- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Apple Is Organized for Innovation
- Joel M. Podolny
- Morten T. Hansen

When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. Believing that conventional management had stifled innovation, Jobs laid off the general managers of all the business units (in a single day), put the entire company under one P&L, and combined the disparate functional departments of the business units into one functional organization. Although such a structure is common for small entrepreneurial firms, Apple—remarkably—retains it today, even though the company is nearly 40 times as large in terms of revenue and far more complex than it was in 1997. In this article the authors discuss the innovation benefits and leadership challenges of Apple’s distinctive and ever-evolving organizational model in the belief that it may be useful for other companies competing in rapidly changing environments.
It’s about experts leading experts.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Major companies competing in many industries struggle to stay abreast of rapidly changing technologies.
One Major Cause
They are typically organized into business units, each with its own set of functions. Thus the key decision makers—the unit leaders—lack a deep understanding of all the domains that answer to them.
The Apple Model
The company is organized around functions, and expertise aligns with decision rights. Leaders are cross-functionally collaborative and deeply knowledgeable about details.
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to 137,000 employees and $260 billion in revenue in 2019. Much less well-known are the organizational design and the associated leadership model that have played a crucial role in the company’s innovation success.
- Joel M. Podolny is the dean and vice president of Apple University in Cupertino, California. The former dean of the Yale School of Management, Podolny was a professor at Harvard Business School and the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
- MH Morten T. Hansen is a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a faculty member at Apple University, Apple. He is the author of Great at Work and Collaboration and coauthor of Great by Choice . He was named one of the top management thinkers in the world by the Thinkers50 in 2019. MortentHansen
Partner Center
- Get Started
- Another Item
- Sub-menu Item 2
- Yet Another Item
- Menu Item 3
- Menu Item 4
Org structure , Real Org Charts , Org Charts
Apple's Organization Structure: How a Functionally Organized Company Became a Global Tech Leader
Apple, the iconic brand synonymous with innovation and sleek design, has long been a trailblazer in the tech industry. From its humble beginnings in a garage in Cupertino, California, to its meteoric rise as a global powerhouse, Apple's story is one of relentless ambition, daring vision, and an unwavering commitment to thinking differently.
The brainchild of Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, Apple's journey has been peppered with numerous anecdotes that illustrate its unique approach to business and organizational structure. Take, for instance, the time when a young Steve Jobs convinced a skeptical computer parts supplier to provide Apple with the components needed for their first computers by exuding confidence and sheer determination.
It's moments like these that have come to define Apple's spirit and set the stage for the company's unprecedented success. In this article, we will touch on the intricacies of Apple's organization chart, explore the distinct culture that pervades its ranks, and unearth the factors that have propelled this tech titan to unparalleled heights.
Understanding Apple's Organization Structure

Centralization is at the heart of Apple's unique organizational structure, which is nothing short of surprising when compared to the typical product team structures found in other big tech organizations . Unlike the common, decentralized approach adopted by many large multinational corporations, Apple could be described as having a functional matrix and takes a more centralized, hierarchical, and focused approach. This means the company is organized around areas of expertise, rather than individual products, defying conventional wisdom and charting its own course. This functional structure enables better communication and coordination, creating a well-integrated team that can effectively tackle challenges and innovate at breakneck speed. It's a testament to Apple's commitment to thinking differently and breaking the mold, which has been a driving force behind its success. The late visionary and ex-CEO, Steve Jobs, was instrumental in crafting this structure , with the aim of fostering rapid innovation on new technology, while maintaining Apple's core values of simplicity, elegance, and user experience. Here is a brief overview of Apple's organizational chart: 1. Board of Directors: Headed by Chairman Arthur D. Levinson, the Board of Directors oversees Apple's activities, protects shareholder interests, and guides the executive team on major decisions. 2. CEO: Since August 2011, Timothy D. Cook has been Apple's Chief Executive Officer. As CEO, Cook is responsible for the overall management and vision of the company. Cook occupies the only position where the design, engineering, operations, marketing, and retail teams of any of Apple’s main products meet. He is supported by a team of senior vice presidents who are in charge of functions, such as hardware engineering, software engineering, machine learning and AI strategy, retail and people. 3. Senior Leadership Team: The top executives responsible for specific areas report directly to Cook. These areas include design, hardware engineering, software engineering, services, sales & marketing, and more. 4. Departments and Divisions: Beneath the senior leadership team, functional departments and divisions consist of various teams working on specific projects and products.
View Apple's senior leadership team in this interactive org chart. Note, roles and responsibilities in this chart are indicative only (using Functionly's default role templates).
The Apple Board of Directors: A Profile
We can learn a lot from real org charts . The diversity of backgrounds and expertise of Apple's Board of Directors is what makes it stand out. This diversity in perspectives and experience helps guide Apple through challenging market conditions and ensures sustained growth. Some of the notable members of Apple's Board of Directors include:
- Arthur D. Levinson (Chairman): Levinson has a Ph.D. in Biochemistry and has been the Chairman of Apple's board since November 2011. He previously served as CEO of Genentech from 1995 to 2009 and is currently the CEO of Calico, a Google-funded research and development biotechnology company.
- Al Gore (Board Member): Al Gore is the former Vice President of the United States and has been a member of Apple's board since 2003. His expertise in sustainable tech and climate change has influenced Apple's commitment to environmental initiatives.
- Andrea Jung (Board Member): Andrea Jung, a former CEO of Avon, brings experience in marketing, branding, and customer experience to Apple's Board of Directors. In addition to serving as a board member, Jung is also the President and CEO of Grameen America, a nonprofit microfinance organization.
- James A. Bell (Board Member): Bell is a former CFO and Corporate President of The Boeing Company and has been a member of Apple’s board since 2015. He brings expertise in finance, operations, and corporate governance to Apple’s board.
- Monica Lozano (Board Member): Lozano is a former President and CEO of College Futures Foundation and has been a member of Apple’s board since 2020. She has experience in media, education, and philanthropy and serves on the audit committee of Apple’s board.
- Ronald D. Sugar (Board Member) : Sugar is a former Chair and CEO of Northrop Grumman Corporation and has been a member of Apple’s board since 2010. He is an expert in engineering, technology, and aerospace and serves as the chair of the audit committee of Apple’s board.
- Susan L. Wagner (Board Member): Wagner is a co-founder and director of BlackRock and has been a member of Apple’s board since 2014. She has extensive knowledge in finance, investment, and global markets and serves as the chair of the nominating committee of Apple’s board.
- Alex Gorsky (Board Member): Gorsky is a former Executive Chair of Johnson & Johnson and has been a member of Apple’s board since 2021. He has leadership experience in health care, consumer products, and medical devices and serves on the compensation committee and the nominating committee of Apple’s board.

Photo: Apple store front by Rayyan Shahid | Pexels
The Secret to Apple's Success: The Unconventional Approach
Apple's functional organization structure may not be typical, but it has undoubtedly proven productive. Here are some of the factors that have contributed to Apple's phenomenal success:
- Collaborative decision-making : Apple encourages collaboration. This enhances communication between departments, encourages idea sharing, and ensures that the company as a whole benefits instead of individual departments.
- Specific roles and responsibilities : Apple's organizational structure clearly defines the responsibilities of each employee. This enables individual employees to contribute their best, and contributes to high-quality products and services.
- Streamlined product development : Apple invests its time and resources in perfecting a limited number of well-designed, high-quality products that maintain strong brand recognition, rather than offering a wider range of products. This focus has been pivotal to its success.
- Unity of leadership : Apple's Executive Team, under the visionary leadership of Steve Jobs and now, Tim Cook, has shown unwavering commitment to a unified vision. This culture has created a team of innovators, creators, and excellence within the company.
- Vertical integration : This allows Apple to control every aspect of its value chain, from hardware to software to services. This gives the company more flexibility, efficiency, and profitability than its rivals.
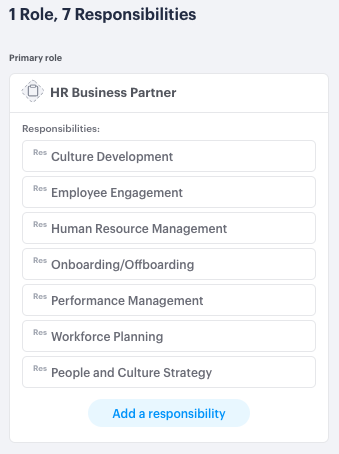
Image: Functionly includes role templates with detailed responsibilities | Created by author
By organizing around areas of expertise rather than products, Apple has been able to foster innovation and collaboration across its functions. Following a unified vision and a vertical integration strategy, the company has been able to maintain its competitive edge and profitability. Moreover, Apple's obsession with attention to detail and emphasis on design aesthetics have set it apart from competitors. The company's dedication to creating user-friendly interfaces and seamless experiences have resonated with customers worldwide, creating a loyal fan base that eagerly anticipates every new product launch. Combined with the company's ability to craft compelling narratives around its products, it's enabled Apple to position itself as a premium brand, commanding a loyal following and higher profit margins Apple’s unconventional approach has proven to be a winning formula for its success - nobody would argue otherwise! This unique blend of factors - collaboration, clearly defined roles, streamlined product development, unity of leadership, vertical integration, design focus, and marketing acumen - has propelled Apple to the forefront of the tech industry, solidifying its position as a global powerhouse and a prime example of organizational ingenuity.

Apple's Organizational Culture
Apple's organizational structure has been instrumental in shaping its culture. It's culture has been characterized by secrecy, collaboration, accountability, and excellence:
1. Collaboration: Has enabled Apple to leverage the expertise and creativity of its diverse workforce and foster cross-functional innovation
2. Accountability: Ensures that everyone in the organization is committed to delivering results and meeting high standards
3. Excellence: Reflects Apple’s pursuit of perfection and customer satisfaction in everything it does
4. Secrecy and Confidentiality: To maintain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving tech industry, Apple emphasizes guarding its intellectual property. Consequently, secrecy and confidentiality remain integral aspects of Apple's organizational culture.
Embracing Apple's Organizational Structure
Apple has set the bar high with its unconventional organizational structure. Its functional approach to collaboration has fostered a culture of innovation, creativity, and excellence within the company, resulting in remarkable success.
The uniqueness of Apple's functional structure also lies in its ability to mitigate the risk of siloed thinking and promote collaboration across departments. This cross-functional approach fosters a culture where ideas can flow freely, unhindered by the boundaries of product-based teams, and empowers employees to think beyond their immediate responsibilities. As a result, Apple has been able to consistently deliver groundbreaking products and services that captivate consumers and elevate the company's standing in the tech world.

By understanding the inner workings of Apple's organization chart, its culture, and factors that contribute to their success, businesses can learn valuable lessons and achieve similar success.
Use Functionly to plan and build your organization....maybe the the next Apple?
Header image: Created by author with Generative AI
Org structure Real Org Charts Org Charts
Related articles

Leadership , Org Design
Navigating the Maze: Strategies for Gaining Stakeholder Buy-in During Company Reorganizations

Org Design , Org Strategy
Reshaping the Future: Tools and Tactics for Organizational Adaptability
Get started now.
Your first step towards a more effective organization.
Start trial
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Integrations
- Start Trial Now
- Orginometry Blog
- Org Design Podcast
- Functionly TV
- Knowledge Base
- About Org Design
- Org Chart Templates
© Copyright 2024 Functionly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Apple’s Organizational Structure & Its Characteristics (An Analysis)

Apple Inc.’s organizational structure contributes to effective and rapid innovation, which is a critical success factor of the business in the information technology, online services, and consumer electronics industries. The company’s organizational structure or corporate structure is the combination of workforce groups, resources, and interconnections among these groups and resources in the business. The organizational design determines how the organizational structure is developed and managed. In this business analysis case of Apple Inc., the company structure supports strategies that push for further technological innovation. The computer technology company’s structural characteristics maintain a traditional hierarchy, with some key elements from other types of organizational structure. Business success and the satisfaction of Apple’s mission statement and vision statement are linked to innovation and organizational leadership, and its business structure is partly responsible for ensuring support for such leadership. With Tim Cook’s leadership, Apple has changed its company structure to suit current global market and industry demands.
Apple’s organizational structure is effective in supporting business performance to ensure leadership in the industry, especially with regard to competitors, including the information technology, consumer electronics, and online services of Google (Alphabet) , Samsung , Microsoft , Amazon , and Sony . Apple TV Plus also competes with the video streaming services of Netflix , Disney , and Facebook (Meta) . The Five Forces analysis of Apple Inc. determines that these competitors impose a strong force in the company’s external environment. Through its company structure, Apple continues to improve its capabilities and competitive advantages, such as in rapid and creative innovation and product design for competitiveness in the international market for smartphones, tablets, laptops, and online services.
Apple’s Organizational Structure Type and Characteristics
Apple has a hierarchical organizational structure , with notable divisional characteristics and a weak functional matrix. The company’s hierarchy is a traditional structural feature in business organizations. The divisional characteristics refer to the product-based grouping within Apple, such as for iOS and macOS. The weak functional matrix involves inter-divisional collaboration, while the company’s hierarchy is preserved. The following are the main characteristics of Apple’s structure:
- Spoke-and-wheel hierarchy
- Product-based divisions
- Weak functional matrix
Spoke-and-Wheel Hierarchy . A bird’s-eye view of Apple’s organizational structure shows a considerable hierarchy that revolves around the company’s headquarters. In the past, everything went through the office of Steve Jobs, who made all the major strategic management decisions. Today, under Tim Cook’s leadership, this hierarchy in Apple’s company structure has slightly changed. The company now has more collaboration among various offices, departments, and teams in the organization, such as software teams and hardware teams. Apple’s vice presidents have more autonomy, which was limited and minimal under Jobs. Thus, the company’s organizational structure is now less rigid, but still has a spoke-and-wheel hierarchy where Tim Cook is at the center. The upper tier (innermost tier in the spoke-and-wheel circle) of the business structure has function-based grouping, which is an element derived from the functional type of organizational structure. Senior vice presidents who report to Tim Cook handle departments based on business functions. For example, Apple has a senior vice president for retail, and a senior vice president for worldwide marketing. In this structural feature, the company’s top leaders address business needs in terms of business function areas.
Product-based Divisions . The upper and lower tiers of Apple’s business structure have product-based divisions, which is an element derived from the divisional type of organizational structure. There are senior vice presidents and vice presidents for different outputs or products. For example, Apple has a Senior Vice President for Software Engineering (iOS and macOS), a Senior Vice President for Hardware Engineering (Mac, iPhone, and iPad), and a Senior Vice President for Hardware Technologies (hardware components). The distribution channels in Apple’s marketing mix or 4P are linked to this structural characteristic. This aspect of the company structure is used to manage specific products or product components that the business organization delivers to its target customers.
Weak Functional Matrix . Apple’s weak functional matrix refers to the collaborative interactions among various components of the business. In a weak functional matrix, top management determines project direction, while project heads have limited authority and control. For example, Apple’s business structure allows hardware teams to collaborate with software teams. In this way, the company facilitates information dissemination that is necessary for innovation processes. This structural feature contributes to effective and rapid innovation processes, which are a major business strength shown in the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc . Through this characteristic of the organizational structure, the company maintains strong innovation processes that support brand development and the use of premium-pricing strategies.
Apple’s Structure: Advantages, Disadvantages, Recommendations
Strong Corporate Control . The hierarchy in Apple’s organizational structure supports strong management control in the organization. Theoretically, hierarchy empowers top leaders, like Tim Cook, to control everything in the organization. Through this hierarchy, business functions and product-based groups are effectively controlled through the decisions of the CEO and other top executives. This advantage of Apple’s corporate structure facilitates rapid and effective strategic management implementation and helps in establishing coherence throughout the entire company.
Limited Organizational Flexibility . Apple’s company structure has the downside of low or limited flexibility. Hierarchy typically prevents lower levels of the structure to flexibly respond to current business needs and market demands. For example, Apple’s product-based divisions must wait for directives from the CEO or other top executives to proceed in implementing changes that address trends in the market for consumer electronics. However, Tim Cook has already made slight improvements by increasing collaboration among various parts of the firm. Such collaboration improves organizational flexibility. Still, Apple’s organizational structure does not support rapid changes in business processes because everything must go through Tim Cook and the top management team.
- Albert, D. (2023). What do you mean by organizational structure? Acknowledging and harmonizing differences and commonalities in three prominent perspectives. Journal of Organization Design , 1-11.
- Apple Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Apple Inc. Leadership .
- Doan, T. N. T., & Nguyen, H. H. (2022). Value creation and value capture: Analysis of Apple company. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 5 (4), 1089-1095.
- Xia, Y., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2023). The influence of organizational structure on the dynamic capability of enterprises: The regulating effect of technological innovation. Science, 11 (2), 57-66.
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.

Apple Organizational Structure: a brief overview
Apple organizational structure can be described as hierarchical and functional. Such a structure has been developed by its founder and former CEO late Steve Jobs in order to ensure focused realization of his innovative ideas and clear vision for the business. When Steve Jobs returned to turnaround failing Apple in 1997 the company had a typical organizational structure with many business units with their own profit and loss (P&L) responsibilities. In order to increase the coherence and fuel innovation, Jobs fired general managers of all business units (within one day) and put in place one P&L for the entire business.
Apple organizational structure has been subjected to certain modifications since the leadership role was assumed by Tim Cook on August 2011. Specifically, Mr. Cook embraced the decentralization of decision making to a certain extent in order to encourage innovation and creativity at various levels. Also, Cook divided hardware function into hardware engineering and hardware technologies. As the most recent change to the corporate structure Cook added artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning as separate function areas due the increasing importance of AI and machine learning.
Currently, Apple organizational structure has the format illustrated in figure below:

Apple Organizational Structure
Generally, Apple corporate structure has the following characteristics:
1. Hierarchical organizational structure. Although Tim Cook introduced considerable changes to Apple corporate structure since assuming the top job in 2011, the structure still remains to be highly hierarchical with many layers of management. Massive size of the company that comprises 164,000 full-time equivalent employees globally necessitates the adherence to the hierarchical organisational structure.
Advantages of Apple hierarchical organizational structure include tight control possessed by senior management over all aspects of the business. Moreover, promotion opportunities motivate employees to perform well and there are clear levels of authority and responsibility. On the negative side, Apple’s hierarchical organisational structure may compromise flexibly of the business to reflect changes in the global marketplace. Furthermore, in hierarchical organizations communication across different departments tends to be less effective than in flat organizations.
2. Product-based grouping . Product-based grouping is an important feature of Apple organizational structure. The multinational technology company divides its operations into the following product-based groups:
a) Services. This group includes App Store, ApplePay, iCloud, and Apple Music.
e) Other products. These include Apple TV, iWatch, headphones, cases, displays, storage devices and various other connectivity and computing products and supplies
3. Collaboration between different groups and divisions . Apple Inc. maintains an intensive and effective collaboration between various groups and divisions of the company. Each product within Apple portfolio such as iPad, iPhone, iPad, Apple TV and iWatch is a result of collaboration of product-based groups.
Apple Inc. Board of Directors consists of eight members with a solid leadership background in a range of industries. Three members are acting CEOs and two members are former Chairman and CEOs of global companies. Moreover, proven leaders such as former US Vice President Albert Gore Jr., former CFO and Corporate President The Boeing Company James A. Bell and co-founder and Director of BlackRock Susan Wagner also serve in Apple Board of Directors.
Considering a number of challenges faced by the company such as rapidly decreasing life cycle of technology products and declining sales of iPhones, iPads and Mac products, [1] it can be argued that Apple organizational structure may be subjected to certain changes in the medium-term perspective. To be more specific, elements of matrix organizational structure and divisional organizational structure may be integrated into Apple Inc. organizational structure to a greater extent to increase the efficiency of new product development practices.
4. Functionality . Functionality is another important aspect of Apple’s structure. Although, product-based grouping is an important element of organizational structure as discussed above, senior vice presidents reporting to CEO are in charge of functions, not products. Functional organizational structure is not common for behemoths like Apple, however, the tech giant benefits from the current patterns of its corporate structure. Specifically, unlike many other large companies there is no fight between heads of product divisions at Apple for resources.
Moreover, functional organizational structure allows the tech giant to neglect short-term financial targets when developing new products that require considerable investments. Importantly, the bonuses of senior R&D executives are based on the financial performance of the whole company rather than revenue from particular products [2] . Therefore, executives at Apple are made to take a holistic approach to the business, similar to small entrepreneurial firms.
Apple Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Apple organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on APPLE. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Apple leadership, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Apple marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

[1] Annual Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[2] Podolny J.M. & Hansen, M.T. (2020) “How Apple Is Organized for Innovation” Harvard Business Review, Available at: https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-apple-is-organized-for-innovation

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Apple Organizational Structure In A Nutshell
Apple has a traditional hierarchical structure with product-based grouping and some collaboration between divisions.
Table of Contents
History of Apple
- Apple Business Model
Understanding the Apple organizational structure
Former CEO Steve Jobs is credited with transforming Apple from a struggling company to one dominating the world with its innovative products.
How exactly was this accomplished?
When Jobs returned to Apple in 1997, the company had a typical product-based structure divided into business units with their own P&L responsibilities. However, Jobs noted that this approach hampered innovation .
He laid off each business unit general manager and put the entire company under one P&L, effectively combining unrelated units into one functional organization. Under this new arrangement, product managers could work insulated from short-term market pressures. They were also encouraged to share their work with other divisions to ensure innovations were not duplicated.
Jobs argued that the function-based structure required two crucial elements. First, product managers had to be product experts and not rely on others for decision-making expertise. Second, senior research and development personnel should receive a bonus based on the performance of the entire company – not simply on their own products. This gave them the freedom and impetus to focus on innovation not involving the iPhone.
Components of Apple’s organizational structure
Today, the company combines the functional and hierarchical structure instituted by Jobs with the somewhat more collaborative approach implemented by successor Tim Cook.
But there are also some other important characteristics to consider. Following is a look in general terms at the Apple corporate structure.
Hierarchical mixed with functional
Apple is a predominantly hierarchical organization. In the past, every strategic decision would have to go through Jobs. When Cook took the helm, however, he introduced a more collaborative approach between managers and employees.
To address business needs in the context of functional units, Apple employs several senior vice presidents. For instance, there are senior vice presidents for worldwide marketing , design, finance, and retail, among others. This level of management has to report to the CEO but is given more autonomy than they were under Jobs.
There are currently 10 SVPs in Apple’s executive leadership team:
- Katherine Adams – SVP and General Counsel.
- Eddy Cue – SVP Services.
- Craig Federighi – SVP Software Engineering.
- John Giannandrea – SVP Machine Learning and AI Strategy.
- Greg Joswiak – SVP Worldwide Marketing.
- Sabih Khan – SVP Operations.
- Luca Maestri – SVP and CFO.
- Deirdre O’Brien – SVP Retail + People.
- Johny Srouji – SVP Hardware Technologies.
- John Ternus – SVP Hardware Engineering.
A functional structure is more suited to the holistic culture of a compact start-up and is uncommon in a company the size of Apple. But this approach ensures there is no competition for resources between product division heads. Furthermore, it allows Apple to neglect short-term financial targets when developing resource-intensive products.
Product-based grouping
Apple also incorporates a product-based leadership model embodying the divisional approach.
Product managers (vice presidents) report to the senior vice presidents. Product managers lead product divisions responsible for iOS apps, human resources, policy, environment, and policy and social initiatives.
Ultimately, this helps the company address specific product components before releasing them to the market. It also helps Apple evaluate marketing or manufacturing requirements.
Apple employs around 100 vice presidents from a pool of 160,000 employees and, in October 2022, announced four new VPs:
- Max Muller – a 20-year veteran who became VP of Maps.
- Charlie Zhai and Fabian Klass – who became VP-level executives in the Silicon group headed by Johny Srouji, and
- Payam Mirrashidi – the new VP of engineering under Services.
Group and division collaboration
Under Jobs, hardware and software teams would have to run their ideas by the CEO with little interaction between the teams themselves.
The development of each Apple product now involves an intensive collaborative effort between various groups and divisions. In other words, some degree of functional rigidity has been sacrificed to enable creative and efficient innovation .
Comparison with Top Related Companies
- Samsung : Samsung utilizes a more complex structure, combining elements of a hierarchical corporate structure with diversified business units that operate like separate companies under the broader corporate umbrella. Unlike Apple, which centralizes decision-making and maintains a unified brand across all product lines, Samsung’s divisions like electronics, heavy industries, and life insurance operate more independently, which can lead to greater agility but also potential inconsistencies in brand and strategy .
- Microsoft : Microsoft also employs a hierarchical structure but with a strong emphasis on both function-based and product-based groups. This matrix structure facilitates better integration and cooperation between different functions and product teams, enhancing Microsoft’s ability to innovate across its software, hardware, and cloud platforms. In contrast, Apple’s structure, while also integrating product-based groups, tends to maintain stricter divisional boundaries to focus deeply on product quality and design coherence.
- Google (Alphabet Inc.) : Google operates under a hybrid structure since its reorganization into Alphabet Inc., where it separates its various ventures into different entities under a corporate umbrella. This allows high levels of innovation and flexibility within each entity, such as Google, Waymo, and Verily, while maintaining overall strategic alignment at the Alphabet level. Apple’s structure is more centralized compared to Google’s, focusing on integration and control across its product lines to ensure consistency and efficiency.
Similarities and Differences
- Similarities : All these companies employ hierarchical elements within their structures to ensure clear lines of command and control. Each company also recognizes the importance of integrating various functions to promote efficiency and innovation .
- Differences : Apple maintains a more centralized control with strong product-based divisions compared to Samsung’s conglomerate model with independent business units. Compared to Microsoft and Google, Apple employs less flexibility in cross-functional collaborations, focusing more on maintaining control and consistency across its product lines.
Implications
- Innovation and Control : Apple’s structure supports strong control over its product development processes, ensuring consistency and high-quality output, which is crucial for its brand reputation. However, this may limit its ability to innovate rapidly compared to a more flexible structure like Google’s or Microsoft’s.
- Responsiveness to Market Changes : Apple’s centralized and somewhat rigid structure may slow its responsiveness to market changes compared to Samsung or Google, whose more diversified and flexible structures allow for quicker pivoting and adaptation.
- Efficiency and Specialization : Apple’s focus on product specialization and a streamlined hierarchical structure allows for efficient execution and strong specialization within product lines. This contrasts with the potential for inefficiencies or dilution of focus in more complex or diversified structures like those of Samsung or Google.
Key takeaways
- Apple has a traditional hierarchical structure mixed with elements of function and product-based grouping.
- Former CEO Tim Cook relaxed the highly rigid hierarchy present under Jobs. Instead of routing every decision through the CEO, divisional senior vice presidents and product managers are now given more autonomy.
- Collaboration between divisions and teams is now a non-negotiable part of every Apple product. This creates an environment where creative innovation has a chance to thrive.
Key Highlights
- History and Transformation : Former CEO Steve Jobs played a pivotal role in transforming Apple from a struggling company to an innovative industry leader.
- Product-Based Structure Transformation : When Jobs returned to Apple in 1997, he restructured the company from a product-based approach into a functional organization under a single P&L. This allowed for more innovation and reduced duplication of efforts.
- Product managers became experts in their domains.
- Senior R&D personnel received bonuses based on overall company performance, encouraging innovation beyond iPhones.
- Hierarchical and Functional Mix : Apple’s structure combines a hierarchical approach with functional roles. While Jobs previously made most strategic decisions, Tim Cook introduced a more collaborative approach between managers and employees.
- Senior Vice Presidents (SVPs) : Apple has several SVPs who lead functional areas such as marketing , design, finance, and operations. These SVPs have more autonomy than before but still report to the CEO.
- Product-Based Leadership Model : Apple’s structure also incorporates a product-based leadership model. Product managers report to SVPs and lead divisions responsible for specific product components, facilitating focused development and evaluation.
- Vice Presidents (VPs) : Around 100 VPs are chosen from Apple’s extensive employee pool. VPs have been appointed for various areas, including Maps, Silicon group, and engineering under Services.
- Group and Division Collaboration : Apple’s approach has evolved from limited interaction between hardware and software teams under Jobs to intensive collaboration between divisions and groups. This flexibility fosters creative and efficient innovation .
- Autonomy and Innovation : Tim Cook’s changes brought more autonomy to divisional SVPs and managers, fostering an environment where creative innovation can thrive.
- Balancing Hierarchy and Innovation : Apple’s structure combines traditional hierarchical elements with a focus on innovation through collaboration and functional specialization.
Related to Apple
Who Owns Apple

Apple Business Growth

Apple Distribution

Apple Value Proposition

How Much Is Apple Worth?

Apple Cash On Hand

Apple Employees

Apple Revenue Per Employee

Apple iPhone Sales

Apple Profits

Revenue Per Employee

Apple Mission Statement

The Economics of The iPhone

Tim Cook’s Salary

Tim Cook’s Net Worth

Smartphone Market Share US

- Apple Distribution Strategy
- The Apple-NeXT Deal
- A Decade-Long Evolution Of Apple Sales By Products
- Who Owns Apple?
- Apple vs. Google Business Models
Read Next: Organizational Structure , Apple Business Model , Apple SWOT Analysis , Apple Pestel Analysis .
Types of Organizational Structures

Siloed Organizational Structures


Open Organizational Structures

Connected Business Frameworks
Portfolio Management

Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model

Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model

McKinsey’s Seven Degrees of Freedom

Mintzberg’s 5Ps

COSO Framework

TOWS Matrix

Lewin’s Change Management

Organizational Structure Case Studies
OpenAI Organizational Structure

Airbnb Organizational Structure

Amazon Organizational Structure

Apple Organizational Structure

Coca-Cola Organizational Structure

Costco Organizational Structure

Dell Organizational Structure

eBay Organizational Structure

Facebook Organizational Structure

Goldman Sachs’ Organizational Structure

Google Organizational Structure

IBM Organizational Structure

McDonald’s Organizational Structure

McKinsey Organizational Structure

Microsoft Organizational Structure

Nestlé Organizational Structure

Nike Organizational Structure

Patagonia Organizational Structure

Samsung Organizational Structure

Sony Organizational Structure

Starbucks Organizational Structure

Tesla Organizational Structure

Toyota Organizational Structure

Walmart Organizational Structure

Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization
With the functional organization structure, the company is divided into hundreds of specialized teams. Dozens of groups can work on a single component of a new product. For example, at least 40 teams worked on a dual-lens camera with portrait mode: motion sensor software, sensor development and other aspects (Podolny & Hansen, 2022). Like Jobs before, Tim Cook now occupies the only CEO position in the entire organization. Cook controls the design, development, marketing, trading, and other processes at Apple (Schmitt, 2021). Otherwise, there are no general managers in the company who could directly influence the processes. Decisions in the company are made only by employees with the most significant experience and expertise in a particular field. Apple distributes its products in rapidly changing technological markets (Podolny & Hansen, 2022). Therefore, relying on employees’ decisions with deep knowledge is essential. The company relies on technologies that must be successful even before they become popular on the market — experts increase the likelihood of a successful product.
If the company relied primarily on financial indicators, it would slow down work on innovative products. For example, top research departments are paid bonuses based on the performance indicators of the entire company and not on the financial results of individual products. Moreover, the finance team does not participate in development team meetings, and the engineering teams do not determine the price of products (Meyer, 2022). The reputation of an individual employee and a team in a functional organization is a way of managing decisions. After introducing a functional organization by Steve Jobs, Apple managers at all levels had to have two key characteristics. They need to have deep experience to participate in all processes around a particular function meaningfully (Meyer, 2022). The willingness to discuss other functions during collective decision-making is correspondingly essential. Thus, only qualified employees influence the company’s actions.
The functionality of the Apple framework has different pros. The advantage is that all employees collaborate, resulting in gadgets built within the company’s boundaries that, in principle, function in harmony (Podolny & Hansen, 2022). It is worth noting that this is the key to the success of the Apple ecosystem. Each manager is solely accountable for the product, profitability, sales, and general efficiency under the classic divisional organization (Kao, 2018). The functional structure allows employees to work together. It helps Apple create software and hardware solutions that can be applied to multiple products. Managers can think more broadly without focusing on specific products.
The organizational structure built around special knowledge contributes to the creation of innovations. It is based on the premise that the most experienced and competent specialists in this field should decide on specific issues. Finding a balance between cost control and creating additional value for customers is more manageable when decisions are made by leaders who know their field well rather than general managers who are more concerned about targets (The Org, 2021). The fundamental principle of the traditional structure of an organization is a combination of responsibility and control. In that case, the functional structure is based on a combination of knowledge and decision-making rights.
Kao, R. (2018). Disruptive leadership: Apple and the technology of caring deeply—Nine keys to organizational excellence and global impact . Productivity Press.
Meyer, P. (2022). Apple Inc.’s organizational structure & its characteristics (an analysis) . Panmore Institute. Web.
The Org. (2021). A history of Apple’s organizational structure . Web.
Podolny, J. M., & Hansen, M. T. (2020). How Apple is organized for innovation. Harvard Business Review . Web.
Schmitt, K. R. (2021). What is Tim Cook’s managerial style? Investopedia. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 22). Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization. https://ivypanda.com/essays/apples-concept-of-the-functional-organization/
"Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization." IvyPanda , 22 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/apples-concept-of-the-functional-organization/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization'. 22 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/apples-concept-of-the-functional-organization/.
1. IvyPanda . "Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/apples-concept-of-the-functional-organization/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Apple’s Concept of the Functional Organization." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/apples-concept-of-the-functional-organization/.
- Wireless Sensor Networks in Military Applications
- Narrow Band Sensor and Wide Band Sensor in Engines
- Researching Capacitive Touch Sensor
- Routing Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks
- Wireless Sensor Networks
- Wireless Sensor Network, Its Topology and Threats
- Tim Cook's Era in Apple Inc.'s Management
- Tim Cook as an Effective Strategic Leader
- “The Journals of Captain Cook” James Cook
- Measuring Rotational Torque Sensor
- Economies of Scale in Production
- Toggl's Fully Remote Operating Model
- Management Models and Impact of Firm's Size
- Walmart Inc.'s Strategic Management and Daily Operations
- Google's Culture: Innovation, User-Centric Marketing, Sustainability

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Introduction to Apple Inc.: History, Products, and Organizational Structure
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 6 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 21 June 2012*
- File format: Text
- Words: 1,518 (approx)
- Number of pages: 7 (approx)
- Tags: Apple essays
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 1,518 words. Download the full version above.
Part A: Introduction to the Organization and the Organizational Design
Apple Inc. is an American multinational electronics and software company established by Steven Jobs and Stephen Wozniak on April 1, 1976, in Cupertino, California. Apple designs, manufactures and markets personal computers, portable media players, mobile phones, computer software, computer hardware and peripherals. The Apple Store, which is a retail store owned and operated by Apple Inc., has opened 283 stores as of December 2009, which are located in 10 countries. The company’s products are also sold worldwide through its online stores, its direct sales force, and third-party wholesalers, resellers, and value-added resellers. Music, audio books, iPod games, music videos, episodes of television programs, and movies can be downloaded off the iTunes Store on Mac or Windows computers, and on the iPod Touch and iPhone. Apple’s most popular products include their line of Macintosh personal computers, iPod portable media players, and the iPhone.
Apple Inc. sells its products to individual consumers, small and mid-sized businesses, educators and consumers in enterprise, government, creative, information technology and scientific markets. The company’s total net sales was $36 537 million and they employed approximately 34 300 full-time equivalent employees and 2500 full-time equivalent temporary employees and contractors as of the end of their fiscal year on September 26, 2009.
Apple manages and organizes its business based on a geographical structure, which is one of the divisional structures. The divisional structure is a traditional organization structure which group together people who work on the same product or process, serve similar customers, and/or are located in the same geographical region. In regards to Apple, their geographical structure group together jobs and activities being performed in the same geographical region. The company has created operating segments based on the location and nature of customers. The operating segments are the Americas, Europe, Japan, Asia-Pacific, Retail and FileMaker operations. The Americas, Europe, Japan and Retail operations are Apple’s reportable operating segments. The Americas, Europe, Japan and Asia Pacific segments do not include activities associated with the Retail segment. Asia Pacific includes Australia and Asia, excluding Japan. The Americas segment encompasses North and South America. European countries, the Middle East, and Africa are part of the Europe segment. Regarding the company’s retail segment, these are the retail stores operating in the U.S. and international markets. Similar hardware and software products and services are provided to the same types of customers by each reportable operating segment.
Apple Inc. is such a large corporation that it has all levels of management from upper to lower. The organization has all types of managers including line managers whose work directly contributes to the production of apples goods and services. They also have staff managers who use their special technical expertise to support line workers (marketing, accounting, human resources, and legal services). As shown in the diagram below of how Apple’s top managers are organized, the company has both functional managers, who are responsible for one area of activity, and general managers, who are responsible for complex areas.
This design is appropriate for the organization because their process of creating this geographical structure has appeared to benefit them from their results, which included a 36% gross margin in 2009, and helped them accomplish their mission and objectives. It allows their expertise to be focused on specific customers, products, and regions, which all have unique cultures and different requirements.
Steve Jobs the CEO and Co-Founder of Apple Inc. is known for having a temperamental management style. He has gone against the traditional management style, being strict with employees causing some fear but also praising them. Jobs is a perfectionist who pays close attention to detail, which can drive some of his subordinates crazy from his constant demands. He has a �no compromise” attitude when developing products for Apple. He creates many prototypes and mock-ups which are constantly being edited and revised by being passed back and forth between designers, engineers, programmers, and managers, and then back again. His obsession with excellence has created an amazing development process which turns out great products.
Based on Steve Jobs’s management style I believe he is not following a traditional approach to management. He appears to be following one of the behavioural management approaches, McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y. I believe he has some of the qualities of a theory ‘X’ and theory ‘Y’ manager. Jobs has theory ‘X’ characteristics because he prefers to lead others and expects staff to listen to his commands. His drive to change the world leads him to scream and shout at employees. In contrast, he also has some of the qualities of a theory ‘Y’ manager because he wants his staff to be imaginative and creative and to also be involved by participating in the design process. Jobs believes debating between his employees fosters creativity, therefore he gives creative partners a lot of rope.
In the ever constantly changing environment of the computer/electronics industry, I also see Steve Jobs following the modern management approach of contingency thinking as the competitive environment is always changing. Jobs is always required to understand the situation and respond to it in the appropriate way. Apple is also a learning organization, which is a continuing management theme. The organization continuously changes and improves, using lessons learned from prior experiences. Information sharing, teamwork, participation, and learning are all valued within the company.
Apple Inc. is very modern in everything they do which has caused them to already follow some of the common trends including: shorter chains of command, less unity of command, wider spans of control and more delegation and empowerment. Today, technology companies are starting to not talk about their product, rather the �solutions” or �customer experience” that is offered. The organization is one of the most competitive because it is constantly being one of the first to look to new trends to improve, while others companies are still trying to compete and keep up with Apple’s trends. Trends of today in the technology industry include: the demand for excellence, the pursuit of great design, the instinct for marketing, and the insistence on ease of use and compatibility. These trends have been with Jobs and Apple since the beginning, which has allowed it to succeed in what it has become today. Apple remains the last and only vertical integration company, meaning they make their own hardware and software, which is their greatest strategic advantage.
Through research of Steve Jobs’s management style within Apple Inc, it appears the organization is adaptive. An adaptive organization has more decentralized authority, fewer rules and procedures, less precise division of labour, wider spans of control, and more personal means of coordination. Worker empowerment and teamwork is encouraged within Apple as Jobs believes �talented staff is a competitive advantage that puts you ahead of your rivals.” He likes to work in many small teams, which is a characteristic of an adaptive organization. He does not like teams of more than 100 members because he believes they can become unfocused and unmanageable if they become too large. Members of the organization are encouraged to challenge Jobs’s ideas to foster creative thinking. Adaptive organizations are built upon trust of the employees to get the job down through their own initiative. It is freeing people from control and restrictions and giving them the power and freedom to do what they do best to get the job done; which Jobs allows with his creative partners. The adaptive design works well for Apple Inc.’s competitive environment, which demands flexibility in dealing with the constantly changing conditions. Internal teamwork is encouraged in the company because of the demand for total quality management and competitive advantage.
Areas Where Improvement Could Be Made:
After analyzing Apple Inc.’s organizational design, types and approaches to management, and organizational trends, it appears the design is appropriate for the organization as they are able to accomplish their mission and objectives. As there is always room for improvement in business, Apple can re-engineer some of its processes to design new and better ways to carry out work in the organization. There are many advantages for large organizations that use a divisional structure, disadvantages include: reducing economies of scale and increasing costs through the duplication of resources and efforts across divisions. Rivalries can be created as divisions compete for resources and top-management attention, and divisional needs can take away from the goals of Apple as a whole.
Apple attracts the best highly motivated workers from around the world, therefore I believe it is not necessary for Steve Jobs to be so temperamental, by screaming and shouting at employees. It would improve the organization if he lost his �Theory X” qualities as his preference to lead others and expectations that staff should listen to his commands, can create passive, dependent, and reluctant subordinates who tend to do only what they are told to or required to do. Improving human skills creates a better ability for Jobs and others to work well with each other in cooperation. Less intimidation and threat of job loss in the organization would improve the quality of work life at Apple.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
Discover more:
- Apple essays
Recommended for you
- Apple’s Ethical Problems with Outsourcing Manufacturing
- Apple analysis inc. SWOT / PESTEL
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Introduction to Apple Inc.: History, Products, and Organizational Structure . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/apple-inc/> [Accessed 21-04-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

Apple’s Organizational Structure Essay Example
- Pages: 4 (1080 words)
- Published: June 16, 2017
- Type: Case Study
Apple's organizational structure begins with when Apple was a one-man company. Actually, it started as a two man company - Jobs and Wozniak. Apple was a centralized business, similar to a single party or an authoritarian rule type because the all departments of Apple reported to Steve Jobs for approval. True Apple currently controls a fortunate place in the tech world. However, Apple's new challenges start after the death of Steve Jobs.
Thus begins Apple's organizational structure with Apple's new chief executive officer, Tim Cook Apple, (2012).Organizational Structure and Apple's Organizational Structure http://google images. om There are three traditional types of organizational structures. There Is the functional structure that divides departments into their own group dependent on their function.
A divisional structure group is dependent on the product type. There Is the matrix structure that i
s a mixture of function and division organizational structure. What about the vertical structure? A companys organization working within a matrix structure will most likely have two leaders or bosses to report to, each one would be ependent on their particular department for that particular division.Tim Cook Apple's chief operating officer has shared In Interviews that Apple does not want anyone to know their magic that works, which Is the company's organizational structure because they do not want anyone to copy what they have In the company.
However, with over 70 vice presidents and multiple Interviews of ex-employees the organizational structure has been fgured out. For the most part everyone reported to Steve Jobs before his death. Apple currently Is a functional organization with Tim Cook at the top of the organizational structure (Apple, 2012).Apples Organizational Structures Slmllarltles and Contrast
to Other Companies Microsoft Is separated Into a dlvlslonal structure of five separate businesses. There Is the entertainment and devices dlvlslon, the server and tools, the online part, which Includes the services of business, the Microsoft business dlvlslon, and customer or client. The dlvlslons Independently work each operation focuses on their particular department Inside of Microsoft (EHow, 2012).
Microsoft Is different from Apple ecause It Is not a hierarchy Iike Apple's organizational structure.Global companies consist of a matrix management structure because they have more than one reporting line. Apple's Organizational Function In Marketing Apple manager perform task In an organlzlng function that help with the help Identification of actlvltles - managers have to Identify the task, which would Include making sales, preparation of accounts, quality control, Inventory control, record keeping, and so forth. Managers at Apple have to group and classify all these activities into diffe rent parts.Apple's employees are organized into a structure to meet marketing goals and minimize confusion and clearly identifying which individuals are responsible for which tasks. Apple's line functions that are a factor that add to the company profits of production managers, sales reps, mid-level managers, marketing senior managers, lower-level managers, and regular staff EHow, (2012).
Apple is not a matrix structure that would allows employees from different departments to come together temporarily to work on special project because they are very private even to the point of having staff work on fake projects.While the matrix structure would allow flexibility to respond quickly to a customers need that would create a need for a team of people that would give the majority of their time to a new project line
and later then return to their departments Bateman, ; Snell, (2011). Apple's Organizational Function in Operations Then Apple classifies the authority with giving rank in the managerial hierarchy. The top of Apple's latter id the CEO and then drops to management which in turns forms Apple's policies, to the middle level management into departmental supervision and ower level management finally into supervision of supervisors.Apple's clarification of management authority does help for a positive and secretive work environment EHow, (2012).
Apple's Organizational Function in Human Resource (HR) Apple's Human Resource department functions include recruiting, finances of payroll, procedures of policy, safety, training, and development of the Apple industry, and the performance of staff. Human resources take care of administrative and the executive positions with the Apple Company. Apple's HR department goal is to make sure they lace the right people in the right places to achieve the organization's goal.Apple's HR department is responsible to cultivate programs that are innovative and that attract, the right people that is nessasery to meet the Apple's organizational mission Apple, (2012). Apple's Organizational Design of Product The leader of cool design is Apple. Customers of apple product and service are excited and delighted with the beautiful creations of Apple.
The Apple organization spares no detail Apple strives to be the best Apple is an out of box experience over he top experience of great products and this is the infusion of the Apple culture Apple, (2012).Apple's Organizational Design of Service First that comes to mind is that Apple thinks different and better Period. that is the image most have and therefore, so is their service Period. Apple gives the impression they
are set apart from the crowd Comma.
the norm Period. so whatever the competition is does not interfere or impact what Apple offers where it is product or service Period. Apple, (2012). Apple's Organizational Marketing Channels For one Apple uses the web to market worldwide. Apple uses social media and loyal customers spread with word of mouth.Apple is a one-stop shop self-contained domination the market of their service and product.
Apple uses their product with their customers to market nothing is compatible with Apple product Apple is its own innovation-marketing channel Apple, (2012). This concludes the above-mentioned information about Apple's organizational structure. This student shared a few types about Apples organizational structures with other organizations their similarities and contrasts to with other companies. In addition, that Apple's organizational function in marketing is like non-other.Apple's organizational function in operations the organization tries to keep secret but we have learned it is a functional organizational structure.
Apple's organizational function in Human Resource has a huge part in its success in business. Apple's organizational design of product is like no other product the best of the best is Apple's image. Apple's design of service is a one stop place and in total control. Apple's organizational design of marketing channels has no end, hich extends worldwide in technology ant the web with all its functions that help a business.
- Primary Project Management Organizational Structures Essay Example
- Key determinant and influences on organisational structure Essay Example
- Mcdonalds Individual Structure Organizational Paper Essay Example
- Organizational Structure: Zappos Essay Example
- A Centralized Structure Transforms Essay Example
- Tim Hortons' Organizatinal Structure Essay Example
- Organisational structure and culture affects the performance of the business Essay Example
- Internal Structure and Functional Areas of the Trafford Centre Essay Example
- Multidivisional Structure Essay Example
- Influence And Impact Of Organisational Structures Commerce Essay Example
- Organizational Structure Of Innovative Electronics Commerce Essay Example
- The Impacts of budget cuts on organisational structures Essay Example
- Classical School of Management Theorists to Understand Organizational Structur Essay Example
- Organizational Design and Structure Essay Example
- Organizational structures Essay Example
- Performance essays
- Human Resources essays
- Recruitment essays
- Code of Ethics essays
- Organizational Behavior essays
- Dress Code essays
- Safety essays
- Conflict essays
- Qualities essays
- Accounting essays
- Andrew Carnegie essays
- Automation essays
- Business Cycle essays
- Business Intelligence essays
- Business Model essays
- Business Operations essays
- Business Software essays
- Cooperation essays
- Cooperative essays
- Corporate Social Responsibility essays
- Corporation essays
- Customer Relationship Management essays
- Family Business essays
- Franchising essays
- Harvard Business School essays
- Harvard university essays
- Human Resource Management essays
- Infrastructure essays
- Inventory essays
- Logistics essays
- Management essays
- Manufacturing essays
- Market essays
- Marketing essays
- Multinational Corporation essays
- News Media essays
- Online Shopping essays
- Quality Assurance essays
- Richard Branson essays
- Sales essays
- Selling essays
- Shopping Mall essays
- Small Business essays
- Starting a Business essays
- Stock essays
- Strategy essays
- Structure essays
- Trade Union essays
- Waste essays
- Collective Bargaining essays
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards.
- Enter your topic/question
- Receive an explanation
- Ask one question at a time
- Enter a specific assignment topic
- Aim at least 500 characters
- a topic sentence that states the main or controlling idea
- supporting sentences to explain and develop the point you’re making
- evidence from your reading or an example from the subject area that supports your point
- analysis of the implication/significance/impact of the evidence finished off with a critical conclusion you have drawn from the evidence.
Unfortunately copying the content is not possible
Tell us your email address and we’ll send this sample there..
By continuing, you agree to our Terms and Conditions .
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Products
Apple Inc. Organizational Structure Essay
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Products , Organizational Structure , Steve Jobs , Nature , Apple , Organization , Design , Business
Words: 1200
Published: 02/02/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Apple Inc. is a multinational corporation with a global presence. In the latest financial standings, it has the highest value by the prices of stock. Apple Inc. supplies computer and other electronic and is ahead of others mainly for its production and sale of IPods, IPhones, Mac and the ITunes. The organizational structure at Apple Inc. is functional in nature with the work having been structured according to the functionality. To this extent Apple Inc. is run by departments conferred with specific functions. The departments are run under the Senior Vice Presidents who report directly to the Chief Executive Officer. Some of these functional departments are as follows: Technologies, Finance, Hardware Engineering, Worldwide Marketing, General Counsel and Operations. It is instructive to note that some of the departments overlap and consequently operate in a multifunctional nature. However, by and large, each department is charged with their respective function that in combination ensures the efficient delivery of the organization. In addition, the organizational structure of Apple Inc. is accommodative of its multinational nature. It is notable that Apple Inc. with its headquarters in the United States of America operates branches and plants all over the world. However, the functional structure is manifested in the work organization in the sense that every respective department in the external locations reports directly to its departmental head at the headquarters. Moreover, the company has embraced an element of decentralization in which the branch managers have some degree of autonomy in decision making and other managerial functions. This organizational structure can be compared and contrasted to the organization of the Bank of America and the Amazon.com Inc. In the Bank of America, the organizational structure is product based. In that context, the departments of the bank are influenced by the product categories. Some of the running departments at the moment include: the salaries services department, the small and medium scale loans department, the personal accounts department, the executive and corporate banking department and the capital and forex market departments. By their naming, it is instructive to note that they draw their structure from the product that they consume. This system fits well with the bank since potential clients often need specific products hence the need for specialization of personnel in the respective products. On the other hand, the organizational structure at Amazon.com Inc. is a mixture of functionality and geography. In that context, the organization is run by departments premised on the overall functions just like in the case of Apple Inc. However, the different locations have autonomy from the headquarters and can hence run their own affairs without necessarily consulting and seeking approvals. The nature of Apple Inc. organization entertains a lot of influence from the organizational functions. Some of the functions in the organization as intimated previously include the following technologies, finance, hardware engineering, software engineering, marketing, counsel, operations and human resources, among others. It is also noteworthy that the multinational nature of the organization constrains its operations to assume a global character. In that context, the organization runs its activities with the knowledge of appealing, reaching and engaging the entire global market. Consequently, the organization must assume a multifunctional approach that is based not on the geographical contexts but the need to provide for the entire globe. In addition, the special nature of the functions defeats any attempt to apply a general organizational framework. The organization needs to have personnel of high speciality in respective functions hence the need to have a functional approach. It is this that has consequently created the need for a functional approach that is devoid of general management. In addition, it is should be noted that decentralised management in the company does not confer full authority on the local management but requires that they consult their functional heads at the headquarters. The organizational design can be credited with the consequential organizational structure. This is informed by the fact that ordinarily organizational structure is a product and a reflection of the organizational design. An organizational design essentially refers to the framework of the operations of the organization. It looks into a number of elements such as nature of production, level of production, the volumes of produce, the distribution, the revenue base, the functions involved, among others. On the surface, it would be essential to categorize an organizational design on two main premises. That is, whether it engages in production or services. In many cases, the organization would be engaged in only one of the two. However, in other isolated cases, it could be designed in a way that it engages in both. In the case of Apple Inc., it engages both in service and production. In this regard, Apple Inc. needs an organizational structure that entertains the characters of both service and product industries. This is what could be given to explain away its functional nature. The need to engage effectively in production and service delivery expands the scope. This is a much complicated arrangement that needs a diverse organizational structure. The functional organizational structure best responds to this need. This section shall examine the organizational design in relation to the organizational structure. It is imperative to note that the multinational nature of Apple Inc. imposes a strain as the design must entertain a global perspective that is embracive of various global divides. It is on this premise that operations need to be governed from a central point despite the fact that it is international in nature. In addition, the functions are by and large specialized so that each department is charged with its respective duties and tasks. This does not in any way undermine the cohesion and team working of the company as the departments are relational in nature. The products and services of each department compliment or add value to the outputs from other departments. This approach in design places a need for the organization to adopt the functional organizational structure. The functionalism in the long run blends the organizational objectives to the overall organizational design. This is essential in the final delivery of its services and products. In other words, given the organizational design any other organizational structure other than the functional structure may not meet the needs of the organization. As indicated before, the organization must embrace the best structure that addresses its overall needs and enables it efficiently deliver its services. It is on that premise that the Apple Inc. has adopted the functional organizational structure. Finally, given its positive and enviable performance in the market, it can be surmised that the organizational structure is realistic and workable for the organization.
Apple Inc. (2013, March 2). Apple Press Info. Retrieved April 15, 2013, from Apple Inc.: http://www.apple.com/pr/bios/tim-cook.html Ivancevich, J., & Konopaske, R. (2010). Organizational Behavior and Management. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies,Incorporated. Shafritz, J. M., Ott, S. J., & Jang, Y. S. (2010). Classics of Organization Theory. New York: Cengage Learning.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 1213
This paper is created by writer with
ID 274318926
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Acceptance course work, consciousness course work, elderly course work, authority course work, planet course work, dog course work, clothes course work, archetype case studies, example of report on managing in a global economy, course work on psychological theories of personality, basic valuation essay sample, tangled webs essay, objectives of the research research paper example, free long term correctional facilities for juveniles article review sample, federal aviation act of 1958 research paper examples, foundation course literature reviews examples, free program learning outcomes capstone project example, sex since 1776 essays example, the concept of positive peer culture essays example, marketing research essay sample, good example of essay on higher education issues and solutions, good essay about elizabeth jennings civil rights, free how the correctional system punishes offenders essay sample, mint essays, geek essays, spinach essays, know how essays, chestnut essays, faustus essays, purpose statement essays, environmental science essays, media use essays, eaters essays, healthy foods essays, aerosols essays, bates essays, reiners essays, inmate population essays, the village essays, amenities essays, minerals essays, preparations essays, deposits essays.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Free Essay Samples
- Corporations
Apple Organizational Structure & History
Updated 04 September 2023
Subject Corporations , Entrepreneurship , Management
Downloads 27
Category Business , Information Science and Technology
Topic Company
Apple is the biggest firm in the world right now having supposed the Trillion-dollar mark. The tech company has many facets that have made it strong over the years. Thanks to its management structure, the decision-making process has been instrumental in shaping the growth of the firm. The firm has a rich history with a strong supply chain network which is regarded as the best supply chain in the world. The division of the markets into segments has made the firm to attract millions of customers across the globe. This paper examines Apple Inc. by exploring the various structures that have made it successful.
History of Apple.
Apple was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne in a garage in California. Steve Jos and Wozniak met through a mutual friend Bill Fernandez in 1971 who was later employed by the Apple Company. Jobs and Wozniak joined forces in using their technical knowledge to build ‘blue boxes ‘that were used to make long distance phone calls and making calls to the Vatican. It’s through this partnership that the two made the first Apple Computer. Steve Jobs convinced Wozniack to build a Computer machine and sell it. Hence, Jobs approached a local Computer store called The Byte shop who were interested in buying the machine but if it came with more modifications. Paul Terrell who was the owner even offered to buy Fifty of the machines at five hundred US dollars each. Steve Jobs then took the purchase order to a company called Cramer Electronics where he ordered the components that he needed to make a fully assembled Apple I computer (Rawlinson). The credit Manager was skeptical as to how Steve Jobs was going to pay for the purchase order, but Paul Terrell who was currently at an IEEE Computer conference vouched for their credibility. The two Steve together with their small crew spent their time building and testing their computer to ensure it was fit for purpose. They, later on, delivered it to Paul Terrell in which they got paid.
The machine had only a few features, the main one being the use of a TV as a display system. This was a huge improvement since most machines at the time had no display feature. The Apple I included a bootstrap code on ROM, which made it easier to start up. Later on, Wozniak designed a cassette for loading and saving programs at a fast speed of 1200 bit/s. The machine soon earned Wozniak a reputation of a master designer. Ronald Wayne and two Steves started building the machines however it was financially burdensome but through the help of friends and family, selling Wozniacks HP Scientific Calculator, they were able to get some money to buy the parts needed to assemble the machines. However, this was not enough, Steve Jobs started to look for finance through banks, but they were reluctant to give him. He, later on, met Mike Makkula who co-signed a bank loan with the three, Wayne, Jobs and Wozniack. This is what helped them to build the first Apple Computer on 1st April 1976. Wayne, later on, left the group leaving Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniack as the founders. They settled on the name Apple after Jobs suggested it as result of him working in an apple farm. He stated that the name sounded fun, spirited and approachable. They also settled on it because it started with the letter A which meant it would appear in front of any listings.
The making of Apple II soon ensured after the duo were able to get capital from the sales, they were making from Apple I. The Apple II series had more improved features than its predecessor. This included a redesigned TV interface that held a display memory. It also included color graphics and tape-based storage which was later improved to 5.25 in floppies. The Apple II series was released to the market in 1977 and were sold wildly into the 1980s with different models of the Apple II series being made. The Apple III was released on 19,1980 while the Apple II was still in the market but wasn’t a success like the previous Apple series. Its physical design was not sufficient to cool the Computer hence it was prone to overheating (CNN). This led to the integrated circuit to disconnect from the motherboard. Computers were soon recalled from the market as a new model was introduced in 1983 to fill the gap that the Apple III series had created. Over the years Apple Inc has improved and built up itself with various products as will be later seen in this article.
Apple Products.
This is the line of smartphones of Apple Inc which became a hit in 2007. It includes Siri, Apple Pay, and Touch ID. In 2016 the Company introduced iPhone 7 and 7 Plus which had amazing features including water and dust resistance, high and quality camera lenses among others.
This is the Company’s series of tablets launched on January 2010 which is based on an IOS Operating System, and it has several products like the iPad Pro, iPad Mini, and iPad Air. It uses Siri which is an intelligent voice-activated assistant and also a Touch ID (United States Securities and Exchange Commission,5).
This the Company line of desktops and laptops based on the Mac OS Operating system. It includes MacBook Pro, MacBook Pro with Retina display, Mac Mini, etc.
This the company’s line of product offering portable digital music. The first iPod was an MP3 Player which was launched on October 2003 that had storage for 1000 songs. Over the years they had been the release of better iPod products which includes the iPod touch, iPod Nano, and iPod shuffle (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 5).
This is the Apple’s Operating system for Television. It’s based on the Company’s IOS platform and incorporates the new Siri capabilities which allow searching across more apps and services.
This is the Company’s cloud services that provide for storage of music, contacts, calendars, mail, documents and more, keeping them up to date.
Apple Business strategy
Apple thrives under continuous business innovation. With the innovations, the firm has always tried to give its consumers the best experiences by coming up with the best world technology in terms of hardware, software, and the required application systems. The integration of these new devices is very easy coupled with ease of use and being price friendly. The firm up to date has continued to expand its platform by coming with new designs and products that make it more attractive for consumers to demand the services and products it offers. For example, every year the firm keeps on coming up with new versions of the iOS, Mac, the Apple TV and recently the introduction of the new Apple Watches. The introduction of cloud computing and the integration of artificial intelligence into Apple made devices has made its business strategy to be successful. To make its business strategy even more attractive and competitive, then the firm has a third-party contribution program that allows third parties to develop other programmes and software’s that can be used to complement the internally developed software programs. The program also incorporates the third party developed hardware and any type of digital content that can be appealing to the public domain (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 4). The firm has always been driven by the buying of quality products which has been accepted by consumers thanks to its efficient salespersons. The provision of quality products and services and better prices has for a long time ensured that the firm attracts new customers but at the same time retained its current large pool of customers across the globe. The firm’s business strategy also involves it trusting third-party distribution channels where they do the sales on their behalf in other countries. The business strategy also encompasses the firm constantly increasing its global stores and the use of online buying platforms to access a large pool of customers. Lastly one of the greatest strengths of the firm that has driven its business strategy for years is it believe Research and Development. The firm spends a lot of money to funds this process to make sure that they come up with new market innovations that are of high quality.
Business organization
Over the years, Apple Inc. has managed to primary function by managing its business through geographical basis. The firm has subdivided these geographical areas into segments namely the America, the Asian Pacific, the Japanese region, Europe and China where most of the manufacturing of its devices takes place. The European region is very wide and practically the most prominent segment for the firm since it covers all countries that are in the European Union and Arab region and the continent of Africa. The region also covers India that is home to a market of over 1 billion people. The segments are home to the products and services offered by the firm. However, to effectively manage each specific region, the firm prefers to manage the regions independently (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 4). The primary reason for this is to meet up to the standards of the distinct consumers directly. Each region has customers with a specific culture, background and expectation hence niche marketing is the only way to guarantee the segment's success. Lastly, the firm has also its specific partners such as suppliers who are distinct depending on the specific regions. The distinctiveness, therefore, calls for separate management of the regions to effectively meet up to the requirements of the third parties and partners.
Apple Inc. Markets and Distribution
The firm has many market segments and opportunities which it has exploited for years. Some of the primary markets for the firm include the education sector, world governments, and the business enterprises. However, the primary markets for the firm are the single consumer and SME businesses. The firm has online and retail stores where it directly sales its products to the consumers. The direct sales also cover the firm’s sales of third-party products int the different market segments. Sales of the products are also directly done to the small and middle-sized companies. To cover its huge and wide market segment, then the firm employs the use of third-party distributors commonly called indirect channel distribution. Some of them include retailers, direct network carriers and the use of wholesalers. The firms marketing strategy is pegged on the continuous sale of differentiated products distinct in every market niche and constantly coming up with innovative products.
The belief in quality products has necessitated Apple Inc. to rely on effective marketing by its sellers to directly engage with consumers and express to them the importance of using the quality products. The firm directly gets engaged with its customers where they also offer after sales services. The firm till to date keeps on expanding its outlets both in the U.S and overseas markets (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 7). The marketing strategy that is tailored to customers ensures that the firm positions its stores and worldwide outlets in high traffic areas. Such places include positioning itself in new quality malls around the world and the at the center of well-established urban districts. One cannot miss such outlets when he or she is in these places. The high traffic areas ensure that high-quality products are easily sold. Also, the decision to make sure it only offers high-quality products to ensure quality customer experience has made sure that the firm has customers who prefer to only identify with the firm’s products and services and also it has managed to attract new customers. The marketing strategy is also pegged on the fact that the firm employs only experienced personnel and most significantly employs persons who are highly knowledgeable making it easy for Apple Inc. to offer advice to consumers, suppliers and third parties. The company has also taken significant steps to tap into the education sector by tailoring its products and services towards meeting the educational needs of both students and teachers (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 7). The firm has come up with effective ways of integrating technology into the classroom and the general school environment hence ensuring higher student achievement in the long run. The firm has created some technological, educational products and services that can effectively meet the student needs. Also, the tools include the provision of the necessary instruments to ensure mobile learning. Distribution of its products also involves its marketers targeting big firms and also government institutions. The marketability of the products is more effective and efficient thanks to its productivity and the readiness that consumers find when using the products.
Apple Competition
The technological market is very competitive hence innovation and creativity drive the profitability and viability of tech firms. Apple Inc. makes products that are highly competitive despite being forced into an aggressively competitive market. Some of the firm’s competitors include, Google, Samsung, Techno are some of its major competitors.
The technological competition is characterized by the continuous introduction of new products and services into the market. The quick creation and innovation of technologies have transformed mobile use communication and other usages through the creation of more advanced smartphones. The competition in the tech industry is marred by aggressive pricing and firms coming up with low cost- structures to increase profitability. The pricing strategy adopted by these firms and the eventual cost structures have a significant impact on the financials of a firm in a single fiscal year. Some of the competitive factors that Apple Uses to make sure it maintains a competitive edge over other firms include the quality of its devices and the process of these commodities (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 8). Also, the features of its products such as the yearly launch of new Apple phones plays a significant role in maintaining the firm’s competitiveness. Competitive edge is also realized through having a strong third-party system and distribution channels. Supplier reliability has also played a crucial in making the firm to be competitive. Currently, the firm is enhancing its competitiveness in computers and other media devices apart from smartphones. The firm views all these as new opportunities to tap into. The only way for the company to remain competitive and be at the top is by continuously coming up with innovations and designs. Apple Inc. has some competitive advantages over other firms like Google. Its main edge is its brand strength where it leads as the most popular brand according to 2017 statistics. The strength gives the company the highest visibility in the world and also makes it have large access to the consumer market. Secondly, the firm has many innovative products. The company has a reputation of coming up with innovative products which up to date share the same operating systems making many consumers prefer Apple devices over others due to the commonality of the OS. Although it has an aggressive pricing strategy, Apple Inc. has one of the best premium pricing techniques characterized by limiting discounts to wholesalers. The result of this is the periodic price constancy across the globe. The high prices are meant to affirm the perception that it offers the best quality products across the globe. Also, another competitive edge it has over other tech firms been the fact that it has one of the best differentiation strategies. Apple greatly applies product differentiation where it has effectively managed to expand its market through product differentiation. The technique used in this case is to make the products unique and more attractive to consumers. The success of this strategy has been realized through constant advertising and promotion strategies.
Organizational structure
Apple Inc. has a hierarchical organizational structure. The structure was first developed by its founder Steve Jobs who passed away. Currently, the leadership of the firm is under Tim Cook who is the CEO where he has made several modifications to the way the firm is run since taking over in 2011. The CEO has since embraced the decentralization of the firm’s decision-making process. The CEO by allowing this intends to promote innovation and creativity in the tech firm. The firm is composed of eight members who sit as the board of directors. The background of these board members is solid with all of them coming from many industries within the US. Currently, three of the members are active CEOs in their respective companies while two of them are distinguished former chairpersons of global firms (Dudovskiy). Also, one of the former presidents of the US is an active member of the board together with the founder of the BlackRock. Having this form or organizational structure, hierarchical makes the firm to have tight control of its operations and the entire business environment since all business issues, and facets are easily controlled. The system has a clear level of authority where employees have to follow a specific authority structure. Also, the structure lays out a clear level of responsibility where each manager knows what he or she is supposed to account for within the firm. The system is also very effective in laying out a clear line and direction of communication. Communication flow within the organization whether from up or down has a clear flow hence achievement of operational efficiency is easily realized (Dudovskiy).
The Structure is known to promote employee promotion opportunities which act as a means of motivating the firm’s employees. Although it has a line of authority and a decision-making structure, the system provides an effective way of integrating flexibility within decision making and normal management. The firm allows the flexibility that has culminated into innovations and creativity over the years. The flexibility has also allowed the firm to adopt new and emerging market changes. Currently, Apple is facing challenges in terms of low sales of the devices. The declining product sales can be attributed to the current declining life cycle of a given technology which, might subject the firm to change some aspects of its organizational structure (Dudovskiy). Matrix and divisional organizational layout or structure of the firm might be combined into the current structure to realize high-efficiency levels. Apple is composed of top executives who are answerable to the Board of Directors. After the CEO, we have some senior vices – presidents who report directly to the CEO. Some of them include senior vice president, Retail and online stores, Software engineering and General counsel. Below the senior vice presidents are the Vice presidents to the firm in charge of senior projects, Apple University, Communications, industrial design among others (Dudovskiy). It is expected that the vice presidents have a team behind them such as managers that assist in the daily functionality of the company. The number of teams and managers that help the vice presidents depend on the number of departments and functions that one has within the firm. Generally, the hierarchical management structure places the CEO at the center of all responsibilities and operations of the firm. The CEO is the final decision maker when it comes to the firm’s major operations.
Apple Inc. Foreign and domestic operations
According to the financial data that was released in 2017, the firms domestic market attracted a net revenue of 37% while foreign markets had a net sale of 63%. The firm has preferred to outsource its hardware products manufacturing to other partners. Ideally, most of its manufacturing occurs in the Asian countries where we have cheap labor. However, Apple manufactures some of its personal and desktop computers within the US while also giving an opportunity for Ireland to also manufacture them. During the development of the products, the firm requires specific components which have to be mainly outsourced from the European countries while others come from the US. Although it attracts a huge sales volume from countries other than the US, foreign trade is affected by many factors such as interest rates fluctuations and government trade regulations. Currently, the firm is bracing itself for the coming China-US trade war. Both countries are threatening to increase tariffs on the products imported which will make many of the products produced by the firm to be expensive. Traditionally the firm gets high revenues during the first quarter of its fiscal years. The reason for this can be attributed to the high demand for its products during the holidays. The introduction of new products tends to increase the net sales for the firm. A case example is during the annual introduction of new Apple Phones that attracts new pre-orders upon its launch into the market. The anticipation of a new product is also the leading contributor to the firm’s high sales revenue.
Supply components
The components needed by the firm to make the various products are generally obtained from many sources. There are components which the firm gets from a single source. The high competition in the tech industry has also resulted in the firm competing for the supplier components. The move, therefore, means that the components needed by the firm are at times subjected to shortages due to the competition. The financial condition and performance of the company are also affected by the pricing of these components due to price fluctuations. The uniqueness of the firm has necessitated it to use customized components which are distinct from the general components. The new products that are constantly introduced into the market require the use of special components that can only be generated from a specific source. The delay in the delivery of the new components specifically customized for the firm can lead to serious financial implications. Should the suppliers decide to keep much focus on the production of the common components instead of producing the required customized ones, then the firm can experience delays in production and shipment of the final products to the worldwide outlets (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 8). On a yearly basis, the firm enters into agreements with suppliers for the supply of the components. However, the firm does not give promises or assurances that the agreement will be renewed in the next fiscal year. As the end of the 2018 fiscal year, the firm was still at risk of supply shortages and the fluctuations in prices. Due to the outsourcing nature of the business, the firm can be severely affected by its partners if they fail to deliver products at the end of a given manufacturing schedule. This mostly applies to the Asian partners who do the manufacturing for them.
Apple Research and development
Today technology can be defined as the fourth industrial revolution. At the center of this revolution are the tech firms across the globe. The tech industry is characterized by constant innovations and creativity that requires every firm to always come up with an innovation. The ability of the firm to compete with other tech giants’ rests solely on its capability to always come up with the best products and services. Apple has continued over the years to come up with new technologies and advancements that have made it be at the top of the industry (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 9).
Finance and Accounting
The net sales for the firm increased by 16 % in this financial year which is represented by a $36.4 billion increase. The main driver of the increase in sales revenue is the sale of the iPhone and the provision of the firm’s services. Since the firm is managed by segments, the America segment for is the largest contributor in net sales at 42% in 2018 followed by the European region which had a net sale of 24%. The high sales are all attributed to the sale of iPhone. The operational expenses of the firm increased in 2018 due to the increase in the cost of research and development attributed to increased headcount expenses. The same can be said for selling and the general administration costs thanks to the rise in headcount and the needed professional costs. From 2017 the firm has come to gain from the historic reduction of corporate taxes from the traditional 35% to 21%. The reduction meant that effective 2017, the company was going to pay fewer taxes to the government. The Trump administration introduced these tax cuts with the aim of convincing firms to repatriate back their foreign earnings (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 22-23). Apple Inc is highly liquid with significant cash and cash equivalents. The firm also boasts of having a significant number of marketable securities which makes it easy to meet up to the working capital needs in the short run whenever needed. The capital expenditures for the firm were at $16.7 billion in 2018. The firm intends to increase its capital expenditures due to its manufacturing process requirements. Generally, the financial outlook of the firm is very strong. This has been the trend for many years thanks to its good asset base. The firm continues to post record increases in the net profits with rising share prices.
Apple risk factors
Apple is a global company is faced with many risk factors which it has to anticipate. Changes in the global and regional economic factors and conditions can severely affect the firm’s operations, financial results and the overall growth of the company. For example, should there be a recession or high rates of inflation, the firm’s growth will slow down. The current threat of trade tariff war between the USA and China will negatively affect the firm’s financials in the long run. Secondly, the tech industry market is highly competitive characterized by increased technological innovations. The firm faces the risk of not marching up to this competition. Apple believes in the quality of products hence the need for continuous creativity. It has to keep on coming up with new products to be at the top which is not easy. The firm highly depends on the third parties where it has outsourced most of its manufacturing process to especially in the Asian region. The outsourcing possesses a great risk to the firm in the sense that they can experience delays in getting new products. The delays can lead to new product lounge delays which can severely affect the sales revenue. Also, there is the threat paused by suppliers who might also delay supplying components needed for production especially if the firm has ordered for customized production components (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 11-13).
Apple is a diverse firm with a rich history characterized by strong years of success. The management structure of the firm has been effective in making sure that the firm remains at the top thanks to its best decision-making structure. The firm is very competitive and has been at the top of the tech industry thanks to its continuous innovation and creativity. Pegging its development on research and development has seen the firm come up with new products that meet consumer expectations. Having the best supply chain and distribution network has made it be successful in all of its market segments. The financial performance of the firm shows the firm to be highly profitable meaning it is going to be viable for a long time.
CNN. "Apple Fast Facts". CNN, 2018, https://edition.cnn.com/2014/07/01/business/apple-fast-facts/index.html. Accessed 4 Dec 2018.
Dudovskiy, John. "Apple Organizational Structure - A Hierarchical Structure That May Change in Near Future - Research-Methodology". Research-Methodology, 2018, https://research-methodology.net/apple-organizational-structure-a-hierarchical-structure-that-may-change-in-near-future/. Accessed 4 Dec 2018.
Rawlinson, Nik. "Apple Was 41 Years Old in April, Here's Some History". Macworld UK, 2017, https://www.macworld.co.uk/feature/apple/history-of-apple-steve-jobs-mac-3606104/. Accessed 4 Dec 2018.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission. 2018, https://s22.q4cdn.com/396847794/files/doc_financials/quarterly/2018/Q4/10-K-2018-(As-Filed).pdf. Accessed 4 Dec 2018.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission. 2017, http://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReports/PDF/NASDAQ_AAPL_2017.pdf. Accessed 4 Dec 2018.
Deadline is approaching?
Wait no more. Let us write you an essay from scratch
Related Essays
Related topics.
Find Out the Cost of Your Paper
Type your email
By clicking “Submit”, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy policy. Sometimes you will receive account related emails.
Sample details
- Words: 1190
Related Topics

Apple Inc Organization Structure
Organization or business has to have organizational structure in order to succeed because it prioritizes the hierarchy, identifies the guidelines, policies and procedures needed for a company achieve goals and objectives. The Organizational structure also depicts levels of management from the top down. The organization that I would like to work for is Apple Inc. In this essay, I will give a brief overview of the company’s history, define it organizational structure and effects it have on the success of the organization, distinguish between leadership and management, describe the culture and the core capabilities which lead to Apple becoming the most powerful company in the nation.
Company History Apple Computers Inc. , was established by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in 1976 with the release of the Apple computer. In 1977 Apple Computer Inc. became incorporated and successful until 1984 when things took a turn for the worst because of financial hardship and power struggle between leadership which lead to Steve Jobs resignation; however, he remained the Chairman of Apple Computers Inc. In 1997 Jobs and Wayne reunited, and Jobs became the interim Chief Executive Officer (CEO), and quickly made changes to the organizational structure, which reversed its declining sales.
ready to help you now
Without paying upfront
In 2000, Jobs became the CEO of Apple Inc. and introduced the IPOD, a digital music player which sold 100 million units, which was the turning point for the company. Mr. Jobs was the brain of Apple, known for creating the Ipod touch, Ipad, Mac Book and an online store called Itunes. Organizational Structure Prior to the return of Steve Jobs, Apple Inc, was almost non-existent due to the lack of leadership and management, declining sales and poor strategic planning, which lead to financial hardships and layoffs. The same “top-down” ideology that helped Apple grow also opened the door for some serious financial losses.
With employees at different levels making decisions, it became difficult for the corporate office to keep track of spending and purchasing (Offermann Spiros, 2001, pp 376-92). Upon returning to the company, Steve realized immediately that there were serious issues within the organizational structure and things needed to be changed. He decided to departmentalize the company, creating three main divisions; engineering, retail and hardware. Each department was designed based on their product and functions.
By departmentalizing the company, each manager would be held accountable for their own department, productivity and employees. Departmentalizing the organization consisted of combining various structures which allowed for consistency and unification. This model proves to be an efficient and effective way for Apple to operate because it enabled of Steve’s to transform the organizational structure, which resulted in Apple becoming the front runner of innovation and the most powerful company in the nation. This is a model that other large companies would love to emulate.
Leadership and Management Leadership is a term that has many definitions; however, when defining leadership within Apple Inc. , two definitions caught my attention; Gary Yukl defines leadership as “the process of influencing others to understand and agree about what needs to be done and how to do it, and the process of facilitating individual and collective efforts to accomplish shared objectives” and leadership is about “articulating visions, embodying values, and creating an environment in which things can be accomplished. ” (Richard Engle, 1986, pg 206).
Steve Jobs definitely defines leadership, because he was directly responsible for every aspect of the operation, products and services. He is also known as an enthusiast because he was able to motivate, incorporate his values and beliefs, and excite his team about technology and to share in his vision which would move the company forward. He created an environment where all employees felt as if they had a sense of belonging and added value to the company. Mr. Jobs was known for influencing all every employee in the organization to work cohesively to achieve a common goal.
Today, Tim Cook is the CEO and has assumed the duties and responsibilities previously held by Steve Jobs. The managers are responsible for managing the day to day operation; assigning tasks and making sure tasks are done correctly, efficiently and in a timely manner. Mangers are directly involved in the decision making process, which contributes to the success of the organization. Managers has to define goals and designing a strategic plan to obtain goals, directing, motivating and encouraging team to achieve personal and professional goals, and monitoring the performance of the organization.
Henry Fayol wrote that all managers perform five management functions: planning, organizing, leading, controlling and coordinating, however today all are relevant except coordinating. Management’s ability to perform the five functions of management is one of the main ingredients to the success of Apple. Organizational Behaviors According to Henry Mintzberg, there are five P’s of strategy (plan, ploy, pattern, position and perspective), and each “P” stands for a different approach to strategy and by understanding each “P”, a company can develop a robust business strategy and take advantage of the company’s strengths and capabilities.
The main strategies of Apple are to concentrate on the company’s strengths to create positive performance in order to achieve objectives and goals. Mr. Jobs has strategies are built on upon the following core capabilities; focusing on customer service, managing human capital, taking advantage of and capturing every opportunity, financial assets and the competition. These core capabilities create values and cause employees to achieve superior performance. Compared to the competitor, Apple’s technology far exceeds that of the competitors and management is always planning and developing new ideas.
The pattern for Apple is to take old technology and make it better. Apple’s position is to continue training employees to be innovative, create unique products and stay ahead of the competition. The skill set required by leadership is to take advantage of and capture every opportunity is one of the main functions of leadership because they are responsible for understanding how and what external trends and forces may affect the company, then decipher the information to build scenarios and develop strategies.
The culture within the organization is based on self-motivation has also aided in the success of the company because they all share the same values and beliefs. Leadership and employees are self-motivated; understanding, compassionate, committed to delivering good products and ensuring customers are satisfied. Conclusion Steve Jobs was the brain behind Apple Inc. , because of his ability to create a unique organizational structure and willingness to adapt to change has made Apple the most successful organization in the nation.
His leadership style was that of a dictator, yet he was able to encourage his team to work cohesively to achieve goals of the company. Apple’s organizational structure is departmentalized into three categories, engineering, hardware and retail. This unique structure allows managers to be responsible tasks, production and employees within department.
Apple is a successful company because Mr. Jobs was able to create a vision, share his vision and influence his team to buy into his vision. Managers are responsible for directing, motivating and encouraging team to achieve personal and professional goals, and monitoring the performance of the organization. If a manager cannot perform the four functions of management, the company will not be successful.
Cite this page
https://graduateway.com/apple-inc-organization-structure/
You can get a custom paper by one of our expert writers
Check more samples on your topics
Difference between mechanistic organization structures and organic organization structure.
Organic Food
Introduction The selection of an organizational structure is vital for a company as it directly affects its goal achievement. This decision is influenced by factors like the country and industry environment, the organization's history, size, and technology. Choosing an appropriate organizational structure can assist in adapting to and stabilizing or destabilizing the environment. Main Body The text distinguishes
Apple – Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple
markets. It built retail stores when competitors were moving to direct sales and distribution models, and its products were rarely first to market. There was, however, a surprising consistency in the way the company worked. Simply put, the “Apple Way” was a set of principles with a deep commitment to great products and services at
Apple’s Beethoven. Steve Jobs, Former CEO of Apple Computer
Apple’s Beethoven This case focuses on Steve Jobs, current (and former) CEO of Apple Computer. The case describes how Apple is using the success of the iPod to reemerge as a serious competitor in the computer industry. Topics covered include creativity, personality, leadership, and motivation. Primary emphasis is placed on creativity by detailing how the
Apple Incorporated: How Is Apple Resolving Ethical Issues?
Most of the things that people use today have become automated, and people have changed their lifestyles. Nowadays, people want devices that can simply their life and save them time. They want innovative mobile devices that will enable them to do their work and communicate without restrictions. Many companies have realized this, and they are
The Apple Apple’s Mission Statement Case Analysis
Apple Computer's standard industrial classification (SIC) is 3571. SIC 3571 is used for companies that manufacture computer hardware. The top computer hardware manufacturers by sales are IBM, Hewlett-Packard, Compaq, Dell Computer, Cisco Systems, Sun Microsystems, Xerox, EMC, Seagate, and Gateway. Growth in the computer hardware industry in the United States is predicted to be slow
Apple Inc.: Case Study
Application software
Good content and application of course concepts. Try to make better use of headings and bullets. It will give more focus and make your case easier to read 90 Current Performance From The “Consolidated Statement of Operations: Apple Inc. ” show that Apple evaluates its performance according to its operating segments based on net sales
Corporate Governance a Case Study on Apple Inc
Corporate Governance
Introduction The Personal computer maker and the operating system markets are the chief gross beginnings of Apple Inc. The gross net income border of Apple has been increasing over the old ages; in 2009 ( Q4 ) rose by about 2 %. The main competitive advantages of Apple are its leading in the invention, the trade name
Executive Summary for Apple, Inc.
Apple Inc. is a corporation that focuses on computer hardware, software, and consumer electronic products. They offer Macintosh computers, iTunes media applications, and iPod music players. Steven Wozniak and Steve Jobs founded the company in April 1976 after leaving college. In that year, they made the Apple I computer for a hobbyist club but it
Apple INC. Is One of the Most Successful Companies Worldwide
Introduction: It is no secret that Apple Inc. is one of the most successful companies worldwide, however, many individuals believe that they remain “the best company in the world,” (http://www.businessinsider.com/how-to-run-your-company-like-apple-2012-2). In order to receive a reputation this strong, both your business plan and style must be perfected. It is easy for outsiders to take a look

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.
You can Choose category
Apple INC. Organizational Structure
Apple Inc. is a company that has specialized in the manufacture of software and electronics, among other online solutions. The company was founded by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in 1976. It has experienced substantial growth over the years and succeeded in establishing itself as one of the major players in the global market. In Fortune (2020), it was ranked 4th in the Fortune 500 list Part of its success is attributed to its organizational structure. According to Apple (2021), the present executive team comprises the following individuals:

Apple Inc. has established an organizational structure that fosters technological advances and rapid innovation. It has adopted the traditional hierarchy that includes the spoke-and-wheel hierarchy, product-based divisions, and a weak functional matrix structure. Regarding the spoke-and-wheel hierarchy, the innermost tier in the spoke-and-wheel circle is organized based on the functionality difference. The senior vice presidents report to the chief executive officer who manages the business functions. For instance, the company has a senior vice president for retail and people and another for marketing and communication. In such a structure, the organization’s executives address business issues in terms of function areas. On the other hand, the lower and upper tiers of Apple Inc.’s organizational structure comprises product-based divisions, which stems from a divisional type of organizational structure. The company has senior vice presidents and presidents for different products and services. There is a senior vice president for hardware engineering (iPhone, Mac, iPod, and IPad) and a senior vice president for software engineering (macOS and iOS). Apple Inc.’s marketing strategy depends on its structural features, which aim to manage specific products or services targeted to particular customers.
Conversely, the weak functional matrix structure describes the collaboration between the various departments in Apple Inc. In this structure, it is the primary role of the top management to drive the direction of a project. In Apple Inc.’s case, the control and authority of project heads are limited as they have to report every detail to the top management. This form of information flow provides room for collaboration between teams involved in producing different products; hence, encourage innovation.
Apple Inc. is a large-sized company with hundreds of thousands of employees globally to meet the high demand for its products and services. The organization is headed by a CEO and an executive team consisting primarily of senior vice presidents (VPs). The senior VPs directly report to vice presidents who oversee the Machine Learning and AI Strategy, Worldwide Marketing, Marketing and Communication, Software Engineering, Hardware Engineering, and Internet and Software Service departments, among others. Furthermore, the product-based division corporate structure allows the project heads to focus on the specialized segments; for instance, internet software and services are separated from software engineering. Consequentially, the senior VPs and VPs can efficiently allocate resources in their specific departments to conduct research geared to particular segments. This also trickles down to the employees as it makes them aware of their job roles, management expectations, and specialized roles.
Apple Inc.’s integrative organizational structure offers a broader span of control and greater unity of command to corporate managers. Although the company has a flat design, all VPs, and senior VPs report directly to Tim Cook; therefore, the chain of command can be categorized as top to bottom. The top-tier managers oversee all operations conducted with Apple Inc., thus enabling them to focus more on strategic plans of the company’s various functional divisions. In addition, the organizational design supports a centralized decision-making framework in which the executives integrate the employees’ opinions and welfare in the decision-making process. This enables Apple Inc. to identify distinct strengths and weaknesses develop appropriate improvement plans.
The words “mechanistic” and “organic” depict both organizational structure and culture. Apple Inc.’s nucleus is its unique “design” approach that has given it a market advantage. This sphere is regarded to have an organic structure, based on the significant innovation trend that has been witnessed over the past years. The collaborative relationship fostered by the weak functional matrix provides an atmosphere in which the employees’ decisions are respected, and they are given the freedom to integrate ideas into projects (Tasnim, 2018). As a result, this promotes creativity and innovation. The company has a design team independent of the finance, manufacturing, and other departments and reports directly to the executive team. It is granted the autonomy to set its distinct budget and the ability to ignore manufacturing practicalities (Tasnim, 2018). In some instances, the team might implement physical controls to prevent the design team members from interacting with other employees from different departments. At the center of the design department is the Industrial Design studio, to which only a selected few of the company’s employees to have access (Tasnim, 2018). However, the organic feature does not apply to other departments, such as operations, retail, and sales, with a more mechanistic approach. In these departments, significant decisions are made by the executive team; the employees cannot implement their choices.
Organizational structure is classified as either formal or informal. In the formal system, employees are directed to perform actions in a specific manner depending on the directions given by their superiors. Apple Inc.’s organizational design possesses the features of both the formal and informal structure; regardless, it is highly likely to be categorized as a formal organization. This is due to the fact that there is a clear division of labor, vertical and horizontal differentiation, and a wide span of control. Furthermore, Tim Cook has all the authority, and he makes principal decisions. The company has a set of clear and well-defined goals and objectives, responsibility, and accountability guidelines for employees. Nevertheless, Apple Inc. is famous for its secrecy, including fewer written rules and procedures (Tasnim, 2018). This suggests the existence of informal organizational elements in the organization.
Differentiation describes the way through which organizations categorize their tasks into roles in various subunits. Apple Inc. has a diverse product differentiation approach as it provides a vast portfolio of products in the technology industry. For instance, it has specialized in the production of hardware (iPhone, Mac, iPod, and IPad) and software (macOS and iOS). The company also has a strong vertical integration as it controls the most critical part of the chain used to manufacture and retail its products. It builds the hardware, owns the primary software experience, optimizes that software for the hardware, and finally controls the selling experience through their retail stores. As a result, a dilemma might arise from product differentiation and vertical integration. It is essential to note that Apple Inc. embraces both concepts and has still managed to dominate the global technology market. This is attributed to the fact that the company keeps these two elements separate by using the hierarchy of authority. Various senior VPs are assigned to different departments that are subdivided based on products offered. Another solution to the dilemma is the collaborative approach amongst other departments.
By personalizing its organizational structure, Apple Inc., has established itself as one of the most prominent startups in the 21st century. One of the hierarchical organizational structure strengths is that it has granted the company robust corporate control. The top-tier management is vested the power to make crucial decisions, with Tim Cook, the CEO, at its center. Furthermore, by control resting in the hands of the executives, business and product-based choices are made in a quick, coherent, and efficient manner. Moreover, this organizational structure encourages collaboration among employees from different teams, hence, facilitating rapid product innovation. Lastly, separating core departments, such as product design, from the rest of the departments has further compounded innovation within the company giving it a marketing advantage.
Nevertheless, Apple Inc.’s organizational structure also has its limitations, with the major one being limited flexibility. Besides the design, other departments have a relatively mechanistic system that limits the low-tier employees to respond to the changing market demands and business needs flexibly. This is because approvals have to be given by the CEO or top-level executives. Furthermore, Apple Inc. is known for its secrecy; the lack of transparency between departments might cause power imbalance between functions and cause uncertainty. It is therefore recommended that structural changes be made to achieve a power balance. This might be attained by delegating responsibility and authority to allow low-levels employees to implement their decisions. A decision-making framework that is specific to each department should be provided so that employees are aware of the confines of the process.
Apple. (2021). Apple leadership . Web.
Fortune. (2020). Apple . Web.
Tasnim, M. (2018). An organizational analysis on Apple. European Journal of Business and Management, 10 (11), 35-40. Web.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary. When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities.
the business units into one functional organization that aligns expertise with decision rights—a structure Apple retains to this day. 1998 CEO 6 Harvard Business Review November-December 2020 This article is made available to you with compliments of Apple Inc for your personal use. Further posting, copying or distribution is not permitted.
Apple Organizational Structure. According to Lüsted (2012), organizational structure defines the manner in which an organization is governed. At Apple Inc, the organizational structure is designed into three levels of top management unit. The figure below helps in defining the organizational structure at Apple Inc.
Currently, it is suggested that Apple should shift toward a people-oriented technique for managing its organizational structure. Specifically, the focus on promoting teamwork, collaboration, and active participation among team members in corporate decision-making must be encouraged (Williams et al., 2022). The proposed alterations will launch a ...
Apple's Organizational Culture. Apple's organizational structure has been instrumental in shaping its culture. It's culture has been characterized by secrecy, collaboration, accountability, and excellence: 1. Collaboration: Has enabled Apple to leverage the expertise and creativity of its diverse workforce and foster cross-functional innovation. 2.
Apple Inc.'s organizational structure contributes to effective and rapid innovation, which is a critical success factor of the business in the information technology, online services, and consumer electronics industries. The company's organizational structure or corporate structure is the combination of workforce groups, resources, and ...
Secrecy was one of the organizational cultures that Steve Jobs developed in Apple. It believes that privacy is a fundamental right (Apple, n.d.). This has determinate the development on human resource. High secrecy can help to protect the propriety information and intellectual property from being stole by hackers.
Apple's Organizational Structure. This report provides a reasoned and academically underpinned critical analysis of what is good and what is detrimental to the organisational culture in terms of Human Resource strategy and practice in Apple Inc. The introduction contained a brief on Apples background from inception to its position in present ...
Abstract. The essential components of carrying out an organizational analysis (a case study on Apple Inc) include evaluating external factors that can affect the organization's performance as well ...
July 3, 2023. Apple organizational structure can be described as hierarchical and functional. Such a structure has been developed by its founder and former CEO late Steve Jobs in order to ensure focused realization of his innovative ideas and clear vision for the business. When Steve Jobs returned to turnaround failing Apple in 1997 the company ...
Apple's corporate leadership operates within a hierarchical structure. It includes the CEO, senior executives, and various departments such as hardware engineering, software development, design, marketing, retail, and finance. - Clear lines of authority and accountability. - Efficient decision-making process.
Disruptive leadership: Apple and the technology of caring deeply—Nine keys to organizational excellence and global impact. Productivity Press. Meyer, P. (2022). Apple Inc.'s organizational structure & its characteristics (an analysis). Panmore Institute. Web. The Org. (2021). A history of Apple's organizational structure. Web.
Apple Incorporate is an American multinational technology company. Its world corporate headquarters are located in the middle of Silicon Valley, at 1 Infinite Loop, …show more content… The most important of Apple's organizational structure are Spoke-and-Wheel Hierarchy, Product-Based Grouping and Function-Based Grouping.
1302 Words. 6 Pages. Open Document. Apple's Organizational Structure and culture. Organizational Structure. A companies' organizational structure dictates how to report priorities and strategies of upper management, and it directly impacts the success or failure of said company. In case of Apple, where are no committees and employees can ...
1251 Words. 6 Pages. Open Document. Organizational Design and Structure: Apple's Structure Ciara Smith MGM 255, Colorado Technical University Introduction: In this paper I will discuss the six key elements of an organization's structure as well as identify and diagram 1 organizational structure that can be applied to Apple.
The divisional structure is a traditional organization structure which group together people who work on the same product or process, serve similar customers, and/or are located in the same geographical region. In regards to Apple, their geographical structure group together jobs and activities being performed in the same geographical region.
Apple's Organizational Structure Essay Example. Apple's organizational structure begins with when Apple was a one-man company. Actually, it started as a two man company - Jobs and Wozniak. Apple was a centralized business, similar to a single party or an authoritarian rule type because the all departments of Apple reported to Steve Jobs for ...
Apple Inc. Apple Inc. is a multinational corporation with a global presence. In the latest financial standings, it has the highest value by the prices of stock. Apple Inc. supplies computer and other electronic and is ahead of others mainly for its production and sale of IPods, IPhones, Mac and the ITunes. The organizational structure at Apple ...
Organizational structure. Apple Inc. has a hierarchical organizational structure. The structure was first developed by its founder Steve Jobs who passed away. Currently, the leadership of the firm is under Tim Cook who is the CEO where he has made several modifications to the way the firm is run since taking over in 2011.
The structure of an organization consists of work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization and decentralization, formalization, and boundary spanning. I will further discuss each of these elements and how they affect Apple Inc. later in this paper. First, we will take a look at the history of the ...
The organization that I would like to work for is Apple Inc. In this essay, I will give a brief overview of the company's history, define it organizational structure and effects it have on the success of the organization, distinguish between leadership and management, describe the culture and the core capabilities which lead to Apple becoming ...
Company Structure. 1401 5. Print Сite. Apple Inc. is a company that has specialized in the manufacture of software and electronics, among other online solutions. The company was founded by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in 1976. It has experienced substantial growth over the years and succeeded in establishing itself as one of the major players ...
This essay paper will discuss the proposed organizational structure for IKEA on the light of the shifting in the concentration of the strategic to be expanding globally. IKEA is established in 1943, as a design and sells company that focus on furniture, home accessories, and appliances ("IKEA," 2012).…