- help_outline help

iRubric: Personal Project - Filipino (Tagalog) rubric
- Communication
- Facebook Group
- Facebook Page
- e-SLM vesion2

RPMS-PPST Resources Downloads
- Anecdotal Record, Learner’s Needs, Progress and Achievement Cardex
- Call Parent and Home Visit Forms
- e-IPCRF Official Copy
- Electronic Self-Assessment Tool (e-SAT)
- Individual Plan for Professional Development (IPPD)
- IPCRF-DEVELOPMENT PLAN
- Mid-year Review Form (MRF)
- National Orientation Materials for RPMS Multi-Year RPMS-PPST and Use of Electronic IPCRF for Teachers
- Performance Monitoring and Coaching Form
- Reflections, Journal Entry on Learner-Centered Teaching Philosophy
- RPMS Guidelines
- RPMS Portfolio with MOVs
- RPMS Tools and Forms
Most Downloaded
- Daily Time Record (eDTR)
- Electronic Class Record
- Enhanced BEEF
- Enrollment Form 2022-2023
- Learning Activity Sheets
- New Sick Leave Form 6
- Self-Learning Modules (SLM)
- Teachers Guide 2021-22
- Your 700+ PowerPoint Templates
Ready Made Rubric Assessment Tools for Performance Task
What is a rubric.

Holistic rubrics
Analytic rubrics, here are examples of ready made rubric assessment tools that you can use in assessing the performance task you give to your learners..
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Research Report
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Story Writing
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Cooking Presentation
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Letter Writing
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Building a Structure
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Group Presentation
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Problem Solving in Math
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Class Debate
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Math Graphing
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Creating a Painting
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Independent Reading
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Poem Recitation
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Poster Making
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Interview
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Music
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Reading Comprehension
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Folk Dance
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Essay Writing
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Role Playing
- Rubric Assessment Tool for Skit/Role Playing

No comments
Post a Comment
Social Counter
- facebook count=667 K Follow
Featured Post
Catch-up fridays reading materials free download.
Catch-up Fridays Reading Materials Free Download exclusive for members Are you looking for an enriching reading experience for learners of a...

Popular Posts

DOWNLOADABLE RESOURCES
- Budget of Work
- Curriculum Guide
- Detailed Lesson Plan
- enhanced enrollment form
- Enhanced TIP Course Books
- learning activity sheet
- Modules with answer key
- Quarterly Assessment
- Reading Materials
- Remedial Reading
- Rubric Assessment Tools
- school calendar 2021-2022
- school calendar 2022-2023
- Self-Learning Modules
- Summative Test
LATEST ISSUANCES
Deped updates, teacher resources.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

KRAYTIRYA SA PAGSULAT NG SANAYSAY Nilalaman (45%) Kaugnayan sa Tema (30%) Paggamit ng Salita (25%) Kabuuan (100

- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Rubrics for Performance Tasks, Essay, Problem Solving, Poster Making, etc.

12 comments:

Wala po bang Filipino JHS? Thank you
thank you this is a big help
Words couldn't contain the gratefulness for your kindness. God bless your prowess
Thanks much po
Thank you po
wala po ba mapeh music1
A big help for us..thank you po.
meron po bang hope 11 / 12
Thank You So much. A big help for me
thank you, very useful,
thank very much po..
Thank you so much! Very helpful.
Search This Blog
- Activity Sheets
- Automated IPCRF
- Automated Test Result
- Brigada Eskwela Forms and Tarpaulin
- Budget or Work
- Bulletin Board Displays
- Catch-Up Fridays Materials
- Certificates
- Class Orientation
- Classroom Basic Information
- Classroom Decoration
- Classroom Structuring
- COT Lesson Plans
- Daily Lesson Log
- DepEd Advisory
- DepEd E-Class Record
- DepEd Forms
- DepEd Modified E-Class Record
- DepEd Official Statement
- DepEd Order
- DepEd Press Release
- DepEd TV Lesson Episodes
- DepEd VIsion Mission Core Values
- Detailed Lesson Plans
- Diagnostic Test
- Educational Games
- English IMs
- Enrollment Forms
- Filipino IMs
- Free Webinars
- Free Webinars. Tutorials
- Grade 1 Activity Sheets
- Grade 1 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 1 DLL
- Grade 1 Periodical Tests
- Grade 1 Summative Tests
- Grade 10 Activity Sheets
- Grade 11 Activity Sheets
- Grade 12 Activity Sheets
- Grade 2 Activity Sheets
- Grade 2 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 2 DLL
- Grade 2 Periodical Tests
- Grade 2 Summative Tests
- Grade 3 Activity Sheets
- Grade 3 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 3 DLL
- Grade 3 Periodical Tests
- Grade 3 Summative Tests
- Grade 4 Activity Sheets
- Grade 4 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 4 DLL
- Grade 4 Periodical Tests
- Grade 4 Summative Tests
- Grade 5 Activity Sheets
- Grade 5 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 5 DLL
- Grade 5 Periodical Tests
- Grade 5 Summative Tests
- Grade 6 Activity Sheets
- Grade 6 CO Lesson Plans
- Grade 6 DLL
- Grade 6 Periodical Tests
- Grade 6 Summative Tests
- Grade 7 Activity Sheets
- Grade 8 Activity Sheets
- Grade 9 Activity Sheets
- Handwriting Worksheets
- Homeroom Guidance Modules
- In-Service Training for Teachers
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan
- Inspiring Stories
- Instructional Materials
- Item Analysis Automated Template
- LAC Session
- LDM Practicum Portfolio
- LDM2 Teacher's Portfolio
- Learner's Individual Record Card
- LEARNER'S PROFILE
- Learners Materials
- Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)
- Lesson Exemplars (MELC-Based)
- Mathematics IMs
- MELC-Based MODULES
- Mid-Year Review Form
- Monthly Celebration
- Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC)
- Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELCs)
- NDEP/GAD/DRRM Corners
- Nutritional Status Template
- Other Materials
- Performance Tasks
- Periodical Test (Quarter 1)
- Periodical Test (Quarter 2)
- Periodical Test (Quarter 3)
- Periodical Test (Quarter 4)
- Reading Articles
- Reading Materials
- Revised PDS (CS Form 212)
- RPMS Portfolio
- RPMS-PPST Materials
- School Effectiveness Toolkit
- School Form 9 (SF9)
- School Forms
- School Signage
- Science IM's
- Self-Learning Modules
- Self-Monitoring Tool
- STUDY NOTEBOOKS for LDM2
- Summative Tests
- Teacher Planner
- Teacher's Forms
- Teacher's Guide
- Teacher's Materials
- Thinking Log for Learners
- Weekly Home Learning Plan
- Weekly Learning Plan
- Weekly Tests
Popular Posts

Recent Posts
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Asignatura na Filipino
Monday, april 18, 2016, rubric sa pagtatalo/debate, 2 comments:.

Maraming salamat po
salamat po at nagamit ko ito bilang reperensya sa aking aralin.. kung inyo pong mamarapatin...salamat po,God Bless.
clear statement of findings in qualitative research
Criteria for good qualitative research: a comprehensive review.
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
73k Accesses
25 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik Aspers & Ugo Corte

Qualitative Research: Ethical Considerations
How to use and assess qualitative research methods
Loraine Busetto, Wolfgang Wick & Christoph Gumbinger
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
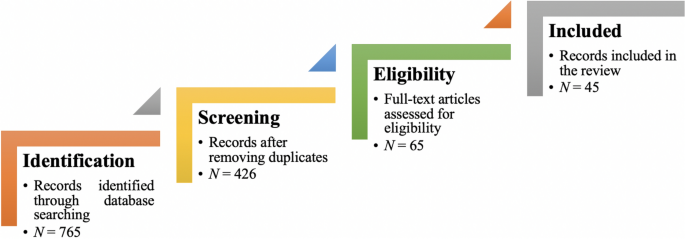
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 1
- How to appraise qualitative research
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Calvin Moorley 1 ,
- Xabi Cathala 2
- 1 Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- 2 Institute of Vocational Learning , School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Calvin Moorley, Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, UK; Moorleyc{at}lsbu.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2018-103044
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
In order to make a decision about implementing evidence into practice, nurses need to be able to critically appraise research. Nurses also have a professional responsibility to maintain up-to-date practice. 1 This paper provides a guide on how to critically appraise a qualitative research paper.
What is qualitative research?
- View inline
Useful terms
Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries or other documents. 3
Authenticity
Title, keywords, authors and abstract.
In a previous paper, we discussed how the title, keywords, authors’ positions and affiliations and abstract can influence the authenticity and readability of quantitative research papers, 4 the same applies to qualitative research. However, other areas such as the purpose of the study and the research question, theoretical and conceptual frameworks, sampling and methodology also need consideration when appraising a qualitative paper.
Purpose and question
The topic under investigation in the study should be guided by a clear research question or a statement of the problem or purpose. An example of a statement can be seen in table 2 . Unlike most quantitative studies, qualitative research does not seek to test a hypothesis. The research statement should be specific to the problem and should be reflected in the design. This will inform the reader of what will be studied and justify the purpose of the study. 5
Example of research question and problem statement
An appropriate literature review should have been conducted and summarised in the paper. It should be linked to the subject, using peer-reviewed primary research which is up to date. We suggest papers with a age limit of 5–8 years excluding original work. The literature review should give the reader a balanced view on what has been written on the subject. It is worth noting that for some qualitative approaches some literature reviews are conducted after the data collection to minimise bias, for example, in grounded theory studies. In phenomenological studies, the review sometimes occurs after the data analysis. If this is the case, the author(s) should make this clear.
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks
Most authors use the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks interchangeably. Usually, a theoretical framework is used when research is underpinned by one theory that aims to help predict, explain and understand the topic investigated. A theoretical framework is the blueprint that can hold or scaffold a study’s theory. Conceptual frameworks are based on concepts from various theories and findings which help to guide the research. 6 It is the researcher’s understanding of how different variables are connected in the study, for example, the literature review and research question. Theoretical and conceptual frameworks connect the researcher to existing knowledge and these are used in a study to help to explain and understand what is being investigated. A framework is the design or map for a study. When you are appraising a qualitative paper, you should be able to see how the framework helped with (1) providing a rationale and (2) the development of research questions or statements. 7 You should be able to identify how the framework, research question, purpose and literature review all complement each other.
There remains an ongoing debate in relation to what an appropriate sample size should be for a qualitative study. We hold the view that qualitative research does not seek to power and a sample size can be as small as one (eg, a single case study) or any number above one (a grounded theory study) providing that it is appropriate and answers the research problem. Shorten and Moorley 8 explain that three main types of sampling exist in qualitative research: (1) convenience (2) judgement or (3) theoretical. In the paper , the sample size should be stated and a rationale for how it was decided should be clear.
Methodology
Qualitative research encompasses a variety of methods and designs. Based on the chosen method or design, the findings may be reported in a variety of different formats. Table 3 provides the main qualitative approaches used in nursing with a short description.
Different qualitative approaches
The authors should make it clear why they are using a qualitative methodology and the chosen theoretical approach or framework. The paper should provide details of participant inclusion and exclusion criteria as well as recruitment sites where the sample was drawn from, for example, urban, rural, hospital inpatient or community. Methods of data collection should be identified and be appropriate for the research statement/question.
Data collection
Overall there should be a clear trail of data collection. The paper should explain when and how the study was advertised, participants were recruited and consented. it should also state when and where the data collection took place. Data collection methods include interviews, this can be structured or unstructured and in depth one to one or group. 9 Group interviews are often referred to as focus group interviews these are often voice recorded and transcribed verbatim. It should be clear if these were conducted face to face, telephone or any other type of media used. Table 3 includes some data collection methods. Other collection methods not included in table 3 examples are observation, diaries, video recording, photographs, documents or objects (artefacts). The schedule of questions for interview or the protocol for non-interview data collection should be provided, available or discussed in the paper. Some authors may use the term ‘recruitment ended once data saturation was reached’. This simply mean that the researchers were not gaining any new information at subsequent interviews, so they stopped data collection.
The data collection section should include details of the ethical approval gained to carry out the study. For example, the strategies used to gain participants’ consent to take part in the study. The authors should make clear if any ethical issues arose and how these were resolved or managed.
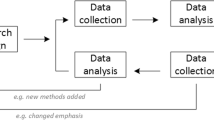
The approach to data analysis (see ref 10 ) needs to be clearly articulated, for example, was there more than one person responsible for analysing the data? How were any discrepancies in findings resolved? An audit trail of how the data were analysed including its management should be documented. If member checking was used this should also be reported. This level of transparency contributes to the trustworthiness and credibility of qualitative research. Some researchers provide a diagram of how they approached data analysis to demonstrate the rigour applied ( figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Example of data analysis diagram.
Validity and rigour
The study’s validity is reliant on the statement of the question/problem, theoretical/conceptual framework, design, method, sample and data analysis. When critiquing qualitative research, these elements will help you to determine the study’s reliability. Noble and Smith 11 explain that validity is the integrity of data methods applied and that findings should accurately reflect the data. Rigour should acknowledge the researcher’s role and involvement as well as any biases. Essentially it should focus on truth value, consistency and neutrality and applicability. 11 The authors should discuss if they used triangulation (see table 2 ) to develop the best possible understanding of the phenomena.
Themes and interpretations and implications for practice
In qualitative research no hypothesis is tested, therefore, there is no specific result. Instead, qualitative findings are often reported in themes based on the data analysed. The findings should be clearly linked to, and reflect, the data. This contributes to the soundness of the research. 11 The researchers should make it clear how they arrived at the interpretations of the findings. The theoretical or conceptual framework used should be discussed aiding the rigour of the study. The implications of the findings need to be made clear and where appropriate their applicability or transferability should be identified. 12
Discussions, recommendations and conclusions
The discussion should relate to the research findings as the authors seek to make connections with the literature reviewed earlier in the paper to contextualise their work. A strong discussion will connect the research aims and objectives to the findings and will be supported with literature if possible. A paper that seeks to influence nursing practice will have a recommendations section for clinical practice and research. A good conclusion will focus on the findings and discussion of the phenomena investigated.
Qualitative research has much to offer nursing and healthcare, in terms of understanding patients’ experience of illness, treatment and recovery, it can also help to understand better areas of healthcare practice. However, it must be done with rigour and this paper provides some guidance for appraising such research. To help you critique a qualitative research paper some guidance is provided in table 4 .
Some guidance for critiquing qualitative research
- ↵ Nursing and Midwifery Council . The code: Standard of conduct, performance and ethics for nurses and midwives . 2015 https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/nmc-publications/nmc-code.pdf ( accessed 21 Aug 18 ).
- Barrett D ,
- Cathala X ,
- Shorten A ,
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Qualitative Data Analysis
23 Presenting the Results of Qualitative Analysis
Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur
Qualitative research is not finished just because you have determined the main findings or conclusions of your study. Indeed, disseminating the results is an essential part of the research process. By sharing your results with others, whether in written form as scholarly paper or an applied report or in some alternative format like an oral presentation, an infographic, or a video, you ensure that your findings become part of the ongoing conversation of scholarship in your field, forming part of the foundation for future researchers. This chapter provides an introduction to writing about qualitative research findings. It will outline how writing continues to contribute to the analysis process, what concerns researchers should keep in mind as they draft their presentations of findings, and how best to organize qualitative research writing
As you move through the research process, it is essential to keep yourself organized. Organizing your data, memos, and notes aids both the analytical and the writing processes. Whether you use electronic or physical, real-world filing and organizational systems, these systems help make sense of the mountains of data you have and assure you focus your attention on the themes and ideas you have determined are important (Warren and Karner 2015). Be sure that you have kept detailed notes on all of the decisions you have made and procedures you have followed in carrying out research design, data collection, and analysis, as these will guide your ultimate write-up.
First and foremost, researchers should keep in mind that writing is in fact a form of thinking. Writing is an excellent way to discover ideas and arguments and to further develop an analysis. As you write, more ideas will occur to you, things that were previously confusing will start to make sense, and arguments will take a clear shape rather than being amorphous and poorly-organized. However, writing-as-thinking cannot be the final version that you share with others. Good-quality writing does not display the workings of your thought process. It is reorganized and revised (more on that later) to present the data and arguments important in a particular piece. And revision is totally normal! No one expects the first draft of a piece of writing to be ready for prime time. So write rough drafts and memos and notes to yourself and use them to think, and then revise them until the piece is the way you want it to be for sharing.
Bergin (2018) lays out a set of key concerns for appropriate writing about research. First, present your results accurately, without exaggerating or misrepresenting. It is very easy to overstate your findings by accident if you are enthusiastic about what you have found, so it is important to take care and use appropriate cautions about the limitations of the research. You also need to work to ensure that you communicate your findings in a way people can understand, using clear and appropriate language that is adjusted to the level of those you are communicating with. And you must be clear and transparent about the methodological strategies employed in the research. Remember, the goal is, as much as possible, to describe your research in a way that would permit others to replicate the study. There are a variety of other concerns and decision points that qualitative researchers must keep in mind, including the extent to which to include quantification in their presentation of results, ethics, considerations of audience and voice, and how to bring the richness of qualitative data to life.
Quantification, as you have learned, refers to the process of turning data into numbers. It can indeed be very useful to count and tabulate quantitative data drawn from qualitative research. For instance, if you were doing a study of dual-earner households and wanted to know how many had an equal division of household labor and how many did not, you might want to count those numbers up and include them as part of the final write-up. However, researchers need to take care when they are writing about quantified qualitative data. Qualitative data is not as generalizable as quantitative data, so quantification can be very misleading. Thus, qualitative researchers should strive to use raw numbers instead of the percentages that are more appropriate for quantitative research. Writing, for instance, “15 of the 20 people I interviewed prefer pancakes to waffles” is a simple description of the data; writing “75% of people prefer pancakes” suggests a generalizable claim that is not likely supported by the data. Note that mixing numbers with qualitative data is really a type of mixed-methods approach. Mixed-methods approaches are good, but sometimes they seduce researchers into focusing on the persuasive power of numbers and tables rather than capitalizing on the inherent richness of their qualitative data.
A variety of issues of scholarly ethics and research integrity are raised by the writing process. Some of these are unique to qualitative research, while others are more universal concerns for all academic and professional writing. For example, it is essential to avoid plagiarism and misuse of sources. All quotations that appear in a text must be properly cited, whether with in-text and bibliographic citations to the source or with an attribution to the research participant (or the participant’s pseudonym or description in order to protect confidentiality) who said those words. Where writers will paraphrase a text or a participant’s words, they need to make sure that the paraphrase they develop accurately reflects the meaning of the original words. Thus, some scholars suggest that participants should have the opportunity to read (or to have read to them, if they cannot read the text themselves) all sections of the text in which they, their words, or their ideas are presented to ensure accuracy and enable participants to maintain control over their lives.
Audience and Voice
When writing, researchers must consider their audience(s) and the effects they want their writing to have on these audiences. The designated audience will dictate the voice used in the writing, or the individual style and personality of a piece of text. Keep in mind that the potential audience for qualitative research is often much more diverse than that for quantitative research because of the accessibility of the data and the extent to which the writing can be accessible and interesting. Yet individual pieces of writing are typically pitched to a more specific subset of the audience.
Let us consider one potential research study, an ethnography involving participant-observation of the same children both when they are at daycare facility and when they are at home with their families to try to understand how daycare might impact behavior and social development. The findings of this study might be of interest to a wide variety of potential audiences: academic peers, whether at your own academic institution, in your broader discipline, or multidisciplinary; people responsible for creating laws and policies; practitioners who run or teach at day care centers; and the general public, including both people who are interested in child development more generally and those who are themselves parents making decisions about child care for their own children. And the way you write for each of these audiences will be somewhat different. Take a moment and think through what some of these differences might look like.
If you are writing to academic audiences, using specialized academic language and working within the typical constraints of scholarly genres, as will be discussed below, can be an important part of convincing others that your work is legitimate and should be taken seriously. Your writing will be formal. Even if you are writing for students and faculty you already know—your classmates, for instance—you are often asked to imitate the style of academic writing that is used in publications, as this is part of learning to become part of the scholarly conversation. When speaking to academic audiences outside your discipline, you may need to be more careful about jargon and specialized language, as disciplines do not always share the same key terms. For instance, in sociology, scholars use the term diffusion to refer to the way new ideas or practices spread from organization to organization. In the field of international relations, scholars often used the term cascade to refer to the way ideas or practices spread from nation to nation. These terms are describing what is fundamentally the same concept, but they are different terms—and a scholar from one field might have no idea what a scholar from a different field is talking about! Therefore, while the formality and academic structure of the text would stay the same, a writer with a multidisciplinary audience might need to pay more attention to defining their terms in the body of the text.
It is not only other academic scholars who expect to see formal writing. Policymakers tend to expect formality when ideas are presented to them, as well. However, the content and style of the writing will be different. Much less academic jargon should be used, and the most important findings and policy implications should be emphasized right from the start rather than initially focusing on prior literature and theoretical models as you might for an academic audience. Long discussions of research methods should also be minimized. Similarly, when you write for practitioners, the findings and implications for practice should be highlighted. The reading level of the text will vary depending on the typical background of the practitioners to whom you are writing—you can make very different assumptions about the general knowledge and reading abilities of a group of hospital medical directors with MDs than you can about a group of case workers who have a post-high-school certificate. Consider the primary language of your audience as well. The fact that someone can get by in spoken English does not mean they have the vocabulary or English reading skills to digest a complex report. But the fact that someone’s vocabulary is limited says little about their intellectual abilities, so try your best to convey the important complexity of the ideas and findings from your research without dumbing them down—even if you must limit your vocabulary usage.
When writing for the general public, you will want to move even further towards emphasizing key findings and policy implications, but you also want to draw on the most interesting aspects of your data. General readers will read sociological texts that are rich with ethnographic or other kinds of detail—it is almost like reality television on a page! And this is a contrast to busy policymakers and practitioners, who probably want to learn the main findings as quickly as possible so they can go about their busy lives. But also keep in mind that there is a wide variation in reading levels. Journalists at publications pegged to the general public are often advised to write at about a tenth-grade reading level, which would leave most of the specialized terminology we develop in our research fields out of reach. If you want to be accessible to even more people, your vocabulary must be even more limited. The excellent exercise of trying to write using the 1,000 most common English words, available at the Up-Goer Five website ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ) does a good job of illustrating this challenge (Sanderson n.d.).
Another element of voice is whether to write in the first person. While many students are instructed to avoid the use of the first person in academic writing, this advice needs to be taken with a grain of salt. There are indeed many contexts in which the first person is best avoided, at least as long as writers can find ways to build strong, comprehensible sentences without its use, including most quantitative research writing. However, if the alternative to using the first person is crafting a sentence like “it is proposed that the researcher will conduct interviews,” it is preferable to write “I propose to conduct interviews.” In qualitative research, in fact, the use of the first person is far more common. This is because the researcher is central to the research project. Qualitative researchers can themselves be understood as research instruments, and thus eliminating the use of the first person in writing is in a sense eliminating information about the conduct of the researchers themselves.
But the question really extends beyond the issue of first-person or third-person. Qualitative researchers have choices about how and whether to foreground themselves in their writing, not just in terms of using the first person, but also in terms of whether to emphasize their own subjectivity and reflexivity, their impressions and ideas, and their role in the setting. In contrast, conventional quantitative research in the positivist tradition really tries to eliminate the author from the study—which indeed is exactly why typical quantitative research avoids the use of the first person. Keep in mind that emphasizing researchers’ roles and reflexivity and using the first person does not mean crafting articles that provide overwhelming detail about the author’s thoughts and practices. Readers do not need to hear, and should not be told, which database you used to search for journal articles, how many hours you spent transcribing, or whether the research process was stressful—save these things for the memos you write to yourself. Rather, readers need to hear how you interacted with research participants, how your standpoint may have shaped the findings, and what analytical procedures you carried out.
Making Data Come Alive
One of the most important parts of writing about qualitative research is presenting the data in a way that makes its richness and value accessible to readers. As the discussion of analysis in the prior chapter suggests, there are a variety of ways to do this. Researchers may select key quotes or images to illustrate points, write up specific case studies that exemplify their argument, or develop vignettes (little stories) that illustrate ideas and themes, all drawing directly on the research data. Researchers can also write more lengthy summaries, narratives, and thick descriptions.
Nearly all qualitative work includes quotes from research participants or documents to some extent, though ethnographic work may focus more on thick description than on relaying participants’ own words. When quotes are presented, they must be explained and interpreted—they cannot stand on their own. This is one of the ways in which qualitative research can be distinguished from journalism. Journalism presents what happened, but social science needs to present the “why,” and the why is best explained by the researcher.
So how do authors go about integrating quotes into their written work? Julie Posselt (2017), a sociologist who studies graduate education, provides a set of instructions. First of all, authors need to remain focused on the core questions of their research, and avoid getting distracted by quotes that are interesting or attention-grabbing but not so relevant to the research question. Selecting the right quotes, those that illustrate the ideas and arguments of the paper, is an important part of the writing process. Second, not all quotes should be the same length (just like not all sentences or paragraphs in a paper should be the same length). Include some quotes that are just phrases, others that are a sentence or so, and others that are longer. We call longer quotes, generally those more than about three lines long, block quotes , and they are typically indented on both sides to set them off from the surrounding text. For all quotes, be sure to summarize what the quote should be telling or showing the reader, connect this quote to other quotes that are similar or different, and provide transitions in the discussion to move from quote to quote and from topic to topic. Especially for longer quotes, it is helpful to do some of this writing before the quote to preview what is coming and other writing after the quote to make clear what readers should have come to understand. Remember, it is always the author’s job to interpret the data. Presenting excerpts of the data, like quotes, in a form the reader can access does not minimize the importance of this job. Be sure that you are explaining the meaning of the data you present.
A few more notes about writing with quotes: avoid patchwriting, whether in your literature review or the section of your paper in which quotes from respondents are presented. Patchwriting is a writing practice wherein the author lightly paraphrases original texts but stays so close to those texts that there is little the author has added. Sometimes, this even takes the form of presenting a series of quotes, properly documented, with nothing much in the way of text generated by the author. A patchwriting approach does not build the scholarly conversation forward, as it does not represent any kind of new contribution on the part of the author. It is of course fine to paraphrase quotes, as long as the meaning is not changed. But if you use direct quotes, do not edit the text of the quotes unless how you edit them does not change the meaning and you have made clear through the use of ellipses (…) and brackets ([])what kinds of edits have been made. For example, consider this exchange from Matthew Desmond’s (2012:1317) research on evictions:
The thing was, I wasn’t never gonna let Crystal come and stay with me from the get go. I just told her that to throw her off. And she wasn’t fittin’ to come stay with me with no money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
A paraphrase of this exchange might read “She said that she was going to let Crystal stay with her if Crystal did not have any money.” Paraphrases like that are fine. What is not fine is rewording the statement but treating it like a quote, for instance writing:
The thing was, I was not going to let Crystal come and stay with me from beginning. I just told her that to throw her off. And it was not proper for her to come stay with me without any money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
But as you can see, the change in language and style removes some of the distinct meaning of the original quote. Instead, writers should leave as much of the original language as possible. If some text in the middle of the quote needs to be removed, as in this example, ellipses are used to show that this has occurred. And if a word needs to be added to clarify, it is placed in square brackets to show that it was not part of the original quote.
Data can also be presented through the use of data displays like tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, and infographics created for publication or presentation, as well as through the use of visual material collected during the research process. Note that if visuals are used, the author must have the legal right to use them. Photographs or diagrams created by the author themselves—or by research participants who have signed consent forms for their work to be used, are fine. But photographs, and sometimes even excerpts from archival documents, may be owned by others from whom researchers must get permission in order to use them.
A large percentage of qualitative research does not include any data displays or visualizations. Therefore, researchers should carefully consider whether the use of data displays will help the reader understand the data. One of the most common types of data displays used by qualitative researchers are simple tables. These might include tables summarizing key data about cases included in the study; tables laying out the characteristics of different taxonomic elements or types developed as part of the analysis; tables counting the incidence of various elements; and 2×2 tables (two columns and two rows) illuminating a theory. Basic network or process diagrams are also commonly included. If data displays are used, it is essential that researchers include context and analysis alongside data displays rather than letting them stand by themselves, and it is preferable to continue to present excerpts and examples from the data rather than just relying on summaries in the tables.
If you will be using graphs, infographics, or other data visualizations, it is important that you attend to making them useful and accurate (Bergin 2018). Think about the viewer or user as your audience and ensure the data visualizations will be comprehensible. You may need to include more detail or labels than you might think. Ensure that data visualizations are laid out and labeled clearly and that you make visual choices that enhance viewers’ ability to understand the points you intend to communicate using the visual in question. Finally, given the ease with which it is possible to design visuals that are deceptive or misleading, it is essential to make ethical and responsible choices in the construction of visualization so that viewers will interpret them in accurate ways.
The Genre of Research Writing
As discussed above, the style and format in which results are presented depends on the audience they are intended for. These differences in styles and format are part of the genre of writing. Genre is a term referring to the rules of a specific form of creative or productive work. Thus, the academic journal article—and student papers based on this form—is one genre. A report or policy paper is another. The discussion below will focus on the academic journal article, but note that reports and policy papers follow somewhat different formats. They might begin with an executive summary of one or a few pages, include minimal background, focus on key findings, and conclude with policy implications, shifting methods and details about the data to an appendix. But both academic journal articles and policy papers share some things in common, for instance the necessity for clear writing, a well-organized structure, and the use of headings.
So what factors make up the genre of the academic journal article in sociology? While there is some flexibility, particularly for ethnographic work, academic journal articles tend to follow a fairly standard format. They begin with a “title page” that includes the article title (often witty and involving scholarly inside jokes, but more importantly clearly describing the content of the article); the authors’ names and institutional affiliations, an abstract , and sometimes keywords designed to help others find the article in databases. An abstract is a short summary of the article that appears both at the very beginning of the article and in search databases. Abstracts are designed to aid readers by giving them the opportunity to learn enough about an article that they can determine whether it is worth their time to read the complete text. They are written about the article, and thus not in the first person, and clearly summarize the research question, methodological approach, main findings, and often the implications of the research.
After the abstract comes an “introduction” of a page or two that details the research question, why it matters, and what approach the paper will take. This is followed by a literature review of about a quarter to a third the length of the entire paper. The literature review is often divided, with headings, into topical subsections, and is designed to provide a clear, thorough overview of the prior research literature on which a paper has built—including prior literature the new paper contradicts. At the end of the literature review it should be made clear what researchers know about the research topic and question, what they do not know, and what this new paper aims to do to address what is not known.
The next major section of the paper is the section that describes research design, data collection, and data analysis, often referred to as “research methods” or “methodology.” This section is an essential part of any written or oral presentation of your research. Here, you tell your readers or listeners “how you collected and interpreted your data” (Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault 2016:215). Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault suggest that the discussion of your research methods include the following:
- The particular approach to data collection used in the study;
- Any theoretical perspective(s) that shaped your data collection and analytical approach;
- When the study occurred, over how long, and where (concealing identifiable details as needed);
- A description of the setting and participants, including sampling and selection criteria (if an interview-based study, the number of participants should be clearly stated);
- The researcher’s perspective in carrying out the study, including relevant elements of their identity and standpoint, as well as their role (if any) in research settings; and
- The approach to analyzing the data.
After the methods section comes a section, variously titled but often called “data,” that takes readers through the analysis. This section is where the thick description narrative; the quotes, broken up by theme or topic, with their interpretation; the discussions of case studies; most data displays (other than perhaps those outlining a theoretical model or summarizing descriptive data about cases); and other similar material appears. The idea of the data section is to give readers the ability to see the data for themselves and to understand how this data supports the ultimate conclusions. Note that all tables and figures included in formal publications should be titled and numbered.
At the end of the paper come one or two summary sections, often called “discussion” and/or “conclusion.” If there is a separate discussion section, it will focus on exploring the overall themes and findings of the paper. The conclusion clearly and succinctly summarizes the findings and conclusions of the paper, the limitations of the research and analysis, any suggestions for future research building on the paper or addressing these limitations, and implications, be they for scholarship and theory or policy and practice.
After the end of the textual material in the paper comes the bibliography, typically called “works cited” or “references.” The references should appear in a consistent citation style—in sociology, we often use the American Sociological Association format (American Sociological Association 2019), but other formats may be used depending on where the piece will eventually be published. Care should be taken to ensure that in-text citations also reflect the chosen citation style. In some papers, there may be an appendix containing supplemental information such as a list of interview questions or an additional data visualization.
Note that when researchers give presentations to scholarly audiences, the presentations typically follow a format similar to that of scholarly papers, though given time limitations they are compressed. Abstracts and works cited are often not part of the presentation, though in-text citations are still used. The literature review presented will be shortened to only focus on the most important aspects of the prior literature, and only key examples from the discussion of data will be included. For long or complex papers, sometimes only one of several findings is the focus of the presentation. Of course, presentations for other audiences may be constructed differently, with greater attention to interesting elements of the data and findings as well as implications and less to the literature review and methods.
Concluding Your Work
After you have written a complete draft of the paper, be sure you take the time to revise and edit your work. There are several important strategies for revision. First, put your work away for a little while. Even waiting a day to revise is better than nothing, but it is best, if possible, to take much more time away from the text. This helps you forget what your writing looks like and makes it easier to find errors, mistakes, and omissions. Second, show your work to others. Ask them to read your work and critique it, pointing out places where the argument is weak, where you may have overlooked alternative explanations, where the writing could be improved, and what else you need to work on. Finally, read your work out loud to yourself (or, if you really need an audience, try reading to some stuffed animals). Reading out loud helps you catch wrong words, tricky sentences, and many other issues. But as important as revision is, try to avoid perfectionism in writing (Warren and Karner 2015). Writing can always be improved, no matter how much time you spend on it. Those improvements, however, have diminishing returns, and at some point the writing process needs to conclude so the writing can be shared with the world.
Of course, the main goal of writing up the results of a research project is to share with others. Thus, researchers should be considering how they intend to disseminate their results. What conferences might be appropriate? Where can the paper be submitted? Note that if you are an undergraduate student, there are a wide variety of journals that accept and publish research conducted by undergraduates. Some publish across disciplines, while others are specific to disciplines. Other work, such as reports, may be best disseminated by publication online on relevant organizational websites.
After a project is completed, be sure to take some time to organize your research materials and archive them for longer-term storage. Some Institutional Review Board (IRB) protocols require that original data, such as interview recordings, transcripts, and field notes, be preserved for a specific number of years in a protected (locked for paper or password-protected for digital) form and then destroyed, so be sure that your plans adhere to the IRB requirements. Be sure you keep any materials that might be relevant for future related research or for answering questions people may ask later about your project.
And then what? Well, then it is time to move on to your next research project. Research is a long-term endeavor, not a one-time-only activity. We build our skills and our expertise as we continue to pursue research. So keep at it.
- Find a short article that uses qualitative methods. The sociological magazine Contexts is a good place to find such pieces. Write an abstract of the article.
- Choose a sociological journal article on a topic you are interested in that uses some form of qualitative methods and is at least 20 pages long. Rewrite the article as a five-page research summary accessible to non-scholarly audiences.
- Choose a concept or idea you have learned in this course and write an explanation of it using the Up-Goer Five Text Editor ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ), a website that restricts your writing to the 1,000 most common English words. What was this experience like? What did it teach you about communicating with people who have a more limited English-language vocabulary—and what did it teach you about the utility of having access to complex academic language?
- Select five or more sociological journal articles that all use the same basic type of qualitative methods (interviewing, ethnography, documents, or visual sociology). Using what you have learned about coding, code the methods sections of each article, and use your coding to figure out what is common in how such articles discuss their research design, data collection, and analysis methods.
- Return to an exercise you completed earlier in this course and revise your work. What did you change? How did revising impact the final product?
- Find a quote from the transcript of an interview, a social media post, or elsewhere that has not yet been interpreted or explained. Write a paragraph that includes the quote along with an explanation of its sociological meaning or significance.
The style or personality of a piece of writing, including such elements as tone, word choice, syntax, and rhythm.
A quotation, usually one of some length, which is set off from the main text by being indented on both sides rather than being placed in quotation marks.
A classification of written or artistic work based on form, content, and style.
A short summary of a text written from the perspective of a reader rather than from the perspective of an author.
Social Data Analysis Copyright © 2021 by Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 15: interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Holger J Schünemann, Gunn E Vist, Julian PT Higgins, Nancy Santesso, Jonathan J Deeks, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group
Key Points:
- This chapter provides guidance on interpreting the results of synthesis in order to communicate the conclusions of the review effectively.
- Methods are presented for computing, presenting and interpreting relative and absolute effects for dichotomous outcome data, including the number needed to treat (NNT).
- For continuous outcome measures, review authors can present summary results for studies using natural units of measurement or as minimal important differences when all studies use the same scale. When studies measure the same construct but with different scales, review authors will need to find a way to interpret the standardized mean difference, or to use an alternative effect measure for the meta-analysis such as the ratio of means.
- Review authors should not describe results as ‘statistically significant’, ‘not statistically significant’ or ‘non-significant’ or unduly rely on thresholds for P values, but report the confidence interval together with the exact P value.
- Review authors should not make recommendations about healthcare decisions, but they can – after describing the certainty of evidence and the balance of benefits and harms – highlight different actions that might be consistent with particular patterns of values and preferences and other factors that determine a decision such as cost.
Cite this chapter as: Schünemann HJ, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Santesso N, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Chapter 15: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
15.1 Introduction
The purpose of Cochrane Reviews is to facilitate healthcare decisions by patients and the general public, clinicians, guideline developers, administrators and policy makers. They also inform future research. A clear statement of findings, a considered discussion and a clear presentation of the authors’ conclusions are, therefore, important parts of the review. In particular, the following issues can help people make better informed decisions and increase the usability of Cochrane Reviews:
- information on all important outcomes, including adverse outcomes;
- the certainty of the evidence for each of these outcomes, as it applies to specific populations and specific interventions; and
- clarification of the manner in which particular values and preferences may bear on the desirable and undesirable consequences of the intervention.
A ‘Summary of findings’ table, described in Chapter 14 , Section 14.1 , provides key pieces of information about health benefits and harms in a quick and accessible format. It is highly desirable that review authors include a ‘Summary of findings’ table in Cochrane Reviews alongside a sufficient description of the studies and meta-analyses to support its contents. This description includes the rating of the certainty of evidence, also called the quality of the evidence or confidence in the estimates of the effects, which is expected in all Cochrane Reviews.
‘Summary of findings’ tables are usually supported by full evidence profiles which include the detailed ratings of the evidence (Guyatt et al 2011a, Guyatt et al 2013a, Guyatt et al 2013b, Santesso et al 2016). The Discussion section of the text of the review provides space to reflect and consider the implications of these aspects of the review’s findings. Cochrane Reviews include five standard subheadings to ensure the Discussion section places the review in an appropriate context: ‘Summary of main results (benefits and harms)’; ‘Potential biases in the review process’; ‘Overall completeness and applicability of evidence’; ‘Certainty of the evidence’; and ‘Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews’. Following the Discussion, the Authors’ conclusions section is divided into two standard subsections: ‘Implications for practice’ and ‘Implications for research’. The assessment of the certainty of evidence facilitates a structured description of the implications for practice and research.
Because Cochrane Reviews have an international audience, the Discussion and Authors’ conclusions should, so far as possible, assume a broad international perspective and provide guidance for how the results could be applied in different settings, rather than being restricted to specific national or local circumstances. Cultural differences and economic differences may both play an important role in determining the best course of action based on the results of a Cochrane Review. Furthermore, individuals within societies have widely varying values and preferences regarding health states, and use of societal resources to achieve particular health states. For all these reasons, and because information that goes beyond that included in a Cochrane Review is required to make fully informed decisions, different people will often make different decisions based on the same evidence presented in a review.
Thus, review authors should avoid specific recommendations that inevitably depend on assumptions about available resources, values and preferences, and other factors such as equity considerations, feasibility and acceptability of an intervention. The purpose of the review should be to present information and aid interpretation rather than to offer recommendations. The discussion and conclusions should help people understand the implications of the evidence in relation to practical decisions and apply the results to their specific situation. Review authors can aid this understanding of the implications by laying out different scenarios that describe certain value structures.
In this chapter, we address first one of the key aspects of interpreting findings that is also fundamental in completing a ‘Summary of findings’ table: the certainty of evidence related to each of the outcomes. We then provide a more detailed consideration of issues around applicability and around interpretation of numerical results, and provide suggestions for presenting authors’ conclusions.
15.2 Issues of indirectness and applicability
15.2.1 the role of the review author.
“A leap of faith is always required when applying any study findings to the population at large” or to a specific person. “In making that jump, one must always strike a balance between making justifiable broad generalizations and being too conservative in one’s conclusions” (Friedman et al 1985). In addition to issues about risk of bias and other domains determining the certainty of evidence, this leap of faith is related to how well the identified body of evidence matches the posed PICO ( Population, Intervention, Comparator(s) and Outcome ) question. As to the population, no individual can be entirely matched to the population included in research studies. At the time of decision, there will always be differences between the study population and the person or population to whom the evidence is applied; sometimes these differences are slight, sometimes large.
The terms applicability, generalizability, external validity and transferability are related, sometimes used interchangeably and have in common that they lack a clear and consistent definition in the classic epidemiological literature (Schünemann et al 2013). However, all of the terms describe one overarching theme: whether or not available research evidence can be directly used to answer the health and healthcare question at hand, ideally supported by a judgement about the degree of confidence in this use (Schünemann et al 2013). GRADE’s certainty domains include a judgement about ‘indirectness’ to describe all of these aspects including the concept of direct versus indirect comparisons of different interventions (Atkins et al 2004, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011b).
To address adequately the extent to which a review is relevant for the purpose to which it is being put, there are certain things the review author must do, and certain things the user of the review must do to assess the degree of indirectness. Cochrane and the GRADE Working Group suggest using a very structured framework to address indirectness. We discuss here and in Chapter 14 what the review author can do to help the user. Cochrane Review authors must be extremely clear on the population, intervention and outcomes that they intend to address. Chapter 14, Section 14.1.2 , also emphasizes a crucial step: the specification of all patient-important outcomes relevant to the intervention strategies under comparison.
In considering whether the effect of an intervention applies equally to all participants, and whether different variations on the intervention have similar effects, review authors need to make a priori hypotheses about possible effect modifiers, and then examine those hypotheses (see Chapter 10, Section 10.10 and Section 10.11 ). If they find apparent subgroup effects, they must ultimately decide whether or not these effects are credible (Sun et al 2012). Differences between subgroups, particularly those that correspond to differences between studies, should be interpreted cautiously. Some chance variation between subgroups is inevitable so, unless there is good reason to believe that there is an interaction, review authors should not assume that the subgroup effect exists. If, despite due caution, review authors judge subgroup effects in terms of relative effect estimates as credible (i.e. the effects differ credibly), they should conduct separate meta-analyses for the relevant subgroups, and produce separate ‘Summary of findings’ tables for those subgroups.
The user of the review will be challenged with ‘individualization’ of the findings, whether they seek to apply the findings to an individual patient or a policy decision in a specific context. For example, even if relative effects are similar across subgroups, absolute effects will differ according to baseline risk. Review authors can help provide this information by identifying identifiable groups of people with varying baseline risks in the ‘Summary of findings’ tables, as discussed in Chapter 14, Section 14.1.3 . Users can then identify their specific case or population as belonging to a particular risk group, if relevant, and assess their likely magnitude of benefit or harm accordingly. A description of the identifying prognostic or baseline risk factors in a brief scenario (e.g. age or gender) will help users of a review further.
Another decision users must make is whether their individual case or population of interest is so different from those included in the studies that they cannot use the results of the systematic review and meta-analysis at all. Rather than rigidly applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria of studies, it is better to ask whether or not there are compelling reasons why the evidence should not be applied to a particular patient. Review authors can sometimes help decision makers by identifying important variation where divergence might limit the applicability of results (Rothwell 2005, Schünemann et al 2006, Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann et al 2013), including biologic and cultural variation, and variation in adherence to an intervention.
In addressing these issues, review authors cannot be aware of, or address, the myriad of differences in circumstances around the world. They can, however, address differences of known importance to many people and, importantly, they should avoid assuming that other people’s circumstances are the same as their own in discussing the results and drawing conclusions.
15.2.2 Biological variation
Issues of biological variation that may affect the applicability of a result to a reader or population include divergence in pathophysiology (e.g. biological differences between women and men that may affect responsiveness to an intervention) and divergence in a causative agent (e.g. for infectious diseases such as malaria, which may be caused by several different parasites). The discussion of the results in the review should make clear whether the included studies addressed all or only some of these groups, and whether any important subgroup effects were found.
15.2.3 Variation in context
Some interventions, particularly non-pharmacological interventions, may work in some contexts but not in others; the situation has been described as program by context interaction (Hawe et al 2004). Contextual factors might pertain to the host organization in which an intervention is offered, such as the expertise, experience and morale of the staff expected to carry out the intervention, the competing priorities for the clinician’s or staff’s attention, the local resources such as service and facilities made available to the program and the status or importance given to the program by the host organization. Broader context issues might include aspects of the system within which the host organization operates, such as the fee or payment structure for healthcare providers and the local insurance system. Some interventions, in particular complex interventions (see Chapter 17 ), can be only partially implemented in some contexts, and this requires judgements about indirectness of the intervention and its components for readers in that context (Schünemann 2013).
Contextual factors may also pertain to the characteristics of the target group or population, such as cultural and linguistic diversity, socio-economic position, rural/urban setting. These factors may mean that a particular style of care or relationship evolves between service providers and consumers that may or may not match the values and technology of the program.
For many years these aspects have been acknowledged when decision makers have argued that results of evidence reviews from other countries do not apply in their own country or setting. Whilst some programmes/interventions have been successfully transferred from one context to another, others have not (Resnicow et al 1993, Lumley et al 2004, Coleman et al 2015). Review authors should be cautious when making generalizations from one context to another. They should report on the presence (or otherwise) of context-related information in intervention studies, where this information is available.
15.2.4 Variation in adherence
Variation in the adherence of the recipients and providers of care can limit the certainty in the applicability of results. Predictable differences in adherence can be due to divergence in how recipients of care perceive the intervention (e.g. the importance of side effects), economic conditions or attitudes that make some forms of care inaccessible in some settings, such as in low-income countries (Dans et al 2007). It should not be assumed that high levels of adherence in closely monitored randomized trials will translate into similar levels of adherence in normal practice.
15.2.5 Variation in values and preferences
Decisions about healthcare management strategies and options involve trading off health benefits and harms. The right choice may differ for people with different values and preferences (i.e. the importance people place on the outcomes and interventions), and it is important that decision makers ensure that decisions are consistent with a patient or population’s values and preferences. The importance placed on outcomes, together with other factors, will influence whether the recipients of care will or will not accept an option that is offered (Alonso-Coello et al 2016) and, thus, can be one factor influencing adherence. In Section 15.6 , we describe how the review author can help this process and the limits of supporting decision making based on intervention reviews.
15.3 Interpreting results of statistical analyses
15.3.1 confidence intervals.
Results for both individual studies and meta-analyses are reported with a point estimate together with an associated confidence interval. For example, ‘The odds ratio was 0.75 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.70 to 0.80’. The point estimate (0.75) is the best estimate of the magnitude and direction of the experimental intervention’s effect compared with the comparator intervention. The confidence interval describes the uncertainty inherent in any estimate, and describes a range of values within which we can be reasonably sure that the true effect actually lies. If the confidence interval is relatively narrow (e.g. 0.70 to 0.80), the effect size is known precisely. If the interval is wider (e.g. 0.60 to 0.93) the uncertainty is greater, although there may still be enough precision to make decisions about the utility of the intervention. Intervals that are very wide (e.g. 0.50 to 1.10) indicate that we have little knowledge about the effect and this imprecision affects our certainty in the evidence, and that further information would be needed before we could draw a more certain conclusion.
A 95% confidence interval is often interpreted as indicating a range within which we can be 95% certain that the true effect lies. This statement is a loose interpretation, but is useful as a rough guide. The strictly correct interpretation of a confidence interval is based on the hypothetical notion of considering the results that would be obtained if the study were repeated many times. If a study were repeated infinitely often, and on each occasion a 95% confidence interval calculated, then 95% of these intervals would contain the true effect (see Section 15.3.3 for further explanation).
The width of the confidence interval for an individual study depends to a large extent on the sample size. Larger studies tend to give more precise estimates of effects (and hence have narrower confidence intervals) than smaller studies. For continuous outcomes, precision depends also on the variability in the outcome measurements (i.e. how widely individual results vary between people in the study, measured as the standard deviation); for dichotomous outcomes it depends on the risk of the event (more frequent events allow more precision, and narrower confidence intervals), and for time-to-event outcomes it also depends on the number of events observed. All these quantities are used in computation of the standard errors of effect estimates from which the confidence interval is derived.
The width of a confidence interval for a meta-analysis depends on the precision of the individual study estimates and on the number of studies combined. In addition, for random-effects models, precision will decrease with increasing heterogeneity and confidence intervals will widen correspondingly (see Chapter 10, Section 10.10.4 ). As more studies are added to a meta-analysis the width of the confidence interval usually decreases. However, if the additional studies increase the heterogeneity in the meta-analysis and a random-effects model is used, it is possible that the confidence interval width will increase.
Confidence intervals and point estimates have different interpretations in fixed-effect and random-effects models. While the fixed-effect estimate and its confidence interval address the question ‘what is the best (single) estimate of the effect?’, the random-effects estimate assumes there to be a distribution of effects, and the estimate and its confidence interval address the question ‘what is the best estimate of the average effect?’ A confidence interval may be reported for any level of confidence (although they are most commonly reported for 95%, and sometimes 90% or 99%). For example, the odds ratio of 0.80 could be reported with an 80% confidence interval of 0.73 to 0.88; a 90% interval of 0.72 to 0.89; and a 95% interval of 0.70 to 0.92. As the confidence level increases, the confidence interval widens.
There is logical correspondence between the confidence interval and the P value (see Section 15.3.3 ). The 95% confidence interval for an effect will exclude the null value (such as an odds ratio of 1.0 or a risk difference of 0) if and only if the test of significance yields a P value of less than 0.05. If the P value is exactly 0.05, then either the upper or lower limit of the 95% confidence interval will be at the null value. Similarly, the 99% confidence interval will exclude the null if and only if the test of significance yields a P value of less than 0.01.
Together, the point estimate and confidence interval provide information to assess the effects of the intervention on the outcome. For example, suppose that we are evaluating an intervention that reduces the risk of an event and we decide that it would be useful only if it reduced the risk of an event from 30% by at least 5 percentage points to 25% (these values will depend on the specific clinical scenario and outcomes, including the anticipated harms). If the meta-analysis yielded an effect estimate of a reduction of 10 percentage points with a tight 95% confidence interval, say, from 7% to 13%, we would be able to conclude that the intervention was useful since both the point estimate and the entire range of the interval exceed our criterion of a reduction of 5% for net health benefit. However, if the meta-analysis reported the same risk reduction of 10% but with a wider interval, say, from 2% to 18%, although we would still conclude that our best estimate of the intervention effect is that it provides net benefit, we could not be so confident as we still entertain the possibility that the effect could be between 2% and 5%. If the confidence interval was wider still, and included the null value of a difference of 0%, we would still consider the possibility that the intervention has no effect on the outcome whatsoever, and would need to be even more sceptical in our conclusions.
Review authors may use the same general approach to conclude that an intervention is not useful. Continuing with the above example where the criterion for an important difference that should be achieved to provide more benefit than harm is a 5% risk difference, an effect estimate of 2% with a 95% confidence interval of 1% to 4% suggests that the intervention does not provide net health benefit.
15.3.2 P values and statistical significance
A P value is the standard result of a statistical test, and is the probability of obtaining the observed effect (or larger) under a ‘null hypothesis’. In the context of Cochrane Reviews there are two commonly used statistical tests. The first is a test of overall effect (a Z-test), and its null hypothesis is that there is no overall effect of the experimental intervention compared with the comparator on the outcome of interest. The second is the (Chi 2 ) test for heterogeneity, and its null hypothesis is that there are no differences in the intervention effects across studies.
A P value that is very small indicates that the observed effect is very unlikely to have arisen purely by chance, and therefore provides evidence against the null hypothesis. It has been common practice to interpret a P value by examining whether it is smaller than particular threshold values. In particular, P values less than 0.05 are often reported as ‘statistically significant’, and interpreted as being small enough to justify rejection of the null hypothesis. However, the 0.05 threshold is an arbitrary one that became commonly used in medical and psychological research largely because P values were determined by comparing the test statistic against tabulations of specific percentage points of statistical distributions. If review authors decide to present a P value with the results of a meta-analysis, they should report a precise P value (as calculated by most statistical software), together with the 95% confidence interval. Review authors should not describe results as ‘statistically significant’, ‘not statistically significant’ or ‘non-significant’ or unduly rely on thresholds for P values , but report the confidence interval together with the exact P value (see MECIR Box 15.3.a ).
We discuss interpretation of the test for heterogeneity in Chapter 10, Section 10.10.2 ; the remainder of this section refers mainly to tests for an overall effect. For tests of an overall effect, the computation of P involves both the effect estimate and precision of the effect estimate (driven largely by sample size). As precision increases, the range of plausible effects that could occur by chance is reduced. Correspondingly, the statistical significance of an effect of a particular magnitude will usually be greater (the P value will be smaller) in a larger study than in a smaller study.
P values are commonly misinterpreted in two ways. First, a moderate or large P value (e.g. greater than 0.05) may be misinterpreted as evidence that the intervention has no effect on the outcome. There is an important difference between this statement and the correct interpretation that there is a high probability that the observed effect on the outcome is due to chance alone. To avoid such a misinterpretation, review authors should always examine the effect estimate and its 95% confidence interval.
The second misinterpretation is to assume that a result with a small P value for the summary effect estimate implies that an experimental intervention has an important benefit. Such a misinterpretation is more likely to occur in large studies and meta-analyses that accumulate data over dozens of studies and thousands of participants. The P value addresses the question of whether the experimental intervention effect is precisely nil; it does not examine whether the effect is of a magnitude of importance to potential recipients of the intervention. In a large study, a small P value may represent the detection of a trivial effect that may not lead to net health benefit when compared with the potential harms (i.e. harmful effects on other important outcomes). Again, inspection of the point estimate and confidence interval helps correct interpretations (see Section 15.3.1 ).
MECIR Box 15.3.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
15.3.3 Relation between confidence intervals, statistical significance and certainty of evidence
The confidence interval (and imprecision) is only one domain that influences overall uncertainty about effect estimates. Uncertainty resulting from imprecision (i.e. statistical uncertainty) may be no less important than uncertainty from indirectness, or any other GRADE domain, in the context of decision making (Schünemann 2016). Thus, the extent to which interpretations of the confidence interval described in Sections 15.3.1 and 15.3.2 correspond to conclusions about overall certainty of the evidence for the outcome of interest depends on these other domains. If there are no concerns about other domains that determine the certainty of the evidence (i.e. risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness or publication bias), then the interpretation in Sections 15.3.1 and 15.3.2 . about the relation of the confidence interval to the true effect may be carried forward to the overall certainty. However, if there are concerns about the other domains that affect the certainty of the evidence, the interpretation about the true effect needs to be seen in the context of further uncertainty resulting from those concerns.
For example, nine randomized controlled trials in almost 6000 cancer patients indicated that the administration of heparin reduces the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), with a risk ratio of 43% (95% CI 19% to 60%) (Akl et al 2011a). For patients with a plausible baseline risk of approximately 4.6% per year, this relative effect suggests that heparin leads to an absolute risk reduction of 20 fewer VTEs (95% CI 9 fewer to 27 fewer) per 1000 people per year (Akl et al 2011a). Now consider that the review authors or those applying the evidence in a guideline have lowered the certainty in the evidence as a result of indirectness. While the confidence intervals would remain unchanged, the certainty in that confidence interval and in the point estimate as reflecting the truth for the question of interest will be lowered. In fact, the certainty range will have unknown width so there will be unknown likelihood of a result within that range because of this indirectness. The lower the certainty in the evidence, the less we know about the width of the certainty range, although methods for quantifying risk of bias and understanding potential direction of bias may offer insight when lowered certainty is due to risk of bias. Nevertheless, decision makers must consider this uncertainty, and must do so in relation to the effect measure that is being evaluated (e.g. a relative or absolute measure). We will describe the impact on interpretations for dichotomous outcomes in Section 15.4 .
15.4 Interpreting results from dichotomous outcomes (including numbers needed to treat)
15.4.1 relative and absolute risk reductions.
Clinicians may be more inclined to prescribe an intervention that reduces the relative risk of death by 25% than one that reduces the risk of death by 1 percentage point, although both presentations of the evidence may relate to the same benefit (i.e. a reduction in risk from 4% to 3%). The former refers to the relative reduction in risk and the latter to the absolute reduction in risk. As described in Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1 , there are several measures for comparing dichotomous outcomes in two groups. Meta-analyses are usually undertaken using risk ratios (RR), odds ratios (OR) or risk differences (RD), but there are several alternative ways of expressing results.
Relative risk reduction (RRR) is a convenient way of re-expressing a risk ratio as a percentage reduction:
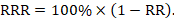
For example, a risk ratio of 0.75 translates to a relative risk reduction of 25%, as in the example above.
The risk difference is often referred to as the absolute risk reduction (ARR) or absolute risk increase (ARI), and may be presented as a percentage (e.g. 1%), as a decimal (e.g. 0.01), or as account (e.g. 10 out of 1000). We consider different choices for presenting absolute effects in Section 15.4.3 . We then describe computations for obtaining these numbers from the results of individual studies and of meta-analyses in Section 15.4.4 .
15.4.2 Number needed to treat (NNT)
The number needed to treat (NNT) is a common alternative way of presenting information on the effect of an intervention. The NNT is defined as the expected number of people who need to receive the experimental rather than the comparator intervention for one additional person to either incur or avoid an event (depending on the direction of the result) in a given time frame. Thus, for example, an NNT of 10 can be interpreted as ‘it is expected that one additional (or less) person will incur an event for every 10 participants receiving the experimental intervention rather than comparator over a given time frame’. It is important to be clear that:
- since the NNT is derived from the risk difference, it is still a comparative measure of effect (experimental versus a specific comparator) and not a general property of a single intervention; and
- the NNT gives an ‘expected value’. For example, NNT = 10 does not imply that one additional event will occur in each and every group of 10 people.
NNTs can be computed for both beneficial and detrimental events, and for interventions that cause both improvements and deteriorations in outcomes. In all instances NNTs are expressed as positive whole numbers. Some authors use the term ‘number needed to harm’ (NNH) when an intervention leads to an adverse outcome, or a decrease in a positive outcome, rather than improvement. However, this phrase can be misleading (most notably, it can easily be read to imply the number of people who will experience a harmful outcome if given the intervention), and it is strongly recommended that ‘number needed to harm’ and ‘NNH’ are avoided. The preferred alternative is to use phrases such as ‘number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome’ (NNTB) and ‘number needed to treat for an additional harmful outcome’ (NNTH) to indicate direction of effect.
As NNTs refer to events, their interpretation needs to be worded carefully when the binary outcome is a dichotomization of a scale-based outcome. For example, if the outcome is pain measured on a ‘none, mild, moderate or severe’ scale it may have been dichotomized as ‘none or mild’ versus ‘moderate or severe’. It would be inappropriate for an NNT from these data to be referred to as an ‘NNT for pain’. It is an ‘NNT for moderate or severe pain’.
We consider different choices for presenting absolute effects in Section 15.4.3 . We then describe computations for obtaining these numbers from the results of individual studies and of meta-analyses in Section 15.4.4 .
15.4.3 Expressing risk differences
Users of reviews are liable to be influenced by the choice of statistical presentations of the evidence. Hoffrage and colleagues suggest that physicians’ inferences about statistical outcomes are more appropriate when they deal with ‘natural frequencies’ – whole numbers of people, both treated and untreated (e.g. treatment results in a drop from 20 out of 1000 to 10 out of 1000 women having breast cancer) – than when effects are presented as percentages (e.g. 1% absolute reduction in breast cancer risk) (Hoffrage et al 2000). Probabilities may be more difficult to understand than frequencies, particularly when events are rare. While standardization may be important in improving the presentation of research evidence (and participation in healthcare decisions), current evidence suggests that the presentation of natural frequencies for expressing differences in absolute risk is best understood by consumers of healthcare information (Akl et al 2011b). This evidence provides the rationale for presenting absolute risks in ‘Summary of findings’ tables as numbers of people with events per 1000 people receiving the intervention (see Chapter 14 ).
RRs and RRRs remain crucial because relative effects tend to be substantially more stable across risk groups than absolute effects (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Review authors can use their own data to study this consistency (Cates 1999, Smeeth et al 1999). Risk differences from studies are least likely to be consistent across baseline event rates; thus, they are rarely appropriate for computing numbers needed to treat in systematic reviews. If a relative effect measure (OR or RR) is chosen for meta-analysis, then a comparator group risk needs to be specified as part of the calculation of an RD or NNT. In addition, if there are several different groups of participants with different levels of risk, it is crucial to express absolute benefit for each clinically identifiable risk group, clarifying the time period to which this applies. Studies in patients with differing severity of disease, or studies with different lengths of follow-up will almost certainly have different comparator group risks. In these cases, different comparator group risks lead to different RDs and NNTs (except when the intervention has no effect). A recommended approach is to re-express an odds ratio or a risk ratio as a variety of RD or NNTs across a range of assumed comparator risks (ACRs) (McQuay and Moore 1997, Smeeth et al 1999). Review authors should bear these considerations in mind not only when constructing their ‘Summary of findings’ table, but also in the text of their review.
For example, a review of oral anticoagulants to prevent stroke presented information to users by describing absolute benefits for various baseline risks (Aguilar and Hart 2005, Aguilar et al 2007). They presented their principal findings as “The inherent risk of stroke should be considered in the decision to use oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients, selecting those who stand to benefit most for this therapy” (Aguilar and Hart 2005). Among high-risk atrial fibrillation patients with prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack who have stroke rates of about 12% (120 per 1000) per year, warfarin prevents about 70 strokes yearly per 1000 patients, whereas for low-risk atrial fibrillation patients (with a stroke rate of about 2% per year or 20 per 1000), warfarin prevents only 12 strokes. This presentation helps users to understand the important impact that typical baseline risks have on the absolute benefit that they can expect.
15.4.4 Computations
Direct computation of risk difference (RD) or a number needed to treat (NNT) depends on the summary statistic (odds ratio, risk ratio or risk differences) available from the study or meta-analysis. When expressing results of meta-analyses, review authors should use, in the computations, whatever statistic they determined to be the most appropriate summary for meta-analysis (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Here we present calculations to obtain RD as a reduction in the number of participants per 1000. For example, a risk difference of –0.133 corresponds to 133 fewer participants with the event per 1000.
RDs and NNTs should not be computed from the aggregated total numbers of participants and events across the trials. This approach ignores the randomization within studies, and may produce seriously misleading results if there is unbalanced randomization in any of the studies. Using the pooled result of a meta-analysis is more appropriate. When computing NNTs, the values obtained are by convention always rounded up to the next whole number.
15.4.4.1 Computing NNT from a risk difference (RD)
A NNT may be computed from a risk difference as
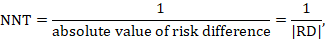
where the vertical bars (‘absolute value of’) in the denominator indicate that any minus sign should be ignored. It is convention to round the NNT up to the nearest whole number. For example, if the risk difference is –0.12 the NNT is 9; if the risk difference is –0.22 the NNT is 5. Cochrane Review authors should qualify the NNT as referring to benefit (improvement) or harm by denoting the NNT as NNTB or NNTH. Note that this approach, although feasible, should be used only for the results of a meta-analysis of risk differences. In most cases meta-analyses will be undertaken using a relative measure of effect (RR or OR), and those statistics should be used to calculate the NNT (see Section 15.4.4.2 and 15.4.4.3 ).
15.4.4.2 Computing risk differences or NNT from a risk ratio
To aid interpretation of the results of a meta-analysis of risk ratios, review authors may compute an absolute risk reduction or NNT. In order to do this, an assumed comparator risk (ACR) (otherwise known as a baseline risk, or risk that the outcome of interest would occur with the comparator intervention) is required. It will usually be appropriate to do this for a range of different ACRs. The computation proceeds as follows:
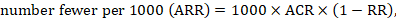
As an example, suppose the risk ratio is RR = 0.92, and an ACR = 0.3 (300 per 1000) is assumed. Then the effect on risk is 24 fewer per 1000:
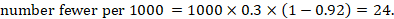
The NNT is 42:
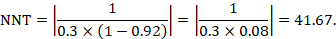
15.4.4.3 Computing risk differences or NNT from an odds ratio
Review authors may wish to compute a risk difference or NNT from the results of a meta-analysis of odds ratios. In order to do this, an ACR is required. It will usually be appropriate to do this for a range of different ACRs. The computation proceeds as follows:
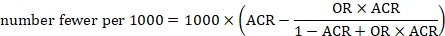
As an example, suppose the odds ratio is OR = 0.73, and a comparator risk of ACR = 0.3 is assumed. Then the effect on risk is 62 fewer per 1000:
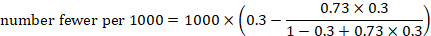
The NNT is 17:
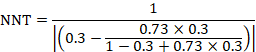
15.4.4.4 Computing risk ratio from an odds ratio
Because risk ratios are easier to interpret than odds ratios, but odds ratios have favourable mathematical properties, a review author may decide to undertake a meta-analysis based on odds ratios, but to express the result as a summary risk ratio (or relative risk reduction). This requires an ACR. Then
It will often be reasonable to perform this transformation using the median comparator group risk from the studies in the meta-analysis.
15.4.4.5 Computing confidence limits
Confidence limits for RDs and NNTs may be calculated by applying the above formulae to the upper and lower confidence limits for the summary statistic (RD, RR or OR) (Altman 1998). Note that this confidence interval does not incorporate uncertainty around the ACR.
If the 95% confidence interval of OR or RR includes the value 1, one of the confidence limits will indicate benefit and the other harm. Thus, appropriate use of the words ‘fewer’ and ‘more’ is required for each limit when presenting results in terms of events. For NNTs, the two confidence limits should be labelled as NNTB and NNTH to indicate the direction of effect in each case. The confidence interval for the NNT will include a ‘discontinuity’, because increasingly smaller risk differences that approach zero will lead to NNTs approaching infinity. Thus, the confidence interval will include both an infinitely large NNTB and an infinitely large NNTH.
15.5 Interpreting results from continuous outcomes (including standardized mean differences)
15.5.1 meta-analyses with continuous outcomes.
Review authors should describe in the study protocol how they plan to interpret results for continuous outcomes. When outcomes are continuous, review authors have a number of options to present summary results. These options differ if studies report the same measure that is familiar to the target audiences, studies report the same or very similar measures that are less familiar to the target audiences, or studies report different measures.

15.5.2 Meta-analyses with continuous outcomes using the same measure
If all studies have used the same familiar units, for instance, results are expressed as durations of events, such as symptoms for conditions including diarrhoea, sore throat, otitis media, influenza or duration of hospitalization, a meta-analysis may generate a summary estimate in those units, as a difference in mean response (see, for instance, the row summarizing results for duration of diarrhoea in Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.b and the row summarizing oedema in Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.a ). For such outcomes, the ‘Summary of findings’ table should include a difference of means between the two interventions. However, when units of such outcomes may be difficult to interpret, particularly when they relate to rating scales (again, see the oedema row of Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.a ). ‘Summary of findings’ tables should include the minimum and maximum of the scale of measurement, and the direction. Knowledge of the smallest change in instrument score that patients perceive is important – the minimal important difference (MID) – and can greatly facilitate the interpretation of results (Guyatt et al 1998, Schünemann and Guyatt 2005). Knowing the MID allows review authors and users to place results in context. Review authors should state the MID – if known – in the Comments column of their ‘Summary of findings’ table. For example, the chronic respiratory questionnaire has possible scores in health-related quality of life ranging from 1 to 7 and 0.5 represents a well-established MID (Jaeschke et al 1989, Schünemann et al 2005).
15.5.3 Meta-analyses with continuous outcomes using different measures
When studies have used different instruments to measure the same construct, a standardized mean difference (SMD) may be used in meta-analysis for combining continuous data. Without guidance, clinicians and patients may have little idea how to interpret results presented as SMDs. Review authors should therefore consider issues of interpretability when planning their analysis at the protocol stage and should consider whether there will be suitable ways to re-express the SMD or whether alternative effect measures, such as a ratio of means, or possibly as minimal important difference units (Guyatt et al 2013b) should be used. Table 15.5.a and the following sections describe these options.
Table 15.5.a Approaches and their implications to presenting results of continuous variables when primary studies have used different instruments to measure the same construct. Adapted from Guyatt et al (2013b)
15.5.3.1 Presenting and interpreting SMDs using generic effect size estimates
The SMD expresses the intervention effect in standard units rather than the original units of measurement. The SMD is the difference in mean effects between the experimental and comparator groups divided by the pooled standard deviation of participants’ outcomes, or external SDs when studies are very small (see Chapter 6, Section 6.5.1.2 ). The value of a SMD thus depends on both the size of the effect (the difference between means) and the standard deviation of the outcomes (the inherent variability among participants or based on an external SD).
If review authors use the SMD, they might choose to present the results directly as SMDs (row 1a, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). However, absolute values of the intervention and comparison groups are typically not useful because studies have used different measurement instruments with different units. Guiding rules for interpreting SMDs (or ‘Cohen’s effect sizes’) exist, and have arisen mainly from researchers in the social sciences (Cohen 1988). One example is as follows: 0.2 represents a small effect, 0.5 a moderate effect and 0.8 a large effect (Cohen 1988). Variations exist (e.g. <0.40=small, 0.40 to 0.70=moderate, >0.70=large). Review authors might consider including such a guiding rule in interpreting the SMD in the text of the review, and in summary versions such as the Comments column of a ‘Summary of findings’ table. However, some methodologists believe that such interpretations are problematic because patient importance of a finding is context-dependent and not amenable to generic statements.
15.5.3.2 Re-expressing SMDs using a familiar instrument
The second possibility for interpreting the SMD is to express it in the units of one or more of the specific measurement instruments used by the included studies (row 1b, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). The approach is to calculate an absolute difference in means by multiplying the SMD by an estimate of the SD associated with the most familiar instrument. To obtain this SD, a reasonable option is to calculate a weighted average across all intervention groups of all studies that used the selected instrument (preferably a pre-intervention or post-intervention SD as discussed in Chapter 10, Section 10.5.2 ). To better reflect among-person variation in practice, or to use an instrument not represented in the meta-analysis, it may be preferable to use a standard deviation from a representative observational study. The summary effect is thus re-expressed in the original units of that particular instrument and the clinical relevance and impact of the intervention effect can be interpreted using that familiar instrument.
The same approach of re-expressing the results for a familiar instrument can also be used for other standardized effect measures such as when standardizing by MIDs (Guyatt et al 2013b): see Section 15.5.3.5 .
Table 15.5.b Application of approaches when studies have used different measures: effects of dexamethasone for pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Karanicolas et al 2008). Reproduced with permission of Wolters Kluwer
1 Certainty rated according to GRADE from very low to high certainty. 2 Substantial unexplained heterogeneity in study results. 3 Imprecision due to wide confidence intervals. 4 The 20% comes from the proportion in the control group requiring rescue analgesia. 5 Crude (arithmetic) means of the post-operative pain mean responses across all five trials when transformed to a 100-point scale.
15.5.3.3 Re-expressing SMDs through dichotomization and transformation to relative and absolute measures
A third approach (row 1c, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ) relies on converting the continuous measure into a dichotomy and thus allows calculation of relative and absolute effects on a binary scale. A transformation of a SMD to a (log) odds ratio is available, based on the assumption that an underlying continuous variable has a logistic distribution with equal standard deviation in the two intervention groups, as discussed in Chapter 10, Section 10.6 (Furukawa 1999, Guyatt et al 2013b). The assumption is unlikely to hold exactly and the results must be regarded as an approximation. The log odds ratio is estimated as
(or approximately 1.81✕SMD). The resulting odds ratio can then be presented as normal, and in a ‘Summary of findings’ table, combined with an assumed comparator group risk to be expressed as an absolute risk difference. The comparator group risk in this case would refer to the proportion of people who have achieved a specific value of the continuous outcome. In randomized trials this can be interpreted as the proportion who have improved by some (specified) amount (responders), for instance by 5 points on a 0 to 100 scale. Table 15.5.c shows some illustrative results from this method. The risk differences can then be converted to NNTs or to people per thousand using methods described in Section 15.4.4 .
Table 15.5.c Risk difference derived for specific SMDs for various given ‘proportions improved’ in the comparator group (Furukawa 1999, Guyatt et al 2013b). Reproduced with permission of Elsevier
15.5.3.4 Ratio of means
A more frequently used approach is based on calculation of a ratio of means between the intervention and comparator groups (Friedrich et al 2008) as discussed in Chapter 6, Section 6.5.1.3 . Interpretational advantages of this approach include the ability to pool studies with outcomes expressed in different units directly, to avoid the vulnerability of heterogeneous populations that limits approaches that rely on SD units, and for ease of clinical interpretation (row 2, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). This method is currently designed for post-intervention scores only. However, it is possible to calculate a ratio of change scores if both intervention and comparator groups change in the same direction in each relevant study, and this ratio may sometimes be informative.
Limitations to this approach include its limited applicability to change scores (since it is unlikely that both intervention and comparator group changes are in the same direction in all studies) and the possibility of misleading results if the comparator group mean is very small, in which case even a modest difference from the intervention group will yield a large and therefore misleading ratio of means. It also requires that separate ratios of means be calculated for each included study, and then entered into a generic inverse variance meta-analysis (see Chapter 10, Section 10.3 ).
The ratio of means approach illustrated in Table 15.5.b suggests a relative reduction in pain of only 13%, meaning that those receiving steroids have a pain severity 87% of those in the comparator group, an effect that might be considered modest.
15.5.3.5 Presenting continuous results as minimally important difference units
To express results in MID units, review authors have two options. First, they can be combined across studies in the same way as the SMD, but instead of dividing the mean difference of each study by its SD, review authors divide by the MID associated with that outcome (Johnston et al 2010, Guyatt et al 2013b). Instead of SD units, the pooled results represent MID units (row 3, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ), and may be more easily interpretable. This approach avoids the problem of varying SDs across studies that may distort estimates of effect in approaches that rely on the SMD. The approach, however, relies on having well-established MIDs. The approach is also risky in that a difference less than the MID may be interpreted as trivial when a substantial proportion of patients may have achieved an important benefit.
The other approach makes a simple conversion (not shown in Table 15.5.b ), before undertaking the meta-analysis, of the means and SDs from each study to means and SDs on the scale of a particular familiar instrument whose MID is known. For example, one can rescale the mean and SD of other chronic respiratory disease instruments (e.g. rescaling a 0 to 100 score of an instrument) to a the 1 to 7 score in Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire (CRQ) units (by assuming 0 equals 1 and 100 equals 7 on the CRQ). Given the MID of the CRQ of 0.5, a mean difference in change of 0.71 after rescaling of all studies suggests a substantial effect of the intervention (Guyatt et al 2013b). This approach, presenting in units of the most familiar instrument, may be the most desirable when the target audiences have extensive experience with that instrument, particularly if the MID is well established.
15.6 Drawing conclusions
15.6.1 conclusions sections of a cochrane review.
Authors’ conclusions in a Cochrane Review are divided into implications for practice and implications for research. While Cochrane Reviews about interventions can provide meaningful information and guidance for practice, decisions about the desirable and undesirable consequences of healthcare options require evidence and judgements for criteria that most Cochrane Reviews do not provide (Alonso-Coello et al 2016). In describing the implications for practice and the development of recommendations, however, review authors may consider the certainty of the evidence, the balance of benefits and harms, and assumed values and preferences.
15.6.2 Implications for practice
Drawing conclusions about the practical usefulness of an intervention entails making trade-offs, either implicitly or explicitly, between the estimated benefits, harms and the values and preferences. Making such trade-offs, and thus making specific recommendations for an action in a specific context, goes beyond a Cochrane Review and requires additional evidence and informed judgements that most Cochrane Reviews do not provide (Alonso-Coello et al 2016). Such judgements are typically the domain of clinical practice guideline developers for which Cochrane Reviews will provide crucial information (Graham et al 2011, Schünemann et al 2014, Zhang et al 2018a). Thus, authors of Cochrane Reviews should not make recommendations.
If review authors feel compelled to lay out actions that clinicians and patients could take, they should – after describing the certainty of evidence and the balance of benefits and harms – highlight different actions that might be consistent with particular patterns of values and preferences. Other factors that might influence a decision should also be highlighted, including any known factors that would be expected to modify the effects of the intervention, the baseline risk or status of the patient, costs and who bears those costs, and the availability of resources. Review authors should ensure they consider all patient-important outcomes, including those for which limited data may be available. In the context of public health reviews the focus may be on population-important outcomes as the target may be an entire (non-diseased) population and include outcomes that are not measured in the population receiving an intervention (e.g. a reduction of transmission of infections from those receiving an intervention). This process implies a high level of explicitness in judgements about values or preferences attached to different outcomes and the certainty of the related evidence (Zhang et al 2018b, Zhang et al 2018c); this and a full cost-effectiveness analysis is beyond the scope of most Cochrane Reviews (although they might well be used for such analyses; see Chapter 20 ).
A review on the use of anticoagulation in cancer patients to increase survival (Akl et al 2011a) provides an example for laying out clinical implications for situations where there are important trade-offs between desirable and undesirable effects of the intervention: “The decision for a patient with cancer to start heparin therapy for survival benefit should balance the benefits and downsides and integrate the patient’s values and preferences. Patients with a high preference for a potential survival prolongation, limited aversion to potential bleeding, and who do not consider heparin (both UFH or LMWH) therapy a burden may opt to use heparin, while those with aversion to bleeding may not.”
15.6.3 Implications for research
The second category for authors’ conclusions in a Cochrane Review is implications for research. To help people make well-informed decisions about future healthcare research, the ‘Implications for research’ section should comment on the need for further research, and the nature of the further research that would be most desirable. It is helpful to consider the population, intervention, comparison and outcomes that could be addressed, or addressed more effectively in the future, in the context of the certainty of the evidence in the current review (Brown et al 2006):
- P (Population): diagnosis, disease stage, comorbidity, risk factor, sex, age, ethnic group, specific inclusion or exclusion criteria, clinical setting;
- I (Intervention): type, frequency, dose, duration, prognostic factor;
- C (Comparison): placebo, routine care, alternative treatment/management;
- O (Outcome): which clinical or patient-related outcomes will the researcher need to measure, improve, influence or accomplish? Which methods of measurement should be used?
While Cochrane Review authors will find the PICO domains helpful, the domains of the GRADE certainty framework further support understanding and describing what additional research will improve the certainty in the available evidence. Note that as the certainty of the evidence is likely to vary by outcome, these implications will be specific to certain outcomes in the review. Table 15.6.a shows how review authors may be aided in their interpretation of the body of evidence and drawing conclusions about future research and practice.
Table 15.6.a Implications for research and practice suggested by individual GRADE domains
The review of compression stockings for prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in airline passengers described in Chapter 14 provides an example where there is some convincing evidence of a benefit of the intervention: “This review shows that the question of the effects on symptomless DVT of wearing versus not wearing compression stockings in the types of people studied in these trials should now be regarded as answered. Further research may be justified to investigate the relative effects of different strengths of stockings or of stockings compared to other preventative strategies. Further randomised trials to address the remaining uncertainty about the effects of wearing versus not wearing compression stockings on outcomes such as death, pulmonary embolism and symptomatic DVT would need to be large.” (Clarke et al 2016).
A review of therapeutic touch for anxiety disorder provides an example of the implications for research when no eligible studies had been found: “This review highlights the need for randomized controlled trials to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic touch in reducing anxiety symptoms in people diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Future trials need to be rigorous in design and delivery, with subsequent reporting to include high quality descriptions of all aspects of methodology to enable appraisal and interpretation of results.” (Robinson et al 2007).
15.6.4 Reaching conclusions
A common mistake is to confuse ‘no evidence of an effect’ with ‘evidence of no effect’. When the confidence intervals are too wide (e.g. including no effect), it is wrong to claim that the experimental intervention has ‘no effect’ or is ‘no different’ from the comparator intervention. Review authors may also incorrectly ‘positively’ frame results for some effects but not others. For example, when the effect estimate is positive for a beneficial outcome but confidence intervals are wide, review authors may describe the effect as promising. However, when the effect estimate is negative for an outcome that is considered harmful but the confidence intervals include no effect, review authors report no effect. Another mistake is to frame the conclusion in wishful terms. For example, review authors might write, “there were too few people in the analysis to detect a reduction in mortality” when the included studies showed a reduction or even increase in mortality that was not ‘statistically significant’. One way of avoiding errors such as these is to consider the results blinded; that is, consider how the results would be presented and framed in the conclusions if the direction of the results was reversed. If the confidence interval for the estimate of the difference in the effects of the interventions overlaps with no effect, the analysis is compatible with both a true beneficial effect and a true harmful effect. If one of the possibilities is mentioned in the conclusion, the other possibility should be mentioned as well. Table 15.6.b suggests narrative statements for drawing conclusions based on the effect estimate from the meta-analysis and the certainty of the evidence.
Table 15.6.b Suggested narrative statements for phrasing conclusions
Another common mistake is to reach conclusions that go beyond the evidence. Often this is done implicitly, without referring to the additional information or judgements that are used in reaching conclusions about the implications of a review for practice. Even when additional information and explicit judgements support conclusions about the implications of a review for practice, review authors rarely conduct systematic reviews of the additional information. Furthermore, implications for practice are often dependent on specific circumstances and values that must be taken into consideration. As we have noted, review authors should always be cautious when drawing conclusions about implications for practice and they should not make recommendations.
15.7 Chapter information
Authors: Holger J Schünemann, Gunn E Vist, Julian PT Higgins, Nancy Santesso, Jonathan J Deeks, Paul Glasziou, Elie Akl, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group
Acknowledgements: Andrew Oxman, Jonathan Sterne, Michael Borenstein and Rob Scholten contributed text to earlier versions of this chapter.
Funding: This work was in part supported by funding from the Michael G DeGroote Cochrane Canada Centre and the Ontario Ministry of Health. JJD receives support from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre at the University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Birmingham. JPTH receives support from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Bristol. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
15.8 References
Aguilar MI, Hart R. Oral anticoagulants for preventing stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and no previous history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005; 3 : CD001927.
Aguilar MI, Hart R, Pearce LA. Oral anticoagulants versus antiplatelet therapy for preventing stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and no history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 3 : CD006186.
Akl EA, Gunukula S, Barba M, Yosuico VE, van Doormaal FF, Kuipers S, Middeldorp S, Dickinson HO, Bryant A, Schünemann H. Parenteral anticoagulation in patients with cancer who have no therapeutic or prophylactic indication for anticoagulation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011a; 1 : CD006652.
Akl EA, Oxman AD, Herrin J, Vist GE, Terrenato I, Sperati F, Costiniuk C, Blank D, Schünemann H. Using alternative statistical formats for presenting risks and risk reductions. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011b; 3 : CD006776.
Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, Moberg J, Brignardello-Petersen R, Akl EA, Davoli M, Treweek S, Mustafa RA, Rada G, Rosenbaum S, Morelli A, Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Group GW. GRADE Evidence to Decision (EtD) frameworks: a systematic and transparent approach to making well informed healthcare choices. 1: Introduction. BMJ 2016; 353 : i2016.
Altman DG. Confidence intervals for the number needed to treat. BMJ 1998; 317 : 1309-1312.
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Zaza S. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004; 328 : 1490.
Brown P, Brunnhuber K, Chalkidou K, Chalmers I, Clarke M, Fenton M, Forbes C, Glanville J, Hicks NJ, Moody J, Twaddle S, Timimi H, Young P. How to formulate research recommendations. BMJ 2006; 333 : 804-806.
Cates C. Confidence intervals for the number needed to treat: Pooling numbers needed to treat may not be reliable. BMJ 1999; 318 : 1764-1765.
Clarke MJ, Broderick C, Hopewell S, Juszczak E, Eisinga A. Compression stockings for preventing deep vein thrombosis in airline passengers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016; 9 : CD004002.
Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences . 2nd edition ed. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.; 1988.
Coleman T, Chamberlain C, Davey MA, Cooper SE, Leonardi-Bee J. Pharmacological interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015; 12 : CD010078.
Dans AM, Dans L, Oxman AD, Robinson V, Acuin J, Tugwell P, Dennis R, Kang D. Assessing equity in clinical practice guidelines. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2007; 60 : 540-546.
Friedman LM, Furberg CD, DeMets DL. Fundamentals of Clinical Trials . 2nd edition ed. Littleton (MA): John Wright PSG, Inc.; 1985.
Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, Beyene J. The ratio of means method as an alternative to mean differences for analyzing continuous outcome variables in meta-analysis: a simulation study. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2008; 8 : 32.
Furukawa T. From effect size into number needed to treat. Lancet 1999; 353 : 1680.
Graham R, Mancher M, Wolman DM, Greenfield S, Steinberg E. Committee on Standards for Developing Trustworthy Clinical Practice Guidelines, Board on Health Care Services: Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011a; 64 : 383-394.
Guyatt GH, Juniper EF, Walter SD, Griffith LE, Goldstein RS. Interpreting treatment effects in randomised trials. BMJ 1998; 316 : 690-693.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008; 336 : 924-926.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, Alonso-Coello P, Falck-Ytter Y, Jaeschke R, Vist G, Akl EA, Post PN, Norris S, Meerpohl J, Shukla VK, Nasser M, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence--indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011b; 64 : 1303-1310.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Santesso N, Helfand M, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Norris S, Meerpohl J, Djulbegovic B, Alonso-Coello P, Post PN, Busse JW, Glasziou P, Christensen R, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 12. Preparing summary of findings tables-binary outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013a; 66 : 158-172.
Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA, Johnston BC, Karanicolas P, Akl EA, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Kupper LL, Martin SL, Meerpohl JJ, Alonso-Coello P, Christensen R, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles-continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013b; 66 : 173-183.
Hawe P, Shiell A, Riley T, Gold L. Methods for exploring implementation variation and local context within a cluster randomised community intervention trial. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2004; 58 : 788-793.
Hoffrage U, Lindsey S, Hertwig R, Gigerenzer G. Medicine. Communicating statistical information. Science 2000; 290 : 2261-2262.
Jaeschke R, Singer J, Guyatt GH. Measurement of health status. Ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference. Controlled Clinical Trials 1989; 10 : 407-415.
Johnston B, Thorlund K, Schünemann H, Xie F, Murad M, Montori V, Guyatt G. Improving the interpretation of health-related quality of life evidence in meta-analysis: The application of minimal important difference units. . Health Outcomes and Qualithy of Life 2010; 11 : 116.
Karanicolas PJ, Smith SE, Kanbur B, Davies E, Guyatt GH. The impact of prophylactic dexamethasone on nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Surgery 2008; 248 : 751-762.
Lumley J, Oliver SS, Chamberlain C, Oakley L. Interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004; 4 : CD001055.
McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Using numerical results from systematic reviews in clinical practice. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997; 126 : 712-720.
Resnicow K, Cross D, Wynder E. The Know Your Body program: a review of evaluation studies. Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine 1993; 70 : 188-207.
Robinson J, Biley FC, Dolk H. Therapeutic touch for anxiety disorders. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 3 : CD006240.
Rothwell PM. External validity of randomised controlled trials: "to whom do the results of this trial apply?". Lancet 2005; 365 : 82-93.
Santesso N, Carrasco-Labra A, Langendam M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Mustafa RA, Heus P, Lasserson T, Opiyo N, Kunnamo I, Sinclair D, Garner P, Treweek S, Tovey D, Akl EA, Tugwell P, Brozek JL, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 3: detailed guidance for explanatory footnotes supports creating and understanding GRADE certainty in the evidence judgments. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 28-39.
Schünemann HJ, Puhan M, Goldstein R, Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH. Measurement properties and interpretability of the Chronic respiratory disease questionnaire (CRQ). COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2005; 2 : 81-89.
Schünemann HJ, Guyatt GH. Commentary--goodbye M(C)ID! Hello MID, where do you come from? Health Services Research 2005; 40 : 593-597.
Schünemann HJ, Fretheim A, Oxman AD. Improving the use of research evidence in guideline development: 13. Applicability, transferability and adaptation. Health Research Policy and Systems 2006; 4 : 25.
Schünemann HJ. Methodological idiosyncracies, frameworks and challenges of non-pharmaceutical and non-technical treatment interventions. Zeitschrift für Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualität im Gesundheitswesen 2013; 107 : 214-220.
Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Reeves BC, Akl EA, Santesso N, Spencer FA, Shea B, Wells G, Helfand M. Non-randomized studies as a source of complementary, sequential or replacement evidence for randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews on the effects of interventions. Research Synthesis Methods 2013; 4 : 49-62.
Schünemann HJ, Wiercioch W, Etxeandia I, Falavigna M, Santesso N, Mustafa R, Ventresca M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Laisaar KT, Kowalski S, Baldeh T, Zhang Y, Raid U, Neumann I, Norris SL, Thornton J, Harbour R, Treweek S, Guyatt G, Alonso-Coello P, Reinap M, Brozek J, Oxman A, Akl EA. Guidelines 2.0: systematic development of a comprehensive checklist for a successful guideline enterprise. CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association Journal 2014; 186 : E123-142.
Schünemann HJ. Interpreting GRADE's levels of certainty or quality of the evidence: GRADE for statisticians, considering review information size or less emphasis on imprecision? Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 75 : 6-15.
Smeeth L, Haines A, Ebrahim S. Numbers needed to treat derived from meta-analyses--sometimes informative, usually misleading. BMJ 1999; 318 : 1548-1551.
Sun X, Briel M, Busse JW, You JJ, Akl EA, Mejza F, Bala MM, Bassler D, Mertz D, Diaz-Granados N, Vandvik PO, Malaga G, Srinathan SK, Dahm P, Johnston BC, Alonso-Coello P, Hassouneh B, Walter SD, Heels-Ansdell D, Bhatnagar N, Altman DG, Guyatt GH. Credibility of claims of subgroup effects in randomised controlled trials: systematic review. BMJ 2012; 344 : e1553.
Zhang Y, Akl EA, Schünemann HJ. Using systematic reviews in guideline development: the GRADE approach. Research Synthesis Methods 2018a: doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1313.
Zhang Y, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt GH, Yepes-Nunez JJ, Akl EA, Hazlewood G, Pardo-Hernandez H, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Qaseem A, Williams JW, Jr., Tugwell P, Flottorp S, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Mustafa RA, Rojas MX, Schünemann HJ. GRADE Guidelines: 19. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences-Risk of bias and indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018b: doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.1001.1013.
Zhang Y, Alonso Coello P, Guyatt G, Yepes-Nunez JJ, Akl EA, Hazlewood G, Pardo-Hernandez H, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Qaseem A, Williams JW, Jr., Tugwell P, Flottorp S, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Mustafa RA, Rojas MX, Xie F, Schünemann HJ. GRADE Guidelines: 20. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences - Inconsistency, Imprecision, and other Domains. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018c: doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.1005.1011.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.
How To Write The Results/Findings Chapter
For qualitative studies (dissertations & theses).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD Cand). Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2021
So, you’ve collected and analysed your qualitative data, and it’s time to write up your results chapter – exciting! But where do you start? In this post, we’ll guide you through the qualitative results chapter (also called the findings chapter), step by step.
Overview: Qualitative Results Chapter
- What (exactly) the qualitative results chapter is
- What to include in your results chapter
- How to write up your results chapter
- A few tips and tricks to help you along the way
What exactly is the results chapter?
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and discuss its meaning), depending on your university’s preference. We’ll treat the two chapters as separate, as that’s the most common approach.
In contrast to a quantitative results chapter that presents numbers and statistics, a qualitative results chapter presents data primarily in the form of words . But this doesn’t mean that a qualitative study can’t have quantitative elements – you could, for example, present the number of times a theme or topic pops up in your data, depending on the analysis method(s) you adopt.
Adding a quantitative element to your study can add some rigour, which strengthens your results by providing more evidence for your claims. This is particularly common when using qualitative content analysis. Keep in mind though that qualitative research aims to achieve depth, richness and identify nuances , so don’t get tunnel vision by focusing on the numbers. They’re just cream on top in a qualitative analysis.
So, to recap, the results chapter is where you objectively present the findings of your analysis, without interpreting them (you’ll save that for the discussion chapter). With that out the way, let’s take a look at what you should include in your results chapter.

What should you include in the results chapter?
As we’ve mentioned, your qualitative results chapter should purely present and describe your results , not interpret them in relation to the existing literature or your research questions . Any speculations or discussion about the implications of your findings should be reserved for your discussion chapter.
In your results chapter, you’ll want to talk about your analysis findings and whether or not they support your hypotheses (if you have any). Naturally, the exact contents of your results chapter will depend on which qualitative analysis method (or methods) you use. For example, if you were to use thematic analysis, you’d detail the themes identified in your analysis, using extracts from the transcripts or text to support your claims.
While you do need to present your analysis findings in some detail, you should avoid dumping large amounts of raw data in this chapter. Instead, focus on presenting the key findings and using a handful of select quotes or text extracts to support each finding . The reams of data and analysis can be relegated to your appendices.
While it’s tempting to include every last detail you found in your qualitative analysis, it is important to make sure that you report only that which is relevant to your research aims, objectives and research questions . Always keep these three components, as well as your hypotheses (if you have any) front of mind when writing the chapter and use them as a filter to decide what’s relevant and what’s not.
Need a helping hand?
How do I write the results chapter?
Now that we’ve covered the basics, it’s time to look at how to structure your chapter. Broadly speaking, the results chapter needs to contain three core components – the introduction, the body and the concluding summary. Let’s take a look at each of these.
Section 1: Introduction
The first step is to craft a brief introduction to the chapter. This intro is vital as it provides some context for your findings. In your introduction, you should begin by reiterating your problem statement and research questions and highlight the purpose of your research . Make sure that you spell this out for the reader so that the rest of your chapter is well contextualised.
The next step is to briefly outline the structure of your results chapter. In other words, explain what’s included in the chapter and what the reader can expect. In the results chapter, you want to tell a story that is coherent, flows logically, and is easy to follow , so make sure that you plan your structure out well and convey that structure (at a high level), so that your reader is well oriented.
The introduction section shouldn’t be lengthy. Two or three short paragraphs should be more than adequate. It is merely an introduction and overview, not a summary of the chapter.
Pro Tip – To help you structure your chapter, it can be useful to set up an initial draft with (sub)section headings so that you’re able to easily (re)arrange parts of your chapter. This will also help your reader to follow your results and give your chapter some coherence. Be sure to use level-based heading styles (e.g. Heading 1, 2, 3 styles) to help the reader differentiate between levels visually. You can find these options in Word (example below).
Section 2: Body
Before we get started on what to include in the body of your chapter, it’s vital to remember that a results section should be completely objective and descriptive, not interpretive . So, be careful not to use words such as, “suggests” or “implies”, as these usually accompany some form of interpretation – that’s reserved for your discussion chapter.
The structure of your body section is very important , so make sure that you plan it out well. When planning out your qualitative results chapter, create sections and subsections so that you can maintain the flow of the story you’re trying to tell. Be sure to systematically and consistently describe each portion of results. Try to adopt a standardised structure for each portion so that you achieve a high level of consistency throughout the chapter.
For qualitative studies, results chapters tend to be structured according to themes , which makes it easier for readers to follow. However, keep in mind that not all results chapters have to be structured in this manner. For example, if you’re conducting a longitudinal study, you may want to structure your chapter chronologically. Similarly, you might structure this chapter based on your theoretical framework . The exact structure of your chapter will depend on the nature of your study , especially your research questions.
As you work through the body of your chapter, make sure that you use quotes to substantiate every one of your claims . You can present these quotes in italics to differentiate them from your own words. A general rule of thumb is to use at least two pieces of evidence per claim, and these should be linked directly to your data. Also, remember that you need to include all relevant results , not just the ones that support your assumptions or initial leanings.
In addition to including quotes, you can also link your claims to the data by using appendices , which you should reference throughout your text. When you reference, make sure that you include both the name/number of the appendix , as well as the line(s) from which you drew your data.
As referencing styles can vary greatly, be sure to look up the appendix referencing conventions of your university’s prescribed style (e.g. APA , Harvard, etc) and keep this consistent throughout your chapter.

Section 3: Concluding summary
The concluding summary is very important because it summarises your key findings and lays the foundation for the discussion chapter . Keep in mind that some readers may skip directly to this section (from the introduction section), so make sure that it can be read and understood well in isolation.
In this section, you need to remind the reader of the key findings. That is, the results that directly relate to your research questions and that you will build upon in your discussion chapter. Remember, your reader has digested a lot of information in this chapter, so you need to use this section to remind them of the most important takeaways.
Importantly, the concluding summary should not present any new information and should only describe what you’ve already presented in your chapter. Keep it concise – you’re not summarising the whole chapter, just the essentials.
Tips and tricks for an A-grade results chapter
Now that you’ve got a clear picture of what the qualitative results chapter is all about, here are some quick tips and reminders to help you craft a high-quality chapter:
- Your results chapter should be written in the past tense . You’ve done the work already, so you want to tell the reader what you found , not what you are currently finding .
- Make sure that you review your work multiple times and check that every claim is adequately backed up by evidence . Aim for at least two examples per claim, and make use of an appendix to reference these.
- When writing up your results, make sure that you stick to only what is relevant . Don’t waste time on data that are not relevant to your research objectives and research questions.
- Use headings and subheadings to create an intuitive, easy to follow piece of writing. Make use of Microsoft Word’s “heading styles” and be sure to use them consistently.
- When referring to numerical data, tables and figures can provide a useful visual aid. When using these, make sure that they can be read and understood independent of your body text (i.e. that they can stand-alone). To this end, use clear, concise labels for each of your tables or figures and make use of colours to code indicate differences or hierarchy.
- Similarly, when you’re writing up your chapter, it can be useful to highlight topics and themes in different colours . This can help you to differentiate between your data if you get a bit overwhelmed and will also help you to ensure that your results flow logically and coherently.
If you have any questions, leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help. If you’d like 1-on-1 help with your results chapter (or any chapter of your dissertation or thesis), check out our private dissertation coaching service here or book a free initial consultation to discuss how we can help you.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

20 Comments
This was extremely helpful. Thanks a lot guys
Hi, thanks for the great research support platform created by the gradcoach team!
I wanted to ask- While “suggests” or “implies” are interpretive terms, what terms could we use for the results chapter? Could you share some examples of descriptive terms?
I think that instead of saying, ‘The data suggested, or The data implied,’ you can say, ‘The Data showed or revealed, or illustrated or outlined’…If interview data, you may say Jane Doe illuminated or elaborated, or Jane Doe described… or Jane Doe expressed or stated.
I found this article very useful. Thank you very much for the outstanding work you are doing.
What if i have 3 different interviewees answering the same interview questions? Should i then present the results in form of the table with the division on the 3 perspectives or rather give a results in form of the text and highlight who said what?
I think this tabular representation of results is a great idea. I am doing it too along with the text. Thanks
That was helpful was struggling to separate the discussion from the findings
this was very useful, Thank you.
Very helpful, I am confident to write my results chapter now.
It is so helpful! It is a good job. Thank you very much!
Very useful, well explained. Many thanks.
Hello, I appreciate the way you provided a supportive comments about qualitative results presenting tips
I loved this! It explains everything needed, and it has helped me better organize my thoughts. What words should I not use while writing my results section, other than subjective ones.
Thanks a lot, it is really helpful
Thank you so much dear, i really appropriate your nice explanations about this.
Thank you so much for this! I was wondering if anyone could help with how to prproperly integrate quotations (Excerpts) from interviews in the finding chapter in a qualitative research. Please GradCoach, address this issue and provide examples.
what if I’m not doing any interviews myself and all the information is coming from case studies that have already done the research.
Very helpful thank you.
This was very helpful as I was wondering how to structure this part of my dissertation, to include the quotes… Thanks for this explanation
This is very helpful, thanks! I am required to write up my results chapters with the discussion in each of them – any tips and tricks for this strategy?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
5 Writing Up the Research Findings
- Published: October 2022
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
A common problem in qualitative interviewing concerns how to reduce or condense the often large amounts of data in interview studies. Chapter 5, on writing up the research findings, uses this problem as a springboard for describing more generally how to report research findings in ways that are both compelling and rigorous. The chapter refers to examples of findings that are based on theoretical readings of qualitative data and also discusses ways of presenting findings that are much freer from social science theory. There are numerous ways of writing up the findings, among them ways that make use of inductive, deductive, and abductive strategies, which are all discussed. The chapter also advocates the use of displays, which are graphic presentations of large amounts of data in ways that include what is central and makes transparent what has been left out.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Clear Study Aims and Hypotheses in a Research Paper
Affiliations.
- 1 From the Department of Anesthesiology, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
- 2 Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care, Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas.
- PMID: 31206443
- DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004230
Publication types
- Anesthesia, Spinal*
- Cesarean Section
- Research Design
- Ultrasonography
- Published: 28 March 2024
Using the consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to integrate innovation recipients’ perspectives into the implementation of a digital version of the spinal cord injury health maintenance tool: a qualitative analysis
- John A Bourke 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- K. Anne Sinnott Jerram 1 , 2 ,
- Mohit Arora 1 , 2 ,
- Ashley Craig 1 , 2 &
- James W Middleton 1 , 2 , 4 , 5
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 390 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
111 Accesses
Metrics details
Despite advances in managing secondary health complications after spinal cord injury (SCI), challenges remain in developing targeted community health strategies. In response, the SCI Health Maintenance Tool (SCI-HMT) was developed between 2018 and 2023 in NSW, Australia to support people with SCI and their general practitioners (GPs) to promote better community self-management. Successful implementation of innovations such as the SCI-HMT are determined by a range of contextual factors, including the perspectives of the innovation recipients for whom the innovation is intended to benefit, who are rarely included in the implementation process. During the digitizing of the booklet version of the SCI-HMT into a website and App, we used the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) as a tool to guide collection and analysis of qualitative data from a range of innovation recipients to promote equity and to inform actionable findings designed to improve the implementation of the SCI-HMT.
Data from twenty-three innovation recipients in the development phase of the SCI-HMT were coded to the five CFIR domains to inform a semi-structured interview guide. This interview guide was used to prospectively explore the barriers and facilitators to planned implementation of the digital SCI-HMT with six health professionals and four people with SCI. A team including researchers and innovation recipients then interpreted these data to produce a reflective statement matched to each domain. Each reflective statement prefaced an actionable finding, defined as alterations that can be made to a program to improve its adoption into practice.
Five reflective statements synthesizing all participant data and linked to an actionable finding to improve the implementation plan were created. Using the CFIR to guide our research emphasized how partnership is the key theme connecting all implementation facilitators, for example ensuring that the tone, scope, content and presentation of the SCI-HMT balanced the needs of innovation recipients alongside the provision of evidence-based clinical information.
Conclusions
Understanding recipient perspectives is an essential contextual factor to consider when developing implementation strategies for healthcare innovations. The revised CFIR provided an effective, systematic method to understand, integrate and value recipient perspectives in the development of an implementation strategy for the SCI-HMT.
Trial registration
Peer Review reports
Injury to the spinal cord can occur through traumatic causes (e.g., falls or motor vehicle accidents) or from non-traumatic disease or disorder (e.g., tumours or infections) [ 1 ]. The onset of a spinal cord injury (SCI) is often sudden, yet the consequences are lifelong. The impact of a SCI is devastating, with effects on sensory and motor function, bladder and bowel function, sexual function, level of independence, community participation and quality of life [ 2 ]. In order to maintain good health, wellbeing and productivity in society, people with SCI must develop self-management skills and behaviours to manage their newly acquired chronic health condition [ 3 ]. Given the increasing emphasis on primary health care and community management of chronic health conditions, like SCI, there is a growing responsibility on all parties to promote good health practices and minimize the risks of common health complications in their communities.
To address this need, the Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool (SCI-HMT) was co-designed between 2018 and 2023 with people living with SCI and their General Practitioners (GPs) in NSW, Australia [ 4 ] The aim of the SCI-HMT is to support self-management of the most common and arguably avoidable potentially life-threatening complications associated with SCI, such as mental health crises, autonomic dysreflexia, kidney infections and pressure injuries. The SCI-HMT provides comprehensible information with resources about the six highest priority health areas related to SCI (as indicated by people with SCI and GPs) and was developed over two phases. Phase 1 focused on developing a booklet version and Phase 2 focused on digitizing this content into a website and smartphone app [ 4 , 5 ].
Enabling the successful implementation of evidence-based innovations such as the SCI-HMT is inevitably influenced by contextual factors: those dynamic and diverse array of forces within real-world settings working for or against implementation efforts [ 6 ]. Contextual factors often include background environmental elements in which an intervention is situated, for example (but not limited to) demographics, clinical environments, organisational culture, legislation, and cultural norms [ 7 ]. Understanding the wider context is necessary to identify and potentially mitigate various challenges to the successful implementation of those innovations. Such work is the focus of determinant frameworks, which focus on categorising or classing groups of contextual determinants that are thought to predict or demonstrate an effect on implementation effectiveness to better understand factors that might influence implementation outcomes [ 8 ].
One of the most highly cited determinant frameworks is the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 9 ], which is often posited as an ideal framework for pre-implementation preparation. Originally published in 2009, the CFIR has recently been subject to an update by its original authors, which included a literature review, survey of users, and the creation of an outcome addendum [ 10 , 11 ]. A key contribution from this revision was the need for a greater focus on the place of innovation recipients, defined as the constituency for whom the innovation is being designed to benefit; for example, patients receiving treatment, students receiving a learning activity. Traditionally, innovation recipients are rarely positioned as key decision-makers or innovation implementers [ 8 ], and as a consequence, have not often been included in the application of research using frameworks, such as the CFIR [ 11 ].
Such power imbalances within the intersection of healthcare and research, particularly between those receiving and delivering such services and those designing such services, have been widely reported [ 12 , 13 ]. There are concerted efforts within health service development, health research and health research funding, to rectify this power imbalance [ 14 , 15 ]. Importantly, such efforts to promote increased equitable population impact are now being explicitly discussed within the implementation science literature. For example, Damschroder et al. [ 11 ] has recently argued for researchers to use the CFIR to collect data from innovation recipients, and that, ultimately, “equitable population impact is only possible when recipients are integrally involved in implementation and all key constituencies share power and make decisions together” (p. 7). Indeed, increased equity between key constituencies and partnering with innovation recipients promotes the likelihood of sustainable adoption of an innovation [ 4 , 12 , 14 ].
There is a paucity of work using the updated CFIR to include and understand innovation recipients’ perspectives. To address this gap, this paper reports on a process of using the CFIR to guide the collection of qualitative data from a range of innovation recipients within a wider co-design mixed methods study examining the development and implementation of SCI-HMT. The innovation recipients in our research are people living with SCI and GPs. Guided by the CFIR domains (shown in the supplementary material), we used reflexive thematic analysis [ 16 ]to summarize data into reflective summaries, which served to inform actionable findings designed to improve implementation of the SCI-HMT.
The procedure for this research is multi-stepped and is summarized in Fig. 1 . First, we mapped retrospective qualitative data collected during the development of the SCI-HMT [ 4 ] against the five domains of the CFIR in order to create a semi-structured interview guide (Step 1). Then, we used this interview guide to collect prospective data from health professionals and people with SCI during the development of the digital version of the SCI-HMT (Step 2) to identify implementation barriers and facilitators. This enabled us to interpret a reflective summary statement for each CFIR domain. Lastly, we developed an actionable finding for each domain summary. The first (RESP/18/212) and second phase (2019/ETH13961) of the project received ethical approval from The Northern Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee. The reporting of this study was conducted in line with the consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) guidelines [ 17 ]. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Procedure of synthesising datasets to inform reflective statements and actionable findings. a Two health professionals had a SCI (one being JAB); b Two co-design researchers had a SCI (one being JAB)
Step one: retrospective data collection and analysis
We began by retrospectively analyzing the data set (interview and focus group transcripts) from the previously reported qualitative study from the development phase of the SCI-HMT [ 4 ]. This analysis was undertaken by two team members (KASJ and MA). KASJ has a background in co-design research. Transcript data were uploaded into NVivo software (Version 12: QSR International Pty Ltd) and a directed content analysis approach [ 18 ] was applied to analyze categorized data a priori according to the original 2009 CFIR domains (intervention characteristics, outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals, and process of implementation) described by Damschroder et al. [ 9 ]. This categorized data were summarized and informed the specific questions of a semi-structured interview guide. The final output of step one was an interview guide with context-specific questions arranged according to the CFIR domains (see supplementary file 1). The interview was tested with two people with SCI and one health professional.
Step two: prospective data collection and analysis
In the second step, semi-structured interviews were conducted by KASJ (with MA as observer) with consenting healthcare professionals who had previously contributed to the development of the SCI-HMT. Healthcare professionals included GPs, Nurse Consultants, Specialist Physiotherapists, along with Health Researchers (one being JAB). In addition, a focus group was conducted with consenting individuals with SCI who had contributed to the SCI-HMT design and development phase. The interview schedule designed in step one above guided data collection in all interviews and the focus group.
The focus group and interviews were conducted online, audio recorded, transcribed verbatim and uploaded to NVivo software (Version 12: QSR International Pty Ltd). All data were subject to reflexive, inductive and deductive thematic analysis [ 16 , 19 ] to better understand participants’ perspectives regarding the potential implementation of the SCI-HMT. First, one team member (KASJ) read transcripts and began a deductive analysis whereby data were organized into CFIR domains-specific dataset. Second, KASJ and JAB analyzed this domain-specific dataset to inductively interpret a reflective statement which served to summarise all participant responses to each domain. The final output of step two was a reflective summary statement for each CFIR domain.
Step three: data synthesis
In the third step we aimed to co-create an actionable finding (defined as tangible alteration that can be made to a program, in this case the SCI-HMT [ 20 ]) based on each domain-specific reflective statement. To achieve this, three codesign researchers (KAS and JAB with one person with SCI from Step 2 (deidentified)) focused on operationalising each reflective statement into a recommended modification for the digital version of the SCI-HMT. This was an iterative process guided by the specific CFIR domain and construct definitions, which we deemed salient and relevant to each reflective statement (see Table 2 for example). Data synthesis involved line by line analysis, group discussion, and repeated refinement of actionable findings. A draft synthesis was shared with SCI-HMT developers (JWM and MA) and refinement continued until consensus was agreed on. The final outputs of step three were an actionable finding related to each reflective statement for each CFIR domain.
The characteristics of both the retrospective and prospective study participants are shown in Table 1 . The retrospective data included data from a total of 23 people: 19 people with SCI and four GPs. Of the 19 people with SCI, 12 participated in semi-structured interviews, seven participated in the first focus group, and four returned to the second focus group. In step 2, four people with SCI participated in a focus group and six healthcare professionals participated in one-on-one semi-structured interviews. Two of the healthcare professionals (a GP and a registrar) had lived experience of SCI, as did one researcher (JAB). All interviews and focus groups were conducted either online or in-person and ranged in length between 60 and 120 min.
In our overall synthesis, we actively interpreted five reflective statements based on the updated CFIR domain and construct definitions by Damschroder et al. [ 11 ]. Table 2 provides a summary of how we linked the updated CFIR domain and construct definitions to the reflective statements. We demonstrate this process of co-creation below, including illustrative quotes from participants. Importantly, we guide readers to the actionable findings related to each reflective statement in Table 2 . Each actionable statement represents an alteration that can be made to a program to improve its adoption into practice.
Participants acknowledged that self-management is a major undertaking and very demanding, as one person with SCI said, “ we need to be informed without being terrified and overwhelmed”. Participants felt the HMT could indeed be adapted, tailored, refined, or reinvented to meet local needs. For example, another person with SCI remarked:
“Education needs to be from the get-go but in bite sized pieces from all quarters when readiness is most apparent… at all time points , [not just as a] a newbie tool or for people with [long-term impairment] ” (person with SCI_02).
Therefore, the SCI-HMT had to balance complexity of content while still being accessible and engaging, and required input from both experts in the field and those with lived experience of SCI, for example, a clinical nurse specialist suggested:
“it’s essential [the SCI-HMT] is written by experts in the field as well as with collaboration with people who have had a, you know, the lived experience of SCI” (healthcare professional_03).
Furthermore, the points of contact with healthcare for a person with SCI can be challenging to navigate and the SCI-HMT has the potential to facilitate a smoother engagement process and improve communication between people with SCI and healthcare services. As a GP suggested:
“we need a tool like this to link to that pathway model in primary health care , [the SCI-HMT] it’s a great tool, something that everyone can read and everyone’s reading the same thing” (healthcare professional_05).
Participants highlighted that the ability of the SCI-HMT to facilitate effective communication was very much dependent on the delivery format. The idea of digitizing the SCI-HMT garnered equal support from people with SCI and health care professionals, with one participant with SCI deeming it to be “ essential” ( person with SCI_01) and a health professional suggesting a “digitalized version will be an advantage for most people” (healthcare professional_02).
Outer setting
There was strong interest expressed by both people with SCI and healthcare professionals in using the SCI-HMT. The fundamental premise was that knowledge is power and the SCI-HMT would have strong utility in post-acute rehabilitation services, as well as primary care. As a person with SCI said,
“ we need to leave the [spinal unit] to return to the community with sufficient knowledge, and to know the value of that knowledge and then need to ensure primary healthcare provider [s] are best informed” (person with SCI_04).
The value of the SCI-HMT in facilitating clear and effective communication and shared decision-making between healthcare professionals and people with SCI was also highlighted, as shown by the remarks of an acute nurse specialist:
“I think this tool is really helpful for the consumer and the GP to work together to prioritize particular tests that a patient might need and what the regularity of that is” (healthcare professional_03).
Engaging with SCI peer support networks to promote the SCI-HMT was considered crucial, as one person with SCI emphasized when asked how the SCI-HMT might be best executed in the community, “…peers, peers and peers” (person with SCI_01). Furthermore, the layering of content made possible in the digitalized version will allow for the issue of approachability in terms of readiness for change, as another person with SCI said:
“[putting content into a digital format] is essential and required and there is a need to put summarized content in an App with links to further web-based information… it’s not likely to be accessed otherwise” (person with SCI_02).
Inner setting
Participants acknowledged that self-management of health and well-being is substantial and demanding. It was suggested that the scope, tone, and complexity of the SCI-HMT, while necessary, could potentially be resisted by people with SCI if they felt overwhelmed, as one person with SCI described:
“a manual that is really long and wordy, like, it’s [a] health metric… they maybe lack the health literacy to, to consume the content then yes, it would impede their readiness for [self-management]” (person with SCI_02).
Having support from their GPs was considered essential, and the HMT could enable GP’s, who are under time pressure, to provide more effective health and advice to their patients, as one GP said:
“We GP’s are time poor, if you realize then when you’re time poor you look quickly to say oh this is a patient tool - how can I best use this?” (healthcare professional_05).
Furthermore, health professional skills may be best used with the synthesis of self-reported symptoms, behaviors, or observations. A particular strength of a digitized version would be its ability to facilitate more streamlined communication between a person with SCI and their primary healthcare providers developing healthcare plans, as an acute nurse specialist reflected, “ I think that a digitalized version is essential with links to primary healthcare plans” (healthcare professional_03).
Efficient communication with thorough assessment is essential to ensure serious health issues are not missed, as findings reinforce that the SCI-HMT is an educational tool, not a replacement for healthcare services, as a clinical nurse specialist commented, “ remember, things will go wrong– people end up very sick and in acute care “ (healthcare professional_02).
The SCI-HMT has the potential to provide a pathway to a ‘hope for better than now’ , a hope to ‘remain well’ and a hope to ‘be happy’ , as the informant with SCI (04) declared, “self-management is a long game, if you’re keeping well, you’ve got that possibility of a good life… of happiness”. Participants with SCI felt the tool needed to be genuine and
“acknowledge the huge amount of adjustment required, recognizing that dealing with SCI issues is required to survive and live a good life” (person with SCI_04).
However, there is a risk that an individual is completely overwhelmed by the scale of the SCI-HMT content and the requirement for lifelong vigilance. Careful attention and planning were paid to layering the information accordingly to support self-management as a ‘long game’, which one person with SCI reflected in following:
“the first 2–3 year [period] is probably the toughest to get your head around the learning stuff, because you’ve got to a stage where you’re levelling out, and you’ve kind of made these promises to yourself and then you realize that there’s no quick fix” (person with SCI_01).
It was decided that this could be achieved by providing concrete examples and anecdotes from people with SCI illustrating that a meaningful, healthy life is possible, and that good health is the bedrock of a good life with SCI.
There was universal agreement that the SCI-HMT is aspirational and that it has the potential to improve knowledge and understanding for people with SCI, their families, community workers/carers and primary healthcare professionals, as a GP remarked:
“[different groups] could just read it and realize, ‘Ahh, OK that’s what that means… when you’re doing catheters. That’s what you mean when you’re talking about bladder and bowel function or skin care” (healthcare professional_04).
Despite the SCI-HMT providing an abundance of information and resources to support self-management, participants identified four gaps: (i) the priority issue of sexuality, including pleasure and identity, as one person with SCI remarked:
“ sexuality is one of the biggest issues that people with SCI often might not speak about that often cause you know it’s awkward for them. So yeah, I think that’s a that’s a serious issue” (person with SCI_03).
(ii) consideration of the taboo nature of bladder and bowel topics for indigenous people, (iii) urgent need to ensure links for SCI-HMT care plans are compatible with patient management systems, and (iv) exercise and leisure as a standalone topic taking account of effects of physical activity, including impact on mental health and wellbeing but more especially for fun.
To ensure longevity of the SCI-HMT, maintaining a partnership between people with SCI, SCI community groups and both primary and tertiary health services is required for liaison with the relevant professional bodies, care agencies, funders, policy makers and tertiary care settings to ensure ongoing education and promotion of SCI-HMT is maintained. For example, delivery of ongoing training of healthcare professionals to both increase the knowledge base of primary healthcare providers in relation to SCI, and to promote use of the tools and resources through health communities. As a community nurse specialist suggested:
“ improving knowledge in the health community… would require digital links to clinical/health management platforms” (healthcare professional_02).
In a similar vein, a GP suggested:
“ our common GP body would have continuing education requirements… especially if it’s online, in particular for the rural, rural doctors who you know, might find it hard to get into the city” (healthcare professional_04).
The successful implementation of evidence-based innovations into practice is dependent on a wide array of dynamic and active contextual factors, including the perspectives of the recipients who are destined to use such innovations. Indeed, the recently updated CFIR has called for innovation recipient perspectives to be a priority when considering contextual factors [ 10 , 11 ]. Understanding and including the perspectives of those the innovation is being designed to benefit can promote increased equity and validation of recipient populations, and potentially increase the adoption and sustainability of innovations.
In this paper, we have presented research using the recently updated CFIR to guide the collection of innovation recipients’ perspectives (including people with SCI and GPs working in the community) regarding the potential implementation barriers and facilitators of the digital version of the SCI-HMT. Collected data were synthesized to inform actionable findings– tangible ways in which the SCI-HMT could be modified according of the domains of the CFIR (e.g., see Keith et al. [ 20 ]). It is important to note that we conducted this research using the original domains of the CFIR [ 9 ] prior to Damschroder et al. publishing the updated CFIR [ 11 ]. However, in our analysis we were able to align our findings to the revised CFIR domains and constructs, as Damschroder [ 11 ] suggests, constructs can “be mapped back to the original CFIR to ensure longitudinal consistency” (p. 13).
One of the most poignant findings from our analyses was the need to ensure the content of the SCI-HMT balanced scientific evidence and clinical expertise with lived experience knowledge. This balance of clinical and experiential knowledge demonstrated genuine regard for lived experience knowledge, and created a more accessible, engaging, useable platform. For example, in the innovation and individual domains, the need to include lived experience quotes was immediately apparent once the perspective of people with SCI was included. It was highlighted that while the SCI-HMT will prove useful to many parties at various stages along the continuum of care following onset of SCI, there will be those individuals that are overwhelmed by the scale of the content. That said, the layering of information facilitated by the digitalized version is intended to provide an ease of navigation through the SCI-HMT and enable a far greater sense of control over personal health and wellbeing. Further, despite concerns regarding e-literacy the digitalized version of the SCI-HMT is seen as imperative for accessibility given the wide geographic diversity and recent COVID pandemic [ 21 ]. While there will be people who are challenged by the technology, the universally acceptable use of the internet is seen as less of a barrier than printed material.
The concept of partnership was also apparent within the data analysis focusing on the outer and inner setting domains. In the outer setting domain, our findings emphasized the importance of engaging with SCI community groups, as well as primary and tertiary care providers to maximize uptake at all points in time from the phase of subacute rehabilitation onwards. While the SCI-HMT is intended for use across the continuum of care from post-acute rehabilitation onwards, it may be that certain modules are more relevant at different times, and could serve as key resources during the hand over between acute care, inpatient rehabilitation and community reintegration.
Likewise, findings regarding the inner setting highlighted the necessity of a productive partnership between GPs and individuals with SCI to address the substantial demands of long-term self-management of health and well-being following SCI. Indeed, support is crucial, especially when self-management is the focus. This is particularly so in individuals living with complex disability following survival after illness or injury [ 22 ], where health literacy has been found to be a primary determinant of successful health and wellbeing outcomes [ 23 ]. For people with SCI, this tool potentially holds the most appeal when an individual is ready and has strong partnerships and supportive communication. This can enable potential red flags to be recognized earlier allowing timely intervention to avert health crises, promoting individual well-being, and reducing unnecessary demands on health services.
While the SCI-HMT is an educational tool and not meant to replace health services, findings suggest the current structure would lead nicely to having the conversation with a range of likely support people, including SCI peers, friends and family, GP, community nurses, carers or via on-line support services. The findings within the process domain underscored the importance of ongoing partnership between innovation implementers and a broad array of innovation recipients (e.g., individuals with SCI, healthcare professionals, family, funding agencies and policy-makers). This emphasis on partnership also addresses recent discussions regarding equity and the CFIR. For example, Damschroder et al. [ 11 ] suggests that innovation recipients are too often not included in the CFIR process, as the CFIR is primarily seen as a tool intended “to collect data from individuals who have power and/or influence over implementation outcomes” (p. 5).
Finally, we feel that our inclusion of innovation recipients’ perspectives presented in this article begins to address the notion of equity in implementation, whereby the inclusion of recipient perspectives in research using the CFIR both validates, and increases, the likelihood of sustainable adoption of evidence-based innovations, such as the SCI-HMT. We have used the CFIR in a pragmatic way with an emphasis on meaningful engagement between the innovation recipients and the research team, heeding the call from Damschroder et al. [ 11 ], who recently argued for researchers to use the CFIR to collect data from innovation recipients. Adopting this approach enabled us to give voice to innovation recipient perspectives and subsequently ensure that the tone, scope, content and presentation of the SCI-HMT balanced the needs of innovation recipients alongside the provision of evidence-based clinical information.
Our research is not without limitations. While our study was successful in identifying a number of potential barriers and facilitators to the implementation of the SCI-HMT, we did not test any implementation strategies to impact determinants, mechanisms, or outcomes. This will be the focus of future research on this project, which will investigate the impact of implementation strategies on outcomes. Focus will be given to the context-mechanism configurations which give rise to particular outcomes for different groups in certain circumstances [ 7 , 24 ]. A second potential concern is the relatively small sample size of participants that may not allow for saturation and generalizability of the findings. However, both the significant impact of secondary health complications for people with SCI and the desire for a health maintenance tool have been established in Australia [ 2 , 4 ]. The aim our study reported in this article was to achieve context-specific knowledge of a small sample that shares a particular mutual experience and represents a perspective, rather than a population [ 25 , 26 ]. We feel our findings can stimulate discussion and debate regarding participant-informed approaches to implementation of the SCI-HMT, which can then be subject to larger-sample studies to determine their generalisability, that is, their external validity. Notably, future research could examine the interaction between certain demographic differences (e.g., gender) of people with SCI and potential barriers and facilitators to the implementation of the SCI-HMT. Future research could also include the perspectives of other allied health professionals working in the community, such as occupational therapists. Lastly, while our research gave significant priority to recipient viewpoints, research in this space would benefit for ensuring innovation recipients are engaged as genuine partners throughout the entire research process from conceptualization to implementation.
Employing the CFIR provided an effective, systematic method for identifying recipient perspectives regarding the implementation of a digital health maintenance tool for people living with SCI. Findings emphasized the need to balance clinical and lived experience perspectives when designing an implementation strategy and facilitating strong partnerships with necessary stakeholders to maximise the uptake of SCI-HMT into practice. Ongoing testing will monitor the uptake and implementation of this innovation, specifically focusing on how the SCI-HMT works for different users, in different contexts, at different stages and times of the rehabilitation journey.
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available available upon request and with permission gained from the project Steering Committee.
Abbreviations
spinal cord injury
HMT-Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
Kirshblum S, Vernon WL. Spinal Cord Medicine, Third Edition. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2018.
Middleton JW, Arora M, Kifley A, Clark J, Borg SJ, Tran Y, et al. Australian arm of the International spinal cord Injury (Aus-InSCI) Community Survey: 2. Understanding the lived experience in people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2022;60(12):1069–79.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Craig A, Nicholson Perry K, Guest R, Tran Y, Middleton J. Adjustment following chronic spinal cord injury: determining factors that contribute to social participation. Br J Health Psychol. 2015;20(4):807–23.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Middleton JW, Arora M, Jerram KAS, Bourke J, McCormick M, O’Leary D, et al. Co-design of the Spinal Cord Injury Health Maintenance Tool to support Self-Management: a mixed-methods Approach. Top Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 2024;30(1):59–73.
Middleton JW, Arora M, McCormick M, O’Leary D. Health maintenance Tool: how to stay healthy and well with a spinal cord injury. A tool for consumers by consumers. 1st ed. Sydney, NSW Australia: Royal Rehab and The University of Sydney; 2020.
Nilsen P, Bernhardsson S. Context matters in implementation science: a scoping review of determinant frameworks that describe contextual determinants for implementation outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):189.
Jagosh J. Realist synthesis for Public Health: building an Ontologically Deep understanding of how Programs Work, for whom, and in which contexts. Annu Rev Public Health. 2019;40(1):361–72.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):53.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4(1):50.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Opra Widerquist MA, Lowery JC. Conceptualizing outcomes for use with the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR): the CFIR outcomes Addendum. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):7.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Widerquist MAO, Lowery JC. The updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):75.
Plamondon K, Ndumbe-Eyoh S, Shahram S. 2.2 Equity, Power, and Transformative Research Coproduction. Research Co-Production in Healthcare2022. p. 34–53.
Verville L, Cancelliere C, Connell G, Lee J, Munce S, Mior S, et al. Exploring clinicians’ experiences and perceptions of end-user roles in knowledge development: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):926.
Gainforth HL, Hoekstra F, McKay R, McBride CB, Sweet SN, Martin Ginis KA, et al. Integrated Knowledge Translation Guiding principles for conducting and Disseminating Spinal Cord Injury Research in Partnership. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(4):656–63.
Langley J, Knowles SE, Ward V. Conducting a Research Coproduction Project. Research Co-Production in Healthcare2022. p. 112– 28.
Braun V, Clarke V. One size fits all? What counts as quality practice in (reflexive) thematic analysis? Qualitative Research in Psychology. 2020:1–25.
Tong A, Sainsbury p, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qulaitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. NursingPlus Open. 2016;2:8–14.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Keith RE, Crosson JC, O’Malley AS, Cromp D, Taylor EF. Using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) to produce actionable findings: a rapid-cycle evaluation approach to improving implementation. Implement Science: IS. 2017;12(1):15.
Choukou M-A, Sanchez-Ramirez DC, Pol M, Uddin M, Monnin C, Syed-Abdul S. COVID-19 infodemic and digital health literacy in vulnerable populations: a scoping review. Digit HEALTH. 2022;8:20552076221076927.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Daniels N. Just Health: Meeting Health needs fairly. Cambridge University Press; 2007. p. 397.
Parker SM, Stocks N, Nutbeam D, Thomas L, Denney-Wilson E, Zwar N, et al. Preventing chronic disease in patients with low health literacy using eHealth and teamwork in primary healthcare: protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2018;8(6):e023239–e.
Salter KL, Kothari A. Using realist evaluation to open the black box of knowledge translation: a state-of-the-art review. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):115.
Sebele-Mpofu FY. The Sampling Conundrum in qualitative research: can Saturation help alleviate the controversy and alleged subjectivity in Sampling? Int’l J Soc Sci Stud. 2021;9:11.
Malterud K, Siersma VD, Guassora AD. Sample size in qualitative interview studies: guided by Information Power. Qual Health Res. 2015;26(13):1753–60.
Acknowledgements
Authors of this study would like to thank all the consumers with SCI and healthcare professionals for their invaluable contribution to this project. Their participation and insights have been instrumental in shaping the development of the SCI-HMT. The team also acknowledges the support and guidance provided by the members of the Project Steering Committee, as well as the partner organisations, including NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation, and icare NSW. Author would also like to acknowledge the informant group with lived experience, whose perspectives have enriched our understanding and informed the development of SCI-HMT.
The SCI Wellness project was a collaborative project between John Walsh Centre for Rehabilitation Research at The University of Sydney and Royal Rehab. Both organizations provided in-kind support to the project. Additionally, the University of Sydney and Royal Rehab received research funding from Insurance and Care NSW (icare NSW) to undertake the SCI Wellness Project. icare NSW do not take direct responsibility for any of the following: study design, data collection, drafting of the manuscript, or decision to publish.
John Walsh Centre for Rehabilitation Research, Northern Sydney Local Health District, St Leonards, NSW, Australia
John A Bourke, K. Anne Sinnott Jerram, Mohit Arora, Ashley Craig & James W Middleton
The Kolling Institute, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Burwood Academy Trust, Burwood Hospital, Christchurch, New Zealand
John A Bourke
Royal Rehab, Ryde, NSW, Australia
James W Middleton
State Spinal Cord Injury Service, NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation, St Leonards, NSW, Australia
Contributions
Project conceptualization: KASJ, MA, JWM; project methodology: JWM, MA, KASJ, JAB; data collection: KASJ and MA; data analysis: KASJ, JAB, MA, JWM; writing—original draft preparation: JAB; writing—review and editing: JAB, KASJ, JWM, MA, AC; funding acquisition: JWM, MA. All authors contributed to the revision of the paper and approved the final submitted version.
Correspondence to John A Bourke .
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The first (RESP/18/212) and second phase (2019/ETH13961) of the project received ethical approval from The Northern Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee. All participants provided informed, written consent. All data were to be retained for 7 years (23rd May 2030).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
MA part salary (from Dec 2018 to Dec 2023), KASJ part salary (July 2021 to Dec 2023) and JAB part salary (Jan 2022 to Aug 2022) was paid from the grant monies. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s note.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Cite this article.
Bourke, J.A., Jerram, K.A.S., Arora, M. et al. Using the consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to integrate innovation recipients’ perspectives into the implementation of a digital version of the spinal cord injury health maintenance tool: a qualitative analysis. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 390 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10847-x
Received : 14 August 2023
Accepted : 11 March 2024
Published : 28 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10847-x
- Spinal Cord injury
- Self-management
- Innovation recipients
- Secondary health conditions
- Primary health care
- Evidence-based innovations
- Actionable findings
- Consolidated Framework for implementation research
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Published: 01 April 2024
Midwives’ lived experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini: a qualitative study
- Annie M. Temane 1 ,
- Fortunate N. Magagula 2 &
- Anna G. W. Nolte 1
BMC Women's Health volume 24 , Article number: 207 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Midwives encounter various difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. The study aimed to explore and describe midwives’ experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini.
A qualitative, exploratory, descriptive, contextual research design with a phenomenological approach was followed. Twelve midwives working in maternal health facilities in the Hhohho and Manzini regions in Eswatini were interviewed. Purposive sampling was used to select midwives to participate in the research. In-depth phenomenological interviews were conducted, and Giorgi’s descriptive phenomenological method was used for data analysis.
Three themes emerged from the data analysis: midwives experienced physical and emotional strain in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities, they experienced frustration due to the lack of equipment to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities, and they faced challenges in providing support and holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
Midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium in Eswatini. There is a need to develop and empower midwives with the knowledge and skill to implement guidelines and enact protocols. Moreover, equipment and infrastructure are required to facilitate support and holistic maternity care for women with mobility disabilities.
Globally, few studies have focused on midwives’ views of providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium [ 1 ]. In The Disabled World [ 2 ], the World Health Organisation (WHO) defines ‘disability’ as an umbrella term covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. Furthermore, the WHO defines an ‘impairment’ as a problem in bodily function or structure; an ‘activity limitation’ as a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; and ‘participation restriction’ as a problem experienced by an individual in various life situations [ 2 ]. In this study, mobility disabilities refer to an impairment in the functioning of the upper and lower extremities as experienced by women during pregnancy, labour and the puerperium.
Midwives, as frontline workers in the delivery of maternity care [ 3 ] responsible for the lives of the mother and the baby, are accountable for providing competent and holistic care for women during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. As part of healthcare provision, midwives play an important role in ensuring that every woman, including women with mobility disabilities, receives the best maternity care during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. Moridi et al. [ 4 ] state that women with mobility disabilities are entitled to feel safe, respected and well cared for by midwives, who must be sufficiently prepared to care for these women.
According to the Global Population Report, [ 5 ] more than one billion people have some form of disability. Eswatini is classified as a middle-income setting in the southern African region, measuring 17 000 square kilometres with a population of 1 093 238. Of the population, 76.2% reside in rural areas (833 472), and 23.8% (259 766) reside in urban areas [ 6 ]. The economy is largely agricultural as most industries manufacture agricultural products [ 7 ]. Of the Eswatini population, 146 554 (13%) live with disabilities, with most being women (87 258; 16%), 22,871 (14.1%) and 26,270 (14.3%) of them reside in the Hhohho and Manzini regions respectively [ 8 ]. 15% (125 545) of people with disabilities live in rural areas, and 85% of the disabled population is unemployed [ 8 ], which means most of these individuals are economically disadvantaged. Furthermore, according to the Eswatini Central Statistics Office, 8 26.5% of people with disabilities have a mobility (walking) disability, with 63.5% of these being women.
Midwives may encounter difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities in what may be challenging circumstances [ 9 ]. The WHO [ 10 ] claims people with disabilities do not receive the health services they need and are thus likely to find healthcare providers have inadequate skills. Lawler et al. [ 11 ] argue that ineffective interactions and poor communication with women needing care, particularly among health professionals engaged in providing maternity services, limit these women’s opportunities to participate in decision-making processes during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. According to the University of Johannesburg, [ 12 ] the midwife, together with the mother, have to engage collaboratively in order to come up with opportunities to promote health while removing any challenges that could impede the achievement thereof.
Walsh-Gallagher et al. [ 13 ] postulate that healthcare professionals tend to view women with disabilities as liabilities and regard them as high risk; they often exclude them from the individualised plan of care, which leads to an increase in these women’s fears about their maternity care. These challenges frequently result in health disparities and prevent women with mobility disabilities from receiving optimal maternity care. By exploring midwives’ experiences of this phenomenon, guidelines for support can be developed to extend available knowledge on maternity care for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
Study design
The aim of the study was to explore and describe midwives’ experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini. A qualitative, [ 14 ] exploratory, [ 15 ] descriptive, [ 16 ] contextual [ 17 ] research design with a phenomenological approach [ 18 ] was applied for this study to gain insight and understanding of the research phenomenon [ 19 ]. The phenomenon under study was midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. The participants were approached face-to-face to participate in the study. The researchers followed the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) to report on this qualitative study [ 20 ].
The setting for the study was the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini. The researcher collected data at the site where participants experienced the phenomenon, as emphasised by Yildiz, [ 21 ] within the context in which they were comfortable to be interviewed [ 22 ]. This setting included maternal health facilities in hospitals and public health units.
Population and sampling
The study’s population comprised midwives working in maternal health facilities in hospitals and public health units, that is, one referral hospital and one public health unit in the Hhohho region and two referral hospitals and one public health unit in the Manzini region of Eswatini. Purposive sampling was used to select midwives to participate in the study; [ 16 ] 12 midwives from both regions were included. The midwives were between the ages of 35 and 55, and all midwives were black in race and identified as females. The years of experience in the field ranged between 5 and 15 years. The criteria for inclusion were midwives who had provided maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium for a period of not more than two to three years, willing to participate in the study. The sample size was determined by repetitions of key statements about the research phenomenon during data collection, termed data saturation [ 23 ]. None of the participants refused to participate in the study.
Table 1 summarises the participants’ demographic characteristics.
In-depth phenomenological, face-to-face, individual interviews were conducted to collect data [ 17 ]. The researcher who was a Midwifery lecturer held a Master’s Degree in Maternal and Neonatal science at the time of the study requested approval from the Unit manager to seek permission from the midwives to take part in the study. The midwives were given an information letter which included objectives of the study and the reasons for conducting the study. After recruiting midwives and obtaining their written consent to participate in the study and permission to audio-record the interviews, the researcher set up appointments with them for the interviews, and the data collection process commenced. The central question posed to participants was: How was it for you to care for a woman with a mobility disability during pregnancy, labour and puerperium? A pilot of the tool was performed on the first participant who met the inclusion criteria and possessed the same characteristics as those of the study sample. The pre-testing question yielded positive results, the participant responded to the question asked and there was no need to rephrase it or further test it.
The interviews were conducted from March 2019 to July 2019 and lasted 30–45 min. The researcher conducted interviews until the data became redundant and repetitive, reflecting that saturation had been reached, in congruence with Fouché et al. [ 25 ] In addition, field notes were recorded in a notebook after each in-depth phenomenological interview. No repeat interviews were held. The researcher ensured bracketing by omitting any perceptions from her past experiences that were likely to influence her interpretation of the research findings.
Data analysis
Before data analysis commenced, data were organised in computer files after being transcribed and translated into narrative form. Data from each participant were coded and stored in the relevant file and kept in a safe place; only the researcher could access the information. Back-up copies were made of all the data, and the master copies were stored in a safe to which only the researcher had access.
Data collection and analysis occurred concurrently. The researcher was guided by Giorgi et al.’s [ 26 ] five-step method of data analysis. This entailed the researcher reading all the transcribed data and the entire ‘naïve description’ provided by the participants during the interviews. The demarcation of ‘meaning units’ within narratives followed. In addition, the researcher marked where meaning shifts occurred and transformed meaning units into descriptive expressions. The researcher laid out the general structure of midwives’ experiences. Moreover, an independent coder was provided with the raw data (after signing a confidentiality agreement) to analyse the findings. The researcher and independent coder analysed the data separately and met for a consensus discussion. Both agreed on all the units of analysis, with an inter-coder reliability of 100%.
Measures of trustworthiness
The research was informed by Guba and Lincoln’s [ 27 ] model in relation to credibility, transferability, dependability and confirmability. For credibility, the researcher ensured prolonged engagement in the field [ 28 ], peer debriefing, [ 29 ] member checking, and an external auditor was used [ 25 ]. The study was also presented at a national conference. Transferability refers to the ability to extend the findings of one’s study to comparable environments or participants, as stated by Pitney et al. [ 30 ] The researcher ensured the study’s transferability by providing a richly documented account and in-depth description of all aspects and processes of the study protocol. Data saturation also confirmed transferability [ 23 ]. Dependability is evident in a study when other researchers are able to follow the researcher’s decision trail [ 31 ]. The researcher ensured dependability by densely describing the research process in congruence with Fouché et al.’s [ 25 ] guidelines, so that other researchers can follow similar steps of the same research methodology. Confirmability occurs when the research is judged by the way in which the findings and conclusions achieve their aim and are not the result of the researcher’s prior assumptions and preconceptions [ 32 ]. The researcher ensured this by remaining true to the research process through reflexivity and not compromising the research process in any way [ 28 ]. In addition, the researcher engaged an independent coder and provided a chain of evidence of the entire research process to enable an audit. Therefore, all forms of collected data, including raw data, reflexive journals, [ 29 ] notes and transcriptions, were recorded.
Ethical clearance to conduct this study was obtained from the University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Sciences Higher Degrees Committee (ref. no. HDC-01-50-2018), University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Research Ethics Committee (ref. no. REC-01-82-2018), and the Eswatini National Health Research Review Board (ref. no. NHRRB982/2018). The researcher applied and adhered to the four principles to be considered when conducting research: autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence and justice [ 33 ]. Autonomy was adhered to by affording the participants the right to choose to participate in the study and by signing a written informed consent form a week after it was given to them before the interviews commenced. Beneficence was ensured through doing good and doing no harm to participants by prioritising the participants’ interests above those of the researcher, and did not engage in any practice that jeopardised their rights. Non-maleficence was observed by eradicating any possible harmful risks in the study; the researcher ensured the safety of the participants by conducting interviews in a familiar, private environment where they felt free and safe from harm. Furthermore, justice was observed by treating all participants equally regardless of their biographical, social and economic status.
Three themes and categories emerged from the data analysis. Table 2 summarises the themes and categories of midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini.
Theme 1: physical and emotional efforts required from midwives to provide maternity care to women with mobility disabilities
Category 1.1: midwives experienced that woman with mobility disabilities needed assistance getting onto the bed during labour and delivery.
According to the participants, caring for women with mobility disabilities weighed heavily on them physically as they were required to assist the women onto delivery beds, which were too high for the women to climb up on their own:
“The beds are too high, they need to be adjustable…unless you change her to another room, we only have one in the other room…but to be honest she delivered on the same high bed with the help…It’s uncomfortable even with me who is normal, how about someone who has a disability? Getting the woman onto the bed is also uncomfortable for us we end up having pain on our backs.” (M3) . “The challenge is that I couldn’t help her to climb on to the bed, because I needed someone to assist when she came for postnatal care as she was even carrying 3 babies, I didn’t know what to do…I eventually went out and asked for assistance from my colleague…” (M10) . “I believe that the equipment should accommodate the women with disability, however, ours is not accommodative to the women…there are no special delivery beds, specifically designed for them because in my opinion the beds have to be shorter so they can be able to get on to them easily…yes so that they can be able to climb on the beds” (M1) .
Category 1.2: midwives experienced challenges in manoeuvring women with mobility disabilities during labour
Midwives reported it was difficult to perform some procedures while progressing these women during labour and delivery. This situation called for some adjustment and improvisation on their part, and they were unsure if it was the right thing to do.
“Even though she was a bit uncomfortable and anxious because the leg was just straight and could not bend, I reassured her…She had to remove the artificial leg and remain with the stump. I placed her on the lithotomy position. With the other hand she had to hold on to the ankle of the normal foot, even though it was awkward and difficult to manoeuvre, she managed to deliver the baby.” (M1) . “Luckily for us, she didn’t sustain a tear and we were saved from suturing her cause we foresaw difficulties as how we could have done it as she couldn’t open her thighs well due to the disability…yes I had to get a partner to assist, since she couldn’t even open her thighs. She also couldn’t cooperate possibly because of the pain that is also more reason I asked for my colleague to assist.” (M6) . “…yes…let me make an example, in my case she had a fracture, even if the pelvis was gynaecoid, there were problems of finding the right position for her during delivery, when she had to push the baby out…” (M8) . “The one that I saw did not have one leg. She had come for her postnatal care. We assisted and her on the couch, with my colleague. Since she couldn’t keep her legs open, I asked my colleague to keep one of her legs open whilst I examined her.” (M12) .
Category 1.3: midwives experienced anxiety and the need to exercise patience when caring for women with mobility disabilities
The participants experienced an emotional and psychological burden when caring for women with mobility disabilities. They felt unqualified and foresaw difficulties that triggered anxiety, which led to them not knowing what to do and how to handle these women.
“It was during labour…the woman was limping the woman she was on crutches. The moment she came into the ward I am a human being I just felt sorry for her kutsi (as to) how is she going to take care of the baby, and the hand was somehow deformed.” (M3) . “At first its emotionally draining as an individual you cause you start sympathising…(other midwife chips in)…yes you even find yourself saying things just because you pity her, and in the process they get hurt.” (M6) . “It came as a shock and it was my first experience, it came as a shock as to how I was going to help her as even my experience was limited in that area.” (M7) . “As I was taking care of her it became necessary for me to put myself into her shoes and to bear with her considering her situation….When you see her for the first time you would pity her yet she is now used to it.” (M1) .
Theme 2: lack of equipment to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities
Category 2.1: midwives reported a lack of special beds and infrastructure to meet the needs of women with mobility disabilities.
Midwives reported their frustration at the lack of sufficient equipment like special beds and examination tables, tailored for women with mobility disabilities. It was a challenge to provide maternity care for women without this equipment.
“I believe that the infrastructure and equipment should accommodate the women with mobility disability, however, ours is not accommodative to the women…Usually we don’t have the prenatal ward in the maternity, most women who come in the latent phase have to ambulate, or go to the waiting huts and come back when the labour pains are stronger…There are no special delivery beds, specifically designed for them because in my opinion the beds have to be shorter so they can be able to get on to them easily. We do not even have toilets meant for them.” (M1) . “I was anxious as to how was she going to push how to push cause we do not have the right beds when it was time for pushing I asked for assistance…” (M2) . “The challenge is that I couldn’t help her to climb on to the bed, because I needed someone to assist when she came for postnatal care…the beds need to be adjustable so that they are able to be pushed lower for the mother to move from wheel chair to the bed and we pull the bed up again to examine her.” (M11) .
Theme 3: challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour, and puerperium
Category 3.1: midwives reported a lack of guidelines and protocols in caring holistically for women with mobility disabilities.
Midwives emphasised a lack of guidelines, protocols and knowledge about caring holistically for women with mobility disabilities. This resulted in everyone making their own decisions and doing as they saw fit in caring for these women:
“I think during antenatal care they (the women with mobility disabilities) need to be prepared for labour cause for others the pain is extraordinary, apart from the pain threshold, they also face self-esteem issues, they are looked down upon…I only saw that she was disabled during assessment cause nothing was recorded on the antenatal care card.” (M2) . “I was not aware of the disability at first, I only discovered when she was pushing…she was admitted and progressed by another midwife, I only attended to her when she was pushing… there was nothing written on the nurse’s notes/ handover notes about her disability.” (M5) . “There is no normal practice for a woman with mobility disability when they come and they are in labour, I usually admit regardless of the stage of labour or dilatation…It is not a protocol, it’s a midwife’s prerogative.” (M1) . “We assess and come up with our own discretion even in terms of admitting them (women with mobility disability). Some midwives will admit them regardless of the stage of labour and disregard the protocol that women who come into labour have to ambulate if they are in the latent phase.” (M8) . “There is one that came the past 3 days she has 3 children now and we just scheduled her for c/section because we know that she has been having c/section since she started. Just from looking at the way she walked, we could tell that she couldn’t deliver normally.” (M9) .
Category 3.2: midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support women with mobility disabilities during labour and delivery
Consequent to the challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities, midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support these women during labour and delivery.
“It can depend on the patients themselves, they should decide and we need to be flexible for it to happen…as you can see our labour room also has the issue of privacy…we would need to restructure cause we have beds for 5 or more women in labour room…and then bringing someone from outside could be tricky” (M6) . “Maybe…not sure though, that they can bring their relatives, but maybe, considering staffing limitation…also the issue of discrimination and privacy, they (the women with disabilities) might feel we discriminate against them because they are disabled we now treat them differently.” (M7) . “Maybe if she can (bring her relative) but that’s not necessary, because I can always ask my colleague to assist, unless there is no one…” (M12) .
Childbirth is a special experience that requires a personal connection between the midwife and the woman giving birth, characterised by successful communication and respect [ 34 ]. However, the themes identified in the study indicated that midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium based on their limited capacity and preparedness, and lack of protocols to care for these women. They also reported a lack of supportive equipment for women with mobility disabilities. This posed a challenge for them in attending to these women’s specific needs, and they did not always know how to handle the situation appropriately.
One of the themes centred on midwives’ experiences of the physical and emotional efforts required of them to provide maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. They explained women with mobility disabilities required assistance getting onto the bed during labour and delivery, and more manoeuvring was expected of them (as midwives) as they had to adjust their performance and some procedures. The midwives also reported challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium. Konig-Bachmann et al. [ 35 ] reiterate that caring for women with disabilities requires a level of flexibility, adaptation beyond routine procedures, and demands a high degree of improvisation from healthcare providers to ensure high-quality care. Morrison et al. [ 36 ] also found that healthcare providers reported difficulties with equipment when providing healthcare for women with physical disabilities; particularly the beds being too high for them to access. Smeltzer et al. [ 37 ] similarly allude to the importance of educating and training clinicians to equip them with knowledge and technical skills to provide more effective care to women with physical disabilities.
The midwives also shared that labour and deliveries were further complicated by some women with mobility disabilities not being able to cooperate due to the pain they experienced; others could not change position due to their disability. In a study by Sonalkar et al., [ 38 ] healthcare providers described the gynaecologic examination as challenging to complete as it required patience and the ability to be adaptable to different methods and positioning. Similarly, Konig-Bachmann et al. [ 35 ] indicate that in order to provide high-quality care for women with disabilities, healthcare providers need to exercise strong flexibility, adapt beyond routine procedures, and engage in a high degree of improvisation. Byrnes and Hickey [ 39 ] concur with this study’s findings and state that due to mobility restrictions, it may be difficult to assess the fundal height and foetal growth in women with physical disabilities.
Some midwives reported their caregiving role was emotionally draining as they felt sorry and pitied the women with mobility disabilities; thus, they needed to show compassion and reassure them. According to Mgwili et al., [ 40 ] psychoanalytic thinkers associate pity among staff members upon first contact with a physically disabled person as being instigated by personal feelings, stimulated by the disability. The midwives in this study stated they needed to be more patient and adjust their approach to caring for these women. Tarasoff [ 41 ] and Schildberger et al. [ 42 ] reiterated that healthcare providers seemed uncomfortable with women’s disability, consequently failing to offer needed support. According to Sonalkar et al., [ 38 ] healthcare providers reported there would be less fear and concern about hurting women with disabilities if midwives had increased training. Similarly, Mitra et al. [ 43 ] mentioned that healthcare providers had a general lack of confidence in their ability to provide adequate maternity care for women with physical disabilities.
Another theme was midwives’ challenges in providing competent and quality care for women with mobility disabilities due to a lack of equipment, including special beds and examination tables to meet these women’s needs. The examination, labour and delivery beds were too high and could not be adjusted for the women to get on by themselves, or even with the assistance of a midwife. In addition, the midwives reported there was no prenatal ward or waiting huts where they could place these women during the latent phase of labour. The midwives further emphasised there were no special toilets for women with mobility disabilities, which made it hazardous and difficult for them. Mitra et al. [ 43 ] concur on the barriers to providing maternity care to women with physical disabilities presented from health professionals’ perspectives. The authors indicated that participants from their study reported inaccessible equipment, including examination tables, as a barrier, making it more difficult and time-consuming to care for women with physical disabilities. In addition, Sonalkar et al. [ 38 ] said healthcare providers shared their concern about the lack of adjustable examination tables and transfer equipment, thus presenting a barrier to equitable care for women with disabilities.
Midwives further reported a lack of guidelines and protocols. This resulted in everyone making their own decisions and doing as they saw fit in caring for these women, and, in most instances, not recording the disability at all during antenatal care and admission into labour records. They often only discovered that the woman had a mobility disability at a later stage, when they were in labour. Sonalkar et al. [ 38 ] reported that healthcare providers felt frustrated and overwhelmed by the uncertainty of whether they made the correct decisions when caring for women with physical disabilities due to the lack of guidelines forcing them to use their own judgement. Mitra et al. [ 43 ] determined that most healthcare providers reported a lack of maternity practice guidelines for women with physical disabilities. Also, healthcare providers highlighted the importance of learning about disabilities and having a better understanding of a condition, particularly if it is likely to be exacerbated during pregnancy [ 44 ]. The need to make and read the notes on these women’s antenatal care cards or reports was emphasised.
Due to the lack of clear guidelines and protocols in caring for women with mobility disabilities, the midwives reported they sometimes admitted the woman into the labour ward regardless of the stage of labour, while other midwives did not and wanted them to walk around and come back for admission once they are in the active phase of labour. Furthermore, the midwives explained they often referred these women for caesarean sections right away, regardless of whether the woman could deliver normally due to mere panic from just seeing the disability or based on a previous record of surgery. Smeltzer et al. [ 45 ] researched obstetric clinicians’ experiences and educational preparation in caring for pregnant women with physical disabilities, and they agree on the lack of knowledge among health professionals caring for women with mobility disability.
Devkota et al. [ 46 ] also agree regarding midwives’ inefficiency in providing quality care for women with mobility disabilities. They claim healthcare providers often struggle to understand women with disabilities’ needs as they are not formally trained to provide services to this population. These healthcare providers were found to be undertrained in specific skills that would equip them to provide better and more targeted services for women with disabilities.
Consequent to the challenges in providing holistic care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium, midwives experienced challenges in allowing significant others to support these women. They reported that as much as they needed assistance caring for these women, and as much as the women would prefer to have their family members or significant others assisting them, this is not possible due to the lack of privacy, especially in public health facilities. Walsh-Gallager et al.’s [ 13 ] study on the ambiguity of disabled women’s experiences of pregnancy, childbirth and motherhood resonate with this study’s findings. The authors reported that women with disabilities’ partners were denied access or had their visits curtailed on several occasions due to inflexible hospital visiting policies. Redshaw et al. [ 47 ] reiterated the same in their study; disabled women were less likely to say their companion or partner was welcome to visit, let alone provide any form of assistance. In addition, a study by Bassoumah and Mohammad [ 48 ] reported that women with disabilities were denied their spouses’ support while receiving maternity care. Byrnes and Hickey [ 39 ] also concur that every effort should be made to allow women with disabilities who are in labour to receive support from significant others, and they should be active partners in the labour process.
Limitations
The study was limited to two of the four regions of Eswatini, namely Hhohho and Manzini; hence, the results could not be generalised for the whole country. The study also only focused on mobility disabilities due to time constraints and limited funds. Future research could be conducted to cover all other forms of disabilities.
This study focused on midwives’ lived experiences caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. In-depth phenomenological interviews were conducted, the findings were analysed, and themes were established. The findings illustrate that midwives experienced challenges caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. There is a need to develop and implement guidelines to empower midwives with knowledge and skill to provide support and holistic maternity care, and enact protocols. They should also have access to appropriate equipment and infrastructure specifically tailored towards promoting optimal health for women with mobility disabilities.
The data analysed is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
González-Timoneda A, Hernández Hernández V, Pardo Moya S, Alfaro Blazquez R. Experiences and attitudes of midwives during the birth of a pregnant woman with COVID-19 infection: a qualitative study. Women Birth. 2021;34(5):467.
Disabled World. Definitions of disability [home page on the internet]. C2009 [updated 2021; cited 2023 July 26]. Available from: https://disabled-world.com/definitions/disability-definitions.php .
Aune I, Tysland T, Vollheim SA. Norwegian midwives’ experiences of relational continuity of midwifery care in the primary health care service: a qualitative descriptive study. Nordic J Nurs Res. 2021;4(1):5–13.
Moridi M, Pazandeh F, Hajian S, Potrata B. Midwives’ perspectives of respectful maternity care during childbirth: a qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229941 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
United Nations. Background: International Day of Persons with Disabilities. [homepage on the internet]. c2022 [updated 2022 December 1; cited 2023 July 20]. Available from: https://un.org/en/observances/day-of-persons-with-disabilities/background .
Central Statistics Office. Population and housing census: 2017. Volume 3. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2019a.
Central Statistics Office. National accounts estimates. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2018.
Central Statistics Office. Population and housing census: 2017. Volume 6. Mbabane: Swaziland Government Printing Office; 2019b.
Magqadiyane S. Experiences of midwives for caring un-booked pregnant mothers in a maternity unit at a district hospital in the Eastern Cape Province. Advances in reproductive sciences [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 5];8:186–200. https://doi.org/10.4236/arsci.2020.84016 .
World Health Organisation (WHO). Global report on health equity for persons with disabilities. [homepage on the internet]. c2022 [updated 2022 December 2; cited 2023 July 20]. Available from: https://who.int/health-topics/disability#tab=tab_1 .
Lawler D, Lalor J, Begley C. Access to maternity services for women with physical disability: a systematic review of literature. Int J Childbirth. 2013;3(4):203–17.
University of Johannesburg. Department of nursing paradigm. Johannesburg: University of Johannesburg;2017.
Walsh-Gallagher D, McConkey R, Sinclair M, Clarke R. Normalising birth for women with a disability: the challenges facing practitioners. Midwifery. 2013;29:294–9.
Silverman D, editor. Qualitative research. 5th ed. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2021.
Nassaji H. Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 6];24(4):427–431. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1362168820941288 .
Doyle L, McCabe C, Keogh B, Brady A, McCann M. An overview of the qualitative design within nursing research. Journal of Research in Nursing [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2021 August 6];25(5):444–446. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1744987119880234 .
Hennink M, Hutter I, Bailey A. Qualitative research methods. 2nd ed. London: SAGE; 2020.
Frechette J, Bitzas V, Aubry M, Kilpatrick K, Lavoie-Tremblay M. Capturing lived experience: methodological considerations for interpretive phenomenological inquiry. Int J Qual Meth. 2022;19:2–11.
Flick U. The SAGE handbook of qualitative research design. London: SAGE; 2022.
Book Google Scholar
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Yildiz A. A discussion on accurate and effective data collection for qualitative research. J Curr Researches Educational Stud. 2020;10(2):17–24.
Papakitsou V. Qualitative research: narrative approaches in sciences. Dialogues Clin Neurosci Mental Health. 2020;3(1):63–70.
Johnson JL, Adkins D, Chauvin S. Qualitative research in pharmacy education: a review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ. 2020;84(1):138–46.
Magagula T. The guidelines of maternity care of women with mobility disabilities in the Hhohho and Manzini regions: Eswatini [unpublished thesis]. University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg; 2021.
Fouché CB, Strydom H, Roestenburg WJH, editors. Research at grassroots for social sciences and human services professions. 5th ed. Pretoria: Van Schaik; 2021.
Giorgi A, Giorgi B, Morley J. The descriptive phenomenological psychological method. In: The SAGE handbook of qualitative research in psychology. 2nd edition. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2017.
Guba EG, Lincoln YS. Fourth generation evaluation. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE; 1989.
Rose J, Johnson W. Contextualising reliability and validity in qualitative research: toward more rigorous and trustworthy qualitative social science in leisure research. J Leisure Res. 2020;1:10–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222216.2020.1722042 .
Creswell JW, Creswell JD. Research Design: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. 5th Ed. California: SAGE; 2018.
Pitney WA, Parker J, Singe SM, Potteiger K. Qualitative research in health professions. Thorofare: SLACK Incorporated; 2020.
Leavy P, editor. The Oxford handbook of qualitative research. New York: Oxford University Press; 2020.
Kyngäs H, Mikkonen K, Kääriäinen M, editors. The application of content analysis in nursing science research. 2020. [cited 2022 April 27]. Available from: https://dl1tarjomac.ir/nursing-ebooks/TPC202203.pdf .
Dhai A, McQuoid-Mason DJ. Bioethics, human rights and health law: principles and practice. Cape Town: Juta; 2020.
Hallam J, Howard C, Locke A, Thomas M. Communicating choice: an exploration of mothers’ experiences of birth. J Reprod Infant Psyc. 2016;34(2):175–84.
König-Bachmann M, Zenzmaier C, Schildberger B. Health professionals’ views on maternity care for women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(551):1–11.
Morrison J, Basnet M, Buthathoki B, et al. Disabled women’s maternal and newborn health care in rural Nepal: a qualitative study. Midwifery. 2014;30:1132–9.
Smeltzer S, Wint A, Ecker J, Iezzoni L. Labor, delivery, and anaesthesia experiences of women with physical disability. Birth. 2017;44(4):315–24.
Sonalkar S, Chavez V, McClusky J, Hunter TA, Mollen CJ. Gynaecologic care for women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study of patients and providers. Women Health Iss. 2020;30(2):136–41.
Byrnes L, Hickey M. Perinatal care for women with disabilities: clinical considerations. J Nurse Practitioners. 2016;12(8):506–7.
Mgwili VN, Watermayer B. Physically disabled women and discrimination in reproductive health care: Psychoanalytic reflections. In: Disability and Social Change: A South African agenda [serial online]. 2006. [cited 2020 June 01]. Available from: https://www.hsrcpress.ac.za .
Tarasoff LA. Improving perinatal care for women with physical disabilities [Abstract]. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2016;38(5):501.
Schildberger B, Zenzmaier C, König-Bachmann M. Experiences of Austrian mothers with mobility or sensory impairments during pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium: a qualitative study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2017;17(201):1–11.
Mitra M, Akobirshoev I, Moring N, et al. Access to and satisfaction with prenatal care among pregnant women with physical disabilities: findings from a national survey. J Womens Health. 2017;26(12):1356–63.
Hall J, Hundley V, Collins B, Ireland J. Dignity and respect during pregnancy and childbirth: a survey of experience of disabled women. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2018;18(328):1–13.
Smeltzer S, Mitra M, Long-Bellil L, Iezzoni L, Smith L. Obstetric clinicians’ experiences and educational preparation for caring for pregnant women with physical disabilities: a qualitative study. Disabil Health J. 2018;11(1):8–13.
Devkota HR, Murray EA, Kett M, Groce N. Health care provider’s attitude towards disability and experience of women with disabilities in the use of maternal healthcare service in rural Nepal. Reprod Health. 2017;14(79):1–14.
Redshaw M, Malouf R, Gao H, Gray R. Women with disability: the experience of maternity care during pregnancy, labour and birth and the postnatal period. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2013;13(174):1–14.
Bassoumah B, Mohammed A. The socio-cultural challenges to maternal and neonatal care: the views of women with disabilities receiving maternity care in the Chereponi district of Northern Ghana. Sci Afr. 2020;7:1–10.
The authors would like to acknowledge the midwives in the Hhohho and Manzini regions of Eswatini who participated in the study and provided their own experiences of providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
The research received funding from the University of Johannesburg Postgraduate Supervisor-linked Bursary.
Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Annie M. Temane & Anna G. W. Nolte
Mother and Child Nursing, University of Eswatini, Kwaluseni, Eswatini
Fortunate N. Magagula
F.N.M conducted the research and wrote the manuscript. A.M.T supervised, reviewed, and finalised the manuscript. A.G.W.N co-supervised the study and edited the manuscript for final submission.
Correspondence to Annie M. Temane .
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Ethical clearance to conduct this study was obtained from the University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Sciences Higher Degrees Committee (ref. no. HDC-01-50-2018), University of Johannesburg Faculty of Health Research Ethics Committee (ref. no. REC-01-82-2018) and the Eswatini National Health Research Review Board (ref. no. NHRRB982/2018). Participation in this study was voluntary, and informed consent was obtained from participants before the interviews commenced.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Temane, A.M., Magagula, F.N. & Nolte, A.G.W. Midwives’ lived experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini: a qualitative study. BMC Women's Health 24 , 207 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-024-03032-z
Received : 18 August 2023
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 01 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-024-03032-z
- Experiences
- Maternity care
- Women with mobility disabilities
- Labour and the puerperium
BMC Women's Health
ISSN: 1472-6874
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
Virginia Tech researchers work to make yoga accessible to everyone
The project, a collaboration between the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Virginia Cooperative Extension, and the University Libraries, aims to reach historically underrepresented populations in yoga.
- Max Esterhuizen
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Copy address link to clipboard
Therese Osborn and Mary Frazier do a yoga pose in front of a fountain in the Corporate Research Center in Blacksburg, Virginia. Photo by Max Esterhuizen for Virginia Tech.
From the downward dog to the reverse warrior, yoga’s popularity has blossomed recently, partly because of its accessibility to a wide range of people at a variety of skill levels.
With benefits ranging from physical to mental to social and spiritual, yoga offers an approach to holistic well-being. Virginia Tech researchers are working on ways to broaden its appeal even further.
“The historical underrepresentation in yoga makes this the perfect thing to study in regard to equitable translation of health evidence,” said Mary Frazier, who is pursuing her Ph.D. in the Translational Biology, Medicine, and Health Graduate Program and is the graduate student lead on the project. “So many people think yoga isn’t for them and that’s largely because of how it’s often portrayed. We want to find ways to reach the groups that don’t think yoga is for them – because it could be.”
The underrepresentation of people from rural areas in yoga practices highlights significant accessibility and awareness issues, often due to a lack of local resources and classes that could introduce and nurture an inclusive yoga culture, the researchers said.
Additionally, according to the research team, prevailing narratives around body image within the yoga community can deter many from participating, as the physical component of yoga is easier to capture ‘on screen’ (e.g., photo or video), but the imagery often lacks representation of the diversity of human bodies.
“These challenges underscore the need for a more inclusive approach to yoga, one that embraces and promotes diversity in all forms, from geographical background to body shape, ensuring that the benefits of yoga are accessible to all,” said Samantha Harden, an associate professor in the Department of Human Nutrition, Foods, and Exercise and a Virginia Cooperative Extension specialist.
To help bridge this gap, the research team made up of Harden; Frazier; Brad Frick, a master’s degree student in the School of Communication ; and Therese Osborn, an undergraduate student in public health , as well as Rachel Kaplan, Cassidy Powers, and Kayla Markley, all students in human nutrition, foods, and exercise, created a messaging survey to identify terms and tactics that resonate with the historically underrepresented groups.
The development of a survey aimed at identifying effective tactics and messaging to engage historically underrepresented groups in yoga represents a strategic approach to fostering inclusivity within the practice. Through a collaboration with University Libraries, this research project can leverage advanced data visualization tools and expertise, transforming raw survey data into compelling, easy-to-understand insights that highlight opportunities for outreach and community engagement.
“This partnership not only amplifies the survey's impact through sophisticated analysis but also ensures that the findings are accessible and actionable for stakeholders aiming to create a more inclusive yoga community,” said Harden, who is also affiliated with the Fralin Biomedical Institute.
“It’s going to be interesting to see and transform the raw survey data into insightful and meaningful visualizations," said Michael Stamper, a University Libraries data visualization designer. "Once we can see the stories within that data, we can begin to take notice of and address them.”
The research project also gave Frazier valuable experience as a graduate student.
“This project has been instrumental in advancing my Ph.D. journey, providing a solid foundation for my dissertation on the importance of inclusivity in wellness spaces and highlighting the transformative potential of yoga when it truly embraces diversity in all its forms,” Frazier said. “The research into the underrepresentation of individuals from rural areas in yoga practices has illuminated critical gaps in accessibility and awareness, underscoring the urgent need for community-based interventions and inclusive programming.”
Osborn, a sophomore, was “nervous” when she first joined the lab — it’s the same nervousness that keeps people out of studios: the unknown. She now acknowledges that the experience has equipped her with valuable skills, preparing her for the workforce.
“Dr. Harden, Frazier, Megan Pullin, and the rest of the lab have been so welcoming and encouraging,” Osborn said. “Not only has the lab allowed me to apply what I have learned in my classes, but it has also taught me new things entirely, that help me to feel prepared for the future. This project has taught me how to build a successful survey and analyze qualitative data.”
Tom Soladay
540-232-2501
- College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- College of Liberal Arts and Human Sciences
- Human Nutrition, Foods, and Exercise
- School of Communication
- Translational Biology, Medicine, and Health
- University Libraries
- Virginia Cooperative Extension
- Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine
Related Content

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Galdas P, Darwin Z, Fell J, et al. A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN). Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Aug. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.34.)

A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN).
Appendix 6 critical appraisal skills programme criteria.
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme criteria
View in own window
The main 10 items were scored ‘yes’, ‘no’ or ‘unclear’ whereas the additional prompts were used to facilitate summarising the main strengths, limitations and concerns of each study.
Source: CASP Qualitative Checklist . 281 URL: www.casp-uk.net/#!casp-tools-checklists/c18f8 (accessed 3 September 2013).
Included under terms of UK Non-commercial Government License .
- Cite this Page Galdas P, Darwin Z, Fell J, et al. A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN). Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Aug. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.34.) Appendix 6, Critical Appraisal Skills Programme criteria.
- PDF version of this title (3.9M)
Other titles in this collection
- Health Services and Delivery Research
Recent Activity
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme criteria - A systematic review and metaethno... Critical Appraisal Skills Programme criteria - A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Fundamental Criteria: General Research Quality. Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3.Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy's "Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent ...
The purpose of this paper is to help authors to think about ways to present qualitative research papers in the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. It also discusses methods for reviewers to assess the rigour, quality, and usefulness of qualitative research. Examples of different ways to present data from interviews, observations, and ...
Useful terms. Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries ...
The qualitative research findings presentation, as a distinct genre, conventionally shares particular facets of genre entwined and contextualized in method and scholarly discourse. Despite the commonality and centrality of these presentations, little is known of the quality of current presentations of qualitative research findings.
In this way, it is made clear to the reader that the themes under discussion have emerged from the participants' interviews and not the mind of the researcher. The work of Latif and others 12 gives an example of how qualitative research findings might be presented. Planning and Writing the Report. As has been suggested above, if researchers ...
This chapter provides an introduction to writing about qualitative research findings. It will outline how writing continues to contribute to the analysis process, what concerns researchers should keep in mind as they draft their presentations of findings, and how best to organize qualitative research writing ... and arguments will take a clear ...
cal. The process of qualitative data analysis and synthesis is an ongoing one, involving continual reflection about the findings and asking analytical questions. As such, there is no clear and accepted single set of conven-tions for the analysis and interpretation of qualitative data. Indeed many qualitative researchers would resist this were ...
They also inform future research. A clear statement of findings, a considered discussion and a clear presentation of the authors' conclusions are, therefore, important parts of the review. In particular, the following issues can help people make better informed decisions and increase the usability of Cochrane Reviews:
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
of the research findings. As for all research, ethical considerations are central in qualitative research. These should be discussed, as well as a clear statement made on formal research ethics committee approval or waiver. Gaining appropriate consent and protecting participant identity are important. Consideration must be given to the
One way to ensure that findings are clear and actionable is to present findings as more nuanced, more specific phrases or sentences. ... A findings statement developed from these themes might be something like 'Data transparency supports real time data analysis.' ... rigorous, theoretically-grounded qualitative research can provide an in ...
A clear research question (or aim, objective, or hypothesis, as relevant to the chosen design) is important in focusing attention. ... (the CONSORT statements), qualitative research (COREQ or similar), or reviews (such as PRISMA or ENTREQ).[6,7] Please use them ... on findings and their importance. Again, remember to iterate the story. This ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
This blog post delves into the art of interpreting findings, offering guidance on making sense of coded data, and drawing conclusions that balance the researcher's insights with the perspectives of the participants. THE COMPLEXITY OF INTERPRETATION. Interpreting findings in qualitative research can be both exhilarating and challenging.
Richardson makes clear that one becomes a good writer of qualitative findings only by practicing writing and reading exemplary texts (Richardson & St. Pierre, 2005). She encouraged the researcher to put emphasis on four general aspects in communicating research findings: (1) the substantial contents of the analysis (what has been found out?);
Qualitative research presents "best examples" of raw data to demonstrate an analytic point, not simply to display data. Numbers (descriptive statistics) help your reader understand how prevalent or typical a finding is. Numbers are helpful and should not be avoided simply because this is a qualitative dissertation.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Reay et al. (2019) also highlighted the potential of vignettes for presenting findings from qualitative research. They argued that a one-size-fits-all approach to presenting data is not helpful ...
Clear Study Aims and Hypotheses in a Research Paper Anesth Analg. 2019 Jul;129(1):3. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004230. Authors Patrick Schober 1 , Thomas R Vetter 2 Affiliations 1 From the Department of Anesthesiology, Amsterdam UMC ...
Deductive qualitative analysis (DQA; Gilgun, 2005) is a specific approach to deductive qualitative research intended to systematically test, refine, or refute theory by integrating deductive and inductive strands of inquiry.The purpose of the present paper is to provide a primer on the basic principles and practices of DQA and to exemplify the methodology using two studies that were conducted ...
Procedure. The procedure for this research is multi-stepped and is summarized in Fig. 1.First, we mapped retrospective qualitative data collected during the development of the SCI-HMT [] against the five domains of the CFIR in order to create a semi-structured interview guide (Step 1).Then, we used this interview guide to collect prospective data from health professionals and people with SCI ...
Midwives encounter various difficulties while aiming to achieve excellence in providing maternity care to women with mobility disabilities. The study aimed to explore and describe midwives' experiences of caring for women with mobility disabilities during pregnancy, labour and puerperium in Eswatini. A qualitative, exploratory, descriptive, contextual research design with a phenomenological ...
Disclosing such information in the methodology section is important and increases the transparency and trustworthiness of the research findings. As for all research, ethical considerations are central in qualitative research. These should be discussed, as well as a clear statement made on formal research ethics committee approval or waiver.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
Postpartum women experience unique barriers to maintaining healthy lifestyles after birth. Theory-based behaviour change techniques and intervention strategies can be integrated into postpartum lifestyle interventions to enable women to overcome barriers to change. This study aims to explore barriers and facilitators to engaging in healthy postpartum lifestyle behaviours and develop ...
A key stage common to all systematic reviews is quality appraisal of the evidence to be synthesized. 1,8 There is broad debate and little consensus among the academic community over what constitutes 'quality' in qualitative research. 'Qualitative' is an umbrella term that encompasses a diverse range of methods, which makes it difficult to have a 'one size fits all' definition of ...
Abstract. This study aims to estimate the effect of corporate governance on the performance of commercial banks in Vietnam. By using the qualitative method (interview and survey of experts) and the quantitative method (PLS-SEM data analysis using SmartPLS4), the findings confirm the direct effect of corporate governance on corporate social responsibility (CSR).
The research project also gave Frazier valuable experience as a graduate student. "This project has been instrumental in advancing my Ph.D. journey, providing a solid foundation for my dissertation on the importance of inclusivity in wellness spaces and highlighting the transformative potential of yoga when it truly embraces diversity in all ...
Qualitative research is the appropriate way to address the aim or answer the research question (e.g. the research concerns experiences/views of participants, processes involved, or the nature of interactions) ... Is there a clear statement of findings? Findings are clearly stated (e.g. in the abstract or findings) 10. Is the research valuable?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Susunod, atasan ang mga mag-aaral na magsulat ng sanaysay, na nagpapaalala sa kanila ng mga pamantayan at ang iyong mga inaasahan para sa takdang-aralin. Sa sandaling makumpleto ng mga mag-aaral ang sanaysay, hayaan muna silang mag -iskor ng kanilang sariling sanaysay gamit ang rubric, at pagkatapos ay lumipat sa isang kapareha. (Ang proseso ng ...
Rubrik Sa Pagsulat NG Sanaysay | PDF. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Ae Octaviano. SirAdrian Ae Octaviano. 1y. Bajado Mildred Dalman. True. 2y. Sample Rubrics in Filipino (Part 1).. 😊😊.
Rubric PAgsulat NG Sanaysay Filipino V | PDF. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Ang four-point rubric ay gumagamit ng apat na potensyal na puntos na maaaring makuha ng mag-aaral para sa bawat lugar, tulad ng 1) malakas, 2) umuunlad, 3) umuusbong, at 4) simula. Upang gawing marka ng sulat ang iyong marka ng rubric , hatiin ang mga puntos na nakuha sa mga puntos na posible. Halimbawa: Ang mag-aaral ay nakakakuha ng 18 sa 20 ...
Rubrics (Sanaysay o Essay) | PDF. ito ay basehan sa pagmamarka ng isang sanaysay by meah1bajande.
Rubrik o Ang Pamantayan sa Pagsusulat ng Sanaysay. Mga dapat gawin rubrik sa pagsulat ng sanaysay rubrik sa pagsulat ng sanaysay kategorya introduksyon
Narito ang ilan sa mga rubric na ginamit ng guro sa kanyang mga pagtataya, pangkatang gawain at proyekto. rubric_sa_pakikiisa.pdf. Download File. rubric_sa_pakikipanayam.pdf. Download File.
Preview text. KRAYTERYA Napakahusay 10. Mahusay 8. Katamtaman 6. Papaunlad 3. Nangangailangan ng Gabay 2 Paglalahad ng Paksa. Napakahusay na inilahad ang Paksa sa pamamagitan ng pagiging malikhaing ng pagsulat nito. Mahusay na inilahad ang Paksa sa pamamagitan at may pagkamalikhain sa pagsulat nito.
iRubric SXA94CX: Rubric title Personal Project - Filipino (Tagalog). Built by AlecJMP using iRubric.com. Free rubric builder and assessment tools.
Rubrics para sa Talakayan PAMANTAYAN PUNTOS ISKALA Lumalahok at nasasagot ng tama ang tanong ng guro sa lahat ng talakayan. 5 100 Lumalahok at nasasagot ng tama ang tanong ng guro paminsan-minsan. 4 90 Lumalahok at nasasagot ng tama ang tanong ng kapag hinikayat ng guro.
Hakbang 6: Baguhin ang Iyong Rubric. Pagkatapos gumawa ng mapaglarawang wika para sa lahat ng mga antas (siguraduhin na ito ay parallel, partikular at masusukat), kailangan mong balikan at limitahan ang iyong rubric sa isang pahina. Masyadong maraming mga parameter ang magiging mahirap na tasahin nang sabay-sabay, at maaaring hindi epektibong ...
A Rubric Assessment Tool is an assessment tool, usually in the form of a matrix or grid, that clearly indicates achievement criteria across all the components of any kind of student work, from written to oral to visual. Rubrics are sometimes called "criteria sheets", "grading schemes", or "scoring guides".
Lakas ng bayan! Lakas ng daigdig! PAMANTAYAN PARA SA MGA LALAHOK SA PALIGSAHANG SABAYANG PAGBIGKAS: I. Ang paligsahan ay gaganapin sa Don Bosco Gym sa ika-31 ng Agosto 2012, sa ganap na10:30-12:30.1. Ito ay maaaring lahukan ng mga sumusunod:a. Mga mag-aaral na kasalukuyang kumukuha ng asignaturang Filipino sa kolehiyo.b.
Download for FREE these available rubrics that you can use in rating your learners' performance and outputs. Simply click on the DOWNLOAD link to get your FREE AND DIRECT copies. Rubrics help students, parents, and teacher identify what quality work is. Students can judge their own work and accept more responsibility for the final product.
Rubric for Assessment of the Narrative Essay. 20 POINTS 15 POINTS 10 POINTS 5 POINTS. INTRODUCTION Background/ History/Exposition. CONCLUSION. Well-developed introduction engages the reader and creates interest. Contains detailed background information. Conclusion effectively wraps up the story / reflects the main points..
5-scale rubric: mastery, accomplished, develop, umuusbong, hindi katanggap-tanggap. 4-scale rubric: above proficiency, proficient, approaching proficiency, below proficiency. 3-scale na rubric: namumukod-tangi, kasiya-siya, hindi kasiya-siya. Ang mga deskriptor sa rubric ay iba-iba para sa bawat antas ng mastery.
Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
RUBRIC SA PAGTATALO/DEBATE. Walang mainam na kaisipang ipinahayag tungkol sa paksa. May naipahayag na 2 hanggang 3 kaisipan ang nabanggit tungkol sa paksa. Lubhang malinaw at maayos ang kaisipang naipahayag. May 4 o higit pang kaisipan ang nabanggit tungkol sa paksa. May sapat na katibayang iniharap sa pangangatwiran.
Magsanay sa Paggamit ng Rubric sa Tunay na Gawain ng Mag-aaral. Bago mo panagutin ang iyong mga mag-aaral sa huling grado, subukan ang iyong bagong rubric sa ilang piraso ng aktwal na gawain ng mag-aaral. Para sa pagiging objectivity, maaari mo ring isaalang-alang ang paghingi ng trabaho sa ibang guro mula sa kanyang mga mag-aaral.
2. Gaganapin ang paligsahan sa ika-28 ng Agosto,2009 sa ganap na ika-10 ng... It is generally designed as a grid-type structure that includes criteria, descriptors of performance, and scores. Twinkl Philippines Filipino Resources. What do... essay writing rubrics. Tagalog. rubrics sa pagsulat ng sanaysay. Last Update: 2020-08-29. Usage ...
Rubrics at Paano Gumawa Ng Photo Essay - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf) or view presentation slides online. photo essay