What is a Seminar? The Complete Guide
If you are in the field of delivering training to at least one organization, you must understand the term seminar. A seminar is a meeting or conference designed to increase awareness of an idea or expand understanding of a topic.
Seminars frequently feature lectures, discussions, and workshops. If you are wondering “what is a seminar” or “what is it that a seminar can do for you,” then this article is for you. It’s focused on the what, the when, and the why of seminars.

What is a Seminar and How Does It Work?
A seminar is a meeting or a conference that is usually organized for a particular topic.
Seminars are held in a place that is set up with enough room to accommodate all the intended attendees. This venue can either be outdoors, indoors or even in the case of physical causes, it can be done online.
In education, seminars are used to share information other than acquiring knowledge from the teacher. They are an effective way of passing on other forms of knowledge from different sources.
A seminar may also have a few group exercises and lectures. However, most of the time is spent listening to presentations.
What is the Purpose of a Seminar?
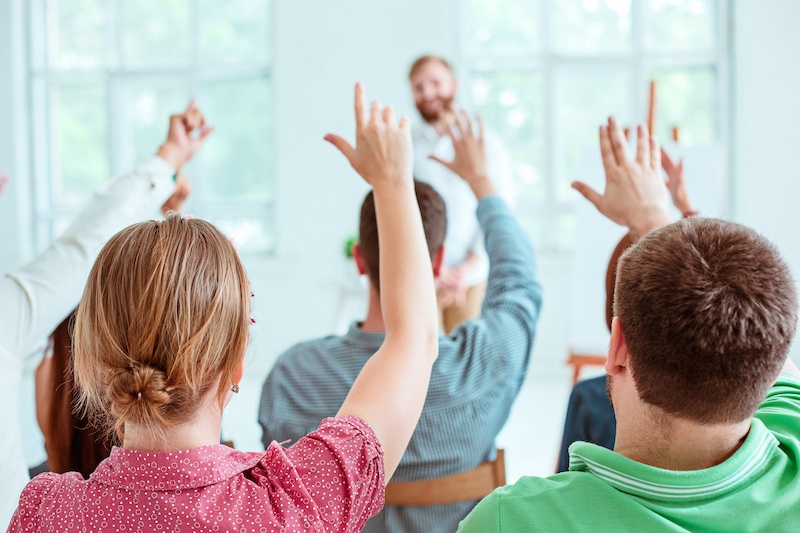
1. providing an opportunity to explore a topic in-depth.
A seminar is a live presentation of a set topic where all participants can ask questions and interact to gain a better understanding.
In a seminar, the facilitator presents information for the entire session and answers questions posed by the audience.
Seminars are beneficial because they provide an opportunity to explore a topic in depth. A seminar allows all participants time to engage with the presenter and with each other in an interactive environment.
2. To sell products, services, or new projects
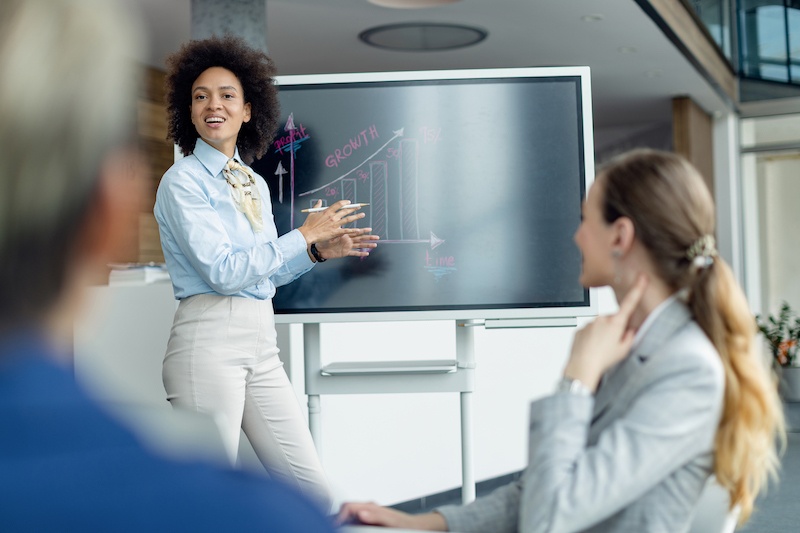
A seminar is an elaborate presentation or lecture, especially by an expert in some field, to teach people about the subject.
Additionally, seminar organizations organize seminars as a means of promoting their products or services to gain new clients. Experts may present seminars with the assistance of multimedia, such as slide projectors.
3. Collaboration, brainstorming, and discussion among participants
A seminar is a form of education through which knowledge, experience, and skills are transferred from the presenter to the attendees.
Seminars are generally held in open groups, and they provide a less formal but more interactive way to learn than lectures and classrooms.
4. To serve as a training tool for businesses
In a seminar, trainees and trainers gain knowledge and skills through a combination of reflexive and informative processes.
Seminars, when conducted correctly can help organizations learn more about their employees and how to handle specific situations in the workplace.
A seminar facilitates the sharing of information between managers and staff members. Business seminars can help improve staff satisfaction through increased morale and creativity, which in turn will lead to higher productivity.
5. To meet new people and develop relationships
A seminar can be a branded event hosted by a company or an educational series hosted by a university. They’re common in markets where recruiting and ongoing training are a priority. They can also be used in ongoing professional development.
Seminars help to meet new people and develop relationships within fields of interest.
How Can Seminars Be Used to Enhance the Learning Process?
1. stimulate the imagination of learners.
Seminars in business and education creatively propel learners’ thinking. Yet, when it is time for them to return to their daily activities, they have to regroup their thoughts and assets gained from the seminar.
In doing so, they will enable themselves to do better things in their organization. Seminars also allow educators the opportunity to add value to the community through the seminars put up by them.
2. Experiment with learning styles
A seminar is a course meant for professionals and others who want to increase their knowledge and/or skills in a specialized area of activity.
Seminars focus on various learning styles and can help in problem-solving and taking informed decisions. In addition to equipping the participants with new skills and tools.
3. Motivate, coach, and empower
A seminar is a session in which you share your knowledge, ideas, and experience with clients to help them. They are generally conducted in a classroom or conference room.
However recently more organizations are using virtual classrooms that run using interactive whiteboard tools or computers.
A seminar is ideal for motivating, coaching, and empowering participants before, during, and after the seminar is conducted.
4. Encourage lifelong learning
There are many ways in which seminars can be used to provide a framework for lifelong learning.
Seminars allow participants to interact with one another, allowing them to gain insights from their experiences, opinions, and ideas on specific subjects. They can also be used as social events, where friendships are formed and old acquaintances are renewed.
5. Serve as a vehicle for exploration and discovery
Seminars are often held to inform or educate. These events can serve as a vehicle for exploration and discovery.
Most seminars, like workshops, include lectures and demonstrations although they ordinarily contain more of the former than the latter.
At any rate, attendees at these events are provided opportunities to ask questions.
In addition, participants might have the opportunity to discuss certain parts of the material presented during breaks or after the seminar is over. This way there is room for the discovery of new things.
What Are the Forms of Seminars Available?
It is often referred to as a “ face-to-face seminar “. A physical seminar is a live event where people come together to hear what the speaker or teacher has to say. It‘s a formal meeting that usually involves highly focused learning.
An instructor can deliver instruction face-to-face in the form of a talk, a lecture, a class, an interview, or a panel discussion.
Online seminars (Webinars)
A webinar is an educational seminar offered via web-based technologies, such as the Internet, online services, or video conferencing .
Unlike seminars, webinars are delivered online making them cost-effective and convenient for learners located around the world to participate.
What Are the Benefits of Attending a Seminar?
1. acquire new skills and knowledge.
Seminars are designed to help individuals up-skill themselves in an area of expertise. This is achieved through the presentation of various topics featuring new, upcoming, and proven concepts.
Additionally, learning new skills can enable individuals to build up their vocational knowledge which they can use to succeed in their professional careers.
2. You will be able to practice your public speaking
A seminar can help you get comfortable with speaking in front of large crowds.
We all get nervous when speaking in front of groups, but after doing it once or twice it won’t be so scary. With practice, it becomes easier to speak in front of crowds, and seminars are perfect for that.
3. Gain practical experience in your field
Attending a seminar will allow you to gain practical experience in your field. By applying the speaker’s ideas, you can also improve your work management skills, improve your abilities, and expand your knowledge base.
4. Get answers to your questions
A seminar will answer most, if not all, of your questions. Exhibitors and seminar leaders do their best to address the specific concerns of the audience. Besides, the main purpose of a seminar is to help you learn from industry experts.
It will answer the questions you have about your work and thus, help you in your journey to the top.
5. Build relationships with people you meet at seminars
People with similar interests to yours are likely to be at seminars. This is a great networking opportunity.
Furthermore, networking helps you build lasting relationships with others in your industry. These types of relationships will also help you improve your ventures in any area of life, including business.
What Skills Do You Need for Presenting in a Seminar?
Presenting is a skill. Like all skills, the more you do it the better you become at it. If you are new to presenting or teaching, why not audio record one of your first few sessions and listen to it afterward?
Try it for an hour or two each day, and in a relatively short number of weeks, you will find that your improvement will be remarkable. The presenter’s world is full of danger lurking in all manner of forms that can sabotage any presentation.
Thankfully, some strategies are easy to implement that can significantly increase the effectiveness of any presentation. Below are some tips on preparing for a seminar.
What Are the Tips to Prepare for a Seminar?
1. know your message.
You’ve done the research; now it’s time to find the audience. The first step in putting together your seminar is to know exactly what you want to say. This isn’t easy if you’re an expert in several areas.
Ideally, write an outline for each of your speeches and practice them (out loud) to see how they sound. If your message is well-supported by its arguments, it will be easier for you to present.
2. Consider the goal of the audience
Public seminars can be a great way to get your name out there about what you do. But it is important to be aware of what an audience expects from a seminar. One of the goals of a seminar is to provide information to meet your audience’s needs.
The style and manner of the delivery determine the level of success of any seminar. Also, your goal is to help others understand your topic and help them see how it applies to their situations.
3. Who will be at the seminar
Identify who will be attending the seminar before kick-off. This will help you determine the content, activities, or handouts you need to have ready. It also reveals how to best market your seminar as a result.
Are you targeting industry leaders only or is this a training seminar that everyone from the novice level will attend? In addition, what is the maximum capacity of the audience you can address?
When you consider these questions, it will help you have a clue of how to go about your presentation.
4. Anticipate possible questions
The traditional notion of a seminar is that it is a formal event. The attendants ask questions to clarify their doubts about the topic for easy understanding. As a presenter, it is very difficult to guess what an audience is thinking about the subject in advance.
To address this, you must first research the client and their industry. What they have been through in the past will be an indication of what questions they will ask during the seminar.
Anticipating possible questions from the audience will help you convey your message concisely and effectively.
5. Provide value and remove objections
You want to hold a conference or seminar, but you are not sure what you should do to make it successful. You already have the best topic selected, now all you need is to bring it to life.
Give the audience something of value. This might be an offer of free information that has value, or it might be something tangible, like a light lunch or free samples.
How is a seminar different from a conference or symposium?
Conferences and symposiums are run by one or a few people for a very specific purpose or subject matter.
Seminars, on the other hand, are typically set up in a more general format to educate a larger audience on particular subject areas.
Who can organize a seminar?
You can organize a seminar when, say, you have a burning topic that you think is important and others should know about.
Or you run an organization that wants to attract more members. Either way, a seminar is a great way to get your name out there.
Final Thoughts
A seminar is a meeting of people with similar interests, objectives, or professions to discuss issues related to their field. It provides a flexible learning atmosphere that allows participants to interact with one another and with the presenter.
Seminars also allow students to network with other students and professionals in their major or career field.
Seminars in the academic world may exist to inform people about online learning and why it’s important. For more information, check out the articles on online learning . You will find them informative and helpful.
The blog, LMS Hero provides high-quality information on e-learning and education to the general public as well as experts. You are welcome to explore the blog at your leisure.
Thanks for reading.
You may also like:
- Start a Seminar Business: Earn Big With This Guide
- What Are Adaptive Skills? [Definition, Types & Benefits]
- Soft Skills List: See 17 Crucial Soft Skills Every Professional Needs
- What Are Entrepreneurial Skills? 10 Benefits of Entrepreneurial Skills
- What Are Social Skills? [Definition, Types & Benefits]
People Also Read:

Why Do Waiters Get Paid So Little [+ How To Make More Money]

Navigating Workplace Norms: Can You Email A Resignation Letter?

Difference Between Roles And Responsibilities

Does Suspension Mean Termination?

Moral Claim: Definition, Significance, Contemporary Issues, & Challenges

Why Can’t You Flush The Toilet After A Drug Test?
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of seminar
- panel discussion
- round-robin
Examples of seminar in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'seminar.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
German, from Latin seminarium nursery
1863, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Dictionary Entries Near seminar
seminal vesicle
Cite this Entry
“Seminar.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/seminar. Accessed 14 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of seminar, more from merriam-webster on seminar.
Nglish: Translation of seminar for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of seminar for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about seminar
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 12, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

What is a Seminar and How to Run One Like a Pro
Learn what is a seminar, along with 3 real-life examples and how to run one like a pro. Engage your audience and boost attendance with our insights.
Written by Brillixa Herdhiana
Hosting a seminar can be the ideal solution to engage and educate your clients, partners, or industry peers. It will also strengthen knowledge sharing and collaboration within your company.
Nobody wants to see screens go black or attendees checking their emails during a presentation.
Running a seminar comes with great responsibility, but when approached correctly, it becomes a powerful tool for audience engagement and building connections.
This article provides expert tips on running a successful seminar, ensuring that you make a lasting impact on your target audience and establish meaningful connections.
Discover how to run a seminar like a pro and optimize your event for maximum success.
How to Make Virtual Events Engaging
Livestorm helps teams collaborate and deliver memorable live or on-demand video experiences.
What is a seminar?
A seminar, or a panel discussion , is a focused and interactive educational event where a group of people with shared interests come together to discuss, learn, and exchange ideas .
A subject matter expert or speaker usually leads the discussion and encourages attendees to ask questions and contribute to the discourse at the end. They’re typically conducted in person, but you can also host them online through video conferencing software .
The size, duration, and format largely depends on your specific needs and goals. But the key to a successful seminar is creating an environment that encourages active participation and open dialogue.
Key takeaways of a seminar
- Seminars are effective tools for engaging and educating clients, partners, and teams, but require careful planning and execution .
- There are three main types of seminars : webinars, academic seminars, and professional development seminars, each serving different purposes and audiences.
- Running a successful seminar involves steps such as choosing the right venue or platform, creating a detailed agenda, assembling a competent team, and effectively promoting the event.
- Keeping the audience engaged during the seminar through interactive elements like live polls, Q&A sessions, breakout rooms, and visual collaboration tools is crucial, followed by post-event follow-up and feedback gathering to improve future seminars.
3 different types of seminars
Seminars can cover a wide range of topics, from webinars and academic seminars to professional development. Let’s take a look at three different types of seminars in more detail.
1. Webinars
Webinars are virtual presentations where hosts or guest speakers share their knowledge and expertise of a certain topic with a global audience . Your attendees can access the webinar live or watch the recording on demand.
Here’s an example of upcoming webinars and on-demand events here at Livestorm:
You can use webinars to showcase your products, educate and onboard customers, build brand authority, and improve internal communications and employee training.
2. Academic seminars
At academic seminars, scholars, researchers, and students come together to talk about their research and share findings .
Depending on the context, they can last for a few hours or even span several days like this seminar by Harvard Business School:
Seminars can happen at universities, research centers, conferences, or workshops. Their main aim is to encourage knowledge-sharing, networking, and in-depth discussions.
3. Professional development seminars
**A professional development seminar is a learning event that helps people enhance their job skills and network with other professionals in their industry. **
These seminars typically prioritize practical, hands-on learning. This way, the attendees gain insights they can directly apply in their workplace.
Some companies also host professional development seminars for their employees to help them grow and advance in their careers.
Here’s a professional development seminar example, held by the Tax Executives Institute (TEI):
What are the advantages of running a seminar ?
Seminars are a great way to educate your audience while building authority and trust. Below are some of the most useful ways seminars can benefit your businesses:
1. Educate your audience
Seminars help participants learn from experts and each other, exchange ideas, and solve problems . Your speakers can demonstrate best practices, techniques, or strategies your audience can learn from or emulate.
Whether it’s presenting a product demo or sharing industry insights, seminars let you offer practical tips, advice, or solutions they can use to overcome challenges or improve their skills.
Of course, seminars aren’t just for your customers.
You can also use them for employee training sessions and onboarding. And if your employees work remotely, webinars can be a great way to connect your team. All you need is a suitable virtual training platform .
2. Increase brand visibility and authority
When you hold informative, engaging seminars, you showcase your expertise and authority on a certain topic.
Valuable seminars lead to word-of-mouth recommendations, social media sharing, and increased recognition. Over time, this builds trust and authority, solidifying your brand's position as a go-to resource in your industry.
3. Engage your audience and foster relationships
Seminars help you connect with your audience and get them involved in the discussion. They’re different from other marketing channels in that way.
Seminars don't just engage your audience passively. Instead, they let them ask questions, communicate, and share their own insights.
This active participation creates a deeper, more meaningful connection between you and your audience. It can strengthen your brand, build community, and even improve internal communication for remote teams .
How to run a seminar in 6 steps
A successful seminar needs careful planning , informative content, and the right platform to engage your audience. Here are some steps to run a seminar:
1. Choose your venue or platform
The first step to any successful seminar is the right setting .
As you’re evaluating venue or platform options, consider:
- Your audience: Are they local or global? What kind of problems are they struggling with? Is your seminar meant for external participants or your internal team?
- Technology and equipment: If you’re hosting a webinar, pick a platform that lets you customize your branding, interact with your audience, and simplify attendance.
- Accessibility and inclusivity : Ensure that the venue or platform is accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes providing options for closed captioning or wheelchair access.
- Advanced reporting features: If you’re using a webinar platform, make sure it allows you to measure your event’s performance and attendee engagement with detailed analytics.
2. Create a detailed agenda
A comprehensive agenda provides a clear roadmap for the event which helps your seminar stay on course and runs smoothly.
Here are a few items to include on your agenda:
- List of key topics
- Start and end times
- Interactive elements and sessions
You can also send the agenda to your attendees beforehand so they’re familiar with the schedule and can prepare some questions in advance.
Don’t forget to give your event moderator a time estimate per item to help make sure speakers don’t go over their allotted time.
3. Find your team
Your seminar dream team helps you bring your vision to life, from planning and execution to engaging with the audience.
So choose them carefully and assign them responsibilities based on roles like:
Speaker: The expert who delivers the main content and insights.
Moderator : Guides the flow of the seminar, facilitates discussions, and ensures everything runs smoothly.
Assistant: Provides technical support, manages Q&A sessions, and assists with logistics.
Host or organizer: Oversees the entire event, ensures everything is in order, and communicates with the audience.
You can use Livestorm's roles and permissions to easily establish who can perform functions like starting and ending the event, moderating events, or presenting slides.
4. Promote your seminar
Promote your event through social media and your email list at least two weeks before the date. Segment your email list and advertise the seminar to the ones that will find it most valuable.
With Livestorm, you can even send unlimited customized reminders and follow-up emails to maximize attendance.
Livestorm is also browser-based so participants can just jump into your webinar, no downloads necessary. Finally, it integrates with calendar and scheduler tools like Calendly for a better scheduling process.
5. Keep your audience engaged
During the seminar, keep your participants engaged by:
Conducting live polls: Use your webinar platform’s poll feature to ask questions and include your audience in the conversation.
Running Q&A sessions: Invite your participants to ask questions and dedicate time at the end of the event to answer them. Livestorm’s Q&A tab even lets attendees upvote their favorites so you can prioritize more easily.
Utilizing breakout rooms: Organize breakout rooms and let attendees collaborate and brainstorm in smaller groups.
Collaborating visually: If your meeting platform offers virtual whiteboards, use it for more interactive brainstorming sessions, illustrating ideas, and co-creating with your audience.
6. Follow up and gather feedback
After the event, follow up with both your attendees and no-shows, thank them for their interest, and send them a recording of the webinar .
At Livestorm, we’ve found that 31% of people who register but don’t attend actually watch the recording. So this post-event engagement method is a great way to keep potential customers interested.
Finally track your event analytics to understand your audience, what worked well, and where you can improve.
Whether you’re using Livestorm for internal and corporate communication or external events, you get detailed reports including participation data, replay analytics, and engagement metrics.
Livestorm for your upcoming seminar
The key to interesting and informative seminars is engaging your audience from start to finish.
Participants who aren’t actively involved won’t find much value in your event and they’re less likely to take the action you want them to take afterwards.
That’s why Livestorm is designed specifically to help you keep your audience hooked before, during, and after events.
Here’s how:
Automated emails and pre-built registration pages to make event promotion easier and maximize attendance
Event automation so you can focus you’re not bogged down with manual tasks
Live engagement features like timers, emoji reactions, hand raising, file and media sharing to interact with attendees
Automated recordings and on-demand session links for easy post-event follow up
With Livestorm, your seminars are more than just an event. They're a dynamic, interactive experience that leaves a lasting impact on your audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the seminar .
Seminars serve to educate and engage participants by facilitating interactive discussions, sharing insights, and building meaningful connections within a community.
What is a seminar vs lecture ?
In contrast to lectures, seminars prioritize interactive participation, discussions, and collaboration among participants rather than one-way communication.
What is a seminar class ?
A seminar class in academic settings encourages small-group discussions, critical analysis, and active participation among students, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Engage audiences
Find ideas to promote your events and make them engaging in this free Ebook.
About the author
Brillixa Herdhiana - Growth Manager
Brillixa joined Livestorm as Growth Manager in 2021. Her experience enables her to contribute to business growth through lead generation from ads and organic channels.
Related articles
12 Modern Event Marketing Examples to Inspire Your Strategy
10 min. read
10 Event Marketing Trends for Success
9 min. read
What is Event Marketing? Strategies & Examples
18 min. read
How to Cancel an Event (+ 5 “Event Canceled” Email Templates)
6 min. read
How to Create a Virtual Event Marketing Strategy
11 min. read
The Ultimate Guide to Hosting Virtual Conferences: Steps, Tools & Cost
14 min. read
Keep in touch with Livestorm news and updates
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Are Effective Presentation Skills (and How to Improve Them)
Presentation skills are essential for your personal and professional life. Learn about effective presentations and how to boost your presenting techniques.
![definition of seminar presentation [Featured Image]: The marketing manager, wearing a yellow top, is making a PowerPoint presentation.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1JnKR1F6C7RrqtObyeUr79/acdb15f7a7e894a375012e8d158ada4f/GettyImages-1358219358.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
At least seven out of 10 Americans agree that presentation skills are essential for a successful career [ 1 ]. Although it might be tempting to think that these are skills reserved for people interested in public speaking roles, they're critical in a diverse range of jobs. For example, you might need to brief your supervisor on research results.
Presentation skills are also essential in other scenarios, including working with a team and explaining your thought process, walking clients through project ideas and timelines, and highlighting your strengths and achievements to your manager during performance reviews.
Whatever the scenario, you have very little time to capture your audience’s attention and get your point across when presenting information—about three seconds, according to research [ 2 ]. Effective presentation skills help you get your point across and connect with the people you’re communicating with, which is why nearly every employer requires them.
Understanding what presentation skills are is only half the battle. Honing your presenting techniques is essential for mastering presentations of all kinds and in all settings.
What are presentation skills?
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images.
You'll make presentations at various times in your life. Examples include:
Making speeches at a wedding, conference, or another event
Making a toast at a dinner or event
Explaining projects to a team
Delivering results and findings to management teams
Teaching people specific methods or information
Proposing a vote at community group meetings
Pitching a new idea or business to potential partners or investors
Why are presentation skills important?
Delivering effective presentations is critical in your professional and personal life. You’ll need to hone your presentation skills in various areas, such as when giving a speech, convincing your partner to make a substantial purchase, and talking to friends and family about an important situation.
No matter if you’re using them in a personal or professional setting, these are the skills that make it easier and more effective to convey your ideas, convince or persuade others, and experience success. A few of the benefits that often accompany improving your presentation skills include:
Enriched written and verbal communication skills
Enhanced confidence and self-image
Boosted critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities
Better motivational techniques
Increased leadership skills
Expanded time management, negotiation, and creativity
The better your presenting techniques, the more engaging your presentations will be. You could also have greater opportunities to make positive impacts in business and other areas of your life.
Effective presentation skills
Imagine yourself in the audience at a TED Talk or sitting with your coworkers at a big meeting held by your employer. What would you be looking for in how they deliver their message? What would make you feel engaged?
These are a few questions to ask yourself as you review this list of some of the most effective presentation skills.
Verbal communication
How you use language and deliver messages play essential roles in how your audience will receive your presentation. Speak clearly and confidently, projecting your voice enough to ensure everyone can hear. Think before you speak, pausing when necessary and tailoring the way you talk to resonate with your particular audience.
Body language
Body language combines various critical elements, including posture, gestures, eye contact, expressions, and position in front of the audience. Body language is one of the elements that can instantly transform a presentation that would otherwise be dull into one that's dynamic and interesting.
Voice projection
The ability to project your voice improves your presentation by allowing your audience to hear what you're saying. It also increases your confidence to help settle any lingering nerves while also making your message more engaging. To project your voice, stand comfortably with your shoulders back. Take deep breaths to power your speaking voice and ensure you enunciate every syllable you speak.
How you present yourself plays a role in your body language and ability to project your voice. It also sets the tone for the presentation. Avoid slouching or looking overly tense. Instead, remain open, upright, and adaptable while taking the formality of the occasion into account.
Storytelling
Incorporating storytelling into a presentation is an effective strategy used by many powerful public speakers. It has the power to bring your subject to life and pique the audience’s curiosity. Don’t be afraid to tell a personal story, slowly building up suspense or adding a dramatic moment. And, of course, be sure to end with a positive takeaway to drive your point home.
Active listening
Active listening is a valuable skill all on its own. When you understand and thoughtfully respond to what you hear—whether it's in a conversation or during a presentation—you’ll likely deepen your personal relationships and actively engage audiences during a presentation. As part of your presentation skill set, it helps catch and maintain the audience’s attention, helping them remain focused while minimizing passive response, ensuring the message is delivered correctly, and encouraging a call to action.
Stage presence
During a presentation, projecting confidence can help keep your audience engaged. Stage presence can help you connect with your audience and encourage them to want to watch you. To improve your presence, try amping up your normal demeanor by infusing it with a bit of enthusiasm. Project confidence and keep your information interesting.
Watch your audience as you’re presenting. If you’re holding their attention, it likely means you’re connecting well with them.
Self-awareness
Monitoring your own emotions and reactions will allow you to react well in various situations. It helps you remain personable throughout your presentation and handle feedback well. Self-awareness can help soothe nervousness during presentations, allowing you to perform more effectively.
Writing skills
Writing is a form of presentation. Sharp writing skills can help you master your presentation’s outline to ensure you stay on message and remain clear about your objectives from the beginning until the end. It’s also helpful to have strong writing abilities for creating compelling slides and other visual aids.
Understanding an audience
When you understand your audience's needs and interests, you can design your presentation around them. In turn, you'll deliver maximum value to them and enhance your ability to make your message easy to understand.
Learn more about presentation skills from industry experts at SAP:
How to improve presentation skills
There’s an art to public speaking. Just like any other type of art, this is one that requires practice. Improving your presentation skills will help reduce miscommunications, enhance your time management capabilities, and boost your leadership skills. Here are some ways you can improve these skills:
Work on self-confidence.
When you’re confident, you naturally speak more clearly and with more authority. Taking the time to prepare your presentation with a strong opening and compelling visual aids can help you feel more confident. Other ways to improve your self-confidence include practicing positive self-talk, surrounding yourself with positive people, and avoiding comparing yourself (or your presentation) to others.
Develop strategies for overcoming fear.
Many people are nervous or fearful before giving a presentation. A bad memory of a past performance or insufficient self-confidence can contribute to fear and anxiety. Having a few go-to strategies like deep breathing, practicing your presentation, and grounding can help you transform that fear into extra energy to put into your stage presence.
Learn grounding techniques.
Grounding is any type of technique that helps you steer your focus away from distressing thoughts and keeps you connected with your present self. To ground yourself, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and imagine you’re a large, mature tree with roots extending deep into the earth—like the tree, you can become unshakable.
Learn how to use presentation tools.
Visual aids and other technical support can transform an otherwise good presentation into a wow-worthy one. A few popular presentation tools include:
Canva: Provides easy-to-design templates you can customize
Powtoon: Animation software that makes video creation fast and easy
PowerPoint: Microsoft's iconic program popular for dynamic marketing and sales presentations
Practice breathing techniques.
Breathing techniques can help quell anxiety, making it easier to shake off pre-presentation jitters and nerves. It also helps relax your muscles and get more oxygen to your brain. For some pre-presentation calmness, you can take deep breaths, slowly inhaling through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
While presenting, breathe in through your mouth with the back of your tongue relaxed so your audience doesn't hear a gasping sound. Speak on your exhalation, maintaining a smooth voice.
Gain experience.
The more you practice, the better you’ll become. The more you doanything, the more comfortable you’ll feel engaging in that activity. Presentations are no different. Repeatedly practicing your own presentation also offers the opportunity to get feedback from other people and tweak your style and content as needed.
Tips to help you ace your presentation
Your presentation isn’t about you; it’s about the material you’re presenting. Sometimes, reminding yourself of this ahead of taking center stage can help take you out of your head, allowing you to connect effectively with your audience. The following are some of the many actions you can take on the day of your presentation.
Arrive early.
Since you may have a bit of presentation-related anxiety, it’s important to avoid adding travel stress. Give yourself an abundance of time to arrive at your destination, and take into account heavy traffic and other unforeseen events. By arriving early, you also give yourself time to meet with any on-site technicians, test your equipment, and connect with people ahead of the presentation.
Become familiar with the layout of the room.
Arriving early also gives you time to assess the room and figure out where you want to stand. Experiment with the acoustics to determine how loudly you need to project your voice, and test your equipment to make sure everything connects and appears properly with the available setup. This is an excellent opportunity to work out any last-minute concerns and move around to familiarize yourself with the setting for improved stage presence.
Listen to presenters ahead of you.
When you watch others present, you'll get a feel for the room's acoustics and lighting. You can also listen for any data that’s relevant to your presentation and revisit it during your presentation—this can make the presentation more interactive and engaging.
Use note cards.
Writing yourself a script could provide you with more comfort. To prevent sounding too robotic or disengaged, only include talking points in your note cards in case you get off track. Using note cards can help keep your presentation organized while sounding more authentic to your audience.
Learn to deliver clear and confident presentations with Dynamic Public Speaking from the University of Washington. Build confidence, develop new delivery techniques, and practice strategies for crafting compelling presentations for different purposes, occasions, and audiences.
Article sources
Forbes. “ New Survey: 70% Say Presentation Skills are Critical for Career Success , https://www.forbes.com/sites/carminegallo/2014/09/25/new-survey-70-percent-say-presentation-skills-critical-for-career-success/?sh=619f3ff78890.” Accessed December 7, 2022.
Beautiful.ai. “ 15 Presentation and Public Speaking Stats You Need to Know , https://www.beautiful.ai/blog/15-presentation-and-public-speaking-stats-you-need-to-know. Accessed December 7, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
What is a Presentation?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The formal presentation of information is divided into two broad categories: Presentation Skills and Personal Presentation .
These two aspects are interwoven and can be described as the preparation, presentation and practice of verbal and non-verbal communication.
This article describes what a presentation is and defines some of the key terms associated with presentation skills.
Many people feel terrified when asked to make their first public talk. Some of these initial fears can be reduced by good preparation that also lays the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
A Presentation Is...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team.
A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other ‘speaking engagements’ such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
To be effective, step-by-step preparation and the method and means of presenting the information should be carefully considered.
A presentation requires you to get a message across to the listeners and will often contain a ' persuasive ' element. It may, for example, be a talk about the positive work of your organisation, what you could offer an employer, or why you should receive additional funding for a project.

The Key Elements of a Presentation
Making a presentation is a way of communicating your thoughts and ideas to an audience and many of our articles on communication are also relevant here, see: What is Communication? for more.
Consider the following key components of a presentation:
Ask yourself the following questions to develop a full understanding of the context of the presentation.
When and where will you deliver your presentation?
There is a world of difference between a small room with natural light and an informal setting, and a huge lecture room, lit with stage lights. The two require quite different presentations, and different techniques.
Will it be in a setting you are familiar with, or somewhere new?
If somewhere new, it would be worth trying to visit it in advance, or at least arriving early, to familiarise yourself with the room.
Will the presentation be within a formal or less formal setting?
A work setting will, more or less by definition, be more formal, but there are also various degrees of formality within that.
Will the presentation be to a small group or a large crowd?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a new audience, you will have to build rapport quickly and effectively, to get them on your side.
What equipment and technology will be available to you, and what will you be expected to use?
In particular, you will need to ask about microphones and whether you will be expected to stand in one place, or move around.
What is the audience expecting to learn from you and your presentation?
Check how you will be ‘billed’ to give you clues as to what information needs to be included in your presentation.
All these aspects will change the presentation. For more on this, see our page on Deciding the Presentation Method .
The role of the presenter is to communicate with the audience and control the presentation.
Remember, though, that this may also include handing over the control to your audience, especially if you want some kind of interaction.
You may wish to have a look at our page on Facilitation Skills for more.
The audience receives the presenter’s message(s).
However, this reception will be filtered through and affected by such things as the listener’s own experience, knowledge and personal sense of values.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication to learn why communication can fail.
The message or messages are delivered by the presenter to the audience.
The message is delivered not just by the spoken word ( verbal communication ) but can be augmented by techniques such as voice projection, body language, gestures, eye contact ( non-verbal communication ), and visual aids.
The message will also be affected by the audience’s expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on one particular topic, and you choose to speak on another, the audience is unlikely to take your message on board even if you present very well . They will judge your presentation a failure, because you have not met their expectations.
The audience’s reaction and therefore the success of the presentation will largely depend upon whether you, as presenter, effectively communicated your message, and whether it met their expectations.
As a presenter, you don’t control the audience’s expectations. What you can do is find out what they have been told about you by the conference organisers, and what they are expecting to hear. Only if you know that can you be confident of delivering something that will meet expectations.
See our page: Effective Speaking for more information.
How will the presentation be delivered?
Presentations are usually delivered direct to an audience. However, there may be occasions where they are delivered from a distance over the Internet using video conferencing systems, such as Skype.
It is also important to remember that if your talk is recorded and posted on the internet, then people may be able to access it for several years. This will mean that your contemporaneous references should be kept to a minimum.
Impediments
Many factors can influence the effectiveness of how your message is communicated to the audience.
For example background noise or other distractions, an overly warm or cool room, or the time of day and state of audience alertness can all influence your audience’s level of concentration.
As presenter, you have to be prepared to cope with any such problems and try to keep your audience focussed on your message.
Our page: Barriers to Communication explains these factors in more depth.
Continue to read through our Presentation Skills articles for an overview of how to prepare and structure a presentation, and how to manage notes and/or illustrations at any speaking event.
Continue to: Preparing for a Presentation Deciding the Presentation Method
See also: Writing Your Presentation | Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves | Dealing with Questions Learn Better Presentation Skills with TED Talks
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER 18 Guidelines to qualitative academic seminar presentation
The primary objective of seminar presentation is to enhance presentation skills when persuading, educating, or informing an audience. Specifically, it provides a focus on the fundamental aspects of a quality academic, professional and business communications including structure, preparation and strategy for delivery, using visual aids, and handling question and answer sessions. The presenter/student practices by preparing and delivering an ideal real-life academic/business presentation. Strict adherence to the instructions outlined allows the presenter to evaluate his/her progress and alter any distracting behaviours before and during presentation. It also enables the participant to learn by doing. The aim of this paper is to introduce students to simple principles on how to plan, writs and present their findings as technical conference papers, then act as the mini-conference programme committee members in reviewing each other's submissions. Finally, in addition to the model itself, description of some variations in instantiation and an assessment of the benefits of this general approach and recommendation for adoption by faculties and educators are proffered. Introduction Rarely are the three pillars of academia-research, teaching and service-addressed together, within one intellectually cohesive context in the graduate curriculum. Such a context is important for exposing students to the interrelationships among these facets. Oftentimes, people are confused what a seminar, workshop or conference means. They are sometimes considered to mean the same thing. However, workshop is a brief intensive educational programme for a relatively small group of people that focuses on techniques and skills in a particular field. Seminar on the other hand is a meeting of a group of advanced students studying under a professor/officer with each doing original research and all exchanging results of their findings through reports and discussions. A conference is a meeting of two or more persons/bodies organized for the benefit of discussing matters of common concern, which usually involves formal interchange of views.
Related Papers
JSCI Systemics, Cybernetics, and Informatics
The purposes of this article is to show the differences between traditional and conversational conferences and to suggest that synergic effects might be produced when both models are adequately related in simultaneous events so cybernetic loops might be produced. The effectiveness of both approaches could increase if they are adequately related or oriented to the generation of processes that might integrate both models in the context of the same event, or chain of events. The content of this article is based on a combination of experience, reflection, and action, using the methodologies of Action-Research/reflection, Action-Learning, and Action-Design. After ten years trying to relate these two approaches we learned that they are opposite, but not contradictory with each other. They are, or can be designed as polar opposites which would complement (and even require) each other in a synergic whole, with potential emergent properties as effective learning, interdisciplinary communicat...
Constructivist Foundations
Christoph Brunner
This article is an open peer commentary to Johan Verbeke's target article "Designing Academic Conferences as a Learning Environment: How to Stimulate Active Learning at Academic Conferences?" (http://www.univie.ac.at/constructivism/journal/11/1/098.verbeke). It targets the field of artistic and design research and its attempt to invent new experimental conference formats. After critically examining the conception of "knowledge production" in these discourses, the commentary fosters the need to take into account sensuous and more-than-human elements shaping such emergent conference formats. The comment closes with a constructivist and speculative proposition for the future planning of creative practice events.
Computer Human Interaction
Nico Macdonald
Conferences are still valuable for established attendees and potential new audiences, and the overall audience for events can be increased, helping alleviate competition between professional organisations.In addition professional organisations need to avoid conferences being run-of-the-mill, and taking their audience for granted. They need to widen their primary and secondary audiences by helping potential attendees and presenters find out about events,
Ivan Dunđer
Przegląd Badań Edukacyjnych
Helena Ostrowicka
Ben Sweeting , Michael Hohl
Context: The design of academic conferences, in which settings ideas are shared and created, is, we suggest, of more than passing interest in constructivism, where epistemology is considered in terms of knowing rather than knowledge. Problem: The passivity and predominantly one-way structure of the typical paper presentation format of academic conferences has a number of serious limitations from a constructivist perspective. These limits are both practical and epistemological. While alternative formats abound, there is nevertheless increasing pressure reinforcing this format due to delegates’ funding typically being linked to reading a paper. Method: In this special issue, authors reflect on conferences that they have organised and participated in that have used alternative formats, such as conversational structures or other constructivist inspired approaches, in whole or in part. We review and contextualize their contributions, understanding them in terms of their connections to constructivism and to each other. Results: While this issue is of relevance across disciplinary boundaries, contributions focus on two fields: that of cybernetics/systems, and that of design. We identify the way that conference organization is of particular importance to these fields, being in self-reflexive relationship to them: the environment of a design conference is something that we design; while a conference regarding systems or cybernetics is itself an instance of the sorts of process with which these fields are concerned. Implications: Building on this self-reflexivity and, also, the close connection of design and cybernetics/systems to constructivism, we suggest that conference organization is an area in which constructivism may itself be understood in terms of practice (and so knowing) rather than theory (and so knowledge. This in turn helps connect ideas in constructivism with pragmatic fields, such as knowledge management, and recent discussions in this journal regarding second-order science. Constructivist content: As a setting for the creation of new ideas, the design of conferences is of importance where we understand epistemology in constructivist terms as a process of knowing. Moreover, the particular fields drawn on - design and cybernetics/systems - have close connections to constructivism, as can be seen, for instance, in the work of Ranulph Glanville, on which we draw here.
Chiara Belluzzi
To date, little research has been conducted on conference presentation (CP) introductions with the aim of analysing their moves, especially as far as non academic CP's are concerned. In fact, to the best of my knowledge, no study has ever focused on the non-academic context - apart from numerous public speaking handbooks, which, however, do not apply any scientific method of analysis. Therefore this study sets out to investigate non-academic CP introductions in order to determine whether they coincide with the genre of the academic CP introduction. Such a study will hopefully prove valuable not only in the field of genre analysis, but also in the field of interpreting studies. Since it is possible to determine a move model from the structure of every genre, I will set out to do this for the non-academic CP introduction as well, thus providing the interpreter with a series of speech acts a speaker can reasonably be expected to carry out. Chapter 2 of this dissertation begins with an overview of the literature on the academic CP as a genre from many different perspectives. Then the focus shifts to the introductory section of different academic written and oral genres, in particular to those studies which lead to the definition of their moves and which, therefore, will be useful in the analysis of the structure of non-academic CP introductions. Chapter 3 focuses on the non-academic CP. First, the concept of discourse community is explored in terms of both academic and non-academic discourse, with the aim of achieving a better understanding of the differences between the two as well as of the latter alone. Then a definition of the non-academic CP introduction as a genre will be developed on the basis of Swales’ (1990) criteria and Hasan’s (Halliday and Hasan 1989) notion of ‘context’, in order to determine whether academic and non-academic CP introductions belong to the same genre or not. After the theoretical framework set in the first part of the dissertation, five case studies will be analysed in Chapter 4. Five non-academic presentations were selected and their introductions were transcribed. To these I have applied Rowley-Jolivet and Carter-Thomas’ (2005) move model of academic CP introductions in order to determine whether their model can be applied to non-academic CP introductions as well. The data retrieved is analysed to let new moves emerge, too, so that a move model for non-academic CP introductions can be identified. The usefulness of this model for further and more in-depth studies is mentioned at the end of the chapter In the last chapter a suggestion is made about the application of move models to 11 interpreting studies, in particular as far as simultaneous interpretation is concerned. To be brief, since move models describe the structure shared by the texts of a given genre, they could be used by interpreters to predict the structure of the text they are going to interpret.
European Political Science
Andrew Mycock
Olga Vetrova
Abstract. Students ’ conferences make up the environment where specific competences are combined with generic competences. Our goal is to estimate the potential of the professionally-oriented academic communication in a foreign language in the students ’ conference environment and find out the ways students’ conferences could contribute to the professional competencies formation. Investigated is the polytechnical tertiary school. Integrative in its essence, the project is aimed at fostering the efficiency of the university education, creativity development, ideas generation by specialists-to-be and innovations dissemination, – all of which is supposed to upgrade the standards of tertiary education and raise the quality of vocational training. This goes in accord with the Bologna process and European, and world-wide effort to enhance flexibility and professionalism on the labour market.
RELATED PAPERS
Eduardo Omar Sosa
Teaching & Learning Inquiry
Margaret Wegener
Oddvar Royset
American Antiquity
Presented at the seminar on “Training Workshop on Raising Awareness Regarding Insurance” organized by “Bangladesh Insurance Sector Development Project (BISDP) held on 20 June 2019, in the Conference Room of Hotel Shaikat, Station Road, Chottogram, Bangladesh
Dr. Nazrul Islam
Cadernos de Saúde Pública
João Luiz Pena
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases
lizzet villalobos
sutri handayani
Daniel LONDOÑO
Dicle Üniversitesi Ziya Gökalp Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi
Medine Baran
Anales Del Seminario De Historia De La Filosofia
abraham fernandez
Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography
Mohammed Mosad
Topoi (Rio de Janeiro)
Roger Chartier
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine
The Science of the total environment
American Journal of Kidney Diseases
Lucile Mercadal
Contexto: revista anual de estudios literarios
Norelsy Lima
Etudes Photographiques
Didier Aubert
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Yulia Frank
oswaldo cruz
Nelsi Yunisa
Enzyme Research
Amelia .farres
Applied Sciences
Davor Ljubas
Stefan Bittner
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Customizable, intuitive, and scalable registration forms to sign up attendees with ease.
End-to-end abstract management platform; submission, review, evaluation, program and proceeding export.
Build branded & stunning event websites to engage your attendees.
Personalize your event awarness to expand your reach and drive registrations.
Host interactive virtual events with networking, streaming, engagement tools, and more.
Take a peek at our case studies and other client successes.
Receive guidance, or learn more about troubleshooting.
- Event Registration
- Abstract Management
- Event Marketing
- Virtual Events
- Case Studies
- Knowledge Center
How to Plan, Organize, and Manage a Successful Seminar: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Seminars are integral to academic life, providing a platform for knowledge sharing, networking, and professional growth. Whether you're a student, academic, or industry professional, attending a seminar can be a rewarding experience. In this comprehensive guide, we will not only walk you through the steps of planning and executing a successful seminar but also explore the core elements of a seminar, how attendees participate, and the techniques used to foster an engaging learning environment.
What is a Seminar?
A seminar is an interactive event where experts, researchers, or industry professionals gather to present and discuss their ideas, research findings, and experiences within a specific subject area. It typically involves presentations, panel discussions, workshops, and opportunities for networking and collaboration. Seminars can focus on various topics, from academic research to industry trends, and are usually organized around a central theme.
Participation and Interaction in Seminars
Unlike traditional lectures, seminars encourage active participation and interaction among attendees. Participants are encouraged to engage in discussions, ask questions, and share their thoughts. This two-way exchange of ideas creates a dynamic learning environment and enhances the overall learning experience.
Techniques Used in Seminars
To foster an engaging learning environment, various techniques are used in seminars. Some common techniques include:
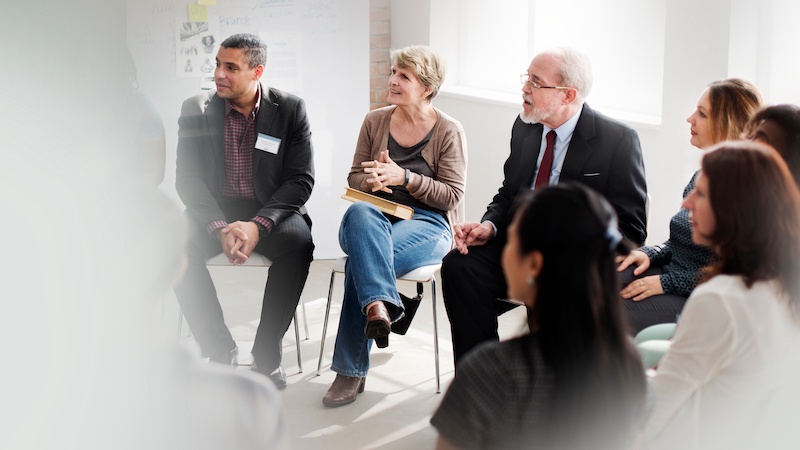

Panel Discussions
Panels are an essential aspect of seminars, offering a platform for in-depth discussions and diverse perspectives on specific topics. Typically, a panel consists of a group of experts or professionals in the field, each providing insights and analysis. The moderator plays a crucial role in guiding the conversation and ensuring that the discussion remains focused and engaging. Panels are highly interactive, allowing audience members to pose questions and share their views, promoting a dynamic exchange of ideas. To make panels more effective, it's essential to curate a diverse set of panelists with contrasting viewpoints, enabling attendees to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Panels are especially valuable for shedding light on complex issues, encouraging critical thinking, and fostering meaningful dialogues among participants. As an attendee, participating in panel discussions provides an excellent opportunity to engage directly with industry experts, expand your knowledge, and network with like-minded individuals. For organizers, creating well-balanced and engaging panels can significantly enhance the overall seminar experience, leaving a lasting impact on participants.
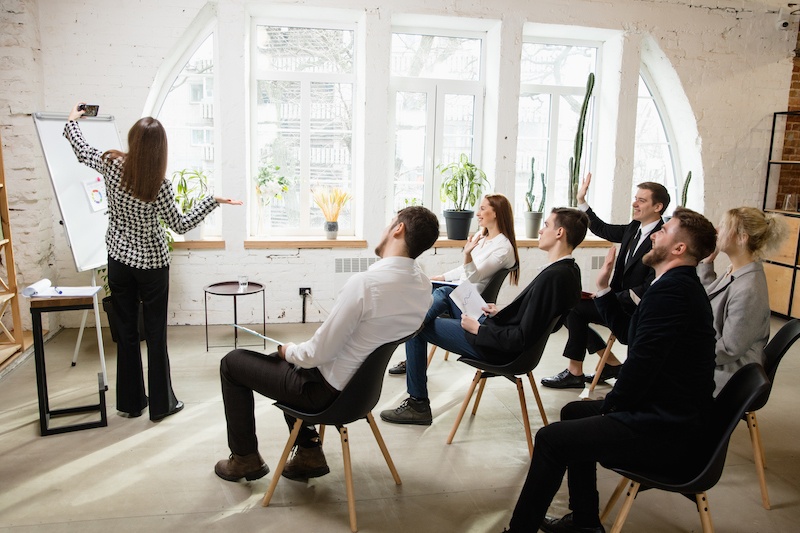

Workshops are an integral part of seminar organization, offering a more hands-on and interactive learning experience. Unlike traditional lectures, workshops focus on active participation and skill-building. They are typically led by experienced facilitators or subject matter experts who guide attendees through practical exercises and activities. Workshops provide a unique opportunity for participants to delve into specific topics, hone their skills, and apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. These sessions can range from small group discussions to immersive training sessions, depending on the seminar's objectives. One of the key benefits of workshops is the opportunity for attendees to engage in problem-solving, collaborate with peers, and receive immediate feedback from facilitators. As an organizer, ensuring that workshops are well-structured, relevant, and align with the overall theme of the seminar is crucial. By offering diverse and skill-enhancing workshops, seminar organizers can create a dynamic and enriched learning environment, leaving attendees with practical takeaways and a memorable learning experience.

Group Activities
Group activities are another essential component of a successful seminar, fostering teamwork, collaboration, and networking among participants. These activities aim to break the ice, encourage interaction, and promote a sense of camaraderie among attendees. Depending on the seminar's nature and objectives, group activities can vary widely, from icebreaker games and team-building exercises to group discussions and brainstorming sessions. The key is to create a supportive and inclusive environment where participants feel comfortable sharing their ideas and engaging with others. Group activities not only enhance the overall learning experience but also provide valuable opportunities for attendees to expand their professional networks. As an organizer, incorporating well-designed group activities can add a sense of excitement and fun to the seminar, making it more enjoyable and memorable for everyone involved. By carefully selecting activities that align with the seminar's goals and themes, organizers can ensure that participants leave the event with new connections, fresh perspectives, and a renewed enthusiasm for their academic or professional pursuits.

Q&A Sessions
Q&A sessions are a fundamental element of seminars that allow participants to engage in direct and interactive discussions with speakers or panelists. These sessions provide a valuable opportunity for attendees to seek clarification, share their insights, and delve deeper into the topics presented during the seminar. Q&A sessions are typically scheduled after each presentation or panel discussion, allowing the audience to ask questions related to the content or express their viewpoints.
To make Q&A sessions effective and inclusive, it's crucial for organizers to set clear guidelines and encourage active participation from the audience. Moderators play a vital role in managing the session, ensuring that questions are relevant and respectful, and giving everyone a chance to contribute. Additionally, utilizing technology such as audience response systems or online platforms can facilitate smooth communication and help manage the flow of questions.
Q&A sessions offer an opportunity for speakers and panelists to showcase their expertise, engage with the audience on a personal level, and address any lingering doubts or concerns. From the attendees' perspective, these sessions provide a chance to gain deeper insights, explore different perspectives, and enrich their understanding of the seminar's subject matter.
To enhance the success of Q&A sessions, organizers can encourage participants to submit questions in advance or use real-time polling to identify the most popular topics for discussion. By fostering a supportive and inclusive atmosphere, Q&A sessions can become a dynamic part of the seminar, sparking thought-provoking discussions and creating lasting impressions for all involved.

Interactive Presentations
Interactive presentations are a dynamic and engaging approach to delivering seminar content. Unlike traditional one-way lectures, interactive presentations encourage active participation from the audience, making the learning experience more immersive and memorable. Various techniques can be incorporated into interactive presentations to stimulate audience involvement and foster meaningful interactions.
One popular method is the use of multimedia elements such as videos, images, and audio clips to enhance the presentation's visual appeal and reinforce key points. This approach captivates attendees' attention and ensures a multi-sensory experience, making the content more accessible and easier to comprehend.
Another effective technique is incorporating audience polling or live quizzes during the presentation. This not only keeps participants engaged but also provides instant feedback to presenters, enabling them to tailor the discussion to the audience's interests and understanding level.
Gamification is another innovative approach to creating interactive presentations. By introducing gamified elements like quizzes, challenges, or group activities, the seminar becomes not only educational but also fun and enjoyable. This approach encourages healthy competition among attendees and motivates them to actively participate.
Additionally, interactive presentations can involve breakout sessions where attendees split into smaller groups to discuss specific topics or case studies. This allows for in-depth exploration of ideas and encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing among participants.
The benefits of interactive presentations are manifold. They foster a sense of inclusivity, as participants feel their opinions are valued and heard. The dynamic nature of these presentations helps maintain audience engagement throughout the seminar, leading to better knowledge retention and a more impactful learning experience.
Planning Your Seminar
✔︎ define your objectives.
Clearly outline the goals and objectives of your seminar. Consider the target audience, theme, and desired outcomes.
✔︎ Choose the Right Venue
Select a venue that can accommodate the number of attendees and offers the necessary facilities, such as audio-visual equipment and Wi-Fi.
✔︎ Invite Engaging Speakers
Attract knowledgeable and influential speakers who can add value to your seminar and spark meaningful discussions.
✔︎ Create an Engaging Agenda
Craft a well-balanced agenda with diverse sessions that cater to the interests of your participants.
✔︎ Implement Effective Marketing
Utilize digital platforms and strategic partnerships to promote your seminar and attract the right audience.
Managing Your Seminar
✔︎ facilitate networking.
Encourage networking opportunities during breaks and networking events to foster meaningful connections among participants.
✔︎ Ensure Smooth Logistics
Thoroughly plan event logistics, including accommodation options, catering, and onsite management.
✔︎ Foster Interaction
Encourage active participation through Q&A sessions, interactive presentations, and group activities.
✔︎ Gather Feedback
Request feedback from participants to evaluate the success of your seminar and identify areas for improvement.
A well-organized seminar provides a platform for participants to engage, learn, and collaborate within their field of interest. By understanding the core elements of a seminar, implementing interactive techniques, and facilitating meaningful networking, you can create a successful and impactful event. Whether you're a seminar organizer or attendee, embracing the spirit of knowledge sharing and collaboration will ensure a rewarding seminar experience for all involved. So, start planning your next seminar today and unlock its potential for growth and innovation in your field.
If you are interested in learning more about the academic event types you can also check our blog post article " Unraveling the Academic Event Landscape: Congresses vs. Conferences - What Sets Them Apart? "
Book an online demo with us.!
Are you looking to streamline your seminar planning and management process? Discover the power of MeetingHand and how it can transform your seminar organization. BOOK A DEMO NOW and join us for an exclusive online product tour. See firsthand how MeetingHand's innovative features and user-friendly interface can make your seminar preparation a breeze. Don't miss this opportunity to experience the future of seminar management with us!
If you enjoyed reading this article, please do not forget to share it with your friends.!
Unlocking the Basics: What is a Senior Seminar?
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on senior seminars! If you’re wondering what a senior seminar is, you’ve come to the right place. Senior seminars are courses designed for advanced students, typically in their final year of undergraduate study, that provide an opportunity to delve deeply into a particular subject matter. These courses are often interdisciplinary, meaning they draw on multiple fields of study to explore a topic in depth.
Senior seminars are a unique opportunity for students to engage in independent research, critical thinking, and collaborative learning, all while under the guidance of a skilled instructor. While these courses differ from traditional lecture-based courses, they are an essential component of higher education, providing students with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in their future careers or further education.
- Senior seminars are courses designed for advanced students in their final year of undergraduate study.
- They provide an opportunity to delve deeply into a particular subject matter through interdisciplinary exploration.
- Senior seminars foster independent research, critical thinking, and collaborative learning.
- These courses are an essential component of higher education, preparing students for their future careers or further education.
The Importance of Senior Seminar
Senior seminars are not just another course requirement to tick off the list. Instead, they hold immense importance in the academic journey of students. These seminars contribute significantly to students’ intellectual growth, personal development, and preparation for the real world.
Intellectual Growth: By participating in senior seminars, students are exposed to in-depth and challenging academic material. They get the opportunity to engage in discussions with peers and professors, allowing them to develop their critical thinking skills and broaden their understanding of complex topics.
Personal Development: Senior seminars require students to complete rigorous research and writing projects, allowing them to hone their analytical and communication skills. Moreover, these seminars encourage collaboration, enhancing teamwork and leadership capabilities.
Preparation for the Real World: Senior seminars prepare students for their future careers or further education by fostering independence, research skills, and a deeper understanding of a specific subject area. The presentation component of senior seminars is particularly crucial in preparing students for the professional world, where effective communication skills are highly valued.
“Senior seminars provide a unique and valuable opportunity for students to engage with challenging material, hone their skills, and prepare for their future careers or further education.”
Unveiling the Benefits of Senior Seminar
Participating in a senior seminar offers a plethora of benefits that extend beyond the classroom. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of taking a senior seminar course :
- Enhanced Critical Thinking Skills: Senior seminars provide an opportunity for students to think critically and creatively about complex issues. By engaging with challenging materials, participants can develop their analytical abilities and gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Strengthened Research Skills: Senior seminars require students to conduct in-depth research and analysis on a specific topic. This process helps to hone research, writing, and presentation skills that can be applied in various academic and professional settings.
- Cultivated Collaboration and Communication: Senior seminars often involve group work and peer-to-peer discussions, providing an opportunity for students to develop their collaboration and communication skills. Through effective communication, students can learn from one another and gain diverse perspectives on complex issues.
- Increased Confidence: Presenting research findings and participating in class discussions can be daunting, but senior seminars provide a supportive environment for students to build confidence in their abilities. This newfound confidence can be applied in future academic and professional endeavors.
- Preparation for Future Career: Senior seminars aim to prepare students for their future careers by providing hands-on experience in research, writing, and presentation skills. These skills are highly valued by employers and are transferable to various fields.
Overall, participating in a senior seminar can lead to personal and intellectual growth, improved academic performance, and enhanced career prospects. Take advantage of the unique opportunities offered by a senior seminar course and reap the benefits!
Senior seminars are often designed to provide students with a capstone experience in their academic journey. As such, these courses typically involve a high level of intellectual rigor and independence.
While the specific curriculum and requirements may vary depending on the institution and program, there are a few commonalities that students can expect.
Overall, senior seminars are designed to challenge students to engage in deeper, more critical thinking and analysis. They provide a unique opportunity for students to pursue a topic of interest in depth and apply their skills to a real-world problem or challenge.
Whether you are pursuing a degree in the humanities, social sciences, or natural sciences, a senior seminar can provide you with an enriching and rewarding academic experience.
Exploring Senior Seminar Topics
Senior seminars cover a vast range of topics, depending on the institution and program. These courses are designed to provide students with a platform to delve deeper into areas of study that they are passionate about. From interdisciplinary subjects to specialized fields of study, senior seminar topics can range from the humanities to the sciences.
Some senior seminar topics may include:
- Globalization and Its Impact
- Environmental Policy and Politics
- Women’s Studies
- Healthcare Management
- Sustainable Agriculture
- Creative Writing Workshop
- Investigative Journalism
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Senior seminars provide an opportunity for students to explore their interests and passions while simultaneously developing critical thinking and research skills. These courses challenge students to look beyond the surface of a topic and consider the underlying complexities and nuances that shape it.
“Senior seminars are a great way to explore topics that you’re interested in, but may not necessarily have the chance to study in-depth elsewhere. It’s not just about learning, but about developing skills that will benefit you in the future.” – John Smith, recent graduate
Senior seminar topics can be interdisciplinary, combining different subjects to provide a unique perspective on a particular issue. This approach encourages students to develop a broader understanding of a topic and cultivate skills in multiple areas.
The Benefits of Exploring Senior Seminar Topics
Exploring senior seminar topics provides students with numerous benefits, both academically and professionally. These courses give students the opportunity to:
- Develop a deeper understanding of their field of study
- Enhance critical thinking and research skills
- Build a strong foundation for future coursework
- Collaborate with peers and develop teamwork skills
- Sharpen communication skills through class discussions and presentations
- Strengthen their resumes and graduate school applications
Senior seminars are a unique and valuable opportunity for students to delve deeper into their areas of interest and develop skills that will benefit them in their future academic and professional endeavors.
The Senior Seminar Presentation
After completing the coursework and research for a senior seminar, students must present their findings in the form of a Senior Seminar Presentation . This culminating event is the highlight of the seminar, allowing students to showcase their knowledge and research skills.
The purpose of the presentation is to demonstrate the student’s ability to analyze and synthesize information, draw conclusions, and communicate effectively. Students present their work to an audience of their peers, professors, and other members of the academic community.
The Senior Seminar Presentation typically takes the form of an oral presentation, but may also include visual aids such as PowerPoint slides or posters. The format can vary depending on the professor’s requirements, but generally, presentations should be clear, concise, and organized.
During the presentation, students are expected to demonstrate their understanding of the course material and their ability to apply critical thinking and research skills. They must be able to answer questions from the audience and defend their ideas and conclusions.
The Senior Seminar Presentation is an excellent opportunity for students to develop their public speaking and presentation skills. It is an essential component of the senior seminar and is an excellent way to show off the benefits of the student’s research efforts.
Understanding the Senior Seminar Course
Senior seminar courses offer a unique and engaging educational experience for students. These courses typically consist of a small group of students and a faculty member, who work together to explore a particular topic in-depth. The seminar format allows for lively discussions and interactive learning, which fosters critical thinking and intellectual growth.
During a senior seminar course , students are expected to participate actively in class discussions, complete reading assignments, and conduct independent research on the seminar topic. Research projects may include writing a paper, creating a presentation, or developing a group project. Collaboration and communication skills are essential in the seminar format and are highly valued in the academic and professional world.
Since senior seminar courses are designed for upper-level students, they are often more challenging than other courses. However, they also offer unique rewards, such as opportunities for independent research and academic exploration. Students who excel in senior seminar courses often emerge from them with a deeper understanding of the seminar topic, improved research skills, and enhanced critical thinking abilities.
Senior seminar courses vary by institution and program, but they typically involve a significant amount of independent work and research. They may be required for certain majors or programs, or they may be optional, allowing students to pursue their interests outside of their primary field of study. Regardless of the specifics, senior seminar courses provide a dynamic, challenging, and rewarding academic experience for students.
Overall, senior seminar courses provide a unique opportunity for students to engage in independent research, explore a particular topic in-depth, and develop essential collaboration and communication skills. If you are considering enrolling in a senior seminar, be prepared to work hard, participate actively, and push yourself intellectually. The rewards of this challenging and engaging academic experience can be significant and long-lasting.
The Purpose of Senior Seminars
Senior seminars serve a critical role in higher education by providing students with a unique opportunity to engage in independent research and critical thinking. The purpose of senior seminars is to prepare students for any future academic or professional pursuits by fostering their intellectual growth, personal development, and research skills.
Senior seminars provide students with an opportunity to explore a specific subject area in-depth, developing a deeper understanding of the field. Through independent research projects, students hone their research skills and learn to think critically about complex problems. The structure of senior seminars encourages students to work independently and collaboratively, fostering the development of leadership and communication skills.
The primary purpose of senior seminars is to expose students to a specific area of study and to provide an opportunity for them to demonstrate mastery of that subject through research and presentation. By the end of the course, students are expected to have developed a strong foundation in their chosen field, making them better equipped for further education or professional pursuits.
Overall, the purpose of senior seminars is to provide students with a comprehensive educational experience that prepares them for their future endeavors. By combining independent research, critical thinking, and collaboration, senior seminars imbue students with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in any field.
In conclusion, senior seminars play a vital role in the academic journey of students. From providing an opportunity for intellectual growth to fostering personal development and preparation for the real world, senior seminars offer a range of benefits. By honing critical thinking skills, fostering collaboration and communication, and exploring a diverse range of topics, students can enhance their academic experience through participation in senior seminars.
Understanding the curriculum and requirements of senior seminars is crucial for ensuring success in these courses. From class discussions and readings to research projects and group work, students can gain a deeper understanding of a specific subject area through their participation in senior seminar courses.
The culminating event of a senior seminar – the presentation – serves as a chance for students to showcase their knowledge and research in a professional manner. By understanding the purpose, format, and expectations surrounding senior seminar presentations, students can effectively communicate their findings and insights.
Overall, senior seminars have a specific purpose in fostering independent thinking, research skills, and a deeper understanding of a subject area. For students, enrolling in a senior seminar course can have a significant impact on their future careers or further education.
Enhancing Your Academic Journey with Senior Seminars
Whether you’re a student considering enrolling in a senior seminar or an educator seeking to enhance your understanding, this comprehensive guide has equipped you with valuable insights into the world of senior seminars. From understanding what a senior seminar is to exploring its importance, benefits, curriculum, and requirements, this guide has provided a detailed and informative overview.
By leveraging the power of senior seminars, students can enhance their academic experience and prepare themselves for future success. So why wait? Enroll in a senior seminar course today and unlock your full potential!
What is a senior seminar?
A senior seminar is a specific course or program designed for senior-level students in higher education. It serves as a culmination of their academic journey, providing an opportunity to explore in-depth topics, conduct research, and present findings.
Why are senior seminars important?
Senior seminars hold great significance in the academic journey as they contribute to students’ intellectual growth, personal development, and preparation for the real world. These seminars encourage critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills, preparing students for their future careers or further education.
What are the benefits of participating in a senior seminar?
Participating in a senior seminar offers a range of benefits. It enhances critical thinking skills, fosters collaboration and communication, provides opportunities for research and independent study, and promotes a deeper understanding of a specific subject area. Senior seminars also allow students to develop presentation and public speaking skills.
What is the typical curriculum and requirements for a senior seminar?
The curriculum and requirements of a senior seminar can vary based on the institution and program. However, typically, senior seminars focus on specific topics or themes and require students to engage in extensive research, critical analysis, and presentations. They may also involve participation in class discussions, readings, and group work.
What topics are covered in senior seminars?
Senior seminar topics can vary widely based on the institution and program. They can include interdisciplinary subjects, specialized areas of study, or specific research projects. The range of topics offered in senior seminars allows students to explore their interests and engage in advanced study within their chosen field.
What is involved in a senior seminar presentation?
The senior seminar presentation is the culminating event of the course. It typically involves showcasing the knowledge and research conducted throughout the seminar in a professional and engaging manner. Presentations can take various formats, including oral presentations, poster presentations, or multimedia presentations.
What can I expect in a senior seminar course?
In a senior seminar course, you can expect a unique educational experience. It may involve intensive class discussions, assigned readings, research projects, group work, and presentations. Senior seminar courses aim to foster independent thinking, research skills, and a deeper understanding of a specific subject area.
What is the purpose of senior seminars?
The purpose of senior seminars is to foster independent thinking, develop research skills, and deepen students’ understanding of a specific subject area. Senior seminars play a vital role in preparing students for their future careers or further education by providing a platform for advanced study and intellectual growth.
Share your love
About the author, related posts, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of seminar in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I attended the seminars for two months .
- I have a seminar to attend before lunch .
- I've already missed five seminars this month through ill-health.
- She gave a brilliant seminar on Dickens.
- I went to most of my seminars at university though I skipped one or two of the lectures .
- academic year
- access course
- Advanced Placement
- asynchronous
- foundation course
- immersion course
- on a course
- the national curriculum
- work placement
seminar | Intermediate English
Seminar | business english, examples of seminar, translations of seminar.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
pitch-perfect
singing each musical note perfectly, at exactly the right pitch (= level)

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Business Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add seminar to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
a small group of students, as in a university, engaged in advanced study and original research under a member of the faculty and meeting regularly to exchange information and hold discussions.
the gathering place of such a group.
a meeting of such a group.
a course or subject of study for advanced graduate students.
any meeting for exchanging information and holding discussions.
Origin of seminar
Words nearby seminar.
- semimonthly
- seminal fluid
- seminal principle
- seminal vesicle
- seminiferous
- seminiferous tubule
Dictionary.com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2024
How to use seminar in a sentence
Companies like Adobe, Unilver and Starbucks are investing in well-being seminars, classes and automated bot systems to meet staff mental health requirements.
“Looks like I was analyzing the Free Exercise and Establishment clauses of the First Amendment for a seminar I took,” he said.
If you are curious about buying or selling a home, I will be holding a virtual homebuyer seminar at the end of September.
If your physical events such as product launch, marketing seminars were canceled or postponed, through which you had plans to gain traction, you could still go that way.
The paper by more than 800 authors is yet to be evaluated by other scientists in a process called “peer review,” but has been presented at a seminar .
Ah, yeah, when you said seminar I thought you attended some sort of corporate speech.
“It made me the coolest guy in my creative-writing seminar ,” he says between drags.
Now, Neilson is proposing legislation that would force couples to complete at least part of the seminar before filing for divorce.
In 2011 the European Aviation Safety seminar identified loss-of-control accidents as “top of the rankings of killer events.”
He held his American-history graduate seminar in his office.
He pointed to the books and said, "I have just been having a seminar here, in Danish literature."
Members of the Society will receive copies of Clark Library seminar papers.
The fourth year work is in the nature of a seminar and is devoted to instruction in bibliography.
These papers are then discussed by the members of the seminar and sharply criticised by Prof. Dziatzko.
Beside these public lectures, Prof Dziatzko gives once a week a bibliographical seminar for a smaller circle.
British Dictionary definitions for seminar
/ ( ˈsɛmɪˌnɑː ) /
a small group of students meeting regularly under the guidance of a tutor, professor, etc, to exchange information, discuss theories, etc
one such meeting or the place in which it is held
a higher course for postgraduates
any group or meeting for holding discussions or exchanging information
Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of seminar noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- Teaching is by lectures and seminars.
- a graduate seminar
- a seminar room
- dissertation
- hall of residence
- acquire/get/lack (an) education/training/ (British English) (some) qualifications
- receive/provide somebody with training/tuition
- develop/design/plan a curriculum/ (especially British English) course/ (North American English) program/syllabus
- give/go to/attend a class/lesson/lecture/seminar
- hold/run/conduct a class/seminar/workshop
- sign up for/take a course/classes/lessons
- go to/start preschool/kindergarten/nursery school
- be in (North American English) the first, second, etc. grade/ (British English) year 1, 2. etc. (at school)
- study/take/drop history/chemistry/German, etc.
- (British English) leave/finish/drop out of/ (North American English) quit school
- (North American English) graduate high school/college
- be the victim/target of bullying
- (British English) play truant from/ (both British English, informal) bunk off/skive off school (= not go to school when you should)
- (both especially North American English) skip/cut class/school
- (British English) cheat in/ (North American English) cheat on an exam/a test
- get/be given a detention (for doing something)
- be expelled from/be suspended from school
- do your homework/ (British English) revision/a project on something
- work on/write/do/submit an essay/a dissertation/a thesis/an assignment/ (North American English) a paper
- finish/complete your dissertation/thesis/studies/coursework
- hand in/ (North American English) turn in your homework/essay/assignment/paper
- study/prepare/ (British English) revise/ (North American English) review/ (North American English, informal) cram for a test/an exam
- take/ (both British English) do/sit a test/an exam
- (especially British English) mark/ (especially North American English) grade homework/a test
- (British English) do well in/ (North American English) do well on/ (especially North American English, informal) ace a test/an exam
- pass/fail/ (especially North American English, informal) flunk a test/an exam/a class/a course/a subject
- apply to/get into/go to/start college/ (British English) university
- leave/graduate from law school/college/ (British English) university (with a degree in computer science)
- study for/take/ (British English) do/complete a law degree/a degree in physics
- (both North American English) major/minor in biology/philosophy
- earn/receive/be awarded/get/have/hold a master’s degree/a bachelor’s degree/a PhD in economics
- In spring 2016 I taught a seminar on Sappho.
- Professor Mackay will give a seminar on Pound's poetry.
- at a/the seminar
- in a/the seminar
Want to learn more?
Find out which words work together and produce more natural-sounding English with the Oxford Collocations Dictionary app. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 Apr 2024 • 8 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

How To Write A Presentation? What should be in a powerful presentation? A great presentation encompasses several key elements to captivate your audience and effectively convey your message. Here’s what you should consider including in a winning presentation:
- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?” Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?” Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….” Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….” Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.17(12); 2021 Dec

Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides
Kristen m. naegle.
Biomedical Engineering and the Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
Introduction
The “presentation slide” is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what is spoken about that slide. Multiple slides are strung together to tell the larger story of the presentation. While there have been excellent 10 simple rules on giving entire presentations [ 1 , 2 ], there was an absence in the fine details of how to design a slide for optimal effect—such as the design elements that allow slides to convey meaningful information, to keep the audience engaged and informed, and to deliver the information intended and in the time frame allowed. As all research presentations seek to teach, effective slide design borrows from the same principles as effective teaching, including the consideration of cognitive processing your audience is relying on to organize, process, and retain information. This is written for anyone who needs to prepare slides from any length scale and for most purposes of conveying research to broad audiences. The rules are broken into 3 primary areas. Rules 1 to 5 are about optimizing the scope of each slide. Rules 6 to 8 are about principles around designing elements of the slide. Rules 9 to 10 are about preparing for your presentation, with the slides as the central focus of that preparation.
Rule 1: Include only one idea per slide
Each slide should have one central objective to deliver—the main idea or question [ 3 – 5 ]. Often, this means breaking complex ideas down into manageable pieces (see Fig 1 , where “background” information has been split into 2 key concepts). In another example, if you are presenting a complex computational approach in a large flow diagram, introduce it in smaller units, building it up until you finish with the entire diagram. The progressive buildup of complex information means that audiences are prepared to understand the whole picture, once you have dedicated time to each of the parts. You can accomplish the buildup of components in several ways—for example, using presentation software to cover/uncover information. Personally, I choose to create separate slides for each piece of information content I introduce—where the final slide has the entire diagram, and I use cropping or a cover on duplicated slides that come before to hide what I’m not yet ready to include. I use this method in order to ensure that each slide in my deck truly presents one specific idea (the new content) and the amount of the new information on that slide can be described in 1 minute (Rule 2), but it comes with the trade-off—a change to the format of one of the slides in the series often means changes to all slides.

Top left: A background slide that describes the background material on a project from my lab. The slide was created using a PowerPoint Design Template, which had to be modified to increase default text sizes for this figure (i.e., the default text sizes are even worse than shown here). Bottom row: The 2 new slides that break up the content into 2 explicit ideas about the background, using a central graphic. In the first slide, the graphic is an explicit example of the SH2 domain of PI3-kinase interacting with a phosphorylation site (Y754) on the PDGFR to describe the important details of what an SH2 domain and phosphotyrosine ligand are and how they interact. I use that same graphic in the second slide to generalize all binding events and include redundant text to drive home the central message (a lot of possible interactions might occur in the human proteome, more than we can currently measure). Top right highlights which rules were used to move from the original slide to the new slide. Specific changes as highlighted by Rule 7 include increasing contrast by changing the background color, increasing font size, changing to sans serif fonts, and removing all capital text and underlining (using bold to draw attention). PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide
When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged. During practice, if you find yourself spending more than a minute on a slide, there’s too much for that one slide—it’s time to break up the content into multiple slides or even remove information that is not wholly central to the story you are trying to tell. Reduce, reduce, reduce, until you get to a single message, clearly described, which takes less than 1 minute to present.
Rule 3: Make use of your heading
When each slide conveys only one message, use the heading of that slide to write exactly the message you are trying to deliver. Instead of titling the slide “Results,” try “CTNND1 is central to metastasis” or “False-positive rates are highly sample specific.” Use this landmark signpost to ensure that all the content on that slide is related exactly to the heading and only the heading. Think of the slide heading as the introductory or concluding sentence of a paragraph and the slide content the rest of the paragraph that supports the main point of the paragraph. An audience member should be able to follow along with you in the “paragraph” and come to the same conclusion sentence as your header at the end of the slide.
Rule 4: Include only essential points
While you are speaking, audience members’ eyes and minds will be wandering over your slide. If you have a comment, detail, or figure on a slide, have a plan to explicitly identify and talk about it. If you don’t think it’s important enough to spend time on, then don’t have it on your slide. This is especially important when faculty are present. I often tell students that thesis committee members are like cats: If you put a shiny bauble in front of them, they’ll go after it. Be sure to only put the shiny baubles on slides that you want them to focus on. Putting together a thesis meeting for only faculty is really an exercise in herding cats (if you have cats, you know this is no easy feat). Clear and concise slide design will go a long way in helping you corral those easily distracted faculty members.
Rule 5: Give credit, where credit is due
An exception to Rule 4 is to include proper citations or references to work on your slide. When adding citations, names of other researchers, or other types of credit, use a consistent style and method for adding this information to your slides. Your audience will then be able to easily partition this information from the other content. A common mistake people make is to think “I’ll add that reference later,” but I highly recommend you put the proper reference on the slide at the time you make it, before you forget where it came from. Finally, in certain kinds of presentations, credits can make it clear who did the work. For the faculty members heading labs, it is an effective way to connect your audience with the personnel in the lab who did the work, which is a great career booster for that person. For graduate students, it is an effective way to delineate your contribution to the work, especially in meetings where the goal is to establish your credentials for meeting the rigors of a PhD checkpoint.
Rule 6: Use graphics effectively
As a rule, you should almost never have slides that only contain text. Build your slides around good visualizations. It is a visual presentation after all, and as they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. However, on the flip side, don’t muddy the point of the slide by putting too many complex graphics on a single slide. A multipanel figure that you might include in a manuscript should often be broken into 1 panel per slide (see Rule 1 ). One way to ensure that you use the graphics effectively is to make a point to introduce the figure and its elements to the audience verbally, especially for data figures. For example, you might say the following: “This graph here shows the measured false-positive rate for an experiment and each point is a replicate of the experiment, the graph demonstrates …” If you have put too much on one slide to present in 1 minute (see Rule 2 ), then the complexity or number of the visualizations is too much for just one slide.
Rule 7: Design to avoid cognitive overload
The type of slide elements, the number of them, and how you present them all impact the ability for the audience to intake, organize, and remember the content. For example, a frequent mistake in slide design is to include full sentences, but reading and verbal processing use the same cognitive channels—therefore, an audience member can either read the slide, listen to you, or do some part of both (each poorly), as a result of cognitive overload [ 4 ]. The visual channel is separate, allowing images/videos to be processed with auditory information without cognitive overload [ 6 ] (Rule 6). As presentations are an exercise in listening, and not reading, do what you can to optimize the ability of the audience to listen. Use words sparingly as “guide posts” to you and the audience about major points of the slide. In fact, you can add short text fragments, redundant with the verbal component of the presentation, which has been shown to improve retention [ 7 ] (see Fig 1 for an example of redundant text that avoids cognitive overload). Be careful in the selection of a slide template to minimize accidentally adding elements that the audience must process, but are unimportant. David JP Phillips argues (and effectively demonstrates in his TEDx talk [ 5 ]) that the human brain can easily interpret 6 elements and more than that requires a 500% increase in human cognition load—so keep the total number of elements on the slide to 6 or less. Finally, in addition to the use of short text, white space, and the effective use of graphics/images, you can improve ease of cognitive processing further by considering color choices and font type and size. Here are a few suggestions for improving the experience for your audience, highlighting the importance of these elements for some specific groups:
- Use high contrast colors and simple backgrounds with low to no color—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment.
- Use sans serif fonts and large font sizes (including figure legends), avoid italics, underlining (use bold font instead for emphasis), and all capital letters—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment [ 8 ].
- Use color combinations and palettes that can be understood by those with different forms of color blindness [ 9 ]. There are excellent tools available to identify colors to use and ways to simulate your presentation or figures as they might be seen by a person with color blindness (easily found by a web search).
- In this increasing world of virtual presentation tools, consider practicing your talk with a closed captioning system capture your words. Use this to identify how to improve your speaking pace, volume, and annunciation to improve understanding by all members of your audience, but especially those with a hearing impairment.
Rule 8: Design the slide so that a distracted person gets the main takeaway
It is very difficult to stay focused on a presentation, especially if it is long or if it is part of a longer series of talks at a conference. Audience members may get distracted by an important email, or they may start dreaming of lunch. So, it’s important to look at your slide and ask “If they heard nothing I said, will they understand the key concept of this slide?” The other rules are set up to help with this, including clarity of the single point of the slide (Rule 1), titling it with a major conclusion (Rule 3), and the use of figures (Rule 6) and short text redundant to your verbal description (Rule 7). However, with each slide, step back and ask whether its main conclusion is conveyed, even if someone didn’t hear your accompanying dialog. Importantly, ask if the information on the slide is at the right level of abstraction. For example, do you have too many details about the experiment, which hides the conclusion of the experiment (i.e., breaking Rule 1)? If you are worried about not having enough details, keep a slide at the end of your slide deck (after your conclusions and acknowledgments) with the more detailed information that you can refer to during a question and answer period.
Rule 9: Iteratively improve slide design through practice
Well-designed slides that follow the first 8 rules are intended to help you deliver the message you intend and in the amount of time you intend to deliver it in. The best way to ensure that you nailed slide design for your presentation is to practice, typically a lot. The most important aspects of practicing a new presentation, with an eye toward slide design, are the following 2 key points: (1) practice to ensure that you hit, each time through, the most important points (for example, the text guide posts you left yourself and the title of the slide); and (2) practice to ensure that as you conclude the end of one slide, it leads directly to the next slide. Slide transitions, what you say as you end one slide and begin the next, are important to keeping the flow of the “story.” Practice is when I discover that the order of my presentation is poor or that I left myself too few guideposts to remember what was coming next. Additionally, during practice, the most frequent things I have to improve relate to Rule 2 (the slide takes too long to present, usually because I broke Rule 1, and I’m delivering too much information for one slide), Rule 4 (I have a nonessential detail on the slide), and Rule 5 (I forgot to give a key reference). The very best type of practice is in front of an audience (for example, your lab or peers), where, with fresh perspectives, they can help you identify places for improving slide content, design, and connections across the entirety of your talk.
Rule 10: Design to mitigate the impact of technical disasters
The real presentation almost never goes as we planned in our heads or during our practice. Maybe the speaker before you went over time and now you need to adjust. Maybe the computer the organizer is having you use won’t show your video. Maybe your internet is poor on the day you are giving a virtual presentation at a conference. Technical problems are routinely part of the practice of sharing your work through presentations. Hence, you can design your slides to limit the impact certain kinds of technical disasters create and also prepare alternate approaches. Here are just a few examples of the preparation you can do that will take you a long way toward avoiding a complete fiasco:
- Save your presentation as a PDF—if the version of Keynote or PowerPoint on a host computer cause issues, you still have a functional copy that has a higher guarantee of compatibility.
- In using videos, create a backup slide with screen shots of key results. For example, if I have a video of cell migration, I’ll be sure to have a copy of the start and end of the video, in case the video doesn’t play. Even if the video worked, you can pause on this backup slide and take the time to highlight the key results in words if someone could not see or understand the video.
- Avoid animations, such as figures or text that flash/fly-in/etc. Surveys suggest that no one likes movement in presentations [ 3 , 4 ]. There is likely a cognitive underpinning to the almost universal distaste of pointless animations that relates to the idea proposed by Kosslyn and colleagues that animations are salient perceptual units that captures direct attention [ 4 ]. Although perceptual salience can be used to draw attention to and improve retention of specific points, if you use this approach for unnecessary/unimportant things (like animation of your bullet point text, fly-ins of figures, etc.), then you will distract your audience from the important content. Finally, animations cause additional processing burdens for people with visual impairments [ 10 ] and create opportunities for technical disasters if the software on the host system is not compatible with your planned animation.
Conclusions
These rules are just a start in creating more engaging presentations that increase audience retention of your material. However, there are wonderful resources on continuing on the journey of becoming an amazing public speaker, which includes understanding the psychology and neuroscience behind human perception and learning. For example, as highlighted in Rule 7, David JP Phillips has a wonderful TEDx talk on the subject [ 5 ], and “PowerPoint presentation flaws and failures: A psychological analysis,” by Kosslyn and colleagues is deeply detailed about a number of aspects of human cognition and presentation style [ 4 ]. There are many books on the topic, including the popular “Presentation Zen” by Garr Reynolds [ 11 ]. Finally, although briefly touched on here, the visualization of data is an entire topic of its own that is worth perfecting for both written and oral presentations of work, with fantastic resources like Edward Tufte’s “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” [ 12 ] or the article “Visualization of Biomedical Data” by O’Donoghue and colleagues [ 13 ].
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the countless presenters, colleagues, students, and mentors from which I have learned a great deal from on effective presentations. Also, a thank you to the wonderful resources published by organizations on how to increase inclusivity. A special thanks to Dr. Jason Papin and Dr. Michael Guertin on early feedback of this editorial.
Funding Statement
The author received no specific funding for this work.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Confusing The Purpose. A seminar is a more interactive event that involves discussion and collaboration between the presenter and the audience. On the other hand, a presentation is a one-way communication where the speaker presents information to the audience.
Definition and Format. Seminars and webinars both act as platforms for sharing information, fostering discussion, and promoting learning. However, they diverge remarkably when it comes to definitions and formats. In essence, a seminar is a more traditional form of learning.
A seminar is a live presentation of a set topic where all participants can ask questions and interact to gain a better understanding. In a seminar, the facilitator presents information for the entire session and answers questions posed by the audience. Seminars are beneficial because they provide an opportunity to explore a topic in depth.
The primary objective of seminar presentation is to enhance presentation skills when persuading, educating, or informing an audience. Specifically, it provides a focus on the fundamental aspects of a quality academic, professional and business communications including structure, preparation and strategy for delivery, using visual aids, and handling question and answer sessions.
seminar: [noun] a group of advanced students studying under a professor with each doing original research and all exchanging results through reports and discussions.
This section focuses on seminar presentations, but most of the information given here is transferable and can be applied to all forms. of public speaking. This section is going to address a number of issues which are all relevant to preparing. and giving presentations and these include: preparing and reading background.
A seminar, or a panel discussion, is a focused and interactive educational event where a group of people with shared interests come together to discuss, learn, and exchange ideas. A subject matter expert or speaker usually leads the discussion and encourages attendees to ask questions and contribute to the discourse at the end.
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
A Presentation Is... A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other 'speaking engagements' such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across ...
The primary objective of seminar presentation is to enhance presentation skills when persuading, educating, or informing an audience. Specifically, it provides a focus on the fundamental aspects of a quality academic, professional and business communications including structure, preparation and strategy for delivery, using visual aids, and handling question and answer sessions.
seminar should tell a scientific story in a way that everyone present can understand and go home with some lesson learned. Purpose of Seminar: A presentation concentrates on teaching something to the audience. A good presentation means that the audience understood the message. The first rule is to place yourself in the mind of your audience.
A seminar is an interactive event where experts, researchers, or industry professionals gather to present and discuss their ideas, research findings, and experiences within a specific subject area. It typically involves presentations, panel discussions, workshops, and opportunities for networking and collaboration.
The Senior Seminar Presentation. After completing the coursework and research for a senior seminar, students must present their findings in the form of a Senior Seminar Presentation. This culminating event is the highlight of the seminar, allowing students to showcase their knowledge and research skills.
SEMINAR meaning: 1. an occasion when a teacher or expert and a group of people meet to study and discuss something…. Learn more.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Seminar. A seminar is a form of academic instruction, either at an academic institution or offered by a commercial or professional organization. It has the function of bringing together small groups for recurring meetings, focusing each time on some particular subject, in which everyone present is requested to participate.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new ...
Noun. ( wikipedia presentation ) ( en noun ) The act of presenting, or something presented. * Hooker. Prayers are sometimes a presentation of mere desires. A dramatic performance. An award given to someone on a special occasion. A lecture or speech given in front of an audience. (medicine) The symptoms and other possible indications of disease ...
Seminar definition: a small group of students, as in a university, engaged in advanced study and original research under a member of the faculty and meeting regularly to exchange information and hold discussions. See examples of SEMINAR used in a sentence.
Definition of seminar noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
The "presentation slide" is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what ...
seminar: 1 n a course offered for a small group of advanced students Type of: class , course , course of instruction , course of study education imparted in a series of lessons or meetings n any meeting for an exchange of ideas Type of: conference a prearranged meeting for consultation or exchange of information or discussion (especially one ...