Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse? Essay
Nursing is a profession that has several significant advantages that motivate people to pursue it. Primarily, it is a field of education that allows people to build successful careers and gain the knowledge and skills to help others. Nurses have an excellent opportunity to get a high-quality education and to work in a decent environment. Furthermore, being a nurse allows people to fulfil their desire to help others and be of service to society in general. Therefore, I want to become a nurse because this profession will enable me to acquire significant knowledge and skills and realize my desire to help others.
Obtaining quality knowledge is one of the main reasons why I want to become a nurse. In this regard, access to a significant amount of evidence-based information for nursing students is vital (Daly & Jackson, 2020). Access to educational information and practice opportunities allows nurses to develop lifelong professional skills, which is a distinct advantage. In addition, the nurse’s professional development combines with the opportunity to help people in difficult situations. It is also essential to understand that nursing work involves several difficulties, including complex learning and stressful working experiences. Nevertheless, I consider these challenges insignificant since the desire to develop and help people allows me to ignore them. Overall, the contributions to society and individuals’ lives provide additional motivation to gain theoretical and practical knowledge.
People’s aspirations to become a nurse are based on the many benefits of this profession. Nursing is an appropriate choice for people who are eager to help others and ready to study and work hard for the greater well-being of society. The nursing profession also offers good educational and working conditions, which provides nurses with the opportunity for continuous professional development. Thus, the possibility of constant professional development and the potential to benefit society are the main reasons I want to become a nurse.
Daly, J., & Jackson, D. (2020). Contexts of Nursing : An introduction . Elsevier.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 17). Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse? https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-profession-why-to-become-a-nurse/
"Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse?" IvyPanda , 17 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-profession-why-to-become-a-nurse/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse'. 17 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse?" January 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-profession-why-to-become-a-nurse/.
1. IvyPanda . "Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse?" January 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-profession-why-to-become-a-nurse/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Nursing Profession: Why to Become a Nurse?" January 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nursing-profession-why-to-become-a-nurse/.
- Elements of Effective Lifelong Learner
- Lifelong Learning in Healthcare
- Lifelong Learning Plan
- Conception of Lifelong Learning in Society
- Consumer Needs and Marketing Research
- Contradictions Between Lifelong Learning and Management
- Eastern Gear Inc.'s Orders Delay Issue and Solution
- Discrepancies Between Aspirations and Reality in Healthcare
- Lifelong Learning and Older Adults Care
- Lifelong Learning in Bedside Nursing
- Professional Burnout Syndrome in Nurses
- How Nursing Professionals Can Benefit From Servant Leadership
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Its Management
- The Educational Perspectives in Nursing
- Mental Health Nurse’s Communication With Patients and Families

find nursing schools near you
What to include: why i want to be a nurse essay.
Why do you want to be a nurse? What is your reason for entering the nursing profession? What drives you?
You will face these questions multiple times throughout your career, but there are two occasions in which answering them could actually define your career.
The first is when you apply to nursing school. You may be asked to complete an essay outlining why you want to become a nurse.
The second time is when you apply for a nursing position and answer that question as part of the interview process.
Whether you're applying for a nursing program or job, it's important to know how to address this question and what sort of answers work best.
What To Include In Your Nursing Essay
To create the perfect nursing essay, one that can help you get into nursing school or find your first job, follow the steps below:
Plan Your Nurse Essay
Before you start writing your nursing essay, think about what you want to include.
Jot down ideas that express your passion for the nursing profession, as well as any personal or familiar experience that led you to take this step.
Be honest. Be open. Summarize your story, highlight your goals, and think about what the nursing profession means to you.
All of these things will be important when structuring your essay.
Show an Emotional Connection to the Profession
Do you have any family members that worked as nurses or doctors? Did you care for a loved one during an illness? Did you require a lot of care at some point in your life?
If so, this should be your lead, and it's probably the most important part of your essay.
Nursing is a lucrative career. You can make a decent salary, enter numerous specialties, and even progress to opening your own practice. There is also a national nursing shortage, so you'll also have plenty of opportunities if you're willing to learn and work. But interviewers don't want to hear that you became a nurse to earn good money and pick up lots of overtime.
Think of it in the context of a talent show. We know that the contestants are there to get famous and make lots of money. But when they stand in front of the camera and appeal for votes, they talk about deceased parents/grandparents, changing their family's life for the better, and making a difference in the world.
It's easy to sympathize with someone who wants to follow in the footsteps of a beloved mother or make a grandparent proud. It's not as easy to sympathize with someone who just wants to drive a Bugatti and wear a Rolex.
Examples :
"My mother is a nurse practitioner. I can see how happy the role makes her and how much it has changed her. I have looked up to her throughout my life and have always wanted to follow in her footsteps."
"I cared for my father when he was ill. I was able to comfort him and assist him in his time of need, and while it was very challenging, it always felt right to me and it's something I would love to do as a career."
Show That You Care
Like all health care workers, nurses are devoted to healing the sick. If you're not a people person, it's probably not the profession for you.
Make it clear that you're a caring person and are willing to devote your life to healing sick people. A good nurse also knows how to comfort distraught family members, so you may want to include this in your essay as well.
If you have any examples of times when you have helped others, include them. This is a good time to talk about volunteer work, as well as other occasions in which you have devoted your time to helping strangers.
"I feel a great sense of pride working with families and patients through difficult times. I like to know that I am making a difference in the lives of others."
"I want to become a nurse so that I can help others in their time of need. I chose nursing as a profession because I feel a great sense of accomplishment when helping others".
Share Your Aspirations
What are your goals for your nursing career? Do you want to become a nurse practitioner? Do you want to specialize as a nurse anesthetist, a critical care nurse, or focus more on pediatrics?
Nurses work across a range of specialties, and it's important to show that you are interested in continuing your education and developing to your full potential.
The goal is to show that you are determined. You are driven to succeed and to better yourself.
If you're just taking your first steps as a nursing student, now is a good time to research into specialties and get an idea of how you want your career to progress.
"I have always been drawn to the nursing profession because it's challenging, demanding, and interesting. I want to push myself every day, engaging my academic interests and satisfying my need to learn and improve as a person."
Describe Your Nursing Skills and Qualifications
If you're applying for an accelerated nursing program or a new nursing job, the interviewer will have access to your qualifications. But they won't know what those qualifications mean to you, what you learned from them, and how you can use them in your career.
It's about problem-solving skills, as well as academic work. It's about experience and personal growth, as well as knowledge acquisition.
This is a good time to talk about internships.
How Do You Write an Introduction to a Nurse Essay?
Starting is always the hardest part, but it's best not to overthink it.
Just start writing about why you want to become a nurse. Don't overthink it. Don't worry too much about the first word or sentence. Everything can be edited, and if you spend too long thinking about those first words, you'll never finish the essay.
Keep it simple, check your work, and edit it until it's perfect and says exactly what you want it to say.
16 Reasons to Choose a Career in Nursing

NurseJournal.org is committed to delivering content that is objective and actionable. To that end, we have built a network of industry professionals across higher education to review our content and ensure we are providing the most helpful information to our readers.
Drawing on their firsthand industry expertise, our Integrity Network members serve as an additional step in our editing process, helping us confirm our content is accurate and up to date. These contributors:
- Suggest changes to inaccurate or misleading information.
- Provide specific, corrective feedback.
- Identify critical information that writers may have missed.
Integrity Network members typically work full time in their industry profession and review content for NurseJournal.org as a side project. All Integrity Network members are paid members of the Red Ventures Education Integrity Network.
Explore our full list of Integrity Network members.

Do you have a passion for caring for people and want to see them get better? Consider a career in nursing.
Registered nurses (RNs) are in demand. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects RN jobs to grow faster than average between 2022-2032. New RN roles will open as an estimated third of nurses over 55 retire, according to the Journal of Nursing Regulation.
Nursing offers many entry-level nursing options , specialties, working environments and pathways for advancement. Learn 16 reasons why choosing a nursing career might be right for you.
1 | Nurses Make a Real Difference
Nurses do much more than perform medical tasks. As a nurse, you can make a real difference in someone’s life. You can offer hope to people, sometimes during the worst time of their life. Nurses often counsel patients and families after a devastating diagnosis, celebrate good news, and become trusted confidantes.
Nurses can also improve their communities through volunteering. In a 2017 survey , 74% of nurses pointed to non-work related activities when asked what they had done to improve their community’s health. Activities included health fairs, health-related volunteering, raising or donating money, and traveling for volunteer work.
“Oftentimes, people are alone in the hospital, and while they (of course) need medical care, they also sometimes just need a friend and to know that someone cares. As a nursing student, this is something you can do even on your first day.”
— Sarah Brooks, ABSN student
2 | Nursing Degree Programs Exist Everywhere
The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) ranks health professions second for the number of associate and bachelor’s graduates. Most large cities have many colleges and universities that offer an associate degree in nursing (ADN) or a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) program .
3 | Nurses Can Pursue Their Education Online
You can get your nursing degree through an accredited online nursing program anywhere in the U.S. Since nursing is a hands-on profession, you will be required to take classes online and complete in-person nursing clinicals in a healthcare setting.
It’s important to ensure any nursing program you attend is accredited by the Accreditation Commission for Education in Nursing or Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education . This is necessary to take the National Council Licensure Examination for RNs (NCLEX-RN) and master NCLEX-style test questions to get your license.
4 | Many Nursing Students Find Financial Aid Opportunities
Student debt can be overwhelming. Even with payback programs, it can take up to a decade to pay off school loans. Fortunately, nursing students have many ways to pay for nursing school .
Some options to reduce total debt include nursing scholarships and grants from various organizations. Financial aid is available for students seeking an associate, bachelor’s, master’s , and even DNP degree. Many hospitals also offer tuition reimbursement programs for staff looking to go back to school to get their ADN or BSN.
Financing your nursing school education doesn’t have to leave you with a lot of debt.
5 | Nurses Can Enter the Workforce Relatively Quickly
Several nursing degrees allow you to enter the workforce quickly. You can earn an ADN, pass the NCLEX-RN, and get your nursing license in as little as two years. Then, if you return to school to complete your bachelor’s degree, you can do it while earning a stable income.
Associate degrees in nursing are one of the highest paying associate degrees. According to Payscale data from October 2023 , graduates of an ADN program make $76,000 per year, which is $23,740 more than graduates of other associate degree programs.
Earning your BSN degree opens more opportunities for career advancement and a higher average annual salary of $92,000, according to Payscale .
6 | Nurses Have a High Level of Job Satisfaction
The 2019 American Mobile Nurses (AMN) Healthcare survey found that 81% of nurses were satisfied or extremely satisfied with their career choice.
When asked if they would encourage others to become a nurse, 70% said “yes.” The survey also found that supporting professional development was tied to job satisfaction.
When employers supported nursing professional development , 52% were extremely satisfied with their jobs. When employers did not support professional development, only 7% were extremely satisfied.
In 2023, the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) reported that 100,000 nurses left nursing during the pandemic because of increased workloads and rising levels of workplace violence , burnout , and nurse bullying .
About 800,000 expressed intent to leave by 2027. Yet, with all the challenges nurses face, nursing schools are still turning away tens of thousands of qualified applicants every year since 2019 because they do not have the nursing faculty to educate aspiring nurses.
Nursing schools nationwide need more nursing faculty. Yet, schools in midwestern states such as Wisconsin, Iowa, and Kansas, have about a 7% nurse faculty vacancy rate compared to about 10% vacancy rate in Southern and Western states, according to the American Association of Colleges of Nursing .
“When I speak with people and tell them my job, almost always the response is, ‘Once when I was sick, I had the best nurse take care of me, and I’ll always remember them helping me.’ It is a wonderful feeling to know we have helped.”
— Elizabeth Clarke, FNP, MSN, RN, MSSW
7 | Nurses Get to Do Exciting Work
Each day with patients can be different. Whether in a clinic, office, a hospital, or an organization, nursing is not dull. In the McKinsey Frontline Workforce Survey from November 2021 by AMN Healthcare, data showed that 32% of nurses had plans to leave their current positions. Only 29% of these nurses planned to stay in a direct patient care role.
The rest of the nurses had plans to move into a non-beside role , further their education, or leave the workforce to focus on their family or other life goals. Nurses who planned to leave direct patient care wanted work-life balance, flexible work hours, safe working environments, better compensation, and more manageable workloads.
“Nursing is incredibly versatile, and there are many ways to learn new skills and apply the ones you already have. It is one of the most exciting and unique things about nursing; you can be a chameleon and constantly change.”
8 | Nursing Is a Respected Field
In 1999, Gallup started a decades-long survey to determine the most ethical and honest profession. In January 2023, Americans ranked nurses in the number one position for an impressive 23 years. The only year nurses were not in the top spot was following September 11, 2001, when firefighters earned the highest score.
In addition to ranking first, nurses earned the highest score to date in 2020 for honesty and ethics. In 2020, the ranking was four percentage points higher than the last recorded high in 2019.
9 | Nurses Can Choose Their Specialty
Nurses are vital to delivering healthcare in many different settings. You can choose from over 100 nursing specialties , so you’ll likely never be bored.
You can focus on a specific population, such as gerontological nursing , or go into a more specialized field, such as a flight nurse or transplant nurse . You can also pursue roles that do not directly work with patients, such as health policy careers .
Nurses can easily move from one specialty to another. For example, after practicing as a dialysis nurse , you may wish to become a traveling nurse. If you are an experienced specialty nurse, you may be able to pick your assignments.
If you want to become a labor and delivery nurse , you may need some hands-on experience and continuing education for nurses before finding a new position.
10 | Nurses Work in a Stable Industry
By 2030, the entire baby boomer generation will have reached age 65. Up to 85% of older adults have at least one chronic health condition, and 60% have at least two. According to the BLS, nurses are in demand to care for a growing population of people with chronic diseases.
The BLS projects that job growth for nurses at all levels is expected to grow faster than average because of this demand. The projected job growth includes 118,600 nurse practitioner (NP) jobs and 177,400 RN jobs.
11 | Nurses Receive Excellent Benefits
Hospitals, clinics, and doctor’s offices may offer excellent benefits to attract and keep qualified professionals. For example, a nurse’s median annual salary of $81,220 is well above $46,310, which is the average annual salary of all occupations.
Travel nurses usually receive added benefits for filling an in-demand position on short notice and for the inconvenience of living and working in another city. They usually receive hazard pay or critical staffing pay in addition to the higher average hourly wage that travel nurses earn compared to staff nurses. These can include benefits to cover travel expenses and a stipend for housing, meals, and other bills.
Benefits for nurses include:
- Paid sick time
- Paid vacation and holidays
- Paid family leave
- Bonuses for working extra shifts or when understaffed
- Health and life insurance
- Tuition reimbursement
- Retirement benefits
- Wellness programs
- Subsidized travel
- Student loan repayment
- Shift differentials where nurses earn more for working holiday, weekend, or night shifts
12 | Nurses Develop Transferable Career Skills
Nursing offers the opportunity to adapt your professional life to fit your lifestyle. For example, you can find work in a variety of geographical locations and work environments. You may choose to work full or part-time and day or night-shift. You can also work shifts as short as four hours or as long as 12 and make more money in shift differentials.
In your first year of nursing school , you’ll develop and hone nursing skills like critical thinking, communication, and organizational skills. You will develop the ability to remain calm and focused in an emergency.
These skills can help you transition from clinical nursing to other non-bedside options , including nursing administration , nonprofit management in nursing , public health nursing , correctional facilities, or being a missionary nurse in clinics across the world.
“Nursing is also a flexible career with so many options. If you don’t like a certain floor or hospital, you can try another one. If you don’t like your current schedule, you can switch it. If you want to further your education and advance your career, there are many ways to do so.”
13 | Nursing Grads Have Smoother New Hire Transitions
All nurses experience orientation or onboarding as they move from an academic to a clinical setting after they graduate as a nurse . For many nurses working in large teaching hospitals, this transition may be eased by the hospital’s one-year nurse residency programs designed to help new nurses successfully transition from school to various work settings for nurses .
Although there is a nursing shortage across the U.S. , it is still challenging to get a premium job. You can improve your success by working while you’re in school to gain nursing experience and complete internships. Nursing students who gain volunteer experience and network while in nursing school also have an advantage when it’s time to apply for their first nursing job.
14 | Nurses Collaborate With Different Healthcare Professionals
Nurses play a unique role in healthcare. They spend a lot of time with patients at the bedside, so they must collaborate with healthcare teams to coordinate patient care and improve outcomes.
The bedside nurse is the hub of patient activity. They know the recommendations of each healthcare professional attending to the patient. Nurses need strong organizational and critical thinking skills to understand how each recommendation affects the overall care plan.
They must also explain the care plan and instructions to patients and their families in an understandable way.
“Nurses are often the first person to assess and examine a patient and to come up with differential diagnoses or an assessment of what the problem may be. From there, the nurse lets the attending physician or provider know the outcomes of the assessment.”
15 | Nurses Have Many Leadership Opportunities
The skills you learn caring for patients can help as you apply to a charge nurse role on the unit. Charge nurses must assign patient care and monitor the staff, making adjustments as needed during the shift.
Nurses with strong nursing leadership skills may go on to positions in administration, such as unit managers, clinical nurse leaders , patient care directors, or chief nursing officers .
You can also take advantage of leadership roles in clinical practice, including advanced practice nurses , clinical nurse specialists , and case managers . Nursing offers several avenues to take additional responsibility and progress up the career ladder.
16 | Nurses Are at the Forefront of the Telemedicine Movement
Telehealth nursing increased significantly during 2020 when healthcare providers began treating patients at home to reduce the spread of COVID-19.
The need for remote telemonitoring for patients in the intensive care unit or at home continues to grow. Remote monitoring can reduce costs for a hospital or physician’s office without sacrificing patient care.
Nurses are integral to patient consultations, taking patient histories and coordinating care at home. They are often the primary source of health education and monitoring. Incorporating telehealth services has given nurses a new tool to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Popular Online RN-to-BSN Programs
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial aid, and more by contacting the universities below.
A Nurse and a Nursing Student Share Why They Choose a Nursing Career

Elizabeth Clarke, FNP, MSN, RN, MSSW
Elizabeth Clarke is a board-certified family nurse practitioner. Her experience spans emergency departments, cardiac units, pediatric urgent care, and occupational health settings. She earned her bachelor of science in nursing and master’s in nursing from the University of Miami in Coral Gables, Florida.
Clarke is a paid member of the Red Ventures Education Integrity Network.

Sarah Brooks
I’m a mom to three daughters, currently enrolled in an accelerated nursing program. Prior to nursing school, I spent over a decade as a writer and editor in the personal finance niche. While I’ve enjoyed it, I’ve always felt a desire to go back to school to become a nurse. With my youngest starting kindergarten last August, I figured there was no better time for me to take the leap and return to school. My career goals include both working as a nurse and continuing to write and edit in the finance and healthcare spaces.
Sarah is a paid member of the Red Ventures freelance Education Student Network.
What experience of making a difference as a nurse would you share with a prospective student to help them understand how nurses make a difference?
I can remember feeling overwhelmed, working my first holiday shift as a new graduate RN.
It was New Year’s Day, my unit was busy and short-staffed. Patients and family members were short-tempered. I ran from patient room to patient room, getting their medications done relatively on time, monitoring vital signs, and ensuring my post-cardiac catheterization patients remained on bed rest.
I had a patient who needed monitoring, she was very sick, but was waiting on testing. She was frustrated, hungry, and thirsty. She was being kept NPO (nothing by mouth), since her doctors still did not know what was wrong with her.
Every time I passed by her room, she would call out and ask for help, needing reassurance. One of the times I stopped in, she began complaining of severe abdominal pain.
I looked at her abdomen and noticed it was beginning to appear distended. Her face was pale with pain, a fine sheen of sweat forming. I auscultated (listened to with my stethoscope) her abdomen, and heard nothing, no bowel sounds. I palpated her abdomen; it was rock hard.
I called the on-call internal medicine physician covering her that day. I quickly gave him a rundown of my concerns, how she looked, and her growing abdomen.
He came right up, we examined her together, and he went running to call a stat surgical consult. He asked me to drop an NG (nasogastric tube) down to see if we could decompress her, standard procedure if you suspect someone has an obstruction or ileus. I grabbed my supplies and my health care technician for help.
We went in and quietly explained to our patient what we needed to do, how we needed to help her, that I would try and get her pain under control and we would figure out what was wrong.
She was clenching her teeth in pain, fear, nausea, all of the above. We started prepping her to put in her NG tube when the surgery resident ran into the room, he began examining her in a brusque manner, pressing hard on her abdomen.
She cried out in pain, I remember quietly asking him if he would let me give her some IV pain medication quickly to minimize her pain while he finished the exam.
He gave me a quick nod and then called his attending on his cell phone in front of the patient, saying he needed an OR, stat. He then turned to my tech and me and told us to get her moving to the third floor OR suites now.
It was a tense moment, my patient did not understand what was happening, she was in severe pain, nauseous, and confused.
As we pushed her down the hall, grabbing additional staff for help, following the resident, I quickly told her they suspected a small bowel obstruction that was becoming worse, twisting her intestines, and they were rushing her so they could get her into the OR as soon as possible.
I remember promising her the on-call surgeon was very good, we would help her, and anesthesia would keep her comfortable so she would not feel any pain.
She asked to hold my hand. She wanted to know if I would be there when she woke up. I told her it depended on the time they finished the surgery, but I promised to tell the recovery room nurses to please hold her hand as they woke her up so she would know she was not alone.
I gave a quick bedside report to the receiving nurse and went back to my unit.
I was working the next day as well, and when I came into my unit, I looked in the system to see where my patient from the day before was. She was in the surgical ICU. I had a busy morning, so later in the afternoon, I asked my charge nurse if I could run down to the SICU to visit my patient, she agreed to watch my beds for me.
When I went into the SICU, I greeted some of my friends who were working and told them about my patient from the day before.
I connected with her nurse, she told me she was doing well, surgery was complicated by a previous liver transplant and lots of scar tissue. She said the surgery report noted the patient was quickly deteriorating and the obstruction was twisting the small bowel.
I went over to my patient’s bed and was surprised to see her awake and very alert. She smiled, reached for my hand, and thanked me. She started to cry, she told me no one had been listening to her when she tried to say something inside her was hurting.
She said she had felt ignored until she got transferred to my unit and I was her nurse. She told me she had felt very scared and discouraged, but when I told her I would take care of her and explained what was going on, she felt safe.
A decade and a half later, this patient is one I always remember even though I have cared for countless others since. I know I made a difference to her and provided excellent nursing care. We often speak of our nurses’ gut — our intuition.
On that New Year’s Day, I trusted my intuition; I knew something was very wrong. I listened to my patient and trusted my nursing assessment. I am glad I was able to make a difference in her life. She had a successful surgery — she survived — and was discharged to rehab for recovery a week later.
Sarah Brooks, ABSN Student
In my experience as a nursing student, it’s nurses that make or break a hospital stay. A kind, compassionate nurse who listens to their patients and does their best to meet their needs will be remembered.
My first shift in clinicals was on a Med-Surg floor specializing in disorders of the respiratory system. I was extremely nervous and had no idea what I was doing medical-wise, but I knew I could at least talk to my patients and provide a sense of comfort.
I had four patients in total and spent about an hour talking with them about why they were admitted to the hospital, how they were feeling, and other details of their lives. When I told them I was leaving for the day, they all individually thanked me for taking the time to sit with them.
Oftentimes, people are alone in the hospital and while they (of course) need medical care, they also sometimes just need a friend and to know that someone cares. As a nursing student, this is something you can do even on your first day.
What reasons do you have for being satisfied with choosing nursing as a career, even amid the challenges in the field right now? Why would you recommend nursing to prospective nursing students?
Nurse Elizabeth Clarke, FNP, MSN, RN, MSSW
I love being a nurse practitioner. I am proud to say I am a BSN RN and a family nurse practitioner.
I often have been with people in their hardest moments — when they are at their sickest, most injured, or most scared. I have been able to provide care, answer questions, hold a hand, and save lives.
Being an RN and now an NP has allowed me to fulfill my desire to help others and serve my patients and their families.
I recently saw a reel on a social media platform where the person filming it was speaking about hard times, and how we can choose to be someone’s light during their darkest hour. To me, this is what being an RN is all about.
We can be someone’s light; we are the helpers. At the end of some of my hardest shifts back when I was an RN, the days where I had too many patients, too high of an acuity, and no time to eat, I always knew I was helping.
Without my care, those patients may not have had their medications on time or had their pre-op workup completed, or been recovered from their procedure, or may have fallen when they tried to move from their bed to the bathroom.
When I speak with people and tell them about my job, almost always the response is, ‘Once when I was sick, I had the best nurse take care of me, and I’ll always remember them helping me.’ It is a wonderful feeling to know we have helped.
Nursing is a second career for me and is something that had been in the back of my mind for many years. I knew I had to at least give it a shot. From what I’ve experienced so far, the rewards of nursing outweigh the hard times by far.
I, personally, am satisfied with choosing nursing as a career because it’s truly a job that makes a difference.
It’s not always going to feel that way, but when push comes to shove, it is us nurses that the patients will remember. It’s up to us whether their hospital stay is an excellent one or a poor one. I love knowing that I’m directly impacting the lives of patients day in and day out.
Nursing is also a flexible career with so many options. If you don’t like a certain floor or hospital, you can try another one. If you don’t like your current schedule, you can switch it.
If you want to further your education and advance your career, there are many ways to do so. There are school nursing, work-from-home nursing jobs, per diem jobs, and more.
While the main thing that drew me to the career was my interest in the medical field and the ability to make a difference in the lives of others, the schedule flexibility and opportunities for advancement helped to solidify my decision.
What do you find exciting about your nursing career?
I work in occupational medicine currently, so while it is not quite as exciting as my days back in the ED or cardiac unit, it does have its moments of excitement and busyness.
One of the most exciting things about being an RN is that you can work almost anywhere in the medical field.
If working with children interests you, choose pediatrics. If surgery is where your interests lie, think about working in the operating room as a scrub nurse, or in the pre or post-operative units prepping and recovering patients.
Are you someone who craves an adrenaline rush to keep you on your toes at work? The emergency department is your place then, there is never a boring moment. From overdoses, to accidents, and illnesses, the ED is hopping.
If you tire or are burnt out in your chosen area, you can switch to a different area of nursing. Nursing is incredibly versatile. There are many ways to learn new skills and apply the ones you already have. It is one of the most exciting and unique things about nursing, you can be a chameleon and constantly change.
The entire job of a nurse is exciting because anytime you walk through the hospital doors, you truly don’t know what you’ll walk into.
You never know if you’ll have a smooth, calm day or a crazy, hectic one. Things can take a turn for the worse at any time and on any floor, so you always need to be prepared and keep an eye on your patients at all times.
I also get excited thinking about my future as a nurse and what that will look like.
Again, this is a career with so many options and opportunities. I’ve toyed with everything from going back to school to pursue my nurse anesthetist degree (CRNA) to working from home as a nurse writer.
Only time and experience will determine what I’ll land on, but I definitely get excited thinking about all the possibilities.
How would you say about how the nurse’s pivotal role in coordinating patient care with the rest of the healthcare helps make nursing a good career choice?
As nurses, we are constantly in contact with other healthcare professionals. From doctors, NPs, or PAs to therapists (physical, occupational, speech or mental health), to registered dieticians, and more, we must collaborate with other professionals regarding what is best for our patients.
Nurses are often the first people to assess and examine a patient and to come up with differential diagnoses or an assessment of what the problem may be.
From there, the nurse lets the attending physician or provider know the outcomes of the assessment. In this way, nurses have a unique position to see, assess and call attention to a problem.
Nurses are excellent at knowing what other care a patient may need, and how to ask for that help. If a nurse sees a patient struggling to swallow, asking for a referral to speech therapy can help ensure the safety of that patient so they do not aspirate.
Nurses are often asked by the provider how the patient is doing and what their needs are – this is an example of the provider realizing the pivotal roles nurses play.
Collaboration in nursing is often mentioned during nursing school, because of this, nurses develop excellent collaboration skills.
Nursing is a great career choice for those who want to help, care, and collaborate for the best outcomes of their patients.
Nurses are the eyes and ears of the hospital. If something goes wrong, it’s almost always a nurse who catches it first. We are the ones in the hospital 24/7.
Doctors, of course, have a pivotal role in determining treatment plans and helping patients recover, but it’s the nurses who play out the treatment plan, see how the patient is responding, and keep the doctor in the loop on any changes.
In my (limited) experience, one thing I’ve really come to learn is that it truly takes a patient care team to treat the patient. All roles are equally necessary and important.
Not only do nurses collaborate with other members of the healthcare team, but also with the family members of the patient. This could be in person or by calling a family member to update them on the status of their loved one.
The nurse not only provides comfort to the patient, but to the family members, as well.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nursing Careers
What are the reasons for choosing nursing as a career.
Most nurses choose to work in the profession to help others live better lives. Whether you work in a hospital, clinic, missionary clinic overseas, administration, or correctional facility, the underlying reason most nurses choose the profession is to help those in need. Another reason is that nursing is a high-paying career with advancement opportunities and flexibility.
How hard is it to become a nurse?
You can become a nurse in as little as two years by completing an ADN. You can further advance your career options and salary by earning a BSN degree. You can do this in two years if you already have an RN license, online or in the classroom and while you continue to work. You can also earn an accelerated BSN degree if you hold a bachelor’s in another field.
What qualities do you need to be a nurse?
Nurses are compassionate, patient, and understanding. They have strong critical thinking, communication, and organizational skills. You may not have these skills at the start of your nursing education but will develop them in your nursing program and hone them in your practice.
How do I know if nursing is right for me?
If you are curious to learn more about health and wellness and have a desire to help others, consider speaking with an admission counselor at your local college or university. You may also want to consider volunteering in a hospital or shadowing a nurse for a shift.
Page last reviewed on November 2, 2023
You might be interested in

The 20 Best Nursing Career Specialties Based On Salary
Interested in nursing, but unsure which career track is best for you? This guide describes the 20 best nursing career specialties and how to get started in these fields.

The 35 Best Specialty Career Choices for Nurses
Explore the best specialty career options available to nurses while reviewing the potential job growth and salary potential for each.

160+ Most Popular Nursing Job & Career Titles
Whatever your healthcare career goals, there’s a nursing specialty that fits your interests. Use this nursing jobs list to explore some of your options.
How to Write a Nursing Essay with a Quick Guide

Ever felt the blank-page panic when assigned a nursing essay? Wondering where to start or if your words will measure up to the weight of your experiences? Fear not, because today, we're here to guide you through this process.
Imagine you're at your favorite coffee spot, armed with a cup of motivation (and maybe a sneaky treat). Got it? Great! Now, let's spill the secrets on how to spin your nursing tales into words that not only get you that A+ but also tug at the heartstrings of anyone reading. We've got your back with nursing essay examples that'll be your inspiration, an outline to keep you on the right path, and more!
What Is a Nursing Essay
Let's start by dissecting the concept. A nursing essay serves as a focused exploration of a specific aspect of nursing, providing an opportunity for students to demonstrate their theoretical knowledge and its practical application in patient care settings.
Picture it as a journey through the challenges and victories of a budding nurse. These essays go beyond the classroom, tackling everything from tricky ethical dilemmas to the impact of healthcare policies on the front lines. It's not just about grades; it's about proving, 'I'm ready for the real deal.'
So, when you read or write a nursing essay, it's not just words on paper. It's like looking into the world of someone who's about to start their nursing career – someone who's really thought about the ins and outs of being a nurse. And before you kick off your nursing career, don't shy away from asking - write my essay for me - we're ready to land a professional helping hand.
How to Start a Nursing Essay
When you start writing a nursing essay, it is like gearing up for a crucial mission. Here's your quick guide from our nursing essay writing service :

Choosing Your Topic: Select a topic that sparks your interest and relates to real-world nursing challenges. Consider areas like patient care, ethical dilemmas, or the impact of technology on healthcare.
Outline Your Route : Plan your essay's journey. Create a roadmap with key points you want to cover. This keeps you on track and your essay on point.
Craft a Strong Thesis: Assuming you already know how to write a hook , kick off your writing with a surprising fact, a thought-provoking quote, or a brief anecdote. Then, state your main argument or perspective in one sentence. This thesis will serve as the compass for your essay, guiding both you and your reader through the rest of your writing.
How to Structure a Nursing Essay
Every great essay is like a well-orchestrated performance – it needs a script, a narrative that flows seamlessly, capturing the audience's attention from start to finish. In our case, this script takes the form of a well-organized structure. Let's delve into the elements that teach you how to write a nursing essay, from a mere collection of words to a compelling journey of insights.

Nursing Essay Introduction
Begin your nursing essay with a spark. Knowing how to write essay introduction effectively means sharing a real-life scenario or a striking fact related to your topic. For instance, if exploring patient care, narrate a personal experience that made a lasting impression. Then, crisply state your thesis – a clear roadmap indicating the direction your essay will take. Think of it as a teaser that leaves the reader eager to explore the insights you're about to unfold.
In the main body, dive into the heart of your essay. Each paragraph should explore a specific aspect of your topic. Back your thoughts with examples – maybe a scenario from your clinical experience, a relevant case study, or findings from credible sources. Imagine it as a puzzle coming together; each paragraph adds a piece, forming a complete picture. Keep it focused and let each idea flow naturally into the next.
Nursing Essay Conclusion
As writing a nursing essay nears the end, resist the urge to introduce new elements. Summarize your main points concisely. Remind the reader of the real-world significance of your thesis – why it matters in the broader context of nursing. Conclude with a thought-provoking statement or a call to reflection, leaving your reader with a lasting impression. It's like the final scene of a movie that leaves you thinking long after the credits roll.
Nursing Essay Outline
Before diving into the essay, craft a roadmap – your outline. This isn't a rigid skeleton but a flexible guide that ensures your ideas flow logically. Consider the following template from our research paper writing service :
Introduction
- Opening Hook: Share a brief, impactful patient care scenario.
- Relevance Statement: Explain why the chosen topic is crucial in nursing.
- Thesis: Clearly state the main argument or perspective.
Patient-Centered Care:
- Definition: Clarify what patient-centered care means in nursing.
- Personal Experience: Share a relevant encounter from clinical practice.
- Evidence: Integrate findings from reputable nursing literature.
Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice
- Scenario Presentation: Describe a specific ethical challenge faced by nurses.
- Decision-Making Process: Outline steps taken to address the dilemma.
- Ethical Frameworks: Discuss any ethical theories guiding the decision.
Impact of Technology on Nursing
- Current Trends: Highlight technological advancements in nursing.
- Case Study: Share an example of technology enhancing patient care.
- Challenges and Benefits: Discuss the pros and cons of technology in nursing.
- Summary of Key Points: Recap the main ideas from each section.
- Real-world Implications: Emphasize the practical significance in nursing practice.
- Closing Thought: End with a reflective statement or call to action.
A+ in Nursing Essays Await You!
Ready to excel? Let us guide you. Click now for professional nursing essay writing assistance.
Nursing Essay Examples
Here are the nursing Essay Examples for you to read.
Writing a Nursing Essay: Essential Tips
When it comes to crafting a stellar nursing essay, a few key strategies can elevate your work from ordinary to exceptional. Here are some valuable tips from our medical school personal statement writer :

Connect with Personal Experiences:
- Approach: Weave personal encounters seamlessly into your narrative.
- Reasoning: This not only adds authenticity to your essay but also serves as a powerful testament to your firsthand understanding of the challenges and triumphs in the nursing field.
Emphasize Critical Thinking:
- Approach: Go beyond describing situations; delve into their analysis.
- Reasoning: Nursing essays are the perfect platform to showcase your critical thinking skills – an essential attribute in making informed decisions in real-world healthcare scenarios.
Incorporate Patient Perspectives:
- Approach: Integrate patient stories or feedback into your discussion.
- Reasoning: By bringing in the human element, you demonstrate empathy and an understanding of the patient's experience, a core aspect of nursing care.
Integrate Evidence-Based Practice:
- Approach: Support your arguments with the latest evidence-based literature.
- Reasoning: Highlighting your commitment to staying informed and applying current research underscores your dedication to evidence-based practice – a cornerstone in modern nursing.
Address Ethical Considerations:
- Approach: Explicitly discuss the ethical dimensions of your topic.
- Reasoning: Nursing essays provide a platform to delve into the ethical complexities inherent in healthcare, showcasing your ability to navigate and analyze these challenges.
Balance Theory and Practice:
- Approach: Connect theoretical concepts to real-world applications.
- Reasoning: By bridging the gap between theory and practice, you illustrate your capacity to apply academic knowledge effectively in the dynamic realm of nursing.
Highlight Interdisciplinary Collaboration:
- Approach: Discuss collaborative efforts with other healthcare professionals.
- Reasoning: Acknowledging the interdisciplinary nature of healthcare underscores your understanding of the importance of teamwork – a vital aspect of successful nursing practice.
Reflect on Lessons Learned:
- Approach: Conclude with a thoughtful reflection on personal growth or lessons from your exploration.
- Reasoning: This not only provides a satisfying conclusion but also demonstrates your self-awareness and commitment to continuous improvement as a nursing professional.
As we wrap up, think of your essay as a story about your journey into nursing. It's not just about getting a grade; it's a way to share what you've been through and why you want to be a nurse.
Imagine the person reading it – maybe a teacher, a future coworker, or someone starting their nursing journey. They're trying to understand your passion and why you care about nursing.
So, when you write, remember it's more than just an assignment. It's your chance to show why nursing matters to you. And if you ever need help – there's always support from our essay writer online .
Ready to Excel in Your Nursing School Essay?
Order now and experience the expertise of our professional writers!
How to Write a Nursing Essay?
How can a nursing essay effectively address ethical considerations, what are some examples of evidence-based practices in nursing essays, related articles.
.webp)
Nursing as a Profession: Old Tensions, New Insights
- First Online: 21 August 2019
Cite this chapter

- Ricardo A. Ayala 2
483 Accesses
This chapter intends to update the social theory of the professions as applied to nursing. It draws on the premise that a profession cannot be defined by a set of structural traits or in reference to characteristics that are idiosyncratic to a dominant culture, questioning available explanations that define nursing as a semi-profession. While addressing the notion of profession in light of its historical origins, it introduces the reader to the main sociological frameworks to analyse the professions, with emphasis on their application to the nursing-as-a-profession rhetoric. This theoretically informed chapter proposes the notion of “social ecology of nursing,” which draws attention to systemic transformations rather than institutional achievements, for more comprehensive analyses of the profession. The focus is thus on the continuous interplay between professions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abbott, A. (1988). The system of professions: An essay on the division of expert labor . Chicago: The University of Chicago.
Book Google Scholar
Abbott, A. (2001). Chaos of disciplines . Chicago: University Chicago Press.
Google Scholar
Abbott, A. (2005). Linked ecologies: States and universities as environments for professions. Sociological Theory, 23 (3), 245–274.
Abbott, A. (2010). Varieties of ignorance. The American Sociologist, 41 (2), 174–189.
Article Google Scholar
Acker, J. (2011). Theorizing gender, race, and class in organizations. In E. Jeanes, D. Knights, & P. Y. Martin (Eds.), Handbook of gender, work and organization (pp. 65–80). Chippenham: Wiley.
Adkins, L. (1995) Gendered work: Sexuality, family and the labour market . Buckingham: Open University Press.
Allan, H. (2001). A ‘good enough’ nurse: Supporting patients in a fertility unit. Nursing Inquiry, 8 (1), 51–60.
Allen, D. (2007). What do you do at work? Profession building and doing nursing. International Nursing Review, 54, 41–48.
Andersen, M. L., & Collins, P. H. (1995). Race, class and gender: An anthology . Boston: Wadsworth.
Anh, T. T., & Winter, R. (2010). Processes of modernisation in two public universities in Vietnam: University managers’ perspectives. In G. Harman, M. Hayden, & T. N. Pham. Reforming higher education in Vietnam: Challenges and priorities (pp. 155–166). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer.
Bixler, G., & Bixler, R. (1959). The professional status of nursing. American Journal of Nursing, 59 (8), 1142–1147.
Bouckaert, B. (2007). The roots of our liberties: On the rise of civil society in the medieval west. New Perspectives on Political Economy, 3 (2), 139–184.
Bourdin, B. (2004). La genèse théologico-politique de l’Etat moderne . Paris: Les Presses Universitaires de France.
Brante, T. (1988). Approaches to the professions. Acta Sociologica, 31 (2), 119–142.
Carr-Saunders, A. M., & Wilson, P. A. (1933). The professions . Oxford: Clarendon.
Clegg, S. R., Harris, M., & Höpfl, H. (2011). Managing modernity: Beyond bureaucracy? Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cody, W., & Kenney, J. (2006). Philosophical and theoretical perspectives for advanced nursing practice . London: Jones & Bartlett.
Collins, R. (1994). Four sociological traditions . New York: Oxford University Press.
Cutcliffe, J., & Wieck, K. L. (2008). Salvation or damnation: Deconstructing nursing’s aspirations to professional status. Journal of Nursing Management, 16, 499–507.
Dahrendorf, R. (1996). Zu einer Theorie des sozialen Konflikts. In T. Bonacker (Ed.), Konflikttheorien. Eine sozialwissenschaftliche Einführung mit Quellen (pp. 279–295). Opladen: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Dahrendorf, R. (2011). The modern social conflict: The politics of liberty . New Brunswick: Transaction Publisher.
Davies, C. (1995). Gender and the professional predicament in nursing . Buckingham: Open University Press.
Davies, C. (2004). Political leadership and the politics of nursing. Journal of Nursing Management, 12 (4), 235–241.
Dingwall, R. (2008). Essays on professions . Aldershot: Ashgate.
Dreher, H. M., & Glasgow, M. E. S. (2011). Role development for doctoral advanced nursing practice . New York: Springer.
Dubar, C., & Tripier, P. (1998). Sociologie des professions . Paris: Colin.
Evetts, J. (2002). New directions in state and international professional occupations: discretionary decision-making and acquired regulation. Work, Employment & Society, 16 (2), 341–353.
Evetts, J. (2013). Professionalism: Value and ideology. Current Sociology, 61 (5–6), 778–796.
Fealy, G. M. (2006). A history of apprenticeship nurse training in Ireland . Abingdon and New York: Routledge.
Flexner, A. (1915). Is social work a profession? In Proceedings of the National Conference of Charities and Correction (pp. 577–590). Chicago: Hildemann.
Freidson, E. (1970). Profession of medicine . New York: Dodd Mead.
Friedman, L. M. (1973). A history of American law . New York: Simon & Schuster.
Godwyn, M., & Gittell, J. H. (2011). Sociology of organizations: Structures and relationships . Los Angeles: Sage Publications.
Gomm, R. (1996). Professions and professionalism. In V. Aitken & H. Jellicoe (Eds.), Behavioural science for health professionals (pp. 104–122). London: Macmillan.
Greiner, D. S., Glick, D. F., Kulbok, P. A., & Mitchell, E. M. (2008). Rural health nursing research review: Global perspectives. Annual Review of Nursing Research, 26 , 261–294.
Group, T. M., & Roberts, J. M. (2001). Nursing, physician control, and the medical monopoly: Historical perspectives on gendered inequality in roles, rights, and range of practice . Bloomington: Indiana University.
Gourdin, G., & Schepers, R. (2009). Hospital governance and the medical practitioner in Belgium. Journal of Health Organization and Management, 23 (3), 319–331.
Grunig, L. A., Toth, E. L., & Hon, L. C. (2008). Women in public relations: How gender influences practice . Hillsdale, NJ: Routledge.
Hahn, H. J. (1995). German thought and culture: From the Holy Roman Empire to the present day . New York: Manchester University Press.
Handel, M. J. (2003). The sociology of organizations: Classic, contemporary, and critical readings . Thousand Oaks and London: Sage.
Hiscott, R. (1998). Career paths of nursing professionals: A study of employment mobility . Ottawa: Carleton University Press.
Hood, L. J. (2006). Leddy S. Leddy & Pepper’s conceptual bases of professional nursing . Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Hughes, E. C. (1958). Men and their work . New York: Free Press.
Jara, P., Behn, V., Ortiz, N., & Valenzuela, S. (2009). Nursing in Chile. In K. L. Breda (Ed.), Nursing and globalization in the Americas: A critical perspective (pp. 55–98). Amityville, New York: Baywood.
Jetin, B. (2010). Industrial upgrading and educational upgrading: Two critical issues for Thailand. In P. Intarakumnerd & Y. Lecler (Eds.), Sustainability of Thailand’s competitiveness: The policy challenges (pp. 78–128). Bangkok: ISEAS-IRASEC.
Johnson, P., Wood, G., Brewster, C., & Brookes, M. (2009). The rise of post-bureaucracy: Theorists’ fancy or organizational praxis? International Sociology, 24 , 37–61.
Jones, R. K., & Stewart, A. (1998). The sociology of the health professionals. In D. Jones et al. (Eds.), Sociology and occupational therapy, an integrated approach (pp. 131–142). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Levay, C., & Waks, C. (2009). Professions and the pursuit of transparency in healthcare: Two cases of soft autonomy. Organization Studies, 30 (5), 509–527.
Mpevo Mpolo, A. (2012). Les quatre tournants manqués de l’Université congolaise: Analyse des réformes académiques du Congo-Zaïre (1971–2011) . Paris: L’Harmattan.
Nancarrow, S. A., & Borthwick, A. M. (2006). Dynamic professional boundaries in the healthcare workforce. Sociology of Health & Illness, 27 (7), 897–919.
Neal, M., & Morgan, J. (2000). The professionalization of everyone? A comparative study of the development of the professions in the United Kingdom and Germany. European Sociological Review, 16 (1), 9–26.
Obong Oula, Q. (2004). Academic dilemmas under neo-liberal education reforms: A review of Makerere University, Uganda. In P. Zeleza & A. Olukoshi (Eds.), African Universities in the twenty-first century (pp. 108–125). Pretoria, South Africa: UNISA Press.
Parsons, T. (1939). The professions and social structure. Social Forces, 17 (4), 457–467.
Porter, S. (1992). The poverty of professionalization: A critical analysis of strategies for the occupational advancement of nursing. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 17 (6), 720–726.
Prest, W. (1987). The professions in early modern England . London: Croom Helm.
Reed, J. (1993). The relationship between semi-professions in acute and long-term care of elderly patients. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 2 (2), 81–87.
Sciulli, D. (2005). Continental sociology of professions today: conceptual contributions. Current Sociology, 53 (6), 915–942.
Shi, L., & Singh, D. A. (2009). The evolution of health services in the United States. In A. M. Barker (Ed.), Advanced practice nursing: Essential knowledge for the profession (pp. 129–160). Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett.
Thornhill, C. J. (2006). German political philosophy: The metaphysics of law . New York: Routledge.
Traynor, M. (1999). Managerialism and nursing: Beyond oppression and profession . London: Routledge.
Traynor, M., Boland, M., & Buus, N. (2010). Professional autonomy in 21st century healthcare: Nurses’ accounts of clinical decision-making. Social Science & Medicine, 71 (8), 1506–1512.
Ueno, C. (1996). Fukugo sabetsu ron [The theory of conceptual discrimination]. In S. Inoue, C. Ueno, M. Osawa, M. Mita, & S. Yoshimi (Eds.), Sabetsu to kyosei no shakaigaku [Sociology for discrimination and coexistence] (pp. 203–232). Tokyo: Iwanami Shoten.
Ushiro, R., & Nakayama, K. (2010). Gender role attitudes of hospital nurses in Japan: Their relation to burnout, perceptions of physician–nurse collaboration, evaluation of care, and intent to continue working. Japan Journal of Nursing Science, 7 (1), 55–64.
Vanderstraeten, R. (2007). Professions in organizations, professional work in education. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 28 (5), 621–635.
Watson, J. (1999). Nursing: Human science and human care—A theory of nursing . Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett.
Weston, W. (2011). The college class at work and home. Society, 48 (3), 236–241.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sociology, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium
Ricardo A. Ayala
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ricardo A. Ayala .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Ayala, R.A. (2020). Nursing as a Profession: Old Tensions, New Insights. In: Towards a Sociology of Nursing. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8887-3_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8887-3_2
Published : 21 August 2019
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-8886-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-8887-3
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res
- v.19(1); Jan-Feb 2014
Nursing professionalism: An evolutionary concept analysis
Fataneh ghadirian.
1 Department of School of Nursing and Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Towhid Sq, Tehran, Iran
Mahvash Salsali
Mohammad ali cheraghi, background:.
Professionalism is an important feature of the professional jobs. Dynamic nature and the various interpretations of this term lead to multiple definitions of this concept. The aim of this paper is to identify the core attributes of the nursing professionalism.
Materials and Methods:
We followed Rodgers’ evolutionary method of concept analysis. Texts published in scientific databases about nursing professionalism between 1980 and 2011 were assessed. After applying the selection criteria, the final sample consisting of 4 books and 213 articles was selected, examined, and analyzed in depth. Two experts checked the process of analysis and monitored and reviewed them.
The analysis showed that nursing professionalism is determined by three attributes of cognitive, attitudinal, and psychomotor. In addition, the most important antecedents concepts were demographic, experiential, educational, environmental, and attitudinal factors.
Conclusion:
Nursing professionalism is an inevitable, complex, varied, and dynamic process. In this study, the importance, scope, and concept of professionalism in nursing, the concept of a beginning for further research and development, and expanding the nursing knowledge are explained and clarified.
I NTRODUCTION
“Professionalization” is an important characteristic of in-service careers.[ 1 ] The concept of professionalization is expressed in the terminology of many job groups and has a long history, especially in social context. Dynamic feature and multiple interpretations of professionalization result in numerous definitions with different functions and nature.[ 2 ] Over the years, many people spoke about professionalization in nursing and its features. Therefore, there are multiple definitions and characteristics for professionalization in nursing.[ 3 , 4 , 5 ] Also, researchers used different methods and tools for its assessment and evaluation.
Nursing profession status is an inter-profession and intra-profession challenge. Whether there is nursing professionalism or not is a challenge among the nurses, sociologists, and historians.[ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ] For many years, other scientists considered nursing as a semi-professional career.[ 3 ] Until 1970, nursing profession was considered as a female work and women were considered as barriers to professionalization in nursing due to their high workload and part-time work.[ 11 ] At that time, some factors such as slow formation of scientific fundamentals of nursing, disagreement in educational requirements for nurses,[ 10 , 12 , 13 ] lack of academic education at the entry level of nursing courses, and lack of theory and theory-based research[ 14 ] were considered as barriers for nursing as a profession.
Gradually, development of education standards and professional certificates led nursing move to professional status.[ 3 ] Having stronger powerful basis for theory and practice and professional education in nursing discipline brought about social cognition. Social understanding about nursing made the society consider nurses as cost–benefit health care providers and independent decision makers. Therefore, nursed could receive more funds and governmental financial aids.[ 15 ]
Today's rapid changes in value systems in society caused nursing to encounter more ethical and philosophical challenges at providing care to its clients. These changes also created new nursing environments that require professional nursing. Accordingly, nursing professionalization definition and its attributes need to be clarified and adapted with rapid changes. For this purpose, concept analysis is a suitable method.
Concepts are the building blocks of theories.[ 16 ] They have important role in theory development. Concept analysis is one of the strategies in concept development. In this strategy, the basic elements of a concept for understanding its structure and function are assessed. During concept analysis process, a researcher, theorist, or clinician becomes familiar with different attributes and definitions of concept and its function.
Evolutionary approach of Rodgers in concept analysis is based on contemporary philosophical thinking on concepts and their roles in knowledge development. In this approach, dynamic features of concepts over time and different social contexts are emphasized.[ 17 ] Form evolutionary perspective, instead of emphasis on “what is it?,” more discovery and assessment are mostly focused. Consequently, this process results in a form of cyclical concept development. With this approach, the final results are the starting point for more concept analysis.[ 17 ] Purpose of concept analysis in this approach is to explain the concept and its attributes more clearly for its further development.[ 18 ]
Accordingly, the purpose of the current study is assessment of “nursing professionalization” concept to understand more about its attributes, antecedents, and consequences. Since the contemporary nursing believed human and other nursing phenomena have constantly a changing and interrelated context, it seems that nursing professionalization is also better understood in the context. This perspective is congruent with evolutionary approach in concept analysis.
M ATERIALS AND M ETHODS
While there are several methods of concept analysis,[ 19 ] an evolutionary approach was selected as the concept of nursing professionalization depends on the context and can be interpreted only when the different parameters appear in a specific context.[ 17 ] Although this approach of studying recommends six preliminary activities [ Table 1 ], Rogers believes that many of these activities take place simultaneously during the study. Study process has a non-linear, rotational, and flexible nature. The six stages merely indicate activities that should take place during the study, and it should not be regarded as a continuous process. In this way, Rogers uses inductive approach and detailed analysis and focuses on the collection and analysis of raw data. In this approach, concepts in the specific social and cultural context of a given profession are studied.[ 17 , 20 ]
Rodgers’ evolutionary concept analysis process

After identifying the concept of interest, the most important step is determining the scope and range of literature.[ 20 ] The scientific databases, PubMed, CINAHL, MEDLINE, ProQuest, and EBM REVIEW, were searched. In a preliminary search, the term “professional nurse” was used. Next, to achieve more precise results, the inclusion criteria were identified. The main criterion for inclusion in the final analysis was the literature published in English from 1980 to 2011 in the context of nursing and health sciences. The exclusion criterion was non-English language articles. Preliminary results of the search gave 250 articles meeting the inclusion criteria, and after deleting the duplicated items (14 items), the number decreased to about 236. In the final stage, 213 articles had the term “professional nurse” in their title or abstract, and their full texts, if available and that too in the nursing field, were chosen. In addition, four books were used in the analysis process to cover the subjects. Books and papers were carefully reviewed and studied. For analyzing, thematic analysis and content analysis were used. All articles in the context of nursing were exactly read, and hints and useful features, antecedents, consequences, related concepts, surrogate terms, and definition of concept were extracted. Then, the data were reviewed several times to allow the researcher to be immersed in, and this enabled deriving key tags and notes to provide clear explanations about every aspect of the concept. Overall, inductive analysis of data was done and themes were identified. Information units consisted of the words and sentences related to the information or responses concerning the following questions: What are the specific characteristics of professional nursing? How do you define nursing professionalization? How do you pretend nursing professionalization? What factors are associated with the incidence of professional nursing? What are the consequences or outcomes of nursing professionalization? Papers based on conceptual analysis of studied information were grouped. In order to ensure impartiality, reliability, and bias reduction, the analysis process was checked by two nursing experts in concept analysis.
Identification of the characteristics of the concept is the first stage of the analysis that leads to the actual definition of the concept.[ 20 , 21 ] Characteristics of a concept, including features and specifications of a concept that have been permanently associated with the concept, help identify the clarity, breadth, and depth of that concept.[ 19 ] In this study, the conceptual dimensions of nursing professionalization were identified as cognitive, affective, and psychomotor dimensions.
Cognitive dimension of nursing professionalization
Nursing education should be able to develop professional knowledge.[ 22 ] All learners should have a basic cognitive framework for understanding the professionalization. It seems that getting all the essential aspects of professional knowledge in all phases of professionalization must be considered and principles of professionalization must be combined at different levels of professional education.[ 23 ] Learner development begins from a basic understanding of the underlying principles of professional conduct and the underlying reasons, and ultimately, the learner should be able to prioritize and make decisions.[ 24 ]
Walton et al . (2010) assigned five stages of training to professional nurse education as follows: (1) create a practical fake identity of a professional nurse in students, (2) trial and error, (3) the seriousness of the conduct; (4) transfer to the bedside, and 5) professionalization.[ 25 ] Some studies suggest that certain training courses such as ethics, research, or professionalization should be included in the professional training program in nursing.[ 26 ] Professional training courses can be temporary and occur during periods of formal or informal education. Professional training in formal programs can be provided with specific workshops and courses of training development modules,[ 27 ] working in small groups on problem-solving, use of role play, simulated patients,[ 28 ] or clinical courses.[ 29 ] On the other hand, usually students learn values and norms in informal trainings.[ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ] For this purpose, there must be a professional learning environment.[ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ] Role modeling and changing the organizational culture can be effective in non-formal education.[ 39 ] Every training program should be designed to meet the expectations concerning professionalization.[ 40 ]
In the area of professional learning, continuing education is very important. UKCCN (United Kingdom Central Council for Nursing) states that all nurses should provide a certificate of professional updating every 3 years.[ 41 ] However, continuing education cannot be considered as the only criterion and antecedent for professionalization, as until mastery of knowledge is not combined with a personal value system and transferred to action, it cannot have a true function.[ 42 ] Making this commitment to continuous learning is the primary task of professional education.[ 43 , 44 , 45 ]
Attitudinal dimension of nursing professionalization
Values are beliefs and ideals that individuals and groups possess.[ 46 ] Professional values are practical standards that create a framework for evaluation of attitudes and ideas influencing behavior in professional clinicians.[ 47 ] Acquisition of professional values is the heart of professional development.[ 48 ]
Many attitudinal items are discussed in the articles and professional experiences concerning nursing professionalization. Although professionalization is a category related to culture, some of its properties are mentioned as to be autonomous, cooperative, retained jurisdiction, membership in professional organizations and professional development, community service and social services, compliance with codes of nursing, conduct and evaluation of nursing theory.[ 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 ] Kim et al . stated that the main features of the nursing professionalization values are classified into three main groups: (1) personal-based features such as the ability to understand the feelings and problems of others, willingness to help others, ability to work with others, tolerance and flexibility in communicating with others; (2) knowledge-based features such as knowledge and skills, scientific accuracy, and ability to research; and (3) state-dependent properties such as willingness to take responsibility and emphasizing on the attractive external appearance.[ 56 ] Core values set forth by AACN (American Association of Critical-Care Nursing) (1998) include human dignity, integrity, autonomy, altruism, and social justice.[ 48 ] These values have also been identified by Horton (2007).[ 57 ] Hall (1982, 1968, 1967) formulated five attributes to the most mature professions such as law and medicine, which are use of professional reference agencies, community service, autonomy, self-regulation, and sense of commitment and professionalism.[ 58 , 59 , 60 ]
In nursing professionalization, the “professional self” is one of the most important attitudinal elements. Professional identity is a secret knowledge that shows the continuation of a profession.[ 61 ] Professional attitude is a sense of experiences that makes up a professional identity.[ 62 ] Professional self-concept is the result of the university system, skills training, and professional development.[ 22 ] Arthur and colleagues (1998) showed that sense of being a professional among graduate students was stronger than among experienced nurses.[ 63 ] Finally, we can say professionalization is a framework for identifying a career in a social context, which emphasizes on attitudinal dimension of professionalization showing the importance of attitude within a profession and its professionals.[ 64 ]
Psychomotor dimension of nursing professionalization
Studies showed among nurses following the standards of practice and psychomotor competences, there are those who value professionalization.[ 65 ] UKCC in 1992, in an article titled “review professional action,” defined the nursing profession by these characteristics: Professional nursing is characterized by clinical working. This view has led to the expansion of the nursing role, so that they allowed getting involved in the therapeutic activities based on their personal qualifications and are actively involved in patient care.[ 66 ] So, professionalization is a certain style of management and implementation through which the professionals know about their commitments and obligations. It is also for those who are self-learning and self-controlled. This is consistent with the word “knowledgeable doer” that can be found in new dialogs in nursing.[ 67 ]
The definition of nursing professionalization in the clinical area is a difficult issue. Barber (1965) defined four properties for a professional manner: High degree of systematic and public knowledge, awareness about the interests of society rather than the personal interests, a high degree of self-control in behavior through moral codes, and existence of a reward system as a sign for success.[ 68 ] In nursing, some scholars have defined codes of professional behavior as: Respecting the dignity, values, and beliefs of the patients, maintaining patients’ trust, making informed decisions, provision of competent and safe care, maintaining standards of activities, presenting the image of nursing, and having a harmony with the law in action.[ 69 ] Lui et al . (2007) stated that the use of codes of professional behavior is important, but it is difficult in clinical practice. The main code of professional behavior in their study was “safe and competent care.”[ 69 ] This item is considered as the main foundation for nursing professionalization by other nursing associations in the West.[ 70 , 71 ]
From another perspective, nursing professionalization consists of behaviors including commitment, encouragement of the colleagues, peer assessments, and support from collective nature of profession. Focus in this view is on marketing and customer orientation.[ 72 ] Mayer (1992) emphasizes that in a modern society, the professions must be of good quality, reasonable, and affordable. He indicates that we can be sure about a professional service when the presented service is market-oriented. Thus, creating an environment where the focus is on value and satisfaction of the customer is important.[ 73 ]
Antecedents of nursing professionalization
The next rotational cycle in the developmental processes of evolutionary concept analysis is determining the antecedents and consequences of the concept.[ 74 ] Identifying the antecedents and consequences is an important part of the analysis because it provides greater clarity about the concept of interest. Antecedents are the events that happened before the concept occurrence and consequences can occur as a result of them.[ 17 ] Professionalization is actually a continuum that occurs during the professional socialization process. Antecedents of nursing professionalization are identified and classified in the following five groups: Demographic factors, factors related to the experience, training-related factors, factors related to the position, and value factors.
Demographic factors
Age is one of the effective factors on nursing professionalization, identified in the studies.[ 75 ] Studies have also shown that ethnic differences can have an impact on professional values.[ 76 ] Gender differences are also the other factors known to influence the professional values.[ 76 , 77 ]
Factors related to the experience
Length of service,[ 32 ] years of experience,[ 15 , 75 , 78 ] previous experiences,[ 78 ] and nursing professional experiences in the health care,[ 22 ] shown in several studies, are directly related to the nursing professionalization and professional attitude. It can be said that maturity in professional experiences has a large impact on professional attitude.
Factors related to the education
Degree,[ 22 , 72 , 79 , 80 , 81 ] membership in professional organiza tions,[ 1 , 4 , 15 , 81 , 82 ] having specialized certification,[ 1 , 15 , 78 , 81 ] the place where the last degree was issued,[ 1 ] political awareness,[ 83 ] educational readiness,[ 78 ] training and socialization,[ 72 ] teachers of nursing,[ 84 , 85 ] and length of the course,[ 1 , 86 ] all have been shown to have a significant relationship with professionalization in academic studies.
Factors related to the position
Position of nurse practitioners,[ 58 , 79 ] type of organization,[ 87 , 88 , 89 ] organizational culture,[ 69 , 90 , 91 ] the appearance of nurses in the workplace,[ 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 ] caregiver employment status,[ 1 ] work place,[ 1 ] existence of a reward system,[ 81 , 97 ] lack of staffs,[ 98 ] increasing the number of patients,[ 98 ] the existence of standards of activity,[ 99 ] lack of time, having stress and fatigue,[ 41 ] patients, clinicians, managers, and co-workers,[ 84 , 85 ] the gap between education and clinical practice,[ 22 ] and expectations of health care organizations,[ 22 ] all have been mentioned as precursors to professionalization in the reviewed studies.
Value factors
Professional satisfaction and organizational commitment,[ 4 ] professional freedom and independence and motivational factors,[ 78 ] belonging, knowing, and acknowledging,[ 100 ] support and guidance, acceptance, willingness, responsibility, and trust,[ 101 , 102 , 103 ] altruism,[ 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 ] and professional identity[ 93 ] have shown a significant relationship with professionalization. Studies showed belonging to a team, answering the questions of the patients and their families, and valuing the work do affect the understanding and meaning of students from professionalization.[ 22 , 93 ]
In general, although several internal and external factors are associated with the level of professionalization in nursing, for becoming a true professional, the experience of working and an educational background are very effective factors.
Consequences of nursing professionalization
Consequences of nursing professionalization consist of two components: Compatible and incompatible. Enhancement of patient care quality and improvement of the outcomes of care,[ 3 , 109 , 110 , 111 ] satisfaction of staffs, customers, clients, and agencies,[ 83 , 91 , 111 , 112 ] enhancement of the professional authority and the power to make decisions,[ 58 ] development of training programs to improve educational efficiency,[ 69 ] reduction of accidents and mistakes and risk management,[ 113 ] non-occurrence of burnout,[ 114 ] creating employment standards,[ 91 ] socialization, professional development, self-concept development, business retention,[ 101 , 102 , 103 ] and increased recognition of patients[ 111 ] are the compatible consequences that have been discussed in several studies.
Although professionalization can be very positive for professional practice, it can create blind spots in organization and stop vital information flow in uncertain conditions. This is because professional groups form their own subculture, especially in their language and communication habits. Therefore, they tend to be separated, even if they are working with other groups in an organization. On the other hand, as the professional members of the profession must accept responsibility, self-regulation, and control of the market for their services, the foundation of professionalization is based on the competition over resources and power that are divided between the characters and organizations.[ 113 ]
Surrogate and related concepts
The term “surrogate” is used for the concepts that express the same meaning of the desired concepts.[ 20 ] In other words, the term explains the meaning of a concept.[ 17 ] Related terms are used to express concepts that are related to the desired concept but do not have necessarily similar characteristics.[ 17 ] Application of related concepts in concept analysis is based on the idea that each concept is a part of a network of concepts. Identifying the related concepts helps us to locate “nursing professionalization” concept in basic knowledge of nursing. During the analysis process, it became clear that the concept of professionalism can be replaced with the words “profession” and “professional.”
Profession and Professor from Latin etymology have the same root (Profess). The meaning of their root is claimed or confessed.[ 2 ] From lexical aspect, profession is a vocation required to higher education and intellectual skills. Many authors have searched for the profession and its indicators. Aydellotle (1990) defined a profession as an organized and sophisticated job through which the clinicians obtain their exclusive knowledge in a protracted course for providing an exclusive, essential, or favorite service. He indicates that the essential features of a profession include having extensive and systematic knowledge, focusing on society interests, controlling the behavior through codes of ethics, having relationships with other professions, and existence of a professional reward system.[ 115 ] Extensive review of studies suggests that the profession is characterized by a series of factors: (1) the body of knowledge acquired through formal education, (2) a high level of competency, (3) inclusion criteria, (4) professional certification process, and (5) a set of behavioral and attitudinal norms, known as professionalization.[ 58 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 ]
Overall, a profession is characterized by the use of standardized knowledge that has three components: (1) an action taken based on underlying basic knowledge or discipline, (2) practical knowledge to solve everyday's problems, and (3) the knowledge based on skills and attitudes to serve to the clients. The articles defining the characteristics of the nursing profession list them as: Strong commitment, long-term and regular education, special body of knowledge and skills, ethics, autonomy, power for standard service, valuing and existence of professional associations.
The word “professional” in Aryanpur dictionary means related to a profession or an occupation, or being seasoned, skilled, and experienced. Dictionary of thesaurus lists the synonyms for the word “professional” as: Qualified, trained, skilled, white-collar professional people like doctors and engineers, expert, experienced, finished, skilled, masterly, efficient, etc.[ 121 ] Being a professional or being a professor means being a person claiming to have expertise in a specific skill or knowledge.[ 122 ] Flexner says professionals are the people who have to adapt to a particular job and have basic and higher education, high intellectual level in performance, sense of responsibility, scientific knowledge based on expertise, interest to develop learning, self-direction, and philanthropy.[ 123 ] Qualified members of a profession have ethical codes and a professional organization as a guide. Sacrifice, altruism, accountability, self-regulation, self-determination, and independence are features of the professional values.[ 7 , 124 ] Jarvis defines a professional as a person who is constantly in search of mastery in a branch of learning that is the foundation of his/her career, so as to be able to provide services to his/her clients.[ 45 ] Freidson, Cho, and Han expressed some professional qualities such as political autonomy, clinical autonomy, professional excellence and dominance, professional autonomy, clinical thinking, self-regulation and professional ethics.[ 125 , 126 , 127 ] In nursing articles, the word “professional” is implied to trained clinicians. In fact, professional employees are different. Their activities are associated with their attitudes and social behaviors.[ 117 , 128 , 129 ] These behaviors and attitudes include a high level of expertise, the freedom to manage work, commitment, knowledge, and a system of peer evaluation for maintaining the ethical standards.[ 130 ] From a marketing perspective, we can say that being a professional means to be obliged to do something that is appropriate for the patient and to accept the responsibility to provide services regardless to one's own interest.[ 58 , 116 ]
An appropriate exemplar of the concept
One of the six activities presented in Rodgers’ approach is identifying an exemplar of the concept, if appropriate. Rogers states that providing an example is essential to clarify a practical implementation of the concept related to the context.[ 17 ] Examples can be expressed by qualitative studies or specific situations.[ 131 ] Despite the strong need felt to provide such an example to clarify the concept further, the complex nature of the concept and features like its multi-dimensionality made it impossible to present a real example. This can be considered as a study limitation.
Interpretation and implications of the concept analysis
The aim of the present study was to assess nursing professionalization in relevant literatures to identify attributes, antecedents, and consequences of the concept. The results showed that nursing professionalization has cognitive, attitudinal, and psychomotor dimensions. Antecedents of nursing professionalization included demographic factors, factors related to education, factors related to experience, factors related to the position, and value factors. Consequences of nursing professionalization included two components of compatible and incompatible mechanisms. Results of the analysis are important because although a lot of literature is available about the nursing professionalization, there is little integration and inference about the concept.
Clinical implications: Professionalization and evolutionary experience
As a special knowledge, professionalization has a skill-oriented and experiential nature. So, focusing on the clinical factors that influence professionalization and providing the perfect context for professional growth and development in clinical practice seems to be one of the essential elements. One of the most important factors in the professionalization was experience, which was confirmed by several studies. Benner in 1984 proposed beginner–expert continuum as a framework for clinical nursing specialty.[ 132 ] He suggests five levels at the continuum: Beginner, advanced, competent, proficient, and expert. Different functional levels represent progressiveg stages of acquired skills and experience. Beginner–specialist's theory implies that through evolutionary experience, nurses are moving from one side to the other side of the continuum, but all nurses do not reach the level of expertise. Several studies have tried to explain the difference between a nurse specialist and beginner.[ 133 , 134 ] One of the most important factors discussed in this difference was years of experience. But this division based on years of experience is not a valid classification.[ 135 , 136 ] Benner et al ., stated that experience singly does not guarantee specialty. They belived that evolutionary experience is associated with expertise, sufficient and especial experiences.[ 137 ]
Implications for research: Professional autonomy path to the professional power
The results of the analysis suggest a variety of researches in future. Although professionalization is not a new concept in nursing, however, studies on this issue seem to have failed to provide a significant step toward a comprehensive solution to achieve it. Therefore, recognition of strategies to achieve professionalization as a major phenomenon among health care providers is essential. The result of the present study suggests professional power and autonomy as a way to achieve nursing professionalization and further researches are considered necessary.
Hall (1982) introduced professional power as the focus on professionalization. He (1968) found that the main features of the professionalization are community service and sense of duty. Meanwhile today, autonomy and membership in professional organizations are most important for nurses.[ 58 , 59 ] He explains the membership in professional organizations as the central reference for self-regulation and professional autonomy at the heart of professionalization. Thereby, it enhances the professional power. One of the main features of nursing professionalization is autonomy. Forsyth and Donisiewics stated that the professions are important, unique, and complex; therefore, professionals should have power to make their own decisions free from external pressures.[ 138 ] Bul (1998) stated that one of the main purposes and attractions to move toward professionalization is development of professional autonomy.[ 139 ] Autonomy is an important component of professionalization that is effective on personal decision making to achieve the goals and the control on job situations. Autonomy not only acts as a buffer against stress but also acts as a mean to empower and strengthen the sense of the personality and professionalism.
Studies have shown that the most important way to achieve a professional power is autonomy, acquired through membership in professional organizations. Hall states that nurses should strongly support the professional organizations because by connecting to professional organizations, they have a more professional feeling and the organizations grow more to support their members.[ 58 , 59 ] If the nurses do not reach to social maturity as a body, it may influence their attitude and the way they are perceived by others. Also, it can act as a confounding factor to reduce the development of nursing as a profession.[ 26 ]
Theoretical implications
This concept analysis is based on an evolutionary approach developed by Rogers. The concept of professionalization is associated with nursing knowledge. This approach with the presentation of a theoretical definition of nursing professionalization is used as a basic starter. This concept analysis is limited based on time and context; therefore, a continuous effort to develop a conceptual framework for the present and future of nursing professionalization is required. Due to the complex nature of the professionalization, various definitions in the literature and the other sciences, especially nursing, are common and expected. According to philosophical foundation of analysis, the result of analysis is not only to reach to what the concept is as a conclusion, but also the basis for further development of the concept. The results of the present analysis can be presented in the definition for the professionalization, as nursing professionalization is a cyclical process, which includes mastery of knowledge, skilful action, and having professional ideology, measured by the top standards. It can promote when excellence is considered as a major criterion for judging actions and attitudes of professionals.
This definition of nursing professionalization not only opens further exploration but also provides the opportunity for further research in order to develop the concept and its application in the field of theory, and research in the fields of education, management, and clinical nursing. On the other hand, acceptance of the above definition is not considered, as acceptance of a unique definition is considered as ignoring other informal factors and variable conditions, which may be a supplement, opposite, or associated with the definition.
D ISCUSSION
Professionalization, depending on times, contexts, and disciplines, has variable protests. Literature analysis of nursing professionalization led us to a variety of different meanings. The results of the present study describe the nursing professionalization as a multi-dimensional concept and it introduced cognitive, attitudinal, and psychomotor dimensions as the main features of nursing professionalization. In the review of studies, antecedents of the concept were demographic factors, factors related to experience, factors related to education, factors related to situation, and value-related factors. Consequences of professionalization in nursing are described by two components of compatible and incompatible. Therefore, nursing professionalization is not always associated with a favorable outcome. Hence, understanding of the professionalization characteristics, antecedents, and its consequences can lead to higher promotion of the status and the importance and application of this concept in the nursing profession. Use of assessment tools to evaluate and investigate this concept can result in further research and extension of the body of knowledge in this profession.
C ONCLUSION
Finally, it can be concluded that nursing professionalism has a complex nature with multi dimensions. This feature requires theorizing in this area. For this purpose, concept analysis considered the first step.
Source of Support: This article didn’t support by any institution
Conflict of Interest: Nil.
R EFERENCES
Essay Sample on Why I Want to Be A Nurse
Nursing is a rewarding and challenging career that has the power to make a real difference in people’s lives. Whether your motivation is to help others, attain financial freedom, or both, writing a “Why I Want To Be A Nurse” essay is an excellent opportunity to express your passion and commitment to the field.
In this article, we’ll explore the reasons why you might want to become a nurse and provide you with helpful tips and inspiration for writing a powerful and persuasive essay .
Why I Want to Be A Nurse (Free Essay Sample)
Nursing is a career that offers a unique combination of hands-on care and emotional support to those in need. There are many reasons why someone might choose to become a nurse, including:
The Empathy and Altruism of Nursing
I have a strong desire to help people and hope to become a nurse. I think nursing is the best way for me to make a difference in other people’s lives because it combines my natural empathy and desire to help people. Nursing gives me a chance to positively touch people’s lives, which has always attracted me to the thought of doing so.
I saw the beneficial effects that nurses may have on people’s life as a child. I have always been moved by the kindness and concern they have for their patients. The small gestures of kindness, like holding a patient’s hand or speaking encouraging words, have always touched me. I think nurses have a special power to change people’s lives and leave a lasting impression, and I want to contribute to that.
Additionally, I think that becoming a nurse is a great and selfless job. To provide for their patients and ensure they are secure and comfortable, nurses put their own needs on hold. I absolutely respect this kind of dedication to helping others, and I aim to exhibit it in my own nursing career.
The Economic Benefits of Nursing
The financial stability that comes with being a nurse is one of the reasons I wish to pursue this career. Nursing is a field that is in high demand, which translates to a wealth of job opportunities and competitive salaries. This profession offers the chance for a stable income, which makes it a good choice for people who want to secure their financial future.
Nursing not only gives economic freedom but also a flexible work schedule that promotes a healthy work-life balance. Many nurses can choose to work part-time or in a variety of places, such as clinics, hospitals, and schools..
A Love for the Science and Art of Nursing
To succeed in the unique field of nursing, one must have both artistic talent and scientific knowledge. This mix is what initially drew me to the thought of becoming a nurse. The human body and its mechanisms have always captivated me, and I enjoy learning about the science that underpins healthcare. But nursing requires more than just a scientific knowledge of the body. It also requires an artistic understanding of the patient and their needs.. Nursing is a demanding and fulfilling job since it combines science and art, which is why I’m drawn to it.
I saw as a child the effect nurses had on patients and their families. Their compassion and understanding have motivated me to seek a profession in nursing because they frequently offer comfort and help in the hardest of situations. My enthusiasm for the science and art of nursing will undoubtedly help me to have a good influence on other people’s lives. I want to work as a nurse and improve the lives of the people I take care of, whether it be by giving medication, educating patients, or just being a reassuring presence.
Continuous Professional Development in Nursing
I think the nursing industry is dynamic and always changing, which gives people a lot of chances to learn and grow. I would have the chance to continuously advance my knowledge and abilities in this sector if I choose to become a nurse. In turn, this would enable me to better care for my patients and stay abreast of professional developments.
There are several different nursing specialties available as well. There are many options, including critical care, pediatrics, gerontology, and surgical nursing. Because of the variety of disciplines available, nurses have the chance to develop their interests and find their niche.
I am certain that a career in nursing will provide me the chance to pursue my passion for healthcare while also allowing me to grow professionally.
Nursing is a fulfilling and noble career that offers a mix of hands-on care, emotional support, and professional growth. I am inspired by the positive impact nurses have on patients and their families and aim to offer my own empathy and compassion. The nursing industry is constantly changing, providing ample opportunities for growth and job prospects with financial stability. The ultimate reward in a nursing career is the satisfaction of making a difference in people’s lives.
Tips for Writing A Compelling Why I Want To Be A Nurse Essay
Now that you understand the reasons why someone might want to become a nurse, it’s time to learn how to write a compelling essay. Here are some tips and strategies to help you get started:
Create an Outline
Before you start writing, it’s important to identify the main points you’ll discuss in your essay. This will help you stay organized and make your essay easier to read.
Start with an Attention-grabbing Introduction
Your introduction is your chance to make a good first impression and engage the reader. Start with a hook that captures the reader’s attention, such as a surprising statistic or personal story .
Be Specific and Personal
Rather than making general statements about why you want to become a nurse, be specific and personal. Share your own experiences, motivations, and passions, and explain why nursing is the right career choice for you.
Highlight your Skills and Qualifications
Nursing is a demanding and complex profession that requires a wide range of skills and qualifications. Be sure to highlight your relevant skills, such as compassion, communication, and problem-solving, and explain how they make you a good fit for the nursing field.
Related posts:
- The Great Gatsby (Analyze this Essay Online)
- Pollution Cause and Effect Essay Sample
- Essay Sample on How Can I Be a Good American
- The Power of Imaging: Why I am Passionate about Becoming a Sonographer
Improve your writing with our guides

Youth Culture Essay Prompt and Discussion

Why Should College Athletes Be Paid, Essay Sample

Reasons Why Minimum Wage Should Be Raised Essay: Benefits for Workers, Society, and The Economy
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


- December 27, 2022
How to Write: Why I Want to Be a Nurse Essay
The Why I Want to Be a Nurse essay is one of the most common components on nursing school applications. There are tons of reasons to become a nurse, but yours are unique – a good nursing essay will stand out and be remembered by those who read it. In addition to general admission, this could even be your ticket to some scholarships for nursing school!
Let’s dive into how to write your Why I Want to Be a Nurse essay and get you into nursing school!
Planning Your Nursing Essay

Before you get into writing anything, you should always complete your pre-writing phase of brainstorming and planning for what you want to write about. Only then can you start considering your structure and details that you want to include.
Step 1: Brainstorm an event or a list of moments that began your interest in nursing.
If this is a lifelong dream, then maybe you can’t remember when you first became interested in nursing. But what moments have helped you continue down this path?
Some people may not have a specific healthcare related experience that inspired them to take this path. That’s okay! You can think broadly and consider times you were satisfied by helping someone with a task or volunteered.
Haven’t taken a writing class in a hot minute? Here are some effective strategies for brainstorming your ideas.
Step 2: Consider what you did to learn more about nursing.
Think about when you began researching nursing as a viable career option. What made nursing more appealing than a different career?
Step 3: Write down what made you decide to choose nursing as a career path.
If you can boil your reasoning down to a sentence or two, then that will be the thesis for your Why I Chose Nursing essay.
What to Include: Why I Want to Be a Nurse Essay
Introduction: your hook and story.

Your test scores and transcripts tell the story of your technical aptitude. But your essay is an opportunity to give your application an emotional route. What experiences have made you passionate about nursing? Have you cared for sick loved ones before? Are there nurses in your family?
Your introduction is where you’ll explain the stake that you have in this. You want the admissions team to understand that you belong in the program. Not just that you have the academic qualifications, but that you’ll be an asset to the entire nursing profession.
In kindergarten, there was an accident while my family was camping. A pot of boiling water tipped over onto my leg. The burns were so bad that I had to be airlifted to a regional hospital. I don’t remember much of the incident itself today, but I remember the nurses who helped me recover. They turned a frightening experience into something much kinder. I want to be able to give that to a child by working as a pediatric nurse.
Paragraph 1: Detail the event or moment you became interested in nursing.
This is a paragraph where you really want to reel the reader in. You’ve hooked them with the broad overview of your story: what sets you apart, why you’re so interested in the nursing profession. Now you can detail a specific moment.
Pick one moment and capture it in as much detail as you can. For example, maybe you remember waiting in a hospital for news about a loved one. Perhaps it was the kindness of a nurse who treated you. Or, in contrast, it was a time that a nurse wasn’t kind, and it made you want to do better for a patient in need.
Despite spending several weeks in the hospital, I didn’t immediately develop a desire to become a nurse. Growing up, I wasn’t sure what I wanted to do with my life. Then in my sophomore year of high school, my neighbor’s son got sick. He was about the same age as I had been when I was in the hospital. When I babysat him, we would swap hospital stories — the good and the bad! And suddenly it dawned on me that if I was a nurse, I could help make those bad stories a little less painful.
Paragraph 2-3: Show how you have used that experience to build your foundation towards nursing school.
Here is where you’ll take your personal experiences into account. Nursing school requires more than just empathy. You will need to have core science credits and an ability to understand the human body. The best nurses are adaptable in the workplace and always willing to learn. You can browse a list of skills nurses need to thrive in the workplace.
I spent a lot of time researching my neighbor’s son’s condition. Though his illness wasn’t terminal, it was degenerative. He began to lose his hearing a few months after his diagnosis. I joined his father in learning sign language to communicate better. During that time period, I spent a lot of time thinking about how so many people have to struggle so hard to communicate.
I want to be a nurse who can give relief to the most vulnerable patients. Every person’s needs are different. A child’s needs are different from a developmentally disabled adult’s, which are different from the needs of someone hard of hearing, and so forth. I’ve seen firsthand the frustration that occurs when communication isn’t easy. So I’ve focused on learning adaptable communication methods and educating myself about the groups that are most overlooked in hospital settings.
Paragraphs 4-5: Detail how you will use your strengths and skills in your nursing career.
This is the point at which you can start to talk about your specific skills, similar to a job interview. You want to highlight any particularly unique aspects, then make sure to solidly establish your core competency. A dream of becoming a nurse can’t just be a dream; you need detail to back it up.
If you know where you want to place your specific focus as a nurse, mention it! Talk about your career goals and how you want to work with your patients and what you hope to learn in doing so.
I think it’s so important for patients to have a nurse that listens to them, and that goes doubly for patients with communication struggles. During my career, I want to continue practicing and using ASL with my patients. I want to improve the quality of care for chronically ill people, especially because so many report anxiety around healthcare settings.
It’s also important to me to keep learning and adapting constantly. I never want to stop learning new skills and refreshing my knowledge. Understanding a patient’s vital signs and demeanor could mean the difference between life and death. In the high-pressure environment of nursing, I strive to have the answers to the questions my patients have – I’ll never stop seeking knowledge.
Conclusion: Reiterate your skills and qualifications, saying why they’d make you a great fit for the program.
The conclusion is fairly straightforward. You’ve provided your thesis: why you want to be a nurse. You’ve explained when the desire started, what experiences support it, and what you plan for the future. Now you just need to tie those things together in a neat summary. Remind the admissions team of why you’re a unique candidate to fit this role.
A long stay in the hospital as a child doesn’t qualify me to be a nurse by itself. But that experience has laid the foundation for my desire to work in healthcare settings. There are a thousand careers that help people, but nursing is personal and dear to me. I want to make sure that any vulnerable patient has access to the care they need, and I can use my adaptability and communication skills to do that.
Related: Stay Organized for the School Year with These Nursing School Planners
Do’s and Don’t’s for Nursing School Essays

Do: Show that you care about people.
Illustrate that you want to help people and have compassion for their suffering. It helps to talk about specific people or groups of people that you care for.
Do: Explain the qualifications that will make you a good fit as a nurse.
Talk about your adaptability, your desire to learn, your interest in the healthcare field, your prior experience – anything that will serve you during your career.
Do: Tell admissions why you want to be a part of their program.
Find a unique aspect of the program to highlight, showing why you want to study there specifically. For example, maybe there’s a school that connects students to underserved rural areas and this is a mission that you are on board with. Spend some time researching the nursing program to be confident in what they offer.
Do: Ask someone to proofread.
You’ll miss typos in your work if you read it a thousand times, so ask for a fresh pair of eyes. It also helps to change the essay to a different font for editing. Here are some more tips to consider offering to your proofreader.
Don’t: Pay for a writing service.
Write your own paper. If you’re worried about your skills, have a peer take a look at your draft, rather than using someone else’s work.
Don’t: Make false claims.
Tell the truth about your motivations, goals, strengths, and driving factors. Don’t make up a backstory or pretend to have skills you don’t.
Don’t: Disregard instructions or criteria.
Pay careful attention to the essay prompt and the criteria. Sometimes you’re expected to answer in less than 300 words, or there are more specific prompts to follow.
Related: Can Nurses Have Tattoos?
Why I Want To Be a Nurse Essay – FAQ
What should i include in a short essay on why i want to be a nurse.
A short essay should still include the main points made here – a short story or introduction, why you became interested in nursing and how that experience has propelled you into nursing, and the skills and experience you will bring to the program.
Should I give more than one reason on why I want to be a nurse?
You should aim to stick with one or two main reasons why you chose nursing – too many reasons will lead to a less effective essay due to a difficulty in following along with your main points.
What do I do if I don’t have a personal story that inspired me to want to become a nurse?
Even if your inspiration is not specific to nursing, you should be ready to tie that into why it’s related to a nursing career. Focus on experiences that required interpersonal skills, great communication skills, or show care for others.
The Why I Want to Be a Nurse essay is your chance to stand out from the crowd. You can show your dedication, compassion, and willingness to learn all through being honest. Just make sure you have your essay proofread before you send it!

- TERMS & DISCLOSURE
- PRIVACY POLICY
BLACK FRIDAY & CYBER MONDAY SAVINGS
Discounted mcat, gre, lsat, nclex, sat, act.
Why Do You Want To Be a Nurse? 15 Reasons to Choose a Career in Nursing

If you’ve started submitting applications to nursing schools or told people that you want to be a nurse, you’re probably hearing the question, “Why do you want to be a nurse?” a lot.
To be honest, it’s a fair question, and each person has their own reasons for wanting to become a nurse. If you’re reading this blog post and wondering if a nursing career is for you, here are the 15 top reasons to choose a career in nursing .
Why Do You Want to Be a Nurse? 15 Reasons
Becoming a nurse is a great career choice with many advantages, including plenty of opportunities for growth and development. Here are the top 15 reasons why you should consider a career in nursing:
1. High Demand for Nurses
Nursing is an increasingly relevant and sought-after career path in today's world. With the aging population, there’s an increasing demand for nursing professionals due to the increased need for both medical and assisted living services.
On top of this, a shortage of physicians has also increased the demand for primary care providers putting nurse practitioners in much higher demand as well.
2. Ability to Start Working Fast
Nursing is an amazing career choice for many reasons, one of them being that you don't necessarily need an extensive education in order to get started.
Becoming a CNA or LPN only requires a 1-2 year associate degree and the starting pay is decent too.
Even if your goal is to become an RN, there are now accelerated BSN programs available at most universities that offer nurses the opportunity to obtain their Bachelor of Science degree in nursing (BSN) quickly so they can begin their careers.
And most of these programs can be completed online (except for some lab and/or clinical components).
3. Great Pay and Benefits
Another awesome advantage of being a nurse is that most nurses earn a really good salary and have excellent benefits. Although nursing salaries vary widely from state to state, the median annual registered nurse salary in 2022 was $81,220, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Licensed practical nurses earn an average salary of $94,538 a year in 2023 , according to Glassdoor.com.
Nurses also receive a number of benefits that can’t be found in other occupations, such as access to excellent health insurance options, retirement savings plans, flexible hours or shifts, paid vacation time, and even educational assistance programs that can help make continuing your education more affordable.
>> Show Me Online RN-to-BSN Programs
4. Incentives to Work in Many Different Areas
Besides a great salary and benefits, nurses are also offered special incentives such as higher pay, relocation assistance, hefty sign-on bonuses, and nursing tuition reimbursement to work in high-need areas.
And there are many places offering these incentives for nurses, from busy urban medical centers to under-served rural and remote communities.
5. Job Security
When it comes to job security, you’ll be hard-pressed to find a job that is more secure and in higher demand.
Currently, there is a nursing shortage , and this shortage is expected to increase over the next decade due to the aging population of Baby Boomers and a growing need for healthcare services related to chronic conditions like diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
6. Professional Respect
An important part of having a great career is knowing that you’re respected for your skills and the work you do. And when it comes to respect and trust, there is no one more trusted than nurses.
For the last 20 years, Gallup has found that the public ranks nurses the highest in terms of their honesty and ethics of any occupation or profession, even higher than physicians. Nursing is an incredible career choice due to the tremendous respect you receive from patients, family, peers, and other medical professionals.
7. Growing Opportunity for Flexible Scheduling
Another important factor when it comes to having a great job and career is a flexible schedule. In fact, a whopping 9 out of 10 employees surveyed said offering flexible scheduling is one of the most important things employers can do to retain employees. And 47.8% said a flexible schedule is even more important than salary.
With an ever-growing demand for healthcare professionals, employers are placing greater emphasis on accommodating remote workers or those who are interested in part-time work.
In addition to regular hospital or clinic settings, nurses can now take advantage of more per-diem nursing opportunities that fit into their busy lives as well.
This opens up the field to those who don’t have the necessary time to commit to a full-time nursing position while still allowing them to contribute meaningful work.
8. Opportunity for Student Loan Forgiveness
Going to school costs a lot of money, even if you go the community college route. Tuition, books, transportation, nursing uniforms and equipment, accommodation, meals, healthcare expenses—the list goes on of the expenses a student has. However, the good news is, many nurses may be eligible for student loan forgiveness programs for nurses .

9. Job Options Across Various Fields
Unlike many other professional fields, nursing offers a huge amount of variety in terms of the type of work you can do and the types of settings you can work in.
If you’d like to work with kids, you can be a school nurse , a pediatric nurse , or work in a PICU with sick children.
Prefer to work with people of all ages for even more variety? Then you can work in a community clinic, emergency department, or as a home care nurse .
And if you have the travel bug and want more adventure, you can be a travel nurse and work almost anywhere you can imagine from large cities to extremely remote locations once you gain some initial nursing experience.
10. Opportunities for Career Advancement
If you’re wondering about opportunities for career advancement, nursing is an excellent career choice for that as well.
As a nurse, there are many ways to work your way up the career ladder through advanced education in Master’s in Nursing and DNP programs.
These programs prepare you to specialize as a nurse—which means a nice boost in salary (usually into the 6-figure category)—and often more autonomy.
And the good news is, there’s high demand for nurse practitioners in a number of different specialties. There are also career paths for nurses who want to pursue healthcare or nursing management, nursing informatics , research or teaching as well.
11. Ability to Make a Difference
If you want a career where you can help people and change their lives, nursing definitely fits the bill. In fact, nursing is an incredibly rewarding career choice because you have the privilege of supporting people when they need your help the most.
As an example, a nurse may help bring a life into the world for new parents or assist someone in managing a chronic condition who would otherwise be lost without a nurse’s teaching and expertise.
In the eyes of those they help, nurses truly are everyday heroes.
12. Transferable Skill Set
The nursing profession is highly marketable and transferable. So those entering the field can expect their experience and training to be valuable from job to job.
For example, the fundamental medical knowledge and expertise that goes hand-in-hand with being a nurse applies no matter where you go or work.
Although certain local regulations, technology, and even cultural norms may have slight variations, having a background as a nurse will still apply no matter where you go.
13. Opportunity for Entrepreneurship
The dream of owning your own business is also a real possibility when you become a nurse. Whether it’s starting your own private practice as a nurse practitioner or consultant, publishing medical research, freelance writing, launching a medical-based app or blog, or developing a new medical product, nurses can capitalize on their expertise and hard work by starting their own company.
Ownership over your career and the ability to create lasting change makes nursing an extremely attractive option for those seeking more than a traditional employment position.
14. Opportunity for Autonomy and Independence
One of the best aspects of nursing as a career is that it encourages autonomy and independence, allowing you to make many decisions on your own.
This is because nurses are given various levels of responsibility depending on their experience and skill level. As a result, this makes nursing an ideal job for those looking for autonomy and independence while still having access to support from their peers, supervisors, and managers.
15. Highly Satisfying Career
Last but not least, nursing is an extremely satisfying career. Despite how difficult the recent pandemic was for nurses, a 2021 career satisfaction survey of 10,788 nurses (including LPNs, RNs, and NPs) found that more than 90% of the nurses surveyed said they were “glad they chose” to be a nurse.
As you can see, there are many great reasons to choose a career in nursing. So what are you waiting for? Jump online and start applying today!

Leona Werezak BSN, MN, RN is the Director of Business Development at NCLEX Education. She began her nursing career in a small rural hospital in northern Canada where she worked as a new staff nurse doing everything from helping deliver babies to medevacing critically ill patients. Learning much from her patients and colleagues at the bedside for 15 years, she also taught in baccalaureate nursing programs for almost 20 years as a nursing adjunct faculty member (yes! Some of those years she did both!). As a freelance writer online, she writes content for nursing schools and colleges, healthcare and medical businesses, as well as various nursing sites.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
How To Answer “Why Do You Want To Be A Nurse?” (With Examples)
- Cover Letter
- Registered Nurse Interview Questions
- Registered Nurse Job Description
- Why Did You Choose Nursing?
When you’re in a nursing interview, you’ll hear the common question “Why do you want to be a nurse ?”, so it’s essential to know how to answer it. Your answer should reflect on what it was that drew you to nursing and tell a story about it, such as the moment it was clear that you wanted to be a nurse.
Whether you want to be a pediatric nurse , emergency department nurse, or travel nurse, we’ll go over how to answer “Why did you choose nursing as a career?”, why interviewers ask this question, as well as some common mistakes to avoid.
Key Takeaways:
Try to think of a story or a moment that made it clear that a nursing career was right for you.
Interviewers ask “Why do you want to become a nurse?” so you can highlight your passion for nursing and what got you interested in the field.
Avoid saying anything negative because it can often be a red flag for interviewers.

How to answer “Why do you want to be a nurse?”
Example answers to “why do you want to be a nurse”, why interviewers ask this interview question, common mistakes to avoid when answering, interview tips for answering this question, possible follow-up questions:, nurse career path faq, final thoughts.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
To answer “Why do you want to be a nurse?” you should first ask yourself questions as to why you want to be a nurse, start at the root, and tell your interviewer a story. Below is a more detailed list of how to answer this interview question .
As yourself questions. Before the interview, ask yourself, putting money and career goals aside, why do YOU want to be a nurse? Consider the following questions to better understand your reasoning:
Do you want to help people?
Does the medical field excite you?
Do you have certain skills, such as communication or concentration under duress, that naturally fit the position?
Do you thrive when you get to build relationships with people?
Do you love both science and working with people?
Focus on these aspects of yourself when you are asked why you are choosing nursing as a career.
Start at the root. If you’ve wanted to be a nurse since you were a kid, start there. If you got into medicine thanks to an impactful college professor , make that your starting point.
Tell a story. Most interviewers prefer narratives over bullet point facts — especially with a personal question like this. Don’t feel like you have to make up some great tale about how a nurse saved the day when you were a child, but bring in real moments when it became clear that nursing was the career for you.
Talk about people and experiences. Nursing is all about building relationships, so your answer should touch on your empathy and ability to form bonds with the people you work with and serve. In this way, your answer will show that you want to be a nurse because you truly enjoy the process of nursing.
Bring it to the future. Close your answer with a nod to the future and what you’d like to accomplish in your brilliant new nursing career. Bringing your answer from the past to the future shows that you’re forward-thinking and determined enough to make your dreams a reality.
Below are example answers to “Why do you want to be a nurse?” for different scenarios such as pediatric or emergency room nursing. Remember to tailor your answers to your specific needs when you answer in your interview.
Pediatric nurse example answer
“I have wanted to get into nursing since I was very young. One of my earliest memories is of a nurse taking care of me when I had to go to the hospital for stitches. She was so kind and gentle with me that I didn’t even cry or panic. I remember leaving thinking that was the kind of person I wanted to be when I grew up. Ever since then, everything I have done has been working towards becoming a nurse.”
Emergency room nurse example answer
“When I was in college I took a course on basic first aid and found it super interesting. I started signing up for volunteer first aid positions and some of my fellow volunteers were nurses. I was curious about their job and the more I learned about what they did the more I found myself excited by the prospect of helping people in medical situations. I made friends with these nurses and they helped guide me through the application process.”
Travel nurse example answer
“Medicine is such an exciting field, and one of the biggest joys of nursing is that I’m always learning new things. I know people who dread getting their necessary CEUs every year, but for me, it’s a perk of the career. “For instance, just last year I completed my certification from the Wilderness Medical Society and can now serve as medical staff on the Appalachian Trail. But from Diabetes for APRNs to Nursing for Infertility courses, I’m always able to maintain my passion for nursing through continuous discovery and wonder at the medical field.”
Critical care nurse example answer
“I believe in helping people, especially in times of extreme need. When I worked as an EMT I was always the one asked to facilitate information between any involved party. I want to expand this skill and I think nursing is a good fit for me. My interests and experience with medical professionals are good for this job.”
Nurse midwife example answer
“I want to be a nurse because I am deeply committed to providing compassionate healthcare to women during one of the most significant and transformative moments of their life. Being a nurse midwife will allow me to empower women by advocating their choices and preferences during childbirth. “Being a nurse midwife will also allow me to make a positive impact on the lives of women and their families. I will be able to provide personalized care, emotional support , and educational resources to help ensure a smooth and empowering birthing experience for my patients.”
Oncology nurse example answer
“I want to be an oncology nurse because this field is driven by a profound desire to make a meaningful difference in the lives of those fighting cancer. I am committed to providing compassionate care to patients during their cancer journey. “Working as an oncology nurse also has the opportunities to be part of cutting-edge research and advancements in cancer treatments. I want to be at the forefront of innovation and help contribute to the improvement of cancer care outcomes.”
The interviewer will ask why you want to be a nurse to know how serious you are about the position. This isn’t a career to take lightly because there are many challenges.
Nursing is a profession with a prerequisite for assisting others in potentially high-stress environments. So by answering this question, you are given the opportunity to highlight not only your skills but more importantly, your passion for nursing and ability to keep cool under pressure.
Additionally, interviewers hope to learn why you got interested in the field in the first place. Telling a story about an impactful experience with a medical professional or about the sense of satisfaction you feel when helping a patient can help illustrate that you’re not only skillful but also have deep compassion for the people you’ll be working with.
You should avoid saying anything negative because it can be a red flag for the interviewer. Here are some other common mistakes you should avoid when answering:
Saying anything negative. A negative response will be a red flag for the interviewer. If you are one to complain or see the worse in a situation, this will make you a difficult coworker in an already difficult field.
Focusing on money or self-serving reasons. Even if the wages are an attractive feature of the profession, mentioning this as a reason will hurt you. The interviewer is looking for an answer that goes beyond your own needs.
Unrelated anecdotes. Don’t get caught up in telling stories about nursing that have nothing to do with you or the job. Remember to keep things relevant and concise.
Your answer should be positive and you should use a personal experience to help you answer and tell a story. Here are some more tips to keep in mind when answering this question:
Be positive. Nothing will concern an interviewer more if you are cynical and negative in an interview where the job requires a strong sense of empathy and selflessness. This does not mean you can’t, nor should, ignore the challenges of the profession. If you can reframe these difficulties with a positive mindset and a “can do” attitude, you will strengthen your impact in the interview.
Be concise. A long-winded, rambling answer may give the impression that you have not considered the question ahead of time. That said, if you rush through your words, you may concern the interviewer as well. So, don’t be afraid to take breaths or have moments of silence, but choose your words carefully and effectively. Concise communication is a huge part of the nursing profession so here is an opportunity to highlight that skill.
Use personal experience. When answering the question “Why did you choose nursing as a career?” it can really help to bring in a personal touch to the response. This creates a unique answer that can help you stand out among other candidates. The personal experience may also reveal a moment of inspiration pointing towards why you chose nursing as a career.
Remember the job description. Use the skills required in the job description and apply them to yourself as you explain your interest in the field. Integrate them with care, you are not trying to restate your resume . Instead, consider how your skills have developed over time and how that relates to your interest in nursing. Remember, skills are developed through some kind of interest too.
Research the organization/department. Wherever you are applying to is going to have unique characteristics. Perhaps the organization focuses on low-income individuals or the elderly or intensive care patients. You may be able to bring this into your answer. Even if you do not, it is still good to give you context. By understanding where you’re applying to, you strengthen the explanation of why you are applying.
Practice your answer. Before the interview, practice this answer, preferably with someone else who can give you feedback such as a friend or family member. However, if you do not have that opportunity, practice in front of a mirror or, better yet, record yourself on your phone and listen back to what you said. In the end, you want to “train” for this question by giving yourself the opportunity to run through it a couple of times with the chance to tweak your response.
After the question “Why did you choose a nursing career?” there will most likely be follow-up questions. Here are some examples of other common interview questions and some tips on how to answer them. This will help you prepare yourself for the direction the interview may take.
What do you think is most difficult about being a nurse? Why?
Be aware of certain challenges of nursing ahead of time. Do some research . The worst thing you can do for yourself is be caught off guard by this question.
How are you at handling stress?
Consider what techniques you use for reducing stress. It is going to be important to show your competency. Consider answering in a way that reveals you to be a team player and aware of the stresses of your coworkers as well.
What are your long-term career goals?
The interviewer is going to be gauging your seriousness in becoming a nurse. It is not a profession that you can just “try-out”, so give an answer that shows sincere consideration for a long-term medical profession. Note: This does not necessarily tie you strictly to nursing. Many managers and hospital administrators come from nursing backgrounds.
Why do you want to work here?
Many interviewers will want to hear about not only your passion for nursing as a career but also how your passions align with their organization.
Look up the mission and vision of the facility before your interview and talk about how that resonates with you, or give an example of how you’ve seen them in action and want to be a part of that.
What drove your interest in this specialty?
Not every nurse fits well in every nursing role, so your interviewers will likely ask you why you want this particular job.
Whether this is the specialty you’ve always worked in or you’re trying something new, structure your answer similarly to your answer to the “Why do you want to be a nurse?” question.
Why would one want to be a nurse?
Many people want to be a nurse because it gives them an opportunity to help people in a meaningful way. Nurses not only perform specialized tasks that are vital to a person’s well-being, but they also get to emotionally support people who are going through an incredibly difficult time.
This can be as simple as being a calm, friendly presence or advocating for them with the rest of the medical staff, but it makes a huge impact on people’s lives.
In addition to this, many people choose to become nurses over another occupation that helps people because they love science and medicine or love the fast-paced, challenging work environment.
What is a good weakness to say in a nursing interview?
A good weakness to say in a nursing interview is a weakness that you’re actively working on. Whether your greatest weakness is that you’re too detailed with your paperwork or say yes to too many people and requests, always follow it up by explaining the steps you’re taking to overcome that weakness.
Hiring managers don’t expect you to be perfect, but they do expect you to be self-aware and take the initiative to minimize the impact of your weak spots.
What are the 6 C’s of nursing?
The 6 C’s of nursing are care, compassion, communication, courage, and commitment. These are principles taught to many nurses to help them learn how to give excellent care to patients.
They also help to set cultural expectations at medical facilities, since all of the nurses are upheld to this standard, no matter what their educational background or specialty.
What are some common nursing interview questions?
Some common nursing interview questions include:
What skills do you think are important for nurses to possess?
Describe your experience as a nurse and what you’ve learned from it.
How would you manage an uncooperative patient?
How well do you thrive in a fast-paced environment?
There are so many nursing jobs out there and nurses are in high demand. You will want to know what you’re getting yourself into before you are asked at the interview what brings you to the field.
Knowledge is power, so knowing your response to “Why did you choose a nursing career?” is crucial for success. This is your moment to shine and show why you are the best candidate for the job.
Those who are able to answer with sincerity and empathy are the types of nurses all organizations will want. So get yourself ready and figure out ahead of time why you want to be a nurse.
Nightingale College – How To Ace Your Nursing Job Interview: Questions, Answers & Tips
The College of St. Scholastica – Why do you want to be a nurse? Students share their sentiments
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Conor McMahon is a writer for Zippia, with previous experience in the nonprofit, customer service and technical support industries. He has a degree in Music Industry from Northeastern University and in his free time he plays guitar with his friends. Conor enjoys creative writing between his work doing professional content creation and technical documentation.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts
Registered Nurse (RN) Vs. Nurse Practitioner (NP)

Should A Resume Be Past Or Present Tense?

How To Get Your First Job

When Is Grad School Worth It?
- Career Advice >
- Get The Job >
- Why Do You Want To Be A Nurse
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Why I Chose Nursing as a Career, Essay Example
Pages: 3
Words: 908
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Personally nursing has always been the right choice as a career. Nursing allows me to have the contact with a number of patients, enabling me to make a different in their treatment. Additionally, I have always looked forward to being part of the health care system, as a responsible first-line in a patient’s stay. For me nursing is the right choice to make that difference in the care and treatment of a patient.
The healthcare of an individual is one of the most important aspects in life. After all, everyone has worried or has had issues with their health, at least to some extent. Many individuals worry about illnesses and other conditions, such as cancer and other unfortunate topics that can alter their life in a negative manner. As a result, the medical care of individuals is concentrated upon and is a leading area of research and supplementary fields.
Personally I have experienced this in my life. In my stay at hospitals, and even health clinics, I have had experiences that have exposed me to the health care system and the dedicated staffs that fill these centers. While I do what I can to stay healthy, I, as most other people, have a reasonable level of worry about having a serious condition in my life.
Family and friends have also had such experiences. There have been times that I have accompanied loved ones to the hospital or even to a doctor. In these experiences you come to realize the important role of doctors, nurses, and other parts of the staff that make up these centers. You also realize how valuable they are as those who can take care of yourself, a loved one, and others in your community when you think about it.
In these experiences and general awareness, this has drawn me to consider choosing nursing. Personally I desire to have that kind of an impact in one’s life. As a valuable part of a person’s healthcare, I feel that this responsibility is important.
Role of the Nurse
As a distinct part of the healthcare system, from hospitals to other types of healthcare centers, the nurse plays a valuable role. As previously mentioned, members of healthcare such as doctors, nurses, and other are an individual’s way to finding relief for whatever condition may elicit their presence in such a center. Yet, even in this distinction, there is a further one in the role of a nurse.
In many cases the nurse is the first line in terms of members of a healthcare-related staff. The nurse serves an important role in addressing the patient’s issues and performing tasks related to the reason for the patient’s visit. In this capacity I find it engaging to have this type of a presence for a patient. I am drawn to be able to be one of the first members of a valuable healthcare staff to provide services for the patient’s condition or reason for appearing.
Interaction with Patients
One of the most crucial points to why I chose nursing as a career is in regards to the interaction with patients. As a part of the healthcare system, nurses have a valuable place in the staff to cater to the needs of patients. Nurses are able to answer any questions and speak to the patients about anything that is needed during their stay at the health care center.
Being able to be a large part of a patient’s stay is important to me. I desire to interact with the patients to make their stay better in any way possible. Having this level of contact with patients is important in my desire to add to the experience of the patient. Having this level of contact not only improves the level of their health-related care, but also the overall experience beyond merely receiving medical attention.
Additionally, the experience is much more enjoyable when dedicated nurses, and other members of the staff, create this kind of environment. In my and other individuals’ experiences that I have spoken to, nurses can provide a calming or engaging environment just with their presence. As a nurse I will be able to give any means of support to a patient as I am able, from calming their worries to having a casual conversation to make their stay more pleasant. For me this is a difference that moves beyond medical attention.
Nursing is an important position across a great deal of health care centers. A nurse plays a valuable role in a patient’s stay in a hospital or other medical center. As a valuable team of health care providers, the nurse is often the first health care professional to have contact with the patient. As a career this is desirable for me to be exposed to patients in this capacity.
The exposure to patients in many kinds of healthcare settings is another more direct response to why I chose nursing as a career. The overall experience from the perspective of the patient is not constrained to medical attention, although this is certainly an important part of a nurse’s duty. Having the ability to interact with so many patients on a normal basis allows the nurse to go above and beyond this to improve the patient’s experience. The nurse is able to provide support and other means to improve his or her experience and stay in a medical center. These valuable roles and experiences capture why I chose nursing as a career, which allows me to play a valuable role in a patient’s experience.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Air and Water Pollution, Research Paper Example
Ban on Whaling, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
Online Nursing Essays
Top Quality Nursing Papers
Why I Want To Be A Nurse Essay

Applying for nursing school is an exciting step towards a rewarding career helping others. The nursing school essay, also known as a personal statement, is a critical part of the application. This is your chance to showcase your passion for the nursing profession and explain why you want to become a nurse.
This guide will show you exactly what admission committees are looking for in a strong nursing school application essay. Let’s walk through how to plan, write, and polish your “why I want to be a nurse” personal statement so it stands out from the competition.
What To Include In Your Nursing Essay
Writing a compelling nursing school essay requires advanced planning and preparation. Follow these tips to create an effective personal statement:
Plan Your Nurse Essay
The first step is to carefully conceptualize your nursing school admissions essay. Jot down some notes answering these key questions:
- Why do you want to go into nursing?
- What personal experiences or traits draw you to the field of nursing?
- How have you demonstrated commitment to caring for others?
- What are your academic and professional qualifications for nursing?
From here, you can start mapping out a logical flow of key points to cover in your nursing school application essay.
Show an Emotional Connection to the Profession
Admission committees want to see that you have genuine passion and empathy for the nursing career choice. Dedicate part of your personal statement to describing your intrinsic motivations and positive impacts for desiring to become a nurse.
Avoid cliché reasons like “I want to help people.” Instead, get specific by sharing a personal anecdote that emotionally moved you towards nursing.
Here’s an example of how you could open your nursing school entrance essay by highlighting a meaningful patient-care interaction:
“Holding Mrs. Wilson’s trembling hand, I watched her fearful eyes relax as I reassured her that the medical team would take excellent care of her. At that moment, providing empathetic comfort to calm her nerves despite the clinical chaos around us, I knew deep down that nursing was my calling.”
This introduction immediately establishes an emotional pull towards the human side of healthcare. From here, explain how this or similar experiences instilled a drive in you to become a nurse.
Show That You Care
Much of nursing is providing compassionate, person-centered care. Therefore, your “why I want to be a nurse” essay should emphasize your ability to be caring, empathetic, patient, and comforting to others.
Share examples that showcase your natural inclination for caregiving:
“Volunteering at the Red Cross shelter after the wildfires by comforting displaced families demonstrated my patience and attentiveness to those suffering. Even as some evacuees grew frustrated by the chaos, I calmly reassured them that we would do everything possible to assist with their recoveries and ensure they felt cared for.”
This example highlights key soft skills needed in nursing as a career, like compassion, active listening, the desire to help, and providing a calming presence under pressure.
Share Your Aspirations
A strong application essay will also articulate your goals and vision for contributing to the nursing field. What are you hoping to achieve through a career in nursing?
Here is an example of discussing aspirations in a nursing school personal statement:
“My long-term aspiration is to become a nurse leader by earning an advanced degree and management experience. I aim to leverage my organizational, communication and critical thinking skills to mentor junior staff, improve operational workflows, and advocate for policies that enhance quality of care. In nursing, I’ve found my true calling – to provide critical care, and help others by being a source of compassion and driving excellence in healthcare delivery.”
This type of self-motivated, forward-looking vision demonstrates maturity, strong goals, and natural leadership qualities.
Describe Your Nursing Skills and Qualifications
Finally, your nursing school entrance essay should summarize the skills; profession offers, and experience that makes you an excellent candidate for the nursing program. Highlight relevant strengths like:
- Academic achievements (science/healthcare courses, GPA, etc.)
- Extracurricular activities (volunteering, internships, etc.)
- Relevant work experience (patient care roles like CNA, medical assistant, etc.)
- Other transferable skills (communication, leadership, teamwork, critical thinking, etc.)
For example:
“My passion for science, healthcare experience as a CNA, and volunteering at a community health fair have prepared me to thrive in the intellectually stimulating and collaborative nursing curriculum. I bring dedication, attention to detail, and a strong work ethic as demonstrated by my 3.8 GPA studying Biology at the University of Michigan.”
With application essays, it’s all about showcasing why you would make an outstanding addition to the nursing program, making a difference through your qualifications and intangible traits.
How Do You Write an Introduction to a Nurse Essay?
Now that you’ve brainstormed content ideas, it’s time to turn them into a polished personal statement. Here are some tips for crafting an attention-grabbing introduction to your nursing school essay:
Hook the Reader with a Personal Story
One of the most engaging ways to start writing your essay is by recounting a brief personal story that illuminates your drive to become a nurse. This can immediately immerse the reader in your intrinsic motivations.
For example , you could open with an anecdote describing a meaningful instance of care and comfort you provided to someone in need:
“Tears streamed down Mrs. Hernandez’s face as she told me about losing her husband to cancer last year. As a hospice volunteer, I held her hand, listening intently to her painful story of grief and loss…”
This type of vivid introduction pulls the reader into the narrative straight away. From here, you can continue sharing details about the scenario and its influence on your desire to pursue nursing.
Illustrate the Human Impact of Nursing
Another compelling way to begin your nursing personal statement is by painting a picture of nursing’s profound impact on patients and their families. This highlights your understanding of the profession’s vital role.
For instance:
“Looking a trembling new mother in the eyes as she first held her newborn, relieved knowing both were safe and healthy after a complicated delivery – that is the human difference nurses make each and every day.”
This type of introduction emphasizes nursing’s profound emotional impact on patients during vulnerable yet joyful moments. It activates the reader’s empathy by bringing them into the vivid scene while showing your own insight into the medical field.
Articulate Passion for Helping Others
Finally, you can start your nursing application essay by asserting your resounding passion for caring for others. This clear expression allows you to succinctly introduce central values like empathy and compassion.
“Ever since I was a young volunteer candy striper in my local hospital, I’ve held an unwavering passion for helping those suffering through the profound act of nursing. I was born to care for others.”
This authoritative opening clearly states your emotional connection to nursing in a compelling yet concise way. You can then build on this assertion of passion through personal examples and further explanation.
No matter how you start your nursing school essay, the introduction should vividly showcase your motivation and why you chose nursing. Set the tone early with your authorship and emotion.
Why I Want To Be A Nurse Essay Examples
Now let’s analyze some complete sample nursing personal statements for inspiration on crafting your own:
Why I Want to Be a Nurse at a Hospital: Essay
Essay on why i want to be a nurse assistant, 1000-word essay on why i want to be a nurse, essay on why i want to be a nurse, why i want to be a nurse: argumentative essay, mental health nursing personal statement, why i want to be a pediatrics nurse, why i want to be a nurse practitioner essay, writing a why i want to become a nurse essay.
To craft a standout nursing school application essay, prospective students should engage the reader with an emotional opening that illuminates their calling to the profession, whether through a compelling personal anecdote or vivid imagery expressing the profound impact of nursing.
The conclusion should be resolved by painting an inspiring vision of how the writer’s skills, values, and determination will be channeled into excellence as a nursing student and future registered nurse, making an empathetic difference in patients’ lives.
With focused, mature writing that radiates passion and preparedness, a “why I want to become a registered nurse” personal statement can stand out amidst the competition as a window into a promising applicant’s commitment to this vital healthcare profession.

Don’t wait until the last minute
Fill in your requirements and let our experts deliver your work asap.
Interview Question: "Why Did You Choose Nursing as a Career?"
- What the Interviewer Wants to Know
- How to Answer Question
Examples of the Best Answers
Tips for giving the best answer, what not to say, possible follow-up questions.
When preparing to interview for a nursing position, it’s helpful to review questions you might be asked. One of the things that interviewers often ask nursing candidates is, "What made you choose nursing as a career ?"
If you have an interview for a nursing position , you want to arrive confident and prepared for your interview. Reviewing questions that interviewers might ask will help you do that.
What the Interviewer Really Wants to Know
When an interviewer for a nursing position asks you questions about why you became a nurse, he or she is trying to learn the personal reasons you may have for becoming a nurse. This question is also posed in order to gauge your enthusiasm for the profession.
The interviewer will seek to identify, from your response, what characteristics and skills you have that make you good at what you do.
Your answers should provide the basis for a discussion about your passion for nursing , your qualifications, and your skill set.
How to Answer the Interview Question “Why Did You Choose Nursing as a Career?”
Because there are so many factors that go into choosing a career, you can answer this question in a variety of ways. When preparing an answer, try to include the reasons the work interests you as well as what strengths you possess that make you an excellent nurse and the best candidate for the job.
You will likely be asked questions relating specifically to nursing , as well as a certain number of general interview questions, so you should prepare some ideas about how you would like to answer them.
Don’t try to memorize an answer, but do jot down a few ideas and talking points that relate to your own experiences and strengths.
4 Ways to Answer: Why Did You Choose Nursing as a Career?
Reviewing sample answers can help you to formulate your own thoughts and give you ideas of what to include to impress the interviewer.
I wanted to do something in my career that is challenging, interesting, and makes a difference in people's lives daily. In the nursing profession, you deal with many aspects of patient care, and I enjoy the variety in the routine.
Why It Works: The interviewer will be pleased to know that the candidate wants to make a difference in people’s lives. The candidate also makes a point to mention that patient care is a priority.
Dealing with patients and their families and helping them through what is often a difficult time for them is extremely satisfying for me.
Why It Works: This works because the candidate is letting the interviewer know that working with patients is of primary importance.
My mother is a nurse and seeing the satisfaction she feels every day by helping people in her job inspired my own interest in the field. I knew from the time that I was very young that nursing was something I wanted to do with my life.
Why It Works: This is a good answer because it shows the candidate’s passion for the nursing profession along with a family history of working in the nursing field.
Throughout college and nursing school, my interest in nursing and my commitment to the field became even stronger as I found that I also had an aptitude for the work. I believe my ability to communicate with people and to explain things clearly in both a technical and non-technical way is one of the things that makes me a good nurse.
Why It Works: This is a very good answer that demonstrates to the interviewer the candidate’s confidence and awareness of the strengths she possesses that enhance her candidacy.
I chose nursing as a career because I love learning new things. As a nurse, I am always challenging myself to keep current on medical trends and training so that I can provide the best care to my patients. Every day as a nurse, I learn something new from my colleagues and patients, which inspires me to explore a deeper knowledge of the techniques and procedures I use.
Why It Works: This works because the candidate shows a willingness to keep current on skills and education necessary in the medical field.
Analyze the Job Posting: It’s a good idea to look carefully at the job posting, as well as the hospital website, to get a feel for what they are specifically looking for in the person who fills the open position, as well as the general culture of the hospital.
Share Your Skill Set: Be prepared to discuss your clinical skill set, as well as your personal qualities, that make you qualified for the job. The interviewer may ask you to provide examples of situations where you applied those skills. You should have a list of your nursing skills with you, preferably on a copy of your resume.
Discuss Patient Scenarios: You will be asked about challenges you have met and problems which you have solved in patient care contexts . Be ready to share specific patient scenarios where you intervened with difficult cases and individuals to help generate positive outcomes.
Show You're a Team Player: Nurses must be effective team members and get along with challenging personalities. Be prepared to share examples of how you have dealt with difficult colleagues.
Practice Your Answer: Prepare a response to this question and then practice your answer, either in front of a friend or the mirror.
Avoid Negativity: Don’t complain about difficult patients, other nurses you’ve known, doctors, or other hospitals.
Avoid Physical Complaints: Don’t complain about the grueling physical aspects of the nursing profession. You chose this career and are applying for this job.
- How do you handle the stress that comes with a nurse’s job? Best Answers
- Why do you want to work here? Best Answers
- Are you organized? Best Answers
Key Takeaways
Prepare for the Interview. Be prepared to discuss both your clinical skill set and personal characteristics that make you a good nurse.
Be Ready to Share Examples. Have some sample patient scenarios and why they were challenging in mind.
Keep it Positive. Don’t complain about past jobs, patients, people, the nature of the work, or anything else.
- Interview Question: "Why Do You Find Nursing Rewarding?"
- Nurse Job Interview Questions About Handling Stress
- Interview Question: "Why Did You Decide to Become a Teacher?"
- Social Work Interview Questions and Tips for Answering
- Common Nursing Interview Questions and Best Answers
- Best Interview Answers: "Why Did You Choose Your College?"
- Speech Pathologist Interview Questions and Answers
- Interview Questions About Why You're Good at Sales
- How to Answer Why Do You Want to Work Here for Nurses
- Call Center Job Interview Questions and Best Answers
- Sales Interview Questions With Examples of the Best Answers
- Interview Question: "How Would You Handle an Angry Customer?"
- Part-Time Job Interview Questions About Your Contributions
- How to Answer “What Interests You Most About This Sales Position?”
- Nurse Interview Questions About Patient Complaints
- Public Relations Interview Questions and Answers
- Open access
- Published: 07 February 2023
What is nursing professionalism? a concept analysis
- Huili Cao 1 , 2 ,
- Yejun Song 3 ,
- Yanming Wu 1 ,
- Yifei Du 1 ,
- Xingyue He 1 ,
- Yangjie Chen 4 ,
- Qiaohong Wang 1 , 4 &
- Hui Yang 1 , 4
BMC Nursing volume 22 , Article number: 34 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
36k Accesses
12 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
Nursing professionalism plays an important role in clinical nursing. However, a clear conceptual understanding of nursing professionalism is lacking.
Walker and Avant’s strategy was used to analyse the concept of nursing professionalism. We searched electronic databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and CINAHL, for studies published from 1965 to 2021. Quantitative or qualitative studies published in English that focused on nursing professionalism were included in the study.
The three attributes of nursing professionalism are multidimensional, dynamic, and culture oriented. Based on the analysis, nursing professionalism is defined as providing individuals care based on the principles of professionalism, caring, and altruism.
Conclusions
This study offers a theoretical definition and conceptual model of nursing professionalism that may be applied to develop standardized assessment tools or nursing professionalism training programs.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The COVID-19 outbreak has exposed deficiencies in the underinvestment of the global health system, including the shortage in nursing resources and nursing staff, and a similar situation is noted in China ( https://www.icn.ch/news/investing-nursing-and-respecting-nurses-rights-key-themes-international-nurses-day-2022 ). An unbalanced number of nurses and patients, high work pressure, lack of social occupational identity and other reasons have led to job burnout, low job satisfaction, and even the resignation of many nurses. Research has also shown that the lack of nursing professionalism adversely affects patient care and patient outcomes [ 1 ]. Ohman [ 2 ] pointed out that lower levels of professionalism may cause negative outcomes, such as turnover and attrition and lower productivity.
In recent years, researchers have tried to solve the above problems through professionalism.
However, nursing professionalism plays a more important role in clinical nursing. Some studies have shown that professionalism can improve the professional knowledge and skills of nurses and ameliorate reductions in institutional productivity and quality [ 3 ]. Higher levels of professionalism can improve nurses’ autonomy and empowerment, increase their recognition and facilitate organizational citizenship behaviours, establish nursing care standards and even improve quality services [ 4 , 5 ].
Nursing professionalism has been discussed for several decades. Hall (1968) developed the Professionalism Inventory Scale [ 6 ]. Miller et al [ 7 ] (1993) first specified the 9 standards criteria of nursing professionalism (educational background; adherence to the code of ethics; participation in the professional organization; continuing education and competency; communication and publication; autonomy and self-regulation; community service; theory use, development, and evaluation; and research involvement.). Yeun et al. (2005) summarized five themes regarding nurses’ perceptions of nursing professionalism: self-concept of the profession, social awareness, professionalism of nursing, the roles of nursing services, and originality of nursing [ 8 ]. Yoder defined nursing professionalism based on six components: acting in the patients’ interests; showing humanism; practising social responsibility; demonstrating sensitivity to people’s cultures and beliefs; having high standards of competence and knowledge; and demonstrating high ethical standards [ 9 ]. Although some researchers have explored the concept of professionalism. How can professionalism be evaluated in nursing clinical practice? Few studies have shown a clear conceptualization of nurses’ professionalism [ 10 , 11 ]. To nurture nursing professionalism, the concept of professionalism must be clarified.
Given that the meaning of professionalism varies across time, contexts, or cultures, it is difficult to define, quantify or measure professionalism [ 12 , 13 ]. The operational definition of nursing professionalism in studies has shortcomings. Sullivan et al. [ 14 ] found professionalism to be a multidimensional concept, but some papers have addressed only one dimension, such as values [ 15 ] or behaviours [ 16 ]. Moreover, professionalism is considered a complex concept. The links and dynamic processes between these different inner characteristics have not been included in the concept. Thus, a comprehensive definition of nursing professionalism, including its characteristics and the relations between them, is necessary.
Recognizing and understanding the concept of nursing professionalism may be an essential step towards providing quality care for people. It may also provide more information for further developing nursing professionalism for nurses.
Method of concept analysis
Walker and Avant’s method used linguistic philosophy techniques to contribute to the philosophical understanding of a concept [ 17 ]. The W & A method is considered a mark of the positivist paradigm, which views the concept as a stable factor that can be reduced or extracted from its context of application [ 18 ]. This study used Walker and Avant’s method, which assumes that nursing professionalism is a relatively mature and stable concept (numerous studies on nursing professionalism have been published to date). This approach to conceptual analysis, although not perfect, is helpful in clarifying the concept of nursing professionalism.
Using the structured method of Walker and Avant enables conceptual clarity to be obtained based on an inductive identification of the concept’s attributes, antecedents and consequences. The concept analysis helps to clarify meanings and develop operational definitions, considering evidence from a wide range of information resources for further research or clinical practice [ 17 , 19 ]. These features make this method particularly useful for the analysis of the concept of ‘nursing professionalism’. The conceptual attributes as well as antecedents and consequences are based on the research team's analysis of the literature using Walker and Avant’s strategy and are not the product of a priori theoretical categories.
Walker and Avant’s [ 17 ] eight-step method includes the following: 1) selecting a concept; 2) determining the aims or purposes of analysis; 3) identifying all uses of the concept; 4) determining the defining attributes of the concept; 5) constructing a model case; 6) constructing borderline, contrary, invented, and illegitimate cases; 7) identifying antecedents and consequences; and 8) defining empirical references.
Selection criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: related to the concept of nursing professionalism; included nurse professionalism, nursing spirit, or nurse spirit; written in the English language; qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods or systematic reviews; published between 1965 and 2021 (when professionalism was first introduced by nursing in 1965); and published in books or dictionaries. We excluded articles published in nonpeer reviewed journals, editorials and letters to the editor.
Data sources
We searched several online databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and CINAHL, for articles published from 1965 to 2021. We searched the words that appear in the title, abstract, and keyword section of the studies.
(((((((((Nursing professionalism[Title]) OR (Nursing professionalism[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nurse professionalism[Title])) OR (Nurse professionalism[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nursing spirit[Title])) OR (Nursing spirit[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nurse spirit[Title])) OR (Nurse spirit[Title/Abstract])).
TI Nursing professionalism OR AB Nursing professionalism OR TI Nurse professionalism OR AB Nurse professionalism OR TI Nursing spirit OR AB Nursing spirit OR TI Nurse spirit OR AB Nurse spirit.
TITLE-ABS-KEY (Nursing professionalism) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Nurse professionalism) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Nursing spirit) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Nurse spirit).
Any quantitative or qualitative studies published in English focusing on nursing professionalism were included in the study. Two researchers independently screened titles and abstracts to determine the selection criteria for electronic retrieval and application. The study was included only when both researchers agreed that the study met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. If the two researchers’ judgements were different, a third person was consulted to resolve the issue. Researchers identified the different usages of the concept and systematically recorded the characteristics of the concept that appeared repeatedly [ 17 ].
We used definitions and examples in the systematic record (Table 2 ) to define a cluster of antecedents, attributes and consequences (Figs. 1 and 2 ) frequently associated with the concept [ 20 ].
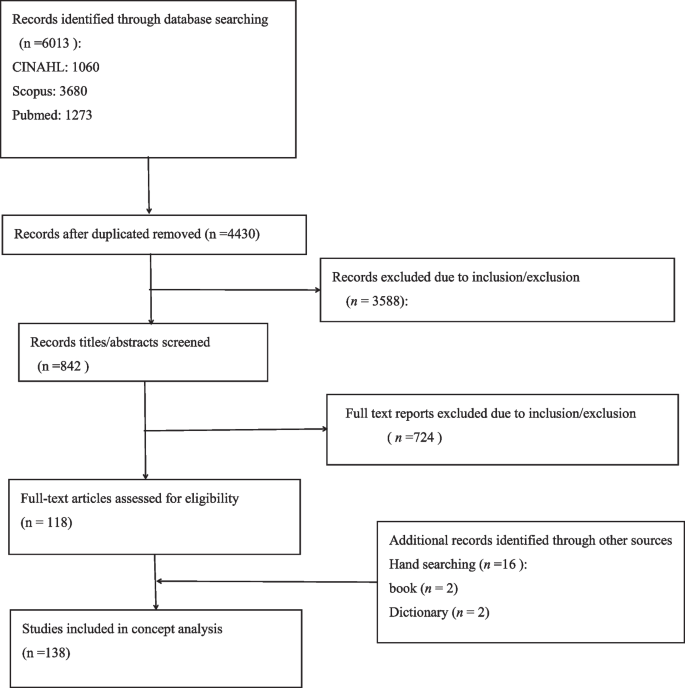
Flowchart of the study selection process of the concept analysis
We identified 6013 studies on nursing professionalism. After excluding duplicates, irrelevant studies, studies that were not original scientific studies or articles, and studies published in languages other than English, 138 studies were selected for analysis. Tables 1 and 2 show some typical literatures used in this study.
Uses of the concept
Dictionary definitions of the concept.
The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines professionalism as ‘the conduct, aims, or qualities that characterize or mark a profession or a professional person’ [ 48 ], whereas the Cambridge Dictionary [ 49 ] defines professionalism as ‘the combination of all the qualities that are connected with trained and skilled people’. These definitions are generic and difficult to use to clarify the factors involved in nursing professionalism.
Definitions of the concept reported in the literature
Hwang et al. [ 50 ] defined professionalism as commitment to a profession and professional identity level. Health-care workers demonstrate professionalism through attitudes, knowledge, and behaviours, which reflect approaches to the regulations, principles, and standards underlying successful clinical practices [ 33 ]. Nursing professionalism reflects the value orientation, concepts of nursing, work attitude and standards of clinical nurses [ 51 ].
Subconcepts
The Nightingale Spirit, named in honour of the founder of professional nursing, refers to the spirit of altruism, caring, and honesty [ 52 ]. In the past, the Nightingale Spirit advocated that nurses are willing to dedicate themselves, but the term currently encompasses more innovation [ 53 ]. E-professionalism is defined as evidence provided by digital means, attitudes and behaviours reflects the traditional models of professionalism [ 54 ]. Nurses use the internet to communicate about work or daily life, blurring the boundaries between individuals and professions; thus, e-professionalism applies to nurses [ 55 ].
The defining attributes of nursing professionalism
The defining attributes of the concept aim to understand its meaning and differentiate it from other related concepts [ 17 ]. The key defining attributes are as follows.
Nursing professionalism is multidimensional
Nursing professionalism is a three-dimensional concept based on the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviours that underlie successful clinical practice [ 33 ].
Professionalism can be conceptualized as a ‘systematic body of knowledge’ with complex configurations of work expertise [ 21 ].
Professionalism refers to the attitude that represents levels of recognition and commitment to a particular profession [ 22 ]. Hall [ 6 ] noted that nurses’ attitudes have a high correspondence with the behaviours of the respondent. Measuring professionalism at the cognitive level can be thought of as measuring potential professionalism at the behavioural level. Researchers noted that given the reduced restrictions of environmental constraints, measuring professionalism at the cognitive level may be more precise than measuring it at the behavioural level [ 23 ].
Nursing professionalism is often described as a set of professional behaviours [ 11 ]. Some researchers judge whether nurses exhibit professionalism through their behaviours. Miller [ 24 ] (1988) developed the Wheel of Professionalism in Nursing Model. The model is considered a framework for understanding professional behaviours among nurses. Kramer [ 56 ] (1975) quantified professionalism by assessing the number of professional books purchased, subscriptions to journals, and the number of articles published.
In addition, the perspective of professional identity formation complements the behaviour-based and attitude-based perspectives on professionalism [ 57 ].
The formation and development of professionalism are dynamic processes
Nursing professionalism is an inevitable, complex, varied, and dynamic process [ 58 ].The professionalism concept is considered ever-changing, replacing static or definitive views [ 59 ].
Socialization process
Nursing professionalism is instilled through a process of socialization in formal nursing education [ 25 ]. Nurses’ socialization process begins with formal, entry-level education to acquire knowledge and skills.
Yeun et al. [ 8 ] (2005) discussed the developmental process of nursing professionalism in which the individual’s thoughts and beliefs are formed by socialization factors through perception. These thoughts and beliefs may in turn influence the individual’s professional image or self-concept, thereby influencing nurses’ actions and performance.
Process of interaction
The dynamic of professionalism is also reflected in the process of interaction. Dehghani et al. [ 26 ]noted that nursing professionalism means the appropriate interaction of the individual and the workplace and the maintenance of interpersonal communication.
Culture oriented
One study showed that altruism is an essential element of medical professionalism in Asia or North America but not Europe [ 27 ]. In China, medical professionalism was influenced by its longstanding Confucian traditions [ 28 ]. Therefore, any definitions of professionalism should match its rooted culture and be validated with respect to the culture and context in which it is applied [ 60 ].
The connotation of nursing professionalism
Professional, having a systematic nursing knowledge system.
The nursing process is considered a method for solving problems or dilemmas in a logical and scientific manner [ 11 ]. Freidson [ 29 ] (2001) noted that professionals perform their specialized work only with the required training and experience. Professionals have specific, tacit, almost esoteric knowledge to do their work [ 61 ]. Miller et al. [ 7 ] considered that a formal university education with a scientific background is critical for professionalism in nursing.
Professional certification
Nurses actively seek specialty certification given their personal commitment to the nursing profession [ 30 ]. Specialty certification promotes nursing professionalism. When attaining the highest levels of clinical knowledge, nursing professionalism also indicates personal responsibility and dedication to best practices [ 31 ].
Lifelong learning and participation in continuing education
Due to professional and ethical obligations, nurses should sustain continuous professional growth and development to maintain individual competence. Professional growth in nursing requires lifelong learning. Lifelong learning includes continuing education and self‐study, seeking advanced degrees, etc. [ 62 ].
Continuing education is one of the indicators of professionalism. Professionals keep up with the latest developments in the field and partake in continuing education. Additionally, continuing education is as important as other criteria for increasing professionalism in nursing [ 7 , 32 ]. Ongoing education brings fresh knowledge to health care, consequently leading to more efficient and quality service for people.
Evidence-based practice
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a hallmark of professionalism [ 33 ]. Dollaghan [ 63 ] (2004) reported that we identify and use the highest quality scientific evidence as an integral part of our efforts to provide the best patient care; EBP is a knowledge base that responds to specific clinical issues in a clear, intelligent, and serious manner while considering clinical practice in the context of the highest-quality scientific evidence available.
Innovation in nursing helps to improve patient care quality and improve nurses’ job performance [ 64 ]. Shen et al. [ 34 ] noted that innovative education plays an important role in the professional quality of undergraduate nursing students.
Striving for excellence
Striving for excellence is a requirement and attribute of nursing professionalism. There is a growing need in nursing practice to possess knowledge and skills in quality improvement science, translational research, and implementation science [ 35 ]. Clinical nurses have the same responsibilities as nursing scientists.
Caring is considered the core attribute of nursing professionalism
The practice of caring is central to nursing [ 65 ]. Caring is defined as the moral ideal of nursing [ 36 ]. Therefore, caring is an important core attribute of nursing professionalism.
Creating a caring-healing environment
Nurses devoted to creating a caring-healing environment embody professionalism. Caring means nurses should create a healing environment at all levels by providing a supportive, protective environment as well as a corrective mental, physical, societal, and spiritual environment for patients. People’s basic needs include a clean environment, comfort measures, safety concerns, and feeling safe or protected [ 65 ].
Displaying kindness/concern/empathy for others
A nurse is defined as someone caring for the ill within the hospital setting [ 66 ]. Caring means showing or having compassion, concern and empathy for others [ 37 ]. Caring behaviours are an interactive and mental process between patients and nurses [ 38 ]. Displaying kindness and concern for others is shown by love, compassion, support and involvement [ 39 ].
Using all methods of knowing support and involvement
‘Human problems reside in ambiguity, paradox, and impermanence’. Therefore, suffering, healing, miraculous cures, and synchronicity are all part of knowing support and involvement.
Researchers suggest that nursing comprises Caritas Nursing, Energy Nursing, Transpersonal Nursing, Holistic Nursing, or Contemplative Nursing…… It goes beyond ordinary nursing. Nursing should have higher standards with excellence for caring, healing, and peace in the world. Therefore, caring means using all methods of knowing support and involvement [ 65 ].
Embracing the unknowns and miracles in life and practising loving
Nursing is a special profession. Nurses confront special circumstances daily and witness people’s struggles with life and death. Everyone has his or her own specific story about his or her experiences and predicaments. Each person seeks his or her own meanings to find inner peace and balance in the midst of fear, doubts, despair, and unknowns. Therefore, the care of nurses is not to blindly sacrifice their own needs but to be a real nurse, embracing the unknowns and miracles in life and caring for patients [ 65 ].
The central tenet of professionalism is to put the needs and best interest of others over self-interests. Altruism is an engagement in caring acts towards others without expecting something in return [ 67 ].
Patients first
To be altruistic means to put others’ needs before your own. Altruism is the selfless concern for others and doing things with the other person’s well-being in mind [ 40 ].
During pandemics, nurses were considered to have a high sense of duty and dedication to patient care [ 41 ]. Front-line nurses perceive high work engagement, especially in self-dedication [ 42 ]. Grøthe et al. [ 43 ] showed that cancer patients in a palliative unit appreciate nurses who have the most dedication and expertise characteristics.
Public service
Due to a strong sense of civic and social responsibility, nurses participate in public service. Nurses volunteer as participants in summer camps, schools, or health-care teams. Nurses are also committed to responding to large-scale crises, such as the terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center in New York, as well as national and international relief efforts, such as tsunamis and Hurricane Katrina [ 44 ].
Disaster and infectious disease rescue
Individuals involved in providing disaster relief face many challenges, experience fatigue and personal suffering, and encounter numerous personal stories of life and death [ 45 ]. Nurses have played a significant role in the fight against infectious diseases such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic [ 68 ]. Nurses are closest with patients. Nurses provide intensive care, regularly assessing and monitoring airways, tubes, medications, and physical therapy. Nurses are also devoted to reducing complications. Nurses assist with daily living activities when patients are unable to care for themselves [ 46 ].
Community service
In addition, emphasizing professionalism means respecting values and commitment to community service delivery [ 69 ].
According to Walker and Avant [ 17 ], cases help further clarify concepts.
Model cases (a real case example)
Model cases help demonstrate all the defining attributes of a concept and helps to better articulate its meaning [ 17 ].
MS A is a 63-year-old nursing director. She worked in clinical nursing and management for 42 years. As she progressed from a new nurse to a nursing expert, she gradually poured her enthusiasm (Multidimensional: Attitudes) into nursing work (Dynamic). She believes that the core of nursing professionalism in China is dedication and responsibility (Culture oriented). In 2020, COVID-19 broke out in Wuhan, China. She led a team to Wuhan to provide support (Multidimensional: Behaviours), reflecting the spirit of altruism (Altruism). She actively promoted exchanges and cooperation among disciplines and the development of academic conferences. She guided students to pay attention to practical innovation and develop evidence-based innovations (Professional). Although she is retired, she still imparts knowledge and experience to students everywhere (Multidimensional: Behaviours). She stated that the development of nursing professionalism is very difficult and requires nursing education and role models. (Multidimensional: Knowledge). The role of a nurse is like that of a mother, bringing care to the people (Caring).
Borderline cases (a real case example)
Borderline cases provide the examples that contain the most defining attributes of the concept [ 17 ].
B is a novice nurse. When working in the infection ward, she was so worried about being infected. She was reluctant to care for patients and wanted to escape from the ward environment. Fortunately, her nurse manager fully understood her situation and helped her adapt to work and reduce her anxiety. B observed that her nurse manager had been helping patients solve problems and giving them comfort and hope. This prompted her to think about what nursing truly means. In 2020, she volunteered to help COVID-19 patients (Altruism).
Related cases (a real case example)
Related cases are related to the concept but do not contain all its defining attributes [ 17 ].
C is a novice nurse. After graduating from nursing school, he became a nurse in the emergency department. He saw many patients who died or recovered, which made him realize the importance of caring (Caring). He said that emergency nurses need strong professionalism (Multidimensional: Attitudes). He participated in social service activities (Multidimensional: Behaviours), for example, promoting knowledge of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (Altruism) in the community. After working for five years, he returned to school for a master’s degree to help the head nurse conduct nursing research or evidence-based practice (Professional). In his Asian cultural milieu, his is embarrassed about his identity as a male nurse (Culture oriented), but he believes he can do well.
Contrary cases (a fictional case example)
A contrary case does not include any defined attributes of the concept [ 17 ].
D is a nurse in paediatrics. She disliked nursing when she was a nursing student and even did enjoy communicating with patients (poor dynamics). She was exhausted after work and felt her life was out of balance. One of the values of the hospital where she worked was dedication, which confused her (Poor culture orientation). She considers it unrealistic to require professionalism (Poor nursing professionalism knowledge) and thinks that taking care of new-borns is particularly troublesome (Poor nursing professionalism attitudes), so she is always careless in her work (Multidimensional: poor attitude). D’s child felt ill last week, so she secretly reduced a patient’s medicine (Poor nursing professionalism behaviours) and took the remaining medicine home for her child (lack of altruism). She stopped doing so after her colleagues sensed something strange. One day, a baby kept crying; D reported it to the doctor and did not make further observations (Poor professional). When the shift nurse took over, she observed abnormal limb activity on one side of the child. The child’s family asked the nurse to bear legal responsibility. D said it was no big deal; she no longer wanted to be a nurse (Poor dynamic, professionalism not established).
- Antecedents
Antecedents are events that occur before the intended concept [ 17 ].
Macro antecedents
Jin [ 28 ] suggested that the conceptualization of professionalism is influenced by culture. Employees defined organizational culture underlies an organization’s values and beliefs [ 70 ]. Nursing professionalism may be supported by a variety of cultures, so a firm understanding of and personal congruence with each particular culture is essential [ 71 ].
Religious beliefs
Religiosity is another contributing factor in the cultivation of altruism [ 72 ]. Taylor noted that nurses’ job motivation and views of the patient and nursing services are affected by their religious beliefs [ 73 ].
Micro antecedents
Snizek [ 74 ] (1972) reported that devotion to work is a professional value originating from a sense of calling to the field. Liaw et al. [ 75 ] (2016) found that nursing students who had caring and compassionate qualities as the most common personal characteristics strongly believed that they were called to nursing.
Individuals who pursue excellence in the workplace may be described as motivated and devoted to their work. Attree [ 76 ] (2005) noted that nurses’ perceived lack of autonomy over their practice could impact quality of care.
Personal characteristics
Nursing professionalism is influenced by various factors, such as educational background, personal interests, professional satisfaction, and professional values [ 77 , 78 , 79 ]. In each country, nurses with higher educational levels may have a higher level of professionalism [ 22 ]. Professionalism is thus a trait related to personal character and upbringing [ 80 ]. Researchers [ 81 ] have demonstrated that professionalism is positively associated with female gender, striving for professional goals, and acceptability. One study found that people’s values tend to shift to emphasize altruism over personal gain as they age [ 79 ]. Nursing professionalism is closely associated with personality traits (extraversion, conscientiousness, and agreeableness) [ 82 ].
Consequences of nursing professionalism
Consequences are events or incidents that are the result of the occurrence of a concept [ 17 ].
Consequences for patients
Professionalism is one of the decisive factors that critically influences patient satisfaction [ 50 ]. Professionalism can also improve practising nurse career development and the quality of service [ 81 ].
Consequences for nurses
Studies have shown that professionalism and a sense of belonging with colleagues and managers affect the satisfaction [ 83 ] and retention rate of nursing students in academic institutions [ 84 ]. Izumi et al. [ 85 ] (2006) found that good nurses felt pride and happiness in caring for patients closely related to their professionalism.
Empirical references
As the last step to concept analysis, empirical references can further clarify the concept and facilitate its measurement [ 17 ].
Hall’s professionalism inventory scale
Hall’s Professionalism Inventory Scale [ 6 ] identified five attitudinal attributes of professionalism: (a) use of professional organizations as major referents, (b) belief in public service, (c) self-regulation, (d) a sense of calling to the field, and (e) autonomy. Nursing researchers used Hall’s Professionalism Inventory Scale to measure professionalism in nursing [ 22 , 47 ]. Snizek [ 74 ] (1972) modified the professionalism scale to more closely match the clinical context of nursing and better reflect the professionalism of nursing staff.
Kramer’s index of professionalism
Kramer (1974) [ 86 ] constructed an index of professionalism that includes indicators of behaviours, such as the number of professional books published, subscriptions to professional journals, hours spent on professional reading, continuing education, participation in professional organizations, number of professional publications, speeches given, committee activity, and participation in research.
The behavioural inventory for professionalism in nursing (BIPN)
The Behavioural Inventory for Professionalism in Nursing [ 7 ] (BIPN) identifies professional behaviours and values among nurses. The nine categories in the BIPN are (1) educational background; (2) adherence to the code of ethics; (3) participation in the professional organization; (4) continuing education and competency; (5) communication and publication; (6) autonomy and self-regulation; (7) community service; (8) theory use, development, and evaluation; and (9) research involvement.
Definition of the concept
Based on the present analysis, we define nursing professionalism as follows: ‘Nursing professionalism is a multidimensional concept manifested by the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviours that underlie successful clinical practice. Nursing professionalism is dynamicized through a process of socialization in formal nursing education. This feature is also reflected in the process of interaction. Therefore, nursing professionalism should match its rooted culture.
The connotations of nursing professionalism include professional, caring, and altruism. These connotations are detailed as follows:
Possesses a systematic nursing knowledge system; professional certification
Exhibits lifelong learning and participation
Participates in evidence-based practice
Demonstrates innovation
Strives for excellence
Creates a caring-healing environment
Displays kindness/concern/empathy for others
Uses various methods of knowing support and involvement
Embraces the unknowns and miracles in life and practices loving
Patient-first
A conceptual model of nursing professionalism is shown in Fig. 2 .
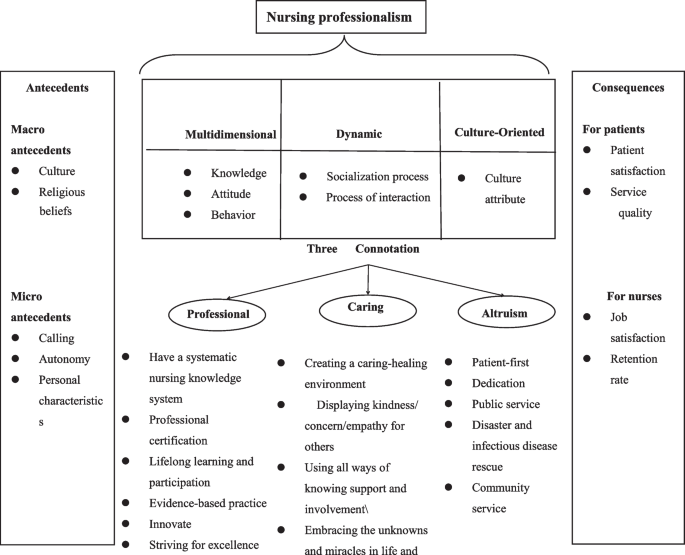
Antecedents, attributes, and consequences of nursing professionalism
Defining the connotation of nursing professionalism
Nursing professionalism has been defined as professional, caring, and altruistic.
Professional values are characteristic of nursing professionalism. Nursing work requires rich knowledge and scientific evidence-based work to improve the quality of nursing services for patients. Nurses need lifelong learning, qualification certification, and participation in academic and practical activities.
Caring is regarded as the core of professionalism. This study suggests creating a caring-healing environment, displaying kindness/concern/empathy for others, employing all methods of knowing support and involvement, embracing the unknowns and miracles in life and practising loving to care for people to obtain high professionalism. This study notes that nursing professionalism emphasizes care for the individual patient and that the nurse does everything possible to create a caring and healing environment for patients. In different health systems worldwide, nurses have incorporated caring about nursing professionalism into everything they do. This characteristic is consistent with Nightingale's view that “Nurses need to be sensitive. A nurse must use her brain, heart and hands to create healing environments to care for the patient’s body, mind and spirit” [ 87 , 88 ].
Nursing has an altruistic nature, and people interested in helping patients are attracted to this profession [ 89 ]. However, some studies have shown that altruistic care is equated with self-sacrifice, self-denial, and unidirectional and unconditional care [ 90 ]. Care for a nurse’s own needs is equally important, but nurses should be able to put aside their own needs when required to focus on the needs of others [ 91 ]. Nurses should view self-care and altruism as dialectical. Self-realization and providing care for others are not conflicting concepts [ 92 ].
Defining the attributes of nursing professionalism
In this study, we defined nursing professionalism as multidimensional, dynamic, and culture oriented.
Nursing professionalism is a multidimensional concept that includes knowledge, attitudes, and behaviour. Previous studies have defined professionalism as the degree of commitment by individuals to the values and behavioural characteristics of a specific career identity [ 6 , 7 ]. However, current research on nursing professionalism is mostly single dimensional. The Behavioural Inventory for Professionalism in Nursing (BIPN) is based on Miller’s model and is used to measure professional behaviours among nurses [ 7 ]. Hall’s Professionalism Inventory Scale [ 6 ] identified five attitudinal attributes of professionalism. This study highlights that it is also necessary to focus on the knowledge dimension of professionalism. Nursing students and nurses should first understand the nursing professionalism that is necessary to become a nurse, which may be the first step in developing professionalism. Nursing students and nurses need to know the values that are necessary to practice the nursing and not have vague impressions. Some studies have shown that nursing students or nurses learn values and norms in informal trainings [ 93 ]. Therefore, this study suggests that the development of assessment tools for the knowledge dimension of professionalism is also necessary. Multidimensional evaluation tools are not available for nursing professionalism. Thus, clarifying the multidimensional nature of nursing professionalism will contribute to the development of multidimensional evaluation tools.
Moreover, understanding the dynamics of professionalism is helpful for cultivating nursing professionalism in stages and steps. Inquiries into medical professionalism should be integrated into the culture of social media interaction [ 94 ]. Nursing educators and managers should dynamically cultivate nursing professionalism in their interactions.
Differences in the connotation of nursing professionalism are noted in different cultures. This study suggests that the cultivation and evaluation of nursing professionalism need to consider the cultural attributes of different regions and countries.
Future research directions
Exploring the antecedents of nursing professionalism can help schools or hospitals cultivate nursing professionalism and develop courses and specific measures.
The macro antecedents of nursing professionalism include culture and religion, and the micro antecedents include calling, autonomy, and personal characteristics. Some researchers have explored methods to cultivate nursing professionalism; for example, role modelling, feedback, group discussions, case-based discussions, reflection, holding ethical rounds, and reports potentially represent more effective methods [ 95 ]. Some researchers have tried to enhance professionalism through social media [ 96 ]. One of the findings this study is that nursing professionalism is complex and its cultivation difficult. Studies have shown that didactic lectures are ineffective for teaching professionalism [ 97 ]. The development of true nursing professionalism requires national advocacy and the immersion of a good professional environment that incorporates professionalism into daily nursing practice. Role modelling is considered an effective method for developing professionalism in nursing [ 98 ]. Therefore, this study suggest that studies should be actively conducted to deeply discuss the causes and processes affecting professionalism and to cultivate and intervene at macro and micro levels as well as the key time periods and populations that form professionalism to truly shape the formation of professionalism. Moreover, an environment for building professionalism [ 99 ] is very important. Williams [ 100 ] (2015) considered that the development of professionalism should begin as early as the first semester of an undergraduate nursing course. One of the themes of nursing students’ professional identity development is ‘doing-learning-knowing-speaking’. Students should develop professionalism in all these areas of nursing practice.
The relationship between nursing professionalism and health outcomes or nurses’ human resources needs to be further studied.
Our research suggests that the ultimate goal of nursing professionalism is to serve patients with professional knowledge and special professional quality. The public has become increasingly aware of certain possibilities, limitations, and consequences of professionalism. COVID-19 significantly increased the discussion of professionalism and patient outcomes.
Improving professionalism has a positive impact on job satisfaction, professional quality of life, and the willingness to continue in the profession [ 101 , 102 , 103 ]. Therefore, it is important to improve support for nurses, create a good environment for professionalism, and establish a training system for professionalism, thus paving the way to enhance training in professionalism and create opportunities for nurses.
Implications for nursing management
In April 2020, the World Health Organization (2020) issued the First State of the World’s Nursing 2020 [ 104 ]. The report highlighted that nursing professionals are the largest occupational group in the health sector, numbering 27.9 million worldwide. Nurses spend more time with patients than any other health care professionals [ 105 ].
Worldwide, nursing professionalism is considered important and associated with expectations. This study clarifies the concept of nursing professionalism and contributes to a framework for developing a theoretical model as well as instruments to measure the concept. A conceptual model of nursing professionalism may increase nurse managers’ insight into nurses’ behaviours and values, creating a good working environment.
Nurse managers should integrate nursing professionalism into their philosophy, mission, and objectives and provide necessary resources, tools, and projects to develop professionalism among nurses. Nurses should cultivate professionalism to provide good nursing services to patients. Further research should explore the relationship between nursing professionalism and patient health outcomes and formulate effective training programs for professionalism.
Limitations
This conceptual analysis has some limitations. First, research on nursing professionalism published in English may be conducted in different countries and cultures. However, it is also necessary to obtain a more comprehensive and mature concept of the study of different national languages. Second, the lack of research on the combination of all elements of professionalism may lead to overestimation of the impact of these subelements on professionalism. Third, the concept analysis focused on the research process and the researchers’ perspectives, possibly reflecting a lack of other professional understandings of nursing professionalism in medical groups. In addition, the concept analysis included a risk of selection bias, extraction bias, and analysis bias because the study selection process, data extraction, and analysis were all conducted by two researchers. Despite these risk, the studies were all described accurately and systematically.
Nursing professionalism is one of the important foundations of clinical nursing. It is multidimensional, dynamic, and culture oriented. Based on the analysis, nursing professionalism has been defined as providing people care based on principles of professionalism, caring, and altruism. The definition, attributes, antecedents, consequences, and reference analysis of the experience of nursing professionalism determined in this study provide a theoretical basis for future research. This information can be used to evaluate nursing professionalism, develop assessment tools, or generate theory-based training courses and interventions.
Availability of data and materials
Data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Hinshaw AS, Smeltzer CH, Atwood JR. Innovative retention strategies for nursing staff. J Nurs Adm. 1987;17:6.
Article Google Scholar
Ohman A. Team social cohesion, professionalism, and patient-centeredness: Gendered care work, with special reference to elderly care—A mixed methods study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:381.
Sahman I. A field study related to determine the effect of professionalism of private hospital management on institutionalization process. Master’s thesis, Gazi University Graduate School of Social Sciences, Department of Management Hospital Management Department; 2008.
Huber TH. Nursing professionalism Kentucky Nurse Association. 2015;63(1):15.
Google Scholar
Hintistan S, Topcuoglu B. Professionalism characteristics of nurses working in internal medicine clinics continuing education. Universal J Public Health. 2017;5:1.
Hall RH. Professionalization and bureaucratization. Am Sociol Rev. 1968;33:1.
Miller BK, Adams D, Beck L. A behavioral inventory for professionalism in nursing. J Prof Nurs. 1993;9:5.
Yeun, E. J., Kwon, Y. M., & Ahn, O. H. (2005). Taehan Kanho Hakhoe chi, 35(6).
Yoder L. Professionalism in nursing. MEDSURG. Nurs. 2017;26:5.
Yamamoto T, Kawaguchi A. Review of the concept of medical professionalism. Bulletin of Faculty of Education: Hokkaido University; 2016. p. 126.
Schwirian PM. Professionalization of Nursing: Current Issues and Trends. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott; 1998.
Swick HM. Medical professionalism and the clinical anatomist. Clinical anatomy (New York, N.Y.). 2006;19(5):393–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20258 .
Al-Eraky MM. Twelve Tips for teaching medical professionalism at all levels of medical education. Med Teach. 2015;37:11.
Sullivan TM, Thiessen AK. Occupational therapy students’ perspectives of professionalism: An exploratory study. Open J Occup Ther. 2015;3:4.
Aguilar A, Stupans I, Scutter S, King S. Exploring professionalism: the professional values of Australian occupational therapists. Aust Occup Ther J. 2012;59:3.
Adam K, Peters S, Chipchase L. Knowledge, skills and professional behaviours required by occupational therapist and physiotherapist beginning practitioners in work-related practice: a systematic review. Australian occupational therapy journal. 2013;60(2):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1630.12006 .
Walker LO, Avant KC. Concept Analysis. In: Walker, L.O., Avant, K.C. (Eds.), Strategies For Theory Construction in Nursing, 5th ed.. London: Pearson; 2014.
Weaver K, Mitcham C. Nursing concept analysis in North America: state of the art. Nurs Philos [Internet]. 2008;9(3):180–94. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-769X.2008.00359.x .
Meleis AI. Theoretical nursing: Development and progress: Fifth edition; 2012.
Nuopponen A. Methods of concept analysis - a comparative study. LSP Journal, -, Language for special purposes, professional communication, knowledge management and cognition; 2010.
Fogarty TJ, Dirsmith MW. Human Resource Development Quarterly. 2001;12(3):247–66.
Wynd CA. Current factors contributing to professionalism in nursing. Journal of professional nursing: official journal of the American Association of Colleges of Nursing. 2003;19(5):251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/s8755-7223(03)00104-2 .
Takada N, Asakura K, Sugiyama S. Developing and validating the Japanese version of professional attitude scale for nurses. Int Nurs Rev. 2021;68(1):24–33.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Miller BK. A model for professionalism in nursing. Today's OR nurse. 1988;10(9):18-23.
Hinshaw AS. Socialization and resocialization of nurses for professional nursing practice. Papers presented at the Sixteenth Conference of the Council of Baccalaureate and Higher Degree Programs; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; 1976. (1977). NLN publications. 1977;(15-1659):1–41.
Dehghani A, Salsali M, Cheraghi MA. Professionalism in Iranian Nursing: Concept Analysis. Int J Nur Knowl. 2016;27:2.
Chandratilake M, McAleer S, Gibson J. Cultural similarities and differences in medical professionalism: a multi-region study. Med Educ. 2012;46:3.
Jin P. The physician charter on medical professionalism from the Chinese perspective: a comparative analysis. J Med Ethics. 2015;41:7.
Bianic TL. Eliot freidson, professionalism, the third logic: on the practice of knowledge, the university of chicago press, chicago, 2001, 251p. 2003;45(3):0-426.
Lamonte M. Test-taking strategies for CNOR certification. AORN J. 2007;85(2):315–32.
Stucky CH, Wymer JA. Progressing toward specialty certification as the National Standard for Nursing. Nurs forum. 2020;55:3.
Karadağ A, Hisar F, Elbaş NO. The level of professionalism among nurses in Turkey. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2007;39:4.
Cornett BS. A principal calling: professionalism and health care services. J Commun Disord. 2006;39:4.
Shen Y, Xie W, Wang X, Qu J, Zhou T, Li Y, Mao X, Hou P, Liu Y. Impact of innovative education on the professionalism of undergraduate nursing students in China. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;98:104647.
Boehm LM, Stolldorf DP, Jeffery AD. Implementation Science Training and Resources for Nurses and Nurse Scientists. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020;52:1.
Watson J. Nursing: Human science and human care. New York: National League for Nursing; 1988.
Collins H. Collins English Dictionary – Complete and unabridged. 12th ed. London: Harper Collins Publishers; 2014.
Papastavrou E, Karlou C, Tsangari H, Efstathiou G, Sousa VD, Merkouris A, et al. Cross-cultural validation and psychometric properties of the greek version of the caring behaviors inventory: a methodological study. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice. 2011.
Jooste K. The principles and practice of nursing and health care. Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers; 2010.
Kubsch S, Tyczkowski B, Passel C. Altruism and the Difficult Patient. Journal of holistic nursing : official journal of the American Holistic Nurses’ Association. 2021;39(1):43–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0898010120933123 .
Fernandez R, Lord H, Halcomb E, Moxham L, Middleton R, Alananzeh I, Ellwood L. Implications for COVID-19: A systematic review of nurses’ experiences of working in acute care hospital settings during a respiratory pandemic. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;111: 103637.
Zhang M, Zhang P, Liu Y, Wang H, Hu K, Du M. Influence of perceived stress and workload on work engagement in front-line nurses during COVID-19 pandemic. J Clin Nurs. 2021;30:11–2.
Goldie J. Assessment of professionalism: a consolidation of current thinking. Medical teacher. 2013;35:2.
Riley JM, Beal JA. Public service: Experienced nurses’ views on social and civic responsibility. Nursing outlook. 2010;58:3.
McDonald L. Florence Nightingale and Irish nursing. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(17–18):2424–33.
Liu Q, Luo D, Haase JE, Guo Q, Wang XQ, Liu S, Xia L, Liu Z, Yang J, Yang BX. The experiences of health-care providers during the COVID-19 crisis in China: a qualitative study. Lancet Global Health. 2020;8:6.
Kim-Godwin YS, Baek HC, Wynd CA. Factors influencing professionalism in nursing among Korean American registered nurses. J Prof Nurs 2010;26:4.
Merriam-Webster. (2019). Professionalism. https://www.merriam webster.com/dictionary/professionalism.
Cambridge Dictionary. (2019). Professionalism. https://www.dictionary.
Hwang JI, Lou F, Han SS, Cao F, Kim WO, Li P. Professionalism: the major factor influencing job satisfaction among Korean and Chinese nurses. Int Nurs Rev. 2009;56:3.
Zulipiye T, Waili A, d., Litifu, K., Jingying, R., & Yi, Y. Study on the current situation and influencing factors of nursing students’professional spirit in a mescal college in Xinjian. Chinese J Med Educ Res. 2018;17:7.
Jha V, Bekker HL, Duffy SR, Roberts TE. Perceptions of professionalism in medicine: a qualitative study. Medical education. 2006;40(10):1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02567.x .
Qian W, Zhiguang D. Scientific connotation of Nightingale′s spirit and its inheritance and promotion. Chinese Nurs Res. 2019;33:19.
Cain J, Romanelli F. E-professionalism: a new paradigm for a digital age - sciencedirect. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning. 2009;1(2):66-70.
Villa-García L, Rodriguez Blanco O. Social networks in health care: Ethical implications and nursing professionalism. Las redes sociales en el cuidado de la salud: implicaciones éticas y profesionalismo enfermero. Enfermeria clinica (English Edition). 2020;30(1):66–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enfcli.2019.08.006 .
KRAMER, & MARLENE. Reality shock: why nurses leave nursing. American Journal of Nursing. 1975;75(5):891.
Barnhoorn P, Houtlosser M, Ottenhoff-de Jonge M, Essers G, Numans M, Kramer A. A practical framework for remediating unprofessional behavior and for developing professionalism competencies and a professional identity. Med Teach. 2019;41:3.
Ghadirian F, Salsali M, Cheraghi MA. Nursing professionalism: An evolutionary concept analysis. Iranian journal of nursing and midwifery research. 2014;19(1):1-10.
Evetts J. Professionalism: Value and ideology. Current Sociology. 2013;61:5–6.
Hodges BD, Ginsburg S, Cruess R, Cruess S, Delport R, Hafferty F, Ho MJ, Holmboe E, Holtman M, Ohbu S, Rees C, Ten Cate O, Tsugawa Y, Van Mook W, Wass V, Wilkinson T, Wade W. Assessment of professionalism: recommendations from the Ottawa 2010 Conference. Med Teach. 2011;33:5.
Kruse FM, Ligtenberg WMR, Oerlemans AJM, Groenewoud S, Jeurissen PPT. How the logics of the market, bureaucracy, professionalism and care are reconciled in practice: an empirical ethics approach. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):1024. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05870-7 .
Bell L. 2. code of ethics for nurses with interpretive statements. AJN The American Journal of Nursing. 2003;103(4):84-84.
Dollaghan C. Evidence-based practice: myths and realities. Asha Leader. 2004;9:7.
Weng RH, Chen WP, Huang CY, Hung CH, Hsu CT. Can nurse innovation improve customer perception of service quality and experience? J Clin Nurs. 2016;25:13–4.
Watson J. Nursing: The philosophy of science and caring. Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Company; 1979.
Oxford English Dictionary. (2019). Retrieved from https://www.oed.com
Swank JM, Ohrt JH, Robinson E. A qualitative exploration of counseling students' perception of altruism. Journal of Humanistic Counseling. 2013;52(1):23-38.
WHO. Disease Outbreaks. Available online: http://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/en/ (Accessed 13 July 2020).
Kim-Godwin YS, Baek HC, Wynd CA. Factors influencing professionalism in nursing among Korean American registered nurses. J Prof Nurs. 2010;26:4.
Braskamp LA, Maehr ML. Spectrum: An organizational development tool [Manual]. Champaign, IL: Metritech, Inc.cambridge.org/fr/dictionnaire/anglais/professionalism; 1985.
Del Bueno DJ, Vincent PM. Organizational culture: how important is it? J Nurs Adm. 1986;16:10.
Alavi A, Zargham-Boroujeni A, Yousefy A, Bahrami M. Altruism, the values dimension of caring self-efficacy concept in Iranian pediatric nurses. Journal of education and health promotion. 2017;6:8.
Taylor EJ, Carr MF. Nursing ethics in the seventh-day adventist religious tradition. Nurs Ethics. 2009;16:6.
Snizek W. Hall’s professionalism scale: An empirical reassessment. Am Sociol Rev. 1972;37:1.
Liaw SY, Wu LT, Holroyd E, Wang W, Lopez V, Lim S, Chow YL. Why not nursing? Factors influencing healthcare career choice among Singaporean students. Int Nurs Rev. 2016;63:4.
Attree M. Nursing agency and governance: registered nurses’ perceptions. J Nurs Manag. 2005;13:5.
Freund AM, Blanchard-Fields F. Age-related differences in altruism across adulthood: making personal financial gain versus contributing to the public good. Dev Psychol. 2014;50:4.
Wu Q, Sun X, Shi Y, Zhang S. The research progress of nurse professionalism and its influencing factors. Chin Med Ethics. 2015;28:04.
Tanaka M, Taketomi K, Yonemitsu Y, Kawamoto R. Professional behaviours and factors contributing to nursing professionalism among nurse managers. J Nurs Manag. 2016;24:1.
Birden H, Glass N, Wilson I, Harrison M, Usherwood T, Nass D. Teaching professionalism in medical education: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 25. Medical teacher. 2013;35(7):e1252-66.
Selic P, Cerne A, Klemenc-Ketis Z, Petek D, Svab I. Attitudes toward professionalism in medical students and its associations with personal characteristics and values: what actually makes a difference? [Response to Letter]. Advances in medical education and practice. 2019;10:689–692. https://doi.org/10.2147/AMEP.S227510 .
Masmouei B, Bazvand H, Harorani M, Bazrafshan MR, Karami Z, Jokar M. Relationship between personality traits and nursing professionalism. Journal of Client-Centered Nursing Care(3). 2020.
Jeffreys MR. Jeffreys’s Nursing Universal Retention and Success model: overview and action ideas for optimizing outcomes A-Z. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;35:3.
Welling S. Applying the Constructs from the Sense of Belongingness to Improve Job Satisfaction and Employee Retention. Sigma Theta Tau International's 26th International Nursing Research Congress. STTI; 2016.
Izumi S, Konishi E, Yahiro M, Kodama M. Japanese patients’ descriptions of “the good nurse”: personal involvement and professionalism. ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 2006;29:2.
Kramer M. Reality shock: Why nurses leave nursing. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1974.
Riegel F, Crossetti MDGO, Martini JG, Nes AAG. Florence Nightingale’s theory and her contributions to holistic critical thinking in nursing. Rev Bras Enferm. 2021;74(2): e20200139. https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2020-0139 .
Nightingale. Notes on nursing : what it is and what it is not - commemorative edition; 1992.
Smith R, Lagarde M, Blaauw D, Goodman C, English M, Mullei K, Pagaiya N, Tangcharoensathien V, Erasmus E, Hanson K. Appealing to altruism: an alternative strategy to address the health workforce crisis in developing countries? J Public Health (Oxf). 2013;35:1.
Pettersen T. The ethics of care: normative structures and empirical implications. Health Care Anal. 2011;19:1.
Hem MH, Halvorsen K, Nortvedt P. Altruism and mature care: some rival moral considerations in care ethics. Nurs Ethics. 2014;21:7.
Van Nistelrooij I, Leget C. Against dichotomies: On mature care and self-sacrifice in care ethics. Nurs Ethics. 2017;24:6.
Lempp H, Seale C. The hidden curriculum in undergraduate medical education: Qualitative study of medical students perceptions of teaching. BMJ. 2004;329:770–3.
Hsieh JG, Kuo LC, Wang YW. Learning medical professionalism - the application of appreciative inquiry and social media. Medical education online. 2019;24:1.
Birden HH, Usherwood T. “They liked it if you said you cried”: how medical students perceive the teaching of professionalism. Med J Aust. 2013;199:6.
Kind T, Patel PD, Lie D, Chretien KC. Twelve tips for using social media as a medical educator. Med Teach. 2014;36:4.
Lockman JL, Yehya N, Schwartz AJ, Cronholm PF. Professionalism in pediatric anesthesiology: Affirmation of a definition based on results of a nationally administered survey of pediatric anesthesiologists. Paediatr Anaesth. 2019;29:4.
Vinales J. J. (2015). The mentor as a role model and the importance of belongingness. British journal of nursing (Mark Allen Publishing), 24(10), 532–535. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2015.24.10.532 .
Phillips RL, Jr. The Built Environment for Professionalism. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine: JABFM. 2020;33(Suppl):S57–S61. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2020.S1.190441 .
Williams MG, Burke LL. Doing Learning Knowing Speaking: How Beginning Nursing Students Develop Their Identity as Nurses. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2015;36:1.
Manojlovich M, Ketefian S. The effects of organizational culture on nursing professionalism: implications for health resource planning. The Canadian journal of nursing research = Revue canadienne de recherche en sciences infirmieres. 2002;33(4):15–34.
Jang I, Kim Y, Kim K. Professionalism and professional quality of life for oncology nurses. Journal of clinical nursing. 2016;25(19–20):2835–45.
Rimmer A. Improving professionalism will increase job satisfaction, says RCP. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2018;363: k5216.
World Health Organization. State of the World’s Nursing Report – 2020. (2020–04–06) [2020–05–10], Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/nursing-report-2020 [in English].
Butler R, Monsalve M, Thomas GW, Herman T, Segre AM, Polgreen PM, Suneja M. Estimating Time Physicians and Other Health Care Workers Spend with Patients in an Intensive Care Unit Using a Sensor Network. Am J Med. 2018;131:8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Hui Yang for the great efforts made in designing the research. We would like to thank linbo Li for providing valuable suggestions for this study.
Postgraduate Education Innovation Program of Shanxi Province in China (No. 2020BY067).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030001, Shanxi, People’s Republic of China
Huili Cao, Yanming Wu, Yifei Du, Xingyue He, Qiaohong Wang & Hui Yang
Linfen Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University (Linfen People’s Hospital), Linfen, 041000, Shanxi, People’s Republic of China
The Third Peoples Hospital of Taiyuan, Taiyuan, 030001, Shanxi, People’s Republic of China
The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030001, Shanxi, People’s Republic of China
Yangjie Chen, Qiaohong Wang & Hui Yang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Hl C and HY made substantial contributions to conception and design. HL C, YJ S, YM W, YF D Collectioned and analysis the data. Hl C was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. XY H, YJ C, QH W revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hui Yang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Our study was approved by the ethical committee of The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University,Shanxi, China,(approval no. 2020K061).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cao, H., Song, Y., Wu, Y. et al. What is nursing professionalism? a concept analysis. BMC Nurs 22 , 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-01161-0
Download citation
Received : 07 May 2022
Accepted : 23 December 2022
Published : 07 February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-01161-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Nursing professionalism
- Concept analysis
- Consequences
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Why I Love Being a Nurse

This blog has been updated on March 22, 2023.
Learn more about Carson-Newman's online FNP nursing programs .
Nursing is one of the most professionally, personally, and spiritually rewarding careers there is.
People are driven to a career in nursing for a variety of reasons. Carson-Newman wanted to better understand and document some of these reasons, which is why we reached out to 15 registered nurses, including three of our own FNP students, to get their perspectives on a simple question: What do you find most rewarding about a career in nursing ?
Read on to discover some of the responses we received and compare these answers to your own experience.
Earn Your MSN-FNP Part-Time For Less than $30k
Nancy brook, rn, msn, cfnp.
'One of the most rewarding aspects of a career in nursing is the ability to connect with our patients on such an intimate level. While we often meet under very difficult circumstances—being present as people face serious health challenges or injuries, witnessing the moment of birth or the end of life—we get to know our patients very quickly and have the opportunity to play an important role in their lives.
"I became a nurse so that I could have an impact on the lives of others and have a career that felt very meaningful . After 25 years of helping patients and their families navigate cancer and mentoring new nurses, I believe that at the end of the day, no matter how challenging, I have impacted someone’s life for the better."
Catherine Burger, RN, MS, MSOL, NEA-BC
"What I find to be the most rewarding about being a nurse is the numerous career paths that are available within the profession. For example, in my nearly 30-year career I have been blessed to work in labor and delivery, the Intensive Care Unit, home health, informatics, leadership, clinical practice, and ambulatory care. As a contributing writer for registerednursing.org, I now get to educate my colleagues and future nurses on current events and issues.
"I initially chose a nursing career just out of high school as I wanted to work in the field of medicine, and I knew I could complete the degree within two years. After many years and many advanced degrees, I still love being of help to people at all stages of life. I am very proud of my nursing profession and I love that nurses are still the most trusted profession to the public: a responsibility we should never take for granted."
Elizabeth Mason, RN, MSN - Carson-Newman FNP Student

"After working for a while, I went back to school and became a nursing instructor in the classroom and clinical. It is the perfect balance of hands-on patient care and teaching the next generation of nurses. I love [when] my students have that “ah-ha” moment as they put together the big picture of the patient, their diagnosis, medications, and treatment plans. I love seeing the growth of new nursing students to their preceptorship. It is always a blessing to see them in the hospital later as nurses succeeding at their calling."
Sandy Griffin, LPN, CHPLN
"I really love going to bed knowing I made a difference. As an LPN at a hospice, that difference is usually making sure our patients are as comfortable as possible, but we often have the opportunity to help the patients’ families too. It’s satisfying to know they feel more at ease after they see the care we provide.
"I chose a nursing career partially because I loved biology and anatomy and partially to have a career with which I could support myself and be independent. The further I got into my nursing education, I realized how rewarding it was to be able to make people who are sick and uncomfortable feel better, even if it’s just a little. Treating people with kindness and respect goes a long way. I found my nursing career home in hospice. It hasn’t always been easy, but it has always been worth it.
"I have loved empowering and supporting patients and families to know that they are able to get through anything. Working for a hospice agency, I have been able to help patients have dignity at some of the most vulnerable times in their lives. Being with patients and their families at the end of life is a privilege. It has been an honor to have been with so many at that time.
"I also love the pride I feel in my work. Being a nurse is one of the most challenging jobs someone could do. It’s physically and mentally demanding at times. However, at the end of the day, you feel amazing satisfaction and pride. Being able to help those in need for a living is unlike any other profession."
MaryAnn Ciambriello, RN, BSN
"The most rewarding thing about being a nurse is making a difference in the lives of others. It may be your patients, their families, or your students. Nursing offers us so many arenas to practice in. As an RN, I have worked in the delivery room, in home care, in a prison, as a high school nurse, and as the director of nurses in assisted living facilities. Now, I am the owner of a few businesses.
"What motivated me to be an RN? My dad chose my profession for me. I was studying business in college and he thought that I should become an RN. So, like any good daughter, I dropped my business studies and became an RN; however, I did go back to complete two business degrees.
"What do I love about nursing? I love that this profession allows us the opportunity to work in so many diverse areas. We are not pigeonholed into just the hospital—the sky's the limit in this profession.
"In nursing, you just have to follow your passion and purpose and stay true to yourself. Always remember to have empathy and to give the best care possible."
Shantay Carter, RN, BSN

"Knowing that my care, touch, voice, and time can help a patient make it through the night is one of the most rewarding feelings. Sometimes, it's the little things that you do for your patient that make a difference. The nursing profession has opened so many doors for me. It has allowed me to become an author and run a successful non-profit organization that addresses the needs in my community. My specialty is orthopedics and trauma, and I love working in this area."
Lauren Mochizuki, RN, BSN
"What I find most rewarding about my career as a nurse is that I have the opportunity to help people in their most vulnerable, and unexpected, moments. For some, coming to the emergency department can be one of the worst days of their lives. As their nurse, my job is to make them feel safe, comfortable, and cared for.
"There are many things that motivated me to choose nursing as a career. First, I love people. I love chatting with them, being around them, and taking care of them—it is very fulfilling to my soul. The second reason is that the schedule is wonderful for being a mother. I now have the opportunity to work per diem and work around my husband's schedule so I can spend lots of time with our children.
"Lastly, I love that it provides great compensation so that I can contribute to my family financially. Five years ago, my husband and I paid off $266,000 of debt, and I am so thankful for my various nursing jobs that allowed me to work to reach this goal. I also love the culture of nursing in my emergency department. It feels like we understand each other, like we can look at each other in a certain way and know what we are thinking. We can sense when something is wrong in each other or celebrate our personal victories. I have the privilege to work among great nurses and that makes the entire shift more enjoyable."
Cynthia Attaway, RN, MSN - Carson-Newman FNP Student

"I am a part time nursing instructor for a community college, and the first to be allowed in the acute hospital setting. The human connection cannot be experienced in simulation and observing the science of human caring was emotional during the pandemic.
"Nursing is the best—high technology, and high touch."
Chris Caulfield, RN, NP-C
"As a nurse, I have a flexible career that allows me to pursue my passions while also having a significant positive impact on patients at need. I was initially attracted to the nursing profession as I loved working with the elderly and had a strong interest in human physiology. There were flexible nursing programs in my local area that were affordably priced, so it was easy for me to start my RN program. I was also very excited by the opportunities to obtain advanced practice certifications and licenses through distanced-based programs that were flexible and could work around my personal commitments.
"Throughout my nursing career, I’ve had the great opportunity to work in many different fields including long-term care, psychiatric nursing, urgent care, labor relations, and nursing informatics. As you work in different specialties, your knowledge continues to grow and your ability to think outside the box increases. As an advanced practice nurse (FNP-C), I’ve gained a deeper understanding of the health care system, which had a significant contribution in leading me to success in my most recent venture-backed technology startup. I’ve been able to take this knowledge and create a system that focuses on allowing nurses to work a flexible schedule via their mobile app, while also helping to address the staffing shortage crises experienced in long-term care facilities.
"Over the past three years, I’ve had over 10,000 nursing professionals join my organization to pick up shifts on the side. With almost unlimited opportunities, I continue to recommend the nursing profession to countless numbers of family members, friends, and acquaintances. I’ve yet to find another career choice that allows the flexibility and options that nursing does."
Tina Baxter, APRN, GNP-BC

"As a nurse, I have the privilege of helping others when they are the most vulnerable. I witness some of their greatest triumphs and their greatest defeats. There is nothing better than attending a birth, holding the hand of someone who is dying, or helping someone achieve a better life through improving their health. It is a legacy that will live on long after you are gone. The patients and families will remember your warm smile, your gentle touch, the knowledge you shared, and the fact that you cared for them.
"As a student in health care, I realized I was more concerned about how a person got ill and how to prevent it, rather than just how to treat it. I wanted to understand how I could help a person not only get healthy but stay healthy. That’s what nurses do. We teach our patients to take care of themselves and to optimize their health.
"One of the things I love about being a nurse is that this career is flexible . I have been a bedside nurse, a nursing professor, a mentor, a supervisor/manager/charge nurse, an entrepreneur, a nurse scientist, a nurse educator, a legal nurse consultant, a wellness practitioner, a nurse practitioner, and coming soon, a nurse author with my first book. I would say that being a nurse is pretty fabulous."
Andrea Tran, RN, IBCLC
"The most rewarding thing I have found about being a nurse is the personal connection that I am able to make with patients. No matter how long it has been, a patient remembers their nurse. They may or may not remember the nurse’s name, but they remember if they were kind and compassionate. A good nurse always is.
"I became a nurse in response to nothing short of “a calling.” I was visiting my grandmother with my mother. She had gone into another room to visit with someone else she knew, and I went to get her. I noticed that the other patient in the room was in a lot of pain, and I had such a strong and deep desire to help them. I decided then and there that I would become a nurse.
"I have spent my entire career with women during the childbearing period. It is mostly wonderful, but when it is not, it is terrible.
"Getting to share in the joy of a new family creates so much happiness. Helping new parents step into their new world with education and support puts me in my happy place."
Nancy Congleton, RN, Author

"What initially motivated me to become a nurse was that my husband and I were sinking financially. We both worked full time, our home was small and affordable, our vehicles were not brand new, and yet we were barely making it. At a young age I found myself intrigued by the medical profession and, after discovering that I could have my associate’s degree in nursing and become an RN in approximately three years, I went for it. What started as a financial necessity has become so much more. I thoroughly enjoy caring for my patients and love mentoring new nurses.
"The things I love most about being a nurse include the variety of areas to practice in, the constant opportunities to focus on others, and those 12-hour shifts! If I had to go back to a Monday–Friday schedule, I don't know if I'd survive!"
Megan McHatten, RN, BSN, CNOR
"As an operating room nurse at a trauma center, there are times that can be pretty stressful and fast paced. Recently, a trauma was called and about six of us rushed to the OR to set up. All we typically know during these events are the very basics, and in this case, a motor vehicle accident had occurred, and we needed to do an exploratory laparotomy. Within about two minutes, we had the supplies and instruments opened, scrub techs were setting up, and anesthesia was getting ready. I looked around and was so proud to be a part of a team that could, within minutes, be ready to potentially save someone's life. Those are times when I am proud to be a perioperative nurse and I find them especially rewarding.
"What motivated me to choose this career? High demand, good pay, multiple specialties to work in, the ability to move forward with my career if I choose (i.e. nurse practitioner, administration) and the feeling of making a difference.
"I love the feeling when our team has a great surgical case, and everyone is working together like a well-oiled machine. I love knowing that many of my patients will begin their healing journey in my OR. I love the endless amount of learning and science that the health care field offers."
Maria Kindrai, RN, MSN - Carson-Newman FNP Student

"As a nurse, I have learned to appreciate every moment spent at the bedside of a patient. Caring for others has always been a priority but during a pandemic it has been heightened. This one on one time with someone is certainly time when both the patient and the nurse have the opportunity for growth and to learn from one another."
Donna Mathezing, RN
"30 years of being a nurse and I have never had a regret about my career choice. I knew when I was five years old that helping people and talking with them was what I was meant to do.
"I have worked in all critical care areas from emergency to the cardiovascular ICU to the general systems ICU; I now work in the post-operative care unit and have 10 years of experience flying with our air ambulance service in a helicopter. I get to make a profound difference every single day. That profound difference is different for every patient, depending on what they need from me at their time of need. That could be something simple like holding a hand, letting them cry on my shoulder, giving pain medications so their loved one is comfortable, or just reassuring them that we will take care of them!
"Being with people at what is sometimes the worst moments of their lives or the best moments (diagnosis is negative or the birth of a baby) is a privilege and one I take very seriously. Being with a family as their loved one is passing away is the ultimate compliment for a nurse. Death is a sacred and scary time for many, and to be allowed within that sacred circle to offer support and comfort is what is rewarding about nursing.
"If I can walk away after my shift knowing that I have eased a person’s worry or fear and brought some sort of peace to them, then my day is fulfilled. And the best part of that is that I get many opportunities every day that I work."
Learn more about Carson-Newman's online nursing programs for registered nurses with their bachelor's or master's.
Request your free program brochure, about carson-newman’s online fnp programs.
Founded in 1851, Carson-Newman is a nationally ranked Christian liberal arts university. An online, yet personal, learning environment connects you with fellow students, faculty, and staff. Faith and learning are combined to create evidence-based online graduate nursing programs designed to transform you into a more autonomous caregiver.
Through its online program and student-centric curriculum, Carson-Newman provides a life-changing education where students come first. Designed for working nurses, Carson-Newman’s affordable FNP programs feature 100% online coursework with no mandatory log-in times, clinical placement service, and exceptional individualized support that prepare graduates to pass the FNP licensure exam.
If you’re ready for the next step in your nursing career, consider the online Master of Science in Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner offered by Carson-Newman University and accredited by the CCNE.
For those who already hold an MSN degree, consider pursuing a Post-Master’s FNP Certificate to enjoy all the leadership opportunities, job satisfaction and autonomy of a family primary care provider. For more information, visit onlinenursing.cn.edu.
Request Information
Download Brochure

Carson-Newman University • 1646 Russell Ave. Jefferson City, TN • © Copyright 2024 Carson-Newman University. All rights reserved. • Sitemap • Privacy Policy | California Privacy Notice
- Nursing School
“Why Do You Want to Be a Nurse?” Nursing School Interview Question

Preparing your “Why do you want to be a nurse” answer for an interview is key. The question will always be asked in a nursing school interview, which is why you must strategically plan out your answer, and take some time to reflect on this difficult question.
Not everybody puts thought into the “why” behind this question. Some people seem to act entirely on instinct, but you can’t afford to do so with your career – your future. Not to mention the fact that you need to have a professional, snappy, and thoughtful response to any (and every) question brought forward in an admissions interview.
Some nursing school interview questions are a chore to get through, but with some careful consideration, the question of why will be so foundational that you’ll never regret having explored it. This isn’t just something you have to answer, this is a question you want – even need – to answer.
In this article, you will find different answer samples to the “Why do you want to be a nurse” question, how to find a personal answer unique to you, and how to structure your answer to create an amazing impression on the interview day.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 10 min read
Why are you asked this question.
Having an answer to this question is more than important, it’s necessary. It’s necessary for your interview, but it’s also necessary for yourself.
Imagine being the interviewer for a moment and seeing a candidate who looks great on paper, with strong academic record, a great nursing school personal statement , good letters of reference, and a demonstrable track record of excellence all-around demonstrated in their nursing school application resume . But in the interview, that candidate responds with, “I don’t know,” to the question of why they are selecting the career that they are. The interviewer’s likeliest response? Complete dismissal. If this question isn’t answered properly, it will corrupt the entire interview, and possibly even destroy the application altogether.
That’s why they ask the question. Would you select a candidate who didn’t know why they were even applying to nursing?
Of course not. If you were generous, you’d take the candidate aside and advise them to take more time to think about their future.
Which presents another reason why you need to answer the question: you owe it to yourself. This is who you want to be, after all. Make sure you put some thought into it. What the interviewer is asking of you is to not just explain why you’re a good candidate, but why nursing is important to you. So the main thing is to put your connection to the profession on display.
This question really is for the admissions committee to understand whether you fit with this career path. Your “why” will demonstrate whether you will be a positive addition to this profession.
Before you start composing your answer to this question, it’s important to reflect on your own reasons for pursuing this career. There are thousands of potential reasons and each one is legitimate in its own way. We have compiled a list of suggestions that may help you pinpoint your own “why” behind your decision.
Patient Care
One of the most common reasons that nurses give for “why nursing?” is to care for patients. Nurses spend more time with patients than any other medical professionals . They spend close to twice as long with patients as personal visitors (more than friends and family) and almost three times as many minutes with patients as other medical staff (physicians, physician assistants, and medical students).
Directly caring for patients is the biggest part of nursing, and an excellent potential aspect of your answer to the question of “why” you want to be a nurse. If you love working with patients, it could be an ideal entry into your answer to this question.
\u201cHuman connection has always been important to me. Nursing is an opportunity for me to help people at their most vulnerable.\u201d ","label":"Example statement","title":"Example statement"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
Heat of a Team
Nurses work together as a team to care for their patients. Although each nurse is assigned certain patients, they will help each other out. Being part of a team is exciting for a lot of people, and perhaps this is one aspect of the profession that excites you. Knowing that somebody has your back, and you have theirs, is a big plus in any career.
Not just part of a nursing team, healthcare requires many specialists across disciplines, and nurses are a part of that team.
\u201cI love working with other people and knowing that I\u2019m part of a work-family. Nurses come together to share their workload in a way that I find encouraging. I would love to be the kind of person who can be counted on by my colleagues, and who has a good support network as part of the job.\u201d ","label":"Example Statement","title":"Example Statement"}]" code="tab2" template="BlogArticle">
Physically, mentally, and emotionally, nursing is a challenge. The profession demands excellence and endurance from all aspects of life. Many people find challenges exciting and rewarding, and it might be beneficial to let an interviewer see that hardworking, never-back-down side to your character.
\u201cI am someone who rises to a challenge, who doesn\u2019t quit, and who won\u2019t back down from hardship. If I fail, I try again. I know that nursing is tough, but that toughness is something I admire in others and in the profession, and I think I would be ideally suited for a place where I can be challenged. ","label":"Example Statement","title":"Example Statement"}]" code="tab3" template="BlogArticle">
Constant Learning
You’re a curious mind who loves to experience new things? Nursing is perfect.
Nursing is a multi-facetted profession, and there is always more to learn and explore. Whether travel nursing, working with children, or with the elderly, you can find something (or everything) within the field.
One of the most interesting areas to learn is in pure medical knowledge. Nurses have to deal with many different areas of medical science, so the opportunities for educational growth are exponential.
Although less altruistic than some other answers, it can be beneficial to let an interviewer know that you will love a career in nursing for these rewarding aspects as well.
\u201cLife is a journey, and an adventure, and nursing provides a place to be a kind of adventurer. There is so much this profession offers, so many different ways to learn and grow, and I look forward to a life of, not just helping people, but exploration.\u201d ","label":"Example Statement","title":"Example Statement"}]" code="tab4" template="BlogArticle">
Nursing exposes a person to a wide variety of medical experiences, and that can lead to excellent insights into the field at large and lead to other, perhaps unexpected, career paths.
There are a lot of growth opportunities within the nursing field. A nurse might strive to become a nurse practitioner – very similar to an R.N. or R.P.N., but with some powers granted and further responsibilities. They can diagnose illnesses, order tests, or give prescriptions, for example. It’s like a halfway point between nurse and doctor. If this is your ambition, do not hesitate to express that you want a career where you will be able to grow, learn, and advance as a professional!
Nurses may also explore other medical professions. While you may be hesitant to express your desire to go from nurse to doctor , you should know that these kinds of transitions are not rare. Nurses who transition to being physicians or other medical professional have a huge advantage in terms of experience and clinical knowledge! You should feel free to express your dedication and commitment to nursing, as well as your aspirations for other professional avenues. Whether you want to grow within nursing or beyond, admissions committees like applicants who show ambition.
\u201cI want to experience the medical field in its fullest, and I believe there is no better first step on that journey than nursing.\u201d ","label":"Example Statement","title":"Example Statement"}]" code="tab5" template="BlogArticle">
Want help preparing for your nursing school application and interview?
How to Plan Your Answer
All of the reasons we list above are good. But you need more than just a parroted reason. Reason without passion is just an excuse.
There is a deeper reason for entering this field. Use this question to display that depth and your passion for nursing.
The personal why is about how the profession connects with you. There was a point in your life when you knew you wanted this for yourself. Maybe a family member was a nurse? Maybe somebody you knew was hospitalized, but the nursing staff at their hospital made their recovery infinitely better. Maybe that person was you: sick or injured, your life and health, improved by the nurses who cared for you.
Start with a good, captivating opening statement. Make it short, to the point, and formulate it in such a way that you will set up the rest of your answer. A good attention-grabbing statement might be a cataclysmic life event, a profound quote, or a statement that generates intrigue. Think of the beginnings of your favorite books or films. They start with something that grabs attention (“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times,” for instance). You want to ensnare an audience, not just say, “I always wanted to be a nurse.”
For example: “We were miles from help, cell phones dead or no bars, and blood was everywhere. I was holding onto my belt, pulling it tight enough to stop the flow, talking my friend back to a state of calmness, and hoping like heck that my lack of belt wouldn’t mean my pants would fall down imminently. I didn’t know it at the time, but being the calm one in a crisis, remembering my first aid knowledge, and making it through all that trauma was what would lead me to become a nurse.”
Keep to one or two main examples as to why you are pursuing nursing, show your connection to nursing beyond just, “it’s a job”, and throw in personal flair to accent your statement. Outlining one or two examples or reasons will allow you to include interesting details and expand on these reasons in more depth.
The personal connection is a good place to start. When did you realize you wanted to be a nurse? Why do you love it? Those catalyst points in your life that made you choose nursing are a great start.
A concluding statement – as short and punchy as your opening line – is the best way to wrap things up. You might let the interviewer know your career goals and how their program will help you get to where you want to go.
Make sure to keep your answer to 1 or 2 minutes long. You do not want to ramble on and on, thus losing the attention of your interviewers.
How to Practice Your “Why Do You Want to Be a Nurse?” Answer
Once you have an experience or two to focus on, spend some time thinking about how you want to present these talking points. Once you have an idea, start practicing. Remember, you do not want to memorize your answer, but you also want to have a clearly laid out format for your response. One of the worst things you can do is come to the interview unprepared, saying something like this, for example:
“I like helping people. I was once hurt and the nurses at the hospital helped me.”
That’s no good. Put effort, details, stories, and energy into the answer. This is the reason why you’re entering your next stage of life, so allow your excitement to shine through. Make a mini-story out of it.
It will help you a lot to practice your answer in mock interviews, making sure that your answer sounds natural, thorough, and professional.
“Why Do You Wat to Be a Nurse?” Sample Answer #1
“I have always needed to help people. As a kid, if my younger siblings got a scrape on the knee, I was right there with my mom, helping to bandage them up. I think I was just mostly in the way.
But that need to care and heal never went away. When I was older, I took first-aid classes and loved it. I loved learning how to help, knowing that if there was a problem I could be right there making things better.
The day that I knew specifically I wanted to be a nurse was after applying my first-aid knowledge directly. A friend of mine got hurt at school, slipped and had a bad fall down some stairs. I used my first-aid to keep them calm and check for any breaks or other issues before helping get them to the school nurse. While I was in the nurse's office, I felt like I was part of something already. Later, I spoke with the school nurse about my career path, and she was helpful, thoughtful, and encouraging.
Nursing is perfect for me. More than any other profession, nursing will give me an opportunity to care for people. It lets me do more than just give medicine, it connects me to people, and make a real difference in their lives.
That human element, making small differences day-to-day, and really helping people – all of that is deeply connected to who I am, who I want to be, and to nursing. Nursing and me are a perfect fit.”
“Nursing is a one-hundred percent career, and I am a one-hundred percent person.
Challenge is exciting to me. Rock climbing is a hobby of mine, and I love it because it’s active and requires commitment. I’ve always been passionate like that.
Another thing I’m deeply passionate about is going where I’m needed. I remember my aunt talking one time about being a nurse, and about the struggles that she and the other nurses went through. I remember her being really upset about it, but I also remember thinking, ‘Oh, they need people.’ And, as I said, I go where I’m needed.
From there I started learning as much as I could about nursing, taking elective classes in school, reading about the profession, and talking to my aunt about the job. The more I learned, the more I knew this was my path.
Nursing is a place where I can make a difference, be needed, and be challenged, and I am looking forward to all of that – one-hundred percent.”
The answer to this question is as personal as it is imperative. Really think about why you want to be a nurse above all else, and you’ll have your answer. Once you know the “why”, you might get thrashed a lot on your journey, but you will always have sight of your destination.
You also have the perfect answer for your interview. But with all that incredible insight into your life and who you want to be, that’s almost a by-product, isn’t it?
An in-depth answer, one that properly communicates your connection to nursing, is going to take up more than a couple sentences. Keep your answer to 1 or 2 minutes long.
No, and in fact, we strongly discourage memorization. Memorizing your answer comes off as disingenuous. Additionally, you run the risk of messing up your script and freezing in the middle of your answer. Instead, just focus on remembering your talking points.
Do plan out your answer carefully before your interview, practice it, but from that point on, just worry about holding the main points in your head. You don’t need to memorize the whole thing.
Everybody has a different approach to their writing processes, but one fast, fairly simple way to deal with writer’s block is to give yourself permission to take five minutes and free associate. You could use pen and paper, word processors, or record yourself talking aloud, but through whichever method you choose, just start getting out ideas about nursing and why you’re interested in it.
Another approach would be to think about the first time you considered nursing as a career and why. Those memories will give you excellent insight and a good starting place to plan your answer.
We recommend sticking to one or two events or reasons that led to your decision.
Since you don’t have time to get into every facet of every aspect of why you want to be a nurse, you’re going to want to stick to one or two primary reasons. You will weaken your statement if you have too many points.
To have a strong answer, you need to incorporate personal or professional events or experiences that led you to pursue nursing. Why did you decide to pursue this career? What interests you about it? What events took place to lead you to apply to nursing school? These events do not necessarily need to be related to nursing directly, but you can connect them to nursing. For example, maybe your volunteer or work experiences demonstrate exceptional communication and interpersonal skills? Whatever it is, make sure you can connect your passion for nursing, and your experiences in your answer.
Chronologically is probably clearest. It will let you, and the interviewer, track the story better.
Keep in mind classical story structure, with a beginning, middle, and end, and use that as a rough guide.
Just pause, take a breath, and remember the first thing your wanted to say. Since you’ll have practiced beforehand, the rest will come back to you. Since you’ve arranged your answer as a small story, the structure helps with remembering as well, and because you haven’t scripted anything, it doesn’t need to be exactly as you’ve rehearsed it.
You need to go back to your story and really look at it with a critical eye. Ask yourself if there are any details you’re including that aren’t really necessary. Try to weed it out.
What is extraneous to your story will pop out if you reconsider that story structure of beginning-middle-end. If you’ve started talking about a certain event in childhood that led to another event that led to your deciding to be a nurse, are you taking any digressions along the way? Including any anecdotes that, while nice, don’t support your main story?
If you’re having trouble sticking to two minutes, be ruthless in your editing.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions.
1.Why you want nursing? 2.what is customer service important
BeMo Academic Consulting
Thanks for your contribution, Rylie!
Get Started Now
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webclass:
How to improve your nursing school interview practice score by 27% , using the proven strategies they don’t want you to know.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Defining Professionalism Among Doctors and Nurses
More from our inbox:, ronna mcdaniel in the rearview mirror, the problem isn’t ohio, senator sherrod brown says, suppressing third parties, a chorus of boos for trash talk in baseball, it’s an animals’ world.

To the Editor:
Re “ How ‘Professionalism’ in the Medical World Can Be a Minefield ” (Science Times, March 19):
Doctors and nurses have answered a calling to care — specifically, in healing the sick. They don’t think about whether their off-duty attire meets traditional definitions of appropriateness, even though some people think that is what defines or constitutes “professionalism.”
But larger questions remain. How do we train medical professionals to be leaders in their field — to commence difficult conversations about death, to manage C-suite demands and requests, to work as a team with others, or to assuage patients’ concerns in a way that fosters compassion and trust?
Hospital executives and medical staff leaders who invest in professionalism training will be rewarded with happier, healthier patients, and doctors and nurses who bring joy and love to their work.
Robert Eisinger Robert Minkes Dr. Eisinger is chief administrative officer at the Healthcare Experience Foundation. Dr. Minkes is a physician coach at the foundation.
Regulating professionalism in medical school is challenging. While it’s crucial to instill traits like reliability and responsibility in future physicians, professionalism can also feel like a weapon wielded arbitrarily.
Some people of color worry over seemingly trivial matters like hairstyle, influenced by the prevailing notion that white people’s hair is the standard for a polished and professional look.
Personally, as an Iranian Canadian, I straightened my naturally curly hair for medical school interviews. One friend — a Black classmate who wore braids — confided that he also considered altering his appearance for interviews but decided against it, realizing he wouldn’t want to attend a school that deemed his appearance unprofessional. Another friend, a South Asian man with well-kempt but long, curly hair, was told he looked unprofessional by a clinical examiner.
Fortunately, our medical school ultimately acknowledged that professional standards shouldn’t be based on white norms around appearance. Now, as a practicing physician, I proudly wear my hair curly all the time.
Shima Shakory Toronto
Re “ NBC News Undoes Hire of McDaniel ” (Business, March 27), about the abrupt dismissal of Ronna McDaniel, the head of the Republican National Committee under former President Donald Trump:
Ms. McDaniel, who was hired by the network as an on-air political contributor, engaged in questionable and probably illegal behavior in Michigan after the 2020 election. Furthermore, she continues to profess that the election was rigged.
Those two facts alone would disqualify her from any journalistic assignment anywhere. The only conclusion to this episode is that NBC erred in its decision to hire her in the first place.
Richard Brody Mercer Island, Wash.
As the NBC News leaders backtrack on an inexplicable decision to give credence to an election denier, Ronna McDaniel, we should all take note. Those who stood up for truth in reporting won that battle.
We, the people, have the same battle to win at the polls. We should never excuse election deniers. And the only way to beat them is to show up.
Cheryl Davidson Culpeper, Va.
Re “ What’s the Matter With Ohio? ,” by Paul Krugman (column, March 22):
Nothing is wrong with Ohioans. The problem is decades of bad trade policy, written at the behest of multinational corporations and pushed by the coastal elite in both parties and in the media, that devastated Ohio communities like the one I grew up in.
The damage to our economy, and to Ohioans’ faith in their government, won’t be repaired overnight. We need investment in American manufacturing and American workers, and we need to level the playing field with Chinese-government-subsidized companies that cheat our trade laws.
And we know that the same corporate apologists who pushed the failed policies of the past will seize on any excuse to try to drag us backward.
Sherrod Brown Cleveland The writer, a Democrat, is a United States senator from Ohio.
Re “ Democrats Try to Derail Bids by 3rd Parties ” (front page, March 21):
Laws and rules that keep parties and candidates from appearing on ballots have the same purpose and effect as laws and rules that deny people the right to vote: suppressing the votes of political opponents.
Thomas F. Schlafly St. Louis
Re “ Nothing Makes Baseball Fun Like Trash Talk ,” by Rafi Kohan (Opinion guest essay, March 24):
So, yes, more taunting in baseball. Remember, it all leaches out into the general public. Just what our uncivil body politic, drowning in hatred and teeming with guns, needs.
Not everyone is equipped or inclined to deal calmly with the casual badinage that defines our society. Our streets are filled with people — many quite well armed — who don’t cope well with disrespect. Many shoot or get shot.
Nice time capsule, Mr. Kohan. Please let’s keep it sealed.
Stephen D. Craig Charlotte, N.C.
Just what we need: more verbal abuse and insults in the public sphere. I get the point that it would be entertaining to some people to watch and listen to this, but isn’t this just what this country is struggling with on the internet: the ease with which we can taunt and tease with no repercussions?
If that’s entertainment, I want no part of it.
Kate Washton Bronxville, N.Y.
What a horrible idea. There are plenty of other sports that have trash talk; watch them. We already have to read about Donald Trump’s trash talk every day. Baseball is a welcome respite. Let’s watch the best players win on the basis of their skills in the sport, not at being jerks.
Mark Stowitts Redlands, Calif.
Re “ New York Is Wilder Than You Think ,” by Emma Marris (Opinion guest essay, March 17):
I live in a suburb adjacent to Albany, and two days ago, a red fox came onto my deck and looked in my window. Occasionally I see a deer, raccoon or opossum in the “forever wild” area beyond my house. A friend who lives about three miles away reported seeing a black bear in his backyard. I do feed the birds and squirrels.
This reminds me that these wild animals are not intruding on us, but rather that we, in occupying their lands, are the real intruders. They were all here long before we occupied their lands.
Arlen Westbrook Delmar, N.Y.

Nursing Home Basics: Who Qualifies, Who Pays, and Other Helpful Facts
Why it matters.
Understanding how nursing homes work can be confusing because standards for eligibility, insurance coverage, etc. vary from state to state in the US.
In this second article in our series on nursing homes ( read Part I here ), we answer some commonly asked questions about nursing home structures and functions.
Who Is Eligible to Enter a Nursing Home?
People qualify for nursing home/facility level of care (NFLOC) if they are unable to live alone safely in the community. There is no federal definition of NFLOC and the exact rules governing level of care vary from state to state. Despite this lack of consistency, the following four areas are commonly considered when a state determines a person’s level of care need: physical functional ability; health issues/medical needs; cognitive impairment; and behavioral issues. In many states, there has been significant rebalancing toward home and community-based services and away from nursing home care. Check state websites for updated information on specific eligibility requirements.
Who Pays for Nursing Home Care?
Medicare is the federal health insurance program for people in the US who are 65 or older, some younger people with disabilities, people with End-Stage Renal Disease. A common misconception is that Medicare will pay for all nursing home costs. This is not true.
Post-acute care (PAC) or skilled nursing facility (SNF) care is usually covered by Medicare or private insurance up to 100 days (100 percent for 20 days and then 80 percent for 80 days based on certain criteria). Long-term care (meals, room and board, and basic health services) is often paid for privately until funds are spent down. A “ spend down ” is how someone with Medicare may qualify for Medicaid — a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to some people with limited income and resources — even if their income is higher than a state's Medicaid limit. Under a spend down, a state lets the person subtract their non-covered medical expenses and cost sharing (like Medicare premiums and deductibles) from their available income. Each state’s Medicaid program covers approximately 70 percent of nursing home care. Long-term care insurance can also pay for nursing home care, but relatively few people have it.
The average cost of a nursing home is over $90,000 per year but this varies state to state. Multiple organizations provide information about nursing home costs and Medicaid daily rates online, including the American Council on Aging .
Who Oversees and Regulates Nursing Home Quality and Safety?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) oversees nursing home quality and safety at the federal level. Several divisions have regulations that pertain to nursing homes.
The CMS Division of Nursing Homes develops and oversees most nursing home regulations. CMS delegates nursing home surveys and inspections to a designated organization in each state, usually the State Survey Agency (SSA). SSAs conduct annual, recertification, and complaint surveys and assess compliance with regulations. There is also a Special Focus Facility program for a small number of low-performing nursing homes that receive more intensive oversight and guidance on quality improvement in each state.
How Do We Measure Nursing Home Quality?
Because definitions of quality may vary, there are different methods used by federal, state, or private organizations to collect and analyze quality data. Here are a few examples:
- Minimum Data Set (MDS) is a standardized assessment tool required by CMS that measures health status in nursing home residents. All nursing homes that accept Medicare or Medicaid must submit the MDS regularly for each resident to receive payment.
- National Healthcare Safety Network is an electronic system for infection reporting, including COVID and other data that goes to CDC.
- CMS Five Star Quality Rating System gathers information from inspections (surveys), quality measures, and staffing from each nursing home and makes this information publicly available on the CMS website.
- Medicare’s Care Compare allows users to locate and compare data from nursing homes.
What are Quality Innovation Networks-Quality Improvement Organizations (QIN-QIOs)?
QIN-QIOs focus on working with nursing homes, states, and regions to improve quality of life and quality of care across settings, including nursing homes. QIN-QIOs have their own separate line item in the US federal budget to support the national program which covers all 50 states and US territories . QIN-QIOs are not part of state survey agencies or the survey process. Their focus is on quality improvement, support, education, and training, which are often provided free or at very low cost.
Who Works in Nursing Homes?
Women make up most of the nursing home workforce, particularly direct care workers such as certified nursing assistants (CNAs). ( Almost 90 percent of nursing assistants are female). Many are single parents. People of color comprise most of the US nursing assistant workforce.
Most nursing assistants are low-income wage earners. Many live at or near the federal poverty level and almost half receive some type of public assistance. Nursing homes typically pay CNAs the minimum wage, but this is not necessarily a livable wage depending on where they live. For this reason, CNAs often work in multiple settings and have multiple jobs. For many CNAs, English is not their first language, and they may have limited English proficiency. Many are immigrants.
What Are Some Challenges Faced by the Nursing Home Workforce?
There are many issues facing nursing home CNAs today and some new opportunities. The National Association of Health Care Assistants (NAHCA) conducted a survey of 1,420 CNAs in July 2023. When asked about their jobs, many CNAs reported that low wages and benefits would be the primary reasons they intend to seek another type of employment. They also cited unstable or inadequate hours, lack of supervisor’s/manager’s support, lack of career advancement or professional development, and feeling under-valued.
High rates of turnover (in some cases over 100 percent in a year) and the need for stronger, stable leadership are important reasons to better support CNAs and other direct care workers. Creating and testing standardized career ladders or lattices and providing more training and education on topics of interest to CNAs represent opportunities to promote better retention and reduce turnover. Another way to respond to CNA concerns is by becoming an Age-Friendly Health Systems Nursing Home .
Alice Bonner, PhD, RN, is IHI’s Senior Advisor for Aging. Amanda Meier, BSW, MA, is IHI’s Project Manager, Age-Friendly Health Systems. If you have any questions or ideas about nursing homes or related policy issues, please feel free to reach out to Alice Bonner ( [email protected] ) or Amanda Meier ( [email protected] ).
You may also be interested in:
The Basics We (and Policymakers) Should Know about Nursing Homes
Centering What Matters: The Core of Age-Friendly Care
Related Insights

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nursing is a profession that has several significant advantages that motivate people to pursue it. Primarily, it is a field of education that allows people to build successful careers and gain the knowledge and skills to help others. Nurses have an excellent opportunity to get a high-quality education and to work in a decent environment.
The protracted Covid-19 pandemic highlights the need to fully define what nurses do through the lens of what we, the authors, call the exemplary practice life for all nurses. Recently there have been calls that recognize the need to clearly describe the roles and expectations of nurses ( Godsey et al., 2020; Ulrich et al., 2020 ).
Nursing as a Profession Essay. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. The nursing profession has been a cornerstone of healthcare for centuries. Yet, it has only recently been given due recognition as an essential part of the medical team.
ALSN has a focus on nursing administration and leadership as well as research at both the graduate and undergraduate levels. 4. Nurse CEOs are even more likely to be seen as no longer belonging to the nursing profession. Some have allowed their licenses to lapse; some do not use "RN" after their names.
Jot down ideas that express your passion for the nursing profession, as well as any personal or familiar experience that led you to take this step. Be honest. Be open. Summarize your story, highlight your goals, and think about what the nursing profession means to you. All of these things will be important when structuring your essay.
The 2019 American Mobile Nurses (AMN) Healthcare survey found that 81% of nurses were satisfied or extremely satisfied with their career choice. When asked if they would encourage others to become a nurse, 70% said "yes.". The survey also found that supporting professional development was tied to job satisfaction.
Nursing professionalism is a multidimensional concept that includes knowledge, attitudes, and behaviour. Previous studies have defined professionalism as the degree of commitment by individuals to the values and behavioural characteristics of a specific career identity [ 6, 7 ].
Here's your quick guide from our nursing essay writing service: Choosing Your Topic: Select a topic that sparks your interest and relates to real-world nursing challenges. Consider areas like patient care, ethical dilemmas, or the impact of technology on healthcare. Outline Your Route: Plan your essay's journey.
Abstract. This chapter intends to update the social theory of the professions as applied to nursing. It draws on the premise that a profession cannot be defined by a set of structural traits or in reference to characteristics that are idiosyncratic to a dominant culture, questioning available explanations that define nursing as a semi-profession.
Learning how to craft a compelling nursing school essay can yield excellent results when applying for nursing school. Follow these 10 nursing school tips for a more impactful essay. 1. Read the Essay Guidelines Thoroughly. Following the directions is essential, as every nursing school establishes its own nursing school essay policies, topics ...
Nursing profession status is an inter-profession and intra-profession challenge. Whether there is nursing ... nursing field, were chosen. In addition, four books were used in the analysis process to cover the subjects. Books and papers were carefully reviewed and studied. For analyzing, thematic analysis and content analysis were used. ...
The nursing industry is constantly changing, providing ample opportunities for growth and job prospects with financial stability. The ultimate reward in a nursing career is the satisfaction of making a difference in people's lives. Tips for Writing A Compelling Why I Want To Be A Nurse Essay
Offering to mentor a colleague or student can also deepen the bonds within a team and serve as a professional growth experience for all. 4. Maintain a positive attitude. To succeed as a nurse, it's important to maintain a positive attitude. Patients look to you not only for excellent care, but also for emotional support.
Paragraph 1: Detail the event or moment you became interested in nursing. This is a paragraph where you really want to reel the reader in. You've hooked them with the broad overview of your story: what sets you apart, why you're so interested in the nursing profession. Now you can detail a specific moment.
Here are the top 15 reasons why you should consider a career in nursing: 1. High Demand for Nurses. Nursing is an increasingly relevant and sought-after career path in today's world. With the aging population, there's an increasing demand for nursing professionals due to the increased need for both medical and assisted living services.
Below are example answers to "Why do you want to be a nurse?" for different scenarios such as pediatric or emergency room nursing. Remember to tailor your answers to your specific needs when you answer in your interview. Pediatric nurse example answer. "I have wanted to get into nursing since I was very young.
Interaction with Patients. One of the most crucial points to why I chose nursing as a career is in regards to the interaction with patients. As a part of the healthcare system, nurses have a valuable place in the staff to cater to the needs of patients. Nurses are able to answer any questions and speak to the patients about anything that is ...
The nursing school essay, also known as a personal statement, is a critical part of the application. This is your chance to showcase your passion for the nursing profession and explain why you want to become a nurse. This guide will show you exactly what admission committees are looking for in a strong nursing school application essay.
Why It Works: This is a very good answer that demonstrates to the interviewer the candidate's confidence and awareness of the strengths she possesses that enhance her candidacy. I chose nursing as a career because I love learning new things. As a nurse, I am always challenging myself to keep current on medical trends and training so that I ...
Nursing professionalism is dynamicized through a process of socialization in formal nursing education. This feature is also reflected in the process of interaction. Therefore, nursing professionalism should match its rooted culture. The connotations of nursing professionalism include professional, caring, and altruism.
Nursing is one of the most professionally, personally, and spiritually rewarding careers there is. People are driven to a career in nursing for a variety of reasons. Carson-Newman wanted to better understand and document some of these reasons, which is why we reached out to 15 registered nurses, including three of our own FNP students, to get ...
A nursing career goal essay is a required document for many nursing programs. Depending on the program you're applying for, this essay may range from 500 to 3,000 words in length. Clearly communicating your short- and long-term goals in a strong essay helps program leaders understand your reasons for joining the program and the value you plan ...
Directly caring for patients is the biggest part of nursing, and an excellent potential aspect of your answer to the question of "why" you want to be a nurse. If you love working with patients, it could be an ideal entry into your answer to this question. Example statement. "Human connection has always been important to me.
Here are six key factors to contemplate before embarking on a nursing career: 1. Caring is Key: As a nurse, you become a vital part of patients' support networks, often playing a crucial role in their comfort and well-being. Establishing connections with patients can be immensely fulfilling, but it also presents challenges.
Ojima Abalaka. To the Editor: Re " How 'Professionalism' in the Medical World Can Be a Minefield " (Science Times, March 19): Doctors and nurses have answered a calling to care ...
Nursing is not on the DHS's STEM degree program list. However, it is on other lists. For example, the Higher Education Research Institute at UCLA includes nursing, medicine, dentistry, and several other health professional fields on its list of STEM disciplines.
301 Moved Permanently. openresty
Why It MattersUnderstanding how nursing homes work can be confusing because standards for eligibility, insurance coverage, etc. vary from state to state in the US. In this second article in our series on nursing homes (read Part I here), we answer some commonly asked questions about nursing home structures and functions.Who Is Eligible to Enter a Nursing Home?People qualify for nursing home ...
At a time when registered nurses are going on strike to protest staffing shortages, thousands of applicants who want to enter or advance in the profession are being turned away from nursing schools.