Direct & Inverse Proportions/Variations
In these lessons, we will learn how to solve direct proportions (variations) and inverse proportions (inverse variations) problems. (Note: Some texts may refer to inverse proportions/variations as indirect proportions/variations.)
Related Pages: Direct Variations Proportion Word Problems More Algebra Lessons
The following diagram gives the steps to solve ratios and direct proportion word problems. Scroll down the page for examples and step-by-step solutions.
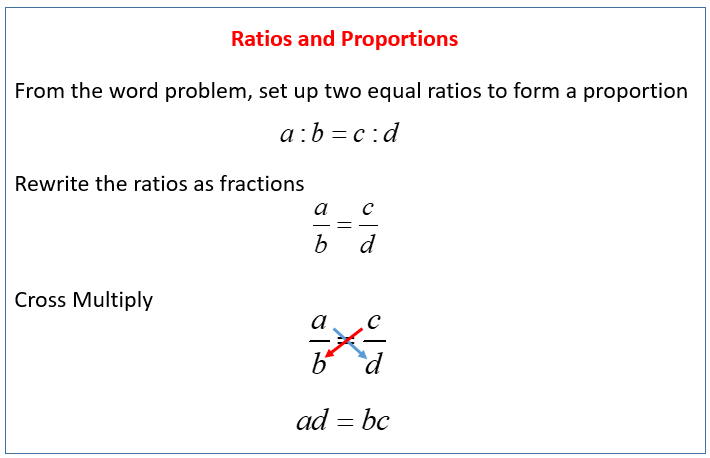

Direct Proportions/Variations
Knowing that the ratio does not change allows you to form an equation to find the value of an unknown variable.
Example : If two pencils cost $1.50, how many pencils can you buy with $9.00?
How To Solve Directly Proportional Questions?
Example 1: F is directly proportional to x. When F is 6, x is 4. Find the value of F when x is 5. Example 2: A is directly proportional to the square of B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 3.
How To Use Direct Proportion?
How To Solve Word Problems Using Proportions?
This video shows how to solve word problems by writing a proportion and solving 1. A recipe uses 5 cups of flour for every 2 cups of sugar. If I want to make a recipe using 8 cups of flour, how much sugar do I use? 2. A syrup is made by dissolving 2 cups of sugar in 2/3 cups of boiling water. How many cups of sugar should be used for 2 cups of boiling water? 3. A school buys 8 gallons of juice for 100 kids. how many gallons do they need for 175 kids?
Solving More Word Problems Using Proportions
1. On a map, two cities are 2 5/8 inches apart. If 3/8 inches on the map represents 25 miles, how far apart are the cities (in miles)? 2. Solve for the sides of similar triangles using proportions
Inverse Proportions/Variations Or Indirect Proportions
Two values x and y are inversely proportional to each other when their product xy is a constant (always remains the same). This means that when x increases y will decrease, and vice versa, by an amount such that xy remains the same.
Knowing that the product does not change also allows you to form an equation to find the value of an unknown variable
Example : It takes 4 men 6 hours to repair a road. How long will it take 8 men to do the job if they work at the same rate?
Solution : The number of men is inversely proportional to the time taken to do the job. Let t be the time taken for the 8 men to finish the job. 4 × 6 = 8 × t 24 = 8t t = 3 hours
Usually, you will be able to decide from the question whether the values are directly proportional or inversely proportional.
How To Solve Inverse Proportion Questions?
This video shows how to solve inverse proportion questions. It goes through a couple of examples and ends with some practice questions Example 1: A is inversely proportional to B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 8 Example 2: F is inversely proportional to the square of x. When A is 20, B is 3. Find the value of F when x is 5.
How To Use Inverse Proportion To Work Out Problems?
How to use a more advanced form of inverse proportion where the use of square numbers is involved.
More examples to explain direct proportions / variations and inverse proportions / variations
How to solve Inverse Proportion Math Problems on pressure and volume?
In math, an inverse proportion is when an increase in one quantity results in a decrease in another quantity. This video will show how to solve an inverse proportion math problem. Example : The pressure in a piston is 2.0 atm at 25°C and the volume is 4.0L. If the pressure is increased to 6.0 atm at the same temperature, what will be the volume?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

Direct Proportion: Definition, Formula, Symbol, Examples, FAQs
What is direct proportion in math, difference between direct proportion and inverse proportion, how to use direct proportion to solve problems, solved examples of direct proportion, practice problems on direct proportion, frequently asked questions about direct proportion.
Direct proportion or direct variation is a type of proportion in which the ratio of two quantities stays constant.
Suppose a variable y varies directly with x, then it means that if x increases, y increases by the same factor. If x decreases, then there is a proportionate decrease in y also.
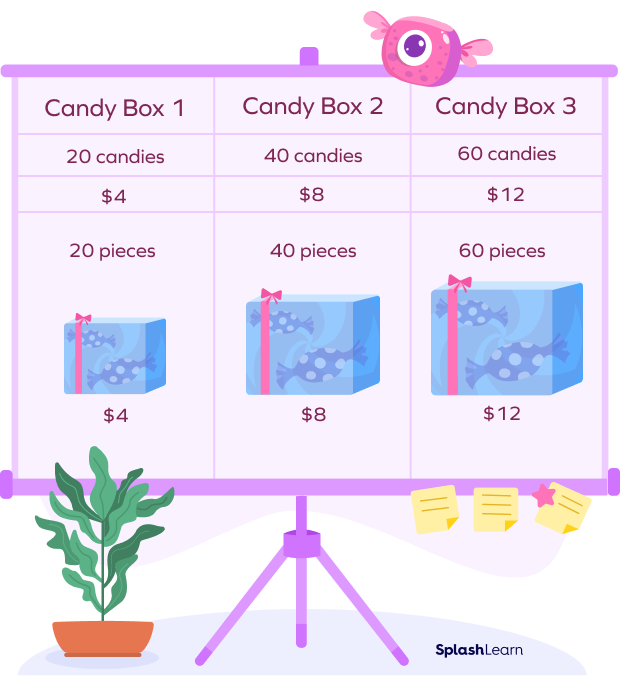
Direct Proportion Example:
The cost of the candy increases as the number of the same increases.
Direct Proportion Symbol
The “directly proportional symbol” or “direct proportional symbol” is $\propto$.
We read x ∝ y as “x is directly proportional to y.”
It means that x is dependent on y.
We read y ∝ x as “y is directly proportional to x.”
It means that y is dependent on x.
Direct Proportion Formula
If y is directly proportional to x, then the direct proportion formula or the direct proportion equation is given by y=kx, where k is a constant of proportionality.

Constant of Proportionality
From the direct proportion formula, we have y = kx.
The fixed value $k = \frac{y}{x}$ is called the constant of proportionality and it represents the constant ratio between the two quantities that are in direct proportion. k can be any non-zero real number.
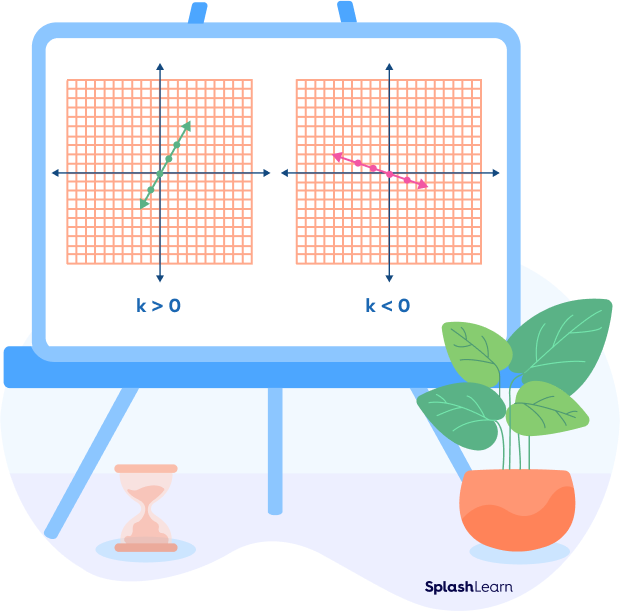
Direct Proportion Graph
If you construct a graph of a direct proportion, it always comes out to be a straight line passing through the origin (0, 0).
The slope of this line is k.
- If k is negative, the line goes down from left to right.
- If k is positive, the line rises from left to right.
Direct proportion and inverse proportion are two kinds of proportional relationships in math describing the relation between two variables. Here are their key differences in the table below:

Let’s understand this with the help of an example.
Example: If 20 pens cost $25, what would be the cost of 100 pens?
Here, the cost of pens is directly proportional to the number of pens.
Note down the given values of x and y.
Since the quantities are in direct proportion, their ratio is constant.
$\frac{20}{25} = \frac{100}{?}$
By cross multiplying, we get
$20 \times ?= 100 \times 25$
? $= \$125$
100 pens will cost $\$125$.
Facts about Direct Proportion
- Prior to $\propto$ (symbol), a double colon (::) was used.
- The proportionality symbol $(\propto)$ was used by William Emerson (London, 1768) for the first time.
- The link between the two variables is no longer a direct proportion if the proportionality ratio changes.
In this article, we learned about direct proportion, its graph, formula, equation, and examples. Let’s solve a few examples and practice problems to understand the concept better.
1. If 8 rooms are required for 24 guests, how many rooms would be required to accommodate 12 guests?
Here, $\frac{24}{8} = \frac{w}{12}$
Cross-multiply:
$w \times 8 = 12 \times 24$
Therefore, for 12 guests, a total of 36 rooms will be required.
2. If 4 tasks take 8 hours for completion, how many tasks can be completed in 20 hours?
Let’s write the constant ratios.
$\frac{4}{8} = \frac{n}{20}$
In 20 hours, 10 tasks can be completed.
3. What will 10 movie tickets cost if the price of 6 tickets is $\$36$ ?
6 tickets cost $\$36$.
Let 10 movie tickets cost $y.
$\frac{6}{36} = \frac{10}{6}$
$y \times 6 = 36 \times 10$
4. If a task is completed in 20 days by 5 workers, how long will it take 10 workers to perform the same task?
Solution:
This problem can again be solved using the direct proportion formula.
Let the number of days for 10 workers to complete the task be x.
$\frac{5}{10} = \frac{20}{x}$
Cross-multiply
$5x = 10 \times 20$
$x = \frac{(10 \times 20)}{5}$
Therefore, 10 workers will require 40 days to complete the same task.
5. How far can John run in 60 minutes if he can cover 9 miles in 90?
Solution:
Use the direct proportion formula for this problem.
Let the distance John covers in 60 minutes be x.
$\frac{9}{90} = \frac{x}{60}$
Cross-multiply.
$\frac{9 \times 60} = 90x$
$x = \frac{(9 \times 60)}{90}$
Therefore, John can run 6 miles in an hour.
Attend this quiz & Test your knowledge.
If x is directly proportional to y, we write it as
If a car travels 75 miles on 3 gallons of gas, how many miles can it travel on 5 gas gallons, the graph for direct proportionality is, on the graph of a direct proportion, the constant of proportionality represents the.
Is y being inversely proportional to x the same thing as y being directly proportional to $\frac{1}{x}$ ?
Yes, y being inversely proportional to x the same thing as y being directly proportional to the reciprocal of x, which is $\frac{1}{x}$.
How do we know whether any two variables are directly proportional or not?
We can confirm the direct proportionality of any two variables if their ratio remains constant. This is expressed mathematically as $\frac{y}{x} = k$. Here, k is the constant of proportionality.
What are the uses of direct proportion?
Direct proportion is a universal concept profoundly used in different fields to explain and predict relationships between variables. The direct proportion has multiple practical uses in various fields, including mathematics, science, engineering, finance, art, population rates, and many others.
What is an independent variable and dependent variable in direct proportion?
For given two quantities, the cause and effect relationship decides the independent variable and the dependent variable. The independent variable is the cause, and the dependent variable is the variable whose value depends on the independent variable. We can define them based on the context.
is $x \propto y$ same as $y \propto x$ ?
No, these two statements are not the same.
$x \propto y$ means that x is directly proportional to y.
$y \propto x$ means that y is directly proportional to x.
RELATED POSTS
- Average Speed Formula: Definition, Examples, Facts, FAQs
- Decimal to Octal: Steps, Methods, Conversion Table
- Relatively Prime
- Meters to Yards Conversion – Definition, Formula, Steps, Examples
- How to Calculate Percent Difference – Definition, Formula, Examples

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free
- Math Article
Direct Proportion
Direct proportion or direct variation is the relation between two quantities where the ratio of the two is equal to a constant value. It is represented by the proportional symbol, ∝ . In fact, the same symbol is used to represent inversely proportional , the matter of the fact that the other quantity is inverted here.
For example, x and y are two quantities or variables which are linked with each other directly, then we can say x ∝ y. When we remove the proportionality symbol, the ratio of x and y becomes equal to a constant, such as x/y = C, where C is a constant. But in the case of inverse proportion, x and y are denoted as x ∝ 1/y or xy = C.
Direct proportion Examples in Real Life
In our day-to-day life, we observe that the variations in the values of various quantities depending upon the variation in values of some other quantities.

For example: if the number of individuals visiting a restaurant increases, earning of the restaurant also increases and vice versa. If more number of people are employed for the same job, the time taken to accomplish the job decreases.
Sometimes, we observe that the variation in the value of one quantity is similar to the variation in the value of another quantity that is when the value of one quantity increases then the value of other quantity also increases in the same proportion and vice versa. In such situations, two quantities are termed to exist in direct proportion.

Some more examples are:
- Speed is directly proportional to distance.
- The cost of the fruits or vegetable increases as the weight for the same increases.
Direct Proportion Symbol and Constant of Proportionality
The symbol for “direct proportional” is ‘∝’ (One should not confuse with the symbol for infinity ∞). Two quantities existing in direct proportion can be expressed as;
k is a non-zero constant of proportionality.
Where x and y are the value of two quantities and k are a constant known as the constant of proportionality . If x 1 , y 1 is the initial values and x 2 , y 2 are the final values of quantities existing in direct proportion. They can be expressed as,
Example: a machine manufactures 20units per hour
The units that machine manufactures is directly proportional to how many hours it has worked.
More works the machine does, more are the units manufactured; in direct proportion.
This could be written as:
Units ∝ Hours Worked
- If it works 2 hours we get 40 Units
- If it works 4 hours we get 80 Units
Direct proportion Questions and Answers
Q.1 : An electric pole, 7 meters high, casts a shadow of 5 meters. Find the height of a tree that casts a shadow of 10 meters under similar conditions.
Solution : Let the height of the tree be x meters. We know that if the height of the pole increases the length of shadow will also increase in same proportion. Hence, we observe that the height of the tree and the length of its shadow exist in direct proportion. In other words height of pole is directly proportional to the length of its shadow. Thus,
x = 14 meters
Q.2 : A train travels 200 km in 5 hours. How much time it will take to cover 600 km?
Solution : Let the time taken be T hours. We know that time taken is directly proportional to distance covered. Hence,
T = 15 hours

Q. 3 : The scale of a map is given as 1:20000000 . Two cities are 4cm apart on the map. Find the actual distance between them.
Solution : Map distance is 4 cm.
Let the actual distance be x cm, then 1:20000000 = 4:x .
1/20000000 = 4/x
⇒ x = 80000000 cm = 800 km
For a detailed discussion on the concept of direct proportion and developing a relationship between two quantities based on direct proportion, inverse proportion and other topics download BYJU’S – The Learning App from Google Play Store and watch interactive videos. Also, take free tests to practice for exams.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
It’s good
last minute exam help thank you
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This video shows how to solve inverse proportion questions. It goes through a couple of examples and ends with some practice questions. Example 1: A is inversely proportional to B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 8. Example 2: F is inversely proportional to the square of x. When A is 20, B is 3. Find the value of F when x is 5.
Direct Proportion Graph. If you construct a graph of a direct proportion, it always comes out to be a straight line passing through the origin (0, 0). The slope of this line is k. If k is negative, the line goes down from left to right. If k is positive, the line rises from left to right. Difference between Direct Proportion and Inverse Proportion
Direct Proportion. Direct proportion or direct variation is the relation between two quantities where the ratio of the two is equal to a constant value. It is represented by the proportional symbol, ∝. In fact, the same symbol is used to represent inversely proportional, the matter of the fact that the other quantity is inverted here.