- Our Mission

8 Tips to Power-Up Your Classroom Presentations
Last month, I attended a Back to School Night for parents, sitting through presentation after presentation by teachers, some with slides that helped make their presentation a delight to listen to, and others . . . well, that's why I'm writing this blog post.
The goal of a classroom presentation is to aid you in effectively conveying information in a way that allows students (or their parents) to remember what you said. Unfortunately, for some, the presentation becomes a crutch, and they begin to rely on the slides to tell their story, rather than to help them tell the story.
I've been creating presentations using software like PowerPoint and KeyNote for 20 years, and I've learned a lot about how to most effectively communicate. Here's what I've found.
1. Use as Many Slides as You Need
It's a common myth that better presentations use fewer slides. This is simply not the case. I once sent an education conference presentation to the organizers so they could preview it in advance of my speaking. They wrote back, concerned that my 45-minute presentation had 116 slides. I looked it over and realized they were right! I revised it and sent a presentation with 135 slides back to them. I finished my talk with 5 minutes to spare -- just enough time to take questions -- and the presentation was a huge success.
The number of slides in your presentation is irrelevant. What matters is how well your slides communicate and how much time you spend talking about each slide. Spending five minutes on five slides will almost always be more engaging to your students than spending five minutes on a single slide, even when the information is exactly the same.
In the movie Amadeus , the Emperor of Austria complains to Mozart that his music has "too many notes." Mozart responds, "There are just as many notes as are required. Neither more nor less." Use as many slides as you need to make your point. No more. No less.
2. Minimize Verbosity
Your slides are there to support what you are saying, not to say it for you. Keep your word count low, and only place one main point on a slide, plus three to five sub-points if absolutely needed. Remember tip #1 above -- don't be afraid to use more slides. They're free! Also, the language in your slides doesn't need to be in complete sentences. Pare the text to as few words as possible, using what's there only to emphasize and reinforce -- not replace -- the words coming out of your mouth.

3. Maximize Visuals
Photos, figures and icons work as visual memory triggers. They help your students remember what it is you're saying. Any time you can add a visual that helps illustrate or reinforce the points you're making in your slides, you should use it. One great way to do this on the cheap is to use public domain or creative commons photos you can find on Flickr or Google .
4. Reduce Noise
Many teachers like to add banners, headers, footers, page numbers and more noise to their slides. Unless the information needs to be on every slide for a vital reason (which is rare), you should remove it. All these redundant elements do is create distractions from the content of your slides. I find this to be especially true of page numbers. Imagine if a movie included a time code at the bottom, constantly reminding you how long you had been watching. All this does is serve to take the viewer out of the moment. Page numbers in slides really don't provide any useful information -- they just remind your students how long they've been watching.
Pursuant to tips #1 and #2, you're not going to win awards by cramming the most content on the fewest slides. Make text and visuals as large as you can. Not only does this make them easier to see and read, but larger images and text make a greater impact to aid memory. There's nothing wrong with filling an entire slide with a photo, and then placing text right on top. You may have to use a transparent background immediately behind the text so that it's clearly readable, but the overall effect is almost always more memorable than just some text beside an image.

6. Highlight What You Are Talking About
While you are presenting, your students may be momentarily distracted taking notes, thinking about what you are saying, glancing out the window, possibly even daydreaming. When they refocus on your slides, though, they need to quickly pick back up where you are, or you risk losing them again.
- Use contrast or call-outs to clearly show the area of the slide you are talking about.
- Reveal bullet points or table rows one at a time so that the last one visible is the one you are talking about.
- Use arrows, circles or other pointers to show what you are referencing in specific parts of an illustration, photo or graph.
- Animate and reveal parts of illustrations and graphs (where possible) to build your story rather than showing everything at once.
- Use bold type or different colors to highlight the keywords in any lengthy text.
7. Transition Changes
Humans suffer from an affliction called change blindness -- we have a hard time seeing changes unless there is a clear transition between the states. This is especially a problem in presentations where slides may look very much alike. Most programs include transitions that can be used between slides or on elements in the slides themselves.
My favorite transition is the cross-dissolve -- where the first slide fades down while the next slide fades up -- but different transitions can help illustrate points in your presentation. Are you talking about combustion or the fire of London? Use a flame transition. Talking about photography or Hollywood movies? Use the flashbulb transition. Even "cheesy" transitions help overcome change blindness and aid student memory at the same time.
8. Repeat Yourself Redundantly
It’s OK to repeat the same slide more than once -- especially when using images -- if you are reminding students of an earlier point. Obviously, this is not a license to be monotonous. However, if you want to tie separate ideas together, emphasize a point or splash in a little comic relief, it's perfectly fine to repeat a slide.
Bonus Tip: Make it Funny!
There's little doubt that emotional responses can aid memory. While it can be difficult to apply this power in a classroom slide presentation, humor is easy enough, and adding a bit of levity to your presentations at the right points can work to give students vital memory hooks.
Remember, the point of presentation slides is not to replace you as the teacher, but to help your students understand and remember what you are teaching. Overwhelming them with too much information can be just as harmful as underwhelming them with too little.
The Ultimate Guide to Effective Teacher Presentations: Strategies & Tips

Dianne Adlawan

Teachers, by nature, are considered professional presenters. Their main responsibility is to talk in front of their students to relay educational knowledge, sharpen their minds and skills, and even serve as a second guide alongside their parents. They also speak in front of parents, co-teachers, and school administrators. This just means that preparing for a presentation is already not new to them.
Still, teachers can become so comfortable with their presentation routine that their techniques turn into autopilot. The result of a repetitive task can become tiring and not challenging anymore which may result in students losing interest or attention span in the process.
The tips featured in this article are dedicated to these hard-working professionals. This will help them prepare and perform a better presentation in front of any type of audience.

Why You Should Prepare for a Presentation
- Preparation helps you build to structure your thoughts to create a well-organized presentation. By taking the time to prepare, you can decide what information is most important, plan the flow of the presentation, and make sure that everything is connected and easy to follow.
- Second, it allows you to think ahead of the questions that your audience might ask. Especially if you’re giving a presentation to a group of various audiences, who are curious about the topic at hand. By preparing in advance, you’ll be able to answer any questions they may have, which will not only increase their understanding but also boost your credibility as a teacher.
- Lastly, preparation helps you make the most of your time. Advanced preparation ahead of the presentation can ensure that you’re not wasting time trying to organize your thoughts at the last minute.
Effects of an Organized and Well-Planned Presentation
An audience engages with a speaker who knows their words and poses a confident attitude. While the projector may display clear and concise slides, the presenter is the main ingredient to every presentation.
For teachers, a well-planned lesson presentation helps the teacher maintain the attention and interest of their students, which is crucial for effective learning. Additionally, being organized and prepared will help teachers convey their ideas more effectively and it will help the teacher to feel more confident, which also impacts their teaching and in turn can help to build trust and rapport with their students.
Possible Outcomes of An Unprepared Presentation
Let’s suppose you haven’t allocated enough time to plan and prepare for an important presentation. What could be the potential outcomes?
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Lack of preparation can lead to increased anxiety and stress, which can not only hinder your ability to deliver a convincing presentation but also hurt your mental health and work balance. It can cause a “mental block,” causing you to lose focus and concentration during your delivery.
- Poor Presentation Delivery: Without proper preparation, your presentation can appear scattered and disjointed. This can lead to an incoherent message that fails to convince your audience.
- Diminished credibility: Delivering an unprepared presentation can harm your reputation as a professional. It can portray you as disorganized and unreliable which could lead your colleagues or students to question your competence and reliability.
Effective Visual and Content Organization Tips
Consider this as the first stage towards an effective teacher presentation. Before moving on to improving your verbal communication cues, let’s enhance first your presentation visuals and content.
Visual Tips
1. add powerpoint animations and different media.
Establishing an attractive slideshow is one of the keys to a successful presentation. This will put a good impression on your audience that you’re prepared just by seeing how well-designed your presentation is. Of course, images add to slideshow attraction, but consider adding another forms of media such as GIFs and videos, as well as animations! Microsoft PowerPoint has a lot of fun & captivating features that you may not be aware of. Check out this example of an easy yet appealing Slide Zoom trick in PowerPoint that you can add to your presentation to wow your audience.
@classpoint.io Did someone say FREE??? Yes, we did. Here are free websites to help you upgrade your next PowerPoint presentation! 😎 #powerpoint #presentation #design #studytok #edutok #tutorial #tipsandtricks #ai ♬ original sound – r & m <33
Read Next: Make Your Presentations POP With This PowerPoint Animation Template
2. Use Readable Font Styles
Make sure to use the best font style that makes your presentation look sleek, readable, and won’t strain your audience’s eyes while reading. We all want to use a fancy font, trust me, I get it. But most of the time, simplicity is beauty, especially if you’re presenting a professional-looking slideshow. Font styles such as Poppins, Tahoma, Verdana, Montserrat, and Helvetica are great examples of font styles that screams simple yet professional to look at.
On the other hand, font styles such as Bradley Hand, Comic Sans, and Chiller are not ideal choices as they are not meant to captivate your audience’s eyes. And another tip is to stick to two or three fonts only!
3. Use Relevant Graphics
Selecting graphics for designing your presentation depends on your audience and the goals you aim to achieve with the presentation. For example, if you are presenting in front of students and your goal is to keep them engaged, motivated, and actively participating, then you might consider incorporating charts, tables, and relevant shapes into your design.
It’s important to remember that your presentation design should align with the theme of your topic.
Free Websites to Upgrade your Presentation Graphics:
- Craiyon. com
- The Noun Project
4. Use Audience Engagement tools to Activate Learning
Want the quickest solution to an engaged audience? Well, it’s audience interactive activities! Adding interactive activities to your presentation can help keep your audience engaged and interested. One of the easiest ways to do this is to use ClassPoint, an audience engagement tool added right into PowerPoint presentations.
With ClassPoint, you no longer need to worry about strategies to keep your students engaged, as this tool transforms PowerPoint into a teacher presentation tool with a teacher toolbelt and student quizzes , polls, and games that make presentations more fun & engaging.
By combining ClassPoint with your presentation techniques, you can focus solely on setting up your lesson content in PowerPoint and allow ClassPoint to handle the rest for achieving a learning-activated presentation lesson .
🔍 Learn more about ClassPoint, the teacher add-in for better lessons & student engagement 👍
5. Use a Laser Pointer
Help focus your audience attention by using a laser pointer!
With the help of a laser pointer device, teachers are able to attract the attention of their audiences and concentrate on essential points in their presentations. Highlighting these main ideas and terms assists the speaker in organizing their speech, preventing distraction, and increasing retention of the information presented.
You can use a physical laser pointer & clicker, or with the addition of ClassPoint into PowerPoint, presenters can easily turn their cursor into a laser or a spotlight . This can make it even easier for students to follow along and is a convenient tool for creating a more captivating teacher presentation.
Secret tip: if you write on your slide with the laser, it will leave disappearing ink! 🪄
Content Tips
1. research and fact-check your presentation.
As educators, it is crucial to equip ourselves with reliable and accurate information before presenting to our students. We have a responsibility to not only educate them but to also mold them into critical thinkers who are equipped with factual knowledge. Without thorough fact-checking, we risk disseminating misinformation and hindering their intellectual growth.
To avoid such situations, we must prioritize research and fact-checking before presenting any information. Conducting research helps us not only in finding accurate information but also in ensuring that the sources we use are reliable and credible. Moreover, taking the time to fact-check demonstrates our commitment to providing students with high-quality education and the desire to create a safe and accurate learning environment.
2. Be Prepared to Anticipate Questions during the Presentation
It is important to be well-prepared for a presentation especially anticipating and addressing questions. This applies particularly to a teacher presentation, as educators face varied expectations and questions. Adequate preparation allows you to organize ideas and justifications, and it can deepen understanding, boost confidence, and improve adaptability. Addressing questions, makes your audiences feel heard and appreciated. This will result in comprehensive presentations, enhanced confidence, improved information flow, and an atmosphere of respect and understanding.
A great & visual way you can elaborate, or explain your material in new ways, is by using ClassPoint’s whiteboard tools added to PowerPoint. ClassPoint’s added toolbar presents teachers with unlimited whiteboard slides they can open whenever they need, and user-friendly yet comprehensive pen tools with available shapes, and text boxes. Plus you can also use ClassPoint’s quick poll or other question types to assess students’ understanding with hard data & insights.
Addressing questions well makes your audience or students feel heard & appreciated leading to improved learning, enhanced confidence, and a respectful, safe learning environment.
3. Provide an Outline Structure of your Content
When you are preparing your presentation, it is best to first create an effective outline structure that will guide your presentation flow and help you focus on the main learning objective. But what you may not be doing, is offering that outline structure to your students, but you should!
Providing students with a clear understanding of what this lesson is about, the structure of the lesson, and what they will be able to take away from it is important. By doing so, you can help students stay focused and follow along with the material. Additionally, you are setting expectations and ensuring that everyone is on the same page, which can help promote student autonomy. So, include an outline at the start of your presentation lesson.
Step-by-Step Strategies for a Successful Presentation
Before presentation, know your audience, your students, or observers.
Once you have completed your deck, you may want to add a guide script and any additional notes with important points you don’t want to forget or you want to highlight in your presentation to impress your students .
Practice your presentation delivery/lesson
Practice delivering your presentation give you a chance to fine-tune your content and get your facts down. This will help you become more comfortable with the material and identify areas that need improvement. You can practice in front of a mirror, record yourself and watch it back, or even rehearse with a colleague or friend. When practicing, pay attention to your posture, tone of voice, and pacing. By doing so, you’ll be able to deliver a confident and engaging presentation that will captivate your audience.
Use a friendly tone of voice and pace
Adjust your tone to match your message, and avoid speaking too quickly so that your audience will get the chance to absorb the information you’re sharing. By being mindful of these aspects, you will capture your audience’s attention and leave them feeling informed and inspired.
Use engaging body language
Body language is essential for engaging your audience during a presentation. Stand up straight, make eye contact, and use hand gestures to emphasize important points. You can also move around the classroom to keep your students’ attention. By using engaging body language, you’ll be able to convey your message more effectively and keep your students interested throughout the presentation. You’ve got this!
During Presentation
Create an icebreaker.
Having an icebreaker is a warm-up for your students’ brains, allowing you to focus and engage with the material being presented. It also helps break down any barriers or tension between the presenter and the audience, making for a more relaxed and welcoming atmosphere. Additionally, an icebreaker provides an opportunity for the presenter to showcase their creativity and personality, adding an extra level of excitement and engagement to the presentation.
Good thing that ClassPoint has numerous features to help you perform an entertaining and unforgettable icebreaker. Here are some examples that you can use during an icebreaker.
- Quick Poll : Quick Poll allows you to create interactive polls right inside your presentation. When used as an icebreaker, it can engage the audience, initiate discussions, and provide valuable insights that help tailor the content to participants’ preferences.
- Word Cloud: Presenters can ask thought-provoking questions related to the topic or general interest. Using Word Cloud, the audiences can answer through their mobile which can be instantly seen as collective responses, with the most frequently mentioned words appearing larger.
- Short Answer : In short answer, you can challenge your audiences’ thought process in a short-form writing activity with no options to get from to test their ability to understand.
- Image Upload : Using single image, audiences can interpret what they feel like, or their mood using only the photos in their gallery or surroundings. A creative yet fun way for an icebreaker!
Speak clearly
Effective communication is crucial when presenting important information to students. Speaking clearly helps ensure that students understand the concepts being taught and follow instructions effectively. As a teacher, it’s important to focus on clear speech to promote effective communication and help your students comprehend the material being presented.
Pay attention to your audience’s attention
Since distractions are aplenty, attention spans are dwindling, it’s important for presenters to captivate their audience’s attention right from the beginning. For teachers, when speaking in front of your class, you should not only focus on the content of your presentation but also on your students’ attention.
To ensure that your students won’t start drifting away or zoning out, start with a compelling opening that immediately grabs their attention. Use vivid storytelling, examples, or demonstrations to engage your students and drive home your message. Don’t forget the power of humor, and never be afraid to be yourself – authentic, passionate, and confident.
Add Personality: share short relatable stories
“A great personality makes everyone feel energized; just like a flower’s fragrance that freshens ups the complete surrounding.” 29 Personality Quotes to Achieve Greatness
As to what is stated in the quote, having a positive and vibrant personality affects the overall mood of your surrounding, it can capture the audience’s attention and maintain their interest throughout the presentation. While the ultimate goal is to deliver a presentation rich with new learnings and knowledge, adding humor can do no harm to lift up the mood in the room. You might want to start by segueing a short story that your students can relate to and make interactions by encouraging them to share a story too or ask questions.
Post-Presentation Reflection
Take the comments by heart.
Receiving feedback from your students is a great way for evaluating the efficacy of a teacher presentation. This can help you identify areas where you can improve and tailor your teaching tactics to better suit the needs of your students. Listening to your students’ feedback can also promote a feeling of cooperation and enable them to become more actively involved in the learning experience. So, don’t be afraid to ask for feedback and take it to heart in order to continually improve your presentations.
Experienced educators understand that they are perpetually crafting their skills, and feedback from their audience brings an opportunity for professional advancement. In addition, accepting audience feedback illustrates esteem and worth for the students’ views. It promotes a feeling of cooperation and enables students to become more actively involved in the learning experience.
Preparing for a presentation is essential for teachers to deliver engaging and impactful content to their students. By structuring thoughts, anticipating questions, and preparing ahead, teachers can achieve a well-organized presentation that will enhance the students’ understanding and leave them feeling confident.
By following our strategies and tips teachers can achieve successful lessons using PowerPoint presentations. And, with the help of an advanced educational technology tool like ClassPoint, teachers can create dynamic and memorable presentations that their students will enjoy and actively participate in.
Try out ClassPoint today and experience a whole teacher presentation in PowerPoint! ✨
About Dianne Adlawan
Try classpoint for free.
All-in-one teaching and student engagement in PowerPoint.
Supercharge your PowerPoint. Start today.
500,000+ people like you use ClassPoint to boost student engagement in PowerPoint presentations.

Effective Communication in the Classroom

Why is It Important?
In a student-centered classroom, the instructor should not be speaking all of the time. However, when you are speaking, students count on you to: provide clarity by highlighting key ideas; elaborate on difficult concepts; and provide clear instructions for in-class activities. These messages should be backed up by appropriate visual aids that reinforce what you are talking about: board work, slides, and/or handouts.
In-class communication can be thought of as consisting of verbal, vocal, and visual channels.
Verbal channel
The verbal channel relates to word choice: the same content or point can be delivered in different ways using different words. Those differences in delivery affect how students comprehend and engage with the material.
The verbal channel can clarify and reinforce course content by:
- Defining and using discipline-specific vocabulary.
- Verbally outlining your presentation. Verbal indicators can signal transitions between ideas, helping students make connections to their prior knowledge and experiences, follow along, and organize their notes.
The verbal channel can also be used to send growth messages and create an inclusive classroom. For example, the way you respond to students’ questions and incorrect answers can be an opportunity to create a warm classroom climate but are often not something we consider rehearsing.
When a student asks a question:
- Try to call on them by name. This will help to create a sense of belonging.
- Thank them for their question to motivate them to ask questions again in the future.
- If a question is common, say so. This will help the student see that others’ have needed clarification on this point as well.
If you pose a question and a student responds with an incorrect answer:
- Thank the student for responding.
- If the student’s response is in line with a common error, say so, so they do not feel alone in their misunderstanding.
- Ask the student about the process that they used to come up with the answer to better understand where they made a misstep. This emphasizes process over product and also teaches good troubleshooting strategies.
- If a student’s answer is partially correct, ask another student to add on or clarify the response.
Certain verbal phrases can detract from a presentation by being distracting, signaling a lack of instructor preparation, or by making students feel insecure in their ability to succeed in the course.
We all use some filler phrases habitually, and we should strive to minimize them. However, over-focusing on avoiding filler phrases can distract from a clear presentation. The best strategy is to practice avoiding filler phrases when rehearsing a lecture, but when actually teaching to focus on communicating with the students.
Vocal channel
The vocal channel includes aspects of speech such as volume, pacing, and tone. The vocal channel can be used to draw students attention and convey enthusiasm.
Visual channel
The visual channel includes all visual aids that support your message, including you (!), anything that you write on the board, project on the projector, or distribute as a handout.
Your physical appearance—posture, attire, expressions—are all part of your presentation and affect how students listen to you and receive your message. Here are some ways your appearance affects your presentation:
- Presence/Position/Posture : standing up straight conveys confidence and authority.
- Eye contact : helps you connect with your audience and keep your students engaged. You may tend to focus your gaze on a particular side of the classroom. Consciously make eye contact in a “W” pattern across the room.
- Movement : too much movement can be distracting, but well-timed movements emphasize key points or physically signal a transition between points – reinforce the information you’re presenting.
Plan what you will actually write on the board so you can make sure it’s organized, large, and legible. If you have limited experience writing on the board, try to practice in the room in which you will be teaching. You may be surprised at how large you have to write so that it is legible from the back of the room.
At MIT, most classrooms are outfitted with multiple, movable boards. Visit your classroom in advance to know the layout of the boards and use this information in your planning. For example, with movable boards, consider the order in which you will fill them to maximize the amount of information students can see at any given point. Students will want to write down everything that you write on the board.
Practice drawing important schematics. If a schematic is necessary but challenging to draw, consider supplementing your board work with a slide, which can also be distributed to students as a handout. Consider using color to highlight ideas, group items, or add clarity to diagrams.
Slide design
The digital nature of slides makes it easy to include more information than students can process on them. In general, try to keep the mantra of “less is more” in mind to reduce the likelihood of cognitive overload and including extraneous information.
When creating slides, words and images are better than words alone. Relevant images can help to support and clarify your message. That said, there are times when images may not be appropriate and you just need to use text. In these cases, summarize the ideas using phrases and avoid full sentences on your slide.
Simple animations of having bullets appear in a synchronized manner with your oration will help to reduce cognitive overload and help students stay focused on what you are saying. Key ideas can also be highlighted by using bolding and color.
Managing Nerves
Stage fright is natural. Almost everyone gets some degree of stage fright. Below are some things you can do at different stages of your preparation to minimize the effects of stage fright.
While preparing for class
- Acknowledge your fears by writing them down or sharing them with a friend or a trusted colleague. This will help you identify specific things you can practice to reduce your nerves.
- Practice your presentation. Try to make your practice as realistic as possible: practice in your assigned classroom with an audience of friends, colleagues, or a video camera.
Shortly before class
- Warm up your body by stretching, walking around, and standing up straight.
- Do breathing exercises to warm up your vocal cords and to regulate your breathing.
- Drink water to stay hydrated.
- Use relaxation or meditation resources to reduce nerves, like the MIT Community Wellness Relaxation Line, 617-253-2256 (CALM)
During class
- Use pauses to give yourself a chance to breathe and think. You can use longer pauses between major ideas or during active learning exercises to get a drink of water from your water bottle.
- If you find your speech rushing, try taking a longer pause after your next point. Take a couple of deep breaths and get comfortable with silence to reset your rate of speech.
- If you find yourself pacing or moving a lot, try planting your feet or putting your hands on a table or podium (if it doesn’t ruin your posture) to ground yourself. Once you’ve reset, give yourself more freedom to move around the room and interact with your students.
Additional resources
Mit school of engineering communication lab.
The Communication Lab is a discipline-specific peer-coaching program for MIT’s School of Engineering that helps graduate students with their scientific writing, speaking, and visual design.
MIT Writing and Communication Center
MIT Comparative Media Studies/Writing offers innovative programs that apply critical analysis, collaborative research, and design across a variety of media arts, forms, and practices.
Center for Teaching
Making better powerpoint presentations.
Print Version
Baddeley and Hitch’s model of working memory.
Research about student preferences for powerpoint, resources for making better powerpoint presentations, bibliography.
We have all experienced the pain of a bad PowerPoint presentation. And even though we promise ourselves never to make the same mistakes, we can still fall prey to common design pitfalls. The good news is that your PowerPoint presentation doesn’t have to be ordinary. By keeping in mind a few guidelines, your classroom presentations can stand above the crowd!
“It is easy to dismiss design – to relegate it to mere ornament, the prettifying of places and objects to disguise their banality. But that is a serious misunderstanding of what design is and why it matters.” Daniel Pink
One framework that can be useful when making design decisions about your PowerPoint slide design is Baddeley and Hitch’s model of working memory .

As illustrated in the diagram above, the Central Executive coordinates the work of three systems by organizing the information we hear, see, and store into working memory.
The Phonological Loop deals with any auditory information. Students in a classroom are potentially listening to a variety of things: the instructor, questions from their peers, sound effects or audio from the PowerPoint presentation, and their own “inner voice.”
The Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad deals with information we see. This involves such aspects as form, color, size, space between objects, and their movement. For students this would include: the size and color of fonts, the relationship between images and text on the screen, the motion path of text animation and slide transitions, as well as any hand gestures, facial expressions, or classroom demonstrations made by the instructor.
The Episodic Buffer integrates the information across these sensory domains and communicates with long-term memory. All of these elements are being deposited into a holding tank called the “episodic buffer.” This buffer has a limited capacity and can become “overloaded” thereby, setting limits on how much information students can take in at once.
Laura Edelman and Kathleen Harring from Muhlenberg College , Allentown, Pennsylvania have developed an approach to PowerPoint design using Baddeley and Hitch’s model. During the course of their work, they conducted a survey of students at the college asking what they liked and didn’t like about their professor’s PowerPoint presentations. They discovered the following:
Characteristics students don’t like about professors’ PowerPoint slides
- Too many words on a slide
- Movement (slide transitions or word animations)
- Templates with too many colors
Characteristics students like like about professors’ PowerPoint slides
- Graphs increase understanding of content
- Bulleted lists help them organize ideas
- PowerPoint can help to structure lectures
- Verbal explanations of pictures/graphs help more than written clarifications
According to Edelman and Harring, some conclusions from the research at Muhlenberg are that students learn more when:
- material is presented in short phrases rather than full paragraphs.
- the professor talks about the information on the slide rather than having students read it on their own.
- relevant pictures are used. Irrelevant pictures decrease learning compared to PowerPoint slides with no picture
- they take notes (if the professor is not talking). But if the professor is lecturing, note-taking and listening decreased learning.
- they are given the PowerPoint slides before the class.
Advice from Edelman and Harring on leveraging the working memory with PowerPoint:
- Leverage the working memory by dividing the information between the visual and auditory modality. Doing this reduces the likelihood of one system becoming overloaded. For instance, spoken words with pictures are better than pictures with text, as integrating an image and narration takes less cognitive effort than integrating an image and text.
- Minimize the opportunity for distraction by removing any irrelevant material such as music, sound effects, animations, and background images.
- Use simple cues to direct learners to important points or content. Using text size, bolding, italics, or placing content in a highlighted or shaded text box is all that is required to convey the significance of key ideas in your presentation.
- Don’t put every word you intend to speak on your PowerPoint slide. Instead, keep information displayed in short chunks that are easily read and comprehended.
- One of the mostly widely accessed websites about PowerPoint design is Garr Reynolds’ blog, Presentation Zen . In his blog entry: “ What is Good PowerPoint Design? ” Reynolds explains how to keep the slide design simple, yet not simplistic, and includes a few slide examples that he has ‘made-over’ to demonstrate how to improve its readability and effectiveness. He also includes sample slides from his own presentation about PowerPoint slide design.
- Another presentation guru, David Paradi, author of “ The Visual Slide Revolution: Transforming Overloaded Text Slides into Persuasive Presentations ” maintains a video podcast series called “ Think Outside the Slide ” where he also demonstrates PowerPoint slide makeovers. Examples on this site are typically from the corporate perspective, but the process by which content decisions are made is still relevant for higher education. Paradi has also developed a five step method, called KWICK , that can be used as a simple guide when designing PowerPoint presentations.
- In the video clip below, Comedian Don McMillan talks about some of the common misuses of PowerPoint in his routine called “Life After Death by PowerPoint.”
- This article from The Chronicle of Higher Education highlights a blog moderated by Microsoft’s Doug Thomas that compiles practical PowerPoint advice gathered from presentation masters like Seth Godin , Guy Kawasaki , and Garr Reynolds .
Presenting to Win: The Art of Telling Your Story , by Jerry Weissman, Prentice Hall, 2006
Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery , by Garr Reynolds, New Riders Press, 2008
Solving the PowerPoint Predicament: using digital media for effective communication , by Tom Bunzel , Que, 2006
The Cognitive Style of Power Point , by Edward R. Tufte, Graphics Pr, 2003
The Visual Slide Revolution: Transforming Overloaded Text Slides into Persuasive Presentations , by Dave Paradi, Communications Skills Press, 2000
Why Most PowerPoint Presentations Suck: And How You Can Make Them Better , by Rick Altman, Harvest Books, 2007

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to do a class presentation (11 steps)

The best class presentations combine strong content and visuals with an engaging presentation style. This post offers 11 steps for creating memorable and high-performing class presentations.
1. Review assignment guidelines
Before you can strategize about how to start a class presentation, you need to be certain that you understand the assignment details. Consult materials that your instructor provided, like rubrics, to determine what your presentation needs to cover and what form it should take.
For instance, are you presenting individually or as part of a group? How long should the presentation be? Are you required to have visuals? Knowing these details will help you to plan a successful class presentation.
2. Make a presentation plan
Once you've reviewed the specific assignment details, it's time to make a presentation plan. You can start by making an outline of your talking points. Outlines for class presentations will look similar to those for papers, with sections and subsections that work through your main ideas. You'll want to be precise about what points are essential to communicate to your audience. Also, take some time to decide on a completion timeline to ensure that you're ready on presentation day. Remember to build in time for practice!
3. Choose your visuals
At this point, you'll also want to determine what kind of visual aid(s) you want to use: a handout or a digital presentation, or both? Keep in mind the assignment requirements, but also the audience and the presentation format. For example, are you presenting to a large audience? If so, a handout might not be efficient. Are you presenting in-person or online? If you're preparing an online presentation, a PowerPoint or Google slides presentation will help your audience follow along.
4. Fill out your outline and keep it simple
Now that you've developed a plan for completing your class presentation, you can begin to build out the actual content. If you've created a basic outline, fill it in with some substance. Remember to keep it simple. At around 10-15 minutes, the average in-class presentation can only effectively communicate around three main points. Avoid long quotes or monologues. Your audience may find it difficult to follow longer textual components.
5. Design your visuals with minimal text
Along similar lines, don't simply plop your outline or textual notes into your visuals. Visual aids should be just that: aids that allow your audience to better visualize the main points of your presentation. Large blocks of text on a PowerPoint can be hard to see, so work on creating a digital aid that is mostly comprised on images. When text is appropriate, use bullet points and active words that your audience can remember.
6. Allow time for revisions
Once you've compiled your notes and created your visuals, take some time away from the project. You'll return to your work with fresh eyes. Then, allow time for revision: be sure to proofread your notes, slides, and/or handouts and make sure your visuals are clear. Check to see if any images that you're using appear pixelated on a larger screen and make sure your text is readable from a distance.
7. Check your citations
Many in class presentations will require citations, especially if they are accompanying a paper or another class research project. You can use BibGuru's citation generator to create your citations and copy them to your slides or handout. Consult your assignment guidelines, or ask your instructor, to find out what citation style is required.
8. Practice...and practice again
Give yourself time to practice your presentation in front of an audience before the big day. Familiarize them with the assignment guidelines, as needed, and ask them to time you. You'll need to know if your presentation meets the time requirements. After the first run though, consider these questions:
- Is your presentation too long or too short?
- Are you hitting the main points in a logical sequence that your audience can follow?
- Are your visuals clear?
- Is your delivery fluid or are you pausing too often to look at your notes?
- Are you making eye contact with your audience?
Use your answers to these questions to determine what, if at all, you need to change and then schedule another practice. You should practice your presentation as many times as you need to in order to achieve a fluid delivery.
9. Prepare for technical difficulties
Since most class presentations will include a digital element, be prepared to troubleshoot if there are technical difficulties on presentation day. Always have a back-up plan and be sure to save your visuals in multiple places. Keep a copy of your notes and slides in your email, on a thumb drive, and/or on the cloud. Practice enough so that, in the event that you can't get your visual aid to work, you can still deliver your presentation.
10. Take the stage with confidence
If you've followed your plan, practiced thoroughly, and prepared for possible technical difficulties, you should be ready to take the stage with confidence. Nervousness is absolutely natural, but try your best to relax and breathe. A few shoulder rolls and deep breaths right before the presentation can go a long way to making you feel more focused and centered.
11. Connect with your audience
From the first moment of your presentation, you'll want to establish a strong connection with your audience. Smile, make eye contact, and modulate your voice appropriately. Remember, people exhibit all kinds of facial expressions when they are listening or concentrating, so try not to pay too much attention to individual faces.
Also, although your instructor will be the one grading you, don't simply present to them. Include the entire class in your gaze. Finally, be careful about pace. If you have a tendency to speed up your speech when you're nervous, make a conscious effort to slow down.
The bottom line
Following the tips above will enable you to confidently deliver a class presentation to your instructor and classmates, or to any audience. With solid preparation and ample practice, your next class presentation will be a memorable success.
Frequently Asked Questions about class presentations
The most successful presentations begin with a hook. This could be a short, yet compelling story, an eye-catching visual with brief analysis, or an inspiring quote or statistic. No matter how you begin, ensure that you can fluidly transition to the main substance of your presentation in a way that your audience can easily follow.
Regardless of the subject of your presentation, you can make it interesting for your audience by engaging them through consistent eye contact, a relaxed and confident delivery style, and interactivity. For instance, to keep your audience engaged, you might try including questions or brief activities in your presentation.
Wrap up your presentation by summarizing your key points. You can also end with a provocative question or thought. You should also thank your audience for listening.
Good presentations are well-organized, time-sensitive, clear, and delivered with confidence.
The most common presentation mistakes include: not engaging your audience, using visuals that are overloaded with text, and not practicing enough.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7.4 Public Speaking and Class Presentations
Learning objectives.
- Know how to overcome nervousness and anxiety associated with public speaking and giving class presentations.
- Effectively use the six-step process to prepare for and deliver a class presentation.
- Create effective visual aids for use in class presentations.
- Work with a group to successfully plan and deliver a class presentation.
Public speaking—giving an oral presentation before a class or another group of people—is a special form of interaction common in education. You will likely be asked to give a presentation in one of your classes at some point, and your future career may also involve public speaking. It’s important to develop skills for this form of communication.
Public speaking is like participating in class—sharing your thoughts, ideas, and questions with others in the group. In other ways, however, public speaking is very different. You stand in front of the class to speak, rather than from your usual seat—and for most students, that changes the psychology of the situation. You also have time outside of class to prepare your presentation, allowing you to plan it carefully—and, for many, giving more time to worry about it and experience even more anxiety!
Overcoming Anxiety
Although a few people seem to be natural public speakers, most of us feel some stage fright or anxiety about having to speak to a group, at least at first. This is completely normal. We feel like everyone is staring at us and seeing our every flaw, and we’re sure we’ll forget what we want to say or mess up. Take comfort from knowing that almost everyone else is dreading giving class presentations the same as you are! But you can learn to overcome your anxiety and prepare in a way that not only safely gets you through the experience but also leads to success in your presentation. The following are proven strategies for overcoming anxiety when speaking in public:
- Understand anxiety. Since stage fright is normal, don’t try to deny that you’re feeling anxious. A little anxiety can help motivate you to prepare and do your best. Accept this aspect of the process and work to overcome it. Anxiety is usually worst just before you begin and but eases up once you’ve begun.
- Understand that your audience actually wants you to succeed. They’re not looking for faults or hoping you’ll fail. Other students and your instructors are on your side, not your enemy. They likely won’t even see your anxiety.
- Reduce anxiety by preparing and practicing. The next section discusses the preparation process in more detail. The more fully you prepare and the more often you have practice, the more your anxiety will go away.
- Focus on what you’re saying, not how you’re saying it. Keep in mind that you have ideas to share, and this is what your classmates and instructors are interested in. Don’t obsess about speaking, but focus on the content of your presentation. Think, for example, of how easily you share your ideas with a friend or family member, as you naturally speak your mind. The same can work with public speaking if you focus on the ideas themselves.
- Develop self-confidence. As you prepare, you will make notes you can refer to during the presentation. You’re not going to forget what you want to say. The more you practice, the more confident you’ll become.
Guidelines for Presentations
Preparing and delivering a presentation in class (or in business or other settings) is a process very similar to the learning process discussed in Chapter 4 “Listening, Taking Notes, and Remembering” , Chapter 5 “Reading to Learn” , and Chapter 6 “Preparing for and Taking Tests” and the writing process discussed in Chapter 8 “Writing for Classes” . The process breaks down into these six basic steps:
- Analyze your audience and goals
- Plan, research, and organize your content
- Draft and revise the presentation
- Prepare speaking notes
- Practice the presentation
- Deliver the presentation
Step 1: Analyze Your Audience and Goals
Who will see and hear your presentation—and why? Obviously, other students and the instructor. But you still need to think about what they already know, and don’t know, about your topic. If your topic relates to subject matter in class lectures and readings, consider what background information they already have and be careful not to give a boring recap of things they already know. It may be important, however, to show how your specific topic fits in with subjects that have been discussed already in class, especially in the beginning of your presentation, but be sure to focus on your new topic.
New terms and concepts may become familiar to you while doing your research and preparation, but remember to define and explain them to other students. Consider how much explanation or examples will be needed for your audience to grasp your points. If your topic involves anything controversial or may provoke emotion, consider your audience’s attitudes and choose your words carefully. Thinking about your audience will help you find ways to get their attention and keep them interested.
Be sure you are clear about the goals for the presentation. Are you primarily presenting new information or arguing for a position? Are you giving an overview or a detailed report? Review the assignment and talk with the instructor if you’re unsure. Your goals guide everything in the presentation: what you say, how much you say, what order you say it in, what visual aids you use, whether you use humor or personal examples, and so forth.
Step 2: Plan, Research, and Organize Your Content
Starting with the assignment and your goals, brainstorm your topic. Jot notes on specific topics that seem important. Often you’ll do reading or research to gather more information. Take notes as you would with any reading. As you research the topic at this stage, don’t worry at first about how much content you are gathering. It’s better to know too much and then pick out the most important things to say than to rush ahead to drafting the presentation and then realize you don’t have enough material.
Organizing a presentation is similar to organizing topics in a class paper and uses the same principles. Introduce your topic and state your main idea (thesis), go into more detail about specific ideas, and conclude your presentation. Look for a logical order for the specifics in the middle. Some topics work best in chronological (time) order or with a compare-and-contrast organization. If your goal is to persuade the audience, build up to the strongest reason. Put similar ideas together and add transitions between different ideas.
While researching your topic and outlining your main points, think about visual aids that may help the presentation.
Also start thinking about how much time you have for the presentation, but don’t limit yourself yet in the outline stage.
Step 3: Draft and Revise the Presentation
Unless required by the assignment, you don’t need to actually write out the presentation in full sentences and paragraphs. How much you write depends on your own learning and speaking style. Some students speak well from brief phrases written in an outline, while other students find it easier to write sentences out completely. There’s nothing wrong with writing the presentation out fully like a script if that helps you be sure you will say what you intend to—just so you don’t actually get up and read from the script.
You can’t know for sure how long a presentation will last until you rehearse it later, but you can estimate the time while drafting it. On the average, it takes two to three minutes to speak what can be written on a standard double-spaced page—but with visual aids, pauses, and audience interaction, it may take longer. While this is only a rough guide, you can start out thinking of a ten-minute presentation as the equivalent of a three to four-page paper.
Never wait until the last minute to draft your presentation. Arrange your time to prepare the first draft and then come back to it a day or two later to ask these questions:
- Am I going on too long about minor points? Could the audience get bored?
- Do I have good explanations and reasons for my main points? Do I need more data or better examples? Where would visual aids be most effective?
- Am I using the best words for this topic and this audience? Should I be more or less informal in the way I talk?
- Does it all hold together and flow well from one point to the next? Do I need a better introduction or transition when I shift from one idea to another?
Visual Aids in Presentations
Except for very short informal presentations, most presentations gain from visuals—and visual aids are often expected. If encouraged or allowed to include visuals in your presentation, plan to do so. Consider all possible types:
- Charts or graphs
- Photos or other images
- Video clips
- Handouts (only when necessary—they can be distracting)
Use the available technology, whether it’s an overhead projector, PowerPoint slides, a flip chart, or posters. (Talk to your instructor about resources and software for designing your visuals.) Follow these guidelines:
Design your visuals carefully. Here are some basic rules:
- Use a simple, neutral background. A light-colored background with text in a dark color works best for words; a dark background used like matting works best for photos.
- Minimize the amount of text in visuals—more than eight words per slide is usually too much. Avoid simply presenting word outlines of what you are saying. Make sure text is large enough for the audience to read.
- Don’t use more than two pictures in a slide, and use two only to make a direct comparison. Montages are hard to focus on and distract the viewer from what you’re saying. Use images only when they support your presentation; don’t use clip art just as decoration.
- Don’t put a table of numbers in a visual aid. If you need to illustrate numerical data, use a graph. (Microsoft Excel can make them for you easily.)
- Don’t use sound effects. Use a very brief recording only if directly related to your main points.
- Don’t use visual special effects such as dissolves, spins, box-outs, or other transitions. They are distracting. Use animation sparingly and only if it helps make a point.
- Don’t use so many visuals or move through them so quickly that the audience gives all its attention to them rather than to you.
- Practice your presentation using your visual aids, because they affect your timing.
- Explain visuals when needed but not when they’re obvious.
- Keep your eyes on your audience, only briefly glancing at visuals to stay in synch with them.
- Don’t hand out a printout of your visuals. Your audience should keep their eyes on you instead of fiddling around with paper.
Step 4: Prepare Speaking Notes
As mentioned earlier, it’s not a good idea to read your presentation from a written page rather than deliver it. To keep your audience’s attention, it’s important to make eye contact with them and to use a normal speaking voice—and you can’t do this if you keep your eyes on a written script.
Speaking notes are a brief outline for your presentation. You might write them on index cards or sheets of paper. Include important facts and data as well as keywords for your main ideas, but don’t write too much. (If you forget things later when you start practicing, you can always add more to your outline then.) Be sure to number your cards or pages to prevent a last-minute mix-up.
Think especially about how to open and close your presentation, because these two moments have the most impact of the whole presentation. Use the opening to capture the audience’s attention, but be sure it is appropriate for your audience and the goals. Here are some possibilities for your opening:
- A striking fact or example (illustrating an issue or a problem)
- A brief interesting or humorous anecdote (historical, personal, or current event)
- A question to the audience
- An interesting quotation
Then relate the opening to your topic and your main point and move into the body of the presentation.
Your closing mirrors the opening. Transition from your last point to a brief summary that pulls your ideas together. You might end with a challenge to the audience, a strong statement about your topic, or a personal reflection on what you have been saying. Just make sure you have a final sentence planned so that you don’t end up uncomfortably fumbling around at the end (“Well, I guess that ends my presentation”).
Step 5: Practice the Presentation
Practice may be the most important step. It is also the best way to get over stage fright and gain confidence.
Practice first in an empty room where you imagine people sitting, so that you can move your eyes around the room to this “audience.” The first time through, focus on putting your outlined notes into full sentences in your natural speaking voice. Don’t read your notes aloud. Glance down at your notes only briefly and then look up immediately around the room. Practice two or three times just to find the right words to explain your points and feel more comfortable working with your notes. Time yourself, but don’t obsess over your presentation being the exact length required. If your presentation is much too long, however, adjust it now in your notes so that you don’t start memorizing things that you might accidentally still say later on even though you cut them from your notes.
Once you feel good speaking from your notes, practice to add some more polish to your delivery. You might want to record or videotape your presentation or ask a friend or roommate to watch your presentation. Pay attention to these aspects of how you speak:
- Try to speak in your natural voice, not in a monotone as if you were just reading aloud. If you will be presenting in a large room without a microphone, you will need to speak louder than usual, but still try to use a natural voice.
- In usual conversation, we speed up and slow down and vary the intensity of our words to show how we feel about what we’re saying. Practice changes in your delivery style to emphasize key points.
- Don’t keep looking at your notes. It’s fine if you use words that are different from those you wrote down—the more you rehearse without looking at your notes, the more natural sounding you will be.
- Be sure you can pronounce all new words and technical terms correctly. Practice saying them slowly and clearly to yourself until you can say them naturally.
- Don’t forget transitions. Listeners need a cue when you’re moving to a new idea. Practice phrases such as “ Another important reason for this is…” or “Now let’s move on to why this is so.…”
- Watch out for all those little “filler” words people use so often, such as “like,” “you know,” “well,” and “uh.” They’re very distracting to most audiences. Listen to or watch your tape to see if you are using these fillers or ask your friend to point it out.
- Pay attention to body language when practicing. Stand up straight and tall in every practice session so that you become used to it. Unless you have to stand at a podium to use a fixed microphone in your presentation, practice moving around while you speak; this helps keep the audience watching you. Use hand and arm gestures if they are natural for you, but don’t try to make up gestures for the presentation because they will look phony. Most important, keep your eyes moving over the audience. Practice smiling and pausing at key points.
- Finally, it’s a good idea to be ready in case of an accident. Most likely your presentation will go smoothly, you’ll stay on track with your notes, and your PowerPoint slides will work fine, but sometimes a mishap happens. Be ready to joke about it, rather than becoming flustered. If the computer fails and you lose your visuals, say something like, “Well, that’s a shame, I had some really great photos to show you!” If you drop your index cards or notes, or accidentally skip ahead in your presentation and then have to backtrack, make a joke: “Sorry about that, I was so excited to get to my next point that I’m afraid I lost control there for a moment!” Let your audience laugh with you—they’ll still be on your side, and you can defuse the incident and move on without becoming more nervous.
Step 6: Deliver the Presentation
Be sure to get enough sleep and eat a healthy breakfast. Don’t drink too much caffeine or else you’ll become hyper and nervous. Wear your favorite—and appropriate—clothing and comfortable shoes.
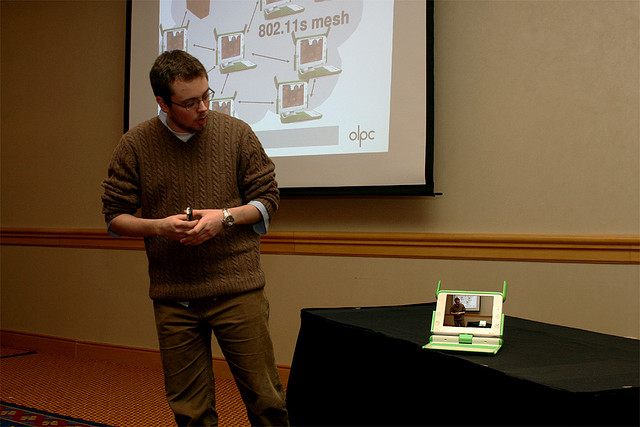

You may use computerized visual aids when you give a presentation to a class.
John Haynes Photography – OLPC – CC BY-ND 2.0.
Remember, your audience is on your side! If you’re still nervous before your turn, take a few deep breaths. Rehearse your opening lines in your mind. Smile as you move to the front of the room, looking at your audience. You’ll see some friendly faces smiling back encouragingly. As you start the presentation, move your eyes among those giving you a warm reception—and if you see some student looking bored or doing something else, just ignore them. But don’t focus on any one person in the audience for too long, which could make them nervous or cause them to look away.
Don’t keep looking at your watch or a clock: If your rehearsal times were close to your assigned time, your presentation will be also. If you do notice that you’re running behind schedule, it may be that you’re saying too much out of nervousness. Use your notes to get back on track and keep the pace moving. But it’s better to deliver your presentation naturally and fluidly and be a bit long or short than to try to change your words and end up sounding unnatural.
At the closing, deliver your last line with confidence, sweeping your eyes over the audience. If appropriate, ask if there are any questions. When you’re done, pause, smile, say “Thank you,” and walk back to your seat.
Later on, ask other students and your instructor for comments. Be open minded—don’t just ask for praise. If you hear a suggestion for improvement, file that in your memory for next time.
Group Presentations
You may be assigned to give a presentation in a small group. The six-step process discussed previously works for group presentations, too, although group dynamics often call for additional planning and shared responsibilities:
- Schedule a group meeting as soon as possible to get started. Don’t let another student put things off. Explain that you’re too busy and won’t have time at the last minute.
- Begin by analyzing your audience and your goals together as a group to make sure everyone understands the assignment the same. Discuss who should do what. While everyone should talk about what content to include, from here onward, you will take on specialized roles. One or more may begin research and gathering information. Others who are good writers may volunteer to draft the presentation, while one or more others may develop the visual aids. Those who have public speaking experience may volunteer to do all or most of the speaking (unless the assignment requires everyone to have a speaking role). You also need a team leader to keep everyone on schedule, organize meetings, and so on. The best team leader is an even-tempered student with good social skills, who can motivate everyone to cooperate.
- Steps 2 and 3 can likely be carried out individually with assigned tasks, but group members should stay in touch. For example, the person developing the visuals should be talking to those doing the researching and drafting to see what visuals are needed and get started finding or creating them.
- Before preparing notes in step 4, meet again to go over the content and plan for visuals. Everyone should be comfortable with the plan so far. Make final decisions about who will do each section of the presentation. Set the time for each segment. Then speakers should prepare their own speaking notes. Let someone with strong speaking skills open or close the presentation (or both), with others doing the other parts.
- The whole group should be present for practice sessions in step 5, even if not everyone is speaking. Those not speaking should take notes and give feedback. If one student is doing most of the presenting, an alternate should be chosen in case the first choice is sick on the scheduled day. The alternate also needs to practice.
- During the delivery, especially if using technology for visual aids, one student should manage the visuals while others do the presenting. If several students present different segments, plan the transition from one to another so that the presentation keeps flowing without pauses.
Additional Resources
For Class Presentations
Using PowerPoint. A step-by-step illustrated tutorial for learning how to create effective visual presentations with PowerPoint. https://www.baruch.cuny.edu/tutorials/powerpoint/
“How to Give a Bad Talk.” A humorous look (with some very good advice) on what not to do when preparing for and giving a class presentation. http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~pattrsn/talks/BadTalk.pdf
Class presentations on YouTube. Search YouTube with the phrase “class presentation” and look for video examples of actual students giving class presentations. Observing and critiquing the presentations of other students are good ways to get started preparing your own and learning from others. Here’s a good example of a student group presentation on a topic we can all relate to (how body language works):
In this presentation, take note of
- how students make good eye contact with the audience;
- the first student’s natural speaking voice and tone, and how she did not have to use her note cards very often (obviously she practiced well);
- some differences among these students;
- the use of PowerPoint slides within the presentation (some better than others);
- the appropriate occasional use of humor;
- the division of presentation responsibilities within the student group;
- each presenter’s interaction with the audience.
Key Takeaways
- Public speaking skills are important because you will likely give presentations in class and perhaps in a future job.
- Overcome anxiety about public speaking by understanding your feelings, preparing well and practicing your delivery, and focusing on your subject.
Follow a six-step process to prepare and deliver a presentation:
- Deliver the presentation and seek feedback
- Use visual aids to support a presentation, creating visuals that are relevant, attractive, and powerful.
- The success of a group presentation depends on effective group meetings, successful division of roles, and repeated group practices.
Checkpoint Exercises
If you have given a class presentation in the past, what worked best for you? (If you have not given a presentation yet as a student, what aspect do you think will be most difficult for you?)
__________________________________________________________________
Name the two most important things you can do to reduce anxiety about a class presentation you will have to give.
For each of the following statements about class presentations, circle T for true or F for false:
Describe how best to use body language (facial expressions, eye movements, gestures, etc.) when giving a presentation.
If you were assigned along with three other students to give a group presentation in the class using this textbook, what would be your preferred role in the preparation stages? Your least preferred role? If you had to take your least preferred role, what single thing would you want to work hardest on to make the presentation successful?
College Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Structuring an Effective Class Session or Presentation
The way you structure and facilitate class sessions or other presentations can have a profound impact on learning. There are evidence-based approaches to designing the learning experience from start to finish to enhance engagement, understanding, and retention of information. This resource is valuable for anyone planning a synchronous (live) learning experience in a variety of contexts, including a class session, presentation, or workshop, in-person or remote.
How do I decide what to include in a class session or presentation?
Start planning by articulating the learning outcomes . What do you want the learner to know or be able to do by the end of that session? For a course, the learning outcomes for a specific class session should fit within the overarching course learning outcomes and help to move students towards achieving those. Use the learning outcomes to make intentional decisions about what content and activities to include in your class session or presentation by assessing their alignment.
As you make these decisions about which content to prioritize for synchronous time together, consider planning for flexibility. Which content is key to cover together, and which activities are vital to your learners’ experiences? Consider structuring your session such that the most vital content happens first to both prioritize it and ensure you have enough time to devote to it. Also plan for content that can be skipped over or moved to the next session in case activities go over time or learners have many questions.
How should I structure a class session or presentation to enhance learning?
When planning a class session or presentation, you should divide the time into segments, starting with an opening and ending with a closing. The main portion between opening and closing should be broken into periods of interactive lecture and individual or group activities, depending on your learning goals.
Starting a Session
The start should be welcoming and set the tone for an interactive learning experience. You might begin by playing music from a shared playlist, asking learners how they are feeling, encouraging them to check in with one another, or posing a lighthearted icebreaker question. Creating this welcoming atmosphere helps support learners’ social-emotional learning.
It is common to share outcome(s), purpose, goals, and/or an agenda at the start of a class session or presentation. In addition, set aside intentional time to “warm up” to the topic, establish context, and connect to learners’ prior knowledge and experiences . An interactive warm up also sets the expectation that the session will be collaborative and interactive. You can engage learners at the start by capturing their attention and curiosity with a “hook”, helping them make connections to prior experiences (academic or personal), or asking them to share beliefs and expectations about a topic. Some examples include:
- What do you know about [Topic]? What do you want to know?
- What do you think is going on in this picture?
- What are your personal thoughts about [topic]?
- What experience do you have with [topic]?
Interactive Content Delivery
Lecturing (i.e., direct oral presentation of information) is efficient and can be effective when the background information is not available or accessible, the facts or problems are conflicting or confusing, or your experience as the presenter will contribute to clarification. Be sure to ask yourself if the best way to understand the content is through oral presentation, or if the content could be explored some other way (e.g., small group exercises or individual reflection). Consider how much of your time will be devoted to lecture, which may depend on how much of the information you want to share will come from the lecture versus assigned course materials (e.g., readings, videos). Is the goal of lecture to supplement the information from course materials, highlight major points, or present separate information?
When designing a lecture-based class session, or any type of presentation, aiming for interaction and engagement will support deeper comprehension and greater retention of information. “We need not abandon the lecture because of its liabilities; rather, we need to find ways to make it work better” (Silver & Perini, 2010). Once you’ve determined what content is best presented through a lecture, there are many ways to improve the lecture presentation:
- “Chunk” the content, or break it up into smaller, focused sections. Aim to speak for no more than a few minutes straight without checking in, even if just with a rhetorical question for learners to ponder as they listen.
- Intersperse active learning activities such as informal discussion, think-pair-share, minute paper, polls, or quick quiz questions ensure that learners are actively processing the information as you present it.
- Use multimedia (e.g., images, audio, video, infographics) throughout your lecture to enhance comprehension and accessibility. However, keep in mind that your multimedia should be focused and related to the course content; avoid .gifs or overly illustrative materials, as these take learners’ focus away from the content and can contribute to extraneous cognitive load.
- Clarify for learners how they should approach taking notes, information they need to commit to memory, and how you expect them to apply the content in the future.
- Allow learners to ask questions at different points within a lecture. Pause periodically to ask, “What questions do you have?” or “What’s on your mind?” After you pose a question, allow “wait time” for a response, giving time for learners to formulate ideas. We may be used to asking, “Do you have any questions?” but students may feel that they are being intrusive or not paying attention if they do have a question. Asking “What questions do you have?” normalizes the fact that students are likely to have questions when learning new content.
Individual or Group Activities
Either before or after presenting content, provide opportunities for learners to interact with the content at a deeper level through individual or group activities. Individually, learners could engage in independent work time or reflection. In small or large groups, learners could discuss the topic in more detail or engage in peer review opportunities. Other ways to encourage reflection, critical thinking, and problem solving, which could be done individually or in groups, include case studies, debates, concepts maps, or game-based instruction.
Ending a Session
At the end of a class session or presentation, be sure to save time to tie everything together and assess learning. It is very common to run out of time and rush to conclude, but end-of-class reflection supports retaining information and helps to clarify what comes next. At the end of a session, you might summarize, or ask learners to summarize, key takeaways, especially in conjunction with revisiting the learning outcomes. Other options include asking learners to submit a written reflection on what they’ve learned, how they might apply what they’ve learned and/or what questions they still have or which concepts were unclear.
Lastly, if teaching a course, you can wrap up by previewing what’s to come, connecting the material to assignments or other work to be completed, or asking questions you want learners to think about before meeting again. You can also provide context on the homework assigned for next class, such as guiding questions for a reading or viewing, or leave time to answer student questions about an upcoming assignment.
How can I make sure my class session or presentation is accessible?
Overall, following the principles of Universal Design for Learning promotes flexibility and adaptation of the learning environment so that all learners can succeed and achieve the intended outcomes. As you consider the guidelines and session structure above, consider how you can provide multiple means of engagement, representation, and action and expression.
Regardless of the structure of your class session or presentation, we highly recommend you use slides or another visual means to communicate information and directions as you progress through the session. Even if your session involves minimal to no “content,” slides, or at least a written agenda, help to keep learners on track with what is being asked of them. If you use slides, decide how and when to make them available. The CTRL accessibility guide provides more detailed guidance for how to ensure slides and documents used in a session are accessible

AU's Center for Teaching, Research & Learning © A Unit of the Office of the Provost American University, Washington, DC
Get in touch!
Address: Hurst 214 Phone: 202-885-2117 Email: [email protected]
Blog > Interactive PowerPoint presentations in class
Interactive PowerPoint presentations in class
03.08.2023 • #powerpoint #tips.
Presentations can be a great way to make your lessons exciting and informative and to informative and to better communicate information to your students. Many students do not feel engaged and integrated enough with normal presentations. To increase the attention span and arouse enthusiasm, interactive elements such as quizzes, word clouds or feedback rounds can help, to significantly increase learning success.
Common problems that arise during presentations in class
Presentations are a central element of the learning process, but they often involve challenges that need to be overcome. We have highlighted four common problems that often accompany presentations in class:
1. Lack of interaction
Standard PowerPoint presentations offer limited opportunities for audience interaction and engagement. They lack features to gather feedback or answer questions in real time and respond to requests.
2. Student passivity
Students are often forced into a passive role when the focus is only on the slides and the presenter simply delivers them in a heavy-handed manner.
3. Time managementt
Creating good presentations can take a lot of time and can be a difficult task for some.
4. Information Overload
Too much information at once, without a break can overwhelm and scare away younger students in particular. It's hard to focus on what's important and grasp the key messages.
4 ideas for interactive presentations in classes
Interactive presentations demonstrably increase learning success and retention. This is also confirmed by a study of the Keele University . The results here show very clearly to what extent involving the audience increases attention as well as knowledge transfer. It was found that the grades of the participants improved by 3.7%, as well as and the failure rate was reduced by 4.4% over the whole school year. were reduced.
1. Interactive classroom engagement
Students can ask questions anonymously and provide interactive feedback. This encourages active participation in the classroom and creates an open learning environment. Teachers could respond spontaneously to questions or interesting discussion points and customize lessons.
Here are some ways to better engage students in the classroom:
- Voting on the desired teaching material : Teachers can include an interactive survey where students choose from a variety of topics they would like to learn more about in class. This allows students to help shape the lesson and contribute their interests.
- Surveys in which subject areas the students need more support : Teachers can start a survey to identify areas where students are having difficulty or need more explanation. This can help to tailor the lessons to the needs of the students.
- Anonymous questions about ambiguities in specific subject areas : For example, students can use SlideLizard to anonymously ask questions about topics they didn't fully understand. These questions can then be discussed in class to clarify misunderstandings and deepen understanding.
2. Brainstorming and unleashing creativity
Interactive slides enable teachers and students to collaboratively brainstorming sessions into the presentation, and to create a presentation. The feature allows ideas to be collected and structured on virtual pinboards. and structure them. The result is an interactive collaboration that unleashes creativity and promotes the exchange of ideas. encourages.
Here are some ideas on how to incorporate brainstorming in the classroom:
- Brainstorming for possible solutions : When addressing complex problems or challenges, teachers can ask students to brainstorm different solutions together on an interactive slide. This encourages teamwork and creative thinking.
- Collection of ideas for projects : Teachers can use an interactive slide where students can collect creative ideas for upcoming projects. These ideas can then be discussed and developed together.
- Solutions for social challenges : Students can brainstorm and discuss ideas for addressing real-world social problems such as poverty, inequality, or pollution.
3. Learning with quizzes
Interactive quizzes are a highlight of PowerPoint presentations. Teachers can check what students have already learned in a playful way and track the learning success. The students in turn experience a motivating sense of achievement when they answer the quiz questions correctly. This makes the learning process not only entertaining, but also effective.
Here are some concrete ideas for how teachers can use quizzes in a meaningful way in the classroom:
- Short knowledge tests during the presentation : Teachers can include a short quiz after each section of a presentation to ensure that students understand the key concepts before moving on to the next section.
- Preparation for exams : Teachers can create more comprehensive quizzes that cover the entire subject matter and help students prepare for upcoming exams.
- Continuous knowledge checks : Teachers can create regular, short quizzes to ensure that knowledge learned builds and deepens consistently over time.
4. Flexibility in teaching through discussions
Additional slides can also be used or set aside to be be flexible to the needs of the students. Teachers can react spontaneously to respond spontaneously to questions or interesting discussion points and individually.
Here are some ways teachers can use discussions to engage students more fully in the classroom:
- Small group discussions : Teachers can divide students into small groups and have them discuss on different slides. Each group can then present their findings or conclusions.
- Feedback and reflexion : After a presentation or lecture, teachers can ask questions on a slide that encourage students to reflect on what they have heard. These questions can then be discussed together.
- Visualize discussions as a word cloud : The students' contributions and thoughts from a discussion can be visualized on a slide as a word cloud. Frequently mentioned words are displayed larger, which draws the focus to dominant topics or trends. This provides a visual summary of the discussion and encourages analysis of the most important aspects.
Tips: Create interactive presentations
One tool that can help you create interactive presentations is SlideLizard. SlideLizard offers a wide range of interactive features, such as word clouds, polls, quizzes or feedback rounds for your teaching. You can integrate the interactive slides directly into your PowerPoint presentation and the results of polls or word clouds during the lesson are automatically visualized in real time. Learn more about interactive teaching with SlideLizard here.
Using interactive PowerPoint presentations with SlideLizard allows teachers to take teaching to a new level and overcome these problems. By combining word clouds, quizzes, interactive feedback sessions, and brainstorming sessions, SlideLizard creates an inspiring learning environment where students can actively participate in the classroom and unlock their potential. Let's use this creative and innovative approach to unleash the potential of visual connection and take teaching in schools to a new level. Learning can be so much fun!
Related articles
About the author.

Annika Fachberger
Annika is dedicated to graphics and videos. At SlideLizard she supports the design team with her creative ideas.
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

Elegant Architecture - Free PowerPoint Template

Corporate Design in Presentations - the Key to Strengthening Corporate Identity
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Valedictory speech.
A valedictory speech is given in order to say goodbye, usually at graduation. It should inspire listeners and functions as a send-off into "real life".
B2C means Business to Customer. A B2C event is hosted by a company for its customers. It's important for gaining new customers and for satisfieing regular clients.
Manuscript Speech
For a manuscript speech, the speaker has an entire manuscript to read from. The benefit is that, as every single word is scripted, no important parts will be missed. However, speeches that are fully written down often seem unnatural and may bore the audience.
Informative Presentations
An information presentation is created when no solution is currently available. Facts, data and figures or study results are presented and current processes are described.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Do a Presentation in Class
Last Updated: March 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,632,731 times.
Doing a presentation in class can be intimidating, but it does not have to be. This wikiHow will give you lots of pointers on how to do a presentation in class with minimal stress.
Planning the Presentation

- Write down keywords or main ideas. If you need to consult your index cards, you're only going to want to scan the index card for information, not read every last word.
- Most of the time, the act of putting information down on your index cards will help you remember the information. So, while you might not strictly need the note cards, it's a nice security blanket to have if you happen to forget what you were going to say.
- You don't want to be reading straight off your notecards during your presentation.

- Practice in front of your family or friends, or in front of the mirror, when you rehearse your presentation. It's probably better to do it in front of friends who you may not know well, as this will help you replicate the feeling of being in front of the class.
- Ask your friends for feedback after you finish your presentation. Was the presentation long enough? How was your eye contact? Did you stammer at all? Were all the points clearly made?
- Make a critique of your practice performance. Challenge yourself to work on all the things that you believe you can improve during the real presentation. When it comes time to deliver the real deal, you'll feel confident knowing that you've worked extra hard on what was toughest for you.

- Get quotes from reliable sources. Good quotes make a good presentation great. Taking what smart people have said and putting it into your presentation not only makes you look smart, it shows the teacher that you spent time thinking about what other people said.
- Make sure your sources are trustworthy. There's nothing that can quite break your confidence like a fact that turns out to not be a fact. Don't always trust the information you get off the Internet.
Delivering the Presentation

- Studies have shown that smiles are infectious; that means that once you smile, it's hard for everyone else not to smile. So if you want your presentation to go off without a hitch, force yourself to smile. That'll make everyone smile; and maybe those smiles will make you actually smile.

- Think about your intention before you talk to your audience. Do you want to educate, enlighten, or entertain this audience? What is the effect that you want to have on the listener?
- Visualize success before, during, and after your presentation. Be humble about what you do — no need for cockiness — but imagine a successful presentation at all times. Don't let the thought of failure creep into your mind.
- In many ways, your confidence is just as important as the information you're delivering. You don't want to spread misinformation, or skimp on doing your research, but a lot of what you'll be graded on — and what the other students come away with — is going to be your level of confidence. Also if you are confident, you will have a better time exchanging ideas with the class.
- If you need a confidence boost, think big picture. After 10 or 15 minutes, your presentation will be over. What will your presentation matter in the long run? Probably not very much. Try to do the best you can, but if you're getting nervous, remind yourself that there are much more important moments in your life to come.

- Have the goal of looking at every person in the classroom at least once. That way, everyone will feel like you've engaged with them. Plus, you'll look like you know what you're talking about.

- Inflection is the kind of movement that radio DJs put into their voice; it's the ramped-up pitch in your voice when it gets excited. You don't want to sound like you've just seen a lion, but you also don't want to sound like you've just seen a squirrel, either. Vary it up to make the presentation more interesting.

- Tell a story, maybe one with a personal note. Stories are great for history or English presentations. Maybe you can tie your presentation into a little anecdote about a famous historical person?
- Ask a provocative question. Ending with a question is a good way of getting your audience to think about your presentation in an interesting way. Is there a certain conclusion you want them to come to?

What Is The Best Way To Start a Presentation?
Community Q&A
- Have good posture. Don't cross or fold your arms, keep them open. Don't slouch and keep your back straight. [8] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Don't forget to look at everyone, not just the floor. Don't stare at anyone in particular but 'skim' the class. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Try not to argue with your audience. This detracts from your presentation. Just tell them they have an interesting point and that you'll check and get back to them. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 1

- Some people may be so tied up before a presentation that they feel faint and may pass out during their speech. If this describes you, make sure you prepare especially hard and keep your blood sugar up before you present. Thanks Helpful 14 Not Helpful 1
- Don't keep your mobile phone in your pocket or it will interfere with the microphone (if any). Thanks Helpful 13 Not Helpful 6
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/ours/oral-presentation-tips-30.htm
- ↑ https://www.uwe.ac.uk/study/study-support/study-skills/presenting-and-working-with-others
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zcfv4wx/articles/zdn3d6f
- ↑ https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~mernst/advice/giving-talk.html
About This Article

The best way to prepare for your class presentation is to practice in front of a friend or family member. When it’s time to present, make eye contact with your audience and use hand motions to illustrate your points. Don’t forget to smile! Finish strong with a final statistic or provocative question. If you’re still nervous, read on for more advice! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Jun 19, 2016
Aug 8, 2016
Mar 30, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Methods for Presenting Subject Matter
- Tips & Strategies
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Teaching Resources
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.A., English, Western Connecticut State University
- B.S., Education, Southern Connecticut State University
The word educate comes from Latin, meaning "to bring up, to rise, and to nourish, to train." To educate is an active enterprise. In comparison, the word teach comes from German, meaning "show, declare, warn, persuade." To teach is a more passive activity.
The difference between these words, educate and teach, has resulted in many different instructional strategies, some more active and some more passive. The teacher has the option to choose one in order to successfully deliver content.
In choosing an active or passive instructional strategy, the teacher must also consider for other factors such as subject matter, the resources available, the time allotted for the lesson, and the background knowledge of the students. What follows is a list of ten instructional strategies that can be used to deliver content regardless of grade level or subject matter.
Lectures are instructor-centered forms of instruction given to a whole class. Lectures come in many different forms, some more effective than others. The least effective form of lecture involves a teacher reading from notes or the text without differentiating for student needs. This makes learning a passive activity and students may quickly lose interest.
The lecture is the most used strategy. An article in "Science Educator" titled "Brain Research: Implications to Diverse Learners" (2005) notes:
"Although lecturing continues to be the most widely employed method in classrooms across the country, research on the way we learn indicates that lecturing is not always very effective."
Some dynamic teachers, however, lecture in a more free-form manner by including students or providing demonstrations. Some skilled lecturers have the ability to engage students using humor or insightful information.
The lecture is often coined as "direct instruction" which can be can be made into a more active instructional strategy when it is part of a mini- lesson .
The lecture portion of the mini-lesson is designed in a sequence where the teacher first makes a connection to previous lessons. Then the teacher delivers the content using a demonstration or a think-aloud . The lecture part of the mini-lesson is revisited after students have an opportunity for hands-on practice when the teacher restates the content one more time.
Socratic Seminar
In a whole group discussion , the instructor and the students share the focus of the lesson. Typically a teacher presents information through questions and answers, trying to ensure that all students are involved in learning. Keeping all students on task, however, may be difficult with large class sizes. Teachers should be aware that using an instructional strategy of whole-class discussions may result in passive engagement for some students who may not participate .
To increase engagement, whole-class discussions may take several different forms. The Socratic seminar is where an instructor asks open-ended questions allowing students to respond and build on each others thinking. According to education researcher Grant Wiggins , the Socratic seminar leads to more active learning when,
"...it becomes the student’s opportunity and responsibility to develop habits and skills that are traditionally reserved for the teacher."
One modification to the Socratic Seminar is the instructional strategy known as the fishbowl. In the fishbowl, a (smaller) inner circle of students respond to questions while a (larger) outer circle of students observes. In the fishbowl, the instructor participates as a moderator only.
Jigsaws and Small Groups
There are other forms of small group discussion. The most basic example is when the teacher breaks the class up into small groups and provides them with talking points that they must discuss. The teacher then walks around the room, checking on the information being shared and ensuring participation by all within the group. The teacher may ask students questions to ensure that everyone's voice is heard.
The Jigsaw is one modification on small group discussion that asks each student to become an expert on a particular topic and then share that knowledge by moving from one group to another. Each student expert then "teaches" the content to the members of each group. All members are responsible to learn all content from one another.
This method of discussion would work well, for example, when students have read an informational text in science or social studies and are sharing information to prepare for questions posed by the instructor.
Literature circles are another instructional strategy that capitalizes on active small group discussions. Students respond to what they have read in structured groups designed to develop independence, responsibility, and ownership. Literature circles can be organized around one book or around a theme using many different texts.
Role Play or Debate
Roleplay is an active instructional strategy that has students take on different roles in a specific context as they explore and learn about the topic at hand. In many ways, role-play is similar to improvisation where each student is confident enough to offer an interpretation of a character or an idea without the benefit of a script. One example could be asking students to participate in a luncheon that is set in a historical period (ex: a Roaring 20s "Great Gatsby" party).
In a foreign language class, students might take on the role of different speakers and use dialogues to help learn the language . It is important that the teacher has a firm plan for including and assessing the students based on their role-playing as more than participation.
The use of debates in the classroom can be an active strategy that strengthens skills of persuasion, organization, public speaking, research, teamwork, etiquette, and cooperation. Even in a polarized classroom, student emotions and biases can be addressed in a debate that begins in research. Teachers can foster critical thinking skills by requiring students to provide evidence to support their claims before any debate.
Hands-on or Simulation
Hands-on learning allows students to participate in an organized activity best evidenced in stations or science experiments. The arts (music, art, drama) and physical education are those recognized disciplines that require hands-on instruction.
Simulations are also hands-on but are different than role-playing. Simulations ask students to use what they have learned and their own intellect to work through an authentic problem or activity. Such simulations might be offered, for example, in a civics class where students create a model legislature in order to create and pass legislation. Another example is having students participate in a stock market game. Regardless of the kind of activity, a post-simulation discussion is important for assessing student understanding.
Because these kinds of active instructional strategies are engaging, students are motivated to participate. The lessons do require extensive preparation and also require the teacher to make clear how each student will be assessed for their participation and then be flexible with the results.
Software Program(s)
Teachers can use a variety of educational software on different platforms to deliver digital content for student learning. The software might be installed as an application or a program that students access on the internet. Different software programs are selected by the teacher for their content ( Newsela ) or for the features that allow students to engage ( Quizlet ) with the material.
Longterm instruction, a quarter or semester, can be delivered over software platforms online such as Odysseyware or Merlot . These platforms are curated by educators or researchers who provide specific subject materials, assessment, and support materials.
Short term instruction, such as a lesson, can be used to engage students in learning content through interactive games ( Kahoot !) or more passive activities such as reading texts.
Many software programs can collect data on student performance which can be used by teachers to inform instruction in areas of weakness. This instructional strategy requires that teacher vets the materials or learns the software processes of the program in order to best use the data that records student performance.
Presentation Through Multimedia
Multimedia methods of presentation are passive methods of delivering content and include slideshows (Powerpoint) or movies. When creating presentations, teachers should be aware of the need to keep notes concise while including interesting and relevant images. If done well, a presentation is a kind of lecture that can be interesting and effective for student learning.
Teachers may want to follow a 10/20/30 rule which means there are no more than 10 slides , the presentation is under 20 minutes, and the font is no smaller than 30 points. Presenters need to be aware that too many words on a slide can be confusing to some students or that reading every word on the slide aloud can be boring for an audience that can already read the material.
Movies present their own set of problems and concerns but can be extremely effective when teaching certain subjects. Teachers should consider the pros and cons of using movies before using them in the classroom.
Independent Reading and Work
Some topics lend themselves well to individual classroom reading time. For example, if students are studying a short story, a teacher might have them read in class and then stop them after a certain time to ask questions and check for understanding. However, it is important that the teacher is aware of student reading levels to make sure that students do not fall behind. Different leveled texts on the same content may be necessary.
Another method some teachers use is to have students select their own reading based on a research topic or simply on their interests. When students make their own choices in reading, they are more actively engaged. On independent reading selections, teachers may want to use more generic questions to assess student understanding such as:
- What did the author say?
- What did the author mean?
- What words are the most important?
Research work in any subject area falls into this instructional strategy.
Student Presentation
The instructional strategy of using student presentations as a way to present content to the class as a whole can be a fun and engaging method of instruction. For example, teachers can divide up a chapter into topics and have the students "teach" the class by presenting their "expert" analysis. This is similar to the Jigsaw strategy used in small group work.
Another way to organize student presentations is to hand out topics to students or groups and have them present information on each topic as a short presentation. This not only helps students learn the material in a deeper manner but also provides them with practice in public speaking. While this instructional strategy is largely passive for the student audience, the student presenting is an active demonstrating a high level of understanding.
Should students choose to use media, they should also adhere to the same recommendations that teachers should use with Powerpoint (ex: a 10/20/30 rule) or for films.
Flipped Classroom
Student use of all manner of digital devices (smartphones, laptops, i-Pads, Kindles) that allow access to content brought the beginning of the Flipped Classroom. More than a switch of homework to classwork, this relatively new instructional strategy is where the teacher moves the more passive elements of learning such as watching a powerpoint or reading a chapter, etc.as an activity outside of the classroom, usually the day or night before. This design of the flipped classroom is where valuable class time is available for more active forms of learning.
In flipped classrooms, one goal would be to guide students to make decisions on how to learn better on their own rather than having the teacher deliver information directly.
One source of materials for the flipped classroom is Khan Academy, This site originally began with videos that explained math concepts using the motto "Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere."
Many students preparing for the SAT for college entry might be interested to know that if they are using Khan Academy, they are participating in a flipped classroom model.
- Whole Group Discussion Pros and Cons
- 6 Tips to Liven Up Your Lectures
- 10 Ways to Keep Your Class Interesting
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Lecturing
- Using Effective Instructional Strategies
- How Scaffolding Instruction Can Improve Comprehension
- 6 Teaching Strategies to Differentiate Instruction
- How to Design Lessons When the Student Can't Read
- Gradual Release of Responsibility Creates Independent Learners
- 5 Keys to Being a Successful Teacher
- Topics for a Lesson Plan Template
- How to Facilitate Learning and Critical Thinking
- Teaching Strategies to Promote Student Equity and Engagement
- Strategies for Teachers to Develop Positive Relationships With Students
- The Pros and Cons of Block Schedules
- How to Make Lesson Plans for Adult Students
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered visual tool ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Visual Academy
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
75 Unique School Presentation Ideas and Topics Plus Templates
Are you tired of seeing the same PowerPoints repeating overused and unoriginal school presentation ideas covering repeated topics in your classes?
You know what I’m talking about; we’ve all been there, and sat through yawn-worthy demonstrations, slides, or presentation videos covering everything from the solar system, someone’s favorite pet, past presidents of a country, to why E=mC squared.

From grade school to university, first graders to college students, we are obligated to create, perform, and observe academic presentations across a plethora of curriculums and classes, and not all of these public speaking opportunities fall into the category of an ‘interesting topic’.
Yet, have no fear! Here at Piktochart, we are here to help you and your classmates. From giving examples of creative and even interactive presentation ideas, providing presentation videos , and suggesting interactive activities to give your five minutes of fame the ‘wow’ factor that it deserves, this article is your guide!
Our massive collection of unique school and college presentation ideas and templates applies if you’re:
- A teacher looking to make your class more engaging and fun with student presentations.
- A student who wants to impress your teacher and the rest of the class with a thought-provoking, interesting topic.
A Curated List of Interesting Topics for School Presentations
Did you know that when it comes to presentations , the more students involved improves retention? The more you know! Yet sometimes, you need a little help to get the wheels moving in your head for your next school presentation .
The great thing about these ideas and topics is you can present them either in face-to-face classes or virtual learning sessions.
Each school presentation idea or topic below also comes with a template that you can use. Create a free Piktochart account to try our presentation maker and get access to the high-quality version of the templates. You can also check out our Piktochart for Education plan .
Want to watch this blog post in video format? The video below is for you!
The templates are further divided into the following categories covering the most popular and best presentation topics. Click the links below to skip to a specific section.
- Unique science presentation topics to cultivate curiosity in class
- Engaging culture and history presentation ideas to draw inspiration from
- Health class presentation topics to help students make healthy lifestyle decisions
- Data visualization ideas to help students present an overwhelming amount of data and information into clear, engaging visuals
- First day of school activity ideas to foster classroom camaraderie
- Communication and media topics to teach students the importance of effective communication
- Topics to help students prepare for life after school
We hope this list will inspire you and help you nail your next school presentation activity.
Unique Science Presentation Topics to Cultivate Curiosity in Class
Science is a broad field and it’s easy to feel overwhelmed with too many topics to choose for your next presentation.
Cultivate curiosity in the science classroom with the following unique and creative presentation ideas and topics:
1. Can life survive in space?

2. Do plants scream when they’re in pain?

3. What are the traits of successful inventors?

4. How vaccines work
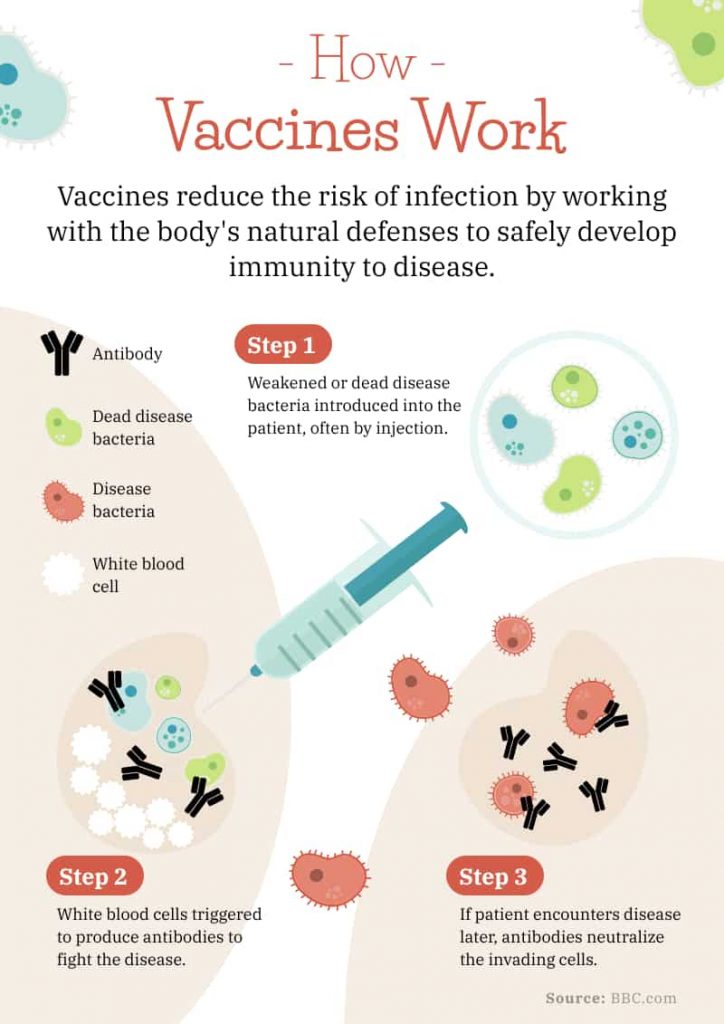
5. Massive destruction of the Koala’s habitat in Australia

6. Left brain versus right brain

7. What are great sources of calcium?

Get access to high-quality, unique school presentation templates by Piktochart for Education.
Create and collaborate in the classroom using Piktochart’s customizable and printable templates for your school reports, presentations, and infographics.
8. Recycling facts you need to know

9. Do you have what it takes to be a NASA astronaut?

10. The rise of robots and AI: Should we be afraid of them?
11. How far down does the sea go?

12. The stages of sleep
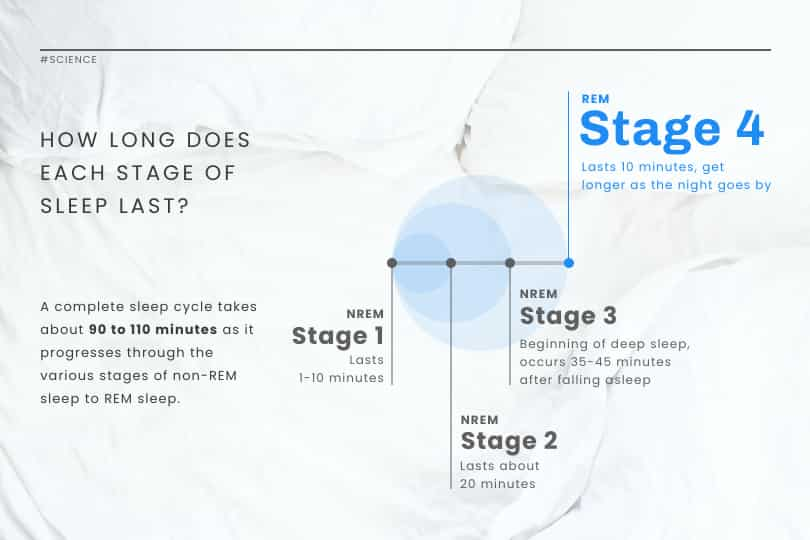
13. Will Mars be our home in 2028?
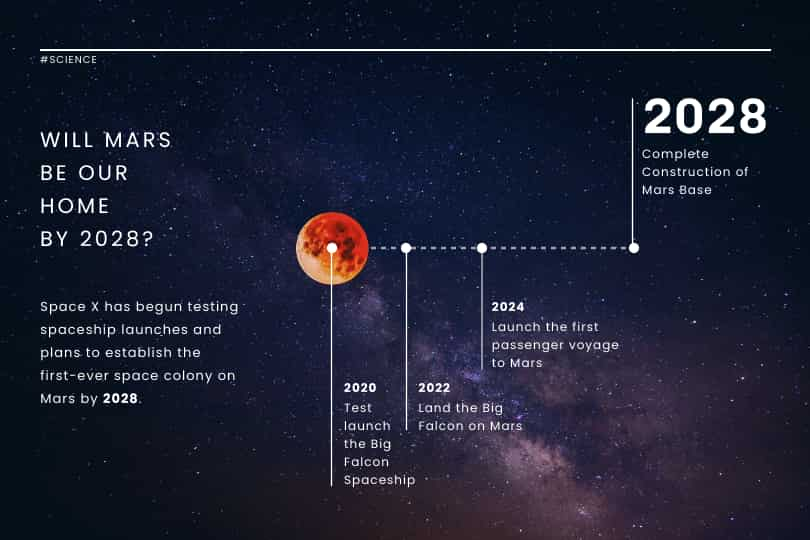
14. A quick look at laboratory safety rules

15. The first person in history to break the sound barrier
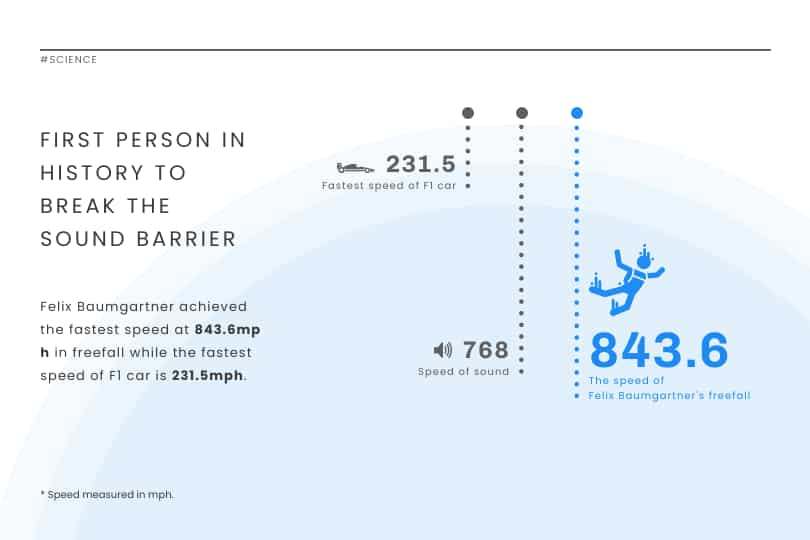
Engaging Culture and History Presentation Ideas to Draw Inspiration From
History is filled with equally inspiring and terrifying stories, and there are lessons that students can learn from the events of the past. Meanwhile, interactive presentations about culture help students learn and embrace diversity.
16. Women in history: A conversation through time

17. The sweet story of chocolate

18. A history lesson with a twist


19. The history of basketball
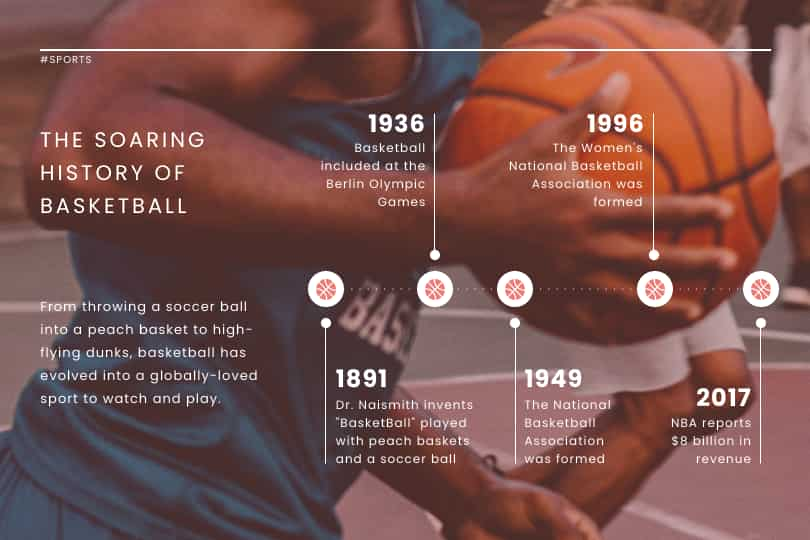
20. The origin of the Halloween celebration
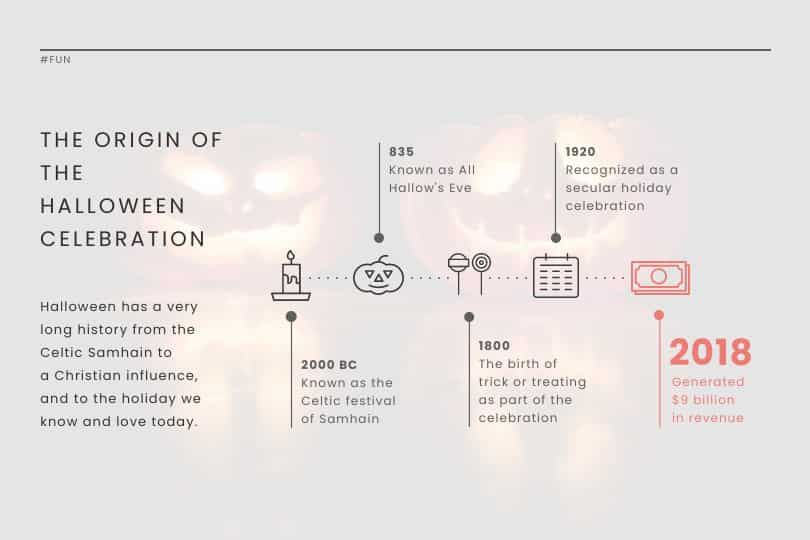
21. AI History
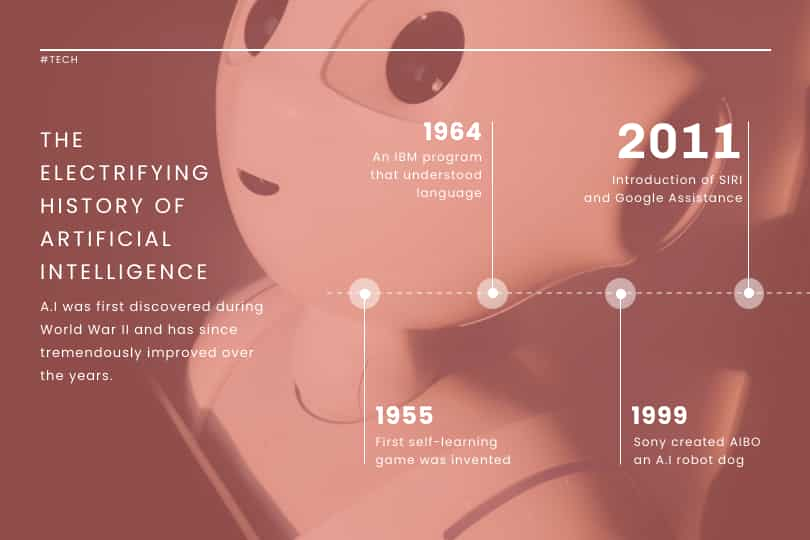
22. What you need to know about New Zealand

23. 1883 volcanic eruption of Krakatoa

24. Roman structures: 2000 years of strength

25. The most famous art heists in history
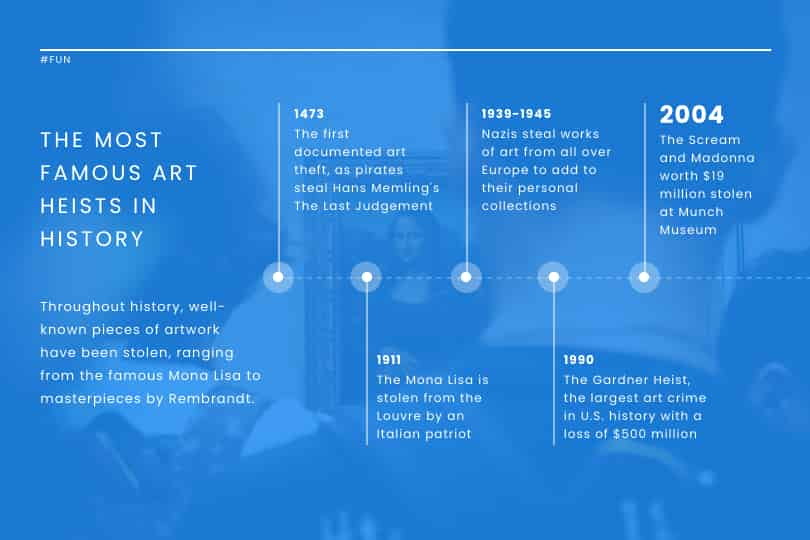
26. Elmo: The story behind a child icon
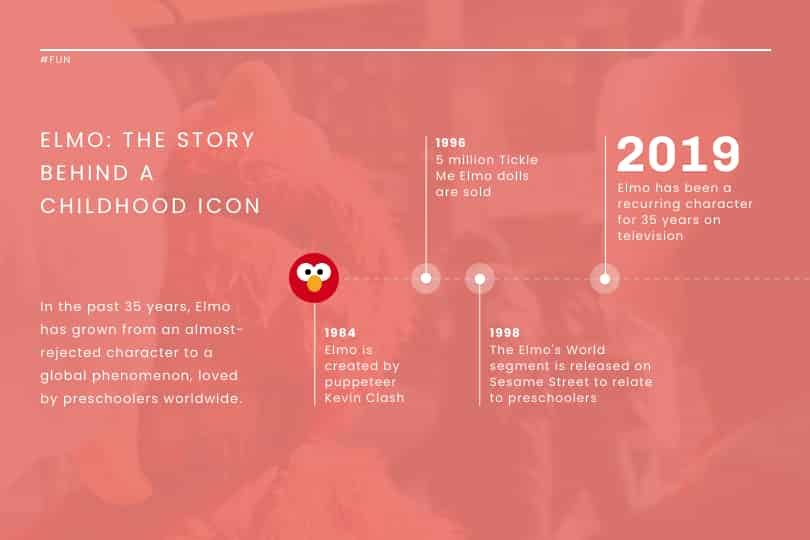
27. 10 things you should know before you visit South Korea
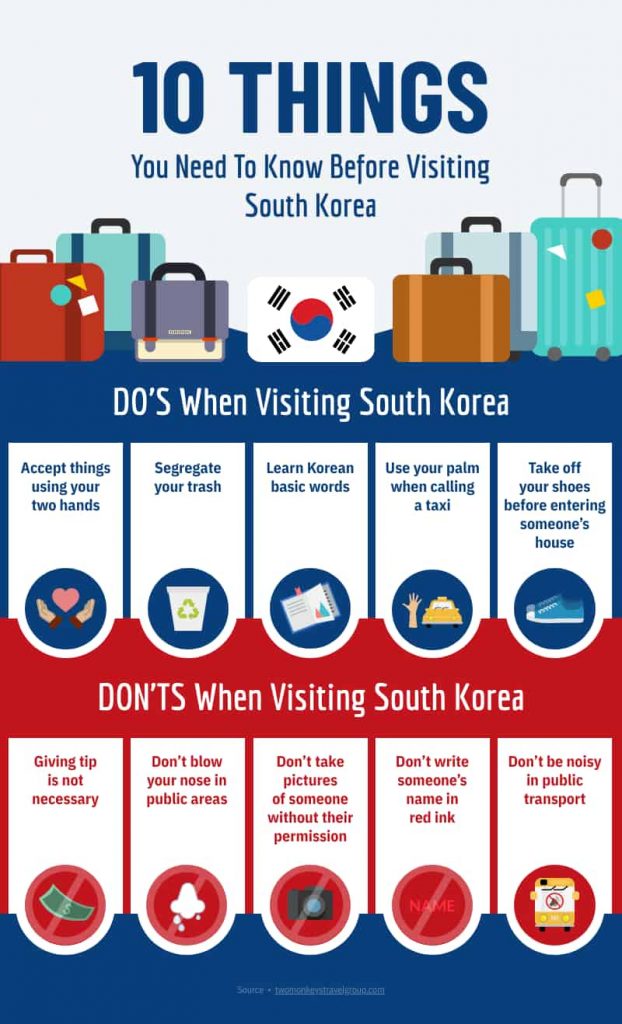
28. 8 things you didn’t know about these 8 countries
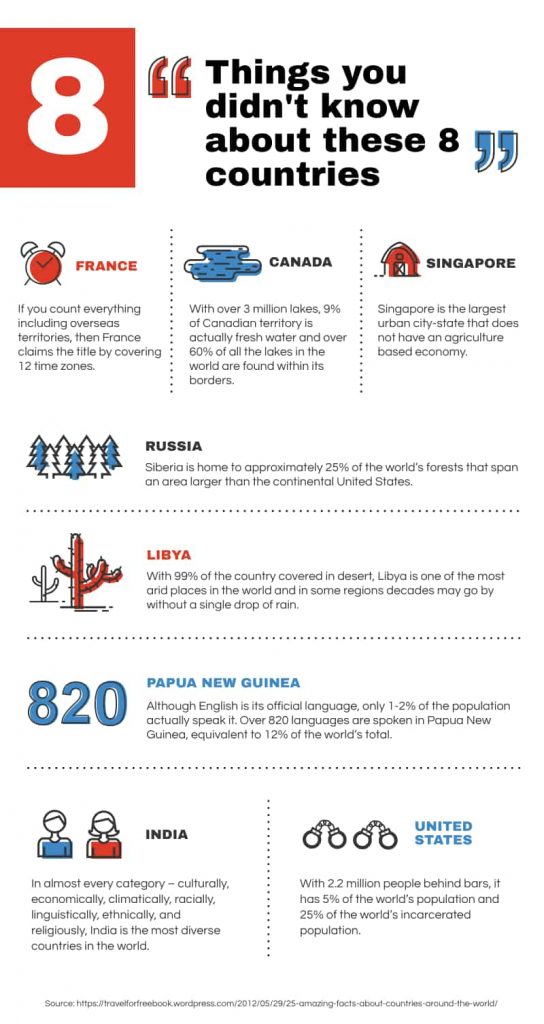
Health Class Presentation Topics to Help Students Make Healthy Lifestyle Decisions
Want to learn how to engage students with healthcare topic ideas? Then consider using these templates for your next interactive presentation.
According to the CDC , school-based health education contributes to the development of functional health knowledge among students. It also helps them adapt and maintain health-promoting behaviors throughout their lives.
Not only will your presentation help with keeping students engaged, but you’ll also increase class involvement with the right slides.
The following examples of health and wellness interactive presentations include fun ideas and topics that are a good start.
29. How to look after your mental health?
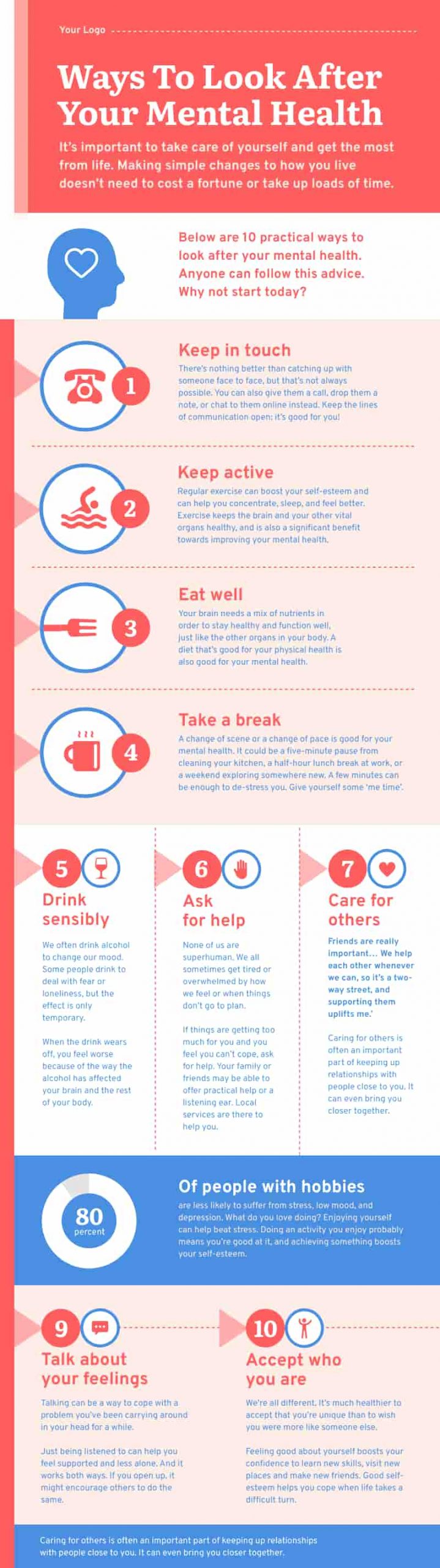
30. The eradication of Polio
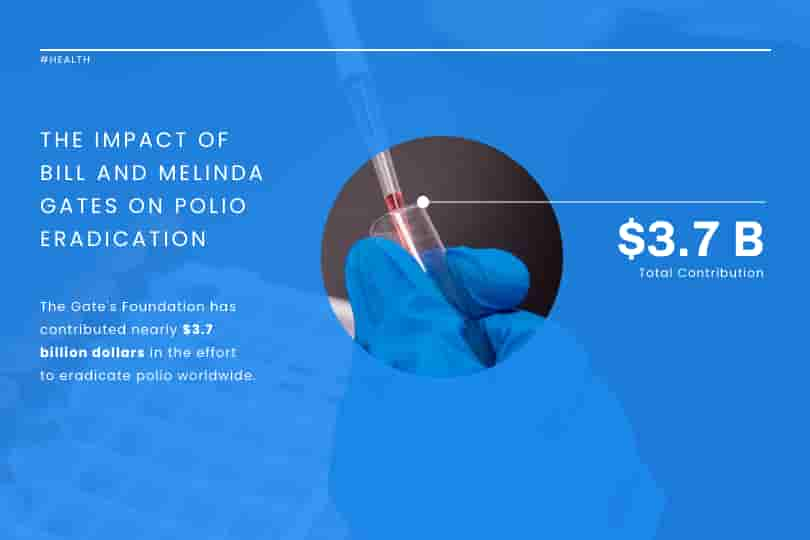
31. How to have a healthy lifestyle

32. 10 handwashing facts

33. Myths and facts about depression

34. Hacks for making fresh food last longer

35. Ways to avoid spreading the coronavirus
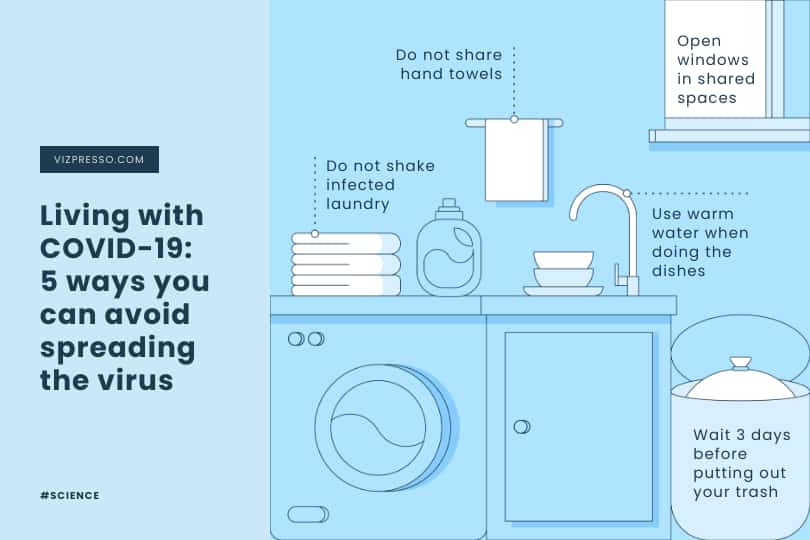
36. Mask protection in 5 simple steps

37. Everything you need to know about the flu

38. All about stress: Prevention, tips, and how to cope
39. The importance of sleep

40. Is milk tea bad for you?

41. How to boost happiness in 10 minutes

42. How dirty are debit and credit cards
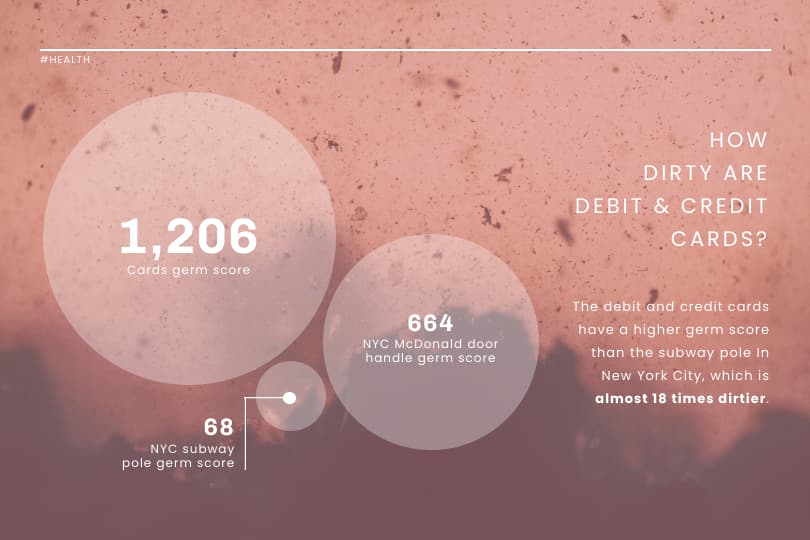
43. Why do you need sunscreen protection

Data Visualization Ideas to Help Students Present Overwhelming Amounts of Data in Creative Ways
Data visualization is all about using visuals to make sense of data. Students need to pull the main points from their extensive research, and present them by story telling while being mindful of their classmates’ collective attention span.
As far as student assignments go, storytelling with data is a daunting task for students and teachers alike. To keep your audience interested, consider using a non linear presentation that presents key concepts in creative ways.
Inspire your class to be master data storytellers with the following data visualization ideas:
44. Are we slowly losing the Borneo rainforest?

45. Skateboard deck design over the years
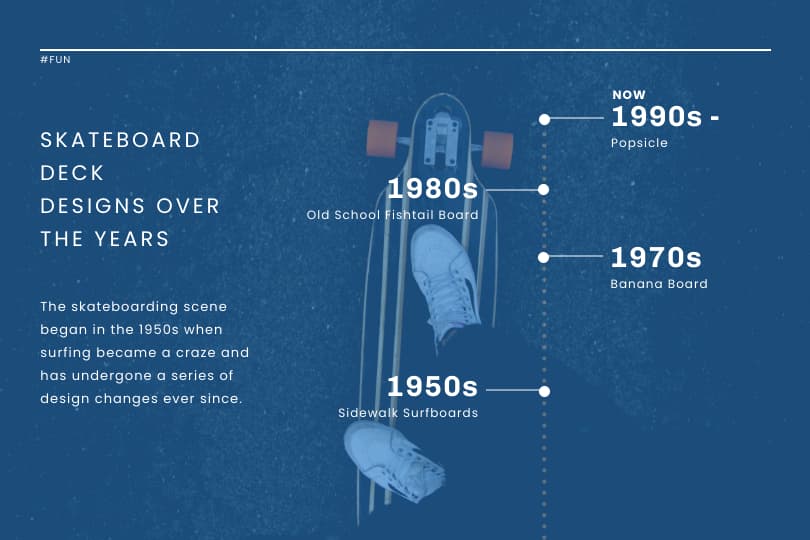
46. Food waste during the Super Bowl
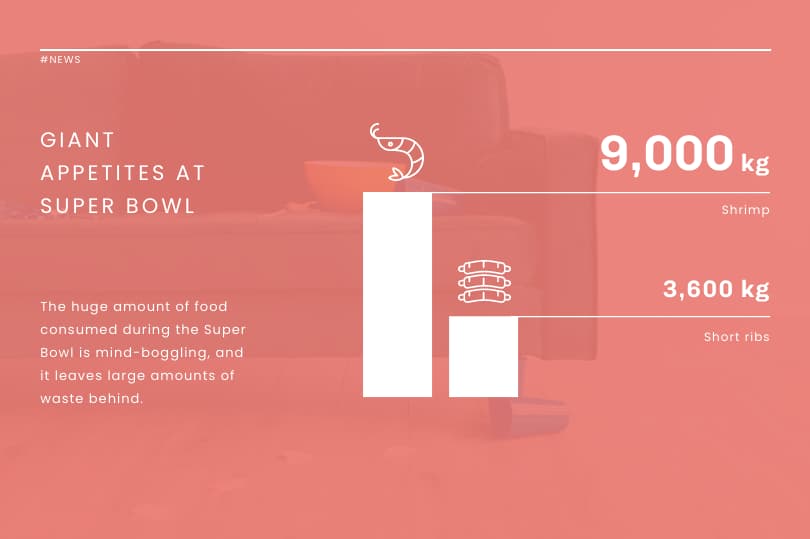
47. The weight of the tallest building in the world
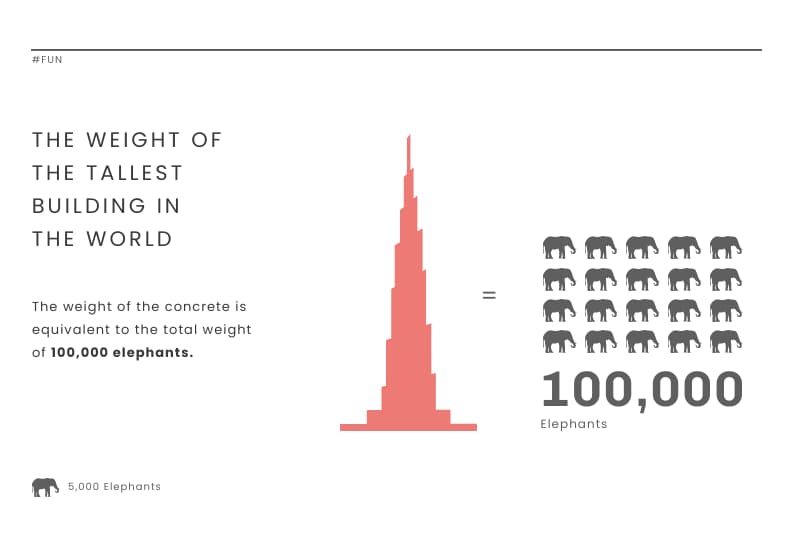
48. Infographic about data and statistics
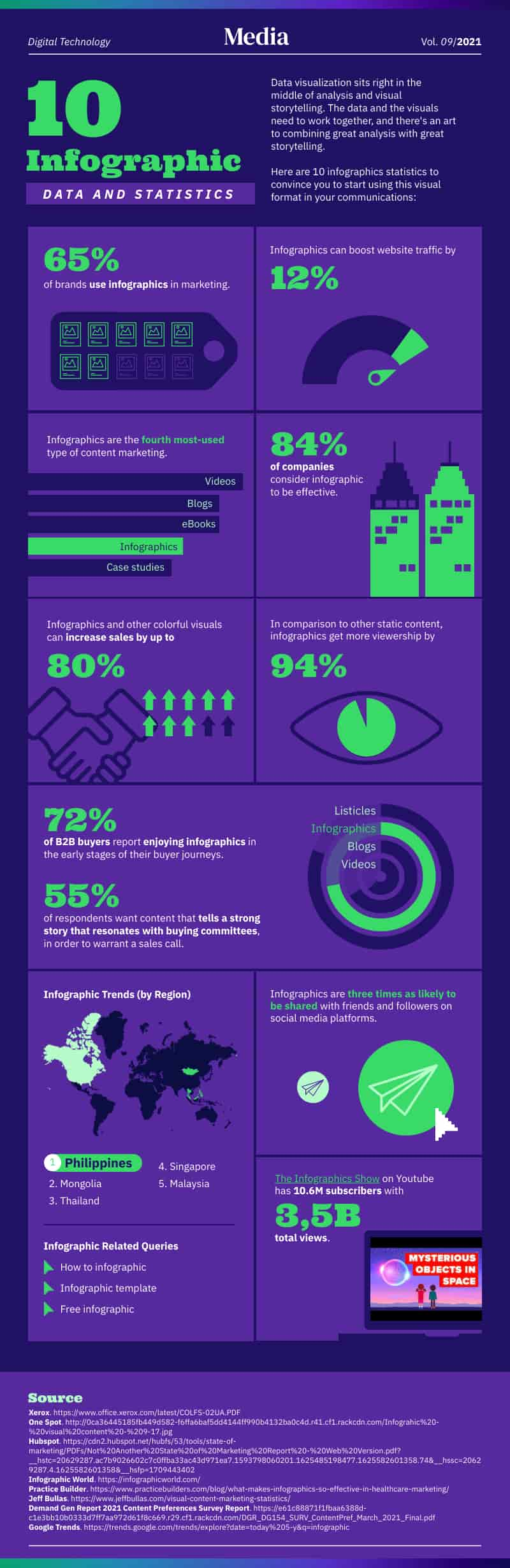
49. Stats about cyberbullying
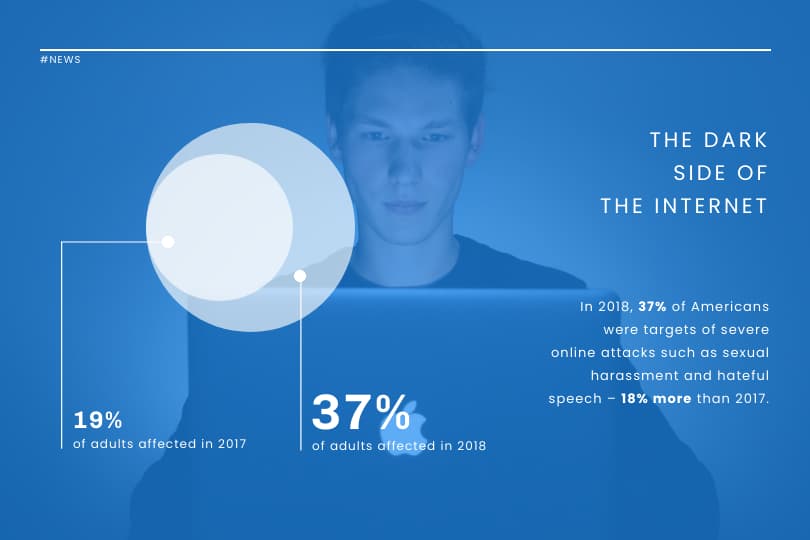
50. How whales combat climate change

First Day of School Interactive Activity Ideas to Foster Whole-class-Camaraderie
Calling all teachers! Welcome your new students and start the school year with the following back-to-school creative presentation ideas and relevant templates for first-day-of-school activities.
These interactive presentations grab the attention of your students and are remarkably easy to execute (which is the main educator’s goal after all)!
51. Meet the teacher
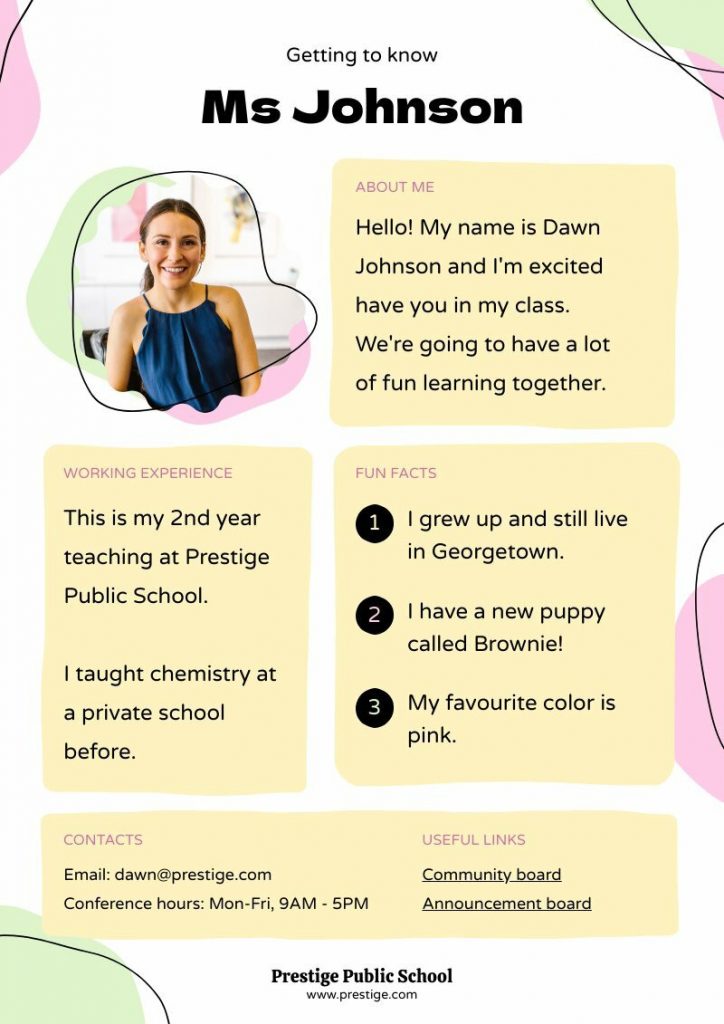
52. Example: all about me

53. Self-introduction

54. Tips on how to focus on schoolwork

55. Course plan and schedule

Give our class schedule maker a try to access more templates for free. You can also access our presentation-maker , poster-maker , timeline-maker , and more by simply signing up .
56. Interpreting a student’s report card (for parents)

57. Introduction of classroom rules

58. Assignment schedule
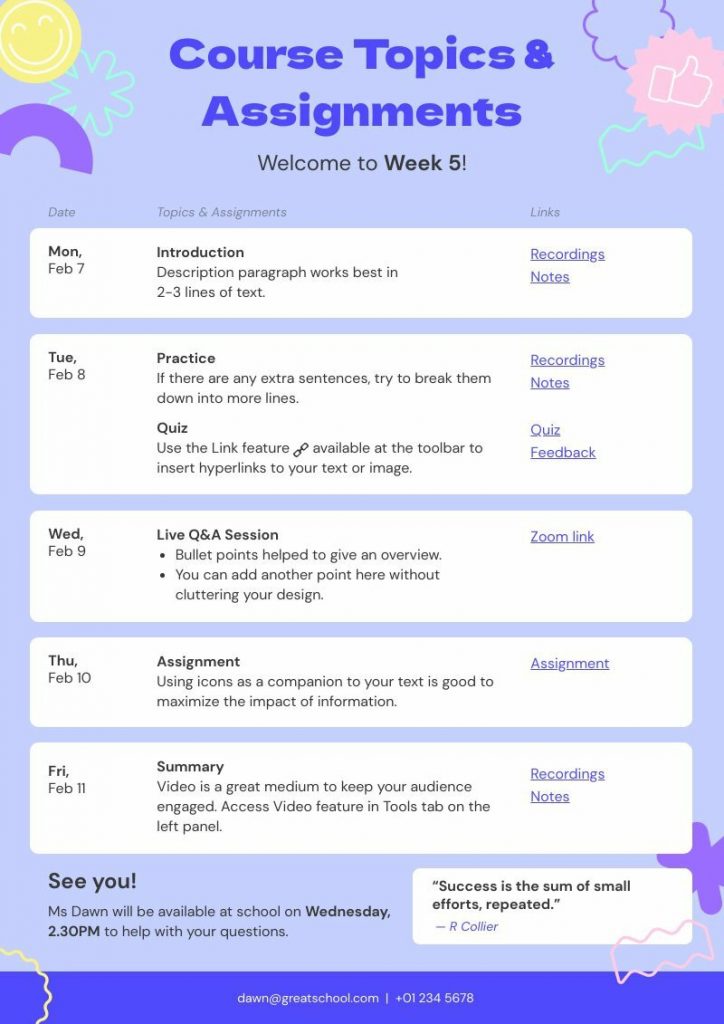
59. Daily planner
60. Course syllabus presentation

61. How to write a class presentation

Topics to Teach Students the Importance of Effective Communication
Visual media helps students retain more of the concepts taught in the classroom. The following media topics and infographic templates can help you showcase complex concepts in a short amount of time.
In addition, interactive presentation activities using these templates also encourage the development of a holistic learning process in the classroom because they help focus on the three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
62. Interactive presentation do’s and don’ts

63. How to create an infographic
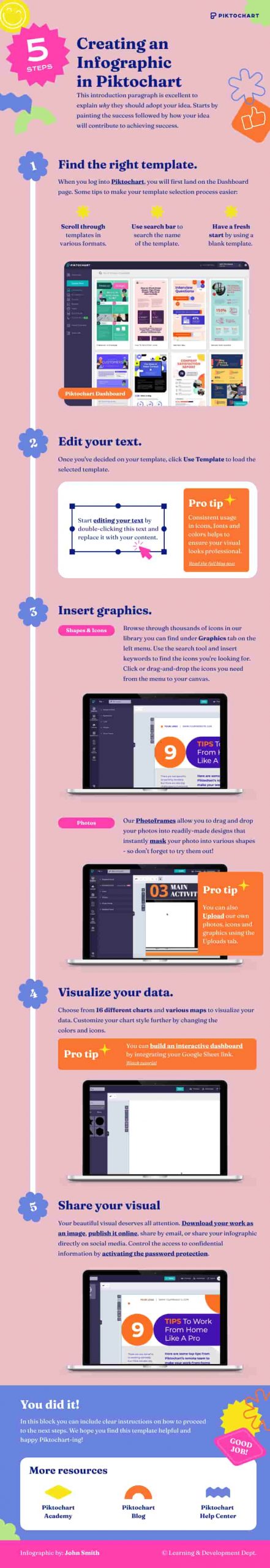
Recommended reading : How to Make an Infographic in 30 Minutes
64. How to improve your internet security and privacy
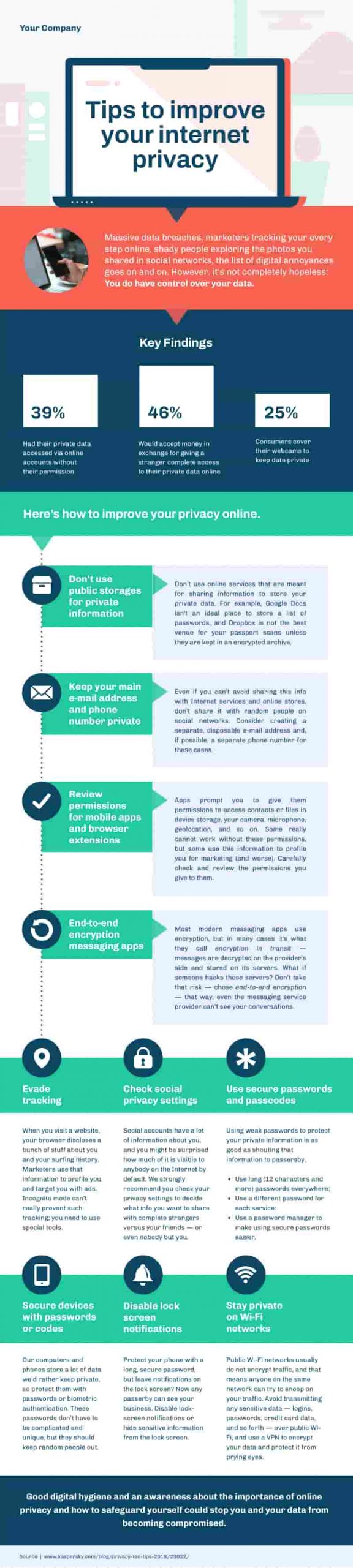
65. What is design thinking?

66. What are your favorite software tools to use in the classroom?

Presentation Topic Ideas to Help Students Prepare for Life After School
One of the things that makes teaching a rewarding career is seeing your students take the learning and knowledge you’ve instilled in them, and become successful, productive adults.
From pitching a business idea to starting your podcast, the following topics are good starting points to prepare students for the challenges after graduation (aka adulting 101):
67. How to make a resume

68. How to start a startup
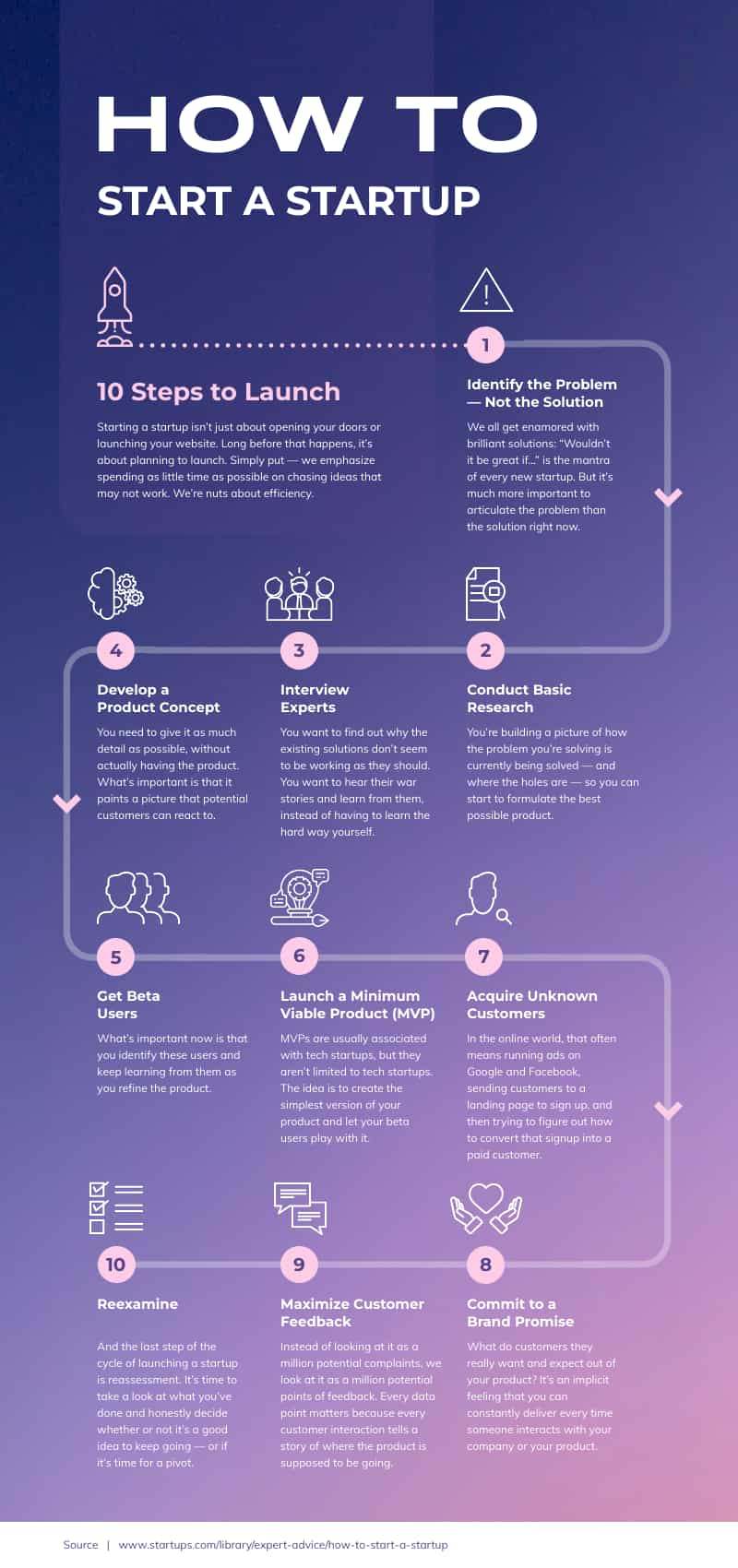
69. Credit card vs. debit card
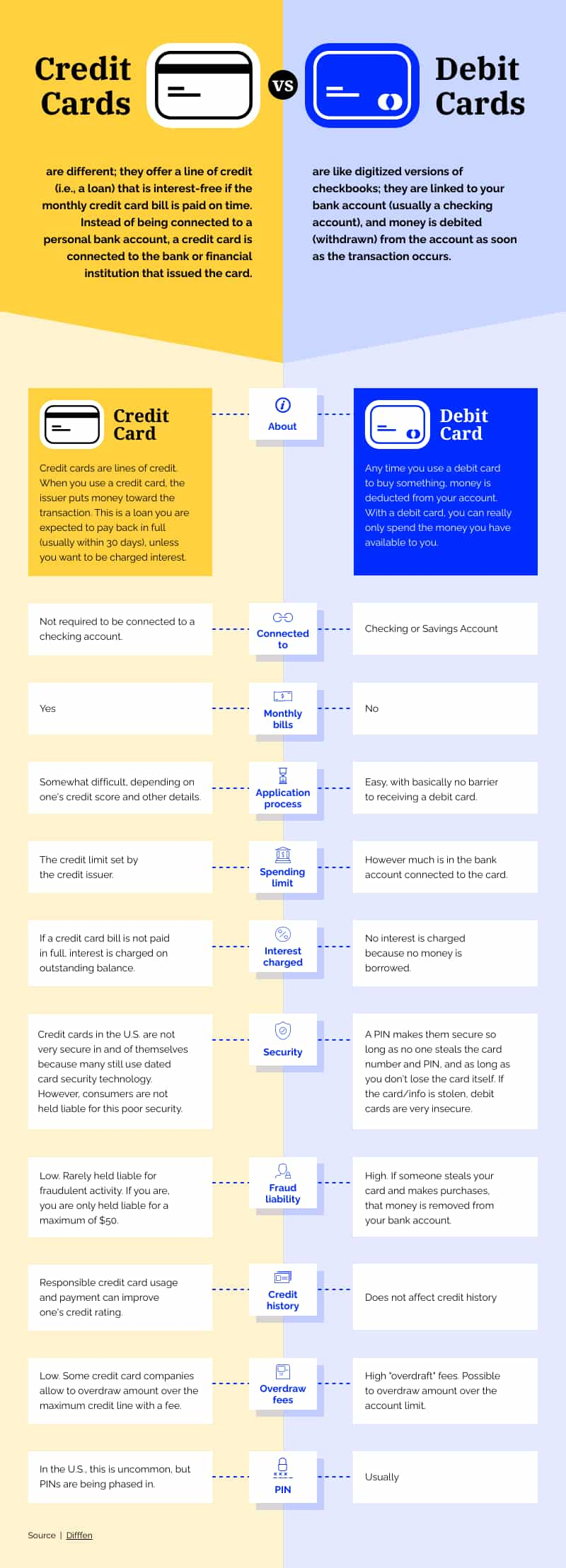
70. Pros and cons of cryptocurrency
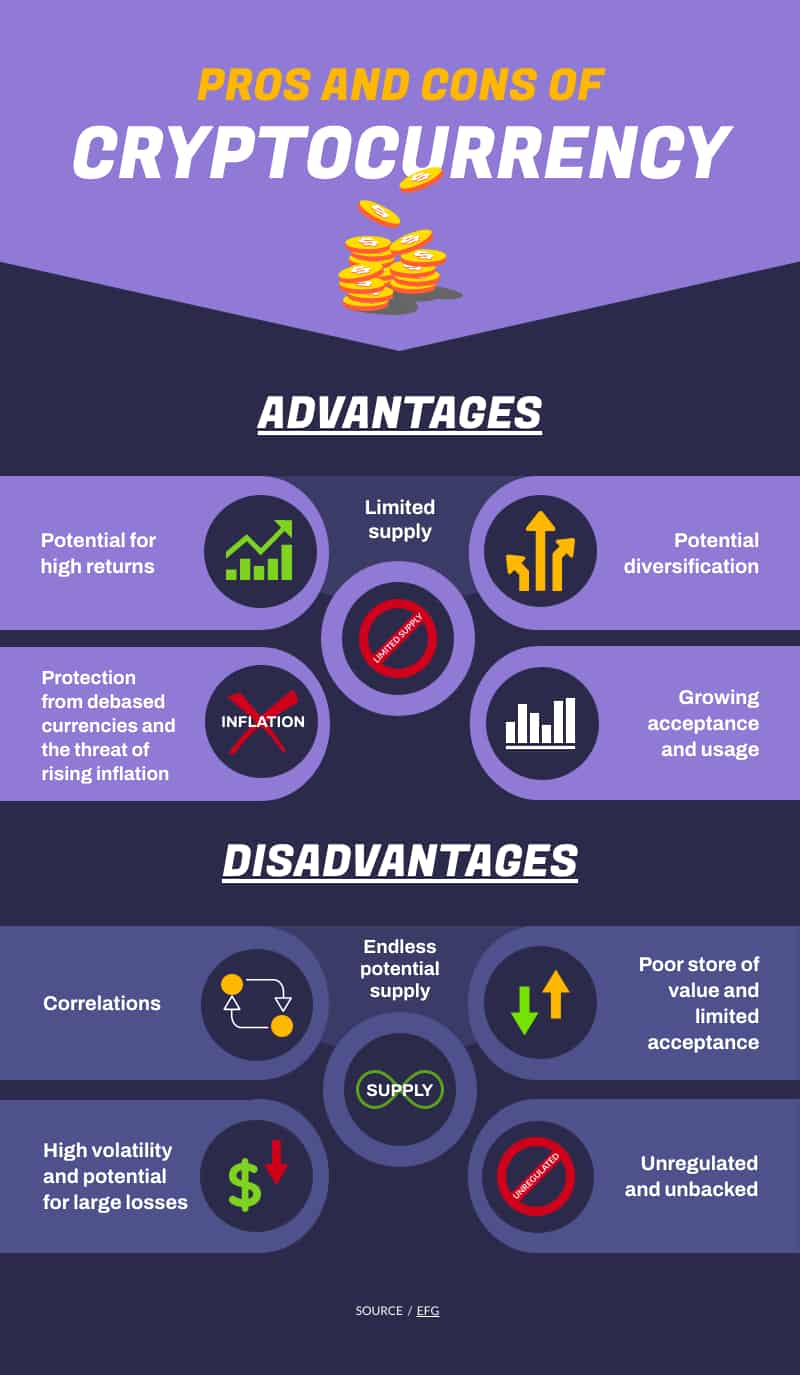
71. How to save on travel
72. How to do a SWOT analysis

73. How to pitch a business idea

74. Habits of successful people

75. Starting your own podcast: A checklist

Find out how a high school teacher like Jamie Barkin uses Piktochart to improve learning in the classroom for her students.
Pro tip: make your presentation as interactive as possible. Students have an attention span of two to three minutes per year of age. To keep minds from wandering off, include some interactive games or activities in the lesson. For example, if you conducted a lesson on the respiratory system, you could ask them to practice breathing techniques.
Maintain eye contact with your students, and you’ll get instant feedback on how interested they are in the interactive presentation.
Make School Presentation Visuals Without the Hassle of Making Them From Scratch
School presentations, when done right, can help teachers engage their classes and improve students’ education effectively by presenting information using the right presentation topic.
If you’re pressed for time and resources to make your school presentation visuals , choose a template from Piktochart’s template gallery . Aside from the easy customization options, you can also print and download these templates to your preferred format.
Piktochart also professional templates to create infographics , posters , brochures , reports , and more.
Creating school-focused, engaging, and interactive presentations can be tedious at first, but with a little bit of research and Piktochart’s handy templates, you’re going to do a great job!
The future of learning is interactivity and collaboration.
Foster interactive and collaborative learning using Piktochart for Education. Share your work, get feedback, and brainstorm on the fly. With Piktochart, everyone’s on the same page. Finally.

Kyjean Tomboc is an experienced content marketer for healthcare, design, and SaaS brands. She also manages content (like a digital librarian of sorts). She lives for mountain trips, lap swimming, books, and cats.
Other Posts
From Chaos to Clarity: Streamlining Your Student Life with a Schedule Builder

Resume with No Experience

15 Infographic Examples for Students (Plus Editable Templates)
Do you want to be part of these success stories, join more than 11 million who already use piktochart to craft visual stories that stick..

- What solution is best for me?
- Download the Government eBook

13 Interactive Presentation Ideas to Engage Students in Class
If you’re a teacher, you’ll know that there’s a lot to think about when you’re in class. It’s important to ensure that what you’re teaching the children is as educational and as interesting as possible - with the aim of engaging the students in the subject and hopefully even enabling them to enjoy learning!
This can be a very difficult balance to strike. However, it’s made easier by these interactive presentation ideas listed in this article, which can engage even the most distracted of students!
How to display presentations
The best classroom gadget to show these presentations on is an interactive display. These are large devices that are mounted to the wall and can connect seamlessly with any video collaboration applications. You can connect interactive displays to the internet and further use them as a powerful classroom teaching tool, to help students learn in a fully interactive and efficient way. We sell interactive displays for classrooms here at Avocor.
Interactive class presentation ideas
Ice breakers.
Many work-related presentations start with an icebreaker, and there’s no reason why a presentation to a class of students should be any different.
The icebreaker question will depend on the class and age of students, but could be something like the following:
- If you could be an animal, what would it be and why?
- What would be your dream place to go on holiday?
- If you could have dinner with three historical characters, who would they be and why?
- If you could make any kind of potion, what would it do?
Incorporating video is one of the best interactive presentation ideas for students. Even if the video is about the same topic as the presentation, the fact that it’s a different type of media will interest the class.
You can either find a suitable video on YouTube or another video software or, if you have a file saved, paste it directly into the presentation .

Questions and answers
Questions and answers are a great way to get the whole class involved. You could invite one student to ask a hypothetical question about the topic, and another could answer.
For example, if you’re learning about Henry VIII and his six wives , you could ask a student to ask a question about them. Their question could be “what was Henry VIII’s favourite food?” or something similar.
When another student answers, you could ask them to explain their answer - for example, if they say “meat and bread”, they might carry on to explain that that was the main diet for royalty at the time.
Songs are a good way to interest younger kids in a topic. You can find songs about all sorts of subjects on YouTube. For example, this seven continents song could be suitable for a Geography song.
Many songs on YouTube have lyrics, so you could encourage your class to practice their reading as they sing along.
Some presentations are made more interactive by external objects - and if you want to engage younger kids, bringing some props can really help the lesson to come alive.
For example, if you’re doing a history lesson about the Ancient Egyptians , you could bring some figures of Tutankhamun, the Sphinx and the ancient pyramids for everybody to see.
Class involvement
Asking for direct class involvement throughout the presentation is a good way to ensure that students stay engaged. For instance, if you’re doing a presentation about animals, you could ask students to make a noise every time you mention a certain animal.
You could ask them to roar each time you mention lions, or make a monkey noise each time you talk about monkeys. This is a great way to ensure that the students are paying attention!
Transitions and animations
A simple way to ensure that your students are paying attention is to use different transitions and animations throughout your presentation.
If you’re teaching older kids or teenagers, you might not want to have too many of these, but younger kids will love seeing every item bounce onto the screen. It’s a wonderful way to get them interested in technology in the classroom !
Quizzes are an effective way to engage students of any age. You can include these at the end of the presentation and they can include questions that you’ve covered in the session.
If your students know that there will be a quiz at the end of the class, they may be more likely to pay attention throughout it! You could also ensure maximum engagement by telling students that there will be prizes for the winner of the quiz - such as stickers or sweets.
Interactive games
Interactive games for class presentations are always a popular way to ensure that students stay engaged! Some examples include:
- noughts and crosses or tic tac toe
- pictionary
- hangman or an alternative like spaceman
- 21 questions
It’s best to make these games related to the subject. For example, the game “21 questions” involves you thinking of a character and students asking questions with a yes or no answer about what character you are.
If you’re teaching a history class, the character could be somebody from history (such as Florence Nightingale or Queen Victoria), or if you’re instructing a science lesson, the character could be a famous scientist (like Einstein or Steven Hawking).
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is another great way to get the class involved. You can use an interactive display to create the brainstorm diagram on. Students can take turns writing on the board, and it can securely connect to any external devices, so any remote class members can join in.
With an interactive display, you can also immediately share the diagram to the rest of the class once it’s finished, so they can keep it to refresh their knowledge of a topic.
For example, if you’re teaching your class about Australia in geography , you could ask their students what they may already know about Australia. They could come up with some items like the following:
- Sydney Opera House
- Aboriginal art
- outback
You could then create a spider diagram with different legs depending on the topic. For this list, there could be an “animals” leg for kangaroos and koalas, an “architecture” leg for the Sydney Opera House, a “landscapes” leg for the rainforest and outback, a “culture” leg for Aboriginal art and a “food” leg for BBQ.
Make a story
Making a story about the topics covered can encourage creativity around the topic. To do this, write down a couple of opening lines to a story related to the topic that you’re teaching.
For example, if you’re teaching students about the Ancient Roman Empire, you could start by saying “Ronald the Roman lived in the British City of Bath, where the Romans had arrived 20 years before. He spent most of his time at work, where he built houses for the rest of the Romans”.
Then, you could invite a student to continue the story, encouraging them to stay as on-topic as possible. You could even give out a prize to the student with the best part of the story. Depending on the size of the class, you could ask every student to contribute.
Stories also work well for English lessons. In these classes, the topic of the story doesn’t matter as much, but you could encourage students to use whatever language they’ve been learning.
For example, if your class has been focused on adjectives, you could ask students to put as many adjectives as possible in each part of their story.
Have a short play
You could take your stories to the next level by creating a short play on one of your slides. This could be based on whatever topic you’re learning about, and you could select a few students to come to the front of the class and read out the lines.
You may wish to create this personally, find a relevant play online or you could even turn a well-known story into a play!
Virtual field trip
One of the most creative interactive school presentation ideas is to take the class on a virtual field trip. This is particularly valuable for geography lessons, where you may learn about places that students might not be able to visit in person, like the Amazon rainforest or even under the sea!
You could link to Google maps, where you could use Google Earth to explore a particular area. Alternatively, there are some YouTube channels that specialise in virtual tours and field trips, such as this one which details all you need to know about rainforests .
If you have a classroom full of students and want to keep them as engaged as possible while teaching them new material, try some of these interactive games for classroom presentations and other ideas!
By incorporating some of these interactive ideas into your presentation, you’ll have the students’ full undivided attention and ensure that they not only enjoy the class but retain the information.
Related Articles
Elevate your space with avocor x series: the award-winning sleek solution for impactful displays, elevate organizational efficiency with avocor: integrating montage & rise vision, enhancing hybrid workspaces: microsoft teams meets avocor l series display, avocor: advances digital collaboration for the hybrid world with google workspace, bigger and better - the 21:9 display sector, get in touch, sign up for our newsletter.
Keep up to date with all the latest from Avocor and partners and get information on upcoming events and exciting product news.

Latest Updates
Useful links, ready to talk.
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
- Slidesgo School
- Presentation Tips
Create Engaging Presentations for Your Online Classroom

Teachers of the world, we are here to help you! Due to the coronavirus pandemic, schools worldwide are transitioning to a completely new model of education: in-person classes are out, distance learning is in. As schools adjust to this new normal, teachers everywhere are scrambling to find the resources they need. Slidesgo can help. Check out our free templates for education and create presentations that are effective , engaging and interactive. They are free, fully-customizable, available in Google Slides and PowerPoint formats and easy to integrate into platforms such as Google Classroom. Of course, creating engaging presentations can be a difficult and time-consuming process. So here are some tips for making more effective presentations for distance learning.
Find a great template that fits your age group and subject
Make one presentation per subject, don’t overload your slides with unnecessary text, enrich your presentations with audio and video, use mind maps, try more graphic organizers, make flashcards, make your presentations engaging and interactive, turn your presentations into stories.
Don’t start from scratch. Find a template! This one simple action will save you an enormous amount of time and effort. Once you have the right template, customize it to suit your needs. At Slidesgo we have made the searching process easy for you, allowing to search by keywords and filter your searches by topic, style, color and more
Online teachers are often overwhelmed by the sheer number of documents and messages that they have to deal with every day. But don’t overload yourself by creating a separate presentation for every class session or topic. The key here is simplicity. Try a different strategy: make just ONE presentation per school subject and add to it as you go. Share it with your students and update it as needed, so it serves as both a teaching tool and a record of what has been learned. And as your presentation gets longer, make it easy to navigate by adding a simple table of contents with links to individual slides or sections.
Using links to go to specific slides
Forget long sentences. Get straight to the point with concise sentences that express key concepts. This is a basic principle for all presentations but it’s even more important for distance learning, where visual learning is key. Students don’t pay attention to slides that are full of lengthy texts. Their attention goes straight to the images and the way the information is presented graphically. But be careful -- don’t overload your slides with images either, or else it will end up looking overcrowded and confusing. Great presentations focus on presenting key ideas with minimal text, concise messages and clear visual organization.
Reducing the text to concise messages
First-time presentation makers usually focus just on text and images. But slides have evolved and expert teachers take advantage of new features to enrich their presentations. Try using an animated gif instead of a still image and you’ll find that conveys your idea much better. Don’t be afraid to use super-short audio and video clips: they are just as easy to insert as a still image and they can add a whole new dimension to your presentations.
Using videos or images
Mind maps are a great way to organize and present content and concepts. They are great to use at the both beginning and end of a unit, when you’re introducing a topic and also when you’re summarizing what’s been learned. They give students an idea of the “big picture” and help them remember key ideas. Mind maps organize information into a logical hierarchy, allowing you to move from a general topic, to key concepts and then to examples. Finally, mind maps give a graphic representation of the relationships between ideas, which promotes deeper understanding. If you’ve never used mind maps before, check out the examples at Slidesgo and get started!
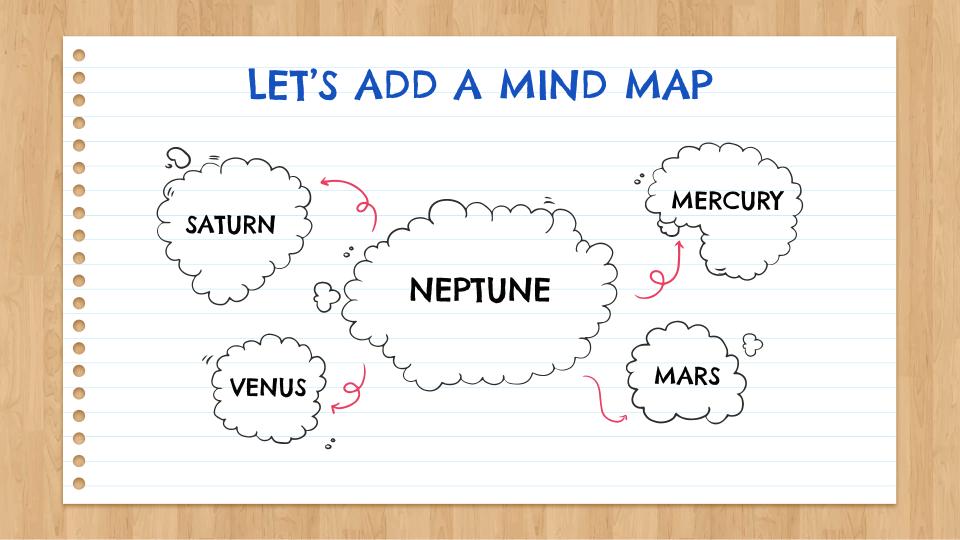
Adding a mind map to organize concepts
Graphic organizers are extremely powerful tools for online learning. If you are a beginner, start by inserting a simple table into your slides to organize information or label images. Next, try using an organizational chart or a graph. Get familiar with the tools from templates to add text fields, bubbles and arrows to connect the parts. You’re off and running! There’s such a wide range of graphic organizers, from flow charts to concept maps, timelines to Venn diagrams. There’s no end to the ways that you can present information visually. At Slidesgo you’ll find presentations and slides with special features for education to make it easier for you to add mind maps and other graphic organizers to your presentations.
Using graphic organizers
Now here’s a simple but effective idea. Flashcards are a great way to present information in bite-sized chunks for students to learn and study. Slide presentations are the perfect way to make flashcards, for any subject at any level. Why not use a slide presentation to make a glossary of new vocabulary? You can include the written word, a picture, audio, video or even have your students collaborate to make their own.

Adding flashcards as means of interaction
Remember that presentations are more than just presenting! To take your presentations to the next level, they should make your students think and encourage them to do something with the material. One simple way to do this is by using links. You can connect your presentation to external websites where your students can do online activities or games and practice what they are learning. Or link your presentation to another document where you test their learning. Finally, remember that your presentations are a great place for you to showcase your students’ work. They will love it if you incorporate what they have done into a presentation for the entire class.
We all love stories! When students feel that there is a story behind what they are learning, it gives them a narrative that connects the parts to the whole and makes their learning more personal and motivating. Include pictures of people in your presentations. Give them names and personalities and bring them to life by animating them. If you think this is impossible, try using Stories by Freepik to choose and animate personalized images. It will add a touch of storytelling to your presentations that your students will love.

Turning your presentation into an actual story
Distance learning places great demands on teachers and requires new tools and solutions. Slidesgo aims to help you by providing presentations that are free, customizable and easy to use. Teachers of the world, thank you!

Do you find this article useful?
Related tutorials.

7 tips to create a positive classroom culture
No matter if it's been ages since you last stepped into a classroom or just a long time ago―there’s probably a particular learning experience you often find yourself thinking about. Maybe it was a passionate teacher who kept the whole class engaged, or perhaps a classmate who lent you a hand with a tricky topic. Positive classroom experiences do leave a lasting mark on us, so it makes perfect sense that people leading a classroom aim to create the finest possible learning setting. In this article, we’ll share some tips to help you turn a regular classroom into a positive space.

How to create a word cloud in Google Slides
There are many ways to improve your Google Slides presentation. From choosing the right font to finding the right template, good presentations keep an audience engaged and convey a message in a clear way.Knowing how to visualize data in a slideshow is one of those actions that have a huge impact on the success of a presentation. At the end of the day, plain data fails to motivate decisions as effectively as clear insights do. This is when powerful visual tools like word clouds step in. Let us tell you all about them.

How to create a word cloud in PowerPoint
In the age of information, showing data has become as important as collecting it. Those who are able to turn big amounts of data into easy-to-understand ideas, are the ones pushing the game forward.At the end of the day, plain data fails to motivate decisions as much as clear insights do. That’s where powerful visual tools such as word clouds step in. We’re here to tell you all about them.

Welcome to Slidesgo Educator Community, Community Circle!
As educators, it's essential to support collaboration and professional development among peers. However, the demands of educating students can sometimes make it challenging to find the time to network with fellow educators. That's why we're excited to introduce our Slidesgo Educator Community, an innovative platform designed especially for educators. In this blog post, we'll dive deeper into why we created this community, what its key features are, and how it can benefit educators.
- Google Classroom
- Google Workspace Admin
- Google Cloud
Get started with Google Slides
Learn how to use Google Slides to create engaging presentations, make fewer class copies, and more.
Find tips and tricks from teachers like you
Explore topics one-by-one.
- What is Google Slides
- Accessing Google Slides
- Creating a presentation in Google Slides
- Adding and editing content
- Presenting Google Slides
- Sharing Google Slides
Discover training lessons and related resources to accelerate your learning
Error loading content :( Please try again later
- {[ item.label ]}
{[ collectionContentCtrl.activeTopic.label ]} All resources ({[ collectionContentCtrl.totalItemsCount ]})
{[ item.eyebrow ]}
{[ item.name ]}
{[ item.description ]}
{[ item.featured_text ]}
No results matching your selection :( Clear filters to show all results
Begin your training with Google Slides
Get support from our help center, you're now viewing content for united states..
For content more relevant to your region, choose a different location:
Home Blog Education How to Present a Lesson Plan
How to Present a Lesson Plan

First days are always exciting, and expectation builds up about the contents of the task ahead, especially if you’re starting a class as a student or professor. This interaction will be significant because it will establish and define the subjects to be covered and the set of expectations flowing from the instructor towards the audience.
Perhaps you are ready to begin your career as a teacher and need some guidance; otherwise, you are a seasoned instructor searching for a refresher in your program. No matter which of the above you represent, the truth of the matter is that you are probably seeking a better way to introduce the subjects you’ll be teaching to your students.
What is a lesson plan?
A lesson plan will be the set of subject matter materials you will be teaching during a specific timeframe. The lesson plan should be an index that students can constantly consult to understand better the parts of the learning journey they will go through during each session.
Teachers and professors should have a lesson plan template that happens in every session. This is different from a syllabus because, in the latter case, the whole curriculum of the program will be laid out; however, for each lesson, there should be one individual lesson plan example to guide the instructor in the set timeframe.
When building the materials for the class or lesson’s attention, it’s always essential to share elements like the purpose or rules that guide the learning process . This article will explore the best way to present a lesson plan and drive a learning session successfully from the instructor or professor’s view.
How to write a lesson plan
Education nowadays guides different sorts of students and target specific learning needs. Therefore, it’s important and relevant to understand how lesson plans can change and be varied to truly implement the best learning path for your students. Once you have this part figured out, the next step is to understand how you will transmit the information and use a PowerPoint Presentation to simplify creating and presenting a lesson plan to your students.
Lesson plans will comprise several different sections that will clarify the first questions students can have: How long will the course be? Will it be an online course ? What will be the main objectives? Which subjects will be discussed along with the class?
1. Introduction
As the lesson begins, it’s essential to place a brief yet descriptive introduction about what the session will cover. A good practice is to create a catchy title for each lesson to have an overall understanding of the information they will be receiving.
Example: Digital Marketing Basics: Industry background, historical review years 1980-2010. In this session, we will cover the birth of digital marketing, including all the touchpoints that shaped today’s industry.
2. Audience
If your class is a one-time-only or recurring session, or even a blended learning journey, it’s essential to explain to your students who this class is for; this will allow them to calibrate their expectations about the matter to be taught ahead.
Example: This lesson is directed to professionals who work in traditional marketing, business owners, or communication specialists seeking to have a profound understanding of how digital marketing came to be.
3. Lesson Objectives
This piece is critical because it will allow the students to assess the intention of each lesson. When thinking about the objectives, it’s vital to consider the acquired skills we expect our students to have at the end of the class. Like any other goals in life or business, each one should be actionable and measurable, meaning after each class, students should be able to use what they have learned and put into action the concepts.
Example : Understand and be able to create a timeline framework of reference to explain the story of the Internet.
4. Materials
Suppose the lesson requires using any specific materials, physical or not, including any software or hardware necessary. In that case, it´s important to list or include within the lesson plan so students can set clear expectations on what they might require. This is particularly important if the session you will be delivering requires them beforehand to bring anything.
Example :
- Computer
- Scratch paper
5. Learning Activities
We´ve covered all the logistics by this point; however, now we need to start sharing the actual activities during the lesson. Ideally, this is a play-by-play of how each activity will guide the lesson towards the already established objectives. To add the list of learning activities that will be helpful for your students, take into account how all of them align with each goal and the requirements students need.
Make sure that you add variety to the activities that you are proposing, go ahead and research trends of how many other teachers or professors, students will appreciate your search to engage them in learning.
Also, consider how much time they will take so that you can note it in the next section.
- Create a timeline on the wall with the most important moments of digital marketing history, including creation of social media, mainstream of email, etc.
Time periods
Pairing each learning activity with a specific timeframe will be useful both for instructors and students. Make sure you calculate a reasonable amount of time for each activity and list it within the lesson plan so everyone can set correct expectations. Assigning time slots for each exercise will also help students and teachers stay on track with the lesson and not waste valuable time invested in learning.
Example : Creation of a timeline – 45 min
How to present a lesson plan
We have now listed the components of the lesson plan structure, everything looks beautiful in the draft, but now we need to start planning how we will present the program to the students. This part is challenging because you have to choose a template that makes sense for you and will be helpful for your students to understand.
A PowerPoint presentation is a great way to showcase all the contents of the lesson plan, however, the trick is to decide how you want to structure it.
Lesson Plan Design
By this point, you’ve structured a lesson plan template that can go through any test. Nevertheless, creating the materials to accompany it can be a key in the commitment generates between the students and the professor.
Design and Style
Before adding any text to your presentation template , think about the requirements you have: Does the academic institution where you work require the use of logos? Do you have to follow any visual guidelines? This might be important for the cohesiveness of your presentation.
It’s essential to think about how you would like to present the lesson plan. You may want to keep it simple and have a 1 pager and talk through it to understand your students fully, or perhaps you need to create one full presentation where every slide will be a relevant piece of information. Let’s explore this a bit further.
One Pager Lesson Plan
If your style is more towards simplicity, this is a great solution: succinct, minimalistic, and straight to the point. You can complete a one-page lesson plan with bullets of the relevant data and send it out to students. A great advantage of this format is that you can either send it as a PDF or even as a single image (JPG or PNG), exporting it directly from PowerPoint.
One significant advantage is that your students will only have to check for one source by choosing this simple format when revising the lesson during the class or afterward.
Several pages lesson plan
Almost like a syllabus, a more extended presentation will include several slides so you can include the information in different formats.
For example, you can use the first slide to include the lesson title; afterward, a new slide can define the purpose or introduction of the lesson. In the upcoming slides, you can include materials, contents, and even ad charts or similar to explain how grades will be affected by each lesson’s assignments on the upcoming slides.
Text in the presentation
It’s always good to follow the reliable practices of presentations and include the necessary information without overwhelming students. Don’t add an excessive amount of text to one slide; actually, make sure that every piece of data is helpful for students to plan their time both during and after class.
However, if you will be sending out the presentation to your students before reviewing it, consider that they will be using it for their reference to follow through with your lesson. So make sure all the information is easy to read and accessible.
Additional elements
Learners of all sorts have become increasingly visual, so don’t be afraid to add infographics, images, photographs, icons or any other elements to make your lesson plan presentation more appealing visually.
Final Words
Remember the lesson plan presentation will be the first approach your students will have with the subject matter. Take your time, enjoy the process, and create comprehensive and attractive lesson plan slides that will inspire your students to have thoughtful and deep learning.
1. 1-Slide Lesson Plan PowerPoint Template
Create a simple and minimalist one-pager lesson plan for your academic uses, course planning, and even as student handouts, with this eye-catching PowerPoint template.
Use This Template

Like this article? Please share
Learning Experience, Learning Styles, Presentation Approaches, Presentation Tips, Presentations Filed under Education
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • March 22nd, 2024
How to Share a Google Slides Presentation
Optimize your presentation delivery as we explore how to share a Google Slides presentation. A must-read for traveling presenters.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.
Leave a Reply
46 Powerful Opening Lines for a Class Presentation
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking

Class presentations can be extremely stressful. The way you open your presentation will determine the way the rest of your presentation goes and how it is accepted by the audience. To make things easier for you, here is a list of powerful opening lines for a Class Presentation.
Before we get into the opening lines, here are some pointers to ensure your presentation has a good structure that will keep the audience engaged.
How to structure a good presentation
State the relevance and purpose to the audience, identify a core message, divide your presentation into three parts, use a simple and clear structure, use engaging and relevant slides, practice and rehearse your delivery, q & a session.
Determine the purpose of your presentation. What do you want your audience to learn or take away from it? Consider the knowledge level, interests, and expectations of your audience. This will help you tailor your content appropriately. Explain why the information is important or relevant to your audience
Identify a single central message that you would like to communicate to your audience. Then build your presentation around that core message. Select a clear and focused topic that aligns with the objectives of the assignment or class.
A presentation can be divided into three parts: an introduction detailing the purpose and structure of the talk; a body covering the main points; and a conclusion summarizing and highlighting the significance of your talk.
A good presentation structure means analyzing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart to the audience, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
Design engaging and suitable slides that support your message and help your audience understand your presentation. Use rhetorical questions, anecdotes, or interactive elements to keep the audience engaged. Incorporate relevant visuals or multimedia to illustrate critical points. Ensure they are clear and legible, and add value to your presentation.
Practice your presentation beforehand to ensure that you can deliver it confidently and effectively.
Invite questions from the audience. Be prepared to respond thoughtfully.
Cite your sources if applicable. This adds credibility to your presentation. In fact, provide any recommended readings or resources for further exploration.
You can divide your presentation in the following manner-
Introduction:.
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement, question, or anecdote related to your topic.
- Presentation Statement : Clearly state the main purpose or argument of your presentation.
- Preview : Provide an overview of what you’ll be covering in the presentation.
- Each main point should be a separate section or slide.
- Present one key idea per slide or section.
- Provide evidence, examples, and supporting details for each point.
- Use visuals like images, graphs, or charts to enhance understanding.
Conclusion:
- Summary : Summarize the main points.
- Restate Thesis : Remind the audience of your main argument.
- Closing Statement : Provide a clear and impactful closing statement.
Structuring a class presentation effectively involves careful planning and organization. By following these steps, you can create a well-structured class presentation that effectively delivers your message and engages your audience.
Here are some additional tips for structuring your class presentation:
- Keep it simple: Don’t try to cram too much information into your presentation. Focus on the most important points you want to communicate.
- Use a variety of presentation techniques : This could include storytelling, humor, and interactive activities.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid using jargon and technical language that your audience may not understand.
- End powerfully: Leave your audience with a memorable thought or call to action.
By following these tips, you can create a class presentation that is informative, engaging, and memorable.
A powerful opening sets the tone for your class presentation and grabs your audience’s attention. Moving ahead to the main part of the article, here is a list of things you can incorporate to make your opening lines for a class presentation rather memorable.
Opening Lines for a class presentation
Ask a rhetorical question, use a startling statistic or fact, quote someone, make a provocative statement, interactive opening, visual description, make historical reference.
This is a great way to grab the audience’s attention and get them thinking about your topic. For example: “Have you ever wondered how the internet works?” or “What are the ethical implications of artificial intelligence?”
1. “Have you ever wondered why [topic] affects each and every one of us?”
2. “What if I told you that [startling fact or statistic]?”
Stories are a great way to connect with your audience and make your presentation more memorable. For example, you could tell a story about a personal experience related to your topic, or a story that illustrates a key point you want to make.
3. “Let me take you back to [a specific moment in time related to your topic].”
4. “I’d like to share a personal story that illustrates the importance of [topic].
This is a great way to grab the audience’s attention and make them want to learn more. For example: “Did you know that 90% of all data has been created in the past two years?” or “One in three people will experience depression at some point in their lives.”
5. “Did you know that [shocking statistic]?”
6. “It might surprise you to learn that [eye-opening fact].”
This is a great way to add credibility to your presentation. For example: “According to Albert Einstein, ‘Imagination is more important than knowledge.'” or “A recent study by Harvard University found that people who meditate regularly are more likely to be happy and successful.”
7. “As [famous figure] once said, ‘ [relevant quote].'”
8. “As Neil Armstrong once said, “That’s one small step for a man, a giant leap for mankind.” I believe space exploration is essential for the development of mankind.”
This is a great way to get the audience’s attention and make them think about your topic in a new way. For example: “The future of work is remote.” or “Artificial intelligence will revolutionize every industry.”
9. “Today, I’m here to challenge how we think about [topic].”
10. “Let’s consider a perspective on [topic] that might be different from what you’ve heard before.”
Other than these, there are certainly other ways of opening your presentation such as:
This is a great way to engage the audience from the beginning of the presentation. This will help keep the audience hooked and trigger their thought process too.
11. “I’d like to begin with a quick exercise. Raise your hand if [question-related to your topic].”
A visual description will help the audience to draw things from their imagination and will keep them engrossed in what you have to say after.
12. “Close your eyes for a moment and imagine [vivid scene related to your topic].”
Humor can never go wrong if you know the audience you are dealing with. A good laugh will always make your presentation go a lot smoother and easier.
13. “They say that [humorous twist on your topic]. But today, we’ll uncover the real story.”
Pick up a historical fact or reference that is quite common or that you can prove happened. This helps engage your audience and they would want to know how is that reference relevant in the context of your topic.
14. “In [specific time period], [relevant historical event] changed the course of [topic].”
Stating something and immediately countering your own statement will confuse the audience into listening to you more keenly. Which is why it serves the purpose of having your audience’s attention.
15. “While most people think [common misconception], the reality is quite different.”
Remember to choose an opening that aligns with your topic and style, and be sure to transition smoothly from your opening into the main content of your presentation. Additionally, practice your opening to ensure you deliver it confidently and engagingly.
Now, let’s look at some examples of opening lines for specific topics of class presentation
Opening lines for specific topics of a class presentation
Climate change, globalization and its effects, mental health awareness, artificial intelligence, gender equality, entrepreneurship, space exploration, cybersecurity, diversity and inclusion, the benefits of reading, the dangers of smoking.
- The challenges of poverty
The importance of recycling
16. “The world is on fire. Or at least it feels that way. The Amazon rainforest is burning, the Arctic is melting, and the Great Barrier Reef is dying. But we can still make a difference.”
17. “Imagine a world where our coastal cities are submerged, and our weather patterns become increasingly erratic.”
18. “In the next few minutes, we’ll confront a reality that demands our immediate attention: the accelerating crisis of climate change.”
19. “Today, our actions in one corner of the globe can have ripple effects thousands of miles away. The world truly is a web of interconnectedness.”
20. “As we discuss globalization, let’s remember that it’s not just about economics. It’s about cultures converging, traditions evolving, and societies adapting.”
21. “We all have mental health. Just like we have physical health. But why is it that we’re so afraid to talk about it? Why is it that we treat mental illness as a taboo topic?”
22. “Close your eyes and think about a time when you or someone you know faced a mental health challenge. It’s more common than you might think.”
23. “Mental health is just as important as physical health, but it is often overlooked.”
24. “One in five adults in the United States experiences mental illness each year.”
25. “Mental health problems can impact anyone, regardless of age, race, or socioeconomic status.”
26. “Imagine a world where machines can think and learn like humans. A world where robots can do our jobs, and self-driving cars can take us anywhere we want to go. This is the world of artificial intelligence.”
27. “From self-driving cars to virtual personal assistants, the rise of artificial intelligence is reshaping the way we live and work.”
28. “Today, we stand on the precipice of an era where machines can not only think but learn and adapt.”
29. “It’s time to talk about gender equality. It’s time to talk about the fact that women still earn less than men, that they are underrepresented in leadership positions, and that they face discrimination and harassment on a daily basis.”
30. “What do Steve Jobs, Mark Zuckerberg, and Elon Musk have in common? They’re all entrepreneurs who started with nothing and built billion-dollar companies. But what does it take to be a successful entrepreneur?”
31. “The cosmos, with its vastness and mysteries, has beckoned explorers and dreamers for centuries. Today, we’re on the cusp of new frontiers.”
32. “As we look up at the night sky, it’s important to remember that each star represents a potential world, waiting to be discovered.”
33. “In an era where our lives are increasingly intertwined with technology, the battleground for our security has shifted to the digital realm.”
34. “Picture this: a breach in cybersecurity can lead to consequences as real and impactful as a physical break-in.”
35. “Diversity isn’t just about ticking boxes on a checklist. It’s about recognizing the richness that comes from embracing different perspectives and experiences.”
36. “In this room, we each bring a unique story and perspective. Together, we have the power to shape a more inclusive world.”
37. “Diversity and inclusion lead to innovation and creativity.”
38. “Reading can improve your vocabulary, grammar, and writing skills.”
39. “Reading can help you to learn about different cultures and perspectives.”
40. “Smoking is the leading preventable cause of death in the United States.”
41. “Smoking causes cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems.”
42. “Secondhand smoke is just as dangerous as smoking itself.”
The challenges of poverty
43. “Poverty is a complex problem that affects millions of people around the world.”
44. “Poverty can lead to hunger, homelessness, and lack of access to education and healthcare.”
45. “We all have a role to play in fighting poverty.”
46. “Did you know that it takes 700 years for a plastic bag to decompose?”
These opening lines can be used as inspiration to create your own powerful opening line for your class presentation. Make sure it sets the tone for the rest of your presentation.
These opening lines are designed to capture attention and provide a strong foundation for your presentation on these specific topics. Remember to follow through with compelling content and a strong conclusion to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
List of other resources for you
As a college student, presentations carry a lot of weight, so How to Give a Presentation in Class as a College Student
As talked about, organizing your presentation is essential, hence Presentation Structures: Everything You Need To Organize Your Talk
Sometimes, you can have a lot of content and not know what to remove, 14 Techniques To Ensure Audience Engagement Through Long Presentations
Doing things at the last minute is not okay, unless and until you know how to get it done effectively. Help! I Have A Presentation Tomorrow & I Am Not Prepared
Sometimes you would not have someone around to practice your presentation, and for that Have A Presentation Coming Up. Here’s How You Can Practice It By Yourself
I hope this is helpful. When choosing an opening line for your presentation, be sure to consider your audience and what you want to achieve with your presentation. You can always try to get in touch with a professional to get advice on your presentation structure and how you present it. For this, check out our personalized coaching services !
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

10 Hand Gestures That Will Make You More Confident and Efficient

Interrupted while Speaking: 8 Ways to Prevent and Manage Interruptions

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.
14 Fun & Interactive Presentation Games for Teams and Students

So you've got an audience to energize, students to engage, or a team that needs a little extra fun — playing an interactive presentation game is an easy way to do just that.
We've done the research and found the best of these games for you: we looked specifically for games that are simple to set up, fun to play, and flexible enough to be used with a variety of presentations and audiences. Most of these activities work virtually with Zoom/PowerPoint and can also be used in person.
Which of these 14 presentation games do you like best? Take a look and let us know your favorites:
1. Live Trivia Competition
A great way to ramp up the excitement and engagement is to enable a little bit of friendly competition. Trivia is an easy way to do this—plus, it can be whole-group inclusive and large-audience friendly (if you use the right tools).
Here's a great trivia game you can run with your team, students, or any large audience. It's already created for you with questions and scoring built in to make it even easier:
Here's how to play:
- Make a free account here: https://slideswith.com/
- Click the slide deck and copy it.
- Launch the trivia game by clicking "Start Event."
- Invite your group to join in and submit answers using their mobile devices (show the winners automatically).
- Interact and play during your presentation!
This trivia game has questions on many topics to keep your audience's attention and appeal to everyone. It only takes 10-15 minutes to play, so it's a great game for long discussions! Also, this interactive activity is free for up to ten participants and is totally customizable.
2. Sing and Swing
To really liven up your group, encourage your listeners to play Sing and Swing. This activity is best for long presentations because it boosts energy, creates a fun, light-hearted environment, and makes people laugh a lot.
Here's how to play:
- Before your presentation, pick a well-known song and rewrite the chorus (replace parts of it with words and phrases from your presentation)
- When you're ready to play, show the song on your screen.
- Invite your audience to sing it with you!
If you have a fun group or a class of energetic students, consider adding choreography to engage your audience even more.

3. 20 Questions
If you want a presentation game that requires your listeners to talk more than you, 20 Questions is the one to play! A classic and simple activity, this game immediately boosts engagement and gets people laughing.
Here's how to play: Have someone put an appropriate image or word on the screen behind you (this can be an audience member you trust or a colleague or co-presenter). To make things more fun, put on a blindfold so that everyone knows you can't cheat. From there, ask 20 "yes or no" questions to guess what's displayed on the screen. Your group should respond "yes" or "no" to guide you to the correct answer.
4. Scavenger Hunt Challenge
To get your audience out of their seats, a scavenger hunt challenge is one of the best interactive games for presentations. It'll immediately energize your audience , team, or students while giving them a fun way to learn.
There are tons of in-person and virtual scavenger hunt ideas you can use to dive deeper into your topic or help everyone learn about one another. But if you want a ready-to-play game that you can instantly launch without having any tech skills, here's a fun one to play:
- Use an email address and password to create a free account here: https://slideswith.com/ (a free account guarantees up to ten people can play at no charge).
- Click the game and press "Copy and use this slide deck."
- In the top right corner, click "Start Event."
- Ask listeners to join the game by using their mobile devices to scan the QR code. Players should continue using their mobile devices to submit answers to questions.
- Have everyone start hunting for items!
This activity is a particularly fun game because it's a photo-hunt, show-and-tell challenge! That means your audience will not only get out of their seats to find items, but they'll also get to take pictures and share and discuss photos of what they find. This conversational element will help engage your group!
5. Group Word Clouds
Whether you're speaking to team members, students, or conference-goers, this activity lets you ask questions and get your listeners' thoughts on specific topics.
This game is the perfect way to start your presentation, especially if you're discussing something with a wide range of opinions or are unsure how much your listeners know about a certain subject. Group Word Clouds is also beneficial if you want to do a quick meeting pulse or know how your listeners feel going into your presentation—understanding their energy levels and mood can help you adjust (if necessary) to get maximum engagement and excitement.
To enjoy this activity, keep things simple by using a tool that already offers a ready-to-play Group Word Clouds game. Here's a popular one you can launch immediately:
- Create a free account by entering an email and password here: https://slideswith.com/
- Click the game and then copy it (the button to do so is right underneath the slide deck).
- Press "Start Event" in the top right corner.
- Tell participants to play by scanning the QR code.
- Create word clouds and have fun!
This interactive game only takes 5-10 minutes to play, so it's a fast, fun way to engage your audience and feel out the room. Players can use their mobile devices to answer questions. This activity is also free for up to 10 people and is easy to personalize.
6. The Get to Know You Game
This activity is one of the best presentation games if you have a small group that doesn't really know each other. The Get to Know You Game is a creative way to do introductions, and it's really simple.
Here's how to play the game: Before the event, ask group members to bring a favorite song or item to the presentation (you can do this by emailing them). When you're ready to play, ask each person to introduce themself, present their song or item, and explain why they picked it. For those sharing a song, have them play it on their phones before they explain why it's their favorite.
7. Live Poll Questions
When you have a large group, it's not easy to find ways to boost engagement—but poll questions are the solutions, especially when they're live and interactive. With this unique setup, large groups engage by answering questions and seeing their answers displayed in a fun way.
Your job is to make sure you actually find a game that showcases responses uniquely to captivate your group. For a quick and great option, here's a popular icebreaker activity that promises to display responses using fun formats like word clouds, donut charts, live graphs, and per-player:
- Create an account for free to access the game: https://slideswith.com/
- Click the slide deck and press the button to copy it.
- Look in the top right corner of the deck and press "Start Event."
- Invite your group to play the game. They only need to use their mobile devices to scan the QR code.
- Start polling your audience!
This activity is one of those fun presentation games everyone will want to enjoy, so invite all of your team members and students to participate. This game can accommodate up to 250 players and takes 5-10 minutes to complete. Tell your group to use their mobile devices to submit their responses.
8. Assumptions
This interactive game is a great way to break up your presentation to see who's paying attention and who can answer questions pertaining to your topic.
- Ask your audience to stand up (for virtual presentations, make sure everyone's video is on).
- Show true or false statements on the screen one by one.
- Tell people to raise a hand if they think the statement is correct and sit down if they think it's incorrect.
- Continue until one person is left standing.
- Award the winner.
This activity can be as short and challenging as you want. Also, if your presentation is long, you can play multiple rounds to break up your speaking time and test your audience throughout your discussion.

9. Controversial Questions
Want to see where your audience, students, or team lands on controversial topics? Then, energize your presentation with a fun, creative game called Controversial Questions. This activity has prompts that inspire lively debates, so it's a great way to get your group excited and chatty.
However, to maintain a positive environment, make sure to find a tool that offers an office-friendly, classroom-friendly, and conference-friendly game. You don't want to sour the mood by creating uncomfortable division during your presentation. To make sure this game is fun and light-hearted, here's a popular one that's suitable for all audiences and ages:
- Sign up for a free account by inputting an email address and password here: https://slideswith.com/pricing
- Click the game and press the button that says, "Copy and use this deck."
- Press "Start Event" (the button is in the top right corner).
- Have participants join the fun by asking them to scan the QR code with their mobile devices.
- Get controversial and play!
This interactive game for presentations asks fun (but appropriate) questions like:
- Does pineapple belong on pizza?
- Does the person flying in the middle seat get both armrests?
- Should the toilet roll go over or under?
Players should use their mobile devices to submit answers. Up to ten people can play for free, and you can customize the game by updating the questions!
10. Word of the Day
With this activity, you can keep your audience, team, or students engaged throughout your entire presentation. This game requires listeners to be alert and recognize whenever you say the word of the day.
Here's how to play: At the beginning of your presentation, tell your group the word of the day (it can also be a phrase if you'd prefer). Say that you'll weave the word into your presentation and that your audience must shout it out whenever you mention it.
11. Mini Activity: Group Icebreaker
Whether you're doing an in-person or virtual presentation, you need to warm up your audience to get things started on a positive note. The best way to do that is with a quick icebreaker game.
However, make sure your questions are fun, positive, and engaging. You can easily do this by finding a game that already has the best icebreaker questions included. Here's one that's ready to play (and requiring no tech skills to launch):
- Input an email address and password to make a free account here: https://slideswith.com/
- Click the deck and copy it (press "Copy and use this deck).
- Click the button in the top right corner that says "Start Event."
- Invite participants to play by asking them to scan the QR code.
- Break the ice to warm up your audience!
Your group should use their mobile devices to submit responses to poll questions. Also, this game accommodates up to 250 players, but only ten people can join for free.
12. Process of Elimination
This activity is one of the best games for presentations because it's simple yet fun and great at helping listeners get to know each other. You can play it at the beginning of your presentation or in the middle to give your group a chance to stretch their legs.
- Before your event, create a list of "yes or no" questions.
- Once you're ready to play, tell your group to stand up (if you're doing a virtual presentation, make sure everyone's video is on).
- Ask each question one by one.
- Tell attendees to stand if their answer is "yes" and sit if their answer is "no."
The questions can relate to your topic or be totally random. Also, if you'd prefer to thin out the number of people standing, you can take a creative twist and ask your questions by saying something like this: "Stay standing if (insert scenario)." When phrasing each question this way, the game will end with one person standing. To acknowledge the winner, you can give them a round of applause or award them a prize.
13. Conference Opener Icebreaker
If you're speaking at a big conference, you need an interactive game for presentations that can get everyone involved and ensure every voice is heard. To achieve these goals, you should create an icebreaker game that works for large groups .
Using an easy, intuitive template is the best step to take. That way, you don't have to start from scratch or spend hours making your game. For a template that requires no code or tech-savviness to build on, here's the best option:
- Sign up by making a free account here: https://slideswith.com/
- Click on the game. On the next page, click the button to copy and use the deck.
- Customize the template using the instructions HERE .
- During your presentation, press "Start Event" in the top right corner.
- Ask the group to use their mobile devices to scan the QR code and join the fun. (Also, make sure participants use their mobile devices to submit answers.)
- Play and engage your audience!
This template has fun, interactive features built in to keep your large audience engaged. Those features include polls, word clouds, and ratings. Just make sure you sign up for a paid plan to accommodate the large number of people in your group—the free account only works for up to ten players.
14. Two Truths and a Lie
This classic game is a fun, energizing way to help your listeners get to know one another. It's perfect for small in-person or virtual groups and is an ideal activity for the beginning of your presentation.
Here's how to play: Pick any topic (for the purposes of this article, the topic will be "movies"). In no particular order, say two movies you've really watched and one you haven't watched. Ask your audience to guess which statement is the lie. The winner picks the next topic and says two truths and a lie.
Be Memorable With Presentation Games
Oftentimes, people forget presentations within a week or even days, and that's because the discussions are boring. But you don't work hard preparing a presentation for it to be forgotten. If you want your message to stick, all you have to do is make it enjoyable without being corny.
If you want to be remembered and actually get people engaged, you need to make your presentation fun and enjoyable, without coming off as corny or desperate to please. Ivan Dimitrijevic, 10 Secrets of Making Every Presentation Fun, Engaging, and Enjoyable
Luckily, the interactive presentation games in this article are unique and exciting—they're far from corny. So, use them for your upcoming presentations to make your messages compelling and memorable.
Subscribe for more articles like this
Try slides with friends for free.
The easiest way to host meetings your team will love
Engagement delivered to your inbox
We'll email you 1-2x per month with brand new, ready-to-run events and ideas. Subscribe to stay ahead of the curve and keep your lessons, meetings, and events fresh and engaging.
Bestiality references allegedly made during presentation at Renmark High School
Warning for readers: This article contains graphic language.
The South Australian Department for Education is investigating a presentation delivered to year 9 girls in a regional high school that allegedly referenced bestiality as being accepted by the LGBTQIA+ community.
Female students said teachers at Renmark High School told them to leave their lessons and attend a presentation in a separate classroom.
Students who attended the presentation on March 22 say two staff from the Headspace centre in the neighbouring town of Berri introduced a "third-party" presenter who facilitated an hour-long presentation focused on relationships.
Parents said they were not notified about the presentation, nor was it consented to.
Students said they were left unsupervised for the duration of the presentation.
Student Courtney White, 14, said she felt confused and blindsided by the presentation.
"We had a teacher that told us to grab a chair and sit in front of the board, and then the Headspace people came in and then [the teacher] left, so then we're sitting in front of a board alone with no teachers, just the Headspace people," she said.
"The first slide of the PowerPoint on the board was 'You can see queerly now' and 'No point hiding.'"
Girls felt 'really uncomfortable'
Fourteen-year-old Emelia Wundenberg said the presenter was graphic when referencing their own sexual preferences and spoke in sexually explicit terms about growing up and being confused about whether they idolised people of the same gender or wanted to be intimate with them.
Students say they were then given an explanation of the initialism LGBTQIA+, with each word and its meaning displayed on the screen.
"There was a slide for what the 'plus' means, and they just started randomly saying words that no-one knew, like bestiality," Emelia said.
"It was on the board when they were showing what the 'plus' meant."
The students said bestiality was then explained in detail and the presenter seemed to imply it was something practised by people who identified as LGBTQIA+.
"They said [the queer community] just accepts all of it, even though … isn't it illegal?" Emelia said.
As the talk went on multiple girls, including Courtney, began to feel uncomfortable and asked to leave the classroom to "go to the bathroom".
"We're all just sitting there like, 'What the hell? What are we doing here? Why are we learning about animals having sex with humans?'" she said.
"It was really disgusting, it was really uncomfortable."
Emelia said many of those who asked to leave the classroom did not return.
When the ABC sought comment from the presenter a response was sent on the person's behalf asking that reporters refrained from reaching out or naming them in its coverage.
'Normal procedure' not followed
Letters seen by the ABC that were sent to parents on behalf of Renmark High School principal Mat Evans stated that the presentation was meant to discuss "respectful relationships".
The letter acknowledged that the school's "normal procedure for notifying parents ahead of specific presentations was not followed".
Mr Evans said the third-party presenter had "been suspended from department schools while the department undertakes an investigation".
"We are undertaking an internal review to ensure that processes around such notifications and procedures with regard to third parties attending at our school are always met," he said.
The ABC contacted the Department for Education, which provided a similar statement and said the presentation was being investigated.
SA education department chief executive Martin Westwell said the presentation was "unacceptable" and "shouldn't have happened".
Speaking with ABC Radio Adelaide on Thursday, Professor Westwell said conversations about sexual health, societal norms, stereotypes and sexuality were normal parts of the Australian curriculum, but the presentation at Renmark High School was not.
"The core idea that students should understand sexuality and other sexualities is, I think, really important — but the way [the presenter] went about it was unacceptable," he said.
"The school has clearly made some mistakes.
"There should have been a teacher in the room when that occurred, but there wasn't and the principal has apologised for that.
"They hadn't reviewed the content.
"There was a few things that went wrong and it ended up with this inappropriate language and a few things being discussed in that session that were just not appropriate."
Support being provided to students
Headspace's national head of clinical leadership Nicola Palfrey said the organisation was aware of concerns raised by members of the Renmark community.
"We take all feedback very seriously and are reviewing how we can support and guide Headspace centres … to ensure presentations they facilitate or deliver are aligned with evidence and best practice and are safe and appropriate for young people," she said.
FocusOne Health Board chair Ian Gartley said the "focus at Headspace Berri, operated under licence by FocusOne Health, is on the mental health and wellbeing of young people".
"We are aware of concerns raised by local members of the Renmark community following a presentation delivered by a lived experience speaker that Headspace Berri facilitated at Renmark High School," he said.
"Our priority right now is ensuring that any young people and their families who may be experiencing distress receive the support they need."
All parties involved in the alleged incident declined to provide the presentation to the ABC.
Following the presentation, a follow-up letter seen by the ABC was sent to parents offering counselling services from the education department, which had arranged a social worker to attend the school to help support affected students.
Parents express shock and outrage
Parents of students who attended the presentation said it was a poor representation of the queer community and had raised many concerns about the school's protocols for third-party presentations.
"Who vetted this material? Who made sure it was safe for 14- and 15-year-old girls? Some of them are still 13," Emelia's mother Kristy Fyfe said.
"It has done a huge disservice to the [queer] community."
Following the presentation, Courtney's mother Nicki Gaylard removed her three children from Renmark High School.
"My kids are in limbo," she said.
"They're not in an education department at this point.
"I'm not putting them anywhere until I know this won't happen again.
"Under no circumstances should a child in that school ever feel trapped and unsafe without someone with their certificate, meaning a teacher."
The ABC has spoken to five other parents whose children attended the presentation.
They substantiated the two girls' claims.
LGBTQIA+ educators condemn 'slur'
Sexuality educators and LGBTQIA+ inclusion advocates Mel Brush and Eleonora Bertsa-Fuchs conduct consent and queer inclusion training for schools, parents and workplaces via their social enterprise Let's Talk About X.
Both are secondary teachers and Mx Bertsa-Fuchs said queer education was important but should be delivered in a safe and appropriate setting.
"The teachers are the people that these young people have a relationship with, that they are familiar with, that they're comfortable with," Mx Bertsa-Fuchs said.
"When you're in a vulnerable situation, like a respectful relationships workshop or seminar, there should be someone in the room that you are familiar with."
Mx Brush said the alleged use of the word bestiality in the presentation was damaging to the queer community.
"It's pretty shocking to think about that term being thrown around like that, especially given how loaded it is, and for a historical context of the way that it's been used as a slur and to discriminate against LGBT+ people," Mx Brush said.
ABC Riverland — local news in your inbox
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Relationships
- Renmark South
- Safety Education
- Secondary Schools

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Page numbers in slides really don't provide any useful information -- they just remind your students how long they've been watching. 5. Go BIG. Pursuant to tips #1 and #2, you're not going to win awards by cramming the most content on the fewest slides. Make text and visuals as large as you can.
The Ultimate Guide to Effective Teacher Presentations: Strategies & Tips. Dianne Adlawan. January 08, 2024. Teachers, by nature, are considered professional presenters. Their main responsibility is to talk in front of their students to relay educational knowledge, sharpen their minds and skills, and even serve as a second guide alongside their ...
Presence/Position/Posture: standing up straight conveys confidence and authority. Eye contact: helps you connect with your audience and keep your students engaged. You may tend to focus your gaze on a particular side of the classroom. Consciously make eye contact in a "W" pattern across the room.
Advice from Edelman and Harring on leveraging the working memory with PowerPoint: Leverage the working memory by dividing the information between the visual and auditory modality. Doing this reduces the likelihood of one system becoming overloaded. For instance, spoken words with pictures are better than pictures with text, as integrating an ...
The best class presentations combine strong content and visuals with an engaging presentation style. This post offers 11 steps for creating memorable and high-performing class presentations. 1. Review assignment guidelines. Before you can strategize about how to start a class presentation, you need to be certain that you understand the ...
Public speaking—giving an oral presentation before a class or another group of people—is a special form of interaction common in education. You will likely be asked to give a presentation in one of your classes at some point, and your future career may also involve public speaking. It's important to develop skills for this form of ...
What is a Class Presentation? A class presentation could be a speech or a presentation in front of your class. It could be as simple as a subject-topic presentation. Or it could be a class presentation for your graduation. Presentations are a fun way of putting across a point, teaching, or expressing yourself.
Creating this welcoming atmosphere helps support learners' social-emotional learning. It is common to share outcome (s), purpose, goals, and/or an agenda at the start of a class session or presentation. In addition, set aside intentional time to "warm up" to the topic, establish context, and connect to learners' prior knowledge and ...
See also 15 Presentation Tools for Teachers. 5 Teacher Tips For Better Presentations In The Classroom. 1. Establish one clear idea. Conventional wisdom of the past used to be about putting as much information and content into a presentation as possible. It was all about trying as hard as you could to come across as an authoritative figure who ...
We have highlighted four common problems that often accompany presentations in class: 1. Lack of interaction. Standard PowerPoint presentations offer limited opportunities for audience interaction and engagement. They lack features to gather feedback or answer questions in real time and respond to requests. 2.
1. Write note cards on index cards. Write main ideas on your index cards. Don't write details, or be stuck with the fate of looking down, staring at your note cards while reading. Put in some fun facts, interactive questions, and other interactive activities on the cards to share with the class. [1]
Student Presentation. The instructional strategy of using student presentations as a way to present content to the class as a whole can be a fun and engaging method of instruction. For example, teachers can divide up a chapter into topics and have the students "teach" the class by presenting their "expert" analysis.
Our massive collection of unique school and college presentation ideas and templates applies if you're: A teacher looking to make your class more engaging and fun with student presentations. A student who wants to impress your teacher and the rest of the class with a thought-provoking, interesting topic.
Interactive games. Interactive games for class presentations are always a popular way to ensure that students stay engaged! Some examples include: noughts and crosses or tic tac toe. pictionary. hangman or an alternative like spaceman. 21 questions. It's best to make these games related to the subject.
Content. Find a great template that fits your age group and subject. Make ONE presentation per subject. Don't overload your slides with unnecessary text. Enrich your presentations with audio and video. Use mind maps! Try more graphic organizers. Make flashcards. Make your presentations engaging and interactive.
Learn how to use Google Slides to create engaging presentations, make fewer class copies, and more. Watch video.
Subscribe Now:http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducationWatch More:http://www.youtube.com/ehoweducationNot everyone enjoys speaking in...
They'll provide you with the foundation you need to realize each presentation idea.) "This or That" Icebreaker. "Virtual Locker" Icebreaker. "Would You Rather" Icebreaker. "What's on Your Phone" Icebreaker. "Get to Know You" Icebreaker. Guess the Word. Spot the Mistakes. Interactive "Slide Deck Book".
What is a class presentation? A class presentation is a structured and formal way of sharing information, ideas, or research with a group of peers and often a teacher or instructor. They are a common activity in educational settings, such as schools, colleges, and universities. Class presentations are usually seen as a more interactive and immersive way of learning.
Text in the presentation . It's always good to follow the reliable practices of presentations and include the necessary information without overwhelming students. Don't add an excessive amount of text to one slide; actually, make sure that every piece of data is helpful for students to plan their time both during and after class.
This is a great way to get the audience's attention and make them think about your topic in a new way. For example: "The future of work is remote." or "Artificial intelligence will revolutionize every industry.". 9. "Today, I'm here to challenge how we think about [topic].". 10.
This activity is also free for up to 10 people and is easy to personalize. . 6. The Get to Know You Game. This activity is one of the best presentation games if you have a small group that doesn't really know each other. The Get to Know You Game is a creative way to do introductions, and it's really simple.
In short: Year 9 girls at Renmark High School say they were given a presentation on "respectful relationships" that included references to bestiality. The ABC understands a teacher was not present ...