- Free Taster Sessions
- 11+ Mock Exams
- 11 Plus Booster Courses
- GCSE Maths Booster Courses
- Free Consultation
- Levelled Reading List
- Student Booklist
- Exam Preparation
- One-to-One Tuition
- Free Taster Session in Seven Kings
- Seven Kings Timetables
- Seven Kings Price List
- Free Taster Session in Loughton
- Loughton Timetables
- Loughton Price List
- Free Resources
- Accessories
- Redbridge Publishing
- Our Processes
- Our Mission – to empower children through education
- Testimonials
- Bancroft’s School
- Beths Grammar School
- Bexley Grammar School
- Chigwell School
- Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School
- City of London School for Boys
- City of London School for Girls
- Forest School
- Haberdashers’ Boys’ School
- Ilford County High School
- King Edward VI Grammar School
- The Latymer School
- Woodford County High School
- 11+ Booster Courses

How to Structure Creative Writing for GCSE (Creative Writing Examples!)
Posted on August, 2022

Structure Creative Writing for Success
Having plenty of ideas for creative writing is one thing, but nailing down the right structure can be a bit more challenging.
There are several steps for children to think about before they begin writing, and that includes creating a structure or plan for how their story will flow.
Creative writing is all about grabbing the reader’s attention immediately, so children in their GCSE years need to understand the importance of structure when writing, in order to organise their ideas and make sure their work reads cohesively.
In this post, we will go through everything your child needs to know from paragraphing, to creating a satisfying ending, providing examples along the way to demonstrate the best way to structure their creative writing.
How Should I Structure Creative Writing?
There are several types of creative writing questions that could come up on the GCSE reading and writing exam. There will be the option to either write creatively based on an image, or a made-up scenario.
Having a solid structure for longer creative writing questions and exercises helps to ensure your child is prepared.
By using a structure that helps to organise your child’s ideas, it helps their writing to flow. It also allows your child to become more confident in their creative writing process.
Planning is more important than you might think, as mark schemes from most exam boards include ‘well-controlled paragraphs’ or something very similar within the top band of criteria for creative writing.
Therefore, children should practise planning out creative writing structures well before their writing exam. Planning gives them time to get into the habit of always providing themselves with a simple, but focused idea of what they are going to write.
Structure Creative Writing with Seven Story Archetypes
Introduction.
Understanding the fundamental structure of a story is crucial for crafting engaging narratives. Beyond basic sequences, story archetypes provide a deeper framework. Christopher Booker , a renowned scholar, identified seven main story archetypes.
Each archetype outlines a distinctive journey and the challenges faced by characters.
1. Overcoming the Monster
This archetype portrays an underdog’s quest to conquer a formidable evil. Examples include the epic tales of Harry Potter battling Lord Voldemort, the classic struggle in Jurassic Park, and the timeless narrative of Jack and the Beanstalk.
2. Rags to Riches
Embarking from a starting point of poverty or despair, characters rise to newfound wealth and success. Witness this transformation in stories like Slumdog Millionaire, The Pursuit of Happyness, and The Wolf of Wall Street.
3. The Quest
A hero’s journey to discover something, overcoming trials and tribulations along the way. Iconic examples include the Fellowship of the Ring’s quest in The Lord of the Rings, Marlin’s journey to find Nemo, and the epic adventures of Odysseus in The Odyssey.
4. Voyage and Return
Protagonists venture into unknown territories, facing adversity before returning home transformed. Dive into this archetype with examples like the curious escapades in Spirited Away, Bilbo Baggins’ journey in The Hobbit, and the enchanting Chronicles of Narnia.
Contrary to our typical perception of humour, this archetype involves destined lovers kept apart by conflicting forces. Delight in the comedic twists of relationships in classics such as 10 Things I Hate About You, When Harry Met Sally, and Notting Hill.
Protagonists with major flaws or errors leading to their inevitable downfall. Witness the unraveling of characters in tragedies like The Great Gatsby, Requiem for a Dream, and the Shakespearean masterpiece Othello.
Characters succumb to darkness but redeem themselves throughout the narrative. Experience the transformative journeys in stories like Atonement, American History X, and the animated Beauty and the Beast.
Application Across Mediums
Beyond literature, these archetypes seamlessly apply to filmmaking and photography. A well-crafted photograph or film can mirror the same narrative arcs, captivating viewers on a visual adventure akin to storytelling. Explore these archetypes to infuse depth and resonance into your creative endeavors.
Paragraphing for a Solid Creative Writing Structure
First of all, paragraphing is central to creative writing as this is what keeps the structure solid.
In order to stick to a creative writing structure, children must know exactly when to end and start a new paragraph, and how much information each paragraph should contain.
For example, introducing the main character, diving into the action of the story, and providing 10 descriptive sentences of the weather and location, could be separated and spread throughout for impact.
Structuring a creative writing piece also involves creating an appropriate timeline of events. Then, you must map out exactly where the story will go from start to finish. This is assuming the writing piece is in sequential order.
Occasionally, there may be a question that requires a non-sequential order.
Master creative writing with our Ultimate Creative Writing Workout!
http://redbridgetuition.co.uk/product/ultimate-creative-writing-workout/
What does a Solid Creative Writing Structure look like?
This list below details every section in a creative writing piece and should look something like this:
- An engaging opening
- A complication
- The development
- The turning point
- A resolution or convincing close
With this structure, it is important to bear in mind that for the AQA GCSE English Language paper 1 reading and creative writing exam.
You can also use Freitag’s pyramid or a story mountain to help you understand the basic structure of a story:
Children will be expected to spend about 50 minutes on the creative writing section. It’s therefore vital to get them into the habit of planning their writing first. As with anything, practice makes perfect.
If you want to find out more about GCSE English Language papers 1 and 2, check out our blog .
We will dive deeper into the creative writing structure further on in this post, but first, let us go through the importance of paragraphing, and how TipTop paragraphs can help to improve children’s writing.
Paragraphing and TipTop Paragraphs
Before children begin to plan out the structure of their stories, it’s essential that they know the importance of paragraphing correctly first.
At this stage of learning, your child should be comfortable in knowing what a paragraph is, and understand that they help with the layout of their stories throughout the whole writing process.
Paragraphs essentially help to organise ideas into dedicated sections of writing based on your child’s ideas. For example, having a paragraph for an introduction, then another paragraph introducing the main character.
This means your child’s writing will be in a logical order and will direct the reader further on into the writing.
Be as creative as Kevin’s booby traps from “ Home Alone “.
To avoid your child straying from their creative writing structure and overloading paragraphs with too much information, there is a simple way to remind them of when they need to start a new paragraph.
TiPToP for a Clearer Creative Writing Structure
Using the TiPToP acronym is such an easy way for you to encourage your child to think about when they need to change paragraphs, as it stands for:
When moving to a different time or location, bringing in a new idea or character, or even introducing a piece of action or dialogue, your child’s writing should be moving on to new paragraphs.
During creative writing practice, your child can ask themselves a series of questions to work out whether they need to move onto a new paragraph to keep their story flowing and reach that top band of criteria.
For example:
- Is the story going into a new day or time period?
- Is the location staying the same or am I moving on?
- Am I bringing in a new idea that I haven’t described yet?
- Am I going to bring in a new character?
Providing opportunities to practise creative writing will help your child to get into the habit of asking themselves these questions as they write, meaning they will stick to the plan they have created beforehand.
Now it’s time to get into the all-important creative writing structure.
Structure Creative Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Producing a creative writing structure should be a simple process for your child, as it just involves organising the different sections of their writing into a logical order.
First, we need to start at the beginning, by creating an engaging opening for any piece of writing that will grab the reader’s attention. You might also be interested to check out this blog on story structure that I found in my research.
This leads us nicely onto step 1…
1. Creating an Engaging Opening
There are several ways to engage the reader in the opening of a story, but there needs to be a specific hook within the first paragraph to ensure the reader continues.
This hook could be the introduction of a word that the reader isn’t familiar with, or an imaginary setting that they don’t recognise at all, leaving them questioning ‘What does this all mean?’
It may be that your child opens their story by introducing a character with a description of their appearance, using a piece of dialogue to create a sense of mystery, or simply describing the surroundings to set the tone. This ‘hook’ is crucial as it sets the pace for the rest of the writing and if done properly, will make the reader feel invested in the story.
Read more about hooks in essays .
If your child needs to work more on description, I definitely recommend utilising the Descriptosaurus :
Additionally, it’s important to include a piece of information or specific object within the opening of the creative writing, as this provides something to link back to at the end, tying the whole storyline together neatly.
Engaging Opening Examples:
- Opening with dialogue – “I wouldn’t tell them, I couldn’t”
- Opening with a question – “Surely they hadn’t witnessed what I had?”
- Opening with mystery/ or a lack of important information – “The mist touched the top of the mountains like a gentle kiss, as Penelope Walker stared out from behind the cold, rigid bars that separated her from the world.”
2. Complication
Providing a complication gets the storyline rolling after introducing a bit of mystery and suspense in the opening.
Treat this complication like a snowball that starts small, but gradually grows into something bigger and bigger as the storyline unfolds.
This complication could be that a secret has been told, and now the main character needs to try and stop it from spreading. Alternatively, you could introduce a love interest that catches the attention of your main character.
In this section, there should be a hint towards a future challenge or a problem to overcome (which will be fleshed out in the development and climax sections) to make the reader slightly aware of what’s to come.
Complication Example:
- Hint to future challenge – “I knew what was coming next, I knew I shouldn’t have told him, now my secret is going to spread like wildfire.”
- Including information to help understand the opening – “Bainbridge Prison was where Penelope had spent the last 2 years, stuffed into a cell the size of a shoebox, waiting for August the 14th to arrive.”
3. Development
The development seamlessly extends from the previous section, providing additional information on the introduced complication.
During this phase, your child should consider the gradual build-up to the writing piece’s climax. For instance, a secret shared in the compilation stage now spreads beyond one person, heightening the challenge of containment.
Here, your child should concentrate on instilling suspense and escalating tension in their creative writing, engaging the reader as they approach the climax.
Development Example:
- Build-up to the challenge/ climax – “I saw him whispering in class today, my lip trembled but I had to force back my tears. What if he was telling them my secret? The secret no-one was meant to know.”
- Focusing on suspense – “4 more days to go. 4 more days until her life changed forever, and she didn’t know yet if it was for better or for worse.”
The climax is the section that the whole story should be built around.
Before creating a structure like this one, your child should have an idea in mind that the story will be based on. Usually this is some sort of shocking, emotion-provoking event.
This may be love, loss, battle, death, a mystery, a crime, or several other events. The climax needs to be the pivotal point; the most exciting part of the story.
Your child may choose to have something go drastically wrong for their main character. They must regardless, need to come up with a way of working this problem into their turning point and resolution. The should think carefully about this will allow the story to be resolved and come to a close.
Climax Example:
- Shocking event: “He stood up and spoke the words I never want to hear aloud. ‘I saw her standing there over the computer and pressing send, she must have done it.’”
- Emotion-provoking event: “The prisoners cheered as Penelope strutted past each cell waving goodbye, but suddenly she felt herself being pulled back into her cell. All she could see were the prison bars once again.”
5. Turning Point or Exposition
After the climax, the story’s turning point emerges, crucial for maintaining reader interest.
During this post-climax phase, address and resolve issues, acknowledging that not every resolution leads to a happy ending.
Turning points need not be confined to the story’s conclusion; they can occur at various junctures, signifying significant narrative shifts.
Even in shorter pieces, introducing turning points early on can captivate the reader.
Creative writing allows for individual storytelling, and effective turning points may differ between your child and you.
Maintain suspense in this section, avoiding premature revelation of the ending despite the climax’s conclusion.
Turning Point Example:
- Turning point: “Little did they know, I was stopping that file from being sent around the whole school. I wasn’t the one to send it, and I had to make sure they knew that.”
- Turning point: “She forced herself through the window, leaving the prison behind her for good this time, or so she thought.”
6. A Resolution or Convincing Close
The resolution should highlight the change in the story, so the tone must be slightly different.
At this stage, the problem resolves (happily or unhappily) and the character/s learns lessons. The close of the story must highlight this.
The writer should also not rush the resolution or end of the story.
It needs to be believable for the reader right until the very end. The writer should allow us to feel what the protagonist is feeling.
This creates emotion and allows your reader to feel fully involved.
Remember the piece of information or specific object that was included in the story’s opening?
Well this is the time to bring that back, and tie all of those loose ends together. You want to leave the reader with something to think about. You can even ask questions as this shows they have invested in the story.
Resolution Example:
- Happy resolution: “He came up to me and curled his hand around mine, and whispered an apology. He knew it wasn’t me, and all I felt was relief. Looks like I should have told them right from the start”
- Unhappy resolution: “All she felt was separation, as she felt those cold, rigid prison bars on her face once more.”
How to Structure Your Creative Writing for GCSE (with Creative Writing Examples!)
To enhance your children’s GCSE creative writing skills, allocate time for practice.
Plan a structure for creative writing to guide children in organising their thoughts and managing time during the GCSE exam.
Apply this structure to various exam questions, such as short stories or describing events.
Focus each creative piece on a climactic event, building anticipation in the beginning and resolving it at the end.
Consider a tutor for GCSE preparation to help children focus on specific areas.
Redbridge Tuition offers experienced tutors for learning from KS2 to GCSE, providing necessary resources for your child’s success.
Get in touch to find out how our tutors could help.
Want a free consultation?
Why not share this post, what our parents and children say.
Just want to use this opportunity to extend my gratitude to Mrs Rupa and the Redbridge Tuition team for the work done with my daughter.…
My daughter has been coming here for 3 weeks now for Key Stage 4 GCSE Maths. All the staff are really friendly and informative and…
Never in a million years did we ever think Mollie would ever achieve one of the ‘top Academic Scholarship Award’ at one of our two chosen…
Just a quick email to say a huge thank you and to show our appreciation for your excellent tuition and the tailored support that you…
Nadein Grey
Thanks to you and your tutors for the confidence you instilled in my daughter to believe in herself. Her maths has improved so much that…
Silo Endeley
My daughter started her 11 plus prep with Redbridge Tuition exactly 1 year prior to the exams. I just wanted to convey my thanks and…
They are a very resourceful team, who structure the activities very carefully and execute it to perfection…
K. S. Kumar
I was over the moon when Nayla’s results arrived as she has managed to secure a place at Woodford County High School. It was no…
Neepa Chowdhury
Thanks for the support given to Konrad last year. He passed his Kent exams with 400 points and his Medway exam with 630 points. He…

Guide to CSSE Creative Writing: How to Gain Top Marks (Examples Included)
Introduction The CSSE creative writing section is a part of the 11 plus exam where many students struggle. Creative writing can be a challenging area…

The Art of Writing: Why It’s Important
Introduction This article will reveal why writing is still an important skill for anyone to improve and master. The Importance of Basic Writing Skills Acquiring…

7 Best Maths Resources for Secondary Students
Introduction This blog delves into the seven indispensable resources tailored for secondary students, encompassing both free and paid options that can significantly enhance a student’s…

Insider GCSE creative writing tips + 106 prompts from past papers
by Hayley | Mar 9, 2023 | Exams , Writing | 0 comments
Are you feeling a little bit twitchy about your child’s English GCSE writing task?
Sciences and humanities – although sometimes daunting in their content – seem a fair bet as ‘revisable’ topics. But the creative writing element of the English Language GCSE is less knowable and ultimately more of a frightening prospect for a student keen to do well.
Preparing for the GCSE writing task? You don’t need to do it alone.
We run a weekly online writing club which prepares students to write high-scoring content. Our “Higher” level club is designed to transform your writing so that you can ace the GCSE language paper.
What is the GCSE writing element of the GCSE Language Paper?
There are 5 key GCSE exam boards: AQA , OCR , Pearson Edexcel , WJEC Eduqas and CCEA . Each board sets their own papers which may appear much the same at first glance (bizarrely they all have a similar front cover layout and fonts). Certainly there is plenty of overlap between their mark schemes and the comments and tips they share in their Examiner Reports.
However, as with all your child’s other subjects, it is essential to know which exam board they are preparing for. You may be surprised to discover that schools pick and choose boards by subject, perhaps choosing AQA for chemistry and OCR for mathematics. Individual school departments have their own preferences. My brother teaches at a school where their English Literature and English Language exams have been split between two different boards. This is unusual though, not the norm!
What forms (question formats) can the test take?
It varies by board.
The AQA board has a writing task in their Question Paper 1 called Explorations in creative reading and writing . Students are given two prompts to choose between. The AQA board also has a second persuasive writing task in Paper 2 called Writers’ viewpoints and perspectives.
Jump ahead to AQA creative writing and persuasive writing prompts from past GCSE papers
The Pearson/Edexcel international iGCSE favoured by many UK private schools has two prompts to choose between for each section. The student is asked to complete a piece of transactional writing (perhaps a persuasive speech or an advertisement leaflet) and additionally a piece of imaginative writing.
Jump ahead to Pearson/Edexcel transactional writing and imaginative writing prompts from past GCSE papers
Interestingly, the WJEC Eduqas board favours non-fiction writing. Unit 2 Reading and Writing: Description, Narration and Exposition gives two prompts to choose between, for an account and an essay perhaps, and Unit 3: Reading and Writing: Argumentation, Persuasion and Instructional sets up a letter, or similar.
Jump ahead to WJEC Eduqas non-fiction writing prompts from past GCSE papers
The OCR board offers two prompts to choose between. One might be a talk for other students and the other might be a letter on a difficult subject .
Jump ahead to OCR creative writing prompts from past GCSE papers
The CCEA board has a writing task in called “ Writing for Purpose and Audience and Reading to Access Non-fiction and Media Texts” and a second writing task which offers a choice between personal writing and creative writing.
Jump ahead to CCEA persuasive writing, personal writing, and creative prompts from past GCSE papers
How long do students have to craft their piece of writing?
Creative writing tests are timed at either 45 minutes or 1 hour. The last thing your child will need is to prepare to write for an hour, only to find they have just three-quarters of an hour on the day. If in doubt, insist that they check with their teacher.
AQA students are given 45 minutes to produce their writing response. The introduction advises: ‘ You are reminded of the need to plan your answer. You should leave enough time to check your work at the end.’ What this means is that 30–35 minutes max is what’s really allowed there for the writing itself.
Pearson/Edexcel allows 45 minutes for each of the two writing tasks.
OCR students are given an hour to complete this section of their exam. The introduction states: ‘You are advised to plan and check your work carefully,’ so they will expect the writing itself to take 45–50 minutes.
How long should the completed GCSE writing task be?
Interestingly, although the mark schemes all refer to paragraphingthey don’t state how many paragraphs they expect to see.
‘A skilfully controlled overall structure, with paragraphs and grammatical features used to support cohesion and achieve a range of effects’ (OCR)
‘Fluently linked paragraphs with seamlessly integrated discourse markers’ (AQA)
Why? Because management of paragraph and sentence length is a structural technique available to the student as part of their writers’ toolkit. If the number of optimal paragraphs were to be spelled out by the board, it would have a negative impact on the freedom of the writer to use their paragraphs for impact or to manage the pace of the reader.
For a general guide I would expect to see 3 to 5 paragraphs in a creative piece and 5 paragraphs in a persuasive piece. Leaflets have a different structure entirely and need to be set out in a particular form to achieve the top notes of the mark scheme.
What are the examiners looking for when they are marking a student’s creative writing paper?
There are two assessment objectives for the writing itself:
- It has to be adapted to the form, tone and register of writing for specific purposes and audiences.
- It has to use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures, with appropriate paragraphing, spelling, punctuation and grammar.
As a GCSE English nerd, I really enjoy delving deeper into the Examiner Reports that each board brings out once the previous cohort’s papers have been marked. They are a fascinating read and never disappoint…
Within their pages, examiners spell out the differences they have spotted between the stronger and the weaker responses.
For example, a creative task set by the AQA board was to describe a photograph of a town at sunset. The examiners explained that some of the strongest responses imagined changes in the scene as darkness descended. They enjoyed reading responses that included personification of the city, and those that imagined the setting in the past, or the weariness of the city. Weaker candidates simply listed what was in the picture or referred directly to the fact it was an image. This chronological-list approach weakened the structure of their work.
No surprises that some weaker students relied heavily on conversation. (As an exam marker myself, I dreaded reading acres of uninspiring direct speech.)
Pearson/Edexcel explain that weaker persuasive pieces (in this case on the value of television) simply listed pros and cons rather than developed ideas fully to clarify their own opinions. The higher-level responses here were quirky and engaging, entertaining the reader with a range of appropriate techniques and making the argument their own.
What accommodations are possible for students who have specific learning difficulties?
The UK Government’s Guide for Schools and Colleges 2022: GCSE, AS and A Levels includes information about changes to assessments to support ‘disabled students.’ Their definition of disabled includes specific learning difficulties (dyslexia, dyspraxia, ADHD, ADD, ASD etc).
Exam boards can make a wide range of adjustments to their assessments. Some of the most common adjustments are:
- modified papers (for example, large print or braille exam papers)
- access to assistive software (for example, voice recognition systems or computer readers)
- help with specific tasks (for example, another person might read questions to the student or write their dictated answers)
- changes to how the assessment is done (for example, an oral rather than a written assessment, word-processing rather than hand-writing answers)
- extra time to complete assessments
- exemptions from an assessment
The exam board will expect paperwork to be in place where your child’s specific needs are formally reported by an appropriate professional (Educational Psychologist, Clinical Psychologist, Consultant). The report needs to be recent, but how recent is difficult to confirm.
If your child is likely to need adjustments to their access arrangements you will need to discuss this with their school in plenty of time before the exam itself.
A close friend of mine realised in the final few weeks before her son’s GCSE exams that his tinnitus would have a negative impact on his performance. She approached the school to ask if he might take his exams in a separate room to minimise noise disturbance. Unfortunately, it was far too late by then to apply, and her son was denied the request.
Your child’s school will explain the process for applying for special arrangements and will be able to advise you on what your expectations should be. Never presume your child will be given what they need – but plenty of requests are successful, so stay positive and make sure your paperwork is in order beforehand.
Tips and strategies for writing a high scoring GCSE creative writing paper:
1. learn the formats.
Know the different formats and conventions of the different GCSE writing tasks. There is a standard layout for a leaflet, for example, where including contact details and a series of bullet points is part of the mark scheme. Not knowing these conventions will knock back a student’s score.
2. Plan ahead
Prepare a planning structure for each of the written forms you might encounter during the exam. It may need to be flexed on the day, but it will banish fear of the blank page and allow you to get started.
3. Prepare sentence-openings
Familiarise yourself with appropriate sentence-openings for each type of GCSE writing task. Fronted adverbials of time and place will improve the quality of a creative piece, whereas access to varied and specific conjunctions might push up the mark of a transactional piece.
4. Check your speaking
Ask your family to check your speech at home. Every now and then try to flip a sentence into formal language, using more interesting synonyms for your usual spoken vocabulary. This will help you to write formally on paper, avoiding colloquialisms.
5. Forget finishing
Finishing is less important than you might imagine. Sloppy, hurried work is your enemy. GCSE examiners will follow your clear planning and mark you accordingly, even if you’ve not managed to complete that final paragraph.
6. Note the details
The question often gives additional information the examiner would like to see included. Note it in your plan to make sure it doesn’t get forgotten.
7. Start strong
Use your best sentence-opener at the start of each paragraph. It will set you up as someone to be taken seriously.
8. Cut back dialogue
Keep dialogue contained in a single paragraph. Focus on description of the speaker and their actions before noting the second character’s reply.
9. Revise
Do this by prepping work as above. Nothing beats it.
Would you like me to transform your child’s writing in my higher writing club?
Each week in my higher writing club , we spend 20 minutes on Zoom together. After the task has been introduced, the students write for 15 minutes. Next, they upload their work for 1:1 video marking.
There is no point prepping essays/creative pieces for the GCSE English Language exam if your child’s writing is poor. First, their scruffy presentation, attention to detail, punctuation, grammar and vocabulary need to be addressed.
After 2 months in the higher writing club your child’s written technique and fluency will be transformed by our 1–2-1 video marking system (consistent messaging is achieved by matching your child with their own teacher).
Each weekly activity is drawn directly from the GCSE English Language Subject Content and Assessment Objectives , published by the English Department of Education.
Here’s an example of a student’s writing, BEFORE they joined our club:

It is chaotic, poorly-presented and nonsensical. Letter-sizing is confused and the student is clearly anxious and repeatedly scribbling through small errors.
Below is the same student 2 months later:

Observe the rich vocabulary, authorial techniques (the jagged rocks are ‘like shards of broken glass’) and general fluency and sophistication.
Real and recent GCSE example questions/prompts from each of the 5 key exam boards
Aqa english language gcse questions, paper 2 writers’ viewpoints and perspectives:.
- ‘Our addiction to cheap clothes and fast fashion means young people in poorer countries have to work in terrible conditions to make them. We must change our attitude to buying clothes now.’ Write an article for a magazine or website in which you argue your point of view on this statement. ( Source )
- ‘People have become obsessed with travelling ever further and faster. However, travel is expensive, dangerous, damaging and a foolish waste of time!’ Write an article for a news website in which you argue your point of view on this statement. ( Source )
- ‘Cars are noisy, dirty, smelly and downright dangerous. They should be banned from all town and city centres, allowing people to walk and cycle in peace.’ Write a letter to the Minister for Transport arguing your point of view on this statement. ( Source )
- ‘All sport should be fun, fair and open to everyone. These days, sport seems to be more about money, corruption and winning at any cost.’ Write an article for a newspaper in which you explain your point of view on this statement. ( Source )
Paper 1 Explorations in creative reading and writing:
- A magazine has asked for contributions for their creative writing section. Either write a description of an old person as suggested by the picture below or write a story about a time when things turned out unexpectedly. ( Source )

- Your school or college is asking students to contribute some creative writing for its website. Either, describe a market place as suggested by the picture below or write a story with the title, ‘Abandoned’. ( Source )

- Your local library is running a creative writing competition. The best entries will be published in a booklet of creative writing. Either, write a description of a mysterious place, as suggested by the picture below or write a story about an event that cannot be explained. ( Source )

- A magazine has asked for contributions for their creative writing section. Either, describe a place at sunset as suggested by the picture below or write a story about a new beginning. ( Source )
OCR English Language GCSE questions
Paper: communicating information and ideas.
- Either, Write a post for an online forum for young people about ‘A moment that changed my life’.
- Or, You are giving a talk at a parents’ information evening about why all children should study science at school. Explain your views. ( Source )
- Either, Write a letter to a friend to describe a challenging and unpleasant task you once had to do.
- Or, Write a short guide for new workers about how to deal successfully with difficult customers. ( Source )
- Either, “Was it worth it?” Write an article for a magazine to describe a time when you had to do something difficult.
- Or, Write a speech for an event to congratulate young people who have achieved something remarkable. ( Source )
- Either, Write the words of a talk to advise pet owners how to make life more enjoyable for their pet and themselves.
- Or, Write an article for a travel magazine to describe your dramatic encounter with an animal. ( Source )
- Either, ‘How I prefer to spend my time.’ Write the words of a talk to young people about your favourite activity
- Or, Write a magazine article to persuade parents to allow their teenage children more freedom. You are not required to include any visual or presentational features. ( Source )
- Either, Write a talk for other students about a person you either admire strongly or dislike intensely
- Or, Write a letter to a friend to explain a difficult decision you had to make. ( Source )
Paper: Exploring effects and impact
- Either, Hunger satisfied. Use this as the title for a story.
- Or, Write about a time when you were waiting for something. ( Source )
- Either, The Taste of Fear Use this as the title for a story.
- Or, Write about a time when you were exploring a particular place. ( Source )
- Either, Alone. Use this as the title for a story.
- Or, Describe a time when you found yourself in a crowd or surrounded by people. ( Source )
- Either, Land at Last. Use this as the title for a story.
- Or, Imagine you have visited somewhere for the first time and are now reporting back on your experience. ( Source )
- Either, The Playground Use this as the title for a story
- Or, Write about a memory you have of playing a childhood game. ( Source )
- Either, It seemed to me like I had been magically transported. Use this as the title for a story.
- Or, Describe a place where you have felt comfortable. ( Source )
Pearson Edexcel English Language iGCSE questions
Paper 1: transactional writing.
- Either, ‘In our busy twenty-first century lives, hobbies and interests are more important than ever.’ Write an article for a newspaper expressing your views on this statement.
- Or, ‘We are harming the planet we live on and need to do more to improve the situation.’ You have been asked to deliver a speech to your peers in which you explain your views on this statement. ( Source )
- ‘ Zoos protect endangered species from around the world.’ ‘No wild animal should lose its freedom and be kept in captivity. Write an article for a magazine in which you express your views on zoos.
- Write a review of an exciting or interesting event that you have seen. ( Source )
- Your local newspaper has published an article with the headline ‘Young people today lack any desire for adventure’. Write a letter to the editor of the newspaper expressing your views on this topic.
- ‘The key to success in anything is being prepared.’ Write a section for a guide giving advice on the importance of preparation. ( Source )
- You and your family have just returned from a holiday that did not turn out as you expected. Write a letter to the travel agent with whom you booked your holiday, explaining what happened.
- A magazine is publishing articles with the title ‘Friendship is one of the greatest gifts in life’. Write your article on this topic. ( Source )
- ‘Important lessons I have learned in my life.’ You have been asked to deliver a speech to your peers on this topic.
- Your local/school library wants to encourage young people to read more. Write the text of a leaflet explaining the benefits of reading. ( Source )
- ‘Most memorable journeys.’ A website is running a competition to reward the best articles on this subject. Write an article for the competition about a memorable journey.
- ‘Cycling is one form of exercise that can lead to a healthier lifestyle.’ Write a guide for young people on the benefits of exercise. ( Source )
- ‘Television educates, entertains and helps global understanding.’ ‘Television is to blame for society’s violence and greed and delivers one-sided news.’ You have been asked to deliver a speech in which you express your views and opinions on television.
- ‘Choosing a career is one of the most important decisions we ever make.’ Write the text of a leaflet that gives advice to young people on how to choose a career. ( Source )
- Write the text for a leaflet aimed at school students which offers advice on how to deal with bullying.
- A museum is planning to open a new exhibition called ‘Life in the Twenty-First Century’. ( Source )
Paper 2: Imaginative writing
- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, enjoyed success
- Write a story with the title ‘A Surprise Visitor’.
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that begins ‘I did not have time for this’ ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, challenged an unfair situation.
- Write a story with the title ‘Bitter, Twisted Lies’.
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that begins ‘It was a new day …’ You may wish to base your response on one of these images. ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, visited a new place.
- Write a story with the title ‘The Storm’
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that ends ‘I decided to get on with it.’ ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, saw something surprising.
- Write a story with the title ‘The Meeting’.
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that starts ‘Suddenly, without warning, there was a power cut.’ ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, went on a long journey.
- Write a story with the title ‘A New Start’
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that begins ‘I tried to see what he was reading. ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, felt proud.
- Write a story with the title ‘The Hidden Book’.
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that begins ‘It was like a dream’ ( Source )

- Write about a time when you, or someone you know, had to be brave
- Write a story with the title ‘Everything Had Changed’
- Look at the two images below. Choose one and write a story that begins ‘It was an unusual gift’. ( Source )

WJEC Eduqas English Language GCSE questions
Unit 2 reading and writing: description, narration and exposition.
- Write an account of a time when you enjoyed or hated taking part in an outdoor activity.
- “It’s essential that more people are more active, more often.” (Professor Laura McAllister, Chair of Sport Wales) Write an essay to explain how far you agree with this view, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- Describe an occasion when you did something you found rewarding.
- Famous chefs such as Jamie Oliver and Mary Berry have spoken of the need for better food and better education about food in schools. Write an essay to explain your views on this subject, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- Write an account of a visit to a dentist or a doctor’s surgery.
- NHS staff, such as doctors and nurses, provide excellent service in difficult circumstances. Write an essay to explain your views on this subject, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- Write an article for a travel magazine describing somewhere interesting that you have visited.
- You see the following in your local newspaper: ‘Young people are selfish. They should all be made to volunteer to help others.’ Write an essay to explain your views on this subject, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- Describe an occasion when technology made a difference to your life.
- Write an account of a time you were unwilling to do something. ( Source )
- Describe a time when you faced a challenge
- Write an essay explaining why charity is important, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- Write an account of a time when you did something for the first time.
- “It’s time for us to start making some changes. Let’s change the way we eat, let’s change the way we live, and let’s change the way we treat each other.” Tupac Shakur Write an essay on the subject of change, giving clear reasons and examples. ( Source )
- “School uniform is vitally important in all schools.” Write an essay explaining your views on this, giving clear reasons and examples.
- Describe a time when you had to create a good impression. ( Source )
Unit 3: Reading and writing: Argumentation, persuasion and instructional
- Your school/college is considering using more Fairtrade items in its canteen. Although this will help to support Fairtrade farmers, it will mean an increase in the price of meals. You feel strongly about this proposal and decide to write a letter to your Headteacher/Principal giving your views. ( Source )
- Increasing litter levels suggest we have lost all pride in our beautiful country. Prepare a talk for your classmates in which you give your opinions on this view. ( Source )
- Write a guide for other students persuading them to stay safe when using social media and the internet. ( Source )
- According to your PE teacher, ‘Swimming is the very best form of exercise.’ You have been asked to prepare a talk for your classmates in which you give your views about swimming. ( Source )
- You read the following in a newspaper: ‘Plastic is one of the biggest problems faced by our planet. Why would we use something for a few minutes that has been made from a material that’s going to last forever?’ Write a letter to the newspaper giving your views on the use of plastic. ( Source )
- “People today never show enough kindness to one another. We must make more effort to be kind.” Write a talk to give on BBC Wales’ new programme Youth Views persuading young people to be kind to others. ( Source )
- ‘We have enough problems in the world without worrying about animals.’ Write an article for the school or college magazine giving your views on this statement.
- You would like to raise some money for an animal charity. Write a talk for your classmates persuading them to donate to your chosen charity. ( Source )
CCEA English Language GCSE questions
Unit 1: writing for purpose and audience and reading to access non-fiction and media texts.
- Write a speech for your classmates persuading them to agree with your views on the following issue: “Young people today are too worried about their body image.” ( Source )
- Write an article for your school magazine persuading the readers to agree with your views on the following question: “Should school uniform have a place in 21st century schools?” ( Source )
- Write a speech for your classmates persuading them to agree with your views on the following question: “Are celebrities the best role models for teenagers?” ( Source )
- Write an article for your school magazine persuading the readers to agree with your views on the following statement: “Advertising is just another source of pressure that teenagers don’t need!” ( Source )

Unit 4: Personal or creative writing and reading literacy and non-fiction texts
- Either, Personal writing: Write a personal essay for the examiner about what you consider to be one of the proudest moments in your life.
- Or, Creative writing: Write your entry for a creative essay writing competition. The audience is teenagers. You may provide your own title. ( Source )
- Write a personal essay for the examiner about an experience that resulted in a positive change in your life.
- Write a creative essay for the examiner. The picture below is to be the basis for your writing. You may provide your own title. ( Source )

- Personal writing: Write a speech for your classmates about the most interesting person you have ever met.
- Creative writing: Write a creative essay for your school magazine. The picture below is to be the basis for your writing. You may provide your own title. ( Source )

- Personal writing: Write a personal essay for the examiner describing your dream destination.
- Creative writing: Write a creative essay for publication in your school magazine. The picture below is to be the basis for your creative writing. You may provide your own title. (Source)

Get 1:1 support and personalized feedback on your GCSE creative writing practice
For 1–2-1 writing support for your pre-GCSE child, join the Griffin Teaching Higher Writing Club—online weekly writing classes specifically tailored to English GCSE creative writing preparation.
In just 20 minutes per week and their writing will be transformed.
Writing skills - creative and narrative writing
Part of English Writing skills
Imaginative or creative writing absorbs readers in an entertaining way. To succeed with this kind of writing you will need to write in a way that is individual, original and compelling to read.
Responding to Prompts
Imagine you’re in an exam and you are asked to write a creative piece called ‘The Party’. What does this title make you think of?Before you decide what you’d write, it’s useful to remember that you do whatever you want with the prompt as long as it’s somehow connected to a party.
- It doesn’t have to be something that really happened
- It doesn’t have to be based on exactly what the title says or is
- It can be as abstract or as mundane as you want it to be.
So this means that for the title ‘The Party’, you could write a lovely descriptive piece about your dream birthday party, or a personal account of a party you attended that was very good – or very bad. You could write a story about a political party, or a doll’s tea party, or a party held by fans to watch the final episode of a TV show everyone is very excited about, or a party that didn’t actually happen because no one turned up. The most important thing is that you choose a story you can write well, showing off your skill in using language effectively and keeping your reader entertained.
Original ideas
There is no formula for having a great idea – but to begin your writing, you do need, at least, some kind of idea. Then you need to find ways to turn your idea into something a reader would enjoy reading. This is the creative part, taking something ordinary and turning it into something extraordinary.
For example, think about writing a description of a coastline. You might start to think straight away about a crowded beach - children playing, deck chairs, sun shining, happy sounds; but, if you stop for a moment, you’ll recall that that's been done before. It's okay, but it's hardly original.

The 'plot hook' in this example is 'What could possibly go wrong?'.
Establish the time and place, as well as the general situation. This can also be used to help develop a suitable mood or atmosphere. It can sometimes help to use a familiar place that your reader can relate to in some way. At this stage, you need to 'set up' the story and begin to introduce the main character(s).
Fiction trigger (or inciting incident)
Use your narrator to tell of an incident or event that the reader feels will spark a chain of events. This helps make the reader feel that the story has really started. From this point, life cannot be quite the same for your main character (that is your protagonist). There is a problem that has to be faced and overcome.
The fiction trigger can be an event that really starts the story. It will develop from the 'plot hook'. If the story is about a day out at the zoo, then maybe an animal has escaped. If it is about a robbery, it might be the event that makes a character consider carrying out a robbery; and if it is about an accident, it will be the event that causes it to happen.
Keeping up the momentum (plot development or rising action)This section builds the tension – keeps the reader absorbed and guessing where it will all lead.
This is where you will move the story forward and will use lots of techniques to keep the reader guessing, 'What will happen next?!'
The problem reaches a head, with suspense creating lots of tension for the reader– showing the reader the possible result of what has come before.
This is not the end of your story – not quite. It will be the key event but your protagonist will, somehow, overcome it and all will be well.
Conclusion (the resolution)
This must leave your reader with a sense of satisfaction, or it could be a twist in the tale leaving questions that linger in the mind.
This is the ending of your story – where all loose ends are tied up to the satisfaction of the reader. A good story will cause the reader to go, 'Hmm – I liked that' or even 'Wow'
By following this story structure, and planning under each of the above headings, you should be able to come up with a tense plot for your own story, one that will engage and absorb your reader.
Writing techniques
Throughout your own story, you will also need to use writing techniques that will work to keep your reader engaged and absorbed. An important skill is to put clear images of the setting and characters in your reader’s mind, as well as to create a sense of atmosphere that suits each part of the story.
- Narration - the voice that tells the story, either first person (I/me) or third person (he/him/she/her). This needs to have the effect of interesting your reader in the story with a warm and inviting but authoritative voice.
- Description - describing words such as adjectives close adjective A word which describes a noun or pronoun. , adverbs close adverb An adverb gives more information about the verb, an adjective or another adverb. , similes close simile A literary technique where a comparison is made between two things using ‘as’ or ‘like’. and metaphors close metaphor Makes a direct comparison by presenting one thing as if it were something else with the characteristic. For example describing a brave person as a lion. that add detail. This is told by the narrator. It helps engage readers by creating vivid pictures and feelings in their 'mind’s eye'.
- Dialogue - the direct speech of characters, shown inside quotation marks. We all judge characters by what they talk about and by the way they speak. This makes dialogue a key technique for creating interest and realism.
- Alliteration - repetition of the same beginning sounds in nearby words.This can create a useful emphasis, maybe to highlight a sound or movement, or to intensify feeling or even to bind words together.
- Connotation - a word’s meaning can be literal, as in 'It looked like a cat', or it can create connotations as in 'As soon as the food reached the table, the boy pounced on it like a cat.' A connotation is a meaning created by a special use of a word in a particular way or context. It works by adding some kind of emotion or a feeling to a word’s usual meaning. All literature depends upon using language that creates connotations. They engage the reader because they evoke reactions and feelings.
- Pathetic fallacy - personification is a kind of metaphor and when nature is described in this way, it is called a use of pathetic fallacy. This can help suggest a suitable atmosphere or imply what the mood of the characters is at a certain point, eg in a ghost story, the storm clouds could be said to 'glower down angrily upon the group of youngsters'. A pathetic fallacy can add atmosphere to a scene. It can even give clues to the reader as to what is to come, acting as a kind of foreshadowing close foreshadow Hint at something that will happen later and have greater significance .
- Personification - this is a technique of presenting objects as if they have feelings, eg 'the rain seemed to be dancing merrily on the excited tin roof.' This creates a sense of emotion and mood for the reader.
- Repetition - the action of repeating a word or idea. This can add emphasis or create an interesting pattern of sound or ideas.
- Onomatopoeia - use of words which echo their meaning in sound, for example, 'whoosh' 'bang'. Using this can add emotion or feeling that helps give the reader a vivid sense of the effect being described.
- Simile - a kind of description. A simile compares two things so that the thing described is understood more vividly, eg 'The water was as smooth as glass.' (Hint - 'like' or 'as' are key words to spot as these create the simile). A simile can create a vivid image in the reader’s mind, helping to engage and absorb them.
- Symbolism - we grow up learning lots of symbols and these can be used in stories to convey a lot of meaning as well as feeling in a single idea or word, eg a red rose can symbolise romantic love; a heavy buckled belt can hint at the power held by the character; an apple can even symbolize temptation if it is used in a way that the reader links to the apple that tempted Eve in the biblical Garden of Eden.
- Impact - symbols help writers pack a lot of meaning into just a single word. They work to engage the reader, too, for the reader automatically gets involved in working out the meaning.
Examples of narration
First person narrator.
I held on to the tuft of grass and slowly looked down - I was too shocked to speak. One moment I had been strolling along the cliff with Vicki, the next I was hanging over the edge. And where was Vicki?
The only thing you shouldn't do is swap the narrative point of view during the story - don’t start with 'I' and then switch to 'he', as it is likely to confuse your reader.
Third person narrator
Steve held on to the tuft of grass and slowly looked down - he was too shocked to speak. One moment he had been strolling along the cliff with Vicki, the next he was hanging over the edge. And where was Vicki?
Ending a short story
The ending of a story doesn't necessarily have to be happy but it has to make sense in a way that ties up what has happened.
There are different types of story endings, for example:
- The cliff-hanger - this isn’t an ending as such, it’s a way of tempting the reader to read the next chapter or instalment. Charles Dickens wrote his chapters like this as they were originally published in magazines in serial form. For example, does the spy manage to stop the bomb in time?
- The twist-in-the-tale - the reader will feel fairly sure about the ending, but in the final part everything changes and we are surprised. For example, we learn that it isn’t a bomb after all, it’s a birthday present!
- The enigma ending - the story stops, but the reader is left a little unsure what will come to happen, yet is intrigued by the possibilities - and still feels satisfied. For example, the bomb is defused and everyone is safe, but then an army commander reports the theft of another bomb… only this time twice as powerful.
There are many possibilities; but there are two endings you should try to avoid:
- The trick ending - a bomb will inevitably explode and as it does, the narrator wakes up - it was all a dream. This is too clichéd and unsatisfying for modern readers.
- The disconnected ending - the secret agent suddenly stops worrying about the bomb, retires, and goes off to play golf. Readers don't like this because the ending has nothing to do with the story – very unsatisfying.
Whatever kind of story you write, work out a satisfying ending and include it in your plan.
Writing that is creative and imaginative needs to be entertaining. You need to experiment a little and not be frightened to try something new.
What might you write about if the following tasks came up in an exam? Take a few minutes to think about different ways you could interpret the task, and maybe sketch a quick plan for your best idea.
- The Best Day of My Life
- The Mysterious Door
- Never Again
- Stormy Weather
- How to be a Hero
- Sunday at the Beach
- My Life as an Expert
- Greetings from the Future
- What I REALLY Learned at School
More on Writing skills
Find out more by working through a topic
How to write an essay
- count 5 of 7
How to write a conclusion to an essay
- count 6 of 7
Writing skills
- count 7 of 7
Writing skills - tone & style
- count 1 of 7
Writing: Crafting Creative Writing Revision

Supercharge your learning
Filter by Level
Filter by exam board, writing: crafting creative writing, crafting creative writing.
By the end of this page you should know how to respond effectively and efficiently to the writing section tasks in your GCSE exam.
We will learn what’s in the mark scheme , how to plan your answer , and how to give you a few structuring ideas so you understand what the examiner is looking for .
What Are You Being Tested On?
There are only two Assessment Objectives in the writing portion of the exam.
You may remember them from our previous pages…
AO5 and AO6 !
Let’s have a refresher of what these two objectives entail.
From the mark scheme :
- Students should aim to communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively .
- They can select and adapt their tone , style and register for different forms , purposes and audiences .
- Students are able to organise information and ideas, by using structural and grammatical features to support their coherence .
- Students should use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effec t in their writing.
- Students should have consistently accurate spelling and punctuation .
How to Plan your Answer
Thinking about themes:
By the time you get to the writing question, you will actually already have been given clues as to what the theme of this question will be!
Questions in a paper are usually under one theme.
For example :
If the questions from the reading section of Paper 1 focuses on ‘ Oliver Twist ‘ by Charles Dickens, the question might ask you to write a story inspired by the word ‘ alone ’.
Putting pen to paper:
Make a note of some key words or ideas that come up once you’ve read the question through properly.
For example:
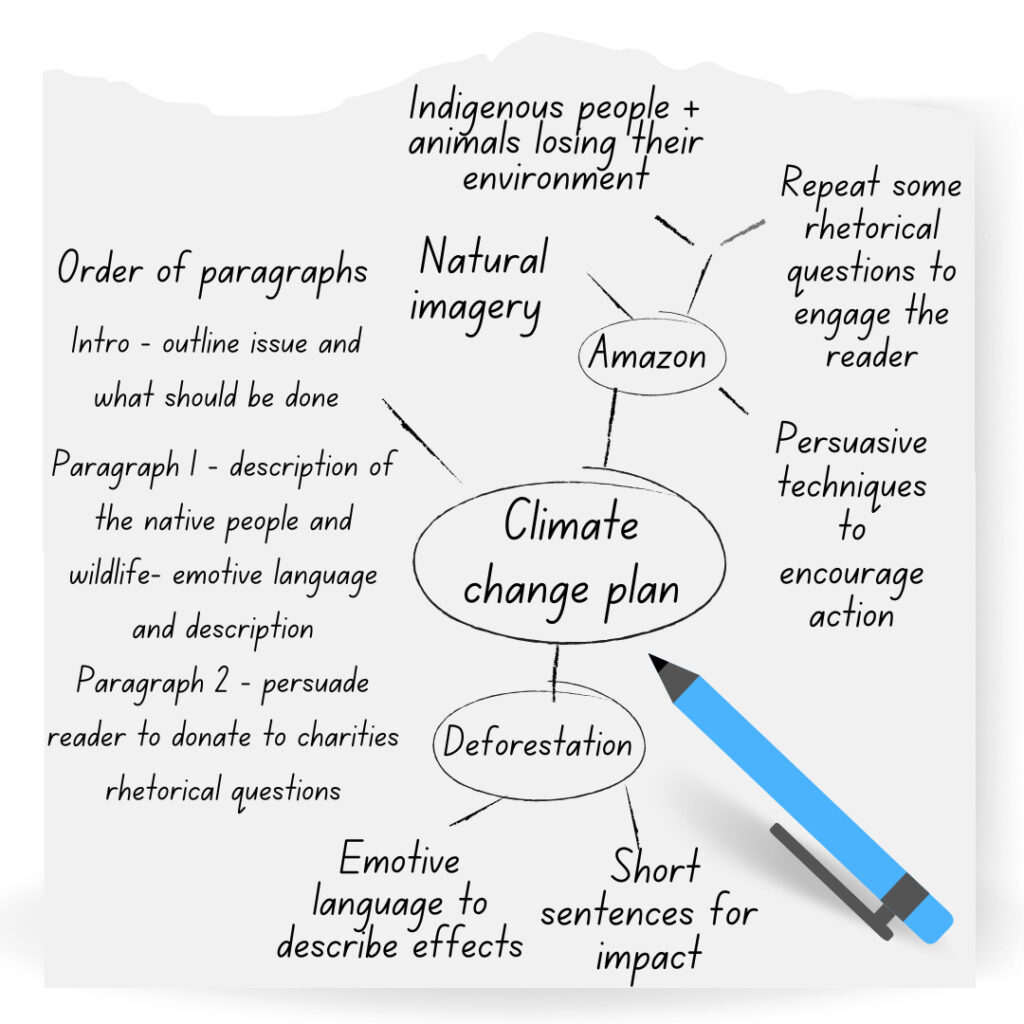
If the focus is on climate change you might write pollution , deforestation , fire , smoke .
Here you can pull out themes or repeated ideas you find interesting or can develop into a creative piece.
In this example , you might write about a deforested section of the Amazon, using language techniques to describe fire and smoke , or presenting climate change in an emotive context.
Think about the individual parts of the question and which angles you could take. Some exam boards , including AQA, will give you an image for example, so you could use this to form the basis of your writing.
This will grab the examiner’s attention by showing that you are able to respond to a prompt and engage in specific questions creatively .
On the other hand, other exam boards, such as Edexcel , might ask for a time in your life when a particular event , which is relevant to the theme , took place.
This does not have to be based on your real life , but you should still aim to make it as interesting as possible.
Who are you writing for?
In some cases, the question may give you a hint as to who your audience is. For example, it may ask you to ‘ write an article for a local magazine ‘ or ‘ write a letter to your local MP ‘.
Once you know the intended audience of your writing, you can decide on the tone and register you should use.
For example, in an article for a local magazine , you might use more informal language, whereas to the MP , you would use a more formal register.
The format will also be dictated, here it’s an article or a letter. You should be familiar with the formatting for a variety of texts before your exam, but we will go through these in depth in the next box!
Why are you writing?
The question may also give you clues about the purpose and aim of your writing, for example ‘write a letter to your local council to complain about the noise levels in your area.’
In instances like this, you would then think about persuasive language techniques you could use in your writing, including emotive language or rhetorical questions for example.

Your 2024 Revision Partner
Structuring
In a creative writing question where you have more free reign, like a story or description , there are different ways to experiment with structure.
- The basic story arc of beginning, middle and end that you may already be familiar with can be subverted , through a different perspective than the expected main character.
- Or the perspective could shift halfway through to give another character’s opinions on the event , creating interest for the reader and showcasing your skills to the examiner !
- Starting the story at the climax of action is a creative way to switch up the structure of your entire answer. You could work backwards and then explain the events that led up to the climax, or describe the aftermath in detail.
If the question specifies a format , like a letter or article, you should use the appropriate structural techniques .

Letter Structure
A letter typically takes a formal tone .
You should include an appropriate greeting : ‘ Dear Sir/Madam ‘
You should also include an appropriate sign-off : ‘ Yours faithfully ‘ if you don’t know who the recipient is, ‘Yours sincerely’ if you do know.
If the letter is to a known audience , you could take a more friendly tone and use first names , e.g., ‘ Dear Mohammed ‘. Your sign-off could match this tone, e.g., ‘ Best wishes ‘.
You should also include the address of the person sending the letter in the top right corner of the page, the address of the person receiving the letter in the top left corner of the page, but slightly underneath the first (these can be made up).

Article Structure
An article should include an engaging headline , which could be an exclamation or question for example.
A strapline is a small line of text under the headline that offers more information on the topic or idea that the headline introduced initially.
Subheadings can be used to organise information in your article. You could make them interesting by adding humour or a rhetorical question to grab the reader’s attention. They should give the reader an idea of what the next paragraph will be about.
Your article should also have a date , and author attribution , e.g., ‘ by David Smith, 25th May 2022 ‘.
Checking Your Answer
It’s a good idea to leave at least five minutes at the end of the exam to check over your answer.
Read through it carefully and make your improvements neatly if needed.
Some questions to think about are:
Could a more sophisticated word choice replace something already there?
- An important part of AO5 and AO6 is using a wide range of sophisticated language, so try to think of some creative swaps for simple words.
Have you got any repeated points that you could remove ?
- AO5 requires you to be concise and clear in your communication, which is hindered by repetition of points. Once you have made a point, try to develop it further by asking what happens next ? What is the impact on the people or things in your writing?
Is your spelling and grammar correct?
- Ensuring the sophisticated language you use is spelled correctly is essential to get the 16 marks available for AO6 in these questions. Check out our more detailed SPaG pages for more information on common mistakes you might make in the exam, and how to fix them!
Is your punctuation placed right ?
- Don’t just stick to full stops and commas in your writing. As long as you use it correctly, get creative with the types of punctuation you use in your answer for a higher AO6 mark. For example, exclamation marks and question marks to create a more conversational tone between the author and the reader. Hyphens , brackets and colons are just a few more you can use in the exam for effect.
Gold Standard Education
Where next?
Previous gcse english language topic, writing: sample questions, gcse english language revision home, go back to the main gcse english language topic list, next gcse english language topic, writing: creative language use.
By clicking continue and using our website you are consenting to our use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy
MME Revision Challenge

Report a Question
You must be logged in to vote for this question..
Your personal data will be used to support your experience throughout this website, to manage access to your account, and for other purposes described in our privacy policy .
- kirstienglishtutor
English Language GCSE: Your Step-By-Step Guide to Creative Writing
Are you preparing for your English language GCSE creative writing task? Feeling a mixture of excitement and anxiety about how to channel your creativity into a structured piece of writing that ticks all the boxes for examiners? You're not alone. Creative writing can seem daunting, but with the right approach and understanding, you can craft a story that not only captivates but also earns you top marks. This guide will walk you through the process of developing your narrative, from the initial brainstorming phase to the final touches before 'pens down'!

Understanding the Assessment Criteria
Before embarking on your creative writing journey, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the assessment criteria is imperative. The evaluators of your English language GCSE creative writing piece will scrutinise several key areas: the coherence of your narrative structure, range of ideas you explore, the variety and complexity of your sentence structures, and the precision of your spelling, punctuation, and grammar. Familiarity with these standards is not just a prerequisite but a strategic tool; it enables you to tailor your creative efforts to meet these benchmarks. As you proceed with each stage of your writing, keep these criteria at the forefront of your mind. They serve as a guiding framework, ensuring that every element of your piece, from the initial plot conception to the final dialogue, contributes towards a cohesive, engaging, and technically proficient narrative. Remember, understanding what is expected is the first step to excelling in your creative writing question.
Finding Your Inspiration
We often talk about 'cultural capital' and how evident it is in the most engaging creative pieces we read when examining. Cultural capital is all around you: let curiosity be your guide, leading you through books that span genres and eras, conversations that challenge and provoke, and the rich tapestry of everyday life. Engage with various forms of art - cinema, paintings, music - to stimulate your senses and uncover fresh perspectives. Record fleeting thoughts, overheard conversations, or the peculiarities of a typical day in a dedicated notebook. This reservoir of ideas will become an invaluable resource to tap into in the exam. Always remember, the seeds of great stories lie in the willingness to explore and the readiness to be inspired by the world around you.
Planning Your Story
After identifying a spark of inspiration, it's crucial to channel that energy into a structured plan for your piece. Crafting an outline is essential, so don't skip the plan! Examiners can always spot an unplanned piece as it will fall apart somewhere around the middle. You only have 50 minutes:: you have time to write a moment, not a movie. Imagine a fascinating five minutes in the picture you've been given as stimulus. Plan a conflict, a contrast or a change that could happen within the five minutes. Remember, a well-thought-out plan not only acts as a roadmap for your writing but also ensures that your narrative remains coherent and compelling from start to finish.
Crafting Descriptive Settings
The environment where your narrative unfolds plays a pivotal role in immersing your audience in the world you’ve created. To craft settings that captivate, employ descriptive language that appeals to the senses. Envision your scene's sights, sounds, smells, and textures, and articulate these in your writing to conjure vivid imagery. Consider the emotional tone your setting imparts; a bustling city street can exude energy and possibility, whereas a secluded forest path might evoke tranquillity or mystery. Reflect on how the environment influences your characters’ actions and decisions, adding depth to your story. A well-drawn setting acts not merely as a backdrop but as a character in its own right, with the power to affect mood, reveal aspects of your characters, and even steer the narrative’s direction. Through thoughtful description, your settings can become memorable landscapes that linger in the reader’s mind long after they've turned the final page.
Don't skip the final five minute check
It feels very tempting to write to the last second but I implore you not to. Even if your spelling, punctuation and grammar is already perfect, the last second tweaks and edits you make could take you from one grade into the next.
Found this helpful? You can sign up for my creative writing guided revision session here .
Recent posts.
5 simple steps to analysing quotations

FICTION AND NON-FICTION WRITING
How to plan and structure a piece of creative writing, this guide deals with how to write a plan for both fiction and non-fiction writing at gcse. it is not a guide for how to write effective fiction and non-fiction. it’s just about how to plan, which is, in itself, both important and challenging. there are other guides on the website which deal with how to actually write the different parts of both fiction and non-fiction pieces., contents of this guide, why planning is essential, two key principles for planning fiction and non-fiction, exam planning vs. non-exam planning, planning fiction, planning non-fiction – writing to argue/persuade.
Summary of this guide
Planning is essential for any creative writing task. You must think about the whole piece before you start writing. You need to have something engaging at the start, and you need to develop your ideas / characters across your piece. You also need to bring your piece to some kind of satisfying resolution, ideally one which links back to your opening. This requires planning. It’s almost impossible to do this without at least some planning. This guide will take you through what it means to write a plan (and also what doesn’t count as a plan), before giving you some tips on how to plan both fiction and non-fiction pieces.
A plan is not the same as some notes or a brainstorm or any similar writing down of ideas. A plan is about structure – you are outlining the order in which you will write your piece :
What will you write first?
What will you write next?
What will you write after that?
And so on, until you get to the end.
In order for a set of ideas to become an actual plan, they must:
Be put in order (key principle 1)
Go from the start to the end (key principle 2).
That’s what a plan is. One way to think about this is to ask yourself what would happen if you gave someone else your ‘plan’ and asked them to write it up in full. How similar would their piece be to what you have in your head? If the plan is an actual plan, then their piece should be quite similar, at least in terms of overall content.
Time constraints matter a lot when it comes to writing a plan. In an exam you will typically have about 45 minutes to plan and write your piece, whether it’s fiction or non-fiction. You should spend 5-10 minutes planning, leaving you 35-40 minutes to write. This means your plan will necessarily be slightly less detailed than it might be if you were planning without time constraints.
That said, this guide will still take you through the ideal approach to planning. Depending on how quickly you are able to think and write, you may need to plan in slightly less detail than we outline here, though the two principles above still hold: your plan must be in order and it must go from the start to the end . It just might need to be a bit less detailed than the examples in this guide.
In an exam, the plan only needs to make sense to you, so you can include fewer small details than we do in the examples in this guide - as long as you plan in your head and know what you want to do, then the plan you write down should be fine.
The first thing you need to understand when planning fiction is the difference between plot structure and narrative structure . Plot structure is the order in which the actual events of a story take place. Narrative structure is the order in which the writer tells the reader about the events in the story. These two structures may be very similar, but they are unlikely to be exactly the same, especially if the story is well structured. You need to plan your narrative structure, not your plot structure , with timeshifts signalled.
The second important thing to bear in mind when planning a short story is the concept of conflict and resolution . In order for a story to have some kind of narrative tension and drive (and therefore to be an actual story, and not just a sequence of events), it must have conflict (e.g. some kind of problem that needs to be overcome), and there must be some kind of resolution at the end (e.g. the problem needs to have been at least somewhat solved). Your plan must include the resolution ; you need to know how your story is going to end before you start writing.
The final thing you need to include in your plan is what you, as the writer, will do in the story. You need to plan how you will tell the story, not just what happens in it. So, you might include things like “describe the café in detail” or “show don’t tell her reaction to the dinosaur” or “increase the tension here”. There are many ways you could plan these kind of directions to yourself, but some common ones are included in the list below:
Description (e.g. describe the man’s elegant hat)
Characterisation (e.g. convey Peter’s awkwardness and insecurity)
Direct speech vs indirect speech (e.g. use indirect speech to convey conversation)
Slow time vs. fast time (e.g. slow-time down – convey Sally’s fear with thoughts)
Show don’t tell (e.g. show don’t tell Grandpa’s frustration)
Timeshift (e.g. timeshift back to the funeral)
Intended effect on the reader (e.g. create suspense with ambiguous threat)
To make all of this a bit clearer, let’s look at two fiction plans, one bad and one good.
Bad fiction plan - not really a plan
Peter is feeling insecure about his new hair cut on his way to school
Thought it was good at first but now he’s worried people will make comments
When he arrives at school people are nice about it
He feels relieved
There’s nothing wrong with the plot here. It is simple, clear and has some conflict (Peter’s fear about his hair cut) and a resolution (people are nice). But as a plan, this is very poor. It doesn’t go into any detail about how the story will be told. It just has the basic plot structure, with very little sense of narrative structure and no sense whatsoever of how the writer will tell the story effectively. If we asked two different people to write this story, two things would happen: first, they would each have to do a lot of work figuring out what to write; second, in the end, they would write the story in very different ways. This means the plan is not clear or specific enough. It is a bad plan.
Good fiction plan - a proper plan
Peter gets out of his mum’s car outside school – thinks a Year 7 is looking at him funny – don’t say why (mystery) – Peter is frowning
Describe the setting outside school – make it clear how busy it all is - how many people there are to judge and laugh
Peter runs fingers through hair – it’s so short
Spots boy from his year going through gate – doesn’t see Peter – relief
Timeshift – tell hair cut episode – make reasons and haircut fears clear
Fast-time – Peter going into school and down corridors (nobody he knows well) – summarise fears – continues to frown
Slow-time – sees friends – walks towards them – create tension – describe their faces and Peter’s thoughts (paranoia) – still frowning
Direct speech – greeting and reply (no mention of hair) – include Peter’s thoughts
As they enter form room Dave (best friend) leans over and says “The hair looks good, mate.”
Peter smiles
This is a much better plan. It’s the same plot as the bad plan, but it actually explains how the story will be told; it’s not just a rough summary of what happens. If two people were given this plan then they would have a good foundation on which to build and they would both write roughly the same story, albeit with different specific details. This is what you want from your plans. It has lots of directions for the writer (direct speech, timeshift, slow and fast time, etc) and it includes enough specifics for the structure of the story to be clear. There is a lot that still needs to be decided in order to actually write the story, but that’s perfectly fine: you’re only writing a plan. This is a good plan.
The first thing you will need to plan for most types of non-fiction is the opening and linked closing . You should be aiming to create a circular structure , where the end of the piece links back to the start in some way to bring about a satisfying ending. This should be included in your plan. You will also need to think very carefully about the opening paragraph of your piece, as this is so important for a successful piece of argue/persuade writing. (There are two separate guides on the website for how to write openings/closings - you should look at part 1 first, obviously.)
You will then need to plan the basic contents of each paragraph – one bullet point per paragraph . For exam pieces you only need a 3 or 4 paragraphs between your opening and closing; you won’t have time to write more. Remember that you will be making an argument in your non-fiction writing, so your paragraphs should build on one another ; this is something you will think about as you plan.
For this part of your plan you might also want to include the type of paragraph you are going to write. Roughly speaking, it will be one of the following three types:
Argument paragraphs – where you explain your view of something and the reasons you hold it (could be abbreviated to ARG in your plan)
Anecdote paragraphs – where you tell a story about your own life (could be abbreviated to AN in your plan)
Real world evidence paragraphs – where you talk about something in the real world which illustrates your point, either something from the news or something from popular culture, like a meme or a TV advert or film or something similar (could be abbreviated to RW in your plan)
You will generally have a mixture of all three of these types in any piece of non-fiction writing, and you don’t have to include them all, but it can help to think in these terms as you plan. (There is a separate guide on how to write these types of paragraphs on the website.)
To make all of this a bit clearer, let’s look at two non-fiction plans, one bad and one good. This is for a question about whether or not it is important for people to go on holidays.
Bad non-fiction plan - not actually a plan
Holidays are a luxury, not a necessity
Lots of people can’t afford to go on holiday
Better to spend the money on essential things like food and clothing
Unfair social pressure
There are the bones of a good piece of persuasive writing here: there is a clear opinion about the importance (or not) of holidays, and there are some ideas that could make an argument. But there is no sense of structure. It is just a series of thoughts jotted down into a list. It’s a good brainstorm for a question about holidays, but it’s a bad plan.
Below is a better plan using the codes suggested above: AN = anecdote paragraph, ARG = argument paragraph, RW = real world evidence paragraph.
Good non-fiction plan - an actual plan
Opening - AN about holiday bores - they’re the worst
ARG - holidays are given too much importance in society - adverts, small talk (where did you go?), etc
RW - cost of living crisis - inflation, fuel, etc - lots of people struggling
ARG - unfair social pressure - better to spend money on essentials, on making the day to day better (e.g. home improvement)
Closing - AN about how to deal with holiday bores - cut them off - “Boring!” - “I didn’t go on holiday” - make them uncomfortable
This is a better plan. It’s still recognisably the same argument as the bad plan, but it’s arranged more clearly into a series of paragraphs which would come together to form a piece of non-fiction writing (an article or a speech, most likely). Each bullet point is a separate paragraph, and there is a clear idea for how to open the piece in an engaging way, with a linked closing at the end. The types of paragraph are also included in the plan using the abbreviations mentioned earlier in the guide (ARG, AN and RW). There is a lot that still needs to be decided in order to actually write the piece, but that’s perfectly fine: you’re only writing a plan. This is a good plan.
Summing up - key things to remember when planning a piece of writing
Planning is not an optional extra – you must plan every piece of writing you produce
A plan conveys the structure of the piece: it must be in order and it must go from the start to the end
When planning fiction, you need to plan the narrative structure of your piece (how you will tell the story, including directions to yourself on what to write) and not the plot structure (the order in which things happen)
When planning fiction, you must know how you will resolve your conflict(s) before you start writing
When planning non-fiction, you need to think carefully about how you will create a circular structure , with an opening and linked closing
When planning non-fiction, you should use one bullet point per paragraph , ideally including the type of paragraph you will write
How to write argue/persuade opinion paragraphs
How to construct different types of sentence.

Miss Huttlestone's GCSE English
Because a whole class of wonderful minds are better than just one!
2 Grade 9 Creative Writing Examples
I recently asked my year 11s to pen a piece of description and/or narrative writing for their mini assessment. I gave them the following prompts:
Your school wants you to contribute to a collection of creative writing.
EITHER: Write a short story as suggested by this picture:

OR: Write a description about a person who has made a strong impression on you.
The following were two COMPELLING and CONVINCING examples of the second choice – one pupil taking ‘you’ as a fictional invitation, the other as a biographical one:
EXAMPLE ONE:
Gradually, I awake and open my eyes only to see the cracked white ceiling which greets me every day. Here I sit, slumped in the bed with the scratchy white sheets hugging me and muffled beeping noises jumping into my ears. Rubbing the sleep crust from my bloodshot eyes, I observe the scene before me. The sound of footsteps overlapping as nurses rush from bed to bed; the metallic tang from stainless steel invading my nostrils; the cold metal bed rail imprisoning and mocking me; the pungent scent of antiseptic troubling me and the blood-curdling cries and moans utterly terrifying me. Using all my strength, I try to imagine I am somewhere else, anywhere else but here.
Crowds, signs, roars: it was 1903 and the suffragette movement had begun. It was a crisp night, refreshing almost and I had taken to the streets. It was like I was possessed by something that night, some urge and deep desire within me that had led me there, surrounded by women like myself. I stood clueless and lost in the crowd; the women yelling ‘Deeds not words’ in unison; passionately parading with large wooden signs and viciously shattering windows with bricks and stones. Despite the violence that was displayed before me, I was not afraid of what was happening and I didn’t deem it unnecessary or improper, in fact I wanted the same as these women, I wanted equality. Abruptly, all of the roars and cheers became muted and faint, one woman walked slowly towards me, her hair messily swooped into an updo, her clothes somewhat dirtied and her chocolate brown corset slightly loosened. There was a glimmer in her eyes as tears seemed to swell within their hazel pools, she seemed inspired, hopeful. After reaching me in the crowd, she held out her hand, gently passing me a sign. Immediately, I clasped it and the yelling and chanting rang loudly in my ears once more. My journey had begun.
Here however, is where it ends. I am aware I do not have much time left, as the doctors have told me so, and spending my last moments in this hospital room is not optimal. However, as I look around I can see beauty within a room which at first glance seems void of it. The hollow medical tubes by my side remind me of the awful act of force feeding I have faced in the past; the shrieks and bawls of patients reflecting the pain women had felt in my time and the bed bars mirroring the prisons we were thrown into and the gates we would chain ourselves too. I know these things may seem far from beautiful, but I can see my past within this room, the power I possessed and the changes I have contributed to today. I know now that I can leave this earth having had an impact. Slowly I close my eyes, I can see her, the women who changed my life many years ago, her name, Emmeline Pankhurst.
EXAMPLE TWO:
I will never forget that day. The hazel pools of her eyes glazed over, and hands delicately placed at her sides. Nobody in the room could quite grasp the fact that this was happening. The crowds of black attire row on row seemed to mimic the thing she loves most in life, the piano. However, this time she had taken the ivory natural keys with her and left everyone else with the sharp tones. You needed both to create beautiful symphonies but all that filled the room was the excruciating silence of her absense. Even the metronone like ticks of the clock seemed to come to a standstill.
It had all began that day, she seemed to open up this whole new world for us to explore together as she placed my fingers onto the keys for the first time. I knew that this was what I was meant to do. She was the most passionately beautiful pianist I had ever seen in my life. Often, I would peer round the oak doorway before my lessons just to catch a glimpse at her. It seemed like nothing in the world mattered to her at the time.
As the years progressed, so did the scope of this world we were exploring. Each sheet of lovingly handwritten sheet music was like a new section of the map we were slowly creating together. Each of her students had their own map. Each as beautiful and each as unique as the pianist. The crotchets and quavers that adorned the staves directed the different paths we could take as my fingers graced the keys. This may not have been a beautiful ballet routine, but this was our dance and it had been carefully choreographed just for us.
That piano room was the safest place in the world. Every inch of it her: the potent scent of her floral perfume; shelves full of scruffy and well loved sheet music; rows upon rows of framed photos of her and her students; the vintage piano which she always kept in tune, it was home. I couldn’t bear the
idea that someone else was going move in and rip away the music room without a second thought. It was her music room.
It was up to me now. Up to me to finish this journey we had begun together.
She may not be with me in person anymore, but she will always live within the world we built together and nothing could ever change that. For she could never truly be gone since she left a piece of her within every one of her students; the passion for piano.

Share this:
Published by.
gcseenglishwithmisshuttlestone
Secondary English teacher in Herts. View all posts by gcseenglishwithmisshuttlestone
2 thoughts on “2 Grade 9 Creative Writing Examples”
This has helped me a lot, I myself am preparing for a narrative test like this and these prompts and descriptive short stories are marvellous! Thank you for sharing this! 🙂
My pleasure!
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Creative Writing: How to Sculpt My Narrative Vision?
Creative writing traditionally stands in opposition to technical writing, so named because it is used to differentiate imaginative and particularly original types of writing from more rigid types. However, creative writing is just as technical, and difficult, as these other types. The assumption is often made that creative writing is a talent – “can I really learn how to write creatively?” – but the true keys to creative writing, whether writing for your own enjoyment, preparing for a school or GCSE exam, are imagination, content, and organisation .

What do these three things mean?
Imagination – the GCSE prompts are usually very open-ended and broad, remind yourself that broad questions are not restrictive, and allow your mind to explore all caveats of the question, and take the reader on a truly original journey
Content – to showcase your ideas you need to be able to show your skill with tone, style, and vocabulary; we will touch on just how to do this later!
Organisation – planning the structure of your answer is key, even though creative writing can be seen as ‘looser’, remember that a good structure is a good way to ensure you are staying in control of the piece. We will touch on how to plan effectively later too!
Focussing on the ‘how’ and developing it:
It can be very daunting when you are presented with a vague prompt to think about how you might achieve all of these things, now we know what they mean let’s look at how we might break them down with an example.
Take the prompt: ‘ Think about a time you were afraid ’.
1) Imagination – where are you going with this? The prompt allows a lot of scope for you as a writer to take this piece wherever you want. You want to plan a piece you are excited by, that you are confident writing, and that is a little bit ‘outside the box’.
We can anticipate many students’ answers describing a spooky forest or a secluded house at night-time; if you are pushing for the higher boundaries, you want to write something that will make the examiner notice you.
Think about the last time you were afraid – how likely is it that you found yourself in a horror-film-esque eerie setting? Perhaps you want to describe the time you auditioned for the school talent show, or your first trip into the dentist alone. You don’t have to be totally avant-garde but remember a skilled writer can create a sense of unease using literary technique alone – don’t rely on a traditional ‘spooky setting’.
2) Content – how are you going to take us there? You want to ensure your communication is convincing and compelling. This means your need to maintain style and tone throughout.
Make a decision about the characteristics of who is narrating your story early on and stick with it (it will often be directed at you, but the examiner doesn’t know you as a person – be creative! If it suits your story to make yourself smarter, more anxious, quieter etc, then do it). Let’s look back to our prompt above. Perhaps you make the decision that you’re writing the piece as you, and you’re incredibly forgetful. This might mean you ask short questions throughout the piece, raising the tension. Maybe you feign confidence and so while the speech of the piece seems assured and at ease, the internal monologue is vastly different, throwing a sense of unease to the narrative early on.
Be ambitious with your vocabulary! Vocabulary is a great way to help set the tone of a piece. Likewise, explore a wide use of linguistic devices (metaphor, simile, imagery, personification, repetition, symbolism – we will come back to these later!)
3) Organisation – how can you plan effectively? When writing a creative piece, first and foremost, you want to ensure you have a varied use of structural features within your paragraphs.
As a rule of thumb, each new paragraph should aim to develop the story and either bring a new idea into the story or develop a previous one. Within each paragraph, aim to show the examiner that you are capable of developing your idea (i.e. continuing the narrative and plot), but also that you are able to detail this from a different perspective.
An effective way to do this is with a structural feature: pick an interesting way to start a new paragraph, focus on contrast, play around with repetition (if you can, play around with the pace of the writing too – see below!), withhold information, use dialogue, experiment with different sentence structures and paragraph lengths, etc.
Some specifics on: ‘linguistic devices’ and ‘structural features’
Linguistic devices and structural features, when used well, can help to make your writing incredibly compelling. Let’s look at some specifics on how we can play around with these and incorporate them into our writing.
1) Linguistic devices
Metaphor and simile – metaphors and similes are both ways to introduce comparisons into your work, which is a good way to bring some variety when describing something instead of just listing off more adjectives. Similes are used specifically with the words ‘like’ or ‘as’ (“life is like a box of chocolates”); metaphors are a direct statement of comparison (“life is a rollercoaster”).
o How can you use these originally? When using these, we want to showcase not just our ability to use them, but also our imagination and vocabulary. With both of these, think of appropriate comparisons which develop the tone of your piece. For example, if you are writing a piece about happiness – ‘his smile was like that of a child at Christmas time’ (simile), or, if you are writing a piece about loneliness – ‘loneliness was a poison’ (metaphor). See how both comparisons match the tone – when writing a happy piece, we use specific things about happiness (e.g. Christmas), when writing a sadder piece, we use sadder objects for comparison (e.g. poison). This will help develop tone and showcase originality.
Imagery – this is used to develop key motifs within the mind of the reader; again, this is a tool for comparison whereby we are comparing something real with something imagined or ultimately non-literal.
o A good way to think of imagery is to appeal to the reader’s senses: how can you create a sensory world for them? Take the brief above once more. We could say “I was afraid when I left the house”, or, we could appeal to sensory imagery: “I pulled my auburn hair into my mouth to chew it as I closed the door to the house. Thud. The air was cold on my cheeks, and my pink nose stood out against the grey sky and grey pavement.” Here, we paint a far richer picture, even though we don’t necessarily develop the story.
Personification - when a personal nature is given to a non-human object. This can be useful when you are faced with long descriptive paragraphs as it serves as another way to break up boring adjective listing.
o Be imaginative and try and include this once in every piece if you can. Remember to tie it in with developing the tone of the piece! I.e. if you are writing a happy piece: “the sun smiled down on me, and I beamed back with gratitude” – this sentence creates an immediately positive atmosphere. However, the sentence: “the wind whispered quietly through the long grass” creates a sense of uncertainty. NB: notice how the weather is an easy and subtle way to help develop a ‘feeling’ throughout your writing.
Repetition – a word or phrase is repeated in order to achieve a certain desired effect. We can use different types of repetition to remain original and keep our writing sophisticated:
o Try repeating only the last few words of a line – “If you don’t doubt yourself, and you can keep a clear head, then you can do it. You can do it.”
o Try repeating the same phrase at the end of following sentences – “On the fields there was blood, in the sea there was blood, on the sand banks there was blood, on the ships there was blood…”
o Try repeating the same words in a new sense to reveal information in a new light – “I don’t dance because I am happy, I am happy because I dance”

2) Structural features
Openings – you want to make sure the start of your text entices the reader, so you may want to start with a very developed complex sentence, with heaps of sensory imagery that immediately immerses the reader in the world of the piece; alternatively, or you may wish to grab their attention in a more direct way – “Bang! Oh god, how was I going to get out of this?”
Contrast – highlighting the difference between two things is a compelling way to describe and develop ideas; we have talked in depth about ways to do this above (simile, metaphor, imagery, sometimes repetition for effect)
Pace – experimenting with the pace of the piece is a very sophisticated way to create a mood. For example, if it is a summer’s day and time does not seem to pass, find a way to highlight this using some of the techniques outlined above – “the sun sat high in the sky, unwavering, for what seemed like forever”, “the sounds of the crickets chirping and the birds merriment overpowered the sound of my watch – we felt truly timeless”. Equally, if you want to build tension, find a way to increase the pace; generally, this can be done by piecing together short, simple sentences: “I knew I had to move fast. Round the door. Up the stairs. Wait. Breathe. Move. Up the next flight. Clear. Move.” Etc, this helps immerse the reader in the mental world of the narrator and as a result they engage far more with the piece.
Dialogue – inserting dialogue into a piece can be a convincing way to introduce new information to a text, think of ways to be inventive with this: does our narrator talk to themselves? What information are we told about additional characters that are introduced? What new approaches have we learned to aid with describing these new characters – and remember – always choose these in line with developing a tone for the piece.
Withholding information – this can be a useful way to build a sense of uncertainty and unease into a piece. Perhaps the narrator is withholding information from other characters, perhaps the narrator is withholding information from the readers themselves! “I knew it had to be done. I didn’t have time to consider the what-if’s and the maybes of it. It had to be done. And it had to be done now.” How much more unsettling is that sentence when we don’t discover what the ‘it’ is – if we want to create humour for a light-hearted piece, perhaps it is getting a tooth removed; if the piece is darker, perhaps the ‘it’ is something far more sinister…
Sentence length – Play around with a variation of simple and complex sentences. Complex sentences can be difficult to construct at first. Remember a few key rules: they are either used effectively to develop one key motif: ‘the snow was white and fell down like tiny elegant dancers in the wind, until at just a moment’s notice, it would land and join a far larger flurry of white across a thousand snow-drenched fields’. Additionally, complex sentences can be used to introduce a lot of new information in one succinct way: ‘It was autumn when he last came, not that I had been counting, but when he last came my hair came only to my shoulders, and I was not yet tall enough to reach the apples on the tree – gosh, what would he think of me now’. The difference between the two is clear, one develops a singular motif and one introduces new ideas quickly – both are effective, and you should aim to be able to write both types well.
While creative writing can seem daunting at first, using the three keys to success (imagination, content and organisation) alongside these advanced linguistic devices and structural features is a great way to develop and succeed in the creative writing exam. Start to enjoy taking the reader on a journey, learn to navigate the realms of description, experiment with tone and you will be well on your way to success!
“Write it like it matters, and it will.” – Libba Bray
By U2 mentor, Hazel (Philosophy & Theology, University of Oxford and a published poet!)
Looking for a Creative Writing tutor to develop written skills?
If you are interested in support for your GCSE English Language or Literature papers, or general Creative Writing endeavours, why not check out our offerings on the GCSE page and book a free consultation to discuss how we can boost your chance of success. We have a large team of predominantly Oxbridge-educated English mentors who are well-placed to develop students’ written skills, teaching how to structure writing, and the literary and rhetorical techniques that this requires.
The ELAT: Our Guide to the Oxbridge English Admission Test in 2024
How to write a formal letter (11+ to gcse).
Paper 1: Creative Writing
In the exam you're normally given two options: a descriptive piece or a narrative piece. neither is worth more or less than the other so it's up to you to choose which suits you best. though describing the same thing for 45 minutes can see a little tough, i'd argue that the description is actually easier than the narrative. the problem with writing a short narrative, is its shortness., to do this well you need to make sure that your plot is very, very , very , very simple . you'll only have 45 minutes to write it, and that doesn't leave a lot of space for character development or events., really, you should be able to tell your storyline in one sentence, any more than that and it's probably too complex for the exam., i've included some of my own below to give you an idea of how much plot i've managed to include....
The Simple Scene
Perspectives
An Unreliable Narrator
Using Description
Read over the stories above and pick one structure that you think you could use. then, google some images and see if you can find a way for your chosen structure to become a story connected to that image. the key with a structure is that you can practice with it, but it will still fit any end you choose., but also, there are literally millions of short stories on the web, simply because writing is such a pleasure and sharing stories is so fundamentally human. to help you filter through some of them, you'll find a list of some of my favourite places below:, https://themolotovcocktail.com/, https://wigleaf.com/, https://blog.reedsy.com/short-stories/, https://www.flashfictiononline.com/.
codexterous
Thoughts about teaching, literature, and teaching literature
Modelling Creative Writing: A Model Example and How We Got There

If you enjoy this blog post, then you’ll love my new book Experiencing English Literature . With dedicated chapters on teaching novels, plays and poetry as well as teaching generative writing, sentence-stems and essay structure, it is filled with actionable strategies ready for the classroom.
You can order it right now HERE !
For the last few lessons with my GCSE class, we’ve been working on creative writing. Up until now, we’ve done a lot of work on refining and rehearsing certain sentence stems, most of which have been taken from Chris Curtis’ superb book, How to Teach English.
This has included doing tasks such as the below with the stem ‘A Year Ago, A Month Ago, Today’.

However, we’ve recently started rehearsing overall text shapes and practising general approaches to planning and generating ideas. One such task included students completing the below planning document (although not for this specific bus image), with this template offering a useful scaffold for prompting the kind of thinking and approach they ought to take.

Whilst the students used the exact same format, the above is actually one that I completed and live modelled. They had another image — the one asking students to write a description suggested by a busy market. The idea was to see how I approached it, but to then apply the same principles to a separate image.
Once we had done this, I then live modelled the first paragraph of my response. As I did so I verbalised the choices being made and even noted these down in the margin so they become more obvious and hopefully clearer.

Once I had live modelled this paragraph they then wrote their own first paragraph, but using their original plan and the market image. Again, as I explained to them, they were seeing from me the underlying approach and principles, but applying that to their own plan and a separate image.
And so we went on: I did the next paragraph, then they did it, and then I did another, and they did another, and so on.
By the end of this process I had incrementally live modelled a full response and they had, in steps, produced their own response to a different question.
Below you’ll find my full version for you to use, if helpful, with your own students.
The Model Response
A year ago I stood brightly polished on my platform. My number 8 shining, twinkling in the sun. A month ago my wheels started to creak. They started to break. They started to crack. My paint chipped. My windows splintered, a long fracture running the length of my shiny skin. Today, I sit waiting. Waiting to be picked up. Thrown away. I sit waiting, the dust and broken mud blowing through the cracked skin of my leather seats. I can hear the magnet hover above my bruised head. Today, my time is up.
20 minutes left.
My headlights, once shiny but now dull, swivel in my steel skull. I stare back into my engine. Once it glistened with oil, slick with grease. But, now it is caked in dust and dirt. I feel the cracks in my mind, splinters of metal sticking into me. My tubes force themselves into my plastic eyes. I feel the groan of my metal bones, the dried oil spread thickly across my rusted mind. Slowly, my eyes swivel outward and I see it again. Hovering. The magnet.
10 minutes left.
As the noise of the magnet grows louder, I remember what it felt like to be brand new. Proudly stood on my platform the now rusted number 8 would shine in silver. My tyres were pumped full of air, almost bouncing jubilantly on the road as I drove through wind. Unstoppable. Through hail. Through rain. Through snow. My mirrors glistened and my seats seemed to hug and cradle my many passenger. Now I am empty. Deflated. Abandoned. My life has been measured in miles and now I have reached my final stop.
5 minutes left.
The magnet snaps onto my back. I feel my steel skin press itself tightly against the metal disk. Pulling. Tearing. Pressing. It begins to lift me high into the air. I hear its chain groan but still it winds me in. Pulls me forward. My eyes swivel downwards and I see what has been left behind. A wing mirror. A bulb. The broken rubber of a broken tyre. A door. I see the pieces of myself discarded in the dust. My number 8, once so bright, is left crumpled on the floor.
One last journey. One last stop. No minutes left.
Share this:
One thought on “ modelling creative writing: a model example and how we got there ”.
Thank you so much for this. It is extremely helpful especially for or what I’m I’m trying to teach at the moment – An Inspector Calls
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Blog at WordPress.com.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Resources you can trust
Creative, imaginative, descriptive and narrative writing
Develop KS3-4 English students' confidence and enjoyment in writing for pleasure with a selection of inspiring classroom resources and activities.

One of the great pleasures – and challenges – of teaching English is helping students to develop their own 'voice' and style as writers of short stories. Assessing their creative, imaginative, descriptive and narrative writing skills at GCSE is a different matter, and can prove to be less rewarding for students, as writing on demand can test even the most confident of writers. The rich collection of creative writing resources on Teachit, generously shared by our fantastic English teacher contributors, are a testament to the creativity, resourcefulness and ingenuity of English teachers as we seek to tease out the best in students' writing. Here is a selection of popular resources for writing classes and lessons, as well as some of our newly published creative and narrative writing resources:
Planning and structuring writing
Story building grids is a flexible writing prompt resource to help students with the first steps of planning the writing process, with suggestions for different literary devices to include (metaphors, similes, alliteration, personification, dialogue, point of view etc.).
Another writing prompt resource, Beth Kemp's Imaginative writing: creating a scene , carefully walks them through the whole planning and writing process. Like a screenplay writer, students learn how to zoom in on key scenes to create pace, tension and atmosphere, while considering point of view and their main characters' traits. This resource also focuses on the importance of re-writing and editing their piece of writing. Fran Nantongwe's delightful and hugely popular The quest for a cure is perfect for younger students and will take your class through a range of different genres and written forms over several English lessons, and also includes some non-fiction tasks.
Word choices
Ditch the adjective is a great new resource by contributor Sally-Ann Griffin, which include a range of writing tips to guide students through the process of making better word choices and focuses on the importance of re-writing.
English teacher Helen Down's Turning pictures into word banks helps students to select really engaging words to use. Writing pyramids is a flexible resource for students to refer to again and again to support their writing experiments.
Story starters
For inspiration for creative writing activities, try Super story starters or Engage your sleeping author! which offers students a range of examples of creative writing and opening sentences which help them to explore different forms (diary, epistolary, historical). With imaginative writing, it's important to inspire students. Stephen Mitchell's Exploring beginnings and Attention-grabbing story starters both encourage students to consider the effect of different story openings. For a series of lessons, try the thoughtful Memory-inspired creative writing . And if you are looking for more imaginative writing, creative writing or narrative writing resources, try our Writing fiction or Writing techniques collection for hundreds of classroom resources for English students and teachers on the following:
- how to create characters and explore character development
- how to experiment with narrative style, such as using the first person or exploring different points of view
- how to explore different genres, settings or plots, and different types of creative writing
- how to use literary devices and techniques.
For non-fiction and creative non-fiction writing, try our Writing non-fiction texts collection.
This article was first published as an Editor's pick newsletter in January 2022.
Share article link
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Twitter
- Share via Pinterest
- Share via Email
Senior Content Lead at Teachit, and former head of English and e-learning.
< Previous Article
Sats 2024: everything you need to know, next article >, developing students' oracy skills: effective speaking and listening, sign up for free.
Sign up to Teachit for access to thousands of free resources
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
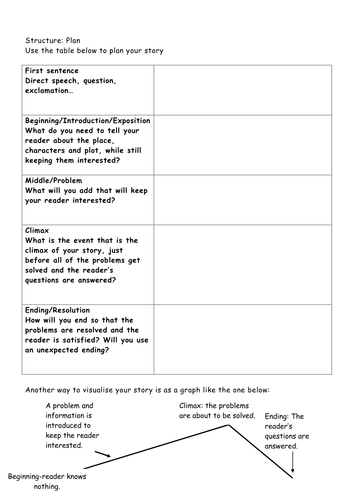
Structure planning sheet Creative writing
Subject: English
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
24 June 2012
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
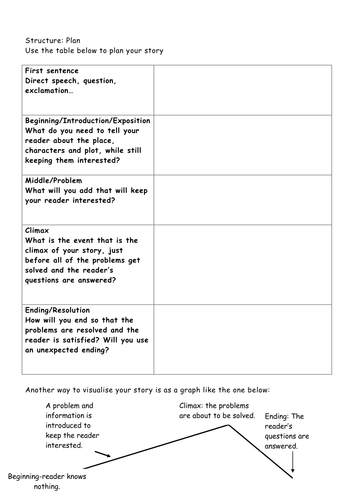
Tes classic free licence
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Great. Thanks for sharing
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Great resource thank you for sharing.
darlene_gedye
Love this resource with accompanying activity. It can be so hard to get students to reveal rather than tell. I think this could be just the ticket to practising this fine art. Thank you.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To enhance your children's GCSE creative writing skills, allocate time for practice. Plan a structure for creative writing to guide children in organising their thoughts and managing time during the GCSE exam. Apply this structure to various exam questions, such as short stories or describing events.
The style of the writing (sentence structure and overall structure) is dynamic and engaging; Below you will find a detailed creative writing model in response to an example of Paper 1 Question 5, under the following sub-headings (click to go straight to that sub-heading): Writing a GCSE English Language story; Structuring your story
Unit 2 Reading and Writing: Description, Narration and Exposition gives two prompts to choose between, for an account and an essay perhaps, and Unit 3: Reading and Writing: Argumentation, Persuasion and Instructional sets up a letter, or similar. Jump ahead to WJEC Eduqas non-fiction writing prompts from past GCSE papers.
Chapter 8: Writing creatively 117 Chapter 8 Writing creatively English Language GCSE Which AOs are covered? AO5 Communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, selecting and adapting tone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences. Organise information and ideas, using structural and grammatical features to support ...
Creative Structure Use. By the end of this page you should have a good understanding of how to creatively use structure to improve the quality of your writing. We will cover perspective and point of view, as well as sentence and paragraph structure. This can help you to create a more complex and sophisticated structure in your entire text.
Narration - the voice that tells the story, either first person (I/me) or third person (he/him/she/her). This needs to have the effect of interesting your reader in the story with a warm and ...
In a creative writing question where you have more free reign, like a story or description, there are different ways to experiment with structure.. The basic story arc of beginning, middle and end that you may already be familiar with can be subverted, through a different perspective than the expected main character.; Or the perspective could shift halfway through to give another character's ...
Are you preparing for your English language GCSE creative writing task? Feeling a mixture of excitement and anxiety about how to channel your creativity into a structured piece of writing that ticks all the boxes for examiners? You're not alone. Creative writing can seem daunting, but with the right approach and understanding, you can craft a story that not only captivates but also earns you ...
Time constraints matter a lot when it comes to writing a plan. In an exam you will typically have about 45 minutes to plan and write your piece, whether it's fiction or non-fiction. You should spend 5-10 minutes planning, leaving you 35-40 minutes to write. This means your plan will necessarily be slightly less detailed than it might be if ...
Break down GCSE English Language Creative Writing into an accessible format with our series of dedicated lessons, beginning with Lesson 1 on structure. The key focus of this lesson is to explore how students can structure a narrative for maximum effect. After completing this GCSE English Language Creative Writing lesson, students will be able to: Understand the different stages of a story ...
This booklet is to support your creative writing practice in preparation for your GCSE Language exam. There are two papers: Paper 1 and Paper 2. In Paper 1, the last ques-tion is 40 marks. It will ask you to write either a description as suggested from a picture, or a short story. 24 of these marks are for the ideas you put on the page. 16 of these
Resource type: Lesson (complete) File previews. pptx, 10.67 MB. docx, 16.34 KB. docx, 717.84 KB. This is a fully differentiated lesson looking at how to use structure effectively in creative writing. The lesson has been designed for anyone studying GCSE English and includes example responses to help learners craft their own response.
A whole lesson looking at how to plan for good structure in pupils' own writing. Very relevant to GCSE. GCSE Creative Writing: Structuring Your Work Lesson Pack contains: Planning the Structure of your Written Work Worksheet [PDF] Planning the Structure of your Written Work Teaching Ideas [PDF]
2 Grade 9 Creative Writing Examples. I recently asked my year 11s to pen a piece of description and/or narrative writing for their mini assessment. I gave them the following prompts: Your school wants you to contribute to a collection of creative writing. EITHER: Write a short story as suggested by this picture:
The true keys to creative writing for the GCSE exam are imagination, content, and organisation. ... Organisation - planning the structure of your answer is key, even though creative writing can be seen as 'looser', remember that a good structure is a good way to ensure you are staying in control of the piece. We will touch on how to plan ...
Lessons and activities. Creative and descriptive writing is a great opportunity for students to explore different themes, audiences and purposes as well as demonstrate their understanding of how structure and punctuation can be used to impact a reader. From creative writing prompts to technique booklets and descriptive writing planning mats, we ...
Paper 1:Creative Writing. Paper 1: Creative Writing. In the exam you're normally given two options: a descriptive piece or a narrative piece. Neither is worth more or less than the other so it's up to you to choose which suits you best. Though describing the same thing for 45 minutes can see a little tough, I'd argue that the description is ...
Proudly stood on my platform the now rusted number 8 would shine in silver. My tyres were pumped full of air, almost bouncing jubilantly on the road as I drove through wind. Unstoppable. Through hail. Through rain. Through snow. My mirrors glistened and my seats seemed to hug and cradle my many passenger.
Examiners love to see students demonstrating their knowledge of how to use these four grammatical beauties in their creative writing, and will reward students for their efforts. 1) Minor: 'Marley was dead.' (Often used for short, snappy introductions and to emphasise a dramatic event.) 2) Simple: 'The door to the old counting-house was ...
Published: 27/01/2022. One of the great pleasures - and challenges - of teaching English is helping students to develop their own 'voice' and style as writers of short stories. Assessing their creative, imaginative, descriptive and narrative writing skills at GCSE is a different matter, and can prove to be less rewarding for students, as ...
A double (two hour) GCSE lesson, practising creative writing using a simple structure. Objective: students will practise the skills of planning and structuring a piece of timed creative writing in response to an image. Outcome: A piece of peer-assessed and corrected creative writing. Powerpoint with prompt image and prompt questions / instructions.
Probably one of the easiest type of poem to start with, the only rule is that each line must start with a letter that, when looking diagonally, spells a word. The amount of lines depends on the length of the word, and there aren't any rules on line length or rhyming. These are great to use during topical writing and great to use with a word mat.
Structure planning sheet Creative writing. Subject: English. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. doc, 48.5 KB. Creative writing scheme range of activities to support writing. See more. to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.