Overview of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management - By DoMS, IIT Madras
Reviewed by Gaurav Dutta 32
Total Quality Management
Introduction
• What is quality?
Dictionary has many definitions: “Essential characteristic,” “Superior,” etc.
Some definitions that have gained wide acceptance in various organizations: “ Quality is customer satisfaction ,” “ Quality is Fitness for Use .”
• The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society for Quality (ASQ) define quality as:
“ The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy given needs. ”
• What is TQM?
A comprehensive, organization-wide effort to improve the quality of products and services, applicable to all organizations.
• What is a customer?
Anyone who is impacted by the product or process delivered by an organization.
External customer : The end user as well as intermediate processors. Other external customers may not be purchasers but may have some connection with the product.
Internal customer : Other divisions of the company that receive the processed product.
• What is a product?
The output of the process carried out by the organization. It may be goods (e.g. automobiles, missile), software (e.g. a computer code, a report) or service (e.g. banking, insurance)
• How is customer satisfaction achieved?
Two dimensions: Product features and Freedom from deficiencies.
• Product features – Refers to quality of design .
Examples in manufacturing industry: Performance, Reliability, Durability, Ease of use, Esthetics etc.
Examples in service industry: Accuracy, Timeliness, Friendliness and courtesy, Knowledge of server etc.
• Freedom from deficiencies – Refers to quality of conformance .
Higher conformance means fewer complaints and increased customer satisfaction.
Why Quality?
Reasons for quality becoming a cardinal priority for most organizations:
• Competition – Today’s market demand high quality products at low cost. Having `high quality’ reputation is not enough! Internal cost of maintaining the reputation should be less.
• Changing customer – The new customer is not only commanding priority based on volume but is more demanding about the “quality system.”
• Changing product mix – The shift from low volume, high price to high volume, low price have resulted in a need to reduce the internal cost of poor quality.
• Product complexity – As systems have become more complex, the reliability requirements for suppliers of components have become more stringent.
• Higher levels of customer satisfaction – Higher customers expectations are getting spawned by increasing competition.
Relatively simpler approaches to quality viz. product inspection for quality control and incorporation of internal cost of poor quality into the selling price, might not work for today’s complex market environment.
Quality perspectives
Everyone defines Quality based on their own perspective of it. Typical responses about the definition of quality would include:
1. Perfection
2. Consistency
3. Eliminating waste
4. Speed of delivery
5. Compliance with policies and procedures
6. Doing it right the first time
7. Delighting or pleasing customers
8. Total customer satisfaction and service
Judgmental perspective
• “goodness of a product.”
• Shewhart’s transcendental definition of quality – “absolute and universally recognizable, a mark of uncompromising standards and high achievement.”
• Examples of products attributing to this image: Rolex watches, Lexus cars.
Product-based perspective
• “function of a specific, measurable variable and that differences in quality reflect differences in quantity of some product attributes.”
• Example: Quality and price perceived relationship.
User-based perspective
• “fitness for intended use.”
• Individuals have different needs and wants, and hence different quality standards.
• Example – Nissan offering ‘dud’ models in US markets under the brand name Datson which the US customer didn’t prefer.
Value-based perspective
• “quality product is the one that is as useful as competing products and is sold at a lesser price.”
• US auto market – Incentives offered by the Big Three are perceived to be compensation for lower quality.
Manufacturing-based perspective
• “the desirable outcome of a engineering and manufacturing practice, or conformance to specification.”
• Engineering specifications are the key!
• Example: Coca-cola – “quality is about manufacturing a product that people can depend on every time they reach for it.”
Quality levels
At organizational level , we need to ask following questions:
• Which products and services meet your expectations?
• Which products and services you need that you are not currently receiving?
At process level , we need to ask:
• What products and services are most important to the external customer?
• What processes produce those products and services?
• What are the key inputs to those processes?
• Which processes have most significant effects on the organization’s performance standards?
At the individual job level , we should ask:
• What is required by the customer?
• How can the requirements be measured?
• What is the specific standard for each measure?
History of quality management
…To know the future, know the past!
• Before Industrial Revolution, skilled craftsmen served both as manufacturers and inspectors, building quality into their products through their considerable pride in their workmanship .
• Industrial Revolution changed this basic concept to interchangeable parts . Likes of Thomas Jefferson and F. W. Taylor (“scientific management” fame) emphasized on production efficiency and decomposed jobs into smaller work tasks. Holistic nature of manufacturing rejected!
• Statistical approaches to quality control started at Western Electric with the separation of inspection division. Pioneers like Walter Shewhart, George Edwards, W. Edwards Deming and Joseph M. Juran were all employees of Western Electric.
• After World War II, under General MacArthur's Japan rebuilding plan, Deming and Juran went to Japan.
• Deming and Juran introduced statistical quality control theory to Japanese industry.
• The difference between approaches to quality in USA and Japan: Deming and Juran were able to convince the top managers the importance of quality .
• Next 20 odd years, when top managers in USA focused on marketing, production quantity and financial performance, Japanese managers improved quality at an unprecedented rate.
• Market started preferring Japanese products and American companies suffered immensely.
• America woke up to the quality revolution in early 1980s. Ford Motor Company consulted Dr. Deming to help transform its operations.
(By then, 80-year-old Deming was virtually unknown in USA. Whereas Japanese government had instituted The Deming Prize for Quality in 1950.)
• Managers started to realize that “quality of management” is more important than “management of quality.” Birth of the term Total Quality Management (TQM) .
• TQM – Integration of quality principles into organization’s management systems .
• Early 1990s: Quality management principles started finding their way in service industry . FedEx, The Ritz-Carton Hotel Company were the quality leaders.
• TQM recognized worldwide : Countries like Korea, India, Spain and Brazil are mounting efforts to increase quality awareness.
• The Deming Philosophy
Definition of quality, “A product or a service possesses quality if it helps somebody and enjoys a good and sustainable market.”
Improve Quality
Decrease cost because of less rework,fewer mistakes
Productivity improves
capture the market with better quality and reduced costs
Stay in business
Long term competitive strength
The Deming philosophy
14 points for management:
1. Create and publish to all employees a statement of the aims and purposes of the company. The management must demonstrate their commitment to this statement.
2. Learn the new philosophy.
3. Understand the purpose of inspection – to reduce the cost and improve the processes.
4. End the practice of awarding business on the basis of price tag alone.
5. Improve constantly and forever the system of production and service.
6. Institute training
7. Teach and institute leadership .
8. Drive out fear. Create an environment of innovation .
9. Optimize the team efforts towards the aims and purposes of the company.
10. Eliminate exhortations for the workforce.
11. Eliminate numerical quotas for production.
12. Remove the barriers that rob pride of workmanship .
13. Encourage learning and self-improvement .
14. Take action to accomplish the transformation.
• “A System of Profound Knowledge”
1. Appreciation for a system - A system is a set of functions or activities within an organization that work together to achieve organizational goals. Management’s job is to optimize the system . (not parts of system, but the whole!). System requires co-operation .
2. Psychology – The designers and implementers of decisions are people . Hence understanding their psychology is important.
3. Understanding process variation – A production process contains many sources of variation. Reduction in variation improves quality . Two types of variations- common causes and special causes . Focus on the special causes. Common causes can be reduced only by change of technology.
4. Theory of knowledge – Management decisions should be driven by facts, data and justifiable theories . Don’t follow the managements fads!
The Juran philosophy
• Pursue quality on two levels:
1. The mission of the firm as a whole is to achieve high product quality .
2. The mission of each individual department is to achieve high production quality .
• Quality should be talked about in a language senior management understands: money (cost of poor quality) .
• At operational level, focus should be on conformance to specifications through elimination of defects- use of statistical methods.
Quality Trilogy –
1. Quality planning : Process of preparing to meet quality goals. Involves understanding customer needs and developing product features.
2. Quality control : Process of meeting quality goals during operations. Control parameters. Measuring the deviation and taking action.
3. Quality improvement : Process for breaking through to unprecedented levels of performance. Identify areas of improvement and get the right people to bring about the change.
The Crosby philosophy
Absolute’s of Management
• Quality means conformance to requirements not elegance.
• There is no such thing as quality problem .
• There is no such thing as economics of quality: it is always cheaper to do the job right the first time .
• The only performance measurement is the cost of quality : the cost of non-conformance.
Basic Elements of Improvement
• Determination (commitment by the top management)
• Education (of the employees towards Zero Defects (ZD))
• Implementation (of the organizational processes towards ZD)
TQM for Middle Management
Process Management
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Process management
• Planning and administering the activities necessary to achieve high quality in business processes ; and also identifying opportunities for improving quality and operational performance – ultimately, customer satisfaction .
• Process simplification reduces opportunities for errors and rework.
• Processes are of two types – value-added processes and support processes.
• Value-added processes – those essential for running the business and achieving and maintaining competitive advantage. (Design process, Production/Delivery process)
• Support processes – Those that are important to an organization’s value-creation processes, employees and daily operations.
• Value creation processes are driven by external customer needs while support processes are driven by internal needs.
• To apply the techniques of process management, a process must be repeatable and measurable .
• Process owners are responsible for process performance and should have authority to manage the process. Owners could range from high-level executive to workers who run a cell.
• Assigning owners ensures accountability .
Process control
• Control is the activity of ensuring the conformance to the requirements and taking corrective action when necessary.
• Two reasons for controlling the process
1. Process control methods are the basis of effective daily management of processes .
2. Long-term improvements can not be made to a process unless the process is first brought under control.
• Short-term corrective action should be taken by the process owners. Long-term remedial action should be the responsibility of the management.
Effective quality control systems include
1. Documented procedures for all key processes
2. A clear understanding of the appropriate equipment and working environment
3. Methods of monitoring and controlling critical quality characteristics
4. Approval processes for equipment
5. Criteria for workmanship: written standards, samples etc.
6. Maintenance activities
Process improvement
• Customer loyalty is driven by delivered value.
• Delivered value is created by business processes.
• Sustained success in competitive markets require a business to continuously improve delivered value.
• To continuously improve value creation ability, a business must continuously improve its value creation processes.
• Continuous process improvement is an old management concept dating back to 1895. However, those approaches were mainly productivity related .
• More recently (1951) Toyota implemented Just-In-Time which relies on zero defects and hence continuous improvement!
Process improvement: Kaizen
• Japanese for gradual and orderly continuous improvement over a long period of time with minimum financial investment, and with participation by everyone in the organization .
• Improvement in all areas of business serves to enhance quality of the firm.
• Three things required for successful kaizen program: operating practices, total involvement, and training.
• Operating practices expose opportunities for improvement. JIT reveals waste and inefficiency as well as poor quality.
• Every employee strives for improvement. Top management views improvement as part of strategy and supports it. Middle management can implement top management’s improvement goals by establishing, maintaining, and upgrading operating standards. Workers can engage through suggestions, small group activity.
• Middle management can help create conducive environment for improvement by improving cooperation amongst departments , and by making employees conscious of their responsibilities for improvement.
• Supervisors can direct their attention more on improvement than supervision, which will facilitate communication.
Kaizen: Implementation
• The Deming cycle : Originally developed by Walter Shewart, but renamed in 1950s because Deming promoted it extensively.
• Plan – Study the current system; identifying problems; testing theories of causes; and developing solutions.
• Do – Plan is implemented on a trial basis. Data collected and documented.
• Study – Determine whether the trial plan is working correctly by evaluating the results.
• Act – Improvements are standardized and final plan is implemented.
• Variation of PDSA cycle: FADE – Focus, Analyze, Develop, Execute cycle !
Juran’s breakthrough sequence:
1. Proof of the need
2. Project identification
3. Organization for breakthrough – two paths identified: symptom to cause (diagnostic) and cause to remedy (remedial) paths.
4. Diagnostic journey
5. Remedial journey
6. Holding the gains.
Process improvement tools
Seven QC Tools
1. Flow charts
2. Check sheets
3. Histograms
4. Pareto diagrams
5. Cause-and-effect diagrams
6. Scatter diagrams
7. Control charts
TQM for the Workforce
Kaizen teams
Quality Circles
Quality circles
• Teams of workers and supervisors that meet regularly to address work-related problems involving quality and productivity.
• Developed by Kaoru Ishikawa at University of Tokyo.
• Became immediately popular in Japan as well as USA.
• Lockheed Missiles and Space Division was the leader in implementing Quality circles in USA in 1973 (after their visit to Japan to study the same).
• Typically small day-to-day problems are given to quality circles. Since workers are most familiar with the routine tasks, they are asked to identify, analyze and solve quality problems in the routine processes.
Additional process improvement tools
Kaizen blitz
• An intense and rapid improvement process in which a team or a department throws all its resources into an improvement project over a short period of time.
• Short time “burst” rather than long range simmer- hence the name.
• Blitz teams usually comprise of employees from all areas involved in the process who understand it and can implement the changes on the spot .
Poka-Yoke (Mistake proofing)
• Approach for mistake-proofing processes using automatic devises or methods to avoid simple human error.
• Developed and refined in the 1960s by the late Shigeo Shingo, a Japanese manufacturing engineer who developed the Toyota production system.
• Focused on two aspects:
1. Prediction – Recognizing that a defect is about to occur and provide a warning.
2. Detection – Recognizing that a defect has occurred and stop the process.
TQM for Top Management
Strategic Quality Management (SQM)
Competitive Advantage
SQM: Hoshin planning
• Hoshin kanri : Japanese for management cycle build around Plan, Do, Check, Act. Elements of this cycle include –
ü Quality policies
ü Quality goals
ü Deployment of goals
ü Plans to meet goals
ü Organizational structure
ü Resources
ü Measurement feedback
ü Review of progress
SQM: Vision/Mission statement
• Developed by taking everyone in confidence. Guide for the Quality journey . Ties quality to overall business goals.
• Vision Statement : Collection of quality policies. A vision statement outlines what a company wants to be. It focuses on tomorrow; it is inspirational ; it provides clear decision-making criteria ; and it is timeless . A vision needs to address three areas: people, culture (or values) and product or service .
• Mission statement : A mission statement outlines what the company is now. It focuses on today ; it identifies the customers; it identifies the critical processes; and it states the level of performance .
• It has been said that a vision is something to be pursued , while a mission is something to be accomplished .
• Mission is what you do best every day, and vision is what the future looks like because you do that mission so exceedingly well.
• For vision – Think leading with inspiration and courage, obsessed with future possibility.
• For mission – Think managing with greatness and untamed strength, improving everything daily.
• Famous vision statement – “ By the end of the decade, we will put a man on the moon. ” JFK.
• Famous mission statement – “ CRUSH REEBOK. ” Nike
SQM: Quality policies
• Prepared to provide guidelines for planning the overall quality program; and defining the action to be taken in situation for which personnel had requested guidelines.
• Policies state: a) a principle to be followed; b) what is to be done .
• Examples of quality policy – For a computer manufacturer: “In selecting suppliers, decision makers are responsible for choosing the best source even if this means internal sources are not selected.”
SQM: Deploying quality goals
• A goal (or objective) is a statement of the desired result to be achieved within a specified period – an aimed-at target .
• These goals then become basis for detailed planning of activities.
• Tactical goals are short range (up to 1 year), whereas strategic goals are long range (say, 5 years).
• Examples of corporate quality goals – For a health product company, the quality goals over the next year could be: “The average leakage rate for …. product shall be reduced to …”
• Note that quality goal statements include quantified data .
Typically Pareto analysis is used to develop the quality goals
Broad goals don’t lead to results. First they have to be deployed as follows:
• Division and subdivision of the goal until specific deeds to be done are identified.
• Allocation of responsibility of doing these deeds.
• Provision for the needed resource.
SQM: Caveats
Reasons of failure of SQM could be
• Lack of leadership by upper management.
• Lack of infrastructure for quality.
• Failure to understand the skepticism about the “new quality program.”
• Management assumption that the exhortation approach will work.
• Failure to start small and learn from pilot programs.
• Reliance on specific techniques as the primary means.
• Underestimating the time and resource required.


Total Quality Management
What do you think of this template.

Product details
Total quality management is the continual process of detecting and reducing or eliminating errors in manufacturing, streamlining supply chain management, improving the customer experience, and ensuring that employees are up to speed with training. Total quality management aims to hold all parties involved in the production process accountable for the overall quality of the final product or service.
Total quality management was developed by William Deming, a management consultant whose work had a great impact on Japanese manufacturing. While Total quality management shares much in common with the Six Sigma improvement process, it is not the same as Six Sigma. Total quality management focuses on ensuring that internal guidelines and process standards reduce errors, while Six Sigma looks to reduce defects.
The focus of the process is to improve the quality of an organization’s outputs, including goods and services, through continual improvement of internal practices. The standards set as part of the Total quality management approach can reflect both internal priorities and any industry standards currently in place.
Industry standards can be defined at multiple levels and may include adherence to various laws and regulations governing the operation of the particular business. Industry standards can also include the production of items to an understood norm, even if the norm is not backed by official regulations.
Total quality management is considered a customer-focused process and aims for continual improvement of business operations. It strives to ensure all associated employees work toward the common goals of improving product or service quality, as well as improving the procedures that are in place for production.
Inspire your company’s staff to be committed to high standards. Total Quality Management is a management framework based on the belief that a company can build long-term success by having all its members, from low-level workers to its highest-ranking executives. It focuses on quality improvement and thus delivering customer satisfaction. This Total Quality Management template models all the facets of Total Quality Management.
The infographics in the first and second slides can be used to highlight different aspects of Total Quality management. Show hierarchy of the components of Total Quality Management with the pyramid in the third slide. The user can come to a good presentation close with the last slide as it summarizes what each alphabet in the TQM acronym really means. It is a fully editable and customizable TQM template for PowerPoint presentations. Users can change colors, texts, and icons to meet requirements.
This template can be used by quality managers when preparing instructions for improving product quality. You can describe in detail what actions need to be taken to improve quality control and what resources and time frame you will need for this.
Product managers can use this template when preparing a report on necessary changes to improve product quality. Marketers and salespeople can use the slides in this template to discuss the competitive advantages of your product and plan actions to improve the quality of the products they produce. Manufacturing managers can use the slides in this template when preparing guidelines for quality control and continuous improvement of work processes in the company.
Extensively used across all industries. The Total Quality Template is great for presentation on management. Ideal for use by management professionals, quality auditors, quality assurance teams, quality controllers, strategic planners, business analysts, project managers, etc… Give the best Total Quality Management presentation and impress your audiences on end with our Total Quality Management template for PowerPoint template.
Related Products
Deployment Process
Flower Petal

Challenges Slide
Pandemic Business Recovery

Big Data Architecture
Technology Stack
Job Interview Presentation
Process Improvement Plan

Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Conceptual Framework
You dont have access, please change your membership plan., great you're all signed up..., verify your account.
PowerSlides.com will email you template files that you've chosen to dowload.
Please make sure you've provided a valid email address! Sometimes, our emails can end up in your Promotions/Spam folder.
Simply, verify your account by clicking on the link in your email.

Aspect Ratio:
File Size: 41.0 MB
Number of Slides: 181
Terms of Usage
Training Presentation/Powerpoint:
Total quality management (tqm).
Description Total Quality Management (TQM) is a holistic approach to achieving long-term success that transcends mere processes or outcomes. At its core, TQM views continuous improvement as a perpetual process rather than a short-lived objective. It instills a mindset where every facet of an organization is seen as a potential source of refinement, from attitudes and practices to systems and structures. TQM is a transformative journey that involves everyone in the organization, fostering a shared commitment to quality and excellence.
The benefits of embracing TQM are as abundant as they are profound. Organizations that integrate TQM principles experience improved operational efficiency, heightened customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and enhanced employee morale. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, TQM empowers organizations to adapt to changing environments, seize opportunities, and exceed customer expectations. TQM doesn't merely lead to success; it becomes a compass guiding organizations towards sustainable excellence.
In today's fast-paced business landscape, the principles of TQM remain as relevant as ever. As markets evolve, customer demands become more intricate, and competition intensifies, TQM equips organizations with the agility to navigate these challenges. Moreover, TQM synergizes harmoniously with Lean, Six Sigma, and Design Thinking methodologies.
By teaching this presentation, employees will understand the importance of making a personal commitment to quality, focus on satisfying both internal and external customer requirements, and working as a team to improve quality.
This TQM PPT training presentation includes quality philosophies from key quality leaders such as W. E. Deming, J. M. Juran and Philip Crosby, and provides a summary of process management, steps for TQM implementation, key tools and techniques for total quality as well as the key business excellence and quality management models.
Note: This training package includes:
1. TQM PPT training presentation (PowerPoint format, 16:9 widescreen)
2. The Inspection Exercise (PowerPoint format, 4:3 standard screen)
Learning Objectives
Explain the meaning of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Identify key leaders in the field of quality and their philosophies
Identify characteristics of the TQM philosophy
Understand the importance of process management and measuring the cost of quality
Describe the key business excellence and quality models
Describe Total Quality leadership attitudes and behaviors
Identify tools and techniques for Total Quality
Define the steps for TQM implementation
Introduction to TQM
Customer Focus
Employee Involvement & Empowerment
Process Management
Cost of Quality
Business Excellence & Quality Management Models
Total Quality Leadership
TQM Implementation
Methods & Tools for Total Quality
Key Takeaways
Yo u may also be interested in the following training presentations (sold separately):
A3 Problem Solving Process & Tools
8D Problem Solving Process & Tools
PDCA Problem Solving Process & Tools
5 Steps of Problem Solving
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Problem Solving & Visualization Tools
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Mistake-Proofing
Total Quality Management
Root Cause Analysis
Reducing the Cost of Quality

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT: TQM Origins, Evolution & key elements
Published by Thomas Hines Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT: TQM Origins, Evolution & key elements"— Presentation transcript:

Organization Development and Change

TOTAL QUALITY APPROACH to QUALITY MANAGEMENT

BS2914 Quality Management & Customer Care 3: TQM Gurus [1] W.Edwards Deming 3: TQM Gurus [1] W.Edwards Deming.

“Statistics is the science of gaining information from numerical data.” -- Moore Definitions of Statistics Statistics: “the science of data involving collecting,

Philosophies and Frameworks

Quality Management Philosophies
Total Quality Management A Great Concept But What is IT ?

Concept of TQM From Quality Gurus

Total Quality Management

Quality is the ability of a product or service to consistently meet or exceed customer expectations. Quality Management.

Quality People: a brief overview of..

Slide 3.1 1999 South-Western College Publishing Chapter 3 Quality Management Philosophies.

THE PRINCIPLES OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT. DEFINING QUALITY Good Appearance? High Price? The Best? Particular Specification? Not necessarily, but always: Fitness.

TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (TQM)

Total Quality Management(TQM) The word “total” conveys the idea that all employees, throughout every function and level of organization, pursue quality.

© 2008 Prentice Hall8-1 Introduction to Project Management Chapter 8 Managing Project Quality Information Systems Project Management: A Process and Team.
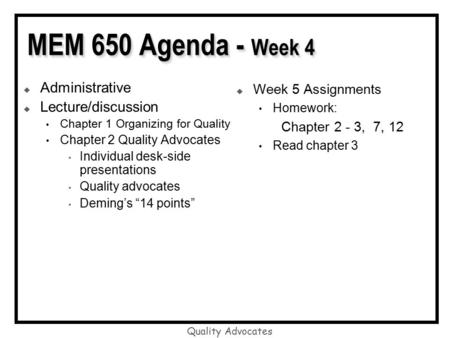
Quality Advocates MEM 650 Agenda - Week 4 Administrative Lecture/discussion Chapter 1 Organizing for Quality Chapter 2 Quality Advocates Individual.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Quality Management PPT Presentations
Quality management concerns the optimization of the quality of a product, a service or a process. Quality management includes the planning, monitoring, control and monitoring of a quality process and the results of the process.
This affects all measures that improve process quality. A common model is the EFQM model and ISO 9001. Benefit from pre-designed checklists, intricate diagrams and model analyses to create a successful quality management presentation. The Total Quality Management (TQM) Toolbox includes all necessary templates and work sheets for the expert recording and control of business processes. Visualize how to increase efficiency and quality of processes and quickly calculate cost models or create strategies to increase profits.
Quality Toolbox PowerPoint Template
The seven basic tools of quality (Q7), seven management tools (M7) and other quality techniques in one set.
TQM Toolbox PowerPoint Template
Quality management templates include diagrams, analysis tools and numerous illustrations for professional business presentations.
EFQM Business Excellence Model PowerPoint Template
Templates with graphics, tables and much more to present the EFQM business excellence model
Quality Auditing PowerPoint Template
Explanations of the quality improvement process and representations of auditor tasks, audit planning and follow-up, and more.
Quality Function Deployment PowerPoint Template
Definitions, explanations and diagrams of the different models and phases of QFD.
Scrum Toolbox PowerPoint Template
Set includes a variety of SCRUM tools like Product Backlogs, Burndown Charts, development tools, checklists and more.
Product Management PowerPoint Template
ABC and GAP analysis, Stage Gate model, Ansoff Matrix and many other analysis models.
Value Proposition PowerPoint Template
Definition, basic knowledge, graphics and various designs of the value proposition for editing in PowerPoint.
Skills Management PowerPoint Template
Skills Management for PowerPoint to classify competences and to illustrate competency models in business presentations.
8D/ 7STEP PowerPoint Template
A comprehensive set of definitions and working templates for the problem-solving methods of 8D and 7STEP.
Kaizen PowerPoint Template
Smart improvement techniques such as PDCA cycle, 5S and Kanban as well as various worksheets to implement Kaizen principles.
Six Sigma PowerPoint Template
Quality management in PowerPoint: Six Sigma incl. all relevant analysis tools such as DMAIC, DMADOV and Gaussian bell curve.
5S TPM Bundle PowerPoint Template
Japanese discipline and tidiness to optimize workflows and production plants.
5S Concept PowerPoint Template
Your workplace has never been this clean: purchase 5S for PowerPoint today and increase efficiency and productivity for your enterprise!
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) PowerPoint Template
The five phases and the eight columns of TPM for an overall improvement of your production plants.
Corporate Services
We’ll optimize your existing PowerPoint presentation and create slides in your corporate design.
New PowerPoint Templates
We are continually bringing you new PowerPoint templates on current business topics and in modern designs.

- Medical Device Validation
- Quality Assurance / Quality Management
- Product and Process Validation
- TQM Tools and Techniques
- Risk Management Process
Introduction to TQM. Total Quality Management...
Information & training. | total quality management., introduction to tqm..
– Product features,
– Process efficiency,
– Service delivery,
– Staff development,
– Systems development,
– Awareness and responsibility towards the environment, etc..
TQM entails meeting customer requirements.
Includes the internal and external customers.
Making continuous improvement part of ongoing activity for all.
Quality development through Inspection (1st era).

Cpk and Ppk Analysis Pareto Analysis Bottleneck Analysis Benchmarking FMEA FTA HAZOP PDCA/DMAIC/DMADV SIPOC Etc. Etc. Etc. Information & Training presentation >>>
Quality development through Quality Control (2nd era).
– Inspection on Product,
– Control on Process.
Quality development through Quality Assurance (3rd era).
Quality development through total quality management (4th era)..

Quality Improvement Techniques
Information & Training. | Total Quality Management Tools and Techniques …
- Continuous improvement utilizing Analytical Techniques.
- Brainstorming
- 5 why’s analysis
- Process Flow Diagrams/Flowcharts/Process Mapping
- Check sheets /Check Lists
- Scatter Diagrams/Scatter Plot
- Cause and Effect/Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagrams
- Identifying sources & causes of variation
- Control/Shewart Charts/DPU Charts
- Cpk and Ppk Analysis
- Pareto Analysis
- Bottleneck Analysis
- Benchmarking
- PDCA/DMAIC/DMADV
- Information & Training presentation >>>
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- What Is Total Quality Management?
- Understanding TQM
- Primary Principles
- How to Implement TQM
- Pros and Cons
- Industries Using TQM
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
What Is Total Quality Management (TQM) and Why Is It Important?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)

What Is Total Quality Management (TQM)?
Total quality management (TQM) is the continual process of detecting and reducing or eliminating errors in manufacturing. It streamlines supply chain management , improves the customer experience, and ensures that employees are up to speed with training. Total quality management aims to hold all parties involved in the production process accountable for the overall quality of the final product or service.
Key Takeaways
- Total quality management (TQM) is an ongoing process of detecting and reducing or eliminating errors.
- Total quality management is used to streamline supply chain management, improve customer service, and ensure that employees are properly trained.
- The focus is to improve the quality of an organization's outputs, including goods and services, through the continual improvement of internal practices.
- Total quality management aims to hold all parties involved in the production process accountable for the overall quality of the final product or service.
- There are often eight guiding principles to TQM that range from focusing on customers, continually improving, and adhering to processes.
Investopedia / Katie Kerpel
Understanding Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total quality management is a structured approach to overall organizational management. The focus of the process is to improve the quality of an organization's outputs, including goods and services, through the continual improvement of internal practices. The standards set as part of the TQM approach can reflect both internal priorities and any industry standards currently in place.
Industry standards can be defined at multiple levels and may include adherence to various laws and regulations governing the operation of a particular business. Industry standards can also include the production of items to an understood norm, even if the norm is not backed by official regulations. Acceptance sampling might be used to check the progress toward the TQM goal.
Example of Total Quality Management
Perhaps the most famous example of TQM is Toyota's implementation of the kanban system. A kanban is a physical signal that creates a chain reaction, resulting in a specific action. Toyota used this idea to implement its just-in-time (JIT) inventory process.
The company decided to keep just enough inventory on hand to fill customer orders as they were generated to make its assembly line more efficient. All parts of Toyota's assembly line are therefore assigned a physical card that has an associated inventory number.
The card is removed and moved up the supply chain right before a part is installed in a car, effectively requesting another of the same part. This allows the company to keep its inventory lean and not overstock unnecessary assets. Effective quality management resulted in better automobiles that could be produced at an affordable price.
History of Total Quality Management
TQM's history often dates back to the early 1900s when Walter A. Shewhart introduced modern quality control. Shewhart produced a landmark piece of industrial work entitled Economic Control of Quality of Manufactured Product in 1931. This exposition is considered one of the founding and basic principles of manufacturing quality control.
Further developments in Shewhart's work introduced new standards in quality management decades later. Joseph M. Juran published a book called What Is Total Quality Control? The Japanese Way . in 1954. The work was based on Juran's experience of being invited to Japan by Japanese scientists and engineers. Juran later co-authored Quality Planning and Analysis , another bestseller in TQM.
Another prominent figure in TQM history is W. Edwards Deming. Also posted in Japan after the Second World War, Deming became involved with the Union of Japanese Scientists and Engineers (JUSE). His career work included several TQM frameworks (Deming's 14 Points, Deming's Seven Deadly Diseases of Management, and The Deming Wheel).
The exact origin of the phrase total quality management is not known, but several parties mentioned above are credited for helping develop the general concept.
Primary Principles of Total Quality Management
TQM is considered a customer-focused process that focuses on consistently improving business operations management . It strives to ensure that all associated employees work toward the common goals of improving product or service quality, as well as improving the procedures that are in place for production. There are several guiding principles that define TQM.
Focus on Customers
Under TQM, your customers define whether your products are high quality. Customer input is highly valued because it allows a company to better understand the needs and requirements in the manufacturing process. Customer surveys may reveal insufficient durability of goods. This input is then fed back into TQM systems to implement better raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and quality control procedures.
Commitment by Employees
Employees must buy into the processes and system if TQM is going to be successful. This includes clearly communicating across departments and leaders what goals, expectations, needs, and constraints are in place. A company adopting TQM principles must be willing to train employees and give them sufficient resources to complete tasks successfully and on time. TQM also strives to reduce attrition and maintain knowledgeable workers.
Improve Continuously
A company should gradually evolve and strive for incremental, small improvements as it learns more about its customers, processes, and competition. This concept of continuous improvement helps a company adapt to changing market expectations. It allows for greater adaptability to different products, markets, customers, or regions. Continuous improvement also drives and widens the competitive advantage that a company has built over related companies.
Adherence to Processes
TQM's systematic approach relies heavily on process flowcharts, TQM diagrams, visual action plans, and documented workflows . Every member engaged in the process must be aware and educated on their part of the process to ensure proper steps are taken at the right time of production. These processes are then continually analyzed to better understand deficiencies in the process.
Strategic and Systematic Approach
A company's processes and procedures should be a direct reflection of the organization's vision, mission , and long-term plan. TQM calls for a system approach to decision making that requires that a company dedicate itself to integrating quality as its core component and making the appropriate financial investments to make that happen.
Data Utilization
The systematic approach of TQM only works if feedback and input is given to evaluate how the process flow is moving. Management must continually rely on production, turnover, efficiency, and employee metrics to correlate the anticipated outcomes with the actual results. TQM relies heavily on documentation and planning, and only by utilizing and analyzing data can management understand if those plans are being met.
Integrate Systems
One way to utilize data is to integrate systems. TQM strategies believe systems should talk to each other, conveying useful information across departments and making smart decisions. When goods or inventory are used in one area, another department should have immediate access to that ERP information. TQM strives to allow everyone to be on the same page at the same time by linking data sources and sharing information across systems.
Communication
Data may transfer between departments freely, but there is a human element to coordinating processes and making sure an entire production line is operating efficiently. Effective communication plays a large part in TQM to motivate employees, educate members along a process, and avoid process errors whether it is normal day-to-day operations or large organizational changes.
Successful TQM requires a company-wide buy-in of every principle. The benefits of TQM quickly diminish if a company does not receive complete buy-in.
How to Implement Total Quality Management
TQM is a unique process. There is not a specific formula for implementing a system that suits every business and each type of industry. But you can create a checklist of issues that might suit your enterprise and proceed with them in chronological order. Some may suit your business while others will not. Select those that you think will provide an advantage.
- Identify your company’s existing culture, its core values, and its systems.
- Use this information to create a system that will serve as your master plan.
- Establish what your customers and clients want and what they expect from your business. Determine how to best meet these expectations and needs.
- Create a team of management and employees to guide and implement your goals and include these efforts in your daily business management process.
- Consistently gather feedback from both employees and customers to gauge your progress.
TQM is not a speedy process. Expect to dedicate an extended period of time to your efforts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TQM
TQM results in a company making a product for less when it's implemented correctly. Companies that engage in TQM provide more consistent products that yield stronger customer loyalty when they emphasize quality and minimize waste.
As TQM touches every department across an organization, a company may reap substantial savings from materials sourcing, production, distribution, or back-office functions. Companies that successfully implement TQM can usually react more quickly to change and proactively plan ahead to avoid obsolescence.
A company must fully engage TQM principles to fully reap the benefits of TQM. This requires substantial buy-in from every department across an organization. This level of commitment is very difficult to achieve, requires substantial financial investment, and necessitates all levels of management to engage in TQM.
The conversion to TQM may be lengthy, and workers may feel resistant to change. A company may be required to replace processes, employees, equipment, or materials in favor of an untested, partially developed TQM plan. More skilled workers may decide to leave the company if they feel TQM processes don't appropriately utilize their skill sets.
Total Quality Management
Delivers stronger, higher quality products to customers
Results in lower company-wide costs
Minimizes waste throughout the entire production and sale process
Enables a company to become more adaptable
May require substantial financial investment to convert to TQM practices
Often requires conversion to TQM practices over a long period of time
May be met with resistance to change
Requires company-wide buy-in to be successful
Industries Using Total Quality Management
TQM originated in the manufacturing sector, but its principles can be applied to a variety of industries. It provides a cohesive vision for systemic change with a focus on long-term change rather than short-term goals. TQM is used in many industries with this in mind, including but not limited to manufacturing, banking and finance, and medicine.
These techniques can be applied to all departments within an individual organization. This helps ensure that all employees are working toward the goals set forth for the company and improving function in each area. Involved departments can include administration, marketing, production, and employee training.
What Does Total Quality Management Do?
TQM oversees all activities and tasks that are necessary to maintain a desired level of excellence within a business and its operations. This includes the determination of a quality policy, creating and implementing quality planning and assurance, and quality control and quality improvement measures.
What Are the Principles of TQM?
Various iterations of TQM have been developed, each with its own set of principles. Certain core elements persist nonetheless. These include good leadership, emphasis on quality, customer priority, error correction and improvement as an ongoing process, and job training.
What Is a TQM Diagram?
A TQM diagram is a visual depiction of the business and process layout. The diagram usually shows different processes or steps, allowing management to see a process, analyze weaknesses or risks in the flow, and strategically adjust how things are done.
Total quality management is the strategic framework that encourages everyone in an organization to focus on quality improvement. The theory holds that customer satisfaction will increase by being operationally excellent. Many principles drive TQM, but the overall purpose is to eliminate errors, streamline processes, and maximize efficiency.
Toyota. " Section 4. Plant Construction and Expansion Item 4. Development and Deployment of the Toyota Production System ."
American Society for Quality. " Walter A. Shewhart ."
American Society for Quality. " Joseph M. Juran ."
British Library. " W Edwards Deming ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/business-people-using-pen-tablet-notebook-are-planning-a-marketing-plan-to-improve-the-quality-of-their-sales-in-the-future--881542122-6767a39f655b4a018019715734dcfbe0.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Home PowerPoint Templates Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management PowerPoint Templates
TQM consists of organization-wide efforts to install and make permanent a climate in which an organization continuously improves its ability to deliver high-quality products and services to customers. Under this category you can download Total Quality Management PowerPoint templates and slide graphics for presentations .
Six Sigma Belts Illustration Scenes

Lean Manufacturing Word Cloud Picture for PowerPoint
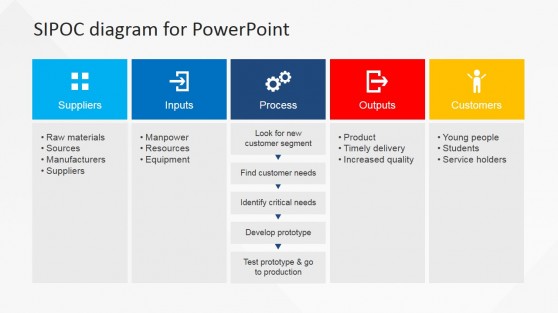
Flat SIPOC PowerPoint Diagram
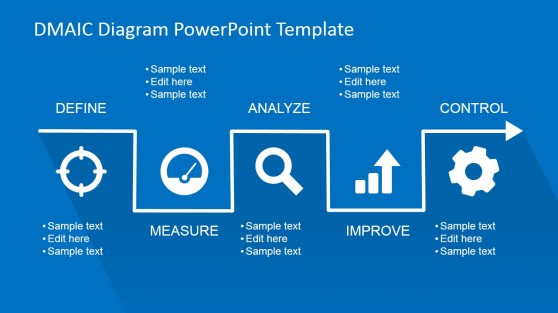
Flat DMAIC PowerPoint Template
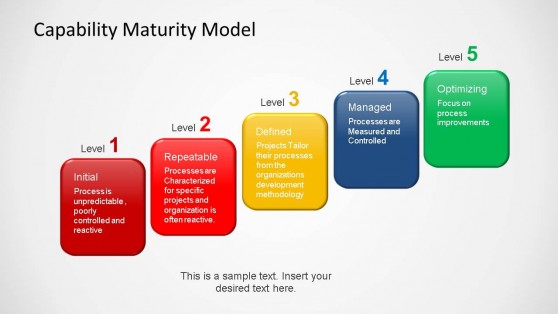
Capability Maturity Model PowerPoint Template
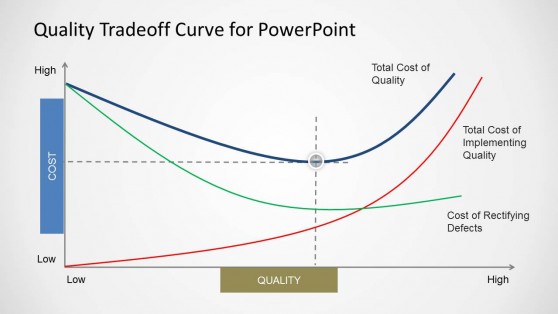
Quality Tradeoff Curve for PowerPoint

Six Sigma Slide Designs for PowerPoint
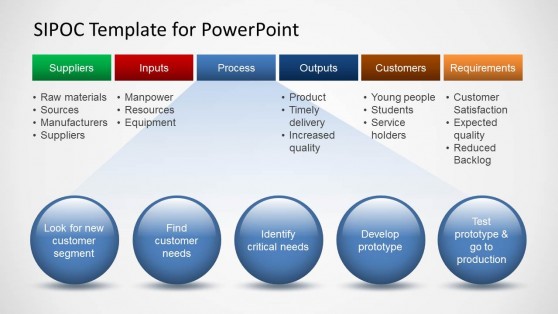
SIPOC Template for PowerPoint
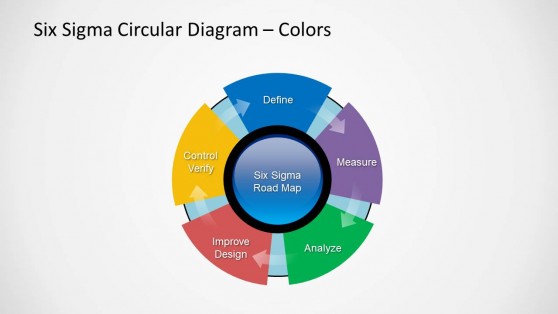
Six Sigma Diagram for PowerPoint
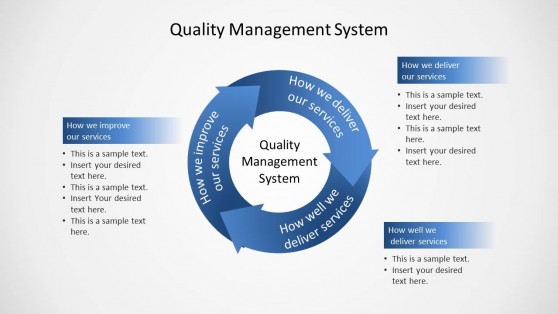
Quality Management System Circular Diagram for PowerPoint
Download unlimited content, our annual unlimited plan let you download unlimited content from slidemodel. save hours of manual work and use awesome slide designs in your next presentation..
Total Quality Management PowerPoint Presentation Slide

Ensure the quality of your product or service is consistent with our content-ready total quality management PowerPoint presentation slides. These capability maturity model integration presentation slides will help you upgrade the standards of your organization. Our quality improvement PPT presentation will help you enhance the quality of your firm outputs. This content ready quality control PowerPoint PPT covers all the relevant slides such as introduction, TQM pyramid, TQM model, customer focus in TQM, planning process in TSM, process management, business process improvement, involvement of people, TQM elements, determinants of product quality, determinants of service quality, importance of good quality, consequences of poor quality, principles and certification, and tools of quality management. It also includes slide on pareto chart, flow chart, fishbone diagram, data and analysis, root cause analysis, opportunity analysis, timeline analysis, force field analysis, SIPOC analysis, 5 why analysis, failure mode effect analysis, musts and wants, cost of quality, quality cost report, quality control, and quality management dashboard. Using these presentation slides, you can explain the content of quality control and quality assessment. So, quickly download this total quality management presentation PPT. Get them in the groove with our Total Quality Management PowerPoint Presentation Slide. Encourage them to follow given directions. Read less

Recommended
More related content, what's hot, what's hot ( 20 ), similar to total quality management powerpoint presentation slide, similar to total quality management powerpoint presentation slide ( 20 ), more from slideteam, more from slideteam ( 20 ), recently uploaded, recently uploaded ( 20 ).
- 1. Total Quality Management Your Company Name Here 1
- 2. Content 2 Introduction • TQM Pyramid • TQM Model • Elements of Quality Management • Determinants of Product/ service Quality • Importance of Good Quality • Consequences of Poor Quality Principles & Certification • General principles of TQM • ISO Certification Tools of Quality Management • Pareto Chart • Flow diagram • Fishbone diagram Data Analysis • Root Cause Analysis • Opportunity Analysis • Timeline Analysis • Force Field Analysis • SIPOC Analysis • Five Why Analysis • FMEA Analysis • Musts & Wants Quality Control • Control Chart • Quality Maintenance Checklist Cost of Quality • Costs of Quality • Quality cost report
- 3. Introduction 3 TQM Pyramid TQM Model Elements of Quality Management Determinants of Good Quality Importance of Good Quality Consequences of Poor Quality
- 4. TQM Pyramid 4 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Customer Driven Values empowerment Continuous Improvement Ownership Management Support Mission planning vision Rewards and Recognition Training,Teams,Awareness Empowerment, Partnership Measurement Information SPC,Cost of Quality, Documentation, Reporting,Testing,Tools,Prevention TQM Culture Leadership Involvement Process Quality This Pyramid Shows The Key Steps An Organization Has To Follow To Achieve The Optimal Quality Levels. You Can Alter These Steps As Per Your Requirements.
- 5. TQM Model 5 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Customer Focus This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Planning Process This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Process Management This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Total Involvement This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Process Improvement TQM Continuous Improvement Below is the TQM model showing the various aspects undertaken to ensure the quality standards. You can alter these aspects as per your needs.
- 6. 6 Customer Focus In TQM Option 1 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Option 2 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Option 3 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Option 4 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Option 5 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Option 6 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 7. 7 Planning Process In TQM 2017 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 2016 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 2015 2018 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 8. Process Management In TQM 8 2014 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 2018 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 2017 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 20162015 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 9. 9 Business Process Improvement Quality Improvement Team Total Participation Systematic Problem Solving Focus Statistical Quality Control Customer Focus
- 10. Involvement Of People 10 This principle recognizes that an organization is nothing without its staff. That their abilities should be used to full effect for business success.
- 11. Continuous Improvement This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Competitive Benchmarking This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Employee Empowerment This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Team Approach This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 11 TQM Elements
- 12. Determinants Of Product Quality 12 Characteristics of the product Performance consistency Resistance and long life of the product Evaluation of quality & reputation Injury risk Design, touch, taste, Fitting, Finishing Some additional features Product Quality Performance Reliability Durability Evaluation Safety Aesthetics Special Features
- 13. Determinants Of Service Quality 13 Determinants Qualities Required Reliability Consistency of performance and dependability Responsiveness Willingness or readiness of employee Competence Required skills and knowledge Access Approachability and ease of contact Courtesy Politeness,respect,consideration,friendliness Communication Keeping customer informed Credibility Trustworthiness,believability,honesty Security Freedom from danger, risk or doubt Understanding/knowing customer Understand the customer’s needs Tangibles Physical evidence of the service
- 14. Importance Of Good Quality 14 Product Liability Company Reputation Higher ProductivityHigher Price Improved Quality Increased profit This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 15. Lost Revenue Lost Customers Increased Costs Lost Productivity Lower Profits Damaged Brand 15 Consequences Of Poor Quality Poor Quality = Increased Business Risk Quality Gap: High Cost Of Failure
- 16. 16 Principles&Certification TQM Principles This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. ISO Certification This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 17. TQM Principles 17 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Customer Focus This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Leadership This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Involvement of People This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Process Approach This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Strategic Approach This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Continual Improvement This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Decision Making This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Supplier Relationship Principles
- 18. ISO Certifications 18 ISO Certification ISO-9001 • Helps Organization to produce Desired Outcome • Ensures Ongoing Controls • Enhance Customer Satisfaction by meeting Customer requirement ISO: 14001 • Helps Organization to reduce waste handling cost • Enhance branding of Organization • Increases profitability by saving energy ISO-27001 • Manages and minimizes risk exposure • Helps you to comply with other regulations • Provide you with a competitive advantage ISO-22301 • Flexibility during disruptions • Competitive advantage • Cost savings • Maintain optimum client delivery level ISO-29990 • Competitive advantage • Helps in establishing company quality model • Increases market presence • Global marketability We have listed down the major certifications wrt to the quality standards which an organization can attain. You can choose the relevant one and grey out the rest.
- 19. Tools of Quality Management 19 Pareto Chart Flow Chart Fishbone Diagram This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 20. Pareto Chart 20 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 1 2 3 5 4 5 Pareto Chart Obesrvation NumberOfDefects This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”. common tool used in ensuring quality standard in the products. Pareto chart would help in indicating the percentage of defects occurred over a period of few observations. This would be help in estimating whether over a time period the defects are reducing or not
- 21. Flow Chart 21 Start Define Collection Elements Specification Required Define specification Yes No Create Collection Plans Create Quality Results Report and analyze results Stop Perform Transaction Flow chart is another tool used in maintain quality standards. This helps in creating a flow for the activities to be followed. We have given an example, you can edit these data points as per your requirements.
- 22. Fishbone Diagram- Cause/ Effect Relationship 22 Cause 1 Cause 2 Cause 3 Cause 4 Cause 6 Cause 5 Cause 7 Cause 8 Cause 9 Cause 11 Cause 10 Cause 12 Description 1 Description 2 Description 3 Description 4 Description 5 Description 6 Problem Quality / Feature Below is the fishbone diagram establishing a cause effect relationship indicating the effect various causes might have on the product/ service quality. You can list down the causes and there effect in the below diagram as per your requirements
- 23. 23 Data & Analysis SIPOC Analysis Opportunity Analysis Root Cause Analysis Timeline Analysis Force Field Analysis FMEA Analysis FMEA
- 24. Root Cause Analysis (1/2) 24 Material CauseCause Measurement Machine Cause Cause Management Cause Man Cause Method Effect This analysis helps in establishing a cause-effect relationship wherein you will list down the causes of the defects and the effect it will have on the final offering. We have listed down 6 broad categories to figure out the causes, you can edit these as per your requirements.
- 25. Root Cause Analysis (2/2) 25 Possible Cause 20% Weight Cause 1 30% Weight Cause 2 40% Weight Cause 3 50% Weight Cause 4 20% Weight Cause 5 What How Who When Status Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here Text Here This analysis helps in establishing a cause-effect relationship wherein you will list down the causes of the defects and the effect it will have on the final offering. We have listed down 6 broad categories to figure out the causes, you can edit these as per your requirements.
- 26. Opportunity Analysis 26 Goals Importance Ability to Complete Low Medium High Low Medium High Description Description Description Description Description Description This Specify the opportunities in the below table wrt to quality and also mention their importance and the ability of the company to complete the same.
- 27. Timeline Analysis 27 Yield Units JAN 93.5% 125 FEB 95% 204 MAR 98% 238 APR 98% 338 MAY 91% 423 JUNE 91% 520 Process Change Provide a timeline for the completion of units manufactured on a monthly basis. This would help in estimating whether or not we are meeting the targets
- 28. Force Field Analysis 28 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 1 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 2 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 3 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 1 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 2 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Example 3 Restricting ForceDriving Force Problem Needs to be solved Mention below the driving and restraining forces in achieving the milestones set by the firm.
- 29. SIPOC Analysis Process Project Name Date Prepared by Notes Suppliers Inputs Process Outputs Customers Provider I/P description I/P Requirements O/P Description O/P Requirements Recipient of output 29 End Boundary Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Start Boundary See High Level Process Steps Below This analysis is used to document a business process from beginning to end. It provides a high level overview of the process.
- 30. 5 Why Analysis 30 Problem / Defect Answer What Caused The Specific Situation Answer Why The Problem Wasn’t Detected Answer What System Failed 1st WHY? 2nd WHY? 3rd WHY? 4th WHY? 5th WHY? Below is a table showing a problem with its various root causes. You have list down the defect and with the help of below analysis table arrive at the root cause of the problem in order to rectify the same.
- 31. Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) Failure Modes Effects Analysis(FMEA) Calculation of Risk Preference Number (RPN) Failure Mode Severity (1-lowest,10-highest) Probability of occurrence (1-lowest,10-highest) Probability of detection (1-lowest,10-highest) RPN A 5 7 4 140 B 6 3 5 90 C 4 5 2 40 Since A has highest priority as it has highest RPN value FMEA 31 FMEA) is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, a manufacturing or assembly process, or a product or service. RPN helps in indicating the failures which have high risk impact. The one’s with high RPN are given priority.
- 32. Musts & Wants Must have Want to have Must covers all those key inputs which are essential for an effective solution Wants covers those non essential inputs which you want to include This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 32
- 33. 33 Cost of Quality Cost of Quality This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Quality Cost Report This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Quality Cost Report Comparison This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 34. Cost of Quality Prevention Cost The cost of any action taken to investigate ,prevent or reduce the risk of a non conformity Appraisal Cost The cost associated with measuring ,checking or evaluating products or services to assure conformance to quality requirements Internal Failure Cost The cost incurred when products and services do not conform to specification External Failure Cost The cost incurred when products and services do not conform to specification Cost of Conformance Cost of Non-Conformance 34 Below slide indicates the four broad categories of quality cost which have an impact on the company performance.
- 35. Quality Cost Report Types of Cost Quality Cost Percentage of sales Prevention Cost Type 1 35,000 10% Type 2 10,000 45,000 Appraisal Cost Type 1 20,000 2.7% Type 2 30,000 50,000 Internal Failure Cost Type 1 50,000 5% Type 2 12,000 62,000 External Failure Cost Type 1 25,000 7% Type 2 30,000 55,000 35 On the basis of various costs, a quality cost report is prepared which comprises of the amount each cost has on the overall product.
- 36. Quality Cost Report (Comparison) Year 1 Year 2 Amount Percent Amount Percent Prevention Cost 00.00 00.00 00.00 00.00 Appraisal Cost 00.00 00.00 00.00 00.00 Internal Failure Cost 00.00 00.00 00.00 00.00 External Failure Cost 00.00 00.00 00.00 00.00 Total Quality Cost 00.00 00.00 00.00 00.00 Total Sales 20,000 25% 10,000 15% 36
- 37. 37 Quality Control Control Chart This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Quality Maintenance Check sheet This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Quality Maintenance Check List This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 38. Quality Control Chart 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 DefectRate Months Anatomy of Control Chart CL Lower control limit Process Improvement LCL UCL Upper control limit Center line Unstable trend 38 Process change We have created a control chart which specifies the defect rate along with their control limits. This would help in controlling the defects in the product and ensure good quality.
- 39. Quality Control Check sheet Name of data recorder Location Data collection date Defect type/event Occurrence Dates Total Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Description 1 9 8 3 20 Description 2 1 4 5 Description 3 10 10 Description 4 3 6 9 Description 5 4 8 Description 6 6 1 7 Description 7 3 3 6 Description 8 2 2 4 Description 9 5 5 Total 0 13 6 20 11 4 0 74 39 This is a table highlighting the defects found and their count. This would help in estimating the numbers of defects occurring on a daily basis so that corrective actions can be implemented instantly.
- 40. 40 Quality Management Dashboard Purpose and Overview Provide an overview of the process you plan to plan to employ to manage quality, describing the items below at a high level Include a problem definition or statement and any relevant background information Scope This section reference any standard and guideline that will be used on the project ,and addresses how compliance with these standards and guidelines will be determined and to which project deliverable they will apply. The project deliverables are then evaluated against these criteria before they are formally approved Roles and Responsibilities Describe who will be involved in the quality management process. What roles and teams will be required? If so how often Metrics and Tools This section describe the product and project and process metrics that will be captured and mentioned for project and any tools that will be used to do so Review and Audit Plan This section specifies the schedule, resources and methods to be used in conducting project review and audits Corrective Plan Provide a high level description of planned procedure used to prevent ,track or resolve problems or issues identified in project processes detected in QA reviews of this project or previous similar projects. Use an error report form 40
- 41. Time 10:15 To10:30 Coffee Break 41
- 42. 42 Chart And Graphs
- 43. Bar Chart 43 This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 FY' 12 FY' 13 FY' 14 FY' 15 FY' 16 FY' 17 FY' 18 Salesinpercentage(%) Financial years
- 44. Rader chart 44 • Product 01 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. • Product 02 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun
- 45. Bubble Chart 45 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 0 10 20 30 40 50 This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”. • Product 01 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. • Product 02 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. • Product 03 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 46. Stacked Bar 46 100 80 -50 -30 90 65 -56 -25 -100-90 -80 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Unit Count • Product 01 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. • Product 02 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 47. Clustered Column 47 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Jan Feb Mar Apr SalesinPercentage(%) Financial Year 2017 • Product 01 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Jan Feb Mar Apr Salesinpercentage(%) Financial Year 2017 • Product 02 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 48. Scatter Chart 48 5 20 10 9 35 15 30 30 56 $0 $10 $20 $30 $40 $50 $60 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% 45% 50% X-Values Y-Values • Product 01 This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 49. Donut Pie Chart 49 Product 03 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Product 02 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Product 01 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Product 04 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 40% 30% 20% 10% This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 50. Open High Low Close 50 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 05-06-2017 06-06-2017 07-06-2017 08-06-2017 09-06-2017 Close High Low • Product 01 This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 51. Area Chart 51 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 DecNovOctSepAugJulJunMayAprMarFebJan InPercentage% Financial Year 2016 • Product 01 • Product 02 This graph/chart is linked to excel, and changes automatically based on data. Just left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
- 52. 52 Additional Slides
- 53. 53 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Vision This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Mission Goal This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Vision & Mission
- 54. Charily Doe This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Mary Clark This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Emily Parker This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Peter Smith This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 54 Our Team Graphic Designer Web DesignerMarketing HeadFinancial Advisor
- 55. 55 Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Text Here This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 01 02 03 About Us
- 56. 56 Awareness This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Quality This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Success This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Our Main Goals
- 57. Comparison 57 vs 55% This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Male 45% This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. Female
- 58. Dashboard 58 0% 50% 100% 75% This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 0% 50% 100% 50% This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 59. Financial 59 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 45% Euro 85% Dollar 30% Pound
- 60. 60 Quotes “ The value of an IDEA LIES IN the using of it.” - Thomas Edison “ MOTIVATION is man your DREAMS put on work clothes.” “ I’m CONSERVATIVE, but I’m not a nut about it.” This is a representative image, and should be replaced by your own image. Just right click and replace image. - Thomas Edison - Benjamin Franklin - George .W. Bush
- 61. Timeline 61 2017 2016 2015 2014 Start Today This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 62. Puzzle 62 04 01 02 03 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 63. Our Target This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 63
- 64. Location 64 USA 80% This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 35% South America Africa 20% Australia 15% Asia 30%
- 65. Circular 65 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. 01 02 03 04
- 66. Venn 66 02 01 03 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 67. Mind Map 67 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 68. Silhouettes 68 01 02 05 04 03 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 69. Hierarchy 69 Name Here Designation Name Here Designation Name Here Designation Name Here Designation This icon is for display purposes only and is completely editable. You can replace this with any other icon from the www.slideteam.net icons section. This icon is for display purposes only and is completely editable. You can replace this with any other icon from the www.slideteam.net icons section. This icon is for display purposes only and is completely editable. You can replace this with any other icon from the www.slideteam.net icons section. This icon is for display purposes only and is completely editable. You can replace this with any other icon from the www.slideteam.net icons section.
- 70. 70 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. IDEA Creation
- 71. Magnifying Glass 71 01 02 03 04 05 This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention. This slide is 100% editable. Adapt it to your needs and capture your audience's attention.
- 72. 72 Thanks for your Business Address # street number, city, state Contact Numbers: 0123456789 Email Address: [email protected]

Total Quality Management
Nov 20, 2014
410 likes | 829 Views
Total Quality Management. Einstein & Athalia. Structure. I. Introduction II. Reasons to learn about TQM III. Cost of quality IV. Total quality management principles V. Tools of TQM VI. Quality process component. Structure (Cont’d). VII. Barriers to TQM VIII.Benefits of TQM
Share Presentation
- quality process
- helps determine
- quality process component
- quality process component cont

Presentation Transcript
Total Quality Management Einstein & Athalia
Structure I. Introduction II. Reasons to learn about TQM III. Cost of quality IV. Total quality management principles V. Tools of TQM VI. Quality process component
Structure (Cont’d) VII. Barriers to TQM VIII.Benefits of TQM IX. Summary
Introduction: • Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management approach that aims for long-term success by focusing on customer satisfaction. TQM is based on the participation of all members of an organization in improving processes, products, services, and the culture in which they work.
II. Reasons To Learn About TQM (Cont’d) A. Managers need to use their technical expertise and the quality process to improve product quality and their firm’s productivity B. Managers need to use their interpersonal skills as a change agent and contest for power in an organization C. Managers need to understand that Quality is a part of production - it is not apart from production
II. Reasons To Learn About TQM (Cont’d) D. Engineers/Mangers need to be creative in improving the engineering process, and recognize that “quality” is not features; that is, a Ford-built Lincoln has more features than a Ford-built Taurus, but it does not necessarily have higher quality E. Engineers/Managers need to think beyond issues of technology, and learn the means whereby people, processes and technology come together
III. Cost of Quality A. Contractors pay a significant price for poor quality resulting from accidents, waste, rework, inefficiencies, poor subcontractor performance and poor communication - these costs are estimated to be between 5% and 30% of the construction cost of a facility B. Cost of nonconformance - includes both direct and indirect costs of not doing things right the first time
III. Cost of Quality 1. Factors a) Accidents b) Omissions c) Errors d) Poor workmanship e) Being late 2. Results a) Rework b) Recalls c) Expediting
III. Cost of Quality (Cont’d) d) Removal of punch list items e) Time extensions f) Litigation costs and damages g) Penalties and liquidated damages h) Increased insurance costs
III. Cost of Quality (Cont’d) C. Cost of Conformance - includes preventive measures 1. Inspection of direct hire work 2. Inspection of subcontractor work 3. Inspection at vendor source of supply 4. Inspection of shipments 5. Review of shop drawings
III. Cost of Quality (Cont’d) 6. All training costs, including safety 7. Facilitator costs 8. Salary of quality coordinator 9. Meetings of the steering committee and quality improvement teams 10. Administration of the quality management program 11. Reward system
IV. Total Quality Management Principles • Provide understanding of and guidance on the application of TQM A.Customer-Driven Organization 1. Organizations depend on their customers and therefore should understand current and future customer needs, meet customer requirements, and strive to exceed customer expectations
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) 2. It requires 10 times as much money to attract a new customer than it requires to keep a customer you already have......keep the present customer happy B. Leadership 1. Leaders establish unity of purpose, direction, and the internal environment of organization; they fully involve people in achieving the organization’s objectives
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) 2. The difference between an average and an outstanding company is the leadership they have C. Involvement of People 1. People are the essence of an organization and their full involvement enables their knowledge and experiences to be used for the organization’s benefit 2. Employees are a company’s greatest asset
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) 3. An individual without information can not take responsibility; an individual with information can and will take responsibility D. Process Approach - A desired result is achieved more effectively when related resources and activities are managed as a process
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) E.System Approach to Management - Identifying, understanding, and managing a system of interrelated processes for a given objective will contribute to the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) F. Continual Improvement 1. Continual improvement is a permanent objective of the organization 2. In the race for quality, there is no finish line 3. Quality comes from within; it comes from the hearts and the minds of the people
IV. Total Quality Management Principles (Cont’d) G. Factual Approach to Decision Making - Effective decisions and actions are based on the analysis of data and information H. Mutually Beneficial Supplier Relationships 1. Mutually beneficial relationships are established to enhance the ability of both organizations to create value 2. Relates to Partnering -Lecture 33
V. Tools of TQM A. Check Sheet - 1. Tabulates frequency of occurrence 2. Easy to use and understand 3. Data gathered here can be used in other tools
V. Tools of TQM (Cont’d) B. Graph 1. Visual display of data 2. Major types a) Line graph b) Bar chart c) Circle diagram (pie chart)
V. Tools of TQM (Cont’d) C. Histogram - 1. Portrays frequency of occurrence 2. Shows various measures of central tendency D. Pareto Chart - 1. Visually portrays problems and causes in order of severity or frequency
V. Tools of TQM (Cont’d) 2. Helps determine which problems or cause to tackle first E. Cause-and-effect diagram 1. Portrays possible causes of a process problem 2. Helps determine root cause
V. Tools of TQM (Cont’d) F. Scatter diagram 1. Indicates the relationship between two variables 2. Displays the strength of that relationship G. Control Chart - 1. Monitors a process to determine magnitude of variation
V. Tools of TQM (Cont’d) 2. Estimates the parameters of a process 3. Reduces the variability of a process H. Flowchart 1. Portrays all the steps in a process 2. Helps understand the process
VI. Quality Process Component A. Motivation - based on recognition, commendation, recommendation, repeat business, reward B. Communication - must be team-wide, involving all partners, as well as thorough, honest, and complete C. Commitment - to the project, to the process, to all the partners, and to the promised result
VI. Quality Process Component (Cont’d) D. Expectations - realistic, reasonable, communicated, understood, and accepted E. Ability - adequate, understood, and consistent F. Involvement - total, all-party, and consistent G. Feedback - thorough, understandable, and complete Follow-up - complete and consistent, as well as long term
VII. Barriers to TQM A. Lack of trained workers/poorly installed equipment/poor workmanship B. Competitive markets C. Poor plans and scheduling specifications/poorly defined work scope D. Bad attitudes E. Lack of competent field managers
VIII. Benefits of TQM A. Better defined project scope and objectives B. Greater communication of objectives C. Teamwork D. Effective planning and scheduling E. Appropriate Training
VIII. Benefits of TQM (Cont’d) F. Improved quality of materials, equipment, and workmanship • Case Studies – Refer to Douglas Electrical Case
IX. Summary • TQM principles • Tools of TQM • Barriers to TQM • Benefits of TQM
- More by User

Total Quality Management Introduction What is quality? Dictionary has many definitions: “Essential characteristic,” “Superior,” etc. Some definitions that have gained wide acceptance in various organizations: “ Quality is customer satisfaction ,” “ Quality is Fitness for Use .”
1.92k views • 69 slides

Total Quality Management. Implementation. Implementation Chart.
500 views • 7 slides

Total Quality Management. Week # 11 5S Prepared by: Khalid Dahleez Faculty of Commerce – the Islamic University of Gaza This material was collected from different sources. WHAT IS 5S?.
1.21k views • 36 slides

Total Quality Management. Week # 8 Business Process Reengineering (BPR) Prepared by: Khalid Dahleez Faculty of Commerce – the Islamic University of Gaza This material was collected from different sources. Business Processes.
967 views • 48 slides

Total Quality Management. Total Quality Management and Continuous Improvement. TQM. Total - made up of the whole Quality - degree of excellence a product or service provides Management - act, art or manner of planning, controlling, directing,….
691 views • 17 slides

Total Quality Management. "Understanding Profound Knowledge" Dr. T. Valesky "Hard work and best efforts will by themselves not produce quality.... the missing ingredient, profound knowledge."
567 views • 21 slides

Total Quality Management. Week # 4 Leadership, Commitment, & Strategy Prepared by: Khalid Dahleez Faculty of Commerce – the Islamic University of Gaza This material was collected from different sources. Total Quality Management Model – major features. Teams. Culture . Process
2.23k views • 74 slides

Total Quality Management. Chapter 5. Management 326. Operations and Operations Strategy. Designing an Operations System. Managing an Operations System. Improving an Operations System. Designing an Operations System. Product Design. Project Management: A Design Tool.
1.54k views • 29 slides

Total Quality Management. Introduction. Total – Made up of the whole(or) Complete. Quality – Degree of Excellence a product or service provides to the customer in present and future. Management – Act , art, or manner of handling , controlling, directing, etc.
1.02k views • 25 slides

TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT. BERNA AKSU İSMET SIDKI UYAR MERT ZORER. History.
632 views • 22 slides

Total Quality Management. a continuous improvement process. Table of Contents. Introduction What is TQM? TQM beliefs Deming’s fourteen points of TQM and his theory Characteristics of Successful TQM Companies Quality TQM principles How to begin Continuous Improvement Reasons to begin now
1.16k views • 47 slides

Total Quality Management. Screen graphic created by : Mustika Lukman Arief, SE.MBA. Total Quality Management and Continuous Improvement. Why TQM?. Ford Motor Company had operating losses of $3.3 billion between 1980 and 1982. Xerox market share dropped from 93% in 1971 to 40% in 1981.
607 views • 15 slides

Total Quality Management. Faculty: J.M.Pant Management Consultant, Trainer and Visiting Professor For any query, contact Mob: 9811030273; e-mail: [email protected] ; [email protected]. Total Quality Management. 1. Main concerns of Manufacturers and Customers Manufacturer Customer
944 views • 60 slides

Total Quality Management. Total Quality Management and Continuous Improvement. Prepared By; Iman P. Hidayat, SE., MSi., Ak. Why TQM?. Ford Motor Company had operating losses of $3.3 billion between 1980 and 1982. Xerox market share dropped from 93% in 1971 to 40% in 1981.
624 views • 15 slides

Total Quality Management. Key concepts The Cost of Quality Tools and Techniques Benefits Implementation. Quality Control. Statistical Methods Process Performance Quality Standards. Inspection. Error Detection Rectification. Total Quality Management. Company Wide Quality Control.
761 views • 22 slides

Total Quality Management. Chapter 5. MGMT 326. Capacity, Facilities, & Work Design. Products & Processes. Quality Assurance. Planning & Control. Foundations of Operations. Managing Quality. Product Design. Introduction. Strategy. Statistical Process Control. Process Design.
516 views • 27 slides

Total Quality Management. ROAD MAP. Introduction Evolution of TQM What is quality? Definitions, Dimensions and customer expectations What is TQM? TQM beliefs Deming’s fourteen points of TQM and his theory Characteristics of Successful TQM Companies Quality TQM principles
1.12k views • 53 slides

Total Quality Management. By: Zaipul Anwar Manager, R & D Dept. Business & Advanced Technology Centre UTM. Total Quality Management (TQM) - A buzzword phrase of the 1980's. Total = quality involves everyone and all activities in the company
812 views • 14 slides

Total Quality Management. This chapter explains the concepts, principles, and philosophy of total quality management. Total Quality Management. The way of managing organization to achieve excellence Total – everything Quality – degree of excellence
1.79k views • 39 slides

Total Quality Management. What is Quality?. Quality involves meeting or exceeding customer expectations. Quality applies to products, services, people, processes, and environments.
531 views • 27 slides

Total Quality Management. Chapter 16. What is Quality?. Quality means user satisfaction: that goods or services satisfy the needs and expectations of the user. Quality and Product Policy. Established by management Product planning wants and needs of the marketplace
2.02k views • 101 slides

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Total quality management powerpoint templates
The total quality management PowerPoint template defines it as a comprehensive as well as structured approach towards organizational management for maintaining standards and improve the quality of products or services with respect to the feedback. The total quality management tool PPT slide describes its aim at the final results in the form of the product or service that an organization aims at providing its clients and customers. The total quality management example presentation template covers all the topics from planning to manufacturing and operations, sales & marketing to post sales support. The total quality management PPT slide design is perfect for the user to emphasize continuous improvement as well as customer satisfaction and involves everyone associated with the business in the process. A user can take the help of the total quality management presentation template to illustrate the importance of maintaining better standards. The total quality management presentation slideshow highlights control over the quality of every single aspect of the business.
The total quality management PowerPoint template defines it as a comprehensive as well as structured approach towards organ..
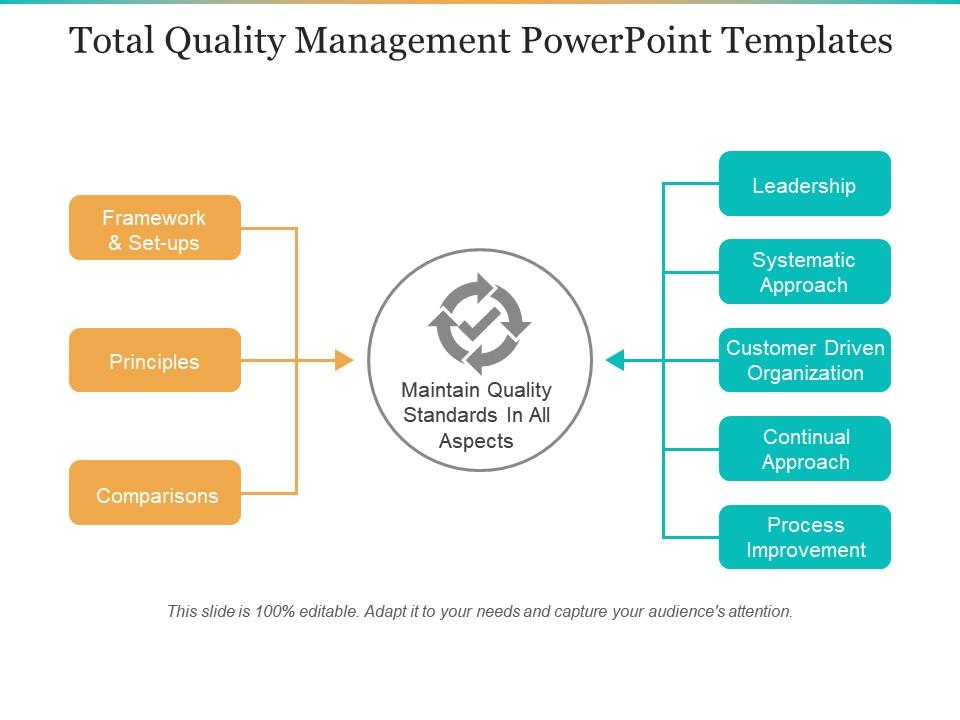
These PPT Slides are compatible with Google Slides
Compatible With Google Slides

- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
Get Presentation Slides in WideScreen
Get This In WideScreen
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
Do you want to remove this product from your favourites?
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Total Quality Management PowerPoint Templates. This slide can be downloaded in different editable formats such as PDF, JPG. Background can be set to any color. You can customize the theme with content that matches your topic of interest. The slide is Google Slides friendly. You can avail of this PPT slide in both standard as well as widescreen size. Because of its high-resolution graphics it can be presented in front of a large number of people.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Diagrams , Business , Marketing , Business Slides , Flat Designs , Concepts and Shapes , Business Review , Management , Quality Management
- Framework And Set Ups ,
- Principles ,
- Comparisons ,
Total quality management powerpoint templates with all 5 slides:
Our Total Quality Management Powerpoint Templates attract expertise. The best brains find them appealing.
Ratings and Reviews
by Delmer Black
June 25, 2021
by Liam Perez
June 24, 2021


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Presentation Transcript. Total Quality Management • TQM is a philosophy which applies equally to all parts of the organization. • TQM can be viewed as anextension of the traditional approach to quality. • TQM places the customer at the forefront of quality decision making. • Greater emphasis on the roles and responsibilities of every ...
5. Total Quality Management Principles: The 8 Primary Elements of TQM are as follows - Total quality management can be summarized as a management system for a customer- focused organization that involves all employees in continual improvement. It uses strategy, data, and effective communications to integrate the quality discipline into the culture and activities of the organization.
capture the market with better quality and reduced costs. Stay in business. . Long term competitive strength. The Deming philosophy. 14 points for management: 1. Create and publish to all employees a statement of the aims and purposes of the company. The management must demonstrate their commitment to this statement.
5. Various Definitions Total quality management (TQM) has been defined as an integrated organizational effort designed to improve quality at every level. The process to produce a perfect product by a series of measures require an organized effort by the entire company to prevent or eliminate errors at every stage in production is called total quality management. According to international ...
Total Quality Management is a management framework based on the belief that a company can build long-term success by having all its members, from low-level workers to its highest-ranking executives. It focuses on quality improvement and thus delivering customer satisfaction. This Total Quality Management template models all the facets of Total ...
2. Total Quality Management (TQM): Definition: Total Quality Management (TQM) is a set of management practices throughout the organization geared to ensure the organization consistently meets or exceed customer requirements. TQM refers to management methods used to enhance quality, based on the participation of all members & aiming all long term success through customers satisfaction ...
This ready-to-use total quality management presentation covers topics like TQM model, customer focus in TQM, planning process in TQM, determinants of product quality, TQM principles, and more. Execute quality management and try to attain a desired level of excellence. Add these professionally designed content-ready Introduction To TQM PPT ...
Slide 1: This slide introduces Total Quality Management with imagery.Add your company name and begin. Slide 2: This slide showcases Content with the following points- Introduction, Principles & Certification, Tools of Quality Management, Data Analysis, Quality Control, Cost of Quality. Slide 3: This is an Introduction slide showing- TQM Pyramid, TQM Model, Elements of Quality Management ...
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a holistic approach to long-term success that views continuous improvement in all aspects of an organization as a process. It aims to radically transform the organization through progressive changes in the attitudes, practices, systems and structures. By teaching this TQM PPT training presentation, employees will understand the importance of quality, focus on ...
2. Top management must provide leadership and support for all quality initiatives. 3. Preventing variability is the key to producing high quality. 4. Quality goals are a moving target, thereby requiring a commitment toward continuous improvement. 5. Improving quality requires the establishment of effective metrics.
1 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT: TQM Origins, Evolution & key elements. 2 What is Quality? Quality is "fitness for use" (Joseph Juran) Quality is "conformance to requirements" (Philip B. Crosby) Quality of a product or services is its ability to satisfy the needs and expectations of the customer. 3 Evolution of Quality Management.
PPT Presentations. Quality management concerns the optimization of the quality of a product, a service or a process. Quality management includes the planning, monitoring, control and monitoring of a quality process and the results of the process. This affects all measures that improve process quality. A common model is the EFQM model and ISO 9001.
Use the total quality management presentation template to maximize the flexibility and profitability of your product. Take the assistance of this professionally designed TQM PowerPoint graphic to establish a company quality model that helps to maintain optimum client delivery level. With the help of quality improvement PPT deck, you can manage ...
Total Quality Management (TQM) Jul 24, 2010 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 436 likes • 144,643 views. Mudassar Salman. 1 of 48. Download now. Total Quality Management (TQM) 1. Chapter 5 - Total Quality Management Mudassar Salman.
Total Quality Management is an organizational philosophy, based on the principle that consistent delivery of customer expectations, can only be achieved if each and every contributor into the customer expectation performs as required, in order to meet the needs of the customer. In TQM the customer is everyone who is provided with a product or ...
Total Quality Management - TQM: Total Quality Management (TQM) is the continuous process of reducing or eliminating errors in manufacturing, streamlining supply chain management , improving the ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Explain the meaning of Total Quality Management (TQM) 2. Identify key leaders in the field of quality and their philosophies 3. Identify characteristics of the TQM philosophy 4. Understand the importance of process management and measuring the cost of quality 5. Describe the key business excellence and quality models 6.
TQM consists of organization-wide efforts to install and make permanent a climate in which an organization continuously improves its ability to deliver high-quality products and services to customers. Under this category you can download Total Quality Management PowerPoint templates and slide graphics for presentations.
PowerPoint presentation slides: Presenting our set of slides with Key Pillars Of Total Quality Management. This exhibits information on five stages of the process. This is an easy to edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Training, Teamwork, Leadership.
Using these presentation slides, you can explain the content of quality control and quality assessment. So, quickly download this total quality management presentation PPT. Get them in the groove with our Total Quality Management PowerPoint Presentation Slide. Encourage them to follow given directions. 1.
Total Quality Management Principles (Cont'd) F. Continual Improvement 1. Continual improvement is a permanent objective of the organization 2. In the race for quality, there is no finish line 3. Quality comes from within; it comes from the hearts and the minds of the people. IV.
The total quality management tool PPT slide describes its aim at the final results in the form of the product or service that an organization aims at providing its clients and customers. The total quality management example presentation template covers all the topics from planning to manufacturing and operations, sales & marketing to post sales ...