
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Academic Proposals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource introduces the genre of academic proposals and provides strategies for developing effective graduate-level proposals across multiple contexts.
Introduction
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals.
For samples of academic proposals, click here .
Important considerations for the writing process
First and foremost, you need to consider your future audience carefully in order to determine both how specific your topic can be and how much background information you need to provide in your proposal. While some conferences and journals may be subject-specific, most will require you to address an audience that does not conduct research on the same topics as you. Conference proposal reviewers are often drawn from professional organization members or other attendees, while journal proposals are typically reviewed by the editorial staff, so you need to ensure that your proposal is geared toward the knowledge base and expectations of whichever audience will read your work.
Along those lines, you might want to check whether you are basing your research on specific prior research and terminology that requires further explanation. As a rule, always phrase your proposal clearly and specifically, avoid over-the-top phrasing and jargon, but do not negate your own personal writing style in the process.
If you would like to add a quotation to your proposal, you are not required to provide a citation or footnote of the source, although it is generally preferred to mention the author’s name. Always put quotes in quotation marks and take care to limit yourself to at most one or two quotations in the entire proposal text. Furthermore, you should always proofread your proposal carefully and check whether you have integrated details, such as author’s name, the correct number of words, year of publication, etc. correctly.
Methodology is often a key factor in the evaluation of proposals for any academic genre — but most proposals have such a small word limit that writers find it difficult to adequately include methods while also discussing their argument, background for the study, results, and contributions to knowledge. It's important to make sure that you include some information about the methods used in your study, even if it's just a line or two; if your proposal isn't experimental in nature, this space should instead describe the theory, lens, or approach you are taking to arrive at your conclusions.
Reasons proposals fail/common pitfalls
There are common pitfalls that you might need to improve on for future proposals.
The proposal does not reflect your enthusiasm and persuasiveness, which usually goes hand in hand with hastily written, simply worded proposals. Generally, the better your research has been, the more familiar you are with the subject and the more smoothly your proposal will come together.
Similarly, proposing a topic that is too broad can harm your chances of being accepted to a conference. Be sure to have a clear focus in your proposal. Usually, this can be avoided by more advanced research to determine what has already been done, especially if the proposal is judged by an important scholar in the field. Check the names of keynote speakers and other attendees of note to avoid repeating known information or not focusing your proposal.
Your paper might simply have lacked the clear language that proposals should contain. On this linguistic level, your proposal might have sounded repetitious, have had boring wording, or simply displayed carelessness and a lack of proofreading, all of which can be remedied by more revisions. One key tactic for ensuring you have clear language in your proposal is signposting — you can pick up key phrases from the CFP, as well as use language that indicates different sections in academic work (as in IMRAD sections from the organization and structure page in this resource). This way, reviewers can easily follow your proposal and identify its relatedness to work in the field and the CFP.
Conference proposals
Conference proposals are a common genre in graduate school that invite several considerations for writing depending on the conference and requirements of the call for papers.
Beginning the process
Make sure you read the call for papers carefully to consider the deadline and orient your topic of presentation around the buzzwords and themes listed in the document. You should take special note of the deadline and submit prior to that date, as most conferences use online submission systems that will close on a deadline and will not accept further submissions.
If you have previously spoken on or submitted a proposal on the same topic, you should carefully adjust it specifically for this conference or even completely rewrite the proposal based on your changing and evolving research.
The topic you are proposing should be one that you can cover easily within a time frame of approximately fifteen to twenty minutes. You should stick to the required word limit of the conference call. The organizers have to read a large number of proposals, especially in the case of an international or interdisciplinary conference, and will appreciate your brevity.
Structure and components
Conference proposals differ widely across fields and even among individual conferences in a field. Some just request an abstract, which is written similarly to any other abstract you'd write for a journal article or other publication. Some may request abstracts or full papers that fit into pre-existing sessions created by conference organizers. Some request both an abstract and a further description or proposal, usually in cases where the abstract will be published in the conference program and the proposal helps organizers decide which papers they will accept.
If the conference you are submitting to requires a proposal or description, there are some common elements you'll usually need to include. These are a statement of the problem or topic, a discussion of your approach to the problem/topic, a discussion of findings or expected findings, and a discussion of key takeaways or relevance to audience members. These elements are typically given in this order and loosely follow the IMRAD structure discussed in the organization and structure page in this resource.
The proportional size of each of these elements in relation to one another tends to vary by the stage of your research and the relationship of your topic to the field of the conference. If your research is very early on, you may spend almost no time on findings, because you don't have them yet. Similarly, if your topic is a regular feature at conferences in your field, you may not need to spend as much time introducing it or explaining its relevance to the field; however, if you are working on a newer topic or bringing in a topic or problem from another discipline, you may need to spend slightly more space explaining it to reviewers. These decisions should usually be based on an analysis of your audience — what information can reviewers be reasonably expected to know, and what will you have to tell them?
Journal Proposals
Most of the time, when you submit an article to a journal for publication, you'll submit a finished manuscript which contains an abstract, the text of the article, the bibliography, any appendices, and author bios. These can be on any topic that relates to the journal's scope of interest, and they are accepted year-round.
Special issues , however, are planned issues of a journal that center around a specific theme, usually a "hot topic" in the field. The editor or guest editors for the special issue will often solicit proposals with a call for papers (CFP) first, accept a certain number of proposals for further development into article manuscripts, and then accept the final articles for the special issue from that smaller pool. Special issues are typically the only time when you will need to submit a proposal to write a journal article, rather than submitting a completed manuscript.
Journal proposals share many qualities with conference proposals: you need to write for your audience, convey the significance of your work, and condense the various sections of a full study into a small word or page limit. In general, the necessary components of a proposal include:
- Problem or topic statement that defines the subject of your work (often includes research questions)
- Background information (think literature review) that indicates the topic's importance in your field as well as indicates that your research adds something to the scholarship on this topic
- Methodology and methods used in the study (and an indication of why these methods are the correct ones for your research questions)
- Results or findings (which can be tentative or preliminary, if the study has not yet been completed)
- Significance and implications of the study (what will readers learn? why should they care?)
This order is a common one because it loosely follows the IMRAD (introduction, methods, results and discussion) structure often used in academic writing; however, it is not the only possible structure or even always the best structure. You may need to move these elements around depending on the expectations in your field, the word or page limit, or the instructions given in the CFP.
Some of the unique considerations of journal proposals are:
- The CFP may ask you for an abstract, a proposal, or both. If you need to write an abstract, look for more information on the abstract page. If you need to write both an abstract and a proposal, make sure to clarify for yourself what the difference is. Usually the proposal needs to include more information about the significance, methods, and/or background of the study than will fit in the abstract, but often the CFP itself will give you some instructions as to what information the editors are wanting in each piece of writing.
- Journal special issue CFPs, like conference CFPs, often include a list of topics or questions that describe the scope of the special issue. These questions or topics are a good starting place for generating a proposal or tying in your research; ensuring that your work is a good fit for the special issue and articulating why that is in the proposal increases your chances of being accepted.
- Special issues are not less valuable or important than regularly scheduled issues; therefore, your proposal needs to show that your work fits and could readily be accepted in any other issue of the journal. This means following some of the same practices you would if you were preparing to submit a manuscript to a journal: reading the journal's author submission guidelines; reading the last several years of the journal to understand the usual topics, organization, and methods; citing pieces from this journal and other closely related journals in your research.
Book Proposals
While the requirements are very similar to those of conference proposals, proposals for a book ought to address a few other issues.
General considerations
Since these proposals are of greater length, the publisher will require you to delve into greater detail as well—for instance, regarding the organization of the proposed book or article.
Publishers generally require a clear outline of the chapters you are proposing and an explication of their content, which can be several pages long in its entirety.
You will need to incorporate knowledge of relevant literature, use headings and sub-headings that you should not use in conference proposals. Be sure to know who wrote what about your topic and area of interest, even if you are proposing a less scholarly project.
Publishers prefer depth rather than width when it comes to your topic, so you should be as focused as possible and further outline your intended audience.
You should always include information regarding your proposed deadlines for the project and how you will execute this plan, especially in the sciences. Potential investors or publishers need to know that you have a clear and efficient plan to accomplish your proposed goals. Depending on the subject area, this information can also include a proposed budget, materials or machines required to execute this project, and information about its industrial application.
Pre-writing strategies
As John Boswell (cited in: Larsen, Michael. How to Write a Book Proposal. Writers Digest Books , 2004. p. 1) explains, “today fully 90 percent of all nonfiction books sold to trade publishers are acquired on the basis of a proposal alone.” Therefore, editors and agents generally do not accept completed manuscripts for publication, as these “cannot (be) put into the usual channels for making a sale”, since they “lack answers to questions of marketing, competition, and production.” (Lyon, Elizabeth. Nonfiction Book Proposals Anybody Can Write . Perigee Trade, 2002. pp. 6-7.)
In contrast to conference or, to a lesser degree, chapter proposals, a book proposal introduces your qualifications for writing it and compares your work to what others have done or failed to address in the past.
As a result, you should test the idea with your networks and, if possible, acquire other people’s proposals that discuss similar issues or have a similar format before submitting your proposal. Prior to your submission, it is recommended that you write at least part of the manuscript in addition to checking the competition and reading all about the topic.
The following is a list of questions to ask yourself before committing to a book project, but should in no way deter you from taking on a challenging project (adapted from Lyon 27). Depending on your field of study, some of these might be more relevant to you than others, but nonetheless useful to reiterate and pose to yourself.
- Do you have sufficient enthusiasm for a project that may span years?
- Will publication of your book satisfy your long-term career goals?
- Do you have enough material for such a long project and do you have the background knowledge and qualifications required for it?
- Is your book idea better than or different from other books on the subject? Does the idea spark enthusiasm not just in yourself but others in your field, friends, or prospective readers?
- Are you willing to acquire any lacking skills, such as, writing style, specific terminology and knowledge on that field for this project? Will it fit into your career and life at the time or will you not have the time to engage in such extensive research?
Essential elements of a book proposal
Your book proposal should include the following elements:
- Your proposal requires the consideration of the timing and potential for sale as well as its potential for subsidiary rights.
- It needs to include an outline of approximately one paragraph to one page of prose (Larsen 6) as well as one sample chapter to showcase the style and quality of your writing.
- You should also include the resources you need for the completion of the book and a biographical statement (“About the Author”).
- Your proposal must contain your credentials and expertise, preferably from previous publications on similar issues.
- A book proposal also provides you with the opportunity to include information such as a mission statement, a foreword by another authority, or special features—for instance, humor, anecdotes, illustrations, sidebars, etc.
- You must assess your ability to promote the book and know the market that you target in all its statistics.
The following proposal structure, as outlined by Peter E. Dunn for thesis and fellowship proposals, provides a useful guide to composing such a long proposal (Dunn, Peter E. “Proposal Writing.” Center for Instructional Excellence, Purdue University, 2007):
- Literature Review
- Identification of Problem
- Statement of Objectives
- Rationale and Significance
- Methods and Timeline
- Literature Cited
Most proposals for manuscripts range from thirty to fifty pages and, apart from the subject hook, book information (length, title, selling handle), markets for your book, and the section about the author, all the other sections are optional. Always anticipate and answer as many questions by editors as possible, however.
Finally, include the best chapter possible to represent your book's focus and style. Until an agent or editor advises you to do otherwise, follow your book proposal exactly without including something that you might not want to be part of the book or improvise on possible expected recommendations.
Publishers expect to acquire the book's primary rights, so that they can sell it in an adapted or condensed form as well. Mentioning any subsidiary rights, such as translation opportunities, performance and merchandising rights, or first-serial rights, will add to the editor's interest in buying your book. It is enticing to publishers to mention your manuscript's potential to turn into a series of books, although they might still hesitate to buy it right away—at least until the first one has been a successful endeavor.
The sample chapter
Since editors generally expect to see about one-tenth of a book, your sample chapter's length should reflect that in these building blocks of your book. The chapter should reflect your excitement and the freshness of the idea as well as surprise editors, but do not submit part of one or more chapters. Always send a chapter unless your credentials are impeccable due to prior publications on the subject. Do not repeat information in the sample chapter that will be covered by preceding or following ones, as the outline should be designed in such a way as to enable editors to understand the context already.
How to make your proposal stand out
Depending on the subject of your book, it is advisable to include illustrations that exemplify your vision of the book and can be included in the sample chapter. While these can make the book more expensive, it also increases the salability of the project. Further, you might consider including outstanding samples of your published work, such as clips from periodicals, if they are well-respected in the field. Thirdly, cover art can give your potential publisher a feel for your book and its marketability, especially if your topic is creative or related to the arts.
In addition, professionally formatting your materials will give you an edge over sloppy proposals. Proofread the materials carefully, use consistent and carefully organized fonts, spacing, etc., and submit your proposal without staples; rather, submit it in a neat portfolio that allows easy access and reassembling. However, check the submission guidelines first, as most proposals are submitted digitally. Finally, you should try to surprise editors and attract their attention. Your hook, however, should be imaginative but inexpensive (you do not want to bribe them, after all). Make sure your hook draws the editors to your book proposal immediately (Adapted from Larsen 154-60).

How to write a research proposal
Drafting your first research proposal can be intimidating if you’ve never written (or seen) one before. Our grad students and admissions staff have some advice on making a start.
Before you make a start
Is it a requirement for your course.
For some research courses in sciences you’ll join an existing research group so you don’t need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience.
Still, for many of our research courses — especially in humanities and social sciences — your research proposal is one of the most significant parts of your application. Grades and other evidence of your academic ability and potential are important, but even if you’re academically outstanding you’ll need to show you’re a good match for the department’s staff expertise and research interests. Every course page on the University website has detailed information on what you’ll need to send with your application, so make sure that’s your first step before you continue:
There are many ways to start, I’ve heard stories about people approaching it totally differently. Yannis (DPhil in Computer Science)
How to begin?
There isn’t one right way to start writing a research proposal. First of all, make sure you’ve read your course page - it’ll have instructions for what to include in your research proposal (as well as anything to avoid), how your department will assess it, and the required word count.
Start small, think big
A research degree is a big undertaking, and it’s normal to feel a bit overwhelmed at first. One way to start writing is to look back at the work you’ve already done. How does your proposed research build on this, and the other research in the area? One of the most important things you’ll be showing through your research project is that your project is achievable in the time available for your course, and that you’ve got (or know how you’ll get) the right skills and experience to pull off your plan.
They don’t expect you to be the expert, you just have to have good ideas. Be willing to challenge things and do something new. Rebecca (DPhil in Medieval and Modern Languages)
However, you don’t have to know everything - after all, you haven’t started yet! When reading your proposal, your department will be looking at the potential and originality of your research, and whether you have a solid understanding of the topic you’ve chosen.
But why Oxford?
An Admissions Officer at one of our colleges says that it’s important to explain why you’re applying to Oxford, and to your department in particular:
“Really, this is all dependent on a department. Look at the department in depth, and look at what they offer — how is it in line with your interests?”
Think about what you need to successfully execute your research plans and explain how Oxford’s academic facilities and community will support your work. Should I email a potential supervisor? Got an idea? If your course page says it’s alright to contact a supervisor (check the top of the How to apply section), it’s a good idea to get in touch with potential supervisors when you come to write your proposal.
You’re allowed to reach out to academics that you might be interested in supervising you. They can tell you if your research is something that we can support here, and how, and give you ideas. Admissions Officer
You’ll find more information about the academics working in your area on your department’s website (follow the department links on your course page ). John (DPhil in Earth Sciences) emailed a professor who had the same research interests as he did.
“Luckily enough, he replied the next day and was keen to support me in the application.”
These discussions might help you to refine your ideas and your research proposal.
Layal says, “I discussed ideas with my supervisor — what’s feasible, what would be interesting. He supported me a lot with that, and I went away and wrote it.”
It’s also an opportunity to find out more about the programme and the department:
“Getting in touch with people who are here is a really good way to ask questions.”
Not sure how to find a potential supervisor for your research? Visit our How-to guide on finding a supervisor .
Asking for help
My supervisors helped me with my research proposal, which is great. You don’t expect that, but they were really helpful prior to my application. Nyree (DPhil in Archaeological Science)
Don’t be afraid to ask for advice and feedback as you go. For example, you could reach out to a supervisor from your current or previous degree, or to friends who are also studying and could give you some honest feedback.
More help with your application
You can find instructions for the supporting documents you’ll need to include in your application on your course page and in the Application Guide.
Applicant advice hub
This content was previously available through our Applicant advice hub . The hub contained links to articles hosted on our Graduate Study at Oxford Medium channel . We've moved the articles that support the application process into this new section of our website.
- Application Guide: Research proposal
Can't find what you're looking for?
If you have a query about graduate admissions at Oxford, we're here to help:
Ask a question
Privacy Policy
Postgraduate Applicant Privacy Policy
- Ask a Librarian
Graduate Funding & Resources
- Assistantships
- Fellowships & Scholarships
Research Proposals
- Office of Prestigious Awards and Fellowships
Developing and writing proposals are important steps in the overall graduate-level research funding process.
- Selected Readings
- GRAPES (Graduate & Postdoctoral Extramural Support) Search for scholarships, grants, fellowships, and postdoctoral awards available to applicants of graduate programs. Designed for UCLA students, this is open for public use.
Books, charts, datasets, videos and reference content including the Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences series ( Little Green Books ), the Qualitative Research Methods series ( Little Blue Books ), and case studies. Helps you create research projects, understand the methods behind them, and create and share lists.
- To create a shareable link to a document, click the Get Link button.
- Creating a Proposal Writing Schedule PowerPoint presentation from The Office Graduate Education - University of Texas at Dallas
- Grant Proposals (or Give Me the Money!) From The Writing Center at University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill
- Grant-Writing Tips for Graduate Students From The Chronicle of Higher Education
- On the Art of Writing Proposals From the Social Science Research Council
- The Proposal Writer's Guide: Overview From The Office of Research at University of Michigan.
- Research Funding: 10 Tips for Writing a Successful Application From The Guardian
- Welcome to Writing Personal Statements Online From Pennsylvania State University
- Write Your Application From the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Academic Phrasebank - University of Manchester The Academic Phrasebank is a general resource for academic writers. It aims to provide you with examples of some of the phraseological ‘nuts and bolts’ of writing organized according to the main sections of a research paper or dissertation.
- Academic Proposals - Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) This resource introduces the genre of academic proposals and provides strategies for developing effective graduate-level proposals across multiple contexts.
- General Application Tips and Advice - ERAU's Office of Prestigious Awards and Fellowships This page from the Office of Prestigious Awards and Fellowships contains tips and advice on how to make the application process easier and better for yourself overall.
- Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal This Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal was created to help empower people to be successful in gaining funds for projects that provide worthwhile social service. A major theme that runs throughout the Guide is a concern for the development of meaningful cooperative relationships - with funding agencies, with community organizations, and with the people you are serving - as a basis for the development of strong fundable initiatives.
- Introduction to Proposal Writing This self-paced online tutorial provides an overview of how to write a standard project proposal to a foundation. Cost is free, and the estimated time to complete is 1 hour.
- Proposal Writing Resources - U. of Illinois Graduate College Provides online resources for starting the proposal process, as well as specific guidance in two main areas: Social Sciences/Humanities and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM).
- Writing a Project Proposal This Hunt Library webinar, presented by Joanne DeTor, provides the Do's and Dont's of proposal writing. Topics covered include: the importance of telling your research story succinctly and persuasively, demystifying the jargon, timelines, budgets, and more. By the end of the webinar, you will feel confident in writing a successful proposal for a grant, thesis, or dissertation.
- << Previous: Fellowships & Scholarships
- Next: Office of Prestigious Awards and Fellowships >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 3:44 PM
- URL: https://guides.erau.edu/graduate-proposals
Hunt Library
Mori Hosseini Student Union 1 Aerospace Boulevard Daytona Beach, FL 32114
Phone: 386-226-6595 Toll-Free: 800-678-9428
Maps and Parking
- Report a Problem
- Suggest a Purchase
Library Information
- Departments and Staff
- Library Collections
- Library Facilities
- Library Newsletter
- Hunt Library Employment
University Initiatives
- Scholarly Commons
- Data Commons
- University Archives
- Open and Affordable Textbooks
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)

Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
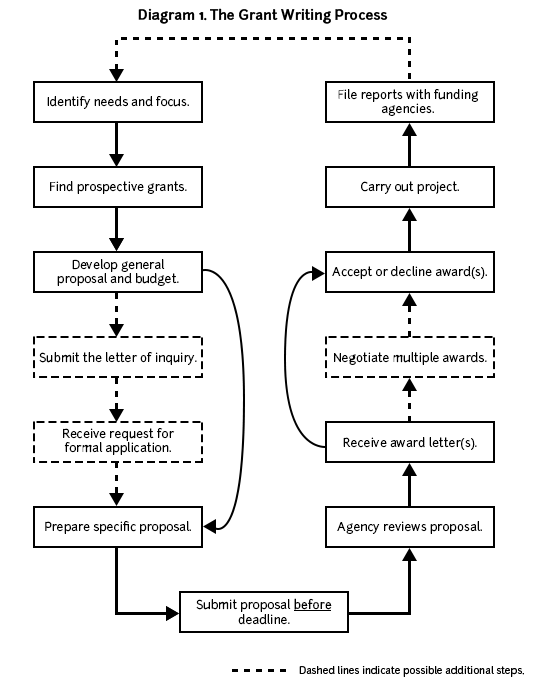
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
Example #3: project timeline in chart format.

Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
NSF Fellowship
The National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship ( NSF GRFP ) is a great way to start a research career. I was a successful applicant in 2010. Below are some details about the program and some tips for applying. You will also find many examples of successful essays and you can even submit your own essays if you are willing to serve as inspiration for the next round of applicants.
Note, this advice was last updated in Sept 2021.
What is it?
The NSF GRFP provides $34,000 to the student and some money to your department for three years. You have the flexibility to defer for up to two years in case you have another source of funding (but you cannot defer to take a year off).
The basic requirements are:
1. US Citizen, US National, or permanent resident
2. Currently a graduating Senior or First/Second year graduate student
3. Graduate students may only apply in their first OR second year (NOT both) . I have some thoughts on which year to apply .
4. Going into science research (does not apply to medical school)
Check out the official requirements at the NSF GRFP website . Here is the more detailed NSF presentation on the requirements. The deadlines are usually the last week of October , but it is never too early to start.
Basic Outline of Application Process
You will need to write two essays:
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals (3 pages)
Graduate Research Statement (2 pages)
You will need to get at least three letters of reference
These essays will be reviewed on the criteria of Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
And that's really it. The challenge is to sell yourself in 5 pages and to successful address the two criteria.
Tips for Getting Started
Read over the official NSF GRFP website , especially their tips .
Look through the NSF GRFP FAQ , with detailed answers here.
Here is a detailed website from Robin Walker . She has a very very thorough guide to the application .
Look at advice from past winners. There are lots of great advice out there, but in an interest to not overload you, here are my personal top choices. You can find more in my examples table at the bottom of the page.
Mallory Ladd - If you can follow her schedule, you should be more than prepared
Claire Bowen - Lots of advice interleaved with excerpts from successful essays
DJ Strouse - Applied under old system, but still great advice.
Blengineers - Fun video series of application tips
Read an example essay. I have posted all of my essays (and others) as well as my ratings sheets at the bottom of this page and organized into them into a table . Personally, I found this extremely useful and I have to give credit to two University of Wisconsin NSF GRFP winners who shared their essays with me, without which I was struggling on how to start the application.
Check out an old guide for reviewers .
For current discussions on the application process, check out this years NSF GRFP discussion at The GradCafe Forums . Some past years discussions include: 2020-2021 , 2019-2020 , 2018-2019 , 2017-2018 , 2016-2017 , 2015-2016 , 2014-2015 , 2013-2014 , 2012-2013 , 2011-2012 , and 2010-2011 .
General Advice
Every essay should address both Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Each essay needs explicit headers of Intellectual Merit / Broader Impacts .
NSF GRFP funds the person, not the project. The most important choice you make is designating the primary field (Chemistry vs Physics & Astronomy, etc). The subfield is less important. If you are an undergrad doing research, I would strongly suggest to make your research proposal related to what you are currently researching as long as: 1. you are going to apply to programs in the same primary field and 2. there is at least a small chance (even if only a few percent) that you could do something related to your proposal in graduate school. NSF will not force you to follow through with the research; instead they just want to see that you can actually write a proposal. I personally wrote about my undergraduate research. It was in physics and I only applied to physics graduate schools (so same primary field), but I was not sure I wanted to continue with it in graduate school, and in fact it ended up being impossible since I did not get into any graduate schools with anyone doing research in my proposed subfield.
Write for a general science audience and assume the reviewer is in your primary field, but not your subfield. This is NSF's tentative review panels , you can see that the only guarantee is that the reviewer is in your primary field.
Ask for letters of reference early and gently remind your writers of the deadline. Get a diverse set of letter writers. I had my current adviser (who was doing research similar to what I proposed), a past research adviser, and my boss at a tutoring center. Therefore, I had two letters addressing my intellectual merit, while one letter addressed broader impacts.
Ask for help. Your current university probably has a writing center . Don't be shy, they will love to help you. Also try asking around your department to find students who have applied previously.
Review Criteria Details
(Below is direct text from NSF but with sentences cut and added highlights)
General Review Criteria
In considering applications, reviewers are instructed to address the two Merit Review Criteria as approved by the National Science Board - Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts. Therefore, applicants must include separate statements on Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts in their written statements in order to provide reviewers with the information necessary to evaluate the application with respect to both Criteria as detailed below.
Reviewers will be asked to evaluate all proposals against two criteria:
Intellectual Merit: the potential to advance knowledge
Broader Impacts: the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.
The following elements should be considered in the review for both criteria:
What is the potential for the proposed activity to
Advance knowledge and understanding within its own field or across different fields (Intellectual Merit); and
Benefit society or advance desired societal outcomes (Broader Impacts)?
To what extent do the proposed activities suggest and explore creative, original, or potentially transformative concepts?
Is the plan for carrying out the proposed activities well-reasoned, well-organized, and based on a sound rationale ? Does the plan incorporate a mechanism to assess success ?
How well qualified is the individual, team, or organization to conduct the proposed activities?
Are there adequate resources available to the PI (either at the home organization or through collaborations) to carry out the proposed activities?
Extra details on Broader Impacts: (additional tips from NSF here )
Broader impacts may be accomplished through the research itself , through the activities that are directly related to specific research projects , or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project . NSF values the advancement of scientific knowledge and activities that contribute to achievement of societally relevant outcomes. Such outcomes include, but are not limited to: full participation of women, persons with disabilities, and underrepresented minorities in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM); improved STEM education and educator development at any level; increased public scientific literacy and public engagement with science and technology; improved well-being of individuals in society; development of a diverse, globally competitive STEM workforce; increased partnerships between academia, industry, and others; improved national security; increased economic competitiveness of the US; and enhanced infrastructure for research and education.
Merit Review Criteria specific to the GRFP
Intellectual Merit Criterion : the potential of the applicant to advance knowledge based on a holistic analysis of the complete application, including the Personal, Relevant Background, and Future Goals Statement, Graduate Research Plan Statement, strength of the academic record, description of previous research experience or publication/presentations, and references.
Broader Impacts Criterion : the potential of the applicant for future broader impacts as indicated by personal experiences, professional experiences, educational experiences and future plans.
Review Criteria: My Two Cents
Here is how I like to think of the review criteria, point by point.
How would answering this research question change science (Intellectual Merit) or society (Broader Impacts)?
Why should I fund you specifically, and not just this research question? What innovation do you specifically bring to the table?
Is there a detailed plan? With built in measures of success?
What are your qualifications?
Can you actual carry out the needed research?
At the end of each essay, you should be able to check off how you answered each point above for BOTH Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals: Essay Prompt from NSF
Prompt in 2021:
Please outline your educational and professional development plans and career goals. How do you envision graduate school preparing your for a career that allows you to contribute to expanding scientific understanding as well as broadly benefit society?
Additional prompt previously provided by NSF:
Describe your personal, educational, and/or professional experiences that motivate your decision to pursue advanced study in science, technology, engineering or mathematics (STEM). Include specific examples of any research and/or professional activities in which you have participated. Present a concise description of the activities, highlight the results and discuss how these activities have prepared you to seek a graduate degree. Specify your role in the activity including the extent to which you worked independently and/or as part of a team. Describe the contributions of your activity to advancing knowledge in STEM fields as well as the potential for broader impacts (See Solicitation, Section VI, for more information about Broader Impacts).
NSF Fellows are expected to become globally engaged knowledge experts and leaders who can contribute significantly to research, education, and innovations in science and engineering. The purpose of this essay is to demonstrate your potential to satisfy this requirement. Your ideas and examples do not have to be confined necessarily to the discipline that you have chosen to pursue.
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals Essay: My Two Cents
Based on the new emphasis NSF GRFP general requirements, I would write the essay in three main sections with two subsections for Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Personal Statement (~1 page). This is where you tell your unique story of either how you became interested in science, what makes you special, and/or any unique perspective you bring to science. Great place to mention if you had to overcome any hardships or would be adding to the diversity of the STEM field. Definitely use this section to highlight Broader Impacts.
Relevant Background (~1 page). Hopefully you already have research experience, so explain how that has prepared you for success in graduate school and beyond. Mainly use this section for Intellectual Merit, but also highly the Broader Impacts of your research experience.
Future Goals (~ 1/2 page). This is where you tie your personal background and scientific background into one cohesive vision for the future.
Intellectual Merit (~1/4 page). Conclude the essay by summarizing all of your contributions to Intellectual Merit. Make sure this is an explicit header.
Broader Impact (~1/4 page). Conclude the essay by summarizing all of your contributions to Broader Impact. Make sure this is an explicit header.
Graduate Research Statement: Essay Prompt from NSF
Present an original research topic that you would like to pursue in graduate school. Describe the research idea, your general approach, as well as any unique resources that may be needed for accomplishing the research goal (i.e. access to national facilities or collections, collaborations, overseas work, etc). You may choose to include important literature citations. Address the potential of the research to advance knowledge and understanding within science as well as the potential for broader impacts on society. The research discussed must be in a field listed in the Solicitation (Section X, Fields of Study).
Graduate Research Statement: My Two Cents
I would recommend structuring the essay as follows:
Introduction
Introduce the scientific problem and its impact on science and society (emphasis on Review Criteria 1)
Research Plan
Show the major steps that need to be accomplished
What is the creative part of your approach?
Have you thought of alternatives for hard or crucial steps?
What skills do you have to make this plan successful?
Intellectual Merit
Have a clear header for this section
Clearly demonstrate that tackling this problem will make an impact and advance science
Try to summarize how you hit all five Review Criteria
Broader Impacts
Paragraphs to address how this research impacts all five Review Criteria.
(Optional). Could use the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts sections as conclusion. If not, e nd with several sentences summarizing your project .
This essay will be Intellectual Merit heavy, but still needs to address Broader Impacts. Show why the broader scientific community / society should care about your research!
Examples of Successful Essays
These are all the essays of recent winners that I could find online. If you want me to link to an example on your website, or if you are willing to share your essays but don't have a site, I can add it to the table if you fill out the contact form below .
Some notes:
Click here to apply your own sort / filters to the table .
Remember the format changed starting in 2014!
If I couldn't figure out the year, I filled in 2013 for old format and 2014 for new formats.
Proposal Column --- Graduate Research Plan ( >= 2014) or Proposed Research ( <= 2013)
Personal Column --- Personal, Relevant Background, and Future Goals ( >= 2014) or Personal ( <= 2013)
Previous Column --- Previous Research Statement ( <= 2013 only)
HM = Honorable Mention
Can't find an example in your area? Tip from GradCafe Forum : politely email past winners !
I've linked to a lot of sites, let me know if any links break! A suggested fix is even better :)
Example essays below, or open in Google Drive
Submit Example Here

NSF GRFP Research Statement
Criteria for success.
- You are eligible for the Fellowship (Be certain to check for restrictions, i.e., only U.S. citizens, nationals, and permanent residents are eligible.)
- Your research proposal convinces a panel of academics that you are qualified to receive the Fellowship, especially with respect to the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria.
- You show that the proposed research is creative, original, and transformative.
- You show that you are actually capable of performing the research.
- Your proposal meets the formatting and page limit criteria.
- Text is grammatically correct and free of typos.
Structure Diagram
According to NSF guidelines, “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts” should be addressed under separate headings. Otherwise, the titles, sizes, and order of sections is flexible within the two-page limit. One example breakdown is shown in the diagram above.
Applications prior to 2018 did not require “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts” to be addressed under separate headings. Be sure to follow the most up-to-date guidelines provided by NSF, especially if you are referencing older examples.
Your research proposal (technically, the “Graduate Research Plan Statement”) is the part of the NSF application where you have an opportunity to lay out a plan for your graduate research career. While the personal statement gives you space to explain the big picture of your past and future career, the research proposal is a place for more detail. Your goal is to convince the selection panel that you are capable of being a successful researcher: that you have the intellectual ability to propose a creative, feasible plan of research.
Unlike many funding opportunities, the NSF GRFP is designed to fund a person rather than a project . The goal of your research proposal is to show that you can propose feasible, original research of an appropriate scope. Even if you are awarded the Fellowship, you will not be limited to the details described in your research proposal.
Analyze Your Audience
Your entire application will be reviewed by “disciplinary and interdisciplinary scientists and engineers, and other professional graduate education experts.” These are academics, usually from your broad area of science (e.g., materials research) but not from your specific area (e.g., optoelectronics). They will judge your application using some combination of the NSF’s official criteria for the Fellowship and their own ideas about what constitutes good science.
The people on the committee read many, many applications. Make it easy for them to figure out that you are qualified for the award by referencing the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria that they use to judge your application. It may be wise to have an “Abstract” or “Executive Summary” at the beginning of the proposal. Use simple language rather than field-specific jargon.
The selection panel knows that this application is for a graduate student fellowship and not for a large grant that might go to a principal investigator. Real grant proposals are big documents with heaps of citations and references. Because this application is about funding you , rather than funding a specific project, the panel is more interested in seeing what your proposal says about you and your ability to write a good proposal rather than about your proposed research. Be sure to keep an emphasis on showing that you are capable and creative, and cite only papers you feel are necessary to provide directly related background (or to highlight your own relevant research if applicable).
Include Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria
The NSF GRFP criteria emphasize “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts.” Do not just make up your own ideas about what these terms mean. Read the solicitation so you know what “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts” mean to the NSF, and show that your proposed research meets those criteria. This is the arguably the most important step in preparing your proposal, because it is by these criteria that your application will be evaluated.
In the 2023 solicitation, NSF defines these terms: “The Intellectual Merit criterion encompasses the potential to advance knowledge… The Broader Impacts criterion encompasses the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.” The NSF also has specific lists of activities that constitute Broader Impacts.
Be sure to include Broader Impacts and Intellectual Merit throughout your proposal as well as in separate, labeled sections. According to the 2023 solicitation, “Applications that do not have separate headings for Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts will not be reviewed.”
Do your homework
A mature and sophisticated proposal for research is more likely to win you the Fellowship. Before sitting down to write, do your homework. Read many papers from the field in which you are proposing research. Make sure the research you are proposing to do hasn’t been done before or isn’t generally regarded as impossible.
Established researchers in your field can also be an excellent resource as you write your proposal. More senior scientists like postdocs and faculty members have a lot of experience crafting research proposals, and they are similar to the kinds of people who will be reviewing your proposal. Finally, your proposal should also be exciting to someone who is in your research area. If a scientist in your field has reservations about whether your project is worth funding, then scientists from other areas might have an even more difficult time believing the research is worth pursuing.
Demonstrate creativity while maintaining credibility
In any research proposal, there is a tradeoff between risk/reward and credibility. Low risk projects, like obvious, simple extensions of your undergraduate thesis research, tend to be very credible: it’s clear that you can do them. They also tend to be low on reward. Projects that are very ambitious and have huge rewards tend to be unbelievable and impossible for a grad student. The key to a successful application frequently involves finding the optimum balance between the two: find a problem that you can probably solve and that demonstrates that you took some initiative, understand your field, and have some creative thoughts.
Relatedly, your research proposal will be judged, in part, on the basis of whether or not the panel members believe you will actually be able to carry it out. It might therefore be wise to name the key resources in your target institution and program. Your success as a graduate student will depend on your advisor’s mentorship, the opportunity for collaboration with other scientists, and the resources that you will have at your target institution. Make it clear that you will have the right equipment and intellectual input that you will need to solve your problem.
Write to a fatigued, non-field-specific audience
It’s more important that all the members of your panel understand your work than that you impress the one member of the panel who happens to be in your field. When you write a paper or a grant, it will probably be minutely reviewed by people much closer to your field of study. However, your panel for the NSF GRFP will not be nearly as field specific, and your application will be one of many that they read. They may very well miss points in your proposal that you think are “subtle” or “implicit.” Explicitly tell them what you’re doing and why, and make it clear even to someone who doesn’t know your field and who may be exhausted after reading many applications.
Lay out concrete hypotheses, approaches, and outcomes
Strong research proposals say what motivates the project, how the project will get done, and what the project’s outcome will mean with respect to the motivating scientific question.
When discussing research approach and outcomes, make it clear that the project has a clear endpoint that is well within the timeline of a Ph.D. It’s great if your project leads into a lifelong line of research, but the NSF GRFP only funds graduate study. To be awarded the Fellowship, you need to be able to complete the proposed research in a few years.
As best you can, describe concrete approaches and outcomes: e.g. Will you develop a new algorithm or design a certain tool? What output will your research generate? Having concrete outcomes can additionally help you show how your proposed research will meet the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts criteria by allowing you to point to specific effects it will have on society.
Content adapted by the MIT Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Communication Lab from an article originally created by the MIT Biological Engineering Communication Lab .
Resources and Annotated Examples
Nsf grfp research statement annotated example 1.
Research statement submitted by senior undergraduate student in 2020 1 MB
NSF GRFP Research Statement Annotated Example 2
Research statement submitted by first-year graduate student in 2021 247 KB

COMMENTS
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
Example research proposal #1: ... A master's is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers. All master's involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; ...
Research and Citation. Overview; Conducting Research; Using Research; APA Style (7th Edition) ... Reading for Graduate School; Sample Academic Proposals; Suggested Resources ... Select the Sample Academic Proposals PDF in the Media box above to download this file and read examples of proposals for conferences, journals, and book chapters. ...
Significance example • My research on identity and development is innovative because it brings together analysis of national discourses about Indians with a study of the practices and choices of the individual Indians whose identities are at issue. I believe this research can be helpful to the nation, development agencies,
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals. For samples of academic proposals ...
Research proposals have a limit on words or pages so you won't be able to analyse the whole existing body of literature. ... • Stakeholders and end-users include, for example, the research community, a professional body or groups of researchers, a particular group of people such as children, older people or doctors, the government, the ...
For some research courses in sciences you'll join an existing research group so you don't need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience. Still, for many of our research courses ...
Covering all aspects of the proposal process, from the most basic questions about form and style to the task of seeking funding, this volume offers clear advice backed up with excellent examples. Included are a number of specimen proposals to help shed light on the important issues surrounding the writing of proposals.
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
Purpose. Your research proposal (technically, the "Graduate Research Plan Statement") is part of an application that should convince the selection panel to award you the Fellowship. The proposal is the part of the application where you get to lay out a plan for your graduate research career. The personal statement gives you space to explain ...
Example: Full proposal submitted by the College of Engineering for an M.S. and Ph.D. Program in Environmental and Ecological Engineering (EEE), Purdue University, West Lafayette ... will provide vital transformative STEM education and world changing research opportunities to graduate students. The program can build upon the strengths of Purdue ...
1.Choose a research topic and develop a working title. Having a strong interest in your research topic will certainly help you to keep going when the journey becomes more challenging. The research topic is the subject of your research, which is a part of a broader field of study.
We break down two research proposal examples/samples, as well as our popular research proposal template, piece by piece. Learn about the key components of a ...
A research proposal is commonly written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project when enrolling for a research-based postgraduate degree. Graduate and post-graduate students also embark on a university dissertation to obtain a degree or get that Ph.D. Although it is just a course assignment, a student must treat the introduction ...
Research Proposal Examples. Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section. 1. Education Studies Research Proposals.
A Sample Research Proposal with Comments A research project or thesis will take at least two semesters to complete. Prior to starting a research, i.e. enrolling in the first semester research course, students must go through the proposal stage, during which students will develop their proposal and have it reviewed by his/her research advisor. ...
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It's targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
Include specific examples of any research and/or professional activities in which you have participated. Present a concise description of the activities, highlight the results and discuss how these activities have prepared you to seek a graduate degree. ... Proposal Column --- Graduate Research Plan ( >= 2014) or Proposed Research ( <= 2013 ...
Your research proposal convinces a panel of academics that you are qualified to receive the Fellowship, especially with respect to the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria. ... especially if you are referencing older examples. Purpose. Your research proposal (technically, the "Graduate Research Plan Statement") is the part of the ...