Should I Pursue A Master’s or A Ph.D.?

The first step in deciding on the right graduate program for you is to figure out which degree will best serve you—a master’s or a doctor of philosophy (Ph.D.). Here are a few factors to consider.

What are your career goals?
- Professional master’s: A good choice if you want to develop a particular skill set in order to practice a particular profession. This type of degree provides coursework focused on learning and practicing skills.
- Research master’s: A good fit if you want to gain expertise in a discipline and know how to teach it. A research master’s typically includes a research project or thesis and comprehensive exams in addition to coursework and provides experience in research and scholarship.
- Ph.D. (doctor of philosophy): Consider this option if your goal is to ground yourself in a body of research and develop the ability to add to that body of knowledge. Ph.D. study includes a major research project in addition to coursework, and a Ph.D. is the highest scholastic degree awarded by American universities. Contrary to common perception, career paths for Ph.D. graduates are quite varied, not just limited to academia. Ph.D. training helps you hones skills such as writing, research, teaching, data analysis, communicating complex topics—all of which can translate into many sectors, including industry, government, nonprofit, and entrepreneurship.
See career data for Duke graduate programs' alumni
How much time do you have to pursue a graduate degree?
Master’s degrees typically take two years to complete, while Ph.D. programs generally take five to seven years ( see Duke programs' time-to-degree ). That is a significant difference in commitment and opportunity costs. It might also play a key role in deciding which factors take higher priority as you evaluate a program. How does the length of the program fit with your career and family plans? How important is the surrounding community if you are going to be there for seven years instead of two? How long are you able or willing to go on a limited income while in graduate school?
How much can you afford to pay for a graduate degree?
Consider your personal financial situation (e.g., how much savings and student loans do you have), as well as how much financial aid you can get. Master’s and Ph.D. programs differ greatly in the amount of financial aid available. Ph.D. programs tend to offer significantly more financial support than master’s programs (but often will have research or teaching requirements).
A typical Ph.D. financial aid package usually includes coverage of tuition and fees, a living stipend, and some level of support for health insurance for a set number of years. For instance, Duke’s standard Ph.D. package covers tuition, mandatory fees, and a stipend for five years, as well as health insurance premiums for six years.
Within an institution, the level of financial support often differs across programs, so be sure to ask your specific program about the financial aid it offers. There are also many national organizations that provide competitive fellowships and scholarships for graduate students.
Know which degree you want to pursue? Here are some key things to look for in a program .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- Master’s vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Published on November 27, 2020 by Lauren Thomas . Revised on June 1, 2023.
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master’s and doctoral degrees:
- A master’s is a 1–2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers.
- A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3–7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research.
A master’s is also the necessary first step to a PhD. In the US, the master’s is built into PhD programs, while in most other countries, a separate master’s degree is required before applying for PhDs.
Master’s are far more common than PhDs. In the US, 24 million people have master’s or professional degrees, whereas only 4.5 million have doctorates.
Table of contents
Master’s vs phd at a glance, which is right for you, length of time required, career prospects, costs and salaries, application process, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about master's and phd degrees.
The table below shows the key differences between the two.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A PhD is right for you if:
- Your goal is to become a professor at a university or some other type of professional researcher.
- You love research and are passionate about discovering the answer to a particular question.
- You are willing to spend years pursuing your research even if you have to put up with a lot of dead ends and roadblocks.
A master’s degree is the better choice if any of the following apply:
- You want to continue studies in your field, but you’re not committed to a career as a professional researcher.
- You want to develop professional skills for a specific career.
- You are willing to pay a higher upfront cost if it means finishing with your degree (and thus being able to work) much faster.
- You want the option to study part-time while working.
The length of time required to complete a PhD or master’s degree varies. Unsurprisingly, PhDs take much longer, usually between 3–7 years. Master’s degrees are usually only 1–2 years.
Length of a master’s
Master’s degrees are usually 2 years, although 1-year master’s degrees also exist, mainly in the UK.
Most of the degree consists of classes and coursework, although many master’s programs include an intensive, semester-long master’s thesis or capstone project in which students bring together all they’ve learned to produce an original piece of work.
Length of a PhD
In the US, a PhD usually takes between 5 and 7 years to complete. The first 2 years are spent on coursework. Students, even those who choose to leave without finishing the program, usually receive a master’s degree at this point.
The next 3–5 years are spent preparing a dissertation —a lengthy piece of writing based on independent research, which aims to make a significant original contribution to one’s field.
Master’s degrees tend to prepare you for a career outside of academia, while PhDs are designed to lead to a career in research.
Careers for master’s graduates
There are two types of master’s degrees: terminal and research-intensive. The career prospects are different for each.
Terminal master’s degrees are intended to prepare students for careers outside of academia. Some degrees, known as professional degrees, specifically prepare students for particular professions; these include the Master of Public Policy (MPP), Master of Business Administration (MBA), Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT), Master of Fine Arts (MFA), and Master of Public Health (MPH) degrees.
Other master’s degrees, usually Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Sciences (MS or MSc) degrees, do not necessarily lead to a specific career, but are intended to be a final degree. Examples include an MS in Communications or MS in Data Analytics.
In research-intensive master’s programs, students take coursework intended to prepare them for writing an original piece of research known as the master’s thesis . Such programs are usually intended to prepare for further study in a doctoral program.
Careers for PhD graduates
As research degrees, PhDs are usually intended to lead to an academic career. A PhD can be thought of like an apprenticeship, where students learn from professional researchers (academics) how to produce their own research.
Most students aspire to become a university professor upon the completion of their degree. However, careers in academia are highly competitive, and the skills learned in a doctoral program often lend themselves well to other types of careers.
Some graduates who find they prefer teaching to producing research go on to be teachers at liberal arts colleges or even secondary schools. Others work in research-intensive careers in the government, private sector, or at think tanks.
Below are a few examples of specific fields and non-academic careers that are common destinations of graduates of those fields.
- Computer Science
- Lab Sciences
Many government jobs, including economists at a country’s central bank, are research-intensive and require a PhD. Think tanks also hire economists to carry out independent research.
In the private sector, economic consulting and technology firms frequently hire PhDs to solve real-world problems that require complex mathematical modeling.
Graduate students from the humanities are sometimes hired by museums, who can make use of their research and writing skills to curate exhibits and run public outreach.
Humanities PhDs are often well-suited to research and grant-writing roles at nonprofits. Since so much of research is funded by grants, PhD students often gain a lot of experience applying for them, which is a useful skill in the nonprofit sector.
There are a wide range of non-academic research jobs for lab scientists with doctorates in subjects like chemistry, biology, ecology and physics.
Many PhD graduates are hired by pharmaceutical companies that need to perform research to create and test their products. Government agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), also hire lab scientists to work on research projects.
Job prospects after graduation vary widely based on the field. In fields like management, computer science, statistics, and economics, there’s little underemployment—even graduates from less well-known programs can easily find jobs that pay well and use the skills they’ve gained from the PhD.
However, in other fields, particularly in the humanities, many PhD graduates have difficulty in the job market. Unfortunately, there are far more PhD graduates than assistant professor roles, so many instead take on part-time and low-paid roles as adjunct instructors. Even non-academic careers can sometimes be difficult for PhDs to move into, as they may be seen as “overqualified” or as lacking in relevant professional experience.
Because career options post-PhD vary so much, you should take the time to figure out what the career prospects are in your field. Doctoral programs often have detailed “placement” records online in which they list the career outcomes of their graduates immediately upon leaving the program. If you can’t find these records, contact the program and ask for them—placement information should play an important role in your choice of PhD program.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Although PhDs take far longer to complete, students often receive a living stipend in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. Master’s degrees are shorter but less likely to be funded.
Both master’s degrees and PhDs lead to increased salaries upon graduation. While PhDs usually earn a bit more than those with a master’s degree, in some fields, the wages are identical, meaning that no financial benefit is gained from going on to a PhD.
Cost of a master’s
The upfront cost of a master’s degree is usually higher than a doctoral degree due to the lower amount of financial aid available. However, increased salaries also arrive faster than with a doctoral degree, because people graduate much earlier from a master’s program.
Some master’s students do receive stipends for their degrees, usually as compensation for being a teaching or research assistant. In addition, many people complete master’s degrees part time while working full-time, which allows them to fund their living costs as well as tuition.
The cost varies significantly by school and program. Public schools are usually cheaper than private ones. Some master’s degrees, such as MBAs, are notoriously expensive, but also result in much higher wages afterwards that make up for the high cost.
The master’s wage premium , or the extra amount that someone with a master’s degree makes than someone with just a high school diploma, is 23% on average. Many universities provide detailed statistics on the career and salary outcomes of their students. If they do not have this online, you should feel free to contact an administrator of the program and ask.
Cost of a PhD
PhDs, particularly outside the humanities, are usually (though not always) funded, meaning that tuition fees are fully waived and students receive a small living stipend. During the last 3–5 years of a PhD, after finishing their coursework (and sometimes before), students are usually expected to work as graduate instructors or research assistants in exchange for the stipend.
Sometimes students can apply for a fellowship (such as the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Program in the United States) that relieves them of any obligations to be a teaching or research assistant. Doctoral programs in the US tend to be better funded than in the rest of the world.
Sometimes, PhD degrees can be completed part-time, but this is rare. Students are usually expected to devote at least 40 hours a week to their research and work as teaching or research assistants.
The main cost of doctoral programs comes in the form of opportunity cost—all the years that students could be working a regular, full-time job, which usually pays much better than a graduate school stipend.
The average wage premium for PhDs is 26%, which is not much higher than the master’s degree premium.
In the US, the application process is similar for master’s and PhD programs. Both will generally ask for:
- At least one application essay, often called a personal statement or statement of purpose .
- Letters of recommendation .
- A resume or CV .
- Transcripts.
- Writing samples.
Applications for both types of programs also often require a standardized test. PhDs usually require the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), which tries to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative, critical thinking , and analytical writing skills. Many master’s programs require this test as well.
Applying for a master’s
Master’s degrees programs will often ask you to respond to specific essay prompts that may ask you to reflect upon not just your academic background, but also your personal character and future career ambitions.
Northwestern University’s Kellogg Business School requires Master’s of Business Administration (MBA) applicants write two essays, one about a recent time they demonstrated leadership and the second about their personal values.
Who you should ask for your letters of recommendation varies by program. If you are applying to a research-intensive master’s program, then you should choose former professors or research supervisors. For other programs, particularly business school, current work supervisors may be a better choice.
Some professional master’s programs require a specific test. For example, to apply to law school, you must take the Law School Admissions Test, or LSAT. For business school, you must take either the GRE or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT).
Applying for a PhD
When applying for a PhD, your resume should focus more on your research background—you should especially emphasize any publications you’ve authored or presentations that you’ve given.
Similarly, your statement of purpose should discuss research that you’ve participated in, whether as an assistant or the lead author. You should detail what exactly you did in projects you’ve contributed to, whether that’s conducting a literature review, coding regressions, or writing an entire article.
Your letters of recommendations should be from former professors or supervisors who can speak to your abilities and potential as a researcher. A good rule of thumb is to avoid asking for recommendations from anyone who does not themselves have a PhD.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Thomas, L. (2023, June 01). Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/masters-vs-phd/
Is this article helpful?

Lauren Thomas
Other students also liked, when to apply for graduate school | month-by-month timeline, how to write a statement of purpose | example, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Pros and Cons of Earning a Master's Degree Before a PhD
Martin Barraud / OJO Images / Getty
- Choosing a Graduate Program
- Tips & Advice
- Admissions Essays
- Recommendation Letters
- Medical School Admissions
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
- M.A., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
As a potential applicant to graduate school you have a great many decisions to make. The initial decisions, such as what field to study , may come easily. However, many applicants struggle with choosing what degree to pursue, whether a master’s degree or PhD is right for them. Others know what degree they want. Those who choose a doctoral degree sometimes wonder if they should first complete a master’s degree. Do you need a master’s degree to apply to a doctoral program?
Is a master’s degree an essential prerequisite for gaining admission to a doctoral program? Usually not. Does a master’s degree improve your odds of admission? Sometimes. Is it in your best interest to earn master’s before applying to PhD programs? It depends.
Pros and Cons of Earning a Master's Before Applying to PhD Programs
There are both advantages and disadvantages to earning a master’s before applying to PhD programs. Below are some of the pros and cons:
Pro: A master’s degree will introduce you to the process of graduate study.
Without a doubt, graduate school is different from college. This is especially true at the doctoral level. A master’s program can introduce to you the process of graduate study and help you understand how it is different from undergraduate study. A master’s program can help you make the transition to graduate school and prepare you for making the transition from college student to graduate scholar.
Pro: A master’s program can help you see if you are ready for doctoral study.
Are you ready for graduate school? Do you have the right study habits? Are you motivated? Can you manage your time? Enrolling in a master’s program can help you see if you have what it takes for success as a graduate student – and especially as a doctoral student.
Pro: A master’s program can help you see if you are interested enough to undertake a PhD
The typical college survey courses present a broad view of a discipline, with little depth. Small college seminars present a topic in more depth but it will not come close to what you will learn in graduate school. It is not until students are immersed in a field that they truly come to know the depth of their interest. Sometimes new grad students realize that the field is not for them. Others complete the master’s degree but realize that they have no interest in pursuing a doctorate.
Pro: A masters may help you get into a doctoral program.
If your undergraduate transcript leaves much to be desired, a master’s program may help you improve your academic record and show that you have the stuff that competent graduate students are made of. Earning a master’s degree shows that you are committed and interested in your field of study. Returning students may seek a master’s degree to obtain contacts and recommendations from faculty.
Pro: A master’s degree can help you change fields.
Are you planning on studying a different field than your college major ? It can be hard to convince a graduate admissions committee that you are interested and committed to a field in which that you have little formal experience. A master’s degree can not only introduce you to the field but can show the admissions committee that you interested, committed, and competent in your chosen field.
Pro: A master’s degree can offer a foot in the door to a particular graduate program.
Suppose you hope to attend a specific graduate program. Taking a few graduate courses, nonmatriculated (or nondegree-seeking) can help you learn about the program and can help faculty learn about you. This is even more true for master’s students. In many graduate programs, master’s and doctoral students take some of the same classes. As a master’s student, you’ll have contact with graduate faculty – often those who teach in the doctoral program. Completing a thesis and volunteering to work on faculty research can help faculty get to know you as a competent and promising researcher. A master’s degree might offer you a foot in the door and a better chance of gaining admission to the department’s doctoral program. However, admission is not guaranteed. Before you choose this option, be sure that you can live with yourself if you don’t gain admission. Will you be happy with a terminal master?
Con: A master’s degree is time-consuming.
Typically a full-time master’s program will require 2 years of study. Many new doctoral students find that their master’s coursework doesn’t transfer. If you enroll in a master’s program recognize that it will likely not make a dent in your required doctoral coursework. Your PhD will likely take an additional 4 to 6 years after earning your master’s degree.
Con: A master’s degree is usually unfunded.
Many students find this a big con: Master’s students usually do not receive much funding. Most master’s programs are paid for out-of-pocket. Are you prepared to potentially have tens of thousands of dollars of debt before you begin your PhD.? If you choose not to seek a doctoral degree, what employment options accompany your master’s degree? While I’d argue that a master’s degree is always of value for your intellectual and personal growth, if the salary-return of your degree is important to you, do your homework and think carefully before enrolling in a master’s program prior to seeking your PhD.
Whether you seek a master’s degree before applying to doctoral programs is a personal decision. Also recognize that many PhD programs award master’s degrees along the way, typically after the first year and completing exams and/or a thesis.
- What Comes After a Master's Degree?
- What Does It Take to Earn a Master's Degree?
- Should I Earn a Taxation Degree?
- Should I Earn a Joint JD/MBA Degree?
- A Note About Masters and Doctoral Comprehensive Exams
- Why Get an MBA?
- How to Earn a Doctorate Degree Online
- Should I Earn an Entrepreneurship Degree?
- Why You Should Get a PhD in Chemistry
- Should I Earn a PhD in Business Administration?
- Should I Earn an Operations Management Degree?
- NonTraditional Applicants to Grad School: 3 Tips for Getting Recommendations
- A Doctor of Philosophy or Doctorate
- Should I Earn an Advertising Degree?
- Should I Earn a Human Resources Degree?
- Should I Earn a Doctorate Degree?
Login or sign up to be automatically entered into our next $10,000 scholarship giveaway
Get Searching
- College Search
- College Search Map
- Graduate Programs
- Featured Colleges
- Scholarship Search
- Lists & Rankings
Articles & Advice
- Ask the Experts
- Campus Visits
- Catholic Colleges and Universities
- Christian Colleges and Universities
- College Admission
- College Athletics
- College Diversity
- Counselors and Consultants
- Education and Teaching
- Financial Aid
- Graduate School
- Health and Medicine
- International Students
- Internships and Careers
- Majors and Academics
- Performing and Visual Arts
- Public Colleges and Universities
- Science and Engineering
- Student Life
- Transfer Students
- Why CollegeXpress
- $10,000 Scholarship
- CollegeXpress Store
- Corporate Website
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- CA and EU Privacy Policy
Articles & Advice > Graduate School > Articles

Master's or PhD: Which One Should You Choose?
You know you want an advanced degree, but just how advanced? Keep reading to discover the key differences between master's and doctoral degrees.
by GradSchools.com Graduate School Directory
Last Updated: Dec 18, 2023
Originally Posted: Jun 20, 2011
Just as there are many reasons people choose to go to graduate school, there are many options from which they may choose. Do you want to attend full-time? Maybe you want to go part-time and work. Or perhaps an online program option will work best for you. But before you can decide on the format type of your program, you need to decide on your program. If you’ve selected a field of study, you may be wondering whether you should get a master's degree or a doctoral degree. Here are some things to consider to help you choose which one is best for you.
3 key differences between programs
Before you can properly weigh the pros and cons of a master’s degree vs. a doctoral program, you must understand the major differences between the two programs. And although that may sound like pros and cons in itself, a pros and cons list is based mainly on your personal preference. So before figuring out preference, you must consider the facts, and these are it.
A graduate degree requires a significant investment of time. Master's degrees require less time than doctoral degrees. Typically a full-time student can acquire a master's degree in about two years. A PhD usually requires at least five to six years and many people take seven to nine years.
The adage "time = money" was never so true as with graduate school. Since a PhD takes longer to complete, it also requires more money. (Not that a master's degree is cheap either!) The flip side to this is that a PhD may yield a higher salary upon completion and is therefore worth the increased cost long term. With both degrees, school costs money (tuition, fees, books, etc.). In addition, however, there is also a significant loss of money if the student is not working or is earning low wages through assistantships or part-time employment. Many people find they must either live a Spartan lifestyle for many years or find themselves strapped with huge loans when they graduate .
Graduate school takes work. Most people are not going to argue with this. However, many students who drifted through college are surprised to find that graduate school requires a much larger commitment in terms of work and intellectual energy. Graduate schools are frequently very competitive. Students who are taking a full course load as well as teaching often find themselves overwhelmed. And of course, the many years of school required for a PhD require perseverance on a scale above and beyond what undergraduates must contemplate. The difference between college and graduate school lies in the ability of the student to focus on their field and the subjects and areas that most interest them. While graduate school requires more work, most students find the work enjoyable since it involves an area in which they are very interested.
Related: Great Expectations: How Grad School Differs From Undergrad
The what ifs of choosing a master's or PhD
So we know that graduate school requires time, money, and commitment for both a master's and a PhD. So which should you choose?
- If all you want is a raise, a PhD is probably not the road to choose. A master’s degree will boost your career possibilities enough for the kind of raise you want.
- If you love learning in and of itself , then the work required for a PhD may be worthwhile. Master's degrees tend to be more career oriented while PhD's tend to be more research oriented since they’re preparing people for highly academic, research-based careers.
- If you want to save time and progress your career, a master's degree has benefits in that it requires less time and money than a doctoral degree but will still set you apart from those who only have a bachelor's. A master's can allow specialization within a field. The degree works well for those who’ve been working in a career for some time and hope to advance within their field.
- If you’re looking for a new path in life, a master's degree can also be an excellent method of changing careers. For those who’ve found their career or undergraduate education aren’t leading them in the direction they would like to go, a master's degree can allow them to start fresh by gaining new knowledge and skills.
- If you want to become a professor, a PhD is practically mandatory. Even for those few who can find teaching positions with only a master's, most schools want to see progress toward a PhD.
- If you really want to impress, a PhD can also be helpful outside the world of academia in today's increasingly competitive job market. Businesses are searching for extremely qualified people who have demonstrated intelligence, perseverance, and the ability to learn. A PhD can open doors.
- If you want to impact the world with original work, PhD work requires original research that contributes new information to your chosen field of study. People interested in pursuing a PhD should love their studies and be excited by the prospect of meaningful contribution.
Related: Choosing the Right Graduate Degree for Your Goals
Making your decision
To summarize, a PhD may be worth it if you truly love your field, enjoy your studies, and want the benefits and prestige associated with the doctoral degree. If you are simply looking to change fields or gain a promotion or do not think you could maintain interest through at least five to six years of school, then a master's is probably a better choice. However, it is worth noting that you may be able to get more financial aid for a PhD Since it takes longer, schools recognize that those trying to acquire their PhD's need more assistance than those who only want a master's degree. This adds an interesting dimension to the application process for two reasons.
First, if you think you may want a PhD but still are not sure, it is probably better to apply to the doctoral program. There is no penalty for changing your mind later and deciding to leave with a master's degree, and it increases your chances of getting financial aid. The second consideration is that the PhD program can be more competitive, and applying to it rather than the master's degree program might decrease your chances of admission. If you are denied entrance to the PhD program, you could ask them to then consider you for the master's degree program, but that may not be allowed.
Related: 7 Important Things to Do Before Applying to Graduate School
We’re glad you came seeking advice on which advanced degree program is right for you. It’s a big decision to make that you shouldn’t take lightly, and seeking the right knowledge to make an informed decision is only going to benefit you. Use this advice, take some time to think it over, and go forward knowing you’re making the best decision for your future goals and career.
Once you’ve made your decision on applying to a master’s or PhD program, start searching for just the right one with our Graduate School Search tool .
Like what you’re reading?
Join the CollegeXpress community! Create a free account and we’ll notify you about new articles, scholarship deadlines, and more.
Tags: advanced degrees applying to grad school doctorate grad school grad students graduate school graduate students master's degree
Join our community of over 5 million students!
CollegeXpress has everything you need to simplify your college search, get connected to schools, and find your perfect fit.

Nazira Abdelkhalek
$2,000 Community Service Scholarship Winner, 2014
I am very honored to be this year’s recipient of the Multicultural Student Community Service Scholarship! This scholarship is vital to helping me achieve and fulfill my dreams, and gives me confidence and motivation as I begin my college career. The CollegeXpress website has been invaluable over the past year as I planned my educational and professional goals. I highly recommend it to all students as they begin to focus on their college and career interests. The website is a wonderful guide to schools and scholarships.
Abhishek Kumar
High School Class of 2022
As a high schooler, I know how hard it is to plan for college. You have to consider a lot of factors: SAT/ACT scores, college searches, scholarships, and more. CollegeXpress has been a helpful resource that solves all these problems. One can easily create a free account and search away. They help you search for scholarships and colleges, they have graduate program search, they have lists and rankings, and so much more. CX also has a lot of articles and advice to read—whether it’s financial aid, test prep, campus visits, internships/careers, or anything. Not only that, CX gives out free scholarship money to students who sign up and create a free CX account. I love CX and will continue to use it! Thank you CollegeXpress for making my college journey easier!

Keydi Banegas
Scholarship for Students of Color Winner, Class of 2022
CollegeXpress is a great application that helped me search for many different scholarships, and it narrows the scholarships depending on how you set your profile. Not only that, but it helps you choose different colleges to apply to by finding matches through the description of your profile. It was the best experience for me.
Joan Franklin
I love this website and have been using it for years with my students. I originally bought products through Wintergreen Orchard House and appreciated having key facts at my fingertips when advising students. Your site is easy to access and offers a wide array of topics I need as a busy college counselor.

Tinuola Dada
$2,000 Community Service Scholarship Winner, 2015
I am very excited to be this year's recipient of the Multicultural Student Community Service Scholarship. This scholarship will bring me ever closer to my academic and professional goals. CollegeXpress has been an exceptional resource to me, and I recommend it to all rising seniors as they begin to navigate the college application process.
- Preparing for the Legal Journey: 9 Tips for Students Interested in Law
- 8 Questions Students of Color Should Ask About Graduate School
- 5 Questions to Ask Before Committing to Graduate School
- On-Campus, Online, or Hybrid: Which Grad School Format Is Right for You?
- Great Graduate Schools and Programs in the Northeast
Colleges You May Be Interested In
Caldwell University
Caldwell, NJ
Moody Theological Seminary
Chicago, IL
Southwest Baptist University
Bolivar, MO
New York University Tandon School of Engineering
Brooklyn, NY
Asbury University
Wilmore, KY
Personalize your experience on CollegeXpress.
With this information, we'll do our best to display content relevant to your interests. By subscribing, you agree to receive CollegeXpress emails and to make your information available to colleges and universities, scholarship programs, and other companies that have relevant/related offers.
Already have an account?
Log in to be directly connected to
Not a CollegeXpress user?
Don't want to register.
Provide your information below to connect with
- Online Degrees
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Transferring Credit
- The Franklin Experience
Request Information
We're sorry.
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at [email protected] , 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.
Popular Posts

Master's vs Doctorate: Which Degree is Right for You?
Graduate degrees are becoming increasingly popular.
According to the world’s largest and most sophisticated database of labor market and talent data from Burning Glass Technologies, 19% of U.S. job openings in the year 2018 requested a graduate degree. And that trend isn’t changing any time soon. In fact, the Bureau of Labor Statistics expects master’s-level occupations to grow by 17% by 2026. Employment for doctoral- and professional-level degree is also projected to grow by about 13%. Both of these projections are much faster than the 7% average for all occupations.
The demand for both master’s and doctorate degrees is high. But how do you know which level of educational attainment is right for you? Does your industry or career aspirations necessitate one degree or another? Will you personally benefit more from a master's or doctorate?
We’ll show you how to take all these factors into consideration to help choose if you should get a master’s degree, or if you should complete your master's and go on to pursue a doctorate degree.
Master's vs Doctorate: What are typical program requirements?
Whether you pursue a master’s degree or doctorate degree program, it’s a significant commitment of time, energy and finances. Before you choose, you should understand the requirements for not only getting into a program, but also completing your master’s or doctorate degree.
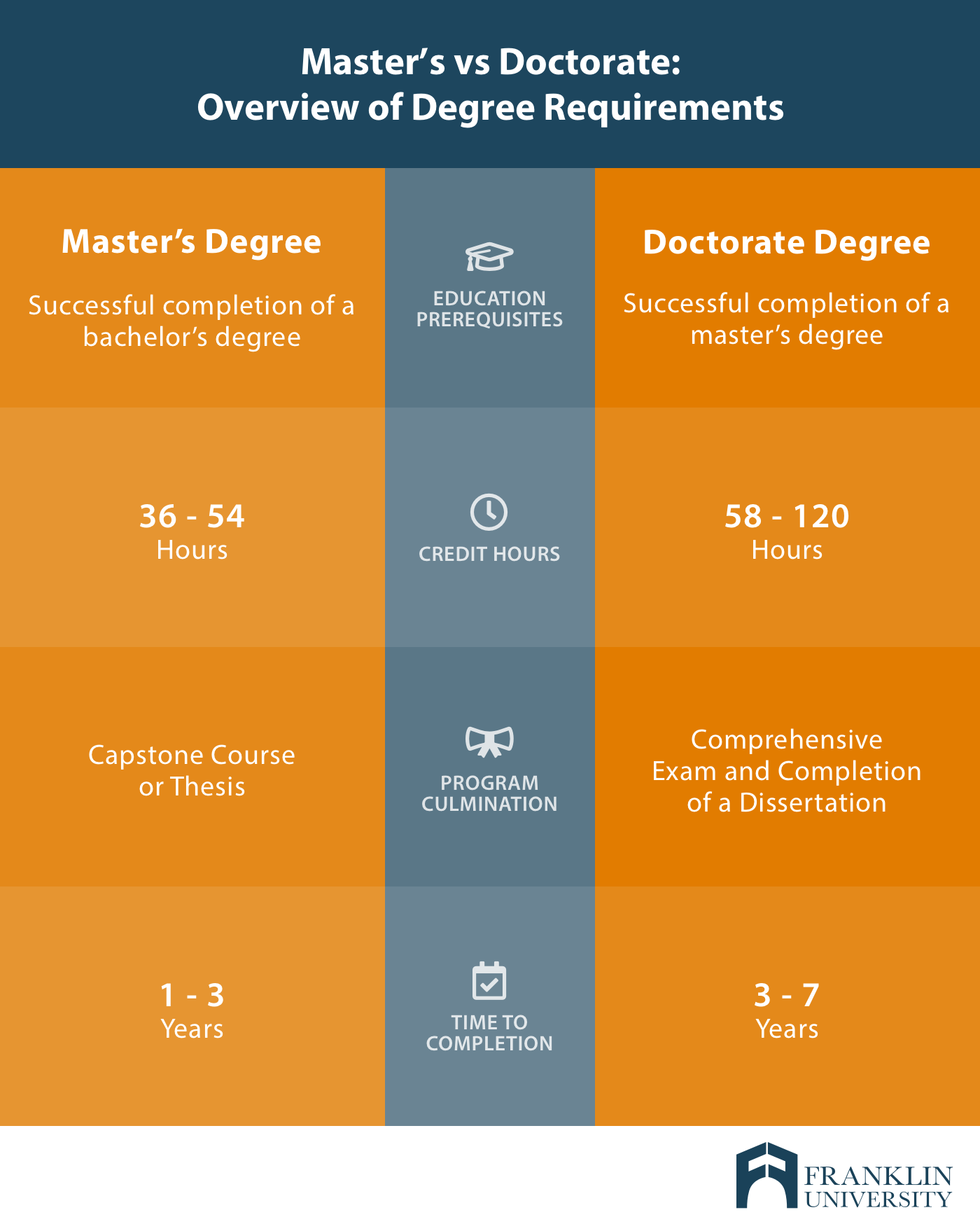
Now that you have an understanding of what committing to a master’s degree or doctorate degree entails, compare the focus of the program and coursework.
Master's vs Doctorate: What’s the difference in content and coursework?
The focus of master’s degrees and doctorate degrees is different.
A master’s degree is designed to deepen career-oriented knowledge and skills. A doctorate degree is a heavily research-based degree, designed to develop critical research,analytical and writing skills in an effort to fill industry knowledge gaps.
Because of these different goals, the makeup of the coursework and content is also distinct.
Master’s programs feature three different types of courses:
- Core courses: These courses are required to complete your master’s degree and are considered essential knowledge to advance your industry expertise.
- Electives: These are a selection of courses that allow you to further specialize your degree with concentrated knowledge in specific areas. They can also be used to broaden your experience in related subject areas.
- Capstone course (or thesis): The culmination of a master’s degree, a capstone course or thesis usually involves conducting research and presenting your findings.
Doctorate programs are broken down into four distinct parts:
- Coursework: These advanced courses are required knowledge for passing your comprehensive exam.
- Research Core: These courses impart essential research, analytical and writing skills to prepare you to complete your dissertation.
- Comprehensive exam: The comprehensive exam tests your understanding of key concepts learned through your coursework. Passing your comprehensive exam is essential to beginning your dissertation.
- Dissertation: You work with a dissertation committee to identify a research topic. Then you complete in-depth research, analysis, and writing before you defend your original research to your dissertation committee.
As you consider these degrees, decide which better fits your academic and professional goals, as well as your personal interests and learning style.
Master's vs Graduate: How much will the degree cost?
We know that cost is a top concern for individuals deciding what degree to pursue. Unfortunately, it’s also one of the most difficult questions to answer. Cost estimates for a master’s degree can be anywhere from $30,000 to $120,000—and costs for doctorates can range just as widely.
If you’re trying to evaluate the cost of a master’s vs doctorate degree you need to look at important factors like:
- Type of institution: Whether you choose a public, private nonprofit or for-profit school will impact how much you pay in tuition. The reputation and rankings of a university also affect the cost of tuition.
- Time to graduation: How many courses you take at one time and the total number of credit hours you need to graduate affect the cost of both master's and doctorates. Doctorates depend highly on an individual’s time and commitment to completing the research and writing of an original dissertation. Also, keep your other personal and professional commitments in mind when estimating how long it will take to earn your degree (and how that will impact cost).
- Transfer credit: If you have a professional certification, or have earned graduate-level course credit, you may be eligible to transfer credit toward your degree. Getting transfer credit can significantly reduce your total cost.
Remember: To complete a doctorate degree you must first complete a master’s degree. So if cost is a top concern, evaluate which institution and program will give you the best value. In some cases, you may even be able to complete both a master’s degree and doctorate degree at a lower cost than a master’s degree at a school with high tuition.
Earning a doctorate is challenging and rewarding, but do you know what to really expect? Download this free guide for tips and insights to help you prepare for success.
Master's vs doctorate: what are the outcomes of each degree.
When it comes to the outcomes of a master’s or doctorate degree, you should look at three key factors: skillset, career prospects and salary expectations. Let’s dive into the differences between the outcomes of these two types of graduate degrees.
- Skillset: Master’s degrees focus on the expert command of industry-specific skills, while working to develop critical-thinking and problem-solving skills. On the other hand, doctorate degrees are nearly the inverse—they heavily focus on research, analysis and writing in support of developing transferable skills that can be used to fill gaps in industry knowledge.
- Career prospects: Career advancement is a primary goal for people who pursue master’s and doctorate degrees. Master’s degrees are seen as career-oriented degrees that prepare you for management and leadership positions. More and more, doctorate degrees are becoming the norm for top executive positions, as well as opportunities to transition your career into academia.
- Income: Both master’s degrees and doctorate degrees significantly increase your salary expectations and lifetime earning potential. But which is worth more? According to the BLS, a master’s degree has the power to boost your earnings by 17% when compared to a bachelor’s degree, while a doctorate degree can bring in a salary 30% higher than a bachelor’s degree. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, an individual with a master’s degree can also earn more than $2.8 million in their lifetime, while a doctorate degree can earn you over $3.5 million.
Comparing the Benefits of Master's vs Doctorate Degrees
There are a lot of factors that go into choosing a master's vs doctorate degree. But as you evaluate all of the different aspects of these programs, make sure to keep your long-term goals in mind. We’ve outlined four key ways to compare the benefits of master's vs doctorate degrees against your goals.
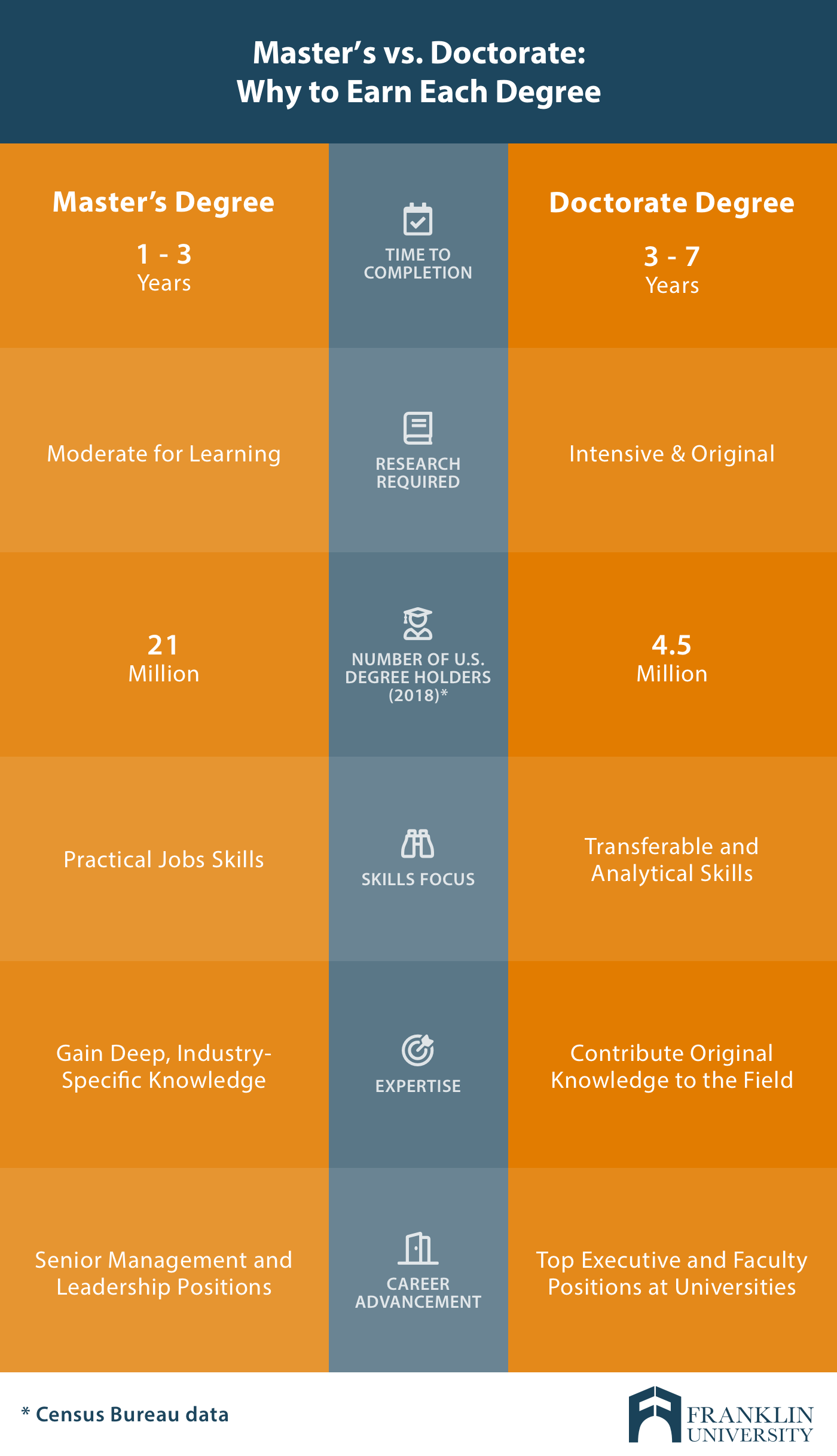
Master's vs Doctorate: Popularity meets possibility with online degrees
As demand increases for advanced degrees, professionals are looking for ways to make getting their graduate degree more attainable. That’s why online master’s and doctorate degrees are more popular than ever. Online degrees offer working professionals the opportunity to get their degree without stalling their career.

Getting your master’s degree or doctorate degree is a lifetime achievement that can help you advance your career. If you’re considering your options for a master’s or doctorate degree, explore Franklin University’s online master’s degrees and online doctorate degrees to find a program that can help you take your career to the next level.

Related Articles

Franklin University 201 S Grant Ave. Columbus , OH 43215
Local: (614) 797-4700 Toll Free: (877) 341-6300 [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Franklin University

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Master’s vs PhD — These are the Main Differences
Updated: July 18, 2022
Published: October 31, 2019

The consideration between earning a master’s vs PhD is not always an easy choice. While many careers and personal aspirations may be complete with just an undergraduate degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s), a lot of people continue their higher education to obtain graduate degrees. These include a master’s and/or a PhD.
Neither a master’s degree nor a PhD is considered to be a walk in the park. Therefore, it’s useful to understand why you would earn either and then decide how far to go.

Photo by Good Free Photos on Unsplash
Definitions: master’s vs phd.
Bost a master’s and PhD are defined as postgraduate degrees, but they require different commitments and styles of learning.
1. Master’s Degree:
Mostly all master’s degrees will require the completion of an undergraduate bachelor’s degree to enroll. They generally all share the same common requirement for a thesis or dissertation to graduate.
Earning a master’s degree through a taught program will result in the completion of a Master of Art (MA), Master of Science (MS), or Master of Philosophy (MPhil). For those who earn their master’s degree through research, they will earn a Master of Research (Mre), in a tailored field of study. There are also degree-specific master’s programs like Master of Business Administration (MBA) and Master of Education (M.Ed).
After earning a master’s degree, the next step is a PhD, which entails both working and performing research at an institution. A PhD is an abbreviation for “Doctor of Philosophy.” It is the highest academic degree one can achieve. As such, it is a time-consuming pursuit that requires a lot of studying and research.
You may be wondering, “Do you need a master’s to get a PhD?”
Technically, the answer is not always. Some students skip a master’s and go straight for their PhD, but they may lack research experience. While it could save money, the transition between a bachelor’s and a PhD is incredibly sharp. It may be harder to complete a PhD without the experience from a master’s.
Yet, some institutions may allow for the possibility to earn both your master’s and PhD in conjunction with one another. This will alleviate the transition between skipping a master’s and going straight to earning a PhD.
Should You Get a Master’s or PhD?
There are many considerations to factor when deciding between a master’s of PhD. For starters, it’s useful to consider the amount of time it will take, the cost, and the benefits and disadvantages of each. It is also of utmost importance to explore your own personal goals and reasons for wanting a graduate degree.
If your desired career of choice requires a PhD, like becoming a university professor, then you have your answer. If you want to start a business and benefit by networking while in school, a Master of Business Administration (MBA) could be a good idea. Consider what you want to pursue as a career and find out the requirements first.
Another useful thing to note is that a master’s degree can be used for a shift in careers. For example, if you attended college and earned a bachelor’s degree in humanities, but now you want to pursue science, you can still earn your master’s degree in a scientific discipline. On the other hand, a PhD is tailored to your field of study and specialty, so it will require that you are sure of your direction when you first earn your master’s degree.
Length of Time
A typical master’s degree program takes about two years full-time. However, there are accelerated programs that can be completed in just a year or so.
A PhD, in general, requires five to six years of studying, teaching, and research. However, it may even take some students up to eight or nine years to graduate. With this significant investment in time, it’s necessary to know if a PhD is right for you before starting.
The cost of both programs varies by institution and enrollment status of part-time versus full-time. However, since a PhD takes longer to complete, it will end up costing more. With that said, if you look into your return on investment, a PhD could end up yielding a higher salary, and therefore end up “costing less.”
Additionally, there is also the possibility of being paid to complete your PhD. Some students may receive an academic stipend, a university fellowship or apprenticeship or a reduced fee to earn their PhD while completing research (or teaching) at an institution. It’s also possible to get financial aid through a scholarship or grant.
As tuition rates continue to rise, it’s useful to look into alternative institutions for affordable education. For example, the University of the People offers a tuition-free master’s program in Business Administration and Education. This means you can study 100% online and graduate for less than the cost of most programs.
Weighing the Benefits
When comparing the two degree types, here are some benefits of each:
- Career-oriented
- Can open the door for more job opportunities
- Costs less than a PhD
- Takes less time than a PhD
- Helps you stand out from those with only an undergraduate degree
- You can perform research in your field of choice
- You become an expert in your field
- The prefix Dr. is added to your name
- You can teach in academia at the highest level
Required Commitment and Reasons to Pursue
Both a master’s and a PhD require a huge amount of hard work and utter commitment. You must be dedicated and motivated to complete either degree. Since most careers only may require a bachelor’s degree, having a master’s or PhD will set you apart from the competition. However, this should not be the sole reason to pursue either.
You may be wondering why would you earn either degree. Here’s a look at some motivational factors:
Reasons to Study for a Master’s
- Your career requires it (see next section)
- You want to advance your subject knowledge
- You want to experience graduate school and network with peers
Reasons to Study for a PhD
- You want to contribute new research to your field of choice
- Your career requires a PhD
- You want to earn the title of Dr.


Photo by Online Marketing on Unsplash
Required degrees by career.
Most people are motivated to pursue higher education because their desired careers require they do so. Here, we will break down those fields that require the completion of a master’s degree as it’s high on the list of reasons why to get one.
- Education Administration: To work as an administrator in an educational institution, you need to hold an advanced degree. A Master’s in Education (M.Ed) will provide you with the necessary knowledge and required skills to succeed in the field.
- Executive Level Business: A Master’s in Business (MBA) will not only place you ahead of the competition to land high-level positions in the field of business, but it can also be the jumping off point for becoming your own boss.
- Environmental Science: With issues in climate change and technological advancement, careers in Environmental Science are growing. As with most scientific careers, it requires a master’s degree where you will learn Applied Ecology, Environmental Policy, Environmental Chemistry, and more.
- Mental Health: To become a licensed practitioner and assist in mental health counseling, you will continue your education through a master’s degree in the field.
- Physical Therapy: Employers of physical therapists often prefer them to obtain a master’s degree in the discipline as the field is highly specialized.
Of course, some careers require a PhD. These careers are easy to spot because they have the prefix Dr. in front of them or the suffix like J.D. (Juris Doctor). To become a lawyer, doctor of medicine, veterinary medicine or psychologist/psychiatrist, you must obtain a PhD in the respective field.
Salary Differences Between Master’s and Ph.D. Graduates
According to a study performed by the Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce , the overall evidence shows that the higher the degree you have, the higher your salary potential. However, the differences vary by subject level and field.
In general, the expected lifetime earnings of those with each degree level is as follows:
- High School Diploma: $973,000
- Bachelor’s Degree: $1.3 million
- Master’s Degree: $2.7 million
- Doctorate Degree: $3.3 million
The Bottom Line
Aside from the financial cost and length of time, the opportunity to earn a master’s and a doctorate degree can offer several benefits.
However, it is an undertaking that requires a lot of dedication and motivation on behalf of the student. As such, it’s important to perform research on your desired career’s requirements, as well as your personal interest in pursuing either a Phd vs master’s.
Related Articles

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, should i get a master's degree 6 factors to consider.
General Education

Whether you've already graduated or are about to graduate from college, if you're asking yourself, "Should I get a master’s degree?" it’s time to dig deep and find the answer. A master's degree can be useful for particular careers — but it's also expensive and time-consuming. So is a master’s degree right for you?
In this guide, we go over what a master's degree is, four key questions to ask yourself before you decide to get one, the pros and cons of getting one, and three tips to help you decide on the best master’s degree program for you.
Feature Image: Illinois Springfield /Flickr
What Is a Master's Degree?
A master’s degree is a graduate degree that indicates you have high-level knowledge of a specific area of study or professional practice. These degrees are the first level of graduate degrees, followed only by doctoral degrees, such as the PhD.
Master's degree graduate programs are offered all over the world at public and private colleges and universities. Most people earn their master's degrees in one to three years of continuous full-time study . In the US, two years is a common length for many master's programs.
In terms of prerequisites, you’ll typically need to have at least a bachelor’s degree in order to enroll in a master’s degree program.
There are many kinds of master’s degrees you can earn. Here are some of the most common:
- Master of Arts (MA)
- Master of Science (MS)
- Master of Fine Arts (MFA)
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- Master of Engineering (ME, MEng)
- Master of Education (MEd)
- Master of Laws (LLM)
- Master of Architecture (MArch)
- Master of Public Administration (MPA)
- Master of Public Health (MPH)
- Master of Public Policy (MPP)
- Master of Social Work (MSW)

Should I Get a Master’s Degree? 4 Questions to Consider
If you’re wondering, "Should I get my master’s?" then it’s important to ask yourself the following four questions before you make any big decisions.
#1: Am I Passionate About the Topic I Want to Study?
First things first, are you passionate about the subject area you want to study at the master’s level? If your answer isn’t a resounding "yes," then it'll be better to reconsider getting a master’s degree — at least in that particular topic.
But why is passion so important?
The reality is that it can be difficult to find the willpower to finish grad school if you’re not all that invested in the topic you’re studying or are only in school because you don’t know what to do with your life.
I myself knew a couple of people who ended up dropping out of master’s programs once they realized it wasn’t actually the topic they wanted to study (for the record, they both switched to different master’s programs).
Leaving a master’s program isn’t a failure by any means, but trust me when I say that your life will be a lot easier if you have a clear idea of what you want to study (and why) before you apply to master’s programs. You don’t want to feel as though you wasted time, energy, and money on a grad program that ultimately didn’t help you reach your academic or professional goals.
Before you decide to go for a master’s degree, try to envision yourself as a grad student, taking classes in the subject, researching it, and writing papers about it. If these thoughts excite you, then this field is likely a good fit for you. If you feel hollow or apathetic, however, you should reconsider whether it's truly worth getting a master’s degree in this subject area.
If you’re really on the fence about earning a master's degree — maybe the topic you’re thinking of studying is completely different from what you majored in as an undergrad — you might want to consider taking some community college courses in that field to help you get a much clearer sense of how grad school will be.
#2: Will Getting a Master’s Degree Help My Career?
Another important question to ask yourself is how this particular master’s degree can help you in your professional goals.
There are two general categories of graduate degrees :
- Academic degrees
- Professional degrees
Academic master’s degrees are primarily focused on increasing your mastery of a specific field of study that connects to your academic and intellectual interests (which you might or might not want to use in your career).
Many students choose to get a master’s degree as a step toward getting a doctoral degree —often a PhD —i n their field of study. Academic grad programs also generally require a master's thesis or capstone project and are more research-oriented.
Examples of academic master's degrees include the MA and MS.
By contrast, professional master’s degrees are much more strongly tied to your career interests, teaching you about the industry you want to enter and equipping you with key skills you will need to succeed professionally.
A professional degree is meant to prepare you for a specific career or field. Many careers, such as lawyers, doctors, and pharmacists, require you to earn a series of professional degrees (usually master's and doctoral degrees).
Examples of professional degrees include the MBA and LLM.
Ultimately, when it comes to getting a master’s degree, you must ask yourself: how much are you expecting your degree to help you in your career? There is no right answer here, though ideally your master’s degree will help you either progress in or jump-start your career.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) , in certain professional fields, having a master’s degree will earn you more money than if you had only a bachelor’s degree. These fields include the following:
- Healthcare and social service
So if you plan to get a master’s degree in any of these four fields, you can rest assured that doing so will most likely have a positive effect on your career trajectory.
If you want to get a master’s degree in a field not listed above, don't freak out just yet —t his doesn’t mean your degree will be totally useless when it comes to your career. As long as you have an idea of how you’d like to use your master's degree and how it can provide you with the critical skills you need to succeed in a specific job, it'll most likely be a good choice to make.

#3: Will I Have to Pay for the Degree?
Unlike doctoral programs, many of which are fully funded for up to five years, master’s degrees in the US are rarely funded. Therefore, it’s important to find out whether you’ll have to pay for your master’s degree — and whether you think the program is worth the price tag.
Again, there’s no right or wrong choice here. Some people are perfectly content to pay for part or even all of their master’s degrees, especially if the degree is essentially guaranteed to help with their careers. Others, however, are adamantly against taking out loans and forking out thousands of dollars for a degree that might not actually help their careers or raise their earning potential.
My personal advice? Try to pay as little as you can for a master’s degree.
Often the cost simply isn’t worth it, especially if you’re planning to get an academic degree and not a professional degree (which is typically more likely to ensure you a steady career).
Remember that master’s programs in the US range significantly in how much they cost. According to the National Center for Education Statistics , the average annual cost (tuition + fees) for grad school in 2012-13 was $16,435.
In my experience, though, this number seems to be on the lower end of the spectrum. As The Best Master’s Degree notes, master’s degree programs in the US can cost in the range of $30,000 to $120,000, with some even exceeding this "maximum"!
This is why I strongly advise looking for master’s programs that award scholarships or fellowships. Grad programs often list scholarships on their program and/or financial aid pages.
You can also look for external scholarships geared toward grad students. For tips, check out our list of 47 grad school scholarships and our guide on how to find grad school scholarships .
#4: Am I OK With Not Working?
A master’s degree is generally a commitment of at least one year — usually two or three — which means you (most likely) won’t be working a full-time job during this time.
Before you decide to do a master’s program, make sure you’re 100% OK with taking a break from working (or, if you’re going straight from undergrad to grad school, delaying entering the workforce).
If you’re young (in your 20s or so), taking a couple years off for school shouldn’t have much of a negative effect on your career trajectory or professional options.
But if you’re older and more established —maybe you have a successful career or a family to care for — taking time off from work to get a master’s degree could have more of a negative impact on your life than you might think.
For one, you likely won't be making much, if any, money while you’re a grad student (unless you’re receiving a stipend or working part-time), so this kind of lifestyle definitely requires sacrifice.
Secondly, it can be difficult to get back into the workforce once you get your master’s degree since you might not have the connections you once had and might lack some practical, on-the-job skills.

6 Pros and Cons of Getting a Master’s Degree
Now that you have a better idea of whether or not a master’s degree is right for you, let’s take a look at the biggest pros and cons of getting one.
Pros of Getting a Master's Degree
It’ll expand your knowledge of a particular subject area: This is perhaps the #1 reason most people opt for a master’s degree, whether it’s mainly to quench your own intellectual curiosity, bolster your career opportunities, or both. Getting a master’s degree also means spending your time reading, researching, and writing — all of which are incredibly valuable, transferable skills.
It can open up new career paths: Whether or not you need a master’s degree to nab a job you want, there’s no doubt getting one will make you more marketable in general and allow you to stand out in a positive light. This advantage is especially applicable to those getting a master’s degree in order to make a career switch.
It can increase your earning potential: According to the BLS, master’s degree holders in 2017 made a median $1,401 a week ; these median wages are higher than what bachelor’s degree holders ($1,173) and high school graduates ($712) made. In other words, earning a master’s degree means higher wages on average. (This is a general trend; weekly earnings can vary a lot depending on factors such as the field, amount of work experience, etc.)
Cons of Getting a Master's Degree
It’s expensive, especially if you don’t get any scholarships: As mentioned, scholarships and fellowships for master’s degree programs are unfortunately pretty rare, which means you’ll most likely have to pay a huge sum of money for your degree out of pocket, through student loans, or both.
It takes a while to get one: Master’s degrees in the US usually take around two years. Even though this isn’t as long as it takes to get a bachelor’s degree, it's still a decent chunk of time you’ll need to be willing to dedicate entirely to school, meaning you’ll be taking valuable time away from accumulating work experience.
It’s not guaranteed to get you a better job or higher salary: Despite the general benefits a master’s degree can have regarding jobs and salary potential, getting a master’s degree does not automatically mean you’ll be nabbing only the best jobs available and getting instant pay raises. A lot of your professional success will depend on not just what type of master’s degree you get but also how you use it, what kind of career you build with it, your location, how good you are at your job, and so on.

What Should You Get a Master’s Degree In? 3 Essential Tips
Even if you know you want to get a master’s degree, sometimes deciding what subject area to get a degree in can be tricky. Here are some tips to help you answer a key question: what should you get a master’s degree in?
Tip 1: Determine Your Biggest Passions and Interests
Regardless of whether your intellectual or professional passions have changed since you got your bachelor’s degree, take time to consider what kinds of topics you’re deeply interested in.
It should be a subject area you can readily envision yourself researching, reading about, and writing about as your day-to-day "job." If the idea of studying this topic excites and inspires you, then it'll likely be a great field for you to pursue a master’s degree in.
But what if you’re equally interested in two topics? In this case, you have a few options:
- Pick the field that’s more relevant to your professional goals: For example, if you’re interested in both English lit and computer science but plan to go into web design in the future, a computer science degree will be far more useful.
- Consider doing a degree or dual degree that combines both fields: For example, if you’re interested in Chinese and law, you might want to look into dual degree programs that let you study both Chinese and law, such as the dual JD/MA program at the University of Michigan .
- Apply to programs in both fields and choose a program to attend based on factors such as location, funding, etc.: If you really can’t decide between the two, then it might be best to just apply to the programs that interest you in both fields. Once you find out which programs you’ve been accepted to, you can make your decision on where to go (and what field to study) based on other important factors to you, such as how much financial aid you received, where the school is located, and how highly ranked the program is.
Tip 2: Consider Your Professional Goals
Before choosing a field in which to get a master’s degree, try to visualize your future career path:
- What kind of industry or field do you want to work in?
- What kinds of jobs do you see yourself working?
- Do these jobs often require or strongly prefer a master’s degree?
It's helpful to first figure out the general field you’re interested in studying at the graduate level. For example, say you majored in English and are now thinking of breaking into writing and editing. Options for possible master’s programs could include the following:
- English/literature
- Creative writing
- Professional writing
- Technical writing
- Communication
- Marketing/advertising
Once you have a general idea of the industry or field you want to have a career in, begin thinking about specific skills and topics you want to learn, and look for master's degree programs that can help you become an expert at these.
Say you're the English major interested in establishing a career in writing and editing. Maybe you’re not as interested in reading as you are in writing. So as a result, you start to think it might be better to look primarily at master’s degree programs that focus on how to write professionally.
In this case, a program that centers on writing as a career versus as an art, such as NYU’s MS in Professional Writing and Emerson’s MA in Publishing and Writing , would be a better fit for your goals.
Of course, this doesn’t mean you can’t apply to other programs, such as creative writing MFAs. But thinking about the skills you want to learn should help you narrow down what kind of program you think will benefit you the most in your future endeavors (whatever those may be).
If you’re struggling to determine what kind of career you want, there's no harm in meeting with a job coach or getting in touch with your undergrad institution’s career services center.

Tip 3: Get to Know the Program
Once you have an idea of what topic you want to study in a master's program and what kind of career you envision yourself having, it’s time to figure out what programs will work best for you.
Here are some actions you can take once you’ve found a program you want to apply to:
- Read the program's official website: Get online and read everything there is to know about the master's program you’re considering. Start with the college or university's official website, and pay special attention to pages that detail specific courses students must take, professors, and graduation requirements.
- Learn about the experiences of real students: Get in touch with current/former students in the master's degree program you want to apply to. These are the people who can tell you what to expect in terms of classes, faculty members, the campus environment, professional networking opportunities, etc.
- Visit the campus, if possible: This isn’t a necessity, but oftentimes seeing the campus and program in-person can give you a clearer picture of how you’ll fit in on a day-to-day basis.
- Get to know the current faculty: This is generally more important for those seeking PhDs, but even for prospective master’s students, it’s definitely helpful to learn more about faculty members by reading their profiles on the school’s website, emailing them, or meeting them in person.
- Find out about funding: This primarily depends on your financial situation and what you’re willing to pay for grad school. But as I mentioned, it’s best to pay as little as you can for your master's degree. Find out whether the program offers scholarships and how many students get one each year. In general, better-funded master's degree programs should be higher on your list of schools — but this doesn’t mean funding is by far the most important factor.
Conclusion: Should I Get My Master’s?
To wrap up, there’s no clear answer to the question, "Should I get a master’s degree?" Indeed, your answer to this will depend on the future you envision for yourself. In other words, what kind of career do you want? And how will a master’s degree help you succeed in your endeavors?
Before you start applying for master’s degree programs, ask yourself these four critical questions:
- Am I passionate about the topic I want to study?
- Will getting a master’s degree help my career?
- Will I have to pay for the degree?
- Am I OK with not working?
There are many pros and cons to getting a master’s degree. The biggest pros are that it’ll teach you more about a specific subject area, open up potential career paths, and possibly increase your earnings. The cons are that master’s degrees can be expensive, take a while to earn, and are by no means 100% guaranteed to nab you a better job or higher salary.
If you’ve decided to get a master’s degree, great! Now, it’s time to answer the next big question: what should you get a master’s degree in? Here are three tips to help you decide on the best program for you:
- Determine your biggest passions and interests
- Consider your professional goals
- Get to know the program
After reading this, you should now have a far clearer vision for your future, regardless of whether there's a master's degree in it or not!
What’s Next?
What exactly is grad school? Learn about why it might be a good idea for you to continue your education beyond undergrad to get a master's or doctoral degree . Also, our expert tips can help you decide whether grad school is worth it for you .
Paying for a master's degree can be tough. That's why it's important you know how to get the most out of FAFSA .

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

MS vs PhD: Which Psychology Degree Should You Get?
An undergraduate degree proves a great starting point for people interested in careers involving psychology. To advance into occupations involving greater responsibility and pay, however, generally requires a graduate degree.
For instance, a master’s degree in psychology is one of the necessities to become a licensed therapist, such as a marriage and family therapist – a career the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts to grow a whopping 16% between 2020-2030. And becoming a psychologist – a position with an average median annual salary of $82,180 – requires earning a doctorate in psychology.
What Are MS and PhD in Psychology Degrees For?
The MS (Master of Science) in Psychology and the PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) in Psychology are degrees for people interested in advanced study in the discipline. Students obtain a greater understanding of human behavior and how to help others. Degree earners are often interested in careers as therapists, licensed psychologists, researchers, or professors.
Choosing Between a Master’s Degree in Psychology vs. a Doctor of Philosophy in Psychology Program
The choice between pursuing a Master’s Degree in Psychology vs. a PhD in Psychology boils down to individual interests and career aspirations. Many students find a MS in Psychology sufficient for the types of jobs they want. Others discover a doctorate necessary for the occupations to which they aspire.
What Is a MS in Psychology?
An MS in Psychology is a graduate degree that prepares recipients for a variety of careers. It also can serve as a building block to entering doctoral studies, and an MS program typically takes about two years to complete. Online MS in Psychology programs sometimes offers accelerated options in which ambitious students can finish in around 18 months.
While coursework varies by institution and personal interests, students in psychology master’s programs often take these classes:
- Lifespan development
- Research methodology
- Cognitive psychology
- Social psychology
- Personality
- Foundations of therapy
- Family systems theory
- Abnormal psychology
Some students focus on general psychology. Others gear their master’s program to a specific area. Some niche choices include:
- Educational psychology
- Forensic psychology
- Clinical psychology
- Industrial-organizational psychology
- Sport psychology
- Health psychology
- Counseling psychology
- Child and adolescent development
- Applied behavior analysis
Who Should Get a MS in Psychology?
Students who want to expand their knowledge of psychology beyond the undergraduate level often seek a master’s degree. Some students pursue an MS to become more attractive candidates to schools when they apply to doctoral programs.
Others enter the workforce after receiving their MS in psychology. They find careers in the following fields:
- Advertising
- Human resources
- Criminal justice
- Social services
- Mental health
What Can You Do with a MS in Psychology?
Individuals who have earned a Master’s in Psychology find their degree a gateway to various types of jobs dealing with people and what influences their behavior. A sample of possible occupations is listed below.
What Is a PhD In Psychology?
A PhD in psychology is the highest-level degree within the discipline. Earning it signifies academic excellence and dedication to the field. In addition to mastering psychological theories and concepts, PhD candidates learn how to advance scientific knowledge through their own original research.
Who Should Get a PhD In Psychology?
Obtaining a PhD in psychology is a rigorous process. It involves classwork, passing an oral exam demonstrating competency, and completing a dissertation. Practicums, internships, and teaching experiences may also be part of the program.
Students thinking about entering such a program should possess a strong background in psychology , such as a bachelor’s and/or master’s degree. They also should look closely at their career goals and decide whether a PhD puts them on the right path.
What Can You Do with a PhD In Psychology?
The expertise obtained from earning a PhD in Psychology opens doors to a variety of careers. Three sample positions include:
Many PhDs remain in academia. They teach classes at colleges and junior colleges as well as perform research in their area of interest within the field of psychology. The BLS lists the mean annual wage for postsecondary psychology teachers as $85,050. 6
Clinical psychologists diagnose and treat a variety of mental, emotional, and behavioral problems. Some specialize in certain areas, such as treating depression or eating disorders. Others work with specific populations, such as children or the elderly. The median yearly salary for a clinical psychologist in 2020 was $79,820 per the BLS. 7
These professionals apply their knowledge of psychology to the workplace. Companies and governmental organizations hire them to examine issues such as productivity, morale, teamwork, hiring, and organizational development. Their suggestions lead to workplace improvements. The BLS reports the median annual salary for an industrial-organizational psychologist in 2020 as $96,270. 7
PsyD Vs PhD at a Glance
Individuals wishing to earn a doctorate have another option besides a PhD in Psychology. They may pursue a PsyD (Doctor of Psychology). Selecting which to earn depends on the student’s educational and career interests.
In general, PsyD programs:
- Focus heavily on applied psychology
- Take 4-7 years to complete
- Attract students interested in working as therapists inc community mental health, hospital, and private practice settings
By comparison, PhD programs in psychology:
- Focus extensively on generating new knowledge through scientific research
- Attract students interested in remaining in academia as professors and researchers, though many do seek licensure and become practicing psychologists
What to Look for in Psychology Graduate Degree Programs
Online vs. on-campus learning.
Whether a student wishes to pursue a master’s degree or a doctorate, choices exist regarding the learning format. Some schools offer graduate-level psychology programs online. Choosing such a route can prove beneficial in terms of access, flexibility, and cost.
Online studies remove geographical barriers when selecting an institution, which opens up a greater pool from which to choose. Remaining at home eliminates expenses related to travel and campus housing, and students with spouses or children do not need to upend their family’s lives to further their education and careers.
Students seeking online degrees should check the terms, however. Some programs include short residency requirements. Likewise, individuals may need to go to campus or other physical sites to complete research projects, internships, practicums, or other hands-on experiences.
Of course, regular on-site programs remain an option for students preferring traditional graduate school. A consistent schedule and the social aspect of attending classes physically alongside others still appeal to many students.
Psychology Certification and Licensure
Psychology-related occupations often require state licensure. Knowing the specifics for the state in which one hopes to find employment can guide educational and career choices and prevent unwelcome surprises down the line.
Psychologists, for example, typically need to complete the following:
- A PsyD or a PhD in Psychology
- An internship
- A post-doc or 1-year supervised professional experience after the internship
- A passing score on the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology
- Completion of a dissertation or case study
States usually require all licensed therapists to complete the following:
- A master’s degree
- A range of 2,000-4,000 hours of post-degree supervised clinical experience
- A successful exam score
Applying to Psychology Doctoral Programs
Acceptance into a Doctoral in Psychology program involves applying to individual institutions. Competition for spots can be substantial, so candidates should apply to several schools in order to increase the chances of getting in.
Some places are more selective than others and may present harder entrance requirements. Someone who has not completed an undergraduate degree in psychology or a sufficient number of psychology courses will likely need to address this gap before seeking admission.
Admissions Requirements for PsyD and PhD Programs
Depending on where a student applies, the prospective school may ask for the following::
- Official transcripts from past collegiate studies at the undergraduate and graduate level, including classes taken, GPA, and degree(s) awarded with date
- Proof of any internships, certifications, or licenses
- A resume of work history, including dates and duties
- A description of other relevant activities, such as volunteer work or participation in professional associations
- Scores from the GRE and the GRE Psychology Test
- 2-3 letters of recommendation that support the candidacy
- Responses to essay prompts
- A personal statement explaining why the student wants to pursue this degree
- Interviews with faculty
Note that some programs look only at candidates who already possess a Master’s Degree in Psychology or a closely related field. Others accept students with a bachelor’s degree into a combined master’s/doctoral program.
Accreditation
Selecting a school with regional accreditation ensures the institution has met certain educational standards. Choose one approved by the U.S. Department of Education or the nonprofit Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA). Your school’s specific graduate psychology program also should be accredited by one or both of these organizations.
Another important factor is checking if the program is accredited by the American Psychological Association (APA). 8 Satisfying licensure requirements in some states can be problematic without APA accreditation. Likewise, employers will often look at only job candidates who graduated from an APA-approved program and completed an APA-accredited internship.
Graduate Psychology Career Resources
The following organizations provide further information on licensure for different careers:
- The Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards
- The National Board for Certified Counselors
- The Association of Marital and Family Therapy Regulatory Boards
- Commission on Rehabilitation Counselor Certification
- Someone possessing a PhD is not a medical doctor. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy. In recognition of the expertise obtained from completing this rigorous course of study, holders of a PhD are entitled to use the title “Doctor” if they so choose.
- One isn’t better than the other, just different. Which degree to pursue depends on individual interests and career aspirations. Aspiring therapists and counselors often choose a master’s program. Those wishing to become licensed psychologists must complete a doctoral program. Also, PhD programs focus heavily on research and often lead to working in an academic setting or consulting.
- Some career options for people who earn a graduate degree in psychology include marriage and family therapist, mental health counselor, substance abuse counselor, counseling psychologist, researcher, and psychology professor.
- A person holding a PhD in psychology is not a medical doctor and usually cannot write prescriptions. A few states do allow psychologists with training in psychopharmacology to prescribe a limited number of psychiatric medications. The majority of prescriptions, however, are written out by psychiatrists since they are MDs.
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/community-and-social-service/marriage-and-family-therapists.htm#tab-1
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/psychologists.htm#tab-1
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/community-and-social-service/substance-abuse-behavioral-disorder-and-mental-health-counselors.htm#tab-1
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/market-research-analysts.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/training-and-development-specialists.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/oes/2017/may/oes251066.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/psychologists.htm#tab-5
- https://www.accreditation.apa.org/accredited-programs

- Second Master’s or PhD? – A Comparison
- Types of Doctorates
A second Master’s degree is best suited for those who want to work in industry, but first either want to acquire additional knowledge in their current field or move to a new one. A PhD is best suited to those who want to gain advanced research skills and expertise in their current field and pursue a career in research or academia.
Introduction
It’s common for Master’s students to be plagued by the thought of what they will do next as they near the end of their current degree. Whether it’s taking a gap year, starting their career or continuing education, one thing is clear: there are many possibilities.
If you decide to stay in education, you’ll likely at some point consider whether it’s better to do a second Master’s or a PhD. You’d be right to give this serious thought, as the two degrees have significant differences, from their costs and durations, to the career paths they offer.
This page explains the differences between a second Master’s and a PhD, the pros and cons of each, and will help you to decide which of the two degrees is best for you.
Second Master’s vs PhD
Level of specialisation, master’s.
A Master’s degree, regardless of whether it’s an MSc, MRes or MPhil, aims to provide you with targeted knowledge that builds on what you would have learnt from your undergraduate degree. Although each type of Master’s degree has its own focus, such as an MSc on practical knowledge and an MPhil on research skills, the specialisation they offer isn’t as in-depth as that offered by a PhD. This is because they have a wider curriculum and usually utilise several teaching methods, including lectures and tutorials, which provide a range of knowledge around several closely related subjects.
PhDs are the highest form of academic qualification you can obtain and offer more specialised knowledge than any Master’s degree. Unlike Master’s degrees, which are based on a mixture of teaching methods and curriculum, PhDs are purely research degrees and focus on a specific research question.
A second Master’s degree will provide you with specialist knowledge in various subjects in your field. A doctoral degree will provide you with research skills and expert knowledge in a single topic within your field.
Programme Duration
Most Master’s courses take one year to complete, with an MPhil two years. However, the exact duration will depend on your specific course, type of Master’s and university.
A PhD lasts on average three to four years , with part-time studies lasting up to eight years.
Since a doctorate lasts several times longer than a Master’s, it requires a much greater commitment.
Programme Cost
The cost of a second Master’s degree will vary depending on its type, subject and host universities. Based on an analysis by FindAMaster’s , which summarises tuition fees from the International and Postgraduate Fees Survey 2019 , the average academic tuition fee per year for a Master’s degree in the UK is:
The average tuition fee per year for a PhD in the UK is £4,407 for home/EU students and £19,600 for international students .
There are other fees associated with doctoral research projects that aren’t present with Master’s studies. These include bench fees, travel costs for collaborations and conferences, and potential writing up fees for late thesis submissions.
Annually, a second Master’s degree is twice as expensive than a PhD for home/EU students, and slightly cheaper for international students. However, considering the typical duration of these programmes, a PhD becomes significantly more expensive; twice as expensive for home/EU students and four times as expensive for international students:
Notes: (1) The tuition fee values for the second Master’s is based on the average fees for an MSc. (2) The above table assumes a second Master’s duration of 1 year and a PhD duration of 4 years. (3) The fees and durations are indicative – the exact values vary depending on the course and university.
It’s also important to bear in mind that many PhD programmes come with funding which covers the cost of their fees. Many funding packages also include a living allowance (known as a stipend) which is comparable to a low salary. It is usually much more difficult to secure non-repayable funding for a Master’s programme unless it’s integrated with a PhD programme.
Employability
The skills and knowledge gained through a Master’s degree are general enough to apply to other relevant disciplines. For example, a Master’s degree in statistics would enable you to work in finance, medical analysis, and specific engineering fields etc. Due to this, a second Master’s could help make you suitable for an even wider range of professional fields.
Because a PhD focuses on advanced research methods and a specific research question as opposed to the broad field, your career path is usually refined to the more advanced positions which require expert knowledge. This doesn’t mean that you cannot apply your skills elsewhere, but most PhD holders remain in their field after completing their studies.
It’s worth noting, however, that there is a growing trend for PhD holders to use the transferable skills they acquired during their degree to successfully reposition themselves in careers outside of academia. In fact, STEM PhD holders are particularly sought after in the financial sector because of their proven ability to perform complex tasks under strict deadlines.
Both a second Master’s and a PhD offer excellent employment opportunities. However, a second Master’s usually offers greater career flexibility across industries, especially at the beginning of a career. A doctorate opens up the more demanding positions within a field, but can sometimes make it more difficult to change industries.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Second Master’s
Improving skills: A second Master’s can strengthen your skills within your current field. For example, suppose you have an MEng in Biomedical Engineering. Here, you know of the technical aspects and their application, but you do not necessarily know how to innovate and develop them further. You could fill this skills gap with an MRes or an MPhil that would provide you with complimentary research and investigatory skills. Improving your skills won’t only help you advance faster in your career faster but may also open up future roles that would not otherwise be available to you.
Career change: After completing your first Master’s degree, you may decide that the field is no longer suitable for you. In these scenarios, a second Master’s degree can facilitate career changes. This will have obvious limitations, for example, you shouldn’t expect to be able to do a Master’s in Biomedical Engineering with a Master’s in Classical Literature, however, if you already have a Master’s in another type of engineering, this transition would be possible.
Bridge between different Industries: In STEM subjects, there is extensive interaction between different industries. Although this interaction has always existed, it has grown steadily as more industries try to innovate and tackle more ambitious projects. There’s an obvious need for multidisciplinary roles, and a second Master’s degree in a relevant subject can make you desirable for this reason.
Disadvantages
Perception: If you carry out a second Master’s in a field unrelated to your first, even if to facilitate a career change, it can lead to potential employers perceiving you as unfocused. Although this shouldn’t be the case for large multidisciplinary organisations, it may deter the more specialised companies.
Salary: While a second relevant Master’s in the same subject field may increase your earning potential, a second unrelated Master’s is unlikely to. Although an unrelated second Master’s isn’t a disadvantage if being used to facilitate a career change, it will probably be an unnecessary use of time and money if you intend to stay within your current career path.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a PhD
Establishing yourself as an Expert: Any individual who holds a doctorate is considered an expert in his or her field. Therefore, a PhD has not only a prestigious status but also opens up roles in advanced research and academia.
Commitment: A PhD shows your willingness, commitment and motivation to learn. This makes you highly desirable for employers, as a strong passion for continuous learning usually correlates with the potential to become industry leaders.
Less freedom: Taking three to four years to complete, a PhD is a huge commitment. As a result, many feel pressured to stay in their field to ensure that their PhD was ‘worth’ it, even if they no longer feel that the field is the right one for them. Although it is still possible to change paths after your doctorate, and many do so successfully, many feel ‘locked’ into their path after they finish their studies.
Over-qualified: You may find it difficult to find a job outside of research or academia, as employers may consider you over-qualified and therefore believe that you will quickly leap from the role to a more challenging one. They may also believe you lack practical work experience compared to your counterpart, who has a Master’s degree and has been working in the industry whilst you were working on your academic studies.
Cost: While PhD programmes can come with funding that helps to finance tuition fees and living costs, the funding usually covers only the first 3.5 years of full-time programmes and the first seven years of part-time programmes. You may be determined to complete your doctorate within this timeframe, but it is not uncommon for students to experience setbacks in their research that take them beyond the period for which they’re funded for. This means they have to pay the rest of the fee themselves, which can be a significant burden for some, especially if they lack the savings to do so.
Deciding between a second Master’s and a PhD may seem like a tough decision, but ultimately it depends on what your career goals are. Therefore, the first thing to do is to ensure you’ve thought about your future and have a good idea of where you want to go after your education.
A second Master’s is best suited to those who want to either gain more specialised knowledge in their current industry or make a job change by transitioning into a new industry. A PhD is best suited for those who want to gain advanced research skills and knowledge in their field and pursue a career in research or academia.
Either way, both options offer great opportunities and will open new doors for you. Which of the two degrees is better for you depends on which door you would like to open.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Masters vs. Doctorate in Clinical Psychology
Know the facts when deciding between a master's or doctorate in clinical psych..
Posted June 13, 2016 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
In choosing a career related to clinical psychology, there are a lot of decisions that must be made. In a previous post we discussed the Ph.D.-PsyD decision. Today, we want to explore another tough decision: Master's (e.g., MA/MS in Psychology, Marriage , and Family (Counseling) Therapy , Mental Health Counseling or MSW) versus Doctorate (Ph.D. or PsyD).
Let’s start with some basic characteristics of each type of degree. First, a Master of Psychology can be in clinical (best suited for those with an interest in psychopathological populations and behavioral health), counseling (best for those interested in vocational and career processes, human diversity, and professional training) or educational (provide counseling services to students, including those with a learning disability or those with behavioral or social problems).
Second, a Master's of Social Work (MSW) degree can be in a clinical direct practice track, or a macro-practice track (i.e., focus on political advocacy, community organizing, policy analysis and/or human services management ).
Third, a PsyD is a Doctor of Psychology degree that is best suited for those with an interest in psychopathological populations and behavioral health, and places greater emphasis on the practice of psychology and less emphasis on research. Finally, a Ph.D. (a Doctor of Philosophy degree) can be obtained in the same domains as a Master’s degree, and puts greater emphasis on research than a PsyD.

The time frame for completing each of these graduate degrees is MSW: 2 years, MA: 2 years, PsyD: 4-6 years, and Ph.D.: 5-7 years. During these years of study, it is important to note that (in general) only Ph.D. students will receive support (tuition paid and a stipend) during their years in graduate school.
Of course, there are funding exceptions, especially in cases where a university only has a Master’s program. In addition, scholarships are sometimes available to MSW, MA and PsyD students, but this is generally rare. Support during graduate school might be very important for you, because you can rack up literally tens of thousands of dollars each year in financial assistance, and the amount of money you will earn with your graduate degree may not be as high as you imagined.
Master’s and PsyD programs, in general, are unable to provide the same type of support as a Ph.D. program. Part of this is tied to the fact that typically only Ph.D. students serve as Teaching Assistants or Research Assistants. Also, because Ph.D. programs have far fewer graduate students than PsyD programs, schools are able to afford to support their Ph.D. students.
As far as deciding to go Master or Doctorate degree, there are several issues to keep in mind. First, the general state of affairs for graduate school acceptance is that there is a hierarchy, with Master's programs being easier to get into than PsyD programs and Ph.D programs being the hardest to get into. For the sake of this post, ease of being accepted is defined in terms of grades and GRE scores, although other factors (e.g., clinical and research experience) do come into play. Of course, there are exceptions to this hierarchy, and you may decide to seek a degree at a for-profit school where grades and GRE score are not deemed as important as a non-profit public or private institution.
Our point is simply that your decision about going for a Master’s or Doctorate degree in a graduate program may be a function of what type of program your grades can get you into. We are not saying this is fair, but we hope you understand that schools need some way to pare down the number of students they will accept, with grades and (especially) GRE scores are seen as two important criteria to make these decisions.
We want to add one more point about all of this. It may be the case that your undergraduate academic record is not strong enough to get into a Doctoral program, but you can get accepted into a Master’s program and you do very well in this program. This can work to your advantage if you still want a Doctorate. The thinking here is that if you do well in the Master’s program, you show a Doctoral program that your undergraduate academic record was not indicative of your true potential. However, your stellar record in your Master’s program can show you have what it takes to continue your education in a Doctoral program.
The second issue to think about is the length of time you will be in graduate school. As stated above, the time in graduate school is shorter for a Master’s student than a Ph.D. student. Of course, this means a typical Master’s student can be earning a real salary a few years before a Ph.D. student. Although this is true, one must keep in mind (1) a Master’s degree leads (on average) to a lower salary than a PhD, and (2) a Master’s student will typically have some debt incurred during their two years in school. Let me add that to find out tuition costs for any APA-accredited graduate program, go to their website and look for the link that says “Student Admissions, Outcomes and Other Data.” I think you will be very surprised to see the tuition costs at graduate programs—they’re pretty high. As stated earlier, a Ph.D. student will typically not have any tuition debt hanging over their head. Thus the extra salary for a Master’s student in the time they are out of graduate school working compared to the stipend of a Ph.D. student will probably be offset by the debt the Master’s student must repay.
Third, whether you go for a Master’s or Doctoral degree, you need to consider issues of accreditation of your graduate program and (for Doctoral degrees) your clinical internship. The reason for this is that graduating from an accredited program will offer a greater range of job opportunities. In fact, some employers will only hire those from accredited graduate programs (e.g., the Veterans Administration). If a school does not indicate that it is accredited (e.g., from the American Psychological Association) it should be viewed with caution. With all of this in mind, you should know that to be licensed (certified to practice by a state) in your chosen field it is often the case that you need an accredited graduate degree or internship. Also, note that licensure requires supervised professional experience, an examination at both the state and national levels. Specific courses may be required if a state deems it necessary.
Fourth, as discussed earlier, you must be clear about the issue of job opportunities and salary. In general, it is the case that Master’s degrees lead to fewer job opportunities and lower salaries than Doctoral degrees. One could argue that this is a function of the amount of training--employers are looking for potential employees who have more experience and supervised training. Some might argue that in this regard, a Doctoral student has a stronger foundation of training than a Master's student.
Fifth, you need to decide how much research training versus clinical practice training you want. If you are hoping for the former, then a Ph.D. is definitely for you. A Master’s in Psychology degree may include some research experience. An MSW and a PsyD will likely offer the least research training. One must keep in mind, however, that regardless of the clinical degree you pursue, there will always be some discussion of research, since the basis of diagnoses, testing, therapeutic techniques, etc. is based on research. The key point here is that certain clinical degrees do not require you to be actually conducting research.
Finally, give some thought to how much independence you want to have when you graduate. This all revolves around the issue of licensure that was raised earlier, and it gets very complicated because every state has its own laws regarding licensure for psychology-related degrees. Make sure you understand the laws for the state where you will practice. Of course, you might not know where you will end up, but you must be aware that the state where you end up living may have very different laws than what you expected or from where you originally were working. An important point to keep in mind about licensure is that once you are licensed, if you decide to go into private practice, your fee schedule is typically market-driven.
With all of this in mind, licensure issues require you to consider the following (also check out this info from the APA ):
You need to see what are the licenses your state approves. For a PsyD and PhD, this is not a problem, because all states will have a license for a Psychologist. The issue gets tricky when you have a Master's degree, because states tend to have different types of licensure for these individuals.
- If your state does not have a license that meets your background, what requirements are needed to get a license in a different area? For example, your Master’s degree may not allow you to be licensed as a Psychologist, but after meeting additional requirements you might get licensed as a Licensed Clinical Counselor.
- You need to be clear which licenses require you to be supervised (by a colleague with a certain license) and which allow for autonomous functioning (i.e., functioning on your own). Keep in mind that an employer typically likes an employee to be autonomous—they do not like paying for two hours of supervision (your time and that of your supervisor).
- When you apply for a license that will eventually allow autonomous functioning, what are the requirements to ultimately receive this license (e.g., supervision hours, direct service hours) that you must fulfill?
In presenting these important factors to think about with regard to a Master's vs. Doctoral degree], we, of course, understand that each individual has unique circumstances that must be taken into account. Still, we hope that presenting these factors gives you some food for thought as you consider your ultimate career path in clinical psychology.
Please note that the comments of Dr. Golding, Dr. Lippert and the others who post on this blog express their own opinion and not that of the University of Kentucky.
Want more? Check out our website for more psychology-related career information.

Jonathan Golding, Ph.D. , is a professor of psychology at the University of Kentucky. Anne Lippert, Ph.D. , is a post-doctoral fellow at the University of Kentucky.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Create Account
Notice of FY 2025 H-1B Cap Initial Registration Selection Process Completion and Cap Season Reminders
H-1B Initial Electronic Registration Selection Process Completed
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services has received enough electronic registrations for unique beneficiaries during the initial registration period to reach the fiscal year (FY) 2025 H-1B numerical allocations (H-1B cap), including the advanced degree exemption (master’s cap). We have randomly selected enough properly submitted registrations for unique beneficiaries projected as needed to reach the H-1B cap and have notified all prospective petitioners with selected beneficiaries that they are eligible to file an H-1B cap-subject petition for such beneficiaries.
Registrants’ online accounts will now show one of the following statuses for each registration (that is, for each beneficiary registered):
- Submitted: The registration has been submitted and is eligible for selection. If the initial selection process has been completed, this registration remains eligible, unless subsequently invalidated, for selection in any subsequent selections for the fiscal year for which it was submitted.
- Selected: Selected to file an H-1B cap petition.
- Not Selected: Not eligible to file an H-1B cap petition based on this registration.
- Denied – duplicate registration: Multiple registrations were submitted by or on behalf of the same registrant for the same beneficiary. If denied as a duplicate registration, all registrations submitted by or on behalf of the same registrant for this beneficiary for the fiscal year are invalid.
- Invalidated – failed payment: A registration was submitted but the payment method was declined, not reconciled, or otherwise invalid.
- Deleted: The submitted registration has been deleted and is no longer eligible for selection.
- Processing submission: USCIS is processing your submission. It may take up to 72 hours for all of your case information to show on the case details page. While it is processing, you will be unable to access your draft.
For more information, visit the H-1B Electronic Registration Process page.
FY 2025 H-1B Cap Petitions May Be Filed Starting April 1
H-1B cap-subject petitions for FY 2025, including those petitions eligible for the advanced degree exemption, may be filed with USCIS beginning April 1, 2024, if filed for a selected beneficiary and based on a valid registration.
Only petitioners with registrations for selected beneficiaries may file H-1B cap-subject petitions for FY 2025.
An H-1B cap-subject petition must be properly filed at the correct filing location (see H-1B Form I-129 Filing Location Change to Lockbox section below) or online at my.uscis.gov and within the filing period indicated on the relevant selection notice. The period for filing the H-1B cap-subject petition will be at least 90 days. Petitioners must include a copy of the applicable selection notice with the FY 2025 H-1B cap-subject petition.
Petitioners must also submit evidence of the beneficiary’s valid passport or travel document used at the time of registration to identify the beneficiary.
Petitioners filing for selected beneficiaries based on their valid registration must still submit evidence or otherwise establish eligibility for petition approval, as registration and selection only pertains to eligibility to file the H-1B cap-subject petition.
For more information, visit the H-1B Cap Season page.
New Fees and Form Edition
On Jan. 31, 2024, USCIS published a final rule that adjusts the fees required for most immigration applications and petitions. The new fees are effective April 1, 2024. Petitions postmarked on or after April 1, 2024 , must include the new fees or we will not accept them. Additionally, there will be a new 04/01/24 edition of Form I-129, Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker . There will be no grace period for filing the new version of Form I-129 because it must include the new fee calculation.
What to Know About Sending Us Your Form I-129.
- We will accept the 05/31/23 edition of this form if it is postmarked before April 1, 2024;
- We will not accept the 05/31/23 edition of this form if it is postmarked on or after April 1, 2024; and
- We will only accept the 04/01/24 edition of this form if it is postmarked on or after April 1, 2024.
We will use the postmark date of a filing to determine which form version and fees are correct but will use the received date for purposes of any regulatory or statutory filing deadlines.
As a reminder, we recently announced a final premium processing fee rule that increased the filing fee for Form I-907, Request for Premium Processing Service , to adjust for inflation, effective Feb. 26, 2024. If we receive a Form I-907 postmarked on or after Feb. 26, 2024, with the incorrect filing fee, we will reject the Form I-907 and return the filing fee. For filings sent by commercial courier (such as UPS, FedEx, and DHL), the postmark date is the date on the courier receipt.
Online Filing and Organizational Accounts
On Feb. 28, 2024, we launched new online organizational accounts that allow multiple people within an organization and their legal representatives to collaborate on and prepare H-1B registrations, H-1B petitions, and any associated Form I-907. Information on organizational accounts is available on the Organizational Accounts Frequently Asked Questions page.
We also launched online filing of Form I-129 and associated Form I-907 for non-cap H-1B petitions on March 25. On April 1, we will begin accepting online filing for H-1B cap petitions and associated Forms I-907 for petitioners whose registrations have been selected.
Petitioners will continue to have the option of filing a paper Form I-129 H-1B petition and any associated Form I-907 if they prefer. However, during the initial launch of organizational accounts, users will not be able to link paper-filed Forms I-129 and I-907 to their online accounts.
H-1B Form I-129 Filing Location Change to Lockbox
Starting April 1, 2024, H-1B and H-1B1 (HSC) Form I-129 petitions are no longer filed directly with the USCIS service centers. All paper-based H-1B and H-1B1 (HSC) Form I-129 petitions are now filed at USCIS lockbox locations. This includes cap, non-cap, and cap-exempt H-1B filings.
We will reject H-1B or H-1B1 (HSC) petitions received at a USCIS service center on or after April 1, 2024. There will be no grace period provided.
USCIS has specific mailing addresses for cases that are subject to the H-1B cap. To determine the correct mailing address, please see our Form I-129 Direct Filing Addresses page.
If a petition is filed at the wrong location, we may reject the petition. Rejected petitions will not retain a filing date. If we reject a petition because it was filed at the wrong location, it may be refiled at the correct location, or online. H-1B cap subject petitions may be refiled at the correct location, or online, as long as the petition is refiled during the designated 90-day filing window listed on the selection notice.
No More Pre-paid Mailers
As of March 25, 2024, we are no longer using prepaid mailers to send out any communication or final notices for any H-1B or H-1B1 (HSC) petitions. With H-1B intake now occurring at the lockbox or online, we will not be able to use any prepaid mailers for H-1B or H-1B1 (HSC) filings.
The process of printing and mailing H-1B petition approval notices by first-class mail is fully automated. For petitions filed online, myUSCIS account holders will also receive an email or text message notification in their myUSCIS account when there is a case status change on a case in their account, followed by a paper notice by mail.
Receipt Notice Delays
When we receive a timely and properly filed H-1B cap subject petition, the petitioner (and, if applicable, the petitioner’s legal representative) will be provided a Form I-797, Notice of Action, communicating receipt of the petition. Due to increased filing volumes typically seen during H-1B cap filing periods, there are instances where a paper petition is timely and properly filed by mail, but issuance of the Form I-797 is delayed. If you are a petitioner and have confirmation from the delivery service that the petition was delivered, but you have not yet received a Form I-797 confirming receipt of the petition, you should not submit a second petition. If you have confirmation from the delivery service that the petition was delivered and you then submit a second H-1B cap petition for the same beneficiary, you will be considered to have submitted multiple H-1B cap petitions. This will result in denial or revocation of both petitions.
If more than 30 days have passed since the confirmation of delivery and you have still not received a Form I-797, you may contact the USCIS Contact Center for assistance.
If you receive notification from the delivery service, or your tracking information suggests that there may be a delay or damage to the package or that the package was misrouted, you should follow the Delivery Service Error Guidance on the H-1B Cap Season webpage.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ph.D. study includes a major research project in addition to coursework, and a Ph.D. is the highest scholastic degree awarded by American universities. Contrary to common perception, career paths for Ph.D. graduates are quite varied, not just limited to academia. Ph.D. training helps you hones skills such as writing, research, teaching, data ...
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master's and doctoral degrees: A master's is a 1-2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers. A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3-7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research. A master's is also the necessary first ...
Your PhD will likely take an additional 4 to 6 years after earning your master's degree. Con: A master's degree is usually unfunded. Many students find this a big con: Master's students usually do not receive much funding. Most master's programs are paid for out-of-pocket.
A Master's degree is a second-cycle academic degree and the first level of graduate study, which means it is after a Bachelor's degree and before a PhD. The Master's degree may allow a concentration within a field so that you may focus your studies in-depth on a particular aspect of a subject.
On paper, Master's programs tend to be cheaper than PhD programs. This difference is not surprising considering the shorter duration required to complete a Master's degree. However, there is usually more funding and financial aid available for PhD students in the form of fellowships, teaching assistantships, or grants.
As we mentioned earlier, having a master's can boost your employability. This is often the case when it comes to graduate schemes. While there are some graduate schemes that accept grads with 2:2s, a lot will specify that they're only open to those with a 2:1 and above OR a postgraduate degree. Particularly if you received a 2:2 at uni, a ...
If all you want is a raise, a PhD is probably not the road to choose. A master's degree will boost your career possibilities enough for the kind of raise you want. If you love learning in and of itself, then the work required for a PhD may be worthwhile. Master's degrees tend to be more career oriented while PhD's tend to be more research ...
A master's degree is designed to deepen career-oriented knowledge and skills. A doctorate degree is a heavily research-based degree, designed to develop critical research,analytical and writing skills in an effort to fill industry knowledge gaps. Because of these different goals, the makeup of the coursework and content is also distinct.
2. PhD: After earning a master's degree, the next step is a PhD, which entails both working and performing research at an institution. A PhD is an abbreviation for "Doctor of Philosophy.". It is the highest academic degree one can achieve. As such, it is a time-consuming pursuit that requires a lot of studying and research.
A Masters degree is the next level of education after the completion of an undergraduate degree, commonly known as a Bachelors. These degree levels are often referred to in terms of cycles so that a Bachelor's is a first-cycle degree, a Masters is a second-cycle and finally, a PhD is the third-cycle of higher education (and the highest).
A master's degree is typically not a requirement to enroll in a Ph.D. program. Earning your master's degree may provide benefits if you choose to do so, however it is rarely a requirement of entering a Ph.D. program. There are a few Ph.D. programs that may require you to earn your master's degree before enrolling, so it is important to check ...
Masters degrees usually involve paying a large sum for tuition. In contrast, for the majority of PhD students, tuition is waived. Earning a PhD is still expensive because it often involves being a ...
A doctorate degree commitment can affect more than just you, so be sure you're factoring that into your decision. Review specifically which PhD would be best for you and your field progression. Research your chosen field carefully and evaluate the job market before you finalize your degree choice. Once you've selected your degree, stay ...
It can increase your earning potential: According to the BLS, master's degree holders in 2017 made a median $1,401 a week; these median wages are higher than what bachelor's degree holders ($1,173) and high school graduates ($712) made. In other words, earning a master's degree means higher wages on average.
9. There are no real breaks. In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done."
The MS (Master of Science) in Psychology and the PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) in Psychology are degrees for people interested in advanced study in the discipline. Students obtain a greater understanding of human behavior and how to help others. Degree earners are often interested in careers as therapists, licensed psychologists, researchers, or ...
Take our quiz to find out which option makes the most sense for you. Search hundreds of top schools for the doctorate YOU want. Choosing the right doctorate degree is a personal decision, but there are some essential questions that can help you focus your efforts on finding the right PhD or professional doctorate program.
Notes: (1) The tuition fee values for the second Master's is based on the average fees for an MSc. (2) The above table assumes a second Master's duration of 1 year and a PhD duration of 4 years. (3) The fees and durations are indicative - the exact values vary depending on the course and university. It's also important to bear in mind ...
You generally earn a Master's in the first two years of a PhD program. They meant that the "Master's route" they laid out—getting a Master's first, then a PhD—would take longer than just getting a PhD. A Master's will allow you to skip early PhD classes in many STEM programs. The time will be about the same.
Finally, a Ph.D. (a Doctor of Philosophy degree) can be obtained in the same domains as a Master's degree, and puts greater emphasis on research than a PsyD. The time frame for completing each ...
If you do a PhD, after you graduate, you'll need to find a job. If you get a job now, you'll already have a job. If you do well you might even command a higher salary in 5 years' time compared to entering the market as a fresh PhD. You might find you don't need a PhD. This could especially be the case if you work with other PhD-holders.
In your case, it's not worth it. Focus on getting research and practical experience. I did a masters before I entered my PhD program! In my experience, I lacked the competitiveness coming out of my undergrad, so I spent time during my masters focusing on research. Not just any research, but the possible route I wanted to take in my PhD, which ...
Masters is a good point to change one's career path. (2) to use the Masters degree to get into a better PhD program. For (1), several programs allow masters students to switch into PhD program after a year. For (2), there is no guarantee you will get into a better PhD program with a masters.
H-1B Initial Electronic Registration Selection Process Completed. U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services has received enough electronic registrations for unique beneficiaries during the initial registration period to reach the fiscal year (FY) 2025 H-1B numerical allocations (H-1B cap), including the advanced degree exemption (master's cap).
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, completely blocking the sun's face. Those within the path of totality will see a total solar eclipse. People outside ...