Language selection

- Search and menus

Study permits and visas
As of January 22, 2024, most students need to provide a provincial attestation letter (PAL) from the province or territory where they plan to study. Some exceptions apply. Find out more .
The most important document you need before you arrive in Canada as an international student is a study permit.
Search colleges & universities
Learn more about study permits and visas:
How to get a study permit, about your study permit, apply for a study permit, biometrics collection, what to do after you apply for a study permit, how to apply for a travel or work visa.
Before you apply for a study permit, you need:
- a letter of acceptance from a designated learning institution (DLI)
- a valid passport or travel document
- a provincial attestation letter (PAL) from the province or territory where you plan to study (required for most students)
- proof of financial support
A designated learning institution is a school approved by a provincial or territorial government to host international students. All primary and secondary schools in Canada are designated learning institutions.
If you plan to attend a post-secondary school, such as a college or university, make sure it’s on the list.
If you need to take certain courses before you are accepted into your program (conditional acceptance), you’ll be given a study permit for the duration of those courses. Once the college or university accepts you into your chosen program, you must apply to extend your study permit.
Note: If you plan to attend a college or university in Quebec, you need a Quebec Acceptance Certificate (CAQ) from the Government of Quebec before you apply for a study permit. Your CAQ can act as your provincial attestation letter for Quebec but it must meet certain requirements. Your school can tell you how to apply for the CAQ.
As an international student with a study permit, you must:
- Always be enrolled at a designated learning institution
- Make progress toward finishing your study program
- Respect the conditions listed on your study permit
- Stop studying if you no longer meet the requirements
- Leave Canada when your permit expires
First, it’s important to confirm that you are eligible to apply for a study permit.
Check your study permit eligibility
There are 2 ways to apply for a study permit: Online or by going to a visa application centre in your country.
We suggest you apply for a study permit as soon as you have a letter of acceptance from a Canadian college or university and provincial attestation. It can take up to 3 months to get a study permit, depending on the country where you are applying.
You may need to give your biometrics (fingerprints and photograph) when applying for a visitor visa, study permit or work permit for Canada. If you need to give your biometrics with your application, you will have to go in person to the Visa Application Centre (VAC) closest to you.
Find out if you need to give your biometrics .
If you’re required to give your biometrics, don’t submit your study permit application by mail. Instead, please submit it at the VAC when they collect your biometrics.
You can check the status of your study permit application on the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada website. The information is updated daily. First, you need to set up an account on the site.
Sometimes, the processing centre will ask you to send more information. Learn more about the application process .
Not everyone needs a travel or work visa, but before you arrive in Canada, you should determine whether your plans require you to get a travel or work visa.
Stays less than 6 months
If your time in Canada will be less than 6 months, you’ll need one of the following visas as an international student:
- A travel visa in your passport if you expect to study in Canada for less than 6 months
- An ETA (Electronic Travel Authorization) if your passport is from a designated country
To find out which travel visa you need, answer these online questions .
Work visa during your studies and beyond
If you are attending a post-secondary program in Canada you may be eligible to work during your studies. You can work part-time without a work permit if you meet all of these requirements:
- You’re a full-time student at a designated learning institution (DLI)
- You’re enrolled in either of the following
- a post-secondary academic , vocational or professional training program or
- a secondary-level vocational training program (Quebec only)
- Your study program
- is at least 6 months long and
- leads to a degree, diploma or certificate
- You’ve started studying
- You have a social insurance number (SIN)
If you want to be part of a work placement while studying, you’ll need to apply for a work permit .
- Work while studying in Canada
- Work in Canada after your studies
- Paths to permanent residency and immigration
- Explore careers in Canada
- Stay in Canada after graduation
- Guide: Applying for a study permit outside Canada
- Get a study permit: Get the right documents
- Save time: Send a complete application
Our partner, Cigna, offers newcomers peace of mind. Get a free quote !
Find the best immigration program for you. Take our free immigration quiz and we’ll tell you the best immigration programs for you!
The International Student Roadmap
Sign up to learn everything you need to know about studying in Canada as an international student.
Updated on January 17, 2024
Find the best immigration programs for you
Advertisement
Sign up for the International Student Roadmap by creating a free Moving2Canada account .

Some international students come to Canada for the world-class schools, while others come to build their options for permanent immigration. However, studying in Canada as an international student can be complicated if you don’t understand the process.
That’s why we designed the International Student Roadmap, a free email-education service that delivers International Student lessons and planning guides directly to your inbox. After you’ve completed the International Student Roadmap, you’ll understand how Canadian education works for international students, from choosing a school to applying for your study permit. Don’t get started on your international student journey without it!

Want to study in Canada?
When it comes to Canadian immigration, knowledge is power. Our website is dedicated to informing our audience about the process of moving to Canada, so that you can make decisions that are best suited for your needs. Empower yourself to be in control of your Canadian journey.
Sign up for the International Student Roadmap when you register for a Moving2Canada account . It’s fast, free, and easy!
Related Content

Introducing Canada’s Innovation Stream Pilot: LMIA-Exempt Work Permits for High-Growth Companies

Educational Credential Assessments for Foreign-Trained Architects: IRCC Announces Changes

What Newcomers Should Know About Canada’s 2024 Federal Budget

FAQ: Navigating Tax Season in Canada for Newcomers

Get immigration help you can trust
Book a consultation with one of Moving2Canada's recommended Canadian immigration consultants. You deserve the best in the business.

Get the latest news & updates
Sign up for the Moving2Canada newsletter to get the latest immigration news and other updates to help you succeed in Canada.
Popular Topics
Search results
results for “ ”
Immigration
Learn everything you need to know about Canadian immigration
If you need help with your immigration, one of our recommended immigration consultant partners can help.
Calculate your estimated CRS score and find out if you're in the competitive range for Express Entry.

Take the quiz

Your guide to becoming a student in Canada
Take our quiz and find out what are the top programs for you.

Watch on YouTube
This guide will help you choose the best bank in Canada for your needs.

Get your guide
News & Features
latest articles

Our Partners
Privacy overview.
Language selection
- Français fr
When I try to submit my Express Entry profile or my application, I get an error. What can I do?
We changed some questions in the education history section in both the online profile and application for Express Entry. Because of this, some people are getting errors when they try to move on to the next step.
In your profile, go to the Study and languages section of the form. Open the Education history sub-section. Scroll to the bottom and click Modify .

You will see the information you already entered. To make sure you filled all the fields, click Check for Completeness at the top of the form.
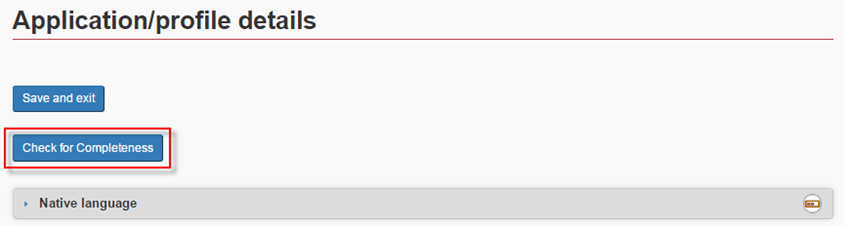
If there is a field you need to correct, you will see a red error message at the top. The question text will also be in red. Fill in the field(s) and click Save and exit .
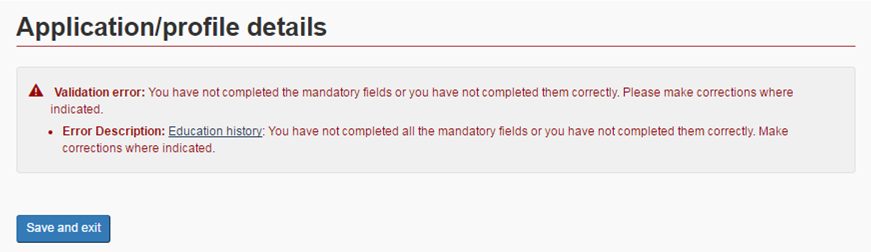
Questions you need to answer are in red
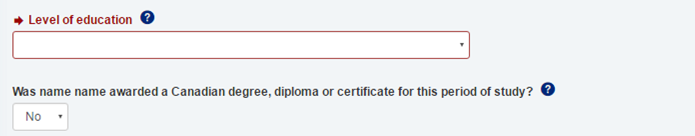
- Repeat these steps for each entry in the section.
If you have been invited to apply, you also need to validate the Personal activities section:
- Go to the Personal history section of the web form.
- Open the Personal activities sub-section and scroll down to the grid of saved entries.
- Click Modify and repeat the steps above for each entry.
Did you find what you were looking for?
If not, tell us why:
You will not receive a reply. Telephone numbers and email addresses will be removed. Maximum 300 characters
Thank you for your feedback
Answers others found useful
- How can I find out what Canadian Language Benchmark (CLB) level my immigration language test results are equivalent to?
- Where can I get an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA)?
- I’m in the Express Entry pool. How can I look for a job in Canada?
- How do I find my National Occupation Classification (NOC) code?
- Why didn’t I get points for my job offer in Express Entry?
- Do I need to include proof of funds for Express Entry?

How to videos

Glossary term
- Economic class

- Forums New posts Search Forums
- Members Registered members Current visitors Recent Activity
- Free Assessment
Should we mention our high school education in the application application
- Thread starter alstar
- Start date Mar 12, 2017
Star Member
Hi Guys, I am about to submit my application as I have uploaded all the necessary documents. One thing that I wanted to clear is that in the educational section should I mention my high school information as well? I am a bachelor's and I have that verified by WES My wife is a masters so she has her bachelor's and masters attested from WES. So in the educational section we have only mentioned that. Do I need to mention my high school details as well? Thanks A
The application says "We will assess <applicants name> secondary and post-secondary periods of study for eligibility for Express Entry, and use them to calculate <applicants name> score. You can tell us about each period of study by filling in the fields below" Now I studied in India and can you tell me what information should I enter besides my bachelors and master degree? As in India we dont label it as secondary or post secondary hence the confusion. Thanks A
Only mention bachelors and masters
xpressentry
High school education was before you turned 18. CIC doesnt care what you did back then and it doesnt give you any points either.
Thank you so much everyone
alstar said: Hi Guys, I am about to submit my application as I have uploaded all the necessary documents. One thing that I wanted to clear is that in the educational section should I mention my high school information as well? I am a bachelor's and I have that verified by WES My wife is a masters so she has her bachelor's and masters attested from WES. So in the educational section we have only mentioned that. Do I need to mention my high school details as well? Thanks I think you need to mention your class 10 and 12th details and also add your certificates along with application. There is no harm in it. moreover also add complete detail of your bachelors and masters even though you have wes for these qualifications. A Click to expand...
Hero Member
DelPiero07 said: Only mention bachelors and masters Click to expand...
xpressentry said: High school education was before you turned 18. CIC doesn't care what you did back then and it doesn't give you any points either. Click to expand...
damitdada said: But, What if I skipped my high school education in between and completed it when I was 21. Should I include that information then....My highest degree is Ph.D. Thanks Click to expand...
History of Post-Secondary in Canada
The history of post-secondary education in canada: part vii – since 2003.
By Alex Usher | President | Higher Education Strategy Associates
The current era of PSE in Canada essentially took shape at the end of the Chretien Era. There has been a little bit of evolution in institutional forms (this is the era in which “polytechnics” arrive and applied research becomes a thing at the college level, and several colleges were converted into universities) but really no change in system architecture.
There are certainly budget changes – rapidly increasing in the period to about 2009, and then levelling off with international student fees replacing government grants thereafter – but they have been slow and incremental. Oil-rich provinces (Alberta, Saskatchewan, Newfoundland) opened the spigots to universities when times were good and then sometimes cut back abruptly when times were bad, but change was for the most part incremental. The system, in a sense, seems to have become too big to revolutionize.
The paradox of this period lies in the way the teaching and research missions interacted. In some respects, teaching became more important because this was a period of huge growth in enrollments. Between 1999 and 2010, FTE enrollment at Canadian universities increased by 50%, partly due to natural growth and partly due to the conversion of seven colleges in BC and Alberta to university status. This was one of the fastest growth rates of tertiary enrolment anywhere in the OECD, and to a considerable extent it was funded through increases in government expenditure.
The sharp increases in student fees that marked the previous era more or less disappeared, to be replaced by a slow but steady drift of between 1-2% after inflation. In other words, tuition fee increases moderated at exactly the time that the system proved high fees were not a barrier to access.
But at the same time, when the system should have been focused on accommodating this new growth, much of the system decided to continue the quest for research-intensity. Encouraged by growth in spending in Ottawa, it was awfully tempting to plow some of those extra student dollars from expansion into more buildings for research, lower teaching loads to accommodate more research (thus creating a need for more sessional teachers and more non-academic staff to pick up work faculty no longer chose to do), and – above all – raise faculty salaries so they were competitive with those in America (the rocketing increase in the value of the dollar around 2006 helped enormously, too). So, to a large extent that’s what everyone did. What we therefore got – and what we still have today – was a system that largely treated the expansion of access as a means to an end for greater research intensity. The fact that the two missions were essentially being funded by two separate levels of government that did not talk to one another did not help matters.
This might have worked, had the crash of 2008 not come along and had the money kept flowing. Post-secondary education was mostly unaffected for the first couple of years, because Canadian governments operated on Keynesian principles and kept spending into the recession that followed. And, of course, the Harper government decided to rescue the construction industry with a huge infrastructure program which for appearance’s sake they decided to locate on college and university campuses (the Trudeau government would dust off exactly the same plans in 2016), which created a temporary illusion of prosperity.
But as the decade ticked by, what Canadian universities received from provincial governments shrunk just a little bit each year in real terms. And the settlements that faculty associations kept winning grew just a little bit each year. And the end of mandatory retirement meant the average age (and therefore wages) of the faculty grew just a little bit each year. It was a long, slow, relentless squeeze. Not enough to create a crisis, but enough to make things uncomfortable, and at a few small universities which happened to experience a bad class recruitment or two (e.g. Acadia) it came pretty close to pushing them to the wall.
Had domestic fees been allowed to rise to compensate, institutions probably would have gone that route. But they couldn’t, so it was exactly at this time that Canadian universities discovered what Australian ones had known for over a decade: you can get international students to pay for stuff your home government and home students won’t! And so began the relentless rise in international student numbers, and it’s suffice to say we’ve more or less just replaced lost government funding with international student dollars and carried on as if nothing had changed.
The other funding challenge was more directly research-related: in conjunction with the run-up in research funding, a lot of universities ramped up their doctoral programs and started hiring more scientists. When the funding escalator stopped, suddenly there were a lot more people competing for funds that were no longer growing. Result: a lot of people with disappointed hopes of academic careers, and significantly decreased success rates on grant competitions (made worse in the medical sciences by CIHR’s bizarre decision to hand out fewer, larger awards). This led to a lot of unhappy scientists who were not in the least mollified by the fact that the Government throughout this period did keep investing fairly heavily in “Big Science” projects like TRIUMF, NEPTUNE, Canada First Research Excellence Grants, etc.
And so that’s about where we sit today. The architecture of the system is almost unchanged from fifteen years ago (BC and Alberta excepted, around the edges). What has changed are the details around research funding, the nature of the funding streams, and to some extent the culture of institutions, which almost regardless of size have taken on more characteristics of American flagship research institutions.
Published in October 2018 by Alex Usher; Higher Education Strategy Associates
Reproduced with Permission
Higher Education Strategy Associates | 20 Maud St, Unit 207, Toronto, ON M5V 2M5 Canada
WEBSITE: higheredstrategy.com EMAIL [email protected]
Related Articles
The history of post-secondary education in canada: part vi – 1993 to 2003, the history of post-secondary education in canada: part v – 1974 to 1993, the history of post-secondary education in canada: part iv – 1960 to 1974, the history of post-secondary education in canada: part iii – 1940 to 1960, search institutions.

Post-Secondary Education Options in Canada
Table of Contents
Canada is one of the best most ideal places for post-secondary education studies in the world. It is highly sought after by many prospective international students. The country has a detailed education system that encourages international students to pursue other endeavors during their Bachelor’s or Master’s degree program and still allows them to stay and work after graduation.
The Canadian government allows each province and territory to deliver its education programs. Despite regional differences, Canadian post-secondary institutions across all levels use similar terms to describe common pathways and credentials. Canada offers a number of certificates, diplomas, bachelor’s and master’s degree programs. These programs qualify students to undertake employment opportunities, they may be useful for immigration purposes.
The length and composition of these programs is also an essential part for potential foreign students, as it may have a direct effect on eligibility for a post-graduation work permit and immigration opportunities in Canada. The undergraduate education system in Canada allows for the completion of senior secondary or high school. The full duration of standard undergraduate education is normally three to five years.
International students should budget a minimum of four years to complete an undergraduate (bachelors) degree program. With a completed bachelor’s degree program, international students may decide to pursue a Master’s degree, which requires completion of a bachelor’s degree.
4 Types of Post-Secondary Education in Canada
Canada tops the charts for the most sought-after schools in the world for quality education. In order to know which program is right for you, you must first understand the different levels of degrees or certificate courses the country offers. There are broadly four different types of post-secondary education each with different purposes.
1. University
A university is a post-secondary educational institution that is authorized to award degrees. Every university offers Bachelor’s Degree programs, and many also offer Master’s Degree programs and Ph.D. programs. Most universities in Canada are public-funded and are autonomous in terms of academic matters such as staff recruitment, quality of programs, and policies and procedures.
A college is a post-secondary educational institution that cannot award degree certifications, though there are some exceptions to this. Instead, they normally offer programs resulting in certificates and/or diplomas.
In general, college courses are more career-oriented programs when compared to universities. A college graduate may complete hands-on, vocational, or practical training in employable skills, like language training, graphic design, or culinary skills. Some Colleges also have training programs or apprenticeships in skilled trade occupations like welding or carpentry.
3. Trade School/Apprenticeships
A skilled trade refers to a specialized occupation, usually focusing on some form of manual labor, which requires basic training and formal education.
A skilled trade does not require a Bachelor’s Degree, so education in the skilled trades usually occurs through trade schools, which are often smaller programs contained within vocational schools or colleges. Once an aspiring tradesperson has acquired sufficient training, they may undertake an apprenticeship. As an apprentice, they work closely with an experienced tradesperson to improve their skills in the trade.
4. Vocational School
Vocational programs equip students with hands-on technical skills required to perform the tasks of a specific job. These programs prepare students to enter into the workforce, either in skilled or low-skilled jobs.
While there are separate terminologies for different types of schools at the post-secondary levels these terms mean different things in various locations around the world, so a college, for example, may be referred to one type of school in Canada but something different in Germany or France. Also, sometimes these schools overlap, there can be colleges affiliated with universities or trade schools within colleges.
Different Types of Degrees in Canada
In Canada, there are different types or levels of degrees for many disciplines and subjects. Basically, these four types of degrees are rendered by universities in the various Canadian provinces and territories:
Associate Degree
An Associate Degree in Canada is a foundational undergraduate program in a field of studies (such as Sciences or Arts). Unlike certificates and diplomas, Associate Degrees comprises a series of general academic subjects such as Associate of Arts (Business) and Associate of Arts (Science).
The Associate Degree allows students to start their studies at one university or college and transfer into third-year coursework at a university, pending approval by the receiving institution.
Bachelor’s Degree
A bachelor’s degree in Canada signifies the completion of four to five years of full-time regular post-secondary education. Subject areas most often include conventional academic subjects in General Sciences, Engineering, Business, the Arts, or Humanities. In this arrangement, students are expected to gain foundational knowledge in their first two years, and then specialize in a major. Some universities offer a fifth professional year course comprising a supervised practicum (for example, for business or teachers’ certifications). Admission into a bachelor’s degree program requires a completed senior secondary or high school program in Canada.
Master’s Degree
Master’s degrees comprise one to three years of advanced post-graduate study, and can also lead to professional practice. Master degrees are conferred by universities and tend to build on previous study areas explored at the undergraduate or bachelor’s level. Programs often expect the student to conduct extensive academic research leading to a major project, thesis, and/or comprehensive examination. Master’s degree programs usually require completion of a bachelor’s degree.
Doctorate Degree
Doctorate degree in Canada comprises at least three to four years’ equivalent full-time study in comprehensive and analytical coursework, followed by an independent thesis or dissertation. PhDs and other doctorate degrees are required for many professions such as university professors and doctors, health care, or high-level administration jobs in government. The average timeframe to complete a Doctorate degree program is four to six years.
Colleges and institutes
Colleges and institutes that usually offer these types of programs issues diplomas and certificates that qualify graduates to work in specific jobs within many fields. These fields include:
- computer and mechanical technologies
- social services
- agriculture
- trades (such as electrician, carpenter, and plumber)
- many others
A growing number of recognized colleges and institutes now offer bachelor’s degrees and, in some cases, master’s degrees.
FAQ for Post-Secondary Education in Canada
Q. Are Post-secondary education free in Canada?
A. Most post-secondary schools in Canada do not offer free education. Though many of them are publicly funded by the federal government and by their respective provincial governments, they do not offer free tuition to both domestic and international students. Only Public high school or secondary is free in Canada for residents of the country.
Q. What is Canadian post-secondary education?
A. Postsecondary Education, also known as tertiary education, is the education level that follows the successful completion of secondary education, often referred to as high school. Postsecondary education includes universities and colleges, as well as trade and vocational schools. Postsecondary education usually leads to a diploma, certification, or academic degree.
Q. What is secondary and post-secondary education in Canada?
A. Secondary or high school is called secondary education in Canada. It is the level of education that preceded post-secondary education. Any studies beyond high school are called post-secondary. Postsecondary education includes universities and colleges, as well as trade and vocational schools.
Q. Is a diploma a post-secondary Education?
A diploma is of two different levels. It can be undergraduate or postgraduate. While an undergraduate diploma does not require a degree, a postgraduate requires completion of a graduation degree. A post-graduate diploma is a diploma course done after your graduation
Q. What are post-secondary education quality assessment boards in Canada?
A. Postsecondary Education Quality Assessment Board is an advisory agency of the federal government. It makes recommendations to the federal Minister on applications for ministerial consent for institutions not authorized to offer all or part of a degree program.
The Board was established to ensure that new degree programs offered by Canadian colleges, universities or private institutions provide the highest quality of education that is expected from degree-granting institutions in Canada.
Q. Which degree is most valuable in Canada?
A. Canada’s post-secondary schools offer a number of degree programs that cut across many fields of endeavors. Most valuable degrees are measured by the high-paying jobs they offer and the demands for them. Based on the highest graduate salaries in Canada, IT and Engineering related degrees are often considered most valuable.
Q. Do colleges and universities in Canada offer the same credentials?
A. Generally speaking, colleges offer certificates and diplomas, while universities offer bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees.
More recently, however, accredited public colleges in Canada now also confer bachelor’s degrees and a limited number of diplomas and graduate certificates. Many Canadian universities also confer post-graduate certificate and diploma programs.
Q. What is the highest degree offered by post-secondary schools?
A. The doctorate degree is the highest degree you can earn in a post-secondary school. This shows that you have achieved the highest level of academic mastery in your chosen field of study, and can work as a university professor, professional researcher, high profile jobs with the government, or in an executive leadership role.
Language selection
- Français fr
Minister Miller issues statement on international student allocations for provinces and territories
From: Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada
The Honourable Marc Miller, Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship, issued the following statement
Ottawa, April 5, 2024— The Honourable Marc Miller, Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship, issued the following statement:
“On January 22, I announced a national cap on study permit applications to address the rapid increase of international students in Canada. Provincial and territorial allocations for 2024 have now been finalized. I would like to take this opportunity to share those figures and explain how we made these decisions.
Net zero first year growth model
“The national cap is based on the amount of expiring study permits this year. This means that the number of international students coming to Canada in 2024 should be the same as the number of students whose permits expire this year. For 2024, the target is 485,000 approved study permits.
“About 20% of students apply for an extension each year and remain in the country. Therefore, IRCC subtracted that amount (97,000) from the target of 485,000 and set aside a small buffer to allow for other variations, resulting in a revised target of 364,000 approved study permits in 2024.
“Accordingly, based on the national approval rate of 60% for study permit applications, the target of 364,000 approved study permits translates into a cap of 606,000 study permit applications received for 2024.
“Some international students are exempt from the cap, such as primary and secondary school students and master’s or doctoral degree students. IRCC deducted the estimated volume of these groups (140,000 based on 2023 data) from the 2024 target number of approved study permits. This resulted in a target of 236,000 approved study permits for 2024, which converts to roughly 393,000 study permit applications to be allocated.
Finalizing provincial and territorial allocations
“IRCC distributed the adjusted number of study permit applications, 393,000, based on the population share of each province and territory. Under this model, some provinces and territories would get more students in 2024 than in 2023, while others would see fewer new students.
“For provinces that would receive more international students in 2024 than in 2023 based on population share, we adjusted their allocation to limit growth to 10% compared to 2023.
“For provinces that would receive fewer international students in 2024 than in 2023, we adjusted their allocation to lessen the negative impact in the first year and support broader regional immigration goals.
“IRCC also topped up allocations for provinces whose approval rate was lower than 60%. The top-ups will help provinces with lower approval rates reach their expected number of approved study permits in 2024.
“As a result, a total of about 552,000 study permit applications have been allocated to provinces and territories under the national cap. These allocations are expected to yield approximately 292,000 approved study permits, representing a 28% reduction from 2023 for the groups included under the cap.
“Many variables may influence the number of new international students who arrive in Canada in 2024, for example
- provinces and territories with room to grow may not end up using their full allocations
- approval rates may change
- in-year adjustments may be required
“These results will help me make decisions on allocations for 2025. I have included the full allocation model below.
“We will continue to work collaboratively with provinces and territories to strengthen the International Student Program and to provide international students with the supports they need to succeed in Canada.”
Allocation model
For further information (media only), please contact:
Bahoz Dara Aziz Press Secretary Minister’s Office Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada [email protected]
Media Relations Communications Sector Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada 613-952-1650 [email protected]
Page details
Language selection
- Français fr
Chapter 1: More Affordable Homes
On this page:, solving the housing crisis, 1.1 building more homes, 1.2 making it easier to own or rent a home, 1.3 helping canadians who can't afford a home.
Fairness for every generation means making housing affordable for every generation.
For generations, one of the foundational promises of Canada's middle class dream was that if you found a good job, worked hard, and saved money, you could afford a home. For today's young adults, this promise is under threat.
Rising rents are making it hard to find an affordable place to call home and rising home prices are keeping homes out of reach for many first-time buyers. The ability of an entire generation of Canadians to achieve the promise of Canada is at risk, despite their sheer grit and hard work. Millennials and Gen Z are watching the middle class dream become less and less achievable. They worry that they won't ever be able to afford the kinds of homes they grew up in. They deserve the same opportunity to own a place of their own as was enjoyed by generations before them.
The government is taking action to meet this moment, and build housing at a pace and scale not seen in generations. We did it when soldiers returned home from the Second World War, and we can build homes like that again. And we can make sure that Canadians at every age can find an affordable home.
On April 12, the government released an ambitious plan to build homes by the millions, Solving the Housing Crisis: Canada's Housing Plan. It includes our plan to make it easier to afford rent and buy a home, and makes sure that the most vulnerable Canadians have support, too. At the heart of our plan is a commitment that no hard-working Canadian should spend more than 30 per cent of their income on housing costs.
Tackling the housing crisis isn't just about fairness, it's also about building a strong economy. When people can afford housing, they can also invest in their local community, supporting local businesses and jobs. When workers can afford to live near their jobs, short commutes turn into high productivity. Businesses want to establish new headquarters in cities where workers can afford to live. When people can more easily save for a down payment, they can pursue their dreams, like starting a business. Housing policy is economic policy.
Budget 2024 and Canada's Housing Plan lay out the government's bold strategy to unlock 3.87 million new homes by 2031 , which includes a minimum of 2 million net new homes on top of the 1.87 million homes expected to be built anyway by 2031. Of the 2 million net new homes, we estimate that the policy actions taken in Budget 2024, Canada's Housing Plan, and in fall 2023 would support a minimum of 1.2 million net new homes.
Given the significant provincial, territorial, and municipal levers that control and influence new housing construction, we call on every order of government to step up, take action, and achieve an additional 800,000 net new homes, at minimum, over this same period.
To get this done, the government will work with every order of government, with for profit and non-profit homebuilders, with Indigenous communities, and with every partner necessary to build the homes needed for Team Canada to restore fairness for every generation.
Working together, we will reach at least 3.87 million new homes by the end of 2031.

Immigrants built Canada. And when new Canadians arrive today, our society is enriched. Canada, like other advanced economies, needs immigrants today more than ever, given our aging population. Immigrants are essential to maintaining a young and capable workforce, to ensuring we can find the doctors, construction workers, nurses, and early childhood educators that we need.
But our ability to successfully welcome new Canadians depends on having the physical capacity to do so properly—in particular having enough homes. That is why current housing pressures mean that Canada is taking a careful look to make sure immigration does not outpace our ability to supply housing for all.
It is important to note that Canada's immigration system has two parts: permanent and temporary.
Throughout Canada's history, permanent immigration has become subject to extensive consultation with communities, provinces, territories, and employers. It is planned and designed in collaboration with Canadian society.
However, temporary immigration, which includes our student and temporary worker programs, has traditionally been demand-driven, determined by the requests from international students and workers, and from employers in Canada.
Canada has recently undertaken a review process for our temporary resident programs, to better align with labour market needs, to protect against abuses in the system, and to match our capacity to build new homes. We will also be setting targets both for the number of permanent residents we welcome, and for temporary residents.
Starting this fall, for the first time, we will expand the Immigration Levels Plan to include both temporary resident admissions and permanent resident admissions.
Our ultimate goal is to ensure a well-managed, responsive, and sustainable immigration system to help balance housing supply with housing demand. We also need to be sure that our temporary worker programs do not create a disincentive for businesses to invest in productivity, or drive down wages in Canada, especially for low-wage workers.
The federal government's plan starts with turbocharging the construction of new homes across the country because the best way to bring down home prices is to increase supply—and quickly. The government is already making the math work for homebuilders by breaking down regulatory and zoning barriers, providing direct low-cost financing, and making more land available. To ensure we have the workers and innovative construction methods needed to build more homes, faster, the government is training and recruiting the next generation of skilled trades workers, and transforming how homes are built to increase construction productivity.
Second, to make it easier to own or rent a home, Budget 2024 announces new action to support renters and lower the costs of homeownership. For renters, new action will help protect them from unfair practices like steep rent increases and renovictions, and unlock new pathways for them to become homeowners, including ensuring they get credit for rental payments. For first-time homebuyers, new support will make it easier to save for their down payment faster and get their first mortgage. And, existing homeowners with mortgages will benefit from new protections from rising payments through the strengthened Canadian Mortgage Charter.
Third, because everyone in Canada deserves a safe and affordable place to call home, this plan is unlocking more homes for Canadians in need. This includes building more affordable units for low- and middle-income Canadians by investing in affordable housing projects and partnering with non-profits, co-ops, the private sector, and other orders of government. This also means offering immediate support for Canadians without shelter and Canadians at risk of becoming homeless.
At the crux of this effort is ensuring that fiscal policy works in tandem with monetary policy, and that Canada's immigration policy works in tandem with housing policy. The government recently announced plans to adjust immigration programming which would lead to about 600,000 fewer temporary residents in Canada compared to current levels. These efforts are critical to creating the necessary conditions to lower interest rates, lower housing demand, and restore housing affordability.
Building enough homes to restore fair prices and make sure everyone has a place to call home is going to take a Team Canada effort. All orders of government—federal, provincial, territorial, and municipal—need to work together to remove all barriers that often slow down the construction of new homes. This includes working together to overcome financial, zoning, and regulatory barriers.
Already, the $4 billion Housing Accelerator Fund is cutting red tape across the country, with 179 agreements with municipalities, provinces, and territories enabling the construction of over 750,000 new homes over the next decade. It is working, so we are topping it up with $400 million to build more homes, faster, in more communities.
Under a new Canada Builds approach, the federal government is offering to partner with provinces and territories that launch their own ambitious housing plans, with federal financing to help rapidly increase housing supply for Canadians in every province and territory.
We must use every possible tool to build homes at a scale and pace not seen since the Second World War. The federal government is announcing a range of new measures to make the math work for homebuilders, unlock the lands needed to build new homes, cut red tape that holds back new construction, attract and train skilled workers, and accelerate the implementation of innovative ways to build more homes, faster.

Key Ongoing Actions
- The Affordable Housing and Groceries Act , which is making it less expensive to build new homes by removing the GST on new purpose-built rental housing projects.
- Over $40 billion through the Apartment Construction Loan Program, which is providing low-cost financing to build more than 101,000 new rental homes across Canada.
- Over $14 billion through the Affordable Housing Fund to build 60,000 new affordable homes and repair 240,000 additional homes.
- $4 billion through the Housing Accelerator Fund, which is incentivizing municipalities to make transformative changes by removing zoning barriers and ramping up housing construction. The Housing Accelerator Fund is already fast-tracking the construction of at least 100,000 homes over the next three years, and more than 750,000 homes across Canada over the next decade.
- Unlocking $20 billion in new financing to build 30,000 more rental apartments per year by increasing the annual limit for Canada Mortgage Bonds from $40 billion to up to $60 billion.
Building Homes on Public Lands
The high cost and scarcity of land present key barriers that prevent key homes from being built. These barriers also contribute to higher costs of building, which are then passed on to Canadians.
Today, governments across Canada are sitting on surplus, underused, and vacant public lands, such as empty office towers or low-rise buildings that could be built on. By unlocking these lands for housing, governments can lower the costs of construction and build more homes, faster, at prices Canadians can afford.
Since 2016, Canada Lands Company has enabled the construction of more than 10,300 new homes on underused federal land, including more than 1,100 affordable homes. Over the next five years, Canada Lands Company currently aims to enable the construction of over 29,200 new homes, with a minimum of 20 per cent affordable units. Canada Lands Company is working to unlock new homes each day, but we need to do more, faster.
To ensure every Canadian has a safe and affordable place to call home, the government will transform its approach to federally owned land and lead a national, Team Canada effort to unlock public lands for housing.
Whenever possible, public land should be used for homes. Moving forward, the federal government will partner with the housing sector to build homes on every possible site across the federal portfolio. By leveraging new approaches to building homes on public lands, such as leasing, the federal government will also be able to maintain the strengths of its balance sheet.
By building homes on public lands,the federal government will lead a Team Canada effort to unlock federal, provincial, territorial, and municipal public lands across the country. The federal government will partner with homebuilders and housing providers to build homes on every possible site across the public portfolio.
With the new Public Lands for Homes Plan , the federal government is announcing an historic shift in its approach to unlock 250,000 new homes by 2031.
To get this done, Budget 2024 announces:
- The federal government will use all tools available to convert public lands to housing, including leasing, acquiring other public lands for housing, and retaining ownership, whenever possible. Keeping land under public ownership and leasing it to builders—instead of selling to the highest bidder—will enable new homes to be affordable, forever. This effort will help housing providers avoid unnecessary upfront capital costs, allowing them to build more affordable housing, all while strengthening the federal government's balance sheet to unlock more homes.
- Review the entire portfolio of federally owned land and properties to rapidly identify sites where new homes can be built;
- Require departments and agencies to offer up specific parcels of land according to specified targets;
- Consult with municipal, provincial, and private sector partners to identify the most promising lands to be made available for housing;
- Publish a new Public Land Bank, encompassing an inventory of available lands, before fall 2024 to accelerate construction on public lands;
- Release a new geo-spatial mapping tool to help homebuilders more easily access and navigate public lands; and,
- Introduce legislation, as required, to facilitate the acquisition and use of public lands for homes, in partnership with other orders of government.
- Cut approval times in half, while abiding by constitutional obligations;
- Initiate redevelopment processes early;
- Bundle multiple properties to be transferred at once;
- Provide leases, including long-term, low-cost leases, for housing providers;
- Transform underused government offices into multi-use properties;
- Transfer land from the federal government to Canada Lands Company for $1, whenever possible, to support more affordable housing;
- Enable housing development on actively used federal properties; and,
- Work with Crown corporations to redevelop their surplus, underutilized, or actively used properties for housing.
- $500 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, on a cash basis, to Public Services and Procurement Canada to launch a new Public Lands Acquisition Fund, which will purchase land from other orders of government to help spur sustainable, mixed-market housing.
- $112.6 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, and $4.3 million in future years, for the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to top up the Federal Lands Initiative to unlock more federal lands for affordable housing providers. This investment, which is expected to unlock a minimum of 1,500 homes, including 600 affordable homes, will also prioritize new approaches, such as leasing, to make federal lands available to affordable housing providers;
- $20 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, for Public Services and Procurement Canada to scale-up its centre of expertise on public lands; and,
- $15 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, for Public Services and Procurement Canada to work with Infrastructure Canada on delivering the new Public Land Bank and geo-spatial mapping tool.
- Nearly 100 homes at Currie in Calgary, Alberta;
- Nearly 500 homes at Wateridge Village in Ottawa, Ontario;
- Over 40 homes at the Village at Griesbach in Edmonton, Alberta;
- 100 homes at Arbo Neighbourhood in Toronto, Ontario; and,
- Over 100 homes at 3155 Chemin de la Côte-de-Liesse in Montréal, Quebec.
- Shannon Park, Dartmouth, Nova Scotia;
- Village at Griesbach, Edmonton, Alberta;
- Downsview, Toronto, Ontario; and,
- Wellington Basin, Montréal, Quebec.
- The Public Lands Action Council will bring all players together to identify specific parcels of land across Canada with high potential for housing and take concerted action to accelerate construction on these lands. This group will also help shape the federal government's approach to building homes on public lands, including the design of the Public Lands Acquisition Fund.
- To support this work, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $1.8 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, for the Privy Council Office to create a Public Lands Action Council Secretariat.
The federal government recognizes that connecting existing federal financing to public lands can accelerate home construction and ensure deeper housing affordability. The federal government will explore leveraging its low-cost financing initiatives, including its new Canada Builds partnership and its new Canada Rental Protection Fund, to encourage housing providers to build more homes on public land.

Building homes on public lands will enable new non-profit housing
Housing Society Co. is a non-profit housing provider and homebuilder that wants to build an apartment building of 125 homes in Edmonton, with at least 30 per cent of its units to be affordable. However, the property Housing Society Co. wants to purchase costs $9 million—representing 25 per cent of total development costs.
Between the land, construction costs, and interest rates, the math just doesn't work to make the project viable. By building homes on public lands, Housing Society Co. will now be able to lease a parcel of land from the federal government at little to no cost upfront and can use rent proceeds to repay the lease over time.
As a result, Housing Society Co. will be able to go forward with the project, and charge affordable rents on a higher percentage of units than initially anticipated.
Building Homes on Canada Post Properties
Canada Post manages a large portfolio of land, including more than 1,700 post offices, in over 1,700 communities across the country. Many of these sites often house one-storey Canada Post buildings, which could be leveraged to build new homes across the country, while maintaining Canada Post services.
The following six Canada Post properties are being assessed for housing development potential:
- 1285 rue Notre-Dame Centre, Trois-Rivières, Quebec;
- 37 rue Saint-Laurent, Beauharnois, Quebec (recently listed for sale);
- 4 rue du Centre Commercial, Roxboro, Quebec;
- 9702 Hardin Street, Fort McMurray, Alberta (recently listed for sale);
- 120 Charles Street, North Vancouver, British Columbia; and,
- 45 Mary Street, Port Moody, British Columbia.
These six properties are just the start. Across Canada Post's portfolio, many more properties could be unlocked for housing, while maintaining high service standards for Canadians, including in rural communities.
- Budget 2024 announces that Canada Post will continue to be a "service first" organization focused on delivering the mail. Additionally, the government will now consider leveraging Canada Post's portfolio of federal properties to contribute to housing supply. This strengthens the expectation that Canada Post embraces innovation to meet the needs of Canadians and their communities.
- As part of its work to build homes on public lands, Budget 2024 announces that the government will take steps to enable Canada Post to prioritize leasing or divestment of post office properties and lands with high potential for housing, where doing so maintains high service standards for Canadians.
- Budget 2024 also announces the government's intention to launch a new Canada Post Housing Program to support affordable housing providers to build on disposed or leased Canada Post properties. Details will be available later this year.

Building Homes on National Defence Lands
National Defence owns 622 properties across every province and territory, totaling 2.2 million hectares, in addition to providing housing to many members of the Canadian Armed Forces. Many of these National Defence properties in cities and communities across Canada are not fully utilized and could be unlocked to build more homes for Canadian Armed Forces members, and civilians, to live in.
- As part of its work to build homes on public lands, Budget 2024 announces that the government is exploring the redevelopment of National Defence properties in Halifax, Toronto, and Victoria that could be suitable for both military and civilian uses.
- The Amherst Armoury in Amherst, Nova Scotia;
- 96 D'Auteuil and 87 St-Louis in Québec City, Quebec;
- The National Defence Medical Centre in Ottawa, Ontario;
- The HMCS Armoury in Windsor, Ontario; and,
- The Brigadier Murphy Armoury in Vernon, British Columbia.
The review of federally owned lands and properties announced as part of the government's work to build homes on public lands is also expected to identify additional National Defence properties with a high potential for housing development.
Those who serve in the Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) stand ready to deploy and relocate in order to defend Canada. Wherever they are posted, service members and their families shouldn't have to worry about finding a suitable home.
Budget 2024 also proposes additional investments for the Department of National Defence to build and renovate housing for CAF personnel on bases across Canada. This would support the construction of up to 1,400 new homes and the renovation of an additional 2,500 existing units for CAF members on base in communities such as Esquimalt, Edmonton, Borden, Trenton, Kingston, Petawawa, Ottawa, Valcartier, and Gagetown. See Chapter 7 for additional details.
Building more on-base housing will not only help meet the housing needs of military personnel but also help address housing demand in surrounding communities, since fewer military personnel will require rentals in these areas.
Converting Underused Federal Offices Into Homes
Sparked by the pandemic, like many organizations in Canada and around the world, the federal government shifted to hybrid work. Today, Public Services and Procurement Canada has over 6 million square metres of office space, of which an estimated 50 per cent is underused or entirely vacant. This is not an effective use of resources, particularly at a time when Canada is facing a shortage of homes.
The federal government is moving forward with a significant disposal effort to reduce its office footprint. This would enable more office buildings, particularly in urban areas, to be converted into homes for Canadians, while also ensuring the responsible use of government resources.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $1.1 billion over ten years, starting in 2024-25, to Public Services and Procurement Canada to reduce its office portfolio by 50 per cent. This funding, which is expected to be fully recovered through substantial short- and long-term cost savings, will help to accelerate the ending of leases and disposal of underused federal properties, and address deferred maintenance. Where applicable, the government will prioritize student and non-market housing in the unlocking of federal office properties.
Reducing the federal office footprint will generate substantial savings, expected to reach $3.9 billion over the next ten years, and $0.9 billion per year ongoing.

Taxing Vacant Lands to Incentivize Construction
At a time when we need to build as quickly as possible, it makes no sense that good land, in good areas, is sitting there, underused. As all orders of government put in place policies to tackle housing supply shortages, there is a concern that some landowners in Canada may be sitting on developable land, hoping to profit from rising land values when the land could instead be used for immediate residential development. Vacant land needs to be used, and it is best used to build homes.
The government is taking significant action to resolve Canada's housing crisis, and the federal government believes owners of vacant land in Canada must also do their part to unlock unused land for homes.
- Budget 2024 announces that the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land. The government will launch consultations later this year.
Building Apartments, Bringing Rents Down
Building rental homes requires significant investment, even more so when interest rates and land prices are high, as in recent years. Access to low-cost financing can help homebuilders move a rental project from being financially unfeasible to feasible. To help more apartment buildings break ground, the government is investing heavily in its low-cost construction financing programs, ensuring homebuilders have the financing needed to keep building.
The Apartment Construction Loan Program plays a crucial role in filling Canada's housing supply shortage by providing developers with the necessary capital to build rental homes. This support accelerates the development of apartments in neighbourhoods where people want to live and work. This is good for people, good for communities, and good for our economy.
- Of this amount, at least $100 million will be used to build homes above existing shops and businesses, especially in big cities where land is scarce and where density is key.
- Extending the terms of the loans offered;
- Extending access to financing to include housing projects for students and seniors;
- Introducing a portfolio approach so builders can move forward on multiple projects at once;
- Providing additional flexibility on affordability, energy efficiency, and accessibility requirements; and,
- Launching a new frequent builder stream to fast-track the application process for proven home builders.
These measures will make it easier, cheaper, and faster to build homes in Canada. For students, it will mean getting the keys to their first home and living close to campus. For young families, it will mean getting a good home near work, opportunity, and in a vibrant neighbourhood. And for seniors, it will mean an affordable place where you can downsize with security and dignity.
Federal financing is complemented by the government's community-building funding, from more early learning and child care spaces to housing-enabling infrastructure funding. This is how we build more affordable, liveable communities.

Lowering costs to build more apartment buildings
Camille Homes Corp. is interested in building a 20-story rental building in Winnipeg, which is expected to cost tens of millions of dollars. Loans for such developments are typically not available through private lenders, unless syndicated through several lenders to diffuse risk, a process which adds significant complexity and time. Private financing, with a prime rate above 7 per cent, is just too costly to make this project viable. Camille Homes Corp. is considering abandoning this project, but instead decides to apply for low-cost financing from the Apartment Construction Loan Program.
The Apartment Construction Loan Program's favourable financing terms, which include competitive interest rates, insurance premiums covered by the program, and longer terms and amortization periods are reducing borrowers' building costs by millions of dollars when compared to private financing.
Low-cost financing and flexible terms, combined with tailored support to meet the project's needs, as well as CMHC's ability to act as a single lender, is making the math on rental buildings work for builders such as Camille Homes Corp. and helping to build more homes across Canada.
Launching Canada Builds
To build homes across the country, we need a Team Canada approach. Provinces and territories control a number of critical levers to unlocking more housing supply, such as zoning rules, development approvals, lands and land use planning, rules for tenants and landlords and the adoption of building codes and regulations.
The federal government is supporting a number of provincial and territorial-led initiatives through cost-shared bilateral housing agreements. Most recently, this includes partnering with British Columbia in support of the BC Builds initiative with $2 billion in low-cost financing through the Apartment Construction Loan Program.
The federal government's partnership with BC Builds is a testament to the progress possible when multiple orders of government work collaboratively to deliver thousands of new rental homes for people in communities across Canada.
- Building on this momentum, Budget 2024 announces Canada Builds , the federal government's intention to leverage its $55 billion Apartment Construction Loan Program to partner with provinces and territories to build more rental housing across the country.
- Complementing federal funds with provincial or territorial investments;
- Building on government, non-profit, community-owned, and vacant lands;
- Considering access to early learning and child care, and the expansion of non-profit child care, in the development process;
- Streamlining the process to cut development approval timelines to no longer than 12 to 18 months; and,
- Meeting the criteria of the Apartment Construction Loan Program, including affordability requirements.
The federal government will initiate discussions with provincial and territorial governments as soon as possible. This transformative approach links portfolios of underused land, homebuilders, and federal and provincial investments. This Team Canada mission will help pave the way for new housing supply across the country.
Topping-Up the Housing Accelerator Fund
In March 2023, the government launched the $4 billion Housing Accelerator Fund to work with municipalities to cut red tape and fast-track the creation of at least 100,000 new homes across Canada. Through 179 agreements signed to date, the government has committed nearly $4 billion to spur the construction of 750,000 new homes across the country over the next decade.
- Building on this success, Budget 2024 proposes to provide an additional $400 million over four years, starting in 2024-25, to the Canada Housing and Mortgage Corporation, to top up the Housing Accelerator Fund. This will help fast track 12,000 new homes in the next three years.

Enabling Communities to Build More Homes
Building more homes in communities that people want to live in requires building more essential infrastructure, like power lines, transit stations, water and wastewater facilities, internet cables, libraries, and recreation centres. Without this infrastructure, communities have trouble growing, and new homes cannot get built.
The federal government is providing support to help growing communities build the infrastructure needed to build more homes, including through the Canada Infrastructure Bank. Budget 2024 also proposes new support for growing communities through a new Canada Housing Infrastructure Fund.
Further details on the federal government's infrastructure funding programs are outlined in Chapter 5.
A New Canada Housing Infrastructure Fund
Building more homes requires putting in place the essential infrastructure to support growing communities and denser, more vibrant, and liveable neighbourhoods.
In particular, communities must invest in effective and reliable water, wastewater, and stormwater infrastructure in order to keep pace with growth and encourage densification. These investments are critical as all orders of government work together to unlock more housing, faster.
- $1 billion available directly to municipalities to support urgent infrastructure needs that will directly enable housing supply.
- Legalize more housing options by adopting zoning that allows four units as-of-right and that permits more "missing middle" homes, including duplexes, triplexes, townhouses, and small multi-unit apartments;
- Implement a three-year freeze on increasing development charges from April 2, 2024, levels for municipalities with a population greater than 300,000;
- Adopt forthcoming changes to the National Building Code to support more accessible, affordable, and climate-friendly housing options;
- Provide pre-approval for construction of designs included in the government's upcoming Housing Design Catalogue; and,
- Implement measures from the forthcoming Home Buyers' Bill of Rights and Renters' Bill of Rights.
- Provinces will have until January 1, 2025, to secure an agreement, and territories will have until April 1, 2025. If a province or territory does not secure an agreement by their respective deadlines, their funding allocation will be transferred to the municipal stream. The federal government will work with territorial governments to ensure the actions in their agreements are suitable to their distinct needs.
To ensure this funding reaches communities of all sizes and needs, provinces must dedicate at least 20 per cent of their agreement-based funding for northern, rural, and Indigenous communities.
Leveraging Transit Funding to Build More Homes
Many Canadians rely on public transit to go to school, to get to work, to see their friends, and to explore their communities. More homes need to be built closer to the services that Canadians count on. Transit that is more accessible and reliable means Canadians can spend more time with their friends and family. It's crucial that all orders of government work together to achieve this.
- Eliminating all mandatory minimum parking requirements within 800 metres of a high-frequency transit line;
- Allowing high-density housing within 800 metres of a high-frequency transit line; and,
- Allowing high-density housing within 800 metres of post-secondary institutions.
- Completing a Housing Needs Assessment for all communities with a population greater than 30,000.
These are long overdue changes that will mean more people can live near transit to access the services and opportunities in their communities, and will allow home construction to happen faster and at more affordable prices.
The Canada Infrastructure Bank's Housing Initiative
As Canada's cities and towns build more homes, they need to build more infrastructure. From water and sewer infrastructure to public transit to high-speed internet, the federal government is providing municipalities with the tools they need to grow.
That is why, since 2017, the Canada Infrastructure Bank has made investment commitments of over $11 billion in more than 50 projects, and catalyzed over $31 billion in total investment, to address critical infrastructure gaps across the country. These include:
- $1.28 billion for the Réseau express métropolitain in Montréal;
- $1.3 billion for rural broadband internet in Ontario;
- $165 million for the City of Calgary to buy zero-emission buses;
- $138.2 million for energy storage to enable increased renewable electricity in Nova Scotia; and,
- Up to $80 million for the Atlin Hydroelectric Expansion in Yukon.
The 2023 Fall Economic Statement announced that the Canada Infrastructure Bank would be exploring further opportunities to support the needs of growing communities by helping to finance the infrastructure needed to build more homes.
In March 2024, the Canada Infrastructure Bank announced the launch of its Infrastructure for Housing Initiative to provide low-cost financing to enable municipalities and Indigenous communities to build housing-enabling infrastructure. Funding for this initiative is sourced from the CIB's existing funding envelope.
Building the infrastructure communities need to build more homes
The Canada Infrastructure Bank (CIB) has already made its first investment commitment under its Infrastructure for Housing Initiative, committing up to $140 million in financing for new and enhanced water and wastewater infrastructure in five communities in Manitoba, including the City of Brandon. The project will support cleaner water and better wastewater treatment, which will provide the enabling infrastructure to support an estimated 15,000 new housing units.
Fast growing communities, like the City of Brandon, require not only significant new home construction but also investments in water and wastewater systems and other local infrastructure. Paying for this new infrastructure can be challenging, especially where the up-front costs would burden existing residents. By lowering the cost of borrowing and taking on some of the risk associated with new development, the CIB's investment can help municipalities build the infrastructure needed to support thousands of new homes across the country.
Changing How We Build Homes
We have to build homes smarter, faster, and at prices Canadians can afford. That means investing in ideas and technology like prefabricated housing factories, mass timber production, panelization, 3D printing, and pre-approved housing design catalogues. We need to bring the same spirit of innovation that we are investing in across the economy, and build homes in a 21st century way.
- To spur the development of innovative housing technologies, Budget 2024 proposes $50 million over two years, beginning in 2024-25, for Next Generation Manufacturing Canada (NGen)—one of Canada's Global Innovation Clusters—to launch a new Homebuilding Technology and Innovation Fund. NGen will seek to leverage an additional $150 million from the private sector, and other orders of government, to support a targeted $200 million investment in housing innovation in Canada. The first projects will aim to be announced this summer.
- Grand River Modular Ltd., in Kitchener, Ontario, to support commercialization efforts to bring modular housing units to market, supported with $188,485 from the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario;
- Structures KSM in Gatineau, Quebec, to acquire innovative, automated production equipment and software to improve the production capacity of roof truss manufacturing, supported with $200,000 from Canada Economic Development for Quebec Regions;
- Nunafab Corp., in Nunavut, to create a modular home production plant in the community of Cambridge Bay where homes can be rapidly built for local housing needs and shipped to other Nunavut communities, supported with $2.15 million from the Canadian Northern Economic Development Agency;
- Island Structural Systems, in Kensington, PEI, an automated facility that will improve the productivity of the PEI residential construction sector, supported with $2 million from the Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency; and,
- Landmark Group of Companies Inc. and Promise Robotics Inc. in Edmonton, Alberta, to establish a mobile, robotic micro-factory to construct housing components, supported with $1 million from Prairies Economic Development Canada.
Any new innovative housing designs funded through the Regional Development Agencies and NGen will feed into the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation's work on the Housing Design Catalogue.
- To help simplify the way Canada builds homes, Budget 2024 announces that the National Research Council will launch consultations with provinces, territories, industry, and fire safety experts to address regulatory barriers, including point block access and single egress designs, and streamline the inspection process. In addition, the National Research Council will identify ways to reduce duplication between factory inspections of modular home components and on-site building inspections, and support efforts to address regulatory barriers to help scale up factory-built housing across the country.
- Budget 2024 also announces that the Apartment Construction Loan Program will earmark at least $500 million to homebuilders that use innovative construction techniques, such as modular housing, for new rental projects.
In the coming months, the government will engage with housing, construction, and building material sectors, along with labour unions, Indigenous housing experts, and other relevant stakeholders, to co-develop a Canadian industrial strategy for homebuilding. Together, we will explore all essential inputs into building homes in Canada, including raw and manufactured materials, supply chains, and building techniques to ensure that all orders of government and industry can achieve our ultimate goal of building homes smarter, faster, and at prices Canadians can afford.
Strengthening innovation and increasing productivity in the residential construction sector is critical to building more homes, faster. In addition to new measures in Budget 2024, the federal government is supporting homebuilders who use new, innovative ways to build more homes, faster.
Existing support to advance innovative construction includes:
- Over $600 million through the Affordable Housing Innovation Fund to support innovative solutions for the next generation of housing in Canada.
- $300 million through the Housing Supply Challenge to develop solutions to remove barriers that hinder housing supply.
- $191.8 million over seven years and $7.1 million per year ongoing to conduct research and development on innovative construction materials and to revitalize national housing and building standards to encourage low-carbon construction solutions.
- $38 million through the Green Construction through Wood program to encourage the use of innovative wood-based building technologies in construction projects.
- $13.5 million per year to make the National Building Codes free to access and to modernize codes, including by reducing barriers to internal trade and aligning building codes across the country.
Further support available for housing and construction innovation and productivity includes:
- The Industrial Research Assistance Program, which helps Canadian small- and medium-sized businesses increase their innovation capacity and take ideas to market.
- The Regional Economic Growth through Innovation program, which helps businesses scale-up new innovative technologies.
- The Strategic Innovation Fund, which helps attract and spur private investment in innovative projects across all regions and sectors of the economy.
Housing Design Catalogue
The government is reviving and modernizing its post-war housing design catalogue, which will provide blueprints that can be used across the country to speed up the construction of new homes.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $11.6 million in 2024-25 to support the development of its Housing Design Catalogue for up to 50 housing designs, such as modular housing, row housing, fourplexes, sixplexes, and accessory dwelling units, that provinces, territories, and municipalities could use to simplify and accelerate housing approvals and builds.
This first phase of the catalogue will be published in fall 2024.
Modernizing Housing Data
To better understand the needs of local housing markets, we need better data. Every order of government should be committed to a data-driven response to the housing crisis.
- To help modernize housing data, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $20 million over four years, starting in 2024-25 for Statistics Canada and the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to modernize and enhance the collection and dissemination of housing data, including municipal-level data on housing starts and completions.
Adding Additional Suites to Single Family Homes
Many homeowners have extra space they could convert into rental suites, such as an unused basement, or a garage that could be converted into a laneway home. Historically, the cost of renovating, combined with municipal red tape, has made this both difficult and costly.
Recent municipal zoning reforms in Canada's major cities, including reforms through Housing Accelerator Fund agreements, are creating new opportunities for homeowners to add additional suites to their properties in support of densification. New rental suites would provide more homes for Canadians and could provide an important source of income for seniors, who would be able to afford continuing to age at home. New suites can also be purpose-built to be barrier-free, to accommodate physical impairments of an aging family member or a child with a disability.
The government is taking action to make it easier for homeowners to increase Canada's supply of housing by adding additional suites to their home.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $409.6 million over four years, starting in 2025-26, to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to launch a new Canada Secondary Suite Loan Program, enabling homeowners to access up to $40,000 in low-interest loans to add secondary suites to their homes. Details of this program will be announced in the coming months.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to make targeted changes to mortgage insurance rules to encourage densification and support the efficient functioning of the housing finance market, by enabling homeowners to add more units to their homes. The government will consult stakeholders on proposed changes to regulations, including for refinancing, maximum loan and home price, as well as other mortgage insurance rules where homeowners are adding additional units.
Low-cost loans to build more secondary suites
Amena and Kareem are young working professionals looking to purchase their first home in Burnaby, British Columbia. They find a single-family home with a separate garage out back. With a single car between them, they think about converting the garage into a laneway home to generate additional income to help pay down their mortgage.
In addition to new flexibilities in mortgage insurance rules to enable Amena and Kareem to access mortgage insurance, for a property value that exceeds the current limit of $1 million, the new secondary suite loan program will help them convert their garage into an adjacent laneway home after the home is purchased.
They apply to the Canada Secondary Suite Loan Program for a low-cost loan of $40,000, to help cover their renovation costs, and once they find a tenant, are able to use new rental income to cover the cost of the loan.
New mortgage flexibilities to add secondary suites
Yuval owns a single-family home in St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador. Despite having accumulated significant equity in his home, Yuval is feeling the strain of mortgage payments, property taxes and other expenses from higher living costs.
Targeted changes to mortgage insurance rules could allow Yuval to refinance his insured mortgage to access his home equity to convert part of his home into a rental suite. This could allow Yuval to earn rental income to offset his mortgage expenses and property taxes, while also providing a much-needed rental accommodation in his neighbourhood.
Accelerating Investment to Build More Apartments
Building on the success of removing 100 per cent of GST from new rental housing projects and providing more low-cost financing to move more apartment building projects forward, the government is taking further action to make the math work for homebuilders.
- Budget 2024 proposes to introduce a temporary accelerated capital cost allowance, at a rate of 10 per cent for eligible new purpose-built rental projects that begin construction on or after Budget Day, and are available for residents to move in before January 1, 2036.
Increasing the capital cost allowance rate from 4 per cent to 10 per cent will incentivize builders by moving projects from unfeasible to feasible, through increased after-tax returns on investment.
The measure does not change the total amount of depreciation expenses being deducted over time, it simply accelerates it. Allowing homebuilders to deduct certain depreciation expenses over a shorter period of time allows homebuilders to recover more of their costs faster, enabling further investment of their money back into new housing projects.
This measure would cost an estimated $1.1 billion over five years, starting in 2024-25.
Building More Student Housing
As universities and colleges expand and attract more students, the demand for student housing is going up. Not every campus is equipped, and that means some students are struggling to afford local rents. And, student demand puts pressure on locals. Building more student housing is good for young people, and makes sure there is a fair rental market for everyone.
To encourage the construction of a wide variety of much needed long-term rental housing that meets the needs of Canadians, the federal government removed 100 per cent of GST from new rental housing built specifically for long-term rental accommodation. However, student residences, given their typically shorter-term and transient nature, may not currently meet the conditions for this rebate.
- Budget 2024 announces that the eligibility conditions for the removal of GST on new student residences will be relaxed for not-for-profit universities, public colleges, and school authorities. This will incentivize Canada's educational institutions to build more student housing by ensuring they benefit from the removal of GST on new student residences. This measure is expected to cost $19 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, and $5 million per year ongoing.
The relaxed eligibility will apply to new student residences that begin construction on or after September 14, 2023, and before 2031, and that complete construction before 2036. Private institutions will not be eligible for this support.
This measure builds on the government's new reform to allow on- and off-campus student housing projects to access the $55 billion Apartment Construction Loan Program.
More Skilled Trades Workers Building Homes
People in the skilled trades are proudly stepping up as part of this generational effort to build housing. But to meet this challenge, Canada needs even more workers and it needs apprenticeships to remain affordable for young people starting their new careers. According to BuildForce Canada, the construction sector faces a shortage of over 60,000 workers by 2032, due to many hard-working construction workers reaching retirement age, combined with demand from accelerating home construction.
To encourage more people to pursue a career in the skilled trades, the federal government is creating apprenticeship opportunities to train and recruit the next generation of skilled trades workers.
- $90 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, for the Apprenticeship Service to help create placements with small and medium-sized enterprises for apprentices. Of this amount, $10 million in 2025-26 would be sourced from existing departmental resources.
- $10 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, for the Skilled Trades Awareness and Readiness Program to encourage Canadians to explore and prepare for careers in the skilled trades. This funding would be sourced from existing departmental resources.
To make it easier for young people who hope to start a career in the skilled trades, in addition to interest-free Canada Apprentice Loan and Employment Insurance Regular Benefits for apprentices on full-time technical training, the government will continue explore options to make apprenticeships more affordable.
Further investments to build Canada's residential construction workforce, such as the recently launched Sustainable Jobs Training Fund, will help young workers gain the specialized skills needed to retrofit homes to increase energy efficiency and lower the costs of homeownership.
Training the next generation of construction workers
Emily is a high school student thinking of pursuing a career as a construction electrician. Through the Skilled Trades Awareness and Readiness Program, Emily can get access to career fairs, mentorship, and job shadowing to explore and prepare for a career in the construction industry.
Jai is a plumbing apprentice seeking to obtain Red Seal Certification. Jai can receive innovative, hands-on training designed to remove accessibility barriers at a small and medium-sized enterprise receiving support through the Apprenticeship Service to offer apprenticeship training opportunities.
Recognizing Foreign Construction Credentials and Improving Labour Mobility
Newcomers with the skills and experience needed to build new homes should be able to join the Canadian labour market without delays.
To enable skilled newcomers to maximize their potential as they build a new life in Canada, the Foreign Credential Recognition Program helps provide training, work placements, wage subsidies, and mentoring to newcomers. For six years, the program has helped over 9,000 skilled newcomers receive work placements and wage subsidies, and another 20,000 workers received low-cost loans and support services to minimize the costs and requirements associated with practicing their trade in Canada.
Building on Budget 2022's five-year $115 million investment in the Foreign Credential Recognition Program:
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $50 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, to Employment and Social Development Canada for the Foreign Credential Recognition Program. At least half of this amount will be to streamline foreign credential recognition in the construction sector to help skilled trades workers build more homes, and the remaining funding will support foreign credential recognition in the health sector. Similar to a recent agreement between federal, provincial and territorial health ministers to recognize foreign credentials for health care professionals, the federal government is calling on provinces and territories to expedite removal of their barriers to foreign credential recognition.
To reduce internal barriers for skilled workers in Canada, the federal government is also calling for provinces and territories to urgently streamline their trades certification standards for interprovincial consistency. This includes streamlining requirements in trades, or sub-trades, that have no or limited equivalents in other jurisdictions. The federal government will continue to collaborate with provincial and territorial apprenticeship authorities to improve labour mobility for workers in these trades.
Ensuring newcomer construction workers can help build more homes
Emmanuel is a newcomer to Canada, with significant experience in the construction sector abroad. Through investments made by the Foreign Credential Recognition Program, Emmanuel can access construction-related training and work opportunities to help him get his education and experience recognized, integrate into the residential construction sector in his province, and contribute to alleviating the housing crisis.
Homeownership is a big part of the middle class dream. If you work hard, and save your money, you should be able to buy a home. That was the deal for generations. But young adults feel like the possibility of owning a home like the one they grew up in is less and less likely, as increases in home prices continue to outpace their salaries and wages. The prospect of owning a home in Canada needs to be as real for young people today, as it was for any other generation.
And for the millions of Canadians who rent, including many who prefer the flexibility that comes with renting, drastic rent increases have pushed what was once an affordable option out of reach.
Canadians need help now, and Canada will work to make homeownership a reality for young Canadians and to protect renters, many of whom are Millennial and Gen Z, and are paying a much higher portion of their earnings towards rents than previous generations.
Budget 2024 takes action to unlock new pathways for young renters to become homeowners, and to protect middle class homeowners from rising mortgage payments.

- The Canadian Mortgage Charter, which details the tailored mortgage relief that the government expects banks to provide borrowers who are facing financial difficulty with the mortgage on their principal residence.
- The new Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, which is a registered savings account that allows Canadians to contribute up to $8,000 per year (up to a lifetime limit of $40,000) for their first down payment.
- The recently doubled First-Time Home Buyers' Tax Credit, which provides up to $1,500 in direct support to home buyers to offset expensive closing costs involved in buying a first home.
- Ensuring the profits from flipping residential real estate are subject to taxation, to unlock more homes for Canadians to live in—because homes are not a speculative financial asset class for investors.
- Making assignment sales fully taxable to ensure homes remain available for Canadians to buy.
- Over $750 million for the Oil to Heat Pump Affordability program, which has to date provided support for over 1,500 low- to median-income households to help them transition from expensive oil heating to more energy efficient, cost-saving electric heat pumps.
- Over $6.7 billion, on a cash basis, for the Canada Greener Homes Grant and Loan programs, which to date have provided over 172,000 grants of up to $5,000 and 58,000 interest-free loans of up to $40,000 to help Canadians save money by making their homes more energy efficient.
Aligning Immigration With Housing Capacity
Immigration enriches Canada's society, our culture, and our economy, but the combination of temporary and permanent immigration experienced last year put strains on Canada's ability to properly welcome and integrate newcomers into Canadian society. The government has taken steps to better manage temporary migration pressures while moderating the pace of its levels plan.
Under the 2024–2026 Immigration Levels Plan, the government has carefully moderated the intake of new permanent residents, moving towards a long-term approach that seeks to strike a balance between meeting the economic imperatives and enhancing the ability of communities to effectively welcome and integrate immigrants.
The government has also recently announced that it will reduce the share of temporary residents to 5 per cent of the overall population over the next three years. This will lead to approximately 600,000 fewer temporary residents in Canada compared to current levels.
Normalizing permanent and temporary immigration levels is critical to ensuring that newcomers have the opportunities and social supports they need to succeed when coming to Canada.
Further, these changes will ensure that newcomers, and all Canadians, have an affordable place to call home. The scale of this reduction is significant in the context of housing demand: in recent years, Canada has built about 220,000 housing units annually.
The government has also taken steps to reduce the volume of asylum claims. In March 2023, Canada and the United States announced the expansion of the Safe Third Country Agreement, which requires asylum claimants to request protection in the first safe country they arrive in, unless they qualify for an exception to the Agreement. This has resulted in significantly fewer individuals claiming asylum at irregular crossings in between Canada's land ports of entry.
Also, on February 29, 2024, the government adjusted the travel requirements for Mexican citizens, who represented 17 per cent of all asylum claims in 2023. While the majority will continue to be able to travel visa-free to Canada, some Mexican nationals will now need to apply for a Canadian visitor visa. This responds to an increase in asylum claims made by Mexican citizens that are refused, withdrawn, or abandoned. In recent years, Mexican nationals represented the top source of asylum claims in Canada.
Stabilizing International Student Intake to Alleviate Housing Pressures
To ensure every Canadian student can find an affordable place to live while pursuing their education, the federal government is taking action to stabilize international student intake across the country. By better aligning temporary immigration pressures to a moderate pace, Canada can ensure a better capacity to welcome newcomers.
In January 2024, the government announced a new cap on the number of study permit applications, which is expected to decrease approved study permits by up to 28 per cent in 2024 for the groups included under the cap. The government also announced new eligibility criteria for the Post-Graduation Work Permit. This will help ease housing demand growth, while also protecting international students from fraudulent institutions and unsafe living conditions.
This builds on the government's announcement last fall to reform the International Student Program. As committed in the 2023 Fall Economic Statement, by fall 2024, the government will launch a new Recognized Institutions Framework to reward post-secondary institutions with high standards around selecting, supporting—including by providing access to housing—and retaining international students.
Taken together, the measures aim to ensure post-secondary students receive the support they need for success, and balance the pressures on student housing by aligning the number of students arriving in Canada with the number of available homes. By alleviating student housing pressures, generations of Canadians and international students today, and tomorrow, will have a more affordable pathway to getting a good education.
Credit for Paying Rent
Every month, millions of Canadian renters pay their rent in full and on-time. The government thinks that should count towards their credit worthiness when applying for their first mortgage, seeking to refinance a mortgage and in many other situations that require credit evaluations. For young Canadians and newcomers to Canada, this is even more important as they have a more difficult time establishing credit history.
More Gen Z and Millennials are renting today than the generations that came before them, with over 54 per cent of people between 25 and 34 years old being renters—and that number jumps to 81 per cent for people under 24 years old. In comparison, 25 per cent of Canadians between 55 and 64 years old are renters today. By making renters' payments count, we can help younger Canadians get ahead.
In Budget 2024, the government is setting a firm expectation with lenders, through its strengthened Canadian Mortgage Charter, to take a renter's on-time payment history into account when performing credit evaluations for mortgage applications.
- Budget 2024 announces that the government is calling on banks, fintechs, and credit bureaus to prioritize launching tools to allow renters to opt-in to reporting their rent payment history to credit bureaus, to strengthen their credit scores and unlock pathways for more renters to become homeowners.
Together, this ability to strengthen one's credit score with on-time rental payment history—and make it easier to qualify for a mortgage, or even a lower rate—works in parallel to the government's efforts to advance consumer-driven banking. Further details on Canada's Framework for Consumer-Driven Banking are in Chapter 3.
Protecting Renters' Rights
Renters face unique challenges to ensuring their homes are properly maintained and that their landlords follow provincial laws. Renters can have a hard time navigating different provincial laws and lack resources to fight disputes with landlords—whether it concerns faulty heating, an illegal rent increase, or an illegal eviction. Tenant organizing and legal services can help renters.
When renters' rights are upheld, it gives people stability and housing security. They can stay in their homes and in their community—taking their kids to the same schools, being close to the same parks, and staying in the same job. It also gives them bargaining power, helping them keep their rent affordable.
The federal government is committed to protecting tenant rights and ensuring that renting a home is fair, open, and transparent.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $15 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, for a new Tenant Protection Fund, which will provide funding to organizations that provide legal and informational services to tenants, as well as for tenants' rights advocacy organizations to raise awareness of renters' rights.
- Budget 2024 also proposes a new Canadian Renters' Bill of Rights, to be developed and implemented in partnership with provinces and territories, to protect renters from unfair practices, make leases simpler, and increase price transparency. The government intends to crack down on renovictions, introduce a nationwide standard lease agreement, and require landlords to disclose historical rent prices of apartments.
Free legal support and advocacy for renters
The heating system in Patrick's apartment breaks down during the winter, threatening his health and safety, but his landlord refuses to arrange urgent repairs because they are on extended vacation. Patrick pays for emergency repairs, but his landlord refuses to fully reimburse his expenses after returning from vacation.
Patrick accesses free, federally funded legal information and advice to navigate his province's tenant dispute resolution process and succeeds in being fully reimbursed for his expenses.
30-Year Amortizations for First-Time Buyers Purchasing New Builds
The high cost of mortgage payments is a barrier for many younger Canadians hoping to buy that first time. Extending mortgage amortizations for first-time buyers purchasing new builds brings that monthly cost down, making it more affordable for first-time buyers, many of whom are young people still working their way up the salary ladder.
To restore generational fairness in the housing market for younger Canadians, the government is strengthening the Canadian Mortgage Charter with new measures to unlock pathways for Millennials and Gen Z to get the keys to their first home.
- Budget 2024 announces the government is strengthening the Canadian Mortgage Charter to allow 30-year mortgage amortizations for first-time home buyers purchasing newly constructed homes. Extending the amortization limits by five years for first-time buyers purchasing new builds will enable more younger Canadians to afford a mortgage and will encourage new supply. This new insured mortgage product will be available to first-time buyers starting August 1, 2024. The government will bring forward regulatory amendments to implement this proposal. Further details will be released in the coming months.
The government will monitor whether housing inflation and supply conditions permit expanding access to 30-year insured mortgage amortizations more broadly.
Combined with the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account to save for a down payment faster and helping renters build their credit score with their on-time rental payment history, new access to 30-year mortgage amortizations will help first-time buyers purchasing new builds to access mortgages with lower monthly payments, making it easier to unlock the door to their first home.
Enhancing the Home Buyers' Plan
As home prices go up and the cost of living rises, saving for a down payment is more and more difficult. The federal government is enhancing the tax savings plans that help young Canadians save for their first home.
Across the country, and particularly in Canada's major cities, home prices have gone up—steeply. Support to help first-time buyers save must keep pace with market prices. That is why the government launched the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, and why in Budget 2024, it is enhancing the Home Buyers' Plan. While home prices have risen—and building more new homes will help to lower prices—the government is unlocking pathways to a down payment so more Canadians can buy a home and build a good middle class life.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to amend the Income Tax Act to increase the Home Buyers' Plan withdrawal limit from $35,000 to $60,000, enabling first-time home buyers to use the tax benefits of an RRSP to save up to $25,000 more for their down payment, faster. The newly increased limit would be available to first-time buyers after April 16, 2024.
- Budget 2024 also announces the government's intention to amend the Income Tax Act to temporarily extend the grace period during which homeowners are not required to repay their Home Buyers' Plan withdrawals to their RRSP by an additional three years. This grace period extension would apply to Home Buyers' Plan participants who made a first withdrawal between January 1, 2022, and December 31, 2025, who will now only have to begin repaying their Home Buyers' Plan withdrawals in the fifth year after the year in which they withdraw. For a couple who withdrew the maximum in 2023, extending the grace period could allow them to defer annual repayments as large as $4,667 by an additional three years.
This measure would reduce federal revenues by an estimated $90 million over six years, starting in 2023-24, and $5 million per year ongoing.
The new Tax-Free First Home Savings Account is a registered savings account that allows Canadians to contribute up to $8,000 per year, and up to a lifetime limit of $40,000, towards their first down payment. To help Canadians reach their savings goals faster, Tax-Free First Home Savings Account contributions are tax deductible on annual income tax returns, like a Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP). And, like a Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA), withdrawals to purchase a first home—including any investment income on contributions—are non-taxable. Tax-free in; tax-free out.
As of April 16, more than 750,000 Canadians have already opened a Tax-Free First Home Savings Account to save for their first down payment—putting homeownership back within reach across the country and helping them reach their savings goals sooner.
Tax-Free First Home Savings Account
Darya is planning to buy a first home in 2029 in Saint John, NB. Starting in 2024, she began contributing $667 per month in her Tax-Free First Home Savings Account. These contributions can be deducted from her income at tax time, providing an annual federal tax refund of $1,640. After five years, Darya has saved $44,000 in her Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, including tax-free investment income, which she uses to make a 10-per-cent down payment on a $350,000 home and pay associated expenses. She can withdraw the full $44,000 tax-free, saving thousands of dollars that can be put towards her new home. In addition, she will claim the First-Time Home Buyers' Tax Credit for $1,500 in tax relief.
Tax-Free First Home Savings Account and Home Buyers' Plan
Mark and Mathieu want to buy a condo in Vancouver this year. They both make between $70,000 and $100,000 annually and contributed the maximum amount in their Tax-Free First Home Savings Account in 2023 and 2024 ($667 per month each), for a total of $32,000 between the two of them. These contributions were deducted from their income at tax time, providing total federal tax refunds of $6,560. Mark and Mathieu also both have $60,000 in their individual RRSPs.
Mark and Mathieu would like to make a 20 per cent down payment on a $760,000 condo to save on mortgage loan insurance premiums and interest payments. The couple is planning to use their Tax-Free First Home Savings Accounts and RRSPs for their $152,000 down payment. With the increased Home Buyers' Plan withdrawal limit, Mark and Mathieu can now withdraw $120,000 from their RRSPs without having to pay $15,000 in taxes, which they would have paid on the amount in excess of the previous Home Buyers' Plan withdrawal limit of $35,000 ($70,000 per couple). They will now have until 2029 to start repaying the $120,000 back to their RRSPs, instead of 2026 as per current rules. They will also claim the First-Time Home Buyers' Tax Credit for an additional $1,500 in tax relief.
The combined value of federal-provincial tax relief offered by the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, compared to a taxable account for a couple living in Ontario, earning about $80,000 and each contributing $8,000 annually is detailed in Chart 1.4. Also shown is the maximum down payment a couple could make when combining the Tax-Free First Home Savings Account, Home Buyers' Plan, and the Home Buyers' Tax Credit.

Enhancing the Canadian Mortgage Charter
The government launched the Canadian Mortgage Charter to help ensure Canadians know about the fair, reasonable, and timely mortgage relief they can seek and receive from their financial institutions.
Mortgage lenders have a range of tools available for providing tailored relief. Lenders will communicate with borrowers facing mortgage hardship to discuss possible approaches based on the borrower's individual circumstances and criteria set by lenders and mortgage insurers.
The federal government and its financial sector agencies, particularly the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada and the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions, are closely monitoring the mortgage relief being offered by financial institutions. While Canadians are continuing to manage the impacts of higher mortgage rates, it is essential that borrowers and lenders remain proactive in identifying and addressing mortgage hardship.
- Using rent payment history for mortgage applications, to help more renters become homeowners by improving their credit score;
- Up to 30-year mortgage amortizations for first-time home buyers purchasing new builds, to make it easier to afford a first mortgage; and,
- More detailed expectations for lenders to proactively contact borrowers, including making permanent mortgage relief measures available, where appropriate; and providing information to help borrowers make informed decisions, such as before renewal.
The Canadian Mortgage Charter sets out the following expectations:
- Proactively contacting homeowners well in advance of their mortgage renewal to inform them of their renewal and refinancing options (e.g., in some circumstances, lenders should contact borrowers at least 24 months in advance to begin discussing options).
- Allowing temporary extensions of the amortization period for mortgage holders at risk and, where appropriate, permanent amortization extensions for those that meet additional criteria set by mortgage insurers and lenders.
- Providing information about additional interest that mortgage holders will pay, over the total length of the mortgage, as a result of amortization extensions.
- Waiving fees and costs that would have otherwise been charged for relief measures, or when mortgage holders take action (e.g., increasing payments) to reduce an extended amortization as their financial situation improves.
- Not requiring insured mortgage holders to requalify under the insured minimum qualifying rate when switching lenders at mortgage renewal.
- Giving borrowers at risk the ability to make lump sum payments to avoid negative amortization or sell their principal residence without any prepayment penalties.
- Not charging interest on interest in the event that mortgage relief measures result in a temporary period of negative amortization.
- Calling on landlords, banks, credit bureaus, and fintech companies to make sure that rental history is taken into account in your credit score.
- Permitting up to 30-year mortgage amortization for first-time buyers purchasing new builds.
Switching mortgage lenders without requalifying for the stress test
Jessica, a new homeowner in Charlottetown, PEI, is nearing the completion of her first five-year term on a $350,000 mortgage for her townhouse. The Mortgage Charter sets an expectation for her bank to send an early notice informing her of her renewal options, which gives her plenty of time to shop around for a better rate. Jessica works with a mortgage broker to evaluate her options and finds a more competitive mortgage rate at a different lender. As a borrower with mortgage insurance, Jessica is able to switch lenders at renewal without needing to requalify under the minimum qualifying rate (the stress test).
Because the Mortgage Charter helped inform Jessica that she could switch lenders without another stress test, Jessica is able to reduce her mortgage rate from 6 per cent to 5.5 per cent and save around $1,000 per year.
Extending amortization and not paying interest on interest
Éric and Maya are new parents in Québec City, Quebec who purchased their first home two years ago. The fixed monthly payment of around $2,300 that they make on their $550,000 variable rate mortgage is no longer covering their mortgage interest costs at the current interest rate, creating a situation where their mortgage balance is growing and interest is being charged on interest.
Éric and Maya receive a letter from their bank informing them of the situation. After discussing options with their bank, Éric and Maya take into account their budget constraints and decide to temporarily extend their amortization by an additional five years to help make their payments more manageable. Because the Mortgage Charter sets expectations for lenders to proactively contact borrowers facing mortgage hardship, Éric and Maya are able to get back to paying down their mortgage balance and avoid about $400 in interest on interest.
When interest rates fall, the bank will work with Éric and Maya to help them return to their original amortization schedule.
Halal Mortgages
Canada is home to a vibrant and growing market of alternative financing products, including halal mortgages, that enable Muslim Canadians, and other diverse communities, to further participate in the housing market.
- Budget 2024 announces that the government is exploring new measures to expand access to alternative financing products, like halal mortgages. This could include changes in the tax treatment of these products or a new regulatory sandbox for financial service providers, while ensuring adequate consumer protections are in place.
In March 2024, the government began consulting financial services providers and diverse communities to understand how federal policies can better support the needs of all Canadians seeking to become homeowners. The government will provide an update in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement .
Strengthening Mortgage Income Verification
Financial institutions maintain rigorous policies to verify borrower income when determining someone's ability to repay their mortgage. Independently verifying borrower income helps financial institutions detect and deter the types of fraud or misrepresentation that can increase the costs of mortgages for all borrowers. However, fraud risks are always evolving—and so too are the tools to combat these risks.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to consult with the mortgage industry on making available a tool through the Canada Revenue Agency to complement the existing strategies of financial institutions to verify borrower income for mortgages.
Banning Foreign Buyers of Canadian Homes
For years, foreign money has been coming into Canada to buy up residential real estate, increasing housing affordability concerns in cities across the country, and particularly major centres. To address this, the government introduced a two-year ban on the purchase of residential property by foreign investors, effective January 1, 2023.
To help ensure that homes are used for Canadians to live in, not as a speculative asset class for foreign investors, on February 4, 2024, the government announced it intends to extend the ban on foreign buying of Canadian homes by an additional two years, to January 1, 2027.
Foreign commercial enterprises and people who are not Canadian citizens or permanent residents will continue to be prohibited from purchasing residential property in Canada.
Cracking Down on Short-Term Rentals
Homes are for Canadians to live in, not speculative assets for investors. The short-term rentals listed on platforms such as Airbnb and VRBO are keeping 18,900 homes off the market in Montréal, Toronto, and Vancouver alone, based on estimates from 2020, meaning families, students, workers, and seniors are having to compete for fewer homes.
To unlock Canada's housing supply for Canadians to live in, in the 2023 Fall Economic Statement, the federal government proposed tax changes to incentivize the return of non-compliant short-term rentals to the long-term market and to support the work of provinces and territories that have restricted short-term rentals.
These changes would apply as of January 1, 2024, to deny income tax deductions on income earned from short-term rentals that do not comply with the relevant provincial or municipal laws. By denying income tax deductions, the government is removing the profit incentive for short-term rental operators.
Some provinces, including Quebec and British Columbia, and municipalities such as Toronto, Montréal, and Vancouver, have already taken action to return short-term rentals to the long-term market for Canadians to live in. To support the work of municipalities to unlock homes for Canadians, the federal government is committed to launching a $50 million short-term rental enforcement fund. The government is currently engaging with stakeholders to design a program that will be responsive to municipal needs, and will announce further details later this year.
Cracking Down on Real Estate Fraud
Cracking down on real estate tax fraud protects home buyers and levels the playing field for those who play by the rules. The government is committed to reinforcing the fairness of the tax system and combatting tax non-compliance across the housing sector.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $73.1 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, and $14.7 million per year ongoing to the Canada Revenue Agency to continue addressing tax non-compliance in real estate transactions. By ensuring that everyone pays their fair share, the government is protecting home buyers from artificial market distortions that increase home prices.
Advancing National Flood Insurance
Unlike previous generations, homeownership now comes with the burdens of paying for the costs of climate change, due to the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters. Put simply, Millennial homeowners have to worry if they can afford flood insurance, or if they can access it at all. This wasn't a common concern for their parents and grandparents.
As announced in Budget 2023, the government intends to deliver a flood reinsurance program and a separate insurance subsidy for households at high risk of flooding.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to establish a subsidiary of the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to deliver flood reinsurance.
- To advance this commitment, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $15 million to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) in 2025-26 to advance implementation of a national flood insurance program by 2025.
The government is advancing work with provinces and territories, in partnership with the insurance industry, to stand-up a low-cost flood insurance program for high-risk properties within the next twelve months.
Flood insurance to protect Canadians' homes
Joaquin and Kariné own a home in an area with a high flood risk. Because there are limited private insurance options available to cover homes in high flood risk areas, they face challenges insuring their home.
Like many Canadian homeowners, their home is a large part of their life savings. Joaquin and Kariné still have a mortgage, which adds to their worries about potential disasters, such as a flood, damaging their property. This situation leaves them with limited financial flexibility and poses a risk to their financial security, should their home suffer damage.
Canada's flood insurance program will help Joaquin and Kariné access insurance coverage and protect their home in a way that is affordable.
Confronting the Financialization of Housing
Housing should be treated as homes for people, instead of a speculative asset class. When purchasing a home, Canadians might expect to be bidding against other potential buyers, not a multi-billion-dollar hedge fund. The role of large, corporate investors in our single-family housing market needs to be addressed.
- Budget 2024 announces that the government intends to restrict the purchase and acquisition of existing single-family homes by very large, corporate investors. The government will consult in the coming months and provide further details in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement .
When you have a home, you have stability, security, and an increased sense of well-being. Everyone deserves this. One of the most heart wrenching realities of the housing crisis is the increase in people struggling to find housing, especially since the pandemic. Making sure everyone has a place to live is the right thing to do, and it's the Canadian thing to do.
A strong and growing community housing sector supports vulnerable people, including those making low incomes, those fleeing violence, and those experiencing homelessness. It also keeps affordable housing affordable, builds new affordable options that meet everyone's needs, and supports strong, diverse communities. Everyone has a right to decent housing, regardless of income.
Budget 2024 will invest to increase the amount of affordable housing in Canada so we can restore what was lost over the past few decades, and help bring chronic homelessness in Canadian communities to an end.
- Over $4 billion towards preventing and reducing homelessness, through Reaching Home, Canada's Homelessness Strategy—including $100 million to support communities in responding to unsheltered homelessness this winter.
- $4 billion through the Rapid Housing Initiative, which is building more than 15,500 affordable homes for people experiencing homelessness or in severe housing need by 2026.
- Nearly $960 million provided since 2017 via the Interim Housing Assistance Program to support provinces and municipalities offering transitional housing support to asylum claimants.
- Over $458 million for the new Greener Affordable Housing stream of the Canada Greener Homes Loan program to provide low-interest loans and grants for energy efficient retrofits of affordable housing, which reduces operational costs for non-profit housing providers.
- Over $4 billion over seven years, starting in 2024-25, to implement an Urban, Rural and Northern Indigenous Housing Strategy and to establish a National Indigenous Housing Centre.
Enhancing the Affordable Housing Fund
Canada's affordable housing stock is too small to meet growing demand, resulting in too many people living in unaffordable and inadequate housing. More affordable housing is particularly needed to ensure persons with disabilities and low-income families can find an affordable place to call home.
This is why the government is investing billions of dollars to support affordable housing providers, to repair existing affordable homes, and to build new ones, through programs such as the $14 billion Affordable Housing Fund.
The 2023 Fall Economic Statement provided an additional $1 billion for the Affordable Housing Fund to support non-profit, co-op, and public housing providers in building more than 7,000 affordable homes.
- To build and maintain more affordable housing, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $976 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, and $24 million in future years, to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to launch a new Rapid Housing stream under the Affordable Housing Fund to build deeply affordable housing, supportive housing, and shelters for our most vulnerable.
Protecting and Expanding Affordable Housing
In the last decade, hundreds of thousands of affordable homes have been lost in Canada—by being destroyed after a lack of maintenance and upkeep, turned into more expensive rental units, or converted into luxury condos. Today, our community housing sector accounts for only 4 per cent of Canada's housing market, while 10 per cent of Canadians are low-income and in need of affordable housing. More must be done. We must protect our affordable housing supply for low- and modest-income families.
The government is committed to expanding and transforming this sector by 2030 and beyond to further support Canadian households, including young Canadians.
- This new Fund will be co-led and co-funded by the federal government and other partners.
- This program will help mobilize investments and financing from the charitable sector, private sector, and other orders of government.
Keeping Non-Profit and Co-op Homes Affordable
In recognition of the financial challenges facing community and social housing providers, such as co-ops, the federal government provides support to affordable housing providers to ensure existing affordable housing can be maintained. To date, the Federal Community Housing Initiative has already delivered nearly $150 million to ensure 47,000 homes can remain affordable for vulnerable Canadians, including persons with disabilities, single-parent families, seniors, and newcomers.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to introduce flexibilities to the Federal Community Housing Initiative to ensure that eligible housing providers can access funding to maintain housing affordability for low-income tenants and co-op members.
Lower Energy Bills for Renters and Homeowners
To address the twin challenges of energy affordability and climate change, the government will launch a Canada Green Buildings Strategy. The strategy will help lower home energy bills and reduce building emissions by supporting energy efficient retrofits. This represents an important next step in meeting Canada's climate targets and helping Canadians save money on their energy bills.
- $800 million over five years, starting in 2025-26, to launch a new Canada Greener Homes Affordability Program that will support the direct installation of energy efficiency retrofits for Canadian households with low- to median-incomes. This program represents the next phase of the Canada Greener Homes Initiative and will be co-delivered with provincial and territorial partners. It will also be complemented by CMHC's Greener Homes Loan program, which provides interest-free loans of up to $40,000 for energy efficiency home retrofits.
- $73.5 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to renew and modernize existing energy efficiency programs that offer tools to building owners like the ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems Standard and the ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager. This funding will also spur the development of better, more ambitious building codes to further reduce emissions and lower energy bills. The federal government will encourage provinces and territories to adopt these top-tier building codes.
- $30 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to continue developing a national approach to home energy labelling, which will empower prospective home buyers with information about the energy efficiency of their new home, with the support of energy auditors.
Natural Resources Canada will announce further details on the Canada Green Buildings Strategy in the coming weeks.
Lowering energy bills for homeowners
Maya and Sophie are homeowners with low incomes and are struggling to afford their energy bills. They want to make their home more cost efficient. Through the Canada Greener Homes Affordability Program (CGHAP), an assessment determines that the most effective energy efficiency upgrades for their home are attic insulation and air sealing. At no cost to Maya and Sophie, CGHAP arranges the direct installation of these upgrades, which will prevent heat from leaking out, improve the comfort of their home, save them money on their energy bills, and reduce their home heating emissions.
Lowering energy bills for renters
Sierra rents an apartment where she faces high heating bills from her baseboard heaters and does not have air conditioning. With the agreement of her landlord, an assessment through CGHAP determines her apartment would be a good candidate for a heat pump. At no cost to Sierra, CGHAP arranges the direct installation of a heat pump that reduces her heating costs and provides air conditioning, leaving her more money at the end of the month, and with a more comfortable home, too.
Addressing Homelessness and Encampments
Homelessness and encampments impact every community in Canada, affecting some of the most vulnerable Canadians, including 2SLGBTQI+ youth, Black and racialized people, persons with disabilities, and Indigenous people. To help ensure everyone has a safe and affordable place to call home, the government has committed over $4 billion through Reaching Home: Canada's Homelessness Strategy, for communities to provide services, transitional housing, and shelter to those who need it most. This is double the funding originally provided for Reaching Home in Budget 2017.
To respond to the urgent needs that communities are facing, the government provided an additional $100 million in 2023-24 to Infrastructure Canada for Reaching Home: Canada's Homelessness Strategy to support emergency funding over the winter for those experiencing or at risk of unsheltered homelessness—including those living in encampments.
- $1.0 billion over four years, starting in 2024-25, to stabilize funding under the program. Recognizing the enduring nature of this challenge, this investment reflects the government's commitment to support organizations that do vitally important work across the country to prevent and reduce homelessness. Of this investment, $50 million will focus on accelerating community-level reductions in homelessness. This investment will support communities across Canada as they adopt best practices and lessons learned from other jurisdictions to reduce the time it takes to move individuals and families into more stable housing.
- $250 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, to address the urgent issue of encampments and unsheltered homelessness. This funding will require provinces and territories to cost-match federal investments, leveraging a total of $500 million. This will help communities scale-up their efforts to train homelessness support workers, respond to the unique experiences of those affected by unsheltered homelessness, including those living in encampments, and renovate and build more shelters and transitional homes for those who need them.
Since Reaching Home was launched, it has supported projects across the country. Existing support to advance innovative construction includes:
- Under the Indigenous Homelessness stream, the Mi'kmaw Native Friendship Society received $904,000 in 2021 to build the Diamond Bailey House in Halifax, with 34 shelter beds, 11 dorm-style rooms and 7 bachelor apartments.
- Under the program's Rural and Remote Homelessness stream, Community Living Huntsville received $125,000 through United Way Simcoe Muskoka to support a transitional housing project that supports adults with developmental disabilities, who have experienced chronic or periodic homelessness, to reach independent living within four years.
Building Homes in Indigenous Communities
Access to safe and affordable housing is critical to improving socio-economic outcomes and ensuring a better future for Indigenous communities. Since 2015 the federal government has committed more than $6.7 billion to support housing in Indigenous communities and a further $4.3 billion to advance an Urban, Rural, and Northern Indigenous Housing strategy set to launch in 2024-25. As of December 31, 2023, Indigenous Services Canada, in collaboration with the Canada Mortgage Housing Corporation, has supported over 22,000 homes in 611 First Nations communities.
As outlined in Chapter 6, Budget 2024 also proposes additional investments to support housing and enabling infrastructure needs in First Nations, Inuit, and Métis communities.
Indigenous households in urban, rural, and northern communities across Canada face challenges accessing adequate and affordable housing. To address this, Budget 2022 and Budget 2023 committed a total of $4.3 billion over seven years, starting in 2024-25, to implement a co-developed Urban, Rural and Northern Indigenous Housing Strategy. The Strategy will be designed and implemented to complement the federal government's previous $6.7 billion in investments to support existing distinctions-based housing strategies for First Nations, Inuit, and Métis.
Informed by Indigenous-led engagements with Indigenous governments, organizations and housing providers, the funding will be delivered directly by First Nations, Inuit, and Métis governments, Modern Treaty holders and Self-Governing Indigenous Governments, and through a new Indigenous-led National Indigenous Housing Centre to ensure support will be provided to all Indigenous people.
Sheltering Asylum Claimants
While providing asylum claimants with a safe place to live falls under provincial and municipal jurisdiction, the federal government recognizes the need for all orders of government to work together to address pressures on the shelter system.
Since 2017, the federal government has provided almost $960 million through the Interim Housing Assistance Program, which helps provincial and municipal governments prevent homelessness for asylum claimants on a cost-sharing basis.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $1.1 billion over three years, starting in 2024-25, to Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada to extend the Interim Housing Assistance Program. Funding in 2026-27 will be conditional on provincial and municipal investments in permanent transitional housing solutions for asylum claimants.
The federal government is working with all orders of government to find long-term solutions to prevent asylum seekers from experiencing homelessness.
Page details

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
298. Jan 8, 2018. #2. Only the Canadian Ph.D. goes in the Education History section. Other degrees need to be listed in the Personal History section only. This way, you. 1. will get the maximum CRS points, 2. will not need to evaluate other degrees, and. 3. will not even need to upload any proofs for these other degrees.
Here are the options: No certificate, diploma or degree. High (secondary) school diploma or equivalency certificate. Non-apprenticeship trades certificate or diploma. Apprenticeship certificate. College, CEGEP or other non-university certificate or diploma from a program of 3 months to less than 1 year. College, CEGEP or other non-university ...
Thank you for your reply. I applied for Visitor Visa and provided by mistake the wrong education history (Secondary School Info.) My intention was not beneficial or Profitable to get a Visitor Visa, it was a mistake as I thought that time +12 (High School) is post-secondary school and therefore, I mentioned all the info about my High School ...
The costs of post-secondary education. All post-secondary schools charge tuition fees for their programs. For Canadian citizens and permanent residents, tuition fees are between $2,500 and $11,400 a year, depending on the school and program you've chosen. Tuition fees can be much higher for international students.
Education part is for getting points, so adding not ECA diploma, you just add unnecessary burden to application. It all can go to Personal history. You basically add non proved docs. About providing too much info, if its proven, its ok. If document is incomplete (non ECA diploma is incomplete for CIC), it might backfire.
work history. address history. education history. Each has a "to" section. This is where you put when you finished that activity or moved from that address. If you are still working or studying, or if you still live at that address, write " today " or the date you are signing the application. If you do not know the exact dates, use your ...
If your time in Canada will be less than 6 months, you'll need one of the following visas as an international student: A travel visa in your passport if you expect to study in Canada for less than 6 months. An ETA (Electronic Travel Authorization) if your passport is from a designated country. To find out which travel visa you need, answer ...
Schools that teach students up to the grade 12 level are known as primary and secondary schools. Primary usually means grades 1-8 and secondary usually means grades 9-12. All primary and secondary schools in Canada can enrol international students. There are special rules for minor children studying in Canada. Post-secondary schools
1940 - 37,225 students, 24% female, 47% arts/science, 12% engineering, 8% medicine. The history of Canadian post-secondary education has two particularly notable things going on with respect to the first four decades of the twentieth century. The first is that western Canada got universities. And the second is that Eastern universities ...
In 1900, Canadian universities together enrolled 6,641 students. 89% were male, 11% female. 44% of students were in the Arts and Science, while 27% were in medicine, and 11% were in Engineering. The key to understanding Canada's somewhat chaotic higher education system lies in understanding two key phenomena: sectarianism and federalism. The former issue historically […]
The Chretien era - roughly 1994 to 2003 - deserves to be remembered as a time of tremendous change in Canadian post-secondary education. Or, as an enormous, stomach-churning, roller-coaster, and mighty odd that a federal politician defined an era in a field of what is essentially provincial. The first defining moment was the fabled 1995 ...
Sep 22, 2021. #1. Error: Give details of all your employment and activities for the past 10 years.-. You're missing details for the past 10 years. Review your entries and make sure you included something for all times periods in the past 10 years. Do not include any entries that you already put for post-secondary education or military/police ...
During the war years, post-secondary education was essentially on hold. But immediately afterwards, in the period from 1945-1960, there were some major developments. The first was dealing with a major surge in enrolments due to returning veterans. In 1944-45, full-time enrolment was 38,516, slightly below where it was in 1938.
T. Inacio, Registered Canadian Immigration Consultant RCIC Membership #511568. 4. Name, address and relationship of any person(s) or institution(s) I will visit: Name Relationship to me Address in Canada. Dalhousie University My university PO Box 15000, Nova Scotia Canada, B3H 4R2. Education.
Oct 30, 2015. 30. 2. Jan 7, 2016. #1. CIC says, we will assess () secondary and post-secondary periods of study for eligibility for Express Entry, and use them to calculate () score. This is mentioned in Application/Profile details, Education Histroy section. Does that mean I need to submit my secondary and higher secondary school education ...
The period roughly from 1959 to the oil crisis of 1973-74 is rightly thought of as a Golden Age for higher education in Canada, much as it is in the United States. Universities ballooned in size and gradually became more research-intensive. A new class of institutions, community colleges, were added to the system.
However, studying in Canada as an international student can be complicated if you don't understand the process. That's why we designed the International Student Roadmap, a free email-education service that delivers International Student lessons and planning guides directly to your inbox.
To fix it: In your profile, go to the Study and languages section of the form. Open the Education history sub-section. Scroll to the bottom and click Modify. You will see the information you already entered. To make sure you filled all the fields, click Check for Completeness at the top of the form. If there is a field you need to correct, you ...
The economic and fiscal history of Canada from the early 70s to the mid-90s is one long, bad disaster movie. Unemployment went over 6% in 1974 and didn't come back down to that level until 2008. For nearly all of the 1980s, it was over 8% and from 1982 to 1994 it was over 10% half the time. The Keynesian medicine that was supposed to get us ...
On the educational history section, it asks to enter any secondary or post secondary education so I thought university degree would suffice. Now that I got ITA incant change my express entry profile. ... Regina, Canada Visa Office..... CPC - Ottawa NOC Code..... 2172/6211 App. Filed..... 26 Nov 15 Doc's Request. 21 Jan 16 - RCMP and 18 May 16 ...
Are you wondering whether you should include your high school education in your Canada immigration application? Join the discussion on this forum and get advice from other applicants who have faced similar questions. You can also find helpful information on other topics related to Canada immigration, such as language proof, passport scan, letter of acceptance, and biometrics appointment.
In some respects, teaching became more important because this was a period of huge growth in enrollments. Between 1999 and 2010, FTE enrollment at Canadian universities increased by 50%, partly due to natural growth and partly due to the conversion of seven colleges in BC and Alberta to university status. This was one of the fastest growth ...
There are broadly four different types of post-secondary education each with different purposes. 1. University. A university is a post-secondary educational institution that is authorized to award degrees. Every university offers Bachelor's Degree programs, and many also offer Master's Degree programs and Ph.D. programs.
The Honourable Marc Miller, Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship, issued the following statement. Ottawa, April 5, 2024—The Honourable Marc Miller, Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship, issued the following statement: "On January 22, I announced a national cap on study permit applications to address the rapid increase of international students in Canada.
Budget 2024 proposes to provide $409.6 million over four years, starting in 2025-26, to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation to launch a new Canada Secondary Suite Loan Program, enabling homeowners to access up to $40,000 in low-interest loans to add secondary suites to their homes.