- General Assembly
- Second Committee

Resolutions on Protecting Global Climate, Eliminating Unilateral Economic Measures, among 16 Texts Approved as Second Committee Concludes Session
The Second Committee (Economic and Financial) today approved 16 resolutions and two decisions, voting on five of them, including one expressing profound alarm that greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise globally, as it concluded its seventy-sixth session.
Further to the text, on “Protection of global climate for present and future generations of humankind”, the General Assembly would emphasize that mitigation and adaptation to climate change represent an immediate global priority. It would urge Member States to adopt environment-responsive approaches to COVID-19 recovery by aligning investments and policies with international agreements to speed up transition to low-emission, climate-resilient, inclusive and sustainable economies.
Addressing that draft, China’s delegate noted that adverse effects of climate change are becoming increasingly visible, highlighting the need for urgent climate action to combat it. The representative of Switzerland expressed regret that the resolution failed to faithfully reflect outcomes of the recent United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland, calling on parties who haven’t done so to submit nationally determined contributions for climate finance.
Among other environmental drafts was one on “Combating sand and dust storms”, by which the Assembly would recognize that these hazards, as well as unsustainable land management practices, pose serious challenges to the development of affected regions. Recognizing that such storms have inflicted substantial economic, social and environmental damage to the world’s arid, semi-arid and dry subhumid areas in recent years, the Assembly would underscore the need to promptly address them.
The text was approved in a recorded vote of 173 in favour to 2 against (Israel, United States), with 1 abstention (Australia).
Several macroeconomic and financial drafts were approved, including one on “Unilateral economic measures as a means of political and economic coercion against developing countries”. By its terms, the Assembly would urge the international community to adopt measures to eliminate the use of unilateral economic, financial or trade measures unauthorized by relevant United Nations organs, inconsistent with international law and the Charter of the United Nations and contravening basic principles of the multilateral trading system.
Speaking to that draft, the representative of the United States said sanctions are an effective, legitimate and peaceful tool for countering threats to peace and security, used against those who threaten human rights, undermine democracy or engage in criminal activities. In contrast, the representative of Iran said unilateral coercive measures aiming to destroy a State’s economy constitute an act of war, passing the red line of terrorism and reaching crimes against humanity.
The text was approved in a recorded vote of 119 in favour to 7 against (Australia, Canada, Israel, Sweden, Ukraine, United Kingdom, United States), with 46 abstentions.
A further text on “Promotion of international cooperation to combat illicit financial flows and strengthening good practices on assets return to foster sustainable development” would have the Assembly call on countries to eliminate base erosion and profit shifting, ensuring that all companies, including multinationals, pay taxes to Governments of countries where economic activity occurs and value is created, according to national and international laws and policies.
Addressing that text, Nigeria’s delegate said illicit financial flows undermine security and inhibit growth, stressing the need for transparency and a redesigned global architecture to tackle them. Adding that such illicit flows need immediate action, she said evidence indicates that recovering and returning their proceeds could generate enough capital to finance the fight against climate change in sub-Saharan Africa by 2030.
A draft was also approved on “Agricultural technology for sustainable development”, by which the Assembly would urge Member States, United Nations organizations and other stakeholders to improve development of sustainable agricultural technologies and their transfer to developing countries. It would encourage international, regional and national efforts to strengthen capacity and foster using local know-how in developing countries, especially that of smallholder and family farmers.
The draft was approved in a recorded vote of 140 in favour to 1 against (Syria), with 34 abstentions.
On that text, Qatar’s delegate, speaking for the Arab Group, said Israel’s submission of the draft, as an occupying authority, is an odious attempt to hide its crimes against Palestinian agriculture and people. Syria’s representative similarly questioned Israel’s eligibility to submit the text, as it continues to hinder agriculture in the occupied Syrian Golan, confiscating land and prohibiting use of natural resources.
Slovenia’s delegate, speaking for the European Union, lauded the draft for addressing progress towards several Sustainable Development Goals, including “zero hunger”, responsible consumption, as well as production, and climate action. The representative of Israel noted that agricultural production and distribution have suffered heavy blows since the onset of COVID-19, stressing that technology is vital in addressing these new realities.
Drafts were also approved on information and communication technologies (ICT); investments for sustainable development; external debt; financing for development update; Environment Assembly; tourism; biological diversity; science, technology and innovation; least developed countries; and coastal zone management.
Draft decisions were approved on the Committee’s work plan for the General Assembly’s seventy-seventh session and two upcoming meetings in 2022.
Also speaking were the representatives of Venezuela, Cuba, Zimbabwe, United Kingdom, Eritrea, Sweden, Liechtenstein, Canada (speaking also for Australia and New Zealand), Republic of Korea, France, Belarus, Guatemala, Japan, Turkey, Antigua and Barbuda, India, Chile, Guinea (for the “Group of 77” developing countries and China), Russian Federation and Morocco. The Observer for the State of Palestine also made a statement.
In addition, a statement was made by Assistant Secretary-General for Policy Coordination and Inter-Agency Affairs Maria-Francesca Spatolisano.
Action on Draft Resolutions
The Second Committee (Economic and Financial) first took up a draft on “Information and communications technologies (ICT) for sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.56), approving it without a vote as orally corrected, withdrawing a previous draft.
By that text, the General Assembly would recognize that a lack of access to affordable and reliable technologies and services remains a critical challenge in many developing countries. All efforts should be deployed to reduce the price of ICT and broadband access, bearing in mind that deliberate interventions, including through research and development and technology transfer on mutually agreed terms, may be necessary to spur the development of lower-cost connectivity options.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would call upon all stakeholders to keep the goal of bridging digital divides an area of priority concern, put into effect sound strategies that contribute to the development of e-government and continue to focus on pro-poor ICT policies and applications, including access to broadband at the grass-roots level, with a view to narrowing the digital divides among and within countries and, in turn, build information and knowledge societies.
The representative of Switzerland said his country joined consensus on the draft, stressing that the enormous challenges in the digital area must be addressed without delay. A digital arena managed by various actors must be inclusive, he said, expressing regret that the draft did not reflect this in a more representative manner.
The representative of the European Union , speaking in its capacity as observer, said the bloc joined consensus, noting that the world during COVID-19 has seen an increase in reliance on digital technology, which has provided an important lifeline for the continuity of work and service delivery. However, this has not been enjoyed by all, she said, stressing that digital transformation must be harnessed for the resilient recovery of all, which was not adequately reflected in the resolution.
The representative of the United States emphasized that closing the digital divide is essential, stating that his country joined consensus on the draft. Regarding operative paragraphs 19 and 32, he referred delegates to the general statement the United States made on 18 November.
Next, it turned to a text on “International financial system and development” (document A/C.2/76/L.21/Rev.1), approving it in a recorded vote of 169 in favour to 1 against (United States), with no abstentions.
By that text, the Assembly would stress the critical importance of a stable, inclusive and enabling global economic environment for the advancement of sustainable development, for the reliable and effective financing of development and for the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, mobilizing public and private, as well as domestic and international resources.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would urge multilateral donors and invite the international financial institutions and regional development banks, within their respective mandates, to review and implement policies that support national efforts to ensure that a higher proportion of resources reach women and girls, particularly in rural and remote areas, and invites multilateral and regional development banks to agree on common indicators for analysing the gender impact of their lending.
Speaking after the vote, the representative of the United States said his country supports the 2030 Agenda and implementation of the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, but voted against the draft due to language that remains unchanged. His country disagrees with references to increasing protectionism, unfair market distorting actions and lack of coherence in the international trading and monetary systems. Moreover, the concessionality of assistance should be determined by the governing bodies of international institutions, he said, referring delegates to the United States statement of 18 November regarding the 2030 Agenda, illicit financial flows and the Addis Ababa Action Agenda.
The representative of France said he tried to vote in favour of the draft, but the ballot was not registered and should be recorded in the proceedings.
The representative of Iran said his country voted in favour of the draft, but due to references made to non-United Nations initiatives in operative paragraph 29, disassociates itself from that text.
The Committee then took up a draft on “External debt sustainability and development” (document A/C.76/L.55), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous text.
By that text, the Assembly would emphasize the special importance of timely, effective, comprehensive and durable solutions to the debt problems of developing countries to promote their economic growth and development.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would stress the need to continue to assist developing countries in avoiding a build-up of unsustainable debt to reduce the risk of relapsing into another debt crisis, considering the challenges posed by the global economic environment and risks for debt sustainability in some developed and developing countries.
The representative of the United States said the draft is particularly timely, as the economic impact of COVID-19 has increased debt risks and set back recovery for various nations. He added, however, that debt transparency is critical to maximize the benefit of relief and allow for fair burden sharing. Also, he said it is outside the scope of the draft to express concern over contracts, referring delegates to his country’s statement on 18 November regarding debt service, trade, technology transfer and debt-related frameworks.
Following that, it acted on a text on “Promoting investments for sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.58), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous draft.
By that text, the Assembly would note with concern that many of the least developed and small island developing States continue to be largely side-lined by foreign direct investment (FDI) that could help to diversify their economies, despite improvements in their investment climates. It would also note with concern the gap in access to capital for micro-, small and medium-sized enterprises, in particular for businesses led by women, young entrepreneurs and persons with disabilities.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would call upon the United Nations system and all relevant stakeholders to support the capacity-building of developing countries in their efforts to close the Sustainable Development Goals investment gaps, especially at the country programme level, and on the use of public finance to leverage private investment for projects benefiting sustainable development.
The representative of the United States said his country joined consensus on the draft, recognizing that FDI in developing countries is vital for sustainable development. Regarding its position on cross-cutting issues mentioned in the text, he referred delegates to his country’s general statement of 18 November.
The Committee then turned to a text on “Follow-up to and implementation of the outcomes of the International Conferences on Financing for Development” (document A/C.2/76/L.59), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous text.
By that text, the Assembly would emphasize the need to work towards the full and timely implementation of the Addis Ababa Action Agenda of the Third International Conference on Financing for Development.
Further to that draft, the Assembly would recognize that, in combating the negative impacts caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and to achieve a sustainable, inclusive and resilient recovery, a functioning global financial safety net, with a strong, quota-based and adequately resourced International Monetary Fund (IMF) at its centre, is important to support a global economic recovery.
The representative of the United States referred delegates to his country’s general statement of 18 November regarding the Addis Ababa Action Agenda.
Next, it took up a draft on “Agricultural technology for sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.20/Rev.1), approving it in a recorded vote of 140 in favour to 1 against (Syria), with 34 abstentions.
By that text, the Assembly would urge Member States, relevant United Nations organizations and other stakeholders to strengthen efforts to improve the development of sustainable agricultural technologies and their transfer and dissemination under mutually agreed terms to developing countries, especially those least developed and encourage international, regional and national efforts to strengthen capacity and foster the utilization of local know-how in developing countries, especially that of smallholder and family farmers.
Further to that draft, the Assembly would encourage Member States, civil society and public and private institutions to develop partnerships to support financial and market services, including training, capacity-building, infrastructure and extension and rural advisory services. It would also call for further efforts by all stakeholders to include smallholder farmers, in particular rural women and youth, in planning and in taking decisions about making appropriate sustainable agricultural technologies and practices accessible and affordable to them.
Before action, Qatar ’s representative, speaking on behalf of the Arab Group, said it had asked for a vote on the draft resolution and will abstain from voting as the “Group of 77” developing countries and China had submitted a draft resolution titled “agricultural technology, food security and nutrition” under agenda item 26, which is of the same substance. Thus, the draft resolution submitted by Israel is a waste of United Nations resources, he said, adding that such submission by Israel, while it is an occupying authority, is odious conduct and an attempt to hide its crimes against Palestinian agriculture and the Palestinian people. Stressing that Israel continues to destroy and waste the assets and resources of the Palestinian people, and has prevented the farming of land by Palestinians, he invited all States to abstain from voting.
Syria ’s representative said the main sponsor of the draft resolution is not morally eligible to submit the text, as it continues to hinder the capacity of the Syrian people in the occupied Syrian Golan to use agriculture, which is their only means of survival, confiscating agricultural land and prohibiting them from using natural resources. Moreover, he said Israel continues to defy several resolutions which invite them to cease their nefarious practices that undermine all socioeconomic aspects of life. Noting that several United Nations reports describe how Israeli policy saps agricultural development, he said the resolution defies the truth reflected in those reports and, in that regard, his delegation would vote against it.
After action, Slovenia ’s representative, speaking on behalf of the European Union, said it had voted in favour of the resolution as it directly addresses progress towards several Sustainable Development Goals, namely those relating to “zero hunger”, responsible consumption and production, and climate action, among others. Welcoming that the resolution highlights the impact of COVID‑19 on agriculture and food systems, she said recovery efforts present a unique opportunity to build back better and greener.
Israel ’s representative said that since the onset of COVID‑19, agricultural production and distribution have suffered heavy blows, causing food prices to rise increasing global hunger and poverty. Meanwhile, as sea levels rise and weather becomes more extreme, climate change is destroying the future of farmers around the globe. Noting that employing technology is an absolute necessity to address those new realities, he said the resolution provides an opportunity to focus on innovation and technology that can help countries around the world. He said there are still Member States, such as Syria and Iran, who chose not to support the resolution out of antisemitism and contempt, as well as others who abstained from voting. He expressed hope that in the future politics will be pushed aside, noting that today’s vote marks an important step towards solving global issues and advancing the Sustainable Development Goals.
The representative of Belarus said her delegation voted in favour of the resolution due to the importance of agricultural technology for sustainable development and ensuring food security, especially in the context of the pandemic. Noting the importance of avoiding actions that could threaten food security, she said thoughtless sanctions and the use of unilateral economic restrictions against whole sectors of the economy linked to food are dragging populations of vulnerable countries to the brink of starvation. Stressing that the use of sanctions is futile, counterproductive and must be stopped, she referred the Committee to her country’s statement delivered on 22 November under agenda item 26.
The representative of the United States said his country remains committed to promoting agricultural development as a means to achieving sustainable development and joins consensus on the resolution. Regarding his country’s position on technology transfer and/or knowledge-sharing, he referred the Committee to his country’s general statement delivered on 18 November.
Iran ’s representative pointed out that his country did not vote in favour of or against the resolution because it does not recognize the “so-called” State of Israel. Noting that “one of the participants” took others’ valuable time by misusing the Committee and raising baseless accusations, he requested the Chair to request that participant to respond to its own responsibilities under the agenda item.
Syria ’s representative said Israel, the occupying Power, has “no shame” to have the audacity to attack another Member State and accuse it of lies, while it pretends to be a peace-loving nation looking to help others in need. The entire world has known the atrocities committed by Israel against the Palestinian and Syrian people for decades, he said.
The observer for the State of Palestine , associating himself with the Arab Group, said Israel, the occupying Power, continues to exploit the Committee’s platform by hiding behind key sustainable development issues to cover up its dreadful acts against Palestinian agriculture. Referring to both General Assembly and Security Council resolutions adopted in relation to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, he said Israel has not respected any of them, adding that it is undermining the Palestinian economy and consolidating its apartheid regime over the Palestinian people. Addressing the representative of Israel, he said “you cannot change the history”, as everything is written in the United Nations archives.
The Committee then took up a draft on “Sustainable tourism and sustainable development in Central America” (document A/C.2/76/L.24/Rev.1), approving it without a vote.
By that text, the Assembly would recognize the major role that sustainable tourism plays in the development of Central American countries, as an instrument of social inclusion that generates decent jobs and improves the quality of life of the population, aimed at achieving poverty eradication.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would call upon Member States and the tourism sector to take effective measures, in the context of sustainable tourism, including ecotourism initiatives, to promote the equal participation of women and the balanced participation of youth, older persons, persons with disabilities, indigenous peoples and local communities, at all levels and in decision-making processes in all areas, and to promote effective economic empowerment, mainly through decent job and income creation.
Speaking after action, Guatemala ’s representative said that her country, as pro tempore chair of the Central American Integration System, had submitted the resolution with the goal of further developing sustainable tourism, incentivizing economic growth, protecting biodiversity and achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Given the region’s richness in majestic tourism locations, the resolution will serve as a benchmark for all stakeholders as they recover from the pandemic, especially those countries dependent on tourism.
Next, it turned to a text titled “Convention on Biological Diversity” (document A/C.2/76/L.54), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous draft.
By that text, the Assembly would urge parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity to ensure the coherence and complementarity of a post-2020 global biodiversity framework with other existing or upcoming international processes, in particular regarding the 2030 Agenda, the Paris Agreement and other related processes, frameworks and strategies.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would note with concern the findings of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, and stress the urgent need to halt the global decline of biodiversity, which is unprecedented in human history, including its main indirect and direct drivers, in particular, changes in land and sea use, direct exploitation of organisms, climate change, pollution and invasion of alien species.
Speaking after action, the representative of the United States said his country remains actively engaged in the work of the Convention on Biological Diversity and supports its objectives. Although it is not a party to the Convention, his country is following closely the process to negotiate the global biodiversity framework. Further, he said the title of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity does not reflect well-defined consensus language or international principles. Naming various declarations and agendas, he referred the Committee to his country’s general statement delivered on 18 November.
The representative of the European Union , in its capacity as observer, noting that it was joining consensus, said that protecting biodiversity is a prerequisite to building stronger economies and safeguarding well-being. For that reason, the Union has pledged to double its external funding for biodiversity protection and conservation, particularly for the most vulnerable countries. The international community must agree on an ambitious and transformative post-2020 global biodiversity framework in 2022, he said, pointing out that the pandemic has underscored the need to redefine mankind’s relationship with nature.
China ’s representative said the first stage of the Fifteenth Conference of Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity was held in Kunming. China’s President attended the “summit” where he announced a contribution of RMB 1.5 billion to create a biodiversity fund of Kunming, a first set of national parks, and a policy system, including for carbon neutrality measures. Going forward, China as host country and chair of the Conference will work with the rest of the international community to push for biodiversity restoration. Referring to subsequent meetings that will take place in 2022, he said China will discharge earnestly its obligations as a host country to ensure the successful outcome of the second stage of the Conference.
Following that, the Committee acted on “Report of the United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)” (document A/C.1/76/L.53), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous text.
By that text, the Assembly would express concern about findings of global environmental assessments indicating that, despite the availability of solutions to common environmental challenges, the planet is increasingly polluted, adversely affected by climate change, quickly losing its biodiversity and experiencing widespread environmental degradation.
Further to the draft, the Assembly would urge support for a sustainable, resilient and inclusive recovery from COVID-19 that protects the planet, stimulates sustainable consumption and production patterns, promotes the One Health approach, revitalizes economies, creates decent and sustainable jobs and makes real progress in eradicating poverty, while enhancing future resilience to similar challenges.
Speaking after action, the representative of the European Union , in its capacity as observer, said his bloc was pleased to join consensus and looks forward to the convening of the resumed meeting of the fifth session of the United Nations Environment Assembly. The resolution sends a strong message on the need to mainstream the environment in the United Nations system, and should mobilize Member States, the United Nations system, and other stakeholders in view of the important milestones ahead. He called on the fifth session of the United Nations Environment Assembly to launch negotiations of an intergovernmental instrument to end plastic pollution. Looking ahead to the second part of the Fifteenth Conference of Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity as well as other environment-related events in 2022, he expressed hope that an ambitious post-biodiversity framework would be adopted.
The representative of the United States said his country strongly supports UNEP and its critical role in galvanizing action to solve many of the world’s environmental problems, adding that it was pleased to join consensus on the resolution. Regarding the 2030 Agenda and the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, he referred to his country’s statement of 18 November.
Next, the Committee turned to a text on “Combating sand and dust storms” (document A/C.2/76/L.36/Rev.1), approving it, as orally corrected, in a recorded vote of 173 in favour to 2 against (Israel, United States), with 1 abstention (Australia).
By that text, the Assembly would recognize that sand and dust storms, as well as unsustainable land management practices, can pose a serious challenge to the sustainable development of affected countries and regions. Also recognizing that they have inflicted over the past few years substantial economic, social and environmental damage on inhabitants of the world’s arid, semi-arid and dry subhumid areas, especially in Africa and Asia, the Assembly would underscore the need to treat them and promptly take measures to address these challenges.
Speaking before action, Israel ’s representative, expressed regret about the call for a vote on the resolution, noting that the draft recalls a United Nations high-level event that had already taken place. The language used does not reflect the language used in the modalities resolution for that event or the language used in the first resolution following the event. It was especially disturbing that the language used is an attempt to rewrite history, deliberately misrepresenting a previously adopted resolution, she said, expressing hope that 2022 will allow the Committee to engage constructively on the resolution.
Speaking after action, the representative of the United States reiterated that the title of the Fifteenth Conference of Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity does not reflect well-defined consensus language or international principles. He expressed regret that the compromise language regarding that text as reflected in other resolutions and agreed during negotiations was removed from the final text. Regarding references to the 2030 Agenda, the Sendai Framework and the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, he referred the Committee to his country’s general statement of 18 November.
The Committee then took up a draft on “Science, technology and innovation for sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.60), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous text.
By its terms, the Assembly would underscore the need to adopt science, technology and innovation strategies as integral elements of national sustainable development plans and strengthen knowledge-sharing on mutually agreed terms and collaboration, scaling up investment in these areas and enhancing technical, vocational and tertiary education and training. Further, it would encourage Member States to strengthen and foster investment in research and development for environmentally sound technologies and promote the involvement of business and financial sectors in developing them.
Further to the text, the Assembly would call on Member States and the United Nations development system to strengthen their support for different science, technology and innovation partnerships with developing countries in primary, secondary and higher, vocational and continuing education, business opportunities for the private sector, and science, technology and innovation infrastructure.
The representative of the United States said his delegation joined consensus, but viewed a reference in preambular paragraph 18 to the Digital Cooperation Organization as representing only one example of multilateral activities outside of the United Nations system relevant to that paragraph. As there are many other organizations doing similar work, the United States does not view the reference as a relevant example, nor does it elevate that organization over other regional organizations. He also pointed out that the reference in operative paragraph 17 refers to “other relevant initiatives” as voluntary initiatives only. Citing other paragraphs, he referred the Committee to the general statement delivered on 18 November.
The representative of the United Kingdom said her delegation joined consensus, but addressed Committee modalities, noting that time spent contesting procedure rather than engaging on substance took away Committee time and resources that could have otherwise addressed how science, technology and innovation affect sustainable development. While pleased to see strong human rights language in that preambular paragraph, she expressed regret at the lack of greater emphasis on a multi-stakeholder approach.
The representative of the Republic of Korea joined consensus, acknowledging that the resolution recognizes the critical role of science, technology and innovation in building resilience to, combating and building back from the pandemic. He welcomed the inclusion of a paragraph affirming that recognizing that human rights offline must apply online as well, expressing support for a human rights-based approach to digital technology.
The representative of Japan said her delegation joined consensus, and it is essential that the technology facilitation mechanism functions agilely to help all Member States learn and collaborate, but noted it is underfunded, with untapped potential. She welcomed reference to “partnership in action” in operative paragraph 10 as a concrete recommendation.
Following that, the Committee took up a draft on “Follow-up to the Fourth United Nations Conference on the Least Developed Countries” (document A/C.2/76/L.57), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous text.
According to that draft, the Assembly would call on the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) to focus its analytical work on least developed countries, emphasizing productive capacities and measuring structural transformation. It would also urge least developed countries and their development partners to use existing initiatives and programmes, such as World Trade Organization (WTO) decisions on duty-free and quota-free market access for least developed countries, preferential rules of origin and aid for trade.
The representative of the United States said his country is committed to supporting least developed countries, including through the ongoing Fifth United Nations Conference on the Least Developed Countries negotiations. He noted the United States does not accept language in operative paragraph 12 calling on countries to increase their official development assistance (ODA) commitments, as emphasis should be on all other forms of development finance. He noted the terms “adequate” and “predictable” in operative paragraph 29 have no internationally agreed definitions, and more inclusive terms should be used. He further referred the Committee to his country’s general statement of 18 November.
The representative of Canada , also speaking for Bangladesh, Co-Chairs of the Preparatory Committee bureau for the Fifth United Nations Conference on the Least Developed Countries, noted Committee negotiations took place under challenging circumstances. She looked forward to resuming deliberations in support of the least developed countries during the next United Nations General Assembly session.
The representative of the United Kingdom said her delegation joined consensus, but expressed disappointment that Committee modalities were often challenged by deletions, treatment of language from an Economic and Social Council resolution as a source text and technical updates. Those activities necessitated convening small groups on procedure rather than substance. She expressed hope that Member States will seize a once in a decade opportunity to strengthen global partnerships, as it is critical that the most vulnerable are placed at the core of commitments.
The representative of the Turkey said that due to Committee modalities, delegates were unable to discuss any substantive issues, voicing hope for substantive discussions in 2022.
The Committee then turned to a text on “Unilateral economic measures as a means of political and economic coercion against developing countries” (document A/C.2/76/L.16/Rev.1), approving it in a recorded vote of 119 in favour to 7 against (Australia, Canada, Israel, Sweden, Ukraine, United Kingdom, United States) with 46 abstentions.
By its terms, the Assembly would urge the international community to adopt urgent and effective measures to eliminate the use of unilateral economic, financial or trade measures, unauthorized by relevant United Nations organs, inconsistent with international law or the Charter of the United Nations or which contravene basic principles of the multilateral trading system.
Further, the Assembly would call on the international community to condemn and reject the use of such measures as political and economic coercion against developing countries that impede full achievement of economic and social development. It would also call on the international community to condemn and reject imposition of unilateral coercive economic measures inconsistent with international law and the Charter, which impede the capacity of targeted countries to respond efficiently to the pandemic and promote post-pandemic recovery.
The representative of the United States , speaking before the vote, said his delegation again opposed the resolution, as sanctions are an effective, legitimate and peaceful tool for countering threats to peace and security, used against those who threaten human rights, undermine democracy or engage in criminal activities. The United States has applied them with specific goals in mind, including protecting the rule of law and human rights. The country also works to minimize unintended consequences, as in tailoring sanctions on Syria and Venezuela, in view of the pandemic. The United States is the leading donor of humanitarian assistance to both countries, providing billions of dollars, and will continue to tailor sanctions to support the flow of legitimate humanitarian goods and assistance. Sanctions are a legitimate way to achieve foreign policy, national security and international objectives, he noted, and the United States is not alone in that view.
The representative of Venezuela , speaking on behalf of the Group of Friends in Defence of the Charter of the United Nations, said unilateral coercive measures, be they economic or political, have become the preferred instrument of certain States to exert pressure on developing countries, and force the sovereign will of another State to obtain advantage over them. They clearly run contrary to spirit and letter of Charter of the United Nations, he said, as these illegal measures attack sustainable development and are also an obstacle to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. He reiterated that increasing recourse to unilateralism impacts the independence of States and their freedom of trade, economic development and efforts to fight the pandemic. They impose pain and suffering on entire populations and should be lifted.
The representative of Slovenia , speaking on behalf of the European Union after the vote, lamented the difficult negotiation process. The bloc abstained due to deterioration of the text compared to previous iterations, leading away from consensus. She noted the Union believes restrictive measures are an important tool in fighting terrorism and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. States hold the primary responsibility to protect human rights. Many transgressions are unacceptable and ending them is a key worldwide priority for the bloc. She noted sanctions should respect the principles of international law, with measures imposed in that context. She expressed regret that none of the bloc’s proposals were taken on board. The European Union and its Member States are the leading donor of COVID-19 vaccines worldwide, including to States under sanctions. She objected to several formulations in the text.
The representative of Cuba , associating himself with the Group of Friends in Defence of the Charter of the United Nations, noted the loss of access to international markets under unilateral coercive measures, and that a heightening of unilateral coercive measures against a number of countries attacks sovereignty and independence of States, and stymies national efforts at development. Those initiatives aim to cause economic and political problems, with no distinction between Governments and populations, attacking the most vulnerable. Cuba has been the victim of the most severe and prolonged coercive measures ever applied against any country, he stressed, causing $9.175 billion in damages from 2019 to 2020 alone. Those measures have been tightened during pandemic, despite calls by Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) to lift them. He noted the United States once again opposed the resolution, showing its disdain for developing countries.
The representative of Zimbabwe , associating herself with the Group of Friends in Defence of the Charter of the United Nations, said her delegation voted in favour of the draft, as unilateral coercive measures transgress international law. Given their extraterritorial nature, they severely impede the socioeconomic advancement of developing countries. Zimbabwe is still suffering under sanctions imposed some 20 years ago, she emphasized, impacting all sectors of its economy. While sanctions are characterized as targeted, she noted, under the pandemic, their effects are more odious, calling for the immediate and unconditional lifting of sanctions on Zimbabwe and other nations.
The representative of the United Kingdom , also speaking on behalf of Australia, Canada and Ukraine, said sanctions are a legitimate tool of foreign policy. The Governments cited voted against the resolution for first time, after having long disagreed with its sentiment and abstaining in previous years. She noted this year’s resolution mischaracterizes sanctions, with no mention that humanitarian exemptions can ensure that sanctions can avoid affecting food, medicine and other aid. They are lawful, transparent and allow for due process protections, with no inconsistency with the Charter of the United Nations.
The representative of China said his delegation voted in favour of the draft. With COVID-19 especially affecting developing countries, the international community must work with more urgency for momentum on development. In recent years, some developing countries have experienced instability fuelled by external interference, he said, and unilateral coercive measures run contrary to the trend of the times and the Charter. No country should coerce another, and the international community must eliminate unilateral or trade measures affecting developing countries. Unilateral coercive measures and the bullying of certain countries do not help solve problems, he said, urging the relevant countries to immediately and completely abolish them.
The representative of Eritrea , associating herself with the Group of Friends in Defence of the Charter of the United Nations, welcomed the resolution, as it is deplorable to witness foreign policy conducted using unilateral coercive measures mainly against developing countries that pursue independence efforts. Illegal unilateral coercive measures are packaged as targeted, she noted, as though they do not adversely affect States. Whether targeted or not, they have no legitimacy, she said, urging those States imposing them to refrain, as “our realities are not those of yours.”
The representative of Iran , associating himself with the Group of Friends in Defence of the Charter of the United Nations, said unilateral coercive measures including sanctions are illegal under international law and the Charter, representing a clear violation of the right to self-determination. Unilateral coercive measures aiming to destroy economy and living standards of a State constitute an act of war, as the effects are analogous. Even if they do not affect humanitarian aid, as alleged by some States, he stressed excluding some States from the international banking system is harmful. Imposing unilateral coercive measures, including illegal economic sanctions, including against some countries suffering under the pandemic, passes the redline of economic terrorism, reaching the level of crimes against humanity.
The representative of Sweden said she had intended to abstain, asking for that vote to be corrected or reflected in the report of the meeting.
Next, the Committee took up a draft on “Promotion of international cooperation to combat illicit financial flows and strengthening good practices on assets return to foster sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.28/Rev.1), approving operative paragraph 3 in a recorded vote of 116 in favour to 41 against, with 7 abstentions (Australia, Canada, Iceland, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Turkey).
The Committee then approved the draft as a whole, without a vote.
By that text, the Assembly would call on all countries to work together to eliminate base erosion and profit shifting and ensure that all companies, including multinationals, pay taxes to Governments of countries where economic activity occurs and value is created, according to national and international laws and policies.
The Assembly would also call on countries to cooperate, according to applicable bilateral or multilateral agreements, in the areas of mutual legal and administrative assistance in tax matters, as well as the automatic exchange of financial account information. Further it would stress that anti-corruption measures should be an integral part of national development policies and strategies.
The representative of the United States , speaking on operative paragraph 3, said fighting corruption is integral to development and security. However, the language undermines constructive work, and his delegation disassociated itself from operative paragraph 3. The United Nations Convention against Corruption is the appropriate venue for experts to consider confiscation and the proceeds from crimes, and the resolution undermines its work. He expressed concern over the endorsement of the High-level Panel on International Financial Accountability, Transparency and Integrity, as the document was not approved by consensus and is not a United Nations document. He also reiterated that some language undermines working against money laundering, corruption and other such crimes. The resolution is not clear on which activities are in question, and does not pay enough attention to transparency, and his delegation does not believe asset recovery should be so directly coupled with sustainable development. He referred the Committee to his country’s statement of 18 November regarding the term “illicit financial flows”.
The representative of the United Kingdom expressed disappointment that the resolution ended up with a paragraph vote containing language the delegation cannot accept. Since 2006, the United Kingdom has frozen, confiscated or returned over £1.1 billion in assets stolen from developing countries. It is not appropriate for the Committee to engage with Faculty Panel, she stated, as it has no official United Nations mandate. She noted the Conference of the States Parties to the United Nations Convention against Corruption will soon meet and is the correct forum for dealing with illicit financing. She expressed hope that, when negotiating the resolution in 2022, the Committee can reach more consensus.
The representative of Liechtenstein said combating illicit financing has been a longstanding priority for his country, but his delegation disassociated from operative paragraph 3 in 2020 as the faculty panel is not endorsed by United Nations membership, and voted against it in 2021. It is misleading that the resolution confuses asset recovery with asset return, he said, and his delegation will still advocate for the Convention on Corruption framework. He encouraged the bi-annualization or tri-annualization of the resolution.
The representative of Canada , also speaking on behalf of Australia and New Zealand, expressed concern over future trends in negotiations on the resolution. Those delegations abstained on operative paragraph 3 over concerns with the substance and process of negotiation. He noted the recent addition of substantive elements, and request for a Secretary-General’s report on the resolution duplicates the request for the Convention on Corruption report. Amendments to the draft were not technical updates and deserved further deliberation, he said, and the Committee could have achieved a better text with modalities respected.
The representative of Switzerland said that his country did not support all recommendations in operative paragraph 3, noting that the definition of illicit financial flows remains open. Elements of corruption require different approaches, and instruments already exist. Creating new coordination bodies will not help implement instruments, he said, and his delegation could not then support the text of operative paragraph 3. A lack of consensus makes efforts in the future more difficult.
The representative of Nigeria said her delegation attaches great importance to “L.28/Rev.1”, as illicit financial flows undermine the security of nations and inhibit growth. In addressing international financial flows, there is a need for transparency and integrity, and a redesigned global architecture to combat them, including establishing of an international ecosystem of laws and institutions. The challenges require taking immediate action, and it was therefore disappointing to see the need for a vote on operative paragraph 3. She expressed appreciation for the flexibility shown by the Group of 77 on the financial action task force referenced in the resolution, and lamented that fractures in the international community appear to be widening. She noted that evidence indicates that recovery and returning proceeds of illicit financial flows of assets could generate enough capital to finance the fight against climate change in Sub Saharan Africa by 2030.
The representative of the Republic of Korea expressed regret that a wholly consensual outcome was not possible. His delegation abstained on operative paragraph 3, while attaching significance to combating illicit financial flows. However, he was not entirely satisfied with the paragraph’s contents for several reasons, noting concern over a vague reference to illicit financial flows, and stating there is no shortage of commitments, mechanisms or bodies tackling components of illicit financial flows, including tax, corruption and criminal activities.
The representative of Sweden said that her country intended to vote no on operative paragraph 3, asking that the record be corrected accordingly.
The representative of Slovenia , speaking on behalf of the European Union on resolution as a whole, said financial integrity is a priority for Sustainable Development Goals. The bloc voted against operative paragraph 3, as the initiative was not as inclusive as hoped. The Faculty Panel report only reflects the views of its members, who did not even agree amongst themselves, she noted. Some language threatens to weaken support for existing bodies and instruments, she said, and the bloc disassociated itself from operative paragraph 3.
Following that, the Committee turned to a draft on “Protection of global climate for present and future generations of humankind” (document A/C.2/76/L.19/Rev.1), rejecting an amendment to paragraph 10 in a recorded vote of 84 against to 62 in favour, with 11 abstentions. It decided to retain the paragraph in a recorded vote of 96 in favour to 51 against, with 9 abstentions (Antigua-Barbuda, Chile, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Fiji, Haiti, Honduras, Maldives).
By that text, the Assembly would express profound alarm that greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise globally, remains deeply concerned that all countries are vulnerable to adverse impacts of climate change and are already experiencing an increase in such impacts. Noting that these include persistent drought, extreme weather events, land degradation, sea level rise, coastal erosion, ocean acidification and retreat of mountain glaciers, the Assembly would emphasize that mitigation of and adaptation to climate change represent an immediate and urgent global priority.
Further to the text, the Assembly would urge Member States to adopt a climate- and environment-responsive approach to COVID‑19 recovery, including by aligning investments and domestic policies with the 2030 Agenda, Paris Agreement goals and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to accelerate a transition to low-emission, climate-resilient, inclusive and sustainable economies.
Also by the text, the Assembly would stress the need to strengthen the global response to climate change by increasing countries’ abilities to adapt to its adverse effects, fostering resilience, accelerating full implementation of the 2030 Agenda and integrating appropriate measures into national policies, strategies and planning. It would further stress the importance of mobilizing means of implementation from all sources, including adequate financial support for mitigation and adaptation, considering the specific needs and special circumstances of developing countries.
Speaking before the vote, the representative of the European Union , speaking in its capacity as observer, said her bloc joined consensus on the draft, despite major deficiencies in the text. Regarding operative paragraph 30, she expressed regret that progress made at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow was not fully reflected in the text, including provisions on transparency and climate finance.
The representative of the United States said the draft’s language in operative paragraph 10 deflects away from the key Sustainable Development Goals, urging Member States to vote yes for the amendment.
Speaking after the vote, the representative of Antigua and Barbuda said his country hoped for consensus on the amendment to ensure that the agreed language in it is maintained, as the amendment was taken from the 2030 Agenda, stating that he abstained from the vote.
The representative of India stressed that developed countries must not neglect their obligations on climate financing, mitigation and adaptation to developing countries. Regarding operative paragraph 10, she lamented that a nation used this to propagate its own agenda, noting that no constructive engagement was made on this paragraph.
The representative of Chile stressed that the outcomes of the Glasgow conference must be fully implemented, especially regarding climate finance and long-term finance, expressing regret that no consensus was achieved on this crucial matter.
The representative of China noted that the adverse effects of climate change are increasingly visible, stressing the urgency for climate action. The Glasgow Climate Change Conference made positive progress, injecting new impetus into the Paris Agreement. The international community should build on this momentum to promote climate mitigation and adaptation in a balanced manner, with developed countries providing the funding.
The representative of Guinea , speaking on behalf of the Group of 77, called on all members of his to vote no to the amendment to operative paragraph 10.
Addressing the draft as a whole, the representative of the Russian Federation stressed the need to ensure consensus on climate issues and adherence to the Paris Agreement. The text should have reflected forests and absorption of greenhouse gases more, he said, expressing regret that the draft failed to do this.
The representative of the United States said his country joined consensus on the draft, but expressed regret that it must disassociate from operative paragraph 10, which promoted a domestic priority of a Member State rather than the 2030 Agenda. He also expressed disappointment in the final language, which failed to reflect the ambition and outcomes of the Glasgow Climate Change Conference.
The representative of the United Kingdom , noting the ambitious and balanced outcome from the Glasgow conference, stressed the importance of all nations coming together on critical steps to protect the climate. The draft contains agreed language on finance and post-2025 finance goals, but fails to include fully updated language as contained in the Glasgow climate platform.
The representative of Switzerland expressed regret that the resolution failed to faithfully reflect the outcomes of the Glasgow conference, calling on parties who have not submitted nationally determined contributions to do so as soon as possible. Stressing the need to make financial flows compatible with low emissions, he called on all to support the development of technology and policies to ensure a transition to low energy systems.
The representative of Canada , also speaking for Norway, Iceland, New Zealand and Australia, expressed disappointment that the Committee was unable to avoid a paragraph vote, stressing that countries must set aside their differences on climate issues.
The Committee then turned to a draft on “Strengthening cooperation for integrated coastal zone management for achieving sustainable development” (document A/C.2/76/L.38/Rev.1), approving it without a vote.
By that text, the Assembly would emphasize that coastal areas are an essential ecological and economic resource, noting that their management and planning, from a sustainable development perspective, need an integrated management approach. It would call on Member States and other actors at the local, national, regional and international levels to address the problem of marine litter, including plastic litter and microplastics, which impacts coastal management.
Further to the text, the Assembly would call on Member States to reduce the level of pollution of coastal areas and protect marine ecosystems and coastal areas in the long term. It would also call on them to develop partnerships allowing the exchange of good practices in integrated coastal zone management, marine spatial planning and the implementation of sustainable economic models and approaches, considering that international cooperation to implement marine spatial planning can contribute to the maintenance of ecosystem integrity and improve the economic profitability of marine management and the use of resources.
Morocco ’s representative, introducing the draft resolution, said the text is a strong illustration of how coastal economies can contribute to sustainable development and to a resilient recovery from COVID‑19. The resolution aims to celebrate efforts made by all Member States, including those without coastal exposure in order to enhance their participation in global trade. It also has enabled the interlinking of various pillars of international cooperation, including North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation. He said his country has adopted a coastal law in 2015, followed by the establishment of a national commission on integrated coastal management, enabling considerable measures in areas such as energy efficiency, public transport and water management. He invited Member States to approve the text by consensus, noting that the resolution is a collective effort for sustainable development.
After action, the representative of the European Union , in its capacity as observer, said his bloc welcomes the resolution, especially the call made therein to address the problem of marine litter and reduce the level of pollution in coastal areas. He warned that without a change in approach, the amount of plastic that ends up in oceans could triple by 2040 to 29 million tons per year. In that regard, he called upon the resumed session of the fifth United Nations Environment Assembly in February to launch negotiations of a much-needed intergovernmental instrument to end plastic pollution. Referring to preambular paragraph 2, which was not open for negotiations in 2021, he said that, while his bloc joins consensus, the omnibus resolution on oceans and law of the sea is and should remain the authoritative source of any reference to the Convention on the Law of the Sea in resolutions of the General Assembly. His bloc’s joining consensus in 2021 does not imply support for language in that preambular paragraph for other resolutions in the future.
Colombia ’s representative said his country’s commitment to strengthening cooperation for integrated coastal zone management is evidenced in his Government’s recent announcement at the twenty-sixth session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change of the extension of its protected marine areas in the East Pacific to 16 million hectares. Noting that while Colombia joins consensus, he said that, with respect to preambular paragraph 2, his country had not ratified the Convention on the Law of the Sea, the provisions of which are not effective nor enforceable against Colombia. As his country does not view that the convention represents the only legal framework regulating ocean activities, it expresses reservation to the reference to that instrument, which is included in the resolution.
The representative of the United States said his country strongly supports the sustainable use and management of coastal zones and marine ecosystems, as well as the launch of negotiations for a global legal instrument on ocean and plastic pollution, at the second session of the fifth United Nations Environment Assembly. While his country joined consensus, regarding references to the 2030 Agenda and the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, he referred the Committee to its statement delivered on 18 November.
Japan ’s representative said that while his delegation decided to join consensus, it regrets that the oral statement by the Secretariat in connection with operative paragraph 14 implying a proposed programme budget for 2023 was issued and circulated after the final informal consultations, without prior information sharing or discussion on the matter. He expressed hope that important aspects, such as programme budgetary implications, would be discussed in detail during informal discussions among Member States for transparency purposes going forward.
The representative of the United Kingdom said that the topic is of particular interest to his country in its role as president of the twenty-sixth session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and leader of the Global Ocean Alliance. With respect to preambular paragraph 2, which was not open for negotiation or amendment, he said his country’s preferred language to refer to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea is contained in a long-standing paragraph accepted in the Committee. After reading that preferred language, he said his country does not consider that language in preambular paragraph 2 would be an appropriate basis for future negotiations.
Turkey ’s representative, said that while her country joins consensus and supports efforts to strengthen cooperation on coastal management, it is not a party to the Convention on the Law of the Sea. That convention is not the only legal framework that regulates all activities in the ocean and sea. She said Turkey disassociates itself form references made in the resolution to that convention and those references should not be interpreted as a change in the legal position of her country on that matter.
Iran ’s representative said that while her country joins consensus, it is not a party to the Convention on the Law of the Sea and thus disassociates itself from all references made in the resolution to that convention, especially in preambular paragraph 2.
Morocco ’s representative, expressing appreciation for the consensus reached on the resolution, assured Japan’s representative that his comments had been taken into account and would also be taken into consideration in the future.
Next, the Committee took up a decision on “Draft programme of work of the Second Committee for the seventy-seventh session of the General Assembly” (document A/C.2/76/L.61), approving it without a vote, withdrawing a previous draft.
By that text, the Assembly would approve the Committee’s draft programme of work for its seventy-seventh session of the Assembly. It would further invite the Second Committee Bureau at the seventy-seventh session, in preparing the draft programme of work and timetable of the Committee for the seventy-seventh session, to consider the provisional programme of work and timetable of the Committee as contained in document A/C.2/76/CRP.2.
Speaking before action, the representative of the European Union , in its capacity as observer, said that a revitalized fit-for-purpose Committee is necessary to address new and emerging challenges. Bound by this year’s modalities, her bloc had not attempted to make further progress on revitalization during negotiations on Committee resolutions. However, it is of utmost importance to keep revitalization of the Committee on its agenda now and in the future, she said, adding that the June 2021 revitalization decision contains many important proposals that would serve as a good basis for progress.
Canada ’s representative, speaking also on behalf of Andorra, Australia, Iceland, Israel, Japan, Liechtenstein, Mexico, New Zealand, Norway, Republic of Korea and the United Kingdom, said the Committee must continue to adapt to current realities and challenges. Their delegations had voiced strong concerns about resolutions that do not currently align with the landmark agreements of 2015, particularly the 2030 Agenda. They had also expressed support to merge resolutions when appropriate, adapt the periodicity of resolutions and to actively consider co-authorship. Noting that the Committee is at a turning point on revitalization, he said the same collaboration and discipline that allowed it to complete its work during the current session, could be used to ensure the Committee also delivers to Member States a sustainable, inclusive and resilient recovery towards achievement of the 2030 Agenda.
The representative of the United States said it was important to continue discussions on revitalization of the Committee, noting progress made over the last two years. The Committee’s decision on revitalization in June contains important proposals that could serve as a good basis for further progress. Noting that there are useful tools that the Committee could adopt to better focus its work, he suggested exploring the possibility of delegations submitting a justification for the introduction or continued consideration of resolutions, indicating how a resolution would support the work of the Committee. Moreover, his delegation is open to considering creative ideas to ensure that the Committee delivers to all its citizens.
The Committee then took up a draft decision on its working methods, approving it without a vote. The decision reads as follows:
“The General Assembly recalls its resolution 75/325 on “Revitalization of the work of the General Assembly”, in particular the provisions relating to working methods, as well as its decisions 75/548B and 73/537B on “Revitalization of the work of the Second Committee”, decides to convene up to two informal meetings of the Second Committee in early 2022 to discuss the working methods of the Committee, and requests the Bureau of the Committee to update the conference room paper on Second Committee working methods, following those discussions.”
The Committee then took up and concluded consideration of its item on “Programme planning”.
Closing Remarks
Maria-Francesca Spatolisano, Assistant Secretary-General for Policy Coordination and Inter-Agency Affairs of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs, said that, despite the limitations posed by the pandemic, the Committee had reached a clear agreement on its methods of work. Recognizing the severe negative impacts of the pandemic on human health, safety and well-being, as well as on lives and livelihoods, the Committee had also provided relevant guidance to current global challenges, examples of which could be found in many of the resolutions it had recently approved. Policy guidance on the challenges faced by groups of countries in special situations was also provided by the Committee, calling for the convening in 2024 of a fourth international conference on small island developing States, as well as deciding to hold the third United Nations Conference on Landlocked Developing Countries, also in 2024. As well, the Committee provided guidance on important topics, such as biological diversity, coastal zone management, and sustainable consumption and production patterns. Noting the Committee’s efficient work during this session, she said the Department of Economic and Social Affairs remains committed to support the Second Committee, as it continues to advance the realization of the 2030 Agenda in the decade of action and delivery.
The Chair said that, given the challenges posed by the pandemic, the Committee had carefully prepared a set of modalities on how to engage with each other over the course of a few months and managed to ensure that its conclusions fell into place with those of the Twenty-Sixth United Nations Climate Change Conference. Further, the Committee managed to respond to the guidance of the Secretary-General’s Food Systems Summit and agreed to start planning for reviewing the work on landlocked developing and small island developing States in 2024, she said, noting that those were not small accomplishments under difficult circumstances. She expressed gratitude to the Bureau, noting that it was first all-women Bureau of the Second Committee in history. She also thanked the facilitators and co-facilitators of resolutions, whose efforts brought together the views of all delegations in the 37 draft resolutions that the Committee had recently approved, as well as the United Nations Offices and the Secretariat for their support. Finally, she thanked delegations for taking the guidance on modalities in stride and for their commitment to engaging efficiently, allowing the Committee to complete its work.
Facebook Twitter Email Print LinkedIn
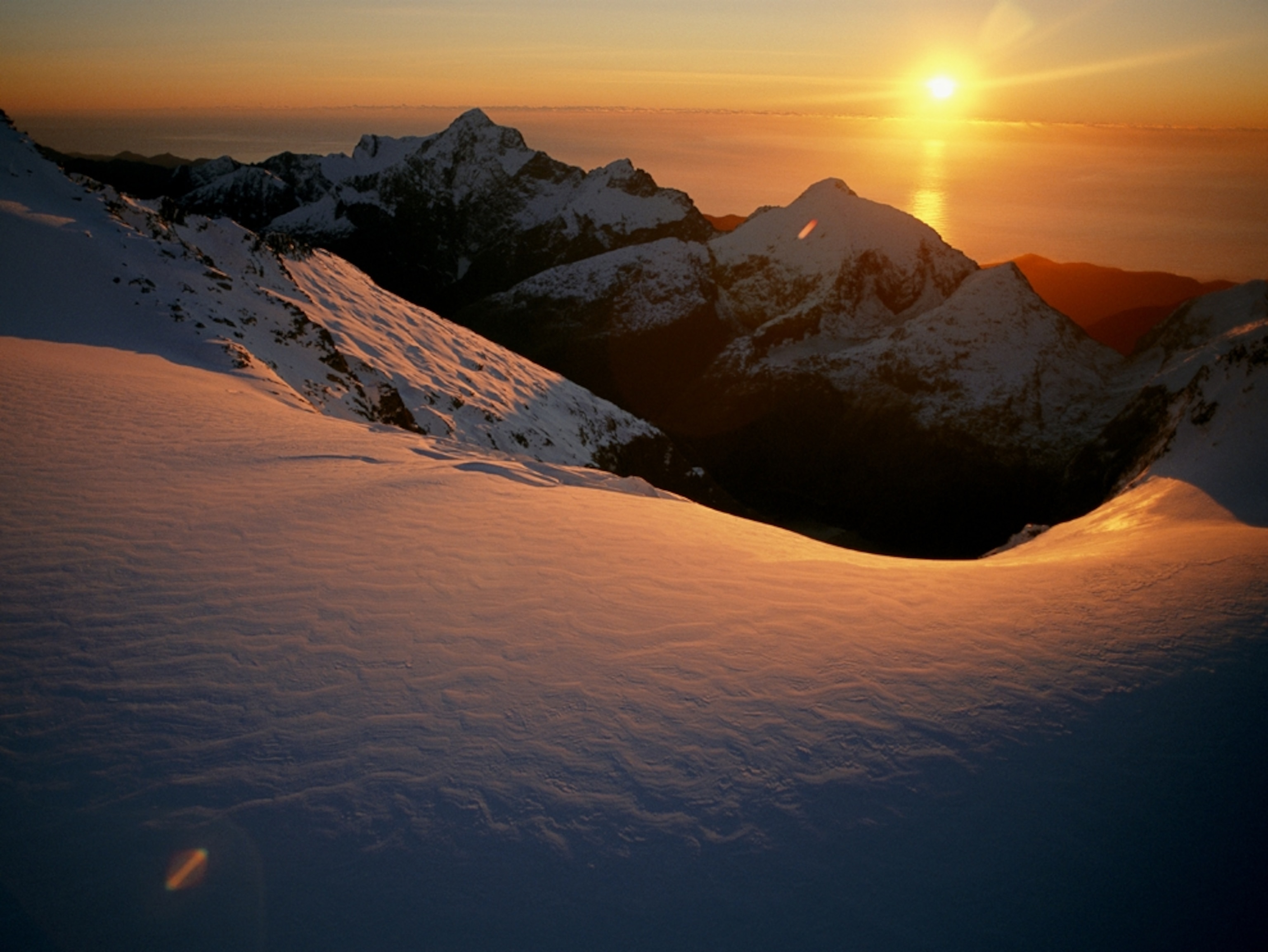

A sunset lights a glacier in New Zealand's Fiordland National Park. Around the world, many glaciers are melting quickly as the planet warms.
- ENVIRONMENT
Are there real ways to fight climate change? Yes.
Humans have the solutions to fight a global environmental crisis. Do we have the will?
The evidence that humans are causing climate change, with drastic consequences for life on the planet, is overwhelming .
Experts began raising the alarm about global warming in 1979 , a change now referred to under the broader term climate change , preferred by scientists to describe the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems. Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also extreme weather events, shifting wildlife populations and habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts.
Over 200 countries—193 countries plus the 27 members of the European Union—have signed the Paris Climate Agreement , a treaty created in 2015 to fight climate change on a global scale. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which synthesizes the scientific consensus on the issue, has set a goal of keeping warming under 2°C (3.6°F) and pursuing an even lower warming cap of 1.5 °C (2.7° F).
But no country has created policies that will keep the world below 1.5 °C, according to the Climate Action Tracker . Current emissions have the world on track to warm 2.8°C by the end of this century.
Addressing climate change will require many solutions —there's no magic bullet. Yet nearly all of these solutions exist today. They range from worldwide changes to where we source our electricity to protecting forests from deforestation.
The promise of new technology
Better technology will help reduce emissions from activities like manufacturing and driving.
Scientists are working on ways to sustainably produce hydrogen, most of which is currently derived from natural gas, to feed zero-emission fuel cells for transportation and electricity.
Renewable energy is growing, and in the U.S., a combination of wind, solar, geothermal, and other renewable sources provide 20 percen t of the nation’s electricity.
New technological developments promise to build better batteries to store that renewable energy, engineer a smarter electric grid, and capture carbon dioxide from power plants and store it underground or turn it into valuable products such as gasoline . Some argue that nuclear power—despite concerns over safety, water use, and toxic waste—should also be part of the solution, because nuclear plants don't contribute any direct air pollution while operating.
Should we turn to geoengineering?
While halting new greenhouse gas emissions is critical, scientists say we need to extract existing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, effectively sucking it out of the sky.
Pulling carbon out of the atmosphere is a type of geoengineering , a science that interferes with the Earth’s natural systems, and it’s a controversial approach to fighting climate change.
Other types of geoengineering involve spraying sunlight-reflecting aerosols into the air or blocking the sun with a giant space mirror. Studies suggest we don’t know enough about the potential dangers of geoengineering to deploy it.
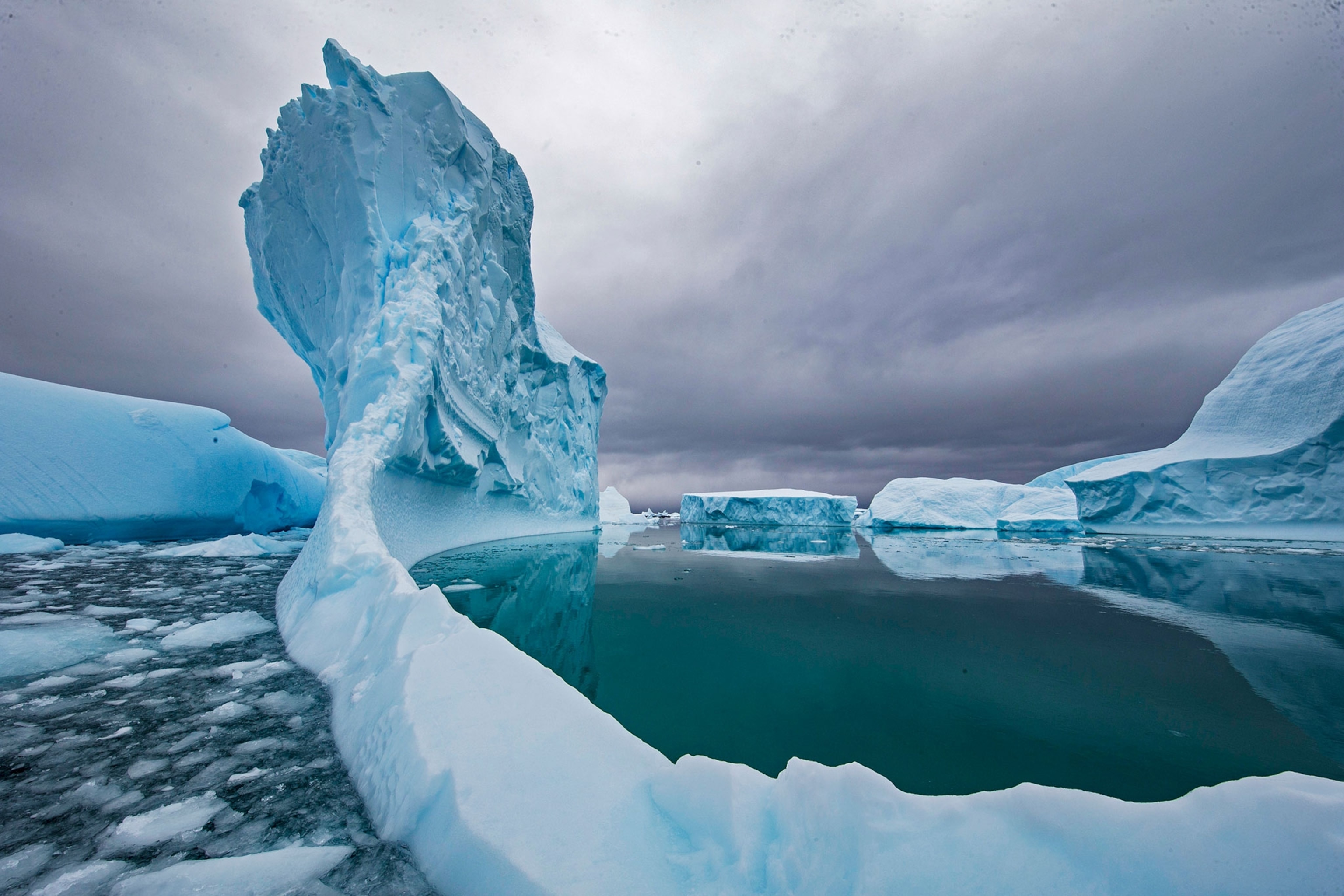

Restoring nature to protect the planet
Planting trees, restoring seagrasses, and boosting the use of agricultural cover crops could help clean up significant amounts of carbon dioxide .
The Amazon rainforest is an important reservoir of the Earth’s carbon, but a study published in 2021, showed deforestation was transforming this reservoir into a source of pollution.
Restoring and protecting nature may provide as much as 37 percent of the climate mitigation needed to reach the Paris Agreement’s 203o targets. Protecting these ecosystems can also benefit biodiversity, providing a win-win for nature .
Adapt—or else
Communities around the world are already recognizing that adaptation must also be part of the response to climate change . From flood-prone coastal towns to regions facing increased droughts and fires, a new wave of initiatives focuses on boosting resilience . Those include managing or preventing land erosion, building microgrids and other energy systems built to withstand disruptions, and designing buildings with rising sea levels in mind.
Last year, the Inflation Reduction Act was signed into law and was a historic investment in fighting and adapting to climate change.
( Read more about how the bill will dramatically reduce emissions. )
Recent books such as Drawdown and Designing Climate Solutions have proposed bold yet simple plans for reversing our current course. The ideas vary, but the message is consistent: We already have many of the tools needed to address climate change. Some of the concepts are broad ones that governments and businesses must implement, but many other ideas involve changes that anyone can make— eating less meat , for example, or rethinking your modes of transport .
"We have the technology today to rapidly move to a clean energy system," write the authors of Designing Climate Solutions . "And the price of that future, without counting environmental benefits, is about the same as that of a carbon-intensive future."
Sarah Gibbens contributed reporting to this article.
LIMITED TIME OFFER
Get a FREE tote featuring 1 of 7 ICONIC PLACES OF THE WORLD
Related Topics
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- AIR POLLUTION
- RENEWABLE ENERGY
You May Also Like

Another weapon to fight climate change? Put carbon back where we found it

Which cities will still be livable in a world altered by climate change?

Could seaweed be the 'fastest and least expensive' tool to fight climate change?

Can we hack DNA in plants to help fight climate change?
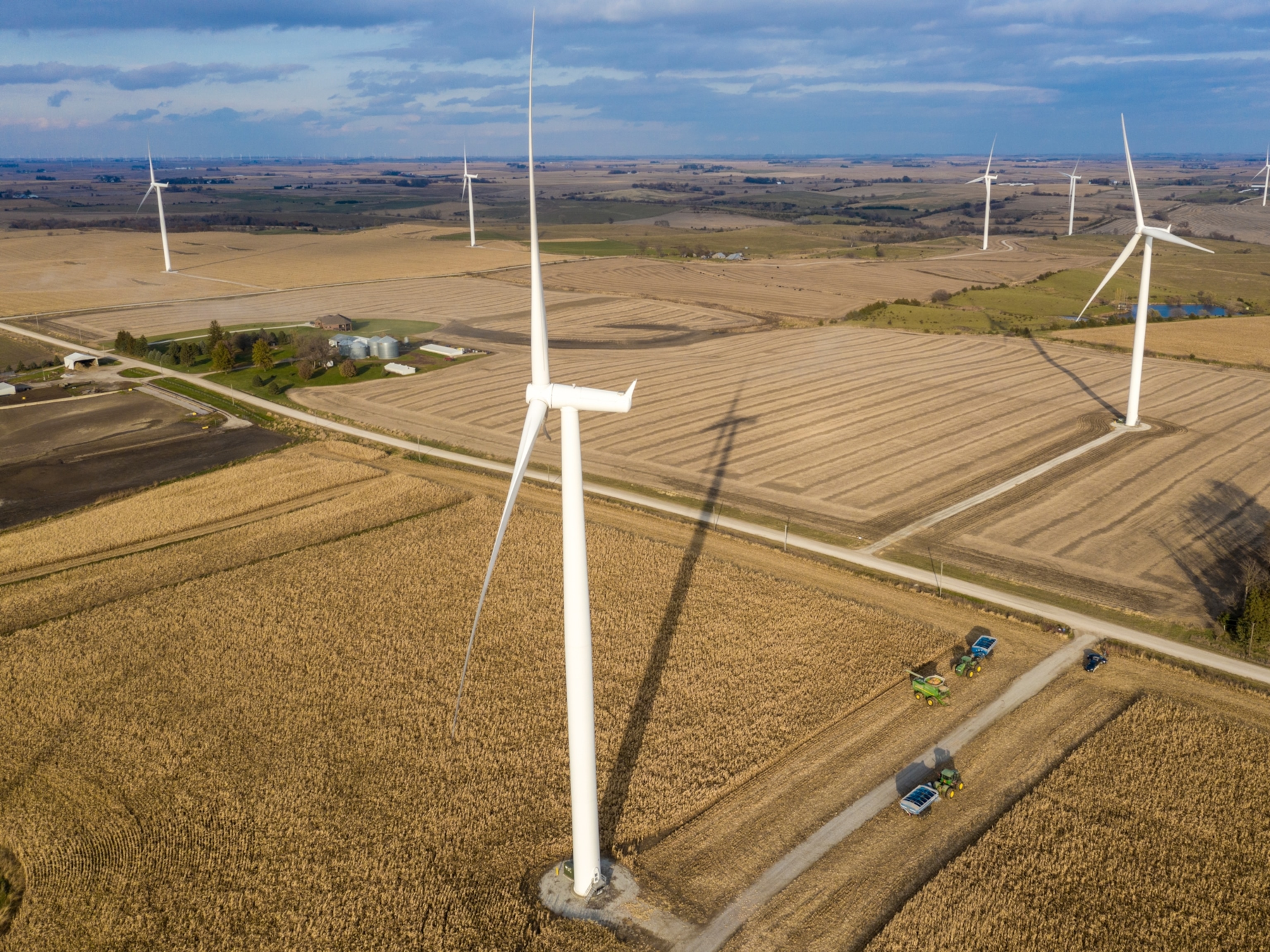

How the historic climate bill will dramatically reduce U.S. emissions
- Paid Content
- Environment
History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Women of Impact
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
November 26, 2007
10 Solutions for Climate Change
Ten possibilities for staving off catastrophic climate change
By David Biello

Mark Garlick Getty Images
The enormity of global warming can be daunting and dispiriting. What can one person, or even one nation, do on their own to slow and reverse climate change ? But just as ecologist Stephen Pacala and physicist Robert Socolow, both at Princeton University, came up with 15 so-called " wedges " for nations to utilize toward this goal—each of which is challenging but feasible and, in some combination, could reduce greenhouse gas emissions to safer levels —there are personal lifestyle changes that you can make too that, in some combination, can help reduce your carbon impact. Not all are right for everybody. Some you may already be doing or absolutely abhor. But implementing just a few of them could make a difference.
Forego Fossil Fuels —The first challenge is eliminating the burning of coal , oil and, eventually, natural gas. This is perhaps the most daunting challenge as denizens of richer nations literally eat, wear, work, play and even sleep on the products made from such fossilized sunshine. And citizens of developing nations want and arguably deserve the same comforts, which are largely thanks to the energy stored in such fuels.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Oil is the lubricant of the global economy, hidden inside such ubiquitous items as plastic and corn, and fundamental to the transportation of both consumers and goods. Coal is the substrate, supplying roughly half of the electricity used in the U.S. and nearly that much worldwide—a percentage that is likely to grow, according to the International Energy Agency. There are no perfect solutions for reducing dependence on fossil fuels (for example, carbon neutral biofuels can drive up the price of food and lead to forest destruction, and while nuclear power does not emit greenhouse gases, it does produce radioactive waste), but every bit counts.
So try to employ alternatives when possible—plant-derived plastics, biodiesel, wind power—and to invest in the change, be it by divesting from oil stocks or investing in companies practicing carbon capture and storage.
Infrastructure Upgrade —Buildings worldwide contribute around one third of all greenhouse gas emissions (43 percent in the U.S. alone), even though investing in thicker insulation and other cost-effective, temperature-regulating steps can save money in the long run. Electric grids are at capacity or overloaded, but power demands continue to rise. And bad roads can lower the fuel economy of even the most efficient vehicle. Investing in new infrastructure, or radically upgrading existing highways and transmission lines, would help cut greenhouse gas emissions and drive economic growth in developing countries.
Of course, it takes a lot of cement, a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, to construct new buildings and roads. The U.S. alone contributed 50.7 million metric tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere in 2005 from cement production, which requires heating limestone and other ingredients to 1,450 degrees Celsius (2,642 degrees Fahrenheit). Mining copper and other elements needed for electrical wiring and transmission also causes globe-warming pollution.
But energy-efficient buildings and improved cement-making processes (such as using alternative fuels to fire up the kiln) could reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the developed world and prevent them in the developing world.
Move Closer to Work —Transportation is the second leading source of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. (burning a single gallon of gasoline produces 20 pounds of CO 2 ). But it doesn't have to be that way.
One way to dramatically curtail transportation fuel needs is to move closer to work, use mass transit, or switch to walking, cycling or some other mode of transport that does not require anything other than human energy. There is also the option of working from home and telecommuting several days a week.
Cutting down on long-distance travel would also help, most notably airplane flights, which are one of the fastest growing sources of greenhouse gas emissions and a source that arguably releases such emissions in the worst possible spot (higher in the atmosphere). Flights are also one of the few sources of globe-warming pollution for which there isn't already a viable alternative: jets rely on kerosene, because it packs the most energy per pound, allowing them to travel far and fast, yet it takes roughly 10 gallons of oil to make one gallon of JetA fuel. Restricting flying to only critical, long-distance trips—in many parts of the world, trains can replace planes for short- to medium-distance trips—would help curb airplane emissions.
Consume Less —The easiest way to cut back on greenhouse gas emissions is simply to buy less stuff. Whether by forgoing an automobile or employing a reusable grocery sack, cutting back on consumption results in fewer fossil fuels being burned to extract, produce and ship products around the globe.
Think green when making purchases. For instance, if you are in the market for a new car, buy one that will last the longest and have the least impact on the environment. Thus, a used vehicle with a hybrid engine offers superior fuel efficiency over the long haul while saving the environmental impact of new car manufacture.
Paradoxically, when purchasing essentials, such as groceries, buying in bulk can reduce the amount of packaging—plastic wrapping, cardboard boxes and other unnecessary materials. Sometimes buying more means consuming less.
Be Efficient —A potentially simpler and even bigger impact can be made by doing more with less. Citizens of many developed countries are profligate wasters of energy, whether by speeding in a gas-guzzling sport-utility vehicle or leaving the lights on when not in a room.
Good driving—and good car maintenance, such as making sure tires are properly inflated—can limit the amount of greenhouse gas emissions from a vehicle and, perhaps more importantly, lower the frequency of payment at the pump.
Similarly, employing more efficient refrigerators, air conditioners and other appliances, such as those rated highly under the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Energy Star program, can cut electric bills while something as simple as weatherproofing the windows of a home can reduce heating and cooling bills. Such efforts can also be usefully employed at work, whether that means installing more efficient turbines at the power plant or turning the lights off when you leave the office .
Eat Smart, Go Vegetarian? —Corn grown in the U.S. requires barrels of oil for the fertilizer to grow it and the diesel fuel to harvest and transport it. Some grocery stores stock organic produce that do not require such fertilizers, but it is often shipped from halfway across the globe. And meat, whether beef, chicken or pork, requires pounds of feed to produce a pound of protein.
Choosing food items that balance nutrition, taste and ecological impact is no easy task. Foodstuffs often bear some nutritional information, but there is little to reveal how far a head of lettuce, for example, has traveled.
University of Chicago researchers estimate that each meat-eating American produces 1.5 tons more greenhouse gases through their food choice than do their vegetarian peers. It would also take far less land to grow the crops necessary to feed humans than livestock, allowing more room for planting trees.
Stop Cutting Down Trees —Every year, 33 million acres of forests are cut down . Timber harvesting in the tropics alone contributes 1.5 billion metric tons of carbon to the atmosphere. That represents 20 percent of human-made greenhouse gas emissions and a source that could be avoided relatively easily.
Improved agricultural practices along with paper recycling and forest management—balancing the amount of wood taken out with the amount of new trees growing—could quickly eliminate this significant chunk of emissions.
And when purchasing wood products, such as furniture or flooring, buy used goods or, failing that, wood certified to have been sustainably harvested. The Amazon and other forests are not just the lungs of the earth, they may also be humanity's best short-term hope for limiting climate change.
Unplug —Believe it or not, U.S. citizens spend more money on electricity to power devices when off than when on. Televisions, stereo equipment, computers, battery chargers and a host of other gadgets and appliances consume more energy when seemingly switched off, so unplug them instead.
Purchasing energy-efficient gadgets can also save both energy and money—and thus prevent more greenhouse gas emissions. To take but one example, efficient battery chargers could save more than one billion kilowatt-hours of electricity—$100 million at today's electricity prices—and thus prevent the release of more than one million metric tons of greenhouse gases.
Swapping old incandescent lightbulbs for more efficient replacements, such as compact fluorescents (warning: these lightbulbs contain mercury and must be properly disposed of at the end of their long life), would save billions of kilowatt-hours. In fact, according to the EPA, replacing just one incandescent lightbulb in every American home would save enough energy to provide electricity to three million American homes.
One Child —There are at least 6.6 billion people living today, a number that is predicted by the United Nations to grow to at least nine billion by mid-century. The U.N. Environmental Program estimates that it requires 54 acres to sustain an average human being today—food, clothing and other resources extracted from the planet. Continuing such population growth seems unsustainable.
Falling birth rates in some developed and developing countries (a significant portion of which are due to government-imposed limits on the number of children a couple can have) have begun to reduce or reverse the population explosion. It remains unclear how many people the planet can comfortably sustain, but it is clear that per capita energy consumption must go down if climate change is to be controlled.
Ultimately, a one child per couple rule is not sustainable either and there is no perfect number for human population. But it is clear that more humans means more greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Fuels —Replacing fossil fuels may prove the great challenge of the 21st century. Many contenders exist, ranging from ethanol derived from crops to hydrogen electrolyzed out of water, but all of them have some drawbacks, too, and none are immediately available at the scale needed.
Biofuels can have a host of negative impacts, from driving up food prices to sucking up more energy than they produce. Hydrogen must be created, requiring either reforming natural gas or electricity to crack water molecules. Biodiesel hybrid electric vehicles (that can plug into the grid overnight) may offer the best transportation solution in the short term, given the energy density of diesel and the carbon neutral ramifications of fuel from plants as well as the emissions of electric engines. A recent study found that the present amount of electricity generation in the U.S. could provide enough energy for the country's entire fleet of automobiles to switch to plug-in hybrids , reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the process.
But plug-in hybrids would still rely on electricity, now predominantly generated by burning dirty coal. Massive investment in low-emission energy generation, whether solar-thermal power or nuclear fission , would be required to radically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. And even more speculative energy sources—hyperefficient photovoltaic cells, solar energy stations in orbit or even fusion—may ultimately be required.
The solutions above offer the outline of a plan to personally avoid contributing to global warming. But should such individual and national efforts fail, there is another, potentially desperate solution:
Experiment Earth —Climate change represents humanity's first planetwide experiment. But, if all else fails, it may not be the last. So-called geoengineering , radical interventions to either block sunlight or reduce greenhouse gases, is a potential last resort for addressing the challenge of climate change.
Among the ideas: releasing sulfate particles in the air to mimic the cooling effects of a massive volcanic eruption; placing millions of small mirrors or lenses in space to deflect sunlight; covering portions of the planet with reflective films to bounce sunlight back into space; fertilizing the oceans with iron or other nutrients to enable plankton to absorb more carbon; and increasing cloud cover or the reflectivity of clouds that already form.
All may have unintended consequences, making the solution worse than the original problem. But it is clear that at least some form of geoengineering will likely be required: capturing carbon dioxide before it is released and storing it in some fashion, either deep beneath the earth, at the bottom of the ocean or in carbonate minerals. Such carbon capture and storage is critical to any serious effort to combat climate change.
Additional reporting by Larry Greenemeier and Nikhil Swaminathan .
Responding to the Climate Threat: Essays on Humanity’s Greatest Challenge

A new book co-authored by MIT Joint Program Founding Co-Director Emeritus Henry Jacoby
From the Back Cover
This book demonstrates how robust and evolving science can be relevant to public discourse about climate policy. Fighting climate change is the ultimate societal challenge, and the difficulty is not just in the wrenching adjustments required to cut greenhouse emissions and to respond to change already under way. A second and equally important difficulty is ensuring widespread public understanding of the natural and social science. This understanding is essential for an effective risk management strategy at a planetary scale. The scientific, economic, and policy aspects of climate change are already a challenge to communicate, without factoring in the distractions and deflections from organized programs of misinformation and denial.
Here, four scholars, each with decades of research on the climate threat, take on the task of explaining our current understanding of the climate threat and what can be done about it, in lay language―importantly, without losing critical aspects of the natural and social science. In a series of essays, published during the 2020 presidential election, the COVID pandemic, and through the fall of 2021, they explain the essential components of the challenge, countering the forces of distrust of the science and opposition to a vigorous national response.
Each of the essays provides an opportunity to learn about a particular aspect of climate science and policy within the complex context of current events. The overall volume is more than the sum of its individual articles. Proceeding each essay is an explanation of the context in which it was written, followed by observation of what has happened since its first publication. In addition to its discussion of topical issues in modern climate science, the book also explores science communication to a broad audience. Its authors are not only scientists – they are also teachers, using current events to teach when people are listening. For preserving Earth’s planetary life support system, science and teaching are essential. Advancing both is an unending task.
About the Authors
Gary Yohe is the Huffington Foundation Professor of Economics and Environmental Studies, Emeritus, at Wesleyan University in Connecticut. He served as convening lead author for multiple chapters and the Synthesis Report for the IPCC from 1990 through 2014 and was vice-chair of the Third U.S. National Climate Assessment.
Henry Jacoby is the William F. Pounds Professor of Management, Emeritus, in the MIT Sloan School of Management and former co-director of the MIT Joint Program on the Science and Policy of Global Change, which is focused on the integration of the natural and social sciences and policy analysis in application to the threat of global climate change.
Richard Richels directed climate change research at the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI). He served as lead author for multiple chapters of the IPCC in the areas of mitigation, impacts and adaptation from 1992 through 2014. He also served on the National Assessment Synthesis Team for the first U.S. National Climate Assessment.
Ben Santer is a climate scientist and John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Fellow. He contributed to all six IPCC reports. He was the lead author of Chapter 8 of the 1995 IPCC report which concluded that “the balance of evidence suggests a discernible human influence on global climate”. He is currently a Visiting Researcher at UCLA’s Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science & Engineering.
Access the Book
View the book on the publisher's website here .
Order the book from Amazon here .

Related Posts
Making the clean energy transition work for everyone.

Letting the Earth answer back: Designing better planetary conversations

Cutting carbon emissions on the US power grid
Study unlocks nanoscale secrets for designing next-generation solar cells

MIT Climate News in Your Inbox
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 18 March 2024
Are we all doomed? How to cope with the daunting uncertainties of climate change
- Adam Sobel 0
Adam Sobel is an atmospheric scientist at Columbia University in New York, and hosts a podcast called Deep Convection .
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Wildfires are getting fiercer faster than anyone predicted — just one factor fuelling an atmosphere of climate doom. Credit: Konstantinos Tsakalidis/Bloomberg/Getty
You have full access to this article via your institution.
How doomed are we? It’s a question I have been asked as a climate scientist many times over the years, sometimes with “doomed” replaced by less printable synonyms.
I struggle to answer it every time. It’s not a scientific question, because the terms are not well defined. What does it mean to be “doomed”? And who is “we”?
Maybe some people really mean it in the most extreme and literal sense: whether global warming is going to single-handedly wipe out the human species in the near future. In that case, it’s easy to talk them down. The evidence doesn’t support that prediction.
But I think that they mostly mean to ask a more subtle question. Something like, “as someone who understands the science on climate change better than most people, what is your emotional reaction to it? How scared are you?”
Fear is an emotion. No scientist, nor anyone else for that matter, can tell you the right amount of it to feel. If you knew that you were going to die in six months, how much fear should you feel? And what should you do in response? You wouldn’t go to a scientist for the answers to these questions.

Scientists under arrest: the researchers taking action over climate change
But having facts to inform our feelings can nonetheless be helpful. Scientists can at least provide some of those. We know that the planet is warming because of human-caused greenhouse-gas emissions. We can project the rate of warming with some confidence over at least the next few decades. At a broad level, we know what many of its effects will be. But when we look more closely, and ask about the societal consequences, things get blurrier.
The global increase in temperature is the simplest and most predictable dimension of climate change. It is also the one that scares me the most, partly because the direction of change is so certain and partly because heat is such a persistent and widespread hazard. For the large proportion of the world where it’s already hot during some or all of the year, just a couple of degrees of warming will cause great societal harm. In places with cooler climates, such as much of Europe, severe heatwaves can sometimes be even more deadly, because people there are less accustomed to heat 1 .
Sea-level rise is another area in which we can be certain about how things are changing, even if we are uncertain about how fast. Extreme rainfall events are becoming heavier and hydrological droughts are worsening owing to faster evaporation of water from hotter soils and plants. Wildfires are becoming more frequent and severe for similar reasons, although they are also affected by forest-management practices.
With some other hazards, however, even the direction of change is uncertain. Individual hurricanes are getting more dangerous, because of strengthening winds and rains, and worsening coastal flooding as sea levels rise. But we don’t know whether hurricanes will become more or less frequent — if the latter, the overall risk they pose might decrease 2 . We also don’t know whether meteorological droughts — lack of rain — will become more or less prevalent, or what changes we should expect with severe convective storms that produce tornadoes and hail 3 .
This scientific uncertainty itself is scary, because it means that some things might well get worse faster than we expect. Scientists always expected warming to exacerbate wildfires in the western United States, but I don’t think anyone predicted that it would happen as soon and as badly as it has.
Threat multiplier
Particularly disturbing is the possibility of ‘tipping points’ — large, possibly abrupt and irreversible changes with planetary-scale consequences 4 , such as the loss of large chunks of the Antarctic or Greenland ice sheets, the emission of large amounts of methane from melted permafrost or sea-floor sediments, or the shutdown of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation. The probabilities of such changes happening soon are all low, but they are hard to estimate with confidence.
Despite all the facts, and the uncertainties in the facts, climate change itself is not really what keeps me up at night. Maybe that’s because my professional training has disconnected me from my emotions on this score. But I think that there is a bigger reason. If we care about climate change because we care about human well-being, then climate change can be only one part of the story.
Humanity faces many existential risks. Wars are being fought today that are already catastrophic for those in the places involved. They could become catastrophic for many more if they expand, especially in a world with many nuclear-armed nations. Loss of biodiversity and ecosystems, for example in the Amazon rainforest, is an immediate, global-scale disaster. The rise of artificial intelligence creates species-level risks, even if our assessment of them is highly speculative. What I personally find the most disturbing is the democratic backsliding in my own country — the United States — as well as in others. This threatens society’s ability to responsibly handle crises, and also tends to create other crises, as authoritarian regimes consolidate and express their power in harmful ways.
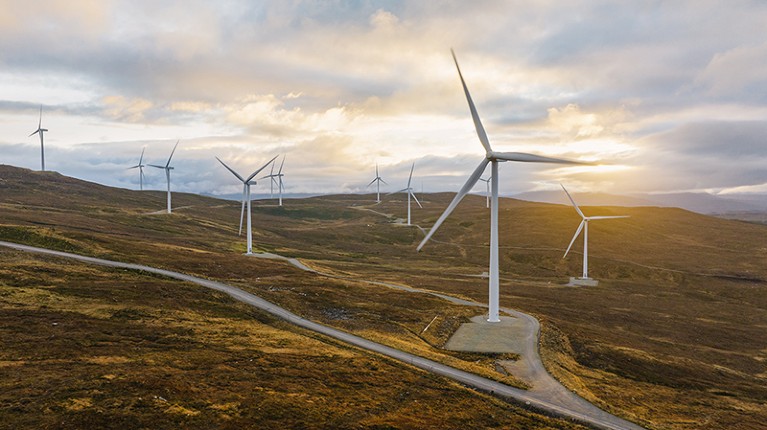

The transition towards cleaner energy sources provides glimmers of climate hope — but citizens must prevail on governments to speed it up. Credit: Getty
Climate is coupled to all these problems, in one way or another. But as scary as many direct consequences of climate change will be at 2 °C of warming or more, the greatest harm, at least in the short term, comes from its role as a ‘threat multiplier’. For example, high rates of migration from low-income countries to the United States and Europe has already been weaponized politically by far-right groups. If warming increases rates of migration, and democracies slide into authoritarianism, is that a result of climate change, or of already polarized and dysfunctional political systems? I don’t know — but I do fear this scenario deeply.
Climate change, in fact, might be one of the more certain components of our future. Social and political developments are even more difficult to predict. Can anyone really predict life on Earth in 2050, let alone 2100, well enough to suggest specific outcomes on a planetary scale, with or without climate change?
And again, even if we did know the planet’s future with perfect certainty, there still wouldn’t be a single right way to feel about it. How good or bad is the present moment, for that matter? The answer to that question depends on our position in the world. In other words: who is “we”?
Emotion and action
The writer Amitav Ghosh is one of the world’s most insightful thinkers on climate, and a friend of mine. He has argued that existential fears about climate change are actually Western fears about the end of colonial power, because in much of the rest of the world — especially for Indigenous people — “catastrophe has already happened”. For people in richer countries searching for the right way to feel about the climate crisis, it’s worth pondering this.
But maybe searching for the right emotion is not the best use of our time. Maybe a more pragmatic and constructive question than “how doomed are we?” is “what should we do about it?”

A giant fund for climate disasters will soon open. Who should be paid first?
Emotions and actions are connected, of course. ‘Doomers’ — climate communicators and activists who focus on the potential for catastrophic outcomes — are criticized for their negative messaging, which some say turns many people off and makes them less likely to act. I am sceptical of this. Greta Thunberg’s message has not been limited to expressions of positive emotion, and it’s hard to think of any climate activist who has been more effective. You could plausibly argue that the 2022 US Inflation Reduction Act, which is possibly the most important piece of federal climate legislation in the nation’s history, wouldn’t have happened without the political pressure applied by her and groups that she inspired.
But “what should we do?” is not a scientific question any more than “how doomed are we?” is. It depends on our values, and on the unscientific question of how to effect social change. Again, I don’t claim to have authoritative answers. I do think, however, that climate scientists such as myself should think a little harder about these questions than perhaps we have.
I have a few basic principles that guide my thinking. One is that democracy is crucial to human well-being, and that we should all support political candidates who think similarly, and oppose authoritarianism. In this regard, the United States has a particularly consequential election coming up this November.
Another principle is that, when it comes to the need to stop using fossil fuels, none of the uncertainties that I’ve catalogued really matter. We know that the negative consequences of warming far outweigh the positive, and that we need to cut emissions much faster than we are now 5 . Future scientific advances won’t change this calculus.
This means that collective, governmental action is essential to speed up the clean-energy transition. As citizens, we should all be politically engaged in ensuring that our countries move further and faster towards this goal. Personal actions that reduce emissions matter too: although insignificant to the global carbon budget on their own, they create a culture that motivates collective action. I am flying less, eating a mostly vegetarian diet and making other low-carbon choices, and I am talking about those choices. I am far from perfect, and I don’t seek to shame anyone else. I know that my steps are largely symbolic. But symbols matter. I take these steps to make climate awareness part of my daily life, and to show to myself and others that I take it seriously.
Treating the symptoms
Climate scientists might consider whether we have a greater responsibility than others, and whether we should seek to bring about positive outcomes through our work. Not all scientific knowledge is relevant to action. As an atmospheric dynamicist, I have come to think that I can have the most positive impact by working not on problems related to climate mitigation — stopping the burning of fossil fuels and other sources of carbon emissions — but on adaptation 6 .
Mitigation is still absolutely crucial. To make a medical analogy, it’s like treating the underlying cause of the disease. But we already know what needs to be done, and the reasons we aren’t doing it are political, not a consequence of scientific uncertainties.

How effective are climate protests at swaying policy — and what could make a difference?
Adaptation, however, is like treating the disease’s symptoms — the impacts of climate change. These are as diverse and specific as the places and ways in which climate affects society generally. Addressing those impacts requires equally diverse, specific and detailed scientific information. For me at least, this is where it’s possible to work towards answering both “what should we do?” and “how doomed are we?” at the same time.
When a national, state or local government writes a climate-adaptation plan, designs infrastructure or develops a policy that influences development in high-risk areas, it needs specific information about the relevant climate risks. Corporations, non-governmental organizations and community groups need the same, if they are taking any action that accounts for climate risk. Because climate change most sharply manifests in extreme events, information about such events’ probabilities and impacts are needed 7 .
Most climate information available from academics or governments doesn’t quite meet this need. Climate-risk-assessment tools and data sets developed to inform the insurance and financial industries are expensive and proprietary. As governments face politically difficult decisions regarding adaptation — for example, how much should taxpayers in low-risk areas pay to support protection of those in high-risk areas? — they will need relevant climate information that has been subject to open scrutiny and debate 8 .
Some uncertainties in climate science are so stubborn that we might not be able to reduce them much in the near term. Scientists such as myself can help by orienting our research towards characterizing the changing hazards, risks and uncertainties, with the granularity and pragmatism needed for decisions on adaptation, in the public domain where all the issues can be hashed out openly.
There are many other answers, of course. The important thing is to remain engaged. That means recognizing that doom is a state of mind, and that uncertainty about the planet’s future is now just part of the human condition. It means doing our best to keep both the climate crisis and the many other dimensions of human and planetary well-being in our view at the same time, both in their global and local dimensions. It means trying to live our values in ways consistent with those realities, as well as we can understand them. And it means recognizing that science has a crucial part to play — but that science can only take us so far.
Nature 627 , 483-485 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00790-6
Ballester, J. et al. Nature Med. 29 , 1857–1866 (2023).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Knutson, T. et al. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 101 , E303–E322 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Gensini, V. in Climate Change and Extreme Events (ed. Fares, A.) 39–56 (Elsevier, 2021).
Google Scholar
Armstrong McKay, D. I. et al. Science 377 , eabn7950 (2022).
Allen, M. R. et al. Special Report: Global Warming of 1.5°C (IPCC, 2018).
Sobel, A. H. Clim. Change 166 , 8 (2021).
President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology Extreme Weather Risk in a Changing Climate: Enhancing Prediction and Protecting Communities (The White House, 2023).
Condon, M. Ariz . St. L. J. 55 , 147–209 (2023).
Download references
Competing Interests
A.S. is on the external advisory board of Jupiter Intelligence, Inc., and receives sponsored research funding in his position at Columbia University from companies in the (re)insurance industry.
Related Articles

- Climate change
- Sustainability

How to achieve safe water access for all: work with local communities
Comment 22 MAR 24

Are we in the Anthropocene yet?
Editorial 20 MAR 24

It’s final: the Anthropocene is not an epoch, despite protest over vote
News 20 MAR 24
‘Global swimways’ on free-flowing rivers will protect key migratory fish species
Correspondence 19 MAR 24
Water shortages means greening southern European cities won’t be easy
Correspondence 12 MAR 24
Pay for trees with carbon credits to deliver urban green spaces for all
Meaningfulness in a scientific career is about more than tangible outputs

Four years on: the career costs for scientists battling long COVID
Career Feature 18 MAR 24
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
“Qiushi” Distinguished Scholar, Zhejiang University, including Professor and Physician
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Postdoctoral Associate
Our laboratory at the Washington University in St. Louis is seeking a postdoctoral experimental biologist to study urogenital diseases and cancer.
Saint Louis, Missouri
Washington University School of Medicine Department of Medicine
Recruitment of Global Talent at the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
The Institute of Zoology (IOZ), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is seeking global talents around the world.
Beijing, China
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
Postdoctoral Fellow-Proteomics/Mass Spectrometry
Location: Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA Department: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Tulane University School of Med...
New Orleans, Louisiana
Tulane University School of Medicine (SOM)
Open Faculty Position in Mathematical and Information Security
We are now seeking outstanding candidates in all areas of mathematics and information security.
Dongguan, Guangdong, China
GREAT BAY INSTITUTE FOR ADVANCED STUDY: Institute of Mathematical and Information Security
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Greenpeace UK
- Email signup
- Donate/Join
What are the solutions to climate change?
Climate change is already an urgent threat to millions of lives – but there are solutions. From changing how we get our energy to limiting deforestation, here are some of the key solutions to climate change.
Climate change is happening now, and it’s the most serious threat to life on our planet. Luckily, there are plenty of solutions to climate change and they are well-understood.
In 2015, world leaders signed a major treaty called the Paris agreement to put these solutions into practice.
Core to all climate change solutions is reducing greenhouse gas emissions , which must get to zero as soon as possible.
Because both forests and oceans play vitally important roles in regulating our climate, increasing the natural ability of forests and oceans to absorb carbon dioxide can also help stop global warming.
The main ways to stop climate change are to pressure government and business to:
- Keep fossil fuels in the ground . Fossil fuels include coal, oil and gas – and the more that are extracted and burned, the worse climate change will get. All countries need to move their economies away from fossil fuels as soon as possible.
- Invest in renewable energy . Changing our main energy sources to clean and renewable energy is the best way to stop using fossil fuels. These include technologies like solar, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal power.
- Switch to sustainable transport . Petrol and diesel vehicles, planes and ships use fossil fuels. Reducing car use, switching to electric vehicles and minimising plane travel will not only help stop climate change, it will reduce air pollution too.
- Help us keep our homes cosy . Homes shouldn’t be draughty and cold – it’s a waste of money, and miserable in the winter. The government can help households heat our homes in a green way – such as by insulating walls and roofs and switching away from oil or gas boilers to heat pumps .
- Improve farming and encourage vegan diets . One of the best ways for individuals to help stop climate change is by reducing their meat and dairy consumption, or by going fully vegan. Businesses and food retailers can improve farming practices and provide more plant-based products to help people make the shift.
- Restore nature to absorb more carbon . The natural world is very good at cleaning up our emissions, but we need to look after it. Planting trees in the right places or giving land back to nature through ‘rewilding’ schemes is a good place to start. This is because photosynthesising plants draw down carbon dioxide as they grow, locking it away in soils.
- Protect forests like the Amazon . Forests are crucial in the fight against climate change, and protecting them is an important climate solution. Cutting down forests on an industrial scale destroys giant trees which could be sucking up huge amounts of carbon. Yet companies destroy forests to make way for animal farming, soya or palm oil plantations. Governments can stop them by making better laws.
- Protect the oceans . Oceans also absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to keep our climate stable. But many are overfished , used for oil and gas drilling or threatened by deep sea mining. Protecting oceans and the life in them is ultimately a way to protect ourselves from climate change.
- Reduce how much people consume . Our transport, fashion, food and other lifestyle choices all have different impacts on the climate. This is often by design – fashion and technology companies, for example, will release far more products than are realistically needed. But while reducing consumption of these products might be hard, it’s most certainly worth it. Reducing overall consumption in more wealthy countries can help put less strain on the planet.
- Reduce plastic . Plastic is made from oil, and the process of extracting, refining and turning oil into plastic (or even polyester, for clothing) is surprisingly carbon-intense . It doesn’t break down quickly in nature so a lot of plastic is burned, which contributes to emissions. Demand for plastic is rising so quickly that creating and disposing of plastics will account for 17% of the global carbon budget by 2050 (this is the emissions count we need to stay within according to the Paris agreement ).
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed, and to feel that climate change is too big to solve. But we already have the answers, now it’s a question of making them happen. To work, all of these solutions need strong international cooperation between governments and businesses, including the most polluting sectors.
Individuals can also play a part by making better choices about where they get their energy, how they travel, and what food they eat. But the best way for anyone to help stop climate change is to take collective action. This means pressuring governments and corporations to change their policies and business practices.
Governments want to be re-elected. And businesses can’t survive without customers. Demanding action from them is a powerful way to make change happen.
Take action
For seven years, a government ban has blocked new onshore wind farms in England – the cheapest, cleanest energy going. With a global energy crisis and sky-high energy bills, now's the time for change. Add your name to tell Rishi Sunak to end the ban on new onshore wind projects in England.
Please fill out all required fields
Thanks for signing
If you can, please chip in to help make this campaign a success.
You don’t have to leave your email address or phone number, but if you do, we’ll use these to keep you updated on how you can get involved through petitions, campaigning, volunteering and donating. You can opt out at any time . We take the security of your data seriously. Your information is safe and secure with us – read our privacy policy
The fossil fuel industry is blocking climate change action
Major oil and gas companies including BP, Exxon and Shell have spent hundreds of millions of pounds trying to delay or stop government policies that would have helped tackle the climate crisis.
Despite the effects of climate change becoming more and more obvious, big polluting corporations – the ones responsible for the majority of carbon emissions – continue to carry on drilling for and burning fossil fuels.
Industries including banks, car and energy companies also make profits from fossil fuels. These industries are knowingly putting money over the future of our planet and the safety of its people.
What are world leaders doing to stop climate change?
With such a huge crisis facing the entire planet, the international response should be swift and decisive. Yet progress by world governments has been achingly slow. Many commitments to reduce carbon emissions have been set, but few are binding and targets are often missed.
In Paris in 2015, world leaders from 197 countries pledged to put people first and reduce their countries’ greenhouse gas emissions. The Paris agreement has the aim of limiting global warming to well below 2ºC and ideally to 1.5°C.
If governments act swiftly on the promises they made in the Paris climate agreement, and implement the solutions now, there’s still hope of avoiding the worst consequences of climate change .
World leaders and climate negotiators meet at annual COPs – which stands for Conference of the Parties (the countries that signed the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, or UNFCCC).
At COPs and other climate talks, nations take stock of their ability to meet their commitments to reduce emissions.
Recently, talks have focused on climate finance – money to help poorer countries adapt to climate change and reduce emissions. Rich countries have pledged $100 billion in annual funding to help developing countries reduce emissions and manage the impacts of climate change. This is yet to materialise, and much more money is needed.
As the impacts of climate change are increasing, important talks have also started on “loss and damage” funding. This is money needed by worst-impacted countries to deal with extreme weather and other climate change impacts.
Global climate change activism
Around the world, millions of us are taking steps to defend our climate. People of all ages and from all walks of life are desperately demanding solutions to the climate emergency.
Over the years, Greenpeace has challenged oil companies chasing new fossil fuels to extract and burn. We’ve also called out the governments for their failure to act fast enough on the climate emergency. Greenpeace activists are ordinary people taking extraordinary action, to push the solutions to climate change.
Indigenous Peoples are most severely affected by both the causes and effects of climate change . They are often on the front lines, facing down deforestation or kicking out fossil fuel industries polluting their water supplies.
Communities in the Pacific Islands are facing sea level rises and more extreme weather. But they are using their strength and resilience to demand world leaders take quicker climate action.
For many of these communities, the fight against climate change is a fight for life itself.
Even in the UK, climate change is impacting people more severely. As a country with the wealth and power to really tackle climate change, it’s never been more important to demand action.
Keep exploring

What can I do to stop climate change?
Individuals can make changes to their lives to reduce their personal carbon footprint. But it’s more important to persuade decision-makers in governments and businesses to drive emissions reductions on a much larger scale. This is the best way to stop climate change getting worse.

What is the UK doing about climate change?
All countries need to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming. So how’s the UK doing?

Renewable energy: a beginner's guide
Clean renewable energy is a vital tool for tackling climate change. Discover how it works and understand the advantages of wind, solar and water power.

Environmental justice, explained
The environmental crisis doesn't affect everyone equally. Often the worst impacts fall on those who are already most exploited by people in power. The fight for environmental justice is about addressing this unfairness, and making sure green solutions don't add to the problem.
What Are the Solutions to Climate Change?
Some solutions are big and will require billions in investment. Some are small and free. All are achievable.

Bundei Hidreka (left), a member of the Orissa Tribal Women's Barefoot Solar Engineers Association, holds up a solar lantern in Tinginaput, India.
Abbie Trayler-Smith/DFID, CC BY-NC-ND 4.0

- Share this page block
Thinking about climate change can be overwhelming. We’ve been aware of its causes for decades now, and all around us, we bear witness to its devastating effects on our communities and ecosystems.
But the good news is that we now know exactly what it will take to win the fight against climate change, and we’re making measurable, meaningful progress. Game-changing developments in clean energy, electric vehicle technology, and energy efficiency are emerging every single day. And countries—including Canada , China , India , and the United States —are coordinating and cooperating at levels never seen before in order to tackle the most pressing issue of our time.
The bottom line: If the causes and effects of our climate crisis are clearer than ever, so are the solutions.
Ending Our Reliance on Fossil Fuels
Greater energy efficiency, renewable energy, sustainable transportation, sustainable buildings, better forestry management and sustainable agriculture, conservation-based solutions, industrial solutions, technological solutions, our choices.
The single-most important thing that we can do to combat climate change is to drastically reduce our consumption of fossil fuels . The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas in our buildings, industrial processes, and transportation is responsible for the vast majority of emissions that are warming the planet —more than 75 percent . In addition to altering the climate , dirty energy also comes with unacceptable ecological and human health impacts.
We must replace coal, oil, and gas with renewable and efficient energy sources. Thankfully, with each passing year, clean energy is making gains as technology improves and production costs go down. But in order to meet the goal of reducing global carbon emissions by at least 45 percent below 2010 levels before 2030—which scientists tell us we must do if we’re to avoid the worst, deadliest impacts of climate change—we must act faster.
There are promising signs. Wind and solar continue to account for ever-larger shares of electricity generation. In 2021, wind and solar generated a record 10 percent of electricity worldwide. And modeling by NRDC has found that wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear could account for as much as 80 percent of U.S. electricity by the end of this decade . (We can also fully realize our clean energy potential if we invest in repairing our aging grid infrastructure and installing new transmission lines.) While this transformation is taking place, automakers—as well as governments—are preparing for a future when the majority of vehicles on the road will produce zero emissions.

Technicians from Solaris Energy carry out the first-annual servicing and cleaning on a heat pump that was installed into a house originally built in the 1930s, in Folkestone, United Kingdom.
Andrew Aitchison / In pictures via Getty Images
Energy efficiency has been referred to as “the first fuel”; after all, the more energy efficient our systems are, the less actual fuel we have to consume, whether rooftop solar energy or gas power. Considered this way, efficiency is our largest energy resource. As the technology harnessing it has advanced over the past 40 years, efficiency has contributed more to the United States’s energy needs than oil, coal, gas, or nuclear power.
What’s more, energy efficiency strategies can be applied across multiple sectors: in our power plants, electrical grids, factories, vehicles, buildings, home appliances, and more. Some of these climate-friendly strategies can be enormously complex, such as helping utility companies adopt performance-based regulation systems , in which they no longer make more money simply by selling more energy but rather by improving the services they provide. Other strategies are extraordinarily simple. For example, weatherproofing buildings, installing cool roofs , replacing boilers and air conditioners with super-efficient heat pumps , and yes, switching out light bulbs from incandescent to LED can all make a big dent in our energy consumption.
Transitioning from fossil fuels to clean energy is the key to winning the fight against climate change. Here are the most common sources of renewable energy —and one source of decidedly nonrenewable energy that often gets included (falsely) in the list.

Engineer Steve Marchi and his team perform a final review of rooftop solar panels as part of the solar expansion project at the Wayne National Forest Welcome Center, in Ohio.
Alex Snyder/Wayne National Forest
Solar energy
Solar energy is produced when light from the sun is absorbed by photovoltaic cells and turned directly into electricity. The solar panels that you may have seen on rooftops or at ground level are made up of many of these cells working together. By 2030, at least one in seven U.S. homes is projected to have rooftop solar panels, which emit no greenhouse gases or other pollutants, and which generate electricity year-round ( in hot or cold weather ) so long as the sun is shining. Solar energy currently accounts for just under 3 percent of the electricity generated in the United States—enough to power 18 million homes —but is growing at a faster rate than any other source. By 2035, it could account for as much as 40 percent of electricity generation. From 2020 through 2026, solar will account for more than half of new electricity generation worldwide.
What to do when the sun doesn’t shine, you might ask. Alongside the boom in solar has been a surge in companion battery storage: More than 93 percent of U.S. battery capacity added in 2021 was paired with solar power plants. Battery storage is key to the clean energy revolution—and adapting to a warming world. Not only are batteries important at night when the sun isn’t out, but on hot days when homes draw a lot of electricity to power air conditioners, battery storage can help manage the energy demand and control the threat of power failures.
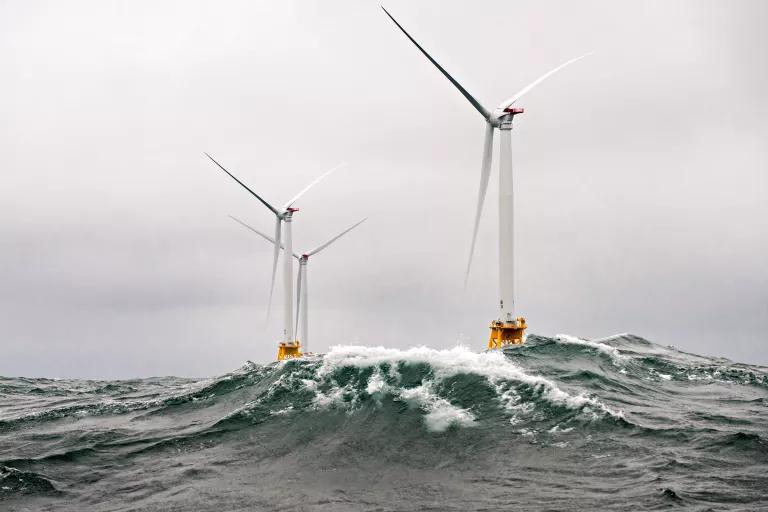

Turbines on Block Island Wind Farm, located 3.8 miles from Block Island, Rhode Island, in the Atlantic Ocean
Dennis Schroeder/NREL, 40481
Wind energy
Unlike solar panels, which convert the sun’s energy directly into electricity, wind turbines produce electricity more conventionally: wind turns the blades of a turbine, which spin a generator. Currently, wind accounts for just above 9 percent of U.S. electricity generation, but it, like solar, is growing fast as more states and utilities come to recognize its ability to produce 100 percent clean energy at a remarkably low cost. Unsurprisingly, states with plenty of wide-open space—including Kansas , Oklahoma , and Texas —have huge capacity when it comes to wind power, but many analysts believe that some of the greatest potential for wind energy exists just off our coasts. Offshore wind even tends to ramp up in the evenings when home electricity use jumps, and it can produce energy during the rainy and cloudy times when solar energy is less available. Smart planning and protective measures , meanwhile, can ensure we harness the massive promise of offshore wind while limiting or eliminating potential impacts on wildlife.
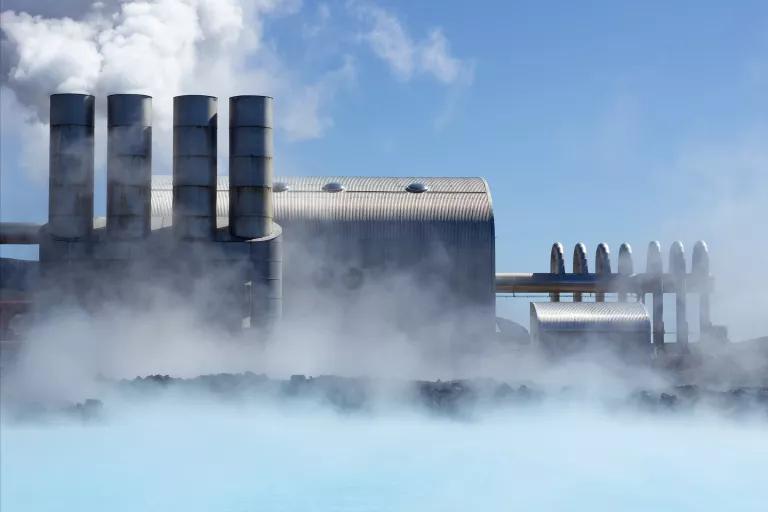

Svartsengi geothermal power plant in Iceland
Daniel Snaer Ragnarsson/iStock
Geothermal and hydroelectric energy
Along with sunlight and wind, water—under certain conditions—can also be a source of renewable energy. For instance, geothermal energy works by drilling deep underground and pumping extremely hot water up to the earth’s surface, where it is then converted to steam that, once pressurized, spins a generator to create electricity. Hydroelectric energy uses gravity to “pull” water downward through a pipe at high speeds and pressures; the force of this moving water is used to spin a generator’s rotor.
Humans have been harnessing heat energy from below the earth’s surface for eons—just think of the hot springs that provided warmth for the people of ancient Rome. Today’s geothermal plants are considered clean and renewable so long as the water and steam they bring up to the surface is redeposited underground after use. Proper siting of geothermal projects is also important, as recent science has linked some innovative approaches to geothermal to an increased risk of earthquakes .
Hydroelectric plants, when small-scale and carefully managed, represent a safe and renewable source of energy. Larger plants known as mega-dams, however, are highly problematic . Their massive footprint can disrupt the rivers on which people and wildlife depend .
Biomass energy
With very few exceptions, generating electricity through the burning of organic material like wood (sourced largely from pine and hardwood forests in the United States), agricultural products, or animal waste—collectively referred to as biomass —does little to reduce carbon emissions, and in fact, does far more environmental harm than good. Unfortunately, despite numerous studies that have revealed the true toll of this form of bioenergy , some countries continue to buy the biomass industry’s false narrative and subsidize these projects. Attitudes are changing but, given the recent wood pellet boom, there is a lot more work to be done.

A new electric bus on King Street in Honolulu, on June 16, 2021
Marco Garcia for NRDC
Transportation is a top source of greenhouse gases (GHG), so eliminating pollution from the billions of vehicles driving across the planet is essential to achieving net-zero global emissions by 2050, a goal laid out in the 2015 Paris climate agreement .
In 2021, electric vehicles (EVs) accounted for less than 8 percent of vehicle sales globally; by 2035 , however, it’s estimated that they’ll account for more than half of all new sales. Governments around the world aren’t just anticipating an all-electric future; they’re bringing it into fruition by setting goals and binding requirements to phase out the sale of gas-powered internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. That year, 2035, is expected to mark a turning point in the adoption of EVs and in the fight against climate change as countries around the world—as well as numerous automakers—have announced goals to phase out gas-powered cars and light trucks . This shift will also benefit our grid: EVs are like a “ battery on wheels ” and have the potential to supply electricity back to the network when demand peaks, helping to prevent blackouts.
It’s also critical that we consider all of the different ways we get around and build sustainability into each of them. By increasing access to public transportation—such as buses, ride-sharing services, subways, and streetcars—as well as embracing congestion pricing , we can cut down on car trips and keep millions of tons of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere every year. And by encouraging zero-emission forms of transportation, such as walking and biking, we can reduce emissions even more. Boosting these alternate forms of transportation will require more than just talk. They require funding , planning, and the building out of supportive infrastructure by leaders across the local, state, and national levels.
To address the full set of impacts of the transportation sector, we need holistic and community-led solutions around things like land-use policies and the way we move consumer goods. Communities closest to ports , truck corridors, rail yards, and warehouses are exposed to toxic diesel emissions and face a high risk of developing acute and chronic public health diseases. Like all climate solutions, long-lasting change in the transportation sector requires building the power of historically marginalized communities.

An Association for Energy Affordability (AEA) worker installs a new energy-efficient window at an apartment in the South Bronx, New York City.
Natalie Keyssar for NRDC
The energy used in our buildings—to keep the lights on and appliances running; to warm them and cool them; to cook and to heat water—makes them the single-largest source of carbon pollution in most cities across the United States. Making buildings more energy efficient, by upgrading windows and adding insulation to attics and walls, for example, will bring these numbers down. That’s why it’s all the more important that we raise public awareness of cost- and carbon-saving changes that individuals can make in their homes and workplaces, and make it easier for people to purchase and install energy-efficient technology, such as heat pumps (which can both heat and cool spaces) and certified appliances through programs like Energy Star in the United States or EnerGuide in Canada.
Beyond the measures that can be taken by individuals, we need to see a dedication from private businesses and governments to further building decarbonization , which simply means making buildings more efficient and replacing fossil fuel–burning systems and appliances with clean-powered ones. Policy tools can help get us there, including city and state mandates that all newly constructed homes, offices, and other buildings be outfitted with efficient all-electric systems for heating, cooling, and hot water; requirements that municipalities and states meet the latest and most stringent energy conservation standards when adopting or updating their building codes would also be impactful. Indeed, many places around the world are implementing building performance standards , which require existing buildings to reduce their energy use or carbon emissions over time. Most important, if these changes are going to reach the scale needed, we must invest in the affordable housing sector so that efficient and decarbonized homes are accessible to homeowners and renters of all incomes .
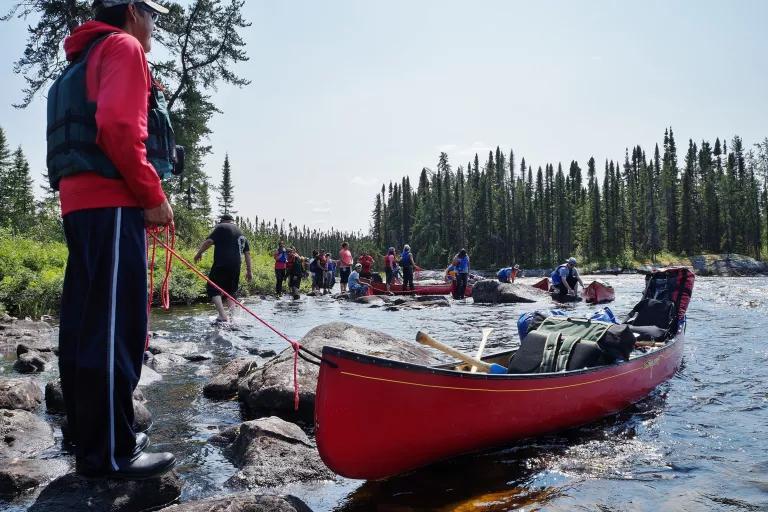

Nicolas Mainville joins a canoe trip with youth from the Cree First Nation of Waswanipi on a river in Waswanipi Quebec, Canada, which is part of the boreal forest.
Nicolas Mainville/Greenpeace
Some of our strongest allies in the fight against climate change are the trees, plants, and soil that store massive amounts of carbon at ground level or underground. Without the aid of these carbon sinks , life on earth would be impossible, as atmospheric temperatures would rise to levels more like those found on Venus .
But whenever we clearcut forests for timber or rip out wetlands for development, we release that climate-warming carbon into the air. Similarly, the widespread overuse of nitrogen-based fertilizers (a fossil fuel product) on cropland and generations of industrial-scale livestock farming practices have led to the release of unprecedented amounts of nitrous oxide and methane, powerful greenhouse gases, into our atmosphere.
We can’t plant new trees fast enough to replace the ones we clearcut in carbon-storing forests like the Canadian boreal or the Amazon rainforest —nor can rows of spindly young pines serve the same function as old-growth trees. We need a combination of responsible forestry policies, international pressure, and changes in consumer behavior to put an end to deforestation practices that not only accelerate climate change but also destroy wildlife habitat and threaten the health and culture of Indigenous communities that live sustainably in these verdant spaces. At the same time, we need to treat our managed landscapes with as much care as we treat wild ones. For instance, adopting practices associated with organic and regenerative agriculture —cover crops, pesticide use reduction, rotational grazing, and compost instead of synthetic fertilizers—will help nurture the soil, yield healthier foods, and pay a climate dividend too.

A school of fish swimming through a mangrove forest in the Caribbean Sea, off Belize
Intact ecosystems suck up and store vast amounts of carbon: Coastal ecosystems like wetlands and mangroves accumulate and store carbon in their roots; our forests soak up about a third of annual fossil fuel emissions; and freshwater wetlands hold between 20 and 30 percent of all the carbon found in the world’s soil. It’s clear we’re not going to be able to address climate change if we don’t preserve nature.
This is one reason why, along with preserving biodiversity, climate experts are calling on global leaders to fully protect and restore at least 30 percent of land, inland waters, and oceans by 2030 , a strategy endorsed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. To help us reach that goal, we must limit industrial impacts on our public lands and waters, continue to protect natural landscapes, support the creation of marine protected areas, uphold bedrock environmental laws, and follow the lead of Indigenous Peoples, many of whom have been faithfully and sustainably stewarding lands and waters for millennia .

Emissions rise from the Edgar Thomson Steel Works, a steel mill in the Braddock and North Braddock communities near Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Getty Images
Heavy industry—the factories and facilities that produce our goods—is responsible for a quarter of GHG emissions in the United States and 40 percent globally. Most industrial emissions come from making a small set of carbon-intensive products: basic chemicals, iron and steel, cement, aluminum, glass, and paper. (Industrial plants are also often major sources of air and water pollutants that directly affect human health.)
Complicating matters is the fact that many industrial plants will stay in operation for decades, so emissions goals for 2050 are really just one investment cycle away. Given these long horizons for building and retrofitting industrial sites, starting investments and plans now is critical. What would successfully decarbonized industrial processes look like? They should sharply reduce heavy industry’s climate emissions , as well as local pollution. They should be scalable and widely available in the next decade, especially so that less developed nations can adopt these cleaner processes and grow without increasing emissions. And they should bolster manufacturing in a way that creates good jobs.
Technology alone won’t save us from climate change (especially not some of these risky geoengineering proposals ). But at the same time, we won’t be able to solve the climate crisis without researching and developing things like longer-lasting EV batteries , nonpolluting hydrogen-based solutions , and reliable, safe, and equitable methods for capturing and sequestering carbon . Because, while these tools hold promise, we have to make sure we don’t repeat the mistakes of the past. For instance, we can take actions to reduce local harms from mining lithium (a critical component of electric vehicle batteries), improve recycling opportunities for solar cells, and not use carbon capture as an excuse to pollute. To accelerate research and development, funding is the critical third leg of the stool: Governments must make investing in clean energy technologies a priority and spur innovation through grants, subsidies, tax incentives, and other rewards.

A protester rings a bell in front of P&G’s headquarters in Cincinnati; the company’s toilet paper brand, Charmin, uses wood pulp from virgin trees in Canada's boreal forest.
Finally, it should go without saying that we, as individuals, are key to solving the climate crisis—not just by continuing to lobby our legislators and speak up in our communities but also by taking climate actions in our daily lives . By switching off fossil fuels in our homes and being more mindful of the climate footprint of the food we eat, our shopping habits, how we get around, our use of plastics and fossil fuels, and what businesses we choose to support (or not to support), we can move the needle.
But it’s when we act collectively that real change happens—and we can do even more than cut down on carbon pollution. Communities banding together have fought back fracking , pipelines , and oil drilling in people’s backyards . These local wins aren’t just good news for our global climate but they also protect the right to clean air and clean water for everyone. After all, climate change may be a global crisis but climate action starts in your own hometown .
We have a responsibility to consider the implications of our choices—and to make sure that these choices are actually helping to reduce the burdens of climate change, not merely shifting them somewhere else. It’s important to remember that the impacts of climate change —which intersect with and intensify so many other environmental, economic, and social issues—fall disproportionately on certain communities, namely low-income communities and communities of color. That’s why our leaders have a responsibility to prioritize the needs of these communities when crafting climate policies. If those on the frontlines aren’t a part of conversations around climate solutions, or do not feel the benefits of things like cleaner air and better job opportunities, then we are not addressing the roots of the climate crisis.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
We need climate action to be a top priority in Washington!
Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
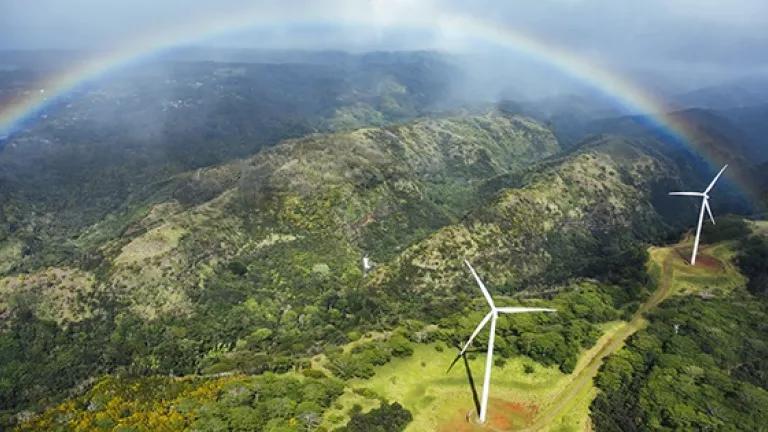

Urge President Biden and Congress to make equitable climate action a top priority in 2024
Related stories.

How to Find Relief During Summer Heat Waves in the City

What Are the Causes of Climate Change?

How to Ditch the Biggest Fossil Fuel Offenders in Your Life
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Better predictive models could reduce clothing returns
Economist Claudia Sahm has a better way to handle recessions
For business leaders: A digital tool for visualizing climate actions
Credit: Stephen Sauer
Ideas Made to Matter
Climate Change
The 5 greatest challenges to fighting climate change
Kara Baskin
Dec 27, 2019
Climate change: Most of the world agrees it’s a danger, but how do we conquer it? What’s holding us back? Christopher Knittel, professor of applied economics at the MIT Sloan School of Management, laid out five of the biggest challenges in a recent interview.
CO2 is a global pollutant that can’t be locally contained
“The first key feature of climate change that puts it at odds with past environmental issues is that it’s a global pollutant, rather than a local pollutant. [Whether] I release a ton of CO2 in Cambridge, Massachusetts, or in London, it does the same damage to the globe,” Knittel said. “Contrast that with local pollutants, where if I release a ton of sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxide in Cambridge, the majority of the damage stays near Cambridge.”
Thus, CO2 is far harder to manage and regulate.
For now, climate change is still hypothetical
The damage caused by most climate change pollutants will happen in the future. Which means most of us won’t truly be affected by climate change — it’s a hypothetical scenario conveyed in charts and graphs. While we’d like politicians and voters to be moved by altruism, this isn’t always the case. In general, policymakers have little incentive to act.
“People [who stand to be] most harmed by climate change aren’t even born yet. Going back to the policymaker’s perspective, she has much less of an incentive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions because those reductions are going to benefit voters in the future and not her current voters,” Knittel said.
There’s no direct link to a smoking gun
Despite the global threat from climate-altering pollutants, it’s hard for scientists to link them to a specific environmental disaster, Knittel said. Without a definitive culprit, it’s easier for skeptics to ignore or explain away climate change effects.
Developing countries contribute to a large share of pollution
Simply put, this isn’t their top priority.
“We’re asking very poor countries that are worried about where their next meal is coming from, or whether they can send their kids to school, to incur costs to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to benefit the world. And that’s a tough ask for a policymaker inside of a developing country,” he said.
Modern living is part of the problem
It’s a tough pill to swallow, but modern conveniences like electricity, transportation, and air conditioning contribute to climate change, and remedies potentially involve significant sacrifice and lifestyle change.
“Although we’ve seen great strides in reductions in solar costs and batteries for electric vehicles, these are still expensive alternatives. There is no free lunch when it comes to overcoming climate change,” Knittel warned.
Writing in the Los Angeles Times recently, Knittel said, “If an evil genius had set out to design the perfect environmental crisis … those five factors would have made climate change a brilliant choice. But we didn’t need an evil genius. We stumbled into it on our own.”
Read next — Climate experts: Clean tech is here, now we need people power
Related Articles

About . Click to expand section.
- Our History
- Team & Board
- Transparency and Accountability
What We Do . Click to expand section.
- Cycle of Poverty
- Climate & Environment
- Emergencies & Refugees
- Health & Nutrition
- Livelihoods
- Gender Equality
- Where We Work
Take Action . Click to expand section.
- Attend an Event
- Partner With Us
- Fundraise for Concern
- Work With Us
- Leadership Giving
- Humanitarian Training
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Donate . Click to expand section.
- Give Monthly
- Donate in Honor or Memory
- Leave a Legacy
- DAFs, IRAs, Trusts, & Stocks
- Employee Giving
Ten solutions to climate change that will actually make a difference
Jun 20, 2022

At this point we need solutions bigger than any one person. But that doesn’t tell the whole story.
There are a lot of differing opinions on whether it's too late to climate change — and, if it's not the best way of going about it. Some say recycling is useless and that individual action means nothing against the larger policy reforms that need to happen. This is, in part, true — although you should absolutely still be recycling. But it doesn’t tell the whole story, and it doesn’t help those who are currently on the frontlines of the climate crisis. Here, we break down 10 solutions to climate change that will actually make a difference — and how you can help make them all a reality.
Stand with the people most affected by climate change
1. shift to renewable energy sources in all key sectors.
The United Nations identified a six-sector solution to climate change, focusing on actions that can be taken by the energy, industry, agriculture, transportation, nature-based solutions, and urban planning. If all of these actions are completed, the UN Environment Programme estimates we could reduce global carbon emissions by 29 to 32 gigatonnes, thereby limiting the global temperature rise to 1.5º C.
One key element of this plan is shifting to renewable energy sources, both at home and at work. “We have the necessary technology to make this reduction by shifting to renewable energy and using less energy,” the UNEP writes of our personal energy consumption (generally, fossil fuels power our homes, keeping the lights on, our rooms warm, and Netflix streaming). But the energy usage of the industrial sector also plays a key role: Addressing issues like methane leaks and switching at large scale to passive or renewable energy-based heating and cooling systems could reduce industrial carbon emissions by 7.3 gigatonnes every year.
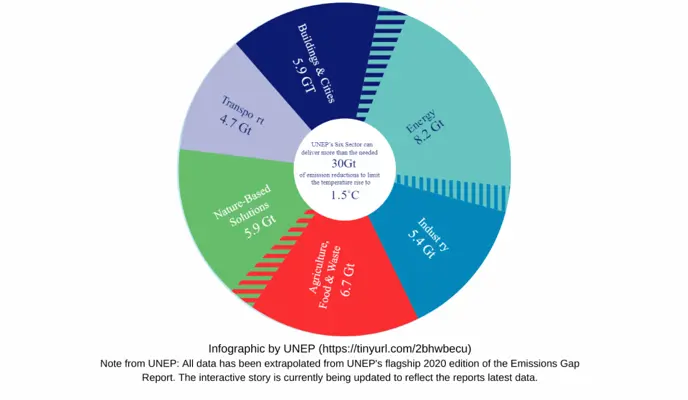
2. Reduce food loss and waste and shift to more sustainable diets
There are a few different ways that climate change and hunger go hand-in-hand. Whether it’s kale or Kobe beef, producing food accounts for some measure of greenhouse gasses. In 2021, the Food and Agriculture Organization estimated we consumed more meat than ever before . By 2050 this will, by some estimates, increase greenhouse gas emissions from food production by 60%. Likewise, many farmers use nitrous-based fertilizers to grow more crops, more quickly to meet demand.
It’s important to reduce food waste at every step of the food system . For us as consumers, we can commit to eating what we buy and composting what we don’t get to in time. We can also switch our focus to plant-based and other sustainable diets, supporting farms that use organic fertilizers and making beef and other meat products the exception rather than the rule at the dinner table.
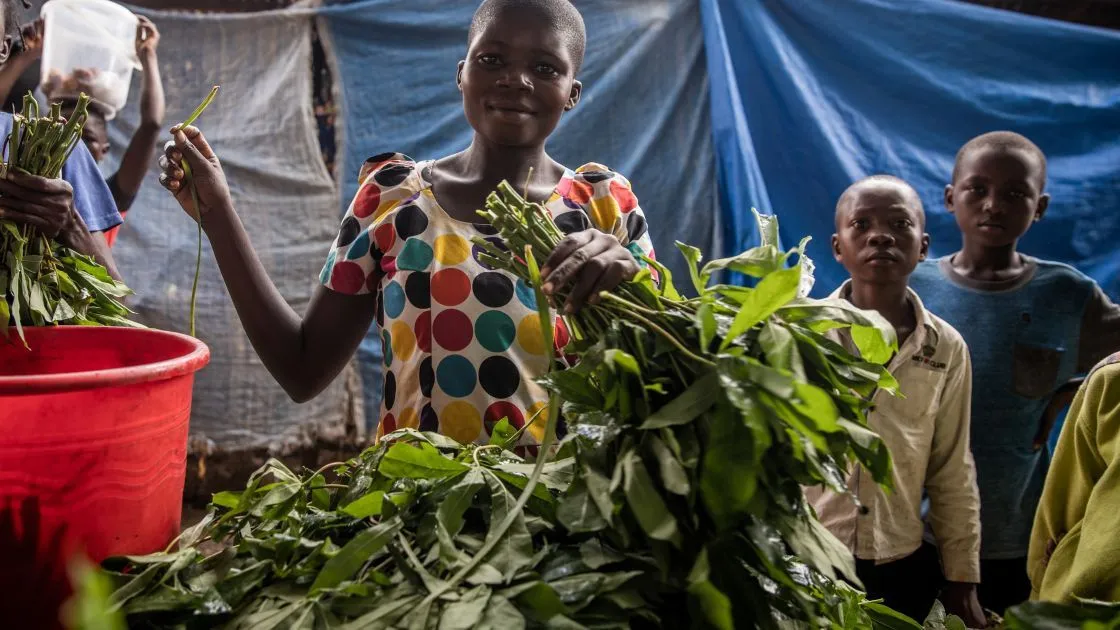

3. Halt deforestation and commit to rebuilding damaged ecosystems
The rapid deforestation of the Earth, especially over the last 60 years, has contributed to climate change, creating “heat islands” out of land that would normally be protected by trees and other flora from overheating. Simply put, this has to stop. There are actions each of us can take as individuals to help halt this—going paperless and buying recycled paper products, planting trees or supporting organizations that do this (like Concern ), and recycling.
But change has to happen at a larger scale here. Illegal logging happens both in the United States and abroad. Last year, world leaders committed to halting this and other harmful practices by 2030 as part of COP26. You can help by holding your own elected leaders to account.
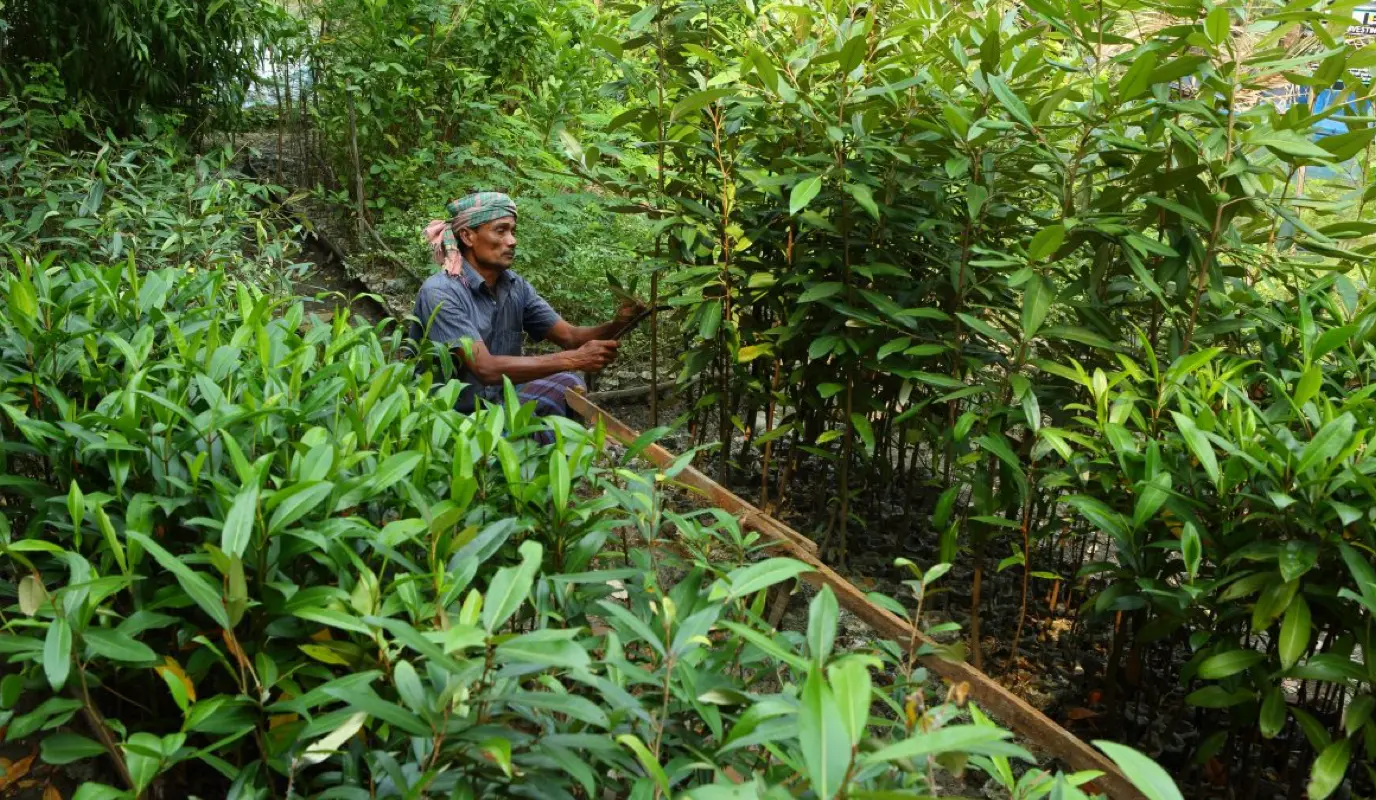

4. Embrace electric vehicles, public transport, and other non-motorized options for getting around
The carbon savings on junking your current car in favor of an electric model are basically nullified if you aren’t seriously in the market for a new vehicle. However, mass adoption of electric vehicles and public transport — along with walking, biking, skating, and scooting — is key to cutting the greenhouse gas emissions from fuel-based motor vehicles.
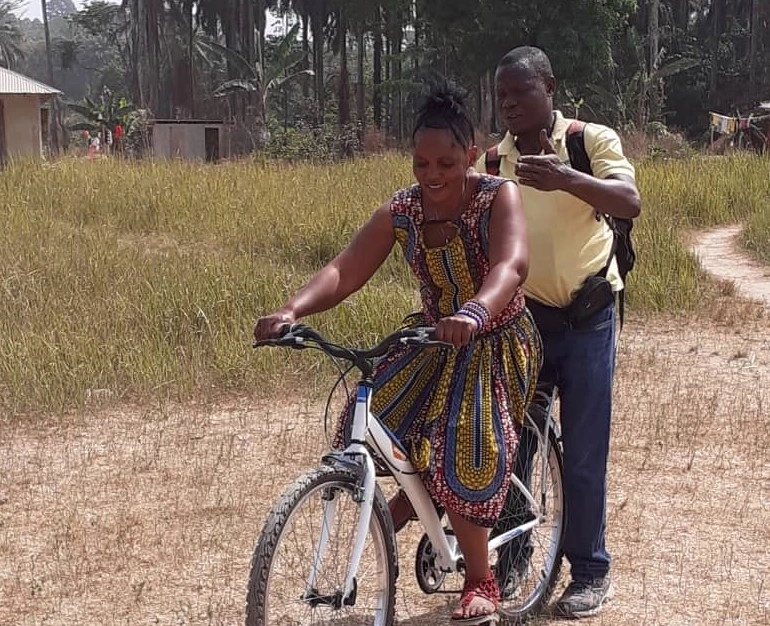

This is another issue you can raise with elected officials. Earlier this year, for example, you may remember hearing that President Biden had been encouraging the US Postal System to adopt electric vans as part of its new fleet. This didn’t come to pass , but it’s changes like these — changes beyond any one person’s transportation method — that need to happen. You can call on your representatives to support these switchovers for delivery vehicles, cab and taxi fleets, ambulances, and other auto-centric services. Or, if your city or town lacks decent public transportation or enough bike lanes or sidewalks to make those alternatives to driving, lobby for those.
5. Subsidize low-carbon alternatives for urban planning
In tandem with low-carbon alternatives for public transportation, governments need to commit to similar measures with our growing cities. New buildings mean a new opportunity to reward green design methods that help to decrease the strain on urban resources, whether they’re apartments or entertainment venues. (Fun fact: The Stavros Niarchos Cultural Center in Athens runs almost entirely off of solar panels during the bright and sunny summer months. ) In cities like New York, we’ve seen the toll that excessive power use can take through rolling blackouts and brown-outs, especially in the summer months. Changes to public infrastructure that reduce our reliance on the power grid will help to keep the system from becoming untenably overloaded.
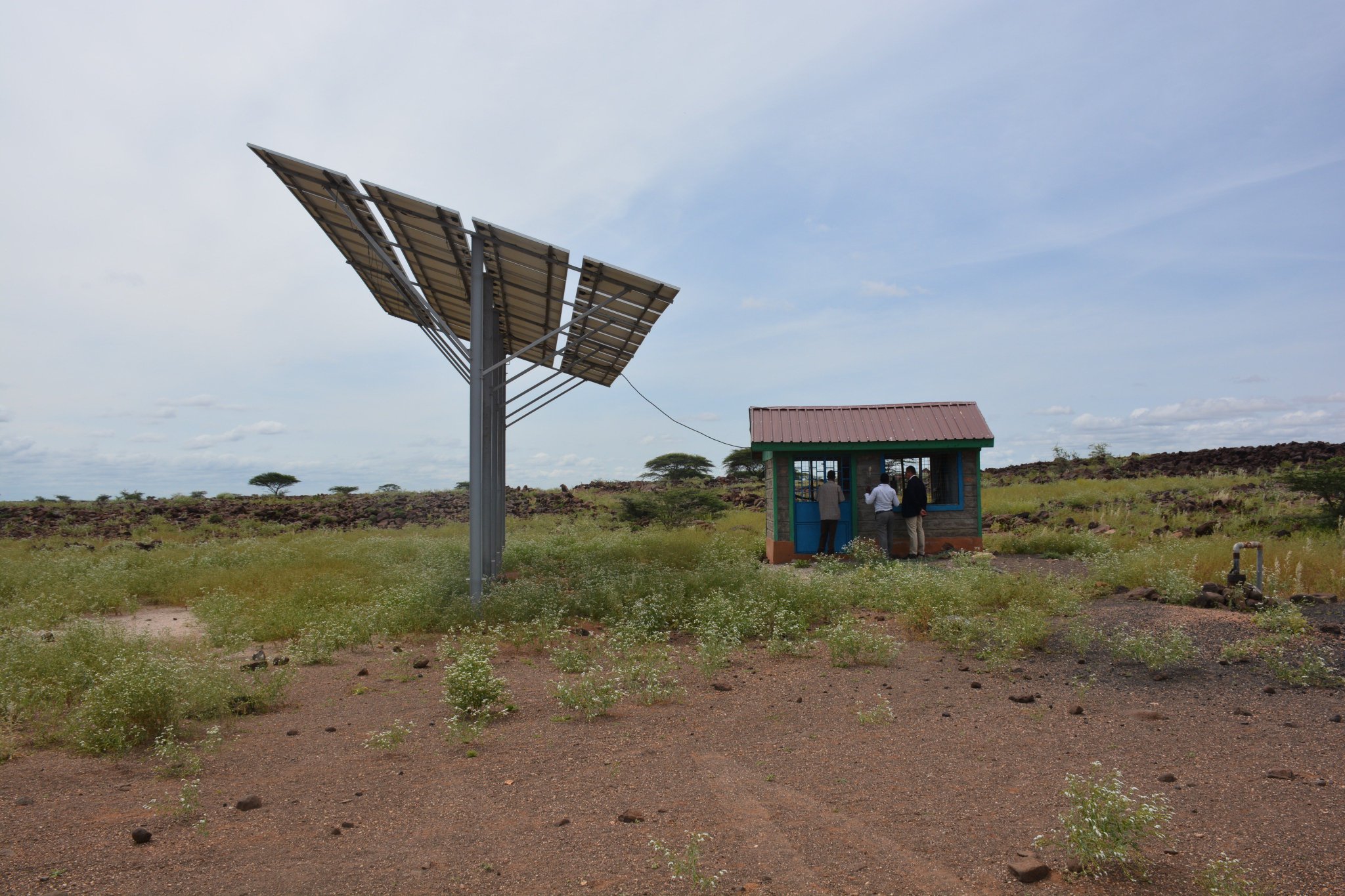

6. Strengthen resilience and climate adaptation methods in MAPA communities
So far, we’ve looked at solutions to climate change that can take place within our own homes and communities. However, these only go so far to mitigate the damage that the climate crisis has already inflicted on a large portion of the world. The most affected people and areas (MAPAs) are largely in the Global South. Many are located in low-income countries without the resources or infrastructure to respond and adapt to climate disasters, even as they become more frequent and destructive.
Countries like the United States and organizations responding to the climate crisis must support MAPA communities, particularly the most vulnerable, in developing and carrying out strategies specific to context and designed to bolster resilience where it’s needed most. Often these communities know what needs to be done to mitigate the effects of climate change, and they simply need to be supported with access to additional research and meteorological data, new technologies, and funding.

What we talk about when we talk about resilience
The word “resilience” has taken on new meanings and contexts in recent years, but at Concern it still has a specific definition relating to our emergency and climate response. Here’s what we mean when we use it.
7. Address poverty and other inequalities that increase vulnerability
The tem MAPA can also apply to individuals within a community. Women, disabled people, children, the elderly, people living in poverty, indigenous peoples, and LGBTQIA+ people are among those who are most likely to be hit harder by climate change because of preexisting societal marginalization. This is why it’s critical that they also have a seat at the decision-making table when it comes to solutions to climate change within their own communities. Ending poverty and the other systemic inequalities that give some people greater access to resources than others will help to offset some of the greatest threats posed by the climate crisis.

8. Invest in disaster risk reduction (DRR)
Disaster Risk Reduction (otherwise known as DRR) protects the lives and livelihoods of communities and individuals who are most vulnerable to disasters or emergencies. Whether the crisis is caused by nature or humans (or a combination of both), DRR limits its negative impact on those who stand to lose the most.
We can’t undo much of climate change’s impact so far, but we can help the communities who are hit hardest by these impacts to prepare for and respond to these emergencies once they strike.
9. Commit to fair financing and climate justice
Of course, DRR strategies and other resilience, adaptation, and mitigation practices cost money. Money that the countries most affected by climate change often lack. As part of a global commitment to climate justice , countries with the highest carbon footprints should be making restitution to those countries with lower footprints, countries that tend to be more vulnerable to global warming.
Countries like the United States must increase investments in disaster prevention and DRR strategies, such as early warning and response systems, forecast-based financing mechanisms, and adapted infrastructure. What’s more, these funds need to be made rapidly dispersible and flexible so that when emergency strikes, they can be accessed more quickly. Additional investment to prevent conflicts over the use of natural resources will also help countries facing both fragile political systems and a high risk for climate-related disasters.

Project Profile
Responding to Pakistan's Internally Displaced (RAPID)
RAPID is a funding program that allows Concern to quickly and efficiently deliver aid to people displaced by conflict or natural disaster.
10. Guarantee these changes in the long-term via policy reform
Few of the solutions listed above are not sustainable without policy reform. You can help by encouraging your elected officials to consider the above points, and to support bills that incorporate one or more of these solutions to climate change, many of which are currently being written and shared at the local and national levels.
Smart climate policy will prioritize people over corporations, consider the framework of climate justice — including land and water rights of indigenous peoples and rural communities, address the intersectional effects of climate change on hunger, poverty, and gender equality, and enforce regulatory frameworks and standards that commit people and institutions to honoring these new standards. Bold and aggressive action must be taken if we’re to reach the goal of not exceeding 1.5º C and mitigating the current effects of climate change by 2030. But it’s not a lost cause yet. It’s on all of us to now support those actions that are needed most.
Support Concern's climate response
Solutions to Climate Change in Action

Ten countries with water stress and scarcity — and how we're helping
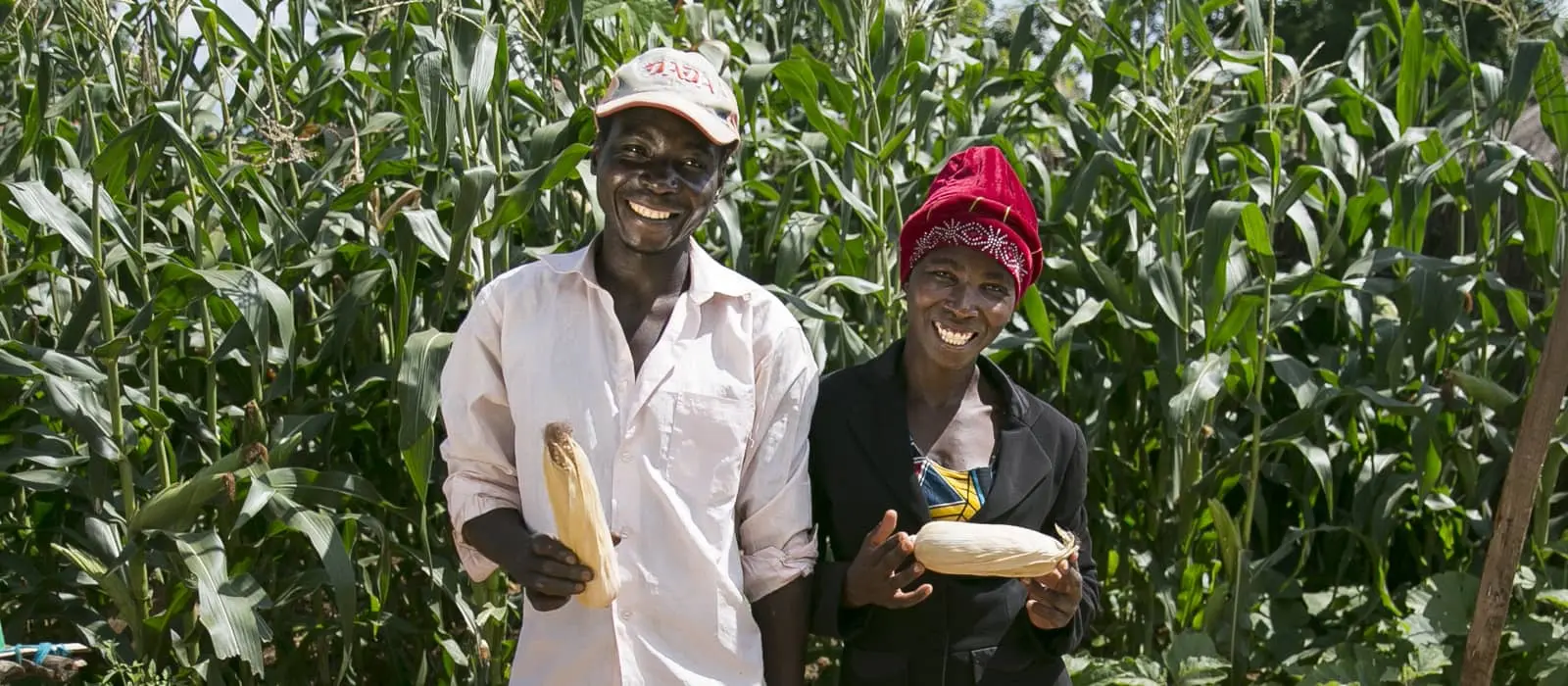

Climate Smart Agriculture: Back to the basics to fight climate change and hunger

Ten of the countries most affected by climate change
Sign up for our newsletter.
Get emails with stories from around the world.
You can change your preferences at any time. By subscribing, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Climate Change: Check Samples in 100, 250 Words
- Updated on
- Sep 21, 2023

Writing an essay on climate change is crucial to raise awareness and advocate for action. The world is facing environmental challenges, so in a situation like this such essay topics can serve as s platform to discuss the causes, effects, and solutions to this pressing issue. They offer an opportunity to engage readers in understanding the urgency of mitigating climate change for the sake of our planet’s future.
Must Read: Essay On Environment
This Blog Includes:
What is climate change, what are the causes of climate change, what are the effects of climate change, how to fight climate change, essay on climate change in 100 words, climate change sample essay 250 words.
Climate change is the significant variation of average weather conditions becoming, for example, warmer, wetter, or drier—over several decades or longer. It may be natural or anthropogenic. However, in recent times, it’s been in the top headlines due to escalations caused by human interference.
Obama at the First Session of COP21 rightly quoted “We are the first generation to feel the impact of climate change, and the last generation that can do something about it.”.Identifying the causes of climate change is the first step to take in our fight against climate change. Below stated are some of the causes of climate change:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Mainly from burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy and transportation.
- Deforestation: The cutting down of trees reduces the planet’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Industrial Processes: Certain manufacturing activities release potent greenhouse gases.
- Agriculture: Livestock and rice cultivation emit methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Climate change poses a huge risk to almost all life forms on Earth. The effects of climate change are listed below:
- Global Warming: Increased temperatures due to trapped heat from greenhouse gases.
- Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels: Ice caps and glaciers melt, causing oceans to rise.
- Extreme Weather Events: More frequent and severe hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb excess CO2, leading to more acidic waters harming marine life.
- Disrupted Ecosystems: Shifting climate patterns disrupt habitats and threaten biodiversity.
- Food and Water Scarcity: Altered weather affects crop yields and strains water resources.
- Human Health Risks: Heat-related illnesses and the spread of diseases.
- Economic Impact: Damage to infrastructure and increased disaster-related costs.
- Migration and Conflict: Climate-induced displacement and resource competition.
‘Climate change is a terrible problem, and it absolutely needs to be solved. It deserves to be a huge priority,’ says Bill Gates. The below points highlight key actions to combat climate change effectively.
- Energy Efficiency: Improve energy efficiency in all sectors.
- Protect Forests: Stop deforestation and promote reforestation.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Adopt eco-friendly farming practices.
- Advocacy: Raise awareness and advocate for climate-friendly policies.
- Innovation: Invest in green technologies and research.
- Government Policies: Enforce climate-friendly regulations and targets.
- Corporate Responsibility: Encourage sustainable business practices.
- Individual Action: Reduce personal carbon footprint and inspire others.
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in Earth’s climate patterns, primarily driven by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global warming. The consequences of climate change are widespread and devastating. Rising temperatures cause polar ice caps to melt, contributing to sea level rise and threatening coastal communities. Extreme weather events, like hurricanes and wildfires, become more frequent and severe, endangering lives and livelihoods. Additionally, shifts in weather patterns can disrupt agriculture, leading to food shortages. To combat climate change, global cooperation, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable practices are crucial for a more sustainable future.
Must Read: Essay On Global Warming
Climate change represents a pressing global challenge that demands immediate attention and concerted efforts. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This results in a greenhouse effect, trapping heat and leading to a rise in global temperatures, commonly referred to as global warming.
The consequences of climate change are far-reaching and profound. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, displacing millions and endangering vital infrastructure. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, have become more frequent and severe, causing devastating economic and human losses. Disrupted ecosystems affect biodiversity and the availability of vital resources, from clean water to agricultural yields.
Moreover, climate change has serious implications for food and water security. Changing weather patterns disrupt traditional farming practices and strain freshwater resources, potentially leading to conflicts over access to essential commodities.
Addressing climate change necessitates a multifaceted approach. First, countries must reduce their greenhouse gas emissions through the transition to renewable energy sources, increased energy efficiency, and reforestation efforts. International cooperation is crucial to set emission reduction targets and hold nations accountable for meeting them.
In conclusion, climate change is a global crisis with profound and immediate consequences. Urgent action is needed to mitigate its impacts and secure a sustainable future for our planet. By reducing emissions and implementing adaptation strategies, we can protect vulnerable communities, preserve ecosystems, and ensure a livable planet for future generations. The time to act is now.
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in Earth’s climate patterns, primarily driven by human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
Five key causes of climate change include excessive greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, notably burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
We hope this blog gave you an idea about how to write and present an essay on climate change that puts forth your opinions. The skill of writing an essay comes in handy when appearing for standardized language tests. Thinking of taking one soon? Leverage Edu provides the best online test prep for the same via Leverage Live . Register today to know more!
Amisha Khushara
With a heart full of passion for writing, I pour my emotions into every piece I create. I strive to connect with readers on a personal level, infusing my work with authenticity and relatability. Writing isn't just a skill; it's my heartfelt expression to touch hearts and minds.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
American Humanist Association
Advocating progressive values and equality for humanists, atheists, and freethinkers, resolution on climate change.
Adopted by the Board of Directors August 21, 2017 | Washington, DC Resolution 2017-001

The Earth’s climate is experiencing destabilization, and our planet’s ability to sustain life as we know it is in crisis. Humanists must join others in leading efforts to reduce human activities causing climate change to ecologically sustainable levels.
Ninety-seven percent of scientists agree that climate change is real and human induced, and the consensus is that we must stabilize global temperatures at the two degree Celsius target to prevent dangerous impacts to humans, flora, and fauna. The consequences of our actions—and inaction—regarding the destruction of our environment for ourselves and future generations mandate a naturalistic social responsibility inherent to humanist values.
WHEREAS human-generated greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel combustion—exacerbated by unsustainable land use such as deforestation—are a leading cause of climate change, and
WHEREAS deforestation and wildfire suppression are making forests more vulnerable to fires and reducing the ability of forests to sequester and store carbon, and
WHEREAS industrial animal production for food is inefficient in terms of land and water usage and often harms the environment due to animal waste, chemical runoff, and bacterial resistance to antibiotics, and
WHEREAS glaciers melting at heightened rates have been and are resulting in rising sea levels, threatening coastal populations and ocean ecology, and
WHEREAS global warming has contributed directly and indirectly to the loss of biodiversity and the destruction of critical biomes, and
WHEREAS the corollaries of these same changes appear to cause shifts in precipitation, resulting in droughts around the globe, and the increase in other extreme weather events, like tsunamis and hurricanes, leading to food insecurity and famine, and decreased access to natural resources like potable water, and
WHEREAS climate change impacts everyone, already vulnerable populations globally will be disproportionately affected, exacerbating unemployment, displacement, and homelessness, and
WHEREAS drastic global climate change is a challenge facing all populations around the world;
THEREFORE, BE IT RESOLVED that the AMERICAN HUMANIST ASSOCIATION , in the pursuit of climate justice,
AFFIRMS its support for the development and proliferation of renewable sources of energy and fuel, particularly wind and solar, and
AFFIRMS its support of sustainable land use, forest conservation, and reforestation, and
AFFIRMS its support for personal and commercial transition toward a plant-based diet, and
AFFIRMS its support of the rights of indigenous peoples who inhabit some of world’s most intact and biodiverse forests, and
AFFIRMS where direct restrictions are insufficient, support for a price on climate-damaging substances and practices through carbon tax and other related disincentives, and
AFFIRMS political and financial incentives for a global industrial refitting of our power infrastructure away from fossil fuels and toward sustainable energy production and storage, and
AFFIRMS its support for international funds for climate change mitigation and adaptation in developing countries, and
AFFIRMS its support for efforts to keep fossil fuels underground, particularly in ecologically and culturally important areas, and
AFFIRMS its support for the validation of climate refugee status, and
AFFIRMS that access to clean and affordable water is necessary and important, and
AFFIRMS its support for a coordinated global effort to manage and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
As humanists, it is crucial that we recognize that the responsibility to create and maintain sustainable methods of living is a collective one. As humanists, we acknowledge the damage done to our environment has been caused by human action and constitutes an existential threat to humanity and many other species that have not already been wiped out. As humanists, we understand that only humans can save ourselves from the climate crises we have created.
THEREFORE, BE IT RESOLVED that the AMERICAN HUMANIST ASSOCIATION calls all humanists to take personal and collective action to save our planet.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures
Kashif abbass.
1 School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, School of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Huaming Song
Muntasir murshed.
3 School of Business and Economics, North South University, Dhaka, 1229 Bangladesh
4 Department of Journalism, Media and Communications, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Haider Mahmood
5 Department of Finance, College of Business Administration, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, 173, Alkharj, 11942 Saudi Arabia
Ijaz Younis
Associated data.
Data sources and relevant links are provided in the paper to access data.
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector’s vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as sufficient production and food supplies are threatened due to irreversible weather fluctuations. In turn, it is challenging the global feeding patterns, particularly in countries with agriculture as an integral part of their economy and total productivity. Climate change has also put the integrity and survival of many species at stake due to shifts in optimum temperature ranges, thereby accelerating biodiversity loss by progressively changing the ecosystem structures. Climate variations increase the likelihood of particular food and waterborne and vector-borne diseases, and a recent example is a coronavirus pandemic. Climate change also accelerates the enigma of antimicrobial resistance, another threat to human health due to the increasing incidence of resistant pathogenic infections. Besides, the global tourism industry is devastated as climate change impacts unfavorable tourism spots. The methodology investigates hypothetical scenarios of climate variability and attempts to describe the quality of evidence to facilitate readers’ careful, critical engagement. Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation and adaptation approaches worldwide in the aforementioned sectors and the associated economic costs. According to the findings, government involvement is necessary for the country’s long-term development through strict accountability of resources and regulations implemented in the past to generate cutting-edge climate policy. Therefore, mitigating the impacts of climate change must be of the utmost importance, and hence, this global threat requires global commitment to address its dreadful implications to ensure global sustenance.
Introduction
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, environmental, socio-political, and socio-economic disciplines (Adger et al. 2005 ; Leal Filho et al. 2021 ; Feliciano et al. 2022 ). Climate change involves heightened temperatures across numerous worlds (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ; Schuurmans 2021 ; Weisheimer and Palmer 2005 ; Yadav et al. 2015 ). With the onset of the industrial revolution, the problem of earth climate was amplified manifold (Leppänen et al. 2014 ). It is reported that the immediate attention and due steps might increase the probability of overcoming its devastating impacts. It is not plausible to interpret the exact consequences of climate change (CC) on a sectoral basis (Izaguirre et al. 2021 ; Jurgilevich et al. 2017 ), which is evident by the emerging level of recognition plus the inclusion of climatic uncertainties at both local and national level of policymaking (Ayers et al. 2014 ).
Climate change is characterized based on the comprehensive long-haul temperature and precipitation trends and other components such as pressure and humidity level in the surrounding environment. Besides, the irregular weather patterns, retreating of global ice sheets, and the corresponding elevated sea level rise are among the most renowned international and domestic effects of climate change (Lipczynska-Kochany 2018 ; Michel et al. 2021 ; Murshed and Dao 2020 ). Before the industrial revolution, natural sources, including volcanoes, forest fires, and seismic activities, were regarded as the distinct sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and H 2 O into the atmosphere (Murshed et al. 2020 ; Hussain et al. 2020 ; Sovacool et al. 2021 ; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente 2022 ; Murshed 2022 ). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) struck a major agreement to tackle climate change and accelerate and intensify the actions and investments required for a sustainable low-carbon future at Conference of the Parties (COP-21) in Paris on December 12, 2015. The Paris Agreement expands on the Convention by bringing all nations together for the first time in a single cause to undertake ambitious measures to prevent climate change and adapt to its impacts, with increased funding to assist developing countries in doing so. As so, it marks a turning point in the global climate fight. The core goal of the Paris Agreement is to improve the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping the global temperature rise this century well below 2 °C over pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5° C (Sharma et al. 2020 ; Sharif et al. 2020 ; Chien et al. 2021 .
Furthermore, the agreement aspires to strengthen nations’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and align financing flows with low GHG emissions and climate-resilient paths (Shahbaz et al. 2019 ; Anwar et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2022a ). To achieve these lofty goals, adequate financial resources must be mobilized and provided, as well as a new technology framework and expanded capacity building, allowing developing countries and the most vulnerable countries to act under their respective national objectives. The agreement also establishes a more transparent action and support mechanism. All Parties are required by the Paris Agreement to do their best through “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) and to strengthen these efforts in the coming years (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2020 ). It includes obligations that all Parties regularly report on their emissions and implementation activities. A global stock-take will be conducted every five years to review collective progress toward the agreement’s goal and inform the Parties’ future individual actions. The Paris Agreement became available for signature on April 22, 2016, Earth Day, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. On November 4, 2016, it went into effect 30 days after the so-called double threshold was met (ratification by 55 nations accounting for at least 55% of world emissions). More countries have ratified and continue to ratify the agreement since then, bringing 125 Parties in early 2017. To fully operationalize the Paris Agreement, a work program was initiated in Paris to define mechanisms, processes, and recommendations on a wide range of concerns (Murshed et al. 2021 ). Since 2016, Parties have collaborated in subsidiary bodies (APA, SBSTA, and SBI) and numerous formed entities. The Conference of the Parties functioning as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA) convened for the first time in November 2016 in Marrakesh in conjunction with COP22 and made its first two resolutions. The work plan is scheduled to be finished by 2018. Some mitigation and adaptation strategies to reduce the emission in the prospective of Paris agreement are following firstly, a long-term goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, secondly, to aim to limit the rise to 1.5 °C, since this would significantly reduce risks and the impacts of climate change, thirdly, on the need for global emissions to peak as soon as possible, recognizing that this will take longer for developing countries, lastly, to undertake rapid reductions after that under the best available science, to achieve a balance between emissions and removals in the second half of the century. On the other side, some adaptation strategies are; strengthening societies’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and to continue & expand international assistance for developing nations’ adaptation.
However, anthropogenic activities are currently regarded as most accountable for CC (Murshed et al. 2022 ). Apart from the industrial revolution, other anthropogenic activities include excessive agricultural operations, which further involve the high use of fuel-based mechanization, burning of agricultural residues, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, national and domestic transportation sectors, etc. (Huang et al. 2016 ). Consequently, these anthropogenic activities lead to climatic catastrophes, damaging local and global infrastructure, human health, and total productivity. Energy consumption has mounted GHGs levels concerning warming temperatures as most of the energy production in developing countries comes from fossil fuels (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2022 ; Usman et al. 2022b ; Abbass et al. 2021a ; Ishikawa-Ishiwata and Furuya 2022 ).
This review aims to highlight the effects of climate change in a socio-scientific aspect by analyzing the existing literature on various sectorial pieces of evidence globally that influence the environment. Although this review provides a thorough examination of climate change and its severe affected sectors that pose a grave danger for global agriculture, biodiversity, health, economy, forestry, and tourism, and to purpose some practical prophylactic measures and mitigation strategies to be adapted as sound substitutes to survive from climate change (CC) impacts. The societal implications of irregular weather patterns and other effects of climate changes are discussed in detail. Some numerous sustainable mitigation measures and adaptation practices and techniques at the global level are discussed in this review with an in-depth focus on its economic, social, and environmental aspects. Methods of data collection section are included in the supplementary information.
Review methodology
Related study and its objectives.
Today, we live an ordinary life in the beautiful digital, globalized world where climate change has a decisive role. What happens in one country has a massive influence on geographically far apart countries, which points to the current crisis known as COVID-19 (Sarkar et al. 2021 ). The most dangerous disease like COVID-19 has affected the world’s climate changes and economic conditions (Abbass et al. 2022 ; Pirasteh-Anosheh et al. 2021 ). The purpose of the present study is to review the status of research on the subject, which is based on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures” by systematically reviewing past published and unpublished research work. Furthermore, the current study seeks to comment on research on the same topic and suggest future research on the same topic. Specifically, the present study aims: The first one is, organize publications to make them easy and quick to find. Secondly, to explore issues in this area, propose an outline of research for future work. The third aim of the study is to synthesize the previous literature on climate change, various sectors, and their mitigation measurement. Lastly , classify the articles according to the different methods and procedures that have been adopted.

Review methodology for reviewers
This review-based article followed systematic literature review techniques that have proved the literature review as a rigorous framework (Benita 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Moreover, we illustrate in Fig. 1 the search method that we have started for this research. First, finalized the research theme to search literature (Cooper et al. 2018 ). Second, used numerous research databases to search related articles and download from the database (Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus Index Journals, Emerald, Elsevier Science Direct, Springer, and Sciverse). We focused on various articles, with research articles, feedback pieces, short notes, debates, and review articles published in scholarly journals. Reports used to search for multiple keywords such as “Climate Change,” “Mitigation and Adaptation,” “Department of Agriculture and Human Health,” “Department of Biodiversity and Forestry,” etc.; in summary, keyword list and full text have been made. Initially, the search for keywords yielded a large amount of literature.

Methodology search for finalized articles for investigations.
Source : constructed by authors
Since 2020, it has been impossible to review all the articles found; some restrictions have been set for the literature exhibition. The study searched 95 articles on a different database mentioned above based on the nature of the study. It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements. The complete procedure yielded 55 articles for our study. We repeat our search on the “Web of Science and Google Scholars” database to enhance the search results and check the referenced articles.
In this study, 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies. Furthermore, this study analyzes closely related areas to provide unique research opportunities in the future. The study also discussed future direction opportunities and research questions by understanding the research findings climate changes and other affected sectors. The reviewed paper framework analysis process is outlined in Fig. 2 .

Framework of the analysis Process.
Natural disasters and climate change’s socio-economic consequences
Natural and environmental disasters can be highly variable from year to year; some years pass with very few deaths before a significant disaster event claims many lives (Symanski et al. 2021 ). Approximately 60,000 people globally died from natural disasters each year on average over the past decade (Ritchie and Roser 2014 ; Wiranata and Simbolon 2021 ). So, according to the report, around 0.1% of global deaths. Annual variability in the number and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades are shown in Fig. 3 . The number of fatalities can be meager—sometimes less than 10,000, and as few as 0.01% of all deaths. But shock events have a devastating impact: the 1983–1985 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis, which struck Myanmar in 2008; and the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti and now recent example is COVID-19 pandemic (Erman et al. 2021 ). These events pushed global disaster deaths to over 200,000—more than 0.4% of deaths in these years. Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are. Historical evidence shows that earlier disaster detection, more robust infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response programmers have substantially reduced disaster deaths worldwide. Low-income is also the most vulnerable to disasters; improving living conditions, facilities, and response services in these areas would be critical in reducing natural disaster deaths in the coming decades.

Global deaths from natural disasters, 1978 to 2020.
Source EMDAT ( 2020 )
The interior regions of the continent are likely to be impacted by rising temperatures (Dimri et al. 2018 ; Goes et al. 2020 ; Mannig et al. 2018 ; Schuurmans 2021 ). Weather patterns change due to the shortage of natural resources (water), increase in glacier melting, and rising mercury are likely to cause extinction to many planted species (Gampe et al. 2016 ; Mihiretu et al. 2021 ; Shaffril et al. 2018 ).On the other hand, the coastal ecosystem is on the verge of devastation (Perera et al. 2018 ; Phillips 2018 ). The temperature rises, insect disease outbreaks, health-related problems, and seasonal and lifestyle changes are persistent, with a strong probability of these patterns continuing in the future (Abbass et al. 2021c ; Hussain et al. 2018 ). At the global level, a shortage of good infrastructure and insufficient adaptive capacity are hammering the most (IPCC 2013 ). In addition to the above concerns, a lack of environmental education and knowledge, outdated consumer behavior, a scarcity of incentives, a lack of legislation, and the government’s lack of commitment to climate change contribute to the general public’s concerns. By 2050, a 2 to 3% rise in mercury and a drastic shift in rainfall patterns may have serious consequences (Huang et al. 2022 ; Gorst et al. 2018 ). Natural and environmental calamities caused huge losses globally, such as decreased agriculture outputs, rehabilitation of the system, and rebuilding necessary technologies (Ali and Erenstein 2017 ; Ramankutty et al. 2018 ; Yu et al. 2021 ) (Table (Table1). 1 ). Furthermore, in the last 3 or 4 years, the world has been plagued by smog-related eye and skin diseases, as well as a rise in road accidents due to poor visibility.
Main natural danger statistics for 1985–2020 at the global level
Source: EM-DAT ( 2020 )
Climate change and agriculture
Global agriculture is the ultimate sector responsible for 30–40% of all greenhouse emissions, which makes it a leading industry predominantly contributing to climate warming and significantly impacted by it (Grieg; Mishra et al. 2021 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Thornton and Lipper 2014 ). Numerous agro-environmental and climatic factors that have a dominant influence on agriculture productivity (Pautasso et al. 2012 ) are significantly impacted in response to precipitation extremes including floods, forest fires, and droughts (Huang 2004 ). Besides, the immense dependency on exhaustible resources also fuels the fire and leads global agriculture to become prone to devastation. Godfray et al. ( 2010 ) mentioned that decline in agriculture challenges the farmer’s quality of life and thus a significant factor to poverty as the food and water supplies are critically impacted by CC (Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Rosenzweig et al. 2014 ). As an essential part of the economic systems, especially in developing countries, agricultural systems affect the overall economy and potentially the well-being of households (Schlenker and Roberts 2009 ). According to the report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, i.e., CH 4, CO 2 , and N 2 O, are increased in the air to extraordinary levels over the last few centuries (Usman and Makhdum 2021 ; Stocker et al. 2013 ). Climate change is the composite outcome of two different factors. The first is the natural causes, and the second is the anthropogenic actions (Karami 2012 ). It is also forecasted that the world may experience a typical rise in temperature stretching from 1 to 3.7 °C at the end of this century (Pachauri et al. 2014 ). The world’s crop production is also highly vulnerable to these global temperature-changing trends as raised temperatures will pose severe negative impacts on crop growth (Reidsma et al. 2009 ). Some of the recent modeling about the fate of global agriculture is briefly described below.
Decline in cereal productivity
Crop productivity will also be affected dramatically in the next few decades due to variations in integral abiotic factors such as temperature, solar radiation, precipitation, and CO 2 . These all factors are included in various regulatory instruments like progress and growth, weather-tempted changes, pest invasions (Cammell and Knight 1992 ), accompanying disease snags (Fand et al. 2012 ), water supplies (Panda et al. 2003 ), high prices of agro-products in world’s agriculture industry, and preeminent quantity of fertilizer consumption. Lobell and field ( 2007 ) claimed that from 1962 to 2002, wheat crop output had condensed significantly due to rising temperatures. Therefore, during 1980–2011, the common wheat productivity trends endorsed extreme temperature events confirmed by Gourdji et al. ( 2013 ) around South Asia, South America, and Central Asia. Various other studies (Asseng, Cao, Zhang, and Ludwig 2009 ; Asseng et al. 2013 ; García et al. 2015 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ) also proved that wheat output is negatively affected by the rising temperatures and also caused adverse effects on biomass productivity (Calderini et al. 1999 ; Sadras and Slafer 2012 ). Hereafter, the rice crop is also influenced by the high temperatures at night. These difficulties will worsen because the temperature will be rising further in the future owing to CC (Tebaldi et al. 2006 ). Another research conducted in China revealed that a 4.6% of rice production per 1 °C has happened connected with the advancement in night temperatures (Tao et al. 2006 ). Moreover, the average night temperature growth also affected rice indicia cultivar’s output pragmatically during 25 years in the Philippines (Peng et al. 2004 ). It is anticipated that the increase in world average temperature will also cause a substantial reduction in yield (Hatfield et al. 2011 ; Lobell and Gourdji 2012 ). In the southern hemisphere, Parry et al. ( 2007 ) noted a rise of 1–4 °C in average daily temperatures at the end of spring season unti the middle of summers, and this raised temperature reduced crop output by cutting down the time length for phenophases eventually reduce the yield (Hatfield and Prueger 2015 ; R. Ortiz 2008 ). Also, world climate models have recommended that humid and subtropical regions expect to be plentiful prey to the upcoming heat strokes (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ). Grain production is the amalgamation of two constituents: the average weight and the grain output/m 2 , however, in crop production. Crop output is mainly accredited to the grain quantity (Araus et al. 2008 ; Gambín and Borrás 2010 ). In the times of grain set, yield resources are mainly strewn between hitherto defined components, i.e., grain usual weight and grain output, which presents a trade-off between them (Gambín and Borrás 2010 ) beside disparities in per grain integration (B. L. Gambín et al. 2006 ). In addition to this, the maize crop is also susceptible to raised temperatures, principally in the flowering stage (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). In reality, the lower grain number is associated with insufficient acclimatization due to intense photosynthesis and higher respiration and the high-temperature effect on the reproduction phenomena (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). During the flowering phase, maize visible to heat (30–36 °C) seemed less anthesis-silking intermissions (Edreira et al. 2011 ). Another research by Dupuis and Dumas ( 1990 ) proved that a drop in spikelet when directly visible to high temperatures above 35 °C in vitro pollination. Abnormalities in kernel number claimed by Vega et al. ( 2001 ) is related to conceded plant development during a flowering phase that is linked with the active ear growth phase and categorized as a critical phase for approximation of kernel number during silking (Otegui and Bonhomme 1998 ).
The retort of rice output to high temperature presents disparities in flowering patterns, and seed set lessens and lessens grain weight (Qasim et al. 2020 ; Qasim, Hammad, Maqsood, Tariq, & Chawla). During the daytime, heat directly impacts flowers which lessens the thesis period and quickens the earlier peak flowering (Tao et al. 2006 ). Antagonistic effect of higher daytime temperature d on pollen sprouting proposed seed set decay, whereas, seed set was lengthily reduced than could be explicated by pollen growing at high temperatures 40◦C (Matsui et al. 2001 ).
The decline in wheat output is linked with higher temperatures, confirmed in numerous studies (Semenov 2009 ; Stone and Nicolas 1994 ). High temperatures fast-track the arrangements of plant expansion (Blum et al. 2001 ), diminution photosynthetic process (Salvucci and Crafts‐Brandner 2004 ), and also considerably affect the reproductive operations (Farooq et al. 2011 ).
The destructive impacts of CC induced weather extremes to deteriorate the integrity of crops (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ), e.g., Spartan cold and extreme fog cause falling and discoloration of betel leaves (Rosenzweig et al. 2001 ), giving them a somehow reddish appearance, squeezing of lemon leaves (Pautasso et al. 2012 ), as well as root rot of pineapple, have reported (Vedwan and Rhoades 2001 ). Henceforth, in tackling the disruptive effects of CC, several short-term and long-term management approaches are the crucial need of time (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, various studies (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ; Patz et al. 2005 ; Pautasso et al. 2012 ) have demonstrated adapting trends such as ameliorating crop diversity can yield better adaptability towards CC.

Schematic description of potential impacts of climate change on the agriculture sector and the appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures to overcome its impact.
Climate change impacts on biodiversity
Global biodiversity is among the severe victims of CC because it is the fastest emerging cause of species loss. Studies demonstrated that the massive scale species dynamics are considerably associated with diverse climatic events (Abraham and Chain 1988 ; Manes et al. 2021 ; A. M. D. Ortiz et al. 2021 ). Both the pace and magnitude of CC are altering the compatible habitat ranges for living entities of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial regions. Alterations in general climate regimes influence the integrity of ecosystems in numerous ways, such as variation in the relative abundance of species, range shifts, changes in activity timing, and microhabitat use (Bates et al. 2014 ). The geographic distribution of any species often depends upon its ability to tolerate environmental stresses, biological interactions, and dispersal constraints. Hence, instead of the CC, the local species must only accept, adapt, move, or face extinction (Berg et al. 2010 ). So, the best performer species have a better survival capacity for adjusting to new ecosystems or a decreased perseverance to survive where they are already situated (Bates et al. 2014 ). An important aspect here is the inadequate habitat connectivity and access to microclimates, also crucial in raising the exposure to climate warming and extreme heatwave episodes. For example, the carbon sequestration rates are undergoing fluctuations due to climate-driven expansion in the range of global mangroves (Cavanaugh et al. 2014 ).
Similarly, the loss of kelp-forest ecosystems in various regions and its occupancy by the seaweed turfs has set the track for elevated herbivory by the high influx of tropical fish populations. Not only this, the increased water temperatures have exacerbated the conditions far away from the physiological tolerance level of the kelp communities (Vergés et al. 2016 ; Wernberg et al. 2016 ). Another pertinent danger is the devastation of keystone species, which even has more pervasive effects on the entire communities in that habitat (Zarnetske et al. 2012 ). It is particularly important as CC does not specify specific populations or communities. Eventually, this CC-induced redistribution of species may deteriorate carbon storage and the net ecosystem productivity (Weed et al. 2013 ). Among the typical disruptions, the prominent ones include impacts on marine and terrestrial productivity, marine community assembly, and the extended invasion of toxic cyanobacteria bloom (Fossheim et al. 2015 ).
The CC-impacted species extinction is widely reported in the literature (Beesley et al. 2019 ; Urban 2015 ), and the predictions of demise until the twenty-first century are dreadful (Abbass et al. 2019 ; Pereira et al. 2013 ). In a few cases, northward shifting of species may not be formidable as it allows mountain-dwelling species to find optimum climates. However, the migrant species may be trapped in isolated and incompatible habitats due to losing topography and range (Dullinger et al. 2012 ). For example, a study indicated that the American pika has been extirpated or intensely diminished in some regions, primarily attributed to the CC-impacted extinction or at least local extirpation (Stewart et al. 2015 ). Besides, the anticipation of persistent responses to the impacts of CC often requires data records of several decades to rigorously analyze the critical pre and post CC patterns at species and ecosystem levels (Manes et al. 2021 ; Testa et al. 2018 ).
Nonetheless, the availability of such long-term data records is rare; hence, attempts are needed to focus on these profound aspects. Biodiversity is also vulnerable to the other associated impacts of CC, such as rising temperatures, droughts, and certain invasive pest species. For instance, a study revealed the changes in the composition of plankton communities attributed to rising temperatures. Henceforth, alterations in such aquatic producer communities, i.e., diatoms and calcareous plants, can ultimately lead to variation in the recycling of biological carbon. Moreover, such changes are characterized as a potential contributor to CO 2 differences between the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods (Kohfeld et al. 2005 ).
Climate change implications on human health
It is an understood corporality that human health is a significant victim of CC (Costello et al. 2009 ). According to the WHO, CC might be responsible for 250,000 additional deaths per year during 2030–2050 (Watts et al. 2015 ). These deaths are attributed to extreme weather-induced mortality and morbidity and the global expansion of vector-borne diseases (Lemery et al. 2021; Yang and Usman 2021 ; Meierrieks 2021 ; UNEP 2017 ). Here, some of the emerging health issues pertinent to this global problem are briefly described.
Climate change and antimicrobial resistance with corresponding economic costs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an up-surging complex global health challenge (Garner et al. 2019 ; Lemery et al. 2021 ). Health professionals across the globe are extremely worried due to this phenomenon that has critical potential to reverse almost all the progress that has been achieved so far in the health discipline (Gosling and Arnell 2016 ). A massive amount of antibiotics is produced by many pharmaceutical industries worldwide, and the pathogenic microorganisms are gradually developing resistance to them, which can be comprehended how strongly this aspect can shake the foundations of national and global economies (UNEP 2017 ). This statement is supported by the fact that AMR is not developing in a particular region or country. Instead, it is flourishing in every continent of the world (WHO 2018 ). This plague is heavily pushing humanity to the post-antibiotic era, in which currently antibiotic-susceptible pathogens will once again lead to certain endemics and pandemics after being resistant(WHO 2018 ). Undesirably, if this statement would become a factuality, there might emerge certain risks in undertaking sophisticated interventions such as chemotherapy, joint replacement cases, and organ transplantation (Su et al. 2018 ). Presently, the amplification of drug resistance cases has made common illnesses like pneumonia, post-surgical infections, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, etc., too difficult and costly to be treated or cure well (WHO 2018 ). From a simple example, it can be assumed how easily antibiotic-resistant strains can be transmitted from one person to another and ultimately travel across the boundaries (Berendonk et al. 2015 ). Talking about the second- and third-generation classes of antibiotics, e.g., most renowned generations of cephalosporin antibiotics that are more expensive, broad-spectrum, more toxic, and usually require more extended periods whenever prescribed to patients (Lemery et al. 2021 ; Pärnänen et al. 2019 ). This scenario has also revealed that the abundance of resistant strains of pathogens was also higher in the Southern part (WHO 2018 ). As southern parts are generally warmer than their counterparts, it is evident from this example how CC-induced global warming can augment the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains within the biosphere, eventually putting additional economic burden in the face of developing new and costlier antibiotics. The ARG exchange to susceptible bacteria through one of the potential mechanisms, transformation, transduction, and conjugation; Selection pressure can be caused by certain antibiotics, metals or pesticides, etc., as shown in Fig. 5 .

A typical interaction between the susceptible and resistant strains.
Source: Elsayed et al. ( 2021 ); Karkman et al. ( 2018 )
Certain studies highlighted that conventional urban wastewater treatment plants are typical hotspots where most bacterial strains exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer (Fig. 5 ). Although at present, the extent of risks associated with the antibiotic resistance found in wastewater is complicated; environmental scientists and engineers have particular concerns about the potential impacts of these antibiotic resistance genes on human health (Ashbolt 2015 ). At most undesirable and worst case, these antibiotic-resistant genes containing bacteria can make their way to enter into the environment (Pruden et al. 2013 ), irrigation water used for crops and public water supplies and ultimately become a part of food chains and food webs (Ma et al. 2019 ; D. Wu et al. 2019 ). This problem has been reported manifold in several countries (Hendriksen et al. 2019 ), where wastewater as a means of irrigated water is quite common.
Climate change and vector borne-diseases
Temperature is a fundamental factor for the sustenance of living entities regardless of an ecosystem. So, a specific living being, especially a pathogen, requires a sophisticated temperature range to exist on earth. The second essential component of CC is precipitation, which also impacts numerous infectious agents’ transport and dissemination patterns. Global rising temperature is a significant cause of many species extinction. On the one hand, this changing environmental temperature may be causing species extinction, and on the other, this warming temperature might favor the thriving of some new organisms. Here, it was evident that some pathogens may also upraise once non-evident or reported (Patz et al. 2000 ). This concept can be exemplified through certain pathogenic strains of microorganisms that how the likelihood of various diseases increases in response to climate warming-induced environmental changes (Table (Table2 2 ).
Examples of how various environmental changes affect various infectious diseases in humans
Source: Aron and Patz ( 2001 )
A recent example is an outburst of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the Republic of China, causing pneumonia and severe acute respiratory complications (Cui et al. 2021 ; Song et al. 2021 ). The large family of viruses is harbored in numerous animals, bats, and snakes in particular (livescience.com) with the subsequent transfer into human beings. Hence, it is worth noting that the thriving of numerous vectors involved in spreading various diseases is influenced by Climate change (Ogden 2018 ; Santos et al. 2021 ).
Psychological impacts of climate change
Climate change (CC) is responsible for the rapid dissemination and exaggeration of certain epidemics and pandemics. In addition to the vast apparent impacts of climate change on health, forestry, agriculture, etc., it may also have psychological implications on vulnerable societies. It can be exemplified through the recent outburst of (COVID-19) in various countries around the world (Pal 2021 ). Besides, the victims of this viral infection have made healthy beings scarier and terrified. In the wake of such epidemics, people with common colds or fever are also frightened and must pass specific regulatory protocols. Living in such situations continuously terrifies the public and makes the stress familiar, which eventually makes them psychologically weak (npr.org).
CC boosts the extent of anxiety, distress, and other issues in public, pushing them to develop various mental-related problems. Besides, frequent exposure to extreme climatic catastrophes such as geological disasters also imprints post-traumatic disorder, and their ubiquitous occurrence paves the way to developing chronic psychological dysfunction. Moreover, repetitive listening from media also causes an increase in the person’s stress level (Association 2020 ). Similarly, communities living in flood-prone areas constantly live in extreme fear of drowning and die by floods. In addition to human lives, the flood-induced destruction of physical infrastructure is a specific reason for putting pressure on these communities (Ogden 2018 ). For instance, Ogden ( 2018 ) comprehensively denoted that Katrina’s Hurricane augmented the mental health issues in the victim communities.
Climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Forests are the global regulators of the world’s climate (FAO 2018 ) and have an indispensable role in regulating global carbon and nitrogen cycles (Rehman et al. 2021 ; Reichstein and Carvalhais 2019 ). Hence, disturbances in forest ecology affect the micro and macro-climates (Ellison et al. 2017 ). Climate warming, in return, has profound impacts on the growth and productivity of transboundary forests by influencing the temperature and precipitation patterns, etc. As CC induces specific changes in the typical structure and functions of ecosystems (Zhang et al. 2017 ) as well impacts forest health, climate change also has several devastating consequences such as forest fires, droughts, pest outbreaks (EPA 2018 ), and last but not the least is the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities. The rising frequency and intensity of another CC product, i.e., droughts, pose plenty of challenges to the well-being of global forests (Diffenbaugh et al. 2017 ), which is further projected to increase soon (Hartmann et al. 2018 ; Lehner et al. 2017 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ). Hence, CC induces storms, with more significant impacts also put extra pressure on the survival of the global forests (Martínez-Alvarado et al. 2018 ), significantly since their influences are augmented during higher winter precipitations with corresponding wetter soils causing weak root anchorage of trees (Brázdil et al. 2018 ). Surging temperature regimes causes alterations in usual precipitation patterns, which is a significant hurdle for the survival of temperate forests (Allen et al. 2010 ; Flannigan et al. 2013 ), letting them encounter severe stress and disturbances which adversely affects the local tree species (Hubbart et al. 2016 ; Millar and Stephenson 2015 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ).
Climate change impacts on forest-dependent communities
Forests are the fundamental livelihood resource for about 1.6 billion people worldwide; out of them, 350 million are distinguished with relatively higher reliance (Bank 2008 ). Agro-forestry-dependent communities comprise 1.2 billion, and 60 million indigenous people solely rely on forests and their products to sustain their lives (Sunderlin et al. 2005 ). For example, in the entire African continent, more than 2/3rd of inhabitants depend on forest resources and woodlands for their alimonies, e.g., food, fuelwood and grazing (Wasiq and Ahmad 2004 ). The livings of these people are more intensely affected by the climatic disruptions making their lives harder (Brown et al. 2014 ). On the one hand, forest communities are incredibly vulnerable to CC due to their livelihoods, cultural and spiritual ties as well as socio-ecological connections, and on the other, they are not familiar with the term “climate change.” (Rahman and Alam 2016 ). Among the destructive impacts of temperature and rainfall, disruption of the agroforestry crops with resultant downscale growth and yield (Macchi et al. 2008 ). Cruz ( 2015 ) ascribed that forest-dependent smallholder farmers in the Philippines face the enigma of delayed fruiting, more severe damages by insect and pest incidences due to unfavorable temperature regimes, and changed rainfall patterns.
Among these series of challenges to forest communities, their well-being is also distinctly vulnerable to CC. Though the detailed climate change impacts on human health have been comprehensively mentioned in the previous section, some studies have listed a few more devastating effects on the prosperity of forest-dependent communities. For instance, the Himalayan people have been experiencing frequent skin-borne diseases such as malaria and other skin diseases due to increasing mosquitoes, wild boar as well, and new wasps species, particularly in higher altitudes that were almost non-existent before last 5–10 years (Xu et al. 2008 ). Similarly, people living at high altitudes in Bangladesh have experienced frequent mosquito-borne calamities (Fardous; Sharma 2012 ). In addition, the pace of other waterborne diseases such as infectious diarrhea, cholera, pathogenic induced abdominal complications and dengue has also been boosted in other distinguished regions of Bangladesh (Cell 2009 ; Gunter et al. 2008 ).
Pest outbreak
Upscaling hotter climate may positively affect the mobile organisms with shorter generation times because they can scurry from harsh conditions than the immobile species (Fettig et al. 2013 ; Schoene and Bernier 2012 ) and are also relatively more capable of adapting to new environments (Jactel et al. 2019 ). It reveals that insects adapt quickly to global warming due to their mobility advantages. Due to past outbreaks, the trees (forests) are relatively more susceptible victims (Kurz et al. 2008 ). Before CC, the influence of factors mentioned earlier, i.e., droughts and storms, was existent and made the forests susceptible to insect pest interventions; however, the global forests remain steadfast, assiduous, and green (Jactel et al. 2019 ). The typical reasons could be the insect herbivores were regulated by several tree defenses and pressures of predation (Wilkinson and Sherratt 2016 ). As climate greatly influences these phenomena, the global forests cannot be so sedulous against such challenges (Jactel et al. 2019 ). Table Table3 3 demonstrates some of the particular considerations with practical examples that are essential while mitigating the impacts of CC in the forestry sector.
Essential considerations while mitigating the climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Source : Fischer ( 2019 )
Climate change impacts on tourism
Tourism is a commercial activity that has roots in multi-dimensions and an efficient tool with adequate job generation potential, revenue creation, earning of spectacular foreign exchange, enhancement in cross-cultural promulgation and cooperation, a business tool for entrepreneurs and eventually for the country’s national development (Arshad et al. 2018 ; Scott 2021 ). Among a plethora of other disciplines, the tourism industry is also a distinct victim of climate warming (Gössling et al. 2012 ; Hall et al. 2015 ) as the climate is among the essential resources that enable tourism in particular regions as most preferred locations. Different places at different times of the year attract tourists both within and across the countries depending upon the feasibility and compatibility of particular weather patterns. Hence, the massive variations in these weather patterns resulting from CC will eventually lead to monumental challenges to the local economy in that specific area’s particular and national economy (Bujosa et al. 2015 ). For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrated that the global tourism industry had faced a considerable decline in the duration of ski season, including the loss of some ski areas and the dramatic shifts in tourist destinations’ climate warming.
Furthermore, different studies (Neuvonen et al. 2015 ; Scott et al. 2004 ) indicated that various currently perfect tourist spots, e.g., coastal areas, splendid islands, and ski resorts, will suffer consequences of CC. It is also worth noting that the quality and potential of administrative management potential to cope with the influence of CC on the tourism industry is of crucial significance, which renders specific strengths of resiliency to numerous destinations to withstand against it (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). Similarly, in the partial or complete absence of adequate socio-economic and socio-political capital, the high-demanding tourist sites scurry towards the verge of vulnerability. The susceptibility of tourism is based on different components such as the extent of exposure, sensitivity, life-supporting sectors, and capacity assessment factors (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). It is obvious corporality that sectors such as health, food, ecosystems, human habitat, infrastructure, water availability, and the accessibility of a particular region are prone to CC. Henceforth, the sensitivity of these critical sectors to CC and, in return, the adaptive measures are a hallmark in determining the composite vulnerability of climate warming (Ionescu et al. 2009 ).
Moreover, the dependence on imported food items, poor hygienic conditions, and inadequate health professionals are dominant aspects affecting the local terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity. Meanwhile, the greater dependency on ecosystem services and its products also makes a destination more fragile to become a prey of CC (Rizvi et al. 2015 ). Some significant non-climatic factors are important indicators of a particular ecosystem’s typical health and functioning, e.g., resource richness and abundance portray the picture of ecosystem stability. Similarly, the species abundance is also a productive tool that ensures that the ecosystem has a higher buffering capacity, which is terrific in terms of resiliency (Roscher et al. 2013 ).
Climate change impacts on the economic sector
Climate plays a significant role in overall productivity and economic growth. Due to its increasingly global existence and its effect on economic growth, CC has become one of the major concerns of both local and international environmental policymakers (Ferreira et al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Abbass et al. 2021b ; Lamperti et al. 2021 ). The adverse effects of CC on the overall productivity factor of the agricultural sector are therefore significant for understanding the creation of local adaptation policies and the composition of productive climate policy contracts. Previous studies on CC in the world have already forecasted its effects on the agricultural sector. Researchers have found that global CC will impact the agricultural sector in different world regions. The study of the impacts of CC on various agrarian activities in other demographic areas and the development of relative strategies to respond to effects has become a focal point for researchers (Chandioet al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Mosavi et al. 2020 ).
With the rapid growth of global warming since the 1980s, the temperature has started increasing globally, which resulted in the incredible transformation of rain and evaporation in the countries. The agricultural development of many countries has been reliant, delicate, and susceptible to CC for a long time, and it is on the development of agriculture total factor productivity (ATFP) influence different crops and yields of farmers (Alhassan 2021 ; Wu 2020 ).
Food security and natural disasters are increasing rapidly in the world. Several major climatic/natural disasters have impacted local crop production in the countries concerned. The effects of these natural disasters have been poorly controlled by the development of the economies and populations and may affect human life as well. One example is China, which is among the world’s most affected countries, vulnerable to natural disasters due to its large population, harsh environmental conditions, rapid CC, low environmental stability, and disaster power. According to the January 2016 statistical survey, China experienced an economic loss of 298.3 billion Yuan, and about 137 million Chinese people were severely affected by various natural disasters (Xie et al. 2018 ).
Mitigation and adaptation strategies of climate changes
Adaptation and mitigation are the crucial factors to address the response to CC (Jahanzad et al. 2020 ). Researchers define mitigation on climate changes, and on the other hand, adaptation directly impacts climate changes like floods. To some extent, mitigation reduces or moderates greenhouse gas emission, and it becomes a critical issue both economically and environmentally (Botzen et al. 2021 ; Jahanzad et al. 2020 ; Kongsager 2018 ; Smit et al. 2000 ; Vale et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2021 ; Verheyen 2005 ).
Researchers have deep concern about the adaptation and mitigation methodologies in sectoral and geographical contexts. Agriculture, industry, forestry, transport, and land use are the main sectors to adapt and mitigate policies(Kärkkäinen et al. 2020 ; Waheed et al. 2021 ). Adaptation and mitigation require particular concern both at the national and international levels. The world has faced a significant problem of climate change in the last decades, and adaptation to these effects is compulsory for economic and social development. To adapt and mitigate against CC, one should develop policies and strategies at the international level (Hussain et al. 2020 ). Figure 6 depicts the list of current studies on sectoral impacts of CC with adaptation and mitigation measures globally.

Sectoral impacts of climate change with adaptation and mitigation measures.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Specific socio-agricultural, socio-economic, and physical systems are the cornerstone of psychological well-being, and the alteration in these systems by CC will have disastrous impacts. Climate variability, alongside other anthropogenic and natural stressors, influences human and environmental health sustainability. Food security is another concerning scenario that may lead to compromised food quality, higher food prices, and inadequate food distribution systems. Global forests are challenged by different climatic factors such as storms, droughts, flash floods, and intense precipitation. On the other hand, their anthropogenic wiping is aggrandizing their existence. Undoubtedly, the vulnerability scale of the world’s regions differs; however, appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures can aid the decision-making bodies in developing effective policies to tackle its impacts. Presently, modern life on earth has tailored to consistent climatic patterns, and accordingly, adapting to such considerable variations is of paramount importance. Because the faster changes in climate will make it harder to survive and adjust, this globally-raising enigma calls for immediate attention at every scale ranging from elementary community level to international level. Still, much effort, research, and dedication are required, which is the most critical time. Some policy implications can help us to mitigate the consequences of climate change, especially the most affected sectors like the agriculture sector;
Warming might lengthen the season in frost-prone growing regions (temperate and arctic zones), allowing for longer-maturing seasonal cultivars with better yields (Pfadenhauer 2020 ; Bonacci 2019 ). Extending the planting season may allow additional crops each year; when warming leads to frequent warmer months highs over critical thresholds, a split season with a brief summer fallow may be conceivable for short-period crops such as wheat barley, cereals, and many other vegetable crops. The capacity to prolong the planting season in tropical and subtropical places where the harvest season is constrained by precipitation or agriculture farming occurs after the year may be more limited and dependent on how precipitation patterns vary (Wu et al. 2017 ).
The genetic component is comprehensive for many yields, but it is restricted like kiwi fruit for a few. Ali et al. ( 2017 ) investigated how new crops will react to climatic changes (also stated in Mall et al. 2017 ). Hot temperature, drought, insect resistance; salt tolerance; and overall crop production and product quality increases would all be advantageous (Akkari 2016 ). Genetic mapping and engineering can introduce a greater spectrum of features. The adoption of genetically altered cultivars has been slowed, particularly in the early forecasts owing to the complexity in ensuring features are expediently expressed throughout the entire plant, customer concerns, economic profitability, and regulatory impediments (Wirehn 2018 ; Davidson et al. 2016 ).
To get the full benefit of the CO 2 would certainly require additional nitrogen and other fertilizers. Nitrogen not consumed by the plants may be excreted into groundwater, discharged into water surface, or emitted from the land, soil nitrous oxide when large doses of fertilizer are sprayed. Increased nitrogen levels in groundwater sources have been related to human chronic illnesses and impact marine ecosystems. Cultivation, grain drying, and other field activities have all been examined in depth in the studies (Barua et al. 2018 ).
- The technological and socio-economic adaptation
The policy consequence of the causative conclusion is that as a source of alternative energy, biofuel production is one of the routes that explain oil price volatility separate from international macroeconomic factors. Even though biofuel production has just begun in a few sample nations, there is still a tremendous worldwide need for feedstock to satisfy industrial expansion in China and the USA, which explains the food price relationship to the global oil price. Essentially, oil-exporting countries may create incentives in their economies to increase food production. It may accomplish by giving farmers financing, seedlings, fertilizers, and farming equipment. Because of the declining global oil price and, as a result, their earnings from oil export, oil-producing nations may be unable to subsidize food imports even in the near term. As a result, these countries can boost the agricultural value chain for export. It may be accomplished through R&D and adding value to their food products to increase income by correcting exchange rate misalignment and adverse trade terms. These nations may also diversify their economies away from oil, as dependence on oil exports alone is no longer economically viable given the extreme volatility of global oil prices. Finally, resource-rich and oil-exporting countries can convert to non-food renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, coal, wind, wave, and tidal energy. By doing so, both world food and oil supplies would be maintained rather than harmed.
IRENA’s modeling work shows that, if a comprehensive policy framework is in place, efforts toward decarbonizing the energy future will benefit economic activity, jobs (outweighing losses in the fossil fuel industry), and welfare. Countries with weak domestic supply chains and a large reliance on fossil fuel income, in particular, must undertake structural reforms to capitalize on the opportunities inherent in the energy transition. Governments continue to give major policy assistance to extract fossil fuels, including tax incentives, financing, direct infrastructure expenditures, exemptions from environmental regulations, and other measures. The majority of major oil and gas producing countries intend to increase output. Some countries intend to cut coal output, while others plan to maintain or expand it. While some nations are beginning to explore and execute policies aimed at a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuel production, these efforts have yet to impact major producing countries’ plans and goals. Verifiable and comparable data on fossil fuel output and assistance from governments and industries are critical to closing the production gap. Governments could increase openness by declaring their production intentions in their climate obligations under the Paris Agreement.
It is firmly believed that achieving the Paris Agreement commitments is doubtlful without undergoing renewable energy transition across the globe (Murshed 2020 ; Zhao et al. 2022 ). Policy instruments play the most important role in determining the degree of investment in renewable energy technology. This study examines the efficacy of various policy strategies in the renewable energy industry of multiple nations. Although its impact is more visible in established renewable energy markets, a renewable portfolio standard is also a useful policy instrument. The cost of producing renewable energy is still greater than other traditional energy sources. Furthermore, government incentives in the R&D sector can foster innovation in this field, resulting in cost reductions in the renewable energy industry. These nations may export their technologies and share their policy experiences by forming networks among their renewable energy-focused organizations. All policy measures aim to reduce production costs while increasing the proportion of renewables to a country’s energy system. Meanwhile, long-term contracts with renewable energy providers, government commitment and control, and the establishment of long-term goals can assist developing nations in deploying renewable energy technology in their energy sector.
Author contribution
KA: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Study design, Formal analysis, Visualization, Revised draft, Writing-review, and editing. MZQ: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Writing-review, and editing. HS: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, literature review, Revised drapt, and writing review and editing. MM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. HM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. IY: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, literature review, and writing review and editing.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
Not applicable.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kashif Abbass, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@ssabbafihsak .
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim, Email: moc.kooltuo@888misaqnahseez .
Huaming Song, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@gnimauh .
Muntasir Murshed, Email: [email protected] .
Haider Mahmood, Email: moc.liamtoh@doomhamrediah .
Ijaz Younis, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@sinuoyzaji .
- Abbass K, Begum H, Alam ASA, Awang AH, Abdelsalam MK, Egdair IMM, Wahid R (2022) Fresh Insight through a Keynesian Theory Approach to Investigate the Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan. Sustain 14(3):1054
- Abbass K, Niazi AAK, Qazi TF, Basit A, Song H (2021a) The aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic period: barriers in implementation of social distancing at workplace. Library Hi Tech
- Abbass K, Song H, Khan F, Begum H, Asif M (2021b) Fresh insight through the VAR approach to investigate the effects of fiscal policy on environmental pollution in Pakistan. Environ Scie Poll Res 1–14 [ PubMed ]
- Abbass K, Song H, Shah SM, Aziz B. Determinants of Stock Return for Non-Financial Sector: Evidence from Energy Sector of Pakistan. J Bus Fin Aff. 2019; 8 (370):2167–0234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Abbass K, Tanveer A, Huaming S, Khatiya AA (2021c) Impact of financial resources utilization on firm performance: a case of SMEs working in Pakistan
- Abraham E, Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev Infect Dis. 1988; 10 (4):677. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adger WN, Arnell NW, Tompkins EL. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob Environ Chang. 2005; 15 (2):77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.12.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akkari C, Bryant CR. The co-construction approach as approach to developing adaptation strategies in the face of climate change and variability: A conceptual framework. Agricultural Research. 2016; 5 (2):162–173. doi: 10.1007/s40003-016-0208-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alhassan H (2021) The effect of agricultural total factor productivity on environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Afr 12:e00740
- Ali A, Erenstein O. Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim Risk Manag. 2017; 16 :183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2016.12.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Hogg ET. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag. 2010; 259 (4):660–684. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sust. 10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
- Araus JL, Slafer GA, Royo C, Serret MD. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2008; 27 (6):377–412. doi: 10.1080/07352680802467736. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aron JL, Patz J (2001) Ecosystem change and public health: a global perspective: JHU Press
- Arshad MI, Iqbal MA, Shahbaz M. Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research. 2018; 23 (2):121–132. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2017.1410192. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashbolt NJ. Microbial contamination of drinking water and human health from community water systems. Current Environmental Health Reports. 2015; 2 (1):95–106. doi: 10.1007/s40572-014-0037-5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asseng S, Cao W, Zhang W, Ludwig F (2009) Crop physiology, modelling and climate change: impact and adaptation strategies. Crop Physiol 511–543
- Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Cammarano D. Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nat Clim Chang. 2013; 3 (9):827–832. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1916. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Association A (2020) Climate change is threatening mental health, American Psychological Association, “Kirsten Weir, . from < https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/07-08/climate-change >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ayers J, Huq S, Wright H, Faisal A, Hussain S. Mainstreaming climate change adaptation into development in Bangladesh. Clim Dev. 2014; 6 :293–305. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2014.977761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Sinha A, Adedoyin FF (2020) Consequences of COVID-19 on the social isolation of the Chinese economy: accounting for the role of reduction in carbon emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(12):1439–1451
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M. The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy. 2022; 185 :1441–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bank W (2008) Forests sourcebook: practical guidance for sustaining forests in development cooperation: World Bank
- Barua S, Valenzuela E (2018) Climate change impacts on global agricultural trade patterns: evidence from the past 50 years. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Development (pp. 26–28)
- Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Colwell RK. Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Glob Environ Chang. 2014; 26 :27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.03.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science. 2009; 323 (5911):240–244. doi: 10.1126/science.1164363. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beesley L, Close PG, Gwinn DC, Long M, Moroz M, Koster WM, Storer T. Flow-mediated movement of freshwater catfish, Tandanus bostocki, in a regulated semi-urban river, to inform environmental water releases. Ecol Freshw Fish. 2019; 28 (3):434–445. doi: 10.1111/eff.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benita F (2021) Human mobility behavior in COVID-19: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 70:102916 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Pons M-N. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015; 13 (5):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3439. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, Van DerHEIJDEN M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Ellers J. Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol. 2010; 16 (2):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02014.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blum A, Klueva N, Nguyen H. Wheat cellular thermotolerance is related to yield under heat stress. Euphytica. 2001; 117 (2):117–123. doi: 10.1023/A:1004083305905. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonacci O. Air temperature and precipitation analyses on a small Mediterranean island: the case of the remote island of Lastovo (Adriatic Sea, Croatia) Acta Hydrotechnica. 2019; 32 (57):135–150. doi: 10.15292/acta.hydro.2019.10. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Botzen W, Duijndam S, van Beukering P (2021) Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks. World Dev 137:105214 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Brázdil R, Stucki P, Szabó P, Řezníčková L, Dolák L, Dobrovolný P, Suchánková S. Windstorms and forest disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric for Meteorol. 2018; 250 :47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown HCP, Smit B, Somorin OA, Sonwa DJ, Nkem JN. Climate change and forest communities: prospects for building institutional adaptive capacity in the Congo Basin forests. Ambio. 2014; 43 (6):759–769. doi: 10.1007/s13280-014-0493-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bujosa A, Riera A, Torres CM. Valuing tourism demand attributes to guide climate change adaptation measures efficiently: the case of the Spanish domestic travel market. Tour Manage. 2015; 47 :233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.09.023. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calderini D, Abeledo L, Savin R, Slafer GA. Effect of temperature and carpel size during pre-anthesis on potential grain weight in wheat. J Agric Sci. 1999; 132 (4):453–459. doi: 10.1017/S0021859699006504. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cammell M, Knight J. Effects of climatic change on the population dynamics of crop pests. Adv Ecol Res. 1992; 22 :117–162. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60135-X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavanaugh KC, Kellner JR, Forde AJ, Gruner DS, Parker JD, Rodriguez W, Feller IC. Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (2):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315800111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cell CC (2009) Climate change and health impacts in Bangladesh. Clima Chang Cell DoE MoEF
- Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Short and long-run impacts of climate change on agriculture: an empirical evidence from China. Int J Clim Chang Strat Manag
- Chaudhary P, Rai S, Wangdi S, Mao A, Rehman N, Chettri S, Bawa KS (2011) Consistency of local perceptions of climate change in the Kangchenjunga Himalaya landscape. Curr Sci 504–513
- Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
- Cooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018; 18 (1):1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen A, Ball S, Bell S, Bellamy R, Kett M. Managing the health effects of climate change: lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. The Lancet. 2009; 373 (9676):1693–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cruz DLA (2015) Mother Figured. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved from, 10.7208/9780226315072
- Cui W, Ouyang T, Qiu Y, Cui D (2021) Literature Review of the Implications of Exercise Rehabilitation Strategies for SARS Patients on the Recovery of COVID-19 Patients. Paper presented at the Healthcare [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Davidson D. Gaps in agricultural climate adaptation research. Nat Clim Chang. 2016; 6 (5):433–435. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diffenbaugh NS, Singh D, Mankin JS, Horton DE, Swain DL, Touma D, Tsiang M. Quantifying the influence of global warming on unprecedented extreme climate events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017; 114 (19):4881–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618082114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dimri A, Kumar D, Choudhary A, Maharana P. Future changes over the Himalayas: mean temperature. Global Planet Change. 2018; 162 :235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.01.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dullinger S, Gattringer A, Thuiller W, Moser D, Zimmermann N, Guisan A. Extinction debt of high-mountain plants under twenty-first-century climate change. Nat Clim Chang: Nature Publishing Group; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dupuis I, Dumas C. Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol. 1990; 94 (2):665–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.665. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Otegui ME. Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: a novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop Res. 2013; 142 :58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2012.11.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Carpici EB, Sammarro D, Otegui M. Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2011; 123 (2):62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.04.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellison D, Morris CE, Locatelli B, Sheil D, Cohen J, Murdiyarso D, Pokorny J. Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Glob Environ Chang. 2017; 43 :51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.01.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elsayed ZM, Eldehna WM, Abdel-Aziz MM, El Hassab MA, Elkaeed EB, Al-Warhi T, Mohammed ER. Development of novel isatin–nicotinohydrazide hybrids with potent activity against susceptible/resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bronchitis causing–bacteria. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021; 36 (1):384–393. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1868450. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- EM-DAT (2020) EMDAT: OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database, Université catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium. from http://www.emdat.be
- EPA U (2018) United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Year in Review
- Erman A, De Vries Robbe SA, Thies SF, Kabir K, Maruo M (2021) Gender Dimensions of Disaster Risk and Resilience
- Fand BB, Kamble AL, Kumar M. Will climate change pose serious threat to crop pest management: a critical review. Int J Sci Res Publ. 2012; 2 (11):1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- FAO (2018).The State of the World’s Forests 2018 - Forest Pathways to Sustainable Development.
- Fardous S Perception of climate change in Kaptai National Park. Rural Livelihoods and Protected Landscape: Co-Management in the Wetlands and Forests of Bangladesh, 186–204
- Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KH. Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2011; 30 (6):491–507. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615687. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano D, Recha J, Ambaw G, MacSween K, Solomon D, Wollenberg E (2022) Assessment of agricultural emissions, climate change mitigation and adaptation practices in Ethiopia. Clim Policy 1–18
- Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Ferreira FA (2020) Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: a comparison of European countries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119770
- Fettig CJ, Reid ML, Bentz BJ, Sevanto S, Spittlehouse DL, Wang T. Changing climates, changing forests: a western North American perspective. J Forest. 2013; 111 (3):214–228. doi: 10.5849/jof.12-085. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fischer AP. Characterizing behavioral adaptation to climate change in temperate forests. Landsc Urban Plan. 2019; 188 :72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.09.024. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flannigan M, Cantin AS, De Groot WJ, Wotton M, Newbery A, Gowman LM. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage. 2013; 294 :54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.022. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fossheim M, Primicerio R, Johannesen E, Ingvaldsen RB, Aschan MM, Dolgov AV. Recent warming leads to a rapid borealization of fish communities in the Arctic. Nat Clim Chang. 2015; 5 (7):673–677. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2647. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Füssel HM, Hildén M (2014) How is uncertainty addressed in the knowledge base for national adaptation planning? Adapting to an Uncertain Climate (pp. 41–66): Springer
- Gambín BL, Borrás L, Otegui ME. Source–sink relations and kernel weight differences in maize temperate hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2006; 95 (2–3):316–326. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.04.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gambín B, Borrás L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: a comparison across crop species. Annals of Applied Biology. 2010; 156 (1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00367.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gampe D, Nikulin G, Ludwig R. Using an ensemble of regional climate models to assess climate change impacts on water scarcity in European river basins. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 573 :1503–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.053. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- García GA, Dreccer MF, Miralles DJ, Serrago RA. High night temperatures during grain number determination reduce wheat and barley grain yield: a field study. Glob Change Biol. 2015; 21 (11):4153–4164. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13009. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garner E, Inyang M, Garvey E, Parks J, Glover C, Grimaldi A, Edwards MA. Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res. 2019; 151 :75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.003. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleditsch NP (2021) This time is different! Or is it? NeoMalthusians and environmental optimists in the age of climate change. J Peace Res 0022343320969785
- Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Toulmin C. Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science. 2010; 327 (5967):812–818. doi: 10.1126/science.1185383. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goes S, Hasterok D, Schutt DL, Klöcking M (2020) Continental lithospheric temperatures: A review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 106509
- Gorst A, Dehlavi A, Groom B. Crop productivity and adaptation to climate change in Pakistan. Environ Dev Econ. 2018; 23 (6):679–701. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X18000232. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gosling SN, Arnell NW. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim Change. 2016; 134 (3):371–385. doi: 10.1007/s10584-013-0853-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM, Ceron J-P, Dubois G. Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Ann Tour Res. 2012; 39 (1):36–58. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2011.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB. Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett. 2013; 8 (2):024041. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024041. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grieg E Responsible Consumption and Production
- Gunter BG, Rahman A, Rahman A (2008) How Vulnerable are Bangladesh’s Indigenous People to Climate Change? Bangladesh Development Research Center (BDRC)
- Hall CM, Amelung B, Cohen S, Eijgelaar E, Gössling S, Higham J, Scott D. On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J Sustain Tour. 2015; 23 (1):4–25. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2014.953544. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartmann H, Moura CF, Anderegg WR, Ruehr NK, Salmon Y, Allen CD, Galbraith D. Research frontiers for improving our understanding of drought-induced tree and forest mortality. New Phytol. 2018; 218 (1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/nph.15048. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Prueger JH. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes. 2015; 10 :4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.wace.2015.08.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Boote KJ, Kimball B, Ziska L, Izaurralde RC, Ort D, Wolfe D. Climate impacts on agriculture: implications for crop production. Agron J. 2011; 103 (2):351–370. doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0303. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P, Van Bunnik B, McNally L, Lukjancenko O, Kjeldgaard J. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun. 2019; 10 (1):1124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08853-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang S (2004) Global trade patterns in fruits and vegetables. USDA-ERS Agriculture and Trade Report No. WRS-04–06
- Huang W, Gao Q-X, Cao G-L, Ma Z-Y, Zhang W-D, Chao Q-C. Effect of urban symbiosis development in China on GHG emissions reduction. Adv Clim Chang Res. 2016; 7 (4):247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2016.12.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Tech Soc 68:101853
- Hubbart JA, Guyette R, Muzika R-M. More than drought: precipitation variance, excessive wetness, pathogens and the future of the western edge of the eastern deciduous forest. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 566 :463–467. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.108. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Butt AR, Uzma F, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Rehman A, Yousaf B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess. 2020; 192 (1):48. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7956-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Uzma F, Ali MU, Butt AR. Regional and sectoral assessment on climate-change in Pakistan: social norms and indigenous perceptions on climate-change adaptation and mitigation in relation to global context. J Clean Prod. 2018; 200 :791–808. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.272. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Intergov. Panel Clim Chang 33 from 10.1017/CBO9781107415324
- Ionescu C, Klein RJ, Hinkel J, Kumar KK, Klein R. Towards a formal framework of vulnerability to climate change. Environ Model Assess. 2009; 14 (1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10666-008-9179-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. Clim Chang Phys Sci Basis Contrib Work Gr I Fifth Assess Rep
- Ishikawa-Ishiwata Y, Furuya J (2022) Economic evaluation and climate change adaptation measures for rice production in vietnam using a supply and demand model: special emphasis on the Mekong River Delta region in Vietnam. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia (pp. 45–53). Springer, Cham
- Izaguirre C, Losada I, Camus P, Vigh J, Stenek V. Climate change risk to global port operations. Nat Clim Chang. 2021; 11 (1):14–20. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00937-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jactel H, Koricheva J, Castagneyrol B (2019) Responses of forest insect pests to climate change: not so simple. Current opinion in insect science [ PubMed ]
- Jahanzad E, Holtz BA, Zuber CA, Doll D, Brewer KM, Hogan S, Gaudin AC. Orchard recycling improves climate change adaptation and mitigation potential of almond production systems. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (3):e0229588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229588. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jurgilevich A, Räsänen A, Groundstroem F, Juhola S. A systematic review of dynamics in climate risk and vulnerability assessments. Environ Res Lett. 2017; 12 (1):013002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa5508. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karami E (2012) Climate change, resilience and poverty in the developing world. Paper presented at the Culture, Politics and Climate change conference
- Kärkkäinen L, Lehtonen H, Helin J, Lintunen J, Peltonen-Sainio P, Regina K, . . . Packalen T (2020) Evaluation of policy instruments for supporting greenhouse gas mitigation efforts in agricultural and urban land use. Land Use Policy 99:104991
- Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F, Virta MP. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2018; 26 (3):220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.005. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohfeld KE, Le Quéré C, Harrison SP, Anderson RF. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science. 2005; 308 (5718):74–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1105375. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kongsager R. Linking climate change adaptation and mitigation: a review with evidence from the land-use sectors. Land. 2018; 7 (4):158. doi: 10.3390/land7040158. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurz WA, Dymond C, Stinson G, Rampley G, Neilson E, Carroll A, Safranyik L. Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature. 2008; 452 (7190):987. doi: 10.1038/nature06777. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamperti F, Bosetti V, Roventini A, Tavoni M, Treibich T (2021) Three green financial policies to address climate risks. J Financial Stab 54:100875
- Leal Filho W, Azeiteiro UM, Balogun AL, Setti AFF, Mucova SA, Ayal D, . . . Oguge NO (2021) The influence of ecosystems services depletion to climate change adaptation efforts in Africa. Sci Total Environ 146414 [ PubMed ]
- Lehner F, Coats S, Stocker TF, Pendergrass AG, Sanderson BM, Raible CC, Smerdon JE. Projected drought risk in 1.5 C and 2 C warmer climates. Geophys Res Lett. 2017; 44 (14):7419–7428. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074117. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemery J, Knowlton K, Sorensen C (2021) Global climate change and human health: from science to practice: John Wiley & Sons
- Leppänen S, Saikkonen L, Ollikainen M (2014) Impact of Climate Change on cereal grain production in Russia: Mimeo
- Lipczynska-Kochany E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 640 :1548–1565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.376. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- livescience.com. New coronavirus may have ‘jumped’ to humans from snakes, study finds, live science,. from < https://www.livescience.com/new-coronavirus-origin-snakes.html > accessed on Jan 2020
- Lobell DB, Field CB. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett. 2007; 2 (1):014002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/2/1/014002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lobell DB, Gourdji SM. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012; 160 (4):1686–1697. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208298. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma L, Li B, Zhang T. New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives: a metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes. Water Res. 2019; 152 :191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.069. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macchi M, Oviedo G, Gotheil S, Cross K, Boedhihartono A, Wolfangel C, Howell M (2008) Indigenous and traditional peoples and climate change. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gland, Suiza
- Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 23–46). Elsevier
- Manes S, Costello MJ, Beckett H, Debnath A, Devenish-Nelson E, Grey KA, . . . Krause C (2021) Endemism increases species’ climate change risk in areas of global biodiversity importance. Biol Conserv 257:109070
- Mannig B, Pollinger F, Gafurov A, Vorogushyn S, Unger-Shayesteh K (2018) Impacts of climate change in Central Asia Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene (pp. 195–203): Elsevier
- Martínez-Alvarado O, Gray SL, Hart NC, Clark PA, Hodges K, Roberts MJ. Increased wind risk from sting-jet windstorms with climate change. Environ Res Lett. 2018; 13 (4):044002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaae3a. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matsui T, Omasa K, Horie T. The difference in sterility due to high temperatures during the flowering period among japonica-rice varieties. Plant Production Science. 2001; 4 (2):90–93. doi: 10.1626/pps.4.90. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meierrieks D (2021) Weather shocks, climate change and human health. World Dev 138:105228
- Michel D, Eriksson M, Klimes M (2021) Climate change and (in) security in transboundary river basins Handbook of Security and the Environment: Edward Elgar Publishing
- Mihiretu A, Okoyo EN, Lemma T. Awareness of climate change and its associated risks jointly explain context-specific adaptation in the Arid-tropics. Northeast Ethiopia SN Social Sciences. 2021; 1 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Millar CI, Stephenson NL. Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science. 2015; 349 (6250):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9933. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mishra A, Bruno E, Zilberman D (2021) Compound natural and human disasters: Managing drought and COVID-19 to sustain global agriculture and food sectors. Sci Total Environ 754:142210 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mosavi SH, Soltani S, Khalilian S (2020) Coping with climate change in agriculture: Evidence from Hamadan-Bahar plain in Iran. Agric Water Manag 241:106332
- Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. 10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Murshed M. Pathways to clean cooking fuel transition in low and middle income Sub-Saharan African countries: the relevance of improving energy use efficiency. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2022; 30 :396–412. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Dao NTT. Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Abbass K, Rashid S. Modelling renewable energy adoption across south Asian economies: Empirical evidence from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Int J Finan Eco. 2021; 26 (4):5425–5450. doi: 10.1002/ijfe.2073. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R. Value addition in the services sector and its heterogeneous impacts on CO2 emissions: revisiting the EKC hypothesis for the OPEC using panel spatial estimation techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (31):38951–38973. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09593-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Al-Tal R, Mahmood H, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2022) Can intra-regional trade, renewable energy use, foreign direct investments, and economic growth reduce ecological footprints in South Asia? Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy. 10.1080/15567249.2022.2038730
- Neuvonen M, Sievänen T, Fronzek S, Lahtinen I, Veijalainen N, Carter TR. Vulnerability of cross-country skiing to climate change in Finland–an interactive mapping tool. J Outdoor Recreat Tour. 2015; 11 :64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2015.06.010. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- npr.org. Please Help Me.’ What people in China are saying about the outbreak on social media, npr.org, . from < https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/01/24/799000379/please-help-me-what-people-in-china-are-saying-about-the-outbreak-on-social-medi >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ogden LE. Climate change, pathogens, and people: the challenges of monitoring a moving target. Bioscience. 2018; 68 (10):733–739. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biy101. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz AMD, Outhwaite CL, Dalin C, Newbold T. A review of the interactions between biodiversity, agriculture, climate change, and international trade: research and policy priorities. One Earth. 2021; 4 (1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.12.008. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz R. Crop genetic engineering under global climate change. Ann Arid Zone. 2008; 47 (3):343. [ Google Scholar ]
- Otegui MAE, Bonhomme R. Grain yield components in maize: I. Ear growth and kernel set. Field Crop Res. 1998; 56 (3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00093-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, . . . Dasgupta P (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Ipcc
- Pal JK. Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics. 2021; 126 (5):4173–4193. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03912-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panda R, Behera S, Kashyap P. Effective management of irrigation water for wheat under stressed conditions. Agric Water Manag. 2003; 63 (1):37–56. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00099-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pärnänen KM, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Kneis D, Berendonk TU, Cacace D, Do TT, Jaeger T. Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci Adv. 2019; 5 (3):eaau9124. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9124. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parry M, Parry ML, Canziani O, Palutikof J, Van der Linden P, Hanson C (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: Working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4): Cambridge University Press
- Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature. 2005; 438 (7066):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nature04188. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patz JA, Graczyk TK, Geller N, Vittor AY. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int J Parasitol. 2000; 30 (12–13):1395–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00141-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pautasso M, Döring TF, Garbelotto M, Pellis L, Jeger MJ. Impacts of climate change on plant diseases—opinions and trends. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2012; 133 (1):295–313. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-9936-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Cassman KG. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004; 101 (27):9971–9975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403720101. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman R, Scholes RJ, Cardoso A. Essential biodiversity variables. Science. 2013; 339 (6117):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1229931. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perera K, De Silva K, Amarasinghe M. Potential impact of predicted sea level rise on carbon sink function of mangrove ecosystems with special reference to Negombo estuary, Sri Lanka. Global Planet Change. 2018; 161 :162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pfadenhauer JS, Klötzli FA (2020) Zonal Vegetation of the Subtropical (Warm–Temperate) Zone with Winter Rain. In Global Vegetation (pp. 455–514). Springer, Cham
- Phillips JD. Environmental gradients and complexity in coastal landscape response to sea level rise. CATENA. 2018; 169 :107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pirasteh-Anosheh H, Parnian A, Spasiano D, Race M, Ashraf M (2021) Haloculture: A system to mitigate the negative impacts of pandemics on the environment, society and economy, emphasizing COVID-19. Environ Res 111228 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Pruden A, Larsson DJ, Amézquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Snape JR. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect. 2013; 121 (8):878–885. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Abbas F, Saeed S, Bakhat HF, Nasim W, Fahad S. The potential applications of picotechnology in biomedical and environmental sciences. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (1):133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06554-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Maqsood F, Tariq T, Chawla MS Climate Change Implication on Cereal Crop Productivity
- Rahman M, Alam K. Forest dependent indigenous communities’ perception and adaptation to climate change through local knowledge in the protected area—a Bangladesh case study. Climate. 2016; 4 (1):12. doi: 10.3390/cli4010012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramankutty N, Mehrabi Z, Waha K, Jarvis L, Kremen C, Herrero M, Rieseberg LH. Trends in global agricultural land use: implications for environmental health and food security. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2018; 69 :789–815. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040256. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021) Towards environmental Sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, Forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
- Reichstein M, Carvalhais N. Aspects of forest biomass in the Earth system: its role and major unknowns. Surv Geophys. 2019; 40 (4):693–707. doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09551-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reidsma P, Ewert F, Boogaard H, van Diepen K. Regional crop modelling in Europe: the impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric Syst. 2009; 100 (1–3):51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2008.12.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie H, Roser M (2014) Natural disasters. Our World in Data
- Rizvi AR, Baig S, Verdone M. Ecosystems based adaptation: knowledge gaps in making an economic case for investing in nature based solutions for climate change. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 2015. p. 48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roscher C, Fergus AJ, Petermann JS, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D. What happens to the sown species if a biodiversity experiment is not weeded? Basic Appl Ecol. 2013; 14 (3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2013.01.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane AC, Müller C, Arneth A, Khabarov N. Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (9):3268–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222463110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Iglesius A, Yang XB, Epstein PR, Chivian E (2001) Climate change and extreme weather events-implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests
- Sadras VO, Slafer GA. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop Res. 2012; 127 :215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salvucci ME, Crafts-Brandner SJ. Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. 2004; 120 (2):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.0173.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santos WS, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Garcez LM, Abad-Franch F. Deforestation effects on Attalea palms and their resident Rhodnius, vectors of Chagas disease, in eastern Amazonia. PLoS ONE. 2021; 16 (5):e0252071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252071. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarkar P, Debnath N, Reang D (2021) Coupled human-environment system amid COVID-19 crisis: a conceptual model to understand the nexus. Sci Total Environ 753:141757 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Schlenker W, Roberts MJ. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009; 106 (37):15594–15598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906865106. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoene DH, Bernier PY. Adapting forestry and forests to climate change: a challenge to change the paradigm. Forest Policy Econ. 2012; 24 :12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.forpol.2011.04.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schuurmans C (2021) The world heat budget: expected changes Climate Change (pp. 1–15): CRC Press
- Scott D. Sustainable Tourism and the Grand Challenge of Climate Change. Sustainability. 2021; 13 (4):1966. doi: 10.3390/su13041966. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D, McBoyle G, Schwartzentruber M. Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Climate Res. 2004; 27 (2):105–117. doi: 10.3354/cr027105. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Semenov MA. Impacts of climate change on wheat in England and Wales. J R Soc Interface. 2009; 6 (33):343–350. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0285. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaffril HAM, Krauss SE, Samsuddin SF. A systematic review on Asian’s farmers’ adaptation practices towards climate change. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 644 :683–695. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.349. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019) Foreign direct Investment–CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Product 217:603–614
- Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in Top-10 polluted countries: Fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
- Sharma R. Impacts on human health of climate and land use change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. Mt Res Dev. 2012; 32 (4):480–486. doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-12-00068.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P. Examining the impacts of economic and demographic aspects on the ecological footprint in South and Southeast Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (29):36970–36982. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09659-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smit B, Burton I, Klein RJ, Wandel J (2000) An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability Societal adaptation to climate variability and change (pp. 223–251): Springer
- Song Y, Fan H, Tang X, Luo Y, Liu P, Chen Y (2021) The effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on ischemic stroke and the possible underlying mechanisms. Int J Neurosci 1–20 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Sovacool BK, Griffiths S, Kim J, Bazilian M (2021) Climate change and industrial F-gases: a critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 141:110759
- Stewart JA, Perrine JD, Nichols LB, Thorne JH, Millar CI, Goehring KE, Wright DH. Revisiting the past to foretell the future: summer temperature and habitat area predict pika extirpations in California. J Biogeogr. 2015; 42 (5):880–890. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner G, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, . . . Midgley P (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Working group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth assessment report: Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1535p
- Stone P, Nicolas M. Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Funct Plant Biol. 1994; 21 (6):887–900. doi: 10.1071/PP9940887. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Su H-C, Liu Y-S, Pan C-G, Chen J, He L-Y, Ying G-G. Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system: from drinking water source to tap water. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 616 :453–461. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.318. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunderlin WD, Angelsen A, Belcher B, Burgers P, Nasi R, Santoso L, Wunder S. Livelihoods, forests, and conservation in developing countries: an overview. World Dev. 2005; 33 (9):1383–1402. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2004.10.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symanski E, Han HA, Han I, McDaniel M, Whitworth KW, McCurdy S, . . . Delclos GL (2021) Responding to natural and industrial disasters: partnerships and lessons learned. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 1–4 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Tao F, Yokozawa M, Xu Y, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z. Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol. 2006; 138 (1–4):82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tebaldi C, Hayhoe K, Arblaster JM, Meehl GA. Going to the extremes. Clim Change. 2006; 79 (3–4):185–211. doi: 10.1007/s10584-006-9051-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Testa G, Koon E, Johannesson L, McKenna G, Anthony T, Klintmalm G, Gunby R (2018) This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
- Thornton PK, Lipper L (2014) How does climate change alter agricultural strategies to support food security? (Vol. 1340): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
- Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag. 2003; 14 (3):207–222. doi: 10.1111/1467-8551.00375. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNEP (2017) United nations environment programme: frontiers 2017. from https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/antimicrobial-resistance - environmental-pollution-among-biggest
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Ene Policy 162:112780
- Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P. Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: Do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Rene. Energy. 2022; 183 :90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.067. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022a) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An advanced panel data simulation. Energy 241:122515
- Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA. What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renew Energy. 2021; 168 :1165–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Urban MC. Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science. 2015; 348 (6234):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4984. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vale MM, Arias PA, Ortega G, Cardoso M, Oliveira BF, Loyola R, Scarano FR (2021) Climate change and biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest: best climatic models, predicted changes and impacts, and adaptation options The Atlantic Forest (pp. 253–267): Springer
- Vedwan N, Rhoades RE. Climate change in the Western Himalayas of India: a study of local perception and response. Climate Res. 2001; 19 (2):109–117. doi: 10.3354/cr019109. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vega CR, Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Uhart SA, Valentinuz OR. Seed number as a function of growth. A comparative study in soybean, sunflower, and maize. Crop Sci. 2001; 41 (3):748–754. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2001.413748x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vergés A, Doropoulos C, Malcolm HA, Skye M, Garcia-Pizá M, Marzinelli EM, Vila-Concejo A. Long-term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016; 113 (48):13791–13796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610725113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheyen R (2005) Climate change damage and international law: prevention duties and state responsibility (Vol. 54): Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
- Waheed A, Fischer TB, Khan MI. Climate Change Policy Coherence across Policies, Plans, and Strategies in Pakistan—implications for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Plan. Environ Manage. 2021; 67 (5):793–810. doi: 10.1007/s00267-021-01449-y. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasiq M, Ahmad M (2004) Sustaining forests: a development strategy: The World Bank
- Watts N, Adger WN, Agnolucci P, Blackstock J, Byass P, Cai W, Cooper A. Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet. 2015; 386 (10006):1861–1914. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weed AS, Ayres MP, Hicke JA. Consequences of climate change for biotic disturbances in North American forests. Ecol Monogr. 2013; 83 (4):441–470. doi: 10.1890/13-0160.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisheimer A, Palmer T (2005) Changing frequency of occurrence of extreme seasonal temperatures under global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32(20)
- Wernberg T, Bennett S, Babcock RC, De Bettignies T, Cure K, Depczynski M, Hovey RK. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science. 2016; 353 (6295):169–172. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8745. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO (2018) WHO, 2018. Antimicrobial resistance
- Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN. Why is the world green? The interactions of top–down and bottom–up processes in terrestrial vegetation ecology. Plant Ecolog Divers. 2016; 9 (2):127–140. doi: 10.1080/17550874.2016.1178353. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiranata IJ, Simbolon K. Increasing awareness capacity of disaster potential as a support to achieve sustainable development goal (sdg) 13 in lampung province. Jurnal Pir: Power in International Relations. 2021; 5 (2):129–146. doi: 10.22303/pir.5.2.2021.129-146. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiréhn L. Nordic agriculture under climate change: a systematic review of challenges, opportunities and adaptation strategies for crop production. Land Use Policy. 2018; 77 :63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu D, Su Y, Xi H, Chen X, Xie B. Urban and agriculturally influenced water contribute differently to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in a mega-city river network. Water Res. 2019; 158 :11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu HX (2020) Losing Steam?—An industry origin analysis of China’s productivity slowdown Measuring Economic Growth and Productivity (pp. 137–167): Elsevier
- Wu H, Qian H, Chen J, Huo C. Assessment of agricultural drought vulnerability in the Guanzhong Plain. China Water Resources Management. 2017; 31 (5):1557–1574. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1594-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie W, Huang J, Wang J, Cui Q, Robertson R, Chen K (2018) Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: the responses from market and trade. China Econ Rev
- Xu J, Sharma R, Fang J, Xu Y. Critical linkages between land-use transition and human health in the Himalayan region. Environ Int. 2008; 34 (2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.08.004. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav MK, Singh R, Singh K, Mall R, Patel C, Yadav S, Singh M. Assessment of climate change impact on productivity of different cereal crops in Varanasi. India J Agrometeorol. 2015; 17 (2):179–184. doi: 10.54386/jam.v17i2.1000. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang B, Usman M. Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sust Prod Cons. 2021; 28 :893–910. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu Z, Razzaq A, Rehman A, Shah A, Jameel K, Mor RS (2021) Disruption in global supply chain and socio-economic shocks: a lesson from COVID-19 for sustainable production and consumption. Oper Manag Res 1–16
- Zarnetske PL, Skelly DK, Urban MC. Biotic multipliers of climate change. Science. 2012; 336 (6088):1516–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.1222732. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M, Liu N, Harper R, Li Q, Liu K, Wei X, Liu S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J Hydrol. 2017; 546 :44–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.040. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does Structural Transformation in Economy Impact Inequality in Renewable Energy Productivity? Implications for Sustainable Development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050

What Is Climate Change?
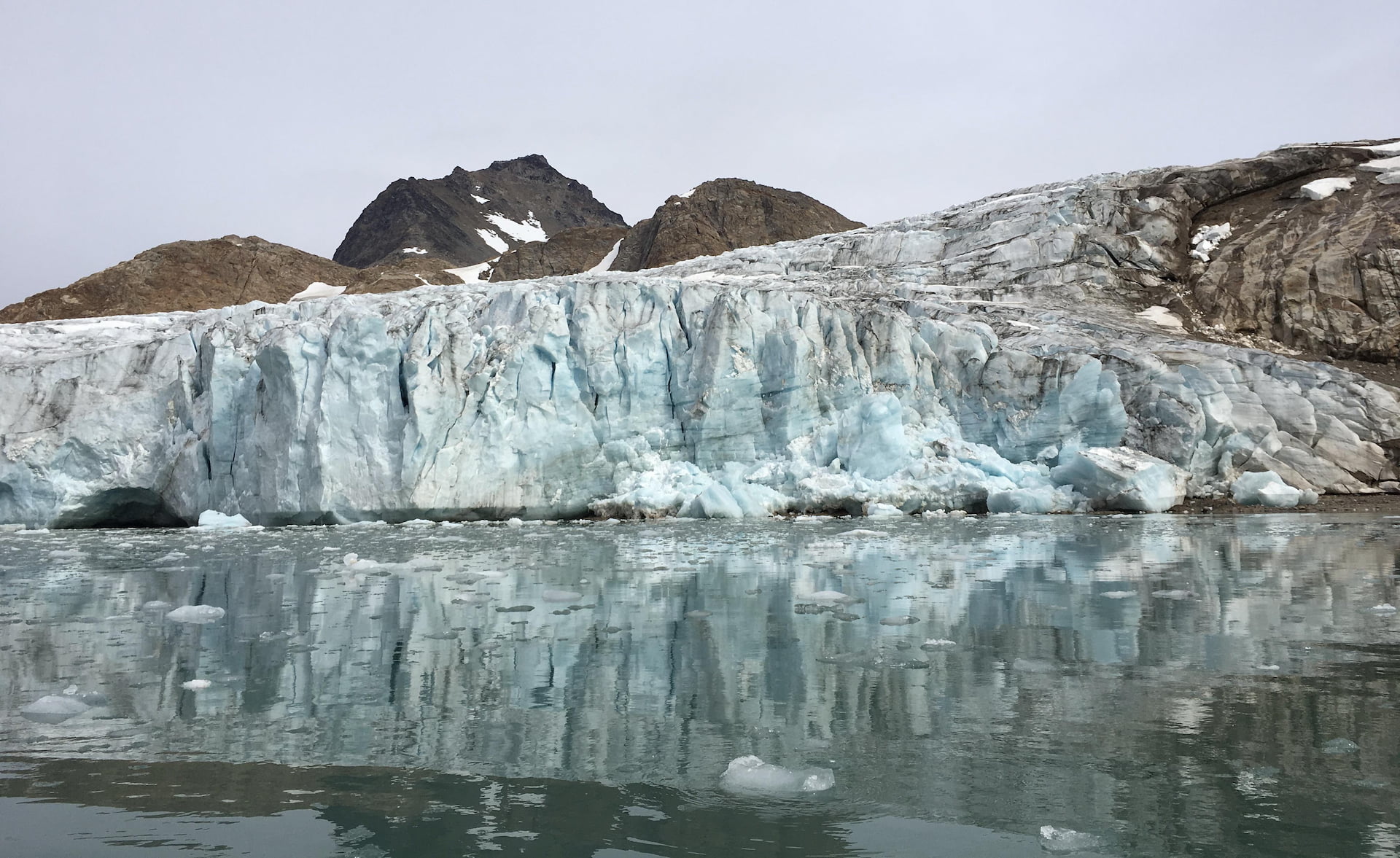

Climate change is a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth’s local, regional and global climates. These changes have a broad range of observed effects that are synonymous with the term.
Changes observed in Earth’s climate since the mid-20th century are driven by human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere, raising Earth’s average surface temperature. Natural processes, which have been overwhelmed by human activities, can also contribute to climate change, including internal variability (e.g., cyclical ocean patterns like El Niño, La Niña and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation) and external forcings (e.g., volcanic activity, changes in the Sun’s energy output , variations in Earth’s orbit ).
Scientists use observations from the ground, air, and space, along with computer models , to monitor and study past, present, and future climate change. Climate data records provide evidence of climate change key indicators, such as global land and ocean temperature increases; rising sea levels; ice loss at Earth’s poles and in mountain glaciers; frequency and severity changes in extreme weather such as hurricanes, heatwaves, wildfires, droughts, floods, and precipitation; and cloud and vegetation cover changes.
“Climate change” and “global warming” are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings. Similarly, the terms "weather" and "climate" are sometimes confused, though they refer to events with broadly different spatial- and timescales.
What Is Global Warming?
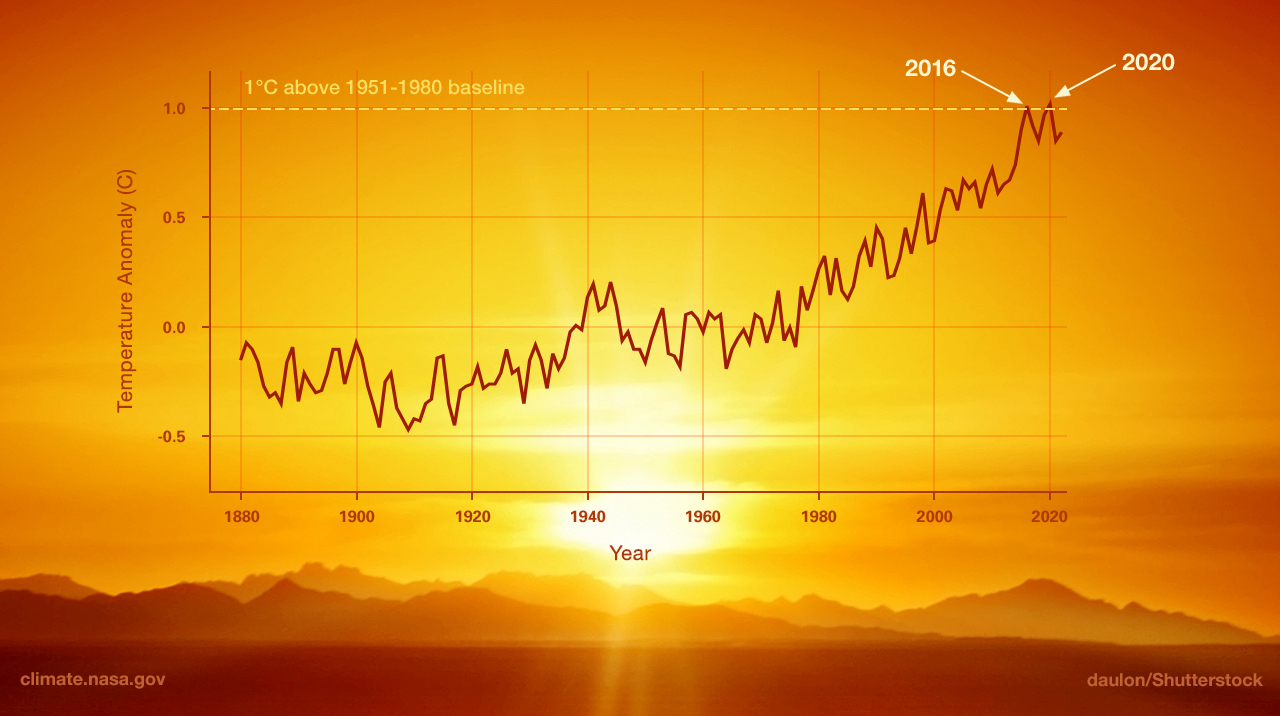
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s surface observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere. This term is not interchangeable with the term "climate change."
Since the pre-industrial period, human activities are estimated to have increased Earth’s global average temperature by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit), a number that is currently increasing by more than 0.2 degrees Celsius (0.36 degrees Fahrenheit) per decade. The current warming trend is unequivocally the result of human activity since the 1950s and is proceeding at an unprecedented rate over millennia.
Weather vs. Climate
“if you don’t like the weather in new england, just wait a few minutes.” - mark twain.
Weather refers to atmospheric conditions that occur locally over short periods of time—from minutes to hours or days. Familiar examples include rain, snow, clouds, winds, floods, or thunderstorms.
Climate, on the other hand, refers to the long-term (usually at least 30 years) regional or even global average of temperature, humidity, and rainfall patterns over seasons, years, or decades.
Find Out More: A Guide to NASA’s Global Climate Change Website
This website provides a high-level overview of some of the known causes, effects and indications of global climate change:
Evidence. Brief descriptions of some of the key scientific observations that our planet is undergoing abrupt climate change.
Causes. A concise discussion of the primary climate change causes on our planet.
Effects. A look at some of the likely future effects of climate change, including U.S. regional effects.
Vital Signs. Graphs and animated time series showing real-time climate change data, including atmospheric carbon dioxide, global temperature, sea ice extent, and ice sheet volume.
Earth Minute. This fun video series explains various Earth science topics, including some climate change topics.
Other NASA Resources
Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio. An extensive collection of animated climate change and Earth science visualizations.
Sea Level Change Portal. NASA's portal for an in-depth look at the science behind sea level change.
NASA’s Earth Observatory. Satellite imagery, feature articles and scientific information about our home planet, with a focus on Earth’s climate and environmental change.
Header image is of Apusiaajik Glacier, and was taken near Kulusuk, Greenland, on Aug. 26, 2018, during NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) field operations. Learn more here . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- XAT Cut Off 2024
- XAT Score vs Percentile 2024
- CAT Score Vs Percentile
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Essay on Climate Change
Climate Change Essay - The globe is growing increasingly sensitive to climate change. It is currently a serious worldwide concern. The term "Climate Change" describes changes to the earth's climate. It explains the atmospheric changes that have occurred across time, spanning from decades to millions of years. Here are some sample essays on climate change.
100 Words Essay on Climate Change
200 words essay on climate change, 500 words essay on climate change.

The climatic conditions on Earth are changing due to climate change. Several internal and external variables, such as solar radiation, variations in the Earth's orbit, volcanic eruptions, plate tectonics, etc., are to blame for this.
There are strategies for climate change reduction. If not implemented, the weather might get worse, there might be water scarcity, there could be lower agricultural output, and it might affect people's ability to make a living. In order to breathe clean air and drink pure water, you must concentrate on limiting human activity. These are the simple measures that may be taken to safeguard the environment and its resources.
The climate of the Earth has changed significantly over time. While some of these changes were brought on by natural events like volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires, etc., many of the changes were brought on by human activity. The burning of fossil fuels, domesticating livestock, and other human activities produce a significant quantity of greenhouse gases. This results in an increase of greenhouse effect and global warming which are the major causes for climate change.
Reasons of Climate Change
Some of the reasons of climate change are:
Deforestation
Excessive use of fossil fuels
Water and soil pollution
Plastic and other non biodegradable waste
Wildlife and nature extinction
Consequences of Climate Change
All kinds of life on earth will be affected by climate change if it continues to change at the same pace. The earth's temperature will increase, the monsoon patterns will shift, the sea level will rise, and there will be more frequent storms, volcano eruptions, and other natural calamities. The earth's biological and ecological equilibrium will be disturbed. Humans won't be able to access clean water or air to breathe when the environment becomes contaminated. The end of life on this earth is imminent. To reduce the issue of climate change, we need to bring social awareness along with strict measures to protect and preserve the natural environment.
A shift in the world's climatic pattern is referred to as climate change. Over the centuries, the climate pattern of our planet has undergone modifications. The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has significantly grown.
When Did Climate Change Begin
It is possible to see signs of climate change as early as the beginning of the industrial revolution. The pace at which the manufacturers produced things on a large scale required a significant amount of raw materials. Since the raw materials being transformed into finished products now have such huge potential for profit, these business models have spread quickly over the world. Hazardous substances and chemicals build up in the environment as a result of company emissions and waste disposal.
Although climate change is a natural occurrence, it is evident that human activity is turning into the primary cause of the current climate change situation. The major cause is the growing population. Natural resources are utilised more and more as a result of the population's fast growth placing a heavy burden on the available resources. Over time, as more and more products and services are created, pollution will eventually increase.
Causes of Climate Change
There are a number of factors that have contributed towards weather change in the past and continue to do so. Let us look at a few:
Solar Radiation |The climate of earth is determined by how quickly the sun's energy is absorbed and distributed throughout space. This energy is transmitted throughout the world by the winds, ocean currents etc which affects the climatic conditions of the world. Changes in solar intensity have an effect on the world's climate.
Deforestation | The atmosphere's carbon dioxide is stored by trees. As a result of their destruction, carbon dioxide builds up more quickly since there are no trees to absorb it. Additionally, trees release the carbon they stored when we burn them.
Agriculture | Many kinds of greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere by growing crops and raising livestock. Animals, for instance, create methane, a greenhouse gas that is 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide. The nitrous oxide used in fertilisers is roughly 300 times more strong than carbon dioxide.
How to Prevent Climate Change
We need to look out for drastic steps to stop climate change since it is affecting the resources and life on our planet. We can stop climate change if the right solutions are put in place. Here are some strategies for reducing climate change:
Raising public awareness of climate change
Prohibiting tree-cutting and deforestation.
Ensure the surroundings are clean.
Refrain from using chemical fertilisers.
Water and other natural resource waste should be reduced.
Protect the animals and plants.
Purchase energy-efficient goods and equipment.
Increase the number of trees in the neighbourhood and its surroundings.
Follow the law and safeguard the environment's resources.
Reduce the amount of energy you use.
During the last few decades especially, climate change has grown to be of concern. Global concern has been raised over changes in the Earth's climatic pattern. The causes of climate change are numerous, as well as the effects of it and it is our responsibility as inhabitants of this planet to look after its well being and leave it in a better condition for future generations.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Geotechnical engineer
The role of geotechnical engineer starts with reviewing the projects needed to define the required material properties. The work responsibilities are followed by a site investigation of rock, soil, fault distribution and bedrock properties on and below an area of interest. The investigation is aimed to improve the ground engineering design and determine their engineering properties that include how they will interact with, on or in a proposed construction.
The role of geotechnical engineer in mining includes designing and determining the type of foundations, earthworks, and or pavement subgrades required for the intended man-made structures to be made. Geotechnical engineering jobs are involved in earthen and concrete dam construction projects, working under a range of normal and extreme loading conditions.
Cartographer
How fascinating it is to represent the whole world on just a piece of paper or a sphere. With the help of maps, we are able to represent the real world on a much smaller scale. Individuals who opt for a career as a cartographer are those who make maps. But, cartography is not just limited to maps, it is about a mixture of art , science , and technology. As a cartographer, not only you will create maps but use various geodetic surveys and remote sensing systems to measure, analyse, and create different maps for political, cultural or educational purposes.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Product Manager
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Operations manager.
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Bank Probationary Officer (PO)
Investment director.
An investment director is a person who helps corporations and individuals manage their finances. They can help them develop a strategy to achieve their goals, including paying off debts and investing in the future. In addition, he or she can help individuals make informed decisions.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
An expert in plumbing is aware of building regulations and safety standards and works to make sure these standards are upheld. Testing pipes for leakage using air pressure and other gauges, and also the ability to construct new pipe systems by cutting, fitting, measuring and threading pipes are some of the other more involved aspects of plumbing. Individuals in the plumber career path are self-employed or work for a small business employing less than ten people, though some might find working for larger entities or the government more desirable.
Construction Manager
Individuals who opt for a career as construction managers have a senior-level management role offered in construction firms. Responsibilities in the construction management career path are assigning tasks to workers, inspecting their work, and coordinating with other professionals including architects, subcontractors, and building services engineers.
Urban Planner
Urban Planning careers revolve around the idea of developing a plan to use the land optimally, without affecting the environment. Urban planning jobs are offered to those candidates who are skilled in making the right use of land to distribute the growing population, to create various communities.
Urban planning careers come with the opportunity to make changes to the existing cities and towns. They identify various community needs and make short and long-term plans accordingly.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Naval Architect
A Naval Architect is a professional who designs, produces and repairs safe and sea-worthy surfaces or underwater structures. A Naval Architect stays involved in creating and designing ships, ferries, submarines and yachts with implementation of various principles such as gravity, ideal hull form, buoyancy and stability.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Veterinary Doctor
Pathologist.
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Speech Therapist
Gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
Hospital Administrator
The hospital Administrator is in charge of organising and supervising the daily operations of medical services and facilities. This organising includes managing of organisation’s staff and its members in service, budgets, service reports, departmental reporting and taking reminders of patient care and services.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Videographer
Multimedia specialist.
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Linguistic meaning is related to language or Linguistics which is the study of languages. A career as a linguistic meaning, a profession that is based on the scientific study of language, and it's a very broad field with many specialities. Famous linguists work in academia, researching and teaching different areas of language, such as phonetics (sounds), syntax (word order) and semantics (meaning).
Other researchers focus on specialities like computational linguistics, which seeks to better match human and computer language capacities, or applied linguistics, which is concerned with improving language education. Still, others work as language experts for the government, advertising companies, dictionary publishers and various other private enterprises. Some might work from home as freelance linguists. Philologist, phonologist, and dialectician are some of Linguist synonym. Linguists can study French , German , Italian .
Public Relation Executive
Travel journalist.
The career of a travel journalist is full of passion, excitement and responsibility. Journalism as a career could be challenging at times, but if you're someone who has been genuinely enthusiastic about all this, then it is the best decision for you. Travel journalism jobs are all about insightful, artfully written, informative narratives designed to cover the travel industry. Travel Journalist is someone who explores, gathers and presents information as a news article.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
Merchandiser.
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Metallurgical Engineer
A metallurgical engineer is a professional who studies and produces materials that bring power to our world. He or she extracts metals from ores and rocks and transforms them into alloys, high-purity metals and other materials used in developing infrastructure, transportation and healthcare equipment.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
ITSM Manager
Information security manager.
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
Business Intelligence Developer
Applications for admissions are open..

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN

NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score upto 100% marks

JEE Main high scoring chapters and topics
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Study 40% syllabus and score upto 100% marks in JEE
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Scientists Just Gave Humanity an Overdue Reality Check. The World Will Be Better for It.

By Stephen Lezak
Mr. Lezak is a researcher at the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford who studies the politics of climate change.
The world’s leading institution on geology declined a proposal on Wednesday to confirm that the planet has entered a new geologic epoch , doubling down on its bombshell announcement earlier this month. The notion that we’re in the “Anthropocene” — the proposed name for a geologic period defined by extensive human disturbance — has become a common theme in environmental circles for the last 15 years. To many proponents, the term is an essential vindication, the planetary equivalent of a long-sought diagnosis of a mysterious illness. But geologists weren’t convinced.
The international geology commission’s decision this week to uphold its vote of 12 to 4 may seem confusing, since by some measures humans have already become the dominant geologic force on the earth’s surface. But setting the science aside for a moment, there’s a reason to celebrate, because the politics behind the Anthropocene label were rotten to begin with.
For starters, the word Anthropocene problematically implies that humans as a species are responsible for the sorry state of the earth’s environments. While technically true, only a fraction of humanity, driven by greed and rapacious capitalism, is responsible for burning through the planet’s resources at an unsustainable rate. Billions of humans still lead lives with relatively modest environmental footprints, yet the terminology of the Anthropocene wrongly lays blame at their feet. Responding to the vote, a group of outside scientists wisely noted in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution that “our impacts have less to do with being human and more to do with ways of being human.”
What’s more, inaugurating a new geologic epoch is an unacceptable act of defeatism. Geologic epochs are not fleeting moments. The shortest one, the Holocene — the one we live in — is 11,700 years long and counting. The idea that we are entering a new epoch defined by human-caused environmental disaster implies that we won’t be getting out of this mess anytime soon. In that way, the Anthropocene forecloses on the possibility that the geologic future might be better than the present.
By placing Homo sapiens center stage, the Anthropocene also deepens a stark and inaccurate distinction between humanity and the planet that sustains us. The idea of “nature” as something separate from humankind is a figment of the Western imagination. We should be wary of language that further separates us from the broader constellation of life to which we belong.
Before the recent vote, the Anthropocene epoch had cleared several key hurdles on the path to scientific consensus. The International Commission on Stratigraphy, the global authority on demarcating the planet’s history, established a dedicated working group in 2009. Ten years later, the group formally recommended adopting the new epoch. But the proposal still had to be approved by a matryoshka doll of committees within the commission and its parent body, the International Union of Geological Sciences.
By all accounts, the process leading up to the vote was highly contentious. After the initial vote was held, scientists in the minority called for it to be annulled , citing procedural issues. This week, the committee’s parent authority stepped in to uphold the results.
Ultimately, what scuttled the proposal was disagreement about where to mark the end of the Holocene. The Anthropocene Working Group had settled on 1952, the year that airborne plutonium residue from testing hydrogen bombs fell across broad stretches of the planet. That ash, scientists reasoned, would leave a sedimentary signature akin to the boundaries that mark ancient geologic transitions. But scientists at the stratigraphy commission objected — what about the dawn of agriculture or the Industrial Revolution? After all, the human footprint on the planet long predates the atomic age.
“It’s very obvious to me that human activity started long before 1952,” Phil Gibbard, a founding member of the Anthropocene Working Group who is the secretary-general of the commission, said when we spoke on Thursday. “It just didn’t make sense to draw a rigid boundary within my lifetime.”
In recent years, philosophers have bandied about alternative names: the Capitalocene , the Plantationocene and even the Ravencene , a reference to the raven who figures widely in North Pacific Indigenous mythology as a trickster figure, reminding humans to be humble amid our destructive capacity. For my part, I’m partial to “post-Holocene,” an admission that the world is vastly different than it was 10,000 years ago, but that we can’t possibly predict — or name — what it might look like in another 10,000 years.
In the end, it might be too late to find a better term. The “Anthropocene” has already entered the popular lexicon, from the cover of The Economist to the title of a Grimes album. The scientists who coined the term do not have the power to extinguish it.
Whatever we choose to call these troubled times, what matters most is that we keep an open mind about what the future holds and maintain an appreciation for the complexity of the issues we face. The scars humanity leaves upon the earth are much too fraught to be represented with a single line drawn across time.
Looking ahead, we should follow the geologists’ lead and keep a healthy skepticism of the A-word. After all, nothing is more hubristic than reckless tyrants who names the world after themselves — think Stalingrad, Constantinople or Alexandria.
Geologists will continue to disagree over what to call the present era. The rest of us must continue the difficult politics of caring for a planet that can (still) support a panoply of life.
Stephen Lezak is a researcher at the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford who studies the politics of climate change.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Climate Change Essay
500+ words essay on climate change.
Climate change is a major global challenge today, and the world is becoming more vulnerable to this change. Climate change refers to the changes in Earth’s climate condition. It describes the changes in the atmosphere which have taken place over a period ranging from decades to millions of years. A recent report from the United Nations predicted that the average global temperature could increase by 6˚ Celsius at the end of the century. Climate change has an adverse effect on the environment and ecosystem. With the help of this essay, students will get to know the causes and effects of climate change and possible solutions. Also, they will be able to write essays on similar topics and can boost their writing skills.
What Causes Climate Change?
The Earth’s climate has always changed and evolved. Some of these changes have been due to natural causes such as volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires etc., but quite a few of them are due to human activities. Human activities such as deforestation, burning fossil fuels, farming livestock etc., generate an enormous amount of greenhouse gases. This results in the greenhouse effect and global warming which are the major causes of climate change.
Effects of Climate Change
If the current situation of climate change continues in a similar manner, then it will impact all forms of life on the earth. The earth’s temperature will rise, the monsoon patterns will change, sea levels will rise, and storms, volcanic eruptions and natural disasters will occur frequently. The biological and ecological balance of the earth will get disturbed. The environment will get polluted and humans will not be able to get fresh air to breathe and fresh water to drink. Life on earth will come to an end.
Steps to be Taken to Reduce Climate Change
The Government of India has taken many measures to improve the dire situation of Climate Change. The Ministry of Environment and Forests is the nodal agency for climate change issues in India. It has initiated several climate-friendly measures, particularly in the area of renewable energy. India took several steps and policy initiatives to create awareness about climate change and help capacity building for adaptation measures. It has initiated a “Green India” programme under which various trees are planted to make the forest land more green and fertile.
We need to follow the path of sustainable development to effectively address the concerns of climate change. We need to minimise the use of fossil fuels, which is the major cause of global warming. We must adopt alternative sources of energy, such as hydropower, solar and wind energy to make a progressive transition to clean energy. Mahatma Gandhi said that “Earth provides enough to satisfy every man’s need, but not any man’s greed”. With this view, we must remodel our outlook and achieve the goal of sustainable development. By adopting clean technologies, equitable distribution of resources and addressing the issues of equity and justice, we can make our developmental process more harmonious with nature.
We hope students liked this essay on Climate Change and gathered useful information on this topic so that they can write essays in their own words. To get more study material related to the CBSE, ICSE, State Board and Competitive exams, keep visiting the BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on climate change Essay
What are the reasons for climate change.
1. Deforestation 2. Excessive usage of fossil fuels 3. Water, Soil pollution 4. Plastic and other non-biodegradable waste 5. Wildlife and nature extinction
How can we save this climate change situation?
1. Avoid over usage of natural resources 2. Do not use or buy items made from animals 3. Avoid plastic usage and pollution
Are there any natural causes for climate change?
Yes, some of the natural causes for climate change are: 1. Solar variations 2. Volcanic eruption and tsunamis 3. Earth’s orbital changes
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

- IMF at a Glance
- Surveillance
- Capacity Development
- IMF Factsheets List
- IMF Members
- IMF Timeline
- Senior Officials
- Job Opportunities
- Archives of the IMF
- Climate Change
- Fiscal Policies
- Income Inequality
Flagship Publications
Other publications.
- World Economic Outlook
- Global Financial Stability Report
- Fiscal Monitor
- External Sector Report
- Staff Discussion Notes
- Working Papers
- IMF Research Perspectives
- Economic Review
- Global Housing Watch
- Commodity Prices
- Commodities Data Portal
- IMF Researchers
- Annual Research Conference
- Other IMF Events
IMF reports and publications by country
Regional offices.
- IMF Resident Representative Offices
- IMF Regional Reports
- IMF and Europe
- IMF Members' Quotas and Voting Power, and Board of Governors
- IMF Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
- IMF Capacity Development Office in Thailand (CDOT)
- IMF Regional Office in Central America, Panama, and the Dominican Republic
- Eastern Caribbean Currency Union (ECCU)
- IMF Europe Office in Paris and Brussels
- IMF Office in the Pacific Islands
- How We Work
- IMF Training
- Digital Training Catalog
- Online Learning
- Our Partners
- Country Stories
- Technical Assistance Reports
- High-Level Summary Technical Assistance Reports
- Strategy and Policies
For Journalists
- Country Focus
- Chart of the Week
- Communiqués
- Mission Concluding Statements
- Press Releases
- Statements at Donor Meetings
- Transcripts
- Views & Commentaries
- Article IV Consultations
- Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP)
- Seminars, Conferences, & Other Events
- E-mail Notification
Press Center
The IMF Press Center is a password-protected site for working journalists.
- Login or Register
- Information of interest
- About the IMF
- Conferences
- Press briefings
- Special Features
- Middle East and Central Asia
- Economic Outlook
- Annual and spring meetings
- Most Recent
- Most Popular
- IMF Finances
- Additional Data Sources
- World Economic Outlook Databases
- Climate Change Indicators Dashboard
- IMF eLibrary-Data
- International Financial Statistics
- G20 Data Gaps Initiative
- Public Sector Debt Statistics Online Centralized Database
- Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Financial Access Survey
- Government Finance Statistics
- Publications Advanced Search
- IMF eLibrary
- IMF Bookstore
- Publications Newsletter
- Essential Reading Guides
- Regional Economic Reports
- Country Reports
- Departmental Papers
- Policy Papers
- Selected Issues Papers
- All Staff Notes Series
- Analytical Notes
- Fintech Notes
- How-To Notes
- Staff Climate Notes
IMF Working Papers
Cross-border impacts of climate policy packages in north america.
Author/Editor:
Jean-Marc Fournier ; Tannous Kass-Hanna ; Liam Masterson ; Anne-Charlotte Paret ; Sneha D Thube
Publication Date:
March 22, 2024
Electronic Access:
Free Download . Use the free Adobe Acrobat Reader to view this PDF file
Disclaimer: IMF Working Papers describe research in progress by the author(s) and are published to elicit comments and to encourage debate. The views expressed in IMF Working Papers are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views of the IMF, its Executive Board, or IMF management.
We quantify cross-border effects of the recent climate mitigation policies introduced in Canada and the U.S., using the global general equilibrium model IMF-ENV. Notably, with the substantial emission reductions from Canada’s carbon tax-led mitigation policies and the U.S.’ Inflation Reduction Act, these two countries would bridge two-thirds of the gap toward their Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) goals. While the broadly divergent policies are believed to elicit competitiveness concerns, we find the aggregate cross-border effects within North America to be very limited and restricted to the energy intensive and trade exposed industries. Potential carbon leakages are also found to be negligible. A more meaningful difference triggered by policy heterogeneity is rather domestic, especially with U.S. subsidies increasing energy output while the Canada model with a carbon tax would marginally decrease it. This analysis is complemented by a stylized model illustrating how such divergence can affect the terms of trade, but also how these effects can be countered by exchange rate flexibility, border adjustments or domestic taxation.
Working Paper No. 2024/068
9798400268960/1018-5941
WPIEA2024068
Please address any questions about this title to [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The resolution sends a strong message on the need to mainstream the environment in the United Nations system, and should mobilize Member States, the United Nations system, and other stakeholders in view of the important milestones ahead. ... Also by the text, the Assembly would stress the need to strengthen the global response to climate change ...
Option 1: Develop a climate plan. Scientists say that in order to prevent the average global temperature from rising more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, the threshold beyond which the dangers of global ...
Over 200 countries—193 countries plus the 27 members of the European Union—have signed the Paris Climate Agreement, a treaty created in 2015 to fight climate change on a global scale.
It would also take far less land to grow the crops necessary to feed humans than livestock, allowing more room for planting trees. Stop Cutting Down Trees —Every year, 33 million acres of ...
Bahçeşehir College is committed to increasing students' awareness of the changing world we live in. This climate change essay competition saw many students submitting well thought out pieces of writing. These essays were marked on their format, creativity, organisation, clarity, unity/development of thought, and grammar/mechanics.
The scientific, economic, and policy aspects of climate change are already a challenge to communicate, without factoring in the distractions and deflections from organized programs of misinformation and denial. Here, four scholars, each with decades of research on the climate threat, take on the task of explaining our current understanding of ...
ESSAY; 18 March 2024; ... Climate change, in fact, might be one of the more certain components of our future. Social and political developments are even more difficult to predict. Can anyone ...
Niklas Hagelberg, UNEP's Climate Change Coordinator. 6. Shop local and buy sustainable. To reduce your food's carbon footprint, buy local and seasonal foods. You'll be helping small businesses and farms in your area and reducing fossil fuel emissions associated with transport and cold chain storage.
In 2015, the Paris Agreement, which is legally binding on climate change, has been accepted by approximately 191 countries to limit global warming to below 2, if possible, to 1.5. The countries have committed to achieve this primary goal and minimise global warming. To accomplish this goal requires all parties to put forward their best efforts ...
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Climate Explained is a collection of short primers that answer diverse climate change questions, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security. Image 1. Example Climate Explained essays on the Yale Climate ...
Improve farming and encourage vegan diets. One of the best ways for individuals to help stop climate change is by reducing their meat and dairy consumption, or by going fully vegan. Businesses and food retailers can improve farming practices and provide more plant-based products to help people make the shift.
Renewable Energy. Transitioning from fossil fuels to clean energy is the key to winning the fight against climate change. Here are the most common sources of renewable energy —and one source of ...
change happens widely because we are burning fossil fuels and that increases gases such as. CO2, methane, and some other gases in the atmosphere" (phone interview). According to the. Australian Greenhouse Office, the world depends on fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and natural. gas for 80% of its energy needs.
Last year a group of scientists published research documenting the exceptional surge from wetlands, which exceeded average projections from even the most pessimistic warming scenarios drawn up by ...
CO2 is a global pollutant that can't be locally contained. "The first key feature of climate change that puts it at odds with past environmental issues is that it's a global pollutant, rather than a local pollutant. [Whether] I release a ton of CO2 in Cambridge, Massachusetts, or in London, it does the same damage to the globe," Knittel ...
Guest Essay. The Best Way to Find Out if We Can Cool the Planet. March 17, 2024. ... As the disastrous effects of climate change mount, Congress has asked federal scientists for a research plan, ...
1. Shift to renewable energy sources in all key sectors. The United Nations identified a six-sector solution to climate change, focusing on actions that can be taken by the energy, industry, agriculture, transportation, nature-based solutions, and urban planning. If all of these actions are completed, the UN Environment Programme estimates we ...
Essay On Climate Change in 100 Words. Climate change refers to long-term alterations in Earth's climate patterns, primarily driven by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global warming. The consequences of climate change are ...
Climate Change Essay. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Climate change is a global phenomenon that affects us all. It can be challenging to wrap your head around such a complex issue, but understanding climate change is an essential ...
August 21, 2017 | Washington, DC. Resolution 2017-001. The Earth's climate is experiencing destabilization, and our planet's ability to sustain life as we know it is in crisis. Humanists must join others in leading efforts to reduce human activities causing climate change to ecologically sustainable levels. Ninety-seven percent of ...
Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, ... It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on "Global Climate Change Impacts ...
Climate change is a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth's local, regional and global climates. These changes have a broad range of observed effects that are synonymous with the term. Changes observed in Earth's climate since the mid-20th century are driven by human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning, […]
[3] Background: In 2019, 27 law students from The University of the South Pacific united in forming Pacific Islands Students Fighting Climate Change, with a campaign for the International Court of Justice to issue an Advisory Opinion on the responsibilities of States in respect to climate change. The resolution, put forward by Vanuatu alongside ...
200 Words Essay on Climate Change. The climate of the Earth has changed significantly over time. While some of these changes were brought on by natural events like volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires, etc., many of the changes were brought on by human activity. The burning of fossil fuels, domesticating livestock, and other human ...
Climate change is one of the most sensitive and talked about issues worldwide. It is a global issue that urges many governments and society as a whole to take action before it is too late to do so. Us humans are battling a war that we caused ourselves, with our selfishness and greed.
Mr. Lezak is a researcher at the University of Cambridge and the University of Oxford who studies the politics of climate change. The world's leading institution on geology declined a proposal ...
This essay examines climate change as a wicked problem and argues that attempts to curb climate change can never be truly effective because of the nature of the problem, the lack of commitment by society to change current lifestyle and the lack of resources to sustain change over the long-term. ... does not have an inherent end that signals a ...
500+ Words Essay on Climate Change. Climate change is a major global challenge today, and the world is becoming more vulnerable to this change. Climate change refers to the changes in Earth's climate condition. It describes the changes in the atmosphere which have taken place over a period ranging from decades to millions of years.
We quantify cross-border effects of the recent climate mitigation policies introduced in Canada and the U.S., using the global general equilibrium model IMF-ENV. Notably, with the substantial emission reductions from Canada's carbon tax-led mitigation policies and the U.S.' Inflation Reduction Act, these two countries would bridge two-thirds of the gap toward their Nationally Determined ...