
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Learning the Importance of Business Management
Understanding the Importance of Business Management is paramount. This blog covers the crucial role that effective management plays in achieving organisational success. Discover the key principles, strategies, and real-world examples that highlight the significance of business management for both new entrepreneurs and established enterprises.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Business Process Improvement Training
- Team Development Training
- Problem Solving Course
- Introduction to Supervising a Team

Business Management is the compass that guides decision-making and the fuel that drives growth. Therefore, it’s time to learn about the importance of managing your business. Not sure how? Read this blog to explore the multifaceted Importance of Business Management. Also, learn how it is crucial for businesses in shaping their organisational structure.
Table of Contents
1) The fundamentals of Business Management
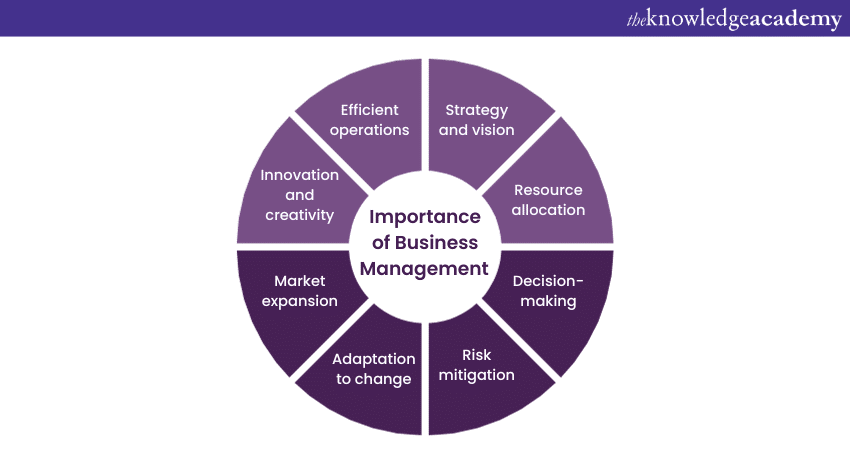
2) Why is Business Management Important?
a) Strategy and vision
b) Resource allocation
c) Decision-making
d) Risk mitigation
e) Adaptation to change
f) Market expansion
g) Innovation and creativity
h) Efficient operations
i) Customer satisfaction
j) Profitability and financial stability
3) Conclusion
The fundamentals of Business Management
Business Management is the backbone of any organisation, providing structure, direction, and purpose to its operations. At its essence, it is an amalgamation of various organisational activities and resources to achieve specific goals and objectives.
It's a multifaceted discipline encompassing many responsibilities, strategies, and techniques. Effective Management of Business ensures that the organisation functions cohesively, adapts to changes, and thrives in a competitive environment. Effective Business Management extends its influence on various aspects of an organisation, including the following:
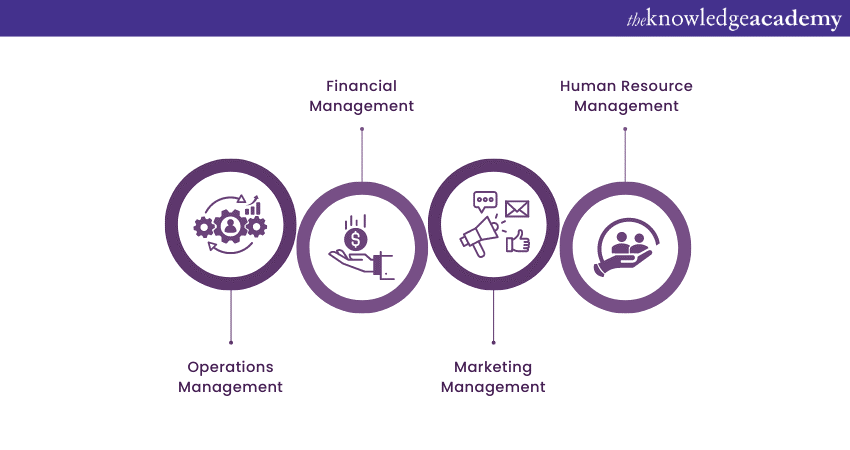
The fundamentals of Business Management revolve around key principles and practices that form the core of effective organisational leadership. At its essence, Business Management encompasses planning, organising, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals and objectives. Let's look at how it works:
a) Planning: This stage involves setting clear goals, developing strategies, and outlining the steps necessary to achieve them. Effective planning provides a roadmap for the organisation's future.
b) Organising: Organi sing involves structuring the resources and workforce to ensure that they align with the established plan. It includes defining roles, responsibilities, and establishing a framework for efficient operations.
c) L eading: Leadership within Business Management is about inspiring and motivating the workforce to achieve the company's goals. It involves effective communication, setting a positive example, and providing guidance.
d) Controlling: Control mechanisms are crucial for monitoring progress and ensuring that the organisation stays on track. This includes assessing performance, identifying variances, and making adjustments when necessary.
In addition to these core functions, Business Management also addresses aspects like strategic thinking, risk management, innovation, resource allocation, and continuous improvement. By mastering these fundamentals, organisations can enhance their decision-making, adapt to change, achieve sustainable growth, and maintain a competitive edge in the dynamic world of business.
Ready to unlock your leadership potential? Explore our Leadership Training and fuel yourself with the skills to inspire teams, drive innovation, and lead with confidence.
Why is Business Management Important?
Business Management is the linchpin of success for any organisation, irrespective of its size or industry. It serves as the guiding force that ensures an enterprise's sustainable growth, profitability, and adaptability. Thus, it’s crucial to understand why Business Management is essential for those aspiring to thrive in today's dynamic business landscape. So, let’s explore the Importance of Business Management, highlighting its role in shaping strategy, resource allocation, decision-making, and risk mitigation:
1) Strategy and v ision
Business Management serves as the backbone of a well-defined strategy and vision for an organisation. A strategic plan outlines an organisation's long-term goals and the steps required to achieve them.
It's the roadmap that guides the company's direction, helping it to stay focused and consistent. Without effective Management of Business operations, an organisation might lack a structured approach to strategic planning. This can lead to confusion, inconsistency, and missed opportunities.
2) Resource a llocation
Efficient resource allocation is pivotal for an organi sation's success. Proper resource allocation involves distributing assets such as finances, human capital, and technology to areas where they are most needed.
Effective Business Management ensures that resources are utilised optimally, avoiding waste and misallocation. Inefficient allocation can lead to budget overruns, poor workforce productivity, and underutilisation of technology and infrastructure.
3) Decision- m aking
The Importance of Business Management is reflected when making important decisions. Business Management provides a structured framework for gathering information, analysing data, and making informed decisions. It allows organisations to consider various factors and potential outcomes before making choices. Without effective management, organisations risk making hasty and uninformed decisions that can lead to costly mistakes and missed opportunities.
4) Risk m itigation
Every business face s risks, whether they are related to economic fluctuations, market competition, or unforeseen events. Effective management involves identifying and assessing these risks. It also includes creating risk mitigation strategies that reduce vulnerabilities and safeguard the organisation. Without a structured approach to risk management, businesses may be ill-prepared to handle unexpected challenges, potentially leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
5) Adaptation to c hange
Today, adaptability has become a key to survival. Effective Business Management equips organisations with strategies and tools to respond to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. It allows them to shift quickly, seize opportunities, and remain competitive. Without such adaptability, businesses risk becoming stagnant, unable to keep up with evolving industry trends.
6) Market e xpansion
Market expansion is a crucial avenue for growth. Business Management provides the framework for assessing market potential and devising market entry strategies. Effective management ensures that an organisation is well-prepared to enter new markets, be it through organic growth, mergers, acquisitions, or international expansion. Without a systematic approach to market expansion, businesses might miss out on untapped opportunities and underperform in their current markets.
Gain an in-depth knowledge of strategic planning, financial management, and operational excellence with our Business Management Training – join today!
7) Innovation and c reativity
Innovation is the lifeblood of businesses in the modern era. Effective Business Management fosters a culture of innovation and creativity within the organisation. Managers encourage employees to think creatively, take calculated risks, and generate new ideas that can lead to groundbreaking products or services. However, a lack of management support for innovation can stifle creativity and hinder an organisation's ability to stand out in a crowded market.
8) Efficient o perations
Efficiency is c rucial to business sustainability. Effective management optimises processes, reduces operational costs, and enhances overall productivity. Efficient operations not only lead to cost savings but also free up resources that can be reinvested in growth initiatives. Without management, businesses may struggle with inefficiencies, leading to higher costs and reduced competitiveness.
9) Customer s atisfaction
Meeting and exceeding customer expectations is paramount for business growth. Without effective management, businesses might overlook critical customer feedback and fail to adapt to changing consumer preferences. Thus, Business Management is crucial to ensure that the organisation is responsive to customer needs and preferences. It helps align processes, products, and services with customer demands, enhancing satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
10) Profitability and f inancial s tability
Business Management includes financial planning, budgeting, and investment decisions. Effective management is instrumental in maintaining profitability and financial stability. It ensures that the organisation's financial health is secure, providing the means for long-term sustainability. A lack of Financial Management can result in financial instability, hampering an organisation's ability to weather economic downturns or invest in future growth.
11) Employee d evelopment and r etention
A skilled and motivated workforce is a valuable asset . Business Management includes human resource aspects such as recruitment, training, and retention strategies. Effective management creates an environment where employees are motivated, engaged, and empowered to contribute to the organisation's growth and success. Without such management, businesses may struggle to attract and retain top talent, leading to skill gaps and high turnover.

12) Compliance and r esponsibility
In today's global business environment, compliance with legal and ethical standards is vital. However, without management oversight, organisations may inadvertently violate regulations. This can result in legal liabilities and reputational damage. Effective Business Management ensures that the organisation adheres to these standards, reducing the risk of legal issues and safeguarding the company's reputation.
13) Environmental r esponsibility
Sustainability is not limited to financial health but extends to environmental responsibility. Without Business Management, businesses may neglect environmental considerations and miss opportunities to embrace sustainability as a competitive advantage. Effective management incorporates strategies for reducing the organisation's environmental footprint. This commitment to environmental responsibility benefits the planet, aligns with the values of socially conscious consumers, and can also lead to cost savings in the long run.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has aided in improving your understanding of the Importance of Business Management and its role in various aspects of business. Business Management is the driver of strategy and the catalyst for adaptation. In commerce, the usefulness of mastering this craft is not just restricted to an individual but beneficial for a larger economy. As businesses brave uncertainties and embrace innovation, the role of Business Management remains pivotal.
Explore our Leadership and Management Skills Course and unlock the keys to effective leadership.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 3rd May 2024
Fri 6th Sep 2024
Fri 15th Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Free Application Code
A $25 Value
Ready to take the next step? Pick your path. We'll help you get there. Complete the form below and receive a code to waive the $25 application fee.
CSU Global websites use cookies to enhance user experience, analyze site usage, and assist with outreach and enrollment. By continuing to use this site, you are giving us your consent to do this. Learn more in our Privacy Statement .
Colorado State University Global

- Admission Overview
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- International Students
- Military & Veteran Students
- Non-Degree Students
- Re-Entry Students
- Meet the Admissions Team
- Tuition & Aid Overview
- Financial Aid
- Tuition & Cost
- Scholarships
- Financial Resources
- Military Benefits
- Student Success Overview
- What to Expect
- Academic Support
- Career Development
- Offices & Services
- Course Catalog
- Academic Calendar
- Student Organizations
- Student Policies
- About CSU Global
- Mission & Vision
- Accreditation
- Why CSU Global
- Our Faculty
- Industry Certifications
- Partnerships
- School Store
- Commitment to Colorado
- Memberships & Organizations
- News Overview
- Student Stories
- Special Initiatives
- Community Involvement
The Importance of Business Management
- April 4, 2022
Recently, we wrote about what business management is and why a Bachelor's Degree in Business Management is worth acquiring. Today, we're going to explore what makes business management so important.
As part of our discussion, we'll go over what business management includes, what roles business managers play in an organization, and why you should consider starting a career in this field.
After you've discovered what makes business management so important, fill out our information request form to receive more information about CSU Global's 100% online Bachelor's of Science Degree in Business Management or our online Master's of Science Degree in Management .
If you're ready to get started, submit your application today!
What is Business Management and Why is it So Important?
Business management is the act of overseeing the organization, coordination, and execution of various business activities. This may include managing different aspects of the business, like sales, marketing, and accounting.
Essentially, business managers are responsible for ensuring that the day-to-day operations function smoothly.
Business management is a crucial part of an organization’s success, and every organization in any industry can benefit from a great business manager who has expertise in best practices and relevant processes.
The core responsibility of a business manager is to ensure that a business remains both operational and profitable, which is what makes business management such an important position.
What Do Business Managers Actually Do?
Business managers are responsible for overseeing a business' finances and operations.
The specific details of any given business manager's duties will depend on their organization and industry, but here are some of their typical responsibilities and tasks:
- Overseeing different departments, including marketing, sales, HR, accounting, and others
- Preparing and managing budgets, payments, and other financial aspects of the business
- Advising stakeholders and leaders on matters of compliance
- Responding to communications from upper management or employees.
- Planning and conducting staff meetings
- Interpreting sales data, customer reviews, and other factors to determine areas for improvement
- Applying critical analysis in decision-making to help increase the organization's value
- Integrating appropriate technology
- Interviewing and observing employees to mitigate problems and come up with innovative solutions
As you might imagine, these responsibilities can apply to individuals working in nearly any industry or field, which is one of the best reasons to consider a career in business management.
Where Do Business Managers Work?
Business managers can find positions in virtually any organization or industry.
While it's common to assume that business managers may only be found in large corporations, they can find work in a much more extensive range of environments.
Below are some of the most common places of work for business managers:
- Restaurants
- Non-profit Organizations
- Construction
While the typical business manager works in-house within an organization, many others serve as independent consultants.
One thing to consider is that getting your Bachelor’s Degree in Business Management doesn’t mean it’s the only potential career for you.
The skills and abilities you’d develop during a B.S. in Business Management Program would lend themselves to many other careers, including roles like:
- Actuarial analyst
- Corporate investment banker
- Data analyst
- Forensic accountant
- Insurance underwriter
- Project manager
- Stockbroker
And should you decide to complete a Master's Degree in Management, you’d be suited for more senior-level, leadership roles, including jobs like:
- Healthcare administrator
- Information systems manager
- Marketing executive
- Chartered management accountant
- Supply chain manager
- Strategy manager
If you’re interested in helping organizations improve their operations and ensure profitability, then business management could be the perfect field for you.
Should You Pursue a Career in Business Management?
Deciding to pursue a career in business management depends on what you enjoy, what you are good at, and what you want to accomplish in terms of your professional goals.
If you have enjoyed successful leadership roles in the past, or if you’re simply interested in learning how to become an effective leader, then business management could be the right choice for you.
Virtually every organization or company needs a business manager, and many of them need several to run different units, departments, or divisions of the company. That means you can find employment as a business manager in pretty much any industry you are interested in, like hospitality, technology, or healthcare.
One compelling reason to study this field is that the skills you learn during your degree program are incredibly transferable. In other words, you'll learn about concepts related to finance, statistics, economics, and even psychology that will make you a manager capable of solving real-world problems.
Accordingly, pursuing an education in business management should lead to developing a versatile set of knowledge and skills that provides you with a range of professional opportunities.
Demand for Business Managers is Projected to Continue Growing
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , employment in management occupations, including the types of roles that are perfect for business management graduates, is expected to grow around 8% by 2031, resulting in nearly a million new jobs. These management positions will be available across a wide range of industries.
Below are the projected growth rates for four of the fastest-growing, relevant positions:
- Medical and Health Services Managers - 28% projected growth
- Financial Managers - 17% projected growth
- Social and Community Service Managers - 12% projected growth
- Public Relations and Fundraising Managers - 8% projected growth
Knowing that the demand for business managers will continue to grow over the coming decade means that your skills should be incredibly relevant to a wide range of jobs, providing you with lots of potential career opportunities.
Business Managers Are Critical to Organizational Success
Business managers play a critical role in ensuring the success of their organization. These professionals monitor and manage everything from budgets to human resources, so their importance cannot be overstated.
Regardless of the industry or organization type, a business manager is most likely involved in running things behind the scenes, planning projects, overseeing budgets, and making the strategic day-to-day decisions that lead to real business success.
Some of the most critical daily tasks that business managers are asked to handle include:
- Ensuring compliance with laws and industry regulations
- Maintaining high standards of operation
- Designing and implementing innovative solutions
- Overseeing budgeting and purchases
Without a capable business manager at the helm of day-to-day operations, organizations are at risk of failing to preserve their operational capacity and profitability.
In this way, the business manager plays a significant role in the process of ensuring an organization’s success, which is what makes this such a great role for anyone looking to have a significant impact on their work.
Business Managers Have Excellent Earnings Potential
Highly skilled business managers are a valuable addition to any organization, and earnings tend to reflect that. Business managers often out-earn other members of an organization, thanks to their critical position.
Recent BLS statistics indicate that the salary expectations for managers in a variety of industries are quite high. The median annual wage for occupations in management as of May 2021 is $123,370 - the highest salary recorded in the BLS database of major occupational groups.
The top-earning positions within management are:
- Computer and Information Systems Managers - 2021 Median Pay: $159,010
- Architectural and Engineering Managers - 2021 Median Pay: $152,350
- Advertising, Promotions, and Marketing Managers - 2021 Median Pay: $137,900
- Natural Sciences Managers - 2021 Median Pay: $137,900
- Financial Managers - 2021 Median Pay: $131,1710
Other management positions in different industries see similarly high wages, so don’t feel like you have to choose one of these areas when it comes time to choose a career specialty.
Once you’ve developed the skills needed to succeed in business management, your knowledge and abilities will transfer easily to a role in nearly any industry, so you can feel free to pursue a career in whatever field is of particular interest to you.
Keep in mind that higher wages come with more experience and education, and that to maximize your earnings potential, you might want to consider completing a Master's of Science Degree in Management.
How to Launch Your Career in Business Management
The best way to start a career in business management begins with earning your degree in the field.
A good business manager is expected to be well-rounded and capable of directing multiple departments within an organization. They should have a solid understanding of economics, statistics, and marketing.
The reason it’s so important to develop your abilities in all these different areas is that business managers are often expected to oversee the work of several people, teams, or departments while maintaining the profitability of the organization.
These concepts - and how they interact in business - are significant areas of study which you’ll focus on during courses in business management. Obtaining your degree proves to potential employers that you have spent the time required to develop your abilities and knowledge in these areas, proving that you’re prepared to take on the difficult role of a business manager.
To increase the odds of launching a successful career in business management, consider enrolling in CSU Global's 100% online Bachelor's Degree in Business Management or our online Master's of Science Degree in Management .
These programs will provide you with everything you need to jumpstart a successful, lifelong career in the exciting and challenging field.
Should You Get Your Business Management Degree Online?
Yes, you should consider getting your business management degree online with CSU Global.
Our accelerated programs are delivered 100% online, so you've got more freedom and flexibility than you would with a traditional on-campus program.
Juggling family and work responsibilities while pursuing a degree can be challenging, but our online courses provide you the freedom to study when it's convenient for you.
Here are a few other advantages you can look forward to if you choose to enroll in one of our online programs:
- Accelerated 8-week courses
- Monthly class start dates
- The freedom to attend your virtual classes from anywhere in the world
If you're ready to get your degree, but require flexibility, then our 100% online programs are the perfect way to complete your educational goals.
Why Should You Pick CSU Global's Online Business Management Program?
Our online business management degree programs are designed to provide you with all the knowledge, skills, and abilities you need to launch or advance your career as a successful business manager.
You can count on your degree being respected in the workforce, as both programs are regionally accredited by the Higher Learning Commission and ACBSP Accredited by the Council of Business Schools and Programs .
In short, if you’re serious about becoming a professional business manager, you’d be hard-pressed to find better options than the programs provided by CSU Global.
Reasons to Choose our B.S. in Business Management program
Our Bachelor’s of Science Degree in Business Management program will provide you with the foundational knowledge you need to drive organizational success by training you to become an effective, skilled, and analytical manager in a professional setting.
This program currently holds several excellent rankings, including:
- A #3 ranking on The Best Online Bachelor’s in Business Intelligence from The Best Schools .
- A #10 ranking on 50 Best Online Business Administration Degrees from Online Schools Report .
- A #10 ranking on Top 15 Online Bachelor's in Business Administration Programs 2021 from Best College Reviews .
Reasons to Choose our M.S. in Management program
Our Master’s of Science Degree in Management program will train you to become a business leader by providing you with the abilities to analyze, communicate, and make effective and strategic business decisions.
This program holds several impressive rankings too, including:
- A #1 ranking on Top 25 Best Online Master’s in Management for 2020 from Best Masters Programs .
- A #1 ranking on Top 25 Best Value Online Master's in Management Degrees for 2020 from Value Colleges .
- A #6 ranking on 15 Online Master’s in Management (MIM) Degrees for 2020 from Great Business Schools .
Obtaining your Master’s Degree in Management will ensure that you’re prepared to move into upper management and executive-level positions.
Furthermore, your degree from CSU Global is sure to impress potential employers since we’re regarded as an expert in higher education, and because we hold several excellent rankings, including:
- A #1 ranking for Best Online Colleges & Schools in Colorado from Best Accredited Colleges .
- A #1 ranking for Best Online Colleges in Colorado from Best Colleges .
- A #10 ranking for Best Online Colleges for ROI from OnlineU .
Finally, to help reduce your costs, we offer competitive tuition rates and a Tuition Guarantee that ensures your affordable tuition rate won't increase for as long as you remain enrolled as a student with us.
To get additional details about our fully-accredited, online Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees in Business Management, please give us a call at (800) 462-7845, or fill out our Information Request Form .
Ready to get started right away? Apply now!
What is Business Management? And Why It Can Be a Great Career Choice
- Share on Facebook
- Follow us on LinkedIn
- Share on Pinterest
- Share via Email

What is Business Management?
Business management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the activities of a business or organization to achieve its goals and objectives. It involves overseeing all aspects of a business, from finance and operations to marketing and human resources. Business managers must be skilled in leadership, communication, and problem-solving, and must be able to make strategic decisions that drive the success of the organization.
Every Organization Needs Leaders
Not everyone can be a leader or manager at work, and many people don’t want the responsibilities of overseeing employees and processes. Fortunately, others feel called to work in management roles and want to make a meaningful impact on their teams and their employers.
Some managers go through company training to learn the skills they need. Others who are new to management “learn by doing,” having to figure things out as they go. Some entry-level managers start the job with formal management education under their belts, which helps them be more confident in their supervisory roles.
Associate Degree in Business Management
If a rewarding career in management is on your life’s bucket list, here’s something that can help you conquer that goal: Get a degree in business management.
The University of Cincinnati Online offers an Associate of Business Management Technology (BMTN) degree program that’s focused, flexible, and designed for today’s modern students.
Our BMTN program prepares you to move into an entry-level supervisory or management position in a wide variety of business settings, with a format that allows you to:
- Study part or full-time . If you attend full-time, you’ll get your associate degree in two years. Your time in the program will move quickly, and you’ll have your degree before you know it.
- Earn a degree online . 100% of the courses are offered online, and there are no campus visits required — a big time-saver for you.
- Learn on your schedule . If you want to study on weeknights or prefer the weekend, the program gives you the flexibility you need to balance your studies with work and family obligations.
- Get the support you need . Our program is 100% engineered for your success. You learn from experienced educators and get access to helpful tools and technical support. We pair you with a Student Success Coordinator who’s with you from enrollment to graduation — they’ll be your biggest champion.
Business Management Curriculum
Our program curriculum is expertly designed to help you excel in the business world. You’ll complete a minimum of 60 credit hours to graduate, studying subjects that include Entrepreneurship, Financial Accounting, Introduction to Marketing, Personal Selling and Sales Management, and Fundamentals of Human Resources.
Completing UC Online’s business management degree equips you with skills that are highly sought after by employers, such as:
- Effectively communicating in a business setting
- Analyzing scenarios and drawing suitable conclusions
- Demonstrating effective team management skills
- Executing the four functions of management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
- Using critical thinking skills to solve problems and make decisions based on accepted business principles
Managers Are in Demand Today
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) expects employment in management occupations to grow 8% between 2021 to 2031, faster than the average for all occupations. With a projected 883,900 new positions opening up, the opportunities for you to work in management are broad.
If you do some research online, you’ll see a variety of entry-level manager positions, including jobs like these:
- Assistant store manager
- Sales support manager
- Assistant office manager
- Customer relationship manager
- Shift manager
Ready to Grow Your Management Expertise?
A career in business management can offer a range of opportunities for personal and professional growth. With the right education and experience, individuals can develop the skills needed to succeed in this challenging and rewarding field. From leading teams and making strategic decisions to navigating complex business environments, business management requires a diverse set of skills and a commitment to lifelong learning.
Pursuing a degree in business management can be a great way to kickstart your career or take your next step in leadership. Whether you aspire to be an entrepreneur, a corporate executive, or a community leader, an associate degree in business management can help you achieve your goals and make a positive impact on the world around you.
The UC Online staff is ready to answer your questions about the Associate of Business Management Technology program. You can connect online with an advisor , or call our associate degree specialists’ team at 833-556-7877 .
We look forward to helping you manage and lead!

Sign up for updates from UC Online
- Name * First Last
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Notice of Non-Discrimination
- Privacy Policy
- Clery and HEOA Notice
- eAccessibility Concerns
© 2024 University of Cincinnati Online Copyright Information
Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business Reflective Essay
Introduction, learning outcomes, key trends in international business, interpretation of the environment, the course and my future career.
Management as a business concept refers to the “on going process that evaluates and controls the business and the industries in which the company operates”. This means that management is undertaken by both the government and the industries or firms operating in a given economy in order to ensure overall economic growth or success.
At the firm level, the managers must evaluate their ability to compete existing and potential competitors. They must also set achievable goals, given their resources and potentials. At the government level, management involves planning for economic development, regulation of industries and supporting emerging industries in order to ensure success.
The management decisions made by both the government and individual firms have a great impact on international business strategy development. This paper is a reflection on the course on management with a focus on international business strategy.
Management is an integral part of developing international business strategy since it determines the approaches used to make decisions, allocation of resources and the ability to achieve the organizational goals and objectives. In regard to the course, learning about the significance of globalization, integration of emerging markets and industrial distributions and their significance on firms was the most appealing aspect of the course.
In particular, the knowledge I gained from the course can be explained as follows. To begin with, globalization has become a key aspect of business environment and will continue to influence critical decisions made by businesses. As the world economy develops, the decisions made by individuals are highly influenced by global trends.
For example, as free trade and open market systems emerge, firms must focus on producing products that meet international standards in order to maintain their competitiveness. One of the major factors that have contributed to globalization is the rapid integration of emerging markets. As countries integrate their markets in order to maximize their synergies, opportunities arise for individual firms.
Such opportunities include a large market, access to cheap labor and raw materials as well as limited regulation. However, integration of markets is also associated with challenges such as high competition and unpredictable business environment. This means that firms must understand the dynamics of the international markets and evaluate their ability to compete in such markets effectively in order to succeed.
Globalization and market integration has led to the rapid growth of multinational corporations. The multinational corporations focus on operating in several countries. This helps them to achieve economies of scale, increase their market shares and profits. However, they also pose high competition especially to the small and medium sized firms at the domestic market.
In many cases, the small and medium sized companies fail within five years of their inception due to their inability to compete in the market. Consequently, internationalization as an expansion strategy is being witnessed as an emerging trend among the small and medium sized firms.
The strategies used by governments to ensure economic growth include industry cluster programs as well as direct financial and nonfinancial support to industries that make significant contributions to economic growth. Such support enables local firms to compete effectively.
Competition
International business is characterized by intense competition as more and more forms join the international market. The presence of cut throat competition is a direct threat to the survival of businesses. Thus managers must be able to evaluate existing and potential competition.
In response to the intense competition, most firms are focusing on internal reorganization as a strategy of creating competitive advantages. Internal reorganization does not only involve changing the management and leadership styles but also involves making significant changes to production methods. The aim of such reorganization is to reduce costs and improve product quality.
Most firms are currently focusing on flatter organizational hierarchies in order to improve efficiency in regard to decision making and strategy development. The customers have become the focus of most business strategies since close relationships with clients helps in overcoming the competition.
Basis of Competition
Owing to the intense competition associated with most markets, firms have found it worthy to focus on a unique way of production that will increase their competitiveness. Besides, each firm normally chooses a strategy that determines the way it will act in the market with the aim of improving its competitiveness.
Firms normally adopt one or a combination of the following strategies at the international market. First, a firm can adopt a differentiation approach to guide its behavior in the market. In this case, the firm targets several market segments with differentiated products. The differentiation helps the firm to position itself as the best in the market.
Second, a firm can adopt a cost based approach. This means that the firm will focus on reducing its production costs with the aim of reducing the price of the final product. By selling at a lower price, the firm will be able to penetrate the market and increase its market share and profitability.
Finally, a focus or niche approach can be adopted to enhance the competitiveness of a firm. It involves concentrating on a particular segment of the market and satisfying the existing needs. These trends indicate that a manager must know the appropriate behavior to adopt for its firm in order to succeed.
Information and Technology
Having the right and accurate information concerning the market and the customers’ needs is a key determinant of the success of a business. Thus future managers need to know how to adopt organizational learning and appropriate technology in order to get the correct information to anchor their strategies.
An effective organizational learning must promote continuous expansion of both the managers’ and their employees’ knowledge. New and better patterns of thinking should be encouraged in the process of strategy development. This will enable managers to develop strategies that are unique in the international market.
The manager should also encourage collective aspiration inline with the overall international strategy. Such shared inspirations help in achieving success. The use of advanced communication and information technology leverages organizational learning.
Currently, the use of e-commerce is a common trend in international business. Most multinational corporations use ecommerce to execute activities such as marketing, sales, and customer service. The main advantage of technologies such as e-ecommerce is that they help in gathering first hand information about the market within a very short time and in a cost effective manner.
Regulation refers to the “administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities”. Managers need to know the regulation trends in the markets in which their businesses are operating. This is due to the fact that regulation dictates the quality of products to be maintained, ownership of businesses, the rights of foreign and domestic firms as well as the level of competition.
Despite the fact that integration of markets and formation of free trade agreements focus on liberalizing markets, regulation is still high in various industries at the international level. It is likely that high regulation will continue to influence international markets in the foreseeable future.
Even though regulation focuses on promoting healthy competition and best practice in international business, it also constrains the expansion capabilities of firms. The emerging economies such as China and India for instance are using protectionist policies to protect their domestic firms from intense competition from their foreign counterparts.
Such policies represent entry barriers to foreign firms since they limit the abilities of the foreign companies to join international markets. The concern about environmental degradation has also led to intense regulation of businesses especially in the manufacturing sector.
Companies are not only expected to avoid polluting the environment but are also expected to participate in its conservation. This represents an increase in the overall costs of operating in a given market. In some industries such as aviation, firms are charged regular fees for the pollution resulting from their operation.
Failure to adhere to the rules used to regulate the industries normally result into severe consequences such as fines. Thus managers must take into account the level of regulation associated with the markets they intend to join in order to develop effective strategies.
Interpreting the business environment involves evaluating the significance of both internal and external factors affecting the performance of a business. Prior to interpreting the business environment, the firm must conduct an environmental analysis in order to understand the environmental factors accordingly.
The most commonly used tools in the analysis include SWOT analysis, Porter’s five forces analysis and PESTEL analysis. The SWOT analysis focuses on evaluating the strength and weaknesses of the firm. It also helps in determining the threats and opportunities available to the firm.
The Porter’s five forces analysis involves evaluating the competition associated with a particular market. The PESTEL analysis helps the firms to study the factors associated with the macro-environment and their effects on businesses. The results of the analysis obtained using the mentioned tools can be interpreted in the following criteria.
Suitability
The environment can be interpreted as either suitable or unsuitable. The interpretation depends on whether the environmental factors make any economic sense or not. For example, availability of good transportation infrastructure is suitable for business success.
Suitability is also determined by the economies of scale or economies of scope associated with the environmental factors. Finally, the environment will be considered suitable if the organization is capable of operating in it with the available resources.
Feasibility
Joining or operating in a given business environment is associated with some costs. For example, joining the international market through foreign direct investment requires the capital to establish new branches.
The costs involved in operating in a given market are justified by the expected returns and the available resources. Thus operating in a given market will be considered feasible if the existing resources will be sufficient and the expected returns will cover the costs and other revenue needs of the organization.
Acceptability
This refers to the possible reactions of various stakeholders such as the workers, customers, community and the shareholders. Acceptability can be interpreted in terms of the expected returns to shareholders’ investment, the overall performance of the business and the risks associated with the environment.
The expected returns are the benefits that will be available to various stakeholders as a result of operating in a particular business environment. For example, shareholders will accept an environment that will enable them to increase their wealth. The employees on the other hand will accept an environment that will guarantee them career progression and job satisfaction.
The risks refer to the “financial and nonfinancial consequences associated with operating in a given business environment”. The financial risks for instance include the chances of incurring huge loses while nonfinancial risks include natural disasters such as floods which can adversely affect businesses.
This discussion indicates that analyzing the business environment alone is not important if the results of the analysis are not interpreted correctly. Thus managers must know how to interpret the environment in which their businesses operate in order to make the right decisions.
This course will help me in my future career in the following ways. First, the concept of globalization and integration of markets will help me in developing strategic plans. Having understood the significance of globalization in terms of its merits and demerits in a business environment, I will be able to make the right decisions in regard to strategic planning.
Second, the course will help me in evaluating business opportunities as well as developing effective strategies of exploiting such opportunities. By being able to evaluate and interpret the business environment correctly, I will be able to choose the right business opportunities.
Besides, I will be able to make the necessary trade-offs in regard to resource allocation in an attempt to achieve the business objectives using the available resources. Finally, the course will enable me to understand the role of government intervention in the economy through programs such as industry clusters. Thus I will be able to indentify the benefits and risks associated with the government’s role in the economy.
The above discussion indicates that development of international business strategies is influenced by the management decisions made by both the firms and the governments. The main futures that managers need to know in developing strategies in future include technological advances, competition, the basis of competition and regulation.
Managers usually interpret the business environment in terms of its suitability, feasibility and acceptability. Correct interpretation of the business environment helps in making the right decisions. This course will thus help me to evaluate the business environment and develop effective strategies.
Akoorie, M., & Scott-kennel, J. (2005). International business strategy: a new Zealand perspective. New York: Pearsons.
Chen, X. (2009). State intervention and business group performance in China. New York: ProQuest LLC.
Choi, H., Clarke, J., & Ferris, S. (2009). The effects of regulation on industry structure and trade generation in the US security industry. Journal of Banking and Finance,33(8) , 1434-1445.
Diego, Q., & Claver, E. (2009). Types of diversification and firm resources: new emperical evidence from the Spanish tourism industry. International Journal of Tourism Reserach, 23(1) , 35-46.
Disney, R., & Haskel, J. (2003). Restructuring and productivity growth in UK manufacturing. Economic Journal, 113(489) , 666-694.
Filip, A. (2009). the effect of globalization in union bargaining and price-cost margins of firms. Review of World Economics, 145(1) , 13-36.
Hargrous, k., & Smith, M. (2008). The advanateg of nations. London: Earth-Scan.
Hunter, J. (2010). Determinats of business success under hypocapital. Journal of Business Research, 56(2) , 113-120.
Kahai, S., & Simmars, W. (2005). The impact of globalization on income inequalities. Global Business and Economic Review, 7(1) , 1-15.
Kent, G. (2009). The importance of internal integration for a successful external integration of the supply chain. Business Logistics in Modern Management, 9(1) , 45-54.
Lee, K., & Olekalis, N. (2010). Nowcasting bsuioness cycle dataing and the interpretation of new information when real time data are available. Economics Review, 10(1) , 17-23.
Machkova, H. (2005). Actual trends in international marketing. Journal of Marketing Management, 20(2) , 47-70.
Upmann, T., & Stahler, F. (2008). Market entry regulation. Review of International Economics, 16(4) , 611-626.
Wright, R. (2000). Trends in international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 1(1) , 109-123.
Xie, W.-J., Gu, G.-F., & Zhou, W.-X. (2010). The growth of primary industry and the population of China’s counties. Statistical Mechanics and its Applied, 389(18) , 3876-3882.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 21). Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-reflections/
"Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business." IvyPanda , 21 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/management-reflections/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business'. 21 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-reflections/.
1. IvyPanda . "Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-reflections/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Importance of The Management Decisions in Every Business." December 21, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-reflections/.
- Some Youth Sports Are Too Intense
- Emerging Markets for International Businesses
- International Business in Emerging Economies
- Emerging Markets: Opportunities and Development
- Vertical vs. Horizontal Integration for Competition
- International Business in Emerging Markets: Videos
- K-12 Intense Study Skills Program Evaluation
- Talents and Competition in Emerging Markets
- Managing Emerging Technologies
- Expansion of Large Food Retailer into Emerging Markets
- Factors Critical to the Implementation of Second Order Change
- Memo to Recommend Plan Change
- Managing Innovations and Entrepreneurship
- Individual Strategic Development
- Human Resources Professionals Associations: The Advancement of HR Skills and Knowledge
Essay on Management: Top 9 Essays
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Management’ for class 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraph, long and short essays on ‘Management’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Importance of Management
1. Essay on the Introduction to Management :
Management is a vital aspect of the economic life of man, which is an organised group activity. It is considered as the indispensable institution in the modern social organisation marked by scientific thought and technological innovations. One or the other form of management is essential wherever human efforts are to be undertaken collectively to satisfy wants through some productive activity, occupation or profession.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is management that regulates man’s productive activities through co-ordinated use of material resources. Without the leadership provided by management, “the resources of production remain resources and never become production”.
In the words of Drucker manager is the life-giving dynamic element in every business. Productive resources-men, money, materials-are entrusted to the organising skill, administrative ability and enterprising initiative of the management.
Modern business is the complex scene of forces of change constantly at work. The size, strategy, structure, motivation of modern enterprises underline the need of creative touch in successfully piloting their affairs. New products, new methods and techniques appear day-after-day to cater to the ever-changing trends of consumers’ tastes and needs. The ceaseless competitive drive to capture markets necessitates intellectual handling of refined requirements of consumers.
Management today is not just an exercise of blind authority or bossism but it implies scientific thinking, accurate planning and meticulous control to ensure quick and better results. Management has become a profession in view of the modern business becoming more sophisticated.
As ownership gets divorced from management, specialisation in business operations becomes more marked. Proprietors, shareholders and even their directors remain comparatively in the background and experts specialising in delicate and intricate matters of industrial techniques play increasingly positive and prominent role in running the business. Professional experts like engineer, scientist, market surveyor, trained executive, researcher, technician, occupy important place in running the affairs of an enterprise today.
Management now a days, therefore, consists of cadre of experts who performs a profitable job to build-up the competitive strength of the firm and they strive to “develop and expand the assets and profits” of the proprietors. According to Drucker, “Management, which is the organ of society specially charged with making resources productive, that is, with the responsibility for organised economic advance, therefore, reflects the basic spirit of the modern age.”
2. Essay on the Meaning and Definition of Management:
It is not an easy job to give the exact meaning of management.
Different writers have used the term “Management” in different senses, which will be clear from the following discussion:
Management as a Process :
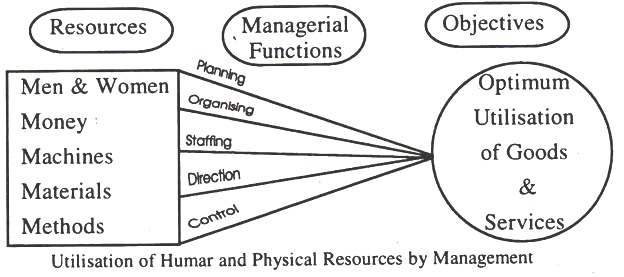
In the words of George R. Terry, “Management is a distinct process consisting of planning, organising actuating and controlling performed to determine and accomplish objectives by the use of human beings and other resources.” The elements of management are: planning, organising, actuating (directing) and controlling.
These are also called the functions of management. It is through the performance of these functions that management is able to effectively utilise manpower and physical resources such as capital, machines, material, etc. to produce goods and services required by the society.
This has been shown in Fig. 1:
Henri Fayol has defined management as a process consisting of five functions: “To manage is to forecast and plan, to organise, to command, to coordinate and to control.”
However, modern authors do not view coordination as a separate function of management. They consider it as the essence of managing. Koontz and O’Donnell have classified the functions of management as follows: planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling. These functions are inter-dependent and interrelated. There is no fixed sequence of their performance. They are performed more or less simultaneously.
Management is regarded a process because it involves a series of functions as shown in:
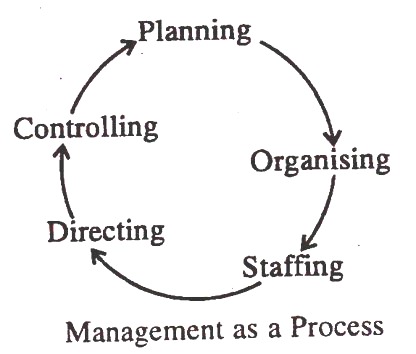
It starts with planning and ends with controlling. But it does not mean that managerial functions are followed in a specific sequence. A manager performs all the managerial functions simultaneously. Moreover, Management is a never-ending process.
There are three features of management as a process:
(i) Management is a social process as it deals with human beings.
(ii) Management is an integrating process as it organises human resources for the efficient use of other resources like capital, materials, technology, machines, etc.
(iii) Management is a continuous process. It is always involved in identifying the organisation problems and solving them.
“Management is the technique of getting things done.”
“Management is the art of getting things done.”
Marry Parker Follet defined management as “an art of getting things done through others”. This is a traditional definition of management. It emphasises that management directs the workers for getting results from them and supervises their performance. The workers are treated merely as a factor of production like materials, machines and capital.
This definition is insufficient in the modern world because of the following reasons:
(i) The above definition is incomplete because workers are treated as a mere means to organisational goals.
(ii) The management tries to manipulate the behaviour of the workers.
(iii) The needs and aspirations of the workers are not considered.
People are not mere cogs in the wheel and so they should not be treated as commodity or mere means to certain ends. Needs and aspirations of the people working in an organisation should not be overlooked. They must be satisfied so as to obtain sustained and consistent effort towards organisational objectives.
Management may be defined as a technique of getting things done through others by satisfying their needs and providing them opportunity for growth and development. According to Harold Koontz, “Management is the art of getting things done through and with people in formally organised groups. It is the art of creating environment in which people can perform as individuals and yet cooperate towards attainment of group goals.”
In order to accomplish results, management must create opportunities, and encourage growth and development of employees and provide guidance and assistance, wherever necessary. All this demands skillful application of the basic principles of the science of management. Managers must have conceptual, technical and social skills in translating the abstract organisational philosophy into concrete action.
Management is the dynamic life-giving element in every organisation. It is the activating element that gets things done through people. It provides the force necessary to transform the resources of a business organisation into desired goods and services. The primary job of management is to convert the disorganised resources of men, machines and materials into a productive organisation.
Management as a Group :
In the words of sociologists, management is a group or a class who together carry out various managerial activities.” Thus, management refers to the group of people in an enterprise who are carrying out management functions.
In other words, all individuals occupying managerial positions are collectively known as management. A manager is a person who performs the managerial functions of planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling.
Since a manager performs the managerial functions, he is a member of the management of the organisation. Used in this sense, management includes all those who manage the affairs of an organisation. But in practice, the term ‘management’ is used to indicate the top management consisting of chairman, managing director or chief executive and Board of Directors.
Management as a Discipline :
As a discipline, management refers to the body of knowledge and a separate field of study. Management is an organised body of knowledge which can be learnt through instructions and teaching. It entails the principles, practices, techniques and skills of management which help in achieving organisational objectives. This discipline is taught widely in schools and colleges in most of the countries of the world.
Management has acquired the status of a discipline because of the following two reasons:
(i) A lot of research is being carried out by the scholars in the field of management. The results of research will be useful for future managers.
(ii) It is a specialised body of knowledge, which is studied and practised in management institutions.
Management as an Activity :
Management is an activity concerned with getting things done through people and directing the efforts of individuals towards a common objective. In the words of Harold Koontz, “Management is the art of getting things done through and with people in formally organised groups.”
Management gets results from the people by satisfying their needs, and expectations, and providing them opportunity for their personal growth. Management is a distinct activity in any organisation which is necessary for the achievement of its objectives.
According to another functional classification management activities are classified as:
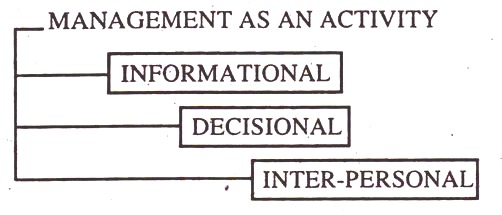
Classification of Management Activities
1. Informational Activities:
Management has to act as a communicative link between subordinates and superiors. On one hand management receives, requests explanations, statements and suggestions from their subordinates and on the other hand it also receives orders and instructions from superiors. In their informational role as managers the requisite information is passed on to both subordinates and superiors.
2. Decisional Activities:
Management being both administrative and executory has to take routine and strategic decisions regarding various operational activities so that the organisation work is executed smoothly. In their decisional role as managers, management can also be termed as innovators, resource allocators, negotiators and crisis managers.
3. Inter personal Activities:
Management being a team work and group activity requires cooperation, coordination and harmonious relationship between individuals and departments. In order to integrate and charrelise best efforts of individuals to attain predetermined objectives of the enterprise, managers in their interpersonal role act as a figure head of the enterprise, as a leader and as a liason.
Other Definitions of Management:
Various writers have given various definitions of the management.
The following are some of the important definition:
According to E.F.L. Brech, “Management is the process of planning and regulating the activities of an enterprise.”
According to Lawrence A. Appley, “Management is the development of people and not the direction of things management is personnel administration.”
According to Koontz and O’Donnell, “It is the task of manager to establish and maintain an internal environment in which people working together in groups can perform effectively and efficiently towards the attainment of group goals.”
According to Kimball and Kimball, “Management embraces all duties and functions that pertain to the initiation of an enterprise, its financing, the establishment of all major policies, the provision of all necessary equipment, the outlining of the general form of organisation under which the enterprise is to operate and the selection of the principal officers. The group of officials in primary control of an enterprise is referred to as “the management.”
According to William Spriegel, “Management is that function of an enterprise, which concerns itself with the direction and control of the various activities to attain the business objectives.”
According to Keith and Gubellini, “Management is the force that integrates men and physical plant into an effective operating unit.”
According to S. George, “Management consists of getting things done through others. Manager is one who accomplishes the objectives by directing the efforts of others.”
According to Newman, Summer, Warren, “The job of management is to make cooperative endeavour to function properly. A manager is one who gets things done by working with people and other resources in order to reach an objective.”
3. Essay on the Characteristics of Management:
The main characteristics of management are as follows:
(i) It is Goal-Oriented:
The important goal of all management activities to achieve the objectives of a business concern. The objectives of the business may be economic, social and humane.
(ii) It is a Process:
When it is used in the sense of a process, it refers to what management does. In other words, it refers to the process of managing, planning, organising, staffing, guiding, directing supervising and controlling.
(iii) It is a Group Activity:
For the success of a business, it is necessary that all human and physical resources are co-ordinated to achieve the maximum levels of productivity. We all know that the combined productivity of various resources will always be higher than the total productivity of each resources.
(iv) Management is Universal:
It is required in all types of organisations, e.g., family, club, university, government, army, business. The basic principles of management are applicable in business as well as in other organisations. However, these principles are flexible and they can be modified to suit different situations.
(v) It is an Art and Science:
It consists of both the elements of science and art. The science of management gives a body of principles or laws for guidance in the solution of specific management problems and objective evaluation of results. The management as an art consists of this use of skill and effort for producing desirable results or situations in specific cases.
(vi) It is a Factor of Production:
Not only the land, labour and capital are of effective use for the production of goods and services but the managerial skills are also used effectively for this purpose.
(vii) Management is Dynamic:
Management denotes is an ever-changing environment, It involves adoption of an organisation to changes in its environment, and modifying the environment for the benefit of the organisation. Therefore, management is a constantly growing process.
(viii) Management is a Profession:
Management is considered to be a profession as it possesses all the attributes of profession as:
(i) A systematic corpus of knowledge,
(ii) A period of apprenticeship, and
(iii) A code of conduct.
(ix) Management is an Important Organ of Society:
Management has become an important organ of society. Management of large scale undertakings influence the economic, social, moral, religious, political and institutional behaviour of the members of the society.
(x) It is a System of Authority:
In every organised group supreme authority must rest somewhere. There should be a clear line of authority from the supreme authority to every individual in the group.

4. Essay on the Nature of Management:
A study of literature of management often gives rise to a question as to whether management is a science or an art. The brief discussion which follows leads us to the conclusion that it is both a science and an art.
Management as a Science :
Science is by definition a body of knowledge gathered by experimentation and observation, artificially tested and expressed in the form of general principles.
Following are the essential features of science:-
1. Systematised Body of Knowledge:
Science being ‘systematic’ is based on cause and effect relationship. It consists of theories and principles which have the capacity to give reasons for past happenings and at the same time, can be used to predict the result of specification in future.
2. Scientific Methods being used:
Personal opinions and individual likes and dislikes don’t influence scientific principles. They are obtained through scientific investigation and reasoning. They are critically tested and can be scientifically proved at any time.
3. Principles based on Experiments:
Observation and testing the validity and truth through experimentation makes a statement, a principle.
4. Universally applicable:
Scientific princAples may be applied in all situations and at all times, exceptions though may be logically explained. These principles, under required given conditions never fail at any place or point of time.
The debate about whether or not managing is a science continues. The answer to this question depends largely on the degree to which the scientific method is used to determine managing principles and solve managing problems.
Management satisfies many of the scientific principles, for e.g.:
1. Management is a systematised body of knowledge. Its principles explaining cause and effect relationship between various variables, e.g., Principle of Unity of Command if not followed leads to inefficiency, confusion and duplication of work.
2. Management principles are evolved on the basis of observation and repeated experimentation. For instance, it is being observed through experiments that if stability in tenure of an employee is not there, his working efficiency decreases.
But, at the same time, there exists many scientific features which do not coincide with those of management.
Briefly, the method of science consists of the following steps:
1. Facts or data are collected in an objective manner.
2. These facts are classified in some way, usually on the basis of similarities or dissimilarities, in an attempt to make the data more meaningful.
3. From the classifications, hypotheses are formulated establishing cause and effect relationships between various given factors.
4. The hypotheses are then tested to determine their reliability and validity.
5. After the hypotheses are verified and if they stand the test of time, they then have interpretive or predictive value when applied to similar phenomena.
In referring to the hope of dream that a true science of management may someday be achieved. Professor Mee states, “This hope probably will be realized in another chapter in another book in another century.” Perhaps the best that can be said is that a science of management is just beginning to emerge.
It has often been stated that even when management attempts to use the method of science (from which managing principles are also derived), management is neither as precise nor as comprehensive as the natural and social sciences.
There are several reasons why this is true:
1. The rational approach and the application of the method of science are relatively new in business and industry. As a result, managing has not developed the comprehensiveness found in other disciplines that have used the scientific approach for a much longer time.
In fact, one of the more significant developments in the last seventy-five years in the field of management has been the tendency toward using the rational approach in solving management problems.
2. Relatively few managers are trained or experienced in using the method of science. Those who are trained may find it too time-consuming and, because of this as well as other limiting factors, seek other ways to reach decisions and to solve problems.
3. Precision measuring instruments and tools are not always available in management. A manager is forced to use relative measurement where absolute measurement is not possible or feasible. To evaluate the performance of a group of supervisors, for example, he may have to use a relative measuring device such as a carefully prepared rating scale. For his purposes, however, the relative measuring technique is just as useful and effective.
4. In the physical sciences, the researcher works with a single variable, holding all other factors constant. Managers can seldom do this. They almost always deal with people, the human element with all its weaknesses. The human element can never be treated as a constant; hence precision is less than in the physical sciences, though equal to that of the social sciences. Businessmen are always dealing with the unpredictable: people, governments and nature.
5. Most importantly, managerial decision-making, unlike problem solving in the sciences, stresses action rather than truth. A manager’s decisions must have practical application. Managers strive for reasonable results under uncertain conditions rather than for perfection. A method, technique, or device only has to be “good enough” to get the job done.
Management as an Art :
Art refers to the skill to put into action a systematized body of knowledge for the achievement of a given task. To get mastery in any skill it is necessary to have the thorough knowledge of the principles of doing the particular task. At the same time it is necessary to possess the tact, the care to be taken, the discretion and proper judgement in applying the principles involved.
Presence of mind, promptness to react to the given situation and correct response demanded by the prevailing condition are all essential to perform skillfully the task undertaken.
Experiences and judgement add to this skill. Management is also an art as it is necessary to apply the principles of management in planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling the whole series of activities all through the managerial process.
Throughout the stages of the process of decision-making and execution of these decisions all the individuals occupying various positions at different levels of management need all the skills involved.
Briefly, these skills are called the planning skills, the organising skills, the staffing skills, the directing skills (how to motivate, to communicate, and to lead) and the controlling skills. Sometimes it is said that a good manager is born and not made. But it has been now established and accepted that it is through learning and training process that skilled managers are developed.
As Koontz and O’Donnell have rightly pointed out the work of managing a business or any group activity is an art. But for this the organised body of knowledge is required. It is certainly a science. Thus art and science are not exclusive terms but complementary ones.
Management as an art has the following features:
(a) Personal Skill:
Human beings apart, there are other factors which vary in their effect and role in the achievement of the managerial tasks. Managers have to apply their skill to deal with them.
(b) Practical Knowledge:
Business enterprises involve risks. Only those who have experience can deal effectively with such risks.
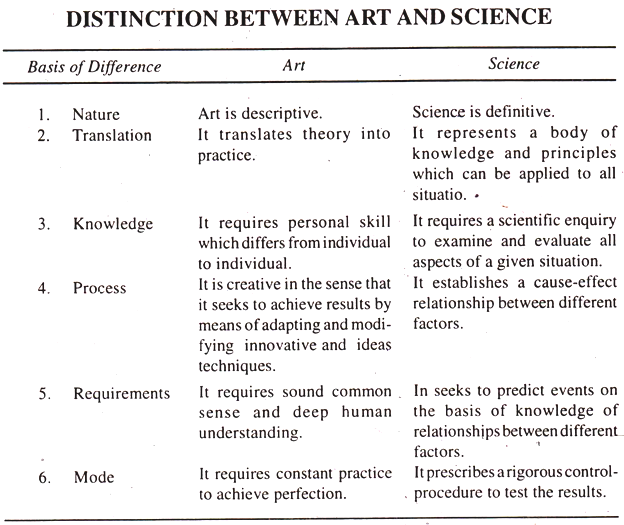
(c) Result Oriented Approach:
Management as an process aims at achieving concrete goals. It aims at utilising available resources optimally by creating a congenial atmosphere.
(d) Personal Judgement:
No doubt there are useful principles of management, but it needs individual judgement to apply them properly and at appropriate time. It means art is necessary.
(e) Continuous Practice:
The art of management is much older than the science of management which as an organised body of knowledge is hardly about ninety to hundred years old.
Management: Both Science and Art :
Management is a combination of an organised body of knowledge and skillful application of this knowledge. According to Brech, “A systematic body of knowledge underlies the competent practice of management”.
Much of this knowledge are to be found in various academic disciplines. Competent performance of various management functions necessarily needs an adequate basis of knowledge and a mature scientific approach.
Thus management is both a science and an art. It is a science because it uses certain principles. It is an art because it requires continuous practice to ensure the best possible result. Thus science and art in management are not mutually exclusive. Both of them exist together in every function of management.
Management as a Profession:
Profession is defined as a composite of intellectual and executive qualities applied to carry out successfully the specified activities for the benefit of others. It is an intellectual field. One enters into it to work without any expectation of a direct share in the profits earned out of the activities to carry out which one might be contributing his specialist knowledge or intellect.
According to George, “Profession is that which has a well-defined body of knowledge, which is learned, intellectual and organised, to which entry is restricted by examination, or education and which is primarily concerned with service to others above self-award.”
Features of Profession:
The above statement makes the following features of profession clear:
1. Existence of a body of knowledge, techniques, skills and specialised knowledge.
2. Formalised methods of acquired training and experience.
3. The establishment of a representative organisation with professionlisation as its goal.
4. The formation of an ethical code for the guidance of its conduct.
5. The charging of fees based on the nature of service extended.
In the light of what has been said above management can be said to be a profession.
The arguments in favour of this statement are given below:
1. Body of knowledge:
All over the world there is marked growth of an organised systematic body of knowledge about management as a process.
2. Formal methods of teaching:
The establishment of professional schools of management in which management as a body of knowledge can be taught is seen everywhere. India is no exception to it as is clear from the establishment of Indian Institutes of Management at Ahmedabad, Calcutta, Bangalore, Lucknow and Postgraduate Departments of Management as well as Institutes/Colleges of Management being established in different parts of the country.
3. Fee as remuneration:
The number of management consultants is increasing Even a large number of well reputed firms are establishing their consultancy agencies.
4. Existence of ethical code:
There is growing emphasis on the ethical basis of management behaviour.
5. Establishment of representative organizations:
Both at the national and international levels management associations have been formed with their membership rules, codes of conduct, etc. All India Management Association, New Delhi.
National Institute of Personnel Management, Calcutta, Institute of Marketing and Management, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, New Delhi, Institute of Costs and Works Accountants of India, Calcutta are the well established associations in India. And many more organisations in the specialised fields/ branches of management are being organised.
Management as Profession: A Controversy :
However, there is no agreement on this point. Questions are asked: Is management a profession? Is it becoming a profession? As it is well known, a large number of business units are operating as sole traders and single entrepreneurship enterprises. By definition and in practice they are managed by proprietor-managers. So is the case with partnership firms and joint Hindu family firms.
But company form of business enterprises in India and corporate organisations in USA and other countries are even by definition the enterprises in which ownership is divorced from management. Even then question remains if all of them are managed by professional managers. As things stand, under law it is the shareholders who elect the Board of Directors from amongst themselves.
Thus the topmost group at the top level management of a company or corporate body are not professional managers. But all the big companies operating on large scale do appoint executives and managers on salary-cum-perks basis. Thus they are the professional managers.
In large companies even the Vice Presidents of marketing, finance, etc. who are on the Board of Directors are the professional managers. So are all those working at the middle level and lower level of management. In case of public undertakings management is in effect with the professional managers. Exceptions to it are Departmental Undertakings such as Railways. Posts & Telegraphs etc. which are controlled by the various departments of the Government.
But there also other than the Minister-in-charge all those looking after the management are professionals. A new trend is becoming more and more marked. Proprietary managers are becoming more interested in acquiring the latest knowledge and technique of management. They are sending their own sons, daughters and other close relatives abroad to acquire degrees and diplomas in management.
Others are joining short- term courses in management run by organisations like Administrative Staff College, Hyderabad. All India Management Association etc. Such persons are now occupying positions at the topmost layers of the managerial hierarchy.
Are these persons to be regarded as proprietary managers or professional managers ? No doubt all the features of profession are not applicable to them. But they do possess other features.
In conclusion, it may be said that all the requirements of profession are not satisfied by managers at the top. But management is, by and large, becoming professionalised, it is more so in the developed nations. But even in India large number of managerial cadres are getting professionalised.
This is applicable to both the public and private sectors. Even the case of smaller enterprises, which are run by proprietary managers, assistance of professionals such as chartered accountants, cost accountants and lawyers are being utilised to a great extent.
5. Essay on the Objectives of Management:
Objectives can be divided into three categories: Individual, Social and Organisational. Recognising the three categories and reacting appropriately to each is a challenge for all modern managers.
(I) Individual Objectives :
Individual objectives are the personal goals each organisation member would like to reach through activity within the organisation. These objectives might include high salary, personal growth and development, peer recognition, and societal recognition.
(II) Social Objectives :
Social objectives deal with the goals of an organisation toward society. Included are obligations to abide by requirements established by the community, such as those pertaining to health, safety, labour practices and price regulation.
Further, they include goals intended to further social and physical improvement of the community and to contribute to desirable civic activities.
It should be noted that most business houses in achieving their primary goals also contribute to their respective communities by creating needed economic wealth, employment and financial support to the community.
(III) Organisational Objectives:
Drucker indicates that the very survival of management may be endangered if managers emphasize only a profit objective. This single-objective emphasis encourages managers to take action that will make money today with little regard for how a profit will be made tomorrow.
In practice, managers should strive to develop and attain variety of objectives in all management areas where activity is critical to the operation and success of the system. Following are the eight key areas in which Drucker advises managers to set management objectives.
1. Market Standing:
Management should set objectives indicating where it would like to b£ in relation to its competitors.
2. Innovation:
Management should set objectives outlining its commitment to the development of new methods of operation.
3. Productivity:
Management should set objectives outlining the target levels of production.
4. Physical and Financial Resources:
Management should set objectives with regard to the use, acquisition and maintenance of capital and monetary resources.
5. Profitability:
Management should set objectives that specify the profit the company would like to generate.
6. Management Performance and Development:
Management should set objectives that specify rates and levels of managerial productivity and growth.
7. Worker Performance and Attitude:
Management should set objectives that specify rates of worker productivity as well as the attitudes workers possess.
8. Public Responsibility:
Management should set objectives that indicate the company’s responsibilities to its customers and society and the extent to which the company intends to live up to those responsibilities.
6. Essay on the Levels of Management:
More of the authors have conceived of three levels of management in any fairly-sized business undertaking.
These are as follows:
1. Top Level Management
2. Middle Level Management
3. Lower level Management
Management is considered as a Three-tier activity. The top tier centres round the determination .of objectives and policies, the middle tier concerned with implementation of policies through the assistance of lower tier of the organisation.
The various tasks in a business enterprise “become structured somewhat like a pyramid, with the highest level of management centred at its apex”.
The managerial set-up of any undertaking, therefore consists of three levels – Top Management, Middle Management and Operating Management or Lower Level Management.
The following chart illustrates Levels of Management in a company form of enterprise of fairly large size:
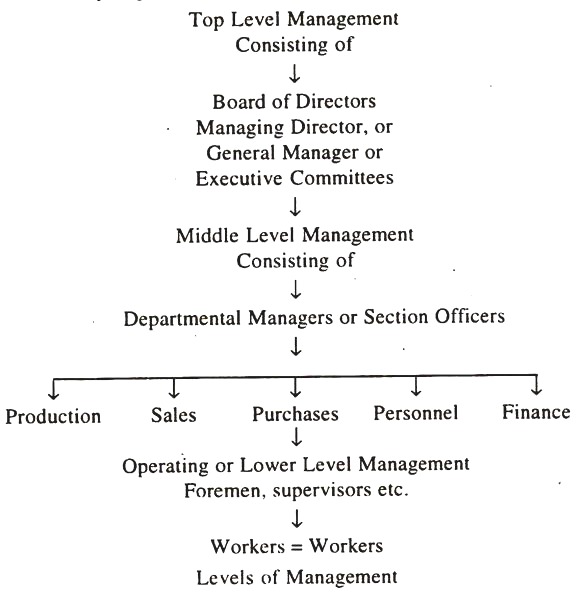
This gradation of level of management is not a watertight arrangement but represents a hierarchy of authority and responsibility designed to secure a systematic sequence of operations. Each level is blended into another through its functions and all the layers of authority constitute an integrated arrangement.
The demarcation of the levels is only to analyse the range of responsibility and span of control and it underlines the principle of specialisation in administrative executive processes.
A. Top Level Management:
Top level management is made up of Board of Directors, its Chairman, Managing Director or General Manager and other key officers responsible for smooth and systematic conduct of the affairs of the enterprise.
The top level management is a concept of functions concerning the manner in which the enterprise should be shaped.
In view of large size of modern companies, the key functions cannot be performed by a single person, and hence a compact group of elected office-bearers, experts and executives form the top management level of enterprises these days. Board of Directors is assisted by Managing Director, General Manger etc. in directing the company’s operations.
Top level management’s work is a creative process and it also involves commitments of high order of responsibility. As Allen observes “top-management work is a work which must be performed at the apex of the organisational pyramid because it cannot be carried out effectively at lower levels.”
Top management is also described “as the policy-making group responsible for the overall direction and success of all company activities.” It is a chief custodian of the property of the enterprise. It is the main mobiliser of resources in men and materials essential for the inception, maintenance, operations and expansion of the undertaking.
It is more basically a panel of planning the company’s operations and in due course shall develop into an evaluating and controlling medium for securing the maximum possible performance. It is concerned with the problems and policies of the entire enterprise.
The functions of top management include:
“Identifying key factors for the survival and growth of the company and devising basic objectives, policies and programmes for dealing with these factors: being sensitive to the inter-dependence of the numerous actions and maintaining a strategic balance in these actions; and keeping an eye on how current activities of the company will cutting with predicted changes-social, political, technological and competitive-and adopting company plans to the anticipated environment.”
Functions of the Managers at the Top Level Management :
The fundamental functions of mangers of the top management may be classified into the following categories:
(1) Determining the objectives.
(2) Framing the policies and making plans to carry out the objectives and policies.
(3) Setting up an organisational framework to conduct the operations as per plans.
(4) Assembling the resources needed to put the plans into operation.
(5) Controlling the operations through organisation.
1. Determining the Objectives :
Objectives are goals which every enterprise seeks to achieve. Most of the companies describe in detail the nature of their activities in the objects clause of their Memoranda of Association. But by and large the general objectives which top management should aim at are survival, profit, business growth, prestige or status and social acceptance.
Production of particular product of specific quality, satisfaction of customer’s needs, earning of profit by production and sales, looking out for expansion and diversification of business, building up an image or reputation of the company in the eyes or estimation of the society are the broad objectives set up by top management.
Objectives also may be specific. They relate to types of activities. Specialty in workmanship, competitive pricing, marketing method, widening the area of sales abroad, relations with the workers, customers, public, government, etc.
2. Framing of Policies :
The objectives are realised through policies framed by the management. Policies signify the decisions taken by the management on different strategic aspects of company’s operations or activities.
Production policy indicates the schedules of production to meet the market demand.
Product policy lays down the standards, specifications, size, design, colour shapes etc. of the product.
Marketing policy describes the channels of selling the product (direct sale or dealership, agency etc.), advertising and sales promotions techniques to be adopted, the sales targets to be attained etc.
Pricing policy emphasises the quality aspect of the product as well as the comparative competitive nature of the rates quoted, discounts allowed etc.
Personnel policy deals with recruitment, placement, training, remuneration, promotion, rewarding and regulating the productivity of the personnel.
Financial policy is concerned with procuring funds required for investment in fixed assets or required to be held over for working capital needs, sources of finance, e.g., borrowing, self-financing, issuing additional capital etc.
Top management has also to devise plans and schemes for precise execution of policies within a given time. Plans set out the course along which operations in different departments are to be conducted as per the criteria laid down in the respective policies.
production schedule, sales campaign, financial arrangements, personnel motivation have to be drawn as to focus and guide the activities of the company in the direction of the realisation of the basic objectives.
3. Organising:
Organisation means division of functions, allocation of duties to the personnel, fixation of range of their responsibility and the scope of their authority and coordination of the activities of the departments of the undertaking. Standardisation of administrative procedures is the main task of organising the enterprise.
Systems and procedures are the methods intended to govern the departmental activities of a company. Organisation ensures smooth flow of work from one stage to another, or from one department to another, so that the whole undertaking is enabled to achieve the targets to the benefit of the company and satisfaction of customers.
4. Assembling the Resources:
Prior to the launching of the plans, the resources of money, men and materials have to be assembled. Executives and operatives are appointed after careful selection on the basis of their merits and the nature of jobs to be handled.
Money capital has to be raised through issue of shares, debentures, etc. and arrangement for working capital has to be made through reserves, bank advance etc.
Then the physical resources-machinery, tools, furniture, buildings, water supply, power, other ancillary equipment-have to be collected as per estimated needs. The management has to find out the sources of finance for implementing the plans and programmes.
5. Controlling :
Top level management does not directly execute work. But the Chief Executive in the top management has the responsibility of exercising supervision over all the departments to make sure that the middle and lower managements are functioning as per the plans.
By controlling we mean instituting checks or comparisons of actual results with the planned targets. It implies evaluation or measurement of the work turned out in each section or department with reference to the goals envisaged in the basic plans and policies of the company.
The top level management lays down the standards of performance for the purpose of comparison of the actual results with the planned performance. Standard cost per unit, sales quotas, net profit per unit of sales are some of the reliable criteria for comparison.
Top level management finds out to what extent the performance has been upto the mark and identifies in the course the sources of strength and weakness in the different phases of organisation and operations.
Top level management has to act as coordinator and regulator of the activities of the undertaking in its different dimensions. It will call for reports, statistical data, special studies, accounting records to know the position of performance and to apply regulatory checks wherever and whenever necessary.
B. Middle Level Management:
Middle level management is concerned with the task of implementing the policies and plans chalked out by the top management. Middle management comprises departmental heads and other executive officers attached to different departments.
These departmental managers and officers are expected to take concrete steps for actual realisation of the objectives and operational results visualised in the plans finalised by the top officers of the organisation. “This group is responsible for the execution and interpretation of policies throughout the organisation and for the successful operation of assigned division or departments.”
Managers at the middle level management level exercise the usual functions of management in respect of their own departments. They have to plan the operations, issue instructions to their assistants, collect the resources required and control the work of the men under them and evaluate the results achieved by their department with reference to the plans formulated by the top management.
If the top management is endowed with the authority of policy-making, middle management is entrusted with the programming of efforts essential for implementing the basic pre-determined policies.
Functions of Managers at the Middle Level Management :
The functions of the managers at the middle level management can be broadly summarised as follows:
(i) Interpretation of policies framed by top level management.
(ii) Preparing the organisational set-up in their departments for fulfilling the objective implied in various business policies.
(iii) Finding out the suitable personnel and assigning duties and responsibilities to them for the execution of the plans of the concerned departments.
(iv) Compiling detailed instructions regarding operations and issuing them to the assistants and operatives to focus and guide their efforts accordingly.
(v) Motivating the personnel for higher productivity and rewarding them for their merit, capacity or calibre.
(vi) Cooperating with other departments so as to evolve a smoothly functioning organisation.
(vii) Collecting reports, statistical information and other records about the work turned out in respective departments and forwarding the same with their observations to the top level management.
(viii) Recommending to the top management, new or revised policies for their departments to secure better performance.
Middle level management managers are responsible for all the leading functions within each department. They provide “the guidance and the structure for a purposeful enterprise”.
The top management’s plans and ambitious expectations cannot be fruitfully realised without the key officers at the middle level management.
Managerial Structure at the Middle Level Management :
Generally the following functions at the middle level management are performed through the various departments under the departmental managers or heads.
1. Production department headed by works manager is concerned with the following functions:
(i) To collect the work orders and issue them to concerned sections.
(ii) To guide the foremen, and prescribe methods and process to be followed in execution of the work allotted.
(iii) To devise a system of inspection of factory functioning, the components, semi-finished and finished products.
(iv) Assembling the tools, equipment, plant, qualified personnel etc. to execute the production’s plan.
(v) Controlling the factory expenses.
2. Engineering Department headed by chief engineer has to perform the following functions:
(i) Production-planning, routing, scheduling.
(ii) Plant layout suited to the execution of production plans.
(iii) Designing the products, their specifications, standards, quality, workmanship etc.
(iv) Research in methodology of production for improving technical efficiency.
(v) Plant and tools maintenance and development of the full capacity of production.
(vi) Economy in production costs and resource consumption.
3. Personnel Department:
It is headed by the chief personnel officer, labour officer. He has to devise selection procedure and training schemes: he has to maintain service records of the staff and formulate methods of remuneration in conformity with the productivity and cost of living. He has to assure wholesome working conditions to the personnel and look after their social and economic security and welfare.
4. Stores Department headed by stores manager is concerned with systematic organisation of purchasing raw materials, stores articles, tools, equipment, spare parts, etc. and proper custody of the materials with the responsibility of issuing them to the requisitioning departments.
He has to sort and arrange neatly the stockpile of materials etc. and keep an up to date record of materials, stores, tools, etc. received, issued, consumed, balance held in stock, etc.
5. Office Manager is in-charge of secretarial work of correspondence, filing, indexing, use of office appliances, maintenance of records and reports pertaining to the different departments.
6. Accounts Department:
The chief Accountant is responsible for maintaining up-to-date accounts of financial transactions and recording sales, purchases, receipts and payments.
He is also required to compile periodically the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance sheet of the firm.
He should ensure that monthly financial statements indicating the position of the firm are placed before the Board and other top management officials.
7. Costing Department:
In bigger enterprises a separate department for costing is constituted and cost accountant is appointed to administer the functions of the section.
Costing department is entrusted with the main functions of ascertaining the prime and supplementary costs and submission of cost-sheets to the top level management for appraisal.
Costing department keeps detailed records of costs of completed jobs in progress, costs of materials, labour, factory overhead costs and sales on cost. It helps the management to find out the disparity between estimated costs and actual costs and the reason thereof so that remedial measures can be adopted.
8. Sales Department:
This section is the life-blood of the enterprise because the sales are the barometer of business profits and reputations of the firm. The work of the department is to create demand for the goods for promoting maximum possible sales at quick pace in wider markets.
The vital functions of the department are as follows:
(i) Market research to find out the needs, tastes and buying habits of the consumers.
(ii) Looking out for new markets for the goods.
(iii) Organising advertisement campaigns and other sales promotion activities for creating, maintaining and expanding the demand.
(iv) Collecting orders from the customers through agents, dealers or salesmen.
(v) Executing the orders by timely despatch of goods.
(vi) Supervision of salesmen’s efforts, training and stimulation of salesmen.
(vii) Organising after-sale service and similar sales promotion efforts.
(viii) Looking after proper warehousing, packing and despatch of goods.
(ix) Attending to customers’ complaints and suggestions.
C. Lower Level Management (Operating Management) :
It is described as the lowest level in the administrative framework and actual operations are the responsibility of the rank and file constituting this level of management.
Foremen, supervisors and sub-departmental executives assisted by a number of workers, clerks etc. carry out the actual operations as per schedule. Their authority and responsibility is limited and they have to follow the lines drawn by the higher levels of management.
The plans and policies of the top level management will fail if the foremen and operatives do not fully realise the spirit of sustained work. The quality of the workmanship and quantity of output will depend on the hard labour, discipline and loyalty of the operating personnel. The foremen or supervisors are responsible for executing the work orders allotted to their respective sections.
They pass on the instructions of middle level management to the working force, procure the materials, tools etc. required for the jobs, assign specific duties to individual workmen and guide them in acting upon the instructions and handling the job on hand with ability and accuracy.
They seek to maintain precise standards of quality, prevent wastage of materials by negligent workmen, look to the safety of machines and equipment and ensure steady flow of output as per plans and programmes prescribed by the top level and middle level managements.
They are also responsible for maintaining discipline among the respective batches of workers, preserving and boosting their morale and fostering the team spirit in them.
7. Essay on Theo Haimann’s Three Notions about Management:
According to Theo Haimann management is used in three different senses:
(i) It is used as a noun. It refers to the group of managerial personnel of an enterprise.
(ii) It refers to the processes of managing, planning, organising, staffing, guiding, directing, supervising and controlling.
(iii) It is used apart from the above two—personnel and activity- but it describes the subject, the body of knowledge and the whole practice, the discipline.
I. Management is an art of getting things done through other people :
It is a process of activity consisting of some basic techniques for getting the objective of an enterprise fulfilled through the efforts of people. It is the activating element in any concern for getting things done through people. But today it is thought to be against humanity. At present: “It is the art of getting things done through and with the people informally organized groups.”
The job of management is to give active leadership that unites the productive but passive resources into a fruitful organization.
As per E. Peterson and E.G. Plowman:
“It is a technique by means of which the purposes and objectives of a particular human group are determined, clarified and effectuated.”
As per E.F.L. Breach it has been said as:
“A social process entailing responsibility for the effective of efficient planning and regulation of the operations of an enterprise, such responsibility involving a judgement and decision in determining plan and using data to control performances and progress against plans. The guidance, integration, inspiration and supervision of the personnel comprising enterprise and carrying out its operations.”
Breach signifies that it is not possible to take management in relation to things or mechanical operations of machines but only in relation to the people who are employed to operate or use such things.
As per Prof. Harold Koontz it is:
“The art of getting things done through and with people informally organized groups. It is the art of creating an environment in which people can perform as individuals and yet co-operate towards attainment of groups’ goals. It is art of removing blocks to such performance, a way of optimizing efficiency in reaching goals.”
II. Management is what management does:
The three functions of management are:
(i) Planning,
(ii) Implementing, and
(iii) Controlling.
Planning includes formation of policy and its translation into plans. Implementing includes the execution. Controlling means exercising administrative control over the plans.
In the words of Dr. James Lundy:
“Management is principally a task of planning, co-ordinating, motivating and controlling the efforts of others towards a specific objective. It involves the combining of the traditional factors of production (land, labour and capital) in an optimum manner, paying dues attention, of course, to the particular goals of the organization.”
This definition includes three major management activities of:
(1) Planning is the ascertainment of the course or objectives of a business, division or department to attain maximum profit effectiveness, the establishment of policies and continuous seeking and finding out new and better ways to do things.
(2) Implementing seeks to the doing phases, after preparation of plans, personnel attend their jobs with training of motivation not do rightly. Activities must run to the planning, supervision and direction of the subordinates and at the same time groups efforts are coordinated.
(3) Lastly, controlling seeks to evaluate acts of those who are responsible for executing the plans agreed upon. It consists of: (a) Controlling adherence to plans (b) appraising performance.
III. Management is the development of the people:
Business is not the management of things. As Appley Lowrence puts it: “The development of people and not the direction of things.” It is the selection, training supervision and development of people. These days most of the large as well as medium-sized enterprises are managed by the professional managers i.e., the managers who have got either little or no share in the ownership of the enterprise. They take management as a career.
Mcforland has noted following characteristics of a profession:
1. A body of principles, techniques, skills and specialised knowledge.
2. Formal methods of acquiring training.
3. Laying down of certain ethical codes of guidance of conduct.
4. Charging of fees according to the nature of services rendered.
And management is truly a profession in the sense that it fulfills all these conditions. Management these days is very much a systematised body of knowledge (science) and is an identifiable discipline. It has also developed a number of its tools and techniques.
In India, now there are a number of management institutes and university departments imparting formal management training. But management still, at last so in our country, does not fulfill the last time requirements of being a profession. There is, for example, still no unified ethical code of conduct for the managers as is there for the doctors and lawyers.
8. Essay on the Functions of Management:
Various authors have given various functions of management according to the time and development of the management science.
All these can be classified into the following categories:
(i) Planning
(ii) Organisation
(iii) Direction
(iv) Co-ordination
(v) Control.
These functions of management have been discussed in detail in the following paragraphs:
(i) Planning:
It is deciding in advance what is to be done, how it is to be done and when it is to be done. Planning involves projecting the future course of action for the business as a whole and also for the different sections within it. It helps in bridging the gap between the present and the future.
Planning is possible whenever there is a question of choosing and planning process is possible only when alternatives are there. In fact planning is an intellectual process. It signifies use of rational approach to the solution of problems. The important aspects of planning process are defining and establishing objectives, policies, procedures methods, rules, budgets, programmes and strategies.
(ii) Organisation:
Organisation is the structural relationship in an enterprise between the various factors i.e., men, material and management which combine to achieve the objectives set by the enterprise. In a dynamic society like ours, the organisation is not fixed. If it does not promote the objectives of the enterprise, it must be modified.
(iii) Direction:
Direction consists of command, execution, control, supervision and motivation i.e., achieving the good results. It is concerned with to use Lawrence H. Appley’s maxim “that management is essentially getting things done through the efforts of other people.”
It needs the personal touch. A good manager has to see that his orders are properly carried out and have achieved the desired results. It will need proper supervision by him and control of all the levels below him.
Moreover, his order must always create motivation among subordinates. It is only possible when his orders are of the right type and at the right moment. For it, more of initiative, sincere and tact is required than aggressiveness. A good executive must always be a good leader.
(iv) Co-Ordination:
Co-operation permeates all operating organisations and makes their entire structure more effective by harmonizing and property timing the various activities. It means synchronising the activities of all persons and functions in the enterprise and rooting out personal prestige and vested interests.
Proper co-ordination presupposes a number of conditions which can be summed up as:
(i) Fixed responsibility
(ii) Adequate authority at each executive level
(iii) Organisational structure facilitating
(iv) Co-ordination.
(v) Control:
This includes the setting of the targets or standards and comparing the actuals with standards in order to know the deviations, analysis and probing the reasons for such deviations, fixing of responsibility in terms of persons responsible for negative deviation, and correction of employees performance so that group goals, and plans devised to achieve them are accomplished.
9. Essay on the Importance of Management:
Management is absolutely essential if human efforts are to be effective to meet all round development of the society through productive activity, occupation or profession. It is essential in all organisations and at all levels of organisation in an enterprise. Without the enlightened guidance and leadership made available by management “the productive resources will remain resources and shall never become production”.
Management is a dynamic element which gives life to a business enterprise. The productive resources such as materials, men, and money are entrusted to the administrative ability, enterprising initiative and organising skill of management.
In short, management is important for the following reasons:
(i) Provides Effectiveness to Human Efforts:
It helps achieve better equipment, plants, offices, products, services, human relations. It keeps abreast of changing conditions, and it supplies foresight and imagination. Improvement and progress are its constant watch-words.
(ii) Critical Ingredient in Nation’s Growth:
An underdeveloped nation usually lacks adequate managerial know-how. National development is not solely one of transferring capital, technology, and education to citizens of an undeveloped nations. It is also supplying or developing management which provides the generation and direction of effective human energies. Management know-how utilizes the available resources effectively toward achievement of basic needs.
(iii) Brings Order to Endeavours:
By means of management, apparently isolated events or factual information or beliefs are brought together and significant relationships discerned. These relationships bear on the immediate problem, point out future hurdles to be overcome, and assist in determining a solution to the problem.
(iv) Provides Judgement and Courage:
To determine worthwhile goals, carefully select and utilize resources efficiently by means of applying planning, organising, directing and controlling require a high degree of judgement and the exercise of great courage.
From time to time, gadgets and aids are offered to replace management, but actually at best they assist and do not represent management. Serious consideration of such devices usually points out the need for more management judgement and courage to be used. Nothing takes the place of management.
(v) Helps in Achieving Group Goals:
Management touches and influences the life of nearly every human being. Management makes us aware of our potentials, shows the way toward better accomplishment, reduces obstacles, and causes us to achieve goals that we probably would not otherwise attain.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Management: Top 5 Essays
- Essay on Manpower Planning: Top 5 Essays | Process | Personnel Management
- Essay on Management: Top 7 Essays
- Essay on Strategic Management: Top 7 Essays
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
Essays-Writings.com
Go through academic routine with a smile
Importance of Management

Management is a multidimensional phenomenon that covers the ongoing processes in the organization related both to its internal and external environment. Modern management serves to develop the organizational culture and innovations. It allows organizations to survive and thrive. The importance of this phenomenon is determined by company’s ability to manage economic performance, achieve competitive advantage, social and economic benefits, motivate employees, and more. An immense contribution of innovations depends on the managers’ ability to overcome different challenges such as risks, costs, and time successfully. Effective management contributes to using emerging technologies and improving workplaces. It also helps organizations achieve their goals, make better decisions, be more efficient, and earn more profit. Thus, management plays a vital role in any organization because it involves the coordination of personnel activities.
The Background of the Concept
Management aims to direct, control, staff, and organize employees with the aim to accomplish organizational goals. In addition, it also serves to provide planning of organizational activities. These processes are important in the coordination of human and material resources necessary for the effective achievement of tasks. The literature reveals that with the help of a set of principles, methods, and forms of managing organizations, management helps them to thrive and survive in the modern market (Scott, 2011). Therefore, it can aid business to adapt to such areas of professional activity as economic, marketing, accounting, control, educational, and research.
Management was introduced into business with the need to explain why the organization thrived or collapsed. Researchers in this field try to find out what the success of the organization is. Therefore, they have achieved their goal, using tests and practices by the method of attempts and errors. Organizations form the basis of the world of management that encourages leaders to find the most effective methods of managing employees. Many studies assert that the primary task of management is to create an organizational culture and a creative climate, which stimulate employees to innovate (Scott, 2011). As a rule, managers of various units are initiators of technological and organizational changes.
- Functions of Management
Management has different functions in organizations. Moreover, it permeates the whole company, affecting all spheres of its activities. However, with the diversity of the interaction between management and an organization, it is possible to define the boundaries of activities that constitute the essence of management. Thus, experts have determined that it serves to focus on the quality and competitiveness of products, increase the degree of profit and consumer customer satisfaction, improve the image and reputation of the organization, and ensures financial stability (Griffin, 2017). In addition, management allows companies to ensure the rational use of all types of resources and increase labor productivity. Moreover, it plays an important role in the introduction of the latest achievements of scientific and technical progress. Therefore, managerial functions are rather multifaceted.
Furthermore, creative managers know how to use functions to benefit an organization. Griffin (2017) believes that any enterprise is a complex system that needs to determine management functions, taking into account several factors, such as material, labor and financial resources, equipment, buildings, and others. In addition, it should focus on the management process, involving planning, organizing, regulating, controlling, and accounting. Thus, planning helps organizations determine the main directions of their business, including perspective orientation and early recognition of problems. Moreover, it outlines the state of the facility and provides specific measures aimed at supporting favorable development trends or deterring negative ones. It also creates an objective basis for effective control.
Another function that aims to eliminate deviations from the specified mode of operation is regulation. It allows organizations to redistribute material, technical, and financial resources. Regulation involves the process of developing corrective measures and implementing organizational, technological, economic, and technical decisions that ensure timely and unconditional elimination of identified problems (Dodgson, Gann, & Phillips, 2014). The regulatory function is a flexible instrument, through which the production process is continuously introduced into a strict framework provided by the plan. Therefore, it helps managers implement decisions and monitor their execution.
Management also aims to coordinate, motivate, control, and direct employees that benefit an organization. Thus, coordination allows firms to ensure an even flow of production. In order to achieve coordinated work of units, managers hold meetings with other managers to identify service activities and material support of production. Next, motivation contributes to the better performance of the personnel, and as a result, the organization can delegate rights and duties in accordance with accepted management decisions (Dodgson et al., 2014). Furthermore, the directing function of management allows organizational leaders to influence the behavior of employees. Therefore, the functions mentioned above are the basis for management.
The Purpose of Management
The purpose of management is aimed at the most effective use of workforce to achieve organizational and personal goals. Today, everyone understands that in order to make profit and maintain competitiveness, management must optimize the return on investment of any resources, such as material, financial, and most importantly, human. When an organization really cares about people, its general philosophy, climate, and mood necessarily affect its performance. Consequently, the concept of management is based on two main aspects, which are functional and organizational (Griffin, 2017). From the functional perspective, human resources management involves the following: (1) the definition of the overall strategy; (2) the planning of the personnel needs; (3) staff selection and evaluation; (4) development and training; (5) promotion system, and so on (Griffin, 2017). In fact, organizationally, management covers all employees in the organization that are responsible for working.
Furthermore, management focuses more on practical actions than on conceptual procedures and rules. Thus, it plays a great role in solving problems and tasks assigned. Moreover, it maintains the development of all personnel members and each individual employee, creating necessary working conditions. The recent studies suggest that management is focused on the future since it helps the company develop strategic objectives (Scott, 2011). Moreover, unlike other specialties, it influences employees, encouraging them to gain organizational goals. Managers are key professionals in organizations. Therefore, to perform their activities, managers must play a number of roles, such as interpersonal, informative, communicative, analytical, technical, and decisive.
The goal of the organization is fixed in the form of individual characteristics. In this respect, management helps companies identify activities necessary for their success. Dodgson et al. (2014) believe that strategic management describes how the firm with its available resources is going to compete under current and future conditions. Moreover, it helps the organization meet needs of its customers for a long time. Most companies formulate a strategy they must implement quite successfully. It can solve the issue of the viability of the organization.
The Role of Knowledge Management in Organizations
In the modern economy, the engine of which is information, organizations see much more value in their intellectual assets than in physical. Knowledge management helps support knowledge that needs to be shared being the basis for cooperation. Moreover, it helps to promote innovations. According to the research by Dodgson et al. (2014), knowledge management provides an infrastructure for building electronic and social networks for the development of new products or services. In addition, it facilitates and provides access to various ideas, such as giving other people an opportunity to benefit from them. It also increases possibilities for cooperation and enriches the process of sharing explicit and indirect knowledge among employees. In fact, knowledge management encourages the free movement of ideas.
Furthermore, knowledge management provides necessary information that helps the decision-making process. Oftentimes, it contributes to the generation of new knowledge in by sharing and collaborating with co-workers. Knowledge management uses information and knowledge to bring organization’s actions in line with its mission and vision (Scott, 2011). Moreover, it increases the level of customer satisfaction, improves customer service by streamlining their response time and improves the result and experience gained by customers when using services. Ultimately, it creates competitive advantage, contributing to the achievement of knowledge of the highest quality and the satisfaction of clients’ needs. Therefore, knowledge management is the main engine of innovations in an organization.
Management plays a vital role in an organization since it helps to coordinate such activities as leading, planning, controlling, as well as organizing employees. In addition, management helps organizations develop strategic directions and improve customer satisfaction. It performs many other functions that help companies survive and thrive in a complex business environment. Management creates an organizational culture and innovation climate, which stimulate employees to innovate. Using planning, controlling, and regulating processes, it allows organizations to use their resources rationally and to increase labor productivity to compete. Since managers are key professionals in organizations, they play a number of roles, such as interpersonal, informative, communicative, analytical, technical, and decisive. Moreover, the goal of management is to use information and knowledge in order to bring organization’s actions in line with its mission and vision. Therefore, companies are prone to succeed due to effective management.
Dodgson, ?M., Gann, ?D. M., & Phillips, N. (Eds.). (2014). The Oxford handbook of innovation management. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Griffin, R. W. (2017). Management (12th ed.). Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Scott, J. T. (2011). The concise handbook of management: A practitioner’s approach . New York, NY: Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Recent Entries
- Strategic Management and Competitiveness
- Managing Teams
- Business Management Essay Sample
- Change Management in the Northern Nevada Casino Premier
- Influence of Management Actions
- Change Management
- Conflicts in Groups at the Workplace
- Construction Planning and Scheduling
- How Managers Might Motivate Professional Workers
Business Essay Examples

13 Business Essay Examples for Students
14 min read
Published on: May 1, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to figure out the structure, research, or data required to make your essay stand out? Or frustrated by the lack of inspiration and ideas for your essay?
But don't give up yet! We have a powerful solution that will make your essay writing a breeze. Our list of business essay examples is here to help!
We have compiled expertly written business essay examples that will illustrate how to write a striking business essay.
With our examples, you'll be able to see how to structure your essay and generate creative ideas for your topic. And our tips will help you make the most of these examples.
So, let's dive in and get ready to learn!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Business Essay?
A business essay is a type of academic writing that focuses on business-related topics and issues. These essays can cover a wide range of topics such as marketing, finance, management, entrepreneurship, and more.
The importance of business essay lies in presenting a well-researched and informed analysis. To do this effectively, writers need to conduct extensive research and analysis on the topic at hand.
Referring to examples of business essays can help you gain insight into the structure, tone, and content of a well-written essay.
Business Essay Examples For Students
Here is a list of business writing examples
Business Essay Examples Pdf
Business Essay Example Grade 10
Business Essay Example Grade 11
A Level Business Essay Examples
University Business Essay Examples
International Business Essay Examples
Short Essay About Business
College Essay About Starting A Business
Types of Business Essay with Examples
When it comes to business essay writing, there are several different types that you might encounter.
Here's a brief overview of each type, including their characteristics and an example of each.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific business situation or problem. It involves extensive research and data analysis to provide recommendations.
Case studies often showcase the application of theory to real-world business scenarios.
Research Papers
Research papers involve a more academic approach to business writing. They typically require an extensive literature review, data analysis, and original research.
Business research papers aim to contribute new knowledge to the field of business. These often involve a hypothesis or research question.
Argumentative Essays
Argumentative business essays aim to persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. They present an argument and use evidence and logic to support their claims.
Argumentative essays can address various business topics such as management practices, ethical issues, or market trends.
White Papers
A white paper is a document that provides a detailed explanation of a particular issue or problem, often with recommendations or solutions.
White papers are typically used to educate stakeholders about a specific topic. These are often used in the business-to-business (B2B) context.
Comparative Essays
Comparative business essays compare and contrast two or more topics or ideas. They typically analyze the similarities and differences between the topics to evaluate their pros and cons.
Comparative essays can focus on various aspects such as products, companies, markets, or strategies.
How to Structure Your Business Essays
As you begin writing your business essay, it's important to structure it in a clear and organized way.
Here's a step-by-step guide with business essay samples to help you do just that:
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire essay. It should summarize your main points and highlight your recommendations.
This section should be written after completing the essay, as it gives a clear picture of what the essay covers.
Here is how you start a business essay sample:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the rest of the essay. It should introduce the topic, provide background information, and explain the purpose of the essay.
Here is a business essay introduction example:
Industry Analysis
In this section, you'll conduct a thorough analysis of the industry in which the business operates. You should examine factors such as competition, market trends, and customer behavior.
Here is a sample industry analysis
Key Issues or Problems
This section should identify the main issues or problems faced by the business. You should provide evidence to support your claims and analyze the impact of these issues.
Here is an example paragraph:
Solutions or Recommendation
Here, you'll provide solutions or recommendations to address the issues identified in the previous section. Your solutions should be well-supported and feasible.
For instance:
Implementation Plan
For this part, you'll outline a plan for implementing the solutions or recommendations you've proposed. This is sort of a description of the business model you suggest.
This section should be detailed and include specific action steps.
For example:
Finally, you'll wrap up your essay by summarizing your main points and reiterating your recommendations.
This section should be clear, concise, and impactful.
By following this structure, your business essay will be well-organized, coherent, and easy to follow for your readers.
Tips for Using Business Essay Examples Effectively
Now that you have quite a few business essay examples at hand, you should know how to use them effectively:
- Use them as a guide, not a template : While it's great to learn from examples, you should never copy them outright. Instead, use them as a starting point for your own research and writing.
- Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the essay : Take note of what works well in the example essay, as well as any areas that could be improved. This will help you understand how to make your own essay even better.
- Use them to inform your own research and writing : Pay attention to the research methods, sources, and evidence used in the example essay. This can give you ideas for your own research and help you strengthen your arguments.
- Avoid plagiarism and ensure proper citation: Whenever you use ideas or information from an example, make sure to cite your sources. This will help you avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity.
You now have a plenty of business essay examples on different topics to help you get started!
By following our tips and studying the sample essays, you can confidently write your own essays that are clear, concise, and impactful.
However, if you still find yourself struggling with your business essays, just reach out to our professional business essay writing service .
We have the best online essay writing service and are ready to provide you a high-quality business. Our writing service has subject specialist writers who can tackle any business essay topic.
So why wait? Contact us today and let our AI essay writer take your business essays to the next level!
Cathy A. (Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Business Analytics: What It Is & Why It's Important

- 16 Jul 2019
Business analytics is a powerful tool in today’s marketplace that can be used to make decisions and craft business strategies. Across industries, organizations generate vast amounts of data which, in turn, has heightened the need for professionals who are data literate and know how to interpret and analyze that information.
According to a study by MicroStrategy , companies worldwide are using data to:
- Improve efficiency and productivity (64 percent)
- Achieve more effective decision-making (56 percent)
- Drive better financial performance (51 percent)
The research also shows that 65 percent of global enterprises plan to increase analytics spending.
In light of these market trends, gaining an in-depth understanding of business analytics can be a way to advance your career and make better decisions in the workplace.
“Using data analytics is a very effective way to have influence in an organization,” said Harvard Business School Professor Jan Hammond, who teaches the online course Business Analytics , in a previous interview . “If you’re able to go into a meeting and other people have opinions, but you have data to support your arguments and your recommendations, you’re going to be influential.”
Before diving into the benefits of data analysis, it’s important to understand what the term “business analytics” means.
Check out our video on business analytics below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
What Is Business Analytics?
Business analytics is the process of using quantitative methods to derive meaning from data to make informed business decisions.
There are four primary methods of business analysis:
- Descriptive : The interpretation of historical data to identify trends and patterns
- Diagnostic : The interpretation of historical data to determine why something has happened
- Predictive : The use of statistics to forecast future outcomes
- Prescriptive : The application of testing and other techniques to determine which outcome will yield the best result in a given scenario
These four types of business analytics methods can be used individually or in tandem to analyze past efforts and improve future business performance.
Business Analytics vs. Data Science
To understand what business analytics is, it’s also important to distinguish it from data science. While both processes analyze data to solve business problems, the difference between business analytics and data science lies in how data is used.
Business analytics is concerned with extracting meaningful insights from and visualizing data to facilitate the decision-making process , whereas data science is focused on making sense of raw data using algorithms, statistical models, and computer programming. Despite their differences, both business analytics and data science glean insights from data to inform business decisions.
To better understand how data insights can drive organizational performance, here are some of the ways firms have benefitted from using business analytics.
The Benefits of Business Analytics
1. more informed decision-making.
Business analytics can be a valuable resource when approaching an important strategic decision.
When ride-hailing company Uber upgraded its Customer Obsession Ticket Assistant (COTA) in early 2018—a tool that uses machine learning and natural language processing to help agents improve speed and accuracy when responding to support tickets—it used prescriptive analytics to examine whether the product’s new iteration would be more effective than its initial version.
Through A/B testing —a method of comparing the outcomes of two different choices—the company determined that the updated product led to faster service, more accurate resolution recommendations, and higher customer satisfaction scores. These insights not only streamlined Uber’s ticket resolution process, but saved the company millions of dollars.
2. Greater Revenue
Companies that embrace data and analytics initiatives can experience significant financial returns.
Research by McKinsey shows organizations that invest in big data yield a six percent average increase in profits, which jumps to nine percent for investments spanning five years.
Echoing this trend, a recent study by BARC found that businesses able to quantify their gains from analyzing data report an average eight percent increase in revenues and a 10 percent reduction in costs.
These findings illustrate the clear financial payoff that can come from a robust business analysis strategy—one that many firms can stand to benefit from as the big data and analytics market grows.
Related: 5 Business Analytics Skills for Professionals
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
Beyond financial gains, analytics can be used to fine-tune business processes and operations.
In a recent KPMG report on emerging trends in infrastructure, it was found that many firms now use predictive analytics to anticipate maintenance and operational issues before they become larger problems.
A mobile network operator surveyed noted that it leverages data to foresee outages seven days before they occur. Armed with this information, the firm can prevent outages by more effectively timing maintenance, enabling it to not only save on operational costs, but ensure it keeps assets at optimal performance levels.
Why Study Business Analytics?
Taking a data-driven approach to business can come with tremendous upside, but many companies report that the number of skilled employees in analytics roles are in short supply .
LinkedIn lists business analysis as one of the skills companies need most in 2020 , and the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects operations research analyst jobs to grow by 23 percent through 2031—a rate much faster than the average for all occupations.
“A lot of people can crunch numbers, but I think they’ll be in very limited positions unless they can help interpret those analyses in the context in which the business is competing,” said Hammond in a previous interview .
Skills Business Analysts Need
Success as a business analyst goes beyond knowing how to crunch numbers. In addition to collecting data and using statistics to analyze it, it’s crucial to have critical thinking skills to interpret the results. Strong communication skills are also necessary for effectively relaying insights to those who aren’t familiar with advanced analytics. An effective data analyst has both the technical and soft skills to ensure an organization is making the best use of its data.

Improving Your Business Analytics Skills
If you’re interested in capitalizing on the need for data-minded professionals, taking an online business analytics course is one way to broaden your analytical skill set and take your career to the next level
Through learning how to recognize trends, test hypotheses , and draw conclusions from population samples, you can build an analytical framework that can be applied in your everyday decision-making and help your organization thrive.
“If you don’t use the data, you’re going to fall behind,” Hammond said . “People that have those capabilities—as well as an understanding of business contexts—are going to be the ones that will add the most value and have the greatest impact.”
Do you want to leverage the power of data within your organization? Explore our eight-week online course Business Analytics to learn how to use data analysis to solve business problems.
This post was updated on November 14, 2022. It was originally published on July 16, 2019.

About the Author
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
The Importance of Management to Organization
The activity of any organization requires management since its effective functioning and development, and in general, existence is impossible without it. In addition, the management of an organization determines the attitude of other organizations towards it and has a significant impact on their response management decisions. That is, the interests of many people are connected with management, both in the organization itself and outside it. Modern management aims to ensure that the employees work efficiently, company is successful, stand out among competitors, and conduct business in resource scarcity conditions. To realize all this, the organization’s management must have its own goals, a plan for its achievement and development, motivation, and control over employees. Management is an integral part of the standard and successful functioning of the organization, and each component must perform its work correctly and efficiently.
Management is the ability to achieve goals with the help of the intelligence and work of the members of the organization. In addition, management is a method by which work processes become as efficient as possible and a way of helping to optimize operations (Wienclaw, 2017). Management includes four main functions, such as planning, organization, motivation, and control.
Planning sets goals that the company must achieve in a certain period and coordinates employees’ actions to achieve these goals. The very process of planning the organization’s strategy and coordinating employees’ actions helps managers make managerial decisions. The tasks of strategic planning include the development of an enterprise strategy that will ensure the introduction of innovations in the organization, increase productivity, and ensure each employee’s work. Planning helps create unity of a common goal within the organization and also helps to reduce risk when making decisions.
Strategic planning becomes significant when it is thought out in detail and has the opportunity to be implemented. When the plan is formed, it is necessary to look for ways to implement it (Cohen & Eimicke, 2020). After choosing a fundamental overall strategy, it must be implemented by combining it with other organizational functions. An essential mechanism for linking the strategy is developing plans and guidelines: tactics, policies, procedures, and rules. Tactics are specific short-term strategies. The policy provides general guidelines for action and decision-making. The rules specify precisely what should be done in a particular situation.
The organization’s function is to create an enterprise structure that allows people to work effectively together to achieve its goals. The organization as a process is a function of coordinating many tasks: there are two main aspects of the organizational process. The first is the division of the organization into divisions according to goals and strategies. The second implies the delegation of authority to subordinates of the organization.
As a term used in management theory, delegation means transferring tasks and powers to a person who assumes responsibility for their implementation. Delegation is rarely effective if management does not adhere to the principle of compliance, according to which the scope of authority should correspond to the delegated responsibility.
When planning and organizing work, the manager determines what precisely this organization should do, when, how, and who, in their opinion, should do it. If these decisions are made effectively, the managers get the opportunity to translate their findings into deeds, applying the basic principles of motivation in practice. Motivation is the process of encouraging others to work to achieve the personal goals or goals of the organization. Employees tend to reduce motivation, which significantly reduces the efficiency of the company. In this case, the task of the manager is to motivate them to work more productively.
Each employer determines the methods that assist the entire team in meeting their own needs and achieving a common task. Recognition of achievements and encouragement of employees is a rather complex process that requires considering the quantity and quality of work and all the circumstances of the emergence and development of motives for behavior. Therefore, the manager needs to choose the right motivation system concerning subordinates, and each requires an extraordinary approach.
Control is a process that ensures the achievement of the organization’s goals. It is necessary to detect and resolve emerging problems before they become severe and can also be used to stimulate successful activities. The control process consists of setting standards, changing the actual results achieved, and making adjustments if the results differ significantly from the established criteria. Control is a critical and complex management function. One of the essential features of control, which should be taken into account, is that control should be comprehensive. Regardless of his rank, every manager should exercise control as an integral part of his official duties, even if no one has specifically instructed him to do so.
The behavior of people is not the only factor determining the effectiveness of control. For the control to fulfill its proper task, i.e., to ensure the organization’s goals, it must have several important properties. Control is effective if it has a strategic nature, aims to achieve concrete results, is timely, flexible, simple, and economical. Of course, sometimes, it is challenging to implement an effective control system strategy since it is impossible to link the relationship between human capital and the control strategy (Usman et al., 2021). As a result, this may lead to the fact that the company’s services or products will not be in demand among consumers.
All three articles studied correctly describe the need for management in the organization. It improves the organization of activities and production, increases internal indicators, and maintains the workflow’s pace. Enterprises strive to increase income, increase economic competitiveness, and achieve these goals directly depending on managers who set tasks and help employees fulfill them. Each country and organization has its management method. One way or another, it should be, and its basis should be organization, planning, control, and motivation. Management allows the company to solve several internal and external tasks, provides information, analytical, motivational support, and gives both a short-term effect from the use and a long-term one that builds a development strategy for years to come.
In conclusion, organizations are entirely different and have their unique ways of development. Some people manage to build their business very quickly, achieving their goals one by one. Another organization is characterized by slow growth. Everything may depend simply on the specifics of the company, or maybe on the fact that the organization does not have enough departments that would be engaged in such vital functions as management.
The main task that management sets itself is creating rules and determining the reasons that can lead the company to success in its field. Management by setting and implementing goals is carried out at its core, taking into account the assessment of the potential capabilities of the organization, its provision with the necessary resources, and the conditions of competition.
Cohen, S., Eimicke, W.B. (2020). Management Fundamentals . Columbia University Press.
Usman, A., Wirawan, H., & Zulkifli. (2021). The effect of human capital and physical capital on regional financial condition: the moderating effect of management control system . Heliyon, 7 (5), 1-10. Web.
Wienclaw, R.A. (2017). Strategies of Management : Vol. Second edition. Salem Press.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2022, December 4). The Importance of Management to Organization. https://business-essay.com/the-importance-of-management-to-organization/
"The Importance of Management to Organization." BusinessEssay , 4 Dec. 2022, business-essay.com/the-importance-of-management-to-organization/.
BusinessEssay . (2022) 'The Importance of Management to Organization'. 4 December.
BusinessEssay . 2022. "The Importance of Management to Organization." December 4, 2022. https://business-essay.com/the-importance-of-management-to-organization/.
1. BusinessEssay . "The Importance of Management to Organization." December 4, 2022. https://business-essay.com/the-importance-of-management-to-organization/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "The Importance of Management to Organization." December 4, 2022. https://business-essay.com/the-importance-of-management-to-organization/.
- IBM and HP: Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Lean Six Sigma and Innovation
- The Case of Dunkin’ Donuts: Organizational Structure
- The Concept of Resilience in Business
- Self-Regulation in Organizational Psychology
- Barcelona WD Group Company Management
- Virtual Team Activity: Personal Facts Guessing Game
- Digital Integration of 3D (CAD) Virtual Environment
- Change Management Plan in Locus Fs Company
- Human Resources Management at Amazon
Business Management essay
Business management is essential for me because I have a great desire to successfully manage people and business projects, as well as to develop effective business-related policies. I want to major in business in order to pursue my Bachelor’s Degree and become a true professional in business management. The reason that I am applying for the scholarship is that it will help me to pay for my academic tuition, academic resources (books, programs, etc.) and spend much more time on my studies.
Today I have to work full time in order to advance myself with a degree in business management. I am currently pursuing my Associate’s Degree, but I am not going to stop my education. To become a true professional in business management, it is necessary to learn more about the key business strategies that will help to enhance management practices and develop the proper skills and abilities. I am going forward to achieve my Bachelor’s Degree.
I am currently pursuing a career course that will help me to advance my leadership and management skills and have the opportunity to work in an advanced management field. My specific academic goals contribute to my professional growth. Some of my academic goals include:
- To develop effective leadership and management skills in order to apply these skills in practice;
- To improve my academic performance in order to become more professional in decision making and goal setting practices;
- To develop good technical skills in order to apply new technologies in business practices;
- To learn more about business management strategies that could be applied in practice;
- To learn how to identify and successfully resolve various organizational and business problems;
- To develop my communication skills that are necessary in achieving strategic goals;
- To learn more about strategic planning in business;
- To use my skills and abilities to continue maintaining a “B” average;
- To do everything possible to keep satisfactory attendance.
My career plans depend on my academic achievements and work experience. I know that business management is not an easy field to work in. I will be focused on my professional development. My work experience involves dealing with conflicts within management, problem solving, decision making, critical thinking, discrimination, as well as personal development. I have been well trained to deal with standard operating procedures and implementation of such standards, to satisfy the Department of Defense and be in compliance with the established laws and regulations of our Federal Government.
In addition, I will do my best to develop professional skills in business management practices that will help me to make good management decisions in my future career. To be a good manager, it is very important to develop not only effective interpersonal communication skills, but also good intuition, which helps to make effective management decisions. I need general knowledge in HR management, finance and accounting operations. I know that Bachelor’s programs in this field are effective in achieving the established academic goals. The greatest pleasure for me would be to pass exams successfully. I believe that my personal skills and abilities will be useful in achieving my academic goals. I am self-confident, hard-working and persistent. I know that to become a good manager I should study hard. I know that a good manager should be competent in three key areas: managing people; managing and developing processes and policies; and managing and developing oneself. I believe that my Bachelor’s program in business management will help me to develop the proper skills to become competent in the above mentioned areas. Today I pay due attention to my personal development. I successfully deal with stresses and conflicts. A good manager should know how to avoid stressful situations which may lead to conflicts in the workplace. Besides, I use my creativity in decision making process to demonstrate the best traits of my character. Innovative ideas in business management provide massive opportunities for successful implementation of the established strategic goals.
Thus, it is necessary to conclude that my specific academic goals and career plans will motivate me to study hard. I know that to become a professional in business management, it is necessary to never give up and be quick about solving any problem or overcoming any barrier. I realize that my academic and career goals are the essential goals I should achieve in the nearest future. Achieving these goals will help to succeed in the realization of my personal potential in profession and career. Business management practices guarantee professional success if a manager is goal-oriented and creative. One of my great desires is to pursue my Bachelor’s Degree in order to become a true professional in business management. I believe that I will be able to apply my best skills and abilities to succeed in academic performance and become a well-trained specialist. My work experience will help me to be confident in everything I need to do to attain my academic goals and career plans.
Do you like this essay?
Our writers can write a paper like this for you!
Order your paper here .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Common Leadership Styles — and How to Decide Which to Use When
- Rebecca Knight

Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances call for different approaches.
Research suggests that the most effective leaders adapt their style to different circumstances — be it a change in setting, a shift in organizational dynamics, or a turn in the business cycle. But what if you feel like you’re not equipped to take on a new and different leadership style — let alone more than one? In this article, the author outlines the six leadership styles Daniel Goleman first introduced in his 2000 HBR article, “Leadership That Gets Results,” and explains when to use each one. The good news is that personality is not destiny. Even if you’re naturally introverted or you tend to be driven by data and analysis rather than emotion, you can still learn how to adapt different leadership styles to organize, motivate, and direct your team.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it’s transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to Daniel Goleman, a psychologist best known for his work on emotional intelligence, “Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances may call for different approaches.”
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
Explore Greyhound Nation
- Loyola Today
The growing importance of sustainability in business

As Loyola University Maryland celebrates Earth Month, two professors at Loyola’s Sellinger School of Business define and discuss sustainability and its growing importance to organizations, different business disciplines, and the planet. Stacy Chavez, Ph.D., assistant professor of accounting, and Astrid Schmidt-King, J.D., teaching assistant professor of management and organizations, specialize in sustainability management, corporate social responsibility, sustainability measurement and reporting, and international business.
What is sustainability? Why is it important?
Chavez: Sustainability can be defined in many ways depending on the context. Business sustainability refers to the ability of an organization to survive and prosper into the future. More commonly, and especially important during Earth Month, sustainability refers to the longevity and ability for the people and the planet to survive, to use only what we need to preserve the future.
It is not possible for one person alone to act in a way that will sustain our world for future generations. The more we know about how to be a better global citizen, be it recycling and reducing waste or simply seeking knowledge about how our actions have a domino impact on the world, the more of a positive force we can be.
Why must organizations work toward sustainability?
Schmidt-King: Sustainability exists at many levels: individual, organizational, societal, and global. Not only are organizations, firms and businesses positioned to be agents and engines of innovation and impact, but a sustainable future is a prerequisite for their own survival. Given the scope, reach and operations of businesses, they can create and adopt sustainable business practices that serve and support their business and stakeholders, including the well-being of the ecosystem. Organizations are realizing that doing well and doing good are not mutually exclusive terms. Businesses can find the balance to do both and, in doing so, can be leaders in sustainability.
What are the different kinds of sustainability?
Schmidt-King: Sustainability is a broad term, which can be a challenge and opportunity. In 2015, the United Nations created 17 Sustainable Development Goals focusing on the dimensions of sustainability including people, planet, prosperity, peace, and partnerships. For businesses and organizations, this has translated into terms like the triple bottom line – PPP for people, planet, and profit and ESG for environmental, social, and governance – and calls upon businesses to see their role and responsibility in advancing sustainable strategies and sustainable development. Our sustainability management major at the Sellinger School of Business views sustainability as “how corporations deliver value to people, planet, and profit while creating and sustaining a competitive advantage.”
How do different business disciplines support sustainability?
Chavez: All business disciplines have a role to play in supporting sustainability. Examples include considering green companies or initiatives in financing and investing decisions, proper messaging and handling of sustainability initiatives to prevent greenwashing or misleading claims, and accounting to help with measurement, assurance of information, and presentation of data.
Schmidt-King: McCormick & Co. and Pompeian Olive Oil visited Loyola to speak to our students about their organizations’ integration of sustainability into their business practices and strategies. From management, to marketing, to collecting and assessing data, to reporting, to understanding global trends in areas such as climate and geopolitics, sustainability requires collaboration not only across disciplines, but also across organizational divisions.
How do organizations measure and report on sustainability?
Chavez: The world of sustainability reporting is like the Wild West. Companies may feel pressure from their stakeholders – investors, customers, employees, etc. – to report on certain activities, or they may report based on their mission or ethics. Unlike financial reporting, sustainability reporting is not yet universally mandated or prescribed, so companies have some autonomy as to what topics they choose to report on, how often they report, which published guidelines they use to measure their impact, and the format of their reporting. We are beginning to see mandated emissions (GHG) disclosure proposals, which is the first step in moving towards more uniform reporting on sustainability.
How does sustainability follow the Jesuit commitment of “caring for our common home”?
Schmidt-King: Laudato Si’ is the name of Pope Francis’ encyclical on caring for our common home, planet earth. It calls to action “every person living on this planet” and calls for an integral ecology that sees the interconnectedness of environmental, economic, political, social, cultural, and ethical issues. In 2021, Loyola University Maryland joined the first cohort of Laudato Si’ universities, committing to responding to the cry of the earth and the cry of the poor through fostering ecological economics, adopting sustainable lifestyles, fostering ecological education, fostering ecological spirituality, and building community resilience and empowerment.
Why should students study sustainability?
Chavez: Students should study sustainability because it is quickly becoming ingrained in the corporate world. Having knowledge of the vocabulary, reporting frameworks, specific industry impacts, etc., will help students succeed and contribute to their chosen path. For instance, the accounting industry expects that Loyola’s current freshmen in the Class of 2027 will be involved in auditing sustainability information in their first year of employment. The focus on sustainability is growing in all facets, so it is imperative that our students know the issues.
Schmidt-King: Not that long ago, sustainability was something extra a business would consider. Now it is integral and ingrained in an organization’s strategy and operations. I am proud that Loyola University Maryland was the first institution in Maryland to create a sustainability management major. It is a path that allows students to do well by doing good, and it provides a career path that highlights the critical role of businesses in effectuating meaningful change.
Loyola’s Sellinger School of Business introduced the Bachelor of Business Administration in sustainability management in 2020. On the graduate level, Emerging Leaders MBA students participate in a sustainability colloquium that addresses the question, “How do competent, credible, confident emerging leaders contribute to sustainable value creation for all stakeholders?” Colloquium participants earn a certification in ESG reporting.
Media Relations Contact
If you are a member of the media and have questions about this story, please contact Rita Buettner at [email protected] .
Additional Links
- University Profile
- Media Resources
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Social Media Directory
- Loyola Magazine

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3) Decision-making. The Importance of Business Management is reflected when making important decisions. Business Management provides a structured framework for gathering information, analysing data, and making informed decisions. It allows organisations to consider various factors and potential outcomes before making choices.
Business management is the act of overseeing the organization, coordination, and execution of various business activities. This may include managing different aspects of the business, like sales, marketing, and accounting. Essentially, business managers are responsible for ensuring that the day-to-day operations function smoothly.
By understanding and implementing the four functions of management - the planning function, the organizing function, the leading function, and the controlling function - a manager can steer an organization toward achievement. Through continuous learning and development, managers can adapt to evolving business dynamics and inspire their ...
Management is an important part of business for both commercial and non commercial organizations. Management can be described as an act that brings together all resources belonging to an organization including people with the aim of achieving and utilizing them optimally to achieve overall corporate goals (Watson 2006, 34-40). We will write a ...
Introduction. Business management is the act of unifying people to accomplish the desired goals and objectives of a business. Business management requires the exploitation of the business' resources in the most efficient manner possible. Business management encompasses organizing, planning, leading, controlling, and directing a business ...
Business management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the activities of a business or organization to achieve its goals and objectives. It involves overseeing all aspects of a business, from finance and operations to marketing and human resources. Business managers must be skilled in leadership, communication ...
3. Accounting. Proper management of finances is important to make critical business decisions. Knowing basic business accounting will enable you to answer questions such as how much you can spend on marketing, or whether you have the ability to secure a loan from a bank. By understanding profit margins, cash flow, and managing debts and expenses, you are equipping yourself with the knowledge ...
Project management, planning, and organizational skills: Maximizing productivity. Emotional intelligence: Better managing professional relationships. Networking: Making mutually beneficial connections throughout your company, industry, and beyond. Related: 10 Business Skills Every Professional Needs.
At the government level, management involves planning for economic development, regulation of industries and supporting emerging industries in order to ensure success. The management decisions made by both the government and individual firms have a great impact on international business strategy development.
your article, business report, stock analysis or advertising campaign. Researching a topic The ability to research a topic, filter out the relevant information and sepa-rate the useless or negligible is an essential part of business. Before you can select information you render important for conveying your message, know-
Bill Birchard is an author and writing coach who's worked with many successful businesspeople. He's drawn on that experience and his review of the scientific literature to identify eight ...
Planning is the first and most important function of the management. It is needed at every level of the management. In the absence of planning all the business activities of the organization will become meaningless. The importance of planning has increased all the more in view of the increasing size of organizations.
I have come to realization, this job has a lot of components and it is an everyday challenge, although I have a great fondness for competition as well as challenges. The philosophy of business management considers the fundamental principles that underlie the formation, operation, and the everyday challenges of a business enterprise.
1. Essay on the Introduction to Management: Management is a vital aspect of the economic life of man, which is an organised group activity. It is considered as the indispensable institution in the modern social organisation marked by scientific thought and technological innovations.
Business management is what runs a business. Businesses have changed a lot from the past to now. A lot of the change has to do with technology and just everything throughout a business being updated. Business management is managing a business, which is managing the time, resources, and employees.
The Importance of Innovation. Unforeseen challenges are inevitable in business. Innovation can help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company in the process. Here are three reasons innovation is crucial for your business: It allows adaptability: The recent COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business on a monumental scale. Routine operations ...
Importance of Management. Management is a multidimensional phenomenon that covers the ongoing processes in the organization related both to its internal and external environment. Modern management serves to develop the organizational culture and innovations. It allows organizations to survive and thrive.
What is a Business Essay? A business essay is a type of academic writing that focuses on business-related topics and issues. These essays can cover a wide range of topics such as marketing, finance, management, entrepreneurship, and more. The importance of business essay lies in presenting a well-researched and informed analysis.
Business analytics is the process of using quantitative methods to derive meaning from data to make informed business decisions. There are four primary methods of business analysis: Descriptive: The interpretation of historical data to identify trends and patterns. Diagnostic: The interpretation of historical data to determine why something has ...
Management is the ability to achieve goals with the help of the intelligence and work of the members of the organization. In addition, management is a method by which work processes become as efficient as possible and a way of helping to optimize operations (Wienclaw, 2017). Management includes four main functions, such as planning ...
Business management is essential for me because I have a great desire to successfully manage people and business projects, as well as to develop effective business-related policies. I want to major in business in order to pursue my Bachelor's Degree and become a true professional in business management. The reason that I am applying for the ...
Improves life of workers:-. Management shares some of its profits with the workers. It provides the workers with good working environment and conditions. It also gives the workers many financial and non-financial incentives. All this improves the quality of life of the workers. 5. Improves corporate image:-.
The Importance Of Business Management. Because of the advancements the world has seen throughout the years, companies are able to expand their business overseas. It is a heavy process and if not done correctly it can end up going terribly wrong. When deciding to move a business or deciding to manufacture overseas many factors come out to play.
Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute ...
As Loyola University Maryland celebrates Earth Month, two professors at Loyola's Sellinger School of Business define and discuss sustainability and its growing importance to organizations, different business disciplines, and the planet. Stacy Chavez, Ph.D., assistant professor of accounting, and Astrid Schmidt-King, J.D., teaching assistant professor of management and organizations ...