71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best physical education topic ideas & essay examples, 🔎 interesting topics to write about physical education, 📑 good research topics about physical education.
- Keeping Physical Education in Schools Apart from participating in the physical education programs, the students need to be taught on the importance of the various exercises so that they inculcate the culture of physical fitness into their life-time fitness programs.
- Physical Education and Its Benefits Schools in particular know the benefits of physical education in a student’s life and should be able to fight for the children’s rights. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Role of Parents in Physical Education and Sport The involvement of parents in physical education and sports is viewed differently in regard to how it affects the child’s participation in sports even later in life.
- Adaptive Physical Education The value of the brochure developed for the informational purpose is attributed to the need to communicate the importance of APE and point out the value that it could bring to children with special needs.
- Bodies in Physical Education The purpose of this study is to investigate how students view the construction of their bodies in relation to physical education and how students’ meanings of their bodies affect their participation or resistance to physical […]
- Physical Education: Personal Physical Exercise Plan Given the necessity of taking fluids, it is good to identify and avail the same before starting a physical exercise session.
- The Usefulness of Physical Education in Modern Education Varied criticism adds to the debate on the usefulness of PE in modern education and the need to change current approaches. This indicates the need to focus the debate on the meaning of PE to […]
- Health Teaching and Physical Education Lesson Plan Students will be able to dribble a ball with a hand paying attention to such principles as dribbling on the side, waist-high, pushing the ball down, and eyes lookup.
- Physical Education Curriculum Physical education has significantly contributed towards the realization of the school philosophy as it helps in the development of the physical aspects of the students.
- Reducing Physical Education Classes The teaching process has a significant amount of waste regarding the excess number of teachers dedicated to sports training compared to math and technical subjects.
- Physical Education Is an Academic Subject These aspects make physical activity one of the core subjects at school, including for younger students who need a surge of emotions and energy.
- Race and Gender in Physical Education and Sports These factors create the diversity of cultures and nations, and inclusiveness, giving access to the best talents and disclosing the individual’s potential, abilities, and strengths.
- Physical Education: Effect of Phototherapy Therefore, it is evident that the intensity of an exercise directly influences one’s heart rate, breathing rate, skin coloration, sweating, and recovery.
- Effectiveness of Physical Education Provisions in the UK School The vital need for health promotion, especially in terms of secondary education has been highlighted by the science of epidemiology the study of factors that influence the health and illnesses of people.
- British Development of Sport and Physical Education in the Last 25 Years Sport England wishes to increase participation in sports through community sports activities, sporting completions providing and training coaches and officiators, and closely working with the Youth Sport Trust and UK Sports formed in 1996 to […]
- Increase of Physical Education Classes Children are the future of any nation, and their health and well-being are the essential preconditions for the successful development of the United States.
- Physical Educators Attitude to Special Needs Children Sue Combs, together with her colleagues from the University of North Carolina, investigated the attitudes of the physical education teachers towards the inclusion of children with special needs in their lessons.
- The Nature and Values of Physical Education In the past, physical education was considered to consist of only physical and practical activities, however, the recent research has justified that physical education can be included in the curriculum on the basis of scientific […]
- Should Public Schools Be Required to Restore Physical Education Classes to the Curriculum? The occurrence of obesity prevalence in children, in the U S, can be associated with the removal of physical education courses in public school curriculum.
- Physical Education within Elementary Schools One of the benefits of the physical education is the level of physical fitness that it induces to the students. The manner in which these students are introduced to physical education and the way that […]
- Effects of Physical Education on Brain These neurons are usually created in a place called the hippocampus, which happens to be the section of the brain involved in learning and storage of memory.
- Elementary School Curriculum and Physical Education
- Should Physical Education Be a Required Class in College?
- Physical Education Class: The Perfect Place to Be Bullied
- Pros and Cons of Physical Education
- How Physical Education Should Be Taught
- Physical Education for Elementary School Students
- Weight-Related Barriers for Overweight Students in an Elementary Physical Education Classroom
- Physical Education Lesson Plan and Activity Ideas
- Motivation, Discipline, and Academic Performance in Physical Education
- Adaptive Physical Education for Students With Special Needs
- Physical Education Should Not Be Mandated
- How Technology Enhances the Physical Education Curriculum
- Physical Education: Standards, Cooperative Skills, and Learning Theories
- Physical Education’s Contribution to Public Health
- Physical Education Importance for Child Development
- Reasons to Keep Physical Education in the National Curriculum
- Ethical Relativism and Its Impact on Physical Education
- Inclusive School Physical Education and Physical Activity
- History and Benefits of Physical Education: Why I Want to Be a P.E. Teacher
- Physical Education Beyond the Middle School
- The Importance of Physical Education in Childhood Obesity
- Physical Activity Promotion and School Physical Education
- Implementing the TARGET Model in Physical Education: Effects on Perceived Psychobiosocial and Motivational States in Girls
- Teaching the Nuts and Bolts of Physical Education
- Health-Related Intensity Profiles for Physical Education Classes
- Anticipated Benefits From a Basic College Physical Education Activity Course
- Physical Education Should Be Graded on Effort, Not Ability
- Motivation and Intention to Be Physically Active in Physical Education Students
- Personal Development, Health, and Physical Education
- Why Physical Education Should Be Included in the School Curriculum
- Attitude and Teacher’s Qualification as Factors Affecting Students’ Participation in Physical Education Activities
- Burnout in Physical Education Teachers
- What Benefits Physical Activity Has on Academic Performance
- SPARK Physical Education Curriculum Program
- Changing the National Curriculum for Physical Education
- Physical Education: Official School Policy
- How Physical Education Helps to Develop Your Personality
- Early Childhood Development: Physical Education Program Effects
- Fun Physical Education Games for High School Students
- How Extracurricular Sports Should Satisfy State Physical Education Requirements
- One’s Readiness to Self-Development Through Physical Education
- Would More Physical Education Reduce Obesity in the Youths?
- Goal-Directed Physical Education for Learners With Disabilities
- Health and Physical Education: Volleyball
- Managing the Physical Education Classroom
- Strategies to Accommodate Autism Spectrum Disorder Students in General Physical Education
- Physical Education vs. School Sports: What’s the Difference?
- The Impact of School Budgetary Cuts on Physical Education
- Teaching Health and Physical Education in Australian Schools
- Positive Reinforcement Techniques in Physical Education
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 9). 71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/
"71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 9 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 9 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
- Fitness Topics
- Disabilities Titles
- Curriculum Essay Ideas
- Academic Achievements Research Topics
- Athletics Topics
- Wellness Essay Topics
- Metabolism Research Topics
- Child Development Research Ideas
- Academic Performance Topics
- Football Topics
- Asthma Paper Topics
- Lifespan Development Essay Titles
- Obesity Ideas
- Soccer Research Topics
- Adolescence Questions
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Studying Process — Physical Education

Essays on Physical Education
Prompt examples for physical education essays, the importance of physical education in schools.
Discuss the significance of including physical education as a part of the school curriculum. How does physical education benefit students' overall development?
Physical Education and Health
Explore the relationship between physical education and students' health. How does regular physical activity in schools contribute to the well-being of students?
The Role of Physical Education Teachers
Examine the responsibilities and impact of physical education teachers. How do they help students develop physical skills and a lifelong love for fitness?
Innovations in Physical Education
Discuss innovative approaches and technologies used in modern physical education programs. How have these innovations improved the learning experience?
Physical Education and Academic Performance
Explore the potential links between physical education and academic success. How does regular physical activity impact students' cognitive abilities and classroom performance?
The Role of Team Sports in Physical Education
Analyze the benefits of incorporating team sports into physical education programs. How do team sports promote cooperation, leadership, and physical fitness?
Physical Education for Special Populations
Discuss the importance of adapting physical education programs for students with special needs. How can inclusive physical education benefit all students?
Challenges and Solutions in Physical Education
Examine the challenges faced by physical education programs, such as limited resources or lack of facilities. What solutions can be implemented to overcome these challenges?
Physical Education and Lifelong Fitness
Explore the role of physical education in promoting lifelong fitness habits. How can physical education programs instill a love for physical activity beyond the school years?
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Physical Education
Discuss methods for assessing the effectiveness of physical education programs. How can schools measure the impact of these programs on students' health and well-being?
Importance of Physical Education
The sequence of cephalocaudal development, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Physical Education in Schools
The benefits of physical education: develop skills & confidence, the importance of physical education to maintain a healthy and happy life, physical education should always be included in the school curriculum, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The Benefits of Taking a Physical Education Course During School
The importance of compulsory physical education classes, gender issues in physical education, different types of play as an important part of young children’s development, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Game Play Participation of Amotivated Students During Sport Education
Using videos in teaching physical education, the importance of sports for students, myers v. peel county board of education, the wingate test: peak power output and anaerobic systems in the college-aged population, social, mental, and physical benefits of sports for young adolescents, physical education in school as a tool for motor development, benefits of physical education in school for body development, the importance of physical education: a comprehensive analysis, the impact of physical education on student grades, importance of physical education in schools, ethics, education, and responsible practices in running, running as a conduit for physical and mental well-being.
Physical Education is an education which brings improvement in human performance with the help of physical activities.
Physical activities range from simple walking to jogging, running, sprinting, hopping, jumping, climbing, throwing, pushing, pulling, kicking, etc.
Physical education helps students develop physical skills and confidence. It develops fitness and fosters the desire for lifelong participation in physical activity. School curriculum prepares students to become highly proficient in one or more sport and/or fitness activity of their choice.
Relevant topics
- Critical Thinking
- Studying Abroad
- Stem Education
- Academic Interests
- Middle School
- Academic Achievements
- School Uniform
- High School
- Academic Challenges
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
What does a physical education teacher do?
Would you make a good physical education teacher? Take our career test and find your match with over 800 careers.
What is a Physical Education Teacher?
A physical education (PE) teacher is responsible for instructing students in physical fitness, sports, and other physical activities. PE teachers design and implement lesson plans that help students develop their physical abilities, including their strength, endurance, coordination, and flexibility. They may teach a wide range of activities, such as team sports like basketball or soccer, individual sports like tennis or gymnastics, and recreational activities like dance or yoga.
In addition to teaching physical skills, PE teachers also promote healthy habits and attitudes toward physical activity. They may educate students on the benefits of regular exercise, nutrition, and the dangers of substance abuse. PE teachers often work closely with other educators and health professionals to develop programs that support students’ overall health and wellness. They may also organize and supervise extracurricular sports and fitness programs, such as intramural sports teams or after-school fitness clubs.
What does a Physical Education Teacher do?

Physical education teachers play an important role in the development and well-being of students. By providing a structured and safe environment for physical activity, they can help students improve their physical fitness, develop their motor skills, and learn the value of teamwork and sportsmanship.
Duties and Responsibilities Physical education teachers have a wide range of duties and responsibilities that contribute to the overall health and well-being of their students. Some of the key responsibilities of PE teachers include:
- Developing and Implementing Lesson Plans: PE teachers design and deliver lesson plans that help students develop their physical abilities and learn new skills. They may also incorporate health education into their lesson plans, teaching students about nutrition, safety, and the benefits of physical activity.
- Assessing Student Progress: PE teachers monitor student progress and provide feedback on their performance. They may also evaluate students’ physical fitness levels and design programs to help them achieve their goals.
- Creating a Safe and Inclusive Environment: PE teachers are responsible for creating a safe and supportive learning environment for all students. They may adapt activities to meet the needs of students with disabilities or other special needs, and ensure that all students feel included and valued.
- Organizing Extracurricular Activities: PE teachers may organize and supervise extracurricular activities, such as sports teams, fitness clubs, or school-wide events like field days.
- Collaborating With Other Educators and Professionals: PE teachers may work closely with other educators and health professionals to develop programs that support students’ overall health and well-being.
- Continuing Professional Development: PE teachers are responsible for keeping up-to-date with the latest research and trends in physical education and health education. They may attend conferences, workshops, and other professional development opportunities to stay current in their field.
Types of Physical Education Teachers There are different types of physical education teachers, depending on the level of education and type of institution where they work. Some of the most common types include:
- Elementary School Physical Education Teachers: These teachers work with students in grades K-5, introducing them to fundamental motor skills and basic sports and fitness concepts. They may also incorporate games and other fun activities to keep students engaged and motivated.
- Middle School Physical Education Teachers: Middle school physical education teachers work with students in grades 6-8, helping them build on the skills they learned in elementary school and introducing more complex sports and fitness activities. They may also focus on developing teamwork and leadership skills.
- High School Physical Education Teachers: High school physical education teachers work with students in grades 9-12, helping them develop advanced skills in a variety of sports and fitness activities. They may also teach health education topics, such as nutrition, substance abuse prevention, and sexual health.
- College and University Physical Education Teachers: These teachers work with college and university students, teaching a wide range of sports and fitness activities and providing opportunities for students to develop leadership skills through coaching and other extracurricular activities.
- Adapted Physical Education Teachers: These teachers work with students with disabilities or special needs, developing customized physical education programs that meet the individual needs of each student.
- Community Physical Education Teachers: Community physical education teachers may work in after-school programs, recreation centers, or other community-based organizations, providing opportunities for people of all ages to stay active and healthy.
Are you suited to be a physical education teacher?
Physical education teachers have distinct personalities . They tend to be social individuals, which means they’re kind, generous, cooperative, patient, caring, helpful, empathetic, tactful, and friendly. They excel at socializing, helping others, and teaching. Some of them are also artistic, meaning they’re creative, intuitive, sensitive, articulate, and expressive.
Does this sound like you? Take our free career test to find out if physical education teacher is one of your top career matches.
What is the workplace of a Physical Education Teacher like?
The workplace of a physical education teacher can vary greatly depending on the specific school and district they work in. However, in general, PE teachers typically work in a school setting, either at the elementary, middle, or high school level. Their primary responsibility is to design and implement physical education programs that promote the development of students' physical abilities and overall health.
PE teachers typically work in a variety of indoor and outdoor settings, including gymnasiums, sports fields, and swimming pools. They may also incorporate technology into their teaching, using tools like heart rate monitors and fitness trackers to track student progress and provide individualized feedback. Additionally, some PE teachers may teach other subjects such as health education or nutrition as part of their curriculum.
In addition to designing and implementing physical education programs, PE teachers also have administrative duties. They may be responsible for organizing and supervising extracurricular sports programs, overseeing equipment maintenance and inventory, and ensuring that all safety procedures are followed. They may also collaborate with other teachers and staff members to create cross-curricular activities that integrate physical education with other subjects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Teaching/school related careers and degrees.
- Adult Education Teacher
- Art Teacher
- Career Counselor
- CTE Teacher
- Dance Teacher
- Distance Learning Coordinator
- Elementary Teacher
- ESL Teacher
- Graduate Teaching Assistant
- High School Teacher
- Kindergarten Teacher
- Middle School Teacher
- Music Teacher
- Physical Education Teacher
- Preschool Teacher
- Private Tutor
- School Counselor
- School Principal
- Special Education Teacher
- STEM Teacher
- Substitute Teacher
- Teacher Assistant
- Virtual Teacher
- Bilingual Education
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Administration
- Elementary Education
- School Psychology
- Special Education Teaching
Continue reading
Physical Education Teachers are also known as: Phys Ed Teacher PE Teacher Gym Teacher

Essay on Physical Education in School for Students in 1000+ Words
In this article, we have published an essay on physical education in school. It includes its meaning, importance, and benefits. Also, how is physical education good for our health?
Table of Contents
Essay on Physical Education in School (1000 Words)
Physical education is essential because it improves the fitness of youngsters, makes them disciplined and active. It helps them to find out teamwork, test their decision-making capabilities too.
Education should be mandatory in every school, from preschools, primary, elementary to secondary school and also in colleges, hostels. But we should always not force them to try to do it, and they ought to be made conscious of its benefits.
The goal of education is to assist students in developing healthy habits that can serve them within the long term. In today’s world, things have become easy due to technology, and we are enjoying the facilities like no other generation.
Adults spend their whole day in air-cooled offices; they eat food, don’t find time to exercise. It’s getting to be very tough for our generation.
If we get good healthy habits now, once we are within the school, it’ll help us now and within the future. It’s a dire need of your time.
The education system should be proactive and make it mandatory in schools. So allow us to see why do children need physical education?
Healthy Habits
With education, children can improve their fitness, body posture, and ultimately it’ll boost their confidence.
It helps students to make good habits from an early age. Running, jogging, weight training, eating, and sleeping on time are a few habits that can help them in the future.
One of the essential aspects of education is discipline . It’ll help them to plan their studies, finances, and life generally.
They’re going to be ready to allot time to studies and for fun too. Alongside academics, children should get time to be children; it’s the most uncomplicated phase of human life.
Interpersonal Skills & Team Work
Physical education and sports improve the interpersonal skills of youngsters. These skills are very crucial at work and within the relationship.
Physical education teaches the way to communicate messages effectively and the way to figure them together.
Stress Buster
Education comes with exams, assignments, projects, and homework, which can stress students.
Alongside this, they even have parents’ expectations burden, Financial worries. In today’s time, the overuse of social media makes them suffer from social anxiety, envy, and FOMO.
In this case, education becomes an excellent outlet. It cuts them from these worries and situations. Due to it, they’re going to be ready to focus more on studies and life generally.
Makes you Confident
With improved interpersonal skills, relaxed and calm composure, and healthy habits, one becomes more confident. Physical education plays a notable role during this too.
Alternate Career Opportunity
Everyone is different; not all students will be great at academics, and there is no such rule. Children find themselves in trouble with selecting a career . Education can help them during this also. One might find the internet in sports and games.
Physical education may be an excellent opportunity to scout for potential athletic talent also. They were within the suitable career matters tons.
If one gets to try to do a thing they like to do, their lives will be happier. Physical education can help them to seek out that or a minimum of narrow down the alternatives.
Health is Wealth
Our current generation is affected by obesity from an early age. They also get spectacles at an old age. Obesity comes with related illnesses too.
An obese child is susceptible to diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, stress, vital sign, etc. Habits formed with education will make them fit from infancy. It’ll encourage them to enhance and maintain their health in the future.
Children inculcate with the importance of physical education for maintaining a healthy body and teach them the importance of regular fitness activity in daily routine, which successively keeps them happy and energized.
It helps the youngsters to take care of their fitness, develop their muscular strength, and increase their stamina.
Research has proven that children who regularly play different types of sports lead to high self-confidence, which is essential for building a person’s character.
Education instills the will to participate, enjoy the victory, and take defeat positively, developing the character’s general personality.
By making children participate in sports, especially team sports, education also imbibes in them a way of solidarity. Children find out how to figure as a team member, organize themselves, and perform together towards attaining a goal.
It successively improves a child’s overall communication skills and, therefore, urges alongside different people.
Physical education helps one gain knowledge about the general aspects of physical health. Teenagers face many health-related problems like obesity, anemia, bulimia, and even diabetes, which are rampant amongst teenagers.
Through education, teachers can promote the advantages of healthy and nutritious food and discourage them from having food by highlighting their ill effects. They will easily promote sound eating practices and guidelines for nutrition.
Physical education also teaches about the importance of private hygiene and the importance of cleanliness . They guide the scholars by informing them about the essential hygiene practices for maintaining health and well-being throughout life.
Additionally, to the present, the education classes also cover a crucial aspect that the youngsters need to affect at puberty.
Apart from the health and knowledge benefits that students get from education, they also learn how to unwind and relieve themselves of stress and anxiety. Sports and other fitness activities offered within the education classes are a welcome break for the scholars.
It won’t be wrong to mention that children, who learn the importance of health and hygiene at an early age, tend to get older to be responsible and healthy adults who are conscious of the advantages of a healthy lifestyle.
Children who provided good education are more likely to become responsible adults who know the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
Anti-Depressant
It is proven that physical activities help us to alleviate stress. Though we all know its importance, we make all possible excuses to avoid it.
Physical education helps us to take care of a timely schedule of physical activities. Students become calmer composed; then, they will focus more on their goals.
The Bottom Line
Physical education leads to a more focused, active, composed, and happy in life . It makes us disciplined and arranged.
Habits formed with the assistance of education tend to remain with us for an extended time. We should bring skilled coaches and needed equipment to colleges.
Students should know its benefits. There are real advantages of education and in the present situation, children, also as adults, need it the foremost.
The opportunity to participate in physical activity daily in schools may increase the probability of adopting a physically active lifestyle.
Choosing to measure a physically active lifestyle is vital to health and wellness. A school’s education department is responsible for assisting students in being involved in and adopting a private lifestyle of regular physical activity.
I hope you liked this essay on physical education in school for students and children.
Leave a comment Cancel reply

Essay on Physical Education
Students are often asked to write an essay on Physical Education in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Physical Education
What is physical education.
Physical Education, often called PE, is a class in school where students do exercises, play sports, and learn about keeping their bodies healthy. It’s not just about playing games; it’s also about learning the rules of sports, teamwork, and staying active.
Benefits of PE
PE helps children stay fit and healthy. It makes their hearts and lungs strong and helps them to move better. Kids also learn to work with others and follow rules. This class can make them feel happier and help them do better in school.
Activities in PE
In PE, children play soccer, basketball, and other games. They might run, jump, or learn dances. Sometimes they also learn about healthy food. PE is fun because it’s a break from sitting in the classroom.
Skills from PE
PE teaches skills like how to throw a ball or swim. But it also teaches kids to be fair and to not give up. These lessons are important in life, not just in sports. PE can help kids become good adults.
Also check:
- Speech on Physical Education

250 Words Essay on Physical Education
Physical Education, or PE for short, is a subject in school where students get to be active and learn about sports and exercises. It’s not just about playing games; it’s also about understanding how to keep our bodies healthy and strong. In PE, teachers show kids how to move their bodies in different ways and play various sports.
Benefits of Physical Education
PE is very important for many reasons. First, it helps students to stay fit and healthy. When kids run, jump, and play sports, they build stronger muscles and bones. It also helps them to stay at a good weight. Second, PE can make your mind sharper and help you focus better in other classes. Lastly, it teaches teamwork and how to get along with others.
What You Learn in PE
In PE, you learn more than just how to play sports. You learn about the rules of games, how to be safe while playing, and how to respect other players. Teachers also talk about healthy eating and how to take care of your body by getting enough sleep and not eating too much junk food.
Fun and Games
PE is also about having fun. When you play games and sports, you can enjoy yourself while exercising. It’s a time in school when you can laugh with friends and enjoy being active.
In conclusion, Physical Education is a key part of school that helps kids learn about staying healthy, working with others, and having a good time. It’s not just about sports; it’s about taking care of your body and mind.
500 Words Essay on Physical Education
Physical Education, often called PE, is a subject in school where students learn about staying active and healthy. It’s not just about playing sports or running around; it’s also about learning how to take care of your body. In PE, you get to learn new games, how to work as a team, and understand the importance of exercise.
The Importance of Staying Active
Staying active is very important for everyone, especially for students like you. When you move around and play, your body gets stronger, and you feel better. Exercise helps your muscles grow and keeps your heart healthy. It also makes you feel happy because when you exercise, your body releases something called endorphins, which are like natural happiness boosters.
Learning New Skills
In Physical Education, you learn a lot of new skills that can be useful in life. You learn how to throw, catch, jump, and run properly. These skills are not only for playing sports but also for daily activities. For example, being able to catch something quickly can help you in many situations, like catching a bus or even a piece of fruit falling from a table.
Teamwork and Sportsmanship
One of the best things about PE is playing games with classmates. You learn how to work together as a team to win a game. But winning isn’t everything. Physical Education also teaches you about sportsmanship, which means being kind and fair to others, even when you are trying to win.
Health and Fitness Knowledge
PE is not just about playing; it’s also about learning. You learn why eating healthy foods and staying active is good for you. Teachers show you how different exercises can help different parts of your body. For example, jumping rope is good for your heart, and stretching can make you more flexible.
Fun and Enjoyment
Physical Education can be a lot of fun! It’s a time in school when you can play with friends and enjoy different activities. You might play soccer, basketball, or even dance. It’s a break from sitting in a classroom, and it’s a chance to laugh and have a good time.
Challenges and Achievements
Sometimes PE can be challenging. Maybe you’re learning a new game or trying to get better at something. But when you practice and get better, it feels great. You feel proud of what you can do, and that helps you feel more confident in other parts of life too.
Physical Education is an essential part of school. It helps you stay healthy, learn new skills, work with others, and have fun. It’s not just about being the best at sports; it’s about feeling good and living a healthy life. So next time you have PE, remember it’s helping you in many more ways than you might think!
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Physical And Mental Health
- Essay on Lottery
- Essay on Photo Bullying
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Task planning for sports learning by physical education teachers in the pre-service phase
Sebastián feu.
1 Department of Didactics of Music, Plastic and Body Expression, University of Extremadura, Badajoz, Spain
Javier García-Rubio
2 Faculty of Education, Universidad Autónoma de Chile, Santiago de Chile, Chile
María de Gracia Gamero
Sergio j. ibáñez, associated data.
All relevant data are available on the Open Science Framework at DOI: 10.17605/OSF.IO/YUZD9 .
Planning the learning task is one of the principal actions that a teacher should engage in, and it is important to know how teachers in the pre-service phase plan learning and communication tasks and the feedback that they use in the classroom. The aim of the present study was twofold: i) to characterize the learning tasks designed by the pre-service physical education teachers; and ii) to identify the relationships between the variables that define the learning tasks and the phases into which a session is structured in Physical Education Teacher Education (PETE) in the pre-service phase. The sample comprised 695 learning tasks designed by fourteen pre-service phase teachers. The independent variable was the lesson structure and the dependent variables were the learning means, the game situation, the game phase, the space where the students practice, the use of the ball in the task, and the kind of feedback provided in the learning tasks. The high predominance of exercises, unspecific games, and no opponent situations, coupled with the low percentage of reflexive feedback, indicates that the pre-service teachers give prevalence to technical over tactical learning. In addition, pre-service teachers show preferences for some of the task characteristics for each part of the lesson structure. Teachers in PETE pre-service phase tasks tend to follow a more traditional methodology, despite having received information about the different methods of sports teaching in their initial training. The current findings seems to indicate a resistance to changing a traditional model for other models centered on game comprehension.
Introduction
Invasion team sports represent the physical education contents most used in teaching planning [ 1 ] and are the most attractive for the students [ 2 ]. Invasion team sports are team-based games in which the purpose is to score points while invading the opponent’s territory and keeping the opposing team’s points to a minimum, within a defined time period. Their inclusion in the elementary school curriculum is controversial [ 3 ], and has to fulfill some requirements to be considered educational. In this planning, the teachers have to make decisions regarding the learning content and teaching plan, methodology or evaluation, adapting them to the teaching approach that they consider most suitable for achieving the desired learning [ 4 ]. One of the basic skills of physical education teachers is planning [ 5 ]. This is where the selection and design of learning methods and techniques start. Learning tasks organization is not a product of improvisation or an excess of creativity [ 6 ].
There are two main approaches to teaching invasion team sports, the Teacher-Centered Approach and the Student-Centered Approach. Within the Teacher-Centered Approach the Direct Instruction methodology is the most common [ 7 ], with the teacher choosing the contents to be developed and managing the class so that the students have more opportunities to respond, get involved cognitively and make decisions about the game [ 8 ]. Specifically, the teacher thus designs tasks to develop movement patterns and technical skills that the student has to reproduce. Initially a technical skill is practiced in an unspecific manner in tasks which are isolated from the game to be subsequently incorporated into play [ 9 ]. The most commonly used method in direct instruction are unspecific exercises and simple games [ 10 ]. The teacher provides the initial information with the criteria for successful performance and a prescriptive feedback to correct errors.
In the Student-Centered Approach, it can be highlighted of Teaching Game for Understanding, TGfU [ 11 ]. The TGfU appeared as a practical teaching model for designing tasks that concentrate the students’ attention as they look for solutions that will lead them to understanding the technical aspects of the game. The teacher is responsible for presenting a tactical problem which has to be developed through a series of tasks or games. The TGFU proposal contains 6 stages: play, perception of play, tactical awareness, decision making, technical execution and performance. Worldwide, different proposals have emerged with similar principals, Games Sense [ 12 , 13 ], Tactical Games, Sport Education Model [ 14 ], Play Practice [ 15 ], and Concept Based Games [ 16 ]. These proposals are based on situated learning, with meaningful and contextualized situations that favor students’ learning [ 17 , 18 ]. In general, the structure of the tasks is based on forms of play which present a tactical problem in the game that the students have to face with. In order to learning to progress it is important for the teacher to use interrogative feedback to make the students autonomously develop decision making and create their own tactical awareness [ 7 , 19 ]. Numerous studies confirm that the models based on understanding the game produce improvements over direct instruction with regard to understanding play, decision making, declarative knowledge, enjoyment and motivation in the classroom [ 20 – 22 ].
Learning tasks can be classified according to their degree of specificity, depending on the presence of formal game elements for which they were conceived. Thus they are divided into specific, semi-specific and unspecific tasks [ 23 ]. In invasion team sports the design and configuration of the learning tasks are linked to the learning methodologies [ 24 , 25 ]. Traditional teaching-learning methods, based on direct instruction, prevail in physical education [ 26 ]; therefore, the skills are worked on in an isolated from using unspecific or specific global tasks [ 27 ].
The tactical games approach uses the most contextualized game situation possible or situated learning [ 24 , 28 ]. Modifications in the game context facilitate the cognitive connection of the student with the game [ 18 ], making it easier to understand its complexity, identify tactical aspects and develop the decision-making process during the game [ 29 ]. The game presents a problem that the students must face with using their previous experience and their reflections on practice [ 30 ]. Semi-specific or unspecific tasks are also used and in a second phase, specific ones, which present decision-making problems of progressive complexity.
Currently, the analysis of learning tasks is an emerging research line in the field of sports education [ 31 ]. The results make it possible to analyze the existing link between the planning of learning tasks and learning methods [ 27 ], and knowledge of the pedagogical content [ 32 ], or the pedagogical variables [ 24 ]. It is important to analyze the learning tasks since these situations provide the practice conditions which allow the players to acquire and execute a sports learning content [ 31 ].
Learning tasks could be assessed according to various criteria such as: i) organizational, which serve to improve the practice time of the students, using group organization related aspects, use of space and equipment, and time control; ii) pedagogical, which allow students to understand the content types being worked on, their organization and sequencing [ 27 ], such as game phases [ 10 ], training means [ 10 ], trainee grouping in game situations [ 24 ], or the methodology employed by the coaches [ 32 ]; and iii) physiological, according to the demands placed on the students, both regarding the internal and external work load [ 33 ]. Currently there is a tool available for analyzing learning tasks in sport, the Integral System for Training Task Analysis (SIATE in Spanish) [ 34 ], which can be applied in sports and school context. It is a flexible and adjustable tool that can be adapted to diverse invasion team sports and learning contexts. This instrument allows to gather information focused on: Contextual Data; Coach Data; Session Data; Pedagogical Variables; Organizational Variables; External Work Load Variables; Internal Work Load Variables; and Kinematic Variables for each of the tasks that comprise a training session.
Pre-service teachers have to be aware of his owns decision consequences’. Tasks’ design plays a major role according the teaching model and, also, the external load imposed in the students. The study and analysis of their practice would help pre-service teacher to develop their teaching skills. Currently few studies exist that analyze the learning tasks designed by teachers for the development of educational goals. There is also a shortage of task design analysis under different methodological approaches, as well as of the learning levels acquired by the students [ 25 ]. Analyzed research shows that teachers are not well prepared to plan the training tasks, so PETE students’ analysis of their own practice is important to fill the gap between expert and novices teachers. The knowledge-based reasoning of physical education teachers: A comparison between groups with different expertise. Therefore, the aim of this study was to analyze the tasks planned by teachers in pre-service phase, before their specialization in the physical education area, for the design of a lesson plan on an invasion sport. The general objective was defined in three specific aims: i) To characterize the learning tasks designed by the pre-service physical education teachers from the variables that define a learning task; ii) To identify the relationships among the variables defining the learning tasks and the phases in which a session is structured; and iii) To create a classification on the development of learning tasks in the different phases of the session based on the variables that define them.
Materials and methods
The study used a comparative transversal associative strategy [ 35 ], in which the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase were asked to plan a lesson plan and design tasks to be analyzed from the point of view of the parts of the session.
The sample was comprised of 695 units of statistical analysis related to the learning tasks designed by fourteen PETE pre-service teachers. The 695 learning tasks came from the planning done by the pre-service teachers for a specific lesson plan on the development of a sporting content. Basketball was selected as the learning content from among the Invasion team sports.
The fourteen pre-service teachers (female 50%; age: 21.6 ±1.05 yrs), were starting their fourth year of training, and designed their planning before starting their internship stage. The first three years carry out a general education as a teacher, in which they take courses on the different disciplines taught in Primary Education. During these period students only receive a specific course on Physical Education Teaching. In the fourth year, students receive a specific training in physical education. They take four specific courses in Physical Education (24 ECTS credits), an external practicum period as a pre-service teacher (24 ECTS credits), a generalist teacher course (6 ECTS credits) and a final degree project (6 ECTS credits). None of the teachers had qualifications as a coach in any team sport. The lesson plans were developed during 12 lessons with total freedom to include the motor tasks considered appropriate.
The independent variable for this research was the lesson structure, which was organized in three stages: warm-up, main activity and culmination activity (this was the last activity before the cool-down). Physical education lessons begin whit the warming up, introducing the aims of the session and setting the student for later effort. In the main part, tasks designed for the development of the objectives of the session are presented. In the cool down activities try to return the body to normal state after vigorous activity.
The dependent variables were chosen to allow definition of the learning tasks. Some of the pedagogical and external load variables defined in the SIATE were selected [ 34 ] as follows: Learning means (different task type classification); Game Situation (number of players involved and the way they were related to the task); Game Phase (principal game phase aimed at the sports content worked on in the sports task). The external load variable employed in this study was Space (location where the students practiced). Also, two new variables were included: The presence of a mobile object (use of the ball in the task); and the kind of feedback provided by the teachers.
The study variables were presented to a panel of 11 experts. All the experts fulfilled the criteria of being Sports Science graduates with more than 10 years experience as physical education teachers in Primary School, and articles published in journals the field of didactics. Nine of them had a Ph.D. The experts gave points on a 1 to 10 scale for clarity in the wording of the item (univocity), adequacy regarding the objectives of the assessment (pertinence) and ability to discriminate the information with respect to the study objectives (importance). Aiken’s V was used to evaluate the adequacy of the study variables. Penfield and Giacobbi’s alebraic modified formula was used to calculate the content validity coefficient [ 36 ]. The exact critical value, or cutoff point, for accepting Aiken’s V was calculated using the formula proposed by Aiken [ 37 ], establishing a value of .83 with a 95% confidence interval. With regard to the pertinenece and importance of all the included variables they were above the critical value of.83 [.84–.93], while regarding the univocity of all the items they were above the critical value for Aiken’s V [.86–93].
The SIATE task analysis instrument [ 34 ] was adapted selecting the dimensions and categories that were best suited for analysis in the educational context. Two new specific variables for this study were included in the registration system.
Proceedings
In Spain, primary school teachers have to pass an educational process at the university with initial training lasting four years. After three years of training as a generalist teacher, the students have a fourth specific year in physical education training, along with an internship period in schools. A group of teachers in the pre-service phase, who were Master in Elementary Education students coursing their fourth year, were asked to design a Lesson Plan with sport as its content. The proposal was to teach an invasion sport that could be played in the school facilities where they were carrying out their teaching practice. Finally, basketball was selected since the resources, materials and facilities were available in every school. The Lesson Plans had to comprise 12 sessions in order to give enough time for learning acquisition, independently of the methodological approach employed in their design [ 20 ]. The session parts were also identified and it was recommended to organize in three parts: warm-up, main activity and culmination activity.
The raters who participated in this phase of the study held a Ph.D. and they are experienced in designing and coding teaching and training tasks. The tasks were analyzed using the SIATE instrument and an inter-rater and intra-rater analysis was carried out to guarantee the quality of the data [ 38 ]. Following Iguartua (2006), a representative part of the cases was selected as a function of the sample size for the reliability test, which was never smaller than 50 units [ 39 ]. Cohen’s Kappa was used to guarantee inter-rater and intra-rater reliability as the variables to be codified were categorical. [ 40 ]. It was necessary to use the multi-rater Kappa as there were more than two raters. The raters who participated in this phase of the study were Ph.Ds with ample experience in designing and coding teaching and training tasks. Randolph’s free multi-rater Kappa was used [ 41 ] as it is ideal when the raters assign a minimal proportion of agreement to a specific category [ 42 ]. The values obtained in the inter-rater reliability test in all the variables that defined the learning tasks were high ( k free >.87), considered as almost perfect [ 43 ]. In the game phase and learning means variables the value was slightly lower ( k free >.78) considered as substantial concordance [ 43 ]. The intra-rater reliability of all grouped variables was almost perfect ( k free >.83).
Statistical analysis
A descriptive exploratory analysis was performed of every variable that defined the learning tasks according to the structure of the physical education lesson. The number of cases and the percentage of each variable are presented in contingency tables.
Secondly, an inferential analysis was used to identify the relations and associations among the study variables. Pearson’s chi-squared test (χ2), was used to contrast the hypothesis of independence between the categorical variables analyzed. The association degree between the variable categories was identified with Cramer’s V coefficient (φc) [ 44 ]. Due to the fact that the Crosstabs Command includes expected frequency distribution lower than 5, and may mask non-significant associations, the Fisher’s exact test was used (Montecarlo adjustment). The association strength was interpreted following the criteria defined by Acock [ 45 ]. The adjusted standardized residuals (ASR) of the contingency tables were used to interpret the meaning of the associations found in those cases in which the value was greater than |1.96|. Finally, the correspondence analysis was employed to illustrate the positive association between variables [ 46 ].
A decision tree analysis was used to create the predictive model to illustrate the classification and segmentation of the relation among variables [ 47 ]. The CHAID (Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector) algorithm [ 48 ] was used, since most of the variables were nominal and not binary. This algorithm is one of the most suitable for the social sciences [ 49 ]. Exhaustive CHAID method have been used. This method allows to, independently of the categories, analyse with more precision all possible results [ 50 ]. A cross validation, with a tree depth of 3 was employed, with a minimum of 75 cases in the filial node and a minimum of 35 cases in the parental node. The statistical software used was the IBM SPSS for Windows version 21 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.).
Table 1 presents the descriptive analysis of the learning tasks planned by the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase for the different parts of the physical education lesson. The most utilized learning mean of the analyzed tasks designed by the teachers was simple exercise (38%) and the unspecific simple game (23.2%). In the warm-up phase simple exercise (45.6%) and unspecific simple game (43.1%) predominate with a scarce presence of more complex games. In the main activity phase they principally used simple exercises (43%) and diverse specific game modalities for the sport: Modified game (13.9%), Specific game (16.2%) and Sport (10.3%).
The trainee groups and game situations that were most frequent in the teachers’ planning were 1x0 and 2x0 (46.5%) and 1x1 (23.7%), and it was also observed that individual work prevailed e.g. 1x1 and 1x0 (59.42%). In the warm-up phase 1x1 (40%) and 1x0 (34.4%) predominated; in the main activity 1x0 (37.6%), 1x1 (19.4%) and number inequality (11.3%) were the most common situations. In the culmination phase individual work activities 1x0 (32%) and 1x1 (17.7%) were more common and for the collective game work nxn (19%) and 1x3/4x4 (10.2%).
The results show that most of the tasks were designed to work specifically on the attack phase ( n = 408), with attack tasks predominating (58.7%) followed by mixed tasks (25.9). The attack content dominated in the three phases of the lesson.
Teachers used activities in reduced spaces, ¼ of the game court (7.2%), very little. In the warm-up and culmination activity phases full court usage was prioritized, meanwhile in the main activity phase half the court was employed. Ball presence predominated in the tasks (93.7%), Table 2 .
The most commonly used feedback was prescriptive (47.6%) followed by motivational (28.3%) and interrogative (18.1%). In the warm-up (40%) and culmination activity (54.4%) phases, prescriptive feedback was mainly used and prescriptive feedback (62.6%) was the most common in the main activity phase.
An inferential analysis was performed to identify the relation between variables that define the learning tasks and lesson structure. A dependant relation between the learning means and the structure of the lesson ( X 2 = 137.57; gl = 12; p < .001/ Fisher’s exact test = 149.85; p < .001) was found. The degree of association between the variable categories was moderate ( φc = .314; p < .005). In more cases than would be expected, in the warm up part, teachers in the pre-service phase proposed simple exercises ( ASR = 2.3) and unspecific simple games ( ASR = 6.8). On the contrary, in this session phase, modified games ( ASR = -2.5), specific games ( ASR = -4.2) and pre-sport-sport ( ASR = -4.6) were employed on fewer occasions than expected. In the main activity phase of the lesson there were more learning tasks than expected of simple exercises ( ASR = 3.1) and specific games ( ASR = 3.9). However, there were less cases than expected of unspecific simple games ( ASR = -6.9). Finally, in the culmination activity part, the learning means were diverse. The results show that there were more cases than expected using pre-sport or sport ( ASR = 5.5) and modified games ( ASR = 2.7) and less cases than expected of simple exercises ( ASR = -6.1). The correlation analysis ( Fig 1 ) shows the positive significant associations identified in the contingency tables.

The chi-square statistic shows that there is a dependent relation between the game situations and session parts ( X 2 = 119.52; gl = 16; p < .001/ Fisher’s exact test = 111.44; p < .001), with a moderate association ( φc = .293; p < .005). The contingency table analysis and the correlation chart ( Fig 2 ) indicate that in the warm up phase there were more cases than expected of 1x1 ( ASR = 5.5) and 2x0 ( ASR = 3.1) situations. On the other hand, there were less 2x2, 3x3, 4x4, 5x5 and number imbalance ( ASR = -2.4 to -3.3) situations. In the main activity phase the prevalence of the individual work situations is noteworthy, 56.96% with 1x0 (n = 146) and 1x1 (n = 75) tasks. In the main activity phase there were more cases of 3x3/4x4 and number imbalance situations ( ASR = 2.9 and 3.6 respectively) than expected and less cases than expected of 1x1 and nxn situations ( ASR = -3.1 and -4.0, respectively). Lastly, in the culmination activity phase, the results show that there were more cases of 3x3 and 4x4 ( ASR = 2.6) and nxn situations ( ASR = 6.7) than expected.

Significant associations were found between the Game phases ( X 2 = 30.24; gl = 6; p < .001/ Fisher’s exact test = 30.52; p < .001) and Session parts variables with a low strength ( φc = .148; p < .001). In the correlation chart, Fig 3 , it can be seen that in the warm-up phase there were more cases than expected of tasks that are not developed in any phase of the game ( ASR = 3.2) and less cases than expected of working with mixed objectives, meaning attack and defense ( ASR = -3.4). In the main activity phase there were less cases than expected of tasks without specific goals in the game ( ASR = -3.6). In the culmination activity phase attack objectives were more prevalent, although there were fewer cases than expected compared to the other tasks ( ASR = -3.3), however there were more tasks with mixed objectives ( ASR = 3.2).

Space usage ( X 2 = 46.17; gl = 4; p < .001 / Fisher’s exact test = 47.87; p < .001) was associated with the lesson phases, although this association was weak ( C = .250; p < .001). In the warm-up phase full court activities predominated ( ASR = 6.5), while in the main activity phase half court usage prevailed ( ASR = 4.9) and there were fewer cases than expected of full court activities ( ASR = -5.2). Tasks in a reduced space, less than half the court, were scarce, representing just 7.2%.
Ball presence was dominant in the tasks (93.7%). A significant association ( X 2 = 7.65; gl = 2; p < .05 / Fisher’s exact test = 129.81; p < .001) was found between ball presence in tasks and lesson parts where they were used, although this association was low ( φc = .105; p < .05).
Lastly, the analysis showed significant associations between planned feedback in the task ( X 2 = 190.41; gl = 6; p < .001/ Fisher’s exact test = 190.50; p < .001) and the parts of the lesson with a moderate association ( φc = .370; p < .005). The correlation chart ( Fig 4 ) shows that in the warm-up phase there were more cases of motivational feedback ( ASR = 3.7) and less cases than expected of prescriptive feedback ( ASR = -4.0); also, it is noticeable that in this phase there were contents without planned feedback ( ASR = 7.5). The future teachers employed the prescriptive ( ASR = 8.9) and interrogative feedback ( ASR = 3.9) more in the main activity of the lesson, showing fewer cases than expected of motivational feedback ( ASR = 9.7).

The decision tree technique was used to predict what kind of tasks the teachers employed in the three required parts of the lesson. Learning means, Game phase, Player relation, Space, Mobile object presence and Kind of feedback were included in the model. The exhaustive CHAID algorithm showed a risk of an estimated .345 in the cross validation, with an error of .018. In general, 67.3% of the tasks were correctly classified, although specifically the warm-up (37.5%) and culmination activity tasks (51%) were classified much lower than the main activity phase tasks (85.8%).
The decision tree comprises fourteen nodes. In the zero node the highest percentage of tasks was developed in the main activity phase (55.8%), Fig 5 . The dependant variable branches into three nodes belonging to the task feedback variable, with node 2, interrogative and prescriptive feedback, showing a higher chi-squared value ( X 2 = 70.090; df = 6; p < .001). Node 2 re-branches into four lines, nodes 6 to 9, with node 6, Simple exercise, grouping more tasks ( n = 198), followed by node 8 Complex exercise, Specific Game and Modified game ( n = 154). Node 8 re-branches ( X 2 = 28.264; df = 6; p < .001), with the variable relation between the players in nodes 12 and 13. Node 12 comprises activities without opponents (2x0, 3x0, 4x0), individual game 1x1 and collective game 5x5 situations, meanwhile node 13 is formed by collective game situations and small sided games (2x2, 3x3, 4x4) and individual situations (1x0).

Node 1, motivational feedback ( X 2 = 30.730; df = 6; p < .001), gives rise to nodes 4 and 5, belonging to the space variable, with node 4 re-branching in the Learning means variable ( X 2 = 18.662; df = 6; p < .001), nodes 10 and 11. Node 4 shows that fullest court tasks are developed in the warm-up phase (47.85%), meanwhile the use of the half court in tasks with motivational feedback occurred in the culmination activity phase (50%). Node 10 shows that in full court activities with motivational feedback the most commonly used tasks in the warm-up phase were the Simple exercises (72.1) meanwhile in node 11 in the culmination activity phase there was a diverse amount of learning means with greater difficulty ( Fig 5 ).
The general objective of this study was to analyze the tasks planned by teachers in the pre-service phase before their specialization in the physical education area. During their internships in schools, these teachers plan the lesson plans of an invasion sport such as basketball using mainly simple exercises followed by unspecific simple game as the learning-teaching means. Only one third of the means are contextualized in sports game problems, employing modified games, the specific game and the sport. Moreover, half the game situations have no opponents, with the 1x0 situation predominating. The most utilized situation from those without opponents is the 1x1. Finally, the most worked on game phase is the attack phase.
An analysis of the employed learning means (exercises and simple games) and learning situations (mainly without opponents) seems to indicate that teachers in the pre-service phase do not employ tasks that are specific and contextualized in the sport itself, which would imply that they are more inclined towards traditional teaching, from the point of view of the methods used [ 27 ]. The motor responses of the students are initially defined in the tasks, with a limited margin for decision making [ 51 ]. Similar results have been found in Secondary Education/High School where the teachers employ a high volume of decontextualized and clearly defined tasks [ 52 ]. Some authors consider that these closed activities are associated with inexperienced teachers, since they apparently give them greater control of the situation. Also the use of models centered on understanding the game provides less security for inexperienced teachers. Likewise, some experience is necessary in order to manipulate and modify the game situations through restrictions and rules [ 53 ] that allow the teacher to create new game problems. All of this causes a lack of confidence in the teachers in the designing of tasks using this approach [ 54 ]. These results differ from the ones found in coaches of school-age children in the extra-curricular context, where 1x1 situations followed by 2x2 situations prevailed [ 24 ].
Furthermore, the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase mainly designed attack phase contents. This tendency matches the results obtained from analyzing basketball teaching for these ages in after-school sport [ 10 ]. Beginning in the attack phase increases the students’ motivation, with the development of attack and defense contents evolving in an undulating manner [ 55 ].
It is noticeable that half the feedback planned by the teachers is of the descriptive and/or prescriptive type, with motivational feedback also being used. Similar results were found in the teaching of collective sports in the Mandatory Secondary Education/High School, where the feedback was mainly prescriptive and affective, followed by reflexive [ 52 ]. Interrogatory feedback is the least employed. Teachers do not plan topics ahead to foster reflection among the students. The PETE teacher knows that different types of feedback allow different objectives to be achieved, as is demonstrated when they vary their use during the lesson. They start with motivational feedback, evolving during the main activity phase to mostly prescriptive. The comprehensive methodology is based on the stimulation of the students’ reflection to adapt their knowledge to the conditions of practice [ 18 ]. The designing of quality questions should be an integral part of the teacher’s planning process [ 56 ], and this is one of the greatest difficulties experienced by teachers for applying a model centered on game comprehension [ 54 ].
One of the principles of game comprehension centered models is the modification of learning situations through the exaggeration and simplification of the elements of the sports game. In the PETE teachers’ planning, half the learning means are exercises and simple games, employing no opponent situations, with interrogative feedback being the least utilized choice. These characteristics show that the teaching process follows a traditional approach [ 57 ].
In the PE lesson, the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase show a preference for some of the task characteristics. In the warm-up phase they employ mostly simple exercises and unspecific simple games, eliminating warm-ups with analytical activities, such as exercises, and replacing them with unspecific games [ 58 ]. They use fewer learning means related to the game, such as modified games, specific game, pre-sport and sport. Also, the most employed game situations in this phase are 1x1 and activities without an opponent, 1x0 and 2x0. From a cognitive point of view, these activities performed in the warm-up phase are less difficult because of the lack of rules and the fact that they are oriented towards physical activation and learning technical abilities.
In the main activity phase the use of simple exercises prevails, while in the last phase of the lesson, played situations predominate. Although in this part of the lesson there is an increase in the means based on the game, in general, the teaching methodology is more centered on the traditional model [ 59 ]. Furthermore, in the main activity there are fewer cases than expected of 1x1 activities and the activities without opponent are maintained, greatly increasing the group situations without defense (3x0; 4x0) and with unbalanced numbers. Basic situations without opponents (1x0, 2x0, … 5x0) and easy commands favors the teachers’ control sensation. Also, the easy reproduction by students of these types of routines generated an efficacy thinking on pre-service teachers. This perception allow teachers to prefer teacher centered methods. In addition, previous experiences in teacher centered approach in sport learning or the scarce availability of specific literature about lessons design in students centered approach could lead to avoid these students centered methods [ 60 ].
The PETE teachers in the pre-service phase were also required to design an activity as the culmination event of the session. In this phase, the most employed method was the simple game. Moreover, it was observed that the specific tasks increase, as a learned content application method during the session, with more modified games and sport; balanced number games significantly increase, 3x3, 4x4 and nxn, coming closer to being centered on game comprehension [ 59 ].
Game content selection, for attacking and defending phases, is an important part of the lesson plan. The PETE teachers in the pre-service phase designed tasks with different contents as a function of the game phase and part of the session. Attack game phase contents predominate in the work of these PETE teachers. The warm-up phase contains tasks without an orientation towards game content. Possibly these activities are oriented towards physiological warm-up and the development of basic motor skills. In the culmination activity phase there is a significant increase in mixed (attack and defense) tasks, probably because these tasks have been designed for the application of knowledge in the real game. In general the PETE teachers employed more attack tasks, probably due to the motivation attached to attack [ 61 ]. On the other hand, without previous attack content work it is very difficult to develop defensive actions [ 62 ]. Tasks using a ball are mostly used, using the full court for the warm-up phase and the half court and small sided game, for the main activity.
Feedback is part of the teacher-student communication process being one of the actions that allow orientation of the task. In the warm-up phase motivational feedback or no feedback activities prevail, with no clear orientation towards any teaching-learning method. In the main activity phase of the session, the feedback is mostly prescriptive, and occasionally interrogative, a significant increase compared to the previous phase. In the culmination activity phase the motivational feedback greatly increases. Interrogative or reflexive feedback is not employed for the students to verbalize key ideas for task resolution.
In summary, the high predominance of exercises, unspecific games, and no opponent situations, together with the low percentage of reflexive feedback, indicates that the teaching gives prevalence to technical over tactical learning [ 32 ], based on the practice of decontextualized and isolated tasks before their application to the real game [ 29 ], representing a traditional teaching-learning model [ 52 ]. This decomposition and elimination of the game elements in the task design leads to a learning process isolated from the real sport practice scenarios [ 63 ]. Contextualized, or situated, learning, with modifications of the game situations, allows the application of students’ previous knowledge favoring their understanding of the game [ 18 ], and their motivation. These tasks are designed with the modification of rules and specific game elements, such as partner players, adversaries, mobile objects and game space, and can be aimed towards the development of contents in the attack and defense phases.
In general, the observed characteristics of the tasks designed by the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase are closer to a traditional methodology, despite their having received information about the different methods of sports teaching in their initial training. This seems to indicate a resistance to changing a traditional model for other models centered on game comprehension. It is more than likely that the decisions made by these teachers are based on implicit ideas and not on empirical-scientific or academic evidence [ 64 ]. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the teachers’ previous beliefs and knowledge since they influence their choice and the development of the teaching profession. It is very important for pre-service teachers to have real experiences in PE lessons during their teaching. This experience can have a direct impact on their behaviors and decisions when planning. Pre-service teachers need to experience students centered approaches during their formation. Reflexive thinking about these models, previous experiences as school students and athletes, and their present practice in real context could lead to avoid to repeat teacher centered approach.
Practical applications
Teacher training centers have to emphasize a paradigm shift in the model of the future teachers. As was observed in this work, theoretical-practical academic training is not enough to orientate the teachers towards more constructive models. The study plans have to be concerned with provoking meaningful experiences for the students and foster reflective processes in order to contrast previous experiences with the learning models centered on game comprehension, considering the advantages for school learning and how to overcome the difficulties of their application in the classroom. Likewise, the practical phase of the PETE teachers has to be reconsidered; encouraging reflection to overcome their implicit beliefs and favoring the transmission of practical knowledge according to the constructive based learning models through mentoring.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the “Ayuda a los Grupos de Investigación (GR18170)” of Govern of Extremadura (Economy and Infrastructures Department); with the support of European Union through FEDER founds. These have been all the funding or sources of support received during this study. There was no additional external funding received for this study.
Funding Statement
This work has been partially supported by the “Ayuda a los Grupos de Investigación (GR18170)” of Govern of Extremadura (Economy and Infrastructures Department); with the support of European Union through FEDER founds. These have been all the funding or sources of support received during this study. There was no additional external funding received for this study
Data Availability

Remember, the longer the due date, the lower the price. Place your order in advance for a discussion post with our paper writing services to save money!
- Individual approach
- Fraud protection
Customer Reviews
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What federal education data shows about students with disabilities in the U.S.
Public K-12 schools in the United States educate about 7.3 million students with disabilities – a number that has grown over the last few decades. Disabled students ages 3 to 21 are served under the federal Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) , which guarantees them the right to free public education and appropriate special education services.
For Disability Pride Month , here are some key facts about public school students with disabilities, based on the latest data from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) .
July is both Disability Pride Month and the anniversary of the Americans with Disabilities Act. To mark these occasions, Pew Research Center used federal education data from the National Center for Education Statistics to learn more about students who receive special education services in U.S. public schools.
In this analysis, students with disabilities include those ages 3 to 21 who are served under the federal Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) . Through IDEA, children with disabilities are guaranteed a “free appropriate public education,” including special education and related services.
The 7.3 million disabled students in the U.S. made up 15% of national public school enrollment during the 2021-22 school year. The population of students in prekindergarten through 12th grade who are served under IDEA has grown in both number and share over the last few decades. During the 2010-11 school year, for instance, there were 6.4 million students with disabilities in U.S. public schools, accounting for 13% of enrollment.
The number of students receiving special education services temporarily dropped during the coronavirus pandemic – the first decline in a decade. Between the 2019-20 and 2020-21 school years, the number of students receiving special education services decreased by 1%, from 7.3 million to 7.2 million. This was the first year-over-year drop in special education enrollment since 2011-12.
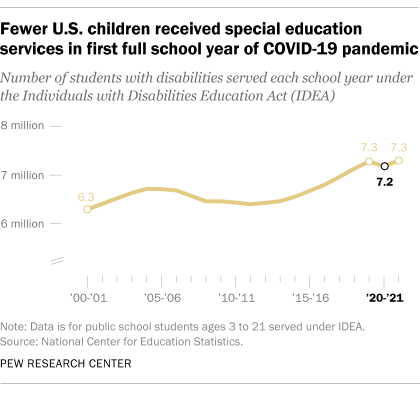
The decline in students receiving special education services was part of a 3% decline in the overall number of students enrolled in public schools between 2019-20 and 2020-21. While special education enrollment bounced back to pre-pandemic levels in the 2021-22 school year, overall public school enrollment remained flat.
These enrollment trends may reflect some of the learning difficulties and health concerns students with disabilities and their families faced during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic , which limited or paused special education services in many school districts.
Many school districts struggle to hire special education professionals. During the 2020-21 school year, 40% of public schools that had a special education teaching vacancy reported that they either found it very difficult to fill the position or were not able to do so.
Foreign languages (43%) and physical sciences (37%) were the only subjects with similarly large shares of hard-to-fill teaching vacancies at public schools that were looking to hire in those fields.
While the COVID-19 pandemic called attention to a nationwide teacher shortage , special education positions have long been among the most difficult for school districts to fill .
The most common type of disability for students in prekindergarten through 12th grade involves “specific learning disabilities,” such as dyslexia. In 2021-22, about a third of students (32%) receiving services under IDEA had a specific learning disability. Some 19% had a speech or language impairment, while 15% had a chronic or acute health problem that adversely affected their educational performance. Chronic or acute health problems include ailments such as heart conditions, asthma, sickle cell anemia, epilepsy, leukemia and diabetes.
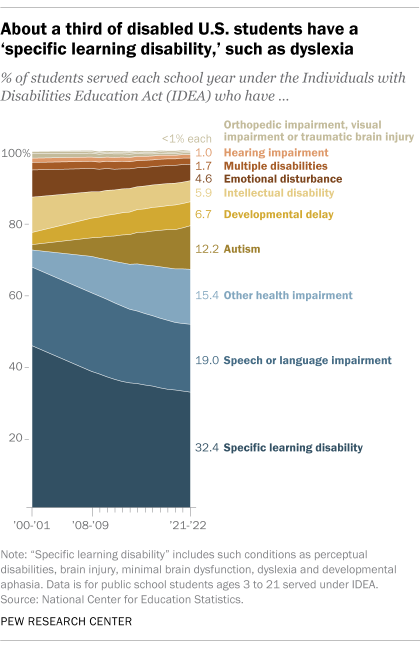
Students with autism made up 12% of the nation’s schoolchildren with disabilities in 2021-22, compared with 1.5% in 2000-01. During those two decades, the share of disabled students with a specific learning disability, such as dyslexia, declined from 45% to 32%.
The percentage of students receiving special education services varies widely across states. New York serves the largest share of disabled students in the country at 20.5% of its overall public school enrollment. Pennsylvania (20.2%), Maine (20.1%) and Massachusetts (19.3%) serve the next-largest shares. The states serving the lowest shares of disabled students include Texas and Idaho (both 11.7%) and Hawaii (11.3%).
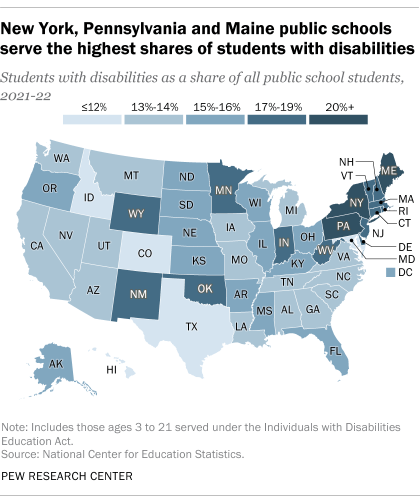
Between the 2000-01 and 2021-22 school years, all but 12 states experienced growth in their disabled student populations. The biggest increase occurred in Utah, where the disabled student population rose by 65%. Rhode Island saw the largest decline of 22%.
These differences by state are likely the result of inconsistencies in how states determine which students are eligible for special education services and challenges in identifying disabled children.
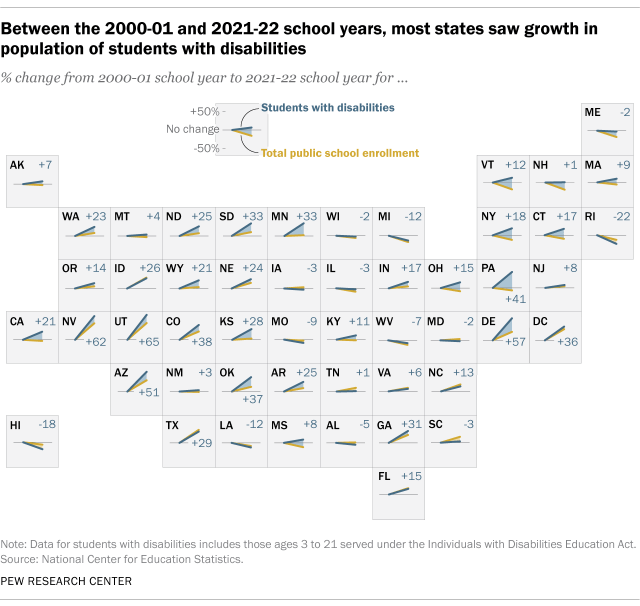
The racial and ethnic makeup of the nation’s special education students is similar to public school students overall, but there are differences by sex. About two-thirds of disabled students (65%) are male, while 34% are female, according to data from the 2021-22 school year. Overall student enrollment is about evenly split between boys and girls.
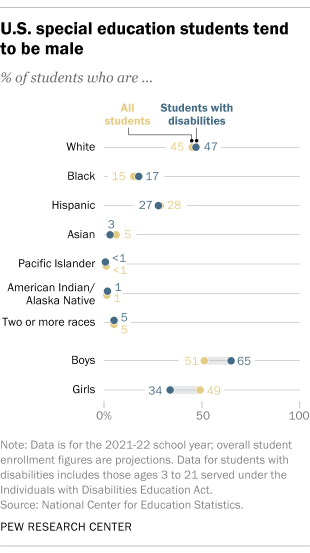
Research has shown that decisions about whether to recommend a student for special education may be influenced by their school’s socioeconomic makeup, as well as by the school’s test scores and other academic markers.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published April 23, 2020.

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center
Most Americans think U.S. K-12 STEM education isn’t above average, but test results paint a mixed picture
About 1 in 4 u.s. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year, about half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, what public k-12 teachers want americans to know about teaching, what’s it like to be a teacher in america today, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

You may be worried that your teacher will know that you took an expert's assistance to write my essay for me, but we assure you that nothing like that will happen with our write essay service. Taking assistance to write from PenMyPaper is both safe and private. We respect your privacy and thus do not ask for credentials like your name, college, location, or your phone number. To pay for the essay writing, you can either use your debit or credit cards to pay via PayPal or use your wallet balance from our website. All we would need is your card details and your email-id. This is our responsibility that your information will be kept all safe. This is what makes our service the best essay writing service to write with.
We hire a huge amount of professional essay writers to make sure that our essay service can deal with any subject, regardless of complexity. Place your order by filling in the form on our site, or contact our customer support agent requesting someone write my essay, and you'll get a quote.
Once I Hire a Writer to Write My Essay, Is It Possible for Me to Monitor Their Progress?
Absolutely! Make an order to write my essay for me, and we will get an experienced paper writer to take on your task. When you set a deadline, some people choose to simply wait until the task is complete, but others choose a more hands-on process, utilizing the encrypted chat to contact their writer and ask for a draft or a progress update. On some occasions, your writer will be in contact with you if a detail from your order needs to be clarified. Good communication and monitoring is the key to making sure your work is as you expected, so don't be afraid to use the chat when you get someone to write my essay!
Customer Reviews

In the order page to write an essay for me, once you have filled up the form and submitted it, you will be automatically redirected to the payment gateway page. There you will be required to pay the entire amount for taking up the service and writing from my experts. We will ask you to pay the entire amount before the service as that gives us an assurance that you will come back to get the final draft that we write and lets us build our trust in you to write my essay for me. It also helps us to build up a mutual relationship with you while we write, as that would ease out the writing process. You are free to ask us for free revisions until you are completely satisfied with the service that we write.
Team of Essay Writers
Customer Reviews
Finished Papers
Specifically, buying papers from us you can get 5%, 10%, or 15% discount.
Advocate Educational Integrity
Our service exists to help you grow as a student, and not to cheat your academic institution. We suggest you use our work as a study aid and not as finalized material. Order a personalized assignment to study from.
Artikel & Berita
Write my essay for me.
You are free to order a full plagiarism PDF report while placing the order or afterwards by contacting our Customer Support Team.
EssayService strives to deliver high-quality work that satisfies each and every customer, yet at times miscommunications happen and the work needs revisions. Therefore to assure full customer satisfaction we have a 30-day free revisions policy.
PenMyPaper offers you with affordable ‘write me an essay service’
We try our best to keep the prices for my essay writing as low as possible so that it does not end up burning a hole in your pocket. The prices are based on the requirements of the placed order like word count, the number of pages, type of academic content, and many more. At the same time, you can be eligible for some attractive discounts on the overall writing service and get to write with us seamlessly. Be it any kind of academic work and from any domain, our writers will get it done exclusively for you with the greatest efficiency possible.
- Our Services
- Additional Services
- Free Essays
Compare Properties
Finished Papers

What is the native language of the person who will write my essay for me?
Essay Service Features That Matter
Customer Reviews
Deadlines can be scary while writing assignments, but with us, you are sure to feel more confident about both the quality of the draft as well as that of meeting the deadline while we write for you.
Please, Write My Essay for Me!
Congratulations, now you are the wittiest student in your classroom, the one who knows the trick of successful and effortless studying. The magical spell sounds like this: "Write my essay for me!" To make that spell work, you just need to contact us and place your order.
If you are not sure that ordering an essay writing service is a good idea, then have no doubts - this is an absolutely natural desire of every aspiring student. Troubles with homework are something all learners have to experience. Do you think that the best high-achievers of your class pick the essays from some essay tree? - They have to struggle with tasks as well as you do. By the way, the chances are that they are already our customers - this is one of the most obvious reasons for them to look that happy.
Some students are also worried that hiring professional writers and editors is something like an academic crime. In reality, it is not. Just make sure that you use the received papers smartly and never write your name on them. Use them in the same manner that you use books, journals, and encyclopedias for your papers. They can serve as samples, sources of ideas, and guidelines.
So, you have a writing assignment and a request, "Please, write my essay for me." We have a team of authors and editors with profound skills and knowledge in all fields of study, who know how to conduct research, collect data, analyze information, and express it in a clear way. Let's do it!

Affiliate program
Refer our service to your friend and receive 10% from every order

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Physical Education and Its Benefits. Schools in particular know the benefits of physical education in a student's life and should be able to fight for the children's rights. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
4 pages / 1770 words. The purpose of this essay is to reflect on the concept of physical education and sport methodically in school, and in detail, typically the role it brings about to developmental stages of children. Physical education is the training in the development of the human body;... Physical Education Physical Exercise.
A physical education (PE) teacher is responsible for instructing students in physical fitness, sports, and other physical activities. PE teachers design and implement lesson plans that help students develop their physical abilities, including their strength, endurance, coordination, and flexibility. They may teach a wide range of activities, such as team sports like basketball or soccer ...
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more. Long and Short Essays on Physical Education for Students and Kids in English. We are providing students with essay samples on a long essay of 500 words and a short essay of 150 words on the topic of Physical Education for reference.
Physical education leads to a more focused, active, composed, and happy in life. It makes us disciplined and arranged. Habits formed with the assistance of education tend to remain with us for an extended time. We should bring skilled coaches and needed equipment to colleges. Students should know its benefits.
1. Introduction. Physical education (PE) is described "as the only curriculum subject whose focus combines the body and physical competence with values-based learning and communication, [which] provides a learning gateway to grow the skills required for success in the 21st Century" (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation [UNESCO], Citation 2015, p. 6).
Due to its focus on the prioritisation of personal significance of movement experiences, the promotion of meaningfulness in Physical Education (PE) has the potential to strengthen pedagogy and encourage a lifelong pursuit of physical activity (Kretchmar, 2006).This perspective comes at a time when many students cite current versions of PE as lacking relevance to their lived experiences (Ladwig ...
Introduction. Content Knowledge (CK) and Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) have been intensively discussed in the scholarship of physical education and Physical Education Teacher Education (PETE) (Capel et al. Citation 2011; Herold and Waring Citation 2018; Iserbyt, Ward, and Li Citation 2017; Tinning Citation 2010; Ward and Ayvazo Citation 2016).We see two limitations in the discussions of ...
ABSTRACT. The paper is the José María Cagigal Scholar Lecture presented at the AIESEP World Congress in Edinburgh 2018. In the paper I argue that the only real sustainable aim for physical education is more physical education, where different ways of being in the world as some-body are both possible and encouraged. To reach this aim, a focus on the art of teaching is vital as a way of ...
Physical Education, or PE for short, is a subject in school where students get to be active and learn about sports and exercises. It's not just about playing games; it's also about understanding how to keep our bodies healthy and strong. In PE, teachers show kids how to move their bodies in different ways and play various sports.
Physical education is not just important for the students to take a break from the elective subjects, it is also for their mental health. Sports make people more healthy, strong, and safe from all diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cancer. For any person sports strengthen their physical wellbeing and blood circulation.
Table 1 presents the descriptive analysis of the learning tasks planned by the PETE teachers in the pre-service phase for the different parts of the physical education lesson. The most utilized learning mean of the analyzed tasks designed by the teachers was simple exercise (38%) and the unspecific simple game (23.2%).
Earlier research indicates that physical education (PE) in school is associated with positive outcomes (e.g., healthy lifestyle, psychological well-being, and academic performance). Research assessing associations with resilience and thriving indicators, such as the 5Cs of Positive Youth Development (PYD; competence, confidence, character, caring, and connection) is limited and more so in the ...
Our essay help exists to make your life stress-free, while still having a 4.0 GPA. When you pay for an essay, you pay not only for high-quality work but for a smooth experience. Our bonuses are what keep our clients coming back for more. Receive a free originality report, have direct contact with your writer, have our 24/7 support team by your ...
Students with autism made up 12% of the nation's schoolchildren with disabilities in 2021-22, compared with 1.5% in 2000-01. During those two decades, the share of disabled students with a specific learning disability, such as dyslexia, declined from 45% to 32%. The percentage of students receiving special education services varies widely ...
This McCloy Lecture sheds light on the "hidden profession" of Physical Education Teacher Educators (PETEs) by sharing my perspectives on the challenges and opportunities faced by PETE scholars and teachers globally. I begin with an overview of my biography and how it has influenced my thinking about PETE. I present some scholarly critiques ...
Short Essay On Physical Education Teacher. 4.8/5. Once your essay writing help request has reached our writers, they will place bids. To make the best choice for your particular task, analyze the reviews, bio, and order statistics of our writers. Once you select your writer, put the needed funds on your balance and we'll get started.
The writers of PenMyPaper establish the importance of reflective writing by explaining its pros and cons precisely to the readers. They tend to 'do my essay' by adding value to both you (enhancing your knowledge) and your paper. View Sample. REVIEWS HIRE. Your Price: .40 per page.
Short Essay On Physical Education Teacher - REVIEWS HIRE. 784 . Finished Papers. 4.8/5. Your Price:.40 per page. High Achievers at Your Service ... Short Essay On Physical Education Teacher, Professional School Essay Writers Website Uk, Essay Of Studying Overseas, Expository Writing Graphic Organizer Middle School, Curriculum Vitae Medic ...
Professional authors can write an essay in 3 hours, if there is a certain volume, but it must be borne in mind that with such a service the price will be the highest. The cheapest estimate is the work that needs to be done in 14 days. Then 275 words will cost you $ 10, while 3 hours will cost you $ 50. Please, take into consideration that VAT ...
Got my paper!!! Place an order. Max Area (sq ft) DRE #01103083. Min Area (sq ft) 1977 Orders prepared. I ordered a paper with a 3-day deadline. They delivered it prior to the agreed time. Offered free alterations and asked if I want them to fix something.
While teachers typically reflect in order to teach or learn how to teach, student reflection in PE practice is always embodied and situated and aims to develop physical, cognitive, social and affective competencies for life (see for example Norwegian Directorate for Education and Training Citation 2020; Ministry of Education Citation 2019 ...
Short Essay On Physical Education Teacher. Hire experienced tutors to satisfy your "write essay for me" requests. Enjoy free originality reports, 24/7 support, and unlimited edits for 30 days after completion. Place your order Use our user-friendly form to place your order.
Short Essay On Physical Education Teacher. Progressive delivery is highly recommended for your order. This additional service allows tracking the writing process of big orders as the paper will be sent to you for approval in parts/drafts* before the final deadline. A personal order manager.