Suitability of vermicomposting for different varieties of organic waste: a systematic literature review (2012–2021)
- Published: 02 November 2022
- Volume 12 , pages 581–602, ( 2022 )

Cite this article
- Kishor Kumar Maharjan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8421-1475 1 , 2 ,
- Prakrit Noppradit 1 &
- Kuaanan Techato 1
660 Accesses
4 Citations
Explore all metrics
The aim of this study was to assess the suitability of vermicomposting for various types of organic waste based on earthworm growth and reproduction as well as nutrient content in final vermicompost. The study was also focused on the kinds of earthworms employed in the research, the countries where vermicomposting research was done, and fundamental operating conditions. To fulfill these aims, we developed research questions and used two reputable databases, namely, SCOPUS and Science Direct. We developed inclusion and exclusion criteria and the papers were taken from the years between 2012 and 2021. This study identified the majority of vermicomposting research related to waste management was conducted in Asian countries (55%) where India has the highest number of paper publications (35%). Research in the field of vermicomposting grew continuously from 2017. Furthermore, Eisenia fetida is a commonly used species for vermicomposting. The majority of vermicomposting experiments were conducted on animal waste, followed by sewage and industrial sludge. According to existing literature, almost all organic wastes can be used for vermicomposting. However, before being used as earthworm feed, these wastes should be pre-composted and should mix with secondary waste in proper proportions. Eighty percent of the papers suggested the importance of pre-composting or treatment before the actual vermicomposting starts.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Vermicomposting of municipal solid waste as a possible lever for the development of sustainable agriculture. A review
Vincent Ducasse, Yvan Capowiez & Joséphine Peigné
Optimizing the vermicomposting of organic wastes amended with inorganic materials for production of nutrient-rich organic fertilizers: a review
Hupenyu Allan Mupambwa & Pearson Nyari Stephano Mnkeni

Vermicomposting—An Effective Method for Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Impact
Adhikary S (2012) Vermicompost, the story of organic gold: a review. Agric Sci 03(07):905–917. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2012.37110
Article Google Scholar
Asian Development Bank [ADB] (2012) Nepal: Capacity building for waste management. Organic Composting (ADB TA 7597- NEP)
Aynehband A, Gorooei A, Moezzi AA (2017) Vermicompost: an eco-friendly technology for crop residue management in organic agriculture. Energy Procedia 141:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.11.090
Behera KK, Alam A, Vats S, Sharma HP, Sharma V (2012) Organic farming history and techniques. In: Lichtfouse E (ed) Sustainable agriculture reviews. Springer, Berlin, pp 287–328
Google Scholar
Belmeskine H, Ouameur WA, Dilmi N, Aouabed A (2020) The vermicomposting for agricultural valorization of sludge from Algerian wastewater treatment plant: impact on growth of snap bean Phaseolus vulgaris L. Heliyon 6(8):04679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04679
Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP (2016) Effect on growth of earthworm and chemical parameters during vermicomposting of pressmud sludge mixed with cattle dung mixture. Procedia Environ Sci 35:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.025
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig A P (2015) Potential utilization of bagasse as feed material for earthworm Eisenia fetida and production of vermicompost. SpringerPlus 4(1) https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-014-0780-y
Boruszko D (2020) Vermicomposting as an alternative method of sludge treatment. J Ecol Eng 21(2):22–28. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/116352
Busato JG, Lima LS, Aguiar NO, Canellas LP, Olivares FL (2012) Changes in labile phosphorus forms during maturation of vermicompost enriched with phosphorus-solubilizing and diazotrophic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 110:390–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.126
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Castillo-González E, Giraldi-Díaz MR, De Medina-Salas L, Sánchez-Castillo MP (2019) Pre-composting and vermicomposting of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and vegetable waste. Appl Sci 9(17). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173564
Castillo-González E, De Medina-Salas L, Giraldi-Díaz MR, Sánchez-Noguez C(2021) Vermicomposting: a valorization alternative for corn cob waste. Appl Sci 11(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125692
China Power (2016) Is China a global leader in research and development? | ChinaPower Project. In Center for Strategic Studies & International Studies. https://chinapower.csis.org/china-research-and-development-rnd/ . Accessed 26 June 2022
Crescent T (2003) Vermicomposting. Development alternatives (DA) sustainable livelihoods [Internet], Available from. http://www.dainet.org/livelihoods/default.htm . Accessed 12 Nov 2012
Crutchik D, Rodríguez-Valdecantos G, Bustos G, Bravo J, González B, Pabón-Pereira C (2020) Vermiproductivity, maturation and microbiological changes derived from the use of liquid anaerobic digestate during the vermicomposting of market waste. Water Sci Technol 82(9):1781–1794. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.427
Das D, Abbhishek K, Banik P, Bhattacharya P (2021) A valorisation approach in recycling of organic wastes using low-grade rock minerals and microbial culture through vermicomposting. Environmental Challenges 5:100225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100225
De Medina-Salas L, Giraldi-Díaz MR, Castillo-González E, Morales-Mendoza LE (2020) Valorization of orange peel waste using precomposting and vermicomposting processes. Sustainability 12(18):6–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187626
Debnath S, Chaudhuri PS (2020) Growth and reproduction of Perionyx excavatus (Perrier) during vermicomposting of different plant residues. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 19(5):1937–1943. https://doi.org/10.46488/NEPT.2020.v19i05.018
Dhiman V (2020) Organic farming for sustainable environment: review of existed policies and suggestions for improvement. Int J Res Rev 7:22–31
Domínguez J (2004) State-of-the-art and new perspectives on vermicomposting research. Earthworm Ecol 401–424. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420039719.ch20
Dominguez and Edwards (2011) Biology and ecology of earthworm species used for vermicomposting. https://doi.org/10.1201/b10453
Edwards CA(2004) Earthworm ecology, 2 nd ed. CRC ress: Boca Raton, FL, USA; ISBN 978–0–8493–1819–1
Ferronato N, Pinedo MLN, Torretta V (2020) Assessment of used baby diapers composting in Bolivia. Sustainability 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125055
FiBL (2019) The world of organic agriculture. In The world of organic agriculture statistic and emerging trends. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781849775991
Ganguly RK, Chakraborty SK (2019) Assessment of qualitative enrichment of organic paper mill wastes through vermicomposting: humification factor and time of maturity. Heliyon 5(5):e01638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01638
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ganguly RK, Chakraborty SK (2021) Valorisation of toxic paper mill waste through vermicomposting: an insight towards cleaner engineering through alleviation of wastes. Clean Eng Technol 2:100070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100070
Garczyńska M, Kostecka J, Paczka G, Hajduk E, Mazur-Paczka A, Butt KR (2020a) Properties of vermicomposts derived from Cameroon sheep dung. Appl Sci 10(15):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155048
Garczyńska M, Paczka G, Podolak A, Mazur-Paczka A, Szura R, Butt KR, Kostecka J (2020b) Effects of Owinema bio-preparation on vermicomposting in earthworm ecological boxes. Appl Sci 10(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020456
Ghorbani M, Sabour MR, Bidabadi M (2021) Vermicomposting smart closed reactor design and performance assessment by using sewage sludge. Waste Biomass Valorization 12(11):6177–6190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01426-w
Hidayati YA, Nurachma S, Badruzzaman DZ, Marlina ET, Harlia E (2021) Utilization of sheep dung and rice straw with indigenous microbial agent to optimize vermicompost production and quality. Biodiversitas 22(12):5445–5451. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d221227
Huang K, Xia H, Wu Y, Chen J, Cui G, Li F, Chen Y, Wu N (2018) Effects of earthworms on the fate of tetracycline and fluoroquinolone resistance genes of sewage sludge during vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 259(88):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.021
Hussain N, Abbasi T, Abbasi SA (2020) Evaluating the fertilizer and pesticidal value of vermicompost generated from a toxic and allelopathic weed ipomoea. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 19(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2018.05.005
Hussain N, Abbasi T, Abbasi SA (2017) Detoxification of parthenium (Parthenium hysterophorus) and its metamorphosis into an organic fertilizer and biopesticide. Bioresour Bioprocess 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0156-6
ISWA (2020) Global assessment of municipal organic waste production and recycling. international solid waste association stationsplein 45 A4.004 3013AK rotterdam the Netherlands
Jjagwe J, Komakech AJ, Karungi J, Amann A, Wanyama J, Lederer J (2019) Assessment of a cattle manure vermicomposting system using material flow analysis: a case study from Uganda. Sustainability 11(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195173
Kapila R, Verma G, Sen A, Nigam A (2021) Evaluation of microbiological quality of vermicompost prepared from different types of organic wastes using Eisenia fetida. Agric Sci Digest 41(3):445–449. https://doi.org/10.18805/ag.D-5275
Karmakar S, Brahmachari K, Gangopadhyay A, Choudhury SR (2012) Recycling of different available organic wastes through vermicomposting. E-J Chem 9(2):801–806. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/945762
Katakula AAN, Handura B, Gawanab W, Itanna F, Mupambwa HA (2021) Optimized vermicomposting of a goat manure-vegetable food waste mixture for enhanced nutrient release. Sci Afr 12:e00727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e00727
Kaur T (2020) Vermicomposting: an effective option for recycling organic wastes. Organic Agriculture: 1–17. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.91892
Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P & Woerden, & Van F (2018) What a waste 2.0 a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. International bank for reconstruction and development. The world bank 1818 H Street NW, Washington, DC
Kujawska J, Wójcik-Oliveira K (2019) Effect of vermicomposting on the concentration of heavy metals in soil with drill cuttings. J Ecol Eng 20(1):152–157. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/93868
Kumar Badhwar V, Singh S, Singh B (2020) Biotransformation of paper mill sludge and tea waste with cow dung using vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 318(August):124097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124097
Lakhotia SC (2018) Why are Indian research journals not making a mark? - the enemy is within. Curr Sci 115(12):2187–2188
Lalander CH, Komakech AJ, Vinneras B (2015) Vermicompost as manure management strategy for urban small-holder animal farms-kampala case study. Waste Manag 39:96-103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.02.009
Lim PN, Wu TY, Clarke C, Nik Daud NN (2015) A potential bioconversion of empty fruit bunches into organic fertilizer using Eudrilus eugeniae. Int J Sci Environ Technol 12(8):2533–2544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0648-2
Liu X, Geng B, Zhu C, Li L, Francis F (2021) An improved vermicomposting system provides more efficient wastewater use of dairy farms using Eisenia fetida. Agron 11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050833
Mago M, Yadav A, Gupta R, Garg VK (2021) Management of banana crop waste biomass using vermicomposting technology. Bioresour Technol 326:124742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124742
Mahaly M, Senthilkumar AK, Arumugam S, Kaliyaperumal C, Karupannan N (2018) Vermicomposting of distillery sludge waste with tea leaf residues. Sustain Environ Res 28(5):223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2018.02.002
Maity S, Bhattacharya S, Chaudhury S (2009) Metallothionein response in earthworms Lampito mauritii (Kinberg) exposed to fly ash. Chemosphere 77(3):319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.011
Majlessi M, Eslami A, Saleh HN, Mirshafieean S, Babaii S (2012) Vermicomposting of food waste: assessing the stability and maturity. J Environ Health Sci Eng 9(1):1–6
Manivannan S, Balamurugan M, Parthasarathi K, Gunasekaran G, Ranganathan LS (2009) Effect of vermicompost on soil fertility and crop productivity – beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Environ Biol 30:275–281
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mashur M, Bilad MR, Hunaepi H, Huda N, Roslan J (2021) Formulation of organic wastes as growth media for cultivation of earthworm nutrient-rich Eisenia foetida. Sustainability 13(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810322
Matheson T (2022) Disposal is not free: fiscal instruments to internalize the environmental costs of solid waste. SSRN Electron J 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3524304
Mohapatra D, Sahoo KK, Sannigrahi AK (2019) Impact of Eisenia fetida populations on bio-conversion of paper mill solid wastes. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 8(1):189–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-019-0288-0
Molavi F, Ehrampoush MH, Ebrahimi AA, Nabi-Meibodi M, Mokhtari M (2020) Evaluating changes in microbial population and earthworms weight during vermicomposting of cow manure containing co-trimoxazole. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(2):403–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00404-8
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mousavi SA, Sader SR, Farhadi F, Faraji M, Falahi F (2020) Vermicomposting of grass and newspaper waste mixed with cow dung using Eisenia fetida: physicochemical changes. Glob Nest J 22(1):8–14. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.003151
Mulla AI, Pathade GR (2020) Optimization of incubation period, pH and moisture content for vermicomposting of biomethanation sludge admixed with fruits and vegetable waste collected from Gultekadi Market Yard, Pune using Eudrilus eugeniae. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 19(2):873–880. https://doi.org/10.46488/NEPT.2020.V19I02.047
Mupambwa HA, Ravindran B, Mnkeni PNS (2016) Potential of effective micro-organisms and Eisenia fetida in enhancing vermi-degradation and nutrient release of fly ash incorporated into cow dung-paper waste mixture. Waste Manag 48:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.10.001
Mupondi LT, Mnkeni PNS, Muchaonyerwa P, Mupambwa HA (2018) Vermicomposting manure-paper mixture with igneous rock phosphate enhances biodegradation, phosphorus bioavailability and reduces heavy metal concentrations. Heliyon 4(8):e00749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00749
Musyoka SN, Liti DM, Ogello EO, Meulenbroek P, Waidbacher H (2020) Using earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to bio-convert agro-industrial wastes for aquaculture nutrition. BioResources 15(1):574–587. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.1.574-587
Nannoni F, Rossi S, Protano G (2014) Soil properties and metal accumulation by earthworms in the Siena urban area (Italy). Appl Soil Ecol 77:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.01.004
Orozco FH, Cegarra J, Trujillo LM, Roig A (1996) Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia foetida: effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biol Fertil Soils 22:162–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384449
Parthasarathi K, Balamurugan M, Prashija KV, Jayanthi L, Basha SA (2016) Potential of Perionyx excavatus (Perrier) in lignocellulosic solid waste management and quality vermifertilizer production for soil health. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 5(1):65–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-016-0118-6
Rameshwar HY, Argaw A (2016) Manurial value of khat waste vermicompost from Awday, Harar town, Ethiopia. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 5(2):105–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-016-0121-y
Raza ST, Tang JL, Ali Z, Yao Z, Bah H, Iqbal H, Ren X (2021) Ammonia volatilization and greenhouse gases emissions during vermicomposting with animal manures and biochar to enhance sustainability. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010178
Raza ST, Bo Z, Ali Z, Liang TJ (2019) Better nutrient recovery and organic waste 51(3):1027–1034.
Rupani PF, Alkarkhi AFM, Shahadat M, Embrandiri A, El-Mesery HS, Wang H, Shao W (2019) Bio-optimization of chemical parameters and earthworm biomass for efficient vermicomposting of different palm oil mill waste mixtures. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(12):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122092
Rupani PF, Embrandiri A, Ibrahim MH, Shahadat M, Hansen S, Mansor NNA (2017) Bioremediation of palm industry wastes using vermicomposting technology: its environmental application as green fertilizer. 3 Biotech 7(3):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0770-1
Sahariah B, Goswami L, Kim KH, Bhattacharyya P, Bhattacharya SS (2015) Metal remediation and biodegradation potential of earthworm species on municipal solid waste: a parallel analysis between Metaphire posthuma and Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 180:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.062
Sánchez-Rosales R, Hernández-Rodríguez A, Ojeda-Barrios D, Robles-Hernández L, González-Franco AC, Parra-Quezad R (2017) Comparison of three systems of decomposition of agricultural residues for the production of organic fertilizers. Chil J Agric Res 77(3):287–292. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392017000300287
Shah RU, Abid M, Qayyum MF, Ullah R (2015) Dynamics of chemical changes through production of various composts/vermicompost such as farm manure and sugar industry wastes. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 4(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-015-0083-5
Sharma KD, Jain S (2020) Municipal solid waste generation, composition, and management: the global scenario. Soc Responsib J 16(6):917–948. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-06-2019-0210
Singh WR, Kalamdhad AS (2016) Transformation of nutrients and heavy metals during vermicomposting of the invasive green weed Salvinia natans using Eisenia fetida. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 5(3):205–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-016-0129-3
Singh CK, Kumar A (2017) Vermicomposting of terrestrial weeds Lantana camara L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. Agric Solid Waste 28:63–69
Sinha RK, Agarwal S, Chauhan K, Valani D (2010) The wonders of earthworms and its vermicompost in farm production: Charles Darwin’s friends of farmers, with potential to replace destructive chemical fertilizers from agriculture. J Agric Sci 1:76–94. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2010.12011
Sohal B, Ahmad Bhat S, Vig AP (2021) Vermiremediation and comparative exploration of physicochemical, growth parameters, nutrients and heavy metals content of biomedical waste ash via ecosystem engineers Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 227:112891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112891
Sosnecka A, Kacprzak M, Rorat A (2016) Vermicomposting as an alternative way of biodegradable waste management for small municipalities. J Ecol Eng 17(3):91–96. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/63310
Światek J, Spitzer T, Grobelak A, Kacprzak M (2019) Effects of biochar addition on vermicomposting of food industry sewage sludge. J Ecol Eng 20(3):36–45. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/97242
Wang Y, Zhang QQ, He K, Zhang Q, Chai L (2013) Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols over China: response to 2000–2015 emission changes of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia. Atomspheric Chem Phys 13(5):2635–2652. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-2635-2013
Wang Y, Han W, Wang X, Chen H, Zhu F, Wang X & Lei C (2017) Speciation of heavy metals and bacteria in cow dung after vermicomposting by the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 245:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.118
Wani KA, Mamta, Rao RJ (2013) Bioconversion of garden waste, kitchen waste and cow dung into value-added products using earthworm Eisenia fetida. Saudi J Biol Sci 20(2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.01.001
Wiethan MMS, Bortolin GS, Pinto RS, Sari BG , da SILVA ACF (2018) Development and multiplication of Eisinea andrei in the manure of cattle subjected to high Trichoderma doses. Bioscience 34(6):1–10. https://doi.org/10.14393/BJ-v34n6a2018-40009
Wu Z, Yin B, Song X, Qiu J, Cao L, Zhao Q (2019) Effects of salinity on earthworms and the product during vermicomposting of kitchen wastes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(23):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234737
Yuvaraj A, Karmegam N, Tripathi S, Kannan S, Thangaraj R (2020) Environment-friendly management of textile mill wastewater sludge using epigeic earthworms: bioaccumulation of heavy metals and metallothionein production. J Environ Manage 254:109813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109813
Zhang H, Li J, Zhang Y, Huang K (2020) Quality of vermicompost and microbial community diversity affected by the contrasting temperature during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051748
Zhang L, Sun X (2016) Influence of bulking agents on physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage composting of green waste. Waste Manage 48:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.032
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Graduate School, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand, for which the authors highly acknowledge. Authors are grateful to Prince of Songkla University for necessary library facilities.
Financial support was received from Graduate School, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Environmental Management, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand
Kishor Kumar Maharjan, Prakrit Noppradit & Kuaanan Techato
Department of Environmental Science, Tri-Chandra Multiple Campus, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal
Kishor Kumar Maharjan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors had contributed to the study. The contributions were as follows:
Kishor Kumar Maharjan: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, data curation, formal analysis. Prakrit Noppradit: review and editing, supervision. Kuaanan Techato: review and editing, supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kishor Kumar Maharjan .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Maharjan, K.K., Noppradit, P. & Techato, K. Suitability of vermicomposting for different varieties of organic waste: a systematic literature review (2012–2021). Org. Agr. 12 , 581–602 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-022-00413-2
Download citation
Received : 01 June 2022
Accepted : 20 October 2022
Published : 02 November 2022
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-022-00413-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Animal manure
- Research questions
- Systematic literature review
- Vermicomposting
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Agriculture Research Guide
- Find Journal Articles
- In The News
- Websites and Organizations
- Reference Books
A Review of the Literature
Literature review examples.
- The Research Process
- APA Citations
Subject Guide

1. Introduction
Not to be confused with a book review, a literature review surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources (e.g. dissertations, conference proceedings, reports) relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of each work. The purpose is to offer an overview of and background on significant literature published on a topic.
2. Components
Similar to primary research, development of the literature review requires four stages:
- Literature search—finding materials relevant to the subject being explored
- Data evaluation—determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic
- Analysis and interpretation—discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature
Literature reviews should comprise the following elements:
- An overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review
- Division of works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative theses entirely)
- Explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research
3. Definition and Use/Purpose
A literature review may constitute an essential chapter of a thesis or dissertation, or may be a self-contained review of writings on a subject. In either case, its purpose is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to the understanding of the subject under review
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration
- Identify new ways to interpret, and shed light on any gaps in, previous research
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort
- Point the way forward for further research
- Place one's original work (in the case of theses or dissertations) in the context of existing literature
The literature review itself, however, does not present new primary scholarship.
Information adapted from UC Santa Cruz University Library .
- Master's Theses Database of master's theses written by CSU, Chico students, from 2009 on. Many of these will contain published examples of literature reviews.
- Proquest Dissertations and Theses: The Humanities and Social Sciences Collection Containes over 2 million dissertations and theses with abstracts, 24 page free previews, and full-text PDF, if available, for dissertations and theses dating back to 1637.
- Sample APA Paper (lit. review begins page 3) Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- << Previous: Find Books
- Next: The Research Process >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2024 12:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csuchico.edu/agriculture_dg
Meriam Library | CSU, Chico
OVERVIEW OF EARTHWORM CASTS AND A COMPARISON WITH COMPOST
WASTE PROCESSING BY EARTHWORMS
Optimal conditions for earthworm activity
· Cool temperature: between 0 and 35 o C
· Not too much water (85% moisture)
Mineralization in the earthworm gut
· As feed passes through the earthworm gut the material is mineralized and plant nutrients are available. The grinding effect of the gizzard and the passage through the gut leads to the formation of a granule (15) (16) .
· Casts have a structure that is similar to a slow release granule: it has an organic matter core and a clay casing (1) .
Casts benefit to plants
· Casts contain the necessary nutrients for plant growth: when added in sufficient amounts, as in 4 -10 Kg casts / m 2 , casts can out-yield NPK fertilizers (100 Kg N / m 2 ) (13) .
· Casts increase plant dry weight and N, P, Mg and K uptake from the soil (12) .
· The presence of earthworms increases plant growth and N uptake as opposed to unfertilized soil (19) .
· Casts have a hormone-like effect that increases germination and growth rate (14) .
Waste preparation for processing by earthworms
· Organic debris are more palatable to earthworms if it’s fresh or incubated for up to 2 weeks. The particle size of organic matter doesn’t matter (23) .
· Earthworms have less requirements than microbes in processing carbon and nitrogen (24) . The C:N ratio which results in the most stable earthworm casts is 25 ( Ndegwa and Thompson, 2000).
· High salinity levels and alkalinity harm earthworms. Earthworms are also sensitive to pesticides (25) .
Types of earthworms used
· Earthworms are chosen for their resistance to extreme conditions and feeding and reproductive rate. They also need to survive handling.
· Eisenia foetida is the most efficient in waste processing, while Eudrilus eugeniae is large, fast growing, reasonably prolific and would be ideal for protein production Eudrilus eugenia (17) .
CASTS OR COMPOST?
Both are organic products which provide the plant with nutrients, good soil aeration and other un-identified advantages (the “organic matter effect”) (10) .
Comparison as to plant nutrients
· Plants treated with compost may still show N deficiency, even when synthetic fertilizer is added. His is due to N immobilization: microorganisms in compost use N for their metabolism (3) .
· More decomposition ( Lignolysis ) occurs and higher levels of Nitrogen are reached when waste is fed to worms than in composting. Casts also increase protein synthesis in plants (7) .
· Compost can be an incomplete fertilizer, most plants have a an increase in yield with the addition of compost, organic N sources can cause a short term yield decrease (18) .
Comparison as to the timing of nutrient release
· Slow nutrient release is more synchronized with plant needs, and leads to higher yields (9) .
· In my master’s thesis ( Chaoui et al, 2003) I showed that casts show a slower nutrient release rate than compost, possibly explaining the higher plant weight to nutrient content ratio.
Comparison as to salinity level
· Ammonium is the main contributor to salinity levels.
· High salinity levels cause osmotic drought.
· NH 4 levels are high in fresh casts but casts stabilize after 2 weeks of aging through nitrification. The acidity level in casts is slightly low, which reduces denitrification (5) . Salinity levels are moderate in casts, since passage through the earthworm gut does not increase the level of some salts (Ca, Mg, Na ) (2) .
· Some composts have high concentrations of ammonium or soluble salts (6) . There are larger amounts of NH 4 than NO 3 in composted domestic waste. High Levels of NH 4 are due to non-stabilized substances (4) . Immature (unfinished) compost can stunt or kill plants, and reduce germination and growth (11) .
Comparison as to pathogens
· Recycling organic waste through earthworms also results in a product with a lower pathogen level than compost (8) .
· Since high temperature are not part of the earthworm cast production process disease suppressing microorganisms that may be present in this material survives in the absence of heat (20) .
· Some composts are suppressive of plant pathogens but heating them to 60 o C for five days reduced suppressiveness . This is why some composts need to be inoculated with disease suppressing microorganisms. Adding nutrients (i.e. reducing competition) also reduces disease suppression by composts (21) .
Comparing Earthworm Casts and Compost as to their processes
Comparison as to time and volume requirement
· Earthworms eat 75% of their weight daily ( Ndegwa , 1999) and the speed or earthworm casts production can be increased by increasing the amount of earthworms. The layer of waste needs to be 1 ft or thinner to prevent anaerobic conditions which hinder earthworm activity.
· A compost pile needs to be 3 cubed feet to hold heat in winter and takes 3-4 months to be cured (22) .
Comparison as to odor problem
· Odorous gases are emitted as compost piles heat up. Specific layering of composting material needs to be used to prevent odor.
· Earthworms don’t require heat to process waste (heat is actually detrimental). In the correct waste to worms ratio fermentation and heat can be prevented, and also odor or flies.
Aeration requirements
· Compost needs aeration (and labor) to maintain aerobic conditions for microbial activity.
· Worms dig canals (burrows) as they process waste which indirectly aerates the processed material.
Literature review on which the above outline is based:
References:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There is an increased recognition that the adoption of earthworm farming (vermiculture) can be a solution for reversing the world's crisis by recycling waste as natural bioreactors for cost-effective and environmentally sound waste management (Aalok et al., 2008).According to Bajsa et al. (2003) sustainability can be reached by vermicomposting organic matter, which involves an accelerated ...
Vermiculture in animal farming: A review on the biological and nonbiological risks related to earthworms in animal feed. ... as reported in literature (Brito-Vega & Espinosa-Victoria, Citation 2009) ... Technique of vermiculture and the process of transforming into earthworm powder, aimed to be incorporated in animal feed, are supposed to ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on VERMICULTURE. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
To limit all these risks, the use of earthworms reared from vermiculture can help to prevent contamination of poultry through feeding. Discover the world's research 25+ million members
Literature reviews related to Vermiculture A review of the use of black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens (L., 1758) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), to compost organic waste in tropical regions Article
Vermiculture is the sustainable solution for total waste management in world (Fraser-Quick, 2002): Diverse organic wastes from various sources (households, farms, businesses and industries) can be efficiently managed by the waste-eater earthworms (Edwards, 1988; 2000; Roe, 2002; Patil, 2005).. a. Municipal organic wastes 1. Food wastes: From homes and restaurants (all raw and cooked kitchen ...
Literature review skeleton. The framework of literature review (Fig. 1) was created to narrow down the subtopics of the review, where it is focused on the role of vermicompost as a potential strategy in circular economy. Then, the effects of vermicompost towards plant yield, quality and bioactive properties were evaluated, to shed light into ...
This review highlights the potential of vermicompost and its derived products as sustainable and eco-friendly solutions for enhancing production and pest management in grain crops. It assesses their impact comprehensively on crops such as maize, wheat, barley, rice, and pearl millet. Vermicompost improves soil quality, increases nutrient availability, boosts crop productivity, and enhances ...
This review attempts as increasing awareness of this local ... organic wastes has been termed vermiculture and the processing of organic wastes by earthworms is known as vermicomposting (Edwards, 2004). ... Therefore the author decided to give a literature overview article about vermicompost, its importance and benefit in agriculture.
LITERATURE REVIEW Vermicompost production methodology Selection of suitable earthworm: Only the earthworms that dwell on the surface should be employed for the production of vermicompost. The subterranean earthworm, which resides beneath the ground, is unsuitable for vermicompost production [2]. The African earthworm (Eudrillus engenial), red worms
Incorporation of vermin culture in the composting system produces "vermicompost", an enriched biofertilizer known to improve the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil. It is applied in granular form and/or in liquid solution (vermiwash), and in both open fields and greenhouses. Vermicompost has been shown to contain plant growth hormones, which stimulate seed germination ...
Murphy BW (2014) Soil organic matter and soil function—review of the literature and underlying data. Department of the Environment, Canberra, Australia. Puga-Freitas R, Blouin M (2015) A review of the effects of soil organisms on plant hormone signalling pathways. Environ Exp Bot 114:104-116. Article CAS Google Scholar
Abstract and Figures. This descriptive-experimental study reports the innovative approach on vermiculture and vermicomposting process undertaken in a state university in Zambales, Philippines ...
review Jorge Dominguez1 and Clive A. Edwards1 IDepartamento de Ecoloxia e Bioloxia Animal, Universidade de Vi go, E-36200 ... earthworms in organic wastes has been termed vermiculture and the processing of organic wastes by earthworms is known as vermicomposting. Vermicomposting, which involves the composting of organic wastes through earthworm ...
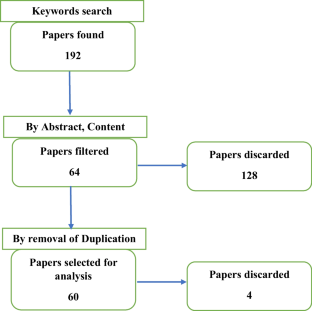
A systematic literature review is a process of identifying, assessing, and interpreting all research findings in order to answer research questions. ... Weeds and other plants residues can be used as vermiculture substrate for varieties of earthworm. The study conducted by Debnath and Chaudhuri found that plant residues (acacia litter, ...
REVIEW ARTICLE Vermiculture in animal farming: A review on the biological and nonbiological risks related to earthworms in animal feed Patrick Byambas1,2*, Jean Luc Hornick1, Didier Marlier3 and Frederic Francis4 Abstract: Earthworms are part of natural diet of some farm animals such as poultry. They are a protein source.
1. Introduction. Not to be confused with a book review, a literature review surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources (e.g. dissertations, conference proceedings, reports) relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of each work.The purpose is to offer an overview of and background on significant literature ...
Literature Review on Vermicomposting. -soil particle bonds. Organic C in those same casts increased by 21 to 43%. Water extractable polysaccharides increased too, maybe due to enrichment of polysaccharides (Zhang & Schrader, 1993). Since internal stability seems to depend on % of , no new ones were formed ( & Dexter, 1990).
vermicomposting, there are only few review papers made for generalization of results. his work was Therefore, t prepared to present a review of the latest research on vermicomposting of different types of organic wastes in the last years, with concentration on the research and applications for developing countries. Trying to draw an
Vermicomposting of Organic Waste : Literature Review. M. Basha, A. S. Elgendyb. Published 2018. Environmental Science, Agricultural and Food Sciences. Purpose : Adoption of new life style, bad management and low budget in many developing countries resulted in massive accumulation of municipal solid waste (MSW) and agricultural wastes causing ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on VERMICOMPOSTING. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
However, vermiculture is not practiced in South Pacific island countries (SPICs) largely due to the lack of awareness of this type of application. We consider the inclusion of vermiculture in this region as a potential means of achieving sustainable organic agricultural practices. This study represents a systematic review in
Vermiculture may be a boon for Fiji which is a small Island nation located in the South Pacific, 3000 km east of Australia and 1930 km south of the equator. It is endowed with excellent climate which is very much suitable for vermicomposting. The land and climate of Fiji are very good for growing horticultural