IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 9 min


# Table of Contents
- IndexError: list assignment index out of range
- (CSV) IndexError: list index out of range
- sys.argv[1] IndexError: list index out of range
- IndexError: pop index out of range
Make sure to click on the correct subheading depending on your error message.
# IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python
The Python "IndexError: list assignment index out of range" occurs when we try to assign a value at an index that doesn't exist in the list.
To solve the error, use the append() method to add an item to the end of the list, e.g. my_list.append('b') .
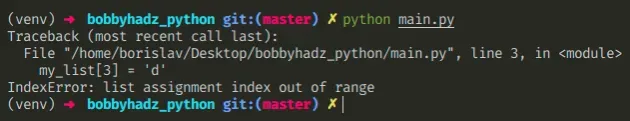
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
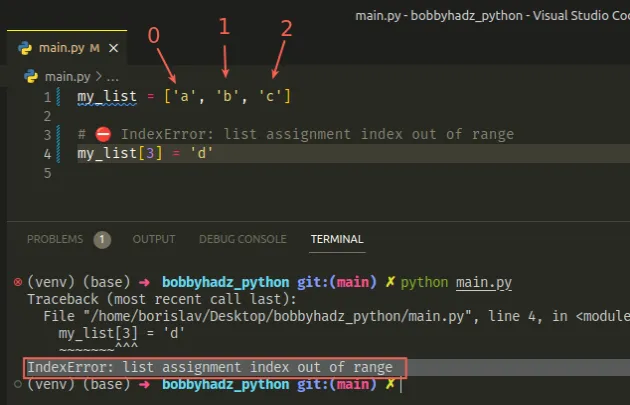
The list has a length of 3 . Since indexes in Python are zero-based, the first index in the list is 0 , and the last is 2 .
Trying to assign a value to any positive index outside the range of 0-2 would cause the IndexError .
# Adding an item to the end of the list with append()
If you need to add an item to the end of a list, use the list.append() method instead.
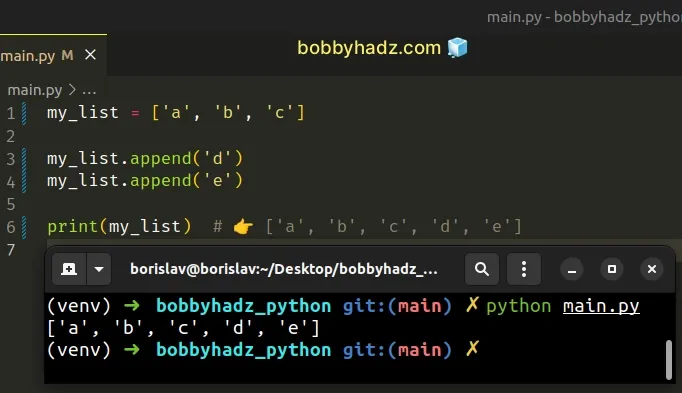
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
The method returns None as it mutates the original list.
# Changing the value of the element at the last index in the list
If you meant to change the value of the last index in the list, use -1 .
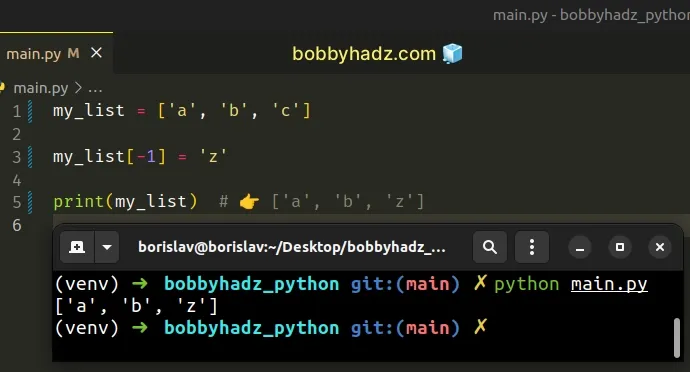
When the index starts with a minus, we start counting backward from the end of the list.
# Declaring a list that contains N elements and updating a certain index
Alternatively, you can declare a list that contains N elements with None values.
The item you specify in the list will be contained N times in the new list the operation returns.
Make sure to wrap the value you want to repeat in a list.
If the list contains a value at the specific index, then you are able to change it.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
If you need to handle the error if the specified list index doesn't exist, use a try/except statement.
The list in the example has 3 elements, so its last element has an index of 2 .
We wrapped the assignment in a try/except block, so the IndexError is handled by the except block.
You can also use a pass statement in the except block if you need to ignore the error.
The pass statement does nothing and is used when a statement is required syntactically but the program requires no action.
# Getting the length of a list
If you need to get the length of the list, use the len() function.
The len() function returns the length (the number of items) of an object.
The argument the function takes may be a sequence (a string, tuple, list, range or bytes) or a collection (a dictionary, set, or frozen set).
If you need to check if an index exists before assigning a value, use an if statement.
This means that you can check if the list's length is greater than the index you are trying to assign to.
# Trying to assign a value to an empty list at a specific index
Note that if you try to assign to an empty list at a specific index, you'd always get an IndexError .
You should print the list you are trying to access and its length to make sure the variable stores what you expect.
# Use the extend() method to add multiple items to the end of a list
If you need to add multiple items to the end of a list, use the extend() method.
The list.extend method takes an iterable (such as a list) and extends the list by appending all of the items from the iterable.
The list.extend method returns None as it mutates the original list.
# (CSV) IndexError: list index out of range in Python
The Python CSV "IndexError: list index out of range" occurs when we try to access a list at an index out of range, e.g. an empty row in a CSV file.
To solve the error, check if the row isn't empty before accessing it at an index, or check if the index exists in the list.
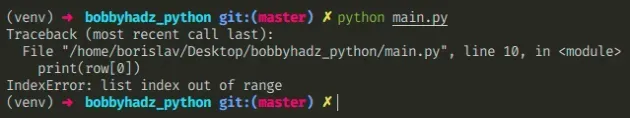
Assume we have the following CSV file.
And we are trying to read it as follows.
# Check if the list contains elements before accessing it
One way to solve the error is to check if the list contains any elements before accessing it at an index.
The if statement checks if the list is truthy on each iteration.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy: None and False .
- 0 (zero) of any numeric type
- empty sequences and collections: "" (empty string), () (empty tuple), [] (empty list), {} (empty dictionary), set() (empty set), range(0) (empty range).
# Check if the index you are trying to access exists in the list
Alternatively, you can check whether the specific index you are trying to access exists in the list.
This means that you can check if the list's length is greater than the index you are trying to access.
# Use a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except block to handle the error.
We try to access the list of the current iteration at index 1 , and if an IndexError is raised, we can handle it in the except block or continue to the next iteration.
# sys.argv [1] IndexError: list index out of range in Python
The sys.argv "IndexError: list index out of range in Python" occurs when we run a Python script without specifying values for the required command line arguments.
To solve the error, provide values for the required arguments, e.g. python main.py first second .
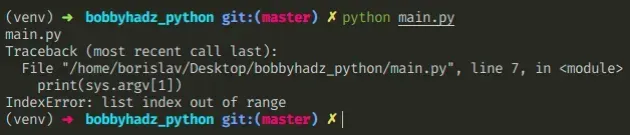
I ran the script with python main.py .
The sys.argv list contains the command line arguments that were passed to the Python script.
# Provide all of the required command line arguments
To solve the error, make sure to provide all of the required command line arguments when running the script, e.g. python main.py first second .
Notice that the first item in the list is always the name of the script.
It is operating system dependent if this is the full pathname or not.
# Check if the sys.argv list contains the index
If you don't have to always specify all of the command line arguments that your script tries to access, use an if statement to check if the sys.argv list contains the index that you are trying to access.
I ran the script as python main.py without providing any command line arguments, so the condition wasn't met and the else block ran.
We tried accessing the list item at index 1 which raised an IndexError exception.
You can handle the error or use the pass keyword in the except block.
# IndexError: pop index out of range in Python
The Python "IndexError: pop index out of range" occurs when we pass an index that doesn't exist in the list to the pop() method.
To solve the error, pass an index that exists to the method or call the pop() method without arguments to remove the last item from the list.
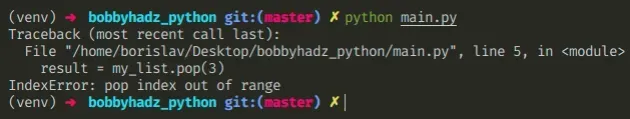
The list has a length of 3 . Since indexes in Python are zero-based, the first item in the list has an index of 0 , and the last an index of 2 .
If you need to remove the last item in the list, call the method without passing it an index.
The list.pop method removes the item at the given position in the list and returns it.
You can also use negative indices to count backward, e.g. my_list.pop(-1) removes the last item of the list, and my_list.pop(-2) removes the second-to-last item.
Alternatively, you can check if an item at the specified index exists before passing it to pop() .
This means that you can check if the list's length is greater than the index you are passing to pop() .
An alternative approach to handle the error is to use a try/except block.
If calling the pop() method with the provided index raises an IndexError , the except block is run, where we can handle the error or use the pass keyword to ignore it.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- IndexError: index 0 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 0
- IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable in Python
- IndexError: pop from empty list in Python [Solved]
- Replacement index 1 out of range for positional args tuple
- IndexError: too many indices for array in Python [Solved]
- IndexError: tuple index out of range in Python [Solved]

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Python indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
An IndexError is nothing to worry about. It’s an error that is raised when you try to access an index that is outside of the size of a list. How do you solve this issue? Where can it be raised?
In this article, we’re going to answer those questions. We will discuss what IndexErrors are and how you can solve the “list assignment index out of range” error. We’ll walk through an example to help you see exactly what causes this error.
Find your bootcamp match
Without further ado, let’s begin!
The Problem: indexerror: list assignment index out of range
When you receive an error message, the first thing you should do is read it. An error message can tell you a lot about the nature of an error.
Our error message is: indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
IndexError tells us that there is a problem with how we are accessing an index . An index is a value inside an iterable object, such as a list or a string.
The message “list assignment index out of range” tells us that we are trying to assign an item to an index that does not exist.
In order to use indexing on a list, you need to initialize the list. If you try to assign an item into a list at an index position that does not exist, this error will be raised.
An Example Scenario
The list assignment error is commonly raised in for and while loops .
We’re going to write a program that adds all the cakes containing the word “Strawberry” into a new array. Let’s start by declaring two variables:
The first variable stores our list of cakes. The second variable is an empty list that will store all of the strawberry cakes. Next, we’re going to write a loop that checks if each value in “cakes” contains the word “Strawberry”.
If a value contains “Strawberry”, it should be added to our new array. Otherwise, nothing will happen. Once our for loop has executed, the “strawberry” array should be printed to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
As we expected, an error has been raised. Now we get to solve it!
The Solution
Our error message tells us the line of code at which our program fails:
The problem with this code is that we are trying to assign a value inside our “strawberry” list to a position that does not exist.
When we create our strawberry array, it has no values. This means that it has no index numbers. The following values do not exist:
We are trying to assign values to these positions in our for loop. Because these positions contain no values, an error is returned.
We can solve this problem in two ways.
Solution with append()
First, we can add an item to the “strawberry” array using append() :
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let’s run our code: [‘Strawberry Tart’, ‘Strawberry Cheesecake’].
Our code works!
Solution with Initializing an Array
Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our “strawberry” array.
To initialize an array, you can use this code:
This will create an array with 10 empty values. Our code now looks like this:
Let’s try to run our code:
Our code successfully returns an array with all the strawberry cakes.
This method is best to use when you know exactly how many values you’re going to store in an array.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Our above code is somewhat inefficient because we have initialized “strawberry” with 10 empty values. There are only a total of three cakes in our “cakes” array that could possibly contain “Strawberry”. In most cases, using the append() method is both more elegant and more efficient.
IndexErrors are raised when you try to use an item at an index value that does not exist. The “indexerror: list assignment index out of range” is raised when you try to assign an item to an index position that does not exist.
To solve this error, you can use append() to add an item to a list. You can also initialize a list before you start inserting values to avoid this error.
Now you’re ready to start solving the list assignment error like a professional Python developer!
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How to Fix the “List index out of range” Error in Python

- learn python
At many points in your Python programming career, you’re going to run into the “List index out of range” error while writing your programs. What does this mean, and how do we fix this error? We’ll answer that question in this article.
The short answer is: this error occurs when you’re trying to access an item outside of your list’s range. The long answer, on the other hand, is much more interesting. To get there, we’ll learn a lot about how lists work, how to index things the bad way and the good way, and finally how to solve the above-mentioned error.
This article is aimed at Python beginners who have little experience in programming. Understanding this error early will save you plenty of time down the road. If you’re looking for some learning material, our Python Basics track includes 3 interactive courses bundled together to get you on your feet.
Indexing Python Lists
Lists are one of the most useful data structures in Python. And they come with a whole bunch of useful methods . Other Python data structures include tuples, arrays, dictionaries, and sets, but we won’t go into their details here. For hands-on experience with these structures, we have a Python Data Structures in Practice course which is suitable for beginners.
A list can be created as follows:
Instead of using square brackets ([]) to define your list, you can also use the list() built-in function.
There are already a few interesting things to note about the above example. First, you can store any data type in a list, such as an integer, string, floating-point number, or even another list. Second, the elements don’t have to be unique: the integer 1 appears twice in the above example.
The elements in a list are indexed starting from 0. Therefore, to access the first element, do the following:
Our list contains 6 elements, which you can get using the len() built-in function. To access the last element of the list, you might naively try to do the following:
This is equivalent to print(x[len(x)]) . Since list indexing starts from 0, the last element has index len(x)–1 . When we try to access the index len(x) , we are outside the range of the list and get the error. A more robust way to get the final element of the list looks like this:
While this works, it’s not the most pythonic way. A better method exploits a nice feature of lists – namely, that they can be indexed from the end of the list by using a negative number as the index. The final element can be printed as follows:
The second last element can be accessed with the index -2, and so on. This means using the index -6 will get back to the first element. Taking it one step further:
Notice this asymmetry. The first error was trying to access the element after the last with the index 6, and the second error was trying to access the element before the first with the index -7. This is due to forward indexing starting at 0 (the start of the list), and backwards indexing starting at -1 (the end of the list). This is shown graphically below:

Looping Through Lists
Whenever you’re working with lists, you’ll need to know about loops. A loop allows you to iterate through all the elements in a list.
The first type of loop we’ll take a look at is the while loop. You have to be a little more careful with while loops, because a small mistake will make them run forever, requiring you to force the program to quit. Once again, let’s try to naively loop through our list:
In this example we define our index, i , to start from zero. After every iteration of our while loop, we print the list element and then go to the next index with the += assignment operator. (This is a neat little trick, which is like doing i=i+1 .)
By the way, if you forget the final line, you’ll get an infinite loop.
We encountered the index error for the same reason as in the first section – the final element has index len(x)-1 . Just modify the condition of the while statement to reflect this, and it will work without problems.
Most of your looping will be done with a for loop, which we’ll now turn our attention to. A better method to loop through the elements in our list without the risk of running into the index error is to take advantage of the range() built-in function. This takes three arguments, of which only the stop argument is required. Try the following:
The combination of the range() and len() built-in functions takes care of worrying about when to stop indexing our list to avoid the index out of range error entirely. This method, however, is only useful if you care about knowing what the index is.
For example, maybe you want to print out the index and the element. In that case, all you need to do is modify the print() statement to print(i, x[i]) . Try doing this for yourself to see the result. Alternatively, you can use The enumerate() function in Python.
If you just want to get the element, there’s a simpler way that’s much more intuitive and readable. Just loop through the elements of the list directly:
If the user inputs an index outside the range of the list (e.g. 6), they’ll run into the list index error again. We can modify the function to check the input value with an if statement:
Doing this prevents our program from crashing if the index is out of range. You can even use a negative index in the above function.
There are other ways to do error handling in Python that will help you avoid errors like “list index out of range”. For example, you could implement a try-exceptaa block instead of the if-else statement.
To see a try-except block in action, let’s handle a potential index error in the get_value() function we wrote above. Preventing the error looks like this:
As you can probably see, the second method is a little more concise and readable. It’s also less error-prone than explicitly checking the input index with an if-else statement.
Master the “List index out of range” Error in Python
You should now know what the index out of range error in Python means, why it pops up, and how to prevent it in your Python programs.
A useful way to debug this error and understand how your programs are running is simply to print the index and compare it to the length of your list.
This error could also occur when iterating over other data structures, such as arrays, tuples, or even when iterating through a string. Using strings is a little different from using lists; if you want to learn the tools to master this topic, consider taking our Working with Strings in Python course. The skills you learnt here should be applicable to many common use cases.
You may also like

How Do You Write a SELECT Statement in SQL?

What Is a Foreign Key in SQL?

Enumerate and Explain All the Basic Elements of an SQL Query
How to fix IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python
by Nathan Sebhastian
Posted on Apr 05, 2023
Reading time: 2 minutes

When programming with Python, you might encounter the following error:
This error occurs when you attempt to assign a value to a list using an index that doesn’t already exist in the list.
This tutorial will show you an example that causes this error and how to fix it in practice
How to reproduce this error
Suppose you create a list in your code as follows:
Next, you assign a new value at index [2] in the list as follows:
You’ll get this error:
The error occurs because the index number [2] doesn’t exist in the animals list. Index assignment in a list only allows you to change existing items.
Because the list has two items, the index number ranges from 0 to 1. Assigning a value to any other index number will cause this error.
How to fix this error
To resolve this error, you need to use the append() method to add a new element to the list.
For example, to add the ‘bird’ item:
As you can see, now the ‘bird’ value is added to the list successfully.
Adding the value using the append() method increases the list index range, which enables you to modify the item at the new index using the list assignment syntax.
To summarize, use the append() method when you’re adding a new element and increasing the size of the list, and use the list assignment index when you want to change an existing item in the list.
I hope this tutorial is helpful. Until next time! 👋
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I'm sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I'll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials. Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Learn more about this website
Connect with me on Twitter
Or LinkedIn
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:

How to Fix – IndexError list assignment index out of range
The IndexError is a common error that occurs in Python when you try to access an index that is out of range for a list. This error can occur when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. In this tutorial, we will discuss how to fix the IndexError list assignment index out of range in Python.
Understanding the Error
Before we dive into the solution, let’s first understand what causes the IndexError list assignment index out of range error. This error occurs when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. For example, consider the following code:
In the above code, we are trying to assign the value 4 to the index 3 of the my_list list. However, the my_list list only has three elements, so the index 3 does not exist. This results in the IndexError list assignment index out of range error.
Fixing the Error
To fix the IndexError list assignment index out of range error, you need to make sure that the index you are trying to access or assign a value to exists in the list. You can use an if statement to check if the index exists in the list.
Note that Python sequences also allow negative indexing so be mindful of this when checking if an index exists in a list or not. Let’s look at an example.
Note that if you’re sure that the given index is not negative, you can just check if the index lies in the range 0 to the length of the list using index < len(my_list) .
Introductory ⭐
- Harvard University Data Science: Learn R Basics for Data Science
- Standford University Data Science: Introduction to Machine Learning
- UC Davis Data Science: Learn SQL Basics for Data Science
- IBM Data Science: Professional Certificate in Data Science
- IBM Data Analysis: Professional Certificate in Data Analytics
- Google Data Analysis: Professional Certificate in Data Analytics
- IBM Data Science: Professional Certificate in Python Data Science
- IBM Data Engineering Fundamentals: Python Basics for Data Science
Intermediate ⭐⭐⭐
- Harvard University Learning Python for Data Science: Introduction to Data Science with Python
- Harvard University Computer Science Courses: Using Python for Research
- IBM Python Data Science: Visualizing Data with Python
- DeepLearning.AI Data Science and Machine Learning: Deep Learning Specialization
Advanced ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- UC San Diego Data Science: Python for Data Science
- UC San Diego Data Science: Probability and Statistics in Data Science using Python
- Google Data Analysis: Professional Certificate in Advanced Data Analytics
- MIT Statistics and Data Science: Machine Learning with Python - from Linear Models to Deep Learning
- MIT Statistics and Data Science: MicroMasters® Program in Statistics and Data Science
🔎 Find Data Science Programs 👨💻 111,889 already enrolled
Disclaimer: Data Science Parichay is reader supported. When you purchase a course through a link on this site, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. Earned commissions help support this website and its team of writers.
If your end goal is to add an element to a list, you can instead use the list append() or insert() functions.
The append() method adds an element to the end of the list, so you don’t have to worry about the index. For example:
Here, we added the element 4 to the end of the list and we didn’t need to provide an index.
If you need to add an element to a specific index in the list, you can use the insert() method. The insert() method takes two arguments: the index where you want to insert the element and the element itself.
In this code, we are using the insert() method to insert the value 4 at the index 3 of the my_list list. Since we are inserting the element at a specific index, the IndexError list assignment index out of range error will be avoided.
The IndexError list assignment index out of range error occurs when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in the list. To fix this error, you need to make sure that the index you are trying to access or assign a value to exists in the list. You can do this by checking the length of the list. If you want to add values to a list, you can use the append() method to add elements to the end of the list, or the insert() method to insert elements at a specific index.
You might also be interested in –
- Understand and Fix IndexError in Python
- Python List Append, Extend and Insert

Piyush is a data professional passionate about using data to understand things better and make informed decisions. He has experience working as a Data Scientist in the consulting domain and holds an engineering degree from IIT Roorkee. His hobbies include watching cricket, reading, and working on side projects.
View all posts
How to Fix Python IndexError: list assignment index out of range
- Python How-To's
- How to Fix Python IndexError: list …
Python IndexError: list assignment index out of range
Fix the indexerror: list assignment index out of range in python, fix indexerror: list assignment index out of range using append() function, fix indexerror: list assignment index out of range using insert() function.

In Python, the IndexError: list assignment index out of range is raised when you try to access an index of a list that doesn’t even exist. An index is the location of values inside an iterable such as a string, list, or array.
In this article, we’ll learn how to fix the Index Error list assignment index out-of-range error in Python.
Let’s see an example of the error to understand and solve it.
Code Example:
The reason behind the IndexError: list assignment index out of range in the above code is that we’re trying to access the value at the index 3 , which is not available in list j .
To fix this error, we need to adjust the indexing of iterables in this case list. Let’s say we have two lists, and you want to replace list a with list b .
You cannot assign values to list b because the length of it is 0 , and you are trying to add values at kth index b[k] = I , so it is raising the Index Error. You can fix it using the append() and insert() .
The append() function adds items (values, strings, objects, etc.) at the end of the list. It is helpful because you don’t have to manage the index headache.
The insert() function can directly insert values to the k'th position in the list. It takes two arguments, insert(index, value) .
In addition to the above two solutions, if you want to treat Python lists like normal arrays in other languages, you can pre-defined your list size with None values.
Once you have defined your list with dummy values None , you can use it accordingly.
There could be a few more manual techniques and logic to handle the IndexError: list assignment index out of range in Python. This article overviews the two common list functions that help us handle the Index Error in Python while replacing two lists.
We have also discussed an alternative solution to pre-defined the list and treat it as an array similar to the arrays of other programming languages.

Zeeshan is a detail oriented software engineer that helps companies and individuals make their lives and easier with software solutions.
Related Article - Python Error
- Can Only Concatenate List (Not Int) to List in Python
- How to Fix Value Error Need More Than One Value to Unpack in Python
- How to Fix ValueError Arrays Must All Be the Same Length in Python
- Invalid Syntax in Python
- How to Fix the TypeError: Object of Type 'Int64' Is Not JSON Serializable
- How to Fix the TypeError: 'float' Object Cannot Be Interpreted as an Integer in Python
Related Article - Python List
- How to Convert a Dictionary to a List in Python
- How to Remove All the Occurrences of an Element From a List in Python
- How to Remove Duplicates From List in Python
- How to Get the Average of a List in Python
- What Is the Difference Between List Methods Append and Extend
- How to Convert a List to String in Python

- Learn Python
- Python Lists
- Python Dictionaries
- Python Strings
- Python Functions
- Learn Pandas & NumPy
- Pandas Tutorials
- Numpy Tutorials
- Learn Data Visualization
- Python Seaborn
- Python Matplotlib
Python IndexError: List Index Out of Range Error Explained
- November 15, 2021 December 19, 2022

In this tutorial, you’ll learn how all about the Python list index out of range error, including what it is, why it occurs, and how to resolve it.
The IndexError is one of the most common Python runtime errors that you’ll encounter in your programming journey. For the most part, these these errors are quite easy to resolve, once you understand why they occur.
Throughout this tutorial, you’ll learn why the error occurs and walk through some scenarios where you might encounter it. You’ll also learn how to resolve the error in these scenarios .
The Quick Answer:
Table of Contents
What is the Python IndexError?
Let’s take a little bit of time to explore what the Python IndexError is and what it looks like. When you encounter the error, you’ll see an error message displayed as below:
We can break down the text a little bit. We can see here that the message tells us that the index is out of range . This means that we are trying to access an index item in a Python list that is out of range, meaning that an item doesn’t have an index position.
An item that doesn’t have an index position in a Python list, well, doesn’t exist.
In Python, like many other programming languages, a list index begins at position 0 and continues to n-1 , where n is the length of the list (or the number of items in that list).
This causes a fairly common error to occur. Say we are working with a list with 4 items. If we wanted to access the fourth item, you may try to do this by using the index of 4. This, however, would throw the error. This is because the 4 th item actually has the index of 3.
Let’s take a look at a sample list and try to access an item that doesn’t exist:
We can see here that the index error occurs on the last item we try to access.
The simplest solution is to simply not try to access an item that doesn’t exist . But that’s easier said than done. How do we prevent the IndexError from occurring? In the next two sections, you’ll learn how to fix the error from occurring in their most common situations: Python for loops and Python while loops.
Need to check if a key exists in a Python dictionary? Check out this tutorial , which teaches you five different ways of seeing if a key exists in a Python dictionary, including how to return a default value.
Python IndexError with For Loop
You may encounter the Python IndexError while running a Python for loop. This is particularly common when you try to loop over the list using the range() function .
Let’s take a look at the situation where this error would occur:
The way that we can fix this error from occurring is to simply stop the iteration from occurring before the list runs out of items . The way that we can do this is to change our for loop from going to our length + 1, to the list’s length. When we do this, we stop iterating over the list’s indices before the lengths value.
This solves the IndexError since it causes the list to stop iterating at position length - 1 , since our index begins at 0, rather than at 1.
Let’s see how we can change the code to run correctly:
Now that you have an understanding of how to resolve the Python IndexError in a for loop, let’s see how we can resolve the error in a Python while-loop.
Want to learn more about Python for-loops? Check out my in-depth tutorial that takes your from beginner to advanced for-loops user! Want to watch a video instead? Check out my YouTube tutorial here .
Python IndexError with While Loop
You may also encounter the Python IndexError when running a while loop.
For example, it may be tempting to run a while loop to iterate over each index position in a list. You may, for example, write a program that looks like this:
The reason that this program fails is that we iterate over the list one too many times. The reason this is true is that we are using a <= (greater than or equal to sign). Because Python list indices begin at the value 0, their max index is actually equal to the number of items in the list minus 1.
We can resolve this by simply changing the operator a less than symbol, < . This prevents the loop from looping over the index from going out of range.
In the next section, you'll learn a better way to iterate over a Python list to prevent the IndexError .
Want to learn more about Python f-strings? Check out my in-depth tutorial , which includes a step-by-step video to master Python f-strings!
How to Fix the Python IndexError
There are two simple ways in which you can iterate over a Python list to prevent the Python IndexError .
The first is actually a very plain language way of looping over a list. We don't actually need the list index to iterate over a list. We can simply access its items directly.
This directly prevents Python from going beyond the maximum index.
Want to learn how to use the Python zip() function to iterate over two lists? This tutorial teaches you exactly what the zip() function does and shows you some creative ways to use the function.
But what if you need to access the list's index?
If you need to access the list's index and a list item, then a much safer alternative is to use the Python enumerate() function.
When you pass a list into the enumerate() function, an enumerate object is returned. This allows you to access both the index and the item for each item in a list. The function implicitly stops at the maximum index, but allows you to get quite a bit of information.
Let's take a look at how we can use the enumerate() function to prevent the Python IndexError .
We can see here that we the loop stops before the index goes out of range and thereby prevents the Python IndexError .
Check out some other Python tutorials on datagy, including our complete guide to styling Pandas and our comprehensive overview of Pivot Tables in Pandas !
In this tutorial, you learned how to understand the Python IndexError : list item out of range. You learned why the error occurs, including some common scenarios such as for loops and while loops. You learned some better ways of iterating over a Python list, such as by iterating over items implicitly as well as using the Python enumerate() function.
To learn more about the Python IndexError , check out the official documentation here .
Nik Piepenbreier
Nik is the author of datagy.io and has over a decade of experience working with data analytics, data science, and Python. He specializes in teaching developers how to use Python for data science using hands-on tutorials. View Author posts

1 thought on “Python IndexError: List Index Out of Range Error Explained”
from django.contrib import messages from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from home.forms import RewardModeLForm from item.models import Item from person.models import Person from .models import Reward, YoutubeVideo # Create your views here.
def home(request): my_reward = Reward.objects.all()[:1] # First Div last_person_post = Person.objects.all()[:1] last_item_post = Item.objects.all()[:1] # 2nd Div lost_person = Person.objects.filter(person=”L”).all()[:1] lost_item = Item.objects.filter(category=”L”).all()[:2] # End 2 div
home_found = Person.objects.all()[:3] home_item = Item.objects.all()[:3] videos = YoutubeVideo.objects.all()[:3] context = { ‘my_reward’: my_reward, ‘lost_person’: lost_person, ‘lost_item’: lost_item, ‘home_found’: home_found, ‘home_item’: home_item, ‘videos’: videos, } if last_person_post[0].update > last_item_post[0].update: context[‘last_post’] = last_person_post else: context[‘last_post’] = last_item_post
return render(request, ‘home/home.html’, context)
# Reward Function
def reward(request): if request.method == ‘POST’: form = RewardModeLForm(request.POST or None) if form.is_valid(): instance = form.save(commit=False) instance.user = request.user instance.save() messages.add_message(request, messages.SUCCESS, ‘Reward Updated .’) return redirect(‘home’) else: form = RewardModeLForm() context = { ‘form’: form, } return render(request, ‘home/reward.html’, context) index out of rage
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
List Index Out of Range – Python Error Message Solved

In this article you'll see a few of the reasons that cause the list index out of range Python error.
Besides knowing why this error occurs in the first place, you'll also learn some ways to avoid it.
Let's get started!
How to Create a List in Python
To create a list object in Python, you need to:
- Give the list a name,
- Use the assignment operator, = ,
- and include 0 or more list items inside square brackets, [] . Each list item needs to be separated by a comma.
For example, to create a list of names you would do the following:
The code above created a list called names that has four values: Kelly, Nelly, Jimmy, Lenny .
How to Check the Length of a List in Python
To check the length of a list in Python, use Python's build-in len() method.
len() will return an integer, which will be the number of items stored in the list.
There are four items stored in the list, therefore the length of the list will be four.
How to Access Individual List Items in Python
Each item in a list has its own index number .
Indexing in Python, and most modern programming languages, starts at 0.
This means that the first item in a list has an index of 0, the second item has an index of 1, and so on.
You can use the index number to access the individual item.
To access an item in a list using its index number, first write the name of the list. Then, inside square brackets, include the intiger that corresponds with the item's index number.
Taking the example from earlier, this is how you would access each item inside the list using its index number:
You can also use negative indexing to access items inside lists in Python.
To access the last item, you use the index value of -1. To acces the second to last item, you use the index value of -2.
Here is how you would access each item inside a list using negative indexing:
Why does the Indexerror: list index out of range error occur in Python?
Using an index number that is out of the range of the list.
You'll get the Indexerror: list index out of range error when you try and access an item using a value that is out of the index range of the list and does not exist.
This is quite common when you try to access the last item of a list, or the first one if you're using negative indexing.
Let's go back to the list we've used so far.
Say I want to access the last item, "Lenny", and try to do so by using the following code:
Generally, the index range of a list is 0 to n-1 , with n being the total number of values in the list.
With the total values of the list above being 4 , the index range is 0 to 3 .
Now, let's try to access an item using negative indexing.
Say I want to access the first item in the list, "Kelly", by using negative indexing.
When using negative indexing, the index range of a list is -1 to -n , where -n the total number of items contained in the list.
With the total number of items in the list being 4 , the index range is -1 to -4 .
Using the wrong value in the range() function in a Python for loop
You'll get the Indexerror: list index out of range error when iterating through a list and trying to access an item that doesn't exist.
One common instance where this can occur is when you use the wrong integer in Python's range() function.
The range() function typically takes in one integer number, which indicates where the counting will stop.
For example, range(5) indicates that the counting will start from 0 and end at 4 .
So, by default, the counting starts at position 0 , is incremented by 1 each time, and the number is up to – but not including – the position where the counting will stop.
Let's take the following example:
Here, the list names has four values.
I wanted to loop through the list and print out each value.
When I used range(5) I was telling the Python interpreter to print the values that are at the positions 0 to 4 .
However, there is no item in position 4.
You can see this by first printing out the number of the position and then the value at that position.
You see that at position 0 is "Kelly", at position 1 is "Nelly", at position 2 is "Jimmy" and at position 3 is "Lenny".
When it comes to position four, which was specified with range(5) which indicates positions of 0 to 4 , there is nothing to print out and therefore the interpreter throws an error.
One way to fix this is to lower the integer in range() :
Another way to fix this when using a for loop is to pass the length of the list as an argument to the range() function. You do this by using the len() built-in Python function, as shown in an earlier section:
When passing len() as an argument to range() , make sure that you don't make the following mistake:
After running the code, you'll again get an IndexError: list index out of range error:
Hopefully this article gave you some insight into why the IndexError: list index out of range error occurs and some ways you can avoid it.
If you want to learn more about Python, check out freeCodeCamp's Python Certification . You'll start learning in an interacitve and beginner-friendly way. You'll also build five projects at the end to put into practice and help reinforce what you learned.
Thanks for reading and happy coding!
Read more posts .
If this article was helpful, share it .
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
- Free Python 3 Tutorial
- Control Flow
- Exception Handling
- Python Programs
- Python Projects
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Database
- Data Science With Python
- Machine Learning with Python
- Filter Python list by Predicate in Python
- How to Fix: ValueError: All arrays must be of the same length
- How to Fix: Invalid value encountered in true_divide
- Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
- How to Fix: Can only compare identically-labeled series objects
- How to Replace Values in a List in Python?
- How to Fix: if using all scalar values, you must pass an index
- How to Fix: Length of values does not match length of index
- Internal working of list in Python
- How to Fix: NameError name ‘pd’ is not defined
- How to Fix: ValueError: Trailing data?
- How to Fix: ValueError: Operands could not be broadcast together with shapes?
- How to Fix: ValueError: cannot convert float NaN to integer
- How to Fix: columns overlap but no suffix specified
- How to Fix: RuntimeWarning: Overflow encountered in exp
- How to Fix: TypeError: ‘numpy.float’ object is not callable?
- How to Fix: TypeError: cannot perform reduce with flexible type
- Python Initialize List of Lists
- How To Combine Multiple Lists Into One List Python
Python List Index Out of Range – How to Fix IndexError
In Python, the IndexError is a common exception that occurs when trying to access an element in a list, tuple, or any other sequence using an index that is outside the valid range of indices for that sequence. List Index Out of Range Occur in Python when an item from a list is tried to be accessed that is outside the range of the list. Before we proceed to fix the error, let’s discuss how indexing work in Python .
What Causes an IndexError in Python
- Accessing Non-Existent Index: When you attempt to access an index of a sequence (such as a list or a string) that is out of range, an Indexerror is raised. Sequences in Python are zero-indexed, which means that the first element’s index is 0, the second element’s index is 1, and so on.
- Empty List: If you try to access an element from an empty list, an Indexerror will be raised since there are no elements in the list to access.
Example: Here our list is 3 and we are printing with size 4 so in this case, it will create a list index out of range.
Similarly, we can also get an Indexerror when using negative indices.
How to Fix IndexError in Python
- Check List Length: It’s important to check if an index is within the valid range of a list before accessing an element. To do so, you can use the function to determine the length of the list and make sure the index falls within the range of 0 to length-1.
- Use Conditional Statements: To handle potential errors, conditional statements like “if” or “else” blocks can be used. For example, an “if” statement can be used to verify if the index is valid before accessing the element. if or try-except blocks to handle the potential IndexError . For instance, you can use a if statement to check if the index is valid before accessing the element.
How to Fix List Index Out of Range in Python
Let’s see some examples that showed how we may solve the error.
- Using Python range()
- Using Python Index()
- Using Try Except Block
Python Fix List Index Out of Range using Range()
The range is used to give a specific range, and the Python range() function returns the sequence of the given number between the given range.
Python Fix List Index Out of Range u sing Index()
Here we are going to create a list and then try to iterate the list using the constant values in for loops.
Reason for the error – The length of the list is 5 and if we are an iterating list on 6 then it will generate the error.
Solving this error without using Python len() or constant Value: To solve this error we will take the index of the last value of the list and then add one then it will become the exact value of length.
Python Fix List Index Out of Range using Try Except Block
If we expect that an index might be out of range, we can use a try-except block to handle the error gracefully.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Python How-to-fix
- python-list
- Google Introduces New AI-powered Vids App
- Dolly Chaiwala: The Microsoft Windows 12 Brand Ambassador
- 10 Best Free Remote Desktop apps for Android in 2024
- 10 Best Free Internet Speed Test apps for Android in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Data Analysis
- Deep Learning
- Large Language Model
- Machine Learning
- Neural Networks

How to Fix list assignment index out of range in Python
Learn what causes IndexError: list assignment index out of range errors in Python and how to avoid and fix them by using valid indexes and methods like len(), append(), and insert().
One of the most common errors that Python programmers encounter is the IndexError: list assignment index out of range. This error occurs when you try to assign a value to an index that does not exist in a list. In this article, we will explain what causes this error, how to avoid it, and how to fix it if it happens.
What is a list assignment index out of range error?
A list is a data structure that stores multiple values in a single variable. You can access the values in a list by using their index, which is a number that represents their position in the list. The first value in a list has an index of 0, the second value has an index of 1, and so on.
For example, consider the following list:
You can access the first value in the list by using fruits[0] , which returns "apple" . You can also assign a new value to an existing index by using the same syntax. For example, you can change the second value in the list by using fruits[1] = "pear" , which updates the list to ["apple", "pear", "orange"] .
However, if you try to assign a value to an index that is out of range, meaning that it is either negative or greater than or equal to the length of the list, you will get an IndexError: list assignment index out of range. For example, if you try to assign a value to fruits[3] , you will get an error because the list only has three values, and the valid indexes are 0, 1, and 2.
How to avoid list assignment index out of range errors?
There are two main ways to avoid list assignment index out of range errors:
- Check the length of the list before assigning a value to an index. You can use the len() function to get the number of values in a list. For example, if you want to assign a value to the last index in a list, you can use len(list) - 1 as the index. For example:
- Use the append() method to add a new value to the end of the list. This method automatically increases the length of the list and assigns the new value to the last index. For example:
How to fix list assignment index out of range errors?
If you encounter a list assignment index out of range error, you need to identify which line of code caused the error and what index you tried to assign a value to. Then, you need to either adjust the index to be within the valid range or use another method to add a new value to the list.
For example, suppose you have the following code that tries to create a new list by adding one to each value in another list:
This code will raise an IndexError: list assignment index out of range because new_numbers is an empty list and has no indexes. To fix this error , you can use the append() method instead of indexing:
Alternatively, you can initialize new_numbers with the same length as numbers and fill it with zeros or None values:
In this article, we learned what causes IndexError: list assignment index out of range errors in Python and how to avoid and fix them. We learned that we need to make sure that we use valid indexes when assigning values to lists and that we can use methods like len() , append() , and insert() to manipulate lists without causing errors.
- list assignment index
Python Image Processing With OpenCV
Install python 3.10 on centos/rhel 8 & fedora 35/34, how to overwrite a file in python, why is python so popular, itertools combinations – python, colorama in python, matplotlib log scale in python, how to generate dummy data with python faker, more article, master python int to string conversion, master the python isinstance() function, python not equal (=) operator: syntax, examples, master python null equivalent syntax: a comprehensive guide.
2016 began to contact WordPress, the purchase of Web hosting to the installation, nothing, step by step learning, the number of visitors to the site, in order to save money, began to learn VPS. Linux, Ubuntu, Centos …
Popular Posts
Popular categories.
- Data Analysis 661
- Artificial Intelligence 517
- Security 95
- Database Management 62
- NLP Analytics 60
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
©markaicode.com. All rights reserved - 2022 by Mark
Fixing Python List Assignments: How to Avoid ‘Index Out of Range’ Error
Fixing the ‘Index Out of Range’ error in Python list assignments may seem daunting, but it’s quite simple once you understand the basics. This error occurs when you try to access an index in a list that doesn’t exist. By following a few steps, you can easily correct your code and avoid this common mistake.
Step by Step Tutorial: Fixing Python List Assignments
Before diving into the steps, it’s important to understand that lists in Python are zero-indexed. This means that the first element is at index 0, the second element at index 1, and so on. The ‘Index Out of Range’ error happens when you attempt to access an index that is higher than the last index in your list.
Step 1: Identify the Problematic Index
The first step is to figure out which index is causing the error.
Oftentimes, the error message will tell you exactly which line of code is problematic. Look for the index that is being accessed and compare it with the length of your list. If the index is equal to or larger than the length of your list, that’s your issue.
Step 2: Modify the Index or List
Once you’ve identified the problematic index, you need to either adjust the index or modify the list itself.
If the index is a hardcoded number, consider whether it’s necessary to access that specific index, or if it was a mistake. If the index is a result of a calculation or loop, check the logic to ensure it stays within the bounds of the list. Alternatively, you may need to expand your list by appending additional elements to avoid the error.
Step 3: Test Your Solution
After making the necessary changes, run your code again to see if the error persists.
Testing is crucial because it ensures that your solution works as intended. If the ‘Index Out of Range’ error is gone, congratulations! If not, revisit the previous steps and double-check your logic and list manipulations.
Once you’ve completed these steps, your Python list assignments should be error-free, and you can continue coding without the pesky ‘Index Out of Range’ error.
Tips: Avoiding ‘Index Out of Range’ Errors
- Always check the length of your list before accessing an index.
- Use loops carefully, ensuring that the iteration doesn’t exceed the list’s length.
- Consider using list methods like append() or extend() to dynamically adjust list sizes.
- Utilize exception handling with try and except blocks to catch and handle errors gracefully.
- Familiarize yourself with Python’s list slicing to access ranges of elements safely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ‘index out of range’ mean.
It means that you’re trying to access an element in a list using an index number that doesn’t exist. Since lists are zero-indexed, the last index will always be one less than the length of the list.
Can I use negative indices in Python lists?
Yes, Python allows the use of negative indices to access elements from the end of a list. For example, -1 refers to the last element, -2 to the second to last, and so on.
How do I avoid ‘Index Out of Range’ errors in loops?
Make sure that your loop condition or range doesn’t exceed the list’s length. For example, use for i in range(len(my_list)): to ensure the loop stays within bounds.
What is the best practice for accessing the last element of a list?
You can use the index -1 to access the last element of a list, as it’s more readable and doesn’t require knowing the exact length of the list.
Should I always check the list length before accessing an element by index?
While it’s good practice to be cautious, if you’re certain of the list’s size or the index is well within the expected range, it may not be necessary. However, always validate indices when dealing with dynamic or unknown list sizes.
- Identify the problematic index causing the ‘Index Out of Range’ error.
- Modify the index or list to ensure the index exists within the list.
- Test your code to confirm the error is resolved.
Fixing the ‘Index Out of Range’ error in Python list assignments is a skill that every Python programmer should master. It involves understanding how list indexing works, carefully managing list lengths, and being mindful of looping constructs. Remember, the key to avoiding this error is to ensure that any index you try to access is within the bounds of your list. Keep practicing, and soon, dealing with list assignments and indexes will be second nature. If you ever get stuck, revisit the steps in this article, apply the tips, and consult the frequently asked questions for guidance. Happy coding!

Kermit Matthews is a freelance writer based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania with more than a decade of experience writing technology guides. He has a Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in Computer Science and has spent much of his professional career in IT management.
He specializes in writing content about iPhones, Android devices, Microsoft Office, and many other popular applications and devices.
Read his full bio here .
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- Retrieving the First Key in a Python Dictionary: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Understanding TypeError in Python: Navigating ‘type’ Object Issues
- Troubleshooting VLOOKUP: Fixing Out of Bounds Errors
- Appending Data to CSV Files in Python: A Guide for Efficient Data Analysis
- Ensuring Input Data Falls Within Specified Range in Programming
- 403 Forbidden Errors: How to Fix Them in Nginx Web Servers
- How to Change Home Screen on iPhone 11
- How to Select Multiple Items from a Dropdown List in Excel
- How to Quickly Find a Circular Reference in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Stop Adding Apps to the iPhone 13 Home Screen
- Troubleshooting ‘Bad Gateway’ Errors in Nginx Proxy Manager: A Guide
- 10 Ways to Make Your iPhone 13 Battery Stop Draining So Fast
- How to Add a Bullet Point in Google Docs
- How to Make the iPhone 13 Screen Brighter
- How to Center a Google Docs Table
- Why Can’t I Screen Record? Troubleshooting for Windows & iPhone
- How to Make All Columns Same Width – Google Sheets
- Addressing SQL Table Creation Errors: ‘optimize_for_sequential_key’ Fix
- How to View My Passwords List in Google Chrome
- How to Screen Record iPhone: Step-by-Step Guide
- Documentation
- System Status
- Rollbar Academy
- Software Development
- Engineering Management
- Platform/Ops
- Customer Support
- Software Agency
- Low-Risk Release
- Production Code Quality
- DevOps Bridge
- Effective Testing & QA
How to Fix IndexError: List Index Out of Range in Python

Table of Contents
The IndexError: list index out of range error occurs in Python when an item from a list is attempted to be accessed that is outside the index range of the list. The range of a list in Python is [0, n-1], where n is the number of elements in the list.
Python IndexError Example
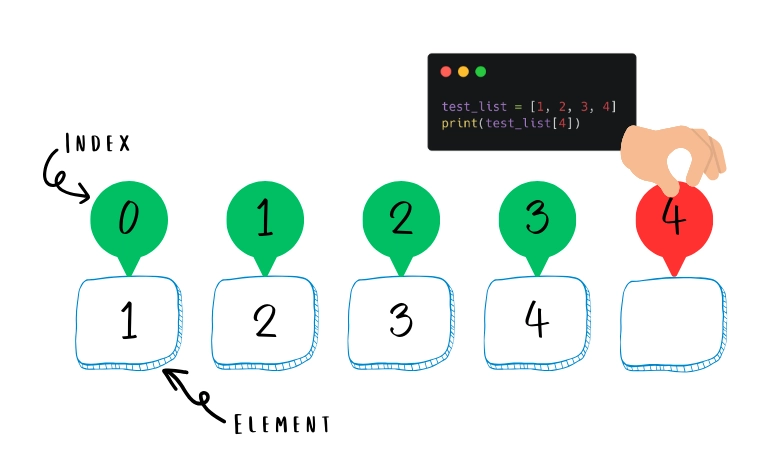
Here’s an example of a Python IndexError: list index out of range thrown when trying to access an out of range list item:
In the above example, since the list test_list contains 4 elements, its last index is 3. Trying to access an element an index 4 throws an IndexError: list index out of range :
How to Fix IndexError in Python
The Python IndexError: list index out of range can be fixed by making sure any elements accessed in a list are within the index range of the list. This can be done by using the range() function along with the len() function.
The range() function returns a sequence of numbers starting from 0 ending at the integer passed as a parameter. The len() function returns the length of the parameter passed. Using these two methods together allows for safe iteration over the list up to its final element, thus ensuring that you stay within the valid index range and preventing the IndexError.
Here's how to use this approach to fix the error in the earlier example:
The above code runs successfully and produces the correct output as expected:
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Python errors easier than ever. Install the Python SDK to identify and fix exceptions today!
Related Resources
How to Catch Multiple Exceptions in Python

How to Handle the Psycopg2 UniqueViolation Error in Python

How to Handle the MemoryError in Python
"Rollbar allows us to go from alerting to impact analysis and resolution in a matter of minutes. Without it we would be flying blind."

Start continuously improving your code today.
List Assignment Index Out of Range Error: An Honest Guide
- Recent Posts
- How to Repost an Image on Instagram: A Stepwise Guide - April 5, 2024
- Instagram Not Loading Pictures: Easy Steps for a Quick Fix - April 5, 2024
- If You Permanently Delete Chat on Instagram: How To Recover - April 5, 2024
In addition, you will experience similar list assignment inconsistencies and mistakes when developing a transformer model for machine translation with a common vocabulary, usually because the value is out of bounds. However, we suggest this profound guide because it teaches how to fix list index out of range in Python with standard debugging techniques and solutions preventing other complications.
JUMP TO TOPIC
– Assigning a Value to a Non-existent Index in the List
– developing a transformer model for machine translation, – writing other statements for the inserted functions, – providing a dictionary for the incorrect containers, why is the list index assignment out of range error happening.
The indexerror: list assignment index out of range 2D array happens because the system cannot assign a value to a non-existent index in the list. We confirmed an identical visual output when developing a transformer model for machine translation with common vocabulary due to an out-of-bounds value.
As you can tell, most culprits confirm issues with the values in the listed indexes or properties. For example, the list index out of range Django code exception ensures your application suffers from problems with the indexed elements or configurations in the main list, although the other components are correct. Consequently, your program displays wronged messages and warnings preventing you from completing the code and reenabling the commands unless removing the indexerror: list index out of range . However, pinpointing the inconsistency is sometimes challenging, especially with complex documents with many lists and values.
Running a value in a non-existent index in the list is the simplest way of reproducing the error log. Hence, we will focus on the system environment to learn more about the culprit, although they differ for all programs and apps. In addition, we will list a few common Python properties to define the project’s purpose and implementation.
The following example lists the environment and traceback calls:
As you can tell, this code snippet ruins the virtual environments and terminates the partial evaluations. Consequently, the abstract packages and lists fail to render the indexes and assigned values. Still, you can only proceed after debugging the program and updating the values, as you will soon learn.
This guide’s other chapter replicating the code exception attempts to create a transformer model for machine translation. The code snippet uses common elements and vocabulary, but the trainers confuse the program after the opening code lines. As a result, the assignment index shows a range of errors and flaws, as confirmed in the following example.
Scan the following code to learn about the primary inputs:
We omitted the broken visual output to keep the chapter as short as possible while reproducing the error log. Thus, launching this code snippet in your document forces your machine to fail and display complex messages specifying the paths and locations. In addition, the dependencies fail to target adequate inputs, which is this error’s another common cause.
Overcome the List Index Assignment Error: 3 Excellent Solutions
You can overcome the list index error log by restructuring the code’s order and checking the boundaries. In addition, this guide suggests writing other statements for the inserted functions . Finally, you could provide a dictionary or an associative array for the incorrect containers and lists.
You can learn more about the corrected document below:
This example checks the boundaries before launching the configurations, which is critical when avoiding the range error and preventing other complications. Still, you could implement the alternative debugging approaches if the code exception persists and affects your assignment indexes.
The following examples teach you about the other statements and conditions:
We inserted a few comments to capture the adjustments because different statements have different purposes. Nevertheless, you will enjoy your programming experience because the error should disappear.
The last debugging approach provides a dictionary or associative array for the incorrect containers. As a result, you clarify the statements’ purpose, helping them check if the index exists in the specific list. However, to round off the solution, you must apply this operation to all invalid code snippets and projections.
We demonstrated the solution in the following code snippet:
Your application should confirm the assignment index is within range and complete the process. On the other hand, you will see a warning preventing other code alterations if the index is out of reach, which is atypical. But again, remember to change the elements after pasting them into your file.
The list index assignment that is out of range error log happens when assigning a value to a non-existent index in the list. Nevertheless, this guide made debugging easy and explained the following necessary points:
- Developing a transformer model for machine translation with common vocabular provokes similar issues
- The debug logs and traceback information is beneficial when finding the broken lists
- You can overcome the list index error log by restructuring the code’s order and checking the boundaries
- Providing a dictionary or associative array for the incorrect containers repairs the program
Assigned lists and indexes are sometimes challenging due to specific boundaries and values. Still, you should overcome most issues with this article’s debugging methods and fixes.
Related posts:
- Conversion Failed When Converting Date And/or Time From Character String.
- Vector Subscript Out of Range: Dissecting The Error
- Could Not Open a Connection to Your Authentication Agent.
- .Map Is Not a Function: A Comprehensive Debugging Guide
- The Insert Statement Conflicted With the Foreign Key Constraint
- The Authenticity of Host Can’t Be Established: Solved
- Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment: How To Solve?
- Import Cycle Not Allowed: How To Solve It in Golang
- Saving Changes Is Not Permitted SQL Server: How To Fix?
- Error 2003 (HY000): Can’t Connect to Mysql Server on ‘Localhost’ (10061)
- Github Permission Denied (Publickey): Causes and Solutions
- Referenceerror: Require Is Not Defined: Finally Repaired
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your list starts out empty because of this: a = [] then you add 2 elements to it, with this code: a.append(3) a.append(7) this makes the size of the list just big enough to hold 2 elements, the two you added, which has an index of 0 and 1 (python lists are 0-based). In your code, further down, you then specify the contents of element j which ...
When your list is empty in python you can not assign value to unassigned index of list. so you have 2 options here:. Use append like : list.append(value); make a loop to assign a value to your list before your main for.Like below: i = 0 while ( i < index_you_want): list[i] = 0 ... #here your main code
But if you try to modify a value whose index is greater than or equal to the length of the list then you will encounter an Indexerror: list assignment index out of range. Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Example. If 'fruits' is a list, fruits=['Apple',' Banana',' Guava']and you try to modify fruits[5] then ...
The Python CSV "IndexError: list index out of range" occurs when we try to access a list at an index out of range, e.g. an empty row in a CSV file. To solve the error, check if the row isn't empty before accessing it at an index, or check if the index exists in the list.
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let's run our code: ['Strawberry Tart', 'Strawberry Cheesecake']. Our code works! Solution with Initializing an Array. Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our "strawberry" array.
How to use the insert() method. Use the insert() method to insert elements at a specific position instead of direct assignment to avoid out-of-range assignments. Example: my_list = [ 10, 20, 30 ] my_list.insert( 3, 987) #Inserting element at index 3 print (my_list) Output: [10, 20, 30, 987] Now one big advantage of using insert() is even if you ...
The elements in a list are indexed starting from 0. Therefore, to access the first element, do the following: >>> print(x[0]) Our list contains 6 elements, which you can get using the len() built-in function. To access the last element of the list, you might naively try to do the following: >>> print(x[6]) IndexError: list index out of range
As you can see, now the 'bird' value is added to the list successfully. Adding the value using the append() method increases the list index range, which enables you to modify the item at the new index using the list assignment syntax.. To summarize, use the append() method when you're adding a new element and increasing the size of the list, and use the list assignment index when you ...
To fix indexerror list assignment index out of range error, make sure that the index you are using for assignment exists in the list.
In Python, the IndexError: list assignment index out of range is raised when you try to access an index of a list that doesn't even exist. An index is the location of values inside an iterable such as a string, list, or array.
IndexError: list index out of range. We can break down the text a little bit. We can see here that the message tells us that the index is out of range. This means that we are trying to access an index item in a Python list that is out of range, meaning that an item doesn't have an index position.
freeCodeCamp is a donor-supported tax-exempt 501(c)(3) charity organization (United States Federal Tax Identification Number: 82-0779546) Our mission: to help people learn to code for free.
Output. blue,red,green Python Fix List Index Out of Range u sing Index(). Here we are going to create a list and then try to iterate the list using the constant values in for loops.
What is a list assignment index out of range error? A list is a data structure that stores multiple values in a single variable. You can access the values in a list by using their index, which is a number that represents their position in the list. The first value in a list has an index of 0, the second value has an index of 1, and so on.
Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window) Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Articles on Python, AWS, Security, Serverless, and Web Development, dedicated to solving issues and streamlining tasks. Start mastering coding today.
The Python IndexError: list index out of range can be fixed by making sure any elements accessed in a list are within the index range of the list. This can be done by using the range() function along with the len() function. The range() function returns a sequence of numbers starting from 0 ending at the integer passed as a parameter.
The element will be added to the specified index within or out of the range at the end of the list. Solution 3: Using list.extend() To add multiple elements to a list without the "IndexError: list assignment index out of range", the "list.extend()" function is used in Python. Here's a code snippet to append one list to another: Code:
Because you're using the values contained in the list as indices; mark takes the values 90, 80, ..., 100. The subscription midterm[90] is obviously out of bounds. To iterate through the items while also having a handle on the position, Python offers enumerate which provides an index along with the current value:
In addition, you will experience similar list assignment inconsistencies and mistakes when developing a transformer model for machine translation with a common vocabulary, usually because the value is out of bounds.
1. The problem is that you have an empty list originally: highest_list = [] And then in the loop you try to access it at index 0: highest_list[0] = ... It's impossible, because it's an empty list and so is not indexable at position 0. A better way to find the mode of a list is to use a collections.Counter object: >>> from collections import ...
I am trying to recognise the text from the uploaded image, for some images; my GUI is returning positive response, but for some other images: it is giving IndexError: list index out of range. I am ...