How to Write a Marketing Research Objective
We all know the old adage: is marketing is an art or a science?
At Seer, we think it’s both. But not necessarily both at the same time. We believe the better question is: which comes first in marketing, art or science?
And if you ask us that question, we’d tell you it’s a science first.
"The science of marketing is all about using data and insights to drive your strategy. The art of marketing is how you express that strategy."
Now that we know we are starting with science, what does that mean exactly?
Well, remember when you were in school and you had to come up with your own science research experiment? Remember what came first? The objective. Why? Because without an objective, you don’t have a testable proposition. And without a testable proposition, you don’t have direction. And we all know that when research doesn’t have a direction, it typically doesn’t garner any groundbreaking takeaways.
So, what does your high school science experiment have to do with marketing research?
Similar to the traditional objective, a great marketing research plan starts with a strong objective. One that is focused, measurable, and effective. Without a clear objective, your marketing research will not be as successful.

What is a Marketing Research Objective?
[TIP] By definition, a "Research Objective" is a statement of purpose that outlines a specific result to achieve within a dedicated time frame and available resources.
Applying this logic to marketing, a marketing research objective is a statement that outlines what you want to know about your customer. Clearly defining your objective at the beginning stages will help you avoid conflicting expectations or wasted collecting irrelevant data.
How Do You Create a Marketing Research Objective?
Start at the end. I know it sounds counterintuitive, but if you start with the desired outcome, you will be able to create a more focused objective. What’s the one thing you want to be able to take away from this research? What do you plan to do with the information? What does success look like? Use this objective as your compass while you navigate your research and analysis.
Typically, it’s easiest to do this in the form of a question. Here are a few examples.
- Example 1: Which features in Product X are most important to our Enterprise customers?
This question will give you a list of features, in order of importance, for your Enterprise customer.
- Example 2: What are the different search triggers amongst our four customer segments?
This question will result in a list of common factors that result in users searching for Service Y.
When you start seeing all the data points, behaviors, and survey responses - curiosity can set in.
An abundance of data can pull you in multiple directions because each finding is interesting in its own right. That’s when your objective comes in. Know the end result you are working toward and stay on that path.
Creating a Research Objective
Once you’ve got your desired outcome, you’ll want to create your objective. A few things to consider as you create your statement:
- Where does this fit into your marketing strategy? Where does this objective fit into your larger marketing strategy? Not only is this helpful when dispersing information internally or getting buy-in, it keeps the research team focused on the higher business objectives attached to this research. Is this part of your company’s focus on brand awareness? A new product launch? An analysis of competitors? These are all very different things.
- Include your target audience. Typically, it’s difficult to understand everything with every user segment so pick which segment you plan to analyze. Is it your Enterprise customers? Customers living in a specific region? A certain demographic segment? Including this in your objective will be a helpful gut check when choosing participants.
- What will you measure? You don’t need to list out all of the data points you plan to measure, but there should be some measurable element in your objective. Is it sentiment? Are you looking for frequencies? What about behavioral trends? Including this in your objective will ensure you pick the most appropriate research methodology to acquire that measurable element.
- A behavior. What is the behavior or action that we are going to be researching? Is navigating your website? Is it purchasing a product? Is it clicking on an ad?
Let’s look at some examples:

Common Marketing Research Objective Pitfalls
While creating an objective may seem relatively straightforward, it can be easy to get wrong. Let’s go over some of the common pitfalls.
Objective is Too Broad
Now, if you follow the outline above, this shouldn’t be an issue because it forces you to get granular with your objective.
- Specific: As part of our rebranding, we are conducting a sentiment analysis with our recurring customers
- Broad: As part of our rebranding, we will ask customers how they feel about it
We want to avoid broad objectives because they can allow curiosity to get the best of us and a once seemingly clear research project can get muddied.
More Than One Objective
Every research project should have one objective and one objective only. Again, while this may seem easy enough to manage, you’d be surprised just how easy it is to sneak those secondary and tertiary objectives into your statement.
- One objective: We aim to understand what questions our customers have when considering purchasing a car
- Two objectives: We aim to understand what questions our customers have when searching for and considering a car
You see, the questions customers may have when searching for a car could be completely different than the questions they have when considering purchasing a car.
Making Assumptions
Avoid making your objective into a hypothesis with absolute statements and assumptions. Your objective should be more of a question than a prediction. That comes later.
- Objective: Uncover the purchase journey of our target demographic
- Assumption: Uncover what part search plays in the purchase journey of our target demographic
This looks unsuspecting, but in reality, we're already assuming that search plays a role in our audience's journey. That could sway the focus of the research.
Once you’ve created your objective, let it (and only it) drive the beginning stages of your marketing research.
Write it on a post-it and stick it on your desk, write it on the whiteboard at every meeting you have, keep it top of mind as you continue your research. It will serve as a compass and help you avoid being led astray by interesting data, curious colleagues, and conflicting agendas.
More Tips for Understanding Your Audience
Check back on the Seer blog for the next installment from our Audience team. Sign up for our newsletter to read the latest blogs on audience, SEO, PPC, and more.

We love helping marketers like you.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive updates and more:
Related Posts

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
Published on July 12, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on November 20, 2023.
Research objectives describe what your research is trying to achieve and explain why you are pursuing it. They summarize the approach and purpose of your project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement . They should:
- Establish the scope and depth of your project
- Contribute to your research design
- Indicate how your project will contribute to existing knowledge
Table of contents
What is a research objective, why are research objectives important, how to write research aims and objectives, smart research objectives, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research objectives.
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process , including how you collect data , build your argument , and develop your conclusions .
Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried out and the actual content of your paper.
Research aims
A distinction is often made between research objectives and research aims.
A research aim typically refers to a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives.
Your research objectives are more specific than your research aim and indicate the particular focus and approach of your project. Though you will only have one research aim, you will likely have several research objectives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Research objectives are important because they:
- Establish the scope and depth of your project: This helps you avoid unnecessary research. It also means that your research methods and conclusions can easily be evaluated .
- Contribute to your research design: When you know what your objectives are, you have a clearer idea of what methods are most appropriate for your research.
- Indicate how your project will contribute to extant research: They allow you to display your knowledge of up-to-date research, employ or build on current research methods, and attempt to contribute to recent debates.
Once you’ve established a research problem you want to address, you need to decide how you will address it. This is where your research aim and objectives come in.
Step 1: Decide on a general aim
Your research aim should reflect your research problem and should be relatively broad.
Step 2: Decide on specific objectives
Break down your aim into a limited number of steps that will help you resolve your research problem. What specific aspects of the problem do you want to examine or understand?
Step 3: Formulate your aims and objectives
Once you’ve established your research aim and objectives, you need to explain them clearly and concisely to the reader.
You’ll lay out your aims and objectives at the end of your problem statement, which appears in your introduction. Frame them as clear declarative statements, and use appropriate verbs to accurately characterize the work that you will carry out.
The acronym “SMART” is commonly used in relation to research objectives. It states that your objectives should be:
- Specific: Make sure your objectives aren’t overly vague. Your research needs to be clearly defined in order to get useful results.
- Measurable: Know how you’ll measure whether your objectives have been achieved.
- Achievable: Your objectives may be challenging, but they should be feasible. Make sure that relevant groundwork has been done on your topic or that relevant primary or secondary sources exist. Also ensure that you have access to relevant research facilities (labs, library resources , research databases , etc.).
- Relevant: Make sure that they directly address the research problem you want to work on and that they contribute to the current state of research in your field.
- Time-based: Set clear deadlines for objectives to ensure that the project stays on track.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, November 20). Research Objectives | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-objectives/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home QuestionPro Marketing
How to Set Marketing Research Goals and Objectives
Marketing research goals.

Begin with the END
Instead of setting your goals and objectives from where you are NOW, imagine yourself ALREADY having achieved your goal – then work backwards and document HOW YOU GOT THERE.
The reason for this is very simple. If you set your goal based on where you are now – there is a good chance that you will get caught up in fixing a problem that is actually irrelevant in getting your business to where you want it to be.
Set your goals and objectives based on your vision for where you want your company to BE and not where it is NOW.
An Example:
If the vision and mission of your business is to help your customers be successful in their business — then imagine your customers being successful and then imagine in what ways you are helping them do that. This may include things you are currently doing — or NOT. And this is the key to creating marketing research goals and objectives that will help you measure the potential market opportunity, the target audience for your products and how they buy.
(I know that this sounds a little way out. But if you’re wondering how some of the successful businesses you see out there got that way — this is IT)
Take Clate Mask and Scott Martineau from InfusionSoft as an example. InfusionSoft is an email marketing intelligence software that automates your sales and marketing process. It’s a high-end software and it isn’t cheap. Clate and Scott found out that their customers really didn’t know how to put marketing messages together — and hence, the software didn’t appear to be “working.”
They quickly realized that if their customers knew what to put INTO the software – the customers would make more than enough money to pay the fee for the software and also refer the software to their friends and colleagues. As a result, they set a goal to have their entire client base double their sales within a 12 month period.
Having set this goal and objective — they were not only fired up and inspired about what was possible for their business. But their customers bought into the very same goal. Suddenly finding out what their customers needed or wanted that would help them grow and prosper was easy.
And what do you think happened to their response rates? Of course, every time they asked their customers what they wanted — these customers were eager to tell them.
So How is this Relevant to YOU?
If you’ve not been successful collecting feedback from your community or if the research you’ve done hasn’t delivered on results — you might want to look at the goals and objectives that you’ve set.
Are these goals and objectives more focused on solving a problem you have today? If so, that problem might be relevant to YOU but not your customer.
Use Social Media Chatter to Help You Find a Meaningful Goal
Enough of the heady stuff. Let’s get to the meat of how you can set these kinds of goals and objectives.
If you don’t already, set up several social media communication channels that include the following:
- Facebook Fan Page
- LinkedIn Company Profile
- LinkedIn Industry Group
- Twitter Account
The next thing you want to do is start posting articles on your blog that focus on your vision and how you are helping you customers be successful. Get active on industry community sites and spaces, ask questions, answer questions and participate. Then, TELL your customers, suppliers, industry experts to participate as well.
If you keep participating and reminding your audience to visit these sites – you will see conversations, get data and start forming relevant, success based goals and objectives.
Trying this backwards strategy of setting goals and objectives might identify new and exciting opportunities for your business.
Reader Interactions
[…] QuestionPro Blog Insights and sneak peeks into QuestionPro.com Skip to content HomeFree Online TrainingFree Webinar Schedule ← How to Set Marketing Research Goals and Objectives […]
[…] How to Set Marketing Research Goals and Objectives (questionpro.com) […]
MORE LIKE THIS

Resident Experience: What It Is and How to Improve It
Mar 27, 2024

11 Best Employee Onboarding and Training Software in 2024
Top 11 Team Engagement Software in 2024
8 Leading Brand Health Tracker to Track Your Brand Reputation
Mar 26, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
Discover the different types of market research, how to conduct your own market research, and use a free template to help you along the way.

MARKET RESEARCH KIT
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research

Updated: 02/21/24
Published: 02/21/24
Today's consumers have a lot of power. As a business, you must have a deep understanding of who your buyers are and what influences their purchase decisions.
Enter: Market Research.
![how to make objectives market research → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Whether you're new to market research or not, I created this guide to help you conduct a thorough study of your market, target audience, competition, and more. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is market research?
Primary vs. secondary research, types of market research, how to do market research, market research report template, market research examples.
Market research is the process of gathering information about your target market and customers to verify the success of a new product, help your team iterate on an existing product, or understand brand perception to ensure your team is effectively communicating your company's value effectively.
Market research can answer various questions about the state of an industry. But if you ask me, it's hardly a crystal ball that marketers can rely on for insights on their customers.
Market researchers investigate several areas of the market, and it can take weeks or even months to paint an accurate picture of the business landscape.
However, researching just one of those areas can make you more intuitive to who your buyers are and how to deliver value that no other business is offering them right now.
How? Consider these two things:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. It‘s very possible that your immediate resources are, in many ways, equal to those of your competition’s immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your customers don't represent the attitudes of an entire market. They represent the attitudes of the part of the market that is already drawn to your brand.
The market research services market is growing rapidly, which signifies a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from roughly $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025 .
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why do market research?
Market research allows you to meet your buyer where they are.
As our world becomes louder and demands more of our attention, this proves invaluable.
By understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired solutions, you can aptly craft your product or service to naturally appeal to them.
Market research also provides insight into the following:
- Where your target audience and current customers conduct their product or service research
- Which of your competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- What's trending in your industry and in the eyes of your buyer
- Who makes up your market and what their challenges are
- What influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Whether there‘s demand for the business initiatives you’re investing in
- Unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be flipped into selling opportunity
- Attitudes about pricing for a particular product or service
Ultimately, market research allows you to get information from a larger sample size of your target audience, eliminating bias and assumptions so that you can get to the heart of consumer attitudes.
As a result, you can make better business decisions.
To give you an idea of how extensive market research can get , consider that it can either be qualitative or quantitative in nature — depending on the studies you conduct and what you're trying to learn about your industry.
Qualitative research is concerned with public opinion, and explores how the market feels about the products currently available in that market.
Quantitative research is concerned with data, and looks for relevant trends in the information that's gathered from public records.
That said, there are two main types of market research that your business can conduct to collect actionable information on your products: primary research and secondary research.
Primary Research
Primary research is the pursuit of first-hand information about your market and the customers within your market.
It's useful when segmenting your market and establishing your buyer personas.
Primary market research tends to fall into one of two buckets:
- Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people.
- Specific Primary Research: This type of research often follows exploratory research. In specific research, you take a smaller or more precise segment of your audience and ask questions aimed at solving a suspected problem.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is all the data and public records you have at your disposal to draw conclusions from (e.g. trend reports, market statistics, industry content, and sales data you already have on your business).
Secondary research is particularly useful for analyzing your competitors . The main buckets your secondary market research will fall into include:
- Public Sources: These sources are your first and most-accessible layer of material when conducting secondary market research. They're often free to find and review — like government statistics (e.g., from the U.S. Census Bureau ).
- Commercial Sources: These sources often come in the form of pay-to-access market reports, consisting of industry insight compiled by a research agency like Pew , Gartner , or Forrester .
- Internal Sources: This is the market data your organization already has like average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other historical data that can help you draw conclusions on buyer needs.
- Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
- Observation-Based Research
- Buyer Persona Research
- Market Segmentation Research
- Pricing Research
- Competitive Analysis Research
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
- Brand Awareness Research
- Campaign Research
1. Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions so you can allow for a natural flow of conversation. Your interviewees can answer questions about themselves to help you design your buyer personas and shape your entire marketing strategy.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups provide you with a handful of carefully-selected people that can test out your product and provide feedback. This type of market research can give you ideas for product differentiation.
3. Product/Service Use Research
Product or service use research offers insight into how and why your audience uses your product or service. This type of market research also gives you an idea of the product or service's usability for your target audience.
4. Observation-Based Research
Observation-based research allows you to sit back and watch the ways in which your target audience members go about using your product or service, what works well in terms of UX , and which aspects of it could be improved.
5. Buyer Persona Research
Buyer persona research gives you a realistic look at who makes up your target audience, what their challenges are, why they want your product or service, and what they need from your business or brand.
6. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research allows you to categorize your target audience into different groups (or segments) based on specific and defining characteristics. This way, you can determine effective ways to meet their needs.
7. Pricing Research
Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy . It gives you an idea of what similar products or services in your market sell for and what your target audience is willing to pay.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses give you a deep understanding of the competition in your market and industry. You can learn about what's doing well in your industry and how you can separate yourself from the competition .
9. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Customer satisfaction and loyalty research gives you a look into how you can get current customers to return for more business and what will motivate them to do so (e.g., loyalty programs , rewards, remarkable customer service).
10. Brand Awareness Research
Brand awareness research tells you what your target audience knows about and recognizes from your brand. It tells you about the associations people make when they think about your business.
11. Campaign Research
Campaign research entails looking into your past campaigns and analyzing their success among your target audience and current customers. The goal is to use these learnings to inform future campaigns.
- Define your buyer persona.
- Identify a persona group to engage.
- Prepare research questions for your market research participants.
- List your primary competitors.
- Summarize your findings.
1. Define your buyer persona.
You have to understand who your customers are and how customers in your industry make buying decisions.
This is where your buyer personas come in handy. Buyer personas — sometimes referred to as marketing personas — are fictional, generalized representations of your ideal customers.
Use a free tool to create a buyer persona that your entire company can use to market, sell, and serve better.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![how to make objectives market research SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

20+ Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

What's a Competitive Analysis & How Do You Conduct One?

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![how to make objectives market research How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![how to make objectives market research 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It

What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
![how to make objectives market research 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Media Center
- E-Books & White Papers
- Knowledge Center
A Basic Guide to Defining Your Market Research Goals
by Caitlin Stewart , on May 29, 2014

1. Define the problem or opportunity and state your objectives
When creating a new goal, it is important to recognize any current problems in a company. You should also work to see whether a problem can be molded into an opportunity. Basic marketing research courses explain that a management problem is any type of issue that needs managerial action in order to resolve the issue. However, a marketing research problem is defined as a statement specifying the type of information needed by the decision maker to help solve the management problem and how that information can be obtained efficiently and effectively. To solve the market research problem, a research team can develop a marketing research objective, which is a goal defining the specific information needed to solve the marketing research problem.
Before you begin a project , make sure you clearly define your objectives and the outcomes you expect from the research that will be conducted. Having a clear and definitive goal is helpful because setting too many goals can dilute a project and increase the chance of having the research fail. By having reasonable goals, you can refer back to them during the project to distinguish whether the research is still keeping the original goals in mind.
2. Develop the research design to meet your objectives
The purpose of a well-developed research design is to confirm theories, measure brand loyalty, describe the population, build a customer profile, or to gain specific information. Based on what you are interested in, deciding whether a descriptive or causal study is needed to meet research objectives is key when starting your project.
Consider all potential issues that could arise during research so you and your research team can be prepared and aware if they occur. For example, if information being gathered is irrelevant to the company’s newly developed objectives, both time and money will be wasted on continuing with that specific research. If this ever occurs, reorganize and consider working with research specialists to help in making sure that the data you are observing is targeted at your specific needs.
3. Collect information relevant to your objectives
Once information and data is needed, sometimes the easiest step is to start looking at secondary data first. Utilizing data sets and examining organized marketing research reports have the potential to clarify your issues or even provide a solution to your research objectives. Secondary data can even alert researchers to other problems and is usually less expensive and faster to gather than primary data.
Once you review or purchase all your secondary data, your researchers can determine whether any further research through surveys or focus groups is necessary. Conducting that research and developing solutions from the information gathered will be required in drawing new conclusions.
4. Create a final report
Create a final report by analyzing all data and organizing it into a useful format for your company’s marketing team. Sorting through conclusions to relate potential solutions to your goals and objectives is central in ensuring your company can make use of the new information both effectively and beneficially.
5. Follow up
Once all findings are organized, you need to choose whether the information gathered is going to be put into use. You should use this stage to identify the areas where marketing techniques can be improved for future research projects. But once all is finished, evaluating whether the information gathered was able to help create solutions and meet your goals is vital. Upper management will need to determine whether the information gathered was a.) worth the cost, and b.) beneficial in meeting the outlined goals.
By knowing what your overall goals and objectives are before you begin a new project, you will help your company and yourself in making sure the research stays on task.
Interested in learning more about using business intelligence to achieve your research goals? Download our free white paper on How to Use Market Research to Launch Your Business.

Thanks for reading!
Caitlin Stewart Marketing Intern, MarketResearch.com

About This Blog
Our goal is to help you better understand your customer, market, and competition in order to help drive your business growth.
Popular Posts
- A CEO’s Perspective on Harnessing AI for Market Research Excellence
- How to Use Market Research for Onboarding and Training Employees
- 10 Global Industries That Will Boom in the Next 5 Years
- Primary Data vs. Secondary Data: Market Research Methods
- 10 Booming Industries in the U.S. to Watch in 202 4 and Beyond
Recent Posts
Posts by topic.
- Industry Insights (814)
- Market Research Strategy (271)
- Food & Beverage (133)
- Healthcare (124)
- The Freedonia Group (120)
- How To's (107)
- Market Research Provider (88)
- Manufacturing & Construction (79)
- Packaged Facts (76)
- Pharmaceuticals (75)
- Telecommunications & Wireless (70)
- Heavy Industry (69)
- Marketing (58)
- Retail (56)
- Profound (55)
- Transportation & Shipping (54)
- Software & Enterprise Computing (53)
- House & Home (50)
- Materials & Chemicals (46)
- Consumer Electronics (45)
- Medical Devices (44)
- Energy & Resources (41)
- Public Sector (40)
- Demographics (37)
- Biotechnology (36)
- Business Services & Administration (36)
- Education (36)
- Custom Market Research (35)
- Diagnostics (34)
- Academic (33)
- E-commerce & IT Outsourcing (32)
- Travel & Leisure (32)
- Financial Services (29)
- Computer Hardware & Networking (26)
- Simba Information (24)
- Kalorama Information (21)
- Knowledge Centers (19)
- Apparel (18)
- Cosmetics & Personal Care (17)
- Social Media (16)
- Advertising (14)
- Big Data (14)
- Market Research Subscription (14)
- Holiday (11)
- Emerging Markets (8)
- Associations (1)
- Religion (1)
MarketResearch.com 6116 Executive Blvd Suite 550 Rockville, MD 20852 800.298.5699 (U.S.) +1.240.747.3093 (International) [email protected]
From Our Blog
Subscribe to blog, connect with us.
.png)
A Comprehensive Guide on How to Perform Market Research

Navigating the intricate world of business often hinges on understanding markets, consumers, and competitors. This understanding is directly rooted in effective market research. While many acknowledge its significance, the detailed process of conducting comprehensive market research can be a challenge for some.
This guide aims to clarify the steps and strategies involved, ensuring businesses can gather insights that are both meaningful and actionable. Dive in to discover the nuances and best practices on how to perform market research, setting the foundation for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Understanding How to Do Market Research
Embarking on the journey of market research can be both exciting and rewarding, as it equips enterprises with market data needed to make strategic decisions. Follow these seven essential market research steps that will steer towards valuable insights.
1. Define Objectives
Before diving into market research, it's crucial to define the research objective. This foundational step forms the groundwork for an effective market research process.
- Start Broad, then Narrow Down : Begin by identifying the overarching goal, such as understanding customer preferences. From there, refine the objective to be more specific, like identifying preferences among a particular demographic or region.
- Align with Business Goals : Ensure that the research objectives are in sync with the company's broader goals. If the aim is market expansion, the research might focus on potential markets or competitor landscapes in new regions.
- Collaborate : Engage multiple departments or stakeholders in the objective-setting process. Different perspectives can offer a more holistic view of what the research should achieve.
- Stay Flexible : While it's essential to have clear objectives, it's equally important to remain adaptable. As the research progresses, new questions or areas of interest might emerge. Being open to refining objectives can lead to unexpected and valuable insights.
2. Choose the Right Market Research Method
Once objectives are crystal clear, the next pivotal step is selecting the appropriate research method. This choice can significantly influence the quality and relevance of the insights gathered.
Different methods offer varying levels of detail. While some provide a broad overview of the market, others delve deep into specific aspects or demographics. The chosen method also often dictates the time, money, and manpower required. Making an informed choice ensures optimal resource utilization without compromising on the quality of insights.
Exploring common research methods:
- Surveys : Ideal for gathering quantitative data, surveys can reach a wide audience and provide insights on general market trends, preferences, or behaviors.
- Interviews : Offering a qualitative perspective, one-on-one interviews can uncover deeper motivations, challenges, or sentiments of the target audience.
- Focus Groups : These are discussions with a small group of participants, providing a mix of qualitative insights and allowing for dynamic interactions and feedback on specific topics or products.
- Observational Research : By studying consumers in their natural environment, businesses can gain unfiltered insights into behaviors, usage patterns, and more.
- Experimental Research : This method tests hypotheses in controlled settings, allowing businesses to understand cause-and-effect relationships, such as the impact of a price change on sales.
3. Determine Target Market Research Audience
Identifying the specific target market research audience allows tailoring research efforts, ensuring relevant and representative data. This step ensures that the data collected is not just accurate but also relevant to the business's goals.
Steps to identify the right audience:
- Segmentation : Divide the broader market into smaller segments based on criteria like demographics, buying behavior, geographic location, or psychographics.
- Prioritization : Not all segments might be equally relevant. Assess which segments align most closely with the business objectives and prioritize them for research.
- Sampling : Instead of surveying an entire segment, a representative sample can be chosen. This sample should be large enough to be statistically significant but manageable in terms of research resources.
- Validation : Ensure that the chosen audience truly represents the desired market segment. This might involve preliminary surveys or checks to confirm their relevance.
Tips for determining the right audience:
- Stay Updated : Market dynamics change, and so do audience behaviors and preferences. Regularly update audience definitions to stay relevant.
- Avoid Biases : Ensure that the selection process is unbiased. Over-relying on certain criteria or overlooking others can skew results.
- Engage Stakeholders : Collaborate with sales, customer service, or other departments that interact directly with customers. Their insights can be invaluable in defining the right audience.
4. Collect Market Research Data
The data collection phase is where the groundwork laid in the previous steps comes to fruition. It's the process of gathering information from the defined audience using the chosen research method. The quality and accuracy of the data collected during this phase will directly influence the insights and conclusions drawn.
Best practices for data collection:
- Ensure Consistency : Whether it's the wording of survey questions or the setting of focus groups, maintaining consistency ensures data reliability across the board.
- Prioritize Data Quality : It's better to have smaller, high-quality data than vast amounts of unreliable information. Implement checks and balances to maintain data integrity.
- Stay Ethical : Always seek consent from participants, maintain their privacy, and be transparent about how the data will be used.
- Test and Refine : Before rolling out on a larger scale, test the data collection methods on a smaller group to identify and rectify potential issues.
5. Analyze the Market Research Data
After the meticulous process of data collection, the next step is analysis. This phase transforms raw data into meaningful insights, providing a clearer understanding of the market landscape, consumer behaviors, and potential opportunities or challenges.
Key data analysis techniques:
- Statistical Analysis : Using tools and software, data can be subjected to various statistical tests to identify significant patterns or trends.
- Qualitative Analysis : For data from interviews or focus groups, thematic analysis can be employed to identify recurring themes or sentiments.
- Comparative Analysis : By comparing current data with past data sets or benchmarking against industry standards, businesses can gauge their performance and position in the market.
- Predictive Analysis : Leveraging historical data and statistical algorithms, businesses can forecast future trends or behaviors.
- Visual Data Analysis : Tools that create graphs, charts, and heat maps can help in visualizing complex data sets, making patterns more discernible.
6. Interpret the Results
With data analysis complete, the next crucial step of market research is interpretation. This phase involves making sense of the analyzed data, drawing conclusions, and understanding the implications for the business. It's where the numbers and patterns are translated into strategic insights that can guide decision-making.
Steps for effective interpretation:
- Relate to Objectives : Revisit the initial research objectives and assess how the results address them. This ensures the interpretation remains aligned with the research's purpose.
- Consider External Factors : Understand external market dynamics, economic factors, or industry trends that might influence the results. This provides a holistic view of the findings.
- Draw Conclusions : Based on the data and its analysis, draw clear conclusions. These should be concise, actionable, and directly related to the research objectives.
- Recommend Actions : Based on the conclusions, suggest actionable steps the business can take. This turns the research into a strategic tool for growth.
7. Present the Findings
After the rigorous processes of data collection, analysis, and interpretation, it's time to communicate the insights. Presenting the findings is about packaging the market research results in a manner that's clear, compelling, and actionable for stakeholders, ensuring that the research's value is fully realized.
Key elements of an effective presentation:
- Executive Summary : Start with a concise overview of the research objectives, methods, and key findings. This provides a snapshot for those who might not delve into the details.
- Visual Aids : Utilize charts, graphs, and infographics to represent data visually . This makes complex data sets more digestible and highlights key patterns or trends.
- Detailed Findings : Delve into the specifics of the results, ensuring that stakeholders have access to both the broad strokes and the finer details.
- Recommendations : Based on the interpreted results, outline actionable recommendations for the business. This turns insights into clear next steps.
- Q&A Session : Allow stakeholders to ask questions or seek clarifications. This ensures a thorough understanding and can also provide additional perspectives.

Prompts to Build Reports in Minutes
Unlock ChatGPT's potential in building marketing reports and dashboards with this comprehensive guide. 5 steps to build your next market research report.
Example of Market Research
Imagine launching a new product and wanting to understand the market's response. Market research becomes the guiding compass, gauging customer interest through methods like surveys and focus groups.
Gauging Customer Interest
Market research becomes your trusted ally in deciphering the minds and hearts of your target customers. Through surveys, focus groups, and feedback mechanisms , you gain valuable insights into what sparks their interest and captures their attention. Unveiling the features, benefits, and packaging that resonate most with consumers allows you to tailor your product offerings to meet their desires precisely.
Identifying Competitors
Market research identifies competitors, their market size, and what sets the product apart. In the fiercely competitive business landscape, knowing who your competitors are and what sets you apart is essential. Armed with this knowledge, your enterprise can carve out a distinct niche and craft a unique value proposition that resonates with your audience.
Determining Optimal Pricing Strategies
Pricing is crucial. Market research guides towards the optimal balance between profitability and customer perception. By assessing consumer willingness to pay and comparing prices of similar products in the market, you can strategically position your offering to attract and retain loyal customers.
Analyzing Consumer Behavior Market Research Data
Data becomes the goldmine of knowledge, and market research is the expert prospector that digs deep to unearth valuable insights. By analyzing consumer behavior data, your enterprise gains a deep understanding of customer preferences, shopping habits, and pain points. This treasure trove of information empowers you to refine your marketing approach, create compelling messaging, and deliver personalized experiences that resonate with your audience on a profound level.
Allocating Resources Effectively
Launching a new product demands efficient resource allocation. Market research guides to invest where they yield the highest returns. By identifying the most promising market segments and channels, you can optimize your marketing efforts, ensuring your message reaches the right audience at the right time.
Aligning Business Strategies With Actual Market Desires
The journey of conducting market research is like navigating through uncharted waters. By defining clear objectives, choosing the right methods, determining the target audience, collecting and analyzing data, interpreting the results, and presenting the findings in a clear and concise manner, an enterprise positions itself to unlock valuable insights. These insights empower strategic decisions, driving growth and success in the fiercely competitive market landscape. It's all about understanding market demand research, competitor landscape, customer preferences, and more, and using this knowledge to steer the enterprise in the right direction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential steps for effective market research.
To succeed in market research, follow these steps. First, define clear goals and insightful research questions. Then, choose suitable research methods aligned with objectives. Identify the specific audience for relevant data. Collect reliable data systematically using tools like surveys. Analyze the data to uncover meaningful trends. Interpret results for strategic decisions. Finally, present findings in a concise report.
How can market research benefit new product launches?
Market research helps new product launches by understanding customer interest. It identifies competitors and pricing strategies. Analyzing consumer behavior data guides better decision-making. Market research optimizes marketing efforts for higher returns.
How does market research refine business marketing approaches?
Market research refines marketing by providing insights, identifying effective strategies, and keeping up with trends. It assesses marketing success, leading to improvements.
What are the primary benefits of using market research in decision-making?
Market research reduces uncertainty, identifies opportunities, minimizes risks, boosts competitiveness, and enhances customer satisfaction.

500+ data sources under one roof to drive business growth. 👇
Analytics that detect nuances for better decision-making

Unshackling Marketing Insights With Advanced UTM Practices
Improvado Labs: experience the latest marketing analytics technology
%20(1).png)
Im provado - A Marketing Analytics Platform
Improvado automates the annoying parts of data management. No more manual anything. Just automate.

From the blog

San Diego | Headquarters
3919 30th St, San Diego, CA 92104
San Francisco
2800 Leavenworth St, Suite 250, San Francisco, CA 94133
Send us an email
How to do market research: The complete guide for your brand
Written by by Jacqueline Zote
Published on April 13, 2023
Reading time 10 minutes
Blindly putting out content or products and hoping for the best is a thing of the past. Not only is it a waste of time and energy, but you’re wasting valuable marketing dollars in the process. Now you have a wealth of tools and data at your disposal, allowing you to develop data-driven marketing strategies . That’s where market research comes in, allowing you to uncover valuable insights to inform your business decisions.
Conducting market research not only helps you better understand how to sell to customers but also stand out from your competition. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about market research and how doing your homework can help you grow your business.
Table of contents:
What is market research?
Why is market research important, types of market research, where to conduct market research.
- Steps for conducting market research
- Tools to use for market research
Market research is the process of gathering information surrounding your business opportunities. It identifies key information to better understand your audience. This includes insights related to customer personas and even trends shaping your industry.
Taking time out of your schedule to conduct research is crucial for your brand health. Here are some of the key benefits of market research:
Understand your customers’ motivations and pain points
Most marketers are out of touch with what their customers want. Moreover, these marketers are missing key information on what products their audience wants to buy.
Simply put, you can’t run a business if you don’t know what motivates your customers.
And spoiler alert: Your customers’ wants and needs change. Your customers’ behaviors today might be night and day from what they were a few years ago.
Market research holds the key to understanding your customers better. It helps you uncover their key pain points and motivations and understand how they shape their interests and behavior.
Figure out how to position your brand
Positioning is becoming increasingly important as more and more brands enter the marketplace. Market research enables you to spot opportunities to define yourself against your competitors.
Maybe you’re able to emphasize a lower price point. Perhaps your product has a feature that’s one of a kind. Finding those opportunities goes hand in hand with researching your market.
Maintain a strong pulse on your industry at large
Today’s marketing world evolves at a rate that’s difficult to keep up with.
Fresh products. Up-and-coming brands. New marketing tools. Consumers get bombarded with sales messages from all angles. This can be confusing and overwhelming.
By monitoring market trends, you can figure out the best tactics for reaching your target audience.
Not everyone conducts market research for the same reason. While some may want to understand their audience better, others may want to see how their competitors are doing. As such, there are different types of market research you can conduct depending on your goal.
Interview-based market research allows for one-on-one interactions. This helps the conversation to flow naturally, making it easier to add context. Whether this takes place in person or virtually, it enables you to gather more in-depth qualitative data.
Buyer persona research
Buyer persona research lets you take a closer look at the people who make up your target audience. You can discover the needs, challenges and pain points of each buyer persona to understand what they need from your business. This will then allow you to craft products or campaigns to resonate better with each persona.
Pricing research
In this type of research, brands compare similar products or services with a particular focus on pricing. They look at how much those products or services typically sell for so they can get more competitive with their pricing strategy.
Competitive analysis research
Competitor analysis gives you a realistic understanding of where you stand in the market and how your competitors are doing. You can use this analysis to find out what’s working in your industry and which competitors to watch out for. It even gives you an idea of how well those competitors are meeting consumer needs.
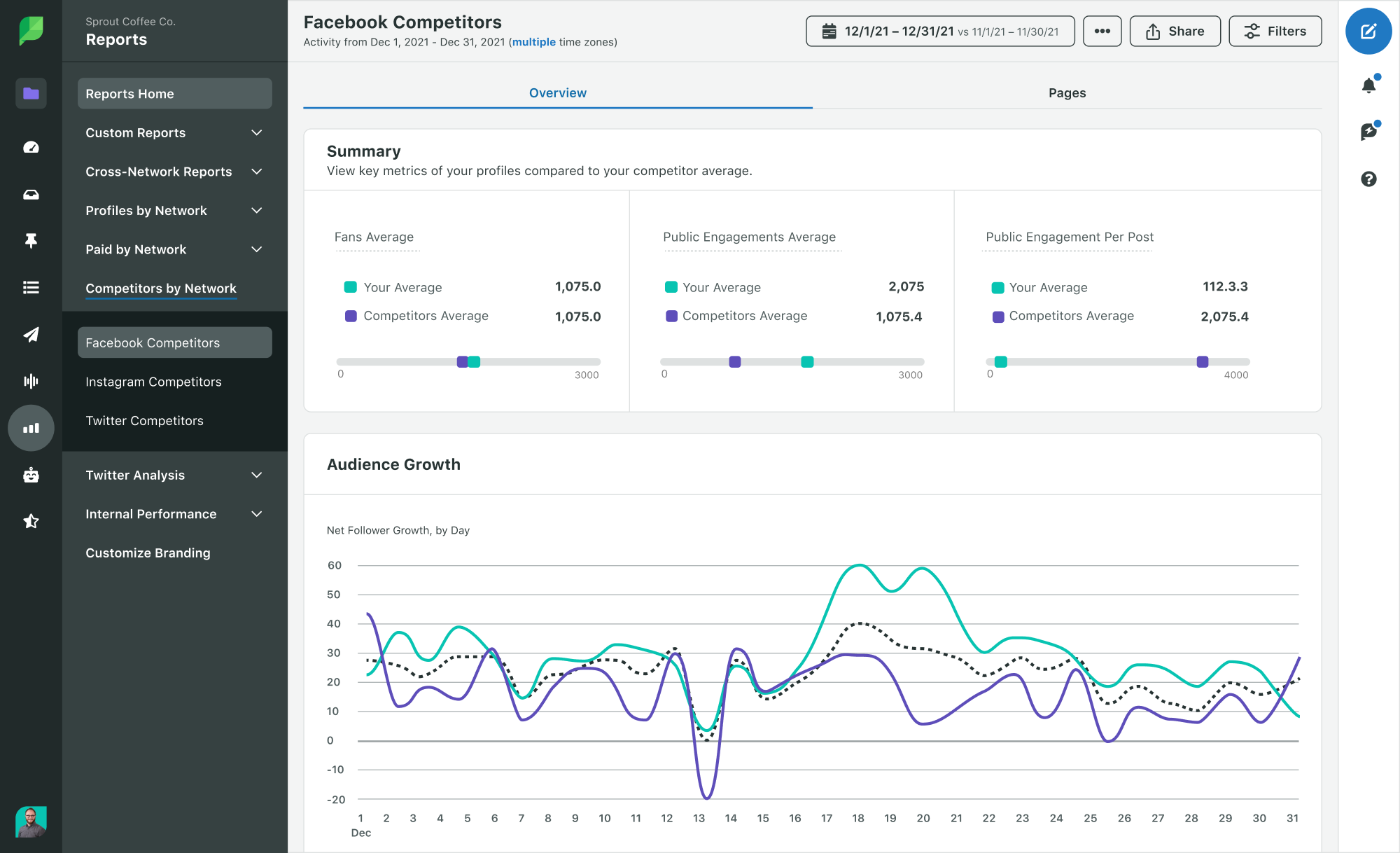
Depending on the competitor analysis tool you use, you can get as granular as you need with your research. For instance, Sprout Social lets you analyze your competitors’ social strategies. You can see what types of content they’re posting and even benchmark your growth against theirs.
Brand awareness research
Conducting brand awareness research allows you to assess your brand’s standing in the market. It tells you how well-known your brand is among your target audience and what they associate with it. This can help you gauge people’s sentiments toward your brand and whether you need to rebrand or reposition.
If you don’t know where to start with your research, you’re in the right place.
There’s no shortage of market research methods out there. In this section, we’ve highlighted research channels for small and big businesses alike.
Considering that Google sees a staggering 8.5 billion searches each day, there’s perhaps no better place to start.
A quick Google search is a potential goldmine for all sorts of questions to kick off your market research. Who’s ranking for keywords related to your industry? Which products and pieces of content are the hottest right now? Who’s running ads related to your business?
For example, Google Product Listing Ads can help highlight all of the above for B2C brands.

The same applies to B2B brands looking to keep tabs on who’s running industry-related ads and ranking for keyword terms too.

There’s no denying that email represents both an aggressive and effective marketing channel for marketers today. Case in point, 44% of online shoppers consider email as the most influential channel in their buying decisions.
Looking through industry and competitor emails is a brilliant way to learn more about your market. For example, what types of offers and deals are your competitors running? How often are they sending emails?

Email is also invaluable for gathering information directly from your customers. This survey message from Asana is a great example of how to pick your customers’ brains to figure out how you can improve your quality of service.

Industry journals, reports and blogs
Don’t neglect the importance of big-picture market research when it comes to tactics and marketing channels to explore. Look to marketing resources such as reports and blogs as well as industry journals
Keeping your ear to the ground on new trends and technologies is a smart move for any business. Sites such as Statista, Marketing Charts, AdWeek and Emarketer are treasure troves of up-to-date data and news for marketers.
And of course, there’s the Sprout Insights blog . And invaluable resources like The Sprout Social Index™ can keep you updated on the latest social trends.
Social media
If you want to learn more about your target market, look no further than social media. Social offers a place to discover what your customers want to see in future products or which brands are killin’ it. In fact, social media is become more important for businesses than ever with the level of data available.
It represents a massive repository of real-time data and insights that are instantly accessible. Brand monitoring and social listening are effective ways to conduct social media research . You can even be more direct with your approach. Ask questions directly or even poll your audience to understand their needs and preferences.

The 5 steps for how to do market research
Now that we’ve covered the why and where, it’s time to get into the practical aspects of market research. Here are five essential steps on how to do market research effectively.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
First off, what are you researching about? What do you want to find out? Narrow down on a specific research topic so you can start with a clear idea of what to look for.
For example, you may want to learn more about how well your product features are satisfying the needs of existing users. This might potentially lead to feature updates and improvements. Or it might even result in new feature introductions.
Similarly, your research topic may be related to your product or service launch or customer experience. Or you may want to conduct research for an upcoming marketing campaign.
Step 2: Choose a buyer persona to engage
If you’re planning to focus your research on a specific type of audience, decide which buyer persona you want to engage. This persona group will serve as a representative sample of your target audience.
Engaging a specific group of audience lets you streamline your research efforts. As such, it can be a much more effective and organized approach than researching thousands (if not millions) of individuals.
You may be directing your research toward existing users of your product. To get even more granular, you may want to focus on users who have been familiar with the product for at least a year, for example.
Step 3: Start collecting data
The next step is one of the most critical as it involves collecting the data you need for your research. Before you begin, make sure you’ve chosen the right research methods that will uncover the type of data you need. This largely depends on your research topic and goals.
Remember that you don’t necessarily have to stick to one research method. You may use a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. So for example, you could use interviews to supplement the data from your surveys. Or you may stick to insights from your social listening efforts.
To keep things consistent, let’s look at this in the context of the example from earlier. Perhaps you can send out a survey to your existing users asking them a bunch of questions. This might include questions like which features they use the most and how often they use them. You can get them to choose an answer from one to five and collect quantitative data.
Plus, for qualitative insights, you could even include a few open-ended questions with the option to write their answers. For instance, you might ask them if there’s any improvement they wish to see in your product.
Step 4: Analyze results
Once you have all the data you need, it’s time to analyze it keeping your research topic in mind. This involves trying to interpret the data to look for a wider meaning, particularly in relation to your research goal.
So let’s say a large percentage of responses were four or five in the satisfaction rating. This means your existing users are mostly satisfied with your current product features. On the other hand, if the responses were mostly ones and twos, you may look for opportunities to improve. The responses to your open-ended questions can give you further context as to why people are disappointed.
Step 5: Make decisions for your business
Now it’s time to take your findings and turn them into actionable insights for your business. In this final step, you need to decide how you want to move forward with your new market insight.
What did you find in your research that would require action? How can you put those findings to good use?
The market research tools you should be using
To wrap things up, let’s talk about the various tools available to conduct speedy, in-depth market research. These tools are essential for conducting market research faster and more efficiently.
Social listening and analytics
Social analytics tools like Sprout can help you keep track of engagement across social media. This goes beyond your own engagement data but also includes that of your competitors. Considering how quickly social media moves, using a third-party analytics tool is ideal. It allows you to make sense of your social data at a glance and ensure that you’re never missing out on important trends.

Email marketing research tools
Keeping track of brand emails is a good idea for any brand looking to stand out in its audience’s inbox.
Tools such as MailCharts , Really Good Emails and Milled can show you how different brands run their email campaigns.
Meanwhile, tools like Owletter allow you to monitor metrics such as frequency and send-timing. These metrics can help you understand email marketing strategies among competing brands.
Content marketing research
If you’re looking to conduct research on content marketing, tools such as BuzzSumo can be of great help. This tool shows you the top-performing industry content based on keywords. Here you can see relevant industry sites and influencers as well as which brands in your industry are scoring the most buzz. It shows you exactly which pieces of content are ranking well in terms of engagements and shares and on which social networks.

SEO and keyword tracking
Monitoring industry keywords is a great way to uncover competitors. It can also help you discover opportunities to advertise your products via organic search. Tools such as Ahrefs provide a comprehensive keyword report to help you see how your search efforts stack up against the competition.

Competitor comparison template
For the sake of organizing your market research, consider creating a competitive matrix. The idea is to highlight how you stack up side-by-side against others in your market. Use a social media competitive analysis template to track your competitors’ social presence. That way, you can easily compare tactics, messaging and performance. Once you understand your strengths and weaknesses next to your competitors, you’ll find opportunities as well.
Customer persona creator
Finally, customer personas represent a place where all of your market research comes together. You’d need to create a profile of your ideal customer that you can easily refer to. Tools like Xtensio can help in outlining your customer motivations and demographics as you zero in on your target market.

Build a solid market research strategy
Having a deeper understanding of the market gives you leverage in a sea of competitors. Use the steps and market research tools we shared above to build an effective market research strategy.
But keep in mind that the accuracy of your research findings depends on the quality of data collected. Turn to Sprout’s social media analytics tools to uncover heaps of high-quality data across social networks.
- Leveling Up
- Marketing Disciplines
The 43 best marketing resources we recommend in 2024
Executing a successful demand generation strategy [with examples]
How customer relationship marketing on social media drives revenue
- Other Platforms
SMS marketing 101: What is SMS Marketing (+ examples)
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
BRAND NEW Two-Day LIVE Summit with 20+ Ecommerce Trailblazers.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, the complete guide to market research: what it is, why you need it, and how to do it.

Written by Mary Kate Miller | June 1, 2021
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Market research is a cornerstone of all successful, strategic businesses. It can also be daunting for entrepreneurs looking to launch a startup or start a side hustle . What is market research, anyway? And how do you…do it?
We’ll walk you through absolutely everything you need to know about the market research process so that by the end of this guide, you’ll be an expert in market research too. And what’s more important: you’ll have actionable steps you can take to start collecting your own market research.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is the organized process of gathering information about your target customers and market. Market research can help you better understand customer behavior and competitor strengths and weaknesses, as well as provide insight for the best strategies in launching new businesses and products. There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four.
“Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research,” says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing . “Market research can help you piece together your [business’s] strengths and weaknesses, along with your prospective opportunities, so that you can understand where your unique differentiators may lie.” Well-honed market research will help your brand stand out from the competition and help you see what you need to do to lead the market. It can also do so much more.
The Purposes of Market Research
Why do market research? It can help you…
- Pinpoint your target market, create buyer personas, and develop a more holistic understanding of your customer base and market.
- Understand current market conditions to evaluate risks and anticipate how your product or service will perform.
- Validate a concept prior to launch.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors have created or overlooked.
- Solve problems that have been left unresolved by the existing product/brand offerings.
- Identify opportunities and solutions for new products or services.
- Develop killer marketing strategies .
What Are the Benefits of Market Research?
Strong market research can help your business in many ways. It can…
- Strengthen your market position.
- Help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Help you identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimize risk.
- Center your customers’ experience from the get-go.
- Help you create a dynamic strategy based on market conditions and customer needs/demands.
What Are the Basic Methods of Market Research?
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more. Throughout this guide, we will cover each of the methods commonly used in market research to give you a comprehensive overview.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own.
This approach is limited, however. It’s likely that the research objectives of these secondary data points differ from your own, and it can be difficult to confirm the veracity of their findings.
Primary Market Research
Primary research is more labor intensive, but it generally yields data that is exponentially more actionable. It can be conducted through interviews, surveys, online research, and your own data collection. Every new business should engage in primary market research prior to launch. It will help you validate that your idea has traction, and it will give you the information you need to help minimize financial risk.
You can hire an agency to conduct this research on your behalf. This brings the benefit of expertise, as you’ll likely work with a market research analyst. The downside is that hiring an agency can be expensive—too expensive for many burgeoning entrepreneurs. That brings us to the second approach. You can also do the market research yourself, which substantially reduces the financial burden of starting a new business .
Secondary Market Research
Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be beneficial to start your market research with secondary sources because it’s widely available and often free-to-access. This information will help you gain a broad overview of the market conditions for your new business.
Identify Your Goals and Your Audience
Before you begin conducting interviews or sending out surveys, you need to set your market research goals. At the end of your market research process, you want to have a clear idea of who your target market is—including demographic information like age, gender, and where they live—but you also want to start with a rough idea of who your audience might be and what you’re trying to achieve with market research.
You can pinpoint your objectives by asking yourself a series of guiding questions:
- What are you hoping to discover through your research?
- Who are you hoping to serve better because of your findings?
- What do you think your market is?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are you testing the reception of a new product category or do you want to see if your product or service solves the problem left by a current gap in the market?
- Are you just…testing the waters to get a sense of how people would react to a new brand?
Once you’ve narrowed down the “what” of your market research goals, you’re ready to move onto how you can best achieve them. Think of it like algebra. Many math problems start with “solve for x.” Once you know what you’re looking for, you can get to work trying to find it. It’s a heck of a lot easier to solve a problem when you know you’re looking for “x” than if you were to say “I’m gonna throw some numbers out there and see if I find a variable.”

How to Do Market Research
This guide outlines every component of a comprehensive market research effort. Take into consideration the goals you have established for your market research, as they will influence which of these elements you’ll want to include in your market research strategy.
Secondary Data
Secondary data allows you to utilize pre-existing data to garner a sense of market conditions and opportunities. You can rely on published market studies, white papers, and public competitive information to start your market research journey.
Secondary data, while useful, is limited and cannot substitute your own primary data. It’s best used for quantitative data that can provide background to your more specific inquiries.
Find Your Customers Online
Once you’ve identified your target market, you can use online gathering spaces and forums to gain insights and give yourself a competitive advantage. Rebecca McCusker of The Creative Content Shop recommends internet recon as a vital tool for gaining a sense of customer needs and sentiment. “Read their posts and comments on forums, YouTube video comments, Facebook group [comments], and even Amazon/Goodreads book comments to get in their heads and see what people are saying.”
If you’re interested in engaging with your target demographic online, there are some general rules you should follow. First, secure the consent of any group moderators to ensure that you are acting within the group guidelines. Failure to do so could result in your eviction from the group.
Not all comments have the same research value. “Focus on the comments and posts with the most comments and highest engagement,” says McCusker. These high-engagement posts can give you a sense of what is already connecting and gaining traction within the group.
Social media can also be a great avenue for finding interview subjects. “LinkedIn is very useful if your [target customer] has a very specific job or works in a very specific industry or sector. It’s amazing the amount of people that will be willing to help,” explains Miguel González, a marketing executive at Dealers League . “My advice here is BE BRAVE, go to LinkedIn, or even to people you know and ask them, do quick interviews and ask real people that belong to that market and segment and get your buyer persona information first hand.”
Market research interviews can provide direct feedback on your brand, product, or service and give you a better understanding of consumer pain points and interests.
When organizing your market research interviews, you want to pay special attention to the sample group you’re selecting, as it will directly impact the information you receive. According to Tanya Zhang, the co-founder of Nimble Made , you want to first determine whether you want to choose a representative sample—for example, interviewing people who match each of the buyer persona/customer profiles you’ve developed—or a random sample.
“A sampling of your usual persona styles, for example, can validate details that you’ve already established about your product, while a random sampling may [help you] discover a new way people may use your product,” Zhang says.
Market Surveys
Market surveys solicit customer inclinations regarding your potential product or service through a series of open-ended questions. This direct outreach to your target audience can provide information on your customers’ preferences, attitudes, buying potential, and more.
Every expert we asked voiced unanimous support for market surveys as a powerful tool for market research. With the advent of various survey tools with accessible pricing—or free use—it’s never been easier to assemble, disseminate, and gather market surveys. While it should also be noted that surveys shouldn’t replace customer interviews , they can be used to supplement customer interviews to give you feedback from a broader audience.
Who to Include in Market Surveys
- Current customers
- Past customers
- Your existing audience (such as social media/newsletter audiences)
Example Questions to Include in Market Surveys
While the exact questions will vary for each business, here are some common, helpful questions that you may want to consider for your market survey. Demographic Questions: the questions that help you understand, demographically, who your target customers are:
- “What is your age?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “What is your gender identity?”
- “What is your household income?”
- “What is your household size?”
- “What do you do for a living?”
- “What is your highest level of education?”
Product-Based Questions: Whether you’re seeking feedback for an existing brand or an entirely new one, these questions will help you get a sense of how people feel about your business, product, or service:
- “How well does/would our product/service meet your needs?”
- “How does our product/service compare to similar products/services that you use?”
- “How long have you been a customer?” or “What is the likelihood that you would be a customer of our brand?
Personal/Informative Questions: the deeper questions that help you understand how your audience thinks and what they care about.
- “What are your biggest challenges?”
- “What’s most important to you?”
- “What do you do for fun (hobbies, interests, activities)?”
- “Where do you seek new information when researching a new product?”
- “How do you like to make purchases?”
- “What is your preferred method for interacting with a brand?”
Survey Tools
Online survey tools make it easy to distribute surveys and collect responses. The best part is that there are many free tools available. If you’re making your own online survey, you may want to consider SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms, or Zoho Survey.
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis is a breakdown of how your business stacks up against the competition. There are many different ways to conduct this analysis. One of the most popular methods is a SWOT analysis, which stands for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.” This type of analysis is helpful because it gives you a more robust understanding of why a customer might choose a competitor over your business. Seeing how you stack up against the competition can give you the direction you need to carve out your place as a market leader.
Social Media Analysis
Social media has fundamentally changed the market research landscape, making it easier than ever to engage with a wide swath of consumers. Follow your current or potential competitors on social media to see what they’re posting and how their audience is engaging with it. Social media can also give you a lower cost opportunity for testing different messaging and brand positioning.
SEO Analysis and Opportunities
SEO analysis can help you identify the digital competition for getting the word out about your brand, product, or service. You won’t want to overlook this valuable information. Search listening tools offer a novel approach to understanding the market and generating the content strategy that will drive business. Tools like Google Trends and Awario can streamline this process.
Ready to Kick Your Business Into High Gear?
Now that you’ve completed the guide to market research you know you’re ready to put on your researcher hat to give your business the best start. Still not sure how actually… launch the thing? Our free mini-course can run you through the essentials for starting your side hustle .

About Mary Kate Miller
Mary Kate Miller writes about small business, real estate, and finance. In addition to writing for Foundr, her work has been published by The Washington Post, Teen Vogue, Bustle, and more. She lives in Chicago.
Related Posts

Create Viral Infographics That Boost Your Organic Traffic
How to Create a Video Sales Letter (Tips and Tricks from a 7-Figure Copywriter)

How to Write a Sales Email That Converts in 2024

What Is a Media Kit: How to Make One in 2024 (With Examples)

Namestorming: How to Choose a Brand Name in 20 Minutes or Less

10 Ways to Increase Brand Awareness without Increasing Your Budget

What Is a Content Creator? A Deep Dive Into This Evolving Industry

Content Creator vs Influencer: What’s the Difference?

How Much Do YouTube Ads Cost? A Beginner’s Pricing Breakdown

How to Get Podcast Sponsors Before Airing an Episode

How Founders Can Overcome Their Sales Fears with AJ Cassata

How to Grow Your YouTube Channel & Gain Subscribers Quickly

How to Write Good Instagram Captions That Hook Your Audience

Discovering the Best CRM for Consultants

10 Instagram Growth Hacks For More Engaged Followers (Without Running Ads)
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.
What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?

Table of contents
There is nothing more embarrassing for a marketer than to hear a client say “…this doesn’t quite address the business questions that we need to answer.” And unfortunately, this is a rather common occurrence in market research reporting that most marketers would care to admit.
So, why do most market research reports fail to meet client expectations? Well, in most cases, because there is more emphasis on methodology and analytic techniques used to craft the report rather than relying on data visualization, creative story-telling, and outlining actionable direction/steps.
Now, our next big question is, how do you avoid your client’s dreaded deer-in-the-headlights reaction when presenting such a report? This blog post will answer this and much more, as we go through the following:
What Is a Market Research Report?
Why is market research important, differences between primary and secondary market research, types of market research, market research reports advantages and disadvantages, how to do market research, how to prepare a market research report: 5 steps, marketing research report templates, marketing research reports best practices, bring your market research reports a step further with databox.
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. The information obtained from conducting market research is then documented in a formal report that should contain the following details:
- The characteristics of your ideal customers
- You customers buying habits
- The value your product or service can bring to those customers
- A list of your top competitors
Every business aims to provide the best possible product or service at the lowest cost possible. Simply said, market research is important because it helps you understand your customers and determine whether the product or service that you are about to launch is worth the effort.
Here is an example of a customer complaint that may result in more detailed market research:
Suppose you sell widgets, and you want your widget business to succeed over the long term. Over the years, you have developed many different ways of making widgets. But a couple of years ago, a customer complained that your widgets were made of a cheap kind of foam that fell apart after six months. You didn’t think at the time that this was a major problem, but now you know it.
The customer is someone you really want to keep. So, you decide to research this complaint. You set up a focus group of people who use widgets and ask them what they think about the specific problem. After the conducted survey you’ll get a better picture of customer opinions, so you can either decide to make the changes regarding widget design or just let it go.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
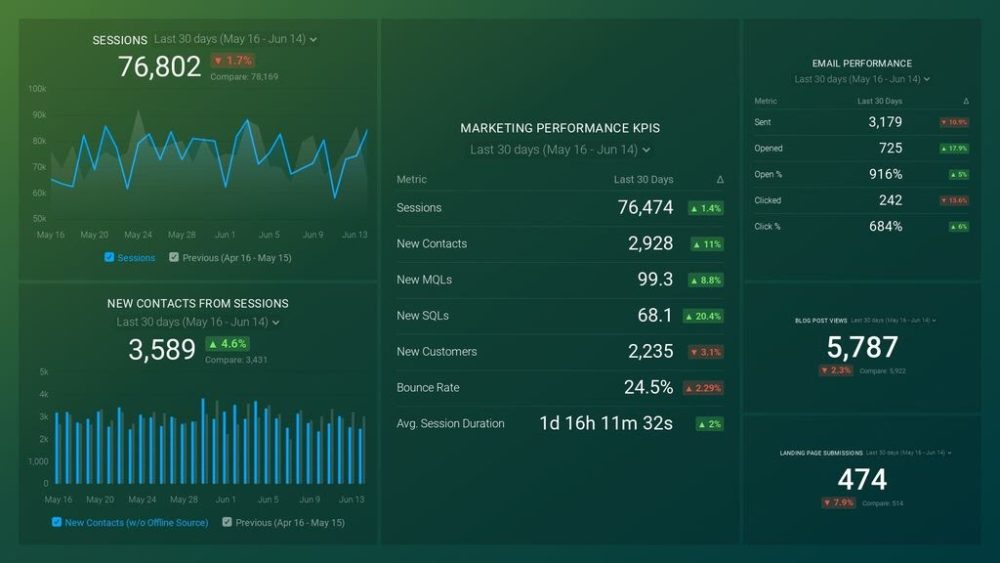
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Marketing research requires both primary and secondary market research. But what does that mean and what are the main differences?
Primary market research takes in information directly from customers, usually as participants in surveys. Usually, it is consisted of:
- Exploratory Primary Research – This type of research helps to identify possible problem areas, and it’s not focused on discovering specific information about customers. As with any research, exploratory primary research should be conducted carefully. Researchers need to craft an interviewing or surveying plan, and gather enough respondents to ensure reasonable levels of statistical reliability.
- Specific Primary Research – This type of research is one of the best ways to approach a problem because it relies on existing customer data. Specific research provides a deeper, more thorough understanding of the problem and its potential solutions. The greatest advantage of specific research is that it lets you explore a very specific question, and focus on a specific problem or an opportunity.
Secondary market research collects information from other sources such as databases, trend reports, market or government statistics, industry content, etc. We can divide secondary market research into 3 categories:
- Public market data – Public sources range from academic journals and government reports to tax returns and court documents. These sources aren’t always easy to find. Many are available only in print in libraries and archives. You have to look beyond search engines like Google to find public source documents.
- Commercial data – Those are typically created by specialized agencies like Pew, Gartner or Forrester. the research agencies are quite expensive, but they provide a lot of useful information.
- Internal data – Your organization’s databases are gold mines for market research. In the best cases, your salespeople can tell you what they think about customers. Your salespeople are your direct sources of information about the market. Don’t underestimate your internal data.
In general, primary research is more reliable than secondary research, because researchers have to interview people directly. But primary research is expensive and time-consuming. Secondary research can be quicker and less expensive.
There are plenty of ways to conduct marketing research reports. Mostly, the type of research done will depend on your goals. Here are some types of market research often conducted by marketers.
Focus Groups
Product/service use research, observation-based research, buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research, competitive analysis research, customer satisfaction and loyalty research, brand awareness research, campaign research.
An interview is an interactive process of asking and answering questions and observing your respondent’s responses. Interviews are one of the most commonly used tools in market research . An interview allows an organization to observe, in detail, how its consumers interact with its products and services. It also allows an organization to address specific questions.
A focus group is a group of people who get together to discuss a particular topic. A moderator leads the discussion and takes notes. The main benefit of focus groups is that they are quick and easy to conduct. You can gather a group of carefully-selected people, give them a product to try out, and get their feedback within a few hours/days.
Product or service use research helps you obtain useful information about your product or service such as:
- What your current customers do with the product/service
- Which features of the product/service are particularly important to your customers
- What they dislike about the product/service
- What they would change about the product/service
Observation-based research helps you to observe your target audience interacting with your product or service. You will see the interactions and which aspects work well and which could be improved. The main point is to directly experience the feedback from your target audience’s point of view.
Personas are an essential sales tool. By knowing your buyers’ pain points and the challenges they face, you can create better content, target messaging, and campaigns for them. Buyer persona research is based on market research, and it’s built around data that describes your customers’ demographics, behaviors, motivations, and concerns. Sales reporting software can significantly help you develop buyer personas when you gain insights after you collected all information.
Market segmentation research is carried out to better understand existing and potential market segments. The objective is to determine how to target different market segments and how they differ from each other. The three most important steps in writing a market segmentation research report are:
- Defining the problem
- Determining the solution [and]
- Defining the market
Related : 9 Customer Segmentation Tips to Personalize Ecommerce Marketing and Drive More Sales
A price that is too high, or too low, can kill a business. And without good market research, you don’t really know what is a good price for your product. Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy.
In a competitive analysis, you define your “competition” as any other entity that competes with you in your market, whether you’re selling a widget or a piece of real estate. With competitive analysis research, you can find out things like:
- Who your competitors are
- What they’ve done in the past
- What’s working well for them
- Their weaknesses
- How they’re positioned in the market
- How they market themselves
- What they’re doing that you’re not
Related : How to Do an SEO Competitive Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
In today’s marketplace, companies are increasingly focused on customer loyalty. What your customers want is your product, but, more importantly, they want it delivered with a service that exceeds their expectations. Successful companies listen to their customers and respond accordingly. That’s why customer satisfaction and loyalty research is a critical component of that basic equation.
Related : 11 Tactics for Effectively Measuring Your Customer Service ROI
Who you are, what you stand for, what you offer, what you believe in, and what your audience thinks of you is all wrapped up in brand. Brand awareness research tells what your target audience knows about your brand and what’s their experience like.
A campaign research report is a detailed account of how your marketing campaign performed. It includes all the elements that went into creating the campaign: planning, implementation, and measurement.
Here are some of the top advantages and disadvantages of doing market research and crafting market research reports.
- Identify business opportunities – A market research report can be used to analyze potential markets and new products. It can give information about customer needs, preferences, and attitudes. Also, it compare products and services.
- A clear understanding of your customers – A market report gives company’s marketing department an in-depth picture about customers’ needs and wants. This knowledge can be used to improve products, prices, and advertising.
- Mitigates risks – 30% of small businesses fail within the first two years. Why is this so? The answer is that entrepreneurs are risk takers. However, there are risks that could be avoided. A good marketing research will help you identify those risks and allow you to mitigate them.
- Clear data-driven insights – Market research encompasses a wide range of activities, from determining market size and segment to forecasting demand, and from identifying competitors to monitoring pricing. All of these are quantified and measurable which means that gives you a clear path for building unique decisions based on numbers.
Disadvantages
- It’s not cheap – Although market research can be done for as little as $500, large markets like the United States can run into millions of dollars. If a research is done for a specific product, the budget may be even much higher. The budget also depends on the quality of the research. The more expensive it is, the more time the research will take.
- Some insights could be false – For example, if you are conducting a survey, data may be inadequate or inaccurate because respondents can, well, simply be dishonest and lie.
Here are the essential steps you need to take when doing market research:
Define your buyer persona
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors, summarize your findings.
The job of a marketing persona is to describe your ideal customer and to tell you what they want, what motivates them, what frustrates them, and what limits them. Finding out these things means you have a better chance of designing your products, services, marketing messages, and brand around real customers. There is no one right way to create a buyer persona, though.
For example, if you’re in an industry focused on education, you could include things like:
- Educational level
- Education background
It’s recommended that you create 3-5 buyer personas for your products, based on your ideal customer.
This should be a representative sample of your target customers so you can better understand their behavior. You want to find people who fit both your target personas and who represent the broader demographic of your market. People who recently made a purchase or purposefully decided not to make one are a good sample to start with.
The questions you use determine the quality of your results. Of course, the quality of your results also depends on the quality of your participants.
Don’t ask questions that imply a yes or no answer. Instead, use open questions. For example, if you are researching customers about yogurt products, you could ask them: „ What have you heard about yogurt ?” or “ What do you think of yogurt ?“.
Avoid questions that use numbers, such as “ How many times a week do you eat yogurt ?”
Avoid questions that suggest a set of mutually exclusive answers, such as “ Do you like yogurt for breakfast, lunch, or dinner ?”
Avoid questions that imply a scale, such as “ Do you like chocolate-flavored yogurt ?”
Market researchers sometimes call one company the top competitor, another middle competitor, and the third one small competitor. However you classify them, you want to identify at least three companies in each category. Now, for each business on your list, list its key characteristics. For example, if your business sells running shoes, a key characteristic might be the product’s quality.
Next, make a list of your small business’s competitive advantages. These include the unique qualities or features of your business that make it the best choice of customers for the products or services it offers. Make a list of these competitive advantages and list them next to the key characteristics you listed for your business.
You have just finished writing your marketing research report. Everything is out there quantified or qualified. You just have to sum it up and focus on the most important details that are going to make a big impact on your decisions. Clear summary leads to a winning strategy!
Related : How to Prepare a Complete Marketing Report: The KPIs, Analysis, & Action Plan You Need
Here’s how to prepare a market research report in 5 simple steps:
Step 1: Cluster the data
Step 2: prepare an outline, step 3: mention the research methods, step 4: include visuals with narrative explanations, step 5: conclude the report with recommendations.
Your first step is to cluster all the available information into a manageable set. Clustering is the process of grouping information together in a way that emphasizes commonalities and minimizes differences. So, in market research, this will help to organize all the information you have about a product, service, or target market and identify your focus areas.
A marketing research report should be written so that other people can understand it:
- Include background information at the beginning to explain who your audience is and what problem you are trying to solve for them.
- In the body of the report, include a description of the methodology – Explain to the reader how your research was done, what was involved, and why you selected the methodology you used.
- Also in the body of the report, include the results of your market research. These may be quantitative or qualitative, but either way they should answer the questions you posed at the beginning.
- Include the executive summary – A summary of the entire report.
The market research methodology section includes details on the type of research, sample size, any limitations of the studies, research design, sample selection, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses used.
Visuals are an essential part of the presentation. Even the best-written text can be difficult to understand. Charts and graphs are easier to understand than text alone, and they help the reader see how the numbers fit the bigger picture.
But visuals are not the whole story. They are only one part of the presentation. Visuals are a cue for the reader. The narrative gives the story, not just the numbers.
Recommendations tend to follow logically from conclusions and are a response to a certain problem. The recommendation should always be relevant to the research rationale, that is, the recommendation should be based on the results of the research reported in the body of the report.
Now, let’s take a look at some dashboard reporting templates you could use to enhance your market research:
- Semrush (Position Tracking) Report
Brand Awareness Report
Sales pipeline performance report, customer success overview report, stripe (mrr & churn) report, semrush (position tracking) report template.
This free SEMRush dashboard template will help you monitor how your website’s search visibility on search engines evolves on a monthly basis. This dashboard contains all of the information you need to make changes and improve the ranking results of your business in Google Search.
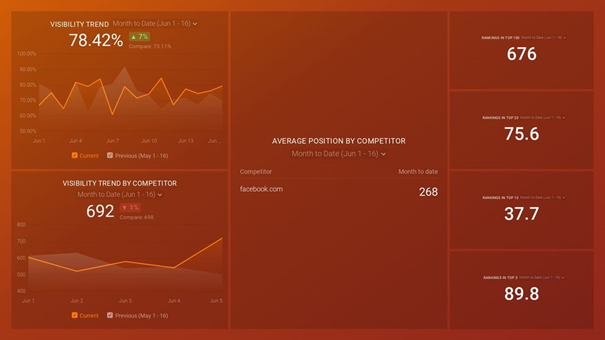
This Brand Awareness Report will help you to get a sense of your brand awareness performance in Google Analytics, Google Organic Search, and Facebook. Use this dashboard to track brand awareness the same way you track other marketing campaigns.
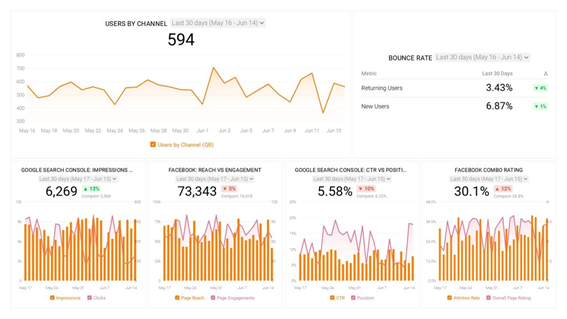
Are your sales and marketing funnel healthy and growing? How is your sales and marketing funnel performing? What are the key conversion rates between your lifecycle stages? With a pipeline performance dashboard , you’ll get all of the answers quickly.
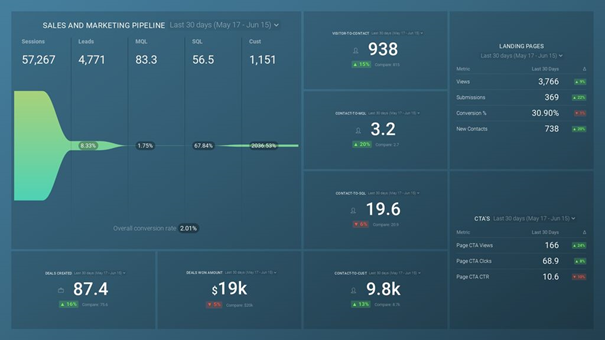
This Customer Success Overview Dashboard allows you to analyze how your customer service team’s responsiveness impacts your business. Use this dashboard to assess the correlation between your customer service performance and churn rate.
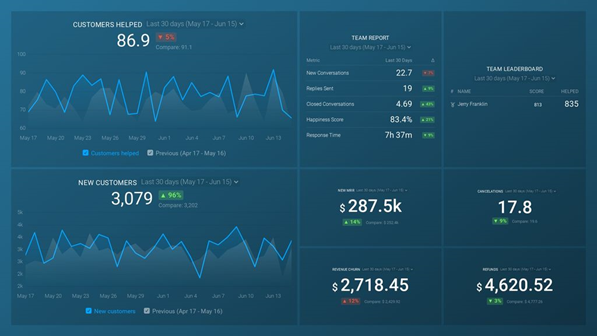
This Stripe dashboard tracks your churn rate and MRR growth in real-time and shows you which customers (and how many of them) you have at any given point in time. All you have to do to get started is to connect your Stripe account.
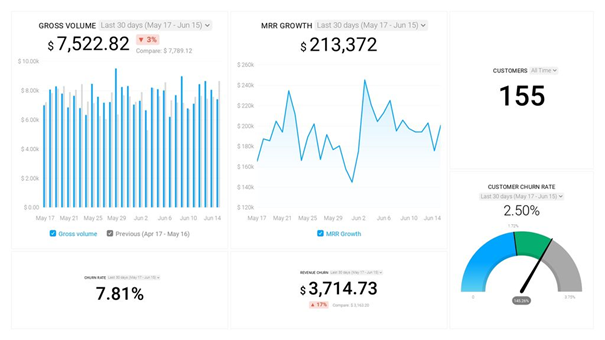
As we said earlier, there are no strict rules when it comes to writing marketing research reports. On the other hand, you must find your focus if you want to write a report that will make a difference. Here are some best practices you should keep in mind when writing a research report.
- Objectives – The objective of a market research report is to define the problems, identify key issues, and suggest recommendations for further research. If you answer them successfully, you’re on the right way.
- Don’t worry about the format – Be creative. The report could be in a form of a PowerPoint presentation, Excel sheet, interactive dashboard or even a video. Use the format that best fits your audience, but make sure to make it easy to read.
- Include an executive summary, scorecard , or a dashboard – This is really important because time is money, and most people don’t have time to waste. So, how to put everything important in a short role? Address all of the objectives and put them in a graphic dashboard or scorecard. Also, you can write an executive summary template (heart of the report) that can be easily updated and read by managers or CEOs.
- Use storytelling – A good story always makes a great point because it’s so memorable. Your research report results can double the effect with a catchy story.
- Keep it short – It’s not a secret that we are reading so little in the digital era. Use a lot of white space and bullet points. Too much text on a page means less focus for the reader.
- Be organized – Maintain the order of information. It’s important for the reader to navigate through the report easily. If they want to find some details or specific information it would be great to divide all sections with appropriate references.
- Methodological information – Methodological details could be boring. Include only the most important details that the reader needs to know to understand the big picture.
- Use images (or other visualizations) whenever you can – A good picture speaks for 1.000 words! If you can communicate the point visually, don’t hesitate to do it. It would be a lot easier for those who don’t like a lot of text to understand your results. But don’t push them where you can’t.
- Create readable graphs – The crown of marketing research reports is a comprehensive graph. Make sure to design precise and attractive graphs that will power up and round your story.
- Use the Appendix – You can include all secondary information such as methodological details and other miscellaneous data in the Appendix at the end of the report.
Market research reports are all about presenting your data in an easy-to-understand way and making calculated decisions about business ideas. But this is something easier said than done.
When busy stakeholders and executives grab a report, they need something that will give them an idea of the results – the big picture that addresses company wide-business goals.
Can a PowerPoint presentation or a PDF report meet those expectations? Most likely not. But a dashboard can.
Keep in mind that even with the best market analysis in the world, your market research report won’t be actionable if you don’t present the data efficiently and in a way that everyone understands what the next steps are. Databox is your key ally in the matter.
Databox dashboards are designed to help you present your market research data with clarity – from identifying what is influencing your business, and understanding where your brand is situated in the market, to gauging the temperature of your niche or industry before a new product/service launch.
Present your research results with efficient, interactive dashboards now by signing up for a free trial .
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Playmaker Spotlight: Tory Ferrall, Director of Revenue Operations March 27, 2024
- New in Databox: Safeguard Your Data With Advanced Security Settings March 18, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Learn / Blog / Article
Back to blog
How to do market research in 4 steps: a lean approach to marketing research
From pinpointing your target audience and assessing your competitive advantage, to ongoing product development and customer satisfaction efforts, market research is a practice your business can only benefit from.
Learn how to conduct quick and effective market research using a lean approach in this article full of strategies and practical examples.

Last updated
Reading time.
A comprehensive (and successful) business strategy is not complete without some form of market research—you can’t make informed and profitable business decisions without truly understanding your customer base and the current market trends that drive your business.
In this article, you’ll learn how to conduct quick, effective market research using an approach called 'lean market research'. It’s easier than you might think, and it can be done at any stage in a product’s lifecycle.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps
What is market research, why is market research so valuable, advantages of lean market research, 4 common market research methods, 5 common market research questions, market research faqs.
We’ll jump right into our 4-step approach to lean market research. To show you how it’s done in the real world, each step includes a practical example from Smallpdf , a Swiss company that used lean market research to reduce their tool’s error rate by 75% and boost their Net Promoter Score® (NPS) by 1%.
Research your market the lean way...
From on-page surveys to user interviews, Hotjar has the tools to help you scope out your market and get to know your customers—without breaking the bank.
The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours.
1. Create simple user personas
A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data from people who use websites and products similar to your own. Start by defining broad user categories, then elaborate on them later to further segment your customer base and determine your ideal customer profile .
How to get the data: use on-page or emailed surveys and interviews to understand your users and what drives them to your business.
How to do it right: whatever survey or interview questions you ask, they should answer the following questions about the customer:
Who are they?
What is their main goal?
What is their main barrier to achieving this goal?
Pitfalls to avoid:
Don’t ask too many questions! Keep it to five or less, otherwise you’ll inundate them and they’ll stop answering thoughtfully.
Don’t worry too much about typical demographic questions like age or background. Instead, focus on the role these people play (as it relates to your product) and their goals.
How Smallpdf did it: Smallpdf ran an on-page survey for a couple of weeks and received 1,000 replies. They learned that many of their users were administrative assistants, students, and teachers.
Next, they used the survey results to create simple user personas like this one for admins:
Who are they? Administrative Assistants.
What is their main goal? Creating Word documents from a scanned, hard-copy document or a PDF where the source file was lost.
What is their main barrier to achieving it? Converting a scanned PDF doc to a Word file.
💡Pro tip: Smallpdf used Hotjar Surveys to run their user persona survey. Our survey tool helped them avoid the pitfalls of guesswork and find out who their users really are, in their own words.
You can design a survey and start running it in minutes with our easy-to-use drag and drop builder. Customize your survey to fit your needs, from a sleek one-question pop-up survey to a fully branded questionnaire sent via email.
We've also created 40+ free survey templates that you can start collecting data with, including a user persona survey like the one Smallpdf used.
2. Conduct observational research
Observational research involves taking notes while watching someone use your product (or a similar product).
Overt vs. covert observation
Overt observation involves asking customers if they’ll let you watch them use your product. This method is often used for user testing and it provides a great opportunity for collecting live product or customer feedback .
Covert observation means studying users ‘in the wild’ without them knowing. This method works well if you sell a type of product that people use regularly, and it offers the purest observational data because people often behave differently when they know they’re being watched.
Tips to do it right:
Record an entry in your field notes, along with a timestamp, each time an action or event occurs.
Make note of the users' workflow, capturing the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘for whom’ of each action.

Don’t record identifiable video or audio data without consent. If recording people using your product is helpful for achieving your research goal, make sure all participants are informed and agree to the terms.
Don’t forget to explain why you’d like to observe them (for overt observation). People are more likely to cooperate if you tell them you want to improve the product.
💡Pro tip: while conducting field research out in the wild can wield rewarding results, you can also conduct observational research remotely. Hotjar Recordings is a tool that lets you capture anonymized user sessions of real people interacting with your website.
Observe how customers navigate your pages and products to gain an inside look into their user behavior . This method is great for conducting exploratory research with the purpose of identifying more specific issues to investigate further, like pain points along the customer journey and opportunities for optimizing conversion .
With Hotjar Recordings you can observe real people using your site without capturing their sensitive information
How Smallpdf did it: here’s how Smallpdf observed two different user personas both covertly and overtly.
Observing students (covert): Kristina Wagner, Principle Product Manager at Smallpdf, went to cafes and libraries at two local universities and waited until she saw students doing PDF-related activities. Then she watched and took notes from a distance. One thing that struck her was the difference between how students self-reported their activities vs. how they behaved (i.e, the self-reporting bias). Students, she found, spent hours talking, listening to music, or simply staring at a blank screen rather than working. When she did find students who were working, she recorded the task they were performing and the software they were using (if she recognized it).
Observing administrative assistants (overt): Kristina sent emails to admins explaining that she’d like to observe them at work, and she asked those who agreed to try to batch their PDF work for her observation day. While watching admins work, she learned that they frequently needed to scan documents into PDF-format and then convert those PDFs into Word docs. By observing the challenges admins faced, Smallpdf knew which products to target for improvement.
“Data is really good for discovery and validation, but there is a bit in the middle where you have to go and find the human.”
3. Conduct individual interviews
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. They allow you to dig deep and explore their concerns, which can lead to all sorts of revelations.
Listen more, talk less. Be curious.
Act like a journalist, not a salesperson. Rather than trying to talk your company up, ask people about their lives, their needs, their frustrations, and how a product like yours could help.
Ask "why?" so you can dig deeper. Get into the specifics and learn about their past behavior.
Record the conversation. Focus on the conversation and avoid relying solely on notes by recording the interview. There are plenty of services that will transcribe recorded conversations for a good price (including Hotjar!).
Avoid asking leading questions , which reveal bias on your part and pushes respondents to answer in a certain direction (e.g. “Have you taken advantage of the amazing new features we just released?).
Don't ask loaded questions , which sneak in an assumption which, if untrue, would make it impossible to answer honestly. For example, we can’t ask you, “What did you find most useful about this article?” without asking whether you found the article useful in the first place.
Be cautious when asking opinions about the future (or predictions of future behavior). Studies suggest that people aren’t very good at predicting their future behavior. This is due to several cognitive biases, from the misguided exceptionalism bias (we’re good at guessing what others will do, but we somehow think we’re different), to the optimism bias (which makes us see things with rose-colored glasses), to the ‘illusion of control’ (which makes us forget the role of randomness in future events).
How Smallpdf did it: Kristina explored her teacher user persona by speaking with university professors at a local graduate school. She learned that the school was mostly paperless and rarely used PDFs, so for the sake of time, she moved on to the admins.
A bit of a letdown? Sure. But this story highlights an important lesson: sometimes you follow a lead and come up short, so you have to make adjustments on the fly. Lean market research is about getting solid, actionable insights quickly so you can tweak things and see what works.
💡Pro tip: to save even more time, conduct remote interviews using an online user research service like Hotjar Engage , which automates the entire interview process, from recruitment and scheduling to hosting and recording.
You can interview your own customers or connect with people from our diverse pool of 200,000+ participants from 130+ countries and 25 industries. And no need to fret about taking meticulous notes—Engage will automatically transcribe the interview for you.
4. Analyze the data (without drowning in it)
The following techniques will help you wrap your head around the market data you collect without losing yourself in it. Remember, the point of lean market research is to find quick, actionable insights.
A flow model is a diagram that tracks the flow of information within a system. By creating a simple visual representation of how users interact with your product and each other, you can better assess their needs.
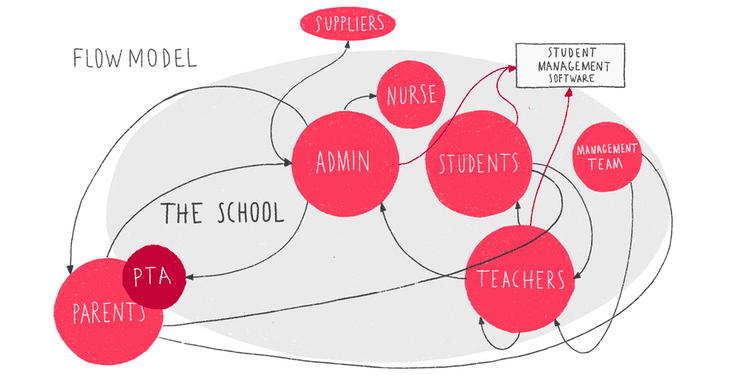
You’ll notice that admins are at the center of Smallpdf’s flow model, which represents the flow of PDF-related documents throughout a school. This flow model shows the challenges that admins face as they work to satisfy their own internal and external customers.
Affinity diagram
An affinity diagram is a way of sorting large amounts of data into groups to better understand the big picture. For example, if you ask your users about their profession, you’ll notice some general themes start to form, even though the individual responses differ. Depending on your needs, you could group them by profession, or more generally by industry.
We wrote a guide about how to analyze open-ended questions to help you sort through and categorize large volumes of response data. You can also do this by hand by clipping up survey responses or interview notes and grouping them (which is what Kristina does).
“For an interview, you will have somewhere between 30 and 60 notes, and those notes are usually direct phrases. And when you literally cut them up into separate pieces of paper and group them, they should make sense by themselves.”
Pro tip: if you’re conducting an online survey with Hotjar, keep your team in the loop by sharing survey responses automatically via our Slack and Microsoft Team integrations. Reading answers as they come in lets you digest the data in pieces and can help prepare you for identifying common themes when it comes time for analysis.
Hotjar lets you easily share survey responses with your team
Customer journey map
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the way a typical prospect becomes a paying customer. It outlines their first interaction with your brand and every step in the sales cycle, from awareness to repurchase (and hopefully advocacy).
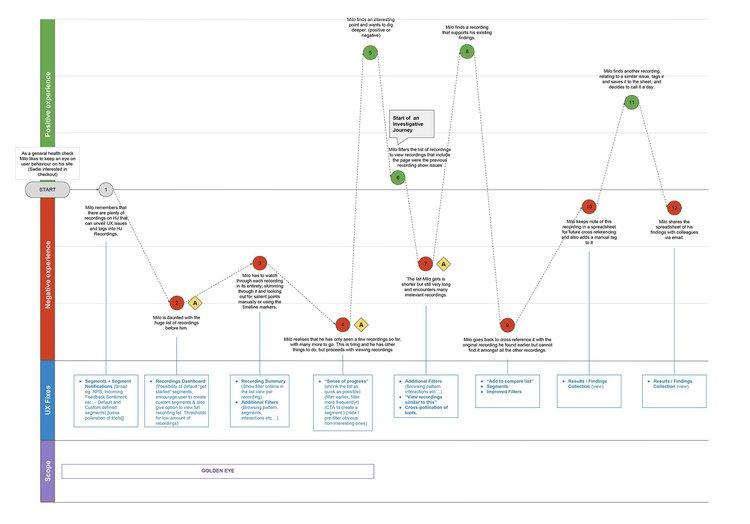
The above customer journey map , created by our team at Hotjar, shows many ways a customer might engage with our tool. Your map will be based on your own data and business model.
📚 Read more: if you’re new to customer journey maps, we wrote this step-by-step guide to creating your first customer journey map in 2 and 1/2 days with free templates you can download and start using immediately.
Next steps: from research to results
So, how do you turn market research insights into tangible business results? Let’s look at the actions Smallpdf took after conducting their lean market research: first they implemented changes, then measured the impact.

Implement changes
Based on what Smallpdf learned about the challenges that one key user segment (admins) face when trying to convert PDFs into Word files, they improved their ‘PDF to Word’ conversion tool.
We won’t go into the details here because it involves a lot of technical jargon, but they made the entire process simpler and more straightforward for users. Plus, they made it so that their system recognized when you drop a PDF file into their ‘Word to PDF’ converter instead of the ‘PDF to Word’ converter, so users wouldn’t have to redo the task when they made that mistake.
In other words: simple market segmentation for admins showed a business need that had to be accounted for, and customers are happier overall after Smallpdf implemented an informed change to their product.
Measure results
According to the Lean UX model, product and UX changes aren’t retained unless they achieve results.
Smallpdf’s changes produced:
A 75% reduction in error rate for the ‘PDF to Word’ converter
A 1% increase in NPS
Greater confidence in the team’s marketing efforts
"With all the changes said and done, we've cut our original error rate in four, which is huge. We increased our NPS by +1%, which isn't huge, but it means that of the users who received a file, they were still slightly happier than before, even if they didn't notice that anything special happened at all.”
Subscribe to fresh and free monthly insights.
Over 50,000 people interested in UX, product, digital empathy, and beyond, receive our newsletter every month. No spam, just thoughtful perspectives from a range of experts, new approaches to remote work, and loads more valuable insights. If that floats your boat, why not become a subscriber?
I have read and accepted the message outlined here: Hotjar uses the information you provide to us to send you relevant content, updates and offers from time to time. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any email.
Market research (or marketing research) is any set of techniques used to gather information and better understand a company’s target market. This might include primary research on brand awareness and customer satisfaction or secondary market research on market size and competitive analysis. Businesses use this information to design better products, improve user experience, and craft a marketing strategy that attracts quality leads and improves conversion rates.
David Darmanin, one of Hotjar’s founders, launched two startups before Hotjar took off—but both companies crashed and burned. Each time, he and his team spent months trying to design an amazing new product and user experience, but they failed because they didn’t have a clear understanding of what the market demanded.
With Hotjar, they did things differently . Long story short, they conducted market research in the early stages to figure out what consumers really wanted, and the team made (and continues to make) constant improvements based on market and user research.
Without market research, it’s impossible to understand your users. Sure, you might have a general idea of who they are and what they need, but you have to dig deep if you want to win their loyalty.
Here’s why research matters:
Obsessing over your users is the only way to win. If you don’t care deeply about them, you’ll lose potential customers to someone who does.
Analytics gives you the ‘what’, while research gives you the ‘why’. Big data, user analytics , and dashboards can tell you what people do at scale, but only research can tell you what they’re thinking and why they do what they do. For example, analytics can tell you that customers leave when they reach your pricing page, but only research can explain why.
Research beats assumptions, trends, and so-called best practices. Have you ever watched your colleagues rally behind a terrible decision? Bad ideas are often the result of guesswork, emotional reasoning, death by best practices , and defaulting to the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion (HiPPO). By listening to your users and focusing on their customer experience , you’re less likely to get pulled in the wrong direction.
Research keeps you from planning in a vacuum. Your team might be amazing, but you and your colleagues simply can’t experience your product the way your customers do. Customers might use your product in a way that surprises you, and product features that seem obvious to you might confuse them. Over-planning and refusing to test your assumptions is a waste of time, money, and effort because you’ll likely need to make changes once your untested business plan gets put into practice.
Lean User Experience (UX) design is a model for continuous improvement that relies on quick, efficient research to understand customer needs and test new product features.
Lean market research can help you become more...
Efficient: it gets you closer to your customers, faster.
Cost-effective: no need to hire an expensive marketing firm to get things started.
Competitive: quick, powerful insights can place your products on the cutting edge.
As a small business or sole proprietor, conducting lean market research is an attractive option when investing in a full-blown research project might seem out of scope or budget.
There are lots of different ways you could conduct market research and collect customer data, but you don’t have to limit yourself to just one research method. Four common types of market research techniques include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and customer observation.
Which method you use may vary based on your business type: ecommerce business owners have different goals from SaaS businesses, so it’s typically prudent to mix and match these methods based on your particular goals and what you need to know.
1. Surveys: the most commonly used
Surveys are a form of qualitative research that ask respondents a short series of open- or closed-ended questions, which can be delivered as an on-screen questionnaire or via email. When we asked 2,000 Customer Experience (CX) professionals about their company’s approach to research , surveys proved to be the most commonly used market research technique.
What makes online surveys so popular?
They’re easy and inexpensive to conduct, and you can do a lot of data collection quickly. Plus, the data is pretty straightforward to analyze, even when you have to analyze open-ended questions whose answers might initially appear difficult to categorize.
We've built a number of survey templates ready and waiting for you. Grab a template and share with your customers in just a few clicks.
💡 Pro tip: you can also get started with Hotjar AI for Surveys to create a survey in mere seconds . Just enter your market research goal and watch as the AI generates a survey and populates it with relevant questions.
Once you’re ready for data analysis, the AI will prepare an automated research report that succinctly summarizes key findings, quotes, and suggested next steps.
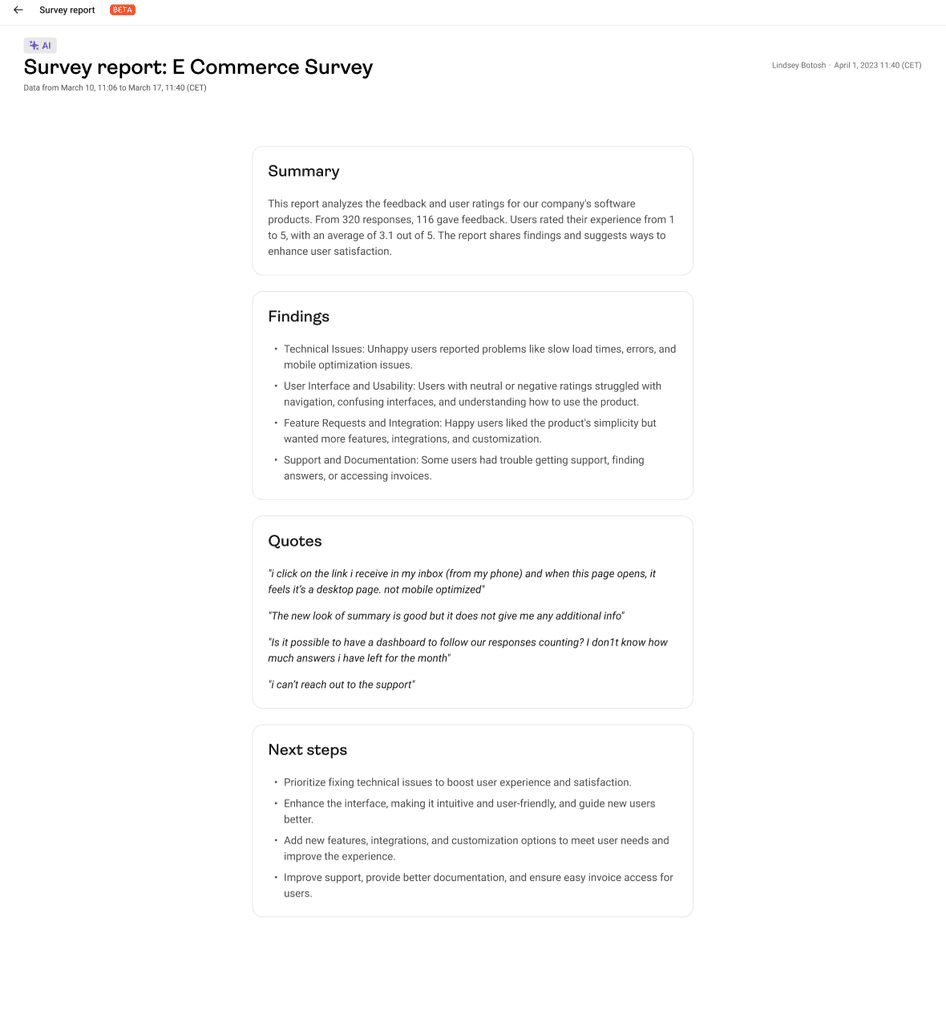
An example research report generated by Hotjar AI for Surveys
2. Interviews: the most insightful
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. Nothing beats a face-to-face interview for diving deep (and reading non-verbal cues), but if an in-person meeting isn’t possible, video conferencing is a solid second choice.
Regardless of how you conduct it, any type of in-depth interview will produce big benefits in understanding your target customers.
What makes interviews so insightful?
By speaking directly with an ideal customer, you’ll gain greater empathy for their experience , and you can follow insightful threads that can produce plenty of 'Aha!' moments.
3. Focus groups: the most unreliable
Focus groups bring together a carefully selected group of people who fit a company’s target market. A trained moderator leads a conversation surrounding the product, user experience, or marketing message to gain deeper insights.
What makes focus groups so unreliable?
If you’re new to market research, we wouldn’t recommend starting with focus groups. Doing it right is expensive , and if you cut corners, your research could fall victim to all kinds of errors. Dominance bias (when a forceful participant influences the group) and moderator style bias (when different moderator personalities bring about different results in the same study) are two of the many ways your focus group data could get skewed.
4. Observation: the most powerful
During a customer observation session, someone from the company takes notes while they watch an ideal user engage with their product (or a similar product from a competitor).
What makes observation so clever and powerful?
‘Fly-on-the-wall’ observation is a great alternative to focus groups. It’s not only less expensive, but you’ll see people interact with your product in a natural setting without influencing each other. The only downside is that you can’t get inside their heads, so observation still isn't a recommended replacement for customer surveys and interviews.
The following questions will help you get to know your users on a deeper level when you interview them. They’re general questions, of course, so don’t be afraid to make them your own.
1. Who are you and what do you do?
How you ask this question, and what you want to know, will vary depending on your business model (e.g. business-to-business marketing is usually more focused on someone’s profession than business-to-consumer marketing).
It’s a great question to start with, and it’ll help you understand what’s relevant about your user demographics (age, race, gender, profession, education, etc.), but it’s not the be-all-end-all of market research. The more specific questions come later.
2. What does your day look like?
This question helps you understand your users’ day-to-day life and the challenges they face. It will help you gain empathy for them, and you may stumble across something relevant to their buying habits.
3. Do you ever purchase [product/service type]?
This is a ‘yes or no’ question. A ‘yes’ will lead you to the next question.
4. What problem were you trying to solve or what goal were you trying to achieve?
This question strikes to the core of what someone’s trying to accomplish and why they might be willing to pay for your solution.
5. Take me back to the day when you first decided you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this goal.
This is the golden question, and it comes from Adele Revella, Founder and CEO of Buyer Persona Institute . It helps you get in the heads of your users and figure out what they were thinking the day they decided to spend money to solve a problem.
If you take your time with this question, digging deeper where it makes sense, you should be able to answer all the relevant information you need to understand their perspective.
“The only scripted question I want you to ask them is this one: take me back to the day when you first decided that you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this kind of a goal. Not to buy my product, that’s not the day. We want to go back to the day that when you thought it was urgent and compelling to go spend money to solve a particular problem or achieve a goal. Just tell me what happened.”
— Adele Revella , Founder/CEO at Buyer Persona Institute
Bonus question: is there anything else you’d like to tell me?
This question isn’t just a nice way to wrap it up—it might just give participants the opportunity they need to tell you something you really need to know.
That’s why Sarah Doody, author of UX Notebook , adds it to the end of her written surveys.
“I always have a last question, which is just open-ended: “Is there anything else you would like to tell me?” And sometimes, that’s where you get four paragraphs of amazing content that you would never have gotten if it was just a Net Promoter Score [survey] or something like that.”
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research asks questions that can’t be reduced to a number, such as, “What is your job title?” or “What did you like most about your customer service experience?”
Quantitative research asks questions that can be answered with a numeric value, such as, “What is your annual salary?” or “How was your customer service experience on a scale of 1-5?”
→ Read more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative user research .
How do I do my own market research?
You can do your own quick and effective market research by
Surveying your customers
Building user personas
Studying your users through interviews and observation
Wrapping your head around your data with tools like flow models, affinity diagrams, and customer journey maps
What is the difference between market research and user research?
Market research takes a broad look at potential customers—what problems they’re trying to solve, their buying experience, and overall demand. User research, on the other hand, is more narrowly focused on the use (and usability ) of specific products.
What are the main criticisms of market research?
Many marketing professionals are critical of market research because it can be expensive and time-consuming. It’s often easier to convince your CEO or CMO to let you do lean market research rather than something more extensive because you can do it yourself. It also gives you quick answers so you can stay ahead of the competition.
Do I need a market research firm to get reliable data?
Absolutely not! In fact, we recommend that you start small and do it yourself in the beginning. By following a lean market research strategy, you can uncover some solid insights about your clients. Then you can make changes, test them out, and see whether the results are positive. This is an excellent strategy for making quick changes and remaining competitive.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Related articles

6 traits of top marketing leaders (and how to cultivate them in yourself)
Stepping into a marketing leadership role can stir up a mix of emotions: excitement, optimism, and, often, a gnawing doubt. "Do I have the right skills to truly lead and inspire?" If you've ever wrestled with these uncertainties, you're not alone.
Hotjar team

The 7 best BI tools for marketers in 2024 (and how to use them)
Whether you're sifting through campaign attribution data or reviewing performance reports from different sources, extracting meaningful business insights from vast amounts of data is an often daunting—yet critical—task many marketers face. So how do you efficiently evaluate your results and communicate key learnings?
This is where business intelligence (BI) tools come in, transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive informed, customer-centric decisions.

6 marketing trends that will shape the future of ecommerce in 2023
Today, marketing trends evolve at the speed of technology. Ecommerce businesses that fail to update their marketing strategies to meet consumers where they are in 2023 will be left out of the conversations that drive brand success.

Geoff Whiting
Search the site:
- WordPress Retainers
- Enterprise Development
- Maintenance & Support
How to Conduct Market Research: A Step-By-Step Guide
Figuring out how to do market research for the first time can be intimidating and confusing. There are so many categories and different methods to choose from. It often seems like an endless list of organizational tasks and preparations.
However cumbersome as it might seem, research has an irreplaceable value for every company, be it a startup or a big corporation. It’s an instrument that leaders must use to keep themselves informed and up-to-date with market changes and make smart choices.
By observing your customers, you gain valuable insights into their personalities, motivations, challenges, and consumer behavior.
Furthermore, the data you gather gives you a glimpse of the processes that control the marketplace. You can gain a strategic edge over seemingly random or meaningless situations by learning more about them.
To sum up, doing your research helps you make better data-based business choices. This leads to better products, satisfied customers, and crushed competition. Sounds good, right?
If you follow through with your research with precision and discipline, you will soon be able to scale your company’s success rate significantly.
Before you read this guide and start your efforts, we advise you to brush up on the basics first and go through our other articles on market research:
- Market Research 101: From Beginner to Advanced
- Conducting Market Research: 6 Methods to Explore
- 15 Essential Market Research Tips for Businesses
Digging deeper into the process will give you the necessary background and confidence to go forth without any concerns.
So, without further ado, let’s roll our sleeves and get started on how to conduct market research. Read on and take notes!
1. Define the Research Goal
The first step of the process is defining your goal. It is important to start with a clear idea of why you are doing the research and what you want to accomplish. If your motivation is vague, you risk straying from your objectives and becoming distracted by irrelevant information.
During your study, you may find other important topics that are not closely related to the problem you are addressing. You should record them and save them for later research in different projects.
Mixing questions regarding too many problems in one survey can confuse the respondents and affect the accuracy of their answers. It can also make the research results too inconsistent. And it’s hard to conclude a bunch of random facts.
By stating the purpose and the problems of your research, you can establish a clear goal guiding everyone throughout the process.
This way, you’ll concentrate your efforts, and, in the end, you’ll be able to make informed decisions based on data.
For example, if you are choosing the pricing model for a new SaaS product, you should perform market research to make sure you’ll pick out the best one for your business. In this case, it should be something like “ Find out the best pricing strategy for the product ”. Some of the objectives can be:
- Identify the target audience.
- Find out what products they are currently using.
- Learn how much they are paying for them.
- Understand how much they are willing to pay.
- Research how they are using similar products.
- Discover what features they’d pay more for.
- Compare your product to the competition, etc.
Ultimately, your goal should be what you want to see accomplished in the future. That’s why it’s best to focus on your plans and targets, rather than on your current problems. Otherwise, you risk being stuck with unsolvable issues rather than with creative solutions.
2. Create Client Personas
When doing market research, you need a group of people who’ll answer your questions and whose opinions are important to your business. To identify these people, you should first create profiles that fit your target audience.
Client personas, or buyer personas , are collective profiles representing your ideal customers’ common qualities. They can be based on your top buyers in an attempt to attract more people like them to your business, or if you are just starting, they can be the product of separate market research.
Every business should have market personas. If you have already created yours – way to go, you are one step ahead! If you have not yet done it, now is a good time.
When building the buyer persona’s profile, you should include the following basic information, and add other specific factors, if there are any:
- Demographic – Age, gender, location, etc.
- Personal Information – Family status, income, interests, etc.
- Work-related details – Company, position, decision-making level, etc.
- Pain Points – Work and personal life struggles, barriers to achieving goals, etc.
For further reference on how to build buyer persona profiles, you can read DevriX’s article:
An Advanced Guide to Creating and Using Buyer Personas to Convert Leads

3. Identify the Sample
A market research sample is a representative group of people who match your client persona profiles. Depending on the scope of the study, you might include in it people who fit one or multiple personas.
Ideally, if you want the results to be representative, you should focus on a single profile. However, if you feel that you will get more information from different types of customers, you can define separate samples for every participating persona and compare the results at the end.
Defining and identifying a representative sample is the foundation of accumulating accurate results. If your participants don’t match the profile you need, their answers will not be relevant to your goals.
Participants for samples can be identified in:
- Your customer database . Clients should be divided into groups matching your buyer persona profiles. If you haven’t already implemented the segmentation , doing it will help you sift through who to invite to participate in the research.
- Competitors’ clients. People who use products similar to yours and fit the profile, but are not currently your customers, are a great addition to your research. By learning about their opinions and preferences, you can attract them as clients in the future.
- Your lead database . Every lead you have in your email list or CRM tool can be a potential candidate for the survey sample. As with existing customers, leads should be segmented not only for research but also for better marketing.
- Social media profiles . Your network of followers on different social media platforms can be a valuable resource in every survey. By announcing the desired profiles participants should fit and encouraging people to share with acquaintances, you can reach many more potential participants.
Your sample must be large enough and also representative of the population you are targeting. Choosing an audience too small or an ill-targeted group of people can make the results of the research biased.
Although there is not a universal minimal number of people to include in your study, it is generally accepted amongst scientists that less than 100 people is insufficient to make up a statistically relevant conclusion. Therefore, to ensure you’ll reach this number, you’ll have to distribute your questions to at least 150 people.
However, if you want to research only your existing customers and they are less than 100 in total, you can still carry out your study but you’ll have to accept a larger error margin .
4. Perform Your Chosen Research Methods
Once your sample is clear, you can move forward to conducting market research. Depending on your goals, you can explore different methods, but we will be using a strategy combining a few of them for this article. This is usually the safest way to guarantee that your results will be comprehensible and on point.
Prep Your Questions
The goals and objectives you set in the initial stages of your research should be organized and formulated into questions you can ask your participants.
Although the phrasing and scope of these will probably change and be refined throughout the different stages of the research, you should consider testing them at the beginning on a small sample. This will allow you to eliminate rookie mistakes and save you some trouble further on in the research.
Do Secondary Research
Before you start studying your audience, you should consider doing secondary research to build a general idea of the market.
You can find paid and free data available in government databases, private research companies, educational institutions, and public libraries.
There is a chance that the information you go through has nothing to do with the goals of your particular research. But it can still help you identify market patterns at scale and configure your following moves.
Try Various Exploratory Methods
The next step is to dive into your specific target audience and see how things are. This can be done via different exploratory research methods.
1. Observation. At this stage, consider starting with observation. This will give you an idea of how your customers act in real-life situations in their natural environment.
2. Focus Group Meetings. You can continue by consolidating your initial impressions in focus group meetings. The moderator can ask the participants about the subjects that got their attention and the discussion that follows can give you additional insights.
3. Personal Interviews. Interviewing individual representatives of your sample will allow you to ask even more follow-up questions and have a chance to learn about your customers’ preferences, goals, and pain points.
Distribute Customer Surveys
You can leverage all the information you’ve gathered in the previous steps to design customer surveys . They will help you acquire the answers to your questions at scale and prove or disprove the hypothesis built in the exploratory stage.
The questions in the surveys should be as simple and easy to understand as possible. Avoid answers that lead the customer in the direction you’d like. This might influence their responses and compromise the results.
5. Analyze the Data and Organize It Into a Report
The data you obtain should be analyzed and organized at the end of every stage of your market research. These preliminary reports will serve you in the process of the study and will make building the final report easier.
Results from the research will be both qualitative and quantitative and should be properly visualized to make sense to everyone to whom they would be presented.
Cold statistics can be overwhelming, but presenting the data in an engaging format can make it more appealing and clear.
Some forms of reporting are customer journey maps and affinity diagrams . Even users who are not technically advanced can take advantage of modern data visualization tools and make research data interesting to the audience of their presentation.
Step-by-Step Market Research
Conducting market research is complicated. It takes a lot of preparation and can seem intimidating at first. But once you become familiar with the basics, you will be able to do it yourself and reap its success.
By using this guide, you can study different aspects of your target market, and get to know your audience on a different level. Leveraging the data and insights you gather will give you a strategic advantage and empower you to make more informed data-based decisions for your business.
Marketing Assistance for Your Business
One of our core specialties as a part of our full-service suite of services is the Inbound Marketing package. If you need expert assistance in keyword generation and SEO, you should get in touch with us. We are a professional WordPress development company profiling in business growth for your next big challenge.
Team DevriX
This article is crafted by DevriX's seasoned marketing team, boasting over four decades of collective expertise in crafting sophisticated marketing funnels, devising comprehensive content frameworks and pillars, implementing engaging email campaigns, and creating impactful social media content designed for scalability.
Our marketing experts specialize in the complete spectrum of inbound marketing strategies. As an accredited HubSpot Agency Partner and a Semrush Partner, we engage in meticulous research, blending our extensive experience with the unique insights of our highly skilled team.
We set benchmarks in content creation by incorporating cutting-edge marketing trends, leveraging in-depth industry research, and utilizing state-of-the-art AI tools for data segmentation and captivating content hooks. Our proficiency extends across a diverse range of sectors, including working with SMEs, Fortune 1000 companies, global B2B brands, major publishing entities, WooCommerce platforms, business directories, and affiliate networks.
More Stories:
Your organization will never be successful without finding your target market and who purchases their products or services. Identifying the main segments of your audience…
The eCommerce industry continues its growth. In 2019, globally, people have spent nearly $3.46 trillion, and with more and more companies expected to jump on…
Webinars are a powerful form of content marketing. They can build your brand, help you generate tons of leads, establish your authority as an industry…
You’ve heard it by now – video is the present and the future of marketing. And the statistics about video marketing for business show it!…
6.3 Steps in a Successful Marketing Research Plan
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- 1 Identify and describe the steps in a marketing research plan.
- 2 Discuss the different types of data research.
- 3 Explain how data is analyzed.
- 4 Discuss the importance of effective research reports.
Define the Problem
There are seven steps to a successful marketing research project (see Figure 6.3 ). Each step will be explained as we investigate how a marketing research project is conducted.
The first step, defining the problem, is often a realization that more information is needed in order to make a data-driven decision. Problem definition is the realization that there is an issue that needs to be addressed. An entrepreneur may be interested in opening a small business but must first define the problem that is to be investigated. A marketing research problem in this example is to discover the needs of the community and also to identify a potentially successful business venture.
Many times, researchers define a research question or objectives in this first step. Objectives of this research study could include: identify a new business that would be successful in the community in question, determine the size and composition of a target market for the business venture, and collect any relevant primary and secondary data that would support such a venture. At this point, the definition of the problem may be “Why are cat owners not buying our new cat toy subscription service?”
Additionally, during this first step we would want to investigate our target population for research. This is similar to a target market, as it is the group that comprises the population of interest for the study. In order to have a successful research outcome, the researcher should start with an understanding of the problem in the current situational environment.
Develop the Research Plan
Step two is to develop the research plan. What type of research is necessary to meet the established objectives of the first step? How will this data be collected? Additionally, what is the time frame of the research and budget to consider? If you must have information in the next week, a different plan would be implemented than in a situation where several months were allowed. These are issues that a researcher should address in order to meet the needs identified.
Research is often classified as coming from one of two types of data: primary and secondary. Primary data is unique information that is collected by the specific researcher with the current project in mind. This type of research doesn’t currently exist until it is pulled together for the project. Examples of primary data collection include survey, observation, experiment, or focus group data that is gathered for the current project.
Secondary data is any research that was completed for another purpose but can be used to help inform the research process. Secondary data comes in many forms and includes census data, journal articles, previously collected survey or focus group data of related topics, and compiled company data. Secondary data may be internal, such as the company’s sales records for a previous quarter, or external, such as an industry report of all related product sales. Syndicated data , a type of external secondary data, is available through subscription services and is utilized by many marketers. As you can see in Table 6.1 , primary and secondary data features are often opposite—the positive aspects of primary data are the negative side of secondary data.
There are four research types that can be used: exploratory, descriptive, experimental, and ethnographic research designs (see Figure 6.4 ). Each type has specific formats of data that can be collected. Qualitative research can be shared through words, descriptions, and open-ended comments. Qualitative data gives context but cannot be reduced to a statistic. Qualitative data examples are categorical and include case studies, diary accounts, interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. By comparison, quantitative data is data that can be reduced to number of responses. The number of responses to each answer on a multiple-choice question is quantitative data. Quantitative data is numerical and includes things like age, income, group size, and height.
Exploratory research is usually used when additional general information in desired about a topic. When in the initial steps of a new project, understanding the landscape is essential, so exploratory research helps the researcher to learn more about the general nature of the industry. Exploratory research can be collected through focus groups, interviews, and review of secondary data. When examining an exploratory research design, the best use is when your company hopes to collect data that is generally qualitative in nature. 7
For instance, if a company is considering a new service for registered users but is not quite sure how well the new service will be received or wants to gain clarity of exactly how customers may use a future service, the company can host a focus group. Focus groups and interviews will be examined later in the chapter. The insights collected during the focus group can assist the company when designing the service, help to inform promotional campaign options, and verify that the service is going to be a viable option for the company.
Descriptive research design takes a bigger step into collection of data through primary research complemented by secondary data. Descriptive research helps explain the market situation and define an “opinion, attitude, or behavior” of a group of consumers, employees, or other interested groups. 8 The most common method of deploying a descriptive research design is through the use of a survey. Several types of surveys will be defined later in this chapter. Descriptive data is quantitative in nature, meaning the data can be distilled into a statistic, such as in a table or chart.
Again, descriptive data is helpful in explaining the current situation. In the opening example of LEGO , the company wanted to describe the situation regarding children’s use of its product. In order to gather a large group of opinions, a survey was created. The data that was collected through this survey allowed the company to measure the existing perceptions of parents so that alterations could be made to future plans for the company.
Experimental research , also known as causal research , helps to define a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more factors. This type of research goes beyond a correlation to determine which feature caused the reaction. Researchers generally use some type of experimental design to determine a causal relationship. An example is A/B testing, a situation where one group of research participants, group A, is exposed to one treatment and then compared to the group B participants, who experience a different situation. An example might be showing two different television commercials to a panel of consumers and then measuring the difference in perception of the product. Another example would be to have two separate packaging options available in different markets. This research would answer the question “Does one design sell better than the other?” Comparing that to the sales in each market would be part of a causal research study. 9
The final method of collecting data is through an ethnographic design. Ethnographic research is conducted in the field by watching people interact in their natural environment. For marketing research, ethnographic designs help to identify how a product is used, what actions are included in a selection, or how the consumer interacts with the product. 10
Examples of ethnographic research would be to observe how a consumer uses a particular product, such as baking soda. Although many people buy baking soda, its uses are vast. So are they using it as a refrigerator deodorizer, a toothpaste, to polish a belt buckle, or to use in baking a cake?
Select the Data Collection Method
Data collection is the systematic gathering of information that addresses the identified problem. What is the best method to do that? Picking the right method of collecting data requires that the researcher understand the target population and the design picked in the previous step. There is no perfect method; each method has both advantages and disadvantages, so it’s essential that the researcher understand the target population of the research and the research objectives in order to pick the best option.
Sometimes the data desired is best collected by watching the actions of consumers. For instance, how many cars pass a specific billboard in a day? What website led a potential customer to the company’s website? When are consumers most likely to use the snack vending machines at work? What time of day has the highest traffic on a social media post? What is the most streamed television program this week? Observational research is the collecting of data based on actions taken by those observed. Many data observations do not require the researched individuals to participate in the data collection effort to be highly valuable. Some observation requires an individual to watch and record the activities of the target population through personal observations .
Unobtrusive observation happens when those being observed aren’t aware that they are being watched. An example of an unobtrusive observation would be to watch how shoppers interact with a new stuffed animal display by using a one-way mirror. Marketers can identify which products were handled more often while also determining which were ignored.
Other methods can use technology to collect the data instead. Instances of mechanical observation include the use of vehicle recorders, which count the number of vehicles that pass a specific location. Computers can also assess the number of shoppers who enter a store, the most popular entry point for train station commuters, or the peak time for cars to park in a parking garage.
When you want to get a more in-depth response from research participants, one method is to complete a one-on-one interview . One-on-one interviews allow the researcher to ask specific questions that match the respondent’s unique perspective as well as follow-up questions that piggyback on responses already completed. An interview allows the researcher to have a deeper understanding of the needs of the respondent, which is another strength of this type of data collection. The downside of personal interviews it that a discussion can be very time-consuming and results in only one respondent’s answers. Therefore, in order to get a large sample of respondents, the interview method may not be the most efficient method.
Taking the benefits of an interview and applying them to a small group of people is the design of a focus group . A focus group is a small number of people, usually 8 to 12, who meet the sample requirements. These individuals together are asked a series of questions where they are encouraged to build upon each other’s responses, either by agreeing or disagreeing with the other group members. Focus groups are similar to interviews in that they allow the researcher, through a moderator, to get more detailed information from a small group of potential customers (see Figure 6.5 ).
Link to Learning
Focus groups.
Focus groups are a common method for gathering insights into consumer thinking and habits. Companies will use this information to develop or shift their initiatives. The best way to understand a focus group is to watch a few examples or explanations. TED-Ed has this video that explains how focus groups work.
You might be asking when it is best to use a focus group or a survey. Learn the differences, the pros and cons of each, and the specific types of questions you ask in both situations in this article .
Preparing for a focus group is critical to success. It requires knowing the material and questions while also managing the group of people. Watch this video to learn more about how to prepare for a focus group and the types of things to be aware of.
One of the benefits of a focus group over individual interviews is that synergy can be generated when a participant builds on another’s ideas. Additionally, for the same amount of time, a researcher can hear from multiple respondents instead of just one. 11 Of course, as with every method of data collection, there are downsides to a focus group as well. Focus groups have the potential to be overwhelmed by one or two aggressive personalities, and the format can discourage more reserved individuals from speaking up. Finally, like interviews, the responses in a focus group are qualitative in nature and are difficult to distill into an easy statistic or two.
Combining a variety of questions on one instrument is called a survey or questionnaire . Collecting primary data is commonly done through surveys due to their versatility. A survey allows the researcher to ask the same set of questions of a large group of respondents. Response rates of surveys are calculated by dividing the number of surveys completed by the total number attempted. Surveys are flexible and can collect a variety of quantitative and qualitative data. Questions can include simplified yes or no questions, select all that apply, questions that are on a scale, or a variety of open-ended types of questions. There are four types of surveys (see Table 6.2 ) we will cover, each with strengths and weaknesses defined.
Let’s start off with mailed surveys —surveys that are sent to potential respondents through a mail service. Mailed surveys used to be more commonly used due to the ability to reach every household. In some instances, a mailed survey is still the best way to collect data. For example, every 10 years the United States conducts a census of its population (see Figure 6.6 ). The first step in that data collection is to send every household a survey through the US Postal Service (USPS). The benefit is that respondents can complete and return the survey at their convenience. The downside of mailed surveys are expense and timeliness of responses. A mailed survey requires postage, both when it is sent to the recipient and when it is returned. That, along with the cost of printing, paper, and both sending and return envelopes, adds up quickly. Additionally, physically mailing surveys takes time. One method of reducing cost is to send with bulk-rate postage, but that slows down the delivery of the survey. Also, because of the convenience to the respondent, completed surveys may be returned several weeks after being sent. Finally, some mailed survey data must be manually entered into the analysis software, which can cause delays or issues due to entry errors.
Phone surveys are completed during a phone conversation with the respondent. Although the traditional phone survey requires a data collector to talk with the participant, current technology allows for computer-assisted voice surveys or surveys to be completed by asking the respondent to push a specific button for each potential answer. Phone surveys are time intensive but allow the respondent to ask questions and the surveyor to request additional information or clarification on a question if warranted. Phone surveys require the respondent to complete the survey simultaneously with the collector, which is a limitation as there are restrictions for when phone calls are allowed. According to Telephone Consumer Protection Act , approved by Congress in 1991, no calls can be made prior to 8:00 a.m. or after 9:00 p.m. in the recipient’s time zone. 12 Many restrictions are outlined in this original legislation and have been added to since due to ever-changing technology.
In-person surveys are when the respondent and data collector are physically in the same location. In-person surveys allow the respondent to share specific information, ask questions of the surveyor, and follow up on previous answers. Surveys collected through this method can take place in a variety of ways: through door-to-door collection, in a public location, or at a person’s workplace. Although in-person surveys are time intensive and require more labor to collect data than some other methods, in some cases it’s the best way to collect the required data. In-person surveys conducted through a door-to-door method is the follow-up used for the census if respondents do not complete the mailed survey. One of the downsides of in-person surveys is the reluctance of potential respondents to stop their current activity and answer questions. Furthermore, people may not feel comfortable sharing private or personal information during a face-to-face conversation.
Electronic surveys are sent or collected through digital means and is an opportunity that can be added to any of the above methods as well as some new delivery options. Surveys can be sent through email, and respondents can either reply to the email or open a hyperlink to an online survey (see Figure 6.7 ). Additionally, a letter can be mailed that asks members of the survey sample to log in to a website rather than to return a mailed response. Many marketers now use links, QR codes, or electronic devices to easily connect to a survey. Digitally collected data has the benefit of being less time intensive and is often a more economical way to gather and input responses than more manual methods. A survey that could take months to collect through the mail can be completed within a week through digital means.
Design the Sample
Although you might want to include every possible person who matches your target market in your research, it’s often not a feasible option, nor is it of value. If you did decide to include everyone, you would be completing a census of the population. Getting everyone to participate would be time-consuming and highly expensive, so instead marketers use a sample , whereby a portion of the whole is included in the research. It’s similar to the samples you might receive at the grocery store or ice cream shop; it isn’t a full serving, but it does give you a good taste of what the whole would be like.
So how do you know who should be included in the sample? Researchers identify parameters for their studies, called sample frames . A sample frame for one study may be college students who live on campus; for another study, it may be retired people in Dallas, Texas, or small-business owners who have fewer than 10 employees. The individual entities within the sampling frame would be considered a sampling unit . A sampling unit is each individual respondent that would be considered as matching the sample frame established by the research. If a researcher wants businesses to participate in a study, then businesses would be the sampling unit in that case.
The number of sampling units included in the research is the sample size . Many calculations can be conducted to indicate what the correct size of the sample should be. Issues to consider are the size of the population, the confidence level that the data represents the entire population, the ease of accessing the units in the frame, and the budget allocated for the research.
There are two main categories of samples: probability and nonprobability (see Figure 6.8 ). Probability samples are those in which every member of the sample has an identified likelihood of being selected. Several probability sample methods can be utilized. One probability sampling technique is called a simple random sample , where not only does every person have an identified likelihood of being selected to be in the sample, but every person also has an equal chance of exclusion. An example of a simple random sample would be to put the names of all members of a group into a hat and simply draw out a specific number to be included. You could say a raffle would be a good example of a simple random sample.
Another probability sample type is a stratified random sample , where the population is divided into groups by category and then a random sample of each category is selected to participate. For instance, if you were conducting a study of college students from your school and wanted to make sure you had all grade levels included, you might take the names of all students and split them into different groups by grade level—freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior. Then, from those categories, you would draw names out of each of the pools, or strata.
A nonprobability sample is a situation in which each potential member of the sample has an unknown likelihood of being selected in the sample. Research findings that are from a nonprobability sample cannot be applied beyond the sample. Several examples of nonprobability sampling are available to researchers and include two that we will look at more closely: convenience sampling and judgment sampling.
The first nonprobability sampling technique is a convenience sample . Just like it sounds, a convenience sample is when the researcher finds a group through a nonscientific method by picking potential research participants in a convenient manner. An example might be to ask other students in a class you are taking to complete a survey that you are doing for a class assignment or passing out surveys at a basketball game or theater performance.
A judgment sample is a type of nonprobability sample that allows the researcher to determine if they believe the individual meets the criteria set for the sample frame to complete the research. For instance, you may be interested in researching mothers, so you sit outside a toy store and ask an individual who is carrying a baby to participate.
Collect the Data
Now that all the plans have been established, the instrument has been created, and the group of participants has been identified, it is time to start collecting data. As explained earlier in this chapter, data collection is the process of gathering information from a variety of sources that will satisfy the research objectives defined in step one. Data collection can be as simple as sending out an email with a survey link enclosed or as complex as an experiment with hundreds of consumers. The method of collection directly influences the length of this process. Conducting personal interviews or completing an experiment, as previously mentioned, can add weeks or months to the research process, whereas sending out an electronic survey may allow a researcher to collect the necessary data in a few days. 13
Analyze and Interpret the Data
Once the data has been collected, the process of analyzing it may begin. Data analysis is the distillation of the information into a more understandable and actionable format. The analysis itself can take many forms, from the use of basic statistics to a more comprehensive data visualization process. First, let’s discuss some basic statistics that can be used to represent data.
The first is the mean of quantitative data. A mean is often defined as the arithmetic average of values. The formula is:
A common use of the mean calculation is with exam scores. Say, for example, you have earned the following scores on your marketing exams: 72, 85, 68, and 77. To find the mean, you would add up the four scores for a total of 302. Then, in order to generate a mean, that number needs to be divided by the number of exam scores included, which is 4. The mean would be 302 divided by 4, for a mean test score of 75.5. Understanding the mean can help to determine, with one number, the weight of a particular value.
Another commonly used statistic is median. The median is often referred to as the middle number. To generate a median, all the numeric answers are placed in order, and the middle number is the median. Median is a common statistic when identifying the income level of a specific geographic region. 14 For instance, the median household income for Albuquerque, New Mexico, between 2015 and 2019 was $52,911. 15 In this case, there are just as many people with an income above the amount as there are below.
Mode is another statistic that is used to represent data of all types, as it can be used with quantitative or qualitative data and represents the most frequent answer. Eye color, hair color, and vehicle color can all be presented with a mode statistic. Additionally, some researchers expand on the concept of mode and present the frequency of all responses, not just identifying the most common response. Data such as this can easily be presented in a frequency graph, 16 such as the one in Figure 6.9 .
Additionally, researchers use other analyses to represent the data rather than to present the entirety of each response. For example, maybe the relationship between two values is important to understand. In this case, the researcher may share the data as a cross tabulation (see Figure 6.10 ). Below is the same data as above regarding social media use cross tabulated with gender—as you can see, the data is more descriptive when you can distinguish between the gender identifiers and how much time is spent per day on social media.
Not all data can be presented in a graphical format due to the nature of the information. Sometimes with qualitative methods of data collection, the responses cannot be distilled into a simple statistic or graph. In that case, the use of quotations, otherwise known as verbatims , can be used. These are direct statements presented by the respondents. Often you will see a verbatim statement when reading a movie or book review. The critic’s statements are used in part or in whole to represent their feelings about the newly released item.
Infographics
As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. For this reason, research results are often shown in a graphical format in which data can be taken in quickly, called an infographic .
Check out this infographic on what components make for a good infographic. As you can see, a good infographic needs four components: data, design, a story, and the ability to share it with others. Without all four pieces, it is not as valuable a resource as it could be. The ultimate infographic is represented as the intersection of all four.
Infographics are particularly advantageous online. Refer to this infographic on why they are beneficial to use online .
Prepare the Research Report
The marketing research process concludes by sharing the generated data and makes recommendations for future actions. What starts as simple data must be interpreted into an analysis. All information gathered should be conveyed in order to make decisions for future marketing actions. One item that is often part of the final step is to discuss areas that may have been missed with the current project or any area of further study identified while completing it. Without the final step of the marketing research project, the first six steps are without value. It is only after the information is shared, through a formal presentation or report, that those recommendations can be implemented and improvements made. The first six steps are used to generate information, while the last is to initiate action. During this last step is also when an evaluation of the process is conducted. If this research were to be completed again, how would we do it differently? Did the right questions get answered with the survey questions posed to the respondents? Follow-up on some of these key questions can lead to additional research, a different study, or further analysis of data collected.
Methods of Quantifying Marketing Research
One of the ways of sharing information gained through marketing research is to quantify the research . Quantifying the research means to take a variety of data and compile into a quantity that is more easily understood. This is a simple process if you want to know how many people attended a basketball game, but if you want to quantify the number of students who made a positive comment on a questionnaire, it can be a little more complicated. Researchers have a variety of methods to collect and then share these different scores. Below are some of the most common types used in business.
Is a customer aware of a product, brand, or company? What is meant by awareness? Awareness in the context of marketing research is when a consumer is familiar with the product, brand, or company. It does not assume that the consumer has tried the product or has purchased it. Consumers are just aware. That is a measure that many businesses find valuable. There are several ways to measure awareness. For instance, the first type of awareness is unaided awareness . This type of awareness is when no prompts for a product, brand, or company are given. If you were collecting information on fast-food restaurants, you might ask a respondent to list all the fast-food restaurants that serve a chicken sandwich. Aided awareness would be providing a list of products, brands, or companies and the respondent selects from the list. For instance, if you give a respondent a list of fast-food restaurants and ask them to mark all the locations with a chicken sandwich, you are collecting data through an aided method. Collecting these answers helps a company determine how the business location compares to those of its competitors. 17
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
Have you ever been asked to complete a survey at the end of a purchase? Many businesses complete research on buying, returning, or other customer service processes. A customer satisfaction score , also known as CSAT, is a measure of how satisfied customers are with the product, brand, or service. A CSAT score is usually on a scale of 0 to 100 percent. 18 But what constitutes a “good” CSAT score? Although what is identified as good can vary by industry, normally anything in the range from 75 to 85 would be considered good. Of course, a number higher than 85 would be considered exceptional. 19
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Effort Score (CES)
Other metrics often used are a customer acquisition cost (CAC) and customer effort score (CES). How much does it cost a company to gain customers? That’s the purpose of calculating the customer acquisition cost. To calculate the customer acquisition cost , a company would need to total all expenses that were accrued to gain new customers. This would include any advertising, public relations, social media postings, etc. When a total cost is determined, it is divided by the number of new customers gained through this campaign.
The final score to discuss is the customer effort score , also known as a CES. The CES is a “survey used to measure the ease of service experience with an organization.” 20 Companies that are easy to work with have a better CES than a company that is notorious for being difficult. An example would be to ask a consumer about the ease of making a purchase online by incorporating a one-question survey after a purchase is confirmed. If a number of responses come back negative or slightly negative, the company will realize that it needs to investigate and develop a more user-friendly process.
Knowledge Check
It’s time to check your knowledge on the concepts presented in this section. Refer to the Answer Key at the end of the book for feedback.
- Defining the problem
- Developing the research plan
- Selecting a data collection method
- Designing the sample
- you are able to send it to all households in an area
- it is inexpensive
- responses are automatically loaded into the software
- the data comes in quickly
- Primary data
- Secondary data
- Secondary and primary data
- Professional data
- It shows how respondents answered two variables in relation to each other and can help determine patterns by different groups of respondents.
- By presenting the data in the form of a picture, the information is easier for the reader to understand.
- It is an easy way to see how often one answer is selected by the respondents.
- This analysis can used to present interview or focus group data.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Dr. Maria Gomez Albrecht, Dr. Mark Green, Linda Hoffman
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Marketing
- Publication date: Jan 25, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/6-3-steps-in-a-successful-marketing-research-plan
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
Marketing Research: Objectives, Types, Steps, Methods
Updated on November 28, 2020 by Ahmad Nasrudin

What’s it: Marketing research is the efforts of systematically collecting and analyzing markets to support more effective marketing decision making. The stages usually include setting objectives, designing research and methods, collecting data, analyzing data, and reporting research results.
Why marketing research is important
Companies need accurate and current information about the marketing environment’s conditions to develop an effective marketing strategy. Demand and competition in the market continue to change from time to time, including about:
- Trending tastes and needs of consumers – for example, people are getting online and leaving conventional media such as print newspapers.
- Changes in the macro-environment , be it political, economic, social, technological, environmental, or regulatory. For example, technology enables companies to explore more data about consumers. Or, COVID-19 can make the economy crash and reduce outdoor activities.
- Competitive dynamics – for example, globalization brings more fierce competition because companies are not only competing with local companies but also globally.
Such changes present both threats and opportunities. Competitive advantage can turn into a disadvantage because companies do not adapt to such changes. They need different strategies and tactics to support a sustainable competitive advantage.
Marketing research objectives
Marketing research aims to identify challenges and opportunities to achieve marketing goals. Companies process data, analyze data, and interpret relevant facts to provide valuable information about it.
Research results also help companies plan, evaluate, and develop marketing strategies and tactics. Management uses it in decision making related to exploiting opportunities, minimizing threats, designing alternative actions, and solving marketing problems.
Meanwhile, the specific objectives of marketing research are:
- Understand what consumers need today – as consumer tastes and preferences change, companies may need different marketing strategies.
- Identifying market gaps – the company may find opportunities to develop new products, which are not being served by products currently on the market.
- Reducing product failure – marketing research information is useful for developing the right marketing mix, so it is profitable and better than competitors.
- Minimizing business risk – companies use research results to anticipate and develop appropriate responses to address threats in their business environment.
- Forecasting future trends – the company anticipates future consumer needs, so it is one step ahead of competitors exploiting market opportunities.
Types of marketing research
Marketing research covers three research areas:
- Market research : about the market, such as market size, profitability level, growth prospects, and competition intensity.
- Product research : about the characteristics and attributes of the right product to satisfy customers
- Consumer research : about consumer needs, tastes, preferences, attitudes, and behavior.
Marketing research can be causal, exploratory, or descriptive.
Causality research is when companies are trying to understand the cause-and-effect relationship of a phenomenon. For example, how much does a company’s advertising affect customer perception?
Descriptive research seeks to understand more about the nature or characteristics of the phenomenon itself. For example, companies try to understand the shopping habits of consumers when they go to the mall.
Exploratory research seeks to understand phenomena more profoundly and is usually useful for developing new products. For example, a company explores the shopping experience to gain insight into what first-time consumers see when shopping, whether price, packaging, store atmosphere, or brand.
Marketing research steps
The marketing stages usually include:
First , determine the problem or research objective. Marketing research covers various aspects of the market, such as product, sales, promotion, distribution, buyer behavior, pricing, and packaging. You cannot investigate them all at once. Therefore, you must be selective and determine what problems you want to answer through research.
Second , determine the research design, whether you want to do exploratory, descriptive, or causality studies.
Third , determine the data collection method. In this section, you have to decide whether to use secondary data or primary data. If it is primary data, will you use surveys, observations, experiments, or consumer panels? Another task is to design data collection forms, questionnaires, and sampling.
Fourth , collect data. Data can be either qualitative or quantitative.
Data collection depends on the research method you use, whether it is primary or secondary research. For example, suppose you decide to use secondary data. In that case, you may have to collect some statistics or reports from government agencies, international agencies, research firms, competitors, or trade associations.
Fifth , analyze and interpret data. Your first task is usually to integrate data into a database. Also, you may need to clean it up, so it’s ready for analysis.
You can use several descriptive or inferential statistical methods to describe the data, depending on your needs. The statistical techniques commonly used for social research are regression analysis, t-test, cluster analysis, factor analysis, cross-tabulation, and conjoint analysis.
Sixth , preparing a research report. You draw conclusions from the results of the analysis and, perhaps, make recommendations. You may need to make a full report or just present your findings in a PowerPoint.
Tables and charts are two tools for summarizing data so that it is easy to read. Both help you explain your findings and support the arguments for your recommendations.
Marketing research methods
Marketing research methods fall into two categories based on its data sources:
- Primary research – you are the first to collect data. This is also known as field research.
- Secondary research – you are second hand collecting data. Also known as desk research because you are collecting data from external sources.
Primary research
You are taking data from original sources, such as consumers. You can use various methods, such as surveys, observations, and focus groups, to collect data.
In a survey, you create a questionnaire containing several questions. You may do it yourself or hire a few people to help you. You then meet with respondents and ask questions in the questionnaire.
Questions may be closed questions for which you have provided alternative answers. Or, it is an open-ended question where you let the respondent answer according to their knowledge.
You can also do interviews without a questionnaire. You have some open-ended questions for you to ask respondents. Then, you record each answer. You can do this face-to-face, over the phone, or via online channels.
Then, you can also interview focus groups. In this case, you gather a few people, say, six to ten people. You then ask for their opinion on a particular topic. You listen to their views or record them.
Under observation, you observe people’s reactions, often without having to get into the conversation directly. If you’re researching shoppers, you’ll probably notice the first shelf they go to, the items they cart, and the items they end up buying at the checkout.
Secondary research
In this method, you rely on data from secondary sources. These sources can come from:
- Publications from government institutions such as central statistical agencies.
- Publications from international institutions such as the world bank and world trade center.
- Publications from research companies like Nielsen.
- Company or other stakeholder reports such as financial reports, annual reports, public presentations and press releases.
- General media such as newspapers and magazines, both print and online.
- Publications from business associations or trade journals.
Secondary research offers the convenience of collecting data, as well as being cheap. You can do it on the table without having to go out on the pitch.
However, unlike primary research, the accuracy of the data is a significant problem for secondary research. You depend on external parties for data quality. It can produce biased information and errors in making conclusions and decisions.
5 NEW ARTICLES

Private Savings: Formula and Explanation
What's it: Private savings equal to the sum of household and business savings. And savings

How to Handle and Resolve Stakeholder Conflicts
Stakeholders have different interests and goals, which are often contradictory. Stakeholder

Where Do Comparative Advantages Come From?
The comparative advantage stems from the ability to produce goods and services at low opportunity

What are the Benefits of International Trade?
Increased access to cheaper and more varied goods and services is key benefits of international

What is the Capital Budgeting Process?
In simple terms, the capital budgeting process involves generating ideas, making proposals about
5 TRENDING ARTICLES
- Business Size: Definition, Measurement, Classification
- Socio-cultural Factors: Examples and How They Impact Business
- International Trade: Why It Matters, Advantages, Disadvantages
- Marketing department: Functions and Responsibilities
- What Are the Effects of Industrialization? [Positive and Negative Impacts]
EXPLORE MORE
- Login to Survey Tool Review Center
- Step by Step Guide to the Market Research Process
Summary: The market research process requires decisions related to budget, target sample, development of data collection tools, fielding, analysis, and reporting. Here is a check list to make the process easier.
5 minutes to read. By author Michaela Mora on March 15, 2022 Topics: Business Strategy , Market Research

The market research process requires making decisions at many steps that can be overwhelming for non-researchers put in charge of research projects.
Consider these practical tips to conduct the following 6 steps during the implementation of a market research project.
Step 1. Define the Problem and Translate It into Research Objectives
- This is the most important step. It sets the direction of the whole market research process. Ask clients how they will use the research results, and what business decisions they will make based on the data. They should be specific. Get a consensus among key stakeholders on the main research objectives. Get them involved from the start.
- Avoid objective creep. Don’t try to research everything under the sky in a project. Focus on what’s needed for decision-making. Trying to cram many things into a project because of budget constraints is often a waste of money as data quality suffers.
- Discuss limitations early in the process. Set clear expectations of what the research will cover and what data it will provide.
- Do secondary research , and check if previous research has been conducted on the same issue to avoid effort duplication and waste of money. Interview key stakeholders to put the research objectives into a greater context.
- Exploratory primary research may be needed with your target market (customers /users, non-customers) to better define the information needs.
- DO NOT select a data collection method before establishing clear objectives and identifying the target population. Think objectives firsts, methods second. Not the other way around.
- How much are the key stakeholders willing to invest in the requested research? Get a number! If there is no commitment to a budget, you will be wasting your time (RFP) and your research vendor’s time (proposal). There is always a trade-off between research quality, deadline, and cost. Make your internal clients aware of that. There is a limit to “ better, faster, and cheaper ” in market research. Push it too hard and you will get fast cheap, crappy research.
Step 2. Formulate the Approach
- Based on the research objective think, which research methodology would be the best fit. Start with the broader categories: Secondary? Primary? Qualitative? Quantitative?
- Based on the decisions that will be made, determine what type of data is needed and expected.
- Example: Need to know how to price a new product before it goes to market? Conjoint Analysis may be a good fit. Check: Conjoint Analysis And Realism In Price Research
- Example: Need to pick the product name that elicits the highest purchase intent from a list of 30? Consider MaxDiff. Check: Making the Case for MaxDiff
- Example: Need to find new growth opportunities? Segmentation research can help to find segments with the highest potential. Check: Segmentation is Key to Success
- The analysis techniques selected will also influence the decision on sample size.
- Ideally, if budget permits do qualitative research before or after quantitative research
- Consider qualitative research for exploration before quantitative and deep-diving after quantitative research.
- Consider quantitative research if a go/no go decision will be made. DO NOT make these types of decisions based only on qualitative research
Step 3. Define The Research Design
Define the target population for the research.
- Who do you want to gather data from? Customers? Non-Customers? Category users? Be realistic. Given your budget, you may or may not be able to reach your target population.
- Sample definition helps decide on what data collection method we use. More than one method may be needed. To read more about mixed-mode data collection check: Mixed Data Collection Modes – Round-Up
- Create clear screening criteria. Discuss them with key stakeholders. Make sure they align with the research objectives.
- Discuss the caveats and limitations of the sample definition and how they will affect the results and decision-making.
- Determine the sample size based on your tolerance for risk. Check Sample Size Matter
- A large sample doesn’t guarantee representativeness. Check: Does A Large Sample Size Guarantee A Representative Sample?
- If you have access to a customer database with emails, use it for studies related to customer retention goals and new product development.
- For customer acquisition, efforts use samples of non-customers in the category.
- If the study is online get bids from multiple online panels.
- Don’t buy third-party email lists and blast them with survey invites. It is illegal (SPAM-CAN Act).
- If you are conducting qualitative research , small samples are expected given the exploration nature of this methodology category. Consider issues of sample size saturation . Depending on the overall research objectives, results from qualitative research may need validation via quantitative research.
Select Data Collection Method (s)
- Objectives, sample plan, analytical plan, and cost have the highest influence on which methods we use. Be open to using hybrid approaches combining qualitative and quantitative data collection methods
- Discuss which methods are the best fit to research the target pop. Some target groups may be difficult to reach with the same method
- If you decide on mixed-mode surveys, be aware of potential measurement errors each mode introduces. Check: Understanding the Pros and Cons of Mixed-Mode Research
- Once the data collection methods are selected, determine if you can do it with internal resources or need a research vendor.
- If time, staff, or lack of tools are limitations, consider outsourcing the project to an external research vendor. For more on this check: When Do You Need A Market Research Vendor ?
- If you are doing surveys, put time into its design. To create surveys that gather quality data check: 10 Things to Consider in Survey Design
- Considering focus groups? Check if it makes sense here: When Using Focus Groups Makes Sense
- If you are doing focus groups, avoid common mistakes. To know which they are, check: Common Mistakes When Doing Focus Groups
- Consider online qualitative research techniques. Check: Online Qualitative Research Techniques Review
Step 4. Collect Data
- Do a soft launch if you are doing online surveys to catch any potential problems.
- Get involved, monitor. early to catch any potential issues that can affect data quality (e.g., bad respondents, programming errors, etc.).
Step 5. Data Processing
- Clean your data. It doesn’t matter if it is quantitative or qualitative data, quality controls are needed.
- Fraudulent research participants are always trying to game the system to get their incentives. Try to catch them on the fly with the help of fraud prevention software and smart programming in recruitment screeners and question design and programming.
- Code open-ended questions to find patterns in the data.
- Create cross-tabulated tables to help organize the data if you do surveys.
- Transcribe interviews and focus group discussions to use tools to organize qualitative data to facilitate thematic analysis.
Step 6. Analyze & Report
- Keep the key objectives in mind to connect market research to business impact. Check: How To Connect Market Research To Business Impact
- Share preliminary results with key stakeholders, discuss, and check if they make sense from a practical standpoint.
- Focus on the story behind the numbers and how it supports your recommendations. Don’t do a data dump. Focus on insights.
Related Articles
- 10 Key Pieces of Advice On How to Do And Use Market Research
- Your Market Research Plan to Succeed As a Startup
- When to Use Different Types of Market Research
- Insightful Planning On A Tight Market Research Budget
- Top Reason Why Businesses Fail & What To Do About It
- Why Faster, Cheaper, and Better Market Research Is a Dangerous Illusion
- How to Align Business Goals With Market Research
- Myths & Misunderstandings About UX – MR Realities Podcast
- Savvy Businesses Realize the Value of Market Research
- Use Research Insights to Connect with Your Customers
- How To Connect Market Research To Business Impact
- Getting The Price Right Takes More Than Guesswork
- What To Value In A Market Research Vendor
- Don’t Let The Budget Dictate Your Market Research Approach
- Don’t Just Trust Your Gut — Do Research
- Market Segmentation Is Key To Success
- How To Use Social Media In Market Research
- 9 Product Development Strategies to Consider
- UX Research Methods For User-Centric Design
- Awareness, Attitude & Usage Metrics That Will Guide Your Success
- When Do You Need A Market Research Vendor?
Subscribe to our newsletter to get notified about future articles
Subscribe and don’t miss anything!
Recent Articles
- Re: Design/Growth Podcast – Researching User Experiences for Business Growth
- Why You Need Positioning Concept Testing in New Product Development
- Why Conjoint Analysis Is Best for Price Research
- The Rise of UX
- Making the Case Against the Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter
- How to Future-Proof Experience Management and Your Business
- When Using Focus Groups Makes Sense
- How to Make Segmentation Research Actionable
- How To Integrate Market Research and UX Research for Desired Business Outcomes
- How To Get Value Out of Your Research Budget
Popular Articles
- Which Rating Scales Should I Use?
- What To Consider in Survey Design
- 6 Decisions To Make When Designing Product Concept Tests
- Write Winning Product Concepts To Get Accurate Results In Concept Tests
- What Is Market Research?
- How to Use Qualitative and Quantitative Research in Product Development
- The Opportunity of UX Research Webinar
- 12 Research Techniques to Solve Choice Overload
- Concept Testing for UX Researchers
- UX Research Geeks Podcast – Using Market Research for Better Context in UX
- A Researcher’s Path – Data Stories Leaders At Work Podcast
- How to Leverage UX and Market Research To Understand Your Customers
- How To Improve Racial and Gender Inclusion in Survey Design

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Do you have the world's best boss? Enter them to win two tickets to Sandals!
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
How to Create a Market Research Plan

Table of Contents
While having a great idea is an important part of establishing a business, you’ll only get so far without laying the proper groundwork. To help your business take off, not only do you need to size up the competition, but you also need to identify who will buy your product, how much it will cost, the best approach to selling it and how many people will demand it.
To get answers to these questions, you’ll need a market research plan, which you can create yourself or pay a specialist to create for you. Market research plans define an existing problem and/or outline an opportunity. From there, the marketing strategy is broken down task by task. Your plan should include objectives and the methods that you’ll use to achieve those objectives, along with a time frame for completing the work.
What should a market research plan include?
A market research plan should provide a thorough examination of how your product or service will fare in a defined area. It should include:
- An examination of the current marketplace and an analysis of the need for your product or service: To know where you fit in the market, it’s important to have a broad understanding of your industry — covering everything from its annual revenue to the industry standards to the total number of businesses operating within it. Start by gathering statistical data from sources like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics and BMI Research and consider the industry’s market size, potential customer base and how external factors such as laws, technology, world events and socioeconomic changes impact it.
- An assessment of the competition: By analyzing your competitors, you can discover strategies to fill market gaps. This involves identifying well-known competitors and noting trends they employ successfully, scrutinizing customer feedback about businesses in your sector, such as through online reviews, and understanding competitors’ product or service offerings. This knowledge can then guide the refinement of your own products or services to differentiate them from others in the market.
- Data about customers: Identify which segment of potential customers in your industry you can effectively target, considering their demographics — such as age, ethnicity, income and location and psychographics, including beliefs, values and lifestyle. Learn about the challenges your customers face in their daily lives and determine how the features and benefits of your offerings address their needs.
- The direction for your marketing in the upcoming year: Your plan should provide a clear roadmap for your marketing strategies for the next year, focusing on approaches to distinguish your brand from competitors. Develop marketing messages that resonate with and display empathy toward your target market and find ways to address customers’ needs and demonstrate value.
- Goals to be met: Outline goals your business would like to achieve and make these goals clear to all employees on your team. Create goals that are realistic and attainable while also making a meaningful impact on the business’s growth. Consider factors including your target number of products or services, the expected number of units to sell based on market size, target market behavior, pricing for each item and the cost of production and advertising.
How to create your market research plan
Doing business without having a marketing plan is like driving without directions. You may eventually reach your destination, but there will be many costly and time-consuming mistakes made along the way.
Many entrepreneurs mistakenly believe there is a big demand for their service or product but, in reality, there may not be, your prices may be too high or too low or you may be going into a business with so many restrictions that it’s almost impossible to be successful. A market research plan will help you uncover significant issues or roadblocks.
Step 1. Conduct a comprehensive situation analysis.
One of the first steps in constructing your marketing plan is to create a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis , which is used to identify your competition, to know how they operate and then to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
When developing a market research plan, it is essential that you do your homework to determine your possible customer base, to gain knowledge about the competition and to have a solid foundation for your marketing strategy.
Step 2: Develop clear marketing objectives.
In this section, describe the desired outcome for your marketing plan with realistic and attainable objectives, the targets and a clear and concise time frame. The most common way to approach this is with marketing objectives, which may include the total number of customers and the retention rate, the average volume of purchases, total market share and the proportion of your potential market that makes purchases.
Step 3: Make a financial plan.
A financial plan is essentia l for creating a solid marketing plan. The financial plan answers a range of questions that are critical components of your business, such as how much you intend to sell, what will you charge, how much will it cost to deliver your services or produce your products, how much will it cost for your basic operating expenses and how much financing will you need to operate your business.
In your business plan, be sure to describe who you are, what your business will be about, your business goals and what your inspiration was to buy, begin or grow your business.
Step 4: Determine your target audience.
Once you know what makes you stand out from your competitors and how you’ll market yourself, you should decide who to target with all this information. That’s why your market research plan should delineate your target audience. What are their demographics and how will these qualities affect your plan? How do your company’s current products and services affect which consumers you can realistically make customers? Will that change in the future? All of these questions should be answered in your plan.
Step 5: List your research methods.
Rarely does one research avenue make for a comprehensive market research plan. Instead, your plan should indicate several methods that will be used to determine the market share you can realistically obtain. This way, you get as much information as possible from as many sources as possible. The result is a more robust path toward establishing the exact footprint you desire for your company.
A good market research plan involves using more than one type of research to obtain the information you need.
Step 6: Establish a timeline.
With your plan in place, you’ll need to figure out how long your market research process will take. Project management charts are often helpful in this regard as they divide tasks and personnel over a timeframe that you have set. No matter which type of project management chart you use, try to build some flexibility into your timeframe. A two-week buffer toward the home stretch comes in handy when a process scheduled for one week takes two — that buffer will keep you on deadline.
Step 7: Acknowledge ethical concerns.
Market research always presents opportunities for ethical missteps. After all, you’ll need to obtain competitor information and sensitive financial data that may not always be readily available. Your market research plan should thus encourage your team to not take any dicey steps to obtain this information. It may be better to state, “we could not obtain this competitor information,” than to spy on the competitor or pressure their current employees for knowledge. Plus, there’s nothing wrong with simply feeling better about the final state of your plan and how you got it there.
Using a market research firm
If the thought of trying to create your own market research plan seems daunting or too time-consuming, there are plenty of other people willing to do the work for you.
You don’t need to pay thousands of dollars for assistance crafting a market research plan. University business schools often provide free resources that can assist you.
Pros of using a market research firm
As an objective third party, businesses can benefit from a market research firm’s impartial perspective and guidance, helping to shape impactful brand strategies and marketing campaigns. These firms, which can help businesses with everything from their marketing campaigns to brand launches, deliver precise results, drawing on their expertise and experience to provide in-depth insights and solutions tailored specifically to your company’s needs.
Even more, working with a market research firm can elevate a brand above the competition, as they provide credible and unique research that is highly valued by the media, enhancing brand credibility and potentially increasing website traffic, social media shares and online visibility.
Cons of using a market research firm
Although hiring a firm can provide businesses with tremendous results, certain downsides can lead a business toward the do-it-yourself route. Most notably, market research firms can be a costly expense that some businesses can’t afford. However, businesses that can allocate the funds will likely see a positive return on investment, as they are paying for the expertise and proficiency of seasoned professionals in the field.
Additionally, finding the right market research firm for your business’s needs can take some time — and even longer, ranging from weeks to months, for a market research firm to complete a plan. This lack of immediate results can be detrimental for businesses that don’t have the time to wait.
Market research firms can charge into the thousands of dollars for a market research plan, but there are ways to get help more affordably, including:
- Outline your plans carefully and spell out objectives.
- Examine as many sources as possible.
- Before paying for any information, check with librarians, small business development centers or market research professors to see if they can help you access market research data for free.
- You may think you’ll need to spend a hefty sum to create a market research plan, but there are plenty of free and low-cost sources available, especially through university business schools that will guide you through the process.
Miranda Fraraccio contributed to this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Market Research?
- How It Works
- Primary vs. Secondary
- How to Conduct Research
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Joules Garcia / Investopedia
Market research examines consumer behavior and trends in the economy to help a business develop and fine-tune its business idea and strategy. It helps a business understand its target market by gathering and analyzing data.
Market research is the process of evaluating the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. It allows a company to define its target market and get opinions and other feedback from consumers about their interest in a product or service.
Research may be conducted in-house or by a third party that specializes in market research. It can be done through surveys and focus groups, among other ways. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples or a small stipend for their time.
Key Takeaways
- Companies conduct market research before introducing new products to determine their appeal to potential customers.
- Tools include focus groups, telephone interviews, and questionnaires.
- The results of market research inform the final design of the product and determine how it will be positioned in the marketplace.
- Market research usually combines primary information, gathered directly from consumers, and secondary information, which is data available from external sources.
Market Research
How market research works.
Market research is used to determine the viability of a new product or service. The results may be used to revise the product design and fine-tune the strategy for introducing it to the public. This can include information gathered for the purpose of determining market segmentation . It also informs product differentiation , which is used to tailor advertising.
A business engages in various tasks to complete the market research process. It gathers information based on the market sector being targeted by the product. This information is then analyzed and relevant data points are interpreted to draw conclusions about how the product may be optimally designed and marketed to the market segment for which it is intended.
It is a critical component in the research and development (R&D) phase of a new product or service introduction. Market research can be conducted in many different ways, including surveys, product testing, interviews, and focus groups.
Market research is a critical tool that companies use to understand what consumers want, develop products that those consumers will use, and maintain a competitive advantage over other companies in their industry.
Primary Market Research vs. Secondary Market Research
Market research usually consists of a combination of:
- Primary research, gathered by the company or by an outside company that it hires
- Secondary research, which draws on external sources of data
Primary Market Research
Primary research generally falls into two categories: exploratory and specific research.
- Exploratory research is less structured and functions via open-ended questions. The questions may be posed in a focus group setting, telephone interviews, or questionnaires. It results in questions or issues that the company needs to address about a product that it has under development.
- Specific research delves more deeply into the problems or issues identified in exploratory research.
Secondary Market Research
All market research is informed by the findings of other researchers about the needs and wants of consumers. Today, much of this research can be found online.
Secondary research can include population information from government census data , trade association research reports , polling results, and research from other businesses operating in the same market sector.
History of Market Research
Formal market research began in Germany during the 1920s. In the United States, it soon took off with the advent of the Golden Age of Radio.
Companies that created advertisements for this new entertainment medium began to look at the demographics of the audiences who listened to each of the radio plays, music programs, and comedy skits that were presented.
They had once tried to reach the widest possible audience by placing their messages on billboards or in the most popular magazines. With radio programming, they had the chance to target rural or urban consumers, teenagers or families, and judge the results by the sales numbers that followed.
Types of Market Research
Face-to-face interviews.
From their earliest days, market research companies would interview people on the street about the newspapers and magazines that they read regularly and ask whether they recalled any of the ads or brands that were published in them. Data collected from these interviews were compared to the circulation of the publication to determine the effectiveness of those ads.
Market research and surveys were adapted from these early techniques.
To get a strong understanding of your market, it’s essential to understand demand, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small number of representative consumers chosen to try a product or watch an advertisement.
Afterward, the group is asked for feedback on their perceptions of the product, the company’s brand, or competing products. The company then takes that information and makes decisions about what to do with the product or service, whether that's releasing it, making changes, or abandoning it altogether.
Phone Research
The man-on-the-street interview technique soon gave way to the telephone interview. A telephone interviewer could collect information in a more efficient and cost-effective fashion.
Telephone research was a preferred tactic of market researchers for many years. It has become much more difficult in recent years as landline phone service dwindles and is replaced by less accessible mobile phones.
Survey Research
As an alternative to focus groups, surveys represent a cost-effective way to determine consumer attitudes without having to interview anyone in person. Consumers are sent surveys in the mail, usually with a coupon or voucher to incentivize participation. These surveys help determine how consumers feel about the product, brand, and price point.
Online Market Research
With people spending more time online, market research activities have shifted online as well. Data collection still uses a survey-style form. But instead of companies actively seeking participants by finding them on the street or cold calling them on the phone, people can choose to sign up, take surveys, and offer opinions when they have time.
This makes the process far less intrusive and less rushed, since people can participate on their own time and of their own volition.
How to Conduct Market Research
The first step to effective market research is to determine the goals of the study. Each study should seek to answer a clear, well-defined problem. For example, a company might seek to identify consumer preferences, brand recognition, or the comparative effectiveness of different types of ad campaigns.
After that, the next step is to determine who will be included in the research. Market research is an expensive process, and a company cannot waste resources collecting unnecessary data. The firm should decide in advance which types of consumers will be included in the research, and how the data will be collected. They should also account for the probability of statistical errors or sampling bias .
The next step is to collect the data and analyze the results. If the two previous steps have been completed accurately, this should be straightforward. The researchers will collect the results of their study, keeping track of the ages, gender, and other relevant data of each respondent. This is then analyzed in a marketing report that explains the results of their research.
The last step is for company executives to use their market research to make business decisions. Depending on the results of their research, they may choose to target a different group of consumers, or they may change their price point or some product features.
The results of these changes may eventually be measured in further market research, and the process will begin all over again.
Benefits of Market Research
Market research is essential for developing brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. Since it is unlikely for a product to appeal equally to every consumer, a strong market research program can help identify the key demographics and market segments that are most likely to use a given product.
Market research is also important for developing a company’s advertising efforts. For example, if a company’s market research determines that its consumers are more likely to use Facebook than X (formerly Twitter), it can then target its advertisements to one platform instead of another. Or, if they determine that their target market is value-sensitive rather than price-sensitive, they can work on improving the product rather than reducing their prices.
Market research only works when subjects are honest and open to participating.
Example of Market Research
Many companies use market research to test new products or get information from consumers about what kinds of products or services they need and don’t currently have.
For example, a company that’s considering starting a business might conduct market research to test the viability of its product or service. If the market research confirms consumer interest, the business can proceed confidently with its business plan . If not, the company can use the results of the market research to make adjustments to the product to bring it in line with customer desires.
What Are the Main Types of Market Research?
The main types of market research are primary research and secondary research. Primary research includes focus groups, polls, and surveys. Secondary research includes academic articles, infographics, and white papers.
Qualitative research gives insights into how customers feel and think. Quantitative research uses data and statistics such as website views, social media engagement, and subscriber numbers.
What Is Online Market Research?
Online market research uses the same strategies and techniques as traditional primary and secondary market research, but it is conducted on the Internet. Potential customers may be asked to participate in a survey or give feedback on a product. The responses may help the researchers create a profile of the likely customer for a new product.
What Are Paid Market Research Surveys?
Paid market research involves rewarding individuals who agree to participate in a study. They may be offered a small payment for their time or a discount coupon in return for filling out a questionnaire or participating in a focus group.
What Is a Market Study?
A market study is an analysis of consumer demand for a product or service. It looks at all of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. These include the product’s price, location, competition, and substitutes as well as general economic factors that could influence the new product’s adoption, for better or worse.
Market research is a key component of a company’s research and development (R&D) stage. It helps companies understand in advance the viability of a new product that they have in development and to see how it might perform in the real world.
Britannica Money. “ Market Research .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1327127856-ce97892716b346b99dcf1d14af294a97.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Marketing91
What is the objective of market research?
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Market research is the practice of researching people’s thoughts, opinions, and behaviors concerning a given product or service. It’s typically conducted by contacting customers to learn what they think about a new product or service before it hits the market.
Market research is a process of identifying important factors in a marketplace. Its purpose is to provide insight that allows a company to make better business decisions and increase profitability.
Table of Contents
10 Objectives of Market Research

Research companies conduct marketing research to optimize marketing effectiveness. Some of the objectives that it serves are –
1) To Know the Target Customers & Bring in New Business
Marketing involves understanding the people who are interested in purchasing a firm’s products or services. This involves gathering information about buyer variables, such as the number of buyers, how frequently they buy, their geographical location, social category, and other relevant factors.
Example –
A company that sells personal care products can conduct market research to identify the target buyers and their needs.
2) To identify a new target audience that they want to pursue based on their last sales figures
In addition to its other purposes, market research is also utilized to discover individuals who could be potential customers but are currently unaware of the company’s products and services. Firms make use of this research to evaluate whether there are any unexplored markets or customer groups that haven’t been targeted yet.
A restaurant may conduct market research to identify potential customers in new neighborhoods.
3) To Measure the Marketing Performance & Impact of Promotional Efforts
In today’s dynamic marketing environment , companies often use various strategies to promote their products or services. The communication mix, which includes advertising , personal selling, and sales promotion , plays a significant role in this regard. Researching the effectiveness of different components of the promotion mix will help the researcher assess their strengths and weaknesses. You can utilize the findings to implement necessary changes that would enhance the outcome.
A company may measure the impact of its promotional efforts by assessing the level of engagement and response across different platforms.
4) To Know the Consumer Response
Market researchers aim to comprehend how consumers respond to their products and services. To achieve this, they collect information about buyers’ preferences, opinions, behaviors, and attitudes . The insights derived from market research will assist researchers in determining what aspects of their offering appeal to customers and what do not.
A tourism company may ask consumers’ opinions about its services to better understand customers’ opinions about its offerings.
5) To Know Market Costs and Profits
There is growing concern worldwide that marketing costs have increased so much that companies are struggling to maximize their profits. Marketing cost reflects the resources a company invests in its marketing efforts and is a key performance indicator. Studying the breakdown of total marketing expenses can help evaluate which marketing strategies are not cost-effective and do not yield satisfactory results.
A food-processing plant may analyze the cost of its marketing activities to determine if they are generating sufficient returns on investment.
6) To Master the External Forces
The company’s policies and strategies are subject to change based on controllable internal factors and uncontrollable external factors.
Companies need precise data about their competitors’ activities, their market share , modifications in foreign markets, government policies, consumer income and expenses, technological advancements, new product substitutes, environmental factors, etc. Firms must continuously adapt to the changing forces in their environment through research. By conducting research, firms can become more innovative and increase their chances of successful survival.
A manufacturing company may conduct research on the impact of rising raw material costs and changes in economic policies to design strategies to overcome this challenge.
7) To Design and Implement Marketing Control
The role of marketing control is to monitor and provide feedback on how well the marketing plan is performing compared to the pre-set standards. Its purpose is to identify and correct deviations and provide data to revise the plan.
Market research can determine whether different messages are resonating more with target customers in different regions. It can also identify areas of the plan that need to be adjusted or improved to meet the company’s objectives.
8) Identifying market gaps
By using market research, you can identify gaps in the market. Companies with limited resources may be unable to go after every opportunity, so understanding what the competition is doing and identifying areas where there is untapped potential gives companies an advantage.
A company may use marketing research to find out what products and services are popular in a certain region. With that information, they can determine if there is an opportunity to expand into that market.
9) Reducing product failure & minimizing business risk
Using marketing research information can help develop a successful marketing mix , leading to profitability and an advantage over competitors. Businesses utilize research findings to predict and prepare suitable measures to deal with potential risks in their operational surroundings.
Market research can help companies identify potential product failures before they launch and adjust their strategy accordingly. It can also provide information on customer preferences that could help them develop new products or services.
10) Forecasting future trends
You will stay ahead of competitors by anticipating future consumer needs and taking advantage of market opportunities by using marketing research. Forecasting can help companies make better decisions on which markets and products to focus on and anticipate changes in consumer preferences.
Market research can supply information about the latest developments in a specific market like the rise in demand for certain products or the increase in interest of specific consumer groups towards particular services. Companies can utilize this data to design more focused marketing campaigns and stay competitive with others in the industry.
Why Marketing Research is Important?
Market research is beneficial for businesses because it enables them to discover customer needs and preferences, gain deeper insights into their intended audience, and make informed decisions regarding product creation, pricing , distribution , and marketing tactics.
- Understanding consumer behavior enables companies to gain insights into their competitors’ strategies and respond appropriately. Additionally, it can aid companies in making business decisions.
- Conducting marketing research is crucial for businesses to achieve success. By analyzing reliable data, companies can gain insights into their target customers and make well-informed decisions.
- By conducting marketing research, businesses can find out what their customers want and like, evaluate how satisfied their customers are, gauge the competition’s performance, and discover new trends in the industry.
Types of Market Research
Mainly two types of market research help a consumer-oriented company in doing effective marketing research and marketing management . Let’s go through both of them right away-
1. Primary Research
Primary research is a method in which a business either directly communicates with its consumers or hires a third party to conduct qualitative research or quantitative research to gather numerical or non-numerical data. It can be done in so many ways to do primary data collection such as –
- Focus Groups
- One-to-One Interviews
- Ethnographic Research
- Customer Surveys
- Questionnaires
2. Secondary Research
Secondary marketing research aims at secondary data and involves analyzing data and insights obtained from sources other than your primary research. This includes both qualitative and quantitative research . The data collected can be useful in determining how to position the product and in making decisions. Some of the ways of doing secondary research are –
- Public Sources
- Commercial Sources
- Company Web Sites
- Other Sources like published market studies, analyst reports, customer emails, customer surveys, recorded meetings, interviews, books, etc
How to Create a Market Research Objective

Some of the steps you need to follow to create an effective marketing research process objective are –
1) Start with a research question –
To create an objective, start by identifying the key questions that your market research needs to answer. Gathering relevant data and information to help reach your desired outcome will be easier if you have a clear focus.
2) Set measurable goals –
For your market research project to succeed, it’s crucial to set specific and achievable goals that can be measured. This involves outlining your objectives and methods for achieving them, so you can monitor progress and assess results.
3) Identify resources –
To reach your goals, it is important to pinpoint helpful resources that can assist you in achieving the desired results. One of these resources includes finding pertinent sources of information , such as surveys and interviews, that are necessary for conducting marketing research.
4) Develop a plan of action –
To achieve your goal, you must create an actionable plan that identifies needed resources and measurable objectives and outlines the steps you will take to collect and use data.
To make sure your marketing research is effective and helps you achieve your desired outcome, follow the steps to create a tailored market research objective for your project. This will ensure that your time and effort spent on market research is not wasted and leads to successful results.
What Questions your Marketing Research Objectives should Answer?
Your marketing research report should answer the following questions to address different scenarios, so you can optimize your marketing strategy for collecting data and solving marketing problems effectively –
1) What strategies can we use to increase sales of our products to our existing customers?
By setting marketing research objectives to determine customer satisfaction levels, such as conducting customer satisfaction surveys, analyzing Net Promoter Score, and retention and churn figures, companies can discover potential strategies to enhance satisfaction and retain customer loyalty .
2) What strategies can we use to attract new customers?
To create different marketing strategies that meet the needs of potential customers and reach them better, companies should set market research objectives to analyze the demographics and geographic location of their target market . They can also use this data to identify the most suitable distribution channels .
3) Is it advisable to create new products for our existing customers?
Businesses may need to address how they can encourage their current customers to try other products or services they offer. Companies can save money by cross-selling to existing customers instead of constantly trying to attract new customers. By providing helpful and convenient solutions through cross-selling, companies can also increase loyalty and satisfaction.
4) Is it advisable to create new products for a new customer base?
Developing new types of products and services for new types of customers is a risky endeavor that companies can embark on. To fully understand market threats and opportunities, companies need to use a comprehensive research plan with specific marketing research objectives.
Conclusion!
To conclude, the objectives of marketing research can be summarized in the following points-
- To identify and comprehend the target audiences, specifically the customers
- To evaluate the purchasing habits of current and potential customers
- To help in determining the preferences and requirements of customers
- To gauge and track the effectiveness of current marketing strategies
- To gain an understanding of the offerings, pricing, and promotional activities of our competitors
- To identify opportunities for market growth and develop new markets
- To predict upcoming market trends, it suggests the steps that you should take
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- What is Primary Market Research? Types & Examples
- Quantitative Market Research
- How to collect primary data for Market research?
- What is Sampling plan and its application in Market research?
- 11 Types Of Quantitative Research options that exist for Market Researchers
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
Industries Overview
Latest articles, social media users trust brands over influencers on finance, apparel, skincare, cash-back rewards drive consumers to open new credit cards, starbucks saying goodbye to global cmo role is part of a larger trend, ai will ‘supercharge’ creativity but exacerbate existing privacy concerns, says vml exec, coca-cola, gap adjust marketing strategies to stay lean, grow, openai’s sora could create a new era for video marketing—but it could also clutter youtube and tiktok, political ad spend is nearly triple what it was in 2016, banking industry chiefs say boring is good—and most customers agree, how the doj’s apple lawsuit could shake up the mobile wallet industry, offsite programmatic retail media ad spending is surging, about emarketer, guide to influencer marketing: trends, tactics, and kpis.
What marketers need to know about its growth and stability

Powerful data and analysis on nearly every digital topic
Want more research .
Sign up for the EMARKETER Daily Newsletter
For many, being a social media influencer has transformed from a side gig into a multimillion dollar business. Creators now have more say in the sponsored content they create for brands as well as the earnings they receive. And as creators continue to prove themselves as influential brand advocates, marketers are tapping these influencers for content beyond social feeds, including TV, out-of-home, and other digital media.
Influencers have also proven resilient amid economic uncertainty and an increasingly crowded space. Influencer marketing spend rose roughly 3.5 times faster in 2023 than social ad spending, according to EMARKETER’s July 2023 forecast.

In this guide, we explore the current state of influencer marketing, and why marketers, social platforms, and media companies should adjust their strategies as the power of the creator economy grows.
- Want to learn more about influencer marketing and other marketing trends? Sign up for the EMARKETER Daily newsletter.
What is the creator economy?
The creator economy , also called the influencer economy, is the interconnected ecosystem of creators, audiences, digital platforms, marketers, and agencies and/or vendors. The creator economy, as defined by EMARKETER’s Creator Economy Explainer report , enables creators to generate revenues in the form of money, goods, or services through their content, usually delivered via social media platforms. Meanwhile, marketers can partner with creators to build awareness for their brands.
Because interaction among stakeholders is constantly evolving, revenue data is sparse. A March 2023 estimate from Citigroup values the creator economy at $65.2 billion in 2023. By 2024, that figure is expected to reach $74.0 billion.
What is influencer marketing?
Influencer marketing involves a celebrity, content creator, subject matter expert, or public figure endorsing a brand’s product or service to drive social proof.
The market is rapidly expanding as influencer types have increased, with influencers filling every conceivable niche and sub-niche interest.
Here are the types of influencers, based on follower count and focuses:
- Mega-influencers: Often celebrity influencers, those accounts with more than 1 million followers
- Macro-influencers: Influencers with a follower count of 100,000 to 999,999
- Mid-tier influencers: Influencers with a follower count of 20,000 to 99,999
- Micro-influencers: Followers ranging between 5,000 to 19,999
- Nano-influencers: A community of 1,000 to 4,999 followers
- Kidfluencers: Gen Alphas with social followings that often review toys and games
- Gaming influencers: Esport and video game players who discuss game strategy and livestream while in-game
- Virtual influencers: Computer-generated avatars like Noonoouri, a fashion model and digital-only popstar
The pandemic sped up changes in influencer marketing that were already underway, such as the trend toward “unfiltered” or less-scripted content, the rise of TikTok, and the popularity of “everyday influencers” with genuine and relatable personalities like Elyse Myers.
Industries like financial services that hadn’t invested in influencer marketing earlier are also learning to navigate the space. And as ecommerce and social media converge, influencers will become increasingly vital intermediaries, helping to connect brands with consumers on social media.
Creators vs. influencers: What’s the difference?
Creators create content. Influencers are creators if the content they develop can sway the purchase decisions of a population regardless of whether they are being paid to promote a product. The term refers to a wide group of people from celebrities to loyal customers. Creators are influencers if their content affects purchase decisions.
Who is a creator?
Everyone has the potential to be a content creator thanks to how the term is defined. Adobe estimates there could be up to 303 million creators worldwide. For context, that figure is close to the US population at the start of 2023, per the US Census Bureau.
Most content creators worldwide are under 41, but there are creators of all ages, including Gen Xers and baby boomers, per Adobe.
Creators over 60 years old, dubbed “granfluencers,” have found popularity on social media due to their cross-generational appeal.
For example, Nonna Pia, a TikTok account with 4 million followers, features a grandmother who cooks classic Italian dishes while her grandson narrates. Similarly, the Instagram account “Excuse My Grandma” follows a grandmother-granddaughter duo as they discuss generational differences in dating, fashion, and more.
Creator categories
Although there is an account for every interest and target audience—from foraging to chiropractic medicine—lifestyle, fashion, and beauty are among the top creator categories.
While broad, these top categories overlap with many other industries, including travel, health, entertainment, food and drink, and art. Cross-category appeal is ideal for brand marketers looking to expand their reach to find like-minded audience demographics.
Areas that have seen recent growth in creator focus include:
Collegiate sports
A 2021 NCAA policy change allows college athletes to be compensated for their name, image, and likeness. College athletes already command large audiences and regularly create content on social media, per August 2022 data from Curastory.
B2B professionals
Industry professionals are increasingly building audiences by sharing B2B content online. For example, a “ LinkedInfluencer ” is an influencer on B2B social platform LinkedIn.
Nearly 1 in 4 people in the US are on LinkedIn, according to EMARKETER’s May 2023 forecast, as both the creator economy and B2B ad spending grow. As buyers get younger and B2B marketing becomes increasingly digital, authenticity and experience will matter more in marketing.
Financial services
In the financial sector, “ finfluencers ” use their social media platform to share videos that cover personal experiences, tips, and advice about investing, budgeting, financial trends, and the economy.
Finfluencers are capitalizing on a widespread lack of financial literacy. However, the quality of the content is controversial because some creators do not have a professional background in finance. Despite concerns, 60% of investors ages 18 to 35 use social media as a source of investment information, according to a Finra Investor Education Foundation report.
The generational response
Younger shoppers are more likely to use social media . About 129.5 million US Gen Zers and millennials will use social media in 2024, per a May 2023 EMARKETER forecast.
Younger shoppers are also more likely to follow and buy from accounts run by influencers. A Q2 2022 Klarna survey found that over 40% of Gen Zers and millennials worldwide follow influencers , compared with one-quarter of Gen Xers and less than 10% of baby boomers.

Millennials
Often considered a millennial concept, influencer culture is embraced by this extremely active social media user base. Close to 70 million US millennials will use social media next year, per EMARKETER’s May 2023 forecast.
Millennials look to trusted influencers for product recommendations, reviews, and as a discovery point for new brands.
They’re also willing to purchase what they see being promoted by their favorite influencers on social media. Over half (54.1%) of US social network users ages 25 to 34 will make a purchase on a social platform in 2024, per September 2023 EMARKETER data.
In 2024, 60.7 million US Gen Zers will use social media, according to EMARKETER’s May 2023 forecast. And while that growth is expected to continue through 2027, Gen Z will remain slightly behind millennial users.
Gen Zers, however, are not as sold on following influencers as their older peers. Less than half (48.6%) use social media to view creator/influencer content, according to a July 2023 EMARKETER survey’s findings.
Where influencers do have an outsize influence over Gen Z is women’s beauty and wellness. Close to 80% of Gen Z women rank creators as their most trusted source for beauty recommendations, a survey conducted by LTK found.
Those recommendations are also turning into online and offline sales. Eighty-three percent of Gen Z women shop for creators’ product suggestions online, and 82% shop for those items in-store.
Influencing by “de-influencing”
While the majority of influencers promote what to buy, some influencers are turning to platforms like TikTok to tell their followers what not to buy. As of January 2024, #deinfluencing videos on TikTok have roughly 1.3 billion views, up considerably from 208 million in February 2023.
Seen as a method to combat overconsumption in a tight economy, deinfluencing videos often offer economical alternatives to expensive products or discuss the pitfalls of fast-fashion shopping hauls.
Creators also use de-influencing videos to share critical commentary to distance themselves from brand controversies and post honest reviews of products that don’t meet expectations. Doing so can help reinforce creator trust through authenticity and transparency.
Influencer marketing spend
In 2024, advertisers will spend $5.89 billion on influencer marketing, a 14.7% increase YoY, according to EMARKETER’s July 2023 forecast, which excludes paid media.
US influencer marketing spend grew more than three times faster than social ad spending in 2023, and it will remain ahead through 2025, according to a July 2023 EMARKETER forecast.
Social platforms are reliant on creators, not the other way around, as creators’ options extend and include owned channels like blogs, podcasts, and newsletters.
A number of well-known creators, such as YouTuber MrBeast and podcaster Alex Cooper, have launched their own audio and video networks.
Although not every creator has a strong enough brand or following to create a successful media business , the growing success of these ventures should signal to brand marketers and entertainment companies that creators can offer much more than an outlet to generate hype or hawk goods.
Where influencers post sponsored content
Creators utilize a number of social media platforms.
To be impactful, influencer content should be engaging, entertaining, and educational, and marketers should work with credible creators who have built trust with their communities.
US marketers will allocate over $1 billion to sponsored content on each of the top four influencer marketing platforms in 2024, according to EMARKETER’s July 2023 forecast. When it comes to influencer monetization , Instagram posts were the top format that creators worldwide were paid by brands to create in December 2022, per a Later and Mavrck December 2022 survey. Here’s a look at the top social media marketing platforms for influencers.

Instagram remains the top platform for sponsored content, per a June 2023 report from Mavrck. About 98% of US creators share brand content via Instagram feed posts, Instagram Stories, and Instagram Reels, while 69.1% go live on the platform.
As of June 2023, more creators worldwide report being paid to create Reels (98.0%) compared with TikTok videos (89.6%).
Creator monetization: In May 2023, Meta began testing a new payout model for Ads on Reels. The monetization program pays creators based on the performance of the Reel, rather than the earnings of the Reel ad, per TechCrunch.

As TikTok’s popularity rises, brand opportunities for paid content is likely to increase as well.
Influencer marketing spending growth on TikTok has grown 27.8%, compared with 12.7% on Instagram, according to EMARKETER’s July 2023 forecast.
In 2024, over half of marketers (54.0%) will use TikTok specifically for influencer marketing, with $1.25 billion in US influencer marketing spend going to the platform, per the same EMARKETER forecast.
Creator monetization: If an influencer promotes a brand’s product on TikTok Shop, the social app’s ecommerce tool, they can earn a commission through product sales. For both brands and influencers, TikTok Shop holds a lot of promise and room for growth. In 2024, we expect 40.7 million TikTok users to make a purchase on the app.
YouTube, like Instagram and TikTok, has a solid hold on influencer marketing. YouTube is the top platform for US adults to follow influencers, according to March 2023 CivicScience data.
EMARKETER forecasts that in 2024, US marketers will spend $1.07 billion on influencer content for YouTube.
Similar to Instagram Reels, YouTube has been emphasizing Shorts as a cost-effective option for marketers.
Livestreaming is also leveraged by YouTube to connect influencers—and, ultimately, the brands they partner with—to followers. One-fourth (25.0%) of internet users say they watch creator- or influencer-led livestreams on YouTube, making it the most popular livestreaming app, ahead of TikTok (18.7%), Facebook (17.4%), and Instagram (14.0%), per an April 2023 survey by The Influencer Marketing Factory.

Creator monetization: YouTube attracts and retains creators in a number of ways. The platform offers a way to connect creator, artist, and brand stores to their YouTube channel, enabling users to more easily find and purchase featured products. YouTube also has affiliate shopping capabilities for creators interested in revenue opportunities.
Other platforms with influencer marketing potential include Facebook, Twitch, and to a lesser extent, Snapchat and X, the social media company formerly known as Twitter.
Despite its waning popularity among users, especially youths, Facebook is still expected to see $1.00 billion in influencer marketing spending next year, per an EMARKETER forecast.
Popular with the esports gaming community, livestreaming app Twitch recently launched a number of features for creators. In July 2023, Twitch announced its Discovery Feed, made up of livestream clips and ad features that help creators share their content from other platforms such as YouTube, TikTok, and Reddit.
Snap has struggled with ad monetization and commands a fraction of influencer marketing spend compared with larger platforms. In 2023, Snap crossed $40 million in influencer marketing spending, and is expected to see growth of 3.4% in 2024.
In October 2023, Snap released Creator Collab Campaigns, a suite of tools to facilitate brand-creator partnerships on the platform. Previously, Snap’s primary focus was helping creators monetize directly on the platform through programs like ad revenue sharing.
X (formerly Twitter)
X saw total US ad revenues decline by 54.9% in 2023 after Elon Musk’s 2022 purchase, according to EMARKETER’s October 2023 forecast, which means it is not an attractive platform for influencer marketing.
The aforementioned June 2023 Mavrck survey found that 45.9% of US creators shared promoted tweets, while a December 2022 Later and Mavrck survey found that 8.3% of creators worldwide have been paid by a brand to post on X.
Influencer marketing strategy
An influencer marketing strategy allows a brand to further its reach and tap new audiences, but narrowing down the right creator to work with requires an understanding of the landscape and what type of partnership will best serve the brand’s objectives.
Influencer marketing hubs: As influencer marketing took off, agencies dedicated to influencers sprang up to help brands manage the opportunity and vice versa.
Acting as a directory, influencer marketing hubs organize creator profiles by follower count per social platform, audience demographics, location, services offered, the price of partnership, and their interests (e.g., fashion, travel, home improvement, etc.), to take the guesswork out of selecting an influencer to partner with.
In addition to facilitating brand-creator relationships and identifying new talent, influencer hubs create campaign narratives, determine KPIs, and amplify influencer-led social campaigns, among other responsibilities.
For creators, working with an influencer marketing agency can be beneficial to scale and manage their own business. As influencer campaigns become more complex, an agency can manage payment, negotiate contracts, handle data analytics and reporting, and oversee other business functions.
Influencer marketing campaigns: An influencer marketing campaign is one that leverages the influence the creator has over their followers.
When in a paid partnership with a brand, the influencer campaign’s objective is to increase awareness, engagement, and, ultimately, sales. In comparison, an unsponsored campaign, while achieving the same objectives to various degrees, can be seen as more trustworthy and authentic by the influencer’s community.
Influencer campaigns fall into two categories:
- User-generated content (UGC) is organic content shared by a social media influencer to promote a brand or product without direct input from the featured brand. The influencer is not paid for UGC posts, and is often not as polished as content created with brand involvement. UGC posts range from product reviews, recommendations, tutorials, and personal experiences with a given good or service.
- Influencer-generated content is a collaboration between a creator and partner brand. These campaigns follow a brand’s creative guidelines—including tone of voice, talking points, aesthetics, and frequency of posts—to produce content fitting for that creator’s audience. As more influencers become trusted partners, brands have loosened the reins, allowing talent to tap into their own creativity for campaigns. Like UGC, influencer-led campaigns are more authentic and engaging, and may prove more effective for the brand involved.
Influencer posts: When paid for by a brand partner, an influencer post is a type of native advertising. When unpaid with no brand involvement, the post is considered UGC.
Most commonly seen on social media platforms, formats include Instagram photos with captions, short-form videos on TikTok, and long-form video content posted to YouTube. Influencers can also post written content on blogging platforms like Substack. Influencers will often promote their posts across various platforms to increase reach, engagement, and effectiveness.
While format is an important aspect of influencer marketing, the post’s creative should be at the forefront. According to EMARKETER’s Influencer Monetization 2023 report, the “three E’s” of influencer marketing should be remembered when creating posts.
“Regardless of the format, each piece of content should be engaging, entertaining, and educational to drive the most impact,” according to EMARKETER analyst Jasmine Enberg. Brands should also trust creators’ input on creative and format decisions because they know what will resonate best with their audience, Enberg continued.
Product launches: Influencers are an ideal way for a brand to launch new products.
When introducing a new product, brands can expand their reach by working with influencers with a similar following as the brand’s target audience. A kitchenware brand, for instance, may work with a popular food influencer to introduce a new range of pots to show off the products, its attributes, and how to buy.
As influencers become brands in their own right, many have launched their own product lines.
Thanks to an engaged and well-known audience, some influencers are able to develop products that align with the interests of the community they’ve built across their social media footprint.
For example, beauty vlogger and influencer Huda Kattan launched her own line of false eyelashes in 2013 after her community expressed an interest. Kattan then expanded the line into a full range of cosmetics. Huda Beauty, named after Kattan’s YouTube channel and blog, is now sold D2C and at Sephora.
Creators with large followings have launched food and beverage products, fitness programs, clothing lines, restaurants, and more to capitalize on their popularity and the value and willingness of their followers to support their businesses. Venturing into their own products also helps creators diversify their revenues and avoid alienating their audiences with too much sponsored content.
Collaboration: Similar to leveraging an influencer’s help to launch a new product, brands also partner with their stable of creators for product collaborations.
Often developed as a one-off or limited-edition product, brand-influencer collaborations can be a great source of product innovation.
In March 2023, Chipotle added two new limited-edition menu items to its quesadilla lineup, the “Keithadilla” and the “Fajita Quesadilla Hack,” which were developed and popularized by TikTok creators Keith Lee and Aleix Frost.
For some influencers, a brand collaboration may be a jumping-off point to developing their own product lines if the collaborative effort was deemed successful.
Common influencer marketing KPIs
These metrics are a good way for brands to measure their return on investment for influencer marketing campaigns:
- Facebook engagement rates (subscribers only): Engagement rate is defined as measurable interactions on social media posts, including likes, comments, favorites, retweets, shares, replies, and reactions, and is calculated based on all these interactions divided by total follower count.
- Facebook posts per week
- Instagram affiliate engagement rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that interacts with an affiliate influencer’s campaign or post on Instagram; this includes likes, comments, and shares.
- Instagram affiliate impression per follower rate : The number of affiliate-generated views that a specific post or piece of content received over a specific period of time on Instagram.
- Instagram affiliate reach : The percentage of followers and viewers from an affiliate influencer’s audience that is exposed to the affiliate influencer’s Instagram.
- Instagram affiliate view rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that views an affiliate influencers’ campaign or post on Instagram.
- Instagram engagement rates : Engagement rate is defined as measurable interactions on social media posts, including likes, comments, favorites, retweets, shares, replies, and reactions, and is calculated based on all these interactions divided by total follower count.
- Instagram posts per week
- Social affiliate clicks : The clicks generated by social influencer efforts, including generating traffic or leads (through affiliate links) to the company’s website.
- Social affiliate conversion rate : The percentage of clicks generated by social influencer efforts, including generating traffic or leads (through affiliate links) to the company’s website that also result in completed orders or purchases.
- Social affiliate engagement rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that interacts with an affiliate influencer’s campaign or post on a social media platform; this includes likes, comments, and shares.
- Social affiliate orders : The orders generated by social influencer efforts, including generating traffic or leads (through affiliate links) to the company’s website.
- Social affiliate sales : The sales or revenues generated by social influencer efforts, including generating traffic or leads (through affiliate links) to the company’s website.
- Social affiliate view rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that views an affiliate influencer’s campaign or post on a social media platform.
- TikTok affiliate engagement rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that interacts with an affiliate influencer’s campaign or post on TikTok; this includes likes, comments, and shares.
- TikTok affiliate view rate : The percentage of an affiliate influencer’s audience that views an affiliate influencer’s campaign or post on TikTok.
- X (formerly Twitter) tweets per week
Want more marketing insights?
Sign up for EMARKETER Daily, our free newsletter.
By clicking “Sign Up”, you agree to receive emails from EMARKETER (e.g. FYIs, partner content, webinars, and other offers) and accept our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . You can opt-out at any time.
Thank you for signing up for our newsletter!
Editor's Picks

Guide to ad agencies and holding companies: What they are and how they support marketing and advertising

Guide to Gen Z: What matters to this generation and what it means for marketers

Guide to Netflix for marketers and advertisers
Industries →, advertising & marketing.
- Social Media
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Browse All →
- Value-Based Care
- Digital Therapeutics
- Online Pharmacy
Ecommerce & Retail
- Ecommerce Sales
- Retail Sales
- Social Commerce
- Connected Devices
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Financial Services
- Wealth Management
More Industries
- Real Estate
- Customer Experience
- Small Business (SMB)
Geographies
- Asia-Pacific
- Central & Eastern Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- North America
- Western Europe
- Data Partnerships
Media Services
- Advertising & Sponsorship Opportunities
Free Content
- Newsletters
Contact Us →
Worldwide hq.
One Liberty Plaza 9th Floor New York, NY 10006 1-800-405-0844
Sales Inquiries
1-800-405-0844 [email protected]
- Advanced Search
Make IDC an Extension of Your Research Process
Get independent analysis for sound investment strategies
Independent Data
Rationalize company and market expectations utilizing independent expertise. More effectively model custom purchasing behavior through market surveys.
Unbiased, Educated Opinions
Gain insight into competitive dynamics across key tech sectors.
Efficient Delivery of Critical Information
A dedicated client relationship manager will ensure timely delivery of data and information.
Differentiated View of IT Markets and Companies
Receive differentiated and directed custom market intelligence. Perform custom analysis on pending technology IPOs.
IDC offers a comphrehensive and innovative research program tailored to the financial services community
IDC's Invenstment Research offerings provide an independent, targeted, and customized research program designed to support the generation of investment ideas, facilitate effective investment decisions, and evaluate technology companies.
How IDC partners with the financial services community
Monitor and build conviction in existing positions.
- Market and company historical data
- Market forecast
- Analyst conference calls/analyst meetings
- Custom SWOT Analysis
- Custom channel checks and surveys
Generate New Ideas (long and short)
- Published reports
- Company primers
- Thematic research - identify technology disruptions and disconnects
Launch Coverage on Companies, Sectors and Technologies
- Market data projections
- Market reports
Build and Maintain Company and Sector Models
- Rationalize and customize data to match company reports
- IDC key market assumptions
Understand Emerging Technologies
- IDC Innovator reports
- IDC 3rd Platform Spending Guides
Engage in Discussions with Industry Experts
- Web conferences
- IDC Directions
Industry Primers
Custom research support.
- Custom survey work
- Custom datacuts
Service Offerings
Investment research service offerings may include access to the following:.
- Global technology research
- Worldwide network of more than 1,300 analyst for 1:1 inquiry calls
- IDC Insights vertical research
- IDC IT Spending Guides
- IDC Quantitative Data Trackers
- IDC's Annual Directions conference and regular web conferences
- Custom Research such as user surveys, company analysis, data cuts from IDC's global analyst network
- Dedicated Client Relationship Manager
To learn more about IDC coverage
Case studies.
See how financial services clients leverage IDC’s global research and data.
Mutual Fund
Determine the potential impact of eu antitrust regulations on google, project description.
A mutual fund company requested datasets and calls with IDC experts to determine the potential impact of EU antitrust regulations on Google. The client has a position in Google in their investment portfolio.
IDC provided the following datasets to help the client answer the question including Google Android’s installed base by country, Android OS shipments and value (e.g. KitKat, Lollipop, Marshmallow, Nougat) with country splits, Android based smartphone market share by vendor with country splits, and Android market share projections in the EU and UK over the next five years.
Update market model and projections for hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs)
A hedge fund regularly uses IDC data to update their market model on HDDs and SSDs which includes suppliers such as Seagate, Samsung, Toshiba, and Western Digital. The client has multiple positions in this market in their investment portfolio.
The client receives off the shelf worldwide quarterly unit and petabyte shipments and revenue for the HDD industry, including supplier unit shipment and revenue market share and quarterly unit shipments, revenue, and capacity shipped for SSDs. Additionally, the client receives custom data on form factor, Terabytes, ASPs, $/GB, interface, etc.
The client also regularly utilizes the HDD and SSD analysts for inquiry calls for a dialogue on market dynamics, trends, and company news.
Private Equity
Determine historical and projected trends of ibm z systems and power systems.
IDC assisted a private equity firm with gathering research on IBM z systems and Power Systems including competitive positioning, historical unit shipments, annual revenue of new sales, and installed base for a potential software deal. The client also requested primers on the server market and several calls with IDC experts.
The client's objective was to determine the short and long-term stability of the current IBM mainframe installed base and the factors keeping the installed base in place as well as the threat from other servers (e.g. x86, hyperscalers).
Investment Bank (Equity Research)
Financial modeling for samsung.
A mobile devices research group creates revenue projections for Samsung and needs market sizing data for the entire mobile sector.
The group gathers relevant IDC forecast and market share reports for trend data to incorporate into their primer and confirms their hypothesis with an advisory call with top IDC industry analysts.
Investment Bank (Banking)
Determine market potential for an initial public offering (ipo) for an emerging technology company.
An investment banking group in the process of bringing a new company to the public markets needed updated market sizing data across several adjacent markets.
The group prepared custom analyses and relevant market share reports to validate product positioning statements for regulatory market filings.
Conducted several insights calls in Identity Access Management, Unified Communications and Collaborative market to provide details on changes with pricing models and potential impacts on emerging solutions.
Custom Project
Create total cost of ownership model for enterprise storage company.
IDC's Storage Team provided insight into an enterprise storage solutions company's (Project Y) competitive offering in the market as part of a due diligence process for an investment bank in support of an investment opportunity.
The IDC team developed 5 custom TCO models to compare Project Y’s offering against 5 competitive vendors forecasting over a 3-year timeframe. Final deliverable included a post-project debriefing with the analyst team.
Meet our Investment Research team. We provide concierge level service to provide our clients with efficient access to IDC’s global resources.
Meaghan Drennen
Research Director, Investment Research
Meaghan Drennen is a Research Director for IDC's Investment Research business and leverages IDC’s research capabilities to support the Tech Investor research program designed to help buy-side institutions make informed investment decisions about companies in the TMT sector. Meaghan provides primary account management to the Tech Investor client base including leading custom research projects and managing the client relationship team.
Michael Hennessey
Group Vice President, Investment Research
Michael Hennessey is a Group Vice President in IDC's Investment research group. Mike has more than 25 years of experience in technology research and financial services. Mike is the co-founder of IDC’s Tech Investor product.
As Group Vice President for IDC’s Investment Research business, Kevin Kane manages IDC’s Tech Investor (TI) and Investment Research Services (IRS) offerings to the Wall Street audience. Clients of the services include hedge funds, mutual funds, private equity firms, venture capital firms, and investment banks (equity research and banking).
Sloane Calvert
Senior Client Relationship Manager
Sloane is an experienced Sr. Client Relationship Manager for IDC’s Financial Services group working with Private Equity, Hedge Funds, Investment Banks to assist in providing Market and Company research including but not limited to, analyst conference calls, published reports, market forecast and historical data & custom research support to efficiently deliver critical information.
Frank DeLuca
Frank DeLuca is a Sr. Client Relationship Manager for IDC’s Financial Services business, including IDC’s Tech Investor (TI) and Investment Research Services (IRS) offerings to the Wall Street audience. Frank works closely with analyst teams across all research areas at IDC to curate IDC syndicated research and data into relevant format for the Wall Street audience.
Deborah Devine
Manager, Client Relationships
Deborah is a Sr. Client Relationship Manager for IDC’s Financial Services team, has previously worked for leading online financial information service providers and management consulting firms, and holds a M.A. degree from University of Connecticut and a M.S. degree from Simmons University.
Business Development Manager
With more than seven years of research experience in the Tech Investor market, Liam is focused on pushing IDC’s customized research content and relevant news to clients. He is also responsible for the theme planning and presentation content of communication activities.
Meg Scagnelli
Associate Client Relationship Manager
Meg is an Associate Client Relationship Manager for IDC’s Financial Services business including Tech Investor (TI) and Investment Research Services (IRS). Meg provides fundamental research support to sell-side, buy-side VC and private equity institutions.
Justin Sessions
Client Relationship Manager
Justin is an experienced Client Relationship Manager for IDC’s Financial Services team, who thoroughly enjoys assisting financial clients from firms such as Private Equity, Venture Capital, Equity Research, and others alike.
Senior Investment Research Manager
Eric curates technology insights from IDC’s global research network for fund managers and investment research professionals in Asia Pacific.
Research Vice President, Investment Research
Doug Bell is Research Vice President for IDCs Investment Research business, including IDC’s Tech Investor (TI) and Investment Research Services (IRS) offerings to the Wall Street audience. Clients of the services include hedge funds, mutual funds, private equity firms, venture capital firms, and investment banks (equity research and banking).
Learn more about IDC’s Investment Research offerings
Follow Polygon online:
- Follow Polygon on Facebook
- Follow Polygon on Youtube
- Follow Polygon on Instagram
Site search
- What to Watch
- What to Play
- PlayStation
- All Entertainment
- Dragon’s Dogma 2
- FF7 Rebirth
- Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
- Baldur’s Gate 3
- Buyer’s Guides
- Galaxy Brains
- All Podcasts
Filed under:
- Genshin Impact guides
Potion event recipes and market news list for Genshin Impact
How to make the best potions for the ‘Alchemical Ascension’ event
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Potion event recipes and market news list for Genshin Impact
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73210048/Alchemical_Ascension_1.0.jpg)
“ Alchemical Ascension ” is the keystone event of Genshin Impact version 4.5, prompting you to mix herbs together to make potions that follow news trends.
Completing the event will also reward a plethora of goodies: furniture, Primogems, a Crown of Insight, and a special weapon that you can only get from this event. The weapon, “ Dialogues of the Desert Sages ,” is a polearm that benefits healers, like Mika and Yaoyao. Again, you can only get this weapon (and its refinement material) from this event, so make sure to grab it before it’s gone.
As usual with Genshin events, “Alchemical Ascension” is split into three parts that are time-gated. Phase one started on March 14, phase two started on March 16, and phase three started on March 18.
You may be worried about messing up your potions early on, but don’t fret too much. As the event progresses, you’ll eventually be able to keep making potions and spamming cycles infinitely, so you can just keep making potions and earning revenue with no worry.
Regardless, we explain how to become a potion expert, potion recipes, and how market news works below.
How to make potions in Genshin Impact’s ‘Alchemical Ascension’ event
As of the first part of the event, you have 10 cycles to make potions. You can only make one potion per cycle and you can end the cycle by talking to Lisa. Throughout different cycles, the market news will tell you what people are into, and thus what potions will sell better.
Each potion is made up of different ingredients . You unlock more as you level up and you can grow them in pots at the potion making area. Each ingredient correlates to a specific efficacy : strength, constitution, dexterity, charisma, wisdom, or balanced. They also each have a different characteristic : endurance, warm, steadying, fragrant, healing, strengthening, relaxing, perception, focus, or technique.
The goal is to place the ingredients, like a puzzle, on to the grid in a way that creates a potion with specific stats and characteristics, leaving as few gaps open as possible.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25337892/GenshinImpact_2024_03_14_14_26_04.png)
As you place pieces, you can see how your potion will turn out on the left side of the screen. Hovering over the ingredient on the right side will also say what it adds to the potion. You’ll just need to keep adding the correlating plants until you get the desired result.
After selling the potions, you can buy upgrades (like a better cauldron or more planting pots) from a woman nearby. Your plants will also upgrade as they get used, unlocking more shapes to use during the puzzle portion of the event. You will also unlock the ability to combine ingredients to level them up, which we do recommend doing before you hit Sucrose’s expert exam, since this will let you craft better potions.
After cycle 10, you’ll be able to purchase bigger upgrades for your shop, like the ability to sell more potions at once. After you unlock enough slots, you ideally just want to stock your shop with high-level potions that cover all the different efficacies and characteristics. This way, you won’t really even have to pay attention to the market news to get rich.
You will eventually be able to buy out the shop’s upgrades completely, so after doing this, you can invest money into enhancing your potions at the cauldron.
Market news requirements, explained
Every couple of cycles, a new newspaper will get delivered to you, talking about the latest trends. As expected, we have to analyze these trends to make potions that suit whatever trend is occurring. However, the game doesn’t directly tell you which efficacy or characteristics are needed per trend — you kind of just have to guess. But you don’t actually, because we list out all the news and their related demands below, along with what cycle they appear in.
Note that in cycles eight through 10, you will get two random trends out of the four we list. From cycles 11 to 22, you’ll get a random group of two from the list every few cycles. From cycle 23 onward, the market news will be randomized from the marked entries below, and they will eventually begin to repeat.
There also appears to be some elements of RNG with what traits get associated per trend, according to both our experience and a few other guides . Each trend can have up to three traits, so if our table has more than three, you’ll have to guess and check. Have no fear, though, as the market news screen will confirm which efficacies and characteristics you got right. As mentioned above, though, you don’t have to stress about getting all the potions perfectly, as you’ll have an unlimited amount of cycles to play though in the end.
Genshin Impact ‘Alchemical Ascension’ market news efficacy and characteristics
Special customers and orders.
Starting in cycle eight, you’ll get some special orders from visiting NPCs. Some may have just straight up requests, whereas Sucrose may appear with more specific requirements to pass a potion-making exam. Everyone’s requests are the same across the board, so there’s no need to worry about an RNG element to get in your way. However, Sucrose’s potions may have different puzzle boards, with the blocking squares in different locations.
Beidou’s potion request
Beidou wants a constitution potion with relaxing characteristics. You can make this by using Calla Lilies and Dandelions . You can use mushrooms and berries to fill in any extra gaps to get those extra points, but don’t use too many. You don’t want their characteristics (endurance and warm, respectively) to overtake the relaxing characteristic.
Sucrose’s beginner alchemy exam
Sucrose wants an intermediate potion with a constitution efficacy. We used tons of Calla Lilies and Sweet Flowers to pass her test.
Diona’s potion request
Just like Beidou, Diona will eventually show up asking for a potion. She wants one with a wisdom efficacy or one that has steadying characteristics. You can use Qingxin or Windwheel Asters for the wisdom effect or Calla Lilies for the steadying effect.
Sucrose’s intermediate alchemy exam
The second time around, Sucrose will want an intermediate potion that has both strength and dexterity efficacies. We specifically used Jueyen Chilis and Horsetails to pass her test, but you can also use Flaming Flowers, Mist Flowers, and Dandelions.
Diluc’s potion request
Diluc wants a potion with both Constitution and Wisdom efficacy or one with Focus and Relaxing characteristics. You can use Calla Lillies , Sweet Flowers , Violetgrass , Qingxin , Windwheel Asters , or Lumidouce Bells if you’re focusing on the efficacies. If you’re focusing on the characteristics, you can use Berries , Zaytun Peaches , or Dandelions to help with that.
Sucrose’s advanced alchemy exam
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25342757/GenshinImpact_2024_03_18_13_09_00.jpg)
For your third exam, Sucrose will ask for an advanced potion that has Wisdom . This shouldn’t be too hard, but to complete the optional objectives (that reward coins), you’ll want to make sure that you fill in as many squares as possible, use five different ingredients, and make sure the potion has the Fragrant characteristic.
We used a mix of Lumidouce Bells , Windwheel Asters , and Qingxin for the Wisdom efficacy, and threw in three Sumeru Roses to give it the Fragrant characteristic. We also used Berries and Mushrooms to fill in the gaps.
Gorou’s potion request
Gorou just wants something that either has a Strength efficacy or an Endurance characteristic. By this point, you should have a ton of potions in your inventory that can probably fulfill his needs.
If you don’t, you can brew one by using Jueyen Chilis , Flaming Flowers , and Mist Flowers .
Sucrose’s expert alchemy exam
Sucrose’s final exam will require you to make an expert potion with a Charisma efficacy. You’ll also want to have Perception and Steadying characteristics to get that additional coin bonus.
We flooded our board with Sumeru Roses , Glaze Lilies , and Marcottes to get the Charisma stat. The Glaze Lilies added Perception, but we threw in some Calla Lilies for the Steadying stat.
Note that if you’re not getting an expert potion from using these ingredients, you may need to level up your ingredients more . Our main Charisma ingredients were all maxed level to make an expert potion.
Traveling merchant distribution strategies
Starting in the third phase of the event, you’ll unlock Atefeh, a traveling merchant who will sell your potions in Sumeru. You’ll need to give her potions that meet her required efficacies and also pick a specific distribution strategy. You can also unlock a Liyue merchant named Deyou by purchasing the “sales expansion contract” in the NPC shop for 600,000 coins.
Both of these merchants will request random efficacies, which you should be able to fulfill from what you just have in your inventory. However, both of the merchants have individual correct distribution strategies. For Atefeh, you want to use “ Akademiya Certification ” and “ Celebrity Endorsement .” For Deyou, use “ Free Sample Delivery ” and “ Hundred-Fold Guarantee .” Using these will net you the highest bonuses per sale.
The next level of puzzles.
Take a break from your day by playing a puzzle or two! We’ve got SpellTower, Typeshift, crosswords, and more.
Sign up for the newsletter Patch Notes
A weekly roundup of the best things from Polygon
Just one more thing!
Please check your email to find a confirmation email, and follow the steps to confirm your humanity.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Loading comments...

Embracer has sold Gearbox — and Borderlands — to Take-Two for $460M

Don’t Starve is getting a board game spin-off

- Dragon’s Dogma 2 guides, walkthroughs, and explainers
How to get to Agamen Volcanic Island in Dragon’s Dogma 2

LG’s tried and true 27-inch 1440p gaming monitor is $210

Honkai: Star Rail Penacony treasure chests locations and map

All pawn specializations in Dragon’s Dogma 2
Baltimore bridge collapse: What happened and what is the death toll so far?
When did the baltimore bridge collapse, what is the death toll so far, why did the bridge collapse, who will pay for the damage and how much will the bridge cost.
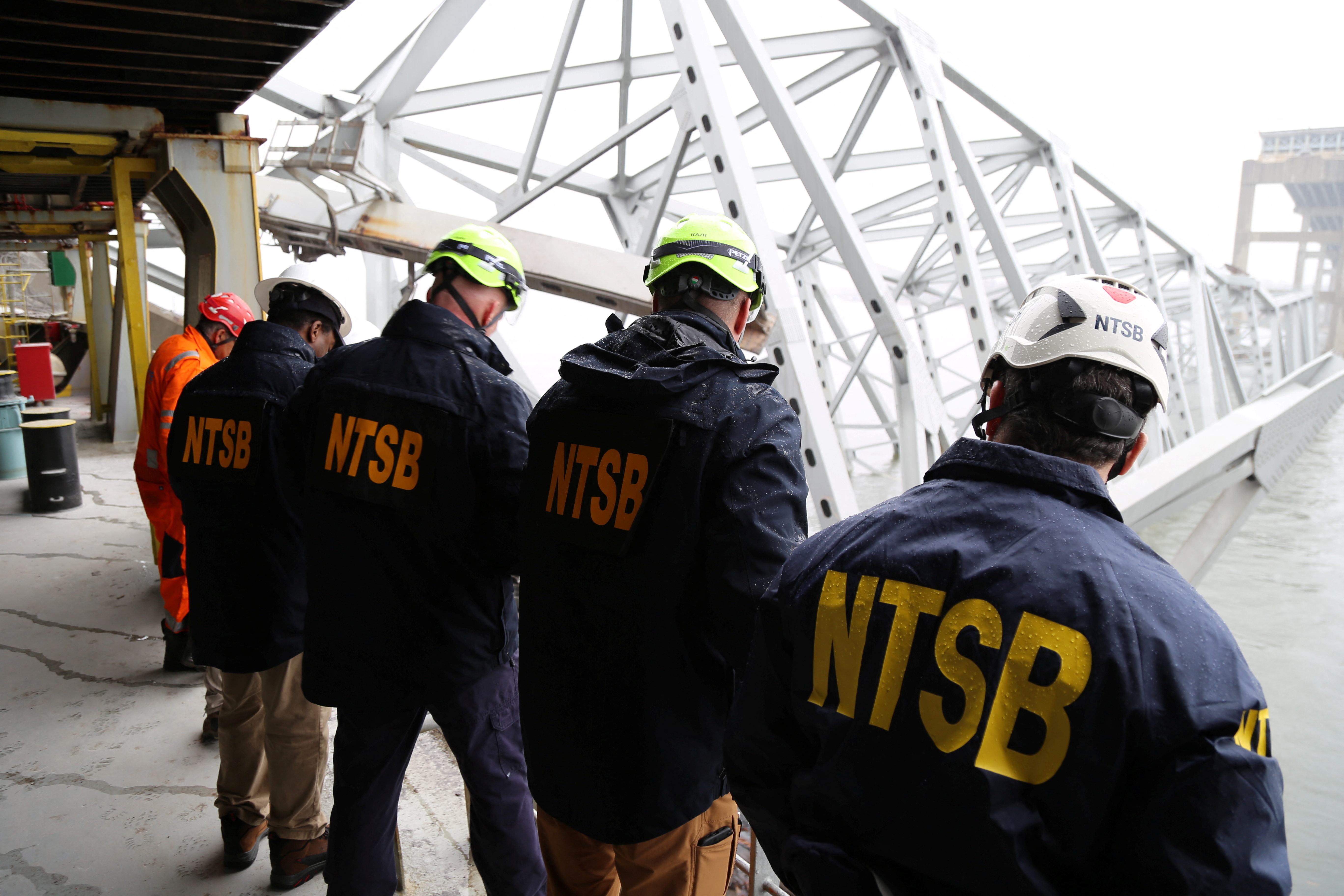

HOW LONG WILL IT TAKE TO REBUILD THE BRIDGE?
What ship hit the baltimore bridge, what do we know about the bridge that collapsed.

HOW WILL THE BRIDGE COLLAPSE IMPACT THE BALTIMORE PORT?

Get weekly news and analysis on the U.S. elections and how it matters to the world with the newsletter On the Campaign Trail. Sign up here.
Writing by Lisa Shumaker; Editing by Daniel Wallis and Josie Kao
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Lisa's journalism career spans two decades, and she currently serves as the Americas Day Editor for the Global News Desk. She played a pivotal role in tracking the COVID pandemic and leading initiatives in speed, headline writing and multimedia. She has worked closely with the finance and company news teams on major stories, such as the departures of Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey and Amazon’s Jeff Bezos and significant developments at Apple, Alphabet, Facebook and Tesla. Her dedication and hard work have been recognized with the 2010 Desk Editor of the Year award and a Journalist of the Year nomination in 2020. Lisa is passionate about visual and long-form storytelling. She holds a degree in both psychology and journalism from Penn State University.
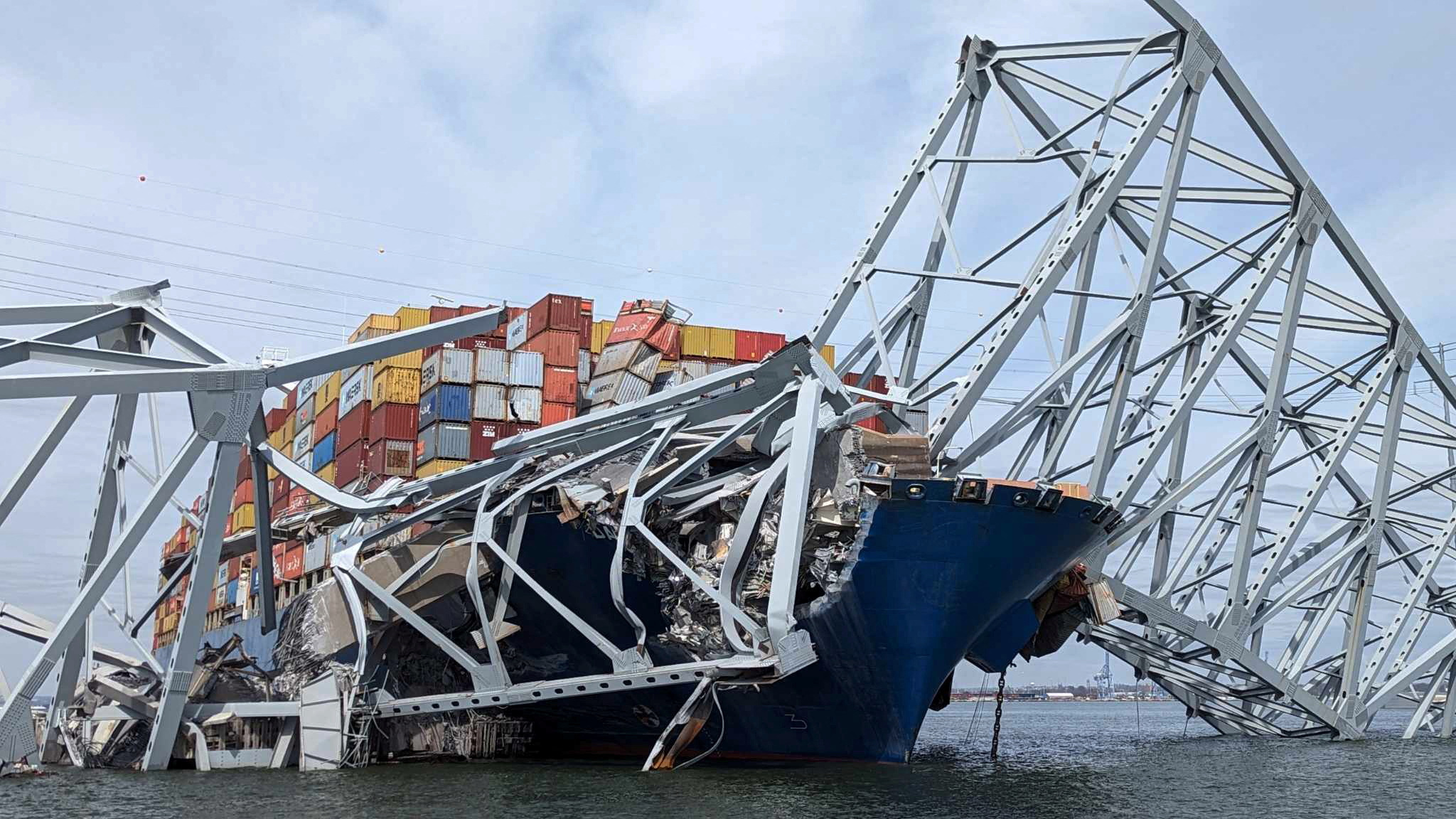

Latvian foreign minister resigns, Latvian public broadcaster says
Latvian Foreign Minister Krisjanis Karins said he would leave his post from April 10, Latvian public broadcaster LSM reported on Thursday.
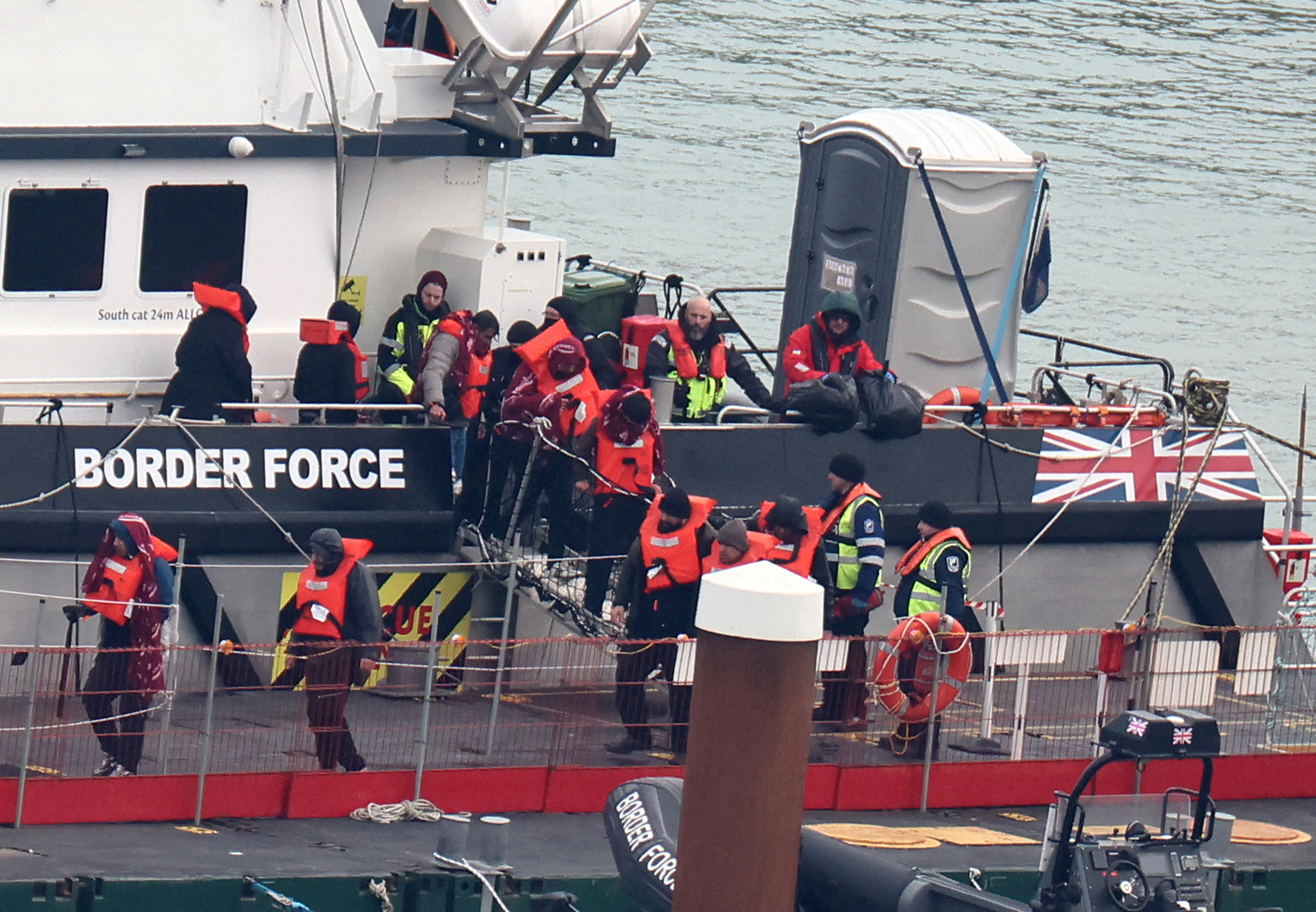

- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- Subscribers For Subscribers
- ELN Write for Entrepreneur
- Store Entrepreneur Store
- Spotlight Spotlight
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Save Big on Lifetime Access to This Stock Market App Through April 2 Learn how to make smarter moves on the market.
By Entrepreneur Store • Mar 27, 2024
Disclosure: Our goal is to feature products and services that we think you'll find interesting and useful. If you purchase them, Entrepreneur may get a small share of the revenue from the sale from our commerce partners.
Everyone knows that there is no "sure thing" on the stock market, but maximizing available data and information can go a long way toward achieving financial success. If you're aiming to expand your business portfolio, there's an app that delivers trusted intel on a daily basis at a surprisingly low price.
Through April 2 at 11:59 p.m. Pacific, you can purchase a lifetime premium plan for the popular Tykr Stock Screener app with an additional $20 off by using coupon code GET20. This low-priced, one-time purchase is primed to pay off with future peace of mind as a more confident trader and potentially in long-term earnings.
Tykr is designed to teach users how to identify high-risk and low-risk investments, providing real-time information on domestic and international stocks alike. This app also generates scores for specific stocks, supplying plenty to consider before making any moves.
Tykr serves up details on more than 30,000 stocks, and a premium plan expands your tool kit to include portfolio trackers and specialized filters. You'll also gain access to a community forum where you can share and compare experiences with other knowledgeable investors.
Tykr has a Trustpilot score of 4.9 out of 5 and a 4.8 rating on our store based on verified buyer reviews, including one from March 2024 that reads, "Tykr Stock Screener is a great product for me. It provides a reliable tool and awesome after-sale service to help make a meaningful stock trading decision. I love the Screener and would certainly recommend it."
Use daily insights to gain stock market confidence by picking up a premium plan to the Tykr Stock Screener app with an extra $20 savings via coupon code GET20 through April 2 at 11:59 p.m. Pacific.
StackSocial prices subject to change.
Entrepreneur Leadership Network® Contributor
Entrepreneur Store
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- She Never Wanted to Start a Business , But Chronic Insomnia Was Motivation — Here's How She Achieved 8 Figures in Sales and 8 Hours of Sleep a Night
- Lock There's a Retirement Crisis on the Horizon — See How Your Savings Compare to the Rest of Your Generation's
- Lock Is There a Superior Diet for the Entrepreneur? The 'Father of Biohacking' Shares What He Eats for High Energy, Low Body Fat and Optimal Output
- This Startup Pays Users to Watch Ads While Streaming Their Favorite Shows
- Lock A Side Hustle Consultant Shares the Most Lucrative Gigs Right Now
- He Owns and Operates a Dozen Popular Nightlife Venues in New York — Here's How He Kept All of His Businesses Afloat in a Crisis
Most Popular Red Arrow
How to improve your soft skills and emotional intelligence in 7 easy steps.
Using these simple but effective approaches will help a person in their business, life and relationships.
Secure Reliable Project Management Support for $25
This project management software comes with tools for generating timesheets, running what-if scenarios, and creating complex schedules.
ZipRecruiter vs. Indeed: Which is the Best Hiring Platform for Small Business
Diving into the strengths and weaknesses of ZipRecruiter and Indeed, we'll help guide small-business owners in choosing the ideal hiring platform.
These Are the 10 Best States for Starting a Side Hustle, New Research Reveals
One side hustle might not be as lucrative as another — and location matters.
I Started a Semi-Passive Side Hustle That Earns $33,000 a Week on Amazon: 'Selling There Is a No-Brainer'
Dr. Jenny Woo wanted to create a product that would help people connect, and it turned out to be a lucrative one.
CEO Gets Dragged After Posting 'Infuriatingly Cringe' Crying Selfie After Laying Off Employees
A LinkedIn post by Braden Wallake, the CEO of HyperSocial, is making the rounds for being out of touch.
Successfully copied link
Want to feel young? Protect your sleep
Feeling sleepy can make you feel ten years older. Researchers at Stockholm University have discovered that sleep affects how old you feel. The study is published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B .
Do you ever find yourself longing for the energy and vitality of your younger years? Feeling young is not just a matter of perception -- it is actually related to objective health outcomes. Previous studies have shown that feeling younger than one's actual age is associated with longer, healthier lives. There is even support for subjective age to predict actual brain age, with those feeling younger having younger brains.
"Given that sleep is essential for brain function and overall well-being, we decided to test whether sleep holds any secrets to preserving a youthful sense of age," says Leonie Balter, researcher at the Department of Psychology, Stockholm University.
In the first study, 429 individuals aged 18 to 70 were asked how old they felt, how many days in the past month they had not gotten enough sleep, and how sleepy they were. It turned out that for each night with insufficient sleep in the past month, participants felt on average 0.23 years older.
In a second study, the researchers tested whether it was indeed the lack of sleep causing participants to feel older. Therefore, they conducted an experimental sleep restriction study involving 186 participants aged 18 to 46. Participants restricted their sleep for two nights -only four hours in bed each night -- and another time slept sufficiently for two nights, with nine hours in bed each night.
After sleep restriction, participants felt on average 4.4 years older compared to when having enjoyed sufficient sleep. The effects of sleep on subjective age appeared to be related to how sleepy they felt. Feeling extremely alert was related to feeling 4 years younger than one's actual age, while extreme sleepiness was related to feeling 6 years older than one's actual age.
"This means that going from feeling alert to sleepy added a striking 10 years to how old one felt," says Leonie Balter, and states that the implications for our daily lives are clear:
"Safeguarding our sleep is crucial for maintaining a youthful feeling. This, in turn, may promote a more active lifestyle and encourage behaviours that promote health, as both feeling young and alert are important for our motivation to be active."
- Sleep Disorder Research
- Insomnia Research
- Healthy Aging
- Staying Healthy
- Sleep Disorders
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Child Development
- Social cognition
- Facial rejuvenation
- Panic attack
- Human parainfluenza viruses
- Fatigue (physical)
- Inferiority complex
Story Source:
Materials provided by Stockholm University . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Leonie J. T. Balter, John Axelsson. Sleep and subjective age: protect your sleep if you want to feel young . Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences , 2024; 291 (2019) DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2024.0171
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Robot, Can You Say 'Cheese'?
- Researchers Turn Back the Clock On Cancer Cells
- Making Long-Term Memories: Nerve-Cell Damage
- A Solar Cell You Can Bend and Soak in Water
- Risk Factors for Faster Brain Aging
- Deep Space Objects Can Become 'Ice Bombs'
- Want to Feel Young? Protect Your Sleep
- Century-Old Powdered Milk in Antarctica
- New Artificial Reef Stands Up to Storms
- Persistent Hiccups in a Far-Off Galaxy
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Avoid making your objective into a hypothesis with absolute statements and assumptions. Your objective should be more of a question than a prediction. That comes later. Objective: Uncover the purchase journey of our target demographic. Assumption: Uncover what part search plays in the purchase journey of our target demographic.
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8. Identify the research problem. Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
Set your goals and objectives based on your vision for where you want your company to BE and not where it is NOW. An Example: If the vision and mission of your business is to help your customers be successful in their business — then imagine your customers being successful and then imagine in what ways you are helping them do that.
Download HubSpot's free, editable market research report template here. 1. Five Forces Analysis Template. Use Porter's Five Forces Model to understand an industry by analyzing five different criteria and how high the power, threat, or rivalry in each area is — here are the five criteria: Competitive rivalry.
1. Define the problem or opportunity and state your objectives. When creating a new goal, it is important to recognize any current problems in a company. You should also work to see whether a problem can be molded into an opportunity. Basic marketing research courses explain that a management problem is any type of issue that needs managerial ...
1. Define Objectives. Before diving into market research, it's crucial to define the research objective. This foundational step forms the groundwork for an effective market research process. Start Broad, then Narrow Down: Begin by identifying the overarching goal, such as understanding customer preferences.
Step 5: Make decisions for your business. Now it's time to take your findings and turn them into actionable insights for your business. In this final step, you need to decide how you want to move forward with your new market insight.
Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer. In other words, it's the process of ...
There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four. "Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research," says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing.
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. ... Objectives - The objective of a market research report is to define the problems, identify key issues ...
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example: This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
Here are a few examples: Increase organic search visibility in the U.S. from 6% to 8% by the end of 2023. Increase search ad impression share from 47% to 65% in the U.S. among Site Audit tool buyers by the end of 2023. Increase marketing podcast audience monthly reach from 300,000 to 500,000 by the end of 2023. How to measure it.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps. The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours. 1. Create simple user personas. A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data ...
1. Define the Research Goal. The first step of the process is defining your goal. It is important to start with a clear idea of why you are doing the research and what you want to accomplish. If your motivation is vague, you risk straying from your objectives and becoming distracted by irrelevant information.
Research objectives are the specific questions that you want to answer in your market research project. They guide the design, data collection, analysis, and reporting of your study.
Market research is defined as the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data about a specific market, industry, or consumer segment. It involves studying customers, competitors, and market dynamics to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and make informed business decisions. Market research provides valuable insights into ...
A marketing research problem in this example is to discover the needs of the community and also to identify a potentially successful business venture. Many times, researchers define a research question or objectives in this first step. Objectives of this research study could include: identify a new business that would be successful in the ...
Marketing research objectives. Marketing research aims to identify challenges and opportunities to achieve marketing goals. Companies process data, analyze data, and interpret relevant facts to provide valuable information about it. Research results also help companies plan, evaluate, and develop marketing strategies and tactics.
Step 1. Define the Problem and Translate It into Research Objectives. This is the most important step. It sets the direction of the whole market research process. Ask clients how they will use the research results, and what business decisions they will make based on the data. They should be specific.
A market research plan will help you uncover significant issues or roadblocks. Step 1. Conduct a comprehensive situation analysis. One of the first steps in constructing your marketing plan is to create a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis, which is used to identify your competition, to know how they operate and ...
Market research is the process of assessing the viability of a new good or service through research conducted directly with the consumer which allows a company to ...
Conclusion! To conclude, the objectives of marketing research can be summarized in the following points-. To identify and comprehend the target audiences, specifically the customers. To evaluate the purchasing habits of current and potential customers. To help in determining the preferences and requirements of customers.
An influencer marketing strategy allows a brand to further its reach and tap new audiences, but narrowing down the right creator to work with requires an understanding of the landscape and what type of partnership will best serve the brand's objectives. Influencer marketing hubs: As influencer marketing took off, agencies dedicated to ...
Objective: Determine market potential for an Initial Public Offering (IPO) for an emerging technology company. Project Description. ... Investment Banks to assist in providing Market and Company research including but not limited to, analyst conference calls, published reports, market forecast and historical data & custom research support to ...
She helped launch the Rift Herald in 2016. " Alchemical Ascension " is the keystone event of Genshin Impact version 4.5, prompting you to mix herbs together to make potions that follow news ...
A U.S. Coast Guard search and rescue helicopter flies over the Dali cargo vessel, which crashed into the Francis Scott Key Bridge causing it to collapse in Baltimore, Maryland, U.S., March 26 ...
Through April 2 at 11:59 p.m. Pacific, you can purchase a lifetime premium plan for the popular Tykr Stock Screener app with an additional $20 off by using coupon code GET20. This low-priced, one ...
The skyrocketing share price comes despite the fact that Trump Media is burning through cash; piling up losses; and its main product, Truth Social, is losing users.
It turned out that for each night with insufficient sleep in the past month, participants felt on average 0.23 years older. In a second study, the researchers tested whether it was indeed the lack ...