Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Year in Review
- Published: 18 December 2019
HIGHLIGHTS OF 2019

The expansion of the Universe is faster than expected
- Adam G. Riess 1
Nature Reviews Physics volume 2 , pages 10–12 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
5801 Accesses
272 Citations
94 Altmetric
Metrics details
This article has been updated
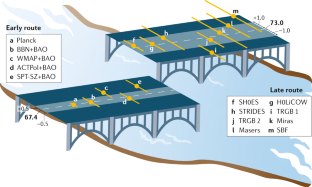
The present rate of the expansion of our Universe, the Hubble constant, can be predicted from the cosmological model using measurements of the early Universe, or more directly measured from the late Universe. But as these measurements improved, a surprising disagreement between the two appeared. In 2019, a number of independent measurements of the late Universe using different methods and data provided consistent results, making the discrepancy with the early Universe predictions increasingly hard to ignore.
Key advances
The local or late Universe measurement of the Hubble constant improved from 10% uncertainty 20 years ago to less than 2% by 2019.
In 2019, multiple independent teams presented measurements with different methods and different calibrations to produce consistent results.
These late Universe estimations disagree at 4 \(\sigma \) to 6 \(\sigma \) with predictions made from the cosmic microwave background in conjunction with the standard cosmological model, a disagreement that is hard to explain or ignore.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Relevant articles
Open Access articles citing this article.
Past-directed scalar field gradients and scalar-tensor thermodynamics
- Andrea Giusti
- , Serena Giardino
- & Valerio Faraoni
General Relativity and Gravitation Open Access 09 March 2023
Requirements on common solutions to the LSND and MiniBooNE excesses: a post-MicroBooNE study
- Waleed Abdallah
- , Raj Gandhi
- & Samiran Roy
Journal of High Energy Physics Open Access 29 June 2022
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
92,52 € per year
only 7,71 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Change history
10 january 2020.
The Competing interest statement is added as it was missing from the previous version.
Riess, A. G. et al. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid standards provide a 1% foundation for the determination of the Hubble constant and stronger evidence for physics beyond ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. 876 , 85 (2019).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Pietrzyn´ski, G. et al. A distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud that is precise to one per cent. Nature 567 , 200–203 (2019).
Reid, M. J., Pesce, D. W. & Riess A. G. An improved distance to NGC 4258 and its implications for the Hubble constant. Astrophys. J. Lett. 886 , L27 (2019).
Wong K. C. et al. H0LiCOW XIII. A 2.4% measurement of H0 from lensed quasars: 5.3σ tension between early and late-Universe probes. Preprint at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.04869 (2019).
Shajib, A. J. et al. STRIDES: A 3.9 per cent measurement of the Hubble constant from the strong lens system DES J0408-5354. Preprint at: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.06306 (2019).
Freedman, W. L. et al. The Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program. VIII. An independent determination of the Hubble constant based on the tip of the red giant branch. Astrophys. J. 882 , 34 (2019).
Yuan, W. et al. Consistent calibration of the tip of the red giant branch in the Large Magellanic Cloud on the Hubble Space Telescope photometric system and a re-determination of the Hubble constant. https://10.3847/1538-4357/ab4bc9 (2019).
Huang, C. D. et al. Hubble Space Telescope observations of Mira variables in the type Ia supernova host NGC 1559: an alternative candle to measure the Hubble constant. Astrophys. J. in the press.
Verde, L., Treu, T. & Riess, A. G. Tensions between the early and the late Universe. Nat. Astron. 3 , 891–895 (2019).
Knox, L & Millea, M. The Hubble hunter’s guide. Preprint at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03663 (2019).
Wu, H. Y. & Huterer, D. Sample variance in the local measurements of the Hubble constant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 471 , 4946–4955 (2017).
Kenworthy, W. D., Scolnic, D. & Riess, A. G. The local perspective on the Hubble tension: local structure does not impact measurement of the Hubble constant. https://10.3847/1538-4357/ab0ebf (2019).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physics & Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Adam G. Riess
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Adam G. Riess .

Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Riess, A.G. The expansion of the Universe is faster than expected. Nat Rev Phys 2 , 10–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-019-0137-0
Download citation
Published : 18 December 2019
Issue Date : January 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-019-0137-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Cosmic growth in f(t) teleparallel gravity.
- Salvatore Capozziello
- Maria Caruana
- Joseph Sultana
General Relativity and Gravitation (2024)
Taiji-TianQin-LISA network: Precisely measuring the Hubble constant using both bright and dark sirens
- Shang-Jie Jin
- Ye-Zhu Zhang
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2024)
Illuminating dark sirens with CSST
- Zong-Hong Zhu
- Serena Giardino
- Valerio Faraoni
General Relativity and Gravitation (2023)
Constraining the Hubble constant to a precision of about 1% using multi-band dark standard siren detections
- Liang-Gui Zhu
- Ling-Hua Xie
- Jianwei Mei
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2022) The present rate of the expansion of our Universe, the Hubble constant, can be predicted from the cosmological model using measurements of the ...