Outside USA: +1‑607‑330‑3200

Critical Thinking Cornell Certificate Program
Overview and courses.
Have you ever known a very intelligent person who made a very bad decision?
Critical problem solving is both a discipline and a skill; one that even very smart people can benefit from learning. Careful thought around decisions can help your teams and organizations thrive. And in today’s age of automation, it’s never been a more essential mindset to develop at every level of a company.
In this certificate program, you will practice a disciplined, systematic approach to problem solving. You will learn how to deeply analyze a problem, assess possible solutions and associated risks, and hone your strategic decision-making skills by following a methodology based on tested actions and sound approaches. Whether you’re interested in preparing for a management role or already lead an execution function, you’ll come away better equipped to confidently tackle any decision large or small, make a compelling business case, and apply influence in your organization in a way that creates the optimal conditions for success.
The courses in this certificate program are required to be completed in the order that they appear.
This program includes a year of free access to Symposium! These events feature several days of live, highly participatory virtual Zoom sessions with Cornell faculty and experts to explore the most pressing leadership topics. Symposium events are held several times throughout the year. Once enrolled in your program, you will receive information about upcoming events.
Throughout the year, you may participate in as many sessions as you wish. Attending Symposium sessions is not required to successfully complete the certificate program.
Course list
Problem-solving using evidence and critical thinking.
Have you ever known a very intelligent person who made a very bad decision? If so, you know that having a high IQ does not guarantee that you automatically make critically thoughtful decisions. Critically thoughtful problem-solving is a discipline and a skill—one that allows you to make decisions that are the product of careful thought, and the results of those decisions help your team and organization thrive.
In this course you will practice a disciplined, systematic approach to problem solving that helps ensure that your analysis of a problem is comprehensive, is based on quality, credible evidence, and takes full and fair account of the most probable counterarguments and risks. The result of this technique is a thoroughly defensible assessment of what the problem is, what is causing it, and the most effective plan of action to address it. Finally, you will identify and frame a problem by assessing its context and develop a well-reasoned and implementable solution that addresses the underlying causes.
Making a Convincing Case for Your Solution
When trying to persuade someone, the tendency is to begin in advocacy mode—for example: “Here's something I want you to agree to.” Most people do not react positively to the feeling of being sold something. The usual reaction is to literally or figuratively start backing up. To make a convincing case, it is more effective to engage with the decision maker as a partner in problem-solving. This makes your counterpart feel less like someone is trying to get them to buy something and more like you are working together to bring about an outcome that is desirable to both parties. Begin by asking yourself: “What is the problem you and the decision maker are solving together?”
By the end of this course, you will have learned how to deeply analyze a problem, possible solutions, and the associated risks as well as the most persuasive and efficient ways of presenting your proposal.
You are required to have completed the following course or have equivalent experience before taking this course:
- Solve Problems Using Evidence and Critical Thinking
Strategic Decision Making
The ability to make effective and timely decisions is an essential skill for successful executives. Mastery of this skill influences all aspects of day-to-day operations as well as strategic planning. In this course, developed by Professor Robert Bloomfield, Ph.D. of Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, you will hone your decision-making skills by following a methodology based on tested actions and sound organizational approaches. You will leave this course better equipped to confidently tackle any decision large or small, and you'll do so in a way that creates the optimal conditions for success.
Navigating Power Relationships
Leaders at every level need to be able to execute on their ideas. In virtually every case, this means that leaders need to be able to persuade others to join in this execution. In order to do so, understanding how to create and utilize power in an organization is critical.
In this course, developed by Professor Glen Dowell, Ph.D., of Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, students will focus on their personal relationship with power as well as how power works in their organization and social network.
Project Management Institute (PMI ® ) Continuing Certification : Participants who successfully complete this course will receive 6 Professional Development Units (PDUs) from PMI ® . Please contact PMI ® for details about professional project management certification or recertification.
Interpreting the Behavior of Others
Applying strategic influence.
Being able to influence others is the most fundamental characteristic of an effective leader, but many people in positions of power don't know specifically how they are influencing others' behavior in positive directions. They let it happen by chance or use their formal authority—getting people to do things because “the boss said so.” But as leaders gets promoted within their organization, using formal authority becomes less effective as they not only need to influence subordinates, but also peers, external stakeholders, and superiors. In this course, Professor Filipowicz explores the three complementary levels of influence. First, you will explore heuristics, or rules of thumb, that people use in order to make decisions. Next, you will learn how to influence through reciprocity by uncovering what the person you want to influence wants and needs. Lastly, you will learn how to alter the social and physical environment in order to get the change in behavior you want. By the end of this course, you'll have the skills to consistently draw out the desired behaviors from your team and from those around you.
Leadership Symposium LIVE
Symposium sessions feature three days of live, highly interactive virtual Zoom sessions that will explore today’s most pressing topics. The Leadership Symposium offers you a unique opportunity to engage in real-time conversations with peers and experts from the Cornell community and beyond. Using the context of your own experiences, you will take part in reflections and small-group discussions to build on the skills and knowledge you have gained from your courses.
Join us for the next Symposium in which we’ll discuss the ways that leaders across industries have continued engaging their teams over the past two years while pivoting in strategic ways. You will support your coursework by applying your knowledge and experiences to relevant topics for leaders. Throughout this Symposium, you will examine different areas of leadership, including innovation, strategy, and engagement. By participating in relevant and engaging discussions, you will discover a variety of perspectives and build connections with your fellow participants from various industries.
Upcoming Symposium: June 4-6, 2024 from 11am – 1pm ET
All sessions are held on Zoom.
Future dates are subject to change. You may participate in as many sessions as you wish. Attending Symposium sessions is not required to successfully complete any certificate program. Once enrolled in your courses, you will receive information about upcoming events. Accessibility accommodations will be available upon request.
How It Works
- View slide #1
- View slide #2
- View slide #3
- View slide #4
- View slide #5
- View slide #6
- View slide #7
- View slide #8
- View slide #9
Faculty Authors

- Certificates Authored
Risa Mish is professor of practice of management at the Johnson Graduate School of Management. She designed and teaches the MBA Core course in Critical and Strategic Thinking, in addition to teaching courses in leadership and serving as faculty co-director of the Johnson Leadership Fellows program.
She has been the recipient of the MBA Core Faculty Teaching Award, selected by the residential program MBA class to honor the teacher who “best fosters learning through lecture, discussion and course work in the required core curriculum”; the Apple Award for Teaching Excellence, selected by the MBA graduating classes to honor a faculty member who “exemplifies outstanding leadership and enduring educational influence”; the “Best Teacher Award”, selected by the graduating class of the Cornell-Tsinghua dual degree MBA/FMBA program offered by Johnson at Cornell and the PBC School of Finance at Tsinghua University; the Stephen Russell Distinguished Teaching Award, selected by the five-year MBA reunion class to honor a faculty member whose “teaching and example have continued to influence graduates five years into their post-MBA careers”; and the Globe Award for Teaching Excellence, selected by the Executive MBA graduating class to honor a faculty member who “demonstrates a command of subject matter and also possesses the creativity, dedication, and enthusiasm essential to meet the unique challenges of an EMBA education.”
Mish serves as a keynote speaker and workshop leader at global, national, and regional conferences for corporations and trade associations in the consumer products, financial services, health care, high tech, media, and manufacturing industries, on a variety of topics, including critical thinking and problem solving, persuasion and influence, and motivating optimal employee performance. Before returning to Cornell, Mish was a partner in the New York City law firm of Collazo Carling & Mish LLP (now Collazo Florentino & Keil LLP), where she represented management clients on a wide range of labor and employment law matters, including defense of employment discrimination claims in federal and state courts and administrative agencies, and in labor arbitrations and negotiations under collective bargaining agreements. Prior to CC&M, Mish was a labor and employment law associate with Simpson Thacher & Bartlett in New York City, where she represented Fortune 500 clients in the financial services, consumer products, and manufacturing industries. She is admitted to practice before the U.S. Supreme Court and state and federal courts in New York and Massachusetts.
Mish is a member of the board of directors of SmithBucklin Corporation, the world’s largest trade association management company, headquartered in Chicago and TheraCare Corporation, headquartered in New York City. She formerly served as a Trustee of the Tompkins County Public Library, Vice Chair of the board of directors of the Community Foundation of Tompkins County, and member of the board of directors of the United Way of Tompkins County.
- Omnichannel Leadership Program
- Corporate Communication
- Intrapreneurship
- Management 360
Critical Thinking
- Performance Leadership
- Executive Leadership
- Change Management

Glen Dowell is an Associate Professor of Management and Organizations at the Johnson Graduate School of Management, Cornell University. He researches in the area of corporate sustainability, with a focus on firm environmental performance. Recent projects have investigated the effect of local demographic factors on changes in pollution levels, the role of corporate merger and acquisition in facilitating changes in facility environmental performance, and the relative influence of financial return and disruption on the commercial adoption of energy savings initiatives.
Professor Dowell’s research has been published in Management Science, Organization Studies, Advances in Strategic Management, Strategic Management Journal, Organization Science, Journal of Management, Industrial and Corporate Change, Journal of Business Ethics, and Administrative Science Quarterly. He is senior editor at Organization Science and co-editor of Strategic Organization, is on the editorial boards of Strategic Management Journal and Administrative Science Quarterly, and represents Cornell on the board of the Alliance for Research in Corporate Sustainability (ARCS). He is also the Division Chair for the Organizations and Natural Environment Division of the Academy of Management.
Professor Dowell teaches Sustainable Global Enterprise and Critical and Strategic Thinking. He is a faculty affiliate for the Center for Sustainable Global Enterprise and a faculty fellow at the Atkinson Center for a Sustainable Future.
- Sustainable Business
- Hotel Management and Owner Relations
- Strategic Healthcare Leadership
- Executive Healthcare Leadership

Since coming to the Johnson Graduate School of Management in 1991, Robert J. Bloomfield has used laboratory experiments to study financial markets and investor behavior. He has also published in all major business disciplines, including finance, accounting, marketing, organizational behavior, and operations research. Professor Bloomfield served as director of the Financial Accounting Standards Research Initiative (FASRI), an activity of the Financial Accounting Standards Board, and is an editor of a special issue of Journal of Accounting Research dedicated to Registered Reports of empirical research. Professor Bloomfield has recently taken on editorship of Journal of Financial Reporting, which is pioneering an innovative editorial process intended to broaden the range of research methods used in accounting, improve the quality of research execution, and encourage the honest reporting of findings.
- Management Accounting for Leaders
- Management Accounting

Allan Filipowicz is clinical professor of management and organizations at the Samuel Curtis Johnson Graduate School of Management at Cornell University. Professor Filipowicz’s research focuses on how emotions drive or impede leadership effectiveness, at both the intrapersonal and interpersonal levels. Within this domain, he studies the relationship between emotions and risky decision making; the influence of humor on both leadership and negotiation effectiveness; the impact of emotional transitions in negotiations; and the relationship between genes, chronotype (morningness–eveningness) and performance. His work has been published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, Journal of Operations Management, International Journal of Forecasting, Creativity Research Journal, Journal of Circadian Rhythms, and Scientific Reports.
Professor Filipowicz teaches Managing and Leading Organizations (recently winning a Best Core Faculty Award), Negotiations, Executive Leadership and Development, Leading Teams, and Critical and Strategic Thinking. He has taught executives across the globe, from Singapore to Europe to the US, with recent clients including Medtronic, Bayer, Google, Pernod Ricard, and Harley-Davidson. Professor Filipowicz received his PhD from Harvard University. He holds an MBA from The Wharton School, an MA in International Affairs from the University of Pennsylvania, and degrees in electrical engineering (MEng, BS) and economics (BA) from Cornell University. His professional experience includes banking (Bankers Trust, New York) and consulting, including running his own boutique consulting firm and four years with The Boston Consulting Group in Paris.
- Adaptive Healthcare Strategy
- Negotiation Mastery
- Psychology of Leadership
Key Course Takeaways
- Respond decisively and consistently when faced with situations that require a decision
- Assess the context of the problem
- Summarize your analysis of the problem
- Analyze potential solutions from multiple perspectives
- Build a compelling business case for your solution
- Improve your ability to exercise influence in your organization and activate your network to achieve goals
- Establish responsibilities and accountabilities to ensure effective follow-through on decisions made
Download a Brochure

What You'll Earn
- Critical Thinking Certificate from Cornell Johnson Graduate School of Management
- 60 Professional Development Hours (6 CEUs)
- 38 Professional Development Units (PDUs) toward PMI recertification
- 30 Professional Development Credits (PDCs) toward SHRM-CP and SHRM-SCP recertification
- 30 Credit hours towards HRCI recertification
Watch the Video
Who should enroll.
- C-level executives, VPs, managers
- Industry leaders with 2-10+ years experience
- Mid-level professionals looking to move into leadership roles
- Engineers and designers leading projects
- Consultants or analysts
- Anyone whose work involves devising, proposing, and defending evidence-based solutions

“eCornell puts you in control of your education entrepreneurship. It allows you to choose what you need to learn and how you need to learn it at the right time.”
Request information now by completing the form below..

Enter your information to get access to a virtual open house with the eCornell team to get your questions answered live.
PHIL102: Introduction to Critical Thinking and Logic
Course introduction.
- Time: 40 hours
- College Credit Recommended ($25 Proctor Fee) -->
- Free Certificate
The course touches upon a wide range of reasoning skills, from verbal argument analysis to formal logic, visual and statistical reasoning, scientific methodology, and creative thinking. Mastering these skills will help you become a more perceptive reader and listener, a more persuasive writer and presenter, and a more effective researcher and scientist.
The first unit introduces the terrain of critical thinking and covers the basics of meaning analysis, while the second unit provides a primer for analyzing arguments. All of the material in these first units will be built upon in subsequent units, which cover informal and formal logic, Venn diagrams, scientific reasoning, and strategic and creative thinking.
Course Syllabus
First, read the course syllabus. Then, enroll in the course by clicking "Enroll me". Click Unit 1 to read its introduction and learning outcomes. You will then see the learning materials and instructions on how to use them.
Unit 1: Introduction and Meaning Analysis
Critical thinking is a broad classification for a diverse array of reasoning techniques. In general, critical thinking works by breaking arguments and claims down to their basic underlying structure so we can see them clearly and determine whether they are rational. The idea is to help us do a better job of understanding and evaluating what we read, what we hear, and what we write and say.
In this unit, we will define the broad contours of critical thinking and learn why it is a valuable and useful object of study. We will also introduce the fundamentals of meaning analysis: the difference between literal meaning and implication, the principles of definition, how to identify when a disagreement is merely verbal, the distinction between necessary and sufficient conditions, and problems with the imprecision of ordinary language.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 5 hours.
Unit 2: Argument Analysis
Arguments are the fundamental components of all rational discourse: nearly everything we read and write, like scientific reports, newspaper columns, and personal letters, as well as most of our verbal conversations, contain arguments. Picking the arguments out from the rest of our often convoluted discourse can be difficult. Once we have identified an argument, we still need to determine whether or not it is sound. Luckily, arguments obey a set of formal rules that we can use to determine whether they are good or bad.
In this unit, you will learn how to identify arguments, what makes an argument sound as opposed to unsound or merely valid, the difference between deductive and inductive reasoning, and how to map arguments to reveal their structure.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 7 hours.
Unit 3: Basic Sentential Logic
This unit introduces a topic that many students find intimidating: formal logic. Although it sounds difficult and complicated, formal (or symbolic) logic is actually a fairly straightforward way of revealing the structure of reasoning. By translating arguments into symbols, you can more readily see what is right and wrong with them and learn how to formulate better arguments. Advanced courses in formal logic focus on using rules of inference to construct elaborate proofs. Using these techniques, you can solve many complicated problems simply by manipulating symbols on the page. In this course, however, you will only be looking at the most basic properties of a system of logic. In this unit, you will learn how to turn phrases in ordinary language into well-formed formulas, draw truth tables for formulas, and evaluate arguments using those truth tables.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 13 hours.
Unit 4: Venn Diagrams
In addition to using predicate logic, the limitations of sentential logic can also be overcome by using Venn diagrams to illustrate statements and arguments. Statements that include general words like "some" or "few" as well as absolute words like "every" and "all" – so-called categorical statements – lend themselves to being represented on paper as circles that may or may not overlap.
Venn diagrams are especially helpful when dealing with logical arguments called syllogisms. Syllogisms are a special type of three-step argument with two premises and a conclusion, which involve quantifying terms. In this unit, you will learn the basic principles of Venn diagrams, how to use them to represent statements, and how to use them to evaluate arguments.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 6 hours.
Unit 5: Fallacies
Now that you have studied the necessary structure of a good argument and can represent its structure visually, you might think it would be simple to pick out bad arguments. However, identifying bad arguments can be very tricky in practice. Very often, what at first appears to be ironclad reasoning turns out to contain one or more subtle errors.
Fortunately, there are many easily identifiable fallacies (mistakes of reasoning) that you can learn to recognize by their structure or content. In this unit, you will learn about the nature of fallacies, look at a couple of different ways of classifying them, and spend some time dealing with the most common fallacies in detail.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 3 hours.
Unit 6: Scientific Reasoning
Unlike the syllogistic arguments you explored in the last unit, which are a form of deductive argument, scientific reasoning is empirical. This means that it depends on observation and evidence, not logical principles. Although some principles of deductive reasoning do apply in science, such as the principle of contradiction, scientific arguments are often inductive. For this reason, science often deals with confirmation and disconfirmation.
Nonetheless, there are general guidelines about what constitutes good scientific reasoning, and scientists are trained to be critical of their inferences and those of others in the scientific community. In this unit, you will investigate some standard methods of scientific reasoning, some principles of confirmation and disconfirmation, and some techniques for identifying and reasoning about causation.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 4 hours.
Unit 7: Strategic Reasoning and Creativity
While most of this course has focused on the types of reasoning necessary to critique and evaluate existing knowledge or to extend our knowledge following correct procedures and rules, an enormous branch of our reasoning practice runs in the opposite direction. Strategic reasoning, problem-solving, and creative thinking all rely on an ineffable component of novelty supplied by the thinker.
Despite their seemingly mystical nature, problem-solving and creative thinking are best approached by following tried and tested procedures that prompt our cognitive faculties to produce new ideas and solutions by extending our existing knowledge. In this unit, you will investigate problem-solving techniques, representing complex problems visually, making decisions in risky and uncertain scenarios, and creative thinking in general.
Completing this unit should take you approximately 2 hours.
Study Guide
This study guide will help you get ready for the final exam. It discusses the key topics in each unit, walks through the learning outcomes, and lists important vocabulary terms. It is not meant to replace the course materials!
Course Feedback Survey
Please take a few minutes to give us feedback about this course. We appreciate your feedback, whether you completed the whole course or even just a few resources. Your feedback will help us make our courses better, and we use your feedback each time we make updates to our courses.
If you come across any urgent problems, email [email protected].
Certificate Final Exam
Take this exam if you want to earn a free Course Completion Certificate.
To receive a free Course Completion Certificate, you will need to earn a grade of 70% or higher on this final exam. Your grade for the exam will be calculated as soon as you complete it. If you do not pass the exam on your first try, you can take it again as many times as you want, with a 7-day waiting period between each attempt.
Once you pass this final exam, you will be awarded a free Course Completion Certificate .
Saylor Direct Credit
Take this exam if you want to earn college credit for this course . This course is eligible for college credit through Saylor Academy's Saylor Direct Credit Program .
The Saylor Direct Credit Final Exam requires a proctoring fee of $5 . To pass this course and earn a Credly Badge and official transcript , you will need to earn a grade of 70% or higher on the Saylor Direct Credit Final Exam. Your grade for this exam will be calculated as soon as you complete it. If you do not pass the exam on your first try, you can take it again a maximum of 3 times , with a 14-day waiting period between each attempt.
We are partnering with SmarterProctoring to help make the proctoring fee more affordable. We will be recording you, your screen, and the audio in your room during the exam. This is an automated proctoring service, but no decisions are automated; recordings are only viewed by our staff with the purpose of making sure it is you taking the exam and verifying any questions about exam integrity. We understand that there are challenges with learning at home - we won't invalidate your exam just because your child ran into the room!
Requirements:
- Desktop Computer
- Chrome (v74+)
- Webcam + Microphone
- 1mbps+ Internet Connection
Once you pass this final exam, you will be awarded a Credly Badge and can request an official transcript .
Saylor Direct Credit Exam
This exam is part of the Saylor Direct College Credit program. Before attempting this exam, review the Saylor Direct Credit page for complete requirements.
Essential exam information:
- You must take this exam with our automated proctor. If you cannot, please contact us to request an override.
- The automated proctoring session will cost $5 .
- This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam (see allowed resources below).
- You will have two (2) hours to complete this exam.
- You have up to 3 attempts, but you must wait 14 days between consecutive attempts of this exam.
- The passing grade is 70% or higher.
- This exam consists of 50 multiple-choice questions.
Some details about taking your exam:
- Exam questions are distributed across multiple pages.
- Exam questions will have several plausible options; be sure to pick the answer that best satisfies each part of the question.
- Your answers are saved each time you move to another page within the exam.
- You can answer the questions in any order.
- You can go directly to any question by clicking its number in the navigation panel.
- You can flag a question to remind yourself to return to it later.
- You will receive your grade as soon as you submit your answers.
Allowed resources:
Gather these resources before you start your exam.
- Blank paper
What should I do before my exam?
- Gather these before you start your exam:
- A photo I.D. to show before your exam.
- A credit card to pay the automated proctoring fee.
- (optional) Blank paper and pencil.
- (optional) A glass of water.
- Make sure your work area is well-lit and your face is visible.
- We will be recording your screen, so close any extra tabs!
- Disconnect any extra monitors attached to your computer.
- You will have up to two (2) hours to complete your exam. Try to make sure you won't be interrupted during that time!
- You will require at least 1mbps of internet bandwidth. Ask others sharing your connection not to stream during your exam.
- Take a deep breath; you got this!
Nominate your advisor for Advisor of the Year 2024
Five advisors will each receive $500, and five Sophia learners will each get a free month of Sophia.
- Critical Thinking
- All courses
- Humanities courses

Critical Thinking reviews
In this class, students will learn how to think more critically by questioning assumptions and biases and being aware of fallacies. Students will learn to interpret and write deductive and inductive arguments and apply to real-life situations.
9305 students successfully completed
39 partners accept credit transfer.* See Partners
3.0 semester credits
Recommended for credit to the ACE® and DEAC college and university networks.

Download Syllabus
Fill in the form to recieve a syllabus for your course..
By providing your information, you consent to receive occasional special promotional offers and education opportunities by email from Sophia Learning or one of its affiliates.
Learning outcomes
Partners who accept this course.
This course transfers into a degree program at these featured institutions
Assignments & grading
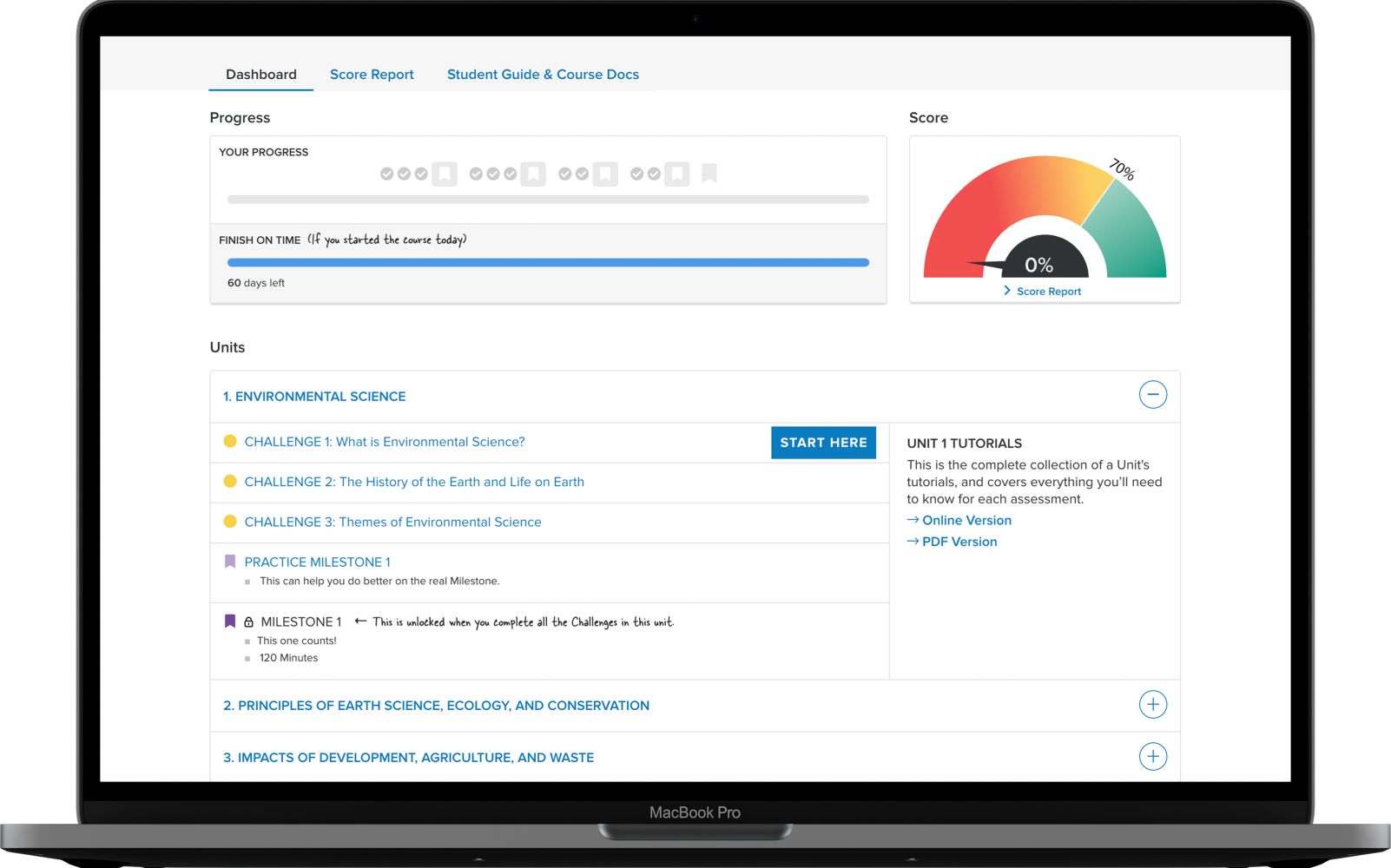
This is a pass/fail course. Students are required to complete all 13 Challenges (formative assessments), 4 Milestones (summative assessments), and 1 Touchstone (project-based or written assessments) with an overall score of 70% or better.

- No credit card required!
- Sophia membership starts with a risk-free trial
* All fields are required.
Inside the Sophia courseroom
Knock out your general education requirements on your terms. Sophia courses are available anytime, anywhere, and most can be accessed from any device.
A revolutionary way to satisfy general education requirements for your degree. On demand. ACE ®-recommended. Low cost.
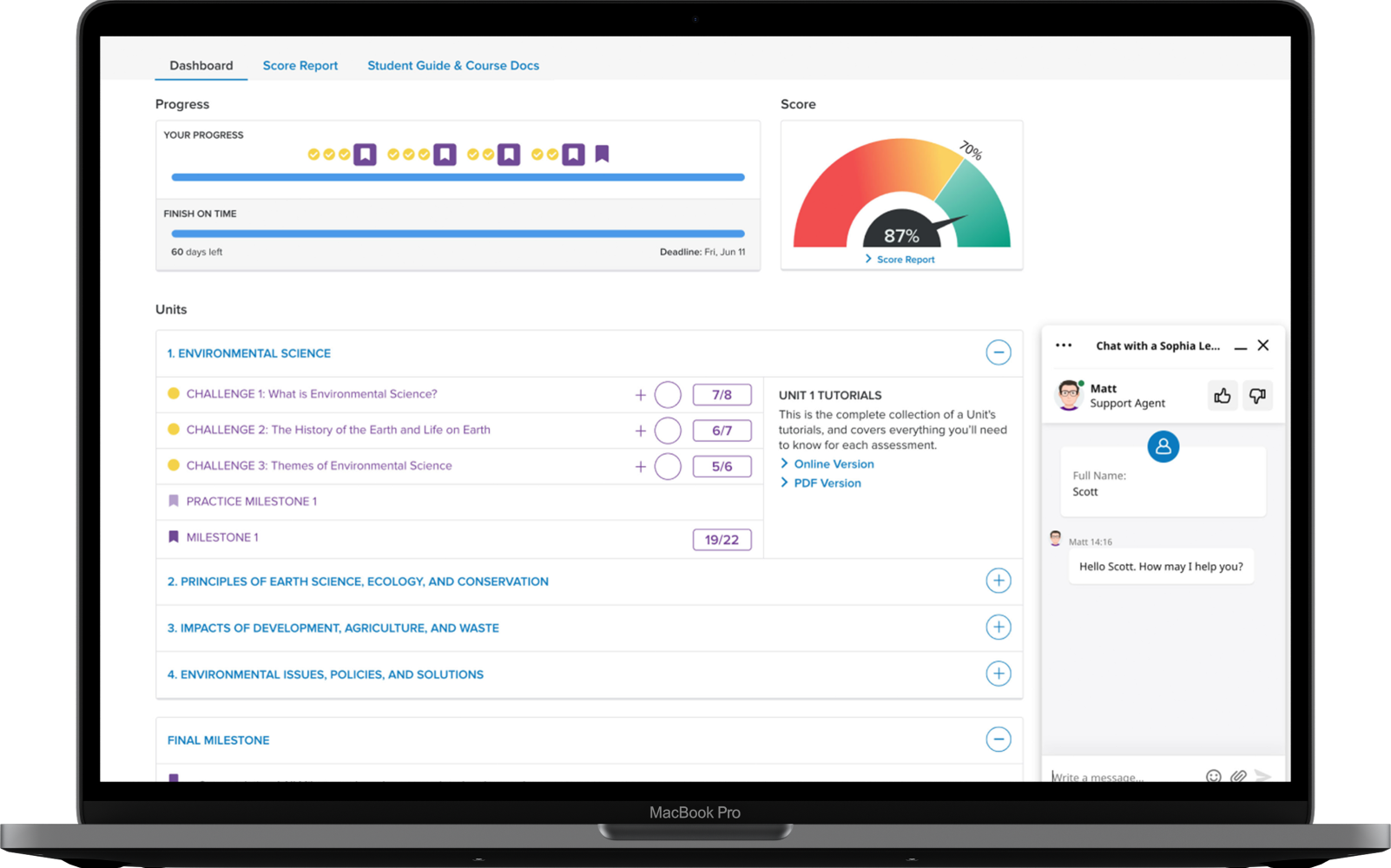
Sophia's Learning Coaches are here for you by phone, email or online chat from the start of your course to ordering your final transcript.
How many courses can I take with the free trial?
Access the course content through the first Challenge of any of Sophia’s 50+ courses.
How do I confirm transfer credit with my school?
Check Sophia’s list of partner schools to see if your school is on the list. If not, contact your registrar to learn about your school’s transfer credit policy and if Sophia coursework can be submitted for transfer.
Can I take courses for credit if I’m not enrolled at a school?
Sophia course completions do not expire and will be available to submit for transfer when you’re ready. At that time, check with your school’s registrar for their credit transfer policies.
What happens to the coursework I’ve already completed once I become a Sophia member?
If you’ve completed the first Challenge during your free trial, you can pick up right where you left off after you become a Sophia member.
What happens to my coursework if I cancel my Sophia membership?
Don’t worry. Your completed courses won’t disappear if you cancel your membership. Those courses will be there for you when you’re ready to submit for transfer.
Will my HR benefits cover the cost of Sophia?
If you have an education benefit through your employer, it may cover your subscription to Sophia. Check with your benefits administrator to find out if you qualify.
- Higher education partnerships
- Corporate partnerships
- Social impact partnerships
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Terms of use
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
Module 5: Thinking and Analysis
Critical thinking, learning objectives.
- Define critical thinking
Thinking comes naturally. You don’t have to make it happen—it just does. But you can make it happen in different ways. For example, you can think positively or negatively. You can think with your heart and you can think with rational judgment. You can also think strategically and analytically, and mathematically and scientifically. These are a few of multiple ways in which the mind can process thought.
What are some forms of thinking you use? When do you use them and why?
As a college student, you are tasked with engaging and expanding your thinking skills. One of the most important thinking skills is critical thinking. Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It’s a “domain-general” thinking skill—not a thinking skill that’s reserved for a one subject alone or restricted to a particular subject area. Critical thinking is used in every domain, from physics to auto mechanics. It is often employed to problem solve when we are puzzled by something or to reveal that there is an error in common ways of thinking about things. Thus, critical thinking is essential for revealing biases.
For example, Galileo used a common form of reasoning called reductio ad absurdum (Latin for “reduce to absurdity) to show that the physics of his day was mistaken. People at that time believed that the heavier something was, the faster it would fall. Galileo knew this common conception was mistaken and he proved it both empirically and conceptually. Here is how he proved it conceptually. Suppose you have two objects, one heavier (call it B) than the other (call it A). Suppose the heavier object falls faster. When you put the lighter object under the heavier object (c), the lighter object should slow down the heavier object. On the other hand gluing together both objects results in a heavier object (c), which should fall even faster than (b). See diagram here . The contradiction proves by reductio ad absurdum that the assumption must be false. This is just one example, but the form of reasoning (reductio ad absurdum) is the same across every domain—from science to religion to auto mechanics. The form of reasoning is just this: assume for the sake of the argument that A is true. If we can then show that A leads to a contradiction (literally where two statements are asserted that cannot possibly be true), then we prove that A is false.
Great leaders have highly attuned critical thinking skills, and you can too. In fact, you probably have a lot of these skills already. Of all your thinking skills, critical thinking may have the greatest value.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. It means asking probing questions like, “How do we know?” or “Is this true in every case or just in this instance?” It involves being skeptical and challenging assumptions, rather than simply memorizing facts or blindly accepting what you hear or read.
Imagine, for example, that you’re reading a history textbook. You wonder who wrote it and why because you detect certain biases in the writing. You find that the author has a limited scope of research focused only on a particular group within a population. In this case, your critical thinking reveals that there are other sides to the story.
Who are critical thinkers, and what characteristics do they have in common? Critical thinkers are usually curious and reflective people. They like to explore and probe new areas and seek knowledge, clarification, and new solutions. They ask pertinent questions, evaluate statements and arguments, and they distinguish between facts and opinion. They are also willing to examine their own beliefs, possessing a manner of humility that allows them to admit lack of knowledge or understanding when needed. They are open to changing their mind. Perhaps most of all, they actively enjoy learning and seeking new knowledge is a lifelong pursuit.
This description may well be you!
No matter where you are on the road to being a critical thinker, you can always more fully develop and finely tune your skills. Doing so will help you develop more balanced arguments, express yourself clearly, read critically, and glean important information efficiently. Critical thinking skills will help you in any profession or any circumstance of life, from science to art to business to teaching. With critical thinking, you become a clearer thinker and problem solver.
The following video from Lawrence Bland presents the major concepts and benefits of critical thinking.
You can view the transcript for “Critical Thinking.wmv” here (opens in new window) .
Supporting Claims with Evidence
Thinking and constructing analyses based on your thinking will bring you in contact with a great deal of information. Some of that information will be factual, and some will not be. You need to be able to distinguish between facts and opinions so you know how to support your arguments. Begin with the following basic definitions:
- Fact: a statement that can be supported by objective evidence such as observation, argument, or research.
- Opinion: a statement whose truth depends on someone’s desire(s) rather than objective evidence. Opinions that cannot be supported by objective evidence are at most subjectively true.
Of course, the tricky part is that most people do not label statements as fact and opinion, so you need to be aware and recognize the difference as you go about honing your critical thinking skills.
You probably have heard the old saying “Everyone is entitled to their own opinions,” which may be true, but conversely not everyone is entitled to their own facts. Facts are true for everyone, not just those who want to believe in them. For example, “mice are mammals” is a fact since it has been established by scientific research. In contrast, “mice make the best pets” is an opinion (since best means whatever one likes the best—and that is a matter of one’s subjective desires).
Facts vs. opinion
Determine if the following statements are facts or opinions based on just the information provided here, referring to the basic definitions above. Some people consider scientific findings to be opinions even when they are convincingly backed by reputable evidence and experimentation. However, remember the definition of fact—verifiable by research or observation. Think about what other research you may have to conduct to make an informed decision.
- Oregon is a state in the United States. (How would this be proven?)
- Beef is made from cattle. (See current legislation concerning vegetarian “burgers.”)
- Increased street lighting decreases criminal behavior. (What information would you need to validate this claim?)
- In 1952, Elizabeth became Queen of England. (What documents could validate this statement?)
- Oatmeal tastes plain. (What factors might play into this claim?)
- Acne is an embarrassing skin condition. (Who might verify this claim?)
- Kindergarten decreases student dropout rates. (Think of different interest groups that may take sides on this issue.)
- Carbohydrates promote weight gain. (Can you determine if this is a valid statement?)
- Cell phones cause brain tumors. (What research considers this claim?)
- Immigration is good for the US economy. (What research would help you make an informed decision on this topic?)
Defending against Bias
Once you have all your information gathered and you have checked your sources for currency and validity, you need to direct your attention to how you’re going to present your now well-informed analysis. Be careful on this step to recognize your own possible biases (metacognition). Facts are verifiable statements; opinions are statements without supporting evidence. Stating an opinion is just that. You could say, “Blue is the best color,” and that would be your opinion. In contrast, suppose you were to conduct research and find the use of blue paint in mental hospitals reduces patients’ heart rates by twenty-five percent and contributes to fewer angry outbursts from patients. In that case, the statement “blue paint in mental hospitals reduces patients’ heart rate by twenty-five percent” would be a fact supported by objective evidence.
Not everyone will accept your analysis, which can be frustrating. Most people resist change and have firm beliefs on both important issues and less significant preferences. With all the competing information surfacing online, on the news, and in general conversation, you can understand how confusing it can be to make any decisions. Look at all the reliable, valid sources that claim different approaches to be the best diet for healthy living: ketogenic, low-carb, vegan, vegetarian, low fat, raw foods, paleo, Mediterranean, etc. All you can do in this sort of situation is conduct your own serious research, check your sources, and write clearly and concisely to provide your analysis of the information for consideration. You cannot force others to accept your stance, but you can show your evidence in support of your thinking, being as persuasive as possible without lapsing into your own personal biases.
critical thinking: clear, reasonable, reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do, often as a result of challenging assumptions
opinions: statements offered without supporting evidence
- College Success. Authored by : Matthew Van Cleave. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking. Provided by : Critical and Creative Thinking Program. Located at : http://cct.wikispaces.umb.edu/Critical+Thinking . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Thinking Critically. Authored by : UBC Learning Commons. Provided by : The University of British Columbia, Vancouver Campus. Located at : https://learningcommons.ubc.ca/student-toolkits/thinking-critically/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- College Success. Authored by : Amy Baldwin; Modified by Lumen Learning. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/7-4-critical-thinking . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Thought-experiment-free-falling-bodies. Provided by : Wikimedia Commons. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Thought-experiment-free-falling-bodies.svg . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Critical Thinking.wmv. Authored by : Lawrence Bland. Located at : https://youtu.be/WiSklIGUblo . License : All Rights Reserved

- College Catalog
- Events Calendar
- Current Students
- Future Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Business & Community
Introduction to Critical Thinking
This introductory-level course is designed to help learners define and identify critical thinking and reasoning skills and develop those skills. Critical thinking is an intellectual model for reasoning through issues to reach well-founded conclusions. It may be the single most valuable skill that one can bring to any job, profession, or life challenge. Being able to ask the right questions, critique an argument, and logically dissect an issue occur constantly in the workplace and our lives.
Learning Outcomes:
- Define critical thinking, reasoning, and logic
- Understand the process of systemic problem-solving
- Identify and overcome barriers to critical thinking
- Articulate common reasoning fallacies
- Engage in critical thinking as it pertains to the workplace
Student Testimonial
"I will be able to implement some of the elements of reasoning questions that are relevant to critical thinking. I feel confident in identifying fallacies as well. The material was well presented." -- Marie, Introduction to Critical Thinking
Course Dates and Times
Course hours: 7 hours .
This workshop is offered through our continuing education online partner.
Register for Introduction to Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking Online Courses
- The Center for Critical Thinking Community Online

- 2019 Blog Entries
- 2020 Blog Entries
- 2021 Blog Entries
- 2022 Blog Entries
- 2023 Blog Entries
- Online Courses for Your Students
- 2023 Webinar Archives
- 2022 Webinar Archives
- 2021 Webinar Archive
- 2020 Webinar Archive
- Guided Study Groups
- Critical Thinking Channel on YouTube
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.

Fall 2024 Online Courses
All participants get complimentary semester-long access to the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online !
Courses also count toward certification in our approach .
Page Contents
• Important Deadlines
• CT700 - How to Infuse Critical Thinking Into Your Instruction
• CT800 - Critical Thinking: Tools for Taking Charge of You Learning and Your Life
• CT701 - How to Infuse Critical Thinking Into Instruction, Part II: Advanced Course
• Our Instructors
• Testimonials
• Frequently Asked Questions
Important Deadlines
August 19, 2024: Last day to drop with a full registration refund.
August 20, 2024: Instruction begins.
September 1, 2024: Last day to register .
October 15, 2024: Last day to drop with a prorated registration refund ($25 minimum refund deduction once the course begins).
December 10, 2024: Semester ends.
Course Offerings
Ct700 - how to infuse critical thinking into your instruction.
This course introduces a substantive conception of critical thinking and how to infuse this concept throughout your instruction. It fosters understanding of how to teach critical thinking skills to students through any subject or discipline, and at any level of instruction. In this course, you will be introduced to the elements of reasoning, universal intellectual standards, and intellectual traits through readings, discussions, and practical application activities. You will redesign lessons and strategies using the concepts and principles of critical thinking. You will practice strategies for Socratic discussions. You will help students learn to consciously use critical thinking concepts and strategies in learning, and in their lives. You will redesign and teach lessons you develop for your own classes - and receive course credit for doing so!
While applying your mind in this course, you will:
- deepen your understanding of the foundations of critical thinking;

- develop skills and abilities in placing fairminded critical thinking at the heart of teaching and learning, including explicitly emphasizing the development of Intellectual Virtues among your students;
- design instruction that fosters explicit critical thinking throughout your course(s);
- help your students learn the tools they need for developing as ethical critical thinkers;
- come to understand the role that native pathologies of human thought play in impeding intellectual development;
- explicitly use the Elements of Reasoning and Intellectual Standards to create critical thinking lessons in your subject area(s);
- help students cultivate their ability to think within key concepts in your subject(s) and discipline(s); and
- create lessons and assessment processes that dovetail with fostering critical thinking at every moment of teaching and learning.
CT800 - Critical Thinking: Tools for Taking Charge of Your Learning and Your Life
Since few people realize the powerful role that thinking plays in their lives, few gain significant command of it. Most people are frequently victims of their thinking; that is, they are hurt rather than helped by it. Most people are their own worst enemies. Their thinking is a continual source of problems, preventing them from recognizing opportunities, keeping them from exerting energy where it will do the most good, poisoning relationships, and leading them down blind alleys.
This course will introduce you to the tools the best thinkers use and will exemplify the activities and practices you can use to begin emulating them. Here are some of the qualities of the best thinkers:
- The best thinkers think about their thinking. They do not take thinking for granted. They do not trust to fate to make them good in thinking. They notice their thinking. They reflect on their thinking. They act upon their thinking.
- The best thinkers are highly purposeful. They do not simply act. They know why they act. They know what they are about. They have clear goals and clear priorities. They continually check their activities for alignment with their goals.

- The best thinkers distinguish their thoughts from their feelings and desires. They know that wanting something to be so does not make it so. They know that one can be unjustifiably angry, afraid, or insecure. They do not let unexamined emotions determine their decisions. They have “discovered” their minds, and they examine the way their minds operate as a result. They take deliberate charge of those operations.
- The best thinkers routinely take thinking apart. They “analyze” thinking. They do not trust the mind to analyze itself automatically. They realize that analyzing thinking is an art one must consciously learn. They realize that it takes knowledge of the parts of thinking, and practice in exercising control over them.
- The best thinkers routinely evaluate thinking, determining its strengths and weaknesses. They do not trust the mind to evaluate itself automatically. They realize that the automatic ways in which the mind evaluates itself are inherently flawed. They realize that evaluating thinking is an art one must consciously learn. They realize that it takes knowledge of the universal standards for thinking, and practice in exercising control over them.
This course, as a whole, will introduce you to the tools of mind that will help you reason well through the problems and issues you face - whether in the classroom, in your personal life, or in your professional life. If you take these ideas seriously, and practice using them, you can take command of the thinking that ultimately will command the quality of your life.
As you apply your mind in this course, you can expect to do the following:
- understand what critical thinking is, how it differs from other forms of human thought, and its foundational principles and concepts;
- become explicitly aware of the barriers to critical thinking development (egocentricity and sociocentricity), as well as how to recognize and overcome their many manifestations in daily life;
- analyze thinking by breaking it down into its fundamental components (the Elements of Thought), and learn how those components work together in reasoning;

- develop Intellectual Virtues, or desirable traits of mind, through practice over time;
- formulate clear, important, relevant questions;
- differentiate between questions of fact, of preference, and of reasoned judgment, and understand the best approaches to take for each of those categories;
- read critically and writing substantively;
- recognize the problem of media bias and propaganda as barriers to critical thought in individuals and human societies;
- develop a clear framework for ethical reasoning and understand how it differs from other modes of thought, such as religious, ideological, political, and legal thinking;
- learn the importance of fairminded critical thinking in self-actualization and the cultivation of fairminded critical homes, workplaces, classrooms, and societies; and
- understand the stages of critical thinking development, as well as determine your current such stage and what is required to ascend to higher stages.
CT701 - How to Infuse Critical Thinking Into Instruction, Part II: Advanced Course
Registration Closed

- Developing effective strategies for fostering fairminded critical thinking in instruction.
- Leading more advanced Socratic dialog.
- Deepening your understanding of the foundations of critical thinking.

- Beginning to outline a Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking within your field of study (showing proficiency in understanding the relationship between critical thinking and your field of study).
- Understanding more deeply the concepts of close reading and substantive writing, in order to better foster these understandings in student thought.
- Placing the concept of fairminded critical thinking at the heart of teaching and learning, including an explicit emphasis on the development of Intellectual Virtues.
- Understanding the roles played by native human pathologies of thought in impeding intellectual development.
- Redesigning lessons with critical thinking at the heart of teaching and learning processes.
- Designing instructional assessment processes that dovetail with fostering critical thinking at every moment in teaching and learning.
General Information
Our instructors.

Testimonials
- 'I told my boss this week during a faculty meeting that this has been the best university course I've ever taken.'
- 'The instruction and course content was phenomenal. . . . this course has added significant value to my life.'
- 'I have really enjoyed this course. . . meetings were engaging and very informative. I plan to attend additional offerings this academic year.'

- "I would like to express my deepest appreciation to you [Dr. Linda Elder] and Richard Paul. You both created a system for life guidance through your very arduous work on critical thinking. Thank you for adding the intellectual virtues to critical thinking. Critical thinking without the intellectual virtues is still narrow-minded thinking. Thanks to [instructor] Paul Bankes [CT700], we could get familiar with fairminded critical thinking this semester in the class. Since I have also attended a couple of courses in psychology, I could better understand what majestic guidance you have created to help us have better lives by improving our way of thinking. I just wanted to say "THANK YOU" for each second you have devoted in this way. I will try to internalize fairminded critical thinking in my life and help to develop this idea as much as I possibly can. I hope one day I can claim that I am from the community of Fairminded Critical Thinking."
- "I would like to extend my sincere gratitude for allowing me to complete the CT700 Course. It has been the most humbling and enlightening experience of my academic life. . . . I will now embark on my vision to make a difference in the South African Education System. Once, again, my gratitude goes out to you . . . "
- "CT700 was an excellent course that changed my thinking and life. It was painful at times and I found it took time for me to meaningfully complete the assignments. As I worked through the first few weeks, I also wondered if I would be able to change my thinking process. By the end of the course, I grew personally and professionally in ways that I wasn’t sure were possible."
Frequently Asked Questions
How do the courses work.
Before the course begins, we email each registrant with the web address of the course and his or her login information. Everything is done through the web: viewing and submitting assignments, communication with the instructor and classmates, etc.
How long do the courses last?
How much time do the courses require each week?
The assignments, if done well, will take an average of 3-4 hours per week for most participants.
Who teaches the courses?
Each course is facilitated by an instructor educated in the Paul-Elder conception of critical thinking, under the direction of the Foundation's Senior Fellows. In recent years, some courses have been instructed by Dr. Paul Bankes , while others have been instructed by Dr. Brian Barnes .
Our registration fee covers the cost of tuition and all course materials. This fee is $942.
Will I receive a certificate of completion?

How will I receive my materials after I register for a course?
The course materials will be available online in a digital format.
What if I need to drop the course?
Please see the 'Important Dates' section at the top of this page.
______________________________________________________________________

A3 - Critical Thinking - Courses
Aas 201. race, racism and critical thinking (3).
Preparatory: Completion of the lower division writing requirement and GE section B4 Mathematics . Introduction to the process of critical thinking through the lens of race-based theories and selected historical and contemporary discourse of African Americans, Asian Americans, European Americans and Latinos on race relations and multiculturalism in American society. Examines contemporary social issues through the use of scholarly studies and a range of cultural texts in order to explore the effects of race and racism on the relationship between language and logic, processes and form of reasoning and practices of critical reflection. Also examines intersection of race, gender and class. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
AFRS 204. Race and Critical Thinking (3)
Prerequisite: Instructor consent. Recommended Corequisite or Preparatory: Completion of the lower division writing requirement. Introduction to the basic concepts of deductive logic as a dimension of critical reasoning and the practical usage of those concepts in discussing, analyzing and critiquing ideas on race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation and other relevant issues of modern society. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
AIS 210. Thinking About Knowing (3)
Preparatory: Completion of the lower division writing requirement is recommended. Introduction to critical thinking through the lens of American Indian Studies and the examination of knowledge production and reproduction. Examine selected historical and contemporary discourse/philosophies of American Indian nations and contemporary social issues, particularly the complex relationship between American Indians and the United States federal government, to make sense of American Indians’ racialized and legal/political status as groups and individuals. Emphasizes critical reading of theory, praxis, and artistic texts to explore critical thinking about research, knowledge, and meaning-making. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
CHS 202. Race, Racism and Critical Thinking (3)
Prerequisite: Completion of the lower division writing requirement. Introduction to the process of critical thinking through the lens of race-based theories and selected historical and contemporary discourse of African Americans, Asian Americans and Chicanos/Latinos on race relations and multiculturalism in American society. Examines contemporary social issues through the use of scholarly studies and a range of cultural texts in order to explore the effects of race and racism on the relationship between language and logic, process and forms of reasoning and practices of critical reflection. Emphasis on the Chicano/Latino racial experience in contemporary America. Examines intersection of race, gender and class. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
COMS 225. Argumentation (3)
Prerequisite: Multiple Measures Placement in GE-level writing. Studies of the strategies used for rhetorical argument. Emphasis is given to ways of finding issues, using evidence and detecting fallacies in rhetorical communications. Includes intensive practice and application in the formulation and critical analysis of argument in rhetorical communications. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
ENGL 215. Critical Thinking About Research Writing (3)
Prerequisite: Completion of the lower division writing requirement. This course will focus on composing and reading practices appropriate to research writing tasks. Students will practice writing effectively and using information technologies. There will be a focus on comprehending and using quantitative and qualitative data and students will be introduced to generating qualitative or quantitative data. Other activities will include drafting and revising documents as well as analyzing information and testing its credibility, including through analyzing logical fallacies. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.) (IC)
GEH 111HON. Places and Spaces (3)
This lower division course is designed to transition students from traditional instruction that focuses on individual subject areas to a more interdisciplinary, integrative approach toward learning. The course adopts a place-based perspective, which will bring students into the field where they will be challenged to consider immediate applications of the material to real-world contexts. This course will include required site visits in and around the San Fernando Valley. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
HIST 202. Critical Thinking in California History (3)
Introduction to the process of critical thinking through the lens of historical evidence and interpretation. Examine how historians use evidence, logic, and reasoning to make historical arguments. Use the history of an increasingly diverse and globalized California to analyze public and political discourse, rhetoric, and historical scholarship. Investigate historical debates around race, immigration, and globalization in California to evaluate bias, fallacies, and disinformation in historical sources and scholarship. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
JS 220. Critical Thinking About Jews on Film (3)
An introduction to the process of critical thinking through analysis of how Jews are represented in the medium of film. In particular, students will consider how this representation is affected by ideologies of race, class, gender and sexuality. Emphasis on the modern history and culture of Jews in America, Europe, Israel and elsewhere. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
PHIL 100. General Logic (4)
Prerequisites: Completion of the lower division writing requirement; GE section B4 Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning or MATH 210 . Not open to students who have completed PHIL 200 . Study of deductive and inductive inferences. Attention to formal and informal fallacies and the relations of logic and language. Emphasis on critical thinking and the attainment of skill in it. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
PHIL 200. Critical Reasoning (3)
Prerequisites: Completion of the lower division writing requirement; GE section B4 Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning or MATH 210 . Not open to students who have completed PHIL 100 . Examination of the relationship between logic and language. Accelerated introduction to the concepts essential to the identification, analysis and evaluation of arguments, with attention to deduction, induction and common fallacies. Emphasis on the application of these concepts. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
PHIL 230. Introduction to Formal Logic (3)
Prerequisites: Completion of the lower division writing requirement; GE section B4 Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning or MATH 210 . Introduction to modern deductive logic, including propositional logic and theory of quantification. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
QS 201. Race and Ethnicity in Queer Studies (3)
Preparatory: Completion of the lower division writing requirement is recommended. Introduction to the process of critical thinking through the lens of race, ethnicity and sexuality. QS 201 offers an exploration of race and ethnicity and its relationship to queer studies, emphasizing critical reading of theory, praxis, and artistic texts. This course also examines the specific development of queer of color critique, its indebtedness to women of color feminism, and its emergence as a response to the whiteness of mainstream queer theory. Students will engage the work of artists, scholars, and activists to interrogate the dominant discourses in the intersections of race, gender, sexuality, class, nation, and diaspora within the context of empire and neoliberalism and in relation to citizenship, welfare, and terrorism. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
RS 204. Religion, Logic and the Media (3)
This course introduces and guides students in the practical use of the basic concepts of deductive logic as a dimension of critical reasoning. Using these concepts, students will discuss, analyze and critique statements that appear in the media (in the U.S. and elsewhere) that have been expressed by religious people and by the media itself. (Available for General Education, Basic Skills A3 Critical Thinking.)
16 Best Free Online Critical Thinking Courses
Written by Argumentful
Critical thinking is one of the most fundamental skills you could focus on. In fact, these skills are so important that many educational institutions have listed them among their central goals. Critical thinking helps you sort the true from the false.
The bad news is that not many people own these skills. Einstein famously said:
“Only two things are infinite, the universe and human stupidity, and I’m not sure about the former.”
The good news though is that you can improve your thinking and you can do it without breaking the bank.
Below are listed 16 of the best free online critical thinking courses with details regarding their contents.
Go on, choose your preferred course and take action today! (You can thank me later😉!)
P.S. Apart from the general critical thinking courses, I’ve included 5 specific ones which focus on today’s burning issues- fake news and climate change , as well as correctly interpreting randomized clinical trials and screening trials. See numbers 12 to 16 below.
Jump to Section
Critical reasoning for beginners, critical thinking classes at fayetteville state university, logical and critical thinking, critical thinking: fundamentals of good reasoning, philosophy and critical thinking, critical thinking & problem solving, introduction to critical thinking and logic, teaching critical thinking through art with the national gallery of art.
- Critical thinking: Reasoned Decision Making
The Science of Everyday Thinking
Critical thinking at university: an introduction, making sense of news, sorting truth from fiction: civic online reasoning, making sense of climate science denial, thinking critically: interpreting randomized clinical trials, thinking critically series: interpreting screening trials.
Offered by : University of Oxford
Description :
4 hours, 6 modules
1: The Nature of Arguments
How to recognise arguments and what the nature of an argument is
2: Different Types of Arguments
Different types of arguments, in particular deductive and inductive arguments
3: Setting Out Arguments Logic Book Style
How to identify and analyse arguments, and how to set arguments out logic book-style to make them easier to evaluate
4: What is a Good Argument? Validity and Truth
How to evaluate arguments and how to tell whether an argument is good or bad, focusing specifically on inductive arguments
5: Evaluating Arguments Part One
Evaluation of arguments – this time deductive arguments – focusing in particular on the notion of validity
6: Evaluating Arguments Part Two
Fallacies: bad arguments that can easily be mistaken for good arguments
Also available on YouTube and iTunes
Offered by : Fayetteville State University
24 videos, 24 hours
Lectures from Spring 2011 Critical Thinking classes at Fayetteville State University held by Gregory B. Sadler. The textbook used was Moore And Parker’s Critical Thinking 9th edition .
- Issues, claims, arguments
- Arguments and non-arguments
- Value Judgments
- Complex arguments, unstated premises
- Deductive and inductive arguments with implicit premises
- Deductive and inductive arguments
- Information sources
- Experts and appeal to authority
- Critical thinking and advertising
- Rhetorical devices
Offered by : University Of Auckland
8 Weeks of study, 4 hours weekly
- Identify common flaws in belief construction
- Recognise and reconstruct arguments
- Evaluate arguments as being good or bad
- Analyse arguments using basic logical tools
- Apply basic logical strategies in areas such as science, moral theories and law
Offered by : IsraelX
9 weeks, 4-6 hours per week
You can create a free account on edx.org and have access to the course for 2 months. After 2 months, you can pay £37 to get unlimited access to the course.
The objective of the course is to improve the student’s ability in the basic skills of critical thinking:
- how to recognize arguments,
- how to interpret them,
- how to evaluate them,
- how to construct them.
Lesson 1. What’s “Critical Thinking?” Lesson 2. What are Arguments Made Of? Lesson 3. From Premises to Conclusions Lesson 4. Recognizing Arguments: Introduction Lesson 5. Argument vs. The Text Containing It Lesson 6. Recognizing Conclusions Lesson 7. Arguments vs. Explanations Lesson 8. Argument Diagrams: Introduction Lesson 9. More about Argument Diagrams Lesson 10. Argument Diagrams: Examples Lesson 11. Hedges Lesson 12. Disclaimers Lesson 13. Examples Lesson 14. Rhetorical Language Lesson 15. Referential Attribution Lesson 16. Principles of Interpretation Lesson 17. Implicit Premises Lesson 18. What’s a Good Argument? Lesson 19. More Virtues of Arguments Lesson 20. Argument Ad Hominem Lesson 21. Argument Ad Verecundiam Lesson 22. Argument Ad Populum Lesson 23. Argument Ad Ignorantiam Lesson 24. Argument Ad Baculum and Ad Misericordiam Lesson 25. Venn Diagrams Lesson 26. Beyond Venn Lesson 27. Modus Ponens Lesson 28. Modus Tollens Lesson 29. Conditionals Lesson 30. Reductio Ad Absurdum Lesson 31. Process of Elimination Lesson 32. Separation of Cases Lesson 33. Truth Trees: An Example Lesson 34. How to Grow Truth Trees Lesson 35. Truth Trees: Another Example Lesson 36. Reflexive Relations Lesson 37. Symmetric Relations Lesson 38. Transitive Relations Lesson 39. Inductive Generalization Lesson 40. What’s a Good Sample? Lesson 41. The New Riddle of Induction Lesson 42. From Induction to Causation Lesson 43. Evaluating Causal Generalizations Lesson 44. Argument from Analogy: Basics Lesson 45. Argument from Analogy: Examples Lesson 46. Who Needs Analogues? Lesson 47. Inference to the Best Explanation Lesson 48. Experimentation Lesson 49. Building an Argument Lesson 50. Writing Up an Argument
Offered by : The University of Queensland
6 weeks, 1-4 hours per week
- How to think with clarity and rigour
- How to identify, analyse and construct cogent arguments
- How to think of solutions to the central problems of philosophy
- How to engage in philosophical conversations with others about topics that matter
Offered by : Rochester Institute of Technology
3 weeks, 4-6 hours per week
- How to perform strategic analysis and assessment
- How to perceive and assess a critical need and design a tailored solution
- How to identify key stakeholders and ensure their needs are met
- How to employ adaptive problem-solving
- How to work through obstacles collaboratively
- How to analyse failure to improve future performance
Offered by : Saylor.org Academy
This course will introduce you to critical thinking, informal logic, and a small amount of formal logic. Its purpose is to provide you with the basic tools of analytical reasoning, which will give you a distinctive edge in a wide variety of careers and courses of study. While many university courses focus on the presentation of content knowledge, the emphasis here is on learning how to think effectively. Although the techniques and concepts covered here are classified as philosophical, they are essential to the practice of nearly every major discipline, from the physical sciences and medicine to politics, law, and the humanities.
- Unit 1: Introduction and Meaning Analysis
- Unit 2: Argument Analysis
- Unit 3: Basic Sentential Logic
- Unit 4: Venn Diagrams
- Unit 5: Fallacies
- Unit 6: Scientific Reasoning
- Unit 7: Strategic Reasoning and Creativity
Offered by : Smithsonian Institution
16 weeks, 3-4 hours per week
- How to use Artful Thinking Routines to strengthen thinking.
- How to facilitate meaningful conversations in your classroom using art for artful learning and artful teaching.
- How to help learners of all levels develop more discerning descriptions, evidence-based reasoning, and meaningful questioning habits.
- Key strategies for using content information to push original thinking deeper.
- Exciting, immersive activities for any type of classroom.
- How to use online teaching resources from the National Gallery of Art, including downloadable Artful Thinking lesson plans
- Unit 0: Welcome (2 hours)
- Unit 1: Diving into Thinking Routines (3-4 hours)
- Unit 2: Observing and Describing (3-4 hours)
- Unit 3: Reasoning with Evidence (3-4 hours)
- Unit 4: Questioning and Investigating (3-4 hours)
Critical thinking: reasoned decision making
Offered by : Tecnológico de Monterrey
4 weeks, 5-8 hours per week
- Identify the theories that support critical thinking
- Employ a methodology for the application of critical thinking
- Relate the elements that make up the stages of critical thinking
- Analyse the standards of critical thinking practice
- Assess the responsibility of perpetuating the intellectual values of the resolution analysis
- Distinguish the vices of thought in decision making
- Apply critical thinking to groups
1. Thinking according to our times
1.1 Why critical thinking?
1.2 The exciting world of thinking and criticism
2. Evaluating our modes of thought
2.1 Intellectual values of a good thinker
2.2 Evaluating our critical thinking skills. Avoiding vices and biased thinking
3. Elements and standards of critical thinking
3.1 Elements of a critical thinking process
3.2 Standards to apply to our thinking modes
4. Articulating our decisions making process
4.1 The logic of our decisions and the behaviour derived from them
4.2 How to improve our critical thinking skills and become a fair-minded thinker
12 weeks, 2-3 hours per week
The course explores the psychology of our everyday thinking: why people believe weird things, how we form and change our opinions, why our expectations skew our judgments, and how we can make better decisions. We’ll discuss and debate topics such as placebos, the paranormal, medicine, miracles, and more.
You will use the scientific method to evaluate claims, make sense of evidence, and understand why we so often make irrational choices. You will begin to rely on slow, effortful, deliberative, analytic, and logical thinking rather than fast, automatic, instinctive, emotional, and stereotypical thinking.
- tools for how to think independently, how to be skeptical, and how to value data over personal experience.
- examining the mental shortcuts that people use and misuse, and apply this knowledge to help make better decisions, and improve critical thinking.
Offered by : University of Leeds
2 weeks, 4 hours weekly
- What is critical thinking?
- A model for critical thinking
- Why is critical thinking important at university?
- Challenges to thinking critically at university
- How can you improve your critical thinking?
- How will critical thinking help you at university?
Offered by : University of Hong Kong
4 weeks, 2-3 hours per week
This course will help you identify reliable information in news reports and become better informed about the world we live in. A discussion on journalism from the viewpoint of the news audience.
- What makes news? The blurred lines between news, promotion and entertainment.
- Why does news matter? Social sharing and the dynamics of the news cycles.
- Who provides information? How to evaluate sources in news reports.
- Where is the evidence? The process of verification.
- When should we act? Recognizing our own biases.
- How do we know what we know? Becoming an active news audience.
You’ll learn to:
- Distinguish news from opinion; media bias from audience bias; assertion from verification
- Apply critical thinking skills to examine the validity of information
- Contextualize the knowledge gained from news report
- Respond quickly to daily news events and make an informed decision
Offered by : Massachusetts Institute of Technology
9 weeks, 2-4 hours per week
Course aimed at fighting fake news and misinformation
Educators—from teachers to librarians—will learn about:
- New knowledge that can be applied in your lessons and resources for your own students.
- How to shift from ineffective information literacy practices towards the kinds of strategies employed by professional fact-checkers.
Unit 1: Search Like a Fact Checker
Unit 2: The Two Big Fact Checker Moves: Lateral Reading & Click Restraint
Unit 3: Evaluating Different Types of Evidence
Unit 4: Adapting Civic Online Reasoning
7 weeks, 2-4 hours per week
WEEK 1: Understanding The Climate Controversy During the first week of the course, we introduce the course content, interact with each other and complete an introductory survey. The week continues with an exploration of political consensus, the drivers and psychology of climate science denial and an overview of the controversy surrounding this topic.
WEEK 2: Global Warming Is Happening In week two, we will look at the indicators of global warming and myths related to temperature and glaciers.
WEEK 3: We Are Causing Global Warming Week three focuses on the ways in which humans cause climate change and the myths associated with the greenhouse effect and the rise in carbon dioxide.
WEEK 4: The Past Tells Us About The Future This week looks at the history of climate change in order to model future climate change. We also address myths related to models.
WEEK 5: We Are Feeling The Impacts Of Climate Change Week five covers climate feedbacks and the impacts of climate change on the environment, society and the weather.
WEEK 6 and 7: Responding to Denial The final weeks of the course look more closely at the psychology of science denial and debunking techniques. We also complete a peer assessment that asks students to practice debunking strategies on real myths that can be found in today’s media.
Approach: mini-lectures, video interviews, quizzes, activities, a peer assessed writing assignment, and readings.
Offered by : Stanford University
1 week, 2-3 hours
This course seeks to fulfil the clinical community’s need to improve skills in the critical evaluation of clinical research papers. Competency in critical appraisal skills can have a significant impact by improving clinical practice, quality of research projects, and peer-review of manuscripts and grants. The course will utilize efficient and engaging videos with relevant clinical examples to cover essential research methodology principles.
- Analyse the concepts of randomization and blinding in reducing bias.
- Develop strategies to critically appraise randomized clinical trials and determine if study results are valid.
- Analyse the key design features of screening studies.
- Develop strategies to critically appraise screening studies and determine if study results are valid.
You May Also Like…

The Importance of Critical Thinking when Using ChatGPT (and Other Large Language Models)
Artificial intelligence has made tremendous strides in recent years, allowing for the creation of conversational AI...

How to Critically Evaluate News and Media Sources
I think we all agree that access to information has never been easier. With the click of a button, we can access an...

Critical Thinking in the Workplace
Imagine that you're in a job interview and the interviewer asks you to describe a time when you had to solve a complex...
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Critical Thinking
Subject area, catalog number, course title, department(s), description, typically offered, academic career, liberal arts, requirement designation, minimum units, maximum units, academic progress units, repeat for credit, course schedule.
- Departments, units, and programs
- College leadership
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Faculty and staff resources
- LAS Strategic Plan

- Apply to LAS
- Liberal arts & sciences majors
- LAS Insider blog
- Admissions FAQs
- Parent resources
- Pre-college summer programs
Quick Links
Request info
- Academic policies and standing
- Advising and support
- College distinctions
- Dates and deadlines
- Intercollegiate transfers
- LAS Lineup student newsletter
- Programs of study
- Scholarships
- Certificates
- Student emergencies
Student resources
- Access and Achievement Program
- Career services
- First-Year Experience
- Honors program
- International programs
- Internship opportunities
- Paul M. Lisnek LAS Hub
- Student research opportunities
- Expertise in LAS
- Research facilities and centers
- Dean's Distinguished Lecture series
- Alumni advice
- Alumni award programs
- Get involved
- LAS Alumni Council
- LAS@Work: Alumni careers
- Study Abroad Alumni Networks
- Update your information
- Nominate an alumnus for an LAS award
- Faculty honors
- The Quadrangle Online
- LAS News email newsletter archive
- LAS social media
- Media contact in the College of LAS
- LAS Landmark Day of Giving
- About giving to LAS
- Building projects
- Corporate engagement
- Faculty support
- Lincoln Scholars Initiative
- Impact of giving
Why is critical thinking important?
What do lawyers, accountants, teachers, and doctors all have in common?

What is critical thinking?
The Oxford English Dictionary defines critical thinking as “The objective, systematic, and rational analysis and evaluation of factual evidence in order to form a judgment on a subject, issue, etc.” Critical thinking involves the use of logic and reasoning to evaluate available facts and/or evidence to come to a conclusion about a certain subject or topic. We use critical thinking every day, from decision-making to problem-solving, in addition to thinking critically in an academic context!
Why is critical thinking important for academic success?
You may be asking “why is critical thinking important for students?” Critical thinking appears in a diverse set of disciplines and impacts students’ learning every day, regardless of major.
Critical thinking skills are often associated with the value of studying the humanities. In majors such as English, students will be presented with a certain text—whether it’s a novel, short story, essay, or even film—and will have to use textual evidence to make an argument and then defend their argument about what they’ve read. However, the importance of critical thinking does not only apply to the humanities. In the social sciences, an economics major , for example, will use what they’ve learned to figure out solutions to issues as varied as land and other natural resource use, to how much people should work, to how to develop human capital through education. Problem-solving and critical thinking go hand in hand. Biology is a popular major within LAS, and graduates of the biology program often pursue careers in the medical sciences. Doctors use critical thinking every day, tapping into the knowledge they acquired from studying the biological sciences to diagnose and treat different diseases and ailments.
Students in the College of LAS take many courses that require critical thinking before they graduate. You may be asked in an Economics class to use statistical data analysis to evaluate the impact on home improvement spending when the Fed increases interest rates (read more about real-world experience with Datathon ). If you’ve ever been asked “How often do you think about the Roman Empire?”, you may find yourself thinking about the Roman Empire more than you thought—maybe in an English course, where you’ll use text from Shakespeare’s Antony and Cleopatra to make an argument about Roman imperial desire. No matter what the context is, critical thinking will be involved in your academic life and can take form in many different ways.
The benefits of critical thinking in everyday life
Building better communication.
One of the most important life skills that students learn as early as elementary school is how to give a presentation. Many classes require students to give presentations, because being well-spoken is a key skill in effective communication. This is where critical thinking benefits come into play: using the skills you’ve learned, you’ll be able to gather the information needed for your presentation, narrow down what information is most relevant, and communicate it in an engaging way.
Typically, the first step in creating a presentation is choosing a topic. For example, your professor might assign a presentation on the Gilded Age and provide a list of figures from the 1870s—1890s to choose from. You’ll use your critical thinking skills to narrow down your choices. You may ask yourself:
- What figure am I most familiar with?
- Who am I most interested in?
- Will I have to do additional research?
After choosing your topic, your professor will usually ask a guiding question to help you form a thesis: an argument that is backed up with evidence. Critical thinking benefits this process by allowing you to focus on the information that is most relevant in support of your argument. By focusing on the strongest evidence, you will communicate your thesis clearly.
Finally, once you’ve finished gathering information, you will begin putting your presentation together. Creating a presentation requires a balance of text and visuals. Graphs and tables are popular visuals in STEM-based projects, but digital images and graphics are effective as well. Critical thinking benefits this process because the right images and visuals create a more dynamic experience for the audience, giving them the opportunity to engage with the material.
Presentation skills go beyond the classroom. Students at the University of Illinois will often participate in summer internships to get professional experience before graduation. Many summer interns are required to present about their experience and what they learned at the end of the internship. Jobs frequently also require employees to create presentations of some kind—whether it’s an advertising pitch to win an account from a potential client, or quarterly reporting, giving a presentation is a life skill that directly relates to critical thinking.
Fostering independence and confidence
An important life skill many people start learning as college students and then finessing once they enter the “adult world” is how to budget. There will be many different expenses to keep track of, including rent, bills, car payments, and groceries, just to name a few! After developing your critical thinking skills, you’ll put them to use to consider your salary and budget your expenses accordingly. Here’s an example:
- You earn a salary of $75,000 a year. Assume all amounts are before taxes.
- 1,800 x 12 = 21,600
- 75,000 – 21,600 = 53,400
- This leaves you with $53,400
- 320 x 12 = 3,840 a year
- 53,400-3,840= 49,560
- 726 x 12 = 8,712
- 49,560 – 8,712= 40,848
- You’re left with $40,848 for miscellaneous expenses. You use your critical thinking skills to decide what to do with your $40,848. You think ahead towards your retirement and decide to put $500 a month into a Roth IRA, leaving $34,848. Since you love coffee, you try to figure out if you can afford a daily coffee run. On average, a cup of coffee will cost you $7. 7 x 365 = $2,555 a year for coffee. 34,848 – 2,555 = 32,293
- You have $32,293 left. You will use your critical thinking skills to figure out how much you would want to put into savings, how much you want to save to treat yourself from time to time, and how much you want to put aside for emergency funds. With the benefits of critical thinking, you will be well-equipped to budget your lifestyle once you enter the working world.
Enhancing decision-making skills
Choosing the right university for you.
One of the biggest decisions you’ll make in your life is what college or university to go to. There are many factors to consider when making this decision, and critical thinking importance will come into play when determining these factors.
Many high school seniors apply to colleges with the hope of being accepted into a certain program, whether it’s biology, psychology, political science, English, or something else entirely. Some students apply with certain schools in mind due to overall rankings. Students also consider the campus a school is set in. While some universities such as the University of Illinois are nestled within college towns, New York University is right in Manhattan, in a big city setting. Some students dream of going to large universities, and other students prefer smaller schools. The diversity of a university’s student body is also a key consideration. For many 17- and 18-year-olds, college is a time to meet peers from diverse racial and socio-economic backgrounds and learn about life experiences different than one’s own.
With all these factors in mind, you’ll use critical thinking to decide which are most important to you—and which school is the right fit for you.
Develop your critical thinking skills at the University of Illinois
At the University of Illinois, not only will you learn how to think critically, but you will put critical thinking into practice. In the College of LAS, you can choose from 70+ majors where you will learn the importance and benefits of critical thinking skills. The College of Liberal Arts & Sciences at U of I offers a wide range of undergraduate and graduate programs in life, physical, and mathematical sciences; humanities; and social and behavioral sciences. No matter which program you choose, you will develop critical thinking skills as you go through your courses in the major of your choice. And in those courses, the first question your professors may ask you is, “What is the goal of critical thinking?” You will be able to respond with confidence that the goal of critical thinking is to help shape people into more informed, more thoughtful members of society.
With such a vast representation of disciplines, an education in the College of LAS will prepare you for a career where you will apply critical thinking skills to real life, both in and outside of the classroom, from your undergraduate experience to your professional career. If you’re interested in becoming a part of a diverse set of students and developing skills for lifelong success, apply to LAS today!
Read more first-hand stories from our amazing students at the LAS Insider blog .
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility

Flipping the Switch: Using the Flipped Classroom to Increase Student Critical Thinking and Engagement
- Alexis Zehler Miami University Author
- Britt Cole Miami University Author
The literature supports the concept of a flipped classroom as a pedagogical approach that can improve critical thinking, enhance clinical judgment, and promote student engagement. This project implemented the flipped classroom concept in two nursing specialty courses, one didactic and one clinical. Data were gathered from both courses using a mixed method approach to evaluate impact. The data demonstrated significant improvement in students’ critical thinking and clinical judgment, increased engagement, and increased positive perceptions of learning when the flipped classroom approach was used in course design

- Requires Subscription PDF
- Application
Access Agreement Journal on Excellence in College Teaching
Before proceeding you must agree to the terms and conditions of usage as outlined below by clicking on the Accept button and/or by both parties’ signatures below. You will have to do this only once. After agreement, you will be redirected back to the main Journal page. A pdf copy of the terms is available for download.
This Access Agreement (the "Agreement") is effective upon processing of payment ("Effective Date") and is entered into by and between the Journal on Excellence in College Teaching (“JECT”) and the Customer (“Customer").
This Agreement constitutes the entire agreement and supersedes and voids all prior communications, understandings, and agreements relating to the Product(s), including any terms of use displayed to Authorized Users via the online site of the Product(s). Alterations to the Agreement and to any Addendum to the Agreement are only valid and binding if they are recorded in writing and signed by both parties
. I. Definitions
"Authorized Users" shall mean individuals who are authorized by the Customer (which shall include those individuals authorized by the Institutions hereunder) to access the Customer's information services whether on-site or off-site via secure authentication and who are affiliated with the Customer as a student (undergraduates and postgraduates), employee (whether on a permanent or temporary basis), or a contractor of the Customer. Individuals who are not a current student, employee, or a contractor of the Customer, but who are permitted to access the Customer's information services from computer terminals within the physical premises of the Customer ("Walk-In Users"), are also deemed to be Authorized Users, but only for the time they are within the physical premises of the Customer. Walk-In Users may not be given means to access the Product(s) when they are not within the physical premises of the Customer.
"Commercial Use" shall mean use for the purpose of monetary reward (whether by or for the Customer or an Authorized User) by means of the sale, resale, loan, transfer, hire, or other form of exploitation of the Product(s). For the avoidance of doubt, neither recovery of direct cost by the Customer from Authorized Users, nor use by the Customer or Authorized Users of the Product(s) in the course of research funded by a commercial organization, shall be deemed to constitute Commercial Use.
"Educational Purposes" shall mean for the purpose of education, teaching, distance learning, private study and/or research as described in Section II below.
"Institutions" shall mean the Customer's participating institutions, if applicable.
"License" shall mean the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and use the Product(s) pursuant to the specific terms and conditions set forth in this Agreement.
"Product(s)" shall mean the products, materials and/or information contained therein that are subject to this Agreement. Product(s) include the Journal on Excellence in College Teaching and the archive of the Learning Communities Journal.
"Reasonable Amount" shall be determined based on guidelines set forth by 17 U.S. Code § 107 (Limitations on exclusive rights, Fair use).
"Secure Authentication" shall mean access to the Product(s) by Internet Protocol ("IP") ranges or by another means of authentication agreed between the Publisher and Customer or Institutions (if applicable) from time to time.
II. Authorized Use of Product(s)
Customer, the Institutions (if applicable), and Authorized Users may use the Product(s) for Educational Purposes as follows:
Analysis . Authorized Users shall be permitted to extract or use information contained in the Product(s) for Educational Purposes, including, but not limited to, text and data mining, extraction and manipulation of information for the purposes of illustration, explanation, example, comment, criticism, teaching, research, or analysis.
Course Packs . Customer, the Institutions, and Authorized Users may use a Reasonable Amount of the Product(s) in the preparation of course packs or other educational materials.
Digital Copy . Customer, the Institutions, and Authorized Users may download and digitally copy a Reasonable Amount of the Product(s).
Display . Customer, the Institutions, and Authorized Users shall have the right to electronically display the Product(s) to the extent necessary to further the intent and purpose of this Agreement.
Electronic Reserve . Customer, the Institutions, and Authorized Users may use a Reasonable Amount of each of the Product(s) in connection with specific courses of instruction offered by Customer.
Interlibrary Loan . The Customer and the Institutions shall be permitted to use Reasonable Amounts of the Content to fulfill occasional requests from other, non-participating institutions, a practice commonly called Interlibrary Loan ("ILL"). Customer and the Institutions shall fulfill such requests in compliance with Section 108 of the United States Copyright Law (17 USC S108, "Limitations on exclusive rights: Reproduction by libraries and archives") and the Guidelines for the Proviso of Subsection 108(2g)(2) prepared by the National Commission on New Technological Uses of Copyrighted Works (CONTU).
The electronic form of the Product(s) may be used as a source for ILL. Customer and the Institutions shall include copyright notices on all ILL transmissions. Notwithstanding anything herein to the contrary, in no event shall any non-secure electronic transmission of files be permitted.
Print Copy . Customer, the Institutions, and Authorized Users may print a Reasonable Amount of the Product(s).
Recover Copying Costs . Customer and the Institutions may charge a reasonable fee to cover costs of copying or printing portions of Product(s) for Authorized Users.
Scholarly Sharing . Authorized Users may transmit to a third party colleague in hard copy or electronically, Reasonable Amounts of the Product(s) for personal use, professional use, or Educational Purposes but in no event for Commercial Use. In addition, Authorized Users have the right to use, with appropriate credit, figures, tables, and brief excerpts from the Product(s) in the Authorized User's own scientific, scholarly, and educational works.
Text Mining . Authorized Users may use the licensed material to perform and engage in text mining/data mining activities for legitimate academic research and other Educational Purposes. Those uses beyond educational use shall require permission from the Publisher.
III. Restrictions
Except as provided herein, the institution shall make reasonable efforts to inform its authorized users not to use, alter, decompile, modify, display, or distribute the Product(s) as follows:
Alter Identification . Remove, obscure, or modify copyright notices, text acknowledging, attributions, or other means of identification or disclaimers as they appear. Alter Product(s).
Alter, decompile, adapt, or modify the Product(s), except to the extent necessary to make it perceptible on a computer screen, or as otherwise permitted in this Agreement. Alteration of words or their order is strictly prohibited.
Commercial Use . No Commercial Use of the Product(s) shall be permitted unless the Customer or an Authorized User has been granted prior written consent by an authorized representative of the Product(s). Use of all or any part of the Product(s) for any Commercial Use or for any purpose other than Educational Purposes.
Distribution . Display or distribute any part of the Product(s) on any electronic network, including without limitation, the Internet, and any other distribution medium now in existence or hereinafter created, other than by a Secure Authentication; print and distribute any portion(s) of the Product(s)s to persons or entities other than the Customer or Authorized Users, except as provided in Section II.
JECT acknowledges that the Customer cannot police or control the actions of its students, faculty, and other Authorized Users with respect to their use of the Product(s). In the event of abuse, the institution shall make prompt and reasonable efforts to heal the breach and notify the publisher.
IV. Term and Termination
This agreement shall commence on the Effective Date and shall remain in effect unless and until terminated as permitted herein (the "Term"). There is no perpetual electronic access to content made available during the term of the agreement.
JECT may terminate this Agreement if Customer violates any of the terms and conditions set forth herein. In the event of any termination of access, JECT will promptly notify the Customer of the basis for termination.
The Customer may terminate this Agreement if sufficient funds are not provided or allotted in future government-approved budgets of the Customer (or reasonably available or expected to become available from other sources at the time the Customer’s payment obligation attaches) to permit the Subscriber, in the exercise of its reasonable administrative discretion, to continue this Agreement.
In the event of any unauthorized use of the Product(s) by an Authorized User, Customer shall cooperate with JECT in the investigation of any unauthorized use of the Product(s) of which it is made aware and shall use reasonable efforts to remedy such unauthorized use and prevent its recurrence. JECT may terminate such Authorized User's access to the Product(s) after first providing reasonable notice to the Customer (in no event less than two (2) weeks) and cooperating with the Customer to avoid recurrence of any unauthorized use. In the event of any termination of access, JECT will promptly notify the Customer
. V. Refunds
In the event that a subscription is canceled by the Customer prior to the subscription end date, the following will be used as guidelines for refunds.
Electronic subscriptions . The Customer shall be entitled to a full refund within 14 days of the start of the most recent subscription term. Refunds requested after 14 days but no later than 60 days from the start of the most recent subscription term will be allowed, minus a 30% processing fee. Refunds will not be granted if requested more than 60 days after the start of the most recent subscription term.
Journal on Excellence in College Teaching Center for Teaching Excellence Miami University 317 Laws Hall Oxford, Ohio 45056
All rights reserved | Miami University | The Journal on Excellence in College Teaching

100 Best universities for Mechanical Engineering in Russia
Updated: February 29, 2024
- Art & Design
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Liberal Arts & Social Sciences
- Mathematics
Below is a list of best universities in Russia ranked based on their research performance in Mechanical Engineering. A graph of 714K citations received by 136K academic papers made by 158 universities in Russia was used to calculate publications' ratings, which then were adjusted for release dates and added to final scores.
We don't distinguish between undergraduate and graduate programs nor do we adjust for current majors offered. You can find information about granted degrees on a university page but always double-check with the university website.
1. Moscow State University
For Mechanical Engineering


2. Tomsk State University

3. St. Petersburg State University

4. Bauman Moscow State Technical University

5. Ufa State Aviation Technical University

6. Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University

7. Tomsk Polytechnic University

8. Ural Federal University

9. South Ural State University

10. National Research University Higher School of Economics

11. Moscow Aviation Institute

12. Novosibirsk State University

13. ITMO University

14. N.R.U. Moscow Power Engineering Institute

15. National Research Nuclear University MEPI

16. Kazan Federal University

17. National University of Science and Technology "MISIS"

18. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology

19. Samara National Research University

20. Moscow State Technological University "Stankin"

21. Novosibirsk State Technical University

22. RUDN University

23. Southern Federal University

24. Saratov State University

25. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University

26. Samara State Technical University

27. Siberian Federal University

28. Kazan National Research Technical University named after A.N. Tupolev - KAI

29. Perm State Technical University

30. Omsk State Technical University

31. Saint Petersburg State Electrotechnical University

32. Moscow Polytech

33. Saint-Petersburg Mining University

34. Magnitogorsk State Technical University

35. Saratov State Technical University

36. Moscow State University of Railway Engineering

37. Lobachevsky State University of Nizhni Novgorod

38. Nizhny Novgorod State Technical University

39. Tula State University

40. Belgorod State Technological University

41. Far Eastern Federal University

42. Novgorod State University
43. belgorod state university.

44. Finance Academy under the Government of the Russian Federation

45. Moscow Medical Academy

46. Kazan State Technological University

47. Russian State University of Oil and Gas
48. siberian state aerospace university.

49. Tambov State Technical University

50. Voronezh State University

51. Siberian State Industrial University

52. Saint Petersburg State Institute of Technology

53. Kalashnikov Izhevsk State Technical University

54. St. Petersburg State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering

55. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia

56. Murmansk State Technical University

57. South-Western State University

58. Ogarev Mordovia State University

59. Tomsk State University of Control Systems and Radioelectronics
60. south-russian state university of economics and service.

61. Perm State University

62. Kuzbass State Technical University

63. Russian National Research Medical University

64. Plekhanov Russian University of Economics

65. Ulyanovsk State Technical University

66. Ulyanovsk State University

67. Penza State University

68. Kuban State University of Technology

69. Polzunov Altai State Technical University

70. Chelyabinsk State University

71. Yaroslavl State University

72. University of Tyumen
73. National Research University of Electronic Technology

74. Leningrad State University

75. Moscow State Pedagogical University

76. Udmurt State University

77. Irkutsk State University

78. North-Eastern Federal University

79. Bashkir State University

80. Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration

81. Kuban State University

82. Kuban State Agricultural University

83. St. Petersburg State University of Aerospace Instrumentation

84. Kemerovo State University

85. Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University

86. Orenburg State University
87. Baltic State Technical University "Voenmeh"

88. Tomsk State University of Architecture and Building

89. Chuvash State University
90. ivanovo state power university.

91. Irkutsk National Research Technical University

92. Orel State University

93. State University of Management

94. Tomsk State Pedagogical University

95. Volgograd State University

96. Petrozavodsk State University

97. Tver State University

98. Northern Arctic Federal University

99. Omsk State Transport University

100. Kaliningrad State Technical University

The best cities to study Mechanical Engineering in Russia based on the number of universities and their ranks are Moscow , Tomsk , Saint Petersburg , and Ufa .
Engineering subfields in Russia

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking course curriculum. edX offers many courses to help learners develop critical thinking skills. For example, a short course on the fundamentals of critical thinking may teach strategic analysis and problem-solving. Others could be more focused on specific applications, such as critical thinking for leaders or entrepreneurs.
She designed and teaches the MBA Core course in Critical and Strategic Thinking, in addition to teaching courses in leadership and serving as faculty co-director of the Johnson Leadership Fellows program. ... SC Johnson College of Business, Cornell University. Since coming to the Johnson Graduate School of Management in 1991, Robert J ...
This specialization introduces general standards of good reasoning and offers tools to improve your critical thinking skills. These skills will help you determine when an argument is being given, what its crucial parts are, and what it assumes implicitly. You will also learn how to apply deductive and inductive standards for assessing arguments ...
Learn Critical Thinking, earn certificates with paid and free online courses from Harvard, Stanford, MIT, University of Pennsylvania and other top universities around the world. Read reviews to decide if a class is right for you.
Free Certificate. This course will introduce you to critical thinking, informal logic, and a small amount of formal logic. Its purpose is to provide you with the basic tools of analytical reasoning, which will give you a distinctive edge in a wide variety of careers and courses of study. While many university courses focus on presenting content ...
Module 1 • 2 hours to complete. In this module, you will be able to apply a model for solving any problem, large or small, in a creative and collaborative way. You will also be able to identify all aspects of a problem and examine role in the problem. You will be able to reframe a goal oriented question. What's included.
This course, designed with incoming college freshmen in mind but open to anyone, provides an essential grounding in critical reasoning skills. Faculty from multiple disciplines at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill offer guidance on applying critical thinking skills in the context of specific disciplines.
Develop your creative and critical thinking skills with New Scientist. Critical thinking and creativity are key skills needed to improve decision-making, whether in a personal context or in the workplace. This three-week course will help sharpen your ability to analyse information and increase your capacity to problem solve creatively.
At the end of the course, you'll be able to: Describe critical thinking in the context of the philosophies that form and define it, and explain why it is important to making good decisions. Recognize, analyze, and construct logical arguments in standard form as distinguished from persuasive arguments. Analyze and assess different types of ...
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
Critical thinking is important because it relates to nearly all tasks, situations, topics, careers, environments, challenges, and opportunities. It's a "domain-general" thinking skill—not a thinking skill that's reserved for a one subject alone or restricted to a particular subject area. Critical thinking is used in every domain, from ...
Introduction to Critical Thinking. This introductory-level course is designed to help learners define and identify critical thinking and reasoning skills and develop those skills. Critical thinking is an intellectual model for reasoning through issues to reach well-founded conclusions. It may be the single most valuable skill that one can bring ...
Course Description. Critical thinking is an intellectual model for reasoning through issues to reach well-founded conclusions. It may be the single-most valuable skill that one can bring to any job, profession, or life challenge. Being able to ask the right questions, critique an argument, and logically dissect an issue occur constantly in the ...
In this course, you will be introduced to the elements of reasoning, universal intellectual standards, and intellectual traits through readings, discussions, and practical application activities. You will redesign lessons and strategies using the concepts and principles of critical thinking. You will practice strategies for Socratic discussions.
A3 - Critical Thinking - Courses. AAS 201. Race, Racism and Critical Thinking (3) Preparatory: Completion of the lower division writing requirement and GE section B4 Mathematics. Introduction to the process of critical thinking through the lens of race-based theories and selected historical and contemporary discourse of African Americans, Asian ...
Introduction to Critical Thinking and Logic. Teaching Critical Thinking through Art with the National Gallery of Art. Critical thinking: Reasoned Decision Making. The Science of Everyday Thinking. Critical Thinking at University: An Introduction. Making Sense of News. Sorting Truth From Fiction: Civic Online Reasoning.
Description. This course explores the process of thinking critically and guides students in thinking more clearly, insightfully, and effectively. Specific examples from students' experiences and from contemporary issues help students develop the abilities to solve problems, analyze issues, and make informed decisions in their academic ...
The importance of critical thinking can be found across a wide set of disciplines. They are not only used in the humanities but are also important to professionals in the social and behavioral sciences, physical sciences, and STEM—and the list does not end there. At the University of Illinois College of Liberal Arts & Sciences, you'll be ...
Course Description. Methods and standards for evaluating various types of beliefs, propositions, and arguments. Includes a study of the connections between language and logic, sources of bias, psychological and philosophical impediments to critical thinking, fallacies and errors of reasoning, explanatory arguments, and moral reasoning. Units: 3.
Develop and practice the reading, writing and critical thinking strategies needed for analyzing and responding to academic texts. Strengthen grammar, organization and vocabulary to improve accuracy and fluency in writing. Prerequisite: either ENGL 101 or placement by test score.
The literature supports the concept of a flipped classroom as a pedagogical approach that can improve critical thinking, enhance clinical judgment, and promote student engagement. This project implemented the flipped classroom concept in two nursing specialty courses, one didactic and one clinical. Data were gathered from both courses using a mixed method approach to evaluate impact.
1755. Statistics Rankings. 2. Bauman Moscow State Technical University. For Mechanical Engineering. # 4 in Russia. # 249 in Europe. Acceptance Rate. 30%.
In 1954, Elemash began to produce fuel assemblies, including for the first nuclear power plant in the world, located in Obninsk. In 1959, the facility produced the fuel for the Soviet Union's first icebreaker. Its fuel assembly production became serial in 1965 and automated in 1982. 1. Today, Elemash is one of the largest TVEL nuclear fuel ...
Sitting. on the tarmac at the Zhukovsky flight-test center about 30. miles southeast of Moscow, the Sukhoi Design Bureau's most power-. ful and capable fighter, the stunning Su-35, gives every impression. of a coiled cobra. Prepared to strike at the slightest warning, it hun-. kers down, nose low, poised on its rough-field landing gear, peering.
EduRank.org is an independent metric-based ranking of 14,131 universities from 183 countries. We utilize the world's largest scholarly papers database with 98,302,198 scientific publications and 2,149,512,106 citations to rank universities across 246 research topics.