- About Amazon (English)
- About Amazon (日本語)
- About Amazon (Français)
- About Amazon (Deutsch)
- Newsroom (Deutsch)
- About Amazon (Italiano)
- About Amazon (Polski)
- About Amazon (Español)
- Press Center (English)
- About Amazon (Português)

Amazon Leadership Principles
Our positions, public policy, our reports, awards and recognition.
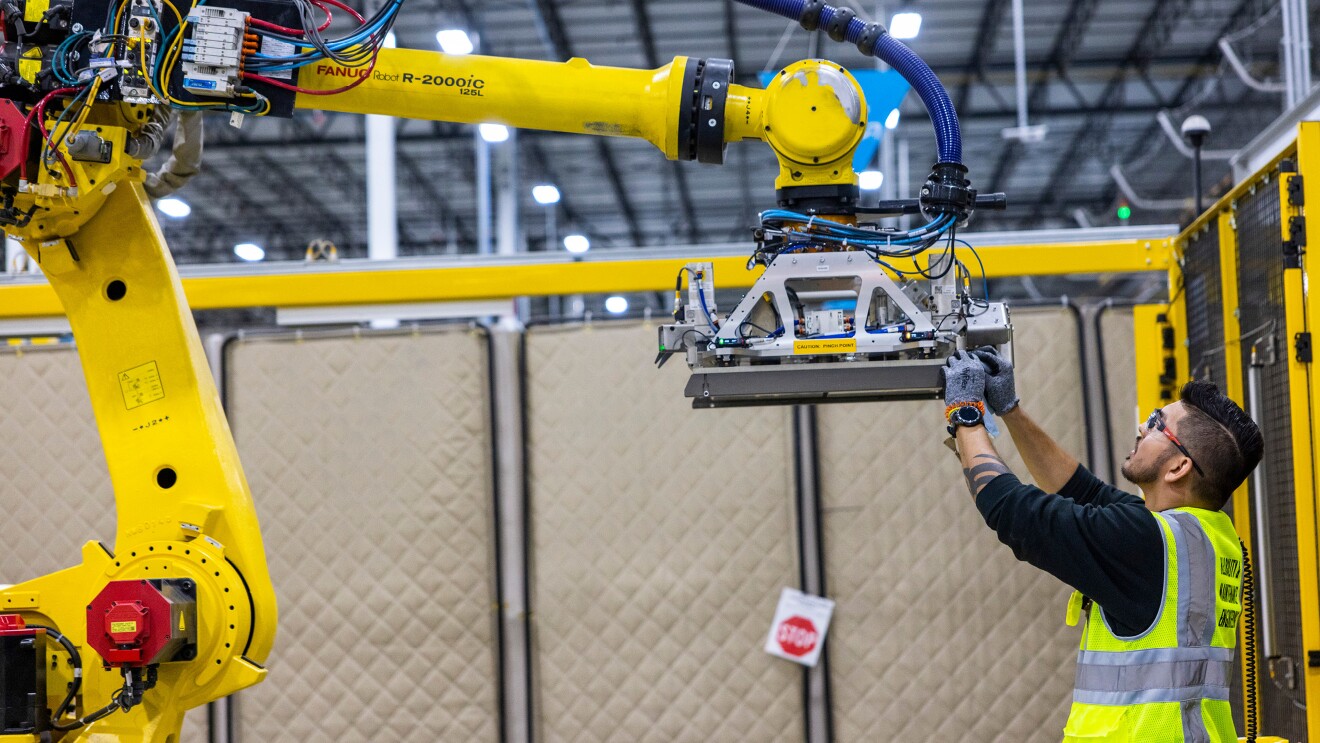

Amazon’s “Day 1” mentality is our approach of doing everything with the energy and entrepreneurial spirit of a new organization on its first day.
Ceo andy jassy’s 2022 letter to shareholders.

Everything you need to know about Amazon Business, one of Amazon’s fastest-growing ventures

Amazon’s safety performance continues to improve year over year

How Amazon employees are driving to new careers in transportation through our Career Choice program

I’m an Amazon apprentice. Here are my top 3 tips for making the most of your career.

Amazon Q4 earnings call: Here’s what CEO Andy Jassy and CFO Brian Olsavsky had to say

I’m an Amazon director who’s held 12 different roles in my 23 years at the company. Here are 4 tips to making a successful career change.

11 Amazon interview tips from recruiters and hiring managers
How to contact Amazon customer service

Amazon named among the world’s most admired companies for the eighth year in a row by ‘Fortune’ magazine
Analysis of Amazon Company
Introduction, company background, organization’s structure and purchasing process, supply chain and purchase function challenges, solutions to the challenges.
Amazon is a giant online retailer that sells everything from books to electronics and clothing. Moreover, the company is a significant provider of cloud services. Given its size and scope, the organization has one of the most complex supply chains. One of the biggest challenges Amazon faces is managing its vast supplier base. The company has over two million suppliers worldwide, and the number is only growing as the enterprise expands into new markets. Keeping track of them and managing relationships is a tremendous hardship. Another challenge Amazon faces is managing inventory as it sells numerous different products. Therefore, there is a need to maintain an extensive list that could be inquiring while still keeping costs low.
The company uses a buyers management system to keep track of its suppliers, permitting it to follow performance, manage orders and payments, and deal with contact information. It assists Amazon in streamlining its administration process and making it more efficient. Nevertheless, Amazon is an extensive organization with a complex organizational structure that requires perfect coordination. For this reason, the procurement process within a giant corporation is especially tricky. It needs to be studied in detail to implement the changes necessary to improve the company’s efficiency. Therefore, the paper will explain the company’s background, structure, and challenges facing its purchasing function and supply chain to offer solutions to the complications. Amazon’s procurement and sourcing process is a multi-component process, and the only analysis of its flow can be an opportunity to implement improvements.
Amazon was founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, who started the company as an online bookstore. Nevertheless, the corporation expanded quickly and began selling other items, such as electronics, furniture, and clothing. Today, Amazon is the largest online retailer globally, with a vast cloud computing business. It has over two million suppliers worldwide and numerous fulfillment centers across the globe (Huang et al., 2020). The company also has a network of third-party warehouses that store and ship inventory, allowing shipping orders to customers quickly and efficiently. However, Amazon has faced some challenges with its supply chain despite the prominent possibilities in recent years. In 2013, it had to deal with a holiday season inventory crunch (Huang et al., 2020). Enterprise had trouble getting enough merchandise to meet customer demand, and the crisis led to long shipping delays and dissatisfied customers.
Moreover, recently Amazon faced an intractable problem with an excessive inventory that had to be sold at a discount which was the reason for lower profits and disgruntled shareholders. One of the specialties that make Amazon’s supply chain complex is the sheer number of products they sell. The enterprise has millions of developments, and it has to keep track of all these products and have enough commodities on hand to meet customer demand. It can be a challenge, significantly when customer demand is most increased during the holiday season. Despite these hardships, Amazon has continued to grow and look for new ways to improve the supply chain and expand operations.
The purchasing function of Amazon is carried out by several distinct departments, each responsible for different types of purchases. Its principal goal is to sell a considerable amount of goods and provide numerous services to satisfy the needs of all customers. The largest unit is the media purchasing department, liable for selling books, music, movies, and other digital content. This department is further divided into sub-units accountable for each type of content (Aćimović et al., 2020). Other central divisions include hardware purchasing, responsible for devices such as the Kindle and Fire TV, and the software department, responsible for accepting applications and games for the Amazon Appstore. Each branch is headed by a manager answerable for the department’s budget and negotiating contracts with suppliers. Below the manager are a team of buyers accountable for selecting the products that the unit will purchase.
The supplier development process at Amazon begins with identifying potential new suppliers that can provide products and services that fit the company’s needs. Once they are placed, the company’s team works with them to assess their capabilities and develop relationships. The selection process at Amazon is based on several factors, including the supplier’s ability to meet quality standards, deliver products on time, and provide competitive prices (Huang et al., 2020). When a supplier is selected, Amazon operates with them to develop a product ordering process that meets the company’s needs. It includes defining the developments or services to be ordered, setting delivery schedules, and establishing payment terms.
Moreover, Amazon company has a particular and organized purchasing process to ensure that they receive the most satisfactory possible products from their suppliers. The first step in this process is developed, and the company managers cooperate with providers to help them improve their offers. Moreover, their leading task is helping them to create new products that Amazon company can offer to their customers. The next stage in the enterprise’s purchasing process is supplier selection. Amazon company carefully selects its suppliers based on various factors, including quality, price, and customer service (Huang et al., 2020). Thus, it can be concluded that the company’s primary purchasing function is to satisfy all customers and provide them with high-quality products. For this purpose, the institution has divided the purchasing process into several stages and created separate departments with specific functions that monitor the supplier’s selection and the methodology of fulfilling their responsibilities.
One of Amazon’s central challenges regarding its purchasing department is ensuring that they get the most suitable products from its suppliers. Therefore, the company efforts to implement a particular and organized buying process to guarantee that they obtain the most pleasing outcomes from their distributors. However, sometimes the providers do not meet the company’s high standards, which can be the reason for receiving products that are not of the best quality. Another challenge that Amazon faces is ensuring that they get the most feasible price for their products. The company works with numerous different suppliers, and each of them has its unique pricing structure (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). Amazon company must ensure that they get the best possible price for their products. It is not always possible to track which purchases will be more profitable and how to save money and avoid losing quality.
Another challenge Amazon faces is managing inventory as it sells numerous different types of products, and there is an urgent need to maintain an extensive list. It can be inquiring about accomplishing while still keeping costs low. Possessing a considerable amount of inventory is expensive and tracking what products are selling sufficiently and which ones are not is likewise challenging (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). It can cause problems with overstocking or understocking certain goods.
Furthermore, one of the most significant issues in the purchasing function at Amazon is the company’s rapidly changing business. The enterprise constantly introduces unknown products and services, which means the purchasing team must continually adapt to unique customer needs. For example, when Amazon launched the Prime membership program, the purchasing team had to start buying eligible products for free two-day shipping (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). Similarly, when the company founded the AmazonFresh grocery delivery service, workers had to begin purchasing fresh food and other perishable items. Moreover, an institution is facing the increasing complexity of managing purchases online. As the website has developed, it has become more difficult for customers to find the products they are looking for, increasing customer returns and additional closing costs. Amazon has difficulty organizing and tracking purchases regarding its size, especially concerning the ratio of a reasonable price to high-quality goods.
Due to the analysis of the company’s website and customer feedback, it was possible to collect enough information for the study to form potential solutions to the concerns. Moreover, the analysis of scientific articles studying the internal work of Amazon enabled to use of them as a qualitative source of data, which was the basis for recommendations that could improve the efficiency of the company. The statistical data obtained from the company’s financial reports made it possible to analyze the most conspicuous omissions in the procurement process and thus suggest necessary improvements (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). Therefore, there are several ways to improve the obtaining procedure at Amazon. One method to enhance it is to centralize the decision-making process. Currently, the purchasing function is decentralized, with each international website having its team of buyers (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). It can cause duplication of efforts and confusion about finding responsible workers for each step.
Therefore, Amazon could streamline the purchasing methodology and make it more efficient by centralizing the decision-making. Another possible solution is to provide the buyers with more authority. Moreover, the customers work closely with the suppliers to ensure that the products they purchase meet Amazon’s high standards (Cui & Bassamboo, 2019). However, they do not have the final vote on whether a product is purchased. It can lead to delays and frustration, while by giving the buyers more authority, the company could speed up the obtaining and make it more efficient.
To improve supplier development, Amazon can work on building more profitable relationships with potential suppliers. It can be accomplished by investing more time in supplier assessment and providing more resources to help them meet the standards. The enterprise can develop a more comprehensive choice criterion that includes quality, delivery, and price to improve supplier selection. To enhance the product ordering process, Amazon might work on streamlining the procedure and making it more profitable. It can be done by automating and improving communication with suppliers.
In conclusion, the purchasing function at Amazon is a critical part of the company’s success. The corporation has an extensive and experienced team of buyers who are experts at negotiating contracts and finding the best deals on Amazon’s products. However, the purchasing function is facing a few challenges, such as the company’s rapidly changing business and the increasing complexity of the Amazon website. Nevertheless, there are some ways in which the purchasing process at Amazon could be improved, including centralizing the decision-making, giving the buyers more authority, automating the order placement process, and investing in better tools and technology. The company faces numerous challenges when managing its vast supplier base and inventory. However, Amazon can use a supplier management system and an inventory administration system to help address these challenges.
Aćimović, S., Mijušković, V., & Milošević, N. (2020). Logistics aspects of goods home delivery: the case of Amazon company. Marketing , 51 (1), 3-11.
Cui, R., Zhang, D. J., & Bassamboo, A. (2019). Learning from inventory availability information: Evidence from field experiments on amazon . Management Science , 65 (3), 1216-1235.
Huang, Y., Liu, H., Li, W., Wang, Z., Hu, X., & Wang, W. (2020). Lifestyles in Amazon: Evidence from online reviews enhanced recommender system. International Journal of Market Research , 62 (6), 689-706.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, May 22). Analysis of Amazon Company. https://studycorgi.com/analysis-of-amazon-company/
"Analysis of Amazon Company." StudyCorgi , 22 May 2023, studycorgi.com/analysis-of-amazon-company/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) 'Analysis of Amazon Company'. 22 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "Analysis of Amazon Company." May 22, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/analysis-of-amazon-company/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Analysis of Amazon Company." May 22, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/analysis-of-amazon-company/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "Analysis of Amazon Company." May 22, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/analysis-of-amazon-company/.
This paper, “Analysis of Amazon Company”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: May 22, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Business History » History and Background of Amazon
History and Background of Amazon
Considered a pioneer in online retailing, Amazon.com, Inc. expanded during the late 1990s to offer the “Earth’s Biggest Selection” of books, CDs, videos, DVDs, electronics, toys, tools, home furnishings and housewares, apparel, and kitchen gadgets. Through third-party agreements, Amazon.com also sells products from well-known retailers including Toysrus.com Inc., Target Corporation, Circuit City Stores Inc., the Borders Group, Waterstones, Expedia Inc., Hotwire, National Leisure Group Inc., and Virgin Wines. Sometimes criticized for its focus on market share over profits, Amazon.com put investor fears to rest when it secured its first net profit during the fourth quarter of 2001.
The Early 1990s: Beginnings
Throughout the 1990s, the popularity of the Internet and World Wide Web swept across the world, and personal computers in most businesses and households got hooked up in some form or another to Internet providers and Web browser software. As use of the Internet became more prevalent in society, companies began looking to the Web as a new avenue for commerce. Selling products over the Internet offered a variety of choices and opportunities. One of the pioneers of e-commerce was Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon.com.
In 1994, Bezos left his job as vice-president of the Wall Street firm D.E. Shaw, moved to Seattle, and began to work out a business plan for what would become Amazon.com. After reading a report that projected annual Web growth at 2,300 percent, Bezos drew up a list of 20 products that could be sold on the Internet. He narrowed the list to what he felt were the five most promising: compact discs, computer hardware, computer software, videos, and books. Bezos eventually decided that his venture would sell books over the Web, due to the large worldwide market for literature, the low price that could be offered for books, and the tremendous selection of titles that were available in print. He chose Seattle as the company headquarters due to its large high-tech work force and its proximity to a large book distribution center in Oregon. Bezos then worked to raise funds for the company while also working with software developers to build the company’s web site. The web site debuted in July 1995 and quickly became the number one book-related site on the Web.
In just four months of operation, Amazon.com became a very popular site on the Web, making high marks on several Internet rankings. It generated recognition as the sixth best site on Point Communications’ “top ten” list, and was almost immediately placed on Yahoo’s “what’s cool list” and Netscape’s “what’s new list.” The site opened with a searchable database of over one million titles. Customers could enter search information, prompting the system to sift through the company database and find the desired titles. The program then displayed information about the selection on a customer’s computer screen, and gave the customer the option to order the books with a credit card and have the books shipped in a just a few days.

Unlike its large competitors, such as Barnes & Noble and Borders, Amazon.com carried only about 2,000 titles in stock in its Seattle warehouse. Most orders through Amazon.com were placed directly through wholesalers and publishers, so no warehouse was needed. Amazon.com would simply receive the books from the other sources, then ship them to the customer. At first, the company operated out of Bezos’ garage, until it was clear that it was going to be a success, necessitating a move to a Seattle office, which served as the customer support, shipping, and receiving area. It was interesting that, because of the Internet, such a small venture could realize such a broad scope so quickly; within a month of launching the web site, Bezos and Amazon.com had filled orders from all 50 states and 45 other countries.
As a pioneer in the world of Internet commerce, Amazon.com strived to set the standard for web businesses. With that goal in mind, Bezos went to work on making the web site as customer friendly as possible and relating the site to all types of customers. For those people who knew what book they were looking for and just wanted quick performance and low cost, Amazon.com offered powerful search capabilities of its expanded 1.5 million-title database. The company also began offering 10 to 30 percent discounts on most titles, making the prices extremely affordable. For other customers who were just looking for something to read in a general area of interest, Amazon.com offered topic areas to browse, as well as lists of bestsellers, award winners, and titles that were recently featured in the media. Finally, for people who could not decide, Amazon.com offered a recommendation center. There a customer could find books based on his or her mood, reading habits, or preferences. The recommendation center also offered titles based on records of books the customer had purchased in the past, if they were return customers to the site.
Other hits with customers were the little touches, such as optional gift wrapping of packages, and the “eye” notification service, which sent customers e-mails alerting them when a new book in their favorite subject or by their favorite author came into stock. The site also offered the ability for customers not only to write their comments about different books and have them published on the site, but to read other customers’ comments about books they were interested in buying.
Going Public in 1997
After less than two years of operation, Amazon.com became a public company in May 1997 with an initial public offering (IPO) of three million shares of common stock. With the proceeds from the IPO, Bezos went to work on improving the already productive web site and on bettering the company’s distribution capabilities.
To help broaden the company’s distribution capabilities, and to ease the strain on the existing distribution center that came from such a high volume of orders, in September 1997 Bezos announced that Amazon.com would be opening an East Coast distribution center in New Castle, Delaware. There was also a 70 percent expansion of the company’s Seattle center. The improvements increased the company’s stocking and shipping capabilities and reduced the time it took to fill customers’ orders. The Delaware site not only got Amazon.com closer to East Coast customers, but also to East Coast publishers, which decreased Amazon.com’s receiving time. With the new centers in place, Bezos set a goal for the company of 95 percent same-day shipping of in-stock orders, getting orders to the customers much faster than before.
Another growth area for Amazon.com was the success of its “Associate’ program. Established in July 1996, the program allowed individuals with their own web sites to choose books of interest and place ads for them on their own sites, allowing visitors to purchase those books. The customer was linked to Amazon.com, which took care of all the orders. Associates were sent reports on their sales and made a 3 to 8 percent commission from books sold on their sites. The Associates program really began to take off in mid-1997, when Amazon.com formed partnerships with Yahoo, Inc. and America Online, Inc. Both companies agreed to give Amazon.com broad promotional capabilities on their sites, two of the most visited sites on the Web. As the success continued, Amazon also struck deals with many other popular sites, including Netscape, GeoCities, Excite, and AltaVista.
As the company continued to grow in 1997, Bezos announced in October that Amazon.com would be the first Internet retailer to reach the milestone of one million customers. With customers in all 50 states and now 160 countries worldwide, what had started in a Seattle garage was now a company with $147.8 million in yearly sales.
Further Expansion in 1998
As Amazon.com ventured into 1998, the company continued to grow. By February, the Associates program had reached 30,000 members, who now earned up to 15 percent for recommending and selling books from their web sites. Four months later, the number of Associates had doubled to 60,000.
The company’s customer database continued to grow as well, with cumulative customer accounts reaching 2.26 million in March, an increase of 50 percent in just three months, and of 564 percent over the previous year. In other words, it took Amazon.com 27 months to serve its first million customers and only six months to serve the second million. This feat made Amazon.com the third largest bookseller in the United States.
Financed by a $75 million credit facility secured in late 1997, Amazon.com continued to reshape its services in 1998. To its catalog of over 2.5 million titles, the company added Amazon.com Advantage, a program to help the sales of independent authors and publishers, and Amazon.com Kids, a service providing over 100,000 titles for younger children and teenagers.
Amazon.com also expanded its business through a trio of acquisitions in early 1998. Two of the companies were acquired to further expand Amazon.com’s business into Europe. Bookpages, one of the largest online booksellers in the United Kingdom, gave Amazon.com access to the U.K. market. Telebook, the largest online bookseller in Germany, added its German titles to the mix. Both companies not only gave Amazon .com access to new customers in Europe, but it also gave existing Amazon.com customers access to more books from around the world. The Internet Movie Database (IMD), the third acquisition, was used to support plans for its move into online video sales. The tremendous resources and information of the IMD served as a valuable asset in the construction of a customer-friendly and informative web site for video sales.
Another big change in 1998 was the announcement of the company’s decision to enter into the online music business. Bezos again wanted to make the site as useful as possible for his customers, so he appealed to them for help. Several months before officially opening its music site, Amazon.com asked its bookstore customers and members of the music profession to help design the new web site.
The music store opened in June 1998, with over 125,000 music titles available. The new site, which began operations at the same time that Amazon.com debuted a redesigned book site, offered many of the same helpful services available at the company’s book site. The database was searchable by artist, song title, or label, and customers were able to listen to more than 225,000 sound clips before making their selection.
Amazon.com ended the second quarter of 1998 as strong as ever. Cumulative customer accounts broke the three million mark, and as sales figures for Amazon.com continued to rise, and more products and titles were added, the future looked bright for this pioneer in the Internet commerce marketplace. With music as a part of the company mix, and video sales on the horizon, Bezos seemed to have accomplished his goal of gathering a strong market share in the online sales arena. As Bezos told Fortune magazine in December 1996: “By the year 2000, there could be two or three big online bookstores. We need to be one of them.”

Growth Continues: 1999 and Beyond
As such, the company’s focus on growth continued. In 1999, it launched an online auction service entitled Amazon Auctions. It also began offering toys and electronics and then divided its product offerings into individual stores on its site to make it easier for customers to shop for certain items. During the holiday season that year, the firm ordered 181 acres of holiday wrapping paper and 2,494 miles of red ribbon, a sign that Bezos expected holiday shoppers to flock to his site as they had in the two past years. Sure enough, sales climbed to $1.6 billion proving that the founder’s efforts to create an online powerhouse had indeed paid off. In 1999, Bezos reached the upper echelon of the corporate world when Time magazine honored him with its prestigious “Person of the Year” award.
While Amazon.com’s growth story was remarkable, Bezos’ focus on market share over profits had made Wall Street uneasy and left analysts speculating whether the company would ever be able to turn a profit. Sales continued to grow as the company added new products to its site–including lawn and patio furniture and kitchen wares. The company however, continued to post net losses. To top it off, the “dot-com boom” of the late 1990s came to a crashing halt in the early years of the new millenium as many startups declared bankruptcy amid intense competition and weakening economies.
Bezos remained optimistic, even as Amazon.com’s share price faltered. During 2001, the company focused on cutting costs. It laid off 1,300 employees and closed a distribution facility. The company also added price reduction to its business strategy, which had traditionally been centered on vast selection and convenience. Amazon.com inked lucrative third-party deals with such well-known retailers as Target Corporation and America Online, Inc. By now, products from Toysrus.com Inc., Circuit City Stores Inc., the Borders Group, and a host of other retailers were available on the Amazon.com site.
Amazon.com’s strategy worked. In 2001, sales grew to $3.12 billion, an increase of 13 percent over the previous year. During the fourth quarter, Amazon.com reached a milestone that many had regarded as unlikely; it secured a net profit of $5 million. In 2002, the company launched its apparel store, which included clothing from retailers The Gap and Lands’ End. Overall, the company reported a net loss of $149 million for the year, an improvement from the $567 million loss reported in 2001. In the fourth quarter of 2002 however, the firm secured a quarterly net profit of $3 million–the second net profit in its history.
While securing quarterly net profits was a major turning point for the young company, a July 2002 Business Week article warned, “after seven years and more than $1 billion in losses, Amazon is still a work in process.” Indeed, the company’s foray into providing the “Earth’s Biggest Selection” had yet to prove it could provide profits on a long-term basis. Nevertheless, Bezos and his Amazon team remained confident that the firm was on the right track. With $3.9 billion in annual sales, Amazon.com had without a doubt come a long way from its start as an online book seller.
Related Posts:
- History and Background of Volkswagen AG
- History and Background of General Motors
- History and Background of Starbucks
- History and Background of United Parcel Service (UPS)
- History and Background of Porsche
- History and Background of The Unilever Company
- History and Background of Qantas Airlines
- History and Background of Oracle
- History and Background of FIAT
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Home — Essay Samples — Business — Amazon — Amazon Company’s Review
Amazon Company's Review
- Categories: Amazon Company E Commerce
About this sample

Words: 892 |
Published: Sep 19, 2019
Words: 892 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business Economics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 626 words
2 pages / 878 words
4 pages / 1702 words
1 pages / 437 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Amazon
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, has evolved from an online bookstore to a global e-commerce giant with diverse business segments including cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. Market structure [...]
Amazon, the global retail and technology giant, has made significant impacts on the global market with its expansive operations and innovative business strategies. However, amidst its success, Amazon has faced scrutiny for its [...]
Amazon is an American multinational technology company founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994. It started as an online bookstore but has since diversified into various other product categories and has become one of the world's largest [...]
The Great Barrier Reef, located off the coast of Queensland, Australia, is the world's largest coral reef system. It is home to a vast array of marine life and plays a crucial role in the global ecosystem. However, in recent [...]
The Amazon Rainforest extends over South America from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Andes Mountains in the west. It is home to the myriad species of fauna and flora, containing 50 percent of the world's biodiversity. [...]
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a farreaching, developing distributed computing stage gave by Amazon. It gives a blend of foundation as an administration (IaaS), stage as an administration (PaaS) and bundled programming as an [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis
History and background.
The selected company is Amazon, which is a technology firm headquartered in Seattle. Founded in 1994, the corporation was initially registered as Cadabra Inc. Today, it is more common as an e-commerce firm that offers goods and services related to artificial intelligence, computing, and digital services such as live streaming (Chan, 2015). Recently, the enterprise was identified as the most profitable retail company in the U.S., surpassing Walmart (Chan, 2015). Interestingly, the corporation is publicly listed on Wall Street and, as of today, has a share value of $3,196.84 per share (Amazon, 2020). The company’s main shareholder is its founder, Jeff Bezos, who is also considered one of the world’s wealthiest people. The company has ventured into strategic partnerships that have allowed it to develop over 16 successful products and services. Such business relationships include one with D.C. Comics, Toys ‘R’ Us, and Nike.
Amazon associates its success with its strong corporate mission. According to the firm’s website, its duty is “to continually raise the bar of the customer experience by using the internet and technology to help clients find, discover and buy anything, and empower businesses and content creators to maximize their success” (Amazon, 2020). Unpacking this statement reveals that the corporation desires to be the most client-centric in the world. Chan (2015) argues that customer behavior has been changing over the years, with more people looking for companies that offer more in terms of the client journey than other traditional approaches. In the recent past, the enterprise has revealed that this specific approach to client engagement has allowed customers to be the focal point of the goods and services they require.
The consumer loyalty and the constant growth of the business’ customer base are evident through their sales and profits growth. A brief analysis of this expansion reveals that the corporation has developed significantly in terms of products and services offered and profits. For example, the company started selling books online, but through research, added other elements such as music, toys, diapers, and even watches. The expansion that led to the various products and services can also be attributed, as mentioned, to strategic partnerships that the business attracted. For instance, they currently have a subsidiary that sells diapers only and targets parents. The firm’s ability to help consumers find whatever product they want makes the corporation that more valuable. In turn, this has led to massive profit growth. The company is currently estimated to collect $280 billion in revenue per year (Amazon, 2019). Apart from the revenue, the enterprise’s 2019 annual report reveals that it also has assets worth $225 billion and a net income of $11 billion (Amazon, 2019). The institution’s total equity stands at approximately $60 billion, with an operating cost of $14 billion.
Primarily, the company has invested fully in digital marketing and advertising. Chan (2015) explains that the firm does not advertise the individual products that can be found on their website, but their processes and convenience for the buyer. This has been achieved through targeted marketing processes such as sponsored search and email marketing. Arguably, the company collects much data from its clients that is then used for targeted marketing and advertising. The firm has also used its social media platforms to advertise its processes and how convenient they are to the public.
One specific event that helped shape Amazon to be the retail giant today is the opening of Microsoft Office in Seattle. This was a significant part of Amazon’s growth as it encouraged the company to relocate from Washington to Seattle, which has become a technological hub (Chan, 2015). A second notable event occurred in 1998 when the company went public. Initially, the company shares were significantly low. However, the company’s growth led the shares to move from the initial $18, and an eventual low of $1.96, to today’s price of over $3000 per share. This also profoundly affected the firm’s profits.
SWOT Analysis
This section focuses on the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of Amazon. One strength of Amazon is that it has a low charge structure. The premise arises from the fact that e-commerce averts some of the capital-intensive elements that traditional shops incur. For instance, Amazon does not store the different merchandise sold on the site. Therefore, the company does not need any storage space, unlike the traditional firms. The nature of the company, where it uses third party sellers, can also be perceived as a strength. Chan (2015) explains that these types of partners provide products that are not available on the Amazon Marketplace platform. Initially, the company allowed these types of sellers to sell directly on Amazon. However, recent developments have led to the establishment of Amazon Prime and Fulfilled by Amazon that target only third-party sellers. Chan (2015) explains that these clients make up 58% of Amazon’s clients. Therefore, one advantage of this is that it has led to the improvement of the bottom line.
A SWOT analysis reveals that the company has several limitations that can be viewed as weaknesses. One such weakness is poor penetration into some growing markets. Chan (2015) argues that developing countries offer broad markets that are yet to be explored by numerous international companies, such as Amazon. Not only has the company failed to target possible clients in the third world countries, but also, it has completely ignored the possibility of entering these markets. The company has not integrated internationally friendly checkout options for its international clients as well. This is a disadvantage as it provides more competitive power to local companies that can make the consumer journey in the purchase of similar products easier. One can argue that Amazon’s business model can also be imitated easily. The risk with this is the fact that competitors can use the same model. It does not help in giving the firm a competitive edge.
Despite the weaknesses, the company has various opportunities for the management further to improve the firm’s standing in the market. One such opportunity is the branching into new developing zones. As mentioned previously, the company has so far ignored the need to penetrate developing continents such as Africa. Arguably, the developing world has a potential market for Amazon due to accessibility to the internet. This has led to more exposure in regards to different brands and options that the target audience would like to purchase. Indeed, Amazon’s user-friendly interface would also appeal to this market. It can be stated that the company also has opportunities in developing start-ups that are targeting the same industry. Currently, start-ups are creating significant competition in the sector. The larger e-commerce platforms have managed to control the market by investing or buying such start-ups (Chan, 2015). It is vital that Amazon also participate in such business relationships in order to remain on top.
The company also has several threats that can be highlighted. The first threat is the ever-changing technology. This affects a part of the company, the growth of artificial intelligence, and new computing advantages. This is a threat, as the company has to keep abreast of all the new technologies in order to remain the biggest shareholder of the market. Chan (2015) also explains that the growth of e-commerce and cloud computing companies are a threat to Amazon. Arguably, this is enhanced by the ever-changing technological advances and the different needs that push these creations. The additional fact that there are policies that encourage the growth of the industry through investing in similar up and coming e-commerce businesses is a threat to Amazon. As previously stated, more start-ups are introducing newer and better ways of engaging with clients through e-commerce. Therefore, the competition is not only in regards to the number of companies that offer the same services but also the quality guaranteed. Amazon has to ensure that it offers high-quality goods and services despite the fact that third party clients control some sections of the company.
Omni-Channel Analysis
An omnichannel analysis of Amazon reveals that the firm has used the strategy to enhance the customer experience. It is critical to note that the omnichannel approach does not necessarily mean that a client can access the company through a physical store, web, or social media. Binnie (2018) explains that this type of approach is a multi-channel approach. On the other hand, an omnichannel approach links all these elements to make the user journey more efficient. It can be broadly stated that the firm’s omnichannel approach has been highly effective in achieving customer-centric experience, as stipulated in the corporate mission statement. Whereas Amazon does not have physical shops, through its omnichannel approach, it developed pop-up kiosks for its clients. Piotrowicz and Cuthbertson (2018) explain that these stores are significantly small and have Amazon-related customer technology. For instance, they have Alexa installed to help clients around the store. One can argue that this has enhanced the corporation’s consumer-centric approach as it has provided a physical store for the market that prefers this over the online stores, but with the same concept used in the highly successful digital platforms.
The firm’s omnichannel approach has also been successful due to its Amazon Fresh Pick-Up approach. Two main things have to be considered when discussing this part of their omnichannel approach. The first is that initially, the company did not offer fresh produce because it did not have physical stores where buyers could pick the items. However, the introduction of the Amazon Fresh Pick-Up stores has allowed the business to broaden its products further and include fresh produce that can be picked on the same day. Interestingly, the same Amazon customer experience, through the firm’s related technology, gives similar buyer experience as their digital store. This is similar to their whole foods section, which also gives purchasers similar experiences. It is arguable that even though the omnichannel has been highly effective in ensuring a client-centric approach, it has not positively affected its bottom line.
The order management solutions used by Amazon tied the physical stores with online platforms. This further enhances the company’s omnichannel approach as all its consumers have to first interact with the brand online. Piotrowicz and Cuthbertson (2018) explain that a significant omnichannel strategy ensures that there is one point of contact before integrating the other aspects that impact customer journeys. Amazon uses its website as this initial point of contact. The buyer can engage the brand in regards to the products or services they need to select whether they want their orders delivered to their locations or prefer to go to the pick-up stores. The order management solution links all these aspects into a seamless single digital transaction for the client. It removes various pain points that the client would otherwise experience. For instance, the client does not need to go to a different page to select the stores closest to them as their location tag narrows this down. Arguably, the solutions employed have not only made work easier for the purchaser who is placing an order but also for the third-party sellers who are using the same platform.
Other elements of the firm’s omnichannel that must be considered include their point of sale, order broker solutions, and merchandising. In regards to the former, the company carefully selects products and services that are to be associated with its brand. As Piotrowicz and Cuthbertson (2018) observe, even the third-party sellers have to be carefully vetted to ensure they are legitimate and truthful about the goods and services they offer. In an attempt to further enhance the consumer-centric approach, the firm also values customer input to make their experiences better (Piotrowicz & Cuthbertson, 2018). This includes giving refunds for damaged or changed products. Arguably, by ensuring that the buyer’s needs come first, the business has been able to slowly progress towards making Amazon the most client-centric firm in the world as denoted in their corporate mission.
Key Competitor
Amazon’s primary competitor is Walmart. As mentioned previously, Walmart was initially considered the biggest and most profitable retail company in the US. However, it has since been surpassed by Amazon, pushing the former to the second position. The companies have various similarities and differences in their retail strategies. One similarity is that they both have focused on making their businesses all about the user journey. Clinehens (2019) argues that an efficient buyer journey not only attracts new clients to a brand, but also ensures customer loyalty. Therefore, one can argue that the success of both Walmart and Amazon can be attributed to their strategic purchaser journeys. On the same not, both companies have arguably removed significant barriers that their clients faced initially in e-commerce. This has further cemented both companies standing in the market and industry.
A second similarity of the strategies employed by both Amazon and Walmart is that they both use emotive marketing and advertising. Debatably, this approach to advertising has worked for both due to the fact that a significant percentage of their audiences are loyal. Clinehens (2019) explains that emotive advertising focuses on the emotions of the consumer. Even though they use different primary channels for advertising, both Amazon and Walmart advertise their process and simplicity in order to appeal to the emotive aspect of marketing.
Despite the similarities, the two retailers are also highly different. First, whereas Amazon is first an e-commerce company, Walmart is primarily a brick-and-mortar store. The premise means that the former firm has focused fully on providing services through the digital space while the latter has physical stores all over the country. Further, Walmart holds a larger percentage of buyers that prefer physical stores even though Amazon has opened up a few stores across the country. Interestingly, Amazon has had to close down some physical stores due to the fact that they received little attention in the market. On the other hand, Walmart has recently entered the e-commerce retailing sector and has little experience in the same. This realization also reveals that the two companies have different strategies as both are trying to enter into spaces that they do not hold strong share.
The two companies are currently using different omnichannel strategies to reach out to their clients and ensure a seamless experience. It is arguable that both companies have heavily invested in their omnichannel, therefore, the approach affects both businesses significantly. As mentioned, Amazon has had to close down some physical shops due to low sales and usage of the same. On the other hand, Walmart is still struggling to fully penetrate the digital space due to a lack of proper experience in the same.
Disputably, Walmart has a positive future. There are several things that make such a prediction possible. The first is the adoption of e-commerce. Indeed, currently, the company is lagging behind in regards to penetrating the e-commerce industry. This is due to its late entry into the space. However, there is a lot of potential in the digital area, and the corporation can still gain advantages over its competitors, such as Amazon. These benefits can experiment in terms of marketing and consumer engagements through online platforms. Walmart has to ensure that its customer involvement is above that of its competitors in order to gain traction and take back its number one spot in the retail market.
It is also arguable that the business has a bright future due to the growth of omnichannel. Many companies realize that the seamless linking between their online and physical presence is key in ensuring the improvement of the bottom line. Walmart has to ensure that their online presence is also effective in order to take advantage of the benefits of omnichannel. The company has to hire the best talents and test different modern ways to better engage with their clients online, even when their physical stores are their biggest asset. It can be added that the firm’s outlook is also positive as more people are looking into online shopping even for groceries, which is Walmart’s biggest product.
Recommendations
One short term recommendation for Amazon is that the corporation stops creating more physical spaces. The recommendation is contradictory to the concept of omnichannel. However, the firm must do more research on the type of physical spaces that will attract their target customers. Currently, the stores have not made much difference in regards to boosting the firm’s sales. Due to this, several stores have been closed in various states, as mentioned earlier. The company must consider what the client needs in regards to a physical store in order to create the best experience for its target market. This recommendation can be described as conservative and one that requires little funds.
A second short term but aggressive suggestion for the business is penetration into developing countries. As stated previously, the company has not been keen on reaching buyers in third world countries. These customers are currently able to purchase products through Amazon and use third parties to get the products delivered to their countries. The enterprise can make international clients’ user journey as efficient and straightforward as for its buyers in the US market. Additionally, the firm has to ensure that payment options provided for international users are easily accessed. This recommendation will require significant investment in advertising and marketing and creating partnerships that allow international shipping.
An intermediate-term recommendation is the establishment of pick-up stores in all the US states. This is a mid-term plan due to two things. First, the spaces will be purely for picking up products purchased online. Therefore, it further cements the corporation’s omnichannel approach. It is important to note that whereas there are people who prefer either digital or brick-and-mortar, there are some products that a significant percentage of the target market prefers to see, feel, and then order. As explained earlier, Amazon is trying to sell fresh produce through its platforms. This sector is already saturated with megastores, such as Walmart. However, Amazon has the advantage of allowing the consumers to order these products online and either get them delivered at their locations or pick them up from an identified store. The physical store is for the part of the market that has to see the groceries first to ensure freshness. This is an aggressive approach to their intermediate plan and will require significant funds.
A more conservative yet intermediate-term recommendation is for the firm to use its database to conduct a study that will inform on the physical stores. The idea to have stores that incorporate Amazon technology and offer the services and goods that the public is interested in is a crucial part of its expansion plan. One can argue that in order to do this efficiently, the management has to conduct a full study of the market and their reactions towards such stores. The research will also help the corporation identify some of the immediate needs of their target audience. The recommendation will require limited funds as the company already has an extensive database.
Bearing all these in mind, one can argue that a viable long term strategy to make the retailer bigger and better is to consider brick-and-mortar as part of their omnichannel. Indeed, whereas this has been tested, the approach towards the same was not made well. The suggested research will allow management to know how many stores are needed and how the physical spaces will look like after design. The long-term recommendation is capital intensive as it is expected that the study will also reveal that the size of the stores will be larger than what has been done so far. It is essential to point out that the business tries to lower costs for the physical stores as much as possible by reducing the size of the space. However, borrowing from stores such as Walmart, despite the efficiency of Amazon tech such as Alexa, people still associate physical stores with human assistants who can help them locate their preferred items.
Amazon. (2020). About us . Web.
Amazon. Annual report 2019 . Web.
Binnie, L. (2018). The future of omni-channel retail: Predictions in the age of Amazon . Emerald Lake Books.
Chan, I. (2015). Examining the cost of Amazon.com’s success using the triple bottom line . Humboldt State University.
Clinehens, L. J. (2019). CX that sings: An introduction to customer journey mapping . Jennifer Clinehens.
Piotrowicz, W., & Cuthbertson, R. (2018). Exploring omnichannel retailing: Common expectations and diverse realities . Springer.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2023, January 8). Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis. https://business-essay.com/amazon-inc-company-analysis/
"Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis." BusinessEssay , 8 Jan. 2023, business-essay.com/amazon-inc-company-analysis/.
BusinessEssay . (2023) 'Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis'. 8 January.
BusinessEssay . 2023. "Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis." January 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/amazon-inc-company-analysis/.
1. BusinessEssay . "Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis." January 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/amazon-inc-company-analysis/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "Amazon Inc.: Company Analysis." January 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/amazon-inc-company-analysis/.
- American International Group’s Star Model Use
- The “Just Do It” Power
- Ryanair & Next Step: Primary Issues and Prospects for the Company
- The Benefits of Global Airline Strategic Alliances
- Annual Reports Provided by Companies
- Pepsi: Consumer Behaviour Report
- PepsiCo’s Strategy Implementation and Strategic Controls
- Merchandizing Strategies Wet Seal Case Study
- Searchie.ai Company’s Strategic Analysis
- Starbucks Corporation’s Compensation Plan
The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure Essay
Being one of the largest multinational corporations in the world, Amazon.com has an organizational structure that reflects the complexity of governing a business on that scale. First and foremost, it is important to note that Amazon’s structure is functional rather than divisional. The company creates departments, such as “worldwide Consumer,” Web Services,” or “Media & Entertainment” based on their function rather than geographical affinity (Amazon, 2021). The advantage of this model is that it offers greater centralization than the divisional structure, in which regional divisions may even begin conflicting with each other to the detriment of global value creation (Luo & Shenkar, 2017). At the same time, functional structure, especially in the business of Amazon’s size, often comes at the cost of restricted adaptability to the specific conditions of regional markets (Luo & Shenkar, 2017). In short, Amazon’s functional structure reflects the leadership’s preference for centralized control and global guidance as opposed to the greater autonomy of regional divisions.
This preference also manifests in the company’s dedication to ensuring stable long-term leadership. Amazon is known for very limited turnover when it comes to its principal executives, such as Jeff Bezos, Andy Jassy, Jamie Gorelick, and others (Kim, 2019). Moreover, research indicates that the high level of trust and camaraderie built over the years among Amazon’s senior managers is one of the defining features of the company’s organizational structure (Kim, 2019). Maintaining a cohesive team with very little turnover signifies Amazon’s dedication to centralization and concentration of control on the top level at the expense of unit autonomy. With this in mind, one may conclude that Amazon maintains a functional organizational structure with a strong emphasis on centralization and top-down control.
Amazon. (2021). Org chart – The official board . Web.
Kim. E. (2019). Amazon’s executive org chart, revealed . CNBC. Web.
Luo, Y., & Shenkar, O. 92017). The multinational corporation as a multilingual community: Language and organization in a global context. In M. Y. Branen & T. Mughan (Eds.), Language in International Business (pp. 59-92). Springer.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, November 28). The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/
"The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." IvyPanda , 28 Nov. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure'. 28 November.
IvyPanda . 2022. "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
- Jeff Bezos’ Managerial Philosophy
- “Invent and Wonder” by Jeff Bezos: Book Review
- Servant Leadership of Jeff Bezos
- Jeff Bezos: The Richest Man in Modern History
- Jamie Dodge Company’s Entry into Japanese Market
- Jeff Bezos and Gladwell’s Success Principles
- Invent and Wander: The Collected Writing of Jeff Bezos
- Jeff Bezos's Leadership and the Amazon Revolution
- Interesting Facts in “Invent & Wander” by Jeffrey Bezos
- "Bullied: The Jamie Nabozny Story" Documentary
- Target Costing Extent Profit: Critical Report
- Cameron Mechanical & Automation, Inc.
- Walmart Organizational Structure
- Holocracy, Heterarchy, and Fractal Organisation
- Business Plan on Fawz Olympic Academy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction and background of Amazon. Amazon is an E-commerce organization based in the US, the company is an enormous internet-based that sells different product range (DVDs, video games, high-techs, furniture, jewelry and many other goods) with products often delivered the next day with worldwide shipping. they also offer web services such ...
Thus, because of its desire to achieve maximum profit, the company allows itself too much, and this is its weak point. This essay, "Amazon: Company Analysis" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly .
Amazon's mission is to be Earth's most customer-centric company, Earth's best employer, and Earth's safest place to work. Customer reviews, 1-Click shopping, personalized recommendations, Prime, Fulfillment by Amazon, AWS, Kindle Direct Publishing, Kindle, Career Choice, Fire tablets, Fire TV, Amazon Echo, Alexa, Just Walk Out technology, Amazon Studios, and The Climate Pledge are some of ...
Introduction and background of Amazon. Amazon is an E-commerce organization based in the US, the company is an enormous internet-based that sells different product range (DVDs, video games, high-techs, furniture, jewelry and many other goods) with products often delivered the next day with worldwide shipping. they also offer web services such as renting data storage which is called "cloud ...
Company Background Amazon was founded by Jeff Bezos. Prior to starting Amazon, Bezos worked in New York as a vice president at D. E. Shaw & Co., a global investment management firm, but decided to quit his job and move to Seattle to take advantage of the incredible growth of the Internet. The Amazon website launched on July 16, 1995.
Amazon.com is a Seattle, Washington-based e-commerce and cloud computing giant whose humble beginnings can be traced to founder Jeff Bezos 's garage, where he began selling books on the still-emerging World Wide Web. Although the company is best known among consumers for its retail platform, a majority of its operating profits (as of 2024 ...
Amazon Company: Introduction, Background, History & Goods Essay Amazon is an E-commerce organization based in the US, the company is an enormous internet-based that sells different product range (DVDs, video games, high-techs, furniture, jewelry and many other goods) with products often ...
Updated: Nov 20th, 2023. Amazon.com is a transnational electronic commerce organization founded in 1994 by an American named Jeff Bezos. The company is the largest online retailer in America dealing with a wide range of consumer products such as books and other products ("Your Amazon.com," 2010).
The New York Times. "Amazon.com Inc". The New York Times 31 January 2012 late ed.: Al. Print. This essay, "Amazon's Business Model" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly .
Company Background. Amazon was founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, who started the company as an online bookstore. Nevertheless, the corporation expanded quickly and began selling other items, such as electronics, furniture, and clothing. ... This paper, "Analysis of Amazon Company", was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database ...
One of the pioneers of e-commerce was Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon.com. In 1994, Bezos left his job as vice-president of the Wall Street firm D.E. Shaw, moved to Seattle, and began to work out a business plan for what would become Amazon.com. After reading a report that projected annual Web growth at 2,300 percent, Bezos drew up a list of 20 ...
It the world's largest online retailer (Holton,2009) and having ranking 43rd in the best 100 global brand in 2009 (Interbrand, 2010). Jeff Bezos founded this company in 1994 and launched it online in 1995 and in 2009 its revenue was US$24.509 billion with 20,700 employees. In 2008, the main domain attracted 615 million visitors.
Amazon Company: Introduction, Background, History & Goods Essay Amazon is an E-commerce organization based in the US, the company is an enormous internet-based that sells different product range (DVDs, video games, high-techs, furniture, jewelry and many other goods) with products often ...
We will write a custom essay on your topic a custom Essay on Amazon Company's Marketing Strategies. 808 writers online . Learn More . According to Byers (2006) Amazon's vision is "to be earth's most customer centric company; to build a place where people can come to find and discover anything they might want to buy online" (p. 3).
Amazon Essay - Company Background and History Pages: 5 (1465 words) Amazon: Online Shopping and Amazon.com Pages: 6 (1512 words) Financial Analysis and Recommendations for Clarkson Lumber Company Pages: 3 (703 words) Amazon's Competitive Strategies and Challenges Pages: 4 (1193 words)
History And Background Of Amazon Marketing Essay. There are so many reasons for adopting mergers and acquisitions strategies in companies. However, in general, the main reason for takeovers is company is seeking improvement in its financial performance. "Mergers and acquisition take place when company takeover its potential competitors to ...
The purpose of this case is to present a balanced and up-to-date business history of the company. Amazon.com's Stock Price Path (Source: Quicken.com, S stands for stock split, Accessed on ...
The company is expanding its business; for example, a subsidiary of Amazon Web Services (AWS) develops and produces cloud services, and it also actively researches in the field of artificial intelligence. The success depends on the informational systems elements and continuous progress concerning customers satisfaction.
Amazon Company's Review. Amazon has developed as an American Multi National Company in E-Commerce because of embracing the most recent advancements in Customer Relationship Management and Information Management and mapping them to its general business methodology. The joining of these advancements has been the main impetus behind its development.
Amazon Company: Introduction, Background, History & Goods Essay Amazon is an E-commerce organization based in the US, the company is an enormous internet-based that sells different product range (DVDs, video games, high-techs, furniture, jewelry and many other goods) with products often ...
In turn, this has led to massive profit growth. The company is currently estimated to collect $280 billion in revenue per year (Amazon, 2019). Apart from the revenue, the enterprise's 2019 annual report reveals that it also has assets worth $225 billion and a net income of $11 billion (Amazon, 2019).
Being one of the largest multinational corporations in the world, Amazon.com has an organizational structure that reflects the complexity of governing a business on that scale. First and foremost, it is important to note that Amazon's structure is functional rather than divisional. The company creates departments, such as "worldwide ...