluated. There are many complexities and nuances in evaluating the research evidence for clinical practice. Evaluation of research behind evidence-based medicine requires critical thinking and good clinical judgment. Sometimes the research findings are mixed or even conflicting. As such, the validity, reliability, and generalizability of available research are fundamental to evaluating whether evidence can be applied in practice. To do so, clinicians must select the best scientific evidence relevant to particular patients—a complex process that involves intuition to apply the evidence. Critical thinking is required for evaluating the best available scientific evidence for the treatment and care of a particular patient.
Good clinical judgment is required to select the most relevant research evidence. The best clinical judgment, that is, reasoning across time about the particular patient through changes in the patient’s concerns and condition and/or the clinician’s understanding, are also required. This type of judgment requires clinicians to make careful observations and evaluations of the patient over time, as well as know the patient’s concerns and social circumstances. To evolve to this level of judgment, additional education beyond clinical preparation if often required.
Sources of Evidence
Evidence that can be used in clinical practice has different sources and can be derived from research, patient’s preferences, and work-related experience. 85 , 86 Nurses have been found to obtain evidence from experienced colleagues believed to have clinical expertise and research-based knowledge 87 as well as other sources.
For many years now, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have often been considered the best standard for evaluating clinical practice. Yet, unless the common threats to the validity (e.g., representativeness of the study population) and reliability (e.g., consistency in interventions and responses of study participants) of RCTs are addressed, the meaningfulness and generalizability of the study outcomes are very limited. Relevant patient populations may be excluded, such as women, children, minorities, the elderly, and patients with multiple chronic illnesses. The dropout rate of the trial may confound the results. And it is easier to get positive results published than it is to get negative results published. Thus, RCTs are generalizable (i.e., applicable) only to the population studied—which may not reflect the needs of the patient under the clinicians care. In instances such as these, clinicians need to also consider applied research using prospective or retrospective populations with case control to guide decisionmaking, yet this too requires critical thinking and good clinical judgment.
Another source of available evidence may come from the gold standard of aggregated systematic evaluation of clinical trial outcomes for the therapy and clinical condition in question, be generated by basic and clinical science relevant to the patient’s particular pathophysiology or care need situation, or stem from personal clinical experience. The clinician then takes all of the available evidence and considers the particular patient’s known clinical responses to past therapies, their clinical condition and history, the progression or stages of the patient’s illness and recovery, and available resources.
In clinical practice, the particular is examined in relation to the established generalizations of science. With readily available summaries of scientific evidence (e.g., systematic reviews and practice guidelines) available to nurses and physicians, one might wonder whether deep background understanding is still advantageous. Might it not be expendable, since it is likely to be out of date given the current scientific evidence? But this assumption is a false opposition and false choice because without a deep background understanding, the clinician does not know how to best find and evaluate scientific evidence for the particular case in hand. The clinician’s sense of salience in any given situation depends on past clinical experience and current scientific evidence.
Evidence-Based Practice
The concept of evidence-based practice is dependent upon synthesizing evidence from the variety of sources and applying it appropriately to the care needs of populations and individuals. This implies that evidence-based practice, indicative of expertise in practice, appropriately applies evidence to the specific situations and unique needs of patients. 88 , 89 Unfortunately, even though providing evidence-based care is an essential component of health care quality, it is well known that evidence-based practices are not used consistently.
Conceptually, evidence used in practice advances clinical knowledge, and that knowledge supports independent clinical decisions in the best interest of the patient. 90 , 91 Decisions must prudently consider the factors not necessarily addressed in the guideline, such as the patient’s lifestyle, drug sensitivities and allergies, and comorbidities. Nurses who want to improve the quality and safety of care can do so though improving the consistency of data and information interpretation inherent in evidence-based practice.
Initially, before evidence-based practice can begin, there needs to be an accurate clinical judgment of patient responses and needs. In the course of providing care, with careful consideration of patient safety and quality care, clinicians must give attention to the patient’s condition, their responses to health care interventions, and potential adverse reactions or events that could harm the patient. Nonetheless, there is wide variation in the ability of nurses to accurately interpret patient responses 92 and their risks. 93 Even though variance in interpretation is expected, nurses are obligated to continually improve their skills to ensure that patients receive quality care safely. 94 Patients are vulnerable to the actions and experience of their clinicians, which are inextricably linked to the quality of care patients have access to and subsequently receive.
The judgment of the patient’s condition determines subsequent interventions and patient outcomes. Attaining accurate and consistent interpretations of patient data and information is difficult because each piece can have different meanings, and interpretations are influenced by previous experiences. 95 Nurses use knowledge from clinical experience 96 , 97 and—although infrequently—research. 98–100
Once a problem has been identified, using a process that utilizes critical thinking to recognize the problem, the clinician then searches for and evaluates the research evidence 101 and evaluates potential discrepancies. The process of using evidence in practice involves “a problem-solving approach that incorporates the best available scientific evidence, clinicians’ expertise, and patient’s preferences and values” 102 (p. 28). Yet many nurses do not perceive that they have the education, tools, or resources to use evidence appropriately in practice. 103
Reported barriers to using research in practice have included difficulty in understanding the applicability and the complexity of research findings, failure of researchers to put findings into the clinical context, lack of skills in how to use research in practice, 104 , 105 amount of time required to access information and determine practice implications, 105–107 lack of organizational support to make changes and/or use in practice, 104 , 97 , 105 , 107 and lack of confidence in one’s ability to critically evaluate clinical evidence. 108
When Evidence Is Missing
In many clinical situations, there may be no clear guidelines and few or even no relevant clinical trials to guide decisionmaking. In these cases, the latest basic science about cellular and genomic functioning may be the most relevant science, or by default, guestimation. Consequently, good patient care requires more than a straightforward, unequivocal application of scientific evidence. The clinician must be able to draw on a good understanding of basic sciences, as well as guidelines derived from aggregated data and information from research investigations.
Practical knowledge is shaped by one’s practice discipline and the science and technology relevant to the situation at hand. But scientific, formal, discipline-specific knowledge are not sufficient for good clinical practice, whether the discipline be law, medicine, nursing, teaching, or social work. Practitioners still have to learn how to discern generalizable scientific knowledge, know how to use scientific knowledge in practical situations, discern what scientific evidence/knowledge is relevant, assess how the particular patient’s situation differs from the general scientific understanding, and recognize the complexity of care delivery—a process that is complex, ongoing, and changing, as new evidence can overturn old.
Practice communities like individual practitioners may also be mistaken, as is illustrated by variability in practice styles and practice outcomes across hospitals and regions in the United States. This variability in practice is why practitioners must learn to critically evaluate their practice and continually improve their practice over time. The goal is to create a living self-improving tradition.
Within health care, students, scientists, and practitioners are challenged to learn and use different modes of thinking when they are conflated under one term or rubric, using the best-suited thinking strategies for taking into consideration the purposes and the ends of the reasoning. Learning to be an effective, safe nurse or physician requires not only technical expertise, but also the ability to form helping relationships and engage in practical ethical and clinical reasoning. 50 Good ethical comportment requires that both the clinician and the scientist take into account the notions of good inherent in clinical and scientific practices. The notions of good clinical practice must include the relevant significance and the human concerns involved in decisionmaking in particular situations, centered on clinical grasp and clinical forethought.
The Three Apprenticeships of Professional Education
We have much to learn in comparing the pedagogies of formation across the professions, such as is being done currently by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. The Carnegie Foundation’s broad research program on the educational preparation of the profession focuses on three essential apprenticeships:
To capture the full range of crucial dimensions in professional education, we developed the idea of a three-fold apprenticeship: (1) intellectual training to learn the academic knowledge base and the capacity to think in ways important to the profession; (2) a skill-based apprenticeship of practice; and (3) an apprenticeship to the ethical standards, social roles, and responsibilities of the profession, through which the novice is introduced to the meaning of an integrated practice of all dimensions of the profession, grounded in the profession’s fundamental purposes. 109
This framework has allowed the investigators to describe tensions and shortfalls as well as strengths of widespread teaching practices, especially at articulation points among these dimensions of professional training.
Research has demonstrated that these three apprenticeships are taught best when they are integrated so that the intellectual training includes skilled know-how, clinical judgment, and ethical comportment. In the study of nursing, exemplary classroom and clinical teachers were found who do integrate the three apprenticeships in all of their teaching, as exemplified by the following anonymous student’s comments:
With that as well, I enjoyed the class just because I do have clinical experience in my background and I enjoyed it because it took those practical applications and the knowledge from pathophysiology and pharmacology, and all the other classes, and it tied it into the actual aspects of like what is going to happen at work. For example, I work in the emergency room and question: Why am I doing this procedure for this particular patient? Beforehand, when I was just a tech and I wasn’t going to school, I’d be doing it because I was told to be doing it—or I’d be doing CPR because, you know, the doc said, start CPR. I really enjoy the Care and Illness because now I know the process, the pathophysiological process of why I’m doing it and the clinical reasons of why they’re making the decisions, and the prioritization that goes on behind it. I think that’s the biggest point. Clinical experience is good, but not everybody has it. Yet when these students transition from school and clinicals to their job as a nurse, they will understand what’s going on and why.
The three apprenticeships are equally relevant and intertwined. In the Carnegie National Study of Nursing Education and the companion study on medical education as well as in cross-professional comparisons, teaching that gives an integrated access to professional practice is being examined. Once the three apprenticeships are separated, it is difficult to reintegrate them. The investigators are encouraged by teaching strategies that integrate the latest scientific knowledge and relevant clinical evidence with clinical reasoning about particular patients in unfolding rather than static cases, while keeping the patient and family experience and concerns relevant to clinical concerns and reasoning.
Clinical judgment or phronesis is required to evaluate and integrate techne and scientific evidence.
Within nursing, professional practice is wise and effective usually to the extent that the professional creates relational and communication contexts where clients/patients can be open and trusting. Effectiveness depends upon mutual influence between patient and practitioner, student and learner. This is another way in which clinical knowledge is dialogical and socially distributed. The following articulation of practical reasoning in nursing illustrates the social, dialogical nature of clinical reasoning and addresses the centrality of perception and understanding to good clinical reasoning, judgment and intervention.
Clinical Grasp *
Clinical grasp describes clinical inquiry in action. Clinical grasp begins with perception and includes problem identification and clinical judgment across time about the particular transitions of particular patients. Garrett Chan 20 described the clinician’s attempt at finding an “optimal grasp” or vantage point of understanding. Four aspects of clinical grasp, which are described in the following paragraphs, include (1) making qualitative distinctions, (2) engaging in detective work, (3) recognizing changing relevance, and (4) developing clinical knowledge in specific patient populations.
Making Qualitative Distinctions
Qualitative distinctions refer to those distinctions that can be made only in a particular contextual or historical situation. The context and sequence of events are essential for making qualitative distinctions; therefore, the clinician must pay attention to transitions in the situation and judgment. Many qualitative distinctions can be made only by observing differences through touch, sound, or sight, such as the qualities of a wound, skin turgor, color, capillary refill, or the engagement and energy level of the patient. Another example is assessing whether the patient was more fatigued after ambulating to the bathroom or from lack of sleep. Likewise the quality of the clinician’s touch is distinct as in offering reassurance, putting pressure on a bleeding wound, and so on. 110
Engaging in Detective Work, Modus Operandi Thinking, and Clinical Puzzle Solving
Clinical situations are open ended and underdetermined. Modus operandi thinking keeps track of the particular patient, the way the illness unfolds, the meanings of the patient’s responses as they have occurred in the particular time sequence. Modus operandi thinking requires keeping track of what has been tried and what has or has not worked with the patient. In this kind of reasoning-in-transition, gains and losses of understanding are noticed and adjustments in the problem approach are made.
We found that teachers in a medical surgical unit at the University of Washington deliberately teach their students to engage in “detective work.” Students are given the daily clinical assignment of “sleuthing” for undetected drug incompatibilities, questionable drug dosages, and unnoticed signs and symptoms. For example, one student noted that an unusual dosage of a heart medication was being given to a patient who did not have heart disease. The student first asked her teacher about the unusually high dosage. The teacher, in turn, asked the student whether she had asked the nurse or the patient about the dosage. Upon the student’s questioning, the nurse did not know why the patient was receiving the high dosage and assumed the drug was for heart disease. The patient’s staff nurse had not questioned the order. When the student asked the patient, the student found that the medication was being given for tremors and that the patient and the doctor had titrated the dosage for control of the tremors. This deliberate approach to teaching detective work, or modus operandi thinking, has characteristics of “critical reflection,” but stays situated and engaged, ferreting out the immediate history and unfolding of events.
Recognizing Changing Clinical Relevance
The meanings of signs and symptoms are changed by sequencing and history. The patient’s mental status, color, or pain level may continue to deteriorate or get better. The direction, implication, and consequences for the changes alter the relevance of the particular facts in the situation. The changing relevance entailed in a patient transitioning from primarily curative care to primarily palliative care is a dramatic example, where symptoms literally take on new meanings and require new treatments.
Developing Clinical Knowledge in Specific Patient Populations
Extensive experience with a specific patient population or patients with particular injuries or diseases allows the clinician to develop comparisons, distinctions, and nuanced differences within the population. The comparisons between many specific patients create a matrix of comparisons for clinicians, as well as a tacit, background set of expectations that create population- and patient-specific detective work if a patient does not meet the usual, predictable transitions in recovery. What is in the background and foreground of the clinician’s attention shifts as predictable changes in the patient’s condition occurs, such as is seen in recovering from heart surgery or progressing through the predictable stages of labor and delivery. Over time, the clinician develops a deep background understanding that allows for expert diagnostic and interventions skills.
Clinical Forethought
Clinical forethought is intertwined with clinical grasp, but it is much more deliberate and even routinized than clinical grasp. Clinical forethought is a pervasive habit of thought and action in nursing practice, and also in medicine, as clinicians think about disease and recovery trajectories and the implications of these changes for treatment. Clinical forethought plays a role in clinical grasp because it structures the practical logic of clinicians. At least four habits of thought and action are evident in what we are calling clinical forethought: (1) future think, (2) clinical forethought about specific patient populations, (3) anticipation of risks for particular patients, and (4) seeing the unexpected.
Future think
Future think is the broadest category of this logic of practice. Anticipating likely immediate futures helps the clinician make good plans and decisions about preparing the environment so that responding rapidly to changes in the patient is possible. Without a sense of salience about anticipated signs and symptoms and preparing the environment, essential clinical judgments and timely interventions would be impossible in the typically fast pace of acute and intensive patient care. Future think governs the style and content of the nurse’s attentiveness to the patient. Whether in a fast-paced care environment or a slower-paced rehabilitation setting, thinking and acting with anticipated futures guide clinical thinking and judgment. Future think captures the way judgment is suspended in a predictive net of anticipation and preparing oneself and the environment for a range of potential events.
Clinical forethought about specific diagnoses and injuries
This habit of thought and action is so second nature to the experienced nurse that the new or inexperienced nurse may have difficulty finding out about what seems to other colleagues as “obvious” preparation for particular patients and situations. Clinical forethought involves much local specific knowledge about who is a good resource and how to marshal support services and equipment for particular patients.
Examples of preparing for specific patient populations are pervasive, such as anticipating the need for a pacemaker during surgery and having the equipment assembled ready for use to save essential time. Another example includes forecasting an accident victim’s potential injuries, and recognizing that intubation might be needed.
Anticipation of crises, risks, and vulnerabilities for particular patients
This aspect of clinical forethought is central to knowing the particular patient, family, or community. Nurses situate the patient’s problems almost like a topography of possibilities. This vital clinical knowledge needs to be communicated to other caregivers and across care borders. Clinical teaching could be improved by enriching curricula with narrative examples from actual practice, and by helping students recognize commonly occurring clinical situations in the simulation and clinical setting. For example, if a patient is hemodynamically unstable, then managing life-sustaining physiologic functions will be a main orienting goal. If the patient is agitated and uncomfortable, then attending to comfort needs in relation to hemodynamics will be a priority. Providing comfort measures turns out to be a central background practice for making clinical judgments and contains within it much judgment and experiential learning.
When clinical teaching is too removed from typical contingencies and strong clinical situations in practice, students will lack practice in active thinking-in-action in ambiguous clinical situations. In the following example, an anonymous student recounted her experiences of meeting a patient:
I was used to different equipment and didn’t know how things went, didn’t know their routine, really. You can explain all you want in class, this is how it’s going to be, but when you get there … . Kim was my first instructor and my patient that she assigned me to—I walked into the room and he had every tube imaginable. And so I was a little overwhelmed. It’s not necessarily even that he was that critical … . She asked what tubes here have you seen? Well, I know peripheral lines. You taught me PICC [peripherally inserted central catheter] lines, and we just had that, but I don’t really feel comfortable doing it by myself, without you watching to make sure that I’m flushing it right and how to assess it. He had a chest tube and I had seen chest tubes, but never really knew the depth of what you had to assess and how you make sure that it’s all kosher and whatever. So she went through the chest tube and explained, it’s just bubbling a little bit and that’s okay. The site, check the site. The site looked okay and that she’d say if it wasn’t okay, this is what it might look like … . He had a feeding tube. I had done feeding tubes but that was like a long time ago in my LPN experiences schooling. So I hadn’t really done too much with the feeding stuff either … . He had a [nasogastric] tube, and knew pretty much about that and I think at the time it was clamped. So there were no issues with the suction or whatever. He had a Foley catheter. He had a feeding tube, a chest tube. I can’t even remember but there were a lot.
As noted earlier, a central characteristic of a practice discipline is that a self-improving practice requires ongoing experiential learning. One way nurse educators can enhance clinical inquiry is by increasing pedagogies of experiential learning. Current pedagogies for experiential learning in nursing include extensive preclinical study, care planning, and shared postclinical debriefings where students share their experiential learning with their classmates. Experiential learning requires open learning climates where students can discuss and examine transitions in understanding, including their false starts, or their misconceptions in actual clinical situations. Nursing educators typically develop open and interactive clinical learning communities, so that students seem committed to helping their classmates learn from their experiences that may have been difficult or even unsafe. One anonymous nurse educator described how students extend their experiential learning to their classmates during a postclinical conference:
So for example, the patient had difficulty breathing and the student wanted to give the meds instead of addressing the difficulty of breathing. Well, while we were sharing information about their patients, what they did that day, I didn’t tell the student to say this, but she said, ‘I just want to tell you what I did today in clinical so you don’t do the same thing, and here’s what happened.’ Everybody’s listening very attentively and they were asking her some questions. But she shared that. She didn’t have to. I didn’t tell her, you must share that in postconference or anything like that, but she just went ahead and shared that, I guess, to reinforce what she had learned that day but also to benefit her fellow students in case that thing comes up with them.
The teacher’s response to this student’s honesty and generosity exemplifies her own approach to developing an open community of learning. Focusing only on performance and on “being correct” prevents learning from breakdown or error and can dampen students’ curiosity and courage to learn experientially.
Seeing the unexpected
One of the keys to becoming an expert practitioner lies in how the person holds past experiential learning and background habitual skills and practices. This is a skill of foregrounding attention accurately and effectively in response to the nature of situational demands. Bourdieu 29 calls the recognition of the situation central to practical reasoning. If nothing is routinized as a habitual response pattern, then practitioners will not function effectively in emergencies. Unexpected occurrences may be overlooked. However, if expectations are held rigidly, then subtle changes from the usual will be missed, and habitual, rote responses will inappropriately rule. The clinician must be flexible in shifting between what is in background and foreground. This is accomplished by staying curious and open. The clinical “certainty” associated with perceptual grasp is distinct from the kind of “certainty” achievable in scientific experiments and through measurements. Recognition of similar or paradigmatic clinical situations is similar to “face recognition” or recognition of “family resemblances.” This concept is subject to faulty memory, false associative memories, and mistaken identities; therefore, such perceptual grasp is the beginning of curiosity and inquiry and not the end. Assessment and validation are required. In rapidly moving clinical situations, perceptual grasp is the starting point for clarification, confirmation, and action. Having the clinician say out loud how he or she is understanding the situation gives an opportunity for confirmation and disconfirmation from other clinicians present. 111 The relationship between foreground and background of attention needs to be fluid, so that missed expectations allow the nurse to see the unexpected. For example, when the background rhythm of a cardiac monitor changes, the nurse notices, and what had been background tacit awareness becomes the foreground of attention. A hallmark of expertise is the ability to notice the unexpected. 20 Background expectations of usual patient trajectories form with experience. Tacit expectations for patient trajectories form that enable the nurse to notice subtle failed expectations and pay attention to early signs of unexpected changes in the patient's condition. Clinical expectations gained from caring for similar patient populations form a tacit clinical forethought that enable the experienced clinician to notice missed expectations. Alterations from implicit or explicit expectations set the stage for experiential learning, depending on the openness of the learner.
Learning to provide safe and quality health care requires technical expertise, the ability to think critically, experience, and clinical judgment. The high-performance expectation of nurses is dependent upon the nurses’ continual learning, professional accountability, independent and interdependent decisionmaking, and creative problem-solving abilities.
This section of the paper was condensed and paraphrased from Benner, Hooper-Kyriakidis, and Stannard. 23 Patricia Hooper-Kyriakidis wrote the section on clinical grasp, and Patricia Benner wrote the section on clinical forethought.
- Cite this Page Benner P, Hughes RG, Sutphen M. Clinical Reasoning, Decisionmaking, and Action: Thinking Critically and Clinically. In: Hughes RG, editor. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008 Apr. Chapter 6.
- PDF version of this page (147K)
In this Page
- Clinical Grasp
Other titles in this collection
- Advances in Patient Safety
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Nurses' reasoning process during care planning taking pressure ulcer prevention as an example. A think-aloud study. [Int J Nurs Stud. 2007] Nurses' reasoning process during care planning taking pressure ulcer prevention as an example. A think-aloud study. Funkesson KH, Anbäcken EM, Ek AC. Int J Nurs Stud. 2007 Sep; 44(7):1109-19. Epub 2006 Jun 27.
- Registered nurses' clinical reasoning skills and reasoning process: A think-aloud study. [Nurse Educ Today. 2016] Registered nurses' clinical reasoning skills and reasoning process: A think-aloud study. Lee J, Lee YJ, Bae J, Seo M. Nurse Educ Today. 2016 Nov; 46:75-80. Epub 2016 Aug 15.
- Combining the arts: an applied critical thinking approach in the skills laboratory. [Nursingconnections. 2000] Combining the arts: an applied critical thinking approach in the skills laboratory. Peterson MJ, Bechtel GA. Nursingconnections. 2000 Summer; 13(2):43-9.
- Review About critical thinking. [Dynamics. 2004] Review About critical thinking. Hynes P, Bennett J. Dynamics. 2004 Fall; 15(3):26-9.
- Review The 'five rights' of clinical reasoning: an educational model to enhance nursing students' ability to identify and manage clinically 'at risk' patients. [Nurse Educ Today. 2010] Review The 'five rights' of clinical reasoning: an educational model to enhance nursing students' ability to identify and manage clinically 'at risk' patients. Levett-Jones T, Hoffman K, Dempsey J, Jeong SY, Noble D, Norton CA, Roche J, Hickey N. Nurse Educ Today. 2010 Aug; 30(6):515-20. Epub 2009 Nov 30.
Recent Activity
- Clinical Reasoning, Decisionmaking, and Action: Thinking Critically and Clinical... Clinical Reasoning, Decisionmaking, and Action: Thinking Critically and Clinically - Patient Safety and Quality
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking
(10 reviews)
Matthew Van Cleave, Lansing Community College
Copyright Year: 2016
Publisher: Matthew J. Van Cleave
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by "yusef" Alexander Hayes, Professor, North Shore Community College on 6/9/21
Formal and informal reasoning, argument structure, and fallacies are covered comprehensively, meeting the author's goal of both depth and succinctness. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Formal and informal reasoning, argument structure, and fallacies are covered comprehensively, meeting the author's goal of both depth and succinctness.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The book is accurate.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
While many modern examples are used, and they are helpful, they are not necessarily needed. The usefulness of logical principles and skills have proved themselves, and this text presents them clearly with many examples.
Clarity rating: 5
It is obvious that the author cares about their subject, audience, and students. The text is comprehensible and interesting.
Consistency rating: 5
The format is easy to understand and is consistent in framing.
Modularity rating: 5
This text would be easy to adapt.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The organization is excellent, my one suggestion would be a concluding chapter.
Interface rating: 5
I accessed the PDF version and it would be easy to work with.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The writing is excellent.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This is not an offensive text.
Reviewed by Susan Rottmann, Part-time Lecturer, University of Southern Maine on 3/2/21
I reviewed this book for a course titled "Creative and Critical Inquiry into Modern Life." It won't meet all my needs for that course, but I haven't yet found a book that would. I wanted to review this one because it states in the preface that it... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
I reviewed this book for a course titled "Creative and Critical Inquiry into Modern Life." It won't meet all my needs for that course, but I haven't yet found a book that would. I wanted to review this one because it states in the preface that it fits better for a general critical thinking course than for a true logic course. I'm not sure that I'd agree. I have been using Browne and Keeley's "Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking," and I think that book is a better introduction to critical thinking for non-philosophy majors. However, the latter is not open source so I will figure out how to get by without it in the future. Overall, the book seems comprehensive if the subject is logic. The index is on the short-side, but fine. However, one issue for me is that there are no page numbers on the table of contents, which is pretty annoying if you want to locate particular sections.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
I didn't find any errors. In general the book uses great examples. However, they are very much based in the American context, not for an international student audience. Some effort to broaden the chosen examples would make the book more widely applicable.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
I think the book will remain relevant because of the nature of the material that it addresses, however there will be a need to modify the examples in future editions and as the social and political context changes.
Clarity rating: 3
The text is lucid, but I think it would be difficult for introductory-level students who are not philosophy majors. For example, in Browne and Keeley's "Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking," the sub-headings are very accessible, such as "Experts cannot rescue us, despite what they say" or "wishful thinking: perhaps the biggest single speed bump on the road to critical thinking." By contrast, Van Cleave's "Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking" has more subheadings like this: "Using your own paraphrases of premises and conclusions to reconstruct arguments in standard form" or "Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives." If students are prepared very well for the subject, it would work fine, but for students who are newly being introduced to critical thinking, it is rather technical.
It seems to be very consistent in terms of its terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 4
The book is divided into 4 chapters, each having many sub-chapters. In that sense, it is readily divisible and modular. However, as noted above, there are no page numbers on the table of contents, which would make assigning certain parts rather frustrating. Also, I'm not sure why the book is only four chapter and has so many subheadings (for instance 17 in Chapter 2) and a length of 242 pages. Wouldn't it make more sense to break up the book into shorter chapters? I think this would make it easier to read and to assign in specific blocks to students.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The organization of the book is fine overall, although I think adding page numbers to the table of contents and breaking it up into more separate chapters would help it to be more easily navigable.
Interface rating: 4
The book is very simply presented. In my opinion it is actually too simple. There are few boxes or diagrams that highlight and explain important points.
The text seems fine grammatically. I didn't notice any errors.
The book is written with an American audience in mind, but I did not notice culturally insensitive or offensive parts.
Overall, this book is not for my course, but I think it could work well in a philosophy course.
Reviewed by Daniel Lee, Assistant Professor of Economics and Leadership, Sweet Briar College on 11/11/19
This textbook is not particularly comprehensive (4 chapters long), but I view that as a benefit. In fact, I recommend it for use outside of traditional logic classes, but rather interdisciplinary classes that evaluate argument read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
This textbook is not particularly comprehensive (4 chapters long), but I view that as a benefit. In fact, I recommend it for use outside of traditional logic classes, but rather interdisciplinary classes that evaluate argument
To the best of my ability, I regard this content as accurate, error-free, and unbiased
The book is broadly relevant and up-to-date, with a few stray temporal references (sydney olympics, particular presidencies). I don't view these time-dated examples as problematic as the logical underpinnings are still there and easily assessed
Clarity rating: 4
My only pushback on clarity is I didn't find the distinction between argument and explanation particularly helpful/useful/easy to follow. However, this experience may have been unique to my class.
To the best of my ability, I regard this content as internally consistent
I found this text quite modular, and was easily able to integrate other texts into my lessons and disregard certain chapters or sub-sections
The book had a logical and consistent structure, but to the extent that there are only 4 chapters, there isn't much scope for alternative approaches here
No problems with the book's interface
The text is grammatically sound
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Perhaps the text could have been more universal in its approach. While I didn't find the book insensitive per-se, logic can be tricky here because the point is to evaluate meaningful (non-trivial) arguments, but any argument with that sense of gravity can also be traumatic to students (abortion, death penalty, etc)
No additional comments
Reviewed by Lisa N. Thomas-Smith, Graduate Part-time Instructor, CU Boulder on 7/1/19
The text covers all the relevant technical aspects of introductory logic and critical thinking, and covers them well. A separate glossary would be quite helpful to students. However, the terms are clearly and thoroughly explained within the text,... read more
The text covers all the relevant technical aspects of introductory logic and critical thinking, and covers them well. A separate glossary would be quite helpful to students. However, the terms are clearly and thoroughly explained within the text, and the index is very thorough.
The content is excellent. The text is thorough and accurate with no errors that I could discern. The terminology and exercises cover the material nicely and without bias.
The text should easily stand the test of time. The exercises are excellent and would be very helpful for students to internalize correct critical thinking practices. Because of the logical arrangement of the text and the many sub-sections, additional material should be very easy to add.
The text is extremely clearly and simply written. I anticipate that a diligent student could learn all of the material in the text with little additional instruction. The examples are relevant and easy to follow.
The text did not confuse terms or use inconsistent terminology, which is very important in a logic text. The discipline often uses multiple terms for the same concept, but this text avoids that trap nicely.
The text is fairly easily divisible. Since there are only four chapters, those chapters include large blocks of information. However, the chapters themselves are very well delineated and could be easily broken up so that parts could be left out or covered in a different order from the text.
The flow of the text is excellent. All of the information is handled solidly in an order that allows the student to build on the information previously covered.
The PDF Table of Contents does not include links or page numbers which would be very helpful for navigation. Other than that, the text was very easy to navigate. All the images, charts, and graphs were very clear
I found no grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The text including examples and exercises did not seem to be offensive or insensitive in any specific way. However, the examples included references to black and white people, but few others. Also, the text is very American specific with many examples from and for an American audience. More diversity, especially in the examples, would be appropriate and appreciated.
Reviewed by Leslie Aarons, Associate Professor of Philosophy, CUNY LaGuardia Community College on 5/16/19
This is an excellent introductory (first-year) Logic and Critical Thinking textbook. The book covers the important elementary information, clearly discussing such things as the purpose and basic structure of an argument; the difference between an... read more
This is an excellent introductory (first-year) Logic and Critical Thinking textbook. The book covers the important elementary information, clearly discussing such things as the purpose and basic structure of an argument; the difference between an argument and an explanation; validity; soundness; and the distinctions between an inductive and a deductive argument in accessible terms in the first chapter. It also does a good job introducing and discussing informal fallacies (Chapter 4). The incorporation of opportunities to evaluate real-world arguments is also very effective. Chapter 2 also covers a number of formal methods of evaluating arguments, such as Venn Diagrams and Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives, but to my mind, it is much more thorough in its treatment of Informal Logic and Critical Thinking skills, than it is of formal logic. I also appreciated that Van Cleave’s book includes exercises with answers and an index, but there is no glossary; which I personally do not find detracts from the book's comprehensiveness.
Overall, Van Cleave's book is error-free and unbiased. The language used is accessible and engaging. There were no glaring inaccuracies that I was able to detect.
Van Cleave's Textbook uses relevant, contemporary content that will stand the test of time, at least for the next few years. Although some examples use certain subjects like former President Obama, it does so in a useful manner that inspires the use of critical thinking skills. There are an abundance of examples that inspire students to look at issues from many different political viewpoints, challenging students to practice evaluating arguments, and identifying fallacies. Many of these exercises encourage students to critique issues, and recognize their own inherent reader-biases and challenge their own beliefs--hallmarks of critical thinking.
As mentioned previously, the author has an accessible style that makes the content relatively easy to read and engaging. He also does a suitable job explaining jargon/technical language that is introduced in the textbook.
Van Cleave uses terminology consistently and the chapters flow well. The textbook orients the reader by offering effective introductions to new material, step-by-step explanations of the material, as well as offering clear summaries of each lesson.
This textbook's modularity is really quite good. Its language and structure are not overly convoluted or too-lengthy, making it convenient for individual instructors to adapt the materials to suit their methodological preferences.
The topics in the textbook are presented in a logical and clear fashion. The structure of the chapters are such that it is not necessary to have to follow the chapters in their sequential order, and coverage of material can be adapted to individual instructor's preferences.
The textbook is free of any problematic interface issues. Topics, sections and specific content are accessible and easy to navigate. Overall it is user-friendly.
I did not find any significant grammatical issues with the textbook.
The textbook is not culturally insensitive, making use of a diversity of inclusive examples. Materials are especially effective for first-year critical thinking/logic students.
I intend to adopt Van Cleave's textbook for a Critical Thinking class I am teaching at the Community College level. I believe that it will help me facilitate student-learning, and will be a good resource to build additional classroom activities from the materials it provides.
Reviewed by Jennie Harrop, Chair, Department of Professional Studies, George Fox University on 3/27/18
While the book is admirably comprehensive, its extensive details within a few short chapters may feel overwhelming to students. The author tackles an impressive breadth of concepts in Chapter 1, 2, 3, and 4, which leads to 50-plus-page chapters... read more
While the book is admirably comprehensive, its extensive details within a few short chapters may feel overwhelming to students. The author tackles an impressive breadth of concepts in Chapter 1, 2, 3, and 4, which leads to 50-plus-page chapters that are dense with statistical analyses and critical vocabulary. These topics are likely better broached in manageable snippets rather than hefty single chapters.
The ideas addressed in Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking are accurate but at times notably political. While politics are effectively used to exemplify key concepts, some students may be distracted by distinct political leanings.
The terms and definitions included are relevant, but the examples are specific to the current political, cultural, and social climates, which could make the materials seem dated in a few years without intentional and consistent updates.
While the reasoning is accurate, the author tends to complicate rather than simplify -- perhaps in an effort to cover a spectrum of related concepts. Beginning readers are likely to be overwhelmed and under-encouraged by his approach.
Consistency rating: 3
The four chapters are somewhat consistent in their play of definition, explanation, and example, but the structure of each chapter varies according to the concepts covered. In the third chapter, for example, key ideas are divided into sub-topics numbering from 3.1 to 3.10. In the fourth chapter, the sub-divisions are further divided into sub-sections numbered 4.1.1-4.1.5, 4.2.1-4.2.2, and 4.3.1 to 4.3.6. Readers who are working quickly to master new concepts may find themselves mired in similarly numbered subheadings, longing for a grounded concepts on which to hinge other key principles.
Modularity rating: 3
The book's four chapters make it mostly self-referential. The author would do well to beak this text down into additional subsections, easing readers' accessibility.
The content of the book flows logically and well, but the information needs to be better sub-divided within each larger chapter, easing the student experience.
The book's interface is effective, allowing readers to move from one section to the next with a single click. Additional sub-sections would ease this interplay even further.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
Some minor errors throughout.
For the most part, the book is culturally neutral, avoiding direct cultural references in an effort to remain relevant.
Reviewed by Yoichi Ishida, Assistant Professor of Philosophy, Ohio University on 2/1/18
This textbook covers enough topics for a first-year course on logic and critical thinking. Chapter 1 covers the basics as in any standard textbook in this area. Chapter 2 covers propositional logic and categorical logic. In propositional logic,... read more
This textbook covers enough topics for a first-year course on logic and critical thinking. Chapter 1 covers the basics as in any standard textbook in this area. Chapter 2 covers propositional logic and categorical logic. In propositional logic, this textbook does not cover suppositional arguments, such as conditional proof and reductio ad absurdum. But other standard argument forms are covered. Chapter 3 covers inductive logic, and here this textbook introduces probability and its relationship with cognitive biases, which are rarely discussed in other textbooks. Chapter 4 introduces common informal fallacies. The answers to all the exercises are given at the end. However, the last set of exercises is in Chapter 3, Section 5. There are no exercises in the rest of the chapter. Chapter 4 has no exercises either. There is index, but no glossary.
The textbook is accurate.
The content of this textbook will not become obsolete soon.
The textbook is written clearly.
The textbook is internally consistent.
The textbook is fairly modular. For example, Chapter 3, together with a few sections from Chapter 1, can be used as a short introduction to inductive logic.
The textbook is well-organized.
There are no interface issues.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
This textbook is relevant to a first semester logic or critical thinking course.
Reviewed by Payal Doctor, Associate Professro, LaGuardia Community College on 2/1/18
This text is a beginner textbook for arguments and propositional logic. It covers the basics of identifying arguments, building arguments, and using basic logic to construct propositions and arguments. It is quite comprehensive for a beginner... read more
This text is a beginner textbook for arguments and propositional logic. It covers the basics of identifying arguments, building arguments, and using basic logic to construct propositions and arguments. It is quite comprehensive for a beginner book, but seems to be a good text for a course that needs a foundation for arguments. There are exercises on creating truth tables and proofs, so it could work as a logic primer in short sessions or with the addition of other course content.
The books is accurate in the information it presents. It does not contain errors and is unbiased. It covers the essential vocabulary clearly and givens ample examples and exercises to ensure the student understands the concepts
The content of the book is up to date and can be easily updated. Some examples are very current for analyzing the argument structure in a speech, but for this sort of text understandable examples are important and the author uses good examples.
The book is clear and easy to read. In particular, this is a good text for community college students who often have difficulty with reading comprehension. The language is straightforward and concepts are well explained.
The book is consistent in terminology, formatting, and examples. It flows well from one topic to the next, but it is also possible to jump around the text without loosing the voice of the text.
The books is broken down into sub units that make it easy to assign short blocks of content at a time. Later in the text, it does refer to a few concepts that appear early in that text, but these are all basic concepts that must be used to create a clear and understandable text. No sections are too long and each section stays on topic and relates the topic to those that have come before when necessary.
The flow of the text is logical and clear. It begins with the basic building blocks of arguments, and practice identifying more and more complex arguments is offered. Each chapter builds up from the previous chapter in introducing propositional logic, truth tables, and logical arguments. A select number of fallacies are presented at the end of the text, but these are related to topics that were presented before, so it makes sense to have these last.
The text is free if interface issues. I used the PDF and it worked fine on various devices without loosing formatting.
1. The book contains no grammatical errors.
The text is culturally sensitive, but examples used are a bit odd and may be objectionable to some students. For instance, President Obama's speech on Syria is used to evaluate an extended argument. This is an excellent example and it is explained well, but some who disagree with Obama's policies may have trouble moving beyond their own politics. However, other examples look at issues from all political viewpoints and ask students to evaluate the argument, fallacy, etc. and work towards looking past their own beliefs. Overall this book does use a variety of examples that most students can understand and evaluate.
My favorite part of this book is that it seems to be written for community college students. My students have trouble understanding readings in the New York Times, so it is nice to see a logic and critical thinking text use real language that students can understand and follow without the constant need of a dictionary.
Reviewed by Rebecca Owen, Adjunct Professor, Writing, Chemeketa Community College on 6/20/17
This textbook is quite thorough--there are conversational explanations of argument structure and logic. I think students will be happy with the conversational style this author employs. Also, there are many examples and exercises using current... read more
This textbook is quite thorough--there are conversational explanations of argument structure and logic. I think students will be happy with the conversational style this author employs. Also, there are many examples and exercises using current events, funny scenarios, or other interesting ways to evaluate argument structure and validity. The third section, which deals with logical fallacies, is very clear and comprehensive. My only critique of the material included in the book is that the middle section may be a bit dense and math-oriented for learners who appreciate the more informal, informative style of the first and third section. Also, the book ends rather abruptly--it moves from a description of a logical fallacy to the answers for the exercises earlier in the text.
The content is very reader-friendly, and the author writes with authority and clarity throughout the text. There are a few surface-level typos (Starbuck's instead of Starbucks, etc.). None of these small errors detract from the quality of the content, though.
One thing I really liked about this text was the author's wide variety of examples. To demonstrate different facets of logic, he used examples from current media, movies, literature, and many other concepts that students would recognize from their daily lives. The exercises in this text also included these types of pop-culture references, and I think students will enjoy the familiarity--as well as being able to see the logical structures behind these types of references. I don't think the text will need to be updated to reflect new instances and occurrences; the author did a fine job at picking examples that are relatively timeless. As far as the subject matter itself, I don't think it will become obsolete any time soon.
The author writes in a very conversational, easy-to-read manner. The examples used are quite helpful. The third section on logical fallacies is quite easy to read, follow, and understand. A student in an argument writing class could benefit from this section of the book. The middle section is less clear, though. A student learning about the basics of logic might have a hard time digesting all of the information contained in chapter two. This material might be better in two separate chapters. I think the author loses the balance of a conversational, helpful tone and focuses too heavily on equations.
Consistency rating: 4
Terminology in this book is quite consistent--the key words are highlighted in bold. Chapters 1 and 3 follow a similar organizational pattern, but chapter 2 is where the material becomes more dense and equation-heavy. I also would have liked a closing passage--something to indicate to the reader that we've reached the end of the chapter as well as the book.
I liked the overall structure of this book. If I'm teaching an argumentative writing class, I could easily point the students to the chapters where they can identify and practice identifying fallacies, for instance. The opening chapter is clear in defining the necessary terms, and it gives the students an understanding of the toolbox available to them in assessing and evaluating arguments. Even though I found the middle section to be dense, smaller portions could be assigned.
The author does a fine job connecting each defined term to the next. He provides examples of how each defined term works in a sentence or in an argument, and then he provides practice activities for students to try. The answers for each question are listed in the final pages of the book. The middle section feels like the heaviest part of the whole book--it would take the longest time for a student to digest if assigned the whole chapter. Even though this middle section is a bit heavy, it does fit the overall structure and flow of the book. New material builds on previous chapters and sub-chapters. It ends abruptly--I didn't realize that it had ended, and all of a sudden I found myself in the answer section for those earlier exercises.
The simple layout is quite helpful! There is nothing distracting, image-wise, in this text. The table of contents is clearly arranged, and each topic is easy to find.
Tiny edits could be made (Starbuck's/Starbucks, for one). Otherwise, it is free of distracting grammatical errors.
This text is quite culturally relevant. For instance, there is one example that mentions the rumors of Barack Obama's birthplace as somewhere other than the United States. This example is used to explain how to analyze an argument for validity. The more "sensational" examples (like the Obama one above) are helpful in showing argument structure, and they can also help students see how rumors like this might gain traction--as well as help to show students how to debunk them with their newfound understanding of argument and logic.
The writing style is excellent for the subject matter, especially in the third section explaining logical fallacies. Thank you for the opportunity to read and review this text!
Reviewed by Laurel Panser, Instructor, Riverland Community College on 6/20/17
This is a review of Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking, an open source book version 1.4 by Matthew Van Cleave. The comparison book used was Patrick J. Hurley’s A Concise Introduction to Logic 12th Edition published by Cengage as well as... read more
This is a review of Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking, an open source book version 1.4 by Matthew Van Cleave. The comparison book used was Patrick J. Hurley’s A Concise Introduction to Logic 12th Edition published by Cengage as well as the 13th edition with the same title. Lori Watson is the second author on the 13th edition.
Competing with Hurley is difficult with respect to comprehensiveness. For example, Van Cleave’s book is comprehensive to the extent that it probably covers at least two-thirds or more of what is dealt with in most introductory, one-semester logic courses. Van Cleave’s chapter 1 provides an overview of argumentation including discerning non-arguments from arguments, premises versus conclusions, deductive from inductive arguments, validity, soundness and more. Much of Van Cleave’s chapter 1 parallel’s Hurley’s chapter 1. Hurley’s chapter 3 regarding informal fallacies is comprehensive while Van Cleave’s chapter 4 on this topic is less extensive. Categorical propositions are a topic in Van Cleave’s chapter 2; Hurley’s chapters 4 and 5 provide more instruction on this, however. Propositional logic is another topic in Van Cleave’s chapter 2; Hurley’s chapters 6 and 7 provide more information on this, though. Van Cleave did discuss messy issues of language meaning briefly in his chapter 1; that is the topic of Hurley’s chapter 2.
Van Cleave’s book includes exercises with answers and an index. A glossary was not included.
Reviews of open source textbooks typically include criteria besides comprehensiveness. These include comments on accuracy of the information, whether the book will become obsolete soon, jargon-free clarity to the extent that is possible, organization, navigation ease, freedom from grammar errors and cultural relevance; Van Cleave’s book is fine in all of these areas. Further criteria for open source books includes modularity and consistency of terminology. Modularity is defined as including blocks of learning material that are easy to assign to students. Hurley’s book has a greater degree of modularity than Van Cleave’s textbook. The prose Van Cleave used is consistent.
Van Cleave’s book will not become obsolete soon.
Van Cleave’s book has accessible prose.
Van Cleave used terminology consistently.
Van Cleave’s book has a reasonable degree of modularity.
Van Cleave’s book is organized. The structure and flow of his book is fine.
Problems with navigation are not present.
Grammar problems were not present.
Van Cleave’s book is culturally relevant.
Van Cleave’s book is appropriate for some first semester logic courses.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Reconstructing and analyzing arguments
- 1.1 What is an argument?
- 1.2 Identifying arguments
- 1.3 Arguments vs. explanations
- 1.4 More complex argument structures
- 1.5 Using your own paraphrases of premises and conclusions to reconstruct arguments in standard form
- 1.6 Validity
- 1.7 Soundness
- 1.8 Deductive vs. inductive arguments
- 1.9 Arguments with missing premises
- 1.10 Assuring, guarding, and discounting
- 1.11 Evaluative language
- 1.12 Evaluating a real-life argument
Chapter 2: Formal methods of evaluating arguments
- 2.1 What is a formal method of evaluation and why do we need them?
- 2.2 Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives
- 2.3 Negation and disjunction
- 2.4 Using parentheses to translate complex sentences
- 2.5 “Not both” and “neither nor”
- 2.6 The truth table test of validity
- 2.7 Conditionals
- 2.8 “Unless”
- 2.9 Material equivalence
- 2.10 Tautologies, contradictions, and contingent statements
- 2.11 Proofs and the 8 valid forms of inference
- 2.12 How to construct proofs
- 2.13 Short review of propositional logic
- 2.14 Categorical logic
- 2.15 The Venn test of validity for immediate categorical inferences
- 2.16 Universal statements and existential commitment
- 2.17 Venn validity for categorical syllogisms
Chapter 3: Evaluating inductive arguments and probabilistic and statistical fallacies
- 3.1 Inductive arguments and statistical generalizations
- 3.2 Inference to the best explanation and the seven explanatory virtues
- 3.3 Analogical arguments
- 3.4 Causal arguments
- 3.5 Probability
- 3.6 The conjunction fallacy
- 3.7 The base rate fallacy
- 3.8 The small numbers fallacy
- 3.9 Regression to the mean fallacy
- 3.10 Gambler's fallacy
Chapter 4: Informal fallacies
- 4.1 Formal vs. informal fallacies
- 4.1.1 Composition fallacy
- 4.1.2 Division fallacy
- 4.1.3 Begging the question fallacy
- 4.1.4 False dichotomy
- 4.1.5 Equivocation
- 4.2 Slippery slope fallacies
- 4.2.1 Conceptual slippery slope
- 4.2.2 Causal slippery slope
- 4.3 Fallacies of relevance
- 4.3.1 Ad hominem
- 4.3.2 Straw man
- 4.3.3 Tu quoque
- 4.3.4 Genetic
- 4.3.5 Appeal to consequences
- 4.3.6 Appeal to authority
Answers to exercises Glossary/Index
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This is an introductory textbook in logic and critical thinking. The goal of the textbook is to provide the reader with a set of tools and skills that will enable them to identify and evaluate arguments. The book is intended for an introductory course that covers both formal and informal logic. As such, it is not a formal logic textbook, but is closer to what one would find marketed as a “critical thinking textbook.”
About the Contributors
Matthew Van Cleave , PhD, Philosophy, University of Cincinnati, 2007. VAP at Concordia College (Moorhead), 2008-2012. Assistant Professor at Lansing Community College, 2012-2016. Professor at Lansing Community College, 2016-
Contribute to this Page

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Guidelines for Reaching a Reasoned Judgment
Mark Battersby and Sharon Bailin
1. Introduction
When one begins to survey the work on conductive argument, two surprising facts emerge. One is that so little has been written on conductive arguments; the second is that much of what has been written has focused on establishing their existence. One would have thought that even a cursory observation of how arguments are conducted in all areas of life would bring to an observer’s attention not only the existence of such arguments but their ubiquity. Making judgments based on both pro and con considerations is a common phenomenon in numerous domains, as Govier notes: “In my experience they [conductive arguments] naturally occur in law, philosophy, interpretive studies—and in fact in any area, including science, in which there are reasons for and against, or ‘pros and cons’ which we must consider in order to make a judgment on an issue” (Govier 1999b, p.160).
That the ubiquity and importance of conductive reasoning has not been sufficiently recognized may be a function of its “messiness.” Conductive arguments do not fit traditional argument patterns. The premises neither entail the conclusion nor do they support the conclusion in an unambiguous way as some of the “premises” (or anti-premises, as some have called them) actually adduce reasons that count against the conclusion. Indeed, Johnson makes the point that conductive arguments are not easily identified as arguments by either Formal Deductive Logic or positivism (Johnson 2000a, p.92).
Given their lack of conformity to traditional argument patterns, the appraisal of conductive arguments has become a central issue. As they are non-conclusive arguments, one cannot specify the criteria for their formal validity, as Wellman points out. And since they involve reasons against as well as for the conclusion, the problem arises as to how to weigh the various considerations and counter considerations, especially as such a weighing will be dependent on subject matter (Wellman 1971, pp.61–62; Govier 1985, p.261). For these reasons, some theorists have concluded that, “It is difficult to give any general guidelines about appraising conductive arguments” (Govier, p.260). Wellman argues, in fact that, although it is meaningful to refer to the validity of conductive arguments, the only way to establish such validity or lack thereof is by thinking the argument through and feeling its logical force (Wellman 1971, p.79).
It is our belief that there are some general guidelines which can be offered with respect to doing conductive reasoning well and that these guidelines give rise to a set of criteria for identifying inadequate conductive arguments. It is such guidelines and criteria that we elucidate in the remainder of the paper.
2. What Do We Mean by Conductive Reasoning?
Before proceeding with that task, it is necessary to clarify how we are using various terms and to delineate the focus and scope of our project. Our focus is not on the structure or assessment of particular conductive arguments per se but rather on the enterprise of conductive reasoning. By conductive reasoning we are referring to the process of comparative evaluation of a variety of contending positions and arguments with the goal of reaching a reasoned judgment on an issue. We adopt this terminology and focus for a number of reasons.
The first is clarity. What are generally referred to as conductive arguments are most likely themselves constructed of competing arguments which may offer reasons in support of a particular claim, objections to and critiques of arguments offered, or responses to objections. We will call the collection of all arguments in a piece of conductive reasoning a case , and individual arguments, simply arguments. A case, then, is made up of a collection of arguments whose conclusion is intended to support a particular judgment on the issue in question. Let us illustrate with an example (taken from our textbook on inquiry). This dialogue takes place following an extensive evaluation by the two protagonists of the various arguments commonly offered for and against capital punishment.
Phil: You know, Sophia, we’ve looked at a lot of arguments and information on capital punishment, but I think that the conclusion is becoming obvious to me. The weight of arguments clearly points against capital punishment.
Sophia: What made you come to that conclusion?
Phil: Well, it’s pretty clear that there’s little evidence to support the deterrence argument.
Sophia: Agreed.
Phil: And the incapacitation argument is really “overkill” (sorry about that) since the same result can be achieved by less drastic means.
Sophia: Agreed again.
Phil: The issue of cost actually supports the con side since it turns out that capital punishment is much more expensive than life imprisonment.
Sophia: Right again.
Phil: I think that there is something legitimate to the retribution argument in terms of the desire for justice. But retribution can be achieved with life imprisonment. You’ve also convinced me that with capital punishment, we risk an even greater injustice, that of possibly executing an innocent person.
Sophia: I’m with you.
Phil: Then there’s the fact that capital punishment is discriminatory.
Sophia: True.
Phil: And then we’re left with all the moral problems of the state killing some of its citizens and, in particular, some of its citizens who are innocent. That’s a very strong argument against capital punishment.
Sophia: Especially since there are alternatives.
Phil: And given the worldwide trend toward abolition, supported by important organizations like the United Nations, the arguments for capital punishment would have to be very strong to counter that.
Sophia: Which they’re not.
Phil: So, all in all, I have to agree with the abolitionists—we should not have the death penalty (Bailin and Battersby 2016, pp.235-236) .
This dialogue may be seen as exemplifying a conductive argument in the usual sense, offering as it does a number of independent reasons in support of a conclusion as well as addressing objections and counter considerations. As noted above, however, this presentation of the case is preceded by considerable reasoning in the form of an evaluation of individual arguments and a comparative weighing of considerations that leads to the making of this conductive “argument.” Cases are often presented in this way—as summaries of conductive reasoning, using primary claims to support a judgment without an explicit statement of the arguments that provide support for these claims. But good conductive reasoning involves a deeper process of inquiry in which the credibility of primary claims is based on an assessment of the arguments that provide support for these claims and in which competing considerations are explicitly weighed and balanced. This is the process in which Sophia and Phil have been engaged previous to this dialogue. It is this entire process of comparative evaluation and weighing which is the focus of our interest, and not simply the resulting “argument.”
Conductive arguments, in the usual sense, can vary considerably in subject matter and complexity. Both the preceding argument regarding capital punishment and the argument: “I’m tired, but I should go to the store anyway because we need bread” have the structure of a conductive argument. Our focus, however, is on the former. We are interested in the pro and con reasoning which takes place in complex and controversial situations, the kind of comparative evaluation we make in actual contexts of disagreement and debate.
Another reason for focusing on conductive reasoning is our commitment to the view of argumentation as dialectical. According to Blair and Johnson, “To say that argumentation is dialectical … is to identify it as a human practice, an exchange between two or more individuals in which the process of interaction shapes the product” (Blair and Johnson 1987, p.46). Our primary focus is on what will make this process a successful one, thereby leading to an adequate product, i.e., a credible reasoned judgment.
3. Features of Conductive Reasoning
The guidelines and criteria we offer arise from the particular features of conductive reasoning.
The first characteristic of import here is that the appropriate goal of conductive reasoning is not the making of a conclusive argument but rather the making of a reasoned judgment. By a reasoned judgment we mean not simply a judgment for which one has reasons, but a judgment for which one has good reasons, reasons which meet relevant standards. A piece of conductive reasoning can, at best, offer good, but not decisive, reasons to support a conclusion over its competitors. Thus arriving at a reasoned judgment will require an examination and weighing of the reasons offered on different sides of an issue and the balancing of various considerations.
No survey of arguments will be exhaustive, however. The possibility always exists that additional reasons and arguments will be put forward which might affect the outcome of the reasoning. Thus the judgment that is the outcome of the conductive reasoning process is always provisional and open to further examination. In addition, because this type of reasoning takes place in complex contexts with dimensions of uncertainty, there may be more than one judgment that is defensible given the context. For these reasons, conductive reasoning needs to be seen in the context of an ongoing process of critical inquiry.
Conductive reasoning takes place in many domains (as mentioned above). It is common in practical reasoning (Hitchcock 2000, pp.5–8) and in social theory and history (Govier 1985, p.260), but can also take place in virtually any domain, including art interpretation and criticism and scientific inquiry. In addition, reasoning about many contested issues will involve a range of types of considerations (for example, factual, ethical, practical). As a consequence, a variety of different types of considerations will often need to be taken into account in conductive reasoning and the criteria of specific domains of inquiry will often play an important role.
An important feature of conductive reasoning (of the kind which is of interest to us) is that it takes place in the context of a dialectic, of a historical and ongoing process of debate and critique, of competing views and the give-and-take among them. Reasons and arguments have been offered on various sides of the issue in question, objections have been raised to many of the arguments, responses have been offered to some of the objections, and alternative views have been put forth. This constellation of reasons, arguments, objections and responses constitutes what Johnson calls the dialectical environment (Johnson 2007). Having knowledge of the dialectical environment surrounding an issue is central to the enterprise of arriving at a reasoned judgment (Bailin and Battersby 2009). In addition, knowledge of the history of the debate can be of assistance in determining which arguments are salient and should be considered, which are considered strong, and which are considered defeated and why.
In addition to this dialectical context, we have identified several additional aspects of context that we believe are relevant to conductive reasoning by playing a role in the determination of both the significance and the weight of reasons. One is the state of practice, which refers to the current situation with respect to the issue at hand (e.g., is there currently capital punishment in the jurisdiction under discussion, and if not, when was it defeated and why). Knowing where the force of current practice and opinion lie can help us to understand what alternative views are up against and whether (and to what extent) any of these views bears the burden of proof. Knowledge about the intellectual, social, political, and historical contexts that surround an issue can contribute to our understanding of the assumptions that lie behind various positions and why people might hold them. Hitchcock’s observation that students’ problems with conductive reasoning are due in part to a “lack of background knowledge to generate a full enough range and detail of competing considerations” (Hitchcock 2000, p.7) points precisely to the centrality of this kind of contextual knowledge.
The dialectical nature of conductive reasoning implies that the process will be dynamic. Particular arguments are often modified or reframed in response to criticism and objections, and these modifications may in turn result in a reframing of the objections, and so on. As Zenker points out, for example, “Typically, some premises appear only in response to and sometimes integrate an opponent’s objections successfully” (Zenker 2007, p.2). In this spirit, Wohlrapp argues against a view of (non-deductive) argumentation in terms of a sequence of isolated inference steps and for a view in which “premises and conclusions of an argumentation form a ‘retroflexive’ system of mutual support” (Wohlrapp 1998, p.342). One implication of this dynamism is that weighing arguments cannot be simply a matter of placing competing arguments on a metaphorical balance scale because arguments will often change in the process of reasoning. Conductive reasoning will need to give attention to the modification, reframing, and synthesizing of arguments.
Because conductive reasoning involves the comparative weighing of reasons on various sides of an issue and because there will often be good reasons supporting different judgments, how strong the prevailing case is in comparison to the other cases will vary. Thus the strength of the judgments warranted by particular instances of conductive reasoning will vary as well. This feature of conductive reasoning points to the need to apportion the confidence of one’s judgment to the strength of the reasons.
4. Guidelines for Conductive Reasoning
In what follows we offer guidelines for conducting conductive reasoning, and then use these guidelines to identify various fallacies in conductive reasoning that one might see either in the process of reasoning or in a case instantiating such reasoning. These guidelines arise from the dialectical and contextual nature of conductive reasoning reviewed above.
4.1. Appropriately review the “dialectical space,” i.e., identify the relevant arguments and the history of the debate
As noted above, in coming to a reasoned judgment, the first task is to conduct an appropriate inquiry into the relevant arguments, including a review of the history of the debate. In addition to providing information regarding the salience and strength of various arguments, the history of the debate provides a context without which it may be extremely difficult to understand some arguments. For example, the problematic nature of the debate in British Columbia and then across Canada about the wisdom of a carbon tax was largely the result of the fact that most citizens were unaware of the dialectical context of the debate. For many, it was just another “tax grab” by the government with the puzzling and suspicious feature that the money was being returned to the taxpayer. Most simply did not understand the economic argument about carbon being an externality (a cost that was not fed through the market) that needed to be woven into the price structure of goods if there was to be an economically rational revision of the use of carbon fuels. The context was not simply global warming, but an extensive debate that had occurred among policy theorist about how best to implement incentives for reduction of carbon use.
4.2. Consider the full variety of objections to the various arguments and responses to the objections
The arguments pro and con about an issue which are the substance of conductive reasoning need to be identified and evaluated along with their associated objections. It is worth noting that there are at least two kinds of objections to individual arguments that provide the support for the primary claims. We suggest using the following terminology. An under cutter is a critique of an argument offered in support of a primary claim. This critique could attack the premises of the argument or the inference to its conclusion. The goal of an under cutter is to show that the conclusion of the argument is poorly supported so that the argument’s conclusion cannot serve as a credible primary claim in support of the case’s judgment. For example, an under cutter for the argument that capital punishment deters would be evidence showing that jurisdictions which eliminated capital punishment did not experience an increase in murder. Another kind of objection to an argument in a case is a specific counter —a countervailing argument or claim meant to provide a countervailing consideration to a particular primary claim. The claim that capital punishment will inevitably result in the execution of people who are innocent is directly countered by the argument that all socially useful practices have downsides which must be accepted; on this view the execution of innocents is just something that society needs to accept in order to have appropriate punishments for first degree murders. These two kinds of objections directed at particular primary claims differ from general counter arguments or con arguments . Con arguments provide a different kind of objection. For example, the argument that capital punishment is a barbaric practice inappropriate to civilized countries is not an argument directed at any particular argument for capital punishment. Rather, it is a general countervailing consideration or con argument .
4.3. Evaluate individual arguments according to relevant criteria
Since the very concept of conductive reasoning involves marshalling both pro and con arguments and relevant objections, one of the primary requirements for reaching a reasoned judgment is that relevant pro and con arguments must be evaluated (just as one would do with any argument). This is not an assessment of the “weight” to be given to a certain claim in the case, but rather an assessment of credibility of the primary claim given the review of the supportive arguments and objections. For example, one could evaluate the arguments for the claim that capital punishment does not deter using the usual criteria for causal claims in the social sciences. Alternatively, one could point out that the appeal to a police chief’s opinion is a fallacious appeal to authority. One could evaluate the evidence for the claim that historically, innocent individuals have been executed and for the claim that it is unlikely that this problem could be eliminated (the latter by appealing to historical evidence, legal scholars, etc.). Finally, one could evaluate the moral argument that capital punishment is the only appropriate punishment for certain kinds of murder—this would require a largely philosophical inquiry.
4.4. Establish the burden of proof and standard of proof required
One role that the consideration of context plays is to help identify, where appropriate, which side bears the burden of proof and the relevant standard of proof required. In scientific inquiry, the burden of proof bears on any novel theory or on claims counter to well established views. Science is inherently conservative in this way. In the political situation, those who argue for change in statutes or other political arrangements inevitably bear the burden of proof. But the standard here can clearly and reasonably evolve. After fifty years of widespread usage of marijuana and at least some scientific studies, the claim that it is relatively harmless (not harmless, but compared to alcohol…) is widely accepted and therefore claims of relative harmlessness would not bear the same burden of proof as they might have in 1960. Even more decisively, the argument that prohibition would not stop usage seems so obvious that it could almost be assumed in the argument. Returning to the capital punishment debate, the claim that capital punishment is not an effective deterrent against murder is now the accepted view of criminologists and anyone arguing for a deterrence effect would bear the burden of proof.
4.5. Assess possibilities in light of alternatives
Part of the assessment of particular arguments should involve consideration of whether there are better alternatives to the position being advocated. For example, with respect to the claims that capital punishment is necessary for both incapacitation and retribution, the existence of the less morally troubling alternative of life imprisonment provides an alternative that weakens the force of those claims. In addition, since the goal of conductive reasoning is reasoned judgment, an inquirer should not be restricted to only considering alternatives that have been put forward in the past. Part of the resolution of a longstanding controversy may well be to consider totally different alternatives rather than trying to decide which of given alternatives is worthy of support. On the question of the legalization of marijuana, for example, there is a wide range of alternatives to consider. While California contemplates legalization of marijuana, many other jurisdictions are considering just decriminalization for possession, or as in The Netherlands, its sale in only certain “coffee bistros.”
4.6. Take into account the relevant range of considerations
Because reasoning about many contested issues will involve a range of types of considerations (for example, factual, ethical, practical), it is important to ensure that one has taken into account the appropriate range of considerations when attempting to make a reasoned judgment. So, for example, in examining the issue of whether we should eat meat that comes from factory farms, it would be important to take into account both factual considerations about the conditions of animals kept on these farms and ethical considerations regarding whether humans have a moral obligation to animals. In inquiring into the debate over the raising of the minimum wage, it would be important to consider not only statistical information, but also the differing assumptions about equity and merit which are inherent in different positions in the debate. In dealing with public policy issues, it would be important to consider ethical as well as instrumental considerations, ends as well as means, costs as well as benefits, and long term as well as short term consequences.
4.7. Take into account and consider a variety of perspectives
The goal of reasoned judgment involves the attempt to make a decision or assessment from an ideal observer’s or “objective” point of view, striving for the “view from nowhere” as the regulative ideal. Striving for this ideal involves attempting to look at an issue from many relevant perspectives—e.g., in a moral dilemma trying to see the perspective of both the moral actor and those of the victims or beneficiaries of the action. One might consider, for example, the controversy surrounding Peter Singer’s advocacy of the euthanasia of disabled babies. Many disabled groups argued that he had failed to consider their perspective (McBryde Johnson 2003).
4.8. Consider differences in how issues, arguments, and reasons are framed
Opposing arguments are frequently characterized by different ways of framing or setting up the issue. Particular ways of framing may slant an inquiry in a particular direction and reframing may affect the outcome of the reasoning. Kahneman and Tversky (1982) have shown, for example, that the question of whether a decision is framed in terms of losing lives versus saving lives has significant impact on the way most people make the decision. As another example, a deontological approach to moral issues would frame a moral dispute quite differently than would a consequentialist perspective. The debate over carbon tax provides yet another illustration of the significance of framing. After the public outrage in British Columbia about the carbon tax, a PR person suggested that what the government should have done was to reframe the issue from a proposal for a tax increase to a proposal for “tax shifting,” i.e., shifting taxes from income tax to carbon producing activities. The carbon tax would not be a tax increase but a tax shift, which would be more acceptable and intelligible to the average citizen, a claim supported by poll results (Barrett 2008). Recognizing differences in framing can often help one to understand the assumptions underlying opposing arguments and thus to be in a better position to comparatively evaluate them. It also opens up the possibility for a mediation of frames that may lead to a judgment that incorporates the strong points of the opposing views.
4.9. Recognize and attempt to incorporate/synthesize strong points from different positions
Good reasons often do not reside entirely in one or other of the conflicting views. Thus it is important, in arriving at a reasoned judgment, to recognize the valid points in each view. The best-justified judgment is often one that incorporates the strong points in opposing views. In the dialogue, for example, our participants acknowledge that the need for deterrence, incapacitation and retribution are legitimate concerns, but they argue that they can all be addressed through life imprisonment.

4.10. Appropriately weigh and balance different considerations, values, and arguments
A central aspect of arriving at a reasoned judgment involves weighing the various reasons pro and con. Although there will likely be some differences in views about comparative weight, it is possible to justify one’s assignment of weight and to criticize reasoning for inappropriate weighting (see below for a detailed discussion of weighing).
4.11. Consider whether one’s own personal convictions and experiences may be coloring one’s judgment
Since we are focused on the process of arriving at a reasoned judgment, there is a requirement for the participant(s) in this process to be aware of their own biases and prejudices. Increasingly convincing research has demonstrated the difficulty people have in making reliably rational judgments. Efforts, including the sharing of discussion with others, identifying one’s perspectives and biases, and avoiding the more common generic biases such as representativeness (thinking individual events or experiences are representative of what generally happens) and confirmation bias (seeking only instances that provide support for one’s view) can all serve to make it more likely that one comes to a judgment which is truly reasoned. One key strategy to avoid bias in one’s judgment is to give due attention to evidence and arguments that counter one’s own point of view. As noted above, we have built such considerations into the process of inquiry, so there is already an important check on confirmation bias, although other biases may need to be addressed with different strategies. An awareness of the historical basis of one’s views and those of others can also help to undermine an inappropriate confidence in one’s views.
4.12. Make a judgment at the appropriate level of confidence—apportion one’s judgment to the strength of the reasons
Part of rational self-awareness involves assessing how much confidence one should have in one’s judgments given the arguments that one has reviewed. It may be that one can conclude with considerable confidence that capital punishment should not be used by a state, but as current debate about what to do about global warming or the debate about the causes of obesity show, not all judgments can be made with the same degree of confidence, even though there may be an urgent need to act on such judgments. Judgments of the likelihood of descriptive factual claims present one sort of problem, but any judgment about what to do must also take into account future states of affairs that are usually less certain than judgments about current states of affairs. And finally, while there are some accepted general moral principles, their application in particular cases, especially ones where accepted principles conflict, inevitably creates significant uncertainty. The unpredictability of the future means that almost all significant actions need to be based on judgments that are at best less than fully confident. In our text we suggest the following table as a guide.
Judgment and Confidence
A very confident judgment is warranted when the weight of reasons clearly supports the judgment.
A reasonably confident judgment is warranted when the weight of reasons strongly supports the judgment but there are still strong countervailing considerations.
A tentative judgment is warranted when the weight of reasons is not overwhelming but is supportive of one position, and we can make a judgment on balance.
A suspended judgment is warranted when the reasons for different positions are closely balanced or when there is insufficient evidence to make a judgment (Bailin and Battersby 2016, p.243).
5. Failures of Judgment
Our focus to this point has been on offering guidelines for reaching reasoned judgments. We also believe that these guidelines can furnish the basis for identifying certain kinds of problems in particular pieces of conductive reasoning, or cases. A given case can be evaluated in terms of the extent to which it deals with, or fails to deal with, the relevant considerations for reaching a reasoned judgment. We have termed the failures “failures of judgment.” As is the case with traditional informal fallacies, failures of judgment are most useful in identifying bad arguments rather than in specifying good ones. We propose that proffered cases are inadequate to the degree to which they fail to take into account the various relevant considerations. The following is a description of the failures of judgment which we have identified.
- Failure to undertake a comprehensive examination of the various competing arguments
Since reaching a reasoned judgment involves a comparative evaluation of the various reasons and arguments on an issue, the failure to take into account any of the significant arguments on the issue constitutes a serious defect in a case.
- Failure to give appropriate consideration to the burden of proof
Failing to determine where the burden of proof lies or misplacing the burden of proof may result in an inappropriate determination of how much evidence is needed to make a case or of when a case has been made successfully.
- Failure to consider the uncertainty of claims
Taking claims as certain where the evidence in support of the claim is not, in fact, compelling may result in making an unjustified judgment or making a judgment with a greater degree of confidence than is warranted.
- Failure to consider alternative solutions or possibilities
The strength of a case can only be evaluated in light of the alternatives available. Ignoring possible and plausible alternatives would be a ground for criticism of a given case.
- Failure to consider objections
Because argumentation is dialectical, any reasoned case, in addition to offering arguments, must also respond to any known and important objections. Failure to do so significantly weakens the case.
- Failure to consider implications
Many cases concern decisions about what to do. However correct an action may appear on the basis of the arguments provided, failure to consider consequences (typically unintended consequences) significantly weakens the case.
- Failure to consider a range of considerations
Judgments which fail to take into account relevant considerations are faulty for that reason.
- Biased framing
Too narrow framing of an issue or argument, or framing in a way that slants the discussion toward a particular perspective may exclude the consideration of other possibilities and thus bias the judgment.
- “Either-Or” framing
Given that many issues have more than two sides, and that there are often intermediate possibilities between two opposing positions, viewing all issues in terms of ‘either-or’ – as a choice between two opposing positions, can oversimplify issues and result in a failure to recognize other, possibly more reasonable possibilities.
- Inappropriate weighting
This problem consists in giving undue weight to certain aspects of an issue when making a judgment.
- Making a judgment at an inappropriate level of confidence
Asserting a judgment with more or less confidence than warranted by the strength of the reasons constitutes another fallacy of judgment.
6. Weighing and Balancing Considerations
A central notion in discussions of the evaluation of conductive reasoning, including our own, is that of weighing. Whatever guidelines may be offered, in the final analysis, reasons pro and con must be weighed in order to reach a reasoned judgment. Yet weighing is a metaphor that is difficult to cash out in the context of arguments, as numerous theorists have pointed out. Is it possible to quantify the weight or strength of various reasons or arguments? And if it is not, then does the notion become so vague as to be of little use or so subjective as to be devoid of evaluative purchase (Koch 2007c).
It is our view that weighing (which we take as the process) is a meaningful, if imperfect, metaphor, and that although weightings (which we take as the products of weighing) are not quantifiable and will sometimes be the object of disagreement, they are nonetheless not (or not primarily) subjective. Weightings can be justified (or criticized) by appeal to objective factors and considerations, for example by appeal to certain widely shared values and principles. Moreover, arguments can be evaluated in terms of both the likelihood that they are true and the support or weight that they give to the judgment. An argument which, if its conclusion is credible, gives considerable weight to a judgment will add little or no weight if it is doubtful. In the court context, for example, an argument that shows that the accused had a good alibi will largely exclude a conviction, whereas if the alibi is in question, the weight it provides is greatly diminished. On the other hand, the fact that an individual has a credible motive adds relatively little weight given that many people may have motives for committing a certain crime.
The excerpt of the dialogue on capital punishment quoted earlier can be used to illustrate some of these aspects of weighing. It is important to bear in mind, however, that a considerable amount of discussion regarding the relative weight of various arguments has already taken place before this dialogue occurs (e.g., Phil: But you’ve convinced me that with capital punishment, we risk an even greater injustice…) and that this discussion process has been a dynamic one, with some of the arguments being modified or reframed in the course of the reasoning that has led to the presentation of the case that we see in the dialogue excerpt.
When reviewing their previous evaluation of individual arguments, Phil and Sophia agree that two of the pro capital punishment arguments, the deterrence and cost arguments, do not hold up—their conclusions are not justified. They are refuted by under cutter arguments and thus are given no weight. However, in addition to the likelihood that the conclusion is true or credible, the arguments can also be assessed with respect to the amount of support (positive or negative) they provide for the case for capital punishment. And each of the deterrence and cost arguments, if they had been credible, would have added different amounts of weight to the case for capital punishment. If capital punishment really did serve as a significant deterrent to murder, that would be a strong argument in its favor, grounded as it is in the widely shared value of saving the lives of innocent people. Even if it were true, however, that the costs are greater to incarcerate for life than to execute, that would not constitute a strong argument in light of the moral objections to capital punishment because of the prima facie presumption that moral issues should generally trump instrumental issues such as cost.
Another of the pro capital punishment arguments, the incapacitation argument, is recognized as sound in the sense that it is true that dead murderers cannot murder again. Nonetheless it is seen as a rather drastic way of removing murderers from circulation given there are other possibilities and so is not a very strong argument for capital punishment. Thus this argument is weakened by a specific counter argument that there is a less morally troubling alternative, life imprisonment, that can achieve the same goal. The retribution argument, on the other hand, is seen as based on strong grounds—an appeal to justice, which is a widely shared value and one that is inherent to any legal system. Nonetheless, although the legitimacy of the appeal to justice is recognized, the weight of the argument as a justification for capital punishment is lessened because life imprisonment can be seen as an alternative which also meets the demand for justice. For both the incapacitation and retribution arguments, then, their weight in the debate is reduced because of the existence of less problematic alternatives.
The likelihood of executing innocent people is viewed by our two inquirers as a very strong argument against capital punishment, indeed as a consideration which overrides most other considerations, appealing as it does to a very strongly held value (not to kill innocent people) and a basic principle of the law (not to punish the innocent). It is true that any system of punishment will have errors no matter how good a job the system does in trying to avoid them. It is, however, crucial to the strength of the argument that some executions (and other long-term incarcerations) have been shown to have been erroneous. So the execution of innocent people is not just a theoretical possibility or an exceedingly rare occurrence. The frequency of such occurrences and the racial bias evident in many cases, in at least some locations, add to the strength of the argument. The weight given to this argument must still be seen as comparative, however, in that, if it could be shown that capital punishment were a significant deterrent and that it would thereby prevent many more innocents from being murdered than would be victims of system error, a much stronger case could be made for the practice. Because of the comparative nature of these evaluations, numbers, if credible and appropriate, may be significant.
We can also see how an appeal to the question of burden of proof is used to help determine how strong the arguments on various sides would need to be in order to prevail. In this case, the worldwide trend toward abolition sets up a burden of proof on the retentionist side. The determination of burden of proof is less pivotal in this case as the anti- capital punishment arguments have been judged to be considerably stronger, but it can be decisive with respect to issues where the reasons on each side are judged to be more evenly balanced. Consider the criminal trial situation where the burden of proof is clearly on the prosecution. The failure of the defense to decisively undermine the prosecutor’s argument should not result in the defendant being convicted since all the defense needs to do is show that there is a reasonable doubt about the guilt of the accused.
One aspect of weighing that is illustrated in the proceeding is that an important ground for justifying weightings is an appeal to widely shared values and principles. The extent of agreement in this regard should not be underestimated. There would, for example, be widespread agreement that the legal system should instantiate principles of justice; that moral considerations should generally take priority over cost considerations; that the state executing innocent people is extremely ethically problematic. Some of these values and principles are built into various domains and related to the “point of the practice.” It is, for example, a basic principle in law not to convict or punish an innocent person. The alleviation of suffering is a foundational value in medicine. Education is grounded in the learning of the child. Weightings can be legitimately justified in terms of such values and principles, and judgments can be rationally criticized which exhibit inappropriate weightings. We would, for example, be justified in criticizing an educational policy if it was seen to value administrative efficiency over the learning of the child.
An excellent example of this aspect of weighing is provided by Allen in his paper discussing Canada’s Rape Shield decision (Allen 1993) where he cites an excerpt from the opinion of one of the judges regarding the exclusion of possibly prejudicial evidence in rape cases:
When, however, prejudicial evidence is for the defence, the prejudicial effect it would have if admitted must substantially outweigh its probative value before a judge can exclude it. This is because a free and democratic society attaches great importance to the principle that an innocent person must not be convicted (p.106).
Here we have both an explicit statement of a central principle that ought to be appealed to in legal decisions and a judgment about the appropriate weighting of considerations in a particular case based on this principle.
There can, of course, be disagreement, even at times deep disagreement, about the relevant or primary considerations, as seems to be the case, for example, in the abortion debate. It is often the case, however, that there will be agreement on the considerations but disagreement over how to prioritize them or how they play out in particular instances. In the rape shield decision cited by Allen, for example, a dissenting opinion by another of the judges argued that the excluded sexual history evidence “is either irrelevant or so prejudicial that its minimal probative value is overwhelmed by its distorting effect” (Allen 1993, p.107). In this case there is agreement regarding the principles that are relevant, i.e., prejudicial effect vs. probative value, but disagreement about their relative weighting in this particular context. As another example, amongst people toward the left of the political spectrum, there are those who support a carbon tax because they believe that it would have a positive impact on the environment while there are others who oppose it because they believe that it would have a negative impact on economically disadvantaged individuals. Although both groups value both the environment and economic equality, they prioritize these values differently with respect to this particular issue. These differences in judgment may be based to some extent on differences in how the likelihood or the severity of the various possible outcomes is assessed or how the short term versus the long term costs and benefits of the different policies are calculated. But these are differences for which one can offer justifications and about which one can reason.
Another example of an explicit discussion of weighing can be seen in a groundbreaking paper by Cornfield (1959) in the context of the early debate about whether smoking caused lung cancer. Cornfield argued that despite the fact that researchers could not provide a good biological model (i.e., animal experiments) to demonstrate the link between smoking and lung cancer, in this case that criterion should not be given the weight it usually receives in epidemiological reasoning. His argument was that, since smoking exhibited very strong correlations and a strong “dose relationship” with lung cancer, these facts and the fact of the lack of credible alternative explanations for the data should be taken as adequate to establish a causal link between smoking and lung cancer. This was one of the first successful arguments in epidemiology since the late 19 th century to subordinate the biological account to the results of large-scale statistical results.
We take these examples to show that there is a role for a rational examination of weightings and the considerations that lie behind them. In this regard, the two opinions cited in the rape shield case (or the argument by Cornfield) can be seen as models for the role of the justification of weightings. Such an explicit justification of weightings puts them forward for scrutiny in the arena of public reason where they can be the basis for deliberation by others and for ongoing inquiry. Since weighing is a dynamic process, there is always the possibility that arguments and even issues may be reframed, resulting in the dissolution of a disagreement over how values or considerations have been weighed. An example would be a public policy debate, initially framed in terms of the competing rights of various parties being reframed in terms of the welfare of the community. Such a process will not necessarily lead to agreement among the interlocutors, however. But unless and until the issue is considered settled, any evaluation made can be seen as a moment in and contribution to on ongoing public process of reasoning about the issue by others as well as ourselves.
Allen, D. 1993. “Relevance, Conduction and Canada’s Rape-shield Decision.” Informal Logic 15, 2: 105-122.
Bailin, S. and M. Battersby. 2009. “Inquiry: A Dialectical Approach to Teaching Critical Thinking.” In Argument cultures: Proceedings of OSSA 8 CD-ROM, edited by J. Ritola. Windsor, ON: OSSA.
______. 2016. Reason in the Balance: An Inquiry Approach to Critical Thinking , 2 nd Edition. Cambridge, Mass: Hackett; 2010. 1 st Edition, McGraw-Hill Ryerson.
Battersby, M. 2006. “Applied Epistemology and Argumentation in Epidemiology.” Informal Logic 26, 1: 42-61.
Cornfield, J. et al. 1959. “Smoking and Lung Cancer: Recent Evidence and a Discussion of Some Questions.” Journal of the National Cancer Institute 22: 173-203.
Govier. T. 1985. A Practical Study of Argument . Belmond, CA: Wadsworth.
______. 1987. Problems in Argument Analysis and Evaluation . Providence, RI: Foris Publications.
______. 1999. The Philosophy of Argument . Newport News: Vale Press.
Hitchcock, D. 2000. “Statement on Practical Reasoning.” Retrieved from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.29.6897&rep=rep1&type=pdf , downloaded Jan. 16, 2010.
Johnson, R. H. 2000. Manifest Rationality: A Pragmatic Theory of Argument. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
______. 2007. “Anticipating Objections as a Way of Coping with Dissensus.” In Dissensus and the Search for Common Ground , CD-ROM, 1-16, edited by H.V. Hansen, et al . Windsor, ON: OSSA.
Kahneman, D., P. Slovic and A. Tversky. 1982. Judgment Under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kock, C. 2007a. “Is Practical Reasoning Presumptive?” Informal Logic 27, 1: 91-108.
______. 2007b. “Norms of Legitimate Dissensus.” Informal Logic 27, 2: 179-196.
McBryde, Johnson , H. 2003, Feb. 16. “Unspeakable Conversations.” New York Times . Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2003/02/16/ magazine/ unspeakable-conversations.html?ref=petersinger
Wellman, C. 1971. Challenge and Response: Justification in Ethics. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press.
Wohlrapp, H. 1998. “A New Light on Non-deductive Argumentation Schemes.” Argumentation 12: 341-350.
Zenker, F. 2007. “Complexity Without Insight: Ceteris Paribus Clauses in Assessing Conductive Argumentation.” Retrieved from www.frank zenker .de/downloads/ ZENKER _ALTA_2007.pdf , downloaded Jan. 15, 2010.
Inquiry: A New Paradigm for Critical Thinking Copyright © 2018 by Windsor Studies in Argumentation & The Authors is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2: Critical Thinking, Research, Reading, and Writing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 162132

- Nathan Smith et al.
You have likely heard the term “critical thinking” and have probably been instructed to become a “good critical thinker.” Unfortunately, you are probably also unclear what exactly this means because the term is poorly defined and infrequently taught. “But I know how to think,” you might say, and that is certainly true. Critical thinking, however, is a specific skill. This chapter is an informal and practical guide to critical thinking and will also guide you in how to conduct research, reading, and writing for philosophy classes.
Critical thinking is set of skills, habits, and attitudes that promote reflective, clear reasoning. Studying philosophy can be particularly helpful for developing good critical thinking skills, but often the connection between the two is not made clear. This chapter will approach critical thinking from a practical standpoint, with the goal of helping you become more aware of some of the pitfalls of everyday thinking and making you a better philosophy student.
While you may have learned research, reading, and writing skills in other classes—for instance, in a typical English composition course—the intellectual demands in a philosophy class are different. Here you will find useful advice about how to approach research, reading, and writing in philosophy.
- 2.1: The Brain Is an Inference Machine
- 2.2: Overcoming Cognitive Biases and Engaging in Critical Reflection
- 2.3: Developing Good Habits of Mind
- 2.4: Gathering Information, Evaluating Sources, and Understanding Evidence
- 2.5: Reading Philosophy
- 2.6: Writing Philosophy Papers
- 2.7: Summary
- 2.8: Key Terms
- 2.9: Review Questions
Thumbnail: Critical thinking as chess (Unsplash License; Lou Levit via Unsplash )
Chapter 9: Critical Thinking and Reasoning
Objectives and introduction, chapter 6: critical thinking & reasoning.
By Terri Russ, J.D., Ph.D. Saint Mary’s College, Notre Dame, IN
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
- Understand and explain the importance of critical thinking
- Identify the core skills associated with critical thinking
- Demonstrate the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning
- Construct a logically sound and well-reasoned argument
- Avoid the various fallacies that can arise through the misuse of logic
- Apply chapter concepts in final questions and activities
Introduction

“Filos segundo logo” by Filosofias filosoficas. CC-BY .
As we meander through our daily routines, we are surrounded by numerous messages and people trying to get our attention and convince us to do something. We sign into our e-mail accounts and are bombarded with sales pitches to help us get rich quick or promise to fix all of our embarrassing physical problems. We drive to school and see billboards touting tantalizing restaurants or pitching local political candidates. We converse with our friends and family about current events like the crazy car thief who tried to avoid the police by driving down train tracks right into an oncoming train. Throughout all of these exchanges, we must constantly strive to make sense of the messages and determine which are true and which are not true, which are probably and which are improbable, which are intended and which are unintended. When we do this we practice critical thinking . We evaluate the arguments presented and determine if their logic is sound or if they rely on fallacies to build their case. In this chapter you will learn how to use critical thinking in all areas of your life, including preparing and presenting speeches. You will also learn how to construct a logical argument that avoids the pitfalls of fallacious thinking.
- Chapter 6 Objectives, Outline, and Introduction. Authored by : Terri Russ, J.D., Ph.D.. Provided by : Saint Mary's College, Notre Dame, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Filos Segundo Logo. Authored by : Filosofias filosoficas. Located at : http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Filos_segundo_logo.JPG%20 . License : CC BY: Attribution

Privacy Policy
- Increase Font Size
Chapter 6: Critical Thinking

“We cannot change anything if we cannot change our thinking.”
~ Santosh Kalwar
Where Are You Now?
Assess your present knowledge and attitudes.
Where Do You Want to Go?
Think about how you answered the questions above. Be honest with yourself. On a scale of 1 to 10, how would you rate your level of thinking skills at this time?
In the following list, circle the three most important areas in which you think you can improve:
- Applying information
- Analyzing information
- Thinking critically
- Asking questions about information
- Evaluating information
- Coming up with new ideas
- Solving problems
- Making decisions
- Identifying weaknesses in ideas
- Choosing sources for research
Are there other areas in which you can improve your thinking skills? Write down other things you feel you need to work on.
What Is Thought?
- Thinking is the mental process you use to form associations and models of the world. When you think, you manipulate information to form concepts, to engage in problem-solving, to reason, and to make decisions.
- Thought can be described as the act of thinking that produces thoughts, which arise as ideas, images, sounds, or even emotions.
The Cognitive Domain of Learning
The cognitive domain of learning is divided into six main learning-skill levels, or learning-skill stages, which are arranged hierarchically—moving from the simplest of functions like remembering and understanding, to more complex learning skills, like applying and analyzing, to the most complex skills—evaluating and creating. The lower levels are more straightforward and fundamental, and the higher levels are more sophisticated. [1] See Figure 1, below.

The following table describes the six main skill sets within the cognitive domain.
You can explore these concepts further in the two videos, below.
The first is from the Center for Learning Success at Louisiana State University. It discusses Bloom’s with regard to student success in college.
Video: Bloom’s Taxonomy learning levels
This next video is a culturally based way of understanding and applying Bloom’s taxonomy.
Video: Bloom’s Taxonomy Featuring Harry Potter Movies
You can download a transcript of the video here .
Critical Thinking Skills

What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. It means asking probing questions like, “How do we know?” or “Is this true in every case or just in this instance?” It involves being skeptical and challenging assumptions, rather than simply memorizing facts or blindly accepting what you hear or read.
Critical Thinking IS
- Examining assumptions
- Challenging reasoning
- Uncovering biases
Critical Thinking is NOT
- Group thinking
- Blind acceptance of authority
The following video, from Lawrence Bland, presents the major concepts and benefits of critical thinking.
Video: Critical Thinking
What Is Logic, and Why Is It Important in Critical Thinking?
The word logic comes from the Ancient Greek logike , referring to the science or art of reasoning. Using logic, a person evaluates arguments and reasoning and strives to distinguish between good and bad reasoning, or between truth and falsehood. Using logic, you can evaluate ideas or claims people make, make good decisions, and form sound beliefs about the world. [1]
Questions of Logic in Critical Thinking
- What’s happening? Gather the basic information and begin to think of questions.
- Why is it important? Ask yourself why it’s significant and whether or not you agree.
- What don’t I see? Is there anything important missing?
- How do I know? Ask yourself where the information came from and how it was constructed.
- Who is saying it? What’s the position of the speaker and what is influencing them?
- What else? What if? What other ideas exist and are there other possibilities?
Problem-Solving with Critical Thinking
Strategies and action checklist.
- o Identify the problem
- o Provide as many supporting details as possible
- o Provide examples
- o Organize the information logically
- o Use logic to identify your most important goals
- o Identify implications and consequences
- o Identify facts
- o Select your solution
- o Use gathered facts and relevant evidence
- o Support and defend solutions considered valid
- o Defend your solution
Developing Yourself As a Critical Thinker

Critical thinking is a fundamental skill for college students, but it should also be a lifelong pursuit. Below are additional strategies to develop yourself as a critical thinker in college and in everyday life:
- Reflect and practice : Always reflect on what you’ve learned. Is it true all the time? How did you arrive at your conclusions?
- Use wasted time : It’s certainly important to make time for relaxing, but if you find you are indulging in too much of a good thing, think about using your time more constructively. Think about the time of day you are most effective and have the most energy. Plan to do your most difficult work during these times.
- Redefine the way you see things : It can be very uninteresting to always think the same way. Challenge yourself to see familiar things in new ways. Put yourself in someone else’s shoes and consider things from a different angle or perspective. If you’re trying to solve a problem, list all your concerns: what you need in order to solve it, who can help, what some possible barriers might be, etc. It’s often possible to reframe a problem as an opportunity. Try to find a solution where there seems to be none.
- Analyze the influences on your thinking and in your life : Why do you think or feel the way you do? Analyze your influences. Think about who in your life influences you. Do you feel or react a certain way because of social convention, or because you believe it is what is expected of you? Try to break out of any molds that may be constricting you.
- Express yourself : Critical thinking also involves being able to express yourself clearly. Most important in expressing yourself clearly is stating one point at a time. You might be inclined to argue every thought, but you might have greater impact if you focus just on your main arguments. This will help others to follow your thinking clearly. For more abstract ideas, assume that your audience may not understand. Provide examples, analogies, or metaphors where you can.
- Enhance your wellness : It’s easier to think critically when you take care of your mental and physical health. Try taking 10-minute activity breaks to reach 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity each day . Try taking a break between classes and walk to the coffee shop that’s farthest away. Scheduling physical activity into your day can help lower stress and increase mental alertness.
Activity: Reflect on Critical Thinking
- Apply critical thinking strategies to your life
Directions:
- Think about someone you consider to be a critical thinker (friend, professor, historical figure, etc). What qualities does he/she have?
- Review some of the critical thinking strategies discussed on this page. Pick one strategy that makes sense to you. How can you apply this critical thinking technique to your academic work?
- Habits of mind are attitudes and beliefs that influence how you approach the world (i.e., inquiring attitude, open mind, respect for truth, etc). What is one habit of mind you would like to actively develop over the next year? How will you develop a daily practice to cultivate this habit?
- Write your responses in journal form, and submit according to your instructor’s guidelines.
Outside Resources
- Glossary of Critical Thinking Terms
- Critical Thinking Self-Assessment
- Logical Fallacies Jeopardy Template
- Thinking Critically | Learning Commons
- Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking in Everyday Life
- Infact TedTalk #1
- Infact TedTalk #2
- Infact TedTalk #3
- Here Be Dragons
In Real Life

After months of searching for a part-time job, Charles accepted a position as a community organizer with a local non-profit. His primary responsibilities were to register new voters and inform registered voters about ballot issues. Although personally, he was not deeply passionate about voting, politics, or even interested in community issues, he was excited about the flexibility of his new job. Charles only had four classes to take in order to earn his associate’s degree in Business Administration. He needed a flexible schedule in order to complete his courses and work. His supervisor agreed to schedule Charles around his classes as long as Charles met the required weekly goals.
Charles’ first impression of community organizing was that it was going to be really easy. He thought that people would immediately register to vote after he asked them. Charles did not think it was necessary to engage prospective voters in conversation about voting. He simply asked if they wanted to register to vote and if the answer was no, he moved on to the next prospect. Charles did not think it was helpful to practice approaching prospective voters or to learn more about the issues and candidates that were on the upcoming ballot.
After two weeks into the position, Charles’ supervisor expressed dissatisfaction with his performance which made Charles fearful of losing his job. He felt that this job provided the most flexibility for him to continue to attend his classes. However, if Charles did not improve his ability to register more voters, he would lose his job.
Discussion Questions:
- How does Charles’ personal interest in voting and community issues impact his performance?
- How could Charles use critical thinking skills to improve his ability to register more voters?
- What skills do you think Charles might have as a business student that could be useful to him in his new job?
- How could Charles’ supervisor support and guide him in dealing with prospective voters?
Chapter Discussion Questions
- What is the difference between thinking and thought? Give an example of when and how you use each.
- What is critical thinking? Has there ever been a time when you, or someone you have known, has preferred ignorance over being informed? Why?
- What are typical characteristics and attributes of critical thinkers? List them. Are you a critical thinker? Give an example/story where you have used critical thinking skills.
ACAD100: Success Pathways at Lansing Community College, Third Edition by Root,T, Eaton, T, Madigan, M and Menefee, E. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Module 7: Thinking, Reasoning, and Problem-Solving
This module is about how a solid working knowledge of psychological principles can help you to think more effectively, so you can succeed in school and life. You might be inclined to believe that—because you have been thinking for as long as you can remember, because you are able to figure out the solution to many problems, because you feel capable of using logic to argue a point, because you can evaluate whether the things you read and hear make sense—you do not need any special training in thinking. But this, of course, is one of the key barriers to helping people think better. If you do not believe that there is anything wrong, why try to fix it?
The human brain is indeed a remarkable thinking machine, capable of amazing, complex, creative, logical thoughts. Why, then, are we telling you that you need to learn how to think? Mainly because one major lesson from cognitive psychology is that these capabilities of the human brain are relatively infrequently realized. Many psychologists believe that people are essentially “cognitive misers.” It is not that we are lazy, but that we have a tendency to expend the least amount of mental effort necessary. Although you may not realize it, it actually takes a great deal of energy to think. Careful, deliberative reasoning and critical thinking are very difficult. Because we seem to be successful without going to the trouble of using these skills well, it feels unnecessary to develop them. As you shall see, however, there are many pitfalls in the cognitive processes described in this module. When people do not devote extra effort to learning and improving reasoning, problem solving, and critical thinking skills, they make many errors.
As is true for memory, if you develop the cognitive skills presented in this module, you will be more successful in school. It is important that you realize, however, that these skills will help you far beyond school, even more so than a good memory will. Although it is somewhat useful to have a good memory, ten years from now no potential employer will care how many questions you got right on multiple choice exams during college. All of them will, however, recognize whether you are a logical, analytical, critical thinker. With these thinking skills, you will be an effective, persuasive communicator and an excellent problem solver.
The module begins by describing different kinds of thought and knowledge, especially conceptual knowledge and critical thinking. An understanding of these differences will be valuable as you progress through school and encounter different assignments that require you to tap into different kinds of knowledge. The second section covers deductive and inductive reasoning, which are processes we use to construct and evaluate strong arguments. They are essential skills to have whenever you are trying to persuade someone (including yourself) of some point, or to respond to someone’s efforts to persuade you. The module ends with a section about problem solving. A solid understanding of the key processes involved in problem solving will help you to handle many daily challenges.
7.1. Different kinds of thought
7.2. Reasoning and Judgment
7.3. Problem Solving
READING WITH PURPOSE
Remember and understand.
By reading and studying Module 7, you should be able to remember and describe:
- Concepts and inferences (7.1)
- Procedural knowledge (7.1)
- Metacognition (7.1)
- Characteristics of critical thinking: skepticism; identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; reasoning and problem solving skills (7.1)
- Reasoning: deductive reasoning, deductively valid argument, inductive reasoning, inductively strong argument, availability heuristic, representativeness heuristic (7.2)
- Fixation: functional fixedness, mental set (7.3)
- Algorithms, heuristics, and the role of confirmation bias (7.3)
- Effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
By reading and thinking about how the concepts in Module 6 apply to real life, you should be able to:
- Identify which type of knowledge a piece of information is (7.1)
- Recognize examples of deductive and inductive reasoning (7.2)
- Recognize judgments that have probably been influenced by the availability heuristic (7.2)
- Recognize examples of problem solving heuristics and algorithms (7.3)
Analyze, Evaluate, and Create
By reading and thinking about Module 6, participating in classroom activities, and completing out-of-class assignments, you should be able to:
- Use the principles of critical thinking to evaluate information (7.1)
- Explain whether examples of reasoning arguments are deductively valid or inductively strong (7.2)
- Outline how you could try to solve a problem from your life using the effective problem solving sequence (7.3)
7.1. Different kinds of thought and knowledge
- Take a few minutes to write down everything that you know about dogs.
- Do you believe that:
- Psychic ability exists?
- Hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness?
- Magnet therapy is effective for relieving pain?
- Aerobic exercise is an effective treatment for depression?
- UFO’s from outer space have visited earth?
On what do you base your belief or disbelief for the questions above?
Of course, we all know what is meant by the words think and knowledge . You probably also realize that they are not unitary concepts; there are different kinds of thought and knowledge. In this section, let us look at some of these differences. If you are familiar with these different kinds of thought and pay attention to them in your classes, it will help you to focus on the right goals, learn more effectively, and succeed in school. Different assignments and requirements in school call on you to use different kinds of knowledge or thought, so it will be very helpful for you to learn to recognize them (Anderson, et al. 2001).
Factual and conceptual knowledge
Module 5 introduced the idea of declarative memory, which is composed of facts and episodes. If you have ever played a trivia game or watched Jeopardy on TV, you realize that the human brain is able to hold an extraordinary number of facts. Likewise, you realize that each of us has an enormous store of episodes, essentially facts about events that happened in our own lives. It may be difficult to keep that in mind when we are struggling to retrieve one of those facts while taking an exam, however. Part of the problem is that, in contradiction to the advice from Module 5, many students continue to try to memorize course material as a series of unrelated facts (picture a history student simply trying to memorize history as a set of unrelated dates without any coherent story tying them together). Facts in the real world are not random and unorganized, however. It is the way that they are organized that constitutes a second key kind of knowledge, conceptual.
Concepts are nothing more than our mental representations of categories of things in the world. For example, think about dogs. When you do this, you might remember specific facts about dogs, such as they have fur and they bark. You may also recall dogs that you have encountered and picture them in your mind. All of this information (and more) makes up your concept of dog. You can have concepts of simple categories (e.g., triangle), complex categories (e.g., small dogs that sleep all day, eat out of the garbage, and bark at leaves), kinds of people (e.g., psychology professors), events (e.g., birthday parties), and abstract ideas (e.g., justice). Gregory Murphy (2002) refers to concepts as the “glue that holds our mental life together” (p. 1). Very simply, summarizing the world by using concepts is one of the most important cognitive tasks that we do. Our conceptual knowledge is our knowledge about the world. Individual concepts are related to each other to form a rich interconnected network of knowledge. For example, think about how the following concepts might be related to each other: dog, pet, play, Frisbee, chew toy, shoe. Or, of more obvious use to you now, how these concepts are related: working memory, long-term memory, declarative memory, procedural memory, and rehearsal? Because our minds have a natural tendency to organize information conceptually, when students try to remember course material as isolated facts, they are working against their strengths.
One last important point about concepts is that they allow you to instantly know a great deal of information about something. For example, if someone hands you a small red object and says, “here is an apple,” they do not have to tell you, “it is something you can eat.” You already know that you can eat it because it is true by virtue of the fact that the object is an apple; this is called drawing an inference , assuming that something is true on the basis of your previous knowledge (for example, of category membership or of how the world works) or logical reasoning.
Procedural knowledge
Physical skills, such as tying your shoes, doing a cartwheel, and driving a car (or doing all three at the same time, but don’t try this at home) are certainly a kind of knowledge. They are procedural knowledge, the same idea as procedural memory that you saw in Module 5. Mental skills, such as reading, debating, and planning a psychology experiment, are procedural knowledge, as well. In short, procedural knowledge is the knowledge how to do something (Cohen & Eichenbaum, 1993).
Metacognitive knowledge
Floyd used to think that he had a great memory. Now, he has a better memory. Why? Because he finally realized that his memory was not as great as he once thought it was. Because Floyd eventually learned that he often forgets where he put things, he finally developed the habit of putting things in the same place. (Unfortunately, he did not learn this lesson before losing at least 5 watches and a wedding ring.) Because he finally realized that he often forgets to do things, he finally started using the To Do list app on his phone. And so on. Floyd’s insights about the real limitations of his memory have allowed him to remember things that he used to forget.
All of us have knowledge about the way our own minds work. You may know that you have a good memory for people’s names and a poor memory for math formulas. Someone else might realize that they have difficulty remembering to do things, like stopping at the store on the way home. Others still know that they tend to overlook details. This knowledge about our own thinking is actually quite important; it is called metacognitive knowledge, or metacognition . Like other kinds of thinking skills, it is subject to error. For example, in unpublished research, one of the authors surveyed about 120 General Psychology students on the first day of the term. Among other questions, the students were asked them to predict their grade in the class and report their current Grade Point Average. Two-thirds of the students predicted that their grade in the course would be higher than their GPA. (The reality is that at our college, students tend to earn lower grades in psychology than their overall GPA.) Another example: Students routinely report that they thought they had done well on an exam, only to discover, to their dismay, that they were wrong (more on that important problem in a moment). Both errors reveal a breakdown in metacognition.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
In general, most college students probably do not study enough. For example, using data from the National Survey of Student Engagement, Fosnacht, McCormack, and Lerma (2018) reported that first-year students at 4-year colleges in the U.S. averaged less than 14 hours per week preparing for classes. The typical suggestion is that you should spend two hours outside of class for every hour in class, or 24 – 30 hours per week for a full-time student. Clearly, students in general are nowhere near that recommended mark. Many observers, including some faculty, believe that this shortfall is a result of students being too busy or lazy. Now, it may be true that many students are too busy, with work and family obligations, for example. Others, are not particularly motivated in school, and therefore might correctly be labeled lazy. A third possible explanation, however, is that some students might not think they need to spend this much time. And this is a matter of metacognition. Consider the scenario that we mentioned above, students thinking they had done well on an exam only to discover that they did not. Justin Kruger and David Dunning examined scenarios very much like this in 1999. Kruger and Dunning gave research participants tests measuring humor, logic, and grammar. Then, they asked the participants to assess their own abilities and test performance in these areas. They found that participants in general tended to overestimate their abilities, already a problem with metacognition. Importantly, the participants who scored the lowest overestimated their abilities the most. Specifically, students who scored in the bottom quarter (averaging in the 12th percentile) thought they had scored in the 62nd percentile. This has become known as the Dunning-Kruger effect . Many individual faculty members have replicated these results with their own student on their course exams, including the authors of this book. Think about it. Some students who just took an exam and performed poorly believe that they did well before seeing their score. It seems very likely that these are the very same students who stopped studying the night before because they thought they were “done.” Quite simply, it is not just that they did not know the material. They did not know that they did not know the material. That is poor metacognition.
In order to develop good metacognitive skills, you should continually monitor your thinking and seek frequent feedback on the accuracy of your thinking (Medina, Castleberry, & Persky 2017). For example, in classes get in the habit of predicting your exam grades. As soon as possible after taking an exam, try to find out which questions you missed and try to figure out why. If you do this soon enough, you may be able to recall the way it felt when you originally answered the question. Did you feel confident that you had answered the question correctly? Then you have just discovered an opportunity to improve your metacognition. Be on the lookout for that feeling and respond with caution.
concept : a mental representation of a category of things in the world
Dunning-Kruger effect : individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
inference : an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
metacognition : knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
Critical thinking
One particular kind of knowledge or thinking skill that is related to metacognition is critical thinking (Chew, 2020). You may have noticed that critical thinking is an objective in many college courses, and thus it could be a legitimate topic to cover in nearly any college course. It is particularly appropriate in psychology, however. As the science of (behavior and) mental processes, psychology is obviously well suited to be the discipline through which you should be introduced to this important way of thinking.
More importantly, there is a particular need to use critical thinking in psychology. We are all, in a way, experts in human behavior and mental processes, having engaged in them literally since birth. Thus, perhaps more than in any other class, students typically approach psychology with very clear ideas and opinions about its subject matter. That is, students already “know” a lot about psychology. The problem is, “it ain’t so much the things we don’t know that get us into trouble. It’s the things we know that just ain’t so” (Ward, quoted in Gilovich 1991). Indeed, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain wrong. Randolph Smith (2002) wrote a book about critical thinking in psychology called Challenging Your Preconceptions, highlighting this fact. On the other hand, many of students’ preconceptions about psychology are just plain right! But wait, how do you know which of your preconceptions are right and which are wrong? And when you come across a research finding or theory in this class that contradicts your preconceptions, what will you do? Will you stick to your original idea, discounting the information from the class? Will you immediately change your mind? Critical thinking can help us sort through this confusing mess.
But what is critical thinking? The goal of critical thinking is simple to state (but extraordinarily difficult to achieve): it is to be right, to draw the correct conclusions, to believe in things that are true and to disbelieve things that are false. We will provide two definitions of critical thinking (or, if you like, one large definition with two distinct parts). First, a more conceptual one: Critical thinking is thinking like a scientist in your everyday life (Schmaltz, Jansen, & Wenckowski, 2017). Our second definition is more operational; it is simply a list of skills that are essential to be a critical thinker. Critical thinking entails solid reasoning and problem solving skills; skepticism; and an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. Excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills contribute to critical thinking. So, you can consider the subject matter of sections 7.2 and 7.3 to be part of critical thinking. Because we will be devoting considerable time to these concepts in the rest of the module, let us begin with a discussion about the other aspects of critical thinking.
Let’s address that first part of the definition. Scientists form hypotheses, or predictions about some possible future observations. Then, they collect data, or information (think of this as making those future observations). They do their best to make unbiased observations using reliable techniques that have been verified by others. Then, and only then, they draw a conclusion about what those observations mean. Oh, and do not forget the most important part. “Conclusion” is probably not the most appropriate word because this conclusion is only tentative. A scientist is always prepared that someone else might come along and produce new observations that would require a new conclusion be drawn. Wow! If you like to be right, you could do a lot worse than using a process like this.
A Critical Thinker’s Toolkit
Now for the second part of the definition. Good critical thinkers (and scientists) rely on a variety of tools to evaluate information. Perhaps the most recognizable tool for critical thinking is skepticism (and this term provides the clearest link to the thinking like a scientist definition, as you are about to see). Some people intend it as an insult when they call someone a skeptic. But if someone calls you a skeptic, if they are using the term correctly, you should consider it a great compliment. Simply put, skepticism is a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided. People from Missouri should recognize this principle, as Missouri is known as the Show-Me State. As a skeptic, you are not inclined to believe something just because someone said so, because someone else believes it, or because it sounds reasonable. You must be persuaded by high quality evidence.
Of course, if that evidence is produced, you have a responsibility as a skeptic to change your belief. Failure to change a belief in the face of good evidence is not skepticism; skepticism has open mindedness at its core. M. Neil Browne and Stuart Keeley (2018) use the term weak sense critical thinking to describe critical thinking behaviors that are used only to strengthen a prior belief. Strong sense critical thinking, on the other hand, has as its goal reaching the best conclusion. Sometimes that means strengthening your prior belief, but sometimes it means changing your belief to accommodate the better evidence.
Many times, a failure to think critically or weak sense critical thinking is related to a bias , an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice. Everybody has biases, but many people are unaware of them. Awareness of your own biases gives you the opportunity to control or counteract them. Unfortunately, however, many people are happy to let their biases creep into their attempts to persuade others; indeed, it is a key part of their persuasive strategy. To see how these biases influence messages, just look at the different descriptions and explanations of the same events given by people of different ages or income brackets, or conservative versus liberal commentators, or by commentators from different parts of the world. Of course, to be successful, these people who are consciously using their biases must disguise them. Even undisguised biases can be difficult to identify, so disguised ones can be nearly impossible.
Here are some common sources of biases:
- Personal values and beliefs. Some people believe that human beings are basically driven to seek power and that they are typically in competition with one another over scarce resources. These beliefs are similar to the world-view that political scientists call “realism.” Other people believe that human beings prefer to cooperate and that, given the chance, they will do so. These beliefs are similar to the world-view known as “idealism.” For many people, these deeply held beliefs can influence, or bias, their interpretations of such wide ranging situations as the behavior of nations and their leaders or the behavior of the driver in the car ahead of you. For example, if your worldview is that people are typically in competition and someone cuts you off on the highway, you may assume that the driver did it purposely to get ahead of you. Other types of beliefs about the way the world is or the way the world should be, for example, political beliefs, can similarly become a significant source of bias.
- Racism, sexism, ageism and other forms of prejudice and bigotry. These are, sadly, a common source of bias in many people. They are essentially a special kind of “belief about the way the world is.” These beliefs—for example, that women do not make effective leaders—lead people to ignore contradictory evidence (examples of effective women leaders, or research that disputes the belief) and to interpret ambiguous evidence in a way consistent with the belief.
- Self-interest. When particular people benefit from things turning out a certain way, they can sometimes be very susceptible to letting that interest bias them. For example, a company that will earn a profit if they sell their product may have a bias in the way that they give information about their product. A union that will benefit if its members get a generous contract might have a bias in the way it presents information about salaries at competing organizations. (Note that our inclusion of examples describing both companies and unions is an explicit attempt to control for our own personal biases). Home buyers are often dismayed to discover that they purchased their dream house from someone whose self-interest led them to lie about flooding problems in the basement or back yard. This principle, the biasing power of self-interest, is likely what led to the famous phrase Caveat Emptor (let the buyer beware) .
Knowing that these types of biases exist will help you evaluate evidence more critically. Do not forget, though, that people are not always keen to let you discover the sources of biases in their arguments. For example, companies or political organizations can sometimes disguise their support of a research study by contracting with a university professor, who comes complete with a seemingly unbiased institutional affiliation, to conduct the study.
People’s biases, conscious or unconscious, can lead them to make omissions, distortions, and assumptions that undermine our ability to correctly evaluate evidence. It is essential that you look for these elements. Always ask, what is missing, what is not as it appears, and what is being assumed here? For example, consider this (fictional) chart from an ad reporting customer satisfaction at 4 local health clubs.
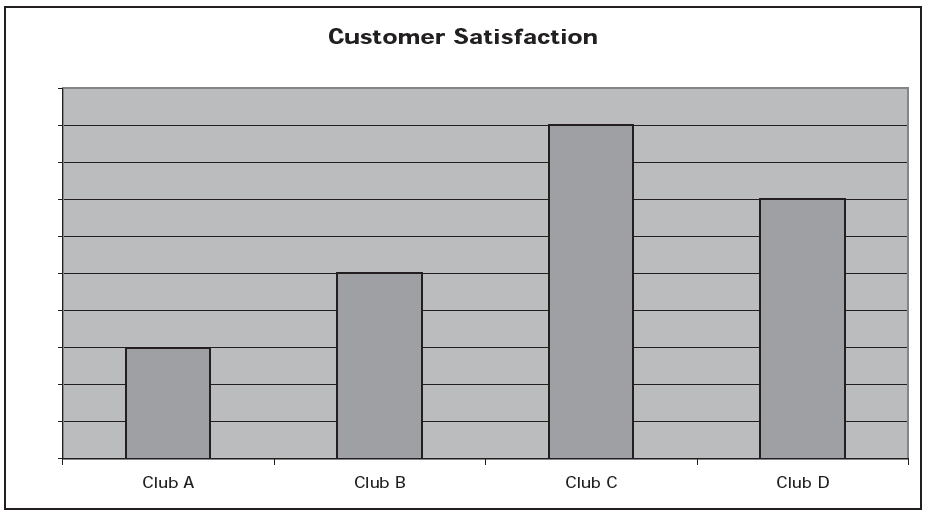
Clearly, from the results of the chart, one would be tempted to give Club C a try, as customer satisfaction is much higher than for the other 3 clubs.
There are so many distortions and omissions in this chart, however, that it is actually quite meaningless. First, how was satisfaction measured? Do the bars represent responses to a survey? If so, how were the questions asked? Most importantly, where is the missing scale for the chart? Although the differences look quite large, are they really?
Well, here is the same chart, with a different scale, this time labeled:
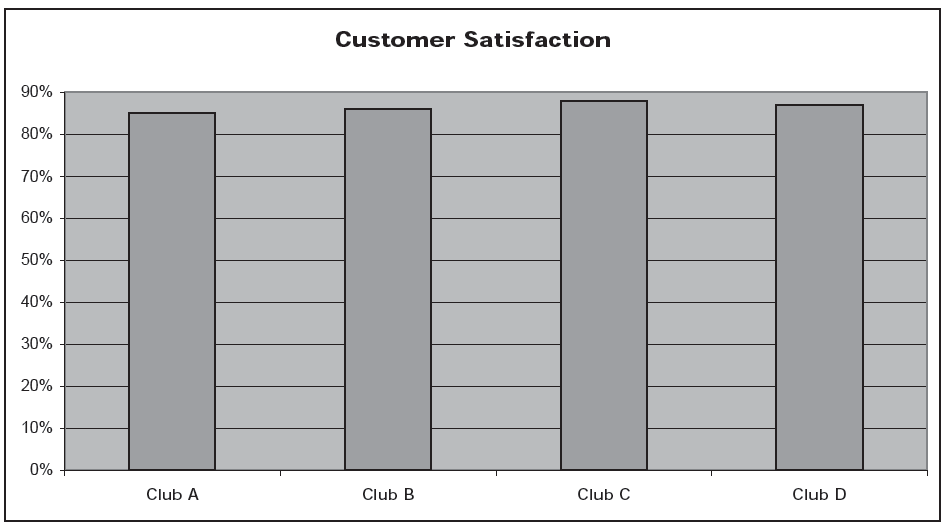
Club C is not so impressive any more, is it? In fact, all of the health clubs have customer satisfaction ratings (whatever that means) between 85% and 88%. In the first chart, the entire scale of the graph included only the percentages between 83 and 89. This “judicious” choice of scale—some would call it a distortion—and omission of that scale from the chart make the tiny differences among the clubs seem important, however.
Also, in order to be a critical thinker, you need to learn to pay attention to the assumptions that underlie a message. Let us briefly illustrate the role of assumptions by touching on some people’s beliefs about the criminal justice system in the US. Some believe that a major problem with our judicial system is that many criminals go free because of legal technicalities. Others believe that a major problem is that many innocent people are convicted of crimes. The simple fact is, both types of errors occur. A person’s conclusion about which flaw in our judicial system is the greater tragedy is based on an assumption about which of these is the more serious error (letting the guilty go free or convicting the innocent). This type of assumption is called a value assumption (Browne and Keeley, 2018). It reflects the differences in values that people develop, differences that may lead us to disregard valid evidence that does not fit in with our particular values.
Oh, by the way, some students probably noticed this, but the seven tips for evaluating information that we shared in Module 1 are related to this. Actually, they are part of this section. The tips are, to a very large degree, set of ideas you can use to help you identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. If you do not remember this section, we strongly recommend you take a few minutes to review it.
skepticism : a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
bias : an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
- Which of your beliefs (or disbeliefs) from the Activate exercise for this section were derived from a process of critical thinking? If some of your beliefs were not based on critical thinking, are you willing to reassess these beliefs? If the answer is no, why do you think that is? If the answer is yes, what concrete steps will you take?
7.2 Reasoning and Judgment
- What percentage of kidnappings are committed by strangers?
- Which area of the house is riskiest: kitchen, bathroom, or stairs?
- What is the most common cancer in the US?
- What percentage of workplace homicides are committed by co-workers?
An essential set of procedural thinking skills is reasoning , the ability to generate and evaluate solid conclusions from a set of statements or evidence. You should note that these conclusions (when they are generated instead of being evaluated) are one key type of inference that we described in Section 7.1. There are two main types of reasoning, deductive and inductive.
Deductive reasoning
Suppose your teacher tells you that if you get an A on the final exam in a course, you will get an A for the whole course. Then, you get an A on the final exam. What will your final course grade be? Most people can see instantly that you can conclude with certainty that you will get an A for the course. This is a type of reasoning called deductive reasoning , which is defined as reasoning in which a conclusion is guaranteed to be true as long as the statements leading to it are true. The three statements can be listed as an argument , with two beginning statements and a conclusion:
Statement 1: If you get an A on the final exam, you will get an A for the course
Statement 2: You get an A on the final exam
Conclusion: You will get an A for the course
This particular arrangement, in which true beginning statements lead to a guaranteed true conclusion, is known as a deductively valid argument . Although deductive reasoning is often the subject of abstract, brain-teasing, puzzle-like word problems, it is actually an extremely important type of everyday reasoning. It is just hard to recognize sometimes. For example, imagine that you are looking for your car keys and you realize that they are either in the kitchen drawer or in your book bag. After looking in the kitchen drawer, you instantly know that they must be in your book bag. That conclusion results from a simple deductive reasoning argument. In addition, solid deductive reasoning skills are necessary for you to succeed in the sciences, philosophy, math, computer programming, and any endeavor involving the use of logic to persuade others to your point of view or to evaluate others’ arguments.
Cognitive psychologists, and before them philosophers, have been quite interested in deductive reasoning, not so much for its practical applications, but for the insights it can offer them about the ways that human beings think. One of the early ideas to emerge from the examination of deductive reasoning is that people learn (or develop) mental versions of rules that allow them to solve these types of reasoning problems (Braine, 1978; Braine, Reiser, & Rumain, 1984). The best way to see this point of view is to realize that there are different possible rules, and some of them are very simple. For example, consider this rule of logic:
therefore q
Logical rules are often presented abstractly, as letters, in order to imply that they can be used in very many specific situations. Here is a concrete version of the of the same rule:
I’ll either have pizza or a hamburger for dinner tonight (p or q)
I won’t have pizza (not p)
Therefore, I’ll have a hamburger (therefore q)
This kind of reasoning seems so natural, so easy, that it is quite plausible that we would use a version of this rule in our daily lives. At least, it seems more plausible than some of the alternative possibilities—for example, that we need to have experience with the specific situation (pizza or hamburger, in this case) in order to solve this type of problem easily. So perhaps there is a form of natural logic (Rips, 1990) that contains very simple versions of logical rules. When we are faced with a reasoning problem that maps onto one of these rules, we use the rule.
But be very careful; things are not always as easy as they seem. Even these simple rules are not so simple. For example, consider the following rule. Many people fail to realize that this rule is just as valid as the pizza or hamburger rule above.
if p, then q
therefore, not p
Concrete version:
If I eat dinner, then I will have dessert
I did not have dessert
Therefore, I did not eat dinner
The simple fact is, it can be very difficult for people to apply rules of deductive logic correctly; as a result, they make many errors when trying to do so. Is this a deductively valid argument or not?
Students who like school study a lot
Students who study a lot get good grades
Jane does not like school
Therefore, Jane does not get good grades
Many people are surprised to discover that this is not a logically valid argument; the conclusion is not guaranteed to be true from the beginning statements. Although the first statement says that students who like school study a lot, it does NOT say that students who do not like school do not study a lot. In other words, it may very well be possible to study a lot without liking school. Even people who sometimes get problems like this right might not be using the rules of deductive reasoning. Instead, they might just be making judgments for examples they know, in this case, remembering instances of people who get good grades despite not liking school.
Making deductive reasoning even more difficult is the fact that there are two important properties that an argument may have. One, it can be valid or invalid (meaning that the conclusion does or does not follow logically from the statements leading up to it). Two, an argument (or more correctly, its conclusion) can be true or false. Here is an example of an argument that is logically valid, but has a false conclusion (at least we think it is false).
Either you are eleven feet tall or the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth.
You are not eleven feet tall
Therefore the Grand Canyon was created by a spaceship crashing into the earth
This argument has the exact same form as the pizza or hamburger argument above, making it is deductively valid. The conclusion is so false, however, that it is absurd (of course, the reason the conclusion is false is that the first statement is false). When people are judging arguments, they tend to not observe the difference between deductive validity and the empirical truth of statements or conclusions. If the elements of an argument happen to be true, people are likely to judge the argument logically valid; if the elements are false, they will very likely judge it invalid (Markovits & Bouffard-Bouchard, 1992; Moshman & Franks, 1986). Thus, it seems a stretch to say that people are using these logical rules to judge the validity of arguments. Many psychologists believe that most people actually have very limited deductive reasoning skills (Johnson-Laird, 1999). They argue that when faced with a problem for which deductive logic is required, people resort to some simpler technique, such as matching terms that appear in the statements and the conclusion (Evans, 1982). This might not seem like a problem, but what if reasoners believe that the elements are true and they happen to be wrong; they will would believe that they are using a form of reasoning that guarantees they are correct and yet be wrong.
deductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
argument : a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
deductively valid argument : an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
Inductive reasoning and judgment
Every day, you make many judgments about the likelihood of one thing or another. Whether you realize it or not, you are practicing inductive reasoning on a daily basis. In inductive reasoning arguments, a conclusion is likely whenever the statements preceding it are true. The first thing to notice about inductive reasoning is that, by definition, you can never be sure about your conclusion; you can only estimate how likely the conclusion is. Inductive reasoning may lead you to focus on Memory Encoding and Recoding when you study for the exam, but it is possible the instructor will ask more questions about Memory Retrieval instead. Unlike deductive reasoning, the conclusions you reach through inductive reasoning are only probable, not certain. That is why scientists consider inductive reasoning weaker than deductive reasoning. But imagine how hard it would be for us to function if we could not act unless we were certain about the outcome.
Inductive reasoning can be represented as logical arguments consisting of statements and a conclusion, just as deductive reasoning can be. In an inductive argument, you are given some statements and a conclusion (or you are given some statements and must draw a conclusion). An argument is inductively strong if the conclusion would be very probable whenever the statements are true. So, for example, here is an inductively strong argument:
- Statement #1: The forecaster on Channel 2 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #2: The forecaster on Channel 5 said it is going to rain today.
- Statement #3: It is very cloudy and humid.
- Statement #4: You just heard thunder.
- Conclusion (or judgment): It is going to rain today.
Think of the statements as evidence, on the basis of which you will draw a conclusion. So, based on the evidence presented in the four statements, it is very likely that it will rain today. Will it definitely rain today? Certainly not. We can all think of times that the weather forecaster was wrong.
A true story: Some years ago psychology student was watching a baseball playoff game between the St. Louis Cardinals and the Los Angeles Dodgers. A graphic on the screen had just informed the audience that the Cardinal at bat, (Hall of Fame shortstop) Ozzie Smith, a switch hitter batting left-handed for this plate appearance, had never, in nearly 3000 career at-bats, hit a home run left-handed. The student, who had just learned about inductive reasoning in his psychology class, turned to his companion (a Cardinals fan) and smugly said, “It is an inductively strong argument that Ozzie Smith will not hit a home run.” He turned back to face the television just in time to watch the ball sail over the right field fence for a home run. Although the student felt foolish at the time, he was not wrong. It was an inductively strong argument; 3000 at-bats is an awful lot of evidence suggesting that the Wizard of Ozz (as he was known) would not be hitting one out of the park (think of each at-bat without a home run as a statement in an inductive argument). Sadly (for the die-hard Cubs fan and Cardinals-hating student), despite the strength of the argument, the conclusion was wrong.
Given the possibility that we might draw an incorrect conclusion even with an inductively strong argument, we really want to be sure that we do, in fact, make inductively strong arguments. If we judge something probable, it had better be probable. If we judge something nearly impossible, it had better not happen. Think of inductive reasoning, then, as making reasonably accurate judgments of the probability of some conclusion given a set of evidence.
We base many decisions in our lives on inductive reasoning. For example:
Statement #1: Psychology is not my best subject
Statement #2: My psychology instructor has a reputation for giving difficult exams
Statement #3: My first psychology exam was much harder than I expected
Judgment: The next exam will probably be very difficult.
Decision: I will study tonight instead of watching Netflix.
Some other examples of judgments that people commonly make in a school context include judgments of the likelihood that:
- A particular class will be interesting/useful/difficult
- You will be able to finish writing a paper by next week if you go out tonight
- Your laptop’s battery will last through the next trip to the library
- You will not miss anything important if you skip class tomorrow
- Your instructor will not notice if you skip class tomorrow
- You will be able to find a book that you will need for a paper
- There will be an essay question about Memory Encoding on the next exam
Tversky and Kahneman (1983) recognized that there are two general ways that we might make these judgments; they termed them extensional (i.e., following the laws of probability) and intuitive (i.e., using shortcuts or heuristics, see below). We will use a similar distinction between Type 1 and Type 2 thinking, as described by Keith Stanovich and his colleagues (Evans and Stanovich, 2013; Stanovich and West, 2000). Type 1 thinking is fast, automatic, effortful, and emotional. In fact, it is hardly fair to call it reasoning at all, as judgments just seem to pop into one’s head. Type 2 thinking , on the other hand, is slow, effortful, and logical. So obviously, it is more likely to lead to a correct judgment, or an optimal decision. The problem is, we tend to over-rely on Type 1. Now, we are not saying that Type 2 is the right way to go for every decision or judgment we make. It seems a bit much, for example, to engage in a step-by-step logical reasoning procedure to decide whether we will have chicken or fish for dinner tonight.
Many bad decisions in some very important contexts, however, can be traced back to poor judgments of the likelihood of certain risks or outcomes that result from the use of Type 1 when a more logical reasoning process would have been more appropriate. For example:
Statement #1: It is late at night.
Statement #2: Albert has been drinking beer for the past five hours at a party.
Statement #3: Albert is not exactly sure where he is or how far away home is.
Judgment: Albert will have no difficulty walking home.
Decision: He walks home alone.
As you can see in this example, the three statements backing up the judgment do not really support it. In other words, this argument is not inductively strong because it is based on judgments that ignore the laws of probability. What are the chances that someone facing these conditions will be able to walk home alone easily? And one need not be drunk to make poor decisions based on judgments that just pop into our heads.
The truth is that many of our probability judgments do not come very close to what the laws of probability say they should be. Think about it. In order for us to reason in accordance with these laws, we would need to know the laws of probability, which would allow us to calculate the relationship between particular pieces of evidence and the probability of some outcome (i.e., how much likelihood should change given a piece of evidence), and we would have to do these heavy math calculations in our heads. After all, that is what Type 2 requires. Needless to say, even if we were motivated, we often do not even know how to apply Type 2 reasoning in many cases.
So what do we do when we don’t have the knowledge, skills, or time required to make the correct mathematical judgment? Do we hold off and wait until we can get better evidence? Do we read up on probability and fire up our calculator app so we can compute the correct probability? Of course not. We rely on Type 1 thinking. We “wing it.” That is, we come up with a likelihood estimate using some means at our disposal. Psychologists use the term heuristic to describe the type of “winging it” we are talking about. A heuristic is a shortcut strategy that we use to make some judgment or solve some problem (see Section 7.3). Heuristics are easy and quick, think of them as the basic procedures that are characteristic of Type 1. They can absolutely lead to reasonably good judgments and decisions in some situations (like choosing between chicken and fish for dinner). They are, however, far from foolproof. There are, in fact, quite a lot of situations in which heuristics can lead us to make incorrect judgments, and in many cases the decisions based on those judgments can have serious consequences.
Let us return to the activity that begins this section. You were asked to judge the likelihood (or frequency) of certain events and risks. You were free to come up with your own evidence (or statements) to make these judgments. This is where a heuristic crops up. As a judgment shortcut, we tend to generate specific examples of those very events to help us decide their likelihood or frequency. For example, if we are asked to judge how common, frequent, or likely a particular type of cancer is, many of our statements would be examples of specific cancer cases:
Statement #1: Andy Kaufman (comedian) had lung cancer.
Statement #2: Colin Powell (US Secretary of State) had prostate cancer.
Statement #3: Bob Marley (musician) had skin and brain cancer
Statement #4: Sandra Day O’Connor (Supreme Court Justice) had breast cancer.
Statement #5: Fred Rogers (children’s entertainer) had stomach cancer.
Statement #6: Robin Roberts (news anchor) had breast cancer.
Statement #7: Bette Davis (actress) had breast cancer.
Judgment: Breast cancer is the most common type.
Your own experience or memory may also tell you that breast cancer is the most common type. But it is not (although it is common). Actually, skin cancer is the most common type in the US. We make the same types of misjudgments all the time because we do not generate the examples or evidence according to their actual frequencies or probabilities. Instead, we have a tendency (or bias) to search for the examples in memory; if they are easy to retrieve, we assume that they are common. To rephrase this in the language of the heuristic, events seem more likely to the extent that they are available to memory. This bias has been termed the availability heuristic (Kahneman and Tversky, 1974).
The fact that we use the availability heuristic does not automatically mean that our judgment is wrong. The reason we use heuristics in the first place is that they work fairly well in many cases (and, of course that they are easy to use). So, the easiest examples to think of sometimes are the most common ones. Is it more likely that a member of the U.S. Senate is a man or a woman? Most people have a much easier time generating examples of male senators. And as it turns out, the U.S. Senate has many more men than women (74 to 26 in 2020). In this case, then, the availability heuristic would lead you to make the correct judgment; it is far more likely that a senator would be a man.
In many other cases, however, the availability heuristic will lead us astray. This is because events can be memorable for many reasons other than their frequency. Section 5.2, Encoding Meaning, suggested that one good way to encode the meaning of some information is to form a mental image of it. Thus, information that has been pictured mentally will be more available to memory. Indeed, an event that is vivid and easily pictured will trick many people into supposing that type of event is more common than it actually is. Repetition of information will also make it more memorable. So, if the same event is described to you in a magazine, on the evening news, on a podcast that you listen to, and in your Facebook feed; it will be very available to memory. Again, the availability heuristic will cause you to misperceive the frequency of these types of events.
Most interestingly, information that is unusual is more memorable. Suppose we give you the following list of words to remember: box, flower, letter, platypus, oven, boat, newspaper, purse, drum, car. Very likely, the easiest word to remember would be platypus, the unusual one. The same thing occurs with memories of events. An event may be available to memory because it is unusual, yet the availability heuristic leads us to judge that the event is common. Did you catch that? In these cases, the availability heuristic makes us think the exact opposite of the true frequency. We end up thinking something is common because it is unusual (and therefore memorable). Yikes.
The misapplication of the availability heuristic sometimes has unfortunate results. For example, if you went to K-12 school in the US over the past 10 years, it is extremely likely that you have participated in lockdown and active shooter drills. Of course, everyone is trying to prevent the tragedy of another school shooting. And believe us, we are not trying to minimize how terrible the tragedy is. But the truth of the matter is, school shootings are extremely rare. Because the federal government does not keep a database of school shootings, the Washington Post has maintained their own running tally. Between 1999 and January 2020 (the date of the most recent school shooting with a death in the US at of the time this paragraph was written), the Post reported a total of 254 people died in school shootings in the US. Not 254 per year, 254 total. That is an average of 12 per year. Of course, that is 254 people who should not have died (particularly because many were children), but in a country with approximately 60,000,000 students and teachers, this is a very small risk.
But many students and teachers are terrified that they will be victims of school shootings because of the availability heuristic. It is so easy to think of examples (they are very available to memory) that people believe the event is very common. It is not. And there is a downside to this. We happen to believe that there is an enormous gun violence problem in the United States. According the the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 39,773 firearm deaths in the US in 2017. Fifteen of those deaths were in school shootings, according to the Post. 60% of those deaths were suicides. When people pay attention to the school shooting risk (low), they often fail to notice the much larger risk.
And examples like this are by no means unique. The authors of this book have been teaching psychology since the 1990’s. We have been able to make the exact same arguments about the misapplication of the availability heuristics and keep them current by simply swapping out for the “fear of the day.” In the 1990’s it was children being kidnapped by strangers (it was known as “stranger danger”) despite the facts that kidnappings accounted for only 2% of the violent crimes committed against children, and only 24% of kidnappings are committed by strangers (US Department of Justice, 2007). This fear overlapped with the fear of terrorism that gripped the country after the 2001 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and US Pentagon and still plagues the population of the US somewhat in 2020. After a well-publicized, sensational act of violence, people are extremely likely to increase their estimates of the chances that they, too, will be victims of terror. Think about the reality, however. In October of 2001, a terrorist mailed anthrax spores to members of the US government and a number of media companies. A total of five people died as a result of this attack. The nation was nearly paralyzed by the fear of dying from the attack; in reality the probability of an individual person dying was 0.00000002.
The availability heuristic can lead you to make incorrect judgments in a school setting as well. For example, suppose you are trying to decide if you should take a class from a particular math professor. You might try to make a judgment of how good a teacher she is by recalling instances of friends and acquaintances making comments about her teaching skill. You may have some examples that suggest that she is a poor teacher very available to memory, so on the basis of the availability heuristic you judge her a poor teacher and decide to take the class from someone else. What if, however, the instances you recalled were all from the same person, and this person happens to be a very colorful storyteller? The subsequent ease of remembering the instances might not indicate that the professor is a poor teacher after all.
Although the availability heuristic is obviously important, it is not the only judgment heuristic we use. Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman examined the role of heuristics in inductive reasoning in a long series of studies. Kahneman received a Nobel Prize in Economics for this research in 2002, and Tversky would have certainly received one as well if he had not died of melanoma at age 59 in 1996 (Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously). Kahneman and Tversky demonstrated repeatedly that people do not reason in ways that are consistent with the laws of probability. They identified several heuristic strategies that people use instead to make judgments about likelihood. The importance of this work for economics (and the reason that Kahneman was awarded the Nobel Prize) is that earlier economic theories had assumed that people do make judgments rationally, that is, in agreement with the laws of probability.
Another common heuristic that people use for making judgments is the representativeness heuristic (Kahneman & Tversky 1973). Suppose we describe a person to you. He is quiet and shy, has an unassuming personality, and likes to work with numbers. Is this person more likely to be an accountant or an attorney? If you said accountant, you were probably using the representativeness heuristic. Our imaginary person is judged likely to be an accountant because he resembles, or is representative of the concept of, an accountant. When research participants are asked to make judgments such as these, the only thing that seems to matter is the representativeness of the description. For example, if told that the person described is in a room that contains 70 attorneys and 30 accountants, participants will still assume that he is an accountant.
inductive reasoning : a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
inductively strong argument : an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
availability heuristic : judging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
representativeness heuristic: judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
Type 1 thinking : fast, automatic, and emotional thinking.
Type 2 thinking : slow, effortful, and logical thinking.
- What percentage of workplace homicides are co-worker violence?
Many people get these questions wrong. The answers are 10%; stairs; skin; 6%. How close were your answers? Explain how the availability heuristic might have led you to make the incorrect judgments.
- Can you think of some other judgments that you have made (or beliefs that you have) that might have been influenced by the availability heuristic?
7.3 Problem Solving
- Please take a few minutes to list a number of problems that you are facing right now.
- Now write about a problem that you recently solved.
- What is your definition of a problem?
Mary has a problem. Her daughter, ordinarily quite eager to please, appears to delight in being the last person to do anything. Whether getting ready for school, going to piano lessons or karate class, or even going out with her friends, she seems unwilling or unable to get ready on time. Other people have different kinds of problems. For example, many students work at jobs, have numerous family commitments, and are facing a course schedule full of difficult exams, assignments, papers, and speeches. How can they find enough time to devote to their studies and still fulfill their other obligations? Speaking of students and their problems: Show that a ball thrown vertically upward with initial velocity v0 takes twice as much time to return as to reach the highest point (from Spiegel, 1981).
These are three very different situations, but we have called them all problems. What makes them all the same, despite the differences? A psychologist might define a problem as a situation with an initial state, a goal state, and a set of possible intermediate states. Somewhat more meaningfully, we might consider a problem a situation in which you are in here one state (e.g., daughter is always late), you want to be there in another state (e.g., daughter is not always late), and with no obvious way to get from here to there. Defined this way, each of the three situations we outlined can now be seen as an example of the same general concept, a problem. At this point, you might begin to wonder what is not a problem, given such a general definition. It seems that nearly every non-routine task we engage in could qualify as a problem. As long as you realize that problems are not necessarily bad (it can be quite fun and satisfying to rise to the challenge and solve a problem), this may be a useful way to think about it.
Can we identify a set of problem-solving skills that would apply to these very different kinds of situations? That task, in a nutshell, is a major goal of this section. Let us try to begin to make sense of the wide variety of ways that problems can be solved with an important observation: the process of solving problems can be divided into two key parts. First, people have to notice, comprehend, and represent the problem properly in their minds (called problem representation ). Second, they have to apply some kind of solution strategy to the problem. Psychologists have studied both of these key parts of the process in detail.
When you first think about the problem-solving process, you might guess that most of our difficulties would occur because we are failing in the second step, the application of strategies. Although this can be a significant difficulty much of the time, the more important source of difficulty is probably problem representation. In short, we often fail to solve a problem because we are looking at it, or thinking about it, the wrong way.
problem : a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
problem representation : noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
Defining and Mentally Representing Problems in Order to Solve Them
So, the main obstacle to solving a problem is that we do not clearly understand exactly what the problem is. Recall the problem with Mary’s daughter always being late. One way to represent, or to think about, this problem is that she is being defiant. She refuses to get ready in time. This type of representation or definition suggests a particular type of solution. Another way to think about the problem, however, is to consider the possibility that she is simply being sidetracked by interesting diversions. This different conception of what the problem is (i.e., different representation) suggests a very different solution strategy. For example, if Mary defines the problem as defiance, she may be tempted to solve the problem using some kind of coercive tactics, that is, to assert her authority as her mother and force her to listen. On the other hand, if Mary defines the problem as distraction, she may try to solve it by simply removing the distracting objects.
As you might guess, when a problem is represented one way, the solution may seem very difficult, or even impossible. Seen another way, the solution might be very easy. For example, consider the following problem (from Nasar, 1998):
Two bicyclists start 20 miles apart and head toward each other, each going at a steady rate of 10 miles per hour. At the same time, a fly that travels at a steady 15 miles per hour starts from the front wheel of the southbound bicycle and flies to the front wheel of the northbound one, then turns around and flies to the front wheel of the southbound one again, and continues in this manner until he is crushed between the two front wheels. Question: what total distance did the fly cover?
Please take a few minutes to try to solve this problem.
Most people represent this problem as a question about a fly because, well, that is how the question is asked. The solution, using this representation, is to figure out how far the fly travels on the first leg of its journey, then add this total to how far it travels on the second leg of its journey (when it turns around and returns to the first bicycle), then continue to add the smaller distance from each leg of the journey until you converge on the correct answer. You would have to be quite skilled at math to solve this problem, and you would probably need some time and pencil and paper to do it.
If you consider a different representation, however, you can solve this problem in your head. Instead of thinking about it as a question about a fly, think about it as a question about the bicycles. They are 20 miles apart, and each is traveling 10 miles per hour. How long will it take for the bicycles to reach each other? Right, one hour. The fly is traveling 15 miles per hour; therefore, it will travel a total of 15 miles back and forth in the hour before the bicycles meet. Represented one way (as a problem about a fly), the problem is quite difficult. Represented another way (as a problem about two bicycles), it is easy. Changing your representation of a problem is sometimes the best—sometimes the only—way to solve it.
Unfortunately, however, changing a problem’s representation is not the easiest thing in the world to do. Often, problem solvers get stuck looking at a problem one way. This is called fixation . Most people who represent the preceding problem as a problem about a fly probably do not pause to reconsider, and consequently change, their representation. A parent who thinks her daughter is being defiant is unlikely to consider the possibility that her behavior is far less purposeful.
Problem-solving fixation was examined by a group of German psychologists called Gestalt psychologists during the 1930’s and 1940’s. Karl Dunker, for example, discovered an important type of failure to take a different perspective called functional fixedness . Imagine being a participant in one of his experiments. You are asked to figure out how to mount two candles on a door and are given an assortment of odds and ends, including a small empty cardboard box and some thumbtacks. Perhaps you have already figured out a solution: tack the box to the door so it forms a platform, then put the candles on top of the box. Most people are able to arrive at this solution. Imagine a slight variation of the procedure, however. What if, instead of being empty, the box had matches in it? Most people given this version of the problem do not arrive at the solution given above. Why? Because it seems to people that when the box contains matches, it already has a function; it is a matchbox. People are unlikely to consider a new function for an object that already has a function. This is functional fixedness.
Mental set is a type of fixation in which the problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past, even though the solution may no longer be useful. It is commonly seen when students do math problems for homework. Often, several problems in a row require the reapplication of the same solution strategy. Then, without warning, the next problem in the set requires a new strategy. Many students attempt to apply the formerly successful strategy on the new problem and therefore cannot come up with a correct answer.
The thing to remember is that you cannot solve a problem unless you correctly identify what it is to begin with (initial state) and what you want the end result to be (goal state). That may mean looking at the problem from a different angle and representing it in a new way. The correct representation does not guarantee a successful solution, but it certainly puts you on the right track.
A bit more optimistically, the Gestalt psychologists discovered what may be considered the opposite of fixation, namely insight . Sometimes the solution to a problem just seems to pop into your head. Wolfgang Kohler examined insight by posing many different problems to chimpanzees, principally problems pertaining to their acquisition of out-of-reach food. In one version, a banana was placed outside of a chimpanzee’s cage and a short stick inside the cage. The stick was too short to retrieve the banana, but was long enough to retrieve a longer stick also located outside of the cage. This second stick was long enough to retrieve the banana. After trying, and failing, to reach the banana with the shorter stick, the chimpanzee would try a couple of random-seeming attempts, react with some apparent frustration or anger, then suddenly rush to the longer stick, the correct solution fully realized at this point. This sudden appearance of the solution, observed many times with many different problems, was termed insight by Kohler.
Lest you think it pertains to chimpanzees only, Karl Dunker demonstrated that children also solve problems through insight in the 1930s. More importantly, you have probably experienced insight yourself. Think back to a time when you were trying to solve a difficult problem. After struggling for a while, you gave up. Hours later, the solution just popped into your head, perhaps when you were taking a walk, eating dinner, or lying in bed.
fixation : when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
functional fixedness : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
mental set : a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
insight : a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
Solving Problems by Trial and Error
Correctly identifying the problem and your goal for a solution is a good start, but recall the psychologist’s definition of a problem: it includes a set of possible intermediate states. Viewed this way, a problem can be solved satisfactorily only if one can find a path through some of these intermediate states to the goal. Imagine a fairly routine problem, finding a new route to school when your ordinary route is blocked (by road construction, for example). At each intersection, you may turn left, turn right, or go straight. A satisfactory solution to the problem (of getting to school) is a sequence of selections at each intersection that allows you to wind up at school.
If you had all the time in the world to get to school, you might try choosing intermediate states randomly. At one corner you turn left, the next you go straight, then you go left again, then right, then right, then straight. Unfortunately, trial and error will not necessarily get you where you want to go, and even if it does, it is not the fastest way to get there. For example, when a friend of ours was in college, he got lost on the way to a concert and attempted to find the venue by choosing streets to turn onto randomly (this was long before the use of GPS). Amazingly enough, the strategy worked, although he did end up missing two out of the three bands who played that night.
Trial and error is not all bad, however. B.F. Skinner, a prominent behaviorist psychologist, suggested that people often behave randomly in order to see what effect the behavior has on the environment and what subsequent effect this environmental change has on them. This seems particularly true for the very young person. Picture a child filling a household’s fish tank with toilet paper, for example. To a child trying to develop a repertoire of creative problem-solving strategies, an odd and random behavior might be just the ticket. Eventually, the exasperated parent hopes, the child will discover that many of these random behaviors do not successfully solve problems; in fact, in many cases they create problems. Thus, one would expect a decrease in this random behavior as a child matures. You should realize, however, that the opposite extreme is equally counterproductive. If the children become too rigid, never trying something unexpected and new, their problem solving skills can become too limited.
Effective problem solving seems to call for a happy medium that strikes a balance between using well-founded old strategies and trying new ground and territory. The individual who recognizes a situation in which an old problem-solving strategy would work best, and who can also recognize a situation in which a new untested strategy is necessary is halfway to success.
Solving Problems with Algorithms and Heuristics
For many problems there is a possible strategy available that will guarantee a correct solution. For example, think about math problems. Math lessons often consist of step-by-step procedures that can be used to solve the problems. If you apply the strategy without error, you are guaranteed to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. This approach is called using an algorithm , a term that denotes the step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution. Because algorithms are sometimes available and come with a guarantee, you might think that most people use them frequently. Unfortunately, however, they do not. As the experience of many students who have struggled through math classes can attest, algorithms can be extremely difficult to use, even when the problem solver knows which algorithm is supposed to work in solving the problem. In problems outside of math class, we often do not even know if an algorithm is available. It is probably fair to say, then, that algorithms are rarely used when people try to solve problems.
Because algorithms are so difficult to use, people often pass up the opportunity to guarantee a correct solution in favor of a strategy that is much easier to use and yields a reasonable chance of coming up with a correct solution. These strategies are called problem solving heuristics . Similar to what you saw in section 6.2 with reasoning heuristics, a problem solving heuristic is a shortcut strategy that people use when trying to solve problems. It usually works pretty well, but does not guarantee a correct solution to the problem. For example, one problem solving heuristic might be “always move toward the goal” (so when trying to get to school when your regular route is blocked, you would always turn in the direction you think the school is). A heuristic that people might use when doing math homework is “use the same solution strategy that you just used for the previous problem.”
By the way, we hope these last two paragraphs feel familiar to you. They seem to parallel a distinction that you recently learned. Indeed, algorithms and problem-solving heuristics are another example of the distinction between Type 1 thinking and Type 2 thinking.
Although it is probably not worth describing a large number of specific heuristics, two observations about heuristics are worth mentioning. First, heuristics can be very general or they can be very specific, pertaining to a particular type of problem only. For example, “always move toward the goal” is a general strategy that you can apply to countless problem situations. On the other hand, “when you are lost without a functioning gps, pick the most expensive car you can see and follow it” is specific to the problem of being lost. Second, all heuristics are not equally useful. One heuristic that many students know is “when in doubt, choose c for a question on a multiple-choice exam.” This is a dreadful strategy because many instructors intentionally randomize the order of answer choices. Another test-taking heuristic, somewhat more useful, is “look for the answer to one question somewhere else on the exam.”
You really should pay attention to the application of heuristics to test taking. Imagine that while reviewing your answers for a multiple-choice exam before turning it in, you come across a question for which you originally thought the answer was c. Upon reflection, you now think that the answer might be b. Should you change the answer to b, or should you stick with your first impression? Most people will apply the heuristic strategy to “stick with your first impression.” What they do not realize, of course, is that this is a very poor strategy (Lilienfeld et al, 2009). Most of the errors on exams come on questions that were answered wrong originally and were not changed (so they remain wrong). There are many fewer errors where we change a correct answer to an incorrect answer. And, of course, sometimes we change an incorrect answer to a correct answer. In fact, research has shown that it is more common to change a wrong answer to a right answer than vice versa (Bruno, 2001).
The belief in this poor test-taking strategy (stick with your first impression) is based on the confirmation bias (Nickerson, 1998; Wason, 1960). You first saw the confirmation bias in Module 1, but because it is so important, we will repeat the information here. People have a bias, or tendency, to notice information that confirms what they already believe. Somebody at one time told you to stick with your first impression, so when you look at the results of an exam you have taken, you will tend to notice the cases that are consistent with that belief. That is, you will notice the cases in which you originally had an answer correct and changed it to the wrong answer. You tend not to notice the other two important (and more common) cases, changing an answer from wrong to right, and leaving a wrong answer unchanged.
Because heuristics by definition do not guarantee a correct solution to a problem, mistakes are bound to occur when we employ them. A poor choice of a specific heuristic will lead to an even higher likelihood of making an error.
algorithm : a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
problem solving heuristic : a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
confirmation bias : people’s tendency to notice information that confirms what they already believe
An Effective Problem-Solving Sequence
You may be left with a big question: If algorithms are hard to use and heuristics often don’t work, how am I supposed to solve problems? Robert Sternberg (1996), as part of his theory of what makes people successfully intelligent (Module 8) described a problem-solving sequence that has been shown to work rather well:
- Identify the existence of a problem. In school, problem identification is often easy; problems that you encounter in math classes, for example, are conveniently labeled as problems for you. Outside of school, however, realizing that you have a problem is a key difficulty that you must get past in order to begin solving it. You must be very sensitive to the symptoms that indicate a problem.
- Define the problem. Suppose you realize that you have been having many headaches recently. Very likely, you would identify this as a problem. If you define the problem as “headaches,” the solution would probably be to take aspirin or ibuprofen or some other anti-inflammatory medication. If the headaches keep returning, however, you have not really solved the problem—likely because you have mistaken a symptom for the problem itself. Instead, you must find the root cause of the headaches. Stress might be the real problem. For you to successfully solve many problems it may be necessary for you to overcome your fixations and represent the problems differently. One specific strategy that you might find useful is to try to define the problem from someone else’s perspective. How would your parents, spouse, significant other, doctor, etc. define the problem? Somewhere in these different perspectives may lurk the key definition that will allow you to find an easier and permanent solution.
- Formulate strategy. Now it is time to begin planning exactly how the problem will be solved. Is there an algorithm or heuristic available for you to use? Remember, heuristics by their very nature guarantee that occasionally you will not be able to solve the problem. One point to keep in mind is that you should look for long-range solutions, which are more likely to address the root cause of a problem than short-range solutions.
- Represent and organize information. Similar to the way that the problem itself can be defined, or represented in multiple ways, information within the problem is open to different interpretations. Suppose you are studying for a big exam. You have chapters from a textbook and from a supplemental reader, along with lecture notes that all need to be studied. How should you (represent and) organize these materials? Should you separate them by type of material (text versus reader versus lecture notes), or should you separate them by topic? To solve problems effectively, you must learn to find the most useful representation and organization of information.
- Allocate resources. This is perhaps the simplest principle of the problem solving sequence, but it is extremely difficult for many people. First, you must decide whether time, money, skills, effort, goodwill, or some other resource would help to solve the problem Then, you must make the hard choice of deciding which resources to use, realizing that you cannot devote maximum resources to every problem. Very often, the solution to problem is simply to change how resources are allocated (for example, spending more time studying in order to improve grades).
- Monitor and evaluate solutions. Pay attention to the solution strategy while you are applying it. If it is not working, you may be able to select another strategy. Another fact you should realize about problem solving is that it never does end. Solving one problem frequently brings up new ones. Good monitoring and evaluation of your problem solutions can help you to anticipate and get a jump on solving the inevitable new problems that will arise.
Please note that this as an effective problem-solving sequence, not the effective problem solving sequence. Just as you can become fixated and end up representing the problem incorrectly or trying an inefficient solution, you can become stuck applying the problem-solving sequence in an inflexible way. Clearly there are problem situations that can be solved without using these skills in this order.
Additionally, many real-world problems may require that you go back and redefine a problem several times as the situation changes (Sternberg et al. 2000). For example, consider the problem with Mary’s daughter one last time. At first, Mary did represent the problem as one of defiance. When her early strategy of pleading and threatening punishment was unsuccessful, Mary began to observe her daughter more carefully. She noticed that, indeed, her daughter’s attention would be drawn by an irresistible distraction or book. Fresh with a re-representation of the problem, she began a new solution strategy. She began to remind her daughter every few minutes to stay on task and remind her that if she is ready before it is time to leave, she may return to the book or other distracting object at that time. Fortunately, this strategy was successful, so Mary did not have to go back and redefine the problem again.
Pick one or two of the problems that you listed when you first started studying this section and try to work out the steps of Sternberg’s problem solving sequence for each one.
a mental representation of a category of things in the world
an assumption about the truth of something that is not stated. Inferences come from our prior knowledge and experience, and from logical reasoning
knowledge about one’s own cognitive processes; thinking about your thinking
individuals who are less competent tend to overestimate their abilities more than individuals who are more competent do
Thinking like a scientist in your everyday life for the purpose of drawing correct conclusions. It entails skepticism; an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions; and excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills.
a way of thinking in which you refrain from drawing a conclusion or changing your mind until good evidence has been provided
an inclination, tendency, leaning, or prejudice
a type of reasoning in which the conclusion is guaranteed to be true any time the statements leading up to it are true
a set of statements in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion
an argument for which true beginning statements guarantee that the conclusion is true
a type of reasoning in which we make judgments about likelihood from sets of evidence
an inductive argument in which the beginning statements lead to a conclusion that is probably true
fast, automatic, and emotional thinking
slow, effortful, and logical thinking
a shortcut strategy that we use to make judgments and solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
udging the frequency or likelihood of some event type according to how easily examples of the event can be called to mind (i.e., how available they are to memory)
judging the likelihood that something is a member of a category on the basis of how much it resembles a typical category member (i.e., how representative it is of the category)
a situation in which we are in an initial state, have a desired goal state, and there is a number of possible intermediate states (i.e., there is no obvious way to get from the initial to the goal state)
noticing, comprehending and forming a mental conception of a problem
when a problem solver gets stuck looking at a problem a particular way and cannot change his or her representation of it (or his or her intended solution strategy)
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver cannot think of a new use for an object that already has a function
a specific type of fixation in which a problem solver gets stuck using the same solution strategy that has been successful in the past
a sudden realization of a solution to a problem
a step-by-step procedure that guarantees a correct solution to a problem
The tendency to notice and pay attention to information that confirms your prior beliefs and to ignore information that disconfirms them.
a shortcut strategy that we use to solve problems. Although they are easy to use, they do not guarantee correct judgments and solutions
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Ken Gray; Elizabeth Arnott-Hill; and Or'Shaundra Benson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
6-1 Discussion Intro to Critical Thinking

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Terms in this set (41) critical thinking. Active thinking in which we evaluate and analyze information in order to determine the best course of action. argument. Statements that combine reasoning with evidence to support an assertion. Logic. the process of reasoning. Fallacies.
Terms in this set (7) What is critical thinking? Active thinking in which we evaluate and analyze information in order to determine the best course of action. What are arguments? Statements that combine reasoning with evidence to support an assertion. What are the seven traits of critical thinkers? Open-Mindedness, Analytic Nature, Systematic by.
A fallacy that occurs when the actual argument appears to be refuted, but in reality a related point is addressed. Syllogism. A form of deductive argument in which the conclusion is inferred from the premises. Most syllogisms contain a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms ...
This page titled 6: Critical Thinking and Reasoning is shared under a CC BY-NC-ND 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Terri Russ@Saint Mary's College (Public Speaking Project) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
Critical Thinking, Chapter 6 - Application to Real Life Dona Warren 5 the entire book. We can then go back to examine the argument in each chapter, each section, each paragraph, if we want. We should remember that the author may present multiple, interrelated, positions and arguments, and adopt a different attitude toward each.
Chapter Objectives. After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Understand and explain the importance of critical thinking. Identify the core skills associated with critical thinking. Demonstrate the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning. Construct a logically sound and well-reasoned argument.
Learning Objectives. After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand and explain the importance of critical thinking. Identify the core skills associated with critical thinking. Demonstrate the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning. Construct a logically sound and well-reasoned argument.
The ability to think critically uses reflection, induction, deduction, analysis, challenging assumptions, and evaluation of data and information to guide decisionmaking. 9, 14, 15 Critical reasoning is a process whereby knowledge and experience are applied in considering multiple possibilities to achieve the desired goals, 16 while considering ...
This is an introductory textbook in logic and critical thinking. The goal of the textbook is to provide the reader with a set of tools and skills that will enable them to identify and evaluate arguments. The book is intended for an introductory course that covers both formal and informal logic. As such, it is not a formal logic textbook, but is closer to what one would find marketed as a ...
Critical thinkers have faith in the power of logic and sound reasoning. Critical thinkers understand that it is in everyone's best interest to encourage and develop sound logic. More importantly, critical thinkers value the power of letting others draw their own conclusions. Recall that critical thinking is an active mode of thinking.
Critical Thinking Chapter 6 Reasoning. What is reasoning? Click the card to flip 👆. • The rational link between evidence and claim. • Making connections, distinctions, and preditions. • Using what is known to reach conclusions about what is unknown. • Thinking critically about the world and how it operates. Click the card to flip ...
In order to practice critical thinking in action, spend some time researching the major arguments each side uses. Because the debates in this area are so complex, you might want to narrow your focus just a bit. For example, you could focus on the issue of minors consenting to abortion or abortion in the case of rape or other sexual assault.
6. Weighing and Balancing Considerations. A central notion in discussions of the evaluation of conductive reasoning, including our own, is that of weighing. Whatever guidelines may be offered, in the final analysis, reasons pro and con must be weighed in order to reach a reasoned judgment.
1.7: Creating a Philosophical Outline. This page titled 1: Introduction to Critical Thinking, Reasoning, and Logic is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by () . What is thinking? It may seem strange to begin a logic textbook with this question. 'Thinking' is perhaps the most intimate and personal thing that ...
This chapter is an informal and practical guide to critical thinking and will also guide you in how to conduct research, reading, and writing for philosophy classes. Critical thinking is set of skills, habits, and attitudes that promote reflective, clear reasoning. Studying philosophy can be particularly helpful for developing good critical ...
Learning Objectives. After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Understand and explain the importance of critical thinking. Identify the core skills associated with critical thinking. Demonstrate the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning. Construct a logically sound and well-reasoned argument.
Chapter 6: Critical Thinking. Image of Studentsin Class by roanokecollege is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ... Using logic, a person evaluates arguments and reasoning and strives to distinguish between good and bad reasoning, or between truth and falsehood. Using logic, you can evaluate ideas or claims people make, make good decisions, and form ...
Appeal to emotion. when a speaker supports an argument by playing on our emotion rather than by producing a real argument. Argument from outrage. attempts to convince us by making us angry rather than by giving a relevant argument. Scare tactics. try to scare us into accepting an irrelevant conclusion.
Chapter 6 critical thinking & reasoning www.publicspeakingproject.org 6-3 critical thinking traits and skills Critical thinkers tend to exhibit certain traits that are common to them. These traits are summarized in Table 6.1 (adapted from Facione, 1990, p. 6): Recall that critical thinking is an active mode of thinking. Instead of just receiving messages and accepting them as is, we consider ...
Critical thinking entails solid reasoning and problem solving skills; skepticism; and an ability to identify biases, distortions, omissions, and assumptions. Excellent deductive and inductive reasoning, and problem solving skills contribute to critical thinking. So, you can consider the subject matter of sections 7.2 and 7.3 to be part of ...
People need to have critical thinking skills to be better at multitasking and to be more efficient in decision-making and problem solving. Critical thinking involves judgment, reasoning, reflection, questioning, metacognition and mental process. The government has introduced various programs and school syllabus to improve critical thinking skills among students.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like analysis, critical thinking, appeal to pity and more.
Philosophy document from Southern New Hampshire University, 1 page, Destyne Ayala Intro to Critical Thinking 6-1 Discussion Discuss a fallacy (as described in the text) that you have encountered at home, work, in text, or in the media. This could also be one that you committed. Explain why the reasoning is fallacious in t
Basic steps of critical thinking when problem-solving: 1. Determine just what the problem is and write it down. ask whether there is a contributing problem chain or series of events. 2. Gather facts and ideas to help you decide what to do about it. 3.