Journal of International Medical Research

Subject Area and Category
- Biochemistry
- Cell Biology
- Biochemistry (medical)
- Medicine (miscellaneous)
SAGE Publications Inc.
Publication type
14732300, 03000605
Information
How to publish in this journal
The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 (green) comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 (yellow) the second highest values, Q3 (orange) the third highest values and Q4 (red) the lowest values.
The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'. SJR is a measure of scientific influence of journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the importance or prestige of the journals where such citations come from It measures the scientific influence of the average article in a journal, it expresses how central to the global scientific discussion an average article of the journal is.
Evolution of the number of published documents. All types of documents are considered, including citable and non citable documents.
This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal. The chart shows the evolution of the average number of times documents published in a journal in the past two, three and four years have been cited in the current year. The two years line is equivalent to journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Journal Self-citation is defined as the number of citation from a journal citing article to articles published by the same journal.
Evolution of the number of total citation per document and external citation per document (i.e. journal self-citations removed) received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal’s documents.
International Collaboration accounts for the articles that have been produced by researchers from several countries. The chart shows the ratio of a journal's documents signed by researchers from more than one country; that is including more than one country address.
Not every article in a journal is considered primary research and therefore "citable", this chart shows the ratio of a journal's articles including substantial research (research articles, conference papers and reviews) in three year windows vs. those documents other than research articles, reviews and conference papers.
Ratio of a journal's items, grouped in three years windows, that have been cited at least once vs. those not cited during the following year.
Leave a comment
Name * Required
Email (will not be published) * Required
* Required Cancel
The users of Scimago Journal & Country Rank have the possibility to dialogue through comments linked to a specific journal. The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. For topics on particular articles, maintain the dialogue through the usual channels with your editor.

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2022. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Int Med Res
Journal of International Medical Research
Journal Abbreviation: J INT MED RES Journal ISSN: 0300-0605
You may also be interested in the following journals
- ► Animal Cells and Systems
- ► Chinese Medical Journal
- ► PLoS One
- ► European Journal of Pharmacology
- ► Neurotherapeutics
- ► Molecular Vision
- ► Current Neurovascular Research
- ► Pharmaceutical Biology
- ► Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
- ► Zebrafish
Top Journals in other
- Ca-A Cancer Journal For Clinicians
- Chemical Reviews
- Nature Materials
- Reviews of Modern Physics
- Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
- Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Cancer Discovery
- BMJ-British Medical Journal
- Advanced Energy Materials
- Advances in Optics and Photonics
Journal Impact

- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Ahead of Print
- Subscription
- Author Guidelines

About the Journal

International Journal of Medical Research Professionals (IJMRP) (An Indexed, Multidisciplinary, Peer-Reviewed, Open-Access, International Medical Research Journal. IJMRP is an Official publication of Ibn Sina Academy of Medieval Medicine & Sciences)
ISSN (online): 2454-6364 ISSN (Print): 2454-6356 Impact Factor: 2.365 Frequency: Bimonthly (6 issues/year) Publication Manager: Muskan Garg

- Editorial Policy
- Publication Charges
- Subscribe to This Journal
- Join As Editor
- Join As Reviewer
- Why Publish in IJMRP
- Downloads Section
Useful Links
- Pubmed Central
Trust Certificate

International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences
About the journal.

International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences (IJRMS) is an open access, international, peer-reviewed general medical journal. The journal's full text is available online at https://www.msjonline.org. The journal allows free access to its contents. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences is dedicated to publishing research in medical science from all disciplines and therapeutic areas of medical science or practice. The journal has a broad coverage of relevant topics across medical science or practice. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences (IJRMS) is one of the fastest communication journals and articles are published online within short time after acceptance of manuscripts. The types of articles accepted include original research articles, review articles, editorial, medical news, case reports, adverse drug reactions, short communications, correspondence, images in medical practice, clinical problem solving, perspectives and new drug updates. It is published monthly and available in print and online version. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences (IJRMS) complies with the uniform requirements for manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals, issued by the International Committee for Medical Journal Editors.
Issues: 12 per year
Email: [email protected] , [email protected]
Print ISSN: 2320-6071 Online ISSN: 2320-6012
Publisher: Medip Academy
DOI prefix: 10.18203
Medip Academy is a member of Publishers International Linking Association, Inc. (PILA), which operates CrossRef (DOI)
Manuscript Submission
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences accepts manuscript submissions through Online Submissions :
Registration and login are required to submit manuscripts online and to check the status of current submissions.
- Registration
Please check out the video on our YouTube Channel:
Steps to register and submit a manuscript: https://youtu.be/YHX7eUWH7bk
Problem Logging In-Clear cookies: https://youtu.be/WVjZVkjB2SQ
If you find any difficulty in online submission of your manuscript, please contact editor at [email protected] , [email protected]
Abbreviation
The correct abbreviation for abstracting and indexing purposes is Int J Res Med Sci.
Abstracting and Indexing information
The International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences is indexed with
- PubMed and PubMed Central (PMC) (NLM ID: 101772888, Selected citations only)
- Index Copernicus
- Index Medicus for South-East Asia Region (WHO)
- Scilit (MDPI)
- Google Scholar
- Journal Index
- Directory of Science
- JournalTOCs
- ResearchBib
- SHERPA/RoMEO
Announcements
Fast track publication service.
Fast track publication service is provided to shorten the time to decision and publication. Authors if they wish can have their article published as Articles in Press within 2 weeks of manuscript submission (Conditional to acceptance and author does prompt corrections).
In Press Articles are accepted, peer reviewed manuscripts, and are citable by the digital object identifier (DOI) assigned at the time of online publication. (For example, PubMed Style: D’souza AS, Samuel CJ, Katumalla FS, Gupta G, Goyal S. A randomized comparison between misoprostol and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and labor induction in patients with unfavorable cervices. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. doi:10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20150678).
If you wish to use fast track publication service, please submit your manuscript and write to editor with manuscript ID at [email protected] , [email protected] or contact the editorial office: +91-8128027277 (WhatsApp) .
Make a Submission
Information.
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Current Issue
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. Copyright © 2023.
Print ISSN: 2320-6071 | Online ISSN: 2320-6012
[email protected] , [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- NATURE INDEX
- 13 March 2024
Four change-makers seek impact in medical research
- Amy Coombs 0 &
- Sandy Ong 1
Amy Coombs is a freelance science writer in Chicago, Illinois.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Sandy Ong is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
SIRI ELDEVIK HÅBERG: Lines of enquiry
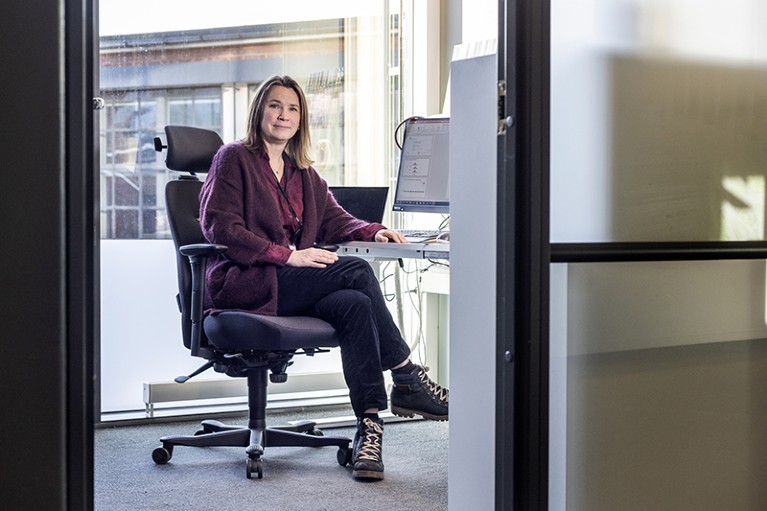

Siri Eldevik Håberg studies whether environmental factors such as smoking are linked to subtle changes to the human genome. Credit: Fredrik Naumann/Panos Pictures for Nature
As a medical student, Siri Eldevik Håberg became fascinated with how the health of a baby can be affected during pregnancy . Smoking, for example, is a proven risk factor for respiratory infection in fetuses — a finding supported by one of Håberg’s earliest studies, which scoured data from tens of thousands of births in Norway to investigate outcomes for a small subset of women who had smoked during, but not after, pregnancy 1 . The analysis was based on data from the Mother, Father, and Child Cohort Study (MoBa) at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH) in Oslo, which today holds biological samples and survey information for nearly 300,000 participants.

Nature Index 2024 Health sciences
Håberg conducted her postdoctoral work in the United States, where she joined a group at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences in Durham, North Carolina. She contributed data analysis to a team that examined 1,062 blood samples from MoBa, drawn from the umbilical cord at the delivery of a baby, and identified 10 genes that were altered in infants born to women who smoked while pregnant. The 2012 study provided important evidence for how non-heritable smoking exposure can cause certain epigenetic effects — subtle changes to the genome that impact the reading of DNA but do not alter the DNA sequence 2 . “We are only beginning to understand the gravity of epigenetic changes during development,” says Håberg.
Now, as director of the Centre for Fertility and Health at the NIPH, Håberg is investigating ways to combine MoBa data with statistics from Norwegian registries on factors such as vaccinations, prescriptions, education and economic status. In one project, she and her colleagues matched babies from the 2012 study with data collected by the Medical Birth Registry of Norway and found that reduced birth weight was strongly correlated with smoking during pregnancy 3 .
Having investigated the effects of smoking on fetal health, Håberg was interested in other factors that could cause epigenetic changes linked to development. In a 2022 study published by Nature Communications 4 , she and her co-authors compared rates of DNA methylation — a process that affects levels of gene expression — for almost 2,000 MoBa newborns. Roughly half of the babies were conceived naturally and half through reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization. Even after controlling for the parents’ DNA methylation rates, differences were found in more than 100 genes, including those related to growth and development. The findings might pave the way for big-data approaches to studies related to reproductive technologies.
Håberg is passionate about connecting specialists from her team with interdisciplinary groups from around the world so that they can explore large amounts of data that hold clues about fetal health. One such project is comparing MoBa data with information from the Danish National Birth Cohort. “It all comes down to finding exciting new ways for teams of specialists to work together,” she says. “It’s great to see so many resources dedicated to questions of early embryonic development.” — Amy Coombs
NARMIN GHAFFARI LALEH: Deeper vision
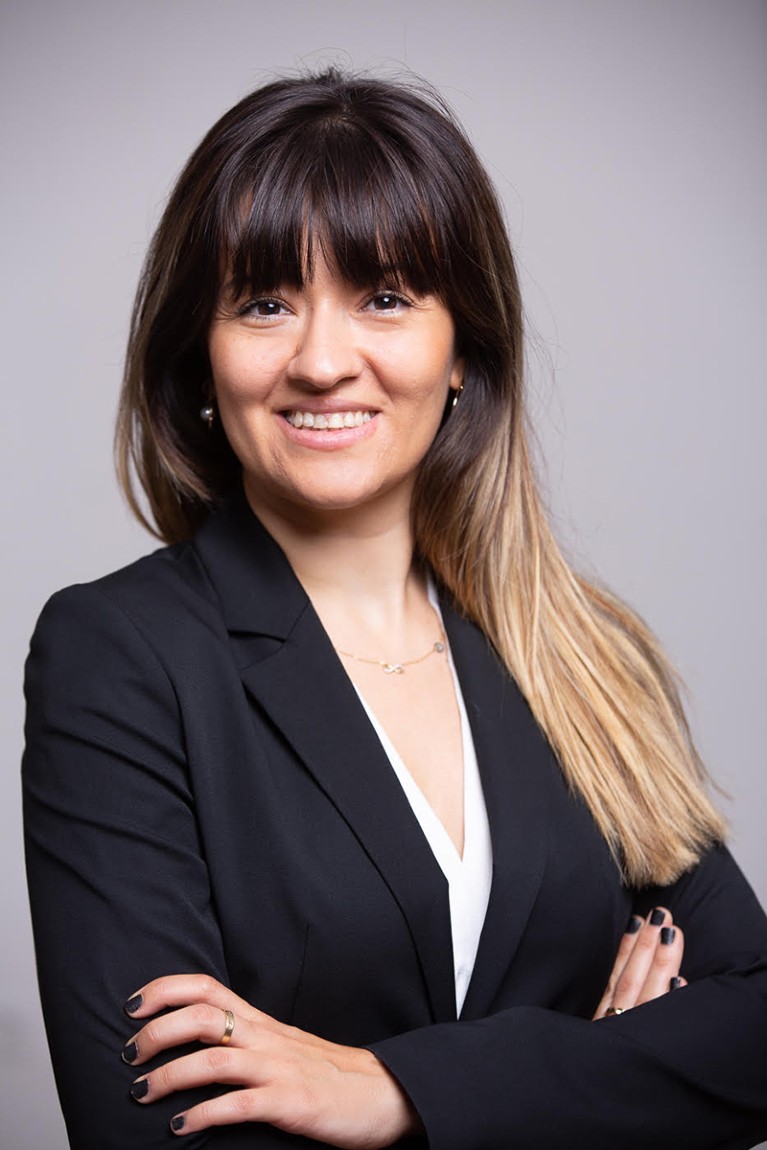

Narmin Ghaffari Laleh. Credit: Courtesy of Narmin Ghaffari Laleh
As a university student studying medical photonics in Jena, Germany, Narmin Ghaffari Laleh was inspired to use her programming skills to help patients and doctors. She sought work experience at local medical-device company, Carl Zeiss Meditec, to explore the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in improving medical-image analysis. Her work there concentrated on eye imaging, where conventional methods of analysis use systems that read each row of pixels, identifying features such as the cornea, lens and retina by tracking their colours and the distance between them. Common variables such as glasses can throw such systems off, however. “These kinds of programs work well until someone puts on glasses or contact lenses and takes a photo,” says Ghaffari Laleh, who was a master’s student at Fredrich Schiller University of Jena at the time.
The model developed by Ghaffari Laleh and her colleagues at the company used deep learning — a machine-learning technique that can identify complex patterns. In testing, their system analysed images with variables such as glasses with greater accuracy and less human oversight than previous methods. “I saw the potential for this sort of program to impact other areas of medicine, because the machine-learning techniques were rapidly becoming more sophisticated and could handle more data, all without the traditional human reviewer,” says Ghaffari Laleh, who built on these findings in her 2020 master’s thesis.
Ghaffari Laleh began her PhD at RWTH Aachen University in Aachen, Germany, in the field of computational pathology — an emerging area of research that aims to improve patient care by using advances in AI and big data. Her focus was on developing systems that can more accurately and efficiently identify visual indicators of cancer and other diseases than methods that rely solely on human specialists. These systems could be particularly useful in the analysis of tissue samples that have been prepared for microscope slides and stained with the widely used haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) dye, which turns cell structures different shades of purple, blue and pink, she says.
In 2022, Ghaffari Laleh co-authored a paper 5 describing how AI could consistently categorize tumours in kidney-tissue slides. “With deep learning, we can detect patterns that the human eye cannot see,” she says.
For a separate study 6 , the team showed how AI trained to identify mutations in a protein associated with bladder cancer could outperform a uropathologist in analysing tissue samples stained with H&E. “We do not aim to replace the urologist, but deep-learning can offer additional analysis,” says Ghaffari Laleh.
To test whether these methods can move to clinical applications, Ghaffari Laleh dedicated her PhD thesis to investigating how applicable these kinds of AI systems could be to a variety of diseases and patient demographics. Her dissertation is pending defence in March.
Ghaffari Laleh hopes to apply her skills to help medical professionals in developing countries who cannot afford to run advanced diagnostics and who struggle to recruit and train skilled professionals. “AI is a much more affordable option,” she says. “If a deep-learning model can analyse data from diverse patient groups from a wide range of countries, then hospitals that lack resources can ship samples for diagnosis.” She’s also working on AI that can read text 7 , ultrasound and radiology image data, with hopes that they can speed up the work of doctors and other specialists worldwide. — Amy Coombs

TAL PATALON: Prolific polymath
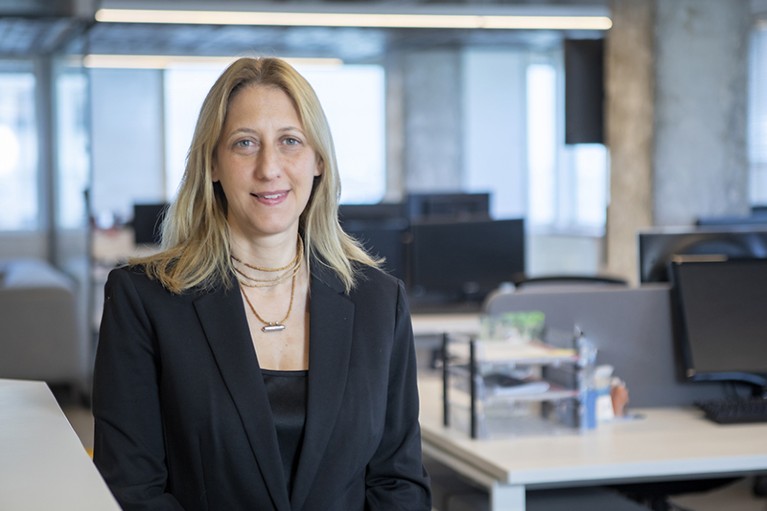

Tal Patalon. Credit: Asaf Brenner
Tal Patalon prides herself on being able to pivot her work to where she thinks her expertise, and that of her team, will be most effective. “For me, it’s all about clinical impact,” she says. As head of Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi (KSM) in Tel Aviv — the research and innovation centre of Maccabi Healthcare Services, one of Israel’s largest health-care providers — Patalon is interested in a range of medical conditions, including parvovirus, mpox, cancer and coeliac disease.
Having the capacity to launch research projects quickly proved invaluable to Patalon and her team during the COVID-19 pandemic, when global treatment and vaccination protocols changed rapidly to keep up with the evolution of the disease. In 2021, as the highly contagious Delta wave was surging through Israel, Patalon co-led a team that scoured the health records of almost 125,000 Israelis, charting coronavirus incidence, symptoms and hospitalization rates over three months.
The team discovered that vaccinated people who had not previously tested positive for COVID-19 were 13 times more likely to be infected by the new variant, compared with previously infected individuals who were unvaccinated. The results showed that the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 confers a natural immunity to those who have been infected, providing valuable evidence that vaccinating them wasn’t an immediate priority 8 . “It was a very big achievement for us,” says Patalon.
Extracting new insights from the vast amounts of public-health data that are being collected globally is key to advancing treatments and keeping one step ahead of infectious diseases, says Patalon. As part of her role at KSM, she oversees the Tipa Biobank, Israel’s largest biosample repository, comprising more than one million blood samples from some 200,000 Maccabi patients. In addition to one-off samples from patients, the biobank collects serial samples — successive samples from the same patient over a period of time. Serial samples are “very rare and highly valuable for research”, says Patalon, especially when it comes to analysing biological changes before and after a diagnosis.
KSM also manages some 30 years’ worth of electronic medical records from more than 2.7 million patients collected by 32 hospital networks that are affiliated with Maccabi. By sharing these data, which have been deidentified, with researchers around the world, Patalon hopes to inform artificial-intelligence-powered innovations in diagnosis and treatment. “These collaborations, I believe, will create the future of medicine,” she says.
Being adaptable as a researcher and a leader is crucial, particularly in times of crisis, says Patalon, whose team has been deeply affected by the war in Gaza .
“This is a time that requires a lot of patience, empathy, emotional support and the building of good relationships. We have to come out of this situation stronger.” — Sandy Ong
SARAH LUO: Hunting hunger pathways
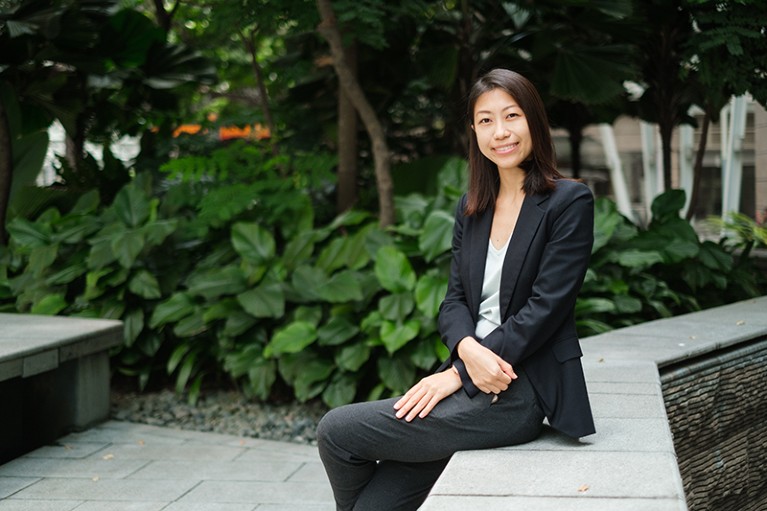

Sarah Luo’s team discovered one of the brain’s many feeding regulatory centres. Credit: Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
Sarah Luo’s fascination with neuroscience sparked when, as an undergraduate student at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in Wisconsin, she was introduced to the work of British neurologist and author, Oliver Sacks.
Known for his empathic approach to patients with conditions such as amnesia, face blindness and Tourette’s syndrome, Sacks “brought a very humanizing perspective to brain disorders”, says Luo. “He showed how even minute changes in certain regions of the brain could lead to profound effects on cognition and behaviour.”
Today, Luo runs a lab at Singapore’s Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), where she studies the connection between hunger and the brain to help patients with metabolic disorders such as diabetes and fatty liver disease. She first studied this connection as a postdoctoral fellow in an adjacent lab, where she was part of a team that discovered a mechanism that regulates feeding.
For many years, researchers had assumed that hunger is regulated by two types of neurons: one that drives hunger and another that suppresses it. But when Luo and her colleagues ran experiments that stimulated certain neurons in a region of the brain called the tuberal nucleus, they could prompt mice to start eating even when they weren’t hungry 9 . “There are actually many feeding regulatory centres in the brain, and we discovered one of them,” she says.
These other centres can deal with “more diverse aspects of eating behaviour”, says Luo, including environmental cues that can incite hunger. In a series of follow-up experiments 10 , Luo and her colleagues observed that when mice were placed in the same feeding chamber where the neurons in the tuberal nucleus had been activated the previous week, they would immediately start eating, even if it was outside their normal feeding times. The results suggest that these neurons not only influence basic feeding behaviour, but also integrate memory and contextual cues into the eating process, says Luo.
Humans experience similar cues. Visiting a favourite restaurant, for example, or returning to the family home can spark an appetite.
“Your neurons might become activated, just because of the environment you’re in,” says Luo. “Those signals might cause you to eat, even if you’re not actually hungry.”
Luo and her team at A*STAR hope to develop treatments that will help to curb excessive food consumption in people with obesity and metabolic conditions by blocking or activating certain neural signals. The trick, she says, is to find and target pathways that run between the brain and organs such as the liver and kidneys, which are more accessible than neural pathways in the brain.
“It would be very invasive to implant an electrode in the brain to activate or inhibit these pathways,” says Luo. But activating pathways that connect to these regions in the brain — by using vagal nerve stimulation, for example, which is a technique used to treat epilepsy that involves implanting a pulse generator under the skin on the chest — would be a more viable option. “Then maybe there will be an easier route for developing therapies to target some of these metabolic diseases,” says Luo. — Sandy Ong
Nature 627 , S8-S10 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00754-w
This article is part of Nature Index 2024 Health sciences , an editorially independent supplement. Advertisers have no influence over the content.
Håberg, S. E., Stigum,, H., Nystad, W. & Nafstad, P. Am. J. Epidemiol. 166 , 679–686 (2007).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Joubert, B. R. et al. Environ. Health Perspect. 120 , 1425–1431 (2012).
Rotroff, D. M. et al. BMC Genomics 17 , 976 (2016).
Håberg, S. E. et al. Nature Commun. 13 , 1896 (2022).
Ghaffari Laleh, N. et al. Med. Image Anal. 79 , 102474 (2022).
Loeffler, C. M. L. et al. Eur. Urol .Focus 8 , 472–479 (2022).
Clusmann, J. et al. Commun. Med. 3 , 141 (2023).
Gazit, S. et al. Clin. Infect. Dis. 75 , e545–e551 (2022).
Luo, S. X. et al. Science 361 , 76–81 (2018).
Mohammad, H. et al. Nature Neurosci. 24 , 1132–1141 (2021).
Download references
Related Articles

Partner content: A holistic approach to health in Japan
Partner content: Can we increase the safety of carbon nanotubes?
Partner content: Building for a digitized, personalized future
Partner content: Translating basic research into medical advances
Partner content: Meds, meals and microbes: gut health on the cancer front line
Partner content: A hotspot for research and development of medical AI
Partner content: What are we learning from the world’s myopia capital?
Partner content: Systems biology: a network view of disease could unearth hidden targets
Partner content: Learning from the pupil: the power of pupillometry
Partner content: Does green tea offer cognitive and sleep benefits?
Partner content: A team effort delivers a new tool for fighting neuroblastoma
Partner content: Shaping the future of medical science - A multidisciplinary paradigm
Partner content: Harnessing AI to see a patient’s unique patterns
Partner content: Improving the outlook for chronic kidney disease
Partner content: From medical robots to a mouse metaverse
Partner content: What comes after clinical trials?
Partner content: Making vitamin D detection much more accessible
Partner content: A new injectable gel could seal wounds after cancer surgery
Partner content: The surprising interplay between metabolism and mind
Partner content: Detecting atrial fibrillation while there’s still time to act
- Bioinformatics
- Machine learning
- Medical research
- Public health

‘Wildly weird’ RNA bits discovered infesting the microbes in our guts
News 29 JAN 24

How to share data — not just equally, but equitably
Editorial 17 OCT 23

Methods section too short? Use online protocols to make complex techniques understandable
Career Column 16 OCT 23

Google AI could soon use a person’s cough to diagnose disease
News 21 MAR 24
Three reasons why AI doesn’t model human language
Correspondence 19 MAR 24

AI image generators often give racist and sexist results: can they be fixed?
News Feature 19 MAR 24
Cutting-edge CAR-T cancer therapy is now made in India — at one-tenth the cost

China’s medical-device industry gets a makeover
Spotlight 20 MAR 24

Whittling down the bacterial subspecies that might drive colon cancer
News & Views 20 MAR 24
Full/Associate & Assistant Professor
We are internationally recognized for our innovative achievements in studying the biology of cancers prevalent in Asia.
National University of Singapore (NUS)
Recruitment of scientific research personnel at National Institute of Pathogen Biology, CAMS&PUMC
Seeking tenure-track and tenured faculty members, and postdoctoral research fellow.
Beijing, China
National Institute of Pathogen Biology, CAMS&PUMC
Associate or Senior Editor, Nature Communications (Electrochemistry)
About Springer Nature Group Springer Nature opens the doors to discovery for researchers, educators, clinicians and other professionals. Every day,...
New York City, New York (US)
Springer Nature Ltd
Applied Bioinformatics Research Scientist
We are hiring an Applied Bioinformatics Research Scientist to identify metabolic vulnerabilities in lung cancer for therapeutic targeting.
Tampa, Florida
H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute
Novo Nordisk Postdoctoral Research Fellowships (5 posts)
We are currently recruiting five Postdoctoral Research Fellows as part of the Novo Nordisk Fellowship Programme at the University of Oxford.
Oxford, Oxfordshire
University of Oxford
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Current Issues
- Registration
- Instructions

- IJBMR- Journal Details
- Why Publish in IJBMR?
- IJBMR-Impact factor
- IJBMR Indexing
- Privacy Statement
- Author Instruction
- Author Registration
- Copyright Form
- IJBMR - Model Cover Letter
- Publication Charges
- Conflict of Interest
- Disclaimer and Copyrights
- Ethical Standards
- Journal Policies
- Peer Review Guidelines
- Reviewer Registration
- Peer Review Process
- Join as reviewer-IJBMR
- Editorial - Peer Review Process
- Join as Editorial Board/Member
- Submit Your Enquiry
An international peer-reviewed publishing online journal Articles are invited. IJBMR - ISSN: 0976 - 6685
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research (IJBMR) publishes papers describing original research in all areas of contemporary biological and medical fields. Submitted original research papers should represent a novel and important contribution to the understanding of any area of biological and medical research and provide mechanistic insights into the process.
All submitted articles should report original, previously unpublished research results, experimental or theoretical, and will be peer-reviewed. Articles submitted to the journal should meet these criteria and must not be under consideration for publication. Manuscripts should follow the style of the journal and are subject to both review and editing.
International Journal of Biological and Medical Research is an international peer-reviewed multidisciplinary online journal published quarterly in the months of January, April, July and October. The journal accepts Original Articles, Review Articles, Case Report and Short Report. Scope of the Article: All Biological & Medical Sciences.
Scope of the Article
All Biological & Medical Sciences like Anesthesiology, Animal Research, Basic medical sciences, Biochemistry, Biotechnology, Bioinformatics, Biophysics, Biology, Cancer biology, Cardiology, Cardio Thoracic Surgery, Dibetology, Dermatology, ENT, Endocrinology, Free radical Biology, General surgery, General Medicine, Genetics, Gastroenterology, Gynecology, Hematology, Herbal Therapy, Human physiology, Immunology, Infertility, Infectious Diseases, Laboratory Medicine & Techniques, Microbiology, Molecular Biology, Nanotechnology, Neonatology, Neurology, Nephrology, Nursing care, Nutrition, Oncology, Orthopedics, Ophthalmology, Pathology, Plant Study, Plant Bio Technology, Pharmacology, Pulmonology, Pediatrics, Psychiatry, Rheumatology, STDs, Stem Cell Research, Toxicology, Urology & Virology, etc...
Abstracted/Indexed in:
Our Journal Indexed in:-

International Journal of Translational Medical Research and Public Health
Review Latest Developments in the field of applied and translational public health and medical research.
Print ISSN : 2576-9502 | Online ISSN : 2576-9499 Frequency of publication: Continuous | Language of publication: English Starting year: 2017 | Format of publication: Online
The International Journal of Translational Medical Research and Public Health (IJTMRPH) is an open access peer-reviewed journal committed to publishing high-quality articles in the field of applied and translational public health and medical research.
- Online submission
- Wider visibility through open access
- Higher impact with wider visibility
- Prompt review
We are accepting new
manuscripts, please submit your
manuscript to us

Abstracting and Indexing Information
Recently published articles.

LETTER TO THE EDITOR | ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
On Utilizing Artificial Intelligence to Impact Healthcare in Low-Income Countries
Marilyn Murrillo
COMMENTARY | MEDICAL EDUCATION EQUITY
An Innovative Approach to E-mentorship for Black Applicants to Graduate Medical Education (GME) Programs
Omar M. Young, Jackyln C. Fuller, Henry W. Lewis III

Original Article | Hepatitis B
Knowledge and Risk Assessment of Hepatitis B Infection among Barbers and Beauty Salon Workers in Mwanza, Tanzania
Semvua Kilonzo, Hyasinta Jaka, Sylvanus Mapunda

Letter to Editor
Cancer Registry in Bangladesh: Challenges and Opportunities
Md. Matiur Rahman, Md. Kaoser Bin Siddique, Mohammad Mahbub Ur Rahim
Published Articles
- February (14)
- February (8)
- December (1)
- January (7)
- January (2)
- September (3)
- January (3)
ISSN (Print): 2576-9502 ISSN (Online): 2576-9499

Privacy Overview

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Impact Factor: 1.6 / 5-Year Impact Factor: 1.9 . JOURNAL HOMEPAGE. SUBMIT PAPER. Journal of International Medical Research is a peer-reviewed open access journal that focuses on innovative clinical and preclinical research, systematic reviews and meta-analyses. All manuscripts must follow ICMJE standards and will receive rigorous peer review ...
Medicine, Research & Experimental (SCIE) 146 out of 189 | Pharmacology & Pharmacy (SCIE) 295 out of 362. The Journal Citation Indicator (JCI) is a measure of citation impact that is normalized by subject category. It is calculated using citations from items published in the JCI year and prior three years, to items published in the prior three ...
Impact Factor: 1.6 / 5-Year Impact Factor: 1.9 . JOURNAL HOMEPAGE. SUBMIT PAPER. Previous issue. Next issue. March 2024. View issue contents Hide issue contents. ... Journal of International Medical Research ISSN: 0300-0605; Online ISSN: 1473-2300; About Sage; Contact us; CCPA - Do not sell my personal information;
Scope. The Journal of International Medical Research is a peer-reviewed, open access journal which focuses on original clinical and preclinical research, systematic and perspective reviews, meta-analyses, pilot studies and case reports, with every article accepted by peer review given a full technical edit to make all papers highly accessible ...
The Impact IF 2022 of Journal of International Medical Research is 1.62, which is computed in 2023 as per its definition. Journal of International Medical Research IF is increased by a factor of 0.25 and approximate percentage change is 18.25% when compared to preceding year 2021, which shows a rising trend.
Articles from The Journal of International Medical Research are provided here courtesy of SAGE Publications. Follow NCBI. Connect with NLM. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894. Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure. Help Accessibility Careers. NLM; NIH; HHS; USA.gov ...
Journal of International Medical Research 2023-2024 Journal's Impact IF is 1.573. Check Out IF Ranking, Prediction, Trend & Key Factor Analysis.
Journal Impact Factor™ ... Journal of International Medical Research is a peer-reviewed open access journal that focuses on innovative clinical and preclinical research, systematic reviews and ...
Journal of International Medical Research. Journal Abbreviation: J INT MED RES. Journal ISSN: 0300-0605. Year. Impact Factor (IF) Total Articles. Total Cites. 2022 (2023 update) 1.6.
» JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL RESEARCH. Abbreviation: J INT MED RES ISSN: 0300-0605 eISSN: 1473-2300 ... Science Citation Index Expanded. Impact Factor (IF): 1.6 Journal Citation Indicator (JCI): 0.33 Citations: 8,478 Open Access Support: Fully Open Access OA journals may be totally free OR paid. For more info, check it on DOAJ.ORG. Country:
Scope/Description: The Journal of International Medical Research is a peer-reviewed, open access journal which focuses on original clinical and preclinical research, systematic and perspective reviews, meta-analyses, pilot studies and case reports, with every article accepted by peer review given a full technical edit to make all papers highly ...
Journal of International Medical Research is exempt from Sage's Gold Open Access APC waiver scheme. This is due to the unique Technical Edit service performed on all provisionally accepted manuscripts. At the point of submission, authors are asked to confirm that they have the publication funds available to pay for their manuscript is accepted.
Introduction. International Medical Research Journal (IMRJ) is a peer reviewed journal produced biannually by Institute for Medical Research (IMR), National Institutes of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH) and has been established since 1997. The journal aims to rapidly disseminate research findings to the scientific community and ...
Gastroenterology, Endocrinology, Oncology and Cardiology are some topics wherein Internal medicine research discussed in the journal have an impact. Journal of International Medical Research emphasizes research on Surgery, which includes concerns such as Complication. Magnetic resonance imaging is a major topic of Radiology research presented ...
International Journal of Medical Research Professionals (IJMRP) (An Indexed, Multidisciplinary, Peer-Reviewed, Open-Access, International Medical Research Journal. IJMRP is an Official publication of Ibn Sina Academy of Medieval Medicine & Sciences) ISSN (online): 2454-6364. ISSN (Print): 2454-6356. Impact Factor: 2.365. Frequency: Bimonthly (6 ...
Journal impact factor (2022): B/C: 1.33. Impact Factor is one of the quantitative tools for ranking, evaluating, categorizing, and comparing journals. It is a measure of the frequency with which the "average article" in a journal has been cited in a particular year or period. The annual impact factor is a ratio between citations and recent ...
Critical Incident Stress Debriefing Experience, Training, and Anticipated Barriers in Emergency Medicine Providers: A Targeted Needs Assessment. Loke, Dana Elizabeth; Dastoor, Jehannaz D.; Fant, Abra L. International Journal of Advanced Medical and Health Research. 10 (1):12-16, Jan-Jun 2023. Abstract.
Impact Factor: 1.6 / 5-Year Impact Factor: 1.9 . JOURNAL HOMEPAGE. SUBMIT PAPER. Journal description ... Journal of International Medical Research (JIMR) is a peer-reviewed open access journal which focuses on original clinical and preclinical research, systematic and perspective reviews, meta-analyses, pilot studies and case reports, with ...
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences (IJRMS) complies with the uniform requirements for manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals, issued by the International Committee for Medical Journal Editors. Issues: 12 per year. Email: [email protected], [email protected]. Print ISSN: 2320-6071 Online ISSN: 2320-6012
Four change-makers seek impact in medical research. ... is a proven risk factor for respiratory infection in fetuses — a ... UNIL is a leading international teaching and research institution ...
International Journal of Biological and Medical Research is an international peer-reviewed multidisciplinary online journal published quarterly in the months of January, April, July and October. The journal accepts Original Articles, Review Articles, Case Report and Short Report. Scope of the Article: All Biological & Medical Sciences.
Impact Factor: 1.6 / 5-Year Impact Factor: 1.9 . JOURNAL HOMEPAGE. SUBMIT PAPER. All articles. Filter. Selecting a filter will update the page's search results. ... Journal of International Medical Research ISSN: 0300-0605; Online ISSN: 1473-2300; About Sage; Contact us; CCPA - Do not sell my personal information;
The International Journal of Translational Medical Research and Public Health (IJTMRPH) is an open access peer-reviewed journal committed to publishing high-quality articles in the field of applied and translational public health and medical research. Online submission. Wider visibility through open access. Higher impact with wider visibility.
Impact Factor: 1.6 / 5-Year Impact Factor: 1.9 . JOURNAL HOMEPAGE. SUBMIT PAPER. Close Add email alerts. You are adding the following journal to your email alerts. ... The Editors of The Journal of International Medical Research focus on publishing high-quality studies across all areas of preclinical and clinical medical research. We have ...