From Associate to Doctorate: A Complete Guide to College Degree Levels

Genevieve Carlton
Contributing Writer
Learn about our editorial process .
Updated April 12, 2024
Hannah Muniz
Contributing Editor
Reviewed by
Stephanie DeBord
Contributing Reviewer

Our Integrity Network
TheBestSchools.org is committed to delivering content that is objective and actionable. To that end, we have built a network of industry professionals across higher education to review our content and ensure we are providing the most helpful information to our readers.
Drawing on their firsthand industry expertise, our Integrity Network members serve as an additional step in our editing process, helping us confirm our content is accurate and up to date. These contributors:
- Suggest changes to inaccurate or misleading information.
- Provide specific, corrective feedback.
- Identify critical information that writers may have missed.
Integrity Network members typically work full time in their industry profession and review content for TheBestSchools.org as a side project. All Integrity Network members are paid members of the Red Ventures Education Integrity Network.
Explore our full list of Integrity Network members.
TheBestSchools.org is an advertising-supported site. Featured or trusted partner programs and all school search, finder, or match results are for schools that compensate us. This compensation does not influence our school rankings, resource guides, or other editorially-independent information published on this site.
Are you ready to discover your college program?
Considering a college degree? First, you'll have to understand the types of degrees and college degree levels.
Different degrees prepare you for different career paths. For example, you can't become a psychologist with just a bachelor's degree — you'd need a master's or doctorate in psychology. And you usually can't become an engineer without at least a bachelor's degree.
Typically, as your university degree level rises, your earning potential increases, and the unemployment rate decreases. That's one more reason it's important to understand the different types of degrees.
What Types of Degrees Are There in College?
There are many types of degrees you can earn in college. College degree levels can be broken down into two categories: undergraduate degrees and graduate degrees.
Here are the college degrees in order, from lowest ranking to highest:
- Associate degree (undergraduate)
- Bachelor's degree (undergraduate)
- Master's degree (graduate)
- Doctoral degree (graduate)
While a doctorate is the highest education level, some fields may stop at a master's. The phrase "terminal degree" refers to the highest degree in a field.
A professional degree is a type of graduate degree — often a doctorate — that prepares you for a professional career in fields like law and medicine.
Popular Online Programs
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial aid, and more by contacting the universities below.
Associate Degree
- Typical Program Length: 1-2 years
- Typical Number of Credits: 60
Most associate degrees prepare you to enter the workforce immediately upon graduation. These programs can be found at community and technical colleges and typically last 1-2 years.
An associate degree can also serve as the foundation for a bachelor's program. You may even be able to transfer some of the credits you earned for your associate degree toward a four-year degree.
Some associate degrees require you to complete an internship or practicum in addition to taking classes. This is particularly common among healthcare and tech degrees.
To apply for an associate degree program , you'll need a high school diploma or equivalent, like a GED certificate. Some schools may require you to submit standardized test scores, such as the ACT or the SAT, as well.
Featured Associate Programs
What can you do with an associate degree.
An associate degree prepares you for vocational, allied health, and support roles. For example, you can become a medical assistant , paralegal , or vet tech with an associate degree.
The highest-paying careers with an associate degree pay over $80,000 per year. See the table below for salary information on other popular associate degree jobs.
Source: BLS
Types of Associate Degrees
Colleges can offer three kinds of associate degrees:
- Associate of Arts (AA)
- Associate of Science (AS)
- Associate of Applied Science (AAS)
Arts, humanities, and creative fields typically offer an AA, whereas social sciences and natural sciences fields often award an AS. Many applied and vocational programs offer an AAS degree.
The type of degree matters if you're planning to transfer into a bachelor's program. Colleges normally offer fewer transfer credits for an AAS degree.
Popular Associate Degrees
- Business Administration
- Business Management
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Cybersecurity
- Early Childhood Education
- Graphic Design
- Healthcare Management
- Information Technology
- Medical Assisting
- Medical Billing and Coding
- Pre-Nursing
- Social Work
Bachelor's Degree
- Typical Program Length: 4 years
- Typical Number of Credits: 120
A bachelor's degree prepares you for many career paths. You'll generally spend four years earning a bachelor's degree at a college or university. You'll take general education classes and courses in your major . You can also choose a minor.
Some colleges offer accelerated bachelor's programs , which take less time — often 2-3 years. Degree-completion programs can also speed up the timeline by awarding you credit for previous college coursework.
You can earn your bachelor's degree online as well. An online degree from an accredited college meets the same standards as that of an in-person degree.
You'll need a high school diploma for admission and may also need to submit SAT or ACT scores.
Featured Bachelor's Programs
What can you do with a bachelor's degree.
In diverse industries like business, tech, and education, a bachelor's degree can prepare you for many entry-level careers. Some of the highest-paying jobs with a bachelor's degree include roles in finance, management, and tech.
Graduates with a four-year degree can also benefit from high demand in many lucrative fields, like software development and engineering. The table below introduces some popular jobs with a bachelor's degree.
Types of Bachelor's Degrees
You can earn a bachelor's degree in many fields. Some of the most common types of bachelor's degrees you'll see include:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA)
- Bachelor of Science (BS)
- Bachelor of Applied Arts (BAA)
- Bachelor of Applied Science (BAS)
- Bachelor of Architecture (B.Arch.)
- Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA)
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA)
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)
The two most popular degrees are a BA and a BS. These degrees cover all arts and sciences majors and some education and engineering degrees.
Popular Bachelor's Degrees
- Civil Engineering
- Communication
- Computer Programming
- Health Informatics
- Health Sciences
- Human Resources
- Mathematics
- Organizational Psychology
- Political Science
- Public Policy
- Supply Chain and Logistics
Master's Degree
- Typical Program Length: 1-3 years
- Typical Number of Credits: 30
A master's degree can help you gain specialized skills and qualify for higher-paying roles. As a graduate student, you'll work closely with experts in your field to explore advanced topics.
While a master's degree typically takes two years, some universities offer accelerated one-year master's programs. You can also enroll in a bachelor's-to-master's program to earn both a bachelor's and master's degree in less time.
Most master's programs require a minimum of 30 credits. Admission and graduation requirements vary depending on the program. For example, many arts and sciences master's programs require GRE scores , while business programs typically require GMAT scores .
Featured Master's Programs
What can you do with a master's degree.
With a master's degree, you can qualify for management-level careers and specialized roles in industries like healthcare, research, and social services. The highest-paying master's degrees include MBAs and nurse practitioner degrees.
Learn more about the earning potential and demand for popular master's degree jobs below.
Types of Master's Degrees
Here are some of the most common types of master's degrees you can earn:
- Master of Arts (MA)
- Master of Science (MS)
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- Master of Education (M.Ed.)
- Master of Fine Arts (MFA)
- Master of Laws (LL.M.)
- Master of Public Administration (MPA)
- Master of Public Health (MPH)
- Master of Public Policy (MPP)
- Master of Science in Nursing (MSN)
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
An MA and an MS are among the most popular master's degrees. Humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences fields typically award an MA or an MS. Other popular options include an MBA and an M.Ed.
Popular Master's Degrees
- Creative Writing
- Data Science
- Engineering
- Healthcare Administration
- Library and Information Science
- Network Security
- Public Health
- Supply Chain Management
Doctoral Degrees
- Typical Program Length: 2-10 years
- Typical Number of Credits: Varies
A doctorate represents the highest degree you can get in academia. There are a few types of doctoral degrees you can get.
Professional doctorates train you for a professional career. For example, law school and med school are two common professional paths. A Ph.D., on the other hand — by far one of the most common types of doctorates — emphasizes theory and research.
In a doctoral program, you'll take graduate-level seminars and courses, take comprehensive exams, conduct original research, and defend a dissertation in front of a faculty committee.
Most applied doctorates take 3-5 years, while a Ph.D. typically requires 4-6 years of coursework. In certain fields, you can earn your doctorate online.
Some doctoral programs require a master's degree for admission, whereas others admit applicants with just a bachelor's degree. You may need to submit standardized test scores depending on the program.
Featured Doctoral Programs
What can you do with a doctorate.
If you want to become a physician , professor , or lawyer, you'll need a doctorate. In many fields, a doctorate translates into higher salaries. Lawyers, pharmacists , and physicists all report median salaries of over $125,000 per year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
The following table shows the earning potential and demand for popular doctoral degree jobs.
Types of Doctoral Degrees
A doctorate is the highest education level, but there are still several types of doctoral degrees. Here are some of the most common you can get:
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)
- Doctor of Medicine (MD)
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
- Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.)
- Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.)
- Juris Doctor (JD)
A Ph.D. is the most popular doctorate. You can earn a Ph.D. in many arts and sciences fields. Other doctorates take their names from the career path associated with the degree.
Popular Doctoral Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Educational Administration
- Educational Leadership
- Human Services
- Legal Studies
- Organizational Leadership
- Public Administration
Frequently Asked Questions About College Degree Levels
What are the four types of college degrees.
The four types of college degrees are associate degrees, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and doctoral degrees. Colleges classify associate and bachelor's degrees as undergraduate degrees and master's and doctoral degrees as graduate degrees.
Within those categories, you can earn many types of degrees. For instance, at the bachelor's level, you could earn a bachelor of arts (BA), a bachelor of science (BS), or a bachelor of fine arts (BFA) degree.
What is a four-year college degree called?
A four-year college degree is called a bachelor's degree. Another term for this degree type is a baccalaureate degree.
Many careers require a bachelor's degree for entry-level roles. For example, most careers in business require you to hold a bachelor's degree. Many roles in tech, education, the public sector, and engineering also require you to have a four-year degree.
Some career paths require a specific major. In many states, you'll need a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) to become a registered nurse . In other fields, your specific major matters less than the quality of your skills.
What is the highest degree?
The highest degree is a doctorate, also called a doctoral degree. In terms of university degree levels, both master's and bachelor's degrees rank below doctorates.
You can earn a doctorate in a wide array of fields, including the social sciences, business, the humanities, education, engineering, and healthcare.
In some fields, however, a master's degree represents the terminal, or highest, degree. For instance, a master of fine arts (MFA) is the terminal degree for creative writing.
What is the hardest college degree?
Most would agree that the hardest college degree is a doctorate. As the highest education level, a doctorate requires significant expertise in the field.
Many Ph.D. programs take six years or more and require you to write a book-length dissertation based on original research.
Because a doctorate represents the top of the university degree levels, it's a relatively uncommon degree. Only around 2% of U.S. adults held a doctorate in 2022, according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
What is the quickest degree?
The fastest degree you can get is either a one-year associate degree or a one-year master's degree. While other types of degrees typically take a minimum of two years, you can earn a master's degree in one year with an accelerated or fast-track program.
You can sometimes add a master's degree to your bachelor's through a 4+1 program, also known as a bachelor's-to-master's program. In this case, some of your coursework counts toward both your undergraduate and graduate degrees, meaning you'll spend an additional year in college to leave with a master's degree.
Explore More College Resources
Highly informative resources to keep your education journey on track.
Take the next step toward your future with online learning.
Discover schools with the programs and courses you’re interested in, and start learning today.
Module 1: Motivating Success
Types of classes in your degree plan, learning objectives.
- Identify differences in types of classes within your degree plan, such as electives and core requirements
Just as you have choices about the delivery format of your courses, you also have choices about where specific courses fit academically into your chosen degree program. For example, you can choose to take various combinations of required courses and elective courses in a given term. Typical college degree programs include both required and elective courses.
- A core course is a course required by your institution, and every student must take it in order to obtain a degree. It’s sometimes also called a general education course. Collectively, core courses are part of a core curriculum. Core courses are always essential to an academic degree, but they are not necessarily foundational to your major.
- A course required in your major , on the other hand, is essential to your specific field of study. For example, as an accounting student you would probably have to take classes like organizational theory and principles of marketing. Your academic adviser can help you learn which courses within your major are required.
- An elective course , in contrast to both core courses and required courses in your major, is a variable component of your curriculum. You choose your electives from a number of optional subjects. Elective courses tend to be more specialized than required courses. They may also have fewer students than required courses.
Most educational programs prefer that students to take a combination of elective and required courses during the same term. This is a good way to meet the demands of your program and take interesting courses outside your focus area at the same time.
Since your required courses will be clearly specified, you may not have many questions about which ones to take or when to take them. But since you get to choose which elective courses you take, some interesting questions may arise.
What are some strategies you can employ to help you decide which electives are right for you? The following article, “ 9 Things No One Tells You About Choosing College Electives ” by Thomas Edison State University, gives helpful advice.
It’s important to track and plan your required and elective courses from the outset. Take advantage of a guidance counselor or another adviser to help you make sure you are on the best trajectory to graduation. Reassess your plan as needed.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
How to Choose Your College Courses
Whether you're undecided or know your major, consider these tips to pick the college courses that are right for you.
Valerie Kirk
From physics to art history, colleges offer hundreds — even thousands — of courses to help you expand your knowledge, explore new interests, and prepare you for your future career.
Interested in climate change? There’s a course for that. How about Greek mythology? There’s a course for that, too.
With so many choices, you may find yourself overwhelmed as you scroll through the course catalog, especially if you are a new college student or you are undecided about your major. Add the need to balance graduation requirements, personal interests, tuition costs, and your very busy schedule, and you may not know where — or how — to start choosing the right courses to meet your specific needs.
The courses you take each semester have a profound impact on your graduation eligibility and college experience. It’s important to spend some time deciding which courses are right for you. When you find a course that interests you, it’s important to look at it in the context of all the other courses you are choosing that semester so you can build an ideal schedule that will inspire you and set you up for success in the coming college years.
Here are a few tips to help you choose the right college courses to meet your individual needs.
Understand the Different Types of Courses
Before getting lost in the course catalog, it’s important to understand the different types of courses that are available to you. From there, you can decide what courses are right for your learning style and where they fit into your college journey.
General education courses
College is a time for exploring new subjects and being exposed to new ideas. To help students expand their knowledge, most colleges require students to take general education courses, typically during the first two years of school.
General education courses include liberal arts and STEM subjects and are usually introductory or beginner level courses. They are also typically included in graduation requirements, so it’s a good idea to know how many general education courses you are required to take to meet your school’s requirements.
A key benefit of taking general education courses in your freshman or sophomore year is that they could help you decide on a major if you are still undecided. For example, you could take astronomy as a required general education science credit and realize you love the subject and seek out additional higher level astronomy classes.
If you took AP classes in high school, check with your college advisor to see if those classes satisfy a general education course requirement and count toward college credit. If they do, you have the opportunity to take other classes that interest you to round out your schedule.
Courses required for your major or minor
If you know what you are going to major and minor in, you will be required to take courses that are specific to that field of study and degree program. These classes are typically intermediate or advanced level courses and may require a prerequisite class.
While typically students choosing these courses have declared their major, you can take them if you are still undecided to help you gain valuable insight into a specific subject.
Elective courses
Electives are classes you can take on any subject you want to explore. These could be additional classes in your major or minor field of study that aren’t required as part of your degree program, but offer you a deeper understanding of certain topics. If you haven’t chosen a major, electives are a good way to learn about different topics that could help you decide.
They may also be on anything outside of your field of study; you have the freedom to take any elective you choose if you can fit it into your schedule. Some colleges build in a certain number of elective courses as part of their graduation requirements, so check ahead of time to know if there’s a required number of electives you have to take.
Remote or hybrid courses
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, some colleges are continuing to offer classes online or with a hybrid schedule. It’s a personal decision as to whether you want to take a course that offers a remote or hybrid schedule, or if you prefer to stick with classes that only meet in-person.
Lecture hall courses
If you attend a larger college or university, some courses may be offered in a lecture hall with hundreds of other students. There is little personal interaction with the professor in lecture courses, but they often require you to attend an additional discussion class with a graduate student. If you have a hard time learning in this type of environment, consider smaller, more personalized formats. You should be able to see the maximum number of students allowed to register for a specific course in the course catalog.
Many courses require hands-on lab work or field work, especially science classes. If you want to try field work or enjoy a more hands-on learning environment, look for classes that offer labs and research the kind of work they include.
Learn more about our Secondary School Program
5 Factors to Consider When Selecting College Courses
Choosing the right college classes goes beyond just checking off the course requirements for your degree program. Each semester presents a unique opportunity to build a class schedule that inspires and challenges you, while also giving you the opportunity to enjoy college life.
Here are five factors to consider as you choose your college courses.
1. Course load
College classes are challenging and require a time commitment in order to succeed. But based on your personal level of aptitude, you may find some subjects easier than others. When building your schedule, be aware of your course load and difficulty level. Mix course levels so you have some classes that may be easier than others to help manage your stress levels.
Consider choosing a variety of subjects —ones that tend to challenge you and ones that you naturally excel at. Also, avoid trying to take too many classes in one semester in your rush to graduation. Check ahead with your academic advisor to make sure you’re still on track to graduate and if so, be mindful of not pushing yourself too hard.
2. Class times
If you struggle to get out of bed in the morning, you may want to avoid that 8 a.m. class held on the other side of campus. Alternatively, if you tend to get tired or lose focus in the afternoon, a 3 p.m. class may not be the best choice.. Consider spreading out your classes throughout the week so you aren’t stuck with a packed schedule every day.
While sometimes you have no choice but to take a course at a time that is not ideal for your schedule, it’s helpful to be aware of class times as you select your courses and choose those that fit into your life.
3. The instructor’s teaching style
When choosing a course, learn about the instructor. Ask others who have taken the class about what it was really like. Read their bio or faculty page, check their LinkedIn profile, or review sites like Rate My Professors . You can even email the instructor ahead of time to ask about how they like to teach the class, the course load, and the general syllabus. Based on what you learn, decide if their teaching style fits with your learning style.
4. Group projects vs. independent work
You can find clues in the course description about the emphasis placed on group projects throughout the semester. If you enjoy group projects, you can seek out those courses. Consider asking students who have already taken the course for examples of these projects to gain a better picture of what’s to come. If you prefer working independently, avoid those classes.
5. Prerequisites
Many higher level courses require prerequisite classes before registering. Be sure you read through the course description to learn if your chosen class has any courses you need to take ahead of time.
Choosing Courses When You Know Your Major
Choosing courses can be easier when you know your major field of study because you likely already have a list of classes you are required to take. However, it’s still important to build a schedule that works for you each semester. Here are four tips for choosing classes when you know your major:
1. Map out graduation requirements
Once you declare your major, learn which classes you are required to take to earn your degree. Then, map out which classes you will take over each semester leading up to your desired graduation date. Be sure to include any general education and elective requirements in your plan.
2. Work with an advisor
You should have — and know — your college advisor, who can talk through your career aspirations and help you build an academic plan to meet your goals each semester. Your advisor will help you keep track of your classes to ensure you are working towards meeting all of the graduation requirements for your degree program.
3. Add electives that interest you
College will challenge you and expose you to different ideas. Electives offer a wide range of options to learn something new, so be sure to take advantage of this opportunity! Research different electives, then round out your schedule with classes that pique your interest.
4. Consider taking a summer school course
Summer school can be a good option to help you fit in all of your degree program requirements or take prerequisite courses to stay on track with your graduation plan. It’s also a great time to take elective courses on subjects that interest you. Class sizes are generally smaller in summer school and you are more likely to receive more personalized attention. If you are feeling adventurous, consider summer study abroad programs .
Choosing Courses When You Are Undecided
If you are undecided about your major , you aren’t alone. Many students who arrive on campus don’t know what they want to do with their careers. Even for those who have declared a major, 30 percent change their major during their first three years of college. Here are three tips for choosing classes when you are still figuring out your major:
1. Meet with an academic advisor
If you are already in college, meeting with a career counselor can help you explore career paths that may be right for you based on your interests. They can also help you decide which classes to take as you think through your career options.
2. Explore summer school
If you are in high school, college summer school courses are a great way to explore your interests. Harvard Summer School offers summer college programs for high school students that provide a glimpse into the college experience. These programs give you the opportunity to take rigorous for-credit and non-credit college courses on a variety of subjects, which could help you determine the types of classes and subjects you may want to take when you start college.
3. Plan ahead
It’s never too early to start thinking about your college journey . By exploring your interests while still in high school, you can build the right class schedule when you get to college that will prepare you for your life and career while also giving you a great college experience.
Learn more about Harvard’ Summer School’s college programs for high school students — the Secondary School Program , which offers more than 200 for-credit college courses in an immersive experience; and the Pre-College Program , which offers non-credit academically rigorous courses.
Explore our pre-college program for high school students
About the Author
Valerie Kirk is a freelance writer and corporate storyteller specializing in customer and community outreach and topics and trends in education, technology, and healthcare. Based in Maryland near the Chesapeake Bay, she spends her free time exploring nature by bike, paddleboard, or on long hikes with her family.
How High School Students Can Set — and Accomplish — Their Goals
Setting and achieving goals can contribute to developing skills for future success.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Types of College Degrees — The Ultimate Guide
All types of college degrees are earned by completing a certain number of credits in a given program at a specific educational level. That said, there are certain factors you need to consider when deciding on the next step in your education.
In this comprehensive guide, we’re providing an in-depth description of the four main types of academic degrees available in the US, followed by the most common programs at each level, the entry requirements, and the cost of obtaining each degree.
What’s the Difference Between College Degree Levels?
Different college degrees equip students with diverse knowledge and skills. Some provide technical knowledge and prepare students to enter the workforce immediately after graduation. Other degree types emphasize developing critical thinking and productivity skills.
Furthermore, different degree types will provide you with various career opportunities. For example, some careers require a minimal college education, whereas others require more intensive study and multiple degrees.
Levels of Degrees in Order
There are multiple types of degrees to choose from, so if you feel unsure about what’s the best educational path for you, read on to discover how college degrees rank from lowest to highest. Additionally, we’re sharing important educational details like the benefits of each degree, the potential career path with that specific education, the requirements to enter the program and obtain the degree, and more.
Undergraduate Types of College Degrees
Undergraduate degree programs are more general compared to graduate programs. Typically, students have five to six courses every semester.
Undergraduate studies are also more flexible than graduate studies, allowing students to switch majors even when they are one or two years in the program. Career-wise, these programs enable students to apply for entry- or manager-level positions. Below, we’re diving deeper into the types of undergraduate degrees.
Associate’s Degree
Community colleges , vocational schools, and junior colleges offer associate degrees. These degrees require a completion of 60 semester credit hours which should take about two years.
After completing the associate degree, graduates are prepared for technical and entry-level roles in the workforce. Also, they can continue their education. About 57% of associate degree recipients who continue their education do so in academic schools, whereas 42.7% attend vocational schools.
Generally, students who earn this type of degree in college and complete their general education courses go to a four-year university to complete their bachelor’s degree program. If the community college is regionally accredited, this can be a great plan for attaining a bachelor’s degree at a significantly lower cost.
The Most Common Types of Associate Degrees
Predictions are that in the 2029-2030 school year, there will be 615,000 female and 392,000 male associate’s degree holders in the US. This stat confirms that associate’s degrees continue to be some of the most popular community college degree types. Read on and discover the most popular types of degrees that can be earned at this level.
Associate in Applied Science
The AAS degree program focuses on one career field, usually technical. It’s perfect for students who want to immediately start building a high-paying career. Potential working positions include web developer, chemical technician, radiologic technologist, geological and petroleum technician.
Associate of Arts
The AA degree studies are focused on liberal arts, general, or pre-professional studies. It’s the broadest of all associate’s degrees. Common AA majors include business administration, law, and psychology. In addition, these types of college degrees prepare graduates for work across a broad range of industries instead of a specific one. As a result, the career options for AA graduates are plenty. They can work as paralegals, customer service representatives, HR managers, art directors, and more.
Associate in Science
The AS degree has broad but more specific scope than an AA degree. Typically, students who intend to pursue education in science-related fields choose AS studies. Earning this degree can pave the way to working in an in-demand field like IT, web development, and healthcare, to name a few.
Entry Requirements
Compared to the requirements for other types of degrees in college, the entry prerequisites for an associate’s degree are less competitive. Considering that the deadlines for these programs are usually longer, it’s not a surprise that they are often an alternative for students who don’t meet the requirements for entering a bachelor’s degree program. Admissions require a high school diploma or equivalent. Some colleges might require a minimum GPA and a completed state’s pre-college curriculum, including math, English, and science courses.
Associate Degree Cost
Comparing the college degrees in order from lowest to highest cost-wise shows that associate programs are the most affordable. The total cost of a degree for in-state students pursuing an associate degree in a public college is $31,496, including $6,754 in tuition costs and $24,742 in additional expenses.
Students would have to pay $68,038 in private, non-profit colleges and $64,758 in private for-profit colleges. These include $33,796 and $30,666 in tuition and $34,242 and $34,092 in additional expenses, respectively.
However, according to college graduation rates , only 13% of students actually graduate within two years, which means the cost is usually much higher than the average.
Bachelor’s Degree
Bachelor’s degree is the most popular of all types of degrees in college. It has a completion rate of 60% and allows graduates to enter the workforce, taking entry- or management-level positions. This undergraduate degree is earned in colleges and universities, and it takes four years to complete. Typically, the program is divided into two years of general education and two years of specialized education.
The general education courses often include English, foreign language, mathematics, and social science. Those enrolled in a bachelor’s degree program need to choose a major area of study like history, biology, finance, or communication.
Bachelor Types of Degrees in College in Order of Popularity
Bachelor’s degree programs are offered in multiple fields. Below, we outline the most popular ones.
Bachelor of Arts
BA lets you focus on specific areas of study in the humanities and social sciences fields like languages, journalism, communication, and international relations. Possible majors in BA programs are English, foreign language, history, fashion merchandising, interior design, psychology, sociology, and political science.
Bachelor of Science
The BSc is a common bachelor degree’s type. It’s very similar to the BA program. The main distinction is in the additional course requirements, with the BSc requiring more science and math courses than BA. BSc also focuses more on combining theoretical knowledge with research practice. BSc programs are offered in numerous fields like natural sciences, mathematics, computer science and IT, and engineering and technology fields.
Bachelor of Fine Arts
The BFA is one of the professional types of college degrees, proving that graduates have gained specific skills to enter the world of fine arts and be actors, singers, authors, dancers, or sculptors. The main difference between BA and BFA is that the program focuses more on majors rather than general studies. The coursework is dedicated to performing or visual arts and may also involve studying liberal arts like psychology, literature, and history.
Bachelor of Business Administration
As one of the basic types of college degrees in business, the BBA programs cover accounting, management, business operations, marketing, and economics courses. At the core of the program are business theory and practice, so students can learn how to analyze complex business issues, approach them from different perspectives, and overcome problems within and between organizations.
Bachelor of Architecture
The Bachelor of Architecture (BArch) involves hands-on experience and theoretical knowledge courses to prepare graduates for employment in the building industry as interior designers, architects, city planners, industrial designers, or other related roles. Students gain fundamental skills and knowledge of architecture while combining theory and history and acquiring digital, technological, legal, artistic, and financial expertise.
Different types of degrees in college involve different requirements. The conditions for enrolling into bachelor’s degree programs might differ from course to course. Generally, students need to have completed high school education and GED or be transfer students from another accredited institution with a minimum GPA of 2.0.
Bachelor Degree Cost
The total cost of a degree for a student living on campus at a public, in-state school is $25,487 per year, which amounts to $101,948 for four years.
As with other types of degrees you can get in college, the cost is higher for out-of-state students who pay on average $43,161 per year or $172,644 for four years. Keep in mind that only 33.3% of students enrolled in bachelor’s degree programs graduate on time—a whopping 57.6% graduate within six years, which increases the cost of attendance to $152,922.
In private schools, the total cost of earning a bachelor’s in a private non-profit institution is estimated at $212,868, whereas in a private for-profit organization is $140,500.
Graduate Types of College Degrees
Graduate degrees provide specialized education on a particular subject or discipline. These studies usually take about three advanced level courses and require higher academic performance.
The studies are fast-paced, more hands-on, and very competitive. Students in graduate programs can work closely with professors and have access to more advanced tools for research purposes. A graduate degree gives better career opportunities and market favorability.
Master’s Degree
A master’s degree is one of the two highest college degrees. It proves the student has a high level of mastery in a specific subject area. The program demands the completion of 30-60 credits which usually takes between one and two years.
The program’s goal is to improve students’ knowledge and technical skills in a specialized area. Students usually decide to pursue a master’s degree to advance in a particular field, boost their job appeal, or find a better-paid role in a senior position.
Master’s Types of College Degrees in Order of Popularity
There are two main types of master’s degrees — course-based and thesis-based. The course-based degree programs are based on structured modules taught through lectures, seminars, or practical work, whereas research-based degree programs require students to do their own research projects in the focus field of study. Additionally, master’s degree programs can be categorized based on the subject matter, specialization level, coursework type, and more.
Master of Arts
A Master of Arts degree is one of the most common types of college degrees in master’s programs. It’s awarded in disciplines that fall under the arts and social sciences category like languages, linguistics, communication, history, geography, and music. The program involves a combination of lectures and seminars and culminates with a student’s dissertation based on a research project.
Master of Science
The Master of Science degree is awarded in science for disciplines like biology, engineering, health, and chemistry. Students enrolled in these kinds of degrees learn through lab work, analysis, and scientific research. The degree holders have high prospects for working in one of the best jobs for the future.
Master of Research
An MRes degree provides training on how to become a researcher. Usually, students pursue this degree if they want to implement research skills and knowledge in their careers or prepare for a PhD program. The MRes program involves courses that focus on research principles, methods, and tools. They need to conduct research and write a thesis to earn the degree.
Professional Master’s Degrees
Professional master’s degrees are specialized kinds of degrees that are more hands-on than traditional master’s degree programs and heavily concentrate on giving students practical skills and knowledge.
Master of Laws
The Master of Laws degree program allows students who have earned a professional law degree to combine basic skills with specialized knowledge acquired through researching specific law areas. Earning an LLM provides great career benefits and helps boost career prospects.
Master of Business Administration
The MBA is one of the most common types of business degrees in college. The program is designed to provide students with the skills and knowledge needed for career advancement in business and management roles. Students go through extensive training in all business aspects. The majority of programs require at least three years of professional experience.
Master of Education
The MEd degree prepares students to pursue a career in education, as well as get certified or specialize in specific areas like special education, curriculum, counseling, instruction, and administration. The programs usually combine both coursework and internship.
Master of Architecture
The MArch degree is one of the most extensive types of degrees you can get in college. It assesses students through internships and a final thesis or project. Students are also required to produce coursework in subjects like building science, architectural history, design, theory, and professional practice. In the end, students get licensed and can consider wide career possibilities.
Postgraduate master’s degrees are open to students who hold a bachelor’s degree or an undergraduate degree in an appropriate subject. Additionally, schools usually require an undergraduate GPA of 3.0. Some schools might also require students to take entrance exams. The professional master’s degrees generally have additional prerequisites like having professional experience or holding specific bachelor’s degrees.
Doctoral Degree
A doctorate is the highest college degree. The standard title for students obtaining a doctorate is Ph.D, which stands for Doctor of Philosophy. It’s the final degree available in a specific discipline.
A doctorate follows the completion of bachelor’s and master’s degrees. That said, some programs also admit students who don’t hold a master’s degree.
The doctorate programs are designed to help students get advanced knowledge and skills and reach the highest level of academic mastery in their chosen field. It takes about four years to complete doctoral types of college programs.
Studies are complex and require a great deal of commitment, focus, energy, and money. In the first year of the program, the content is standard. However, in the next few years, students move toward in-depth analysis and research. Finally, before earning the doctoral degree, students need to defend a thesis in front of an expert panel.
After the program’s completion, the Doctor of Philosophy can work as a university professor, a professional researcher, or take an executive leadership role. Thus, a doctorate often leads to significant professional advancement and tremendous earning potential. In fact, Ph.D holders earn a median weekly pay of $1,885.
Types of Doctoral Degrees
A doctorate is the highest degree in college, and there are several different types of degrees available at this level. If you’re unsure where to start, here are the four key programs available in the US.
Research-Based Doctorate
Research-based doctorates are also known as academic doctorates and are usually awarded for original research in traditional academic subjects. The main focus is on expanding the theoretical understanding of a subject rather than advancing professional practice.
Professional Doctorate
A professional doctorate program focuses on applying research to practical issues, designing effective professional practices, and creating solutions to complex problems in a specific profession. Examples of such types of college programs include Doctor of Business Administration, Doctor of Education, Doctor of Public Health, and Doctor of Nursing Practice, to name a few.
Professional doctorates are awarded to candidates who directly contribute to a specific vocational field by conducting research and analysis. These programs might require the candidate to have specific field experience.
Higher Doctorates
Usually awarded later in one’s career, higher doctorates aim to recognize esteemed practitioners and researchers. They are one of the highest types of educational degrees that candidates don’t need to enroll in; the degree is awarded based on a published scholarly work that establishes the candidates as making a significant contribution to the advancement of the specific field. Examples of higher doctorate degrees might include Doctor of Science, Doctor of Laws, Doctor of Engineering, Doctor of Business, and Doctor of Music.
Honorary Doctorates
Honorary doctorates are awarded to celebrate one’s achievement in a specific field. It’s one of the highest college degrees that aren’t rewarded for academic achievements but for lifetime accomplishments that benefit humanity. Some institutions allow candidates to apply for an honorary degree, whereas others require third-party nominations.
These schools also create their own criteria for acceptance. They may present different types of degrees like Doctor of Laws, Doctor of Fine Arts, Doctor of Humane Letters, and Doctor of Divinity, to name a few.
The Cost of Doctoral Degree
When comparing the college degrees in order from lowest to highest, doctorates are the most expensive. According to the latest data published by Education Data, a doctorate costs on average $114,300. The average cost is higher for some fields like Psychology ($132,200) and Education ($111,900). That said, some programs might offer financial aid in the form of fellowships and assistantships or work within the academic department.
Degree Requirements
The requirements for getting a doctorate vary from program to program. Usually, the research-based doctorate programs require specific coursework, whereas requirements for professional degree programs typically include fieldwork, residencies, or at least internships. It’s important to note that internships increase job offers by 16% . Often, the final step to a doctorate is a comprehensive research work or a dissertation thesis.
How to Choose From the College Degree Levels
When preparing for college and considering which degree level to pursue, the first and most important step is to identify your interests and the career path you want to follow. While you can start working with an associate degree, the higher degree level you reach, the more advanced career opportunities you’ll have.
Furthermore, make sure to do comprehensive research on the position you’d like to have and take note of the job requirements to ensure the degree will make you competitive. Finally, consider your budget and whether you can afford the potential debt. Keep in mind that advanced degrees will cost you more, but the potential salary you’ll earn often outweighs the tuition cost.
People Also Ask
College degrees are first divided into undergraduate and graduate degrees. The two main types under the undergraduate category are associate’s and bachelor’s degrees. The former requires only two years and can be the first step towards earning a bachelor’s degree, which takes four years to complete. The graduate category consists of master’s degree and doctoral degree problems. These degree programs are more extensive and represent a form of field specialization.
The next level after graduating from high school is the associate’s degree. It is the least advanced degree, followed by the bachelor’s, one of the most common degrees. Next comes the master’s, followed by the doctoral degree—the highest degree one can earn in college. Within these four categories, there are different types of degree programs that differ based on the area of study.
A bachelor’s degree program usually requires the completion of 120 credits and takes four years. However, due to social, academic, and financial strains, graduating on time has become nearly impossible. In fact, the average full-time student takes six years to graduate. According to recent data, only 33.3% of students graduate on time, and 57.6% do so within six years.
A two-year degree is called an associate degree. It requires the completion of 60 semester credit hours and prepares students for entry-level work positions. Students can earn an associate’s degree in a community, junior, or technical college. Afterward, they can start working or continue their education by pursuing a bachelor’s degree. Associate of Arts, Associate in Science, and Associate in Applied Science are the three most common types of associate’s degrees.
Doctoral is the highest degree one can earn. It’s also commonly referred to as a “terminal degree” as it’s the highest academic mastery level in a particular field. The degree is awarded to academics who have completed a doctoral program and have prepared research or defended a thesis in front of an examination committee. Professional degrees are also doctoral types of college degrees that focus on a specific vocational field.
Bachelor Studies Barry.edu Best Colleges Best Colleges Best Colleges BLS Caldo Central Christian College Chron College Transfer Edology Education Data Education Data Education Data Find A Masters Find A PhD Find A Professional Doctorate GoGrad Hot Courses Abroad Leeds Masters Portal NYU Pearson Accelerated Schools.com Statista Study.com Study.com Study.com Think Impact US News

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What are the 4 Types of College Degrees?

Understanding the Numbers When reviewing job growth and salary information, it’s important to remember that actual numbers can vary due to many different factors — like years of experience in the role, industry of employment, geographic location, worker skill and economic conditions. Cited projections do not guarantee actual salary or job growth.
Going to college to earn your degree can provide new skills, job opportunities, and salary increases, but what is the best degree for you
Whether you want to earn your first degree, gain new skills to change careers or earn a promotion by building upon your existing education, it’s important to explore how different degrees can help you reach your goals.
Understanding the types of degrees available, how you can advance through degree levels and the amount of time it will take to complete a program is key to choosing the degree that's right for you.
Exploring College Degree Levels
What is a college degree able to do for your career? It all depends on your field of choice and long-term goals.
Explore the list of college degrees, below, in order from lowest to highest. Discover the benefits of different types of degrees and understand how you can work through these levels of education to further your career.
Types of Associate Degrees
If you’re just starting out with higher education or want to add education credentials to real-world experience, an associate degree could be a great fit.
Different types of associate degrees , such as an Associate of Science (AS) or Associate of Arts (AA), are 60 credits and can be completed in 2 years or less , and are a great first step toward earning an entry-level job or promotion. There are job opportunities for associate degree holders across many fields, including:
- Associate in accounting
- Associate in criminal justice
- Associate in digital photography
- Associate in information technology
- Associate in liberal arts
- Associate in marketing

An AS degree will prepare you for jobs available across many industries including marketing, information technology and accounting. While earning an AA degree can help you develop the soft skills employers look for such as problem-solving, critical thinking skills and communication.
Starting with an associate degree is worth it as there are great benefits and opportunities that come with it. Earning an associate degree can have a significant economic impact. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), associate degree holders earn 20% more than workers with only a high school degree.
If you’re unsure about starting a bachelor’s degree program, earning an associate degree is a great way to kickstart your education and enter the workforce before enrolling in a more advanced degree. If you decide to continue on to a bachelor’s degree, your associate degree credits are typically applied toward the four-year degree.
With an associate degree in business administration , for example, you can gain a solid foundation in business principles and practices that will prepare you for entry-level positions. Continuing on to bachelor’s degrees in business administration can help you dive deeper into a specific area of study, such as finance, project management or marketing.
Types of Bachelor Degrees
Designed to be completed in 4 years, bachelor’s degree programs provide in-depth knowledge and skills across a wide variety of career paths to help you stand out in today’s competitive job market.
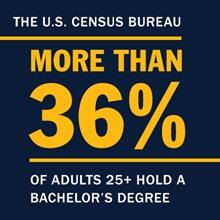
Bachelor's degrees are in high demand. According to a 2020 U.S. Census Bureau report, more than 36% of adults over age 25 hold a bachelor’s degree.

Bachelor’s degrees like Bachelor of Science (BS) and Bachelor of Arts (BA) offer more opportunities to focus your learning on a specialized area of study. With a business administration bachelor’s degree , for example, you can concentrate your studies on anything from finance, accounting and healthcare management to marketing, entrepreneurship and public administration.
Earning a bachelor’s degree opens the door to advancing your education with a graduate-level degree - an increasingly common step for workers looking to further their careers.
Types of Master’s Degrees
Earning a master’s degree is a great way to gain more technical knowledge in your field and set yourself apart from other workers.
With growing opportunities for online master’s degree programs , including programs that can be completed in less than 2 years, this degree path is becoming increasingly popular with full-time working adults.
Employers are also increasing demand for master’s degree holders. According to BLS data, jobs requiring master’s degrees are projected to grow by 16% by 2030.
Earning a master’s degree can open the door to advancement within your company, help you tackle new career goals and can also boost your long-term earning potential. Master’s degree holders’ median weekly earnings were 18% higher than bachelor’s degree holders and 65% higher than associate degree holders, according to BLS.

Master’s degrees, like Master of Science (MS) or Master of Arts (MA), are available across a wide variety of subjects. Master of Business Administration (MBA) programs are among the most well-known master’s degree programs, with opportunities to study finance, accounting, international business, criminal justice, information technology management and more.
If you’re looking to advance your education even further, you may be wondering what comes after a master’s degree. The answer depends on your career goals.
Types of Doctoral Degrees
If you’re looking to advance your education to the highest degree in college , a doctoral degree may be right for you.
Depending on your industry and career goals, there are several types of doctoral degrees to consider. A few include:
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA): A terminal degree tailored to business professionals looking to explore, examine and address business issues.
- Doctor of Education (EdD) : A doctoral degree geared toward leaders (and aspiring leaders) in educational organizations and the education system itself.
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD): An academic doctorate available to a range of fields. A PhD is typically required to become a professor and can help you start a career in research.
Doctoral degrees can take up to 7 years of intense study to complete. After completing doctoral degree coursework, you might sit for comprehensive subject matter exams. A dissertation based on your research interests may also be required and reviewed by a committee of graduate school faculty.
Determining Your Educational Path

While advancing your education can have significant economic impacts, each career has its own unique job requirements and there are often benefits to remaining in the workforce while working toward a college degree. Many companies offer tuition assistance programs, for example, that can help pay for more advanced degrees.
Do some research and reflect on your long-term goals and you’ll be on the path to choosing the college degree level that is right for you.
A degree can change your life. Find the SNHU degree that can help you meet your goals.
Explore more content like this article

How Long Does it Take to Get a Master's Degree?

How to Survive High School and Prepare for College

How Long Does it Take to Get an Associate Degree?
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
U.S. News Guide to College Majors
Options for selecting a college major are numerous and wide-ranging.
Choosing where to attend college is a big decision. But even if you’ve had your sights set on attending your dream school since you were a kid, what will you study there? Some majors, like business, offer courses on a broad range of related topics, while others, like mechanical engineering, present a more specialized track. Deciding what to major in can be overwhelming, but learning about the variety of majors available, coupled with understanding your own strengths, interests and goals, can help you decide which one is right for you.
This guide presents information about some common college majors, the pay associated with those majors and what to expect if you find yourself wanting to change your major.
Understanding College Majors
A college major is a focused area of study. While many undergraduate students must meet general education requirements like taking an English composition or a world history class, the courses associated with a major provide a deeper dive into a subject or specialty area, usually to prepare students for careers in that field.
When considering potential college majors, students should think about the following factors:
- Interests and passions. What do you love and care about? How do you spend your free time? Can you picture yourself still caring about those things throughout your college and professional careers?
- Aptitudes and strengths. What are you good at? Are you an excellent problem solver (in complex situations or when doing math homework)? Do you have a knack for writing or public speaking? Consider how your strengths might benefit you in a variety of careers. At the same time, be aware of your weaknesses. If you faint at the sight of blood, the medical field might not be the right fit for you, for example.
- Career goals and prospects. What do you want to accomplish in your professional career, and how might a college degree help you achieve that? Do your goals align with the demands of the job market? What skills might you need to obtain and which topics might you need to study to reach your goals?
- Flexibility and exploration. Do you want to define your own path and figure out what interests you most throughout your college journey, or do you have more rigid or focused career goals?
Exploring Common College Majors
Stem majors.
The science, technology, engineering and math – collectively known as STEM – fields present a wide variety of in-demand and potentially high-paying jobs. Students with an aptitude and interest for math and science might consider one of these majors, which include:
- Computer Science .
- Engineering .
- Biology .
- Mathematics .
- Physics .
Many STEM subject areas can be subdivided into more focused areas of study, such as mechanical engineering or microbiology , for example.
Social sciences and humanities majors
Chances are, you’ll take some introductory courses for social sciences and humanities regardless of your major. But students who choose to major in one of these subject areas go deeper, on their way toward becoming experts in their field. Social sciences and humanities majors include:
- Psychology .
- Sociology .
- Political Science .
- English Literature .
Business and economics majors
If you declare a business major, you’ll be in good company on your campus. Business is one of the most common undergraduate majors, according to the National Center for Education Statistics . While some majors in this field, like accounting, are more tailored toward a specific career, others, like a general business degree , can provide a broader scope of the subject area. Business and economics majors include:
- Accounting .
- Finance .
- Marketing .
- International Business .
- Economics .
Arts and communication majors
Arts and communication majors likely won’t receive paychecks as large as those their peers in some science or business roles get, but they use their skills to tell stories and convey messages, whether for education or entertainment. Some popular majors for students who want to hone their arts and communication skills include:
- Fine Arts .
- Graphic Design .
- Film and Media Studies.
- Journalism .
- Communication Studies .
Health and medical majors
Jobs in the health care field are always in demand. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, jobs including physical therapist, registered nurse and pharmacist are projected to grow by at least an average rate by 2032. While some roles in this field can be obtained with a bachelor’s degree, others require further schooling. And for students who hope to be accepted into medical school, majoring in a related field for their undergraduate education can lay a firm foundation for the rest of their studies. Health and medical majors include:
- Nursing .
- Premedical Studies .
- Pharmacy .
- Physical Therapy.
- Public Health .
Education majors
Students who have a passion for learning may also desire to foster that same trait in others. Whether they plan to teach at a certain grade level or in a specific subject area, or they hope to be a principal or superintendent someday, students who choose an education major learn how to effectively instruct others. Education majors include:
- Elementary Education .
- Secondary Education.
- Special Education .
- Early Childhood Education .
- Physical Education.
Exploring niche and emerging majors
While college students have been majoring in areas like education and business for decades, other majors have developed over time in response to growing areas of need or interest. Students who want to explore careers in newer or more niche fields might consider majors such as:
- Environmental Science .
- Data Science and Analytics.
- Cybersecurity .
- Sports Management .
- Digital Marketing.
Degrees in more niche subject areas may not be offered by as many schools as the more common majors, so prospective students should keep this in mind as part of their college search.
Additional college majors
High school students who explore a variety of subject areas might discover a college major they’d never thought about before, so be sure to learn as much as you can about anything that interests you while considering your college plans. To assist you in learning what it’s like to major in a variety of areas, U.S. News provides guides on what you need to know about majors like:
- Animal Science .
- Anthropology .
- Architecture .
- Astronomy .
- Biochemistry .
- Biomedical Engineering .
- Business Administration .
- Chemistry .
- Cognitive Science .
- Computer Engineering .
- Criminology .
- Geography .
- Human Biology .
- Human Resources .
- Human Services .
- International Relations .
- Linguistics .
- Management Information and Services .
- Music .
- Nutrition .
- Philosophy .
- Physiology .
- Public Policy .
- Public Relations .
- Real Estate .
- Social Work .
- Statistics .
Pick the Perfect Major
Discover the perfect major for you based on your innate wiring. The Innate Assessment sets you up for success by pairing you with majors, colleges and careers that fit your unique skills and abilities.
Career Paths and Opportunities
Crucially, what a student chooses to major in sets the course for their next steps after graduation. A company looking to hire a graphic designer is more likely to be interested in a candidate who has a degree in graphic design and built a portfolio of design projects while in school than it is in someone who majored in an unrelated field.
While many students’ formal education culminates in a bachelor’s degree, that’s not always the case. For careers that require a master’s, doctorate or professional degree, undergraduates should plan ahead as much as possible. Some graduate programs may only consider applicants who meet minimum GPA requirements, have a bachelor’s degree in a related field or completed relevant coursework in undergrad. Students who know they want to apply for dental school, for example, should look at the prerequisites for dental programs and make sure their major and the courses they take while earning their bachelor’s degree is in line with those requirements.
Other students may want to enter the workforce after graduation and apply for graduate school after gaining a few years of relevant professional experience. Master’s in Business Administration programs tend to prefer applicants who have real-world experience, for instance.
Because jobs in some fields pay more than others, a student’s college major can ultimately affect how much money they make in the future. For example, while both elementary school teachers and information security analysts can obtain their jobs with a bachelor’s degree, their mean annual salaries are dramatically different. Elementary school teachers make an average of $68,000 per year, while information security analysts, who typically have a degree in computer science or a related field, make $119,860 per year on average, according to the BLS.
Highest-paying college majors
Students who major in the STEM fields tend to see some of the highest starting salaries in the workforce. Those who major in engineering or computer science might see a particularly good return on their investment . According to the BLS, computer hardware engineers made an average salary of $140,830 in 2022, while computer network architects made an average of $129,490 and aerospace engineers made an average salary of $127,090. Some employers may prefer employees in these roles to have a master’s degree, while others may hire bachelor’s degree-holders.
Health care professionals like surgeons, emergency medicine physicians and anesthesiologists also have high salaries, but these jobs require years of postgraduate education.
Lowest-paying college majors
While undergraduate students may pay similar tuition rates regardless of their major, the resulting payoff isn’t always the same. Majors in the arts and humanities tend to lead to lower-paying jobs than some roles STEM majors can obtain. According to the BLS, graphic designers made an average of $64,500 in 2022. Archaeologists and anthropologists, many of whom need a master’s or doctoral degree to advance their careers, made an average annual salary of $68,310 in 2022, according to the BLS.
Despite the gap in pay between majors, a college degree generally can pay off in the long run. According to a Georgetown University study , bachelor’s degree holders earn 31% more than associate’s degree holders and 84% more than people whose highest level of education is a high school diploma.
Strategies for Choosing a College Major
When choosing a college major, students should consider their interests and talents as well as career goals and potential future earnings. If multiple options are on the table, think about other resources that might help you narrow your choices, like:
- Meet with a guidance or career counselor at your school. They may be able to help you prioritize what you’re looking for in a career or inform you about a major you haven't considered.
- Learn about programs at your preferred colleges and universities. Sometimes, the decisions of what to study and where to study can go hand in hand. What majors do your dream school and backup schools offer? Which of those majors pique your interest?
- Job shadow or conduct informational interviews. Do any adults in your life have jobs that look like something you might want to do in the future? Do you know any current college students who might want to provide you with insight into the coursework for their major? It’s not uncommon for people to talk to high school students about what they plan to do after graduation, so don't be afraid to ask people about what a typical day on their job looks like. If possible, apply for a job shadowing or internship program with an organization so you can get hands-on experience with that industry and a better idea of whether you might want to pursue it in college.
Majors in high demand
While majors like business have remained consistently popular over the years, others have seen higher or lower enrollment rates depending on the needs of the ever-evolving workforce. Students who major in a STEM or health care field can expect their skills and expertise to be in demand: Among the 10 jobs from which the BLS expects to see the fastest growth by 2032 are nurse practitioners, data scientists, information security analysts, medical and health services managers, physician assistants and software developers. While nurse practitioners and physician assistants typically need a master’s degree, these other roles typically require only a bachelor’s degree.
The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2023 , which examines how jobs might evolve over a five-year period, states that the fastest-growing occupations relative to their size include roles in technology like artificial intelligence and machine learning specialists, as well as sustainability, like renewable energy engineers.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Choosing a Major
While choosing a college major is a big decision, it’s not uncommon for students to change majors at some point during their undergraduate career. But switching majors doesn’t come without risk – you may find yourself taking extra classes to meet the degree requirements for your new major, which can lead to you spending more time and money than it would have cost to follow one degree track from the beginning of your time in college.
Many colleges and universities don’t require students to declare a major until their sophomore year, or until they have completed a certain number of credit hours. So if you’re undecided at the start of your college journey, register for required core classes and take advantage of campus resources and elective courses that can help you find the right major.
Some majors allow students to specialize further by choosing a concentration within their major based on what they intend for their career path. Concentrations vary by institution, but for example, students majoring in sports management might be able to specialize in topics like sports business, analytics, marketing or administration, depending on what area of sports management they want to work in.
Some students find that declaring a double major might help them reach their career goals. Students who double major still only earn one degree – and therefore can still complete their bachelor’s degree in four years – but double majoring means they’ve earned enough credits in two (often related) subject areas for both to be considered a major.
In addition to a major, students commonly declare a minor , a secondary subject area in which to focus. A minor can complement your studies without requiring as many courses in a specialty area as a major. Your chosen minor might not be directly related to your major, but it could help equip you for reaching your career goals. For example, a journalism major who ultimately wants to cover politics may minor in political science, and a fine arts major who hopes to open their own studio someday might choose to minor in business or education.
But even with all these options, students aren’t necessarily limited to specific majors offered at their chosen college or university. Many schools offer an interdisciplinary studies major , or custom study path that incorporates coursework from multiple subject areas to align with a student’s career goals. Students who are interested in interdisciplinary studies or a custom degree should meet with their academic adviser and learn their school’s process for assembling a custom program of study.

Tags: students , education , colleges , college majors , STEM jobs , STEM
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Protests boil over on college campuses.
Lauren Camera April 22, 2024

Supporting Low-Income College Applicants
Shavar Jeffries April 16, 2024

Supporting Black Women in Higher Ed
Zainab Okolo April 15, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

Today NAIA, Tomorrow Title IX?
Lauren Camera April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

How to Decide if an MBA Is Worth it
Sarah Wood March 27, 2024

What to Wear to a Graduation
LaMont Jones, Jr. March 27, 2024

FAFSA Delays Alarm Families, Colleges
Sarah Wood March 25, 2024

Help Your Teen With the College Decision
Anayat Durrani March 25, 2024

Your guide to the different types of college classes

Many teens envision stepping onto their dream campus, but what about stepping into college classrooms? Undergraduate majors, average class size, and other academic programs factor into every student’s college application process, so it’s worth taking a look at the different types of college classes.
Along with questions to ask an academic advisor and on a tour of a college campus , it’s helpful to ask not just about the typical course load and class offerings, but also about what types of classes are offered. After all, a lecture-style class with potentially over one hundred students is a very different experience than a small-group seminar or online class.
That’s all the more reason to know about the myriad of different college course formats!
Often, students will have the choice of several college class formats when they register each semester. Your student may need to take a range of different kinds of classes during their undergraduate years. It’s useful to know not only the basics of what to expect, but what strategies can help students succeed.
7 Types of College Classes (and How to Succeed in Them)
Every college experience is different, so as you look ahead to your teen’s future, it’s good to know the ins and outs of the academic component of that experience. No matter what their major is, however, it’s likely that they will take a mix of different types of classes.
Whether the class is a graduation requirement, a core part of their college major (or two college majors ), or an elective, it’s good to know what students are signing up for! Here are the essentials of what they can expect in seven types of college classes.
Picture a hundred seats facing a lectern and a screen, and you can learn a lot about a lecture-style class. Most often, these large classes consist of entry-level and/or requisite classes for specific majors or for graduation from the university.
Lectures are professor-led, and often require copious amounts of note-taking. Some may involve a participation element, either through traditional Q&A or an electronic participation system (which we’re seeing more and more of these days), but this element is not always present in lectures. These classes often involve working from a textbook or a relatively small number of texts.
At times, it’s easy to feel anonymous in a lecture class, but to succeed in them, it’s important to devote as much attention as to any other type of class. These professors often don’t meet all of their students personally, so attending office hours is particularly important.
2. Sections
Sections go hand in hand with lecture-style classes. In a section, a subset of students enrolled in a lecture meet in smaller groups to discuss course material and complete assignments. Often, sections are led by a teaching assistant or graduate student.
In a typical lecture, students may meet for a professor-led class once per week and meet with their section once or twice per week. These sections are critically important for asking questions, deepening understanding of the content, and collaborating with peers.
3. Independent study
If colleges offer the opportunity for students to take on an independent study, it’s usually at the upper-division level. Students may be able to pursue an independent study as a capstone senior project, or to work through advanced material at their own pace.
In an independent study, students either complete a series of projects, assignments, and readings that are pre-agreed with a professor advisor or of their own design. They may meet weekly or monthly with that advisor, but students will complete the vast majority of the work on their own.
Students should bear in mind that, while the freedom and flexibility that goes with an independent study can be appealing, this type of course won’t work for everyone. It goes without saying that a high level of organization, discipline, and self-direction is essential to success in an independent study.
4. Seminar
These small-group classes, think 25 students or fewer, are usually discussion-heavy and are designed to encourage a high level of engagement from students. Seminars usually consist of a higher number of short readings, the better to explore a specific set of material in depth.
A staple of many humanities departments, seminars are offered at both introductory and advanced levels of study. For a great seminar experience, students should focus on quality (over quantity) of in-class participation and thoughtful written responses on assignments and projects.
5. Online and hybrid courses
More and more common nowadays, online classes can be offered both during the typical academic year and during summer sessions. Most often, online courses at the college level cover introductory-level material.
It is worth noting that online classes offer a higher degree of flexibility for students balancing jobs and other commitments with school. If completing a for-credit internship or study abroad program, for instance, it’s worth looking into the university’s online course options.
Similarly, a hybrid college class involves a combination of online and in-person instruction. Offering the flexible benefits of online courses with a collaborative element, hybrid courses can be a great option for students looking to take on jobs, internships, volunteer work, independent study, or other projects.
Essential to many STEM classes, labs are opportunities for students to conduct extended research and explorations of subject matter. They are often paired with a lecture-style class.
During lab sessions, students will work individually or in groups to gather data, conduct experiments, and solve complex problems. STEM enthusiasts will be familiar with labs from high school, and they will find similarities in the format of college-level labs. In college, labs most often meet at a different time than the lecture and will be longer in duration.
These project-based classes focus on hands-on work and are common in the arts. In a studio class, students will follow an instructor as they learn various techniques and complete assignments that demonstrate mastery of the material.
On a class to class basis, students will likely encounter a mix of short lectures, discussions, and independent work. As coursework for studio classes are often graded holistically in a portfolio format, it’s essential that students keep up with the pace of the course.
Prepare for college with expert guidance
The college application process is as exciting as it can be daunting, and families deserve excellent resources for navigating it. Whether your teen needs personal tutoring for the SAT® or an AP® exam or is looking to boost their extracurricular resume , iD Tech has something for every student.
Plus, check out our recent expert Q & A about how to succeed in STEM in college and beyond, and visit our blog for more college-bound tips and tricks!
Featured Posts
Meet id tech.
Sign up for our emails to learn more about why iD Tech is #1 in STEM education! Be the first to hear about new courses, locations, programs, and partnerships–plus receive exclusive promotions! AI summer camps , coding classes for kids , and more!
Virginia started with iD Tech at the University of Denver in 2015 and has loved every minute since then! A former teacher by trade, she has a master's in education and loves working to embolden the next generation through STEM. Outside the office, you can usually find her reading a good book, struggling on a yoga mat, or exploring the Rocky Mountains.
Related posts
- College Prep How to Write About Virtual Tech Camps on College Applications Universities want to know about applicants’ interests and skills: Virtual Tech Camps speak volumes about both! We recently covered how to write abo
- College Prep Ultimate Guide to College Campuses, Visits, and Tour Questions! In many ways, the campus can define the college experience. From quaint college towns to sprawling cities, each type of campus has uniq
- College Prep 7 College Essay Mistakes & How to Avoid Them College essays are stressful enough. And that blinking mouse cursor on a blank document screen never makes things easier! In fact, this “st
iD Tech Privacy Policy
Id tech privacy policy publish date: 10/26/2023.
internalDrive, Inc. (“iD Tech”) respects your privacy and recognizes the importance of your personal information. We are committed to protecting your information through our compliance with this Privacy Policy.
This Privacy Policy applies to all individuals who visit and/or use iD Tech/internalDrive, Inc.'s websites, services, and products that collect data and/or display these terms ("iD Sites & Services"). This Privacy Policy describes the types of information we may collect when you visit an iD Tech website, open an account or receive iD Tech Services and our practices for using, maintaining, protecting and disclosing that information.
All references to "us," "we," or "our" refer to iD Tech/internalDrive, Inc.
All references to "child" or "children" refer to children under the age of 13.
By accessing or otherwise using any of our iD Sites & Services, you consent to the terms contained in this privacy statement, including the collection, use, and disclosure of data as described below.
California Residents: iD Tech’s PRIVACY NOTICE FOR CALIFORNIA RESIDENTS supplements the information contained in this Privacy Policy and applies solely to visitors, users, and others who reside in the State of California.
I. Information We May Ask You To Provide
Through our iD Sites & Services, we collect information about you and/or your student when you choose to provide it to us. For example, we collect information from you so you can use iD Sites & Services, purchase products and services, register for and obtain an account, request information, apply for a job, register for one of our programs, or verify your age. In general, we may ask you to provide us with the following types of information about you and/your student:
- Contact information such as name, email address, mailing address, phone numbers (note to parents/guardians of children: if we have actual knowledge that a user is under 13 years old, the child will be asked to have their parent or guardian continue the registration process);
- Month, day, and year of birth;
- Gender preference;
- Course interests;
- Billing information such as credit card number and billing address;
- User names to third-party systems (for example, Facebook);
- Information provided on forums or chat rooms within our iD Sites & Services (note to parents/guardians of children: forums and chat rooms permit a child user to enter comments through which the child could provide personal information that would be visible to other users);
- Information included in résumés and job applications; and
- Health, any participation limitations or needs, immunization and allergy information.
Note to Parents/Guardians : We only collect the information described above, from someone we know to be a child, after the child's parent or guardian provides us with verifiable consent, unless one of the limited exceptions discussed below applies. For more information and/or to review these limited exceptions, please see the " Our Commitment to Children’s Privacy " section below. II. Information Collected Automatically Cookies and other Tracking Technologies We may use cookies, web beacons, pixel tags, log files, Local Storage Objects, or other technologies to collect certain information about visitors to and users of iD Sites & Services, such as the date and time you visit iD Sites & Services, the areas or pages of iD Sites & Services that you visit, the amount of time you spend viewing or using iD Sites & Services, the number of times you return to iD Sites & Services, other click-stream or usage data, and emails that you open, forward or click through to iD Sites & Services. For example, we may automatically collect certain information, such as the type of web browser and operating system you use, the name of your Internet Service Provider, Internet Protocol (“IP”) address, software version, and the domain name from which you accessed our iD Sites & Services. We use this information to monitor and improve our iD Sites & Services, support the internal operations of our iD Sites & Services, personalize your online experience, verify e-signatures, and for internal analysis.
We may also use cookies, web beacons, and other similar technologies from third party partners such as Google for measurement services, better targeting advertisements and for marketing purposes. These cookies, web beacons, and other similar technologies allow us to display our promotional material to you on other sites you visit across the internet. Our third-party advertising partners may also use these technologies to identify your browsing interests over time and across different websites to deliver targeted advertisements.
iD Sites & Services do not recognize “Do Not Track” headers or similar mechanisms.
iD Tech partners with Rakuten Advertising, who may collect personal information when you interact with our site. The collection and use of this information is subject to Rakuten’s privacy policy located at https://rakutenadvertising.com/legal-notices/services-privacy-policy/ . Our Sites & Services may also use other third-party plug-ins to provide additional services and benefits. These third parties may collect information about you as well. When we use a third-party plug-in we will attempt to provide you with the identify the plug-in, so you can visit the sites of the third-parties to view the privacy policy under which the information they collect is identified and controlled.
We may also collect geolocation information from your device so we can customize your experience on our iD Sites & Services. In most cases, you are able to turn off such data collection at any time by accessing the privacy settings of your device and/or through the settings in the applicable GPS application. Social Media You also can engage with our content, and other offerings, on or through social media services or other third-party platforms, such as Facebook, or other third-party social media plug-ins, integrations and applications. When you engage with our content on or through social media services or other third-party platforms, plug-ins, integrations or applications, you may allow us to have access to certain information in your profile. This may include your name, email address, photo, gender, birthday, location, an ID associated with the applicable third-party platform or social media account user files, like photos and videos, your list of friends or connections, people you follow and/or who follow you, or your posts or "likes." For a description on how social media services and other third-party platforms, plug-ins, integrations, or applications handle your information, please refer to their respective privacy policies and terms of use, which may permit you to modify your privacy settings.
When we interact with you through our content on third-party websites, applications, integrations or platforms, we may obtain any information regarding your interaction with that content, such as content you have viewed, and information about advertisements within the content you have been shown or may have clicked on. Information from Third Party Services We may also obtain other information, including personal information, from third parties and combine that with information we collect through our Websites. For example, we may have access to certain information from a third-party social media or authentication service if you log in to our Services through such a service or otherwise provide us with access to information from the service. Any access that we may have to such information from a third-party social media or authentication service is in accordance with the authorization procedures determined by that service. If you authorize us to connect with a third-party service, we will access and store your name, email address(es), current city, profile picture URL, and other personal information that the third party service makes available to us, and use and disclose it in accordance with this Policy. You should check your privacy settings on these third-party services to understand and change the information sent to us through these services. For example, you can log in to the Services using single sign-in services such as Facebook Connect or an Open ID provider.
III. Your Ability To Control Cookies And Similar Technologies As noted, we may use cookies or similar technologies to monitor and improve iD Sites & Services, support the internal operations of iD Sites & Services, personalize your online experience, support the e-signature process, and/or for internal analysis. This includes the use of third-party cookies. We use these technologies to keep track of how you are using our iD Sites & Services and to remember certain pieces of general information.
You have the ability to accept or decline cookies. Most web browsers automatically accept cookies, but you can usually modify your browser setting to decline cookies if you prefer. Check the “Tools” or “Help” tab on your browser to learn how to change your cookie and other tracking preferences.
If you choose to decline cookies, you may not be able to fully experience the functions of iD Sites & Services and/or some of our services will function improperly, in particular the inability to log in or manage items in your shopping cart. We do not share cookie data with any third parties. IV. How We May Use Your Information We may use the information we collect from and about you and/or your student for any of the following purposes:
- Allow you to register yourself or your student with iD Sites & Services, or to otherwise register and open an account with us;
- Allow you and/or your student to use iD Sites & Services;
- Fulfill orders, process payments, and prevent transactional fraud;
- Respond to your or your student’s requests or inquiries;
- Provide you or your student with information about our products and services;
- Consider you for employment or a volunteer opportunity;
- Register you or your student in one of our programs;
- Verify your student's age;
- Monitor and improve iD Sites & Services, support the internal operations of iD Sites & Services, personalize your online experience, and for internal analysis;
- Protect the security or integrity of iD Sites & Services and our business;
- Facilitate the sale or potential sale of our business or any of our assets; or
- As required by law.
V. How We Share Information We do not sell or otherwise share your or your student’s information with any third parties, except for the limited purposes described below. Parents/guardians of children under the age of 13 have the option of consenting to the collection and use of their child's personal information without consenting to the disclosure of that information to certain third parties.
1. Law Enforcement And Safety
We may access, preserve, and/or disclose the information we collect and/or content you and/or your student/child provides to us (including information posted on our forums) to a law enforcement agency or other third parties if required to do so by law or with a good faith belief that such access, preservation, or disclosure is reasonably necessary to: (i) comply with legal process; (ii) enforce the Terms and Conditions of iD Sites & Services; (iii) respond to claims that the content violates the rights of third parties; or (iv) protect the rights, property, or personal safety of the owners or users of iD Sites & Services, a third party, or the general public. We also may disclose information whenever we believe disclosure is necessary to limit our legal liability; to protect or defend our rights or property; or protect the safety, rights, or property of others. 2. Service Providers; Colleges and Universities Information collected through iD Sites & Services may be transferred, disclosed, or shared with third parties engaged by us to handle and deliver certain activities, such as housing, meals, payment processing, mail/email distribution, software providers, and to perform other technical and processing functions, such as maintaining data integrity, programming operations, user services, or technology services. We may provide these third parties’ information collected as needed to perform their functions, but they are prohibited from using it for other purposes and specifically agree to maintain the confidentiality of such information. Some of these providers, such as payment processors, may request additional information during the course of offering their services. Before you provide additional information to third-party providers, we encourage you to review their privacy policies and information collection practices. 3. Business Transfer During the normal course of our business, we may sell or purchase assets. If another entity may acquire and/or acquires us or any of our assets, information we have collected about you may be transferred to such entity. In addition, if any bankruptcy or reorganization proceeding is brought by or against us, such information may be considered an asset of ours and may be sold or transferred to third parties. Should a sale or transfer occur, we will use reasonable efforts to try to require that the transferee use personal information provided through our iD Sites & Services in a manner that is consistent with this privacy statement. VI. Our Commitment To Children’s Privacy Protecting the privacy of children is paramount. We understand that users and visitors of our iD Sites & Services who are under 13 years of age need special safeguards and privacy protection. It is our intent to fully comply with the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).
Our iD Sites & Services are intended for general audiences. We do not knowingly permit anyone under 13 years of age to provide us with personal information without obtaining a parent's or guardian’s verifiable consent, except where:
- the sole purpose of collecting the name or online contact information of a parent or child is to provide notice and obtain parental consent;
- the purpose of collecting a parent’s online contact information is to provide voluntary notice to, and subsequently update the parent about, the child’s participation in our iD Sites & Services that do not otherwise collect, use, or disclose childrens' personal information;
- the sole purpose of collecting online contact information from a child is to respond directly on a one-time basis to a specific request from the child, and where such information is not used to re-contact the child or for any other purpose, is not disclosed, and is deleted by us promptly after responding to the child’s request;
- the purpose of collecting a child’s and a parent’s online contact information is to respond directly more than once to the child’s specific request, and where such information is not used for any other purpose, disclosed, or combined with any other information collected from the child;
- the purpose of collecting a child’s and a parent’s name and online contact information, is to protect the safety of a child, and where such information is not used or disclosed for any purpose unrelated to the child’s safety;
- we collect a persistent identifier and no other personal information and such identifier is used for the sole purpose of providing support for the internal operations of iD Sites & Services; or
- otherwise permitted or required by law.
If we receive the verifiable consent of a child's parent or guardian to collect, use, and/or disclose the child's information, we will only collect, use, and disclose the information as described in this privacy statement. Some features of our iD Sites & Services permit a child user to enter comments, such as forums and chat rooms, through which the child could provide personal information that would be visible to other users. If you are the parent or guardian of a child user, please advise your child of the risks of posting personal information on this iD Sites & Services or any other site. VII. Parental/Guardian Rights If you are a parent or guardian, you can review or have deleted your child's personal information, and refuse to permit further collection or use of your child's information. To exercise any of these rights, please email us at [email protected] or send your request to:
iD Tech ∙ PO Box 111720 ∙ Campbell, CA 950011 Client Service Toll Free Number: 1-888-709-8324
VIII. Restrictions On Child Users Children under 13 years of age are prevented from accessing areas of iD Sites & Services which include, but are not restricted to, client account information, unless approved by their parent or guardian and any course content defined as age inappropriate by the Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB). IX. Forums And Chats We may offer forums and chat rooms. Please be aware that anyone may read postings on a forum or in a chat room. Furthermore, any information which is posted to a forum or chat room could include personal information, which would be disclosed and available to all users of that forum or chat room, and is therefore no longer private. We cannot guarantee the security of information that any user discloses or communicates online in public areas such as forums and chat rooms. Those who do so, do so at their own risk. We reserve the right to monitor the content of the forums and chat rooms. If age-inappropriate content or potentially identifiable information is seen, it may be removed or edited by us for security, privacy, and/or legal reasons. We will not republish postings from forums or chat rooms anywhere on the Web. X. Links And Third Parties
At our discretion, we may include or offer third-party websites, products, and services on iD Sites & Services. These third-party sites, products, and services have separate and independent privacy policies. You should consult the respective privacy policies of these third parties. We have no responsibility or liability for the content and activities of linked sites, products, or services.
Our iD Sites & Services may contain links to other third-party websites, chat rooms, or other resources that we provide for your convenience. These sites are not under our control, and we are not responsible for the content available on other sites. Such links do not imply any endorsement of material on our part and we expressly disclaim all liability with regard to your access to such sites. Access to any other websites linked to from iD Sites & Services is at your own risk.
XI. Legal Basis for processing Personal Data and Your Data Protection Rights under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
If you are a resident of the European Economic Area (EEA), iD Tech’s legal basis for collecting and using your personal information as described in this policy depends on the personal Data we collect and the context in which we collect it. ID Tech may process your personal data:
- To provide the services which you requested or purchased;
- Because you have given us permission to do so;
- To provide you with better services, including conducting audits and data analysis;
- For payment processing;
- For marketing; and
- To comply with the law
You have certain data protection rights. iD Tech aims to take reasonable steps to allow you to correct, amend, delete or limit the use of your Personal Data.
If you wish to be informed about what Personal Data we hold about you and if you want it to be removed from our systems, please contact us at [email protected] .
In certain circumstances, you have the following data protection rights:
- The right to access, update, or delete the information we have on you. Whenever made possible, you can access, update, or request deletion of your Personal Data directly within your account settings section. If you are unable to perform these actions yourself, please contact us to assist you.
- The right to have your information corrected if that information is inaccurate or incomplete.
- The right to object. You have the right to object to our processing of your Personal Data.
- The right of restriction. You have the right to request that we restrict the processing of your personal information.
- The right to data portability. You have the right to be provided with a copy of the information we have on you in a structured, machine-readable, and commonly used format.
- The right to withdraw consent. You also have the right to withdraw your consent at any time where iD Tech relied on your consent to process your personal information.
Please note that we may ask you to verify your identity before responding to such requests.
You have the right to complain to a Data Protection Authority about our collection and use of your Personal Data. For more information, please contact your local data protection authority in the European Economic Area (EEA). XII. International Visitors (non GDPR Locations) Our iD Sites & Services are operated and managed on servers located in the United States. If you choose to use our iD Sites & Services from the European Union or other regions of the world with laws governing data collection and uses that differ from the United States, then you recognize and agree that you are transferring your personal information outside of those regions to the United States and you consent to that transfer. XIII. Data Security Commitment To prevent unauthorized access, maintain data accuracy, and ensure the correct use of information, we have put in place reasonable physical, electronic, and managerial procedures to safeguard and secure the information we collect. We also use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol on your account information and registration pages to protect sensitive personal information. Sensitive data is encrypted on our iD Sites & Services and when stored on the servers.
XIV. How You Can Access, Request A Copy, Correct, Or Ask For Information To Be Deleted Access to certain personal Information that is collected from our Services and that we maintain may be available to you. For example, if you created a password-protected account within our Service, you can access that account to review the information you provided.
You may also send an email or letter to the following email or call the number provided to ask for a copy, correction, or ask us to delete your personal Information. Please include your registration information for such services, such as first name, last name, phone, and email address in the request. We may ask you to provide additional information for identity verification purposes or to verify that you are in possession of an applicable email account. Email: [email protected] Phone: 1-888-709-8324 XV. How To Contact Us/Opting Out Of Electronic Communications If you have any questions or concerns about this Privacy Policy or if you have provided your email and/or address and prefer not to receive marketing information, please contact us via email or call at the number provided below. Make sure you provide your name as well as the email(s) and address(es) you wish to have removed.
If you have signed up to receive text messages from us and no longer wish to receive such messages, you may call or email us at the address provided below. Please provide your name, account email, and the number(s) you want removed. Email: [email protected] Phone: 1-888-709-8324 XVI. Terms And Conditions Your use of our iD Sites & Services and any information you provide on our iD Sites & Services are subject to the terms of the internalDrive, Inc. (referred to as “iD Tech”) Terms and Conditions. XVII. Privacy Statement Changes We will occasionally amend this privacy statement. We reserve the right to change, modify, add, or remove portions of this statement at any time. If we materially change our use of your personal information, we will announce such a change on relevant iD Sites & Services and will also note it in this privacy statement. The effective date of this privacy statement is documented at the beginning of the statement. If you have any questions about our privacy statement, please contact us in writing at [email protected] or by mail at PO Box 111720, Campbell, CA 95011. XVIII. Your Credit Card Information And Transactions For your convenience, you may have us bill you or you can pay for your orders by credit card. If you choose to pay by credit card, we will keep your credit card information on file, but we do not display that information at the online registration site. For your security, your credit card security number is not stored in our system.
We use state-of-the-art Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption technology to safeguard and protect your personal information and transactions over the Internet. Your information, including your credit card information, is encrypted and cannot be read as it travels over the Internet. XIX. Social Networking Disclaimer iD Tech provides several opportunities for social networking for both participants and staff on sites such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Flickr, and YouTube. These sites are not affiliated with iD Tech and offer their own individual social networking services. Please read the following Terms and Conditions carefully, as well as the Terms and Conditions of the sites in which iD Tech has created a forum ("Group"). These Terms and Conditions are a legal agreement between you and iD Tech and apply to you whether you are a visitor to these sites or any site with an official iD Tech affiliation. iD Tech is a member of several pre-existing sites (as mentioned above). There may be, however, portions of www.iDTech.com that include areas where participants can post submissions. Any of the above-mentioned "Sites" (or other similar sites) have their own distinct rules and regulations. iD Tech reserves the right to take action to remove any content deemed inappropriate by the sites or by iD Tech standards. iD Tech will not be held liable for any loss of content or disagreements that may arise between the individual social networking site and the user. You understand that by registering for an iD Tech program, your participant(s) may access and upload content to social networking sites. In order to access certain features of the social networking sites or pages on iDTech.com, and to post Member Submissions, the majority of these sites require that the user open an account with them. Please note that these sites have their own individual Terms and Conditions that must be followed. Age requirements are outlined within each Site's Terms and Conditions. You hereby authorize your participant to access social networking sites while at camp and create an account if they choose to do so and if they meet the requirements listed by each site to create an account. Interaction with other users:
- iD Tech is merely providing a medium in which to socialize online with fellow participants. Users are solely responsible for interactions (including any disputes) with other Members and any volunteers that may advise and assist participants with projects and activities via your use of the iD Site & Services.
- You understand that iD Tech does not in any way screen Members or review or police: (i) statements made by Members in their Member Submissions or the Member Submissions in general; or (ii) statements made by Users or any information a User may provide via the iD Site & Services.
- You understand that your participant(s) is solely responsible for, and will exercise caution, discretion, common sense, and judgment in using the various iD Sites & Services and disclosing personal information to other Members or Users.
- On behalf of your participant(s), you agree that they will take reasonable precautions in all interactions with other Members, particularly if they decide to meet a Member offline or in person.
- Your participant's use of the social networking sites with which iD Tech is affiliated, their services, and/or Content and Member Submissions, is at your sole risk and discretion and iD Tech hereby disclaims any and all liability to you or any third party relating thereto.
- On behalf of your participant(s), you agree that they will not harass, threaten, intimidate, bully, stalk, or invade the privacy of any individual in connection with your use of the social networking sites with which iD Tech is affiliated and their services, whether or not an individual is an iD Tech Member; and you further agree not to advocate such activities or to encourage others to engage in any such activities.
- On behalf of your participant(s), you agree they will not give their social networking information to an iD Tech staff member.
- You and your participant(s) should also be aware that under no circumstances are iD Tech employees allowed to give personal contact information for social networking sites. This must be arranged by the participant's parent/guardian through the People Services Department.
XX. Copyright & Intellectual Property Policy: You agree that you and your participant will not use the social networking sites to offer, display, distribute, transmit, route, provide connections to, or store any material that infringes copyrighted works, trademarks, or service marks or otherwise violates or promotes the violation of the intellectual property rights of any third party. internalDrive, Inc. has adopted and implemented a policy that provides for the termination in appropriate circumstances of the accounts of users who repeatedly infringe or are believed to be or are charged with repeatedly infringing the intellectual property or proprietary rights of others. XXI. Disclaimer: BY USING THE SOCIAL NETWORKING SITES OR SUBMITTING A MEMBER SUBMISSION, YOU AGREE THAT INTERNALDRIVE, INC. IS NOT RESPONSIBLE, AND WILL IN NO EVENT BE HELD LIABLE, FOR ANY: (A) LOST, ILLEGIBLE, MISDIRECTED, DAMAGED, OR INCOMPLETE MEMBER SUBMISSIONS; (B) COMPUTER OR NETWORK MALFUNCTION OR ERROR; (C) COMMUNICATION DISRUPTION OR OTHER DISRUPTIONS RELATED TO INTERNET TRAFFIC, A VIRUS, BUG, WORM, OR NON-AUTHORIZED INTERVENTION; OR (D) DAMAGE CAUSED BY A COMPUTER VIRUS OR OTHERWISE FROM YOUR ACCESS TO THE SITE OR SERVICES. THE SITE, SERVICES, INTERNALDRIVE, INC., CONTENT, AND MEMBER SUBMISSIONS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. INTERNALDRIVE, INC. AND ITS SUPPLIERS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THE SITE, SERVICES, INTERNALDRIVE, INC., CONTENT AND MEMBER SUBMISSIONS, WHETHER THE PROVISION OF SERVICES OR YOUR SUBMISSION OF A MEMBER SUBMISSION WILL PRODUCE ANY LEVEL OF PROFIT OR BUSINESS FOR YOU OR LEAD TO ECONOMIC BENEFIT, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF QUALITY, AVAILABILITY, MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT. IN ADDITION, INTERNALDRIVE, INC. MAKES NO REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY THAT THE SITE OR SERVICES WILL BE ERROR FREE OR THAT ANY ERRORS WILL BE CORRECTED. SOME STATES OR JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OF CERTAIN WARRANTIES. ACCORDINGLY, SOME OF THE ABOVE EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. XXII. Indemnification: You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold iD Tech, its officers, directors, employees, and agents, harmless from and against any claims, liabilities, damages, losses, and expenses, including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys' fees and costs, arising out of or in any way connected with: (i) your access to or use of social networking sites, their services, iD Tech Content and Member Submissions; (ii) your violation of these Terms of Use; (iii) your violation of any third-party right, including, without limitation, any intellectual property right, publicity, confidentiality, property, or privacy right; or (iv) any claim that one of your Member Submissions caused damage to a third party or infringed or violated any third-party intellectual property right, publicity, confidentiality, property, or privacy right.
iD Tech Terms & Conditions
Id tech general terms & conditions publish date: october 26, 2023.
These Terms and Conditions apply to all pages found at www.idtech.com and all Programs operated by internalDrive, Inc. (referred to as "iD Tech") including but not limited to iD Tech In-Person programs and iD Tech Online Programs. These terms apply to all lessons, classes, courses, and options offered by iD Tech (hereinafter referred to individually as “Program” or collectively “Programs”).
Privacy Policy: By using iD Tech’s website, registering you or your student for a Program, and/or affirmatively giving your agreement, you are agreeing on your own behalf and that of your student to abide and be bound by the Privacy Policy found HERE and the Terms and Conditions contained and referenced herein.
Online Programs: If you are purchasing, or you or your student is participating in an Online Program you also agree on your own behalf and on behalf of your student, to be bound by the additional terms and conditions found HERE .
On-Campus Programs: If you are purchasing, or you or your student is participating in, an On-Campus Program, you also agree on your own behalf and on behalf of your student to be bound by the additional terms and conditions found HERE .
I. Code of Conduct
To promote the best learning environment possible, all students and parents will be held to this Code of Conduct. Failure to comply with this Code of Conduct or engaging in actions or attitudes that seem to be harmful to the atmosphere, other participants, or staff, in the opinion of iD Tech can lead to removal from a Program or Program(s). iD Tech reserves the right to dismiss students from a Program and prevent a student from attending additional Programs without any prior warning for (1) violating any of the terms of this code of conduct, or (2) if iD Tech determines that a Program is not a suitable and/or productive environment for a student (this includes incidents in which a student does not have sufficient English language skills to participate in the Program; participation in courses requires a high level of English understanding). Refunds will not be given for students dismissed for failure of the student or the parent to abide by the Code of Conduct, or if it is determined that a Program is not suitable for a student. While iD Tech strives to maintain excellent relationships with students, in some rare cases, we may determine that iD Tech is not a compatible environment for every student.
Students and parents/guardians may NEVER:
- Disrupt, bully, intimidate, or harass others;
- Use inappropriate language (for example, students cannot use of swear or curse words, racial, gendered, homophobic/transphobic, stereotypical, or culturally insensitive words, even if done in a joking manner);
- View, display or post any inappropriate material (including sexual content, material depicting inappropriate violence, racism, bullying, etc.) during a Program;
- Share Program information (including lesson plans, etc.) with third-parties, without permission from iD Tech;
- Impersonate another person; or
- Contact instructors outside of the Program.
Students also may NEVER:
- Engage in Internet hacking;
- Create an account on or log into third-party websites without the permission of their instructor;
- Use false information to create an account on or log into third-party websites;
- Share personal information with staff members or ask staff members for their personal information;
- Share or create video or audio recordings of iD Tech staff or another student without the permission of iD Tech.
Students and parents/guardians MUST:
- Follow directions/instructions of iD Tech personnel;
- If online, ensure the student attends the Program in an appropriate, private setting;
- Dress appropriately during the Program;
- Adhere to the terms of use of any sites used, including following the specified age policies; and
- Only share material that is related to lessons and appropriate.
II. Age Policy
iD Tech offers Programs for students ages 7-19. Therefore, students may interact and/or room with a student that is within this age range including 18 or 19 years old. Please note the age range of the Program being registered for.
If a student is 18 or 19 years old and participating in an On-Campus Program, they must successfully pass a criminal and sexual offender background check prior to being allowed to attend. Clients are responsible for all costs and fees associated with any background checks required for a student to attend.
III. Special Accommodations
If a student requires an accommodation to participate, or needs an aid to attend in an iD Tech Program, a parent/guardian must call iD Tech at 1-888-709-8324, no less than three weeks prior to your student’s first day of the Program to make needed arrangements.
If a student requires an aide to participate in an iD Tech Program, the aide must be age 18 or older, may not be a family member, and if it is an On -Campus Program, the aide must successfully pass a criminal and sexual offender background check prior ro being allowed to attend with the student. Aides may also be subject to fingerprinting. Clients are responsible for all direct costs, including background check processing fees, parking, and compensation for the aide’s attendance.
IV. Payment Policy
- Unless otherwise noted, all financial transactions are made and quoted in U.S. Dollars.
- All Payment Plan Fees, fees paid for Online Programs, and the $250 per week deposit for On-Campus Programs are non-refundable and non-transferrable.
- Other than if iD Tech needs to cancel a class, there are no refunds, credits or replacement days for classes missed. If iD Tech needs to cancel a class, iD Tech will either provide you a pro rata credit or reschedule the canceled class(es).
- If iD Tech cancels an entire Program for any reason, the fees paid for the Program will be refunded, less the non-refundable fees, as set out above. Non-refundable fees (other than the Payment Plan Fee, if any) will remain in your account as a fully transferable credit that is valid for three (3) years.
- iD Tech has the right to charge a $25 late fee on any payments not paid by the due date. For balances that are over 30 (thirty) days past due, iD Tech has the right to charge a 1% monthly finance charge and send the balance to a collection agency for collection (collection agency and legal fees may apply).
- All fees (registration, administrative, late, etc.) must be paid prior to the start of a Program, unless a payment plan has been agreed to. Students will be withdrawn from a Program if the Program has not been paid in full prior to the start of the Program, or if at any time a payment is not paid by the due date. No refunds, credits, or make-up classes will be provided if a session is missed due to a delinquent payment.
- By agreeing to a subscription or payment plan, you are authorizing iD Tech to auto charge the credit card on file as agreed at the time of purchase and as set out in My Account.
- A $35 returned check fee will be assessed for any checks returned or card transactions that are not honored.
V. Reservation Changes
To provide outstanding Programs, we may have to limit your ability to make changes (such as registering for a different course or changing attendance dates) and/or cancel a Program. Please reference the Terms and Conditions for specific Programs (linked above) for the rules and restrictions for changes and cancellations for that Program.
VI. Promotions and Discounts
Promotional discounts are limited to one discount per student. There may be other limitations as to how they apply, and codes must be submitted at the time of registration. iD Tech will not honor retroactive adjustments, and the total discounts received cannot exceed the total cost of the products purchased.
The Refer-a-Friend Program is a voluntary Program that applies to Small Group Classes and In-Person Programs.
- Each Referral Code can be used a maximum of 10 times. The code can only be used by students attending iD Tech for the first time (may be limited to certain Programs) and must be applied at the time of registration.
- A tuition credit will be given for each new student that registers for an In-Person Program or Small Group Class using a referral code and attends the course for which they registered.
- The Refer-a-Friend Program does not apply to siblings.
- Students may not refer each other to both qualify for the Refer-a-Friend Discount.
- Tuition credit will be applied after the referred client registers, pays in full and attends the Program. If the referred friend cancels his/her Program, the credit will be removed, and you will be responsible for any account balance that is created as a result of the lost credit.
- All tuition credits must be used in the Program term in which they are earned, can be used to offset Program tuition and other fees incurred, but do not entitle you to any form of payment.
- Tuition credits have no cash value.
VII. Certificates/Vouchers
All certificates/vouchers are non-refundable, non-transferable, and not redeemable for cash. Certificates/vouchers must be redeemed at the time of registration. Certificates/vouchers are valid until the specified expiration date, without exception. They are valid for up to the amount issued, and any amounts not used are forfeited.
VIII. General Releases
- Media Release: As a condition of participation, you authorize iD Tech and its partners to take photos, videos, images, audio, and testimonials of and/or from you and your student and agree that said content may be used by iD Tech in promotional materials, marketing collateral, and online media. These images, testimonials, photos, videos, and audio may be shared and used by corporate partners, the media, or other organizations that work with iD Tech. You also agree that all projects and work created by your student during an iD Tech Program may be used by iD Tech in promotional materials, online, and other print media, and may be shared and used by corporate partners, the media, or other organizations that work with iD Tech. You understand that iD Tech, its owners, agents, partners, facility providers, and employees will not be held liable for damages and injuries associated with use of any content released herein, including any and all claims based on negligence. You agree that all images, testimonials, photos, video, and audio taken at or in connection with an iD Tech Program are the sole and exclusive property of iD Tech, and that iD Tech has a royalty-free, perpetual license to use copies of all student work and projects created at an iD Tech Program.
- Name and Likeness Release: As a condition of participation, you authorize iD Tech and the press to use your student's full name and likeness in print, radio, TV, and other mediums.
- Project/Hardware Release: Some iD Tech Programs are project-based. In such instances, iD Tech will attempt to provide your student with the knowledge to produce a working project. Some iD Tech Programs include take home hardware. In those instances, iD Tech will send home a product or voucher for a product. However, there will be instances when a project or product or product voucher cannot be sent home, posted, or delivered, and you agree that iD Tech is not responsible if the game, project, product or voucher does not work properly and/or is not compatible with outside systems. You release iD Tech from any responsibility for failure to provide a copy of the project or product voucher, or a non-functioning/non-compatible/non-complete game, project, product voucher or product. Refunds will not be issued for not receiving products, product vouchers, or being provided a copy of the project, and/or non-functioning/non-compatible/non-complete projects, product vouchers or products. If you have issues with a product voucher or product, you must contact the manufacturer directly. Product vouchers only cover shipping within the continental U.S. Therefore, if you require the product to be shipped outside the continental US, you are responsible for all shipping and handling costs.
- Software Accounts: Some iD Tech Program activities require creation and/or use of an online account or require an online account to be created for your student. You consent to create or have iD Tech create account(s) as needed for your student to participate in Program activities. During non-instructional time, students may have access to websites that require accounts to be set up. While it is against iD Tech rules for students to set up accounts without their instructor’s permission, there may be instances where a student may create an account without the knowledge of iD Tech or its employees. In such instances, you release iD Tech and its employees from any and all responsibility and liability for accounts created by your student without iD Tech’s knowledge.
- Game Ratings: iD Tech takes its corporate responsibility and iD Tech family values very seriously. However, we cannot guarantee that younger students at iD Tech will avoid all contact with or mention of games rated "T" for Teen, or "M" for Mature. iD Tech will make a concerted effort to minimize both direct and indirect exposure to any games not rated for a student’s age group. Students attending courses designed for older ages have a greater chance of being exposed to materials rated for that older age group. If a student is attending a course for ages 13+, they may be exposed to games rated "M" for Mature by the ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board). You voluntarily assume any and all risks, known or unknown, associated with your student’s exposure to game content at an iD Tech Program.
IX. Indemnification
You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold internalDrive, Inc.,iD Tech, its officers, directors, employees, and agents, harmless from and against any claims, liabilities, damages, losses, and expenses, including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys' fees and costs, arising out of or in any way connected with your student’s participation in an iD Tech Program.
X. Arbitration Agreement
You agree that any dispute other than collection matters, arising out of or relating to this Agreement, you or your student's participation in a Program with internalDrive, Inc., or otherwise arising between the parties, including, without limitation, any statutorily created or protected rights, as permitted by applicable state/provincial or federal laws, shall be settled by arbitration to be held in Santa Clara County, California, in accordance with the Commercial Rules of the American Arbitration Association, and judgment upon the award rendered by the arbitrator(s) may be entered in any court of competent jurisdiction. The prevailing party in the arbitration shall be entitled to recover expenses including costs and reasonable attorneys’ fees associated therewith. Should any part of this contract be found invalid or not enforceable by a court of law, then the remaining portion shall continue to be valid and in force. You hereby acknowledge that you understand the terms of this ARBITRATION AGREEMENT, and you agree to comply with all of its terms and provisions.
XI. Rights Reserved
internalDrive, Inc. reserves the right to update or modify these Terms and Conditions at any time. iD Tech is not a university-sponsored program. iD Tech reserves the right to cancel or modify any and all classes, lessons, Programs or courses for any reason.
XII. Release of Liability
ON BEHALF OF MY SON/DAUGHTER/WARD, I, THE PARENT/GUARDIAN, IN EXCHANGE FOR THE RIGHT OF MY SON/DAUGHTER/WARD TO PARTICIPATE IN ID TECH PROGRAM(S), HEREBY RELEASE INTERNALDRIVE, INC., ITS OWNERS, AGENTS, PARTNERS, FACILITY PROVIDERS, AND EMPLOYEES FROM LIABILITY (INCLUDING CLAIMS BASED UPON NEGLIGENCE) FOR ANY AND ALL DAMAGES OR INJURIES TO MY SON/DAUGHTER/WARD OR DAMAGE OF ANY PERSONAL PROPERTY. I AGREE TO BE FULLY RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY AND ALL SUCH DAMAGES OR INJURIES WHICH MAY RESULT DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY FROM ANY NEGLIGENT ACTS OR ACTIVITIES ASSOCIATED WITH INTERNALDRIVE, INC. HOWEVER, I UNDERSTAND THAT I AM NOT RELEASING INTERNALDRIVE, INC., ITS OWNERS, AGENTS, PARTNERS, FACILITY PROVIDERS, AND EMPLOYEES FROM GROSS NEGLIGENCE OR INTENTIONALLY TORTIOUS CONDUCT. TO THE EXTENT THIS RELEASE CONFLICTS WITH STATE/PROVINCIAL LAW GOVERNING RELEASES, THIS RELEASE IS TO BE GIVEN THE FULLEST FORCE AND EFFECT PERMITTED UNDER STATE/PROVINCIAL LAW. SHOULD ANY PART OF THIS CONTRACT BE FOUND INVALID OR NOT ENFORCEABLE BY A COURT OF LAW, THEN THE REMAINING PORTION SHALL CONTINUE TO BE VALID AND IN FORCE. XIII. Copyright
iD Tech partners with and uses the intellectual property of some amazing companies. You and your student agree to uphold the copyright and trademark rights of iD Tech, their partners, and any company whose products are used at an iD Tech Program.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the ultimate college majors list: 295 degrees to consider.
General Education

When you get to college, you'll need to pick a major—a specific area of study that you'll specialize in. Your major can have a big impact on what you decide to do for work, as well as, obviously, how you spend your time in school.
In this article, we'll give a comprehensive college majors list so you can see what options there are. Review this list of majors (we have hundreds!) so you're well informed on all the different routes you can take as a college student.
What Majors Will My College Have?
While most colleges and universities have similar majors, the specific majors you can choose from depends on the college you go to. Some places have similar types of majors that have different names (for instance, Biology vs Biological Sciences).
If you're curious whether or not your college has a specific major, the best thing to do is check your college's course catalog. You'll be able to see all of the specific majors you can choose from, as well as what courses you can take in of the different majors.
The Complete List of All College Majors
Whatever degree you're thinking about, it's probably on this list of majors. Here's the complete list of college degrees.
List of Majors: Agriculture & Natural Resources Conservation
- Agriculture, General
- Agribusiness Operations
- Agricultural Business & Management
- Agricultural Economics
- Agricultural Mechanization
- Agricultural Production
- Agronomy & Crop Science
- Animal Sciences
- Food Sciences & Technology
- Horticulture Operations & Management
- Horticulture Science
- Natural Resources Conservation, General
- Environmental Science
- Natural Resources Management
- Wildlife & Wildlands Management
List of College Degrees: Architecture
- Architecture, General
- Architectural Environmental Design
- City/Urban/Regional Planning
- Interior Architecture
- Landscape Architecture
College Majors List: Area, Ethnic, and Multidisciplinary Studies
- Area Studies, General (e.g., African, Middle Eastern)
- Asian Area Studies
- European Area Studies
- Latin American Area Studies
- North American Area Studies
- Ethnic & Minority Studies, General
- African American Studies
- American Indian/Native American Studies
- Latino/Chicano Studies
- Women's Studies
- Liberal Arts & General Studies
- Library Science
- Multi/Interdisciplinary Studies
College Majors List: Arts: Visual & Performing
- Art, General
- Art History, Criticism & Conservation
- Fine/Studio Arts
- Cinema/Film
- Cinematography/Film/Video Production
- Design & Visual Communications, General
- Fashion/Apparel Design
- Graphic Design
- Industrial Design
- Interior Design
- Music, General
- Music, Performance
- Music, Theory & Composition
- Photography
- Theatre Arts/Drama
List of College Majors: Business
- Accounting Technician
- Business Administration & Management, General
- Hotel/Motel Management
- Human Resources Development/Training
- Human Resources Management
- International Business Management
- Labor/Industrial Relations
- Logistics & Materials Management
- Marketing Management & Research
- Office Supervision & Management
- Operations Management & Supervision
- Organizational Behavior
- Purchasing/Procurement/Contracts Management
- Restaurant/Food Services Management
- Small Business Management/Operations
- Travel/Tourism Management
- Business/Management Quantitative Methods, General
- Actuarial Science
- Business/Managerial Economics
- Finance, General
- Banking & Financial Support Services
- Financial Planning & Services
- Insurance & Risk Management
- Investments & Securities
- Management Information Systems
- Real Estate
- Sales, Merchandising, & Marketing, General
- Fashion Merchandising
- Tourism & Travel Marketing
- Secretarial Studies & Office Administration

College Majors List: Communications
- Communications, General
- Advertising
- Digital Communications/Media
- Journalism, Broadcast
- Journalism, Print
- Mass Communications
- Public Relations & Organizational Communication
- Radio & Television Broadcasting
- Communications Technology, General
- Graphic & Printing Equipment Operation
- Multimedia/Animation/Special Effects
- Radio & Television Broadcasting Technology
List of College Degrees: Community, Family, and Personal Services
- Family & Consumer Sciences, General
- Adult Development & Aging/Gerontology
- Child Care Services Management
- Child Development
- Consumer & Family Economics
- Food & Nutrition
- Textile & Apparel
- Parks, Recreation, & Leisure, General
- Exercise Science/Physiology/Kinesiology
- Health & Physical Education/Fitness
- Parks/Rec/Leisure Facilities Management
- Sport & Fitness Administration/Management
- Personal Services, General
- Cosmetology/Hairstyling
- Culinary Arts/Chef Training
- Funeral Services & Mortuary Science
- Protective Services, General
- Corrections
- Criminal Justice
- Fire Protection & Safety Technology
- Law Enforcement
- Military Technologies
- Public Administration & Services, General
- Community Organization & Advocacy
- Public Administration
- Public Affairs & Public Policy Analysis
- Social Work
College Majors List: Computer Science and Mathematics
- Computer & Information Sciences, General
- Computer Networking/Telecommunications
- Computer Science & Programming
- Computer Software & Media Applications
- Computer System Administration
- Data Management Technology
- Information Science
- Webpage Design
- Mathematics, General
- Applied Mathematics
List of College Degrees: Education
- Counseling & Student Services
- Educational Administration
- Special Education
- Teacher Education, General
- Curriculum & Instruction
- Early Childhood Education
- Elementary Education
- Junior High/Middle School Education
- Postsecondary Education
- Secondary Education
- Teacher Assisting/Aide Education
- Teacher Education, Subject-Specific
- Agricultural Education
- Art Education
- Business Education
- Career & Technical Education
- English-as-a-Second-Language Education
- English/Language Arts Education
- Foreign Languages Education
- Health Education
- Mathematics Education
- Music Education
- Physical Education & Coaching
- Science Education
- Social Studies/Sciences Education
List of College Majors: Engineering
- Engineering (Pre-Engineering), General
- Aerospace/Aeronautical Engineering
- Agricultural/Bioengineering
- Architectural Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Engineering
- Construction Engineering/Management
- Electrical, Electronics & Communications Engineering
- Environmental Health Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
College Majors List: Engineering Technology and Drafting
- Drafting/CAD Technology, General
- Architectural Drafting/CAD Technology
- Mechanical Drafting/CAD Technology
- Engineering Technology, General
- Aeronautical/Aerospace Engineering Technologies
- Architectural Engineering Technology
- Automotive Engineering Technology
- Civil Engineering Technology
- Computer Engineering Technology
- Construction/Building Technology
- Electrical, Electronics Engineering Technologies
- Electromechanical/Biomedical Engineering Technologies
- Environmental Control Technologies
- Industrial Production Technologies
- Mechanical Engineering Technology
- Quality Control & Safety Technologies
- Surveying Technology
List of College Degrees: English and Foreign Languages
- English Language & Literature, General
- American/English Literature
- Creative Writing
- Public Speaking
- Foreign Languages/Literatures, General
- Asian Languages & Literatures
- Classical/Ancient Languages & Literatures
- Comparative Literature
- French Language & Literature
- German Language & Literature
- Linguistics
- Middle Eastern Languages & Literatures
- Spanish Language & Literature
College Majors List: Health Administration and Assisting
- Health Services Administration, General
- Hospital/Facilities Administration
- Medical Office/Secretarial
- Medical Records
- Medical/Clinical Assisting, General
- Dental Assisting
- Medical Assisting
- Occupational Therapy Assisting
- Physical Therapy Assisting
- Veterinarian Assisting/Technology
List of College Degrees: Health Sciences and Technologies
- Chiropractic (Pre-Chiropractic)
- Dental Hygiene
- Dentistry (Pre-Dentistry)
- Emergency Medical Technology
- Health-Related Professions & Services, General
- Athletic Training
- Communication Disorder Services (e.g., Speech Pathology)
- Public Health
- Health/Medical Technology, General
- Medical Laboratory Technology
- Medical Radiologic Technology
- Nuclear Medicine Technology
- Respiratory Therapy Technology
- Surgical Technology
- Medicine (Pre-Medicine)
- Nursing, Practical/Vocational
- Nursing, Registered
- Optometry (Pre-Optometry)
- Osteopathic Medicine
- Pharmacy (Pre-Pharmacy)
- Physician Assisting
- Therapy & Rehabilitation, General
- Alcohol/Drug Abuse Counseling
- Massage Therapy
- Mental Health Counseling
- Occupational Therapy
- Physical Therapy (Pre-Physical Therapy)
- Psychiatric/Mental Health Technician
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Vocational Rehabilitation Counseling
- Veterinary Medicine (Pre-Veterinarian)
College Majors List: Philosophy, Religion, and Theology
- Theology, General
- Bible/Biblical Studies
- Divinity/Ministry
- Religious Education
College Majors List: Repair, Production and Construction
- Aviation & Airway Science, General
- Aircraft Piloting & Navigation
- Aviation Management & Operations
- Construction Trades (e.g., carpentry, plumbing, electrical)
- Mechanics & Repairers, General
- Aircraft Mechanics/Technology
- Autobody Repair/Technology
- Automotive Mechanics/Technology
- Avionics Technology
- Diesel Mechanics/Technology
- Electrical/Electronics Equip Installation & Repair
- Heating/Air Conditioner/Refrigeration Install/Repair
- Precision Production Trades, General
- Machine Tool Technology
- Welding Technology
- Transportation & Materials Moving (e.g., air, ground, & marine)

List of College Degrees: Sciences: Biological and Physical
- Biology, General
- Biochemistry & Biophysics
- Cell/Cellular Biology
- Marine/Aquatic Biology
- Microbiology & Immunology
- Physical Sciences, General
- Atmospheric Sciences & Meteorology
- Geological & Earth Sciences
List of College Majors: Social Sciences and Law
- Legal Studies, General
- Court Reporting
- Law (Pre-Law)
- Legal Administrative Assisting/Secretarial
- Paralegal/Legal Assistant
- Social Sciences, General
- Anthropology
- Criminology
- International Relations & Affairs
- Political Science & Government
- Psychology, Clinical & Counseling
- Psychology, General
- Urban Studies/Urban Affairs
List of College Degrees: How to Choose
Now that you know what your major options are, here's how to choose a major.
#1: Think About Your Interests
First, consider what you're interested in. You'll spend most of your time taking courses in your major, so you'll want to pick something you actually like studying. If you're not interested in taking Biology classes, then don't major in Biology! Pick something you enjoy and want to learn more about.
#2: Think About Your Job Prospects
While not everyone ends up taking a job in their major's field (I didn't!), many do. The training you receive in your major will help you when you're applying for jobs, especially if you're in a science or technology field where you'll need specific practical skills.
#3: Remember You Can Change
Finally, don't stress about your major! You can always change it. And, as I mentioned before, your major doesn't always align with your job. Ultimately, your major is something that you'll study and (hopefully) enjoy during your time at college. It doesn't have to determine your entire future!
Final Thoughts: List of All College Majors
Your college major is the specific area of study that you'll focus on throughout most of your college career. There are hundreds of college majors you can choose from. Consult this list of all college majors and your college's course catalog to see what your options are. Remember, if you don't like your major, you can always change later!
What's Next?
Wondering what the worst majors are? Our in-depth guide lists the majors with the lowest salaries and highest unemployment rates.
What are the easiest majors ? The hardest majors ? Read all about which majors you might have an easier or more difficult time with here.
Considering double majoring ? We tell you what a double major is and go over the pros and cons of having two majors in college.
Hayley Milliman is a former teacher turned writer who blogs about education, history, and technology. When she was a teacher, Hayley's students regularly scored in the 99th percentile thanks to her passion for making topics digestible and accessible. In addition to her work for PrepScholar, Hayley is the author of Museum Hack's Guide to History's Fiercest Females.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science

Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Course Formats & Required Technology
At Harvard Extension School, we offer flexible course options to help you balance school, career, and other life commitments.
Three Participation Options
Online Synchronous . Most of our courses are held live online (eastern time).
Online Asynchronous . 35% do not require live attendance.
On Campus . 20% provide the option to attend on campus.
We review the content and pedagogy of every course before assigning the participation option, choosing the one that optimizes the highest quality learning outcome. You can search courses by participation option .
Course Formats
Online Synchronous Courses View More
Online synchronous participation happens over Zoom so you can see, hear and speak with your classmates.
When you use the “Online Synchronous” search filter, you’ll find:
- Live attendance web conference courses , held entirely live over Zoom.
- Online synchronous courses with a required on-campus weekend , which have class meetings in Zoom plus a required weekend on campus.
- Flexible attendance courses that offer the option to participate synchronously online . These courses may give you the option to watch class recordings and participate asynchronously online. You may also be able to attend on campus. Please see the meeting information for details about which options are available in your course.
Online Asynchronous Courses View More
In online asynchronous courses, you are not required to attend class at a particular time. Instead you can complete the course work on your own schedule each week.
When you use the “Online Asynchronous” search filter, you’ll find:
- Online courses that give you materials to work through each week with discussion boards or live section meetings for support.
- Streamed Harvard University courses , live Harvard College courses that are recorded so you can participate on demand.
- Flexible attendance courses that offer the option to participate asynchronously . These courses may also give you the option to participate synchronously online or on campus. Please see the meeting information for details about which options are available in your course.
On-Campus Courses View More
When you use the “On Campus” search filter, you’ll find:
- Active learning weekend courses
- 1- or 3-week January session courses
- Some premedical courses
- Online synchronous courses with a required on-campus weekend , which have class meetings over Zoom plus a required weekend on campus.
- Flexible attendance courses that offer the option to participate on campus . These courses may also give you the option to participate online synchronously or asynchronously. Please see the meeting information for details about which options are available in your course.
In Harvard Summer School, we also offer a range of courses on campus, across different subject areas and different parts of term. When searching on the summer term, you’ll find these options.
Labs and Section Meetings View More
For any course type, there may be separate labs or section meetings. Information about the days and times of labs or sections will be listed on the course syllabus or announced by the teaching staff once class begins.
Technology Requirements
Canvas course websites.
Every course has a website, which you can access on the Canvas platform . This will be your home base for the course and where you will find:
- Zoom meeting links (learn more about Zoom requirements )
- The syllabus
- Class materials
- Assignments
Course websites are posted one week before classes start and remain available to enrolled students for a limited time after the term ends. We encourage you to download any course materials or graded assignments you wish to keep before your course ends.
How do I access Canvas? View More
Canvas can be accessed directly at Canvas.Harvard.edu or by logging into MyDCE and clicking the link to Canvas from your Dashboard. To log in to your course website, you must use your HarvardKey. If you do not have a HarvardKey, you may claim one at Key.Harvard.edu . Please note, your HarvardKey login credential is different from your DCEKey. For more information, please see Student ID and Login Information .
I’m logged into MyDCE but am unable to access Canvas. What may be causing this error? View More
To log in to your course website, you must use your HarvardKey. If you do not have a HarvardKey, you may claim one at Key.Harvard.edu . Please note, your HarvardKey login credential is different from your DCEKey. For more information, please see Student ID and Login Information .
I registered for a course but do not see it displayed in Canvas. When should I expect it to appear? View More
After you register, it may take 24 to 48 hours for you to gain access to your course website. All course websites/syllabi will be published 1 week before classes start. If your course website is still missing/unpublished closer to the first day of classes, then please reach out to our Enrollment Services team for advice regarding next steps for access. You can reach them at (617) 495-4024 or via email at [email protected] .
When will the syllabus be posted in Canvas? View More
Each instructor is responsible for submitting their syllabus for review in a timely manner so that it can be posted in our Course Search and Registration system and in Canvas. Many syllabi are available to view underneath the course description within the Course Search and Registration system . All course websites/syllabi will be published 1 week before classes start. If your course website/syllabus is still missing/unpublished closer to the start of classes, then please reach out to our Enrollment Services team for advice regarding next steps for access. You can reach them at (617) 495-4024 or via email at [email protected] .
I recently changed courses but do not see the new courses displayed in Canvas. When should I expect it to appear? View More
After you change courses, it may take 24 to 48 hours for you to gain access to your course website. Please note that some course websites are not published by the instructor(s) until closer to the start of the term. If your course website is still missing/unpublished closer to the start of classes, then please reach out to our Enrollment Services team for advice regarding next steps for access. You can reach them at (617) 495-4024 or via email at [email protected] .
If your course change has occurred on the day that your new course meets on, please contact our Academic Technology team to receive a one-time Zoom link to access your course with. You can reach them at (617) 998-8571 or via email at [email protected] .
Can I access my course website after the course ends? View More
You have limited access to your Canvas course website after the term ends.
- About two weeks after the term ends, course websites move to a read-only state. Your access to course messaging, Canvas-based third-party tools, and course videos ends at that time.
- About six months after the term ends, course websites are removed from your Canvas account, and you can no longer view or access course materials.
- Course syllabi remain available through Simple Syllabus .
Logging In: Using Your HarvardKey
To access your course website, you will log in with your HarvardKey, your University login and password. When you first register for a course, you receive a Harvard University ID number and a prompt to claim your HarvardKey.
The two-step authentication process, which adds additional security to your account, will require periodic use of either a smartphone, app, or landline-based verification. Learn more about the Harvard University ID number and HarvardKey .
Computer Specifications & Internet Connection
Windows and macintosh.
- 2GHz or faster processor, 8GB or more of RAM
- Please maintain an up-to-date operating system and web browser.
We do not support:
- Taking courses on mobile devices
- Linux/Chromebook
- Beta versions of any software
- Operating systems discontinued by manufacturers
Connection Speed
You need a minimum internet speed of 5 Mbps. The recommended speed is 10 Mbps. Check your Internet speed .
If your course uses Zoom and you have not used it before, the program will automatically download when you join your first meeting.
- You are required to use a webcam during class.
- Be prepared to use a microphone during class. We recommend a Logitech H390 headset, but any headset should be adequate.
- You are expected to join from a suitable, quiet location with a computer that permits full participation in the class activities. Please review the full Participation and Attendance requirements. If you do not adhere to all participation requirements you may be removed from your class meeting.
Getting Help
Training and documentation.
- Sign up for Zoom training on our web conference information page or visit our Zoom training video .
- Learn to make the most of our course video player through the Media Player Help Page .
Online Support
Technical questions and computer/software troubleshooting.
- Call (617) 998-8571 Hours: Monday – Thursday, 10 a.m. – 11 p.m. (Summer School hours: Monday – Thursday 9 a.m. – 10 p.m.); Friday, Saturday, and Sunday, 10 a.m. – 8 p.m. Eastern Time
- Email: [email protected]
Enrollment Services (Registration, Access, and General Questions)
- Call (617) 495-4024 Mondays – Fridays, 9 a.m. – 5 p.m., Eastern Time
- Email: [email protected]
Online Technology Status Page
- Check on the status of our course platforms (Canvas, Zoom, etc.)
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
List of 200 College Majors: Which Is Right For You?
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
How to pick a major, will your major impact your college chances, ultimate list of college majors, how to find the right school for your major.
With so many majors and programs available, how do you know which one is the best pick for you? It can be hard to decide when you’re still in high school, honing your interests and figuring out your career goals.
But, knowing what major you’re interested in can play a role in determining the right college for you – so it’s an important factor to consider. That’s why we’ve compiled a list of 200 college majors.
NB: Few schools offer all the majors on this list. Use our school-search tool to find colleges with the program that interests you.
So, among these 200 majors (and more, if you can find them), how do you decide on a program ? Here are factors to consider.
Your personal interests, strengths, and experiences
This combination of factors is probably most important in finding the right major for you. What are your passions? Where do you thrive? What have you achieved in both your academic and extracurricular life? While you can certainly change course in college and try something new, your background can play a pivotal role in shaping your path forward.
Your career goals
Hand-in-hand with your passions are your career goals. What do you want to do after you graduate? While some students end up pursuing careers that are wholly unrelated to their majors in college, others adhere to the same path and find that their undergraduate programs provide ample preparation for their careers.
The requirements
Of course, just because a program seems appealing to you doesn’t mean it’s without its hitches. When you ultimately declare a major in college, you will have looked at the requirements, but it’s also a good idea to study up on what’s typically required while you’re still applying. Take a look at requirements for the same major across different colleges, too, because they often vary, depending on the school. This can also help you narrow down your college list.
The Return on Investment (ROI)
In today’s competitive job market, ROI is critical — especially since college is so expensive. Often, you can find data on how many graduates from a particular program find employment within a certain period of time after graduating. You can also find statistics on the earning potential for specific majors. While this shouldn’t be the sole determining factor in choosing a major — after all, graduates of different majors often go into a variety of careers — it’s certainly something to consider.
Usually, your choice of major won’t have much of an effect on your overall chances of admission to a specific college. One exception is if the college has particularly selective programs or schools that you need to apply to directly. For example, the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School of Business tends to be more selective than the larger university and some other colleges or schools within it, so if you choose to apply to this school, then it will impact your chances of admission.
We advise against trying to apply under a supposedly “easier” major that you believe offers higher chances of admission just because you think you’re more likely to get in. Adcoms are likely to see through this tactic because the major you select won’t align with your profile. Also, bear in mind that at some colleges, such as Cornell University, it can be difficult to transfer internally after you’re accepted if the major you really wanted is in another school within the larger institution.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Agriculture, Outdoor, and Construction
- Aeronautics
- Agricultural Business & Technology
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Economics
- Agricultural Operations
- Animal Sciences
- Construction Engineering Technology
- Construction Management
- Fish and Wildlands Science and Management
- Food Science
- Art History
- Cinematography
- Digital Arts
- Fashion Design
- Game Design
- Graphic Design
- Industrial Design
- Illustration
- Interior Design
- Music Management
- Music Performance
- Photography
- Visual and Performing Arts
- Visual Design
- Actuarial Science
- Advertising
- Business Administration
- Business, Management, and Related Support Services
- Econometrics
- Entrepreneurship
- Fashion Merchandising
- Human Resources Management
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Management Science
- Managerial Economics
- Operations Management
- Organizational Behavior
- Real Estate
- Supply Chain Management
- Early Childhood Education
- Education (Other)
- Elementary Education
- Health and Physical Education
- Language Arts Teacher Education
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Middle School Education
- Music Teacher Education
- Physical Education Teaching and Coaching
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Teacher Education
- Athletic Training
- Clinical Laboratory Science
- Cognitive Science
- Communication Sciences
- Community Health
- Community Health Services
- Dental Hygiene
- Health and Wellness
- Health Care Administration
- Health Information
- Health/Medical Preparatory Programs
- Health Professions and Related Clinical Sciences
- Health Services
- Hospital and Health Care Facilities Administration
- Medical Radiologic Technology
- Nursing Research
- Nursing Science
- Nutrition Sciences
- Public Health
- Public Health Education
- Radiologic Technology
- Respiratory Care Therapy
- Speech-Language Pathology
- Applied Communication
- Biblical Studies
- Communication
- Communication and Media Studies
- Creative Writing
- Digital Communication and Multimedia
- Foreign Languages and Literature
- French Language and Literature
- Gender Studies
- General Studies
- General Studies and Humanities
- Liberal Arts
- Linguistics
- Mass Communication
- Organizational Communication
- Parks, Recreation and Leisure Facilities Management
- Parks, Recreation and Leisure Studies
- Public Relations
- Public Relations/Image Management
- Radio and Television
- Religious Studies
- Rhetoric and Composition
- Spanish Language and Literature
- Speech and Rhetoric
- Talmudic Studies
Law and Politics
- Community Organization and Advocacy
- International Relations
- International Studies
- Legal Assistant
- Legal Studies
- Political Science
- Public Administration
- Public Policy Analysis
- Social Work
Social Science
- Anthropology
- Behavioral Sciences
- Child Development
- Criminology
- Experimental Psychology
- Human Development and Family Studies
- Aerospace Engineering
- Applied Mathematics
- Architecture
- Astrophysics
- Biochemistry
- Biological and Biomedical Sciences
- Biological and Physical Sciences
- Biomedical Engineering
- Biomedical Sciences
- Cellular and Molecular Biology
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Engineering
- Computer and Information Sciences
- Computer Science
- Computer Software Engineering
- Computer Systems Networking
- Conservation
- Earth Science
- Electrical Engineering
- Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Environmental Studies
- Exercise Physiology
- Informatics
- Information Science
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology (IT)
- Kinesiology
- Marine Biology
- Mathematics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Microbiology
- Neuroscience
- Petroleum Engineering
- Physiology, Pathology, and Related Sciences, Other
- Apparel and Textiles
- Corrections and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Electromechanical Technology
- Foods, Nutrition, and Wellness Studies
- Forensic Science and Technology
- Hospitality Administration
- Hotel Management
- Human Sciences (General)
- Human Services
- Law Enforcement Administration
- Police Science
- Sport and Fitness Administration
Program availability is one factor in choosing the right college for you, but there’s plenty more to consider. Using our school-search tool , you can find the best fits for you, filtering by criteria like major, finances, location, size, and more. Find out your real chances of getting into your dream school with CollegeVine’s chancing engine .
Not sure what you want to study? Check out our list of the best colleges for undecided students .
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

The Types of Colleges: The Basics
Find the right college for you., sorting out colleges by their types.
Is a college the same thing as a university? What does "liberal arts" mean? Why are some colleges called public and others private? Knowing the basics in regard to different types of colleges is imperative to making the right decision.
Public and Private Colleges
Public colleges are funded by local and state governments and usually offer lower tuition rates than private colleges, especially for students who are residents of the state where a college is located.
Private colleges rely on tuition, fees, and non-government funding sources. Generous financial aid packages for students are often available thanks to private donations.
For-Profit Colleges
For-profit institutions are businesses that typically offer career training. Although these colleges offer a variety of degree programs, it's wise to exercise caution when applying to a for-profit school. The degree programs often come at a higher cost, meaning students graduate with more debt. Credits earned may not transfer to other colleges so be sure to check with the admissions office at each institution.
Four-year and two-year colleges
Four-year institutions are referred to as undergraduate colleges. Four-year colleges specifically offer bachelor's degree programs. These include universities and liberal arts colleges.
Two-year colleges offer certificate programs that can be completed in under two years. They also offer two-year associate degrees. These include community colleges, vocational-technical colleges, and career colleges.
Liberal Arts Colleges
These institutions offer numerous courses in liberal arts in areas such as literature, history, languages, mathematics, and life sciences. Most of these institutions are private and offer four-year bachelor's degree programs. These colleges prepare students for a multiplicity of careers as well as graduate studies

Universities
Universities are larger institutions that offer a wider variety of academic majors and degree options. These schools provide bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees. Most universities contain several smaller colleges, such as colleges of education, engineering, or health sciences. These colleges can prepare you for a wide range of careers or for graduate study.
Community Colleges
Community colleges offer two-year associate degrees that prepare undergraduates for four-year institutions offering bachelor programs. They also provide career-specific associate degrees and certificates. Community colleges are an affordable option because of their low tuition costs.
What is the difference between a college and a university?
A college is a smaller school that may offer a wide variety of educational programs or more focused specializations for those seeking undergraduate degrees. Standing alone or as part of a larger institution, a college is often a private institution with a lower student population and smaller class sizes. On the other hand, a university is a larger school offering both undergraduate and graduate-level degrees. Because they’re a component of a university's doctoral programs, such institutions also serve as research facilities for educational advancement.
Vocational-Technical and Career Colleges
Vocational-technical and career colleges offer specialized training in a particular industry or career. Areas of study include the culinary arts, firefighting, dental hygiene, and medical-records technology. These colleges usually offer students certificates or associate degree programs.
Colleges with a Special Focus
Some colleges focus on a specific interest or student population. These include:
- Arts colleges
- Single-sex colleges
- Religiously affiliated colleges
- Specialized mission colleges
Arts Colleges
Conservatories and colleges of this variety focus on the arts. In addition to regular coursework, these institutions provide training in areas such as photography, music, theater, sculpture, drawing, or fashion design. Most of these schools offer associate or bachelor's degrees in the fine arts or a specialized field.
Single-Sex Colleges
Some private colleges are specifically for men or women.
Religiously Affiliated Colleges
Some private, higher-education institutions are connected to a religious faith. Such connections may simply be historic in nature. Others incorporate religious study into day-to-day student life.
Specially Designated Colleges
Historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs) focus on educating African American students. Colleges and universities are designated Hispanic-serving institutions (HSIs) when at least 25% of the full-time undergraduate students are Hispanic. HBCUs and HSIs may offer programs, services, and activities targeted to the underrepresented students they serve.
What is better, a university or a college?
Those who prefer a more intimate experience with a greater connection to faculty may prefer a college. However, a university may be better for those looking for a broader range of programs and more learning facilities. The ultimate answer will depend on your personal preferences and the school in question. Both colleges and universities can provide a rewarding educational experience.
What to Do Now That You Know About the Different Types of Colleges
Now that you’re familiar with the types of institutions available, you should decide which one will suit your future goals. It’s often helpful to create a vision board of what you plan to achieve before deciding how you plan to achieve it. Take some time to think about your trajectory while keeping the knowledge of these various types of schools in mind. If you need direction after you assess your needs, you may find it helpful to talk to your school's guidance office, a college recruiter, or a college alum to work through any other questions you might have.
Embarking on a journey through higher education can be both exciting and challenging. Using the information presented here should help you sift through your options so the decisions you make today will serve you better in the future. For more help finding the right colleges for you, check out College Search .
Related Articles
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
College Courses in the Philippines [Complete List]
Last Updated – Jun 14, 2023 @ 1:51 am
After graduating from Highschool some of us already know what course we want to take before starting college.
Unfortunately, some of us are torn between the many choices we are presented with. This list will try and help you decide which courses might be perfect for your skillset including the job you can apply for and an estimate of the salary you can receive.
Related: Top Universities in the Philippines
What is a College Course?
A college course is a class offered by a college or university. These courses are part of a program that will lead you to an undergraduate or graduate degree or a certificate.
These courses can be undertaken online or on campus depending on the specific course or degree you want to attain.
Related: Tuition Fee Guide in the Philippines
Types of College Degrees in the Philippines
There are four types of degrees in college that you can aim for. These are Bachelor’s degrees, Master’s, Doctoral, and Associate(vocational courses).
These degrees give you the choice to further enhance your knowledge of the course/s you have chosen.
Bachelor’s Degree
There are 2 types of Bachelor’s Degrees – Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) and Bachelor of Science. It takes 4 years to finish this degree.
Bachelor of Arts (B.A.)
A BA can allow you to study a wide range of subjects related to both your major as well as general education courses such as writing, art, history, philosophy, and religion.
BA offers more flexibility for you to explore a variety of careers
This broad foundation for your degree can help you pursue an education that reflects your interests and passions.
Bachelor of Science (B.S.)
A BS degree is first and foremost a science degree and usually focuses heavily on science and mathematics courses, building a technical understanding of your major.
BS has more stringent requirements
A BS degree typically has a more substantial major requirement than a BA. A BS major typically requires around 54 credits.
Master’s Degree
A master’s degree can be a viable option for those who want to further their knowledge of a particular subject, explore other areas of interest after having completed an undergraduate degree, or improve their career prospects.
The nature of master’s degree programs means prospective students must be prepared for an intensive learning experience that incorporates their undergraduate studies and/or the experience gained from employment.
A Master’s Degree typically takes 2 years to complete.
Doctoral/Doctorate Degree
A Ph. D. may take 4 to 8 years to complete depending on many factors like the timing of the program design and its complexity.
The doctorate degree is the most advanced degree you can earn, symbolizing that you have mastered a specific area of study or field of profession.
The degree requires a significant level of research and articulation. Those who earn the degree must have researched a subject or topic thoroughly, conducted new research and analysis, and provides new insights on the field.
The doctorate positions the professional for top-tier consulting and education career considerations and advancement in their current profession, and gives them the edge to staying relevant.
Associate Degree
An Associate Degree takes 2 years to finish.
Just like a bachelor’s degree, an associate degree is an academic program taken at the undergraduate stage of your education.
Associate degrees in the Philippines are commonly known as vocational courses and are available as short courses from TESDA (Technical Education and Skills Development Authority) or their partnered institutions.
An associate degree is sufficient to get you basic skills and land you work for your livelihood and to gain experience on the job.
College Courses in the Philippines
In this part of the article, we present you with a list of college courses that can be found in the Philippines.
Humanities is a field of study that deals with the ways humans think and feel and how they express themselves.
Bachelor of Arts in History (AB History)
A 4-year course that studies events from the past and will help you learn about the different civilizations that have existed.
Potential Careers :
- Professional Historian
- School Administrator
- Museum Staff
- Historical Researcher
- Diplomatic Service
Bachelor of Arts in Philosophy (AB Philosophy)
A 4-year course that teaches you the underlying principles of reality, knowledge, morality, and existence and how it applies to other fields.
- Management Trainee
- Human Resources Assistant
- Labor Relations Manager
- Training officer
Bachelor of Fine Arts Major in Industrial Design (BFA)
A 4-year course that teaches how to design and develop usable products and also how to design packaging and systems.
Potential Careers:
- Industrial Designer
- Product Designer
- Multimedia Designer
- Graphic Artist
- Packaging Designer
- Professor/Art Educator
Bachelor of Fine Arts Major in Painting (BFA)
A 4-year course that teaches artistic representations through the use of paint. This program focuses on developing the student’s perceptual and technical skills in painting.
- Illustrator
- Production Designer
- Visual Communicators
- Costume Designer
- Professor/Art Educators
- Art Critics
- Art Historians
- Fine Art Appraiser
Bachelor of Fine Arts Major in Sculpture (BFA)
A 4-year course that teaches you how to express interests and ideas in three-dimensional (3-D) art.
- Food Stylist
Bachelor of Fine Arts Major in Visual Communication (BFA)
A 4-year course that teaches how to use traditional and modern technology to create effective advertisements, web, and new media designs.
- Advertising Artist
- Graphic Designer
- New Media Specialist
- Costume and Fashion Designer
- Professor / Art Educator
Social Sciences
Social Sciences is a collective term for the branches of science that deal with the study of humans, their nature, behavior, and how they interact with one another.
Bachelor of Arts in Economics (AB Economics)
A 4-year course that will help you gain a better understanding of economic systems and their structure. This includes the entities that compose them, their relationship with one another, and how the introduction of external factors can affect not only them but the entire system as well.
- Economics Instructor
- Economic Development Officer
- Government Policy Analyst
- Investment Banker
- Financial Analyst
- Stock Broker
Bachelor of Science in Economics (BS Economics)
Potential Careers:
Bachelor of Arts in Psychology (AB Psychology)
A 4-year course that deals with the study of the way we think and behave.
- Clinical Psychologist
- College Professor
- Human Resources Personnel
- Community Developer
Bachelor of Science in Psychology (BS Political Science)
Bachelor of science in criminology (bs criminology).
A 4-year course that is mainly concerned with the nature of crimes and criminals.
- Law Enforcer
- Forensic Scientist
- Correctional Officer
- Security Consultant
- Firefighter
Bachelor of Arts in Political Science (AB Political Science)
A 4-year course that will teach you the skills needed to make political and policy analyses that can be used to introduce changes that will be beneficial to both the government and the general public.
- Political Analyst
- Paralegal / Legal Assistant
- Contract Specialist
- Program Coordinator
- Executive Assistant
- Administrative Assistant
- Intelligence Analyst
- Corporate Analyst
- Policy Analyst
- College Instructor
Bachelor of Arts in English (AB English)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the structure; development; theories; and applications of languages, and how to use your knowledge of them to write and speak effectively, especially in English.
- Quality Assurance Specialist
- Proofreader
- Copy Editor
- Copy Writer / Content Writer
- Course Development Manager
- Translator / Interpreter
- Advertising Associate/Advertising Executive
- Technical Writer
- Speech Writer
- Language Specialist
- Customer Service Representative
Bachelor of Arts in Linguistics (AB Linguistics)
A 4-year course that will teach you about languages, their origins, development, and their social significance to man .
- Verbal Therapist
Bachelor of Arts in Literature (AB Literature)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the different kinds of literature of the world, their history, forms, structures, modes, techniques, and how you can use your knowledge of them to produce new literary works or review existing ones.
- Editorial Assistant
Bachelor of Arts in Anthropology (AB Anthropology)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the origin and evolution of human beings including gradual changes in their genetic makeup, behavior, languages, and social relations.
- Anthropologist
- Museum Curator
Bachelor of Arts in Sociology (AB Sociology)
A 4-year course that will teach you about human society, its structure, history, development, and how different cultural groups vary from one to another.
- Sociologist
Bachelor of Arts in Filipino (AB Filipino)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the structure of the Filipino language, the things that make it distinct from other languages, literary works that were written in the Filipino language, and how to translate written works from a foreign language to Tagalog and vice versa.
- Filipino Teacher
- Interpreter
Bachelor of Science in Forensic Science (BSFS)
A 4-year course that will train you in using scientific principles and techniques to solve different crimes.
- Questioned Documents Examiner
- Forensic Psychologist
- Forensic Pathologist
- Forensic Accountant
- Insurance Investigator
- Risk Analyst
- Crime Scene Analyst
- Field Technician
- Computer Forensics Expert
Bachelor of Arts in Islamic Studies (AB Islamic Studies)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the study Islam as a way of life in the context of economic, social, cultural, political, and legal aspects.
- Academic Researcher
- Administrator of Islamic Institutions
- Business Consultant
- Foreign Diplomat
- Policy Maker
Natural Sciences
Natural Sciences is a collective term for the branches of science that deal with the study of nature and the rules that apply to it.
Bachelor of Science in Environmental Science (BSES)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the environment and the effects of man’s activities on it. It usually covers such issues as the conservation of natural resources, pollution, deforestation, and overpopulation among a couple of others.
- Environmental Impact Assessor
- Environmental Officer
- Conservation and Resource Management Staff
- Pollution Control Officer (PCO)
- Project Planner
- Technical Personnel
- Environmental Scientist
- Research Assistant
- Research Analyst
- Quality Assurance Analyst
- Environmental Consultant
Bachelor of Science in Forestry (BS Forestry)
A 4-year course that will train you in managing the social, economic, and environmental dimensions of forestry resources, performing research that can advance the growth of forestry science, and educating the public of the proper conservation and development of forest resources through extension activities.
- Farm Supervisor
- Farm Manager
- Horticulturist
- Plant Manager
- Dairy Herdsman
- Processing Plant Manager
- Entomologist
- Pest Control Supervisor
- Farm Aide Technician
- Product Development Officer
Bachelor of Science in Fisheries (BSFi)
A 4-year course that will train you in aquaculture, capture fisheries, post-harvest fisheries, aquatic ecology, and fisheries-related research.
- Fisheries Management
- Fisheries Research
- Fisheries Extension Service
- Fisheries Industries
- Fisheries Instruction
Bachelor of Science in Geology (BS Geology)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the origins of the earth, its traits, and characteristics, composition, and the changes that it goes through. It deals with issues such as pollution and waste disposal, the use and conservation of natural resources, and preventing or reducing the harmful effects of natural disasters.
- Volcanologist
- Seismologist
- Geological Engineer
- Environmental Lawyer
Bachelor of Science in Biology (BS Biology)
A 4-year course that deals with the study of living things.
- Research Assistant in government agencies
- Researcher for industries involved in biotechnology, agriculture, food and nutrition, and pharmaceutics
- Biological Laboratory Technician
Bachelor of Science in Molecular Biology (BS Molecular Biology)
A 4-year course that is primarily concerned with identifying, describing, and manipulating the components of cells and organisms including Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), Ribonucleic acid (RNA), and proteins. Among its many practical applications are the detection of diseases, gene therapy, in vitro fertilization, and DNA profiling to name a few.
Potential Careers –
- Research Technician
- Toxicologist
- Veterinarian
- Wildlife Manager
- Pest Control Officer
- Medical Technologist
- Microbiologist
- Product Safety Officer
Bachelor of Science in Physics (BS Physics)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the laws of nature and how to use these laws to understand and explain how the things around us work.
- Cadet Engineers
- Science Research Specialist
- Process Engineer
- Production Engineer
- Physics Instructor
- Biophysicist
Bachelor of Science in Applied Physics (BS Applied Physics)
A 4-year course that will train you in using the principles of Physics to come up with practical solutions to existing programs in a wide variety of fields including but not limited to medicine, engineering, computer science, and business to name a few.
- Science Research Specialist II
Bachelor of Science in Chemistry (BS Chemistry)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the study of chemicals, their composition, their properties, the way they react with one another, and how you can use your knowledge of this information to come up with helpful products in a wide variety of fields including medicine, food science, and engineering to name a few.
- Analytical Chemist
- Laboratory Chemist
- Chemistry Specialist
- Quality Assurance Executive
- Dispensing Chemist
- Product Specialist
- Research and Development Specialist
Formal Sciences
Formal Sciences is a collective term for the branches of science that deal with the study of theoretical systems.
Contrary to natural sciences which try to understand the nature of things through experiments and observations, formal sciences are more concerned with defining the rules that govern a particular theory.
Bachelor of Science in Computer Science (BSCS)
A 4-year course that is generally concerned with the effective use of computation methods to analyze, solve, and come up with practical solutions for different problems, often through the use of computers or computer programs designed to perform specific tasks.
- Application Developer
- Game Developer
- Software Developer
- Computer Programmer
- Software Engineer
- Web Developer
- Data Analyst
- Systems Analyst
Bachelor of Science in Information Technology (BSIT)
A 4-year course that deals with the processing and distribution of data with emphasis on its application on businesses.
- Network Administrator
- Database Manager
- Technical Support Specialist
- QA Specialist
- Mobile Applications Developer
Bachelor of Science in Information Systems (BSIS)
A 4-year course that will train you in designing, developing, and managing information systems such as office automation systems, transaction processing systems, transport information systems, navigation systems, and other systems that provide related services.
- Database Administrator
- Database Designer
- Financial Analyst/Auditor
- Systems Developer
- Auditor for Information System
Bachelor of Science in Mathematics (BS Mathematics)
A 4-year course that will expose you to the breadth and depth of mathematical theories, concepts, and applications in order to prepare you for future careers that require critical and analytical thinking skills.
- Statistician
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Analyst
- Business Intelligence Head
- Financial Systems Consultant
- Quality Assurance Engineer
- System Administrator
- Mathematics Teacher/Instructor
- Game Designer
- Account Executive
Bachelor of Science in Applied Mathematics (BS Applied Math)
A 4-year course that will train you in using mathematical theories, concepts, and formulas to come up with practical solutions to problems in the fields of business, engineering, and information technology among other things.
- Quality Analyst
- Programs Analyst
- Corporate Development Officer
- Workforce Analyst
- Research Executive
- Statistical
- Leasing Supervisor/Manager
Bachelor of Science in Statistics (BS Stat)
A 4-year course that will teach you about different statistical methods and how to use them to analyze and interpret data .
- Market Research Assistant
- Business Analyst
- Management Information System Staff
Agriculture (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Professions and Applied Sciences is an academic discipline that deals with the practical applications of scientific knowledge in daily real-life activities.
Bachelor of Science in Agriculture
A 4-year course that is concerned with applying the principles of science, ethics, and business management in the production, development, and processing of plants and animals used for food, recreation, industrial, and medical purposes among others.
- Farm Management
- Agriculture and Food Technology
Bachelor of Science in Agribusiness (BS Agribusiness)
A four-year degree program in the Philippines that will train you in in the manufacturing and distribution of farm supplies and other related products according to the country’s bio-physical, socio-cultural, political, economic, and development needs.
- Sales Representatives
- Corporate Planners
- Entrepreneurs
- Business Consultants
- Business Managers
- Researchers
- Extensionist
- Credit Analysts
Bachelor of Science in Agroforestry (BS Agroforestry)
A 4-year course that will train you in producing, managing, and utilizing trees, agricultural crops, animals, and soils for the purpose of conservation and socio-economic productivity.
- Technical Consultant
- Entrepreneur
- Farm supervisor
Architecture and Design (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in architecture (bs architecture).
A 5-year course that is concerned with the design and planning of architectural structures such as residential and commercial buildings, roads, dams, tunnels, bridges, and the like.
- Architectural Design
- Urban Design
- Community Architecture
- Facility Planning
- Construction Technology
- Construction Management
- Building Administration and Maintenance
- Real Estate Development
- Restoration/Conservation
Related: Top Architectural Firms in the Philippines
Bachelor in Landscape Architecture (BLA)
A 4-year course that is mainly concerned with the design and planning of land areas.
- Landscape Design Consultancy
- Site Planning
- Park and Recreation Planning and Administration
- Land Development Planning
- Ecological Planning and Design
- Historic Preservation and Restoration
- Urban and Regional Planning
- Construction and Project Management
Bachelor of Science in Interior Design (BS in Interior Design)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the principles of interior design, space planning, application of colors, basic furniture production, and budget management among other things.
- Visual Design Manager
- Auto-CAD Draftsman
- Interior Designer
- Interior Lighting Designer
Business (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in accountancy (bsa).
A 4-year course that is primarily concerned with the effective management of a person’s, group’s, or company’s financial resources including the proper ways of monitoring and documenting the flow of money or goods within the system and the applicable laws related to it.
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Staff
- Management Accounting Staff
- Tax Accounting Staff
- Internal Audit Staff
- Budget Analyst
- Credit Analyst
- Revenue Officer
- Audit Examiner
- Financial Services Specialist
- Accounting Instructor
- Comptroller
- Senior Information Systems Auditor
- Senior Fraud Examiner
- Senior Forensic Auditor
- National Treasurer
- Commissioner
- Chief Financial Officer
Related: Best Accounting Firms in the Philippines
Bachelor of Science in Accounting Technology (BSAcT)
A 4-year course that will train you in maintaining systematic records of business transactions, verifying and recording them, using computers to calculate, prepare and process financial records.
- Financial Statement Preparers
- Cost Accountant
- Senior Information Systems Internal Auditor
- Senior Forensic Internal Auditor
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration
A 4-year course that will help you learn the ins and outs of running a business as well as the necessary traits and skills that you need to have and develop to become a successful business leader.
- Sales Manager
- Market research Analyst
- Human Resources Specialist
- Loan Officer
- Meeting, Convention, and Event Planner
- Logistician
- Real Estate Appraiser
- Buyer or Purchasing Agent
- Compensation and Benefits Analyst
- Insurance Underwriter
- Labor Relations Specialist
Related: Top Business Services in the Philippines
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration Major in Business Economics (BSBA)
A four-year business course that is concerned with the various factors that affect businesses.
- Field Researcher
- Corporate Planning Analyst
- Stock Trader
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration Major in Financial Management (BSBA major in FM)
A 4-year business course that focuses on the financial aspects of managing a business.
- New Account Personnel
- Credit and Collection Assistant
- Treasury Assistant
- Businessman
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration Major in Human Resource Development (BSBA major in HRDM)
A 4-year course that will prepare you for a career in Human Resource Management (HRM) in various organizations and businesses.
- Recruitment Assistant
- Training and Development Officer
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration Major in Marketing Management (BSBA major in MM)
A 4-year course in the Philippines that will prepare you for a Marketing career in various organizations and businesses.
- Marketing Assistant
- Merchandiser
- PR/Advertising Assistant
- Service Crew
- Junior Sales Trainer
- Receptionist
- Product/Brand Assistant
- Order/Billing Assistant
Bachelor of Science in Business Administration Major in Operations Management (BSBA major in OM)
A 4-year course that revolves around the day to day operation of businesses. This includes the processes involved in the production and distribution of goods, the delivery of services, and managing the equipment and facilities used to run a business.
- Operations Management Assistant
- Technical Staff
- Warehouse Assistant
- Inventory Assistant
- Project Assistant
- Logistics Management
- Stock Personnel
Bachelor of Science in Hotel and Restaurant Management (BS HRM)
A 4-year course that will prepare you for working in the hotel and restaurant industry and managing your own hotel and restaurant business someday. With the help of this course you’ll learn not only how to manage the day to day operations of your hotel or, restaurant, you’ll also learn how to devise day-to-day strategies that can increase your company’s profits.
- Room Attendant
- Food and Beverage Service Attendant
- Bartender/Bar Attendant
- Front Office Clerk
- Head Waiter
- Assistant Cook
- Housekeeping Attendant
- Housekeeping Supervisor
- Banquet Supervisor
Bachelor of Science in Entrepreneurship (BS Entrep)
A 4-year course that will train you in identifying opportunities, developing and preparing business plans, and starting and managing your own business.
Related: How to Become a Consultant
Bachelor of Science in Office Administration (BSOA)
A 4-year course that will train you in performing a wide variety of administrative tasks including but not limited to clerical duties, personnel management, events management, and customer service.
- Clerk/Encoder
- Stenographer/Transcriber
- Office Supervisor
- Office Manager
Bachelor of Science in Real Estate Management (BS REM)
A 4-year course that will train you in real estate salesmanship, brokerage, appraisal, and consultancy including properties that fall within public domain.
- Salesperson
- Accounts Personnel
- Real Estate Appraisal Analyst
- Real Estate Consultant
- Real Estate Consultant Assistant
- Appraisal Assistant
- Government Assessor
Bachelor of Science in Tourism Management (BSTM)
A 4-year course that will train you in developing and implementing tourism campaigns, organizing and managing events, and following policies and standards related to investments, business regulations, procurement, and other miscellaneous procedures.
- Travel account representative
- Tour Coordinator
- Local Tourism Officer
- Airline flight attendant
- Tour Escort
- Staff of the Department of Tourism and other tourism-oriented institutions
Health Sciences (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in medical technology (bs med tech).
A 4-year course that deals with the use of modern technology in detecting, identifying, and predicting the possible course of diseases that can put a person’s health at risk.
- Medical Technologist for hospitals, clinics, and sanitarium
- Medical Technologist for Medico-Legal cases
Bachelor of Science in Midwifery (BS Midwifery)
A 4-year course that will train you in addressing the needs of expecting mothers and their children starting from the early stages of pregnancy up to the first few weeks following childbirth.
- Health Facility Administrator
- Clinic Manager
- Health Program Manager
- College Professor/Trainer
Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)
A 4-year course that revolves around caring for the sick or injured. This does not only involve addressing immediate threats to the patient’s health, but also guiding the patient all the way through physical, mental, and emotional recovery.
- Clinic Nurse
- Community Health Nurse
- Private Nurse
- Company Nurse
- School Nurse
- Military Nurse
Bachelor of Science in Occupational Therapy (BSOT)
A 5-year course that is concerned with using different methods and strategies to help people with serious physical, mental, or emotional conditions that keep them from functioning the way they are supposed to.
- Nursing Homes
- Rehabilitation Centers
Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy (BS Pharmacy)
A 4-year course that is concerned with drugs and other related substances. These include medicinal drugs, cosmetics, and common household products.
- Clinical Researcher
- Quality Control Analyst
- Product Manager
- Food and Drug Regulation Officer
- Military Pharmacist
- Forensic Analyst
Bachelor of Science in Physical Therapy (BSPT)
A 5-year course that is concerned with using various treatments and exercises to restore the function of a broken bone or to compensate for the loss of a certain body part.
- Professional Sports Teams
Bachelor of Science in Radiologic Technology (BS Rad Tech)
A 4-year course that will train you in applying x-ray energy to assist in the diagnosis or treatment of diseases, performing radiographic or nuclear medicine procedures and related techniques to produce images for the interpretation of a licensed medical practitioner, and providing radiation therapy to cancer patients.
- Radiologic Technologist
- Ultrasound Technologist
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologist
- Mammography Technologist
- Computed Tomography Technologist
- Interventional Radiology Technologist
- Radiation Therapy Technologist
- Nuclear Medicine Technologist
Bachelor of Science in Respiratory Therapy (BSRT)
A 4-year course that will train you in providing clinical pulmonary care procedures that will help in the proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases.
- Respiratory Therapist
- Medical Service Practitioner
- Product specialist
- Academic Writer
Bachelor of Science in Speech-Language Pathology
A 4-year course that teaches you to evaluate and assess patients with speech-language or related conditions and planning and implementing SLP interventions for patients in various settings.
- Administrator
Bachelor of Science in Sports Science
A 4-year course that will train you in the application of scientific principles to sporting or other similar physical activities to ensure that optimum performance will be delivered while eliminating or reducing the risk of acquiring injuries in the process.
- Physical Education Teacher
- Sports Coach
- Fitness Trainer
- Umpire/Referee
- Sports Facility Administrator
Education (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor in secondary education (bsed).
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching in secondary school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education can find employment as High School teachers for both public and private High Schools.
Bachelor in Elementary Education (BEED)
A 4-year course that will train you in teaching grade school students.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Elementary Education can find employment as Elementary or Grade School teachers for both public and private elementary schools.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Technology and Livelihood Education (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching TLE subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Technology and Livelihood Education can find employment as a TLE teacher.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Biological Sciences (BSED)
A four-year degree program in the Philippines that will prepare you in teaching Biological Science subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Biological Sciences may find employment as a Biology teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in English (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching English subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of a Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in English may find employment as an English teacher.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Filipino (BSED)
A 4-year course that will help you gain a better understanding of the Filipino language, especially its phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Filipino may find employment as a Filipino teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Mathematics (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching the different branches of Mathematics such as algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics in High School.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Mathematics may find employment as a Math teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Islamic Studies (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching Arabic and Islamic Studies subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Islamic Studies may find employment as a teacher in Islamic Studies in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Music, Arts, Physical and Health Education (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching Music, Arts, PE, and Health subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Music, Arts, Physical and Health Education may find employment as a MAPEH teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Physical Sciences (BSED)
A four-year degree program in the Philippines that will prepare you in teaching Physics, Chemistry, Astronomy, and other related subjects in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Social Studies (BSED)
A 4-year course that will introduce you to governments and politics, economic planning and strategy, and selected laws related to them.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Social Studies may find employment as a Social Studies teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Secondary Education Major in Values Education (BSED)
A 4-year course that will prepare you in teaching Values Education subjects in high school.
- Qualified graduates of Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Values Education may find employment as a Values Education teacher in high school.
Bachelor in Elementary Education Major in Preschool Education (BEED)
A 4-year course that will train you in teaching preschool children .
- Qualified graduates of a Bachelor of Elementary Education Major in Preschool Education can find employment as a Preschool Teacher in both public and private Preschools.
Bachelor in Elementary Education Major in Special Education (BEED)
A 4-year course that will train you in teaching children with special needs.
- Qualified BEED Major in Special Education graduates can find employment as a Special Education (SPED) teacher for both public and private schools and institutions.
Bachelor of Library and Information Science in the Philippines (BLIS)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the different sources of information, how to acquire them, and how to develop and maintain a collection of reference materials. It will also teach you how to manage small and large-scale libraries including management of library facilities, equipment, finances, and library personnel.
- Bibliographer
- Information Scientist
- Media or Audio Visual Specialist
Bachelor of Physical Education (BPE)
A 4-year course that will train you in developing and maintaining the optimal physical fitness and functionality individuals. It has two majors: School Physical Education which is a teacher education training program and Sports and Wellness Management which is a program that caters to the needs of the corporate industry.
- P.E. Teacher
- P.E. Department Head
- Coordinator in Physical Education and Sports Programs
- Fitness and Wellness Supervisor
- Gym Manager
- Recreation Director
- Wellness Trainer
- Events / Tournaments Coordinator
- Sports Tourism Officer
- Sports and Wellness Facilities Manager
Engineering (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in aeronautical engineering (bs aeroe).
A 4-year course that is concerned with aircraft and air transportation.
- Aircraft Structural Engineer
- Aircraft Design Engineer
- Aircraft Power Plant Engineer
- Aircraft Manufacturing Engineer
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineer
- Aircraft Operation/Performance Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Ceramic Engineering (BSCerE)
A 4-year course that will train you in applying knowledge of mathematics, physical sciences, and engineering sciences to the practice of ceramic engineering.
- Production Manager
- Materials Engineer specializing in Ceramic Materials
- Sales Engineer
- Design Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering (BSChE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the application of different sciences (ie. natural, social, formal, applied sciences) to come up with safe, ethical and economic ways of converting raw materials into more valuable products.
- Food and Drug Manufacturing
- Packaging Technologies
- Environmental Management
- Petrochemical Engineering
- Energy Engineering
- Biotechnology
- Paints and Coating Technology
- Semiconductor Technology
- Entrepreneurship
Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering (BSCE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the use of scientific and mathematical principles in the construction of buildings and infrastructures such as roads, bridges, tunnels, dams, airports, and the like.
- City Planner
- Structural Engineer
- Traffic Engineer
- Water Resources Engineer
Related: Top Construction Companies in the Philippines
Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering (BSCpE)
A 4-year course that will train you in the design, development, and maintenance of computer systems including both hardware and software.
- Project Engineer
- Network Systems Administrator
- Data Communications Engineer
- Systems Engineer
- Systems Designer
- Technical Support Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering (BSEE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with electricity, its production, transmission, distribution, and usage. Its curriculum covers everything from the design of electrical systems up to their operation and maintenance as well as cheaper and safer ways of completing engineering projects.
- Power Engineer
- Illumination Engineer
- Distribution Engineer
- Instrumentation and Control Engineer
- Safety Engineer
- Electrical Design Inspection
- Hardware Developer
- Construction Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Electronics and Communications Engineering (BSECE)
A 4-year course that is mainly concerned with the conceptualization, design, and development of any electronic, computer or communication products, systems, services, and processes.
- Broadcast Engineer
- Telecommunications Engineer
- Computer Systems Engineer
- Biomedical Engineer
- Robotics/Mechatronics Engineer
- Optics Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Geodetic Engineering (BSGE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with gathering data related to the earth’s surface and using them to produce spatial information systems, maps, plans, charts, and other products.
- Geodetic Engineer
- Photogrammetrist
- Cartographer
- Remote Sensing Specialist
- Hydrographer</li>
- Information Systems Analyst
- Assessor/Realtor/Appraiser
Bachelor of Science in Geological Engineering (BSGeoE)
A 4-year course that will train you in applying scientific principles to solve engineering and environmental problems such as pollution, landslides, earthquakes, and scouting for mineral resources to name a few.
Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering (BSIE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the design, operation, management, and maintenance of different systems, processes, and facilities to ensure their maximum efficiency. It has three major fields of specialization: Production Engineering; Organization and Decision Systems; and Ergonomics/Human Factors Engineering.
- Project Manager
- Strategic Planner
- Process Developer
Bachelor of Science in Marine Engineering in (BSMarE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the construction and development of marine vessels and their component parts. This may include anything from private vessels such as fishing boats and cruise ships to military vehicles such as submarines, battleships, and aircraft carriers.
- Chief Marine Engineer
- Second Marine Engineer
- O.I.C. of an Engineering Watch
Bachelor of Science in Materials Engineering (BSMatE)
A 4-year course that will teach you about the different materials that are used or can be used to produce a wide array of products including their characteristics, uses, and advantages or disadvantages over the others.
- Materials Engineer
- Quality Engineer
- Technical Service Engineer
Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering (BSME)
A 4-year course that focuses on the fundamental knowledge and skills of mechanical engineering. This revolves around the design, production, and maintenance of machines from simple home appliances, gadgets, and automobiles, to more complicated industrial equipment, robots, and jet engines.
- Power and Energy Engineering
- Automotive Engineering
- Manufacturing Engineering
- Mechatronics and Robotics
- Heating, Ventilating, Air-conditioning and Refrigeration
- Biomedical Engineering
- Instrumentation and Controls
Bachelor of Science in Metallurgical Engineering (BSMetE)
A 4-year course that is mainly concerned with metals and their conversion into useful products.
- Research and Development Engineer
- Failure Analysis and Reliability Engineer
- Metallurgy Process Engineer
- Extractive Metallurgy Engineer
- Foundry Metallurgist
- Heat Treatment Metallurgist
Bachelor of Science in Mining Engineering (BSEM)
A 4-year course that is concerned with mines and mining.
- Mineral Resource Development Operation and Management
- Mine Research and Development
- Mine Environmental and Enhancement Services
- Government Mining Services
Bachelor of Science in Petroleum Engineering (BSPetE)
A 4-year course that is concerned with the extraction of oil, petroleum, and other natural gases from the earth and their subsequent delivery to processing facilities as well as the design and development of new technology that will speed up the process while keeping the operational cost to a minimum.
- Drilling Engineering
- Reservoir Engineering
- Production Engineering
- Pollution Cleanup
- Underwater Waste Disposal
- Mining Engineering
- Coal Manufacturing
- Petroleum Geology
Bachelor of Science in Sanitary Engineering (BSSE)
A 4-year course that is primarily concerned with the designing, planning, operation, and maintenance of sanitation facilities; soil, water, and air pollution control; and the general hygienic projects of residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Sanitary Engineer
- Construction Manager/Engineer
- Environmental Engineer
- Hospital Administrator
- Project Engineer / Manager
- Pollution Control Officer
Media and Communication (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of arts in broadcasting (ab broadcasting).
A 4-year course that will prepare you for a career in the media industry, particularly in television and radio networks.
- Radio or Television Writer
- Radio or Television Director
- Radio or Television Producer
- News Reporter/News Anchor
- Media Manager/Media Consultant
Bachelor of Arts in Communication (AB Communication)
A 4-year course that will prepare you for a career in the media or similar industries – advertising agencies and public relations firms in particular.
- Advertising Manager
- Public Relations Officer
- TV or Radio Production Staff
Bachelor of Science in Development Communication (BS DevComm)
A 4-year course that revolves around the role of communication in the pursuit of development.
- Communication Researcher
- Communication Analyst
- Media Planner/Media Manager
- Project Development Officer
Bachelor of Arts in Journalism (AB Journalism)
A 4-year course that will prepare you for a career in the media industry.
- News Editor
- Media Researcher
- News Analyst
- Broadcast Journalist
- Photojournalist
- Program Director
- Web Content Writer
Bachelor of Arts in Mass Communication
A 4-year course that will train you in the effective use of different media in order to send out specific messages to targeted audiences.
- Scriptwriter
- Broadcaster
- Radio/TV Host
- Account Manager/Account Executive
- Media Manager
- Media Planner
- Production Assistant
- Radio Disc Jockey
- Call Center Agent
Public Administration (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in community development(bs community development).
A 4-year course that will train you in building and developing communities by providing their inhabitants with knowledge and resources that they can use to improve the quality of their lives, not only economically but socially and politically speaking as well.
- Business Developer
- Project Coordinator
- Community Development Specialist
- Community Outreach Worker
Bachelor of Science in Customs Administration (BSCA)
A 4-year course that will train you in handling import and export operations.
- Customs Examiner Appraiser
- Air/Sea Cargo Handling Documentation Clerk
- Bank employee
- Customs Broker
Bachelor of Science in Foreign Service (BS Foreign Service)
A 4-year course that will train you in maintaining peaceful relations with other countries, facilitating the flow of investments from international sources, promoting tourism and addressing the needs of Filipinos working overseas among other things.
- Foreign Service Officer
Bachelor of Science in International Studies(BSIS)
A 4-year course that will teach you about different government systems and the social, economic, cultural, geographical, and political factors that dictate or affect the way they operate.
- International Trade Researcher
- Fiscal Assistant
- Cultural Specialist
- Export Operations Manager
Bachelor of Public Administration (BPA)
A 4-year course that will prepare you for a career in public service.
- Technical Assistant
- Researcher in government agencies, Non-Government Organizations (NGOs), and academic institutions
- Development Manager of small or medium-sized voluntary sector or Non-Government Organizations
- Executives in a government institutions and Government-Owned and Controlled Corporations (GOCCs)
- Executives in national, regional, and international organizations</li>
Bachelor of Science in Public Safety (BSPS)
A 4-year course that will help you acquire knowledge and skills essential to ensuring public safety.
- Philippine National Police
- Bureau of Fire Protection
- Bureau of Jail Management and Penology
Bachelor of Science in Social Work (BS Social Work)
A 4-year course that deals with the study of social units such as families and communities, the various issues that affect them, and how social work can help improve, if not immediately resolve, these conditions.
- Human Resource Developer
- Program Developer
- Social Worker
- Social Welfare Planner
Transportation (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in marine transportation (bsmt).
A 4-year course that will train you in performing and fulfilling the duties and responsibilities of a marine deck officer including navigation, radio communication, and basic safety among other things.
- Chief Officer/Chief Mate
- Master Mariner
- Second Officer/Second Mate
- Third Officer/Third Mate
- O.I.C. of a Navigational Watch
- Navy Officer
- Coast Guard Officer
Nutrition (Professions and Applied Sciences)
Bachelor of science in food technology (bs food tech).
A 4-year course that will train you in applying principles of science and other related fields in the handling, preparation, processing, packaging, storage, and distribution of food to ensure that they remain safe and nutritious.
- Food Scientist
- Nutritionist
- Food Technologist
- Food Safety Officer
- Dietary Technician
- Chemical Specialist for Food
- Commissary Officer
- Savoury Application Technologist
- Food Laboratory Technician
Bachelor of Science in Nutrition and Dietetics (BS ND)
A 4-year course that will train you in planning, implementing, monitoring, and documenting nutrition programs for a given individual, group or community. It will also teach you how to plan and implement all aspects of nutrition care including identification of short and long-term goals, selection of treatment modalities, and monitoring of the client’s or patient’s progress.
- Dietary Director
- Therapeutic Nutritionist
- Administrative Nutritionist
- Teaching Nutritionist
- Public Health Nutritionist
- Clinical Dietitian
- Nutritionist Dietitian in Quality Control Department<
- Nutritionist Dietitian in the Test Kitchen (Product Department)
- Research Nutritionist Dietitian
- Food Service Manager
- Canteen Supervisors
- Menu Planner
- Food Checker
College Courses in the Philippines FAQs
How long does college last in the philippines.
Most private institutions are Catholic non-profit organizations. Most universities offer 4-year degree programs with 2 semesters per year. But it really depends on the course some courses can take up to 8 to 10 years for highly specialized ones (ie: Medicine or Law).
What course has the highest salary in the Philippines?
Courses that have high-income job opportunities in the Philippines include:
- Engineering
What courses in the Philippines require board or licensure exams after graduation?
The Philippine Regulation Commission currently has 45 regulatory boards for professions that require board exams before the actual practice:
- Accountancy
- Aeronautical Engineering
- Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering
- Agriculture
- Architecture
- Certified Plant Mechanic
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Criminology
- Customs Brokers
- Dental Technology
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics Engineering
- Environmental Planning
- Fisheries Technology
- Food Technology
- Geodetic Engineering
- Guidance Counseling
- Interior Design
- Landscape Architecture
- Librarianship
- Master Plumbing
- Mechanical Engineering
- Medical Technology
- Metallurgical Engineering
- Naval Architecture
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Ocular Pharmacology
- Occupational Therapy
- Physical Therapy
- Professional Teachers
- Psycometrician
- Radiologic Technology
- Real Estate Broker
- Respiratory Therapy
- Sanitary Engineering
- Social Work
- Speech Language Pathology
- Veterinary Medicine
- X-ray Technology
Can I take college courses online in the Philippines?
Yes, You may really enroll in online college courses in the Philippines. Numerous colleges and educational institutions in the Philippines now provide online courses and degree programs as online learning has grown in popularity.
With the ability to access lectures, materials, and assignments from any location with an internet connection, these online courses give students flexibility and convenience. Universities in the Philippines, both public and private, provide online learning opportunities.
While some institutions have specific online learning platforms, others provide their courses using well-known online learning platforms or learning management systems. Numerous academic disciplines are covered in these online courses, including business, engineering, healthcare, the arts, and sciences.
It is crucial to confirm that the school and the program you select are certified and recognized by the relevant accrediting organizations or governmental authorities when thinking about online education choices.
By doing this, you can be confident that the education you obtain satisfies a set of high criteria and that employers and other educational institutions will accept your degree or certificate. Before making a choice, it is advised to investigate and contrast various online programs, taking into account aspects like accreditation, course options, faculty credentials, student support services, and tuition costs.
What is a prerequisite?
A prerequisite is a condition that must be met in order to move on to the next step, participate in a certain course, or complete an activity. It is a prerequisite that you must fulfill in order to access something else or qualify for something else.
A course or group of courses that you must successfully finish before enrolling in a higher-level or more advanced course is known as a prerequisite in the context of education. Prerequisites are put in place to make sure that students have the information, abilities, or background needed to succeed in the course that comes after it.
To guarantee you have the underlying knowledge required for the more advanced subject, taking a basic mathematics course could be a requirement if you wish to enroll in an advanced mathematics course. Similar requirements must be met in many degree programs before you may enroll in specialized courses or work on research projects.
Prerequisites can be used in fields other than schooling. In the workplace, certain roles may have criteria that must be met before you can be considered for the position in terms of experience, education, or abilities. In general, requirements serve as a way to create a logical progression of knowledge or experience, ensuring that people have the foundation or credentials needed to succeed in the following stage or activity.
Can I change my course after enrolling?
Yes, in most educational institutions, it is often possible to change your course after enrolling, although the specific policies and procedures may vary between institutions. Here are some general considerations regarding changing your course after enrollment:
- Timeframe: There is usually a specific timeframe within which course changes can be made. This timeframe is typically at the beginning of the academic term or semester. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the institution’s deadlines and procedures for course changes.
- Availability: The availability, of course, changes may depend on factors such as course capacity, availability of seats in the desired course, and any prerequisites or requirements for the new course. If the desired course is full or has specific requirements, it may affect your ability to change courses.
- Academic Advising: It is advisable to consult with an academic advisor or counselor at your educational institution. They can provide guidance on the process, inform you about any implications or considerations, and help you make an informed decision about changing your course.
- Administrative Procedures: Changing your course typically involves administrative procedures, such as filling out a course change request form, meeting with the appropriate department or faculty, and completing any necessary paperwork.
- Implications and Consequences: Changing your course may have implications for your academic progress, graduation timeline, financial considerations (such as tuition fees or scholarships), and eligibility for certain programs or opportunities. It’s important to consider these factors before making a decision.
- Prerequisites and Requirements: If you are considering changing to a course with specific prerequisites or requirements, you may need to fulfill those prerequisites or meet the requirements before being allowed to transfer into the new course.
About Migs Palispis
Miguel Palispis is a freelance writer at Grit PH.
He started his freelancing adventure in 2018 and began doing freelance Audio Engineering work (mixing for bands and Podcasts) and is also currently writing tech news and tech reviews for Gadget Pilipinas.
He is also a musician, foody, gamer, and PC enthusiast.
Education: College of Saint Benilde (Bachelor of Arts in Music Production) Focus: Tech, Finance, and Business
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
We need your help!
Our team is currently conducting research for an upcoming guide focusing on starting a business in the Philippines . We would greatly appreciate your contribution, which should only require a few seconds of your time.
Thank you in advance!
- Digital Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Digital PR & Link Building
- Social Media Marketing
- Digital Advertising (PPC & Social)
- Content Marketing
- Copywriting
- Email Marketing
- Conversion Optimization
- Web/App Development
- Ecommerce Development
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Location of Business * Number of Employees * 1 - 10 11 -50 51 - 100 100 - 500 500+ Phone Number * Email * Insurance Company Standard Insurance AXA Philippines BDO AIG Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Full Name * Company Name * Mobile Number * Email Address * Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Contact Number * Email Address * Target Location Preferred Developer * Ayala Land SM Prime Megaworld Alveo Land DMCI Homes Federal Land Robinsons Land Corp Vista Land and Lifescapes Filinvest Land Shang Properties Century Properties Empire East Rockwell Land Name Submit
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident real estate agents can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed property developments you’re interested to invest in.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Age * Location* Phone Number * Email Address * Insurance Company Sun Life Financial Pru Life U.K. AXA Philippines AIA Philippines Manulife Insular Life BPI-AIA BDO Life Etiqa FWD Insurance Allianz PNB Life Name Get a Quote
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident financial advisors can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed insurance company you’re interested in.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lecture-Style Classes. Many gen-eds, electives, and lower-level major courses will be lecture-style classes. These are large classes held in a lecture hall, a theater-like room that may seat hundreds of students. The professor talks for the entire class while students take notes. Lecture classes are common in first-year courses.
This is a type of dual degree in which a student completes three years of liberal arts study followed by two years of professional or technical study. In the end, students earn two bachelor's degrees, usually a BA and a BS. An example of this is Columbia University's 3-2 Combined Plan program in which students can earn a BA and a BS in five ...
7 Types of College Classes You Can Take. Colleges offer diverse course formats and specialized learning experiences. Studio and lab courses use a hands-on approach to apply theories and techniques. Seminars are discussion-oriented, while lectures feature more structured formats. Online classes offer accessibility through various learning platforms.
Here are the college degrees in order, from lowest ranking to highest: Associate degree (undergraduate) Bachelor's degree (undergraduate) Master's degree (graduate) Doctoral degree (graduate) While a doctorate is the highest education level, some fields may stop at a master's. The phrase "terminal degree" refers to the highest degree in a field ...
The length of residency programs varies by specialty but can last between three and seven years. Those who completed a professional degree have lifetime earnings of more than $4.7 million ...
Typical college degree programs include both required and elective courses. A core course is a course required by your institution, and every student must take it in order to obtain a degree. It's sometimes also called a general education course. Collectively, core courses are part of a core curriculum. Core courses are always essential to an ...
Here are four tips for choosing classes when you know your major: 1. Map out graduation requirements. Once you declare your major, learn which classes you are required to take to earn your degree. Then, map out which classes you will take over each semester leading up to your desired graduation date.
The coursework is dedicated to performing or visual arts and may also involve studying liberal arts like psychology, literature, and history. Bachelor of Business Administration. As one of the basic types of college degrees in business, the BBA programs cover accounting, management, business operations, marketing, and economics courses.
College Majors. A major is a specific subject area that students specialize in. Typically, between one-third and one-half of the courses you'll take in college will be in your major or related to it. Arts and Humanities. Programs in art and humanities take a multidisciplinary approach to education. They combine study of languages, literatures ...
Many schools have course codes that divide courses into 100, 200, 300, and 400-level classes. Lower division courses are usually 100 and 200-level. Most students take lower division courses in ...
Depending on your industry and career goals, there are several types of doctoral degrees to consider. A few include: Doctor of Business Administration (DBA): A terminal degree tailored to business professionals looking to explore, examine and address business issues. Doctor of Education (EdD): A doctoral degree geared toward leaders (and ...
STEM majors. The science, technology, engineering and math - collectively known as STEM - fields present a wide variety of in-demand and potentially high-paying jobs. Students with an aptitude ...
Here are the essentials of what they can expect in seven types of college classes. 1. Lecture. Picture a hundred seats facing a lectern and a screen, and you can learn a lot about a lecture-style class. Most often, these large classes consist of entry-level and/or requisite classes for specific majors or for graduation from the university.
TRY THE TEST. most commonly pursued degrees in the United States. associate degrees can help you transfer to a four-year course. Online courses can be an excellent option. academic and professional degrees can boost your job applications. Originally published on January 3, 2018. Contains contributions by Joanna Zambas.
College Majors List: Computer Science and Mathematics. Computer & Information Sciences, General. Computer Networking/Telecommunications. Computer Science & Programming. Computer Software & Media Applications. Computer System Administration. Data Management Technology. Information Science.
Courses that meet live on campus, including: Active learning weekend courses 1- or 3-week January session courses; Some premedical courses; Online synchronous courses with a required on-campus weekend, which have class meetings over Zoom plus a required weekend on campus. Flexible attendance courses that offer the option to participate on ...
Going to college means adopting a new set of responsibilities; building one's own class schedule is one significant such responsibility. Although college students are expected to choose majors and minors, they still have a lot of flexibility when it comes to choosing specific courses to take. Between general education courses, electives required by one's major and empty space in a semester ...
Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Jan 17, 2024. Earning your academic degree from an online college or university—sometimes called distance learning—has become an increasingly popular choice. Many students have increasingly chosen to earn their degree online in recent years. Nearly 2.5 million undergraduate students in the United ...
She specializes in education, technology and career development. She also writes satire and humor, which has appeared in Slackjaw, Points in Case, Little Old Lady Comedy, Jane Austen's Wastebasket, and Funny-ish. View her work and get in touch at: www.lauraberlinskyschine.com. This is a list of 200 college majors all in one place.
Please note, there are a couple of restrictions though: You can only apply maximum of four courses in any one of medicine, dentistry, veterinary medicine or veterinary science. Usually you can only apply to one course at either the University of Oxford or the University of Cambridge. There are exceptions - visit the University of Oxford and ...
Four-year and two-year colleges. Four-year institutions are referred to as undergraduate colleges. Four-year colleges specifically offer bachelor's degree programs. These include universities and liberal arts colleges. Two-year colleges offer certificate programs that can be completed in under two years. They also offer two-year associate degrees.
Types of College Degrees in the Philippines. There are four types of degrees in college that you can aim for. These are Bachelor's degrees, Master's, Doctoral, and Associate (vocational courses). These degrees give you the choice to further enhance your knowledge of the course/s you have chosen.
4-Year and 2-Year Colleges. Four-year colleges offer bachelor's degree programs. They're sometimes called undergraduate institutions or colleges. Two-year colleges provide associate degree programs and/or may offer certificate programs. Two-year institutions are sometimes called community colleges. They can also be vocational, technical, or ...