
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to develop critical thinking skills

Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test

Jump to section
What are critical thinking skills?
How to develop critical thinking skills: 12 tips, how to practice critical thinking skills at work, become your own best critic.
A client requests a tight deadline on an intense project. Your childcare provider calls in sick on a day full of meetings. Payment from a contract gig is a month behind.
Your day-to-day will always have challenges, big and small. And no matter the size and urgency, they all ask you to use critical thinking to analyze the situation and arrive at the right solution.
Critical thinking includes a wide set of soft skills that encourage continuous learning, resilience , and self-reflection. The more you add to your professional toolbelt, the more equipped you’ll be to tackle whatever challenge presents itself. Here’s how to develop critical thinking, with examples explaining how to use it.
Critical thinking skills are the skills you use to analyze information, imagine scenarios holistically, and create rational solutions. It’s a type of emotional intelligence that stimulates effective problem-solving and decision-making .
When you fine-tune your critical thinking skills, you seek beyond face-value observations and knee-jerk reactions. Instead, you harvest deeper insights and string together ideas and concepts in logical, sometimes out-of-the-box , ways.
Imagine a team working on a marketing strategy for a new set of services. That team might use critical thinking to balance goals and key performance indicators , like new customer acquisition costs, average monthly sales, and net profit margins. They understand the connections between overlapping factors to build a strategy that stays within budget and attracts new sales.
Looking for ways to improve critical thinking skills? Start by brushing up on the following soft skills that fall under this umbrella:
- Analytical thinking: Approaching problems with an analytical eye includes breaking down complex issues into small chunks and examining their significance. An example could be organizing customer feedback to identify trends and improve your product offerings.
- Open-mindedness: Push past cognitive biases and be receptive to different points of view and constructive feedback . Managers and team members who keep an open mind position themselves to hear new ideas that foster innovation .
- Creative thinking: With creative thinking , you can develop several ideas to address a single problem, like brainstorming more efficient workflow best practices to boost productivity and employee morale .
- Self-reflection: Self-reflection lets you examine your thinking and assumptions to stimulate healthier collaboration and thought processes. Maybe a bad first impression created a negative anchoring bias with a new coworker. Reflecting on your own behavior stirs up empathy and improves the relationship.
- Evaluation: With evaluation skills, you tackle the pros and cons of a situation based on logic rather than emotion. When prioritizing tasks , you might be tempted to do the fun or easy ones first, but evaluating their urgency and importance can help you make better decisions.

There’s no magic method to change your thinking processes. Improvement happens with small, intentional changes to your everyday habits until a more critical approach to thinking is automatic.
Here are 12 tips for building stronger self-awareness and learning how to improve critical thinking:
1. Be cautious
There’s nothing wrong with a little bit of skepticism. One of the core principles of critical thinking is asking questions and dissecting the available information. You might surprise yourself at what you find when you stop to think before taking action.
Before making a decision, use evidence, logic, and deductive reasoning to support your own opinions or challenge ideas. It helps you and your team avoid falling prey to bad information or resistance to change .
2. Ask open-ended questions
“Yes” or “no” questions invite agreement rather than reflection. Instead, ask open-ended questions that force you to engage in analysis and rumination. Digging deeper can help you identify potential biases, uncover assumptions, and arrive at new hypotheses and possible solutions.
3. Do your research
No matter your proficiency, you can always learn more. Turning to different points of view and information is a great way to develop a comprehensive understanding of a topic and make informed decisions. You’ll prioritize reliable information rather than fall into emotional or automatic decision-making.

4. Consider several opinions
You might spend so much time on your work that it’s easy to get stuck in your own perspective, especially if you work independently on a remote team . Make an effort to reach out to colleagues to hear different ideas and thought patterns. Their input might surprise you.
If or when you disagree, remember that you and your team share a common goal. Divergent opinions are constructive, so shift the focus to finding solutions rather than defending disagreements.
5. Learn to be quiet
Active listening is the intentional practice of concentrating on a conversation partner instead of your own thoughts. It’s about paying attention to detail and letting people know you value their opinions, which can open your mind to new perspectives and thought processes.
If you’re brainstorming with your team or having a 1:1 with a coworker , listen, ask clarifying questions, and work to understand other peoples’ viewpoints. Listening to your team will help you find fallacies in arguments to improve possible solutions.
6. Schedule reflection
Whether waking up at 5 am or using a procrastination hack, scheduling time to think puts you in a growth mindset . Your mind has natural cognitive biases to help you simplify decision-making, but squashing them is key to thinking critically and finding new solutions besides the ones you might gravitate toward. Creating time and calm space in your day gives you the chance to step back and visualize the biases that impact your decision-making.
7. Cultivate curiosity
With so many demands and job responsibilities, it’s easy to seek solace in routine. But getting out of your comfort zone helps spark critical thinking and find more solutions than you usually might.
If curiosity doesn’t come naturally to you, cultivate a thirst for knowledge by reskilling and upskilling . Not only will you add a new skill to your resume , but expanding the limits of your professional knowledge might motivate you to ask more questions.
You don’t have to develop critical thinking skills exclusively in the office. Whether on your break or finding a hobby to do after work, playing strategic games or filling out crosswords can prime your brain for problem-solving.

9. Write it down
Recording your thoughts with pen and paper can lead to stronger brain activity than typing them out on a keyboard. If you’re stuck and want to think more critically about a problem, writing your ideas can help you process information more deeply.
The act of recording ideas on paper can also improve your memory . Ideas are more likely to linger in the background of your mind, leading to deeper thinking that informs your decision-making process.
10. Speak up
Take opportunities to share your opinion, even if it intimidates you. Whether at a networking event with new people or a meeting with close colleagues, try to engage with people who challenge or help you develop your ideas. Having conversations that force you to support your position encourages you to refine your argument and think critically.
11. Stay humble
Ideas and concepts aren’t the same as real-life actions. There may be such a thing as negative outcomes, but there’s no such thing as a bad idea. At the brainstorming stage , don’t be afraid to make mistakes.
Sometimes the best solutions come from off-the-wall, unorthodox decisions. Sit in your creativity , let ideas flow, and don’t be afraid to share them with your colleagues. Putting yourself in a creative mindset helps you see situations from new perspectives and arrive at innovative conclusions.
12. Embrace discomfort
Get comfortable feeling uncomfortable . It isn’t easy when others challenge your ideas, but sometimes, it’s the only way to see new perspectives and think critically.
By willingly stepping into unfamiliar territory, you foster the resilience and flexibility you need to become a better thinker. You’ll learn how to pick yourself up from failure and approach problems from fresh angles.

Thinking critically is easier said than done. To help you understand its impact (and how to use it), here are two scenarios that require critical thinking skills and provide teachable moments.
Scenario #1: Unexpected delays and budget
Imagine your team is working on producing an event. Unexpectedly, a vendor explains they’ll be a week behind on delivering materials. Then another vendor sends a quote that’s more than you can afford. Unless you develop a creative solution, the team will have to push back deadlines and go over budget, potentially costing the client’s trust.
Here’s how you could approach the situation with creative thinking:
- Analyze the situation holistically: Determine how the delayed materials and over-budget quote will impact the rest of your timeline and financial resources . That way, you can identify whether you need to build an entirely new plan with new vendors, or if it’s worth it to readjust time and resources.
- Identify your alternative options: With careful assessment, your team decides that another vendor can’t provide the same materials in a quicker time frame. You’ll need to rearrange assignment schedules to complete everything on time.
- Collaborate and adapt: Your team has an emergency meeting to rearrange your project schedule. You write down each deliverable and determine which ones you can and can’t complete by the deadline. To compensate for lost time, you rearrange your task schedule to complete everything that doesn’t need the delayed materials first, then advance as far as you can on the tasks that do.
- Check different resources: In the meantime, you scour through your contact sheet to find alternative vendors that fit your budget. Accounting helps by providing old invoices to determine which vendors have quoted less for previous jobs. After pulling all your sources, you find a vendor that fits your budget.
- Maintain open communication: You create a special Slack channel to keep everyone up to date on changes, challenges, and additional delays. Keeping an open line encourages transparency on the team’s progress and boosts everyone’s confidence.

Scenario #2: Differing opinions
A conflict arises between two team members on the best approach for a new strategy for a gaming app. One believes that small tweaks to the current content are necessary to maintain user engagement and stay within budget. The other believes a bold revamp is needed to encourage new followers and stronger sales revenue.
Here’s how critical thinking could help this conflict:
- Listen actively: Give both team members the opportunity to present their ideas free of interruption. Encourage the entire team to ask open-ended questions to more fully understand and develop each argument.
- Flex your analytical skills: After learning more about both ideas, everyone should objectively assess the benefits and drawbacks of each approach. Analyze each idea's risk, merits, and feasibility based on available data and the app’s goals and objectives.
- Identify common ground: The team discusses similarities between each approach and brainstorms ways to integrate both idea s, like making small but eye-catching modifications to existing content or using the same visual design in new media formats.
- Test new strategy: To test out the potential of a bolder strategy, the team decides to A/B test both approaches. You create a set of criteria to evenly distribute users by different demographics to analyze engagement, revenue, and customer turnover.
- Monitor and adapt: After implementing the A/B test, the team closely monitors the results of each strategy. You regroup and optimize the changes that provide stronger results after the testing. That way, all team members understand why you’re making the changes you decide to make.
You can’t think your problems away. But you can equip yourself with skills that help you move through your biggest challenges and find innovative solutions. Learning how to develop critical thinking is the start of honing an adaptable growth mindset.
Now that you have resources to increase critical thinking skills in your professional development, you can identify whether you embrace change or routine, are open or resistant to feedback, or turn to research or emotion will build self-awareness. From there, tweak and incorporate techniques to be a critical thinker when life presents you with a problem.

Elizabeth Perry
Content Marketing Manager, ACC
How to improve your creative skills for effective problem-solving
What is lateral thinking 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas, 6 ways to leverage ai for hyper-personalized corporate learning, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, how divergent thinking can drive your creativity, critical thinking is the one skillset you can't afford not to master, what’s convergent thinking how to be a better problem-solver, can dreams help you solve problems 6 ways to try, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, similar articles, what is creative thinking and why does it matter, discover the 7 essential types of life skills you need, 6 big picture thinking strategies that you'll actually use, what are analytical skills examples and how to level up, how intrapersonal skills shape teams, plus 5 ways to build them, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
Critical Thinking
Developing the right mindset and skills.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
We make hundreds of decisions every day and, whether we realize it or not, we're all critical thinkers.
We use critical thinking each time we weigh up our options, prioritize our responsibilities, or think about the likely effects of our actions. It's a crucial skill that helps us to cut out misinformation and make wise decisions. The trouble is, we're not always very good at it!
In this article, we'll explore the key skills that you need to develop your critical thinking skills, and how to adopt a critical thinking mindset, so that you can make well-informed decisions.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well.
Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly valued asset in the workplace. People who score highly in critical thinking assessments are also rated by their managers as having good problem-solving skills, creativity, strong decision-making skills, and good overall performance. [1]
Key Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinkers possess a set of key characteristics which help them to question information and their own thinking. Focus on the following areas to develop your critical thinking skills:
Being willing and able to explore alternative approaches and experimental ideas is crucial. Can you think through "what if" scenarios, create plausible options, and test out your theories? If not, you'll tend to write off ideas and options too soon, so you may miss the best answer to your situation.
To nurture your curiosity, stay up to date with facts and trends. You'll overlook important information if you allow yourself to become "blinkered," so always be open to new information.
But don't stop there! Look for opposing views or evidence to challenge your information, and seek clarification when things are unclear. This will help you to reassess your beliefs and make a well-informed decision later. Read our article, Opening Closed Minds , for more ways to stay receptive.
Logical Thinking
You must be skilled at reasoning and extending logic to come up with plausible options or outcomes.
It's also important to emphasize logic over emotion. Emotion can be motivating but it can also lead you to take hasty and unwise action, so control your emotions and be cautious in your judgments. Know when a conclusion is "fact" and when it is not. "Could-be-true" conclusions are based on assumptions and must be tested further. Read our article, Logical Fallacies , for help with this.
Use creative problem solving to balance cold logic. By thinking outside of the box you can identify new possible outcomes by using pieces of information that you already have.
Self-Awareness
Many of the decisions we make in life are subtly informed by our values and beliefs. These influences are called cognitive biases and it can be difficult to identify them in ourselves because they're often subconscious.
Practicing self-awareness will allow you to reflect on the beliefs you have and the choices you make. You'll then be better equipped to challenge your own thinking and make improved, unbiased decisions.
One particularly useful tool for critical thinking is the Ladder of Inference . It allows you to test and validate your thinking process, rather than jumping to poorly supported conclusions.
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
Combine the above skills with the right mindset so that you can make better decisions and adopt more effective courses of action. You can develop your critical thinking mindset by following this process:
Gather Information
First, collect data, opinions and facts on the issue that you need to solve. Draw on what you already know, and turn to new sources of information to help inform your understanding. Consider what gaps there are in your knowledge and seek to fill them. And look for information that challenges your assumptions and beliefs.
Be sure to verify the authority and authenticity of your sources. Not everything you read is true! Use this checklist to ensure that your information is valid:
- Are your information sources trustworthy ? (For example, well-respected authors, trusted colleagues or peers, recognized industry publications, websites, blogs, etc.)
- Is the information you have gathered up to date ?
- Has the information received any direct criticism ?
- Does the information have any errors or inaccuracies ?
- Is there any evidence to support or corroborate the information you have gathered?
- Is the information you have gathered subjective or biased in any way? (For example, is it based on opinion, rather than fact? Is any of the information you have gathered designed to promote a particular service or organization?)
If any information appears to be irrelevant or invalid, don't include it in your decision making. But don't omit information just because you disagree with it, or your final decision will be flawed and bias.
Now observe the information you have gathered, and interpret it. What are the key findings and main takeaways? What does the evidence point to? Start to build one or two possible arguments based on what you have found.
You'll need to look for the details within the mass of information, so use your powers of observation to identify any patterns or similarities. You can then analyze and extend these trends to make sensible predictions about the future.
To help you to sift through the multiple ideas and theories, it can be useful to group and order items according to their characteristics. From here, you can compare and contrast the different items. And once you've determined how similar or different things are from one another, Paired Comparison Analysis can help you to analyze them.
The final step involves challenging the information and rationalizing its arguments.
Apply the laws of reason (induction, deduction, analogy) to judge an argument and determine its merits. To do this, it's essential that you can determine the significance and validity of an argument to put it in the correct perspective. Take a look at our article, Rational Thinking , for more information about how to do this.
Once you have considered all of the arguments and options rationally, you can finally make an informed decision.
Afterward, take time to reflect on what you have learned and what you found challenging. Step back from the detail of your decision or problem, and look at the bigger picture. Record what you've learned from your observations and experience.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life.
You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when your beliefs could affect your decisions or actions.
You can demonstrate a high level of critical thinking by validating your information, analyzing its meaning, and finally evaluating the argument.
Critical Thinking Infographic
See Critical Thinking represented in our infographic: An Elementary Guide to Critical Thinking .

You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Managing part-time staff.
Strategies for Your Flexible Workforce
The Influence Model
Using Reciprocity to Gain Influence
Add comment
Comments (1)
priyanka ghogare

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Management Skills

5 Phrases That Kill Collaboration
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How do i manage a hybrid team.
Adjusting your management style to a hybrid world
The Life Career Rainbow
Finding a Work-Life Balance That Suits You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
9 ways to future proof your career.
Staying Relevant for Tomorrow's World
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Pain Points
Main Challenges When Developing Your Critical Thinking
Written by Argumentful
Every day we are constantly bombarded with information and opinions from all directions. The ability to think critically is more important now than it ever was.
Critical thinking allows us to evaluate arguments, identify biases, and make informed decisions based on evidence and reasoning.
However, developing this skill is not easy, and there are many challenges that can stand in our way.
In this article, we will explore the main challenges that people face when trying to develop their critical thinking skills and provide some tips and strategies for overcoming them.
• Challenge #1: Confirmation Bias
• Challenge #2: Logical Fallacies
• Challenge #3: Emotions
• Challenge #4: Lack of Information or Misinformation
• Challenge #5: Groupthink
• Challenge #6: Overconfidence Bias
• Challenge #7: Cognitive dissonance
Challenge #1: Confirmation Bias
What is confirmation bias.
Confirmation bias is a tendency to seek out information that supports your existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts those beliefs . It can be a major obstacle to critical thinking, as it can lead us to only consider evidence that confirms our preconceived notions and dismiss evidence that challenges them.
Raymond S. Nickerson, a psychology professor considers that confirmation bias is a common human tendency that can have negative consequences for decision making and information processing.
For example, in politics, people may only consume news from sources that align with their political ideology and ignore information that challenges their beliefs.
Or in the workplace, managers may only seek out feedback that confirms their leadership style and ignore feedback that suggests they need to make changes.
How do critical thinkers fight confirmation bias?
To overcome confirmation bias, it is important to actively seek out information from a variety of sources and perspectives .
This can involve reading news articles and opinion pieces from a range of sources, engaging in discussions with people who hold different opinions, and being open to changing our own beliefs based on new evidence.
It can also be helpful to regularly question our own assumptions and biases.
Another strategy is to practice “ steel manning ” which involves actively trying to understand and strengthen arguments that challenge our own beliefs, rather than just attacking weaker versions of those arguments.
Nickerson suggests the following strategies that can be used to mitigate confirmation bias:
- Considering alternative explanations : You can make a conscious effort to consider alternative explanations for a given set of data or evidence, rather than simply focusing on information that supports your pre-existing beliefs.
- Seeking out disconfirming evidence : Try to actively seek out evidence that contradicts your pre-existing beliefs, rather than simply ignoring or discounting it.
- Using formal decision-making tools : Use formal decision-making tools, such as decision trees or decision matrices, to help structure your thinking and reduce the influence of biases.
- Encouraging group decision making : Groups can be more effective at mitigating confirmation bias than individuals, since group members can challenge each other’s assumptions and biases.
- Adopting a scientific mindset : You can adopt a more scientific mindset, which involves a willingness to consider multiple hypotheses, test them rigorously, and revise them based on evidence.
Nickerson suggests that these strategies may be effective at mitigating confirmation bias, but notes that they may require effort and practice to implement successfully.
By being aware of confirmation bias and actively working to overcome it, we can all develop a more open-minded approach to critical thinking and make more informed decisions.
Challenge #2: Logical Fallacies
Critical thinking requires the ability to identify and analyze arguments for their strengths and weaknesses. One major obstacle to this process is the presence of logical fallacies.
What are logical fallacies?
Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning that can make an argument appear convincing, even if it is flawed .
There are many types of logical fallacies, including ad hominem attacks , false dichotomies , strawman arguments , and appeals to emotion . These fallacies can appear in everyday discourse, from political debates to advertising campaigns, and can lead to flawed conclusions and decisions.
An example of a logical fallacy is when a politician might use an ad hominem attack to undermine their opponent’s credibility rather than addressing their argument directly.
Similarly, an advertisement might use emotional appeals to distract consumers from the actual merits of a product.
For an engaging introduction into the topic, check out Ali Almossawi’s book on logical fallacies-“ An Illustrated Book of Bad Arguments “. It provides a visually appealing perspective, using illustrations and examples to explain many common fallacies. It is aimed at a general audience, but provides a good overview of the topic for beginners.
How do critical thinkers fight logical fallacies?
To avoid being swayed by logical fallacies, it is important to be able to recognize them.
• One strategy is to familiarize yourself with common fallacies and their definitions .
• Additionally, it is important to analyse an argument’s premises and conclusions to identify any flaws in its reasoning.
• Finally, it can be helpful to question assumptions and consider alternative perspectives to ensure that your thinking is not influenced by logical fallacies.
A good source to do a deep dive into logical fallacies is The Fallacy Files by Gary N. Curtis – This website provides an extensive list of common logical fallacies, along with explanations and examples of each. It emphasizes the importance of being able to identify and avoid fallacies, and provides resources for improving critical thinking skills.
By developing the ability to identify and avoid logical fallacies, you can become a more effective critical thinker and make more informed decisions.
Challenge #3: Emotions
Emotions can have a significant impact on critical thinking and decision-making. Our emotional responses to information can affect our perception of it and bias our judgments. For example, if we have a strong emotional attachment to a particular belief or idea, we may be more likely to dismiss information that contradicts it and accept information that supports it, even if the information is flawed or unreliable.
Additionally, emotional reactions can also lead to impulsive decision-making, where we may act without fully considering all available information or weighing the potential consequences. This can be particularly problematic in high-stakes situations, such as in the workplace or in personal relationships.
Jennifer S. Lerner, Ye Li, Piercarlo Valdesolo, and Karim S. Kassam explore the relationship between emotions and decision making, including the role of emotions in shaping cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and judgment. They suggest that emotions can influence decision making in both positive and negative ways, and that understanding how emotions affect decision making is an important area of research.
How do critical thinkers manage emotions?
To manage the role of emotions in critical thinking, it is important to first become aware of our emotional reactions and biases. This can be done through mindfulness practices, such as meditation or journaling, where we can reflect on our thoughts and feelings without judgment.
It can also be helpful to actively seek out diverse perspectives and information, as exposure to new and varied ideas can help to broaden our understanding and reduce emotional attachments to particular beliefs. Additionally, taking a pause before making a decision or responding to information can provide time to reflect on our emotional reactions and consider all available information in a more rational and objective manner.
Overall, recognizing the impact of emotions on critical thinking and developing strategies for managing them can lead to more informed and effective decision-making.
Challenge #4: Lack of Information or Misinformation
Critical thinking relies heavily on having accurate and reliable information. However, in today’s age of rapid information sharing, it is easy to be inundated with an overwhelming amount of information, and distinguishing fact from fiction can be a daunting task. Additionally, misinformation and propaganda can be intentionally spread to manipulate opinions and beliefs.
Pew Research Center found that many Americans are concerned about the impact of misinformation on democracy and that fake news can erode trust in institutions and hinder critical thinking.
One example of the impact of misinformation is the spread of conspiracy theories, such as the belief that climate change is a hoax. These beliefs can lead to negative consequences for us and society as a whole, such as a lack of action on climate change.
How do critical thinkers overcome the lack of information or misinformation?
To overcome the challenge of misinformation and a lack of information, critical thinkers must develop a habit of fact-checking and verifying information. This means seeking out multiple sources of information and analyzing the credibility and biases of each source. Critical thinkers must also be willing to adjust their beliefs based on new evidence and be open to changing their opinions.
Pew Research Center suggests that media literacy education can help people become more discerning consumers of information.
• A good source for developing media literacy is Unesco’s “ Media and Information Literacy: Curriculum for Teachers “: The publication emphasizes the importance of teaching students to critically evaluate information in order to become informed and responsible citizens. It provides a framework for teaching media and information literacy skills, including critical thinking, and emphasizes the need to teach students how to recognize and avoid misinformation.
• Another source worth checking out is New York Times Events’ video on How to Teach Critical Thinking in an Age of Misinformation . The speakers suggest that educators should focus on teaching students to ask probing questions, evaluate evidence, and consider alternative perspectives. They also note that critical thinking skills are especially important in an age of information overload and misinformation.
• Furthermore, it is important to be aware of your own biases and limitations when seeking out and evaluating information. Confirmation bias, discussed in Challenge #1, can also play a role in accepting misinformation or overlooking important information that does not align with our pre-existing beliefs.
By being diligent and thorough in our information gathering and evaluation, we can overcome the challenge of misinformation and make more informed decisions.
Challenge #5: Groupthink
What is groupthink.
According to Sunstein and Hastie , groupthink occurs when members of a group prioritize consensus and social harmony over critical evaluation of alternative ideas. They suggest that groupthink can lead to a narrowing of perspectives and a lack of consideration for alternative viewpoints, which can result in flawed decision-making. They argue that groupthink is particularly dangerous in situations where group members are highly cohesive, where there is a strong leader or dominant voice, or where the group lacks diverse perspectives.
The desire for group cohesion can lead to a reluctance to challenge the consensus or express dissenting opinions, resulting in flawed decision-making and missed opportunities for innovation.
One example of groupthink is the space shuttle Challenger disaster in 1986 , where NASA engineers failed to recognize and address the risk of launching the shuttle in cold weather due to pressure from superiors and a culture of overconfidence. This led to a catastrophic failure that claimed the lives of all seven crew members.
How do critical thinkers overcome groupthink?
To overcome groupthink, it is important to encourage diversity of thought and promote constructive disagreement.
There are several strategies for avoiding groupthink, including promoting independent thinking and dissenting opinions, encouraging diverse perspectives, and engaging in active listening and critical evaluation of alternative ideas.
This can be achieved by seeking out dissenting views and challenging assumptions, creating a culture of open communication and feedback, and avoiding hierarchies that can stifle innovation and creativity. It is also important to value and reward independent thinking, even if it goes against the prevailing consensus.
For more ways to overcome group think, check out this comprehensive list of strategies from Northwestern school of education and social policy .
Developing critical thinking skills can help you to overcome groupthink and make more informed and effective decisions. By being aware of the challenges of group dynamics and actively seeking out diverse perspectives, you can cultivate a more independent and objective approach to critical thinking, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a more robust and resilient society.
Challenge #6: Overconfidence Bias
Another challenge to developing critical thinking is overconfidence bias, which is the tendency to overestimate our own abilities and knowledge. This bias can lead us to make hasty decisions or overlook important information, which can ultimately hinder our critical thinking skills.
Kahneman explains how the human mind has two modes of thinking: System 1, which is fast and intuitive, and System 2, which is slow and deliberative. He argues that overconfidence bias is a common flaw in System 1 thinking, which can lead us to overestimate our knowledge and abilities. Kahneman suggests that improving critical thinking requires training to recognize and control our overconfidence bias.
Overconfidence bias can occur in various contexts, such as in the workplace, academic settings, or even in personal relationships. For instance, you may be overconfident in your ability to complete a task at work without seeking help or feedback from colleagues, which could result in suboptimal outcomes.
Lichtenstein and Fischhoff conducted a study on overconfidence bias, in which they found that people tend to overestimate their knowledge and abilities in areas where they have limited expertise.
Tversky and Kahneman’s seminal paper on heuristics and biases discusses overconfidence bias as a common flaw in human decision-making. They suggest that overconfidence bias can lead us to make inaccurate judgments and can contribute to a wide range of cognitive biases.
How do critical thinkers overcome overconfidence bias?
To overcome overconfidence bias, you should take a more humble and reflective approach to your own abilities and knowledge. This can involve seeking feedback from others, taking the time to consider different perspectives, and being open to constructive criticism.
Kahneman suggests that improving critical thinking requires training to recognize and control our overconfidence bias.
Moore and Healy offer several strategies for reducing overconfidence bias , including increasing feedback, considering alternative explanations, and using probabilistic reasoning.
Another strategy is to cultivate a growth mindset , which emphasizes the belief that your abilities can be developed through effort and persistence. By adopting this mindset, you can avoid becoming complacent and continue to challenge yourself to develop your critical thinking skills.
Overall, overcoming overconfidence bias requires a willingness to acknowledge our own limitations and to actively seek out opportunities for growth and learning.
Challenge #7: Cognitive dissonance
Cognitive dissonance is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when a person holds two or more conflicting beliefs, values, or ideas. This internal conflict can create feelings of discomfort, which can lead to irrational and inconsistent behaviour. Cognitive dissonance can pose a significant challenge to critical thinking by distorting our perceptions and leading us to accept information that confirms our existing beliefs while dismissing or rationalizing away information that challenges them.
For example, a person who believes that they are a good driver may become defensive and dismissive when presented with evidence of their unsafe driving habits, such as speeding or not using a turn signal. This person may experience cognitive dissonance, as their belief in their driving ability conflicts with the evidence presented to them.
Tavris and Aronson’s book- Mistakes were made (but not by me) examines the phenomenon of cognitive dissonance in everyday life, using real-life examples to illustrate how we justify our beliefs and actions, even in the face of evidence to the contrary. It’s a worthwhile read to understand the psychological mechanisms that underlie cognitive dissonance and the implications of dissonance for understanding interpersonal conflict, group behaviour, and decision-making.
How do critical thinkers overcome cognitive dissonance?
Overcoming cognitive dissonance requires a willingness to confront and examine our own beliefs and assumptions.
Tavris and Aronson offer several strategies for recognizing and overcoming cognitive dissonance.
• we should be aware of the potential for cognitive dissonance to arise in situations where our beliefs, attitudes, or behaviours are inconsistent . By recognizing the possibility of dissonance, we can be more prepared to manage the discomfort that may result.
• we should engage in self-reflection to examine our beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors more closely. By questioning assumptions and considering alternative perspectives, we may be able to reduce the cognitive dissonance we experience.
• we should seek out diverse perspectives and engage in constructive dialogue with others. By listening to and respecting different viewpoints, we can gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and others, which may help to reduce cognitive dissonance.
Finally, the authors emphasize the importance of taking responsibility for our own actions and decisions. By acknowledging mistakes and being accountable for them, we can avoid the temptation to justify our behaviour and maintain consistency with our beliefs and attitudes.
In conclusion, developing effective critical thinking skills is essential for making informed decisions and navigating complex issues. However, there are several challenges that can hinder the development of critical thinking.
Confirmation bias, logical fallacies, emotions, lack of information or misinformation, groupthink, overconfidence bias, and cognitive dissonance are all common challenges that you may face when attempting to engage in critical thinking.
To overcome these challenges, it is important to develop strategies such as seeking out diverse perspectives, fact-checking and verifying information, and managing emotions. Additionally, it is crucial to remain open-minded and willing to consider alternative viewpoints, even if they challenge your existing beliefs. By recognizing and addressing these challenges, you can continue to improve your critical thinking skills and become more effective problem-solvers and decision-makers in your personal and professional lives.
You May Also Like…

The Importance of Critical Thinking when Using ChatGPT (and Other Large Language Models)
Artificial intelligence has made tremendous strides in recent years, allowing for the creation of conversational AI...

How to Critically Evaluate News and Media Sources
I think we all agree that access to information has never been easier. With the click of a button, we can access an...

Critical Thinking in the Workplace
Imagine that you're in a job interview and the interviewer asks you to describe a time when you had to solve a complex...
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- How to apply critical thinking in learning
Sometimes your university classes might feel like a maze of information. Consider critical thinking skills like a map that can lead the way.
Why do we need critical thinking?
Critical thinking is a type of thinking that requires continuous questioning, exploring answers, and making judgments. Critical thinking can help you:
- analyze information to comprehend more thoroughly
- approach problems systematically, identify root causes, and explore potential solutions
- make informed decisions by weighing various perspectives
- promote intellectual curiosity and self-reflection, leading to continuous learning, innovation, and personal development
What is the process of critical thinking?
1. understand .
Critical thinking starts with understanding the content that you are learning.
This step involves clarifying the logic and interrelations of the content by actively engaging with the materials (e.g., text, articles, and research papers). You can take notes, highlight key points, and make connections with prior knowledge to help you engage.
Ask yourself these questions to help you build your understanding:
- What is the structure?
- What is the main idea of the content?
- What is the evidence that supports any arguments?
- What is the conclusion?
2. Analyze
You need to assess the credibility, validity, and relevance of the information presented in the content. Consider the authors’ biases and potential limitations in the evidence.
Ask yourself questions in terms of why and how:
- What is the supporting evidence?
- Why do they use it as evidence?
- How does the data present support the conclusions?
- What method was used? Was it appropriate?
3. Evaluate
After analyzing the data and evidence you collected, make your evaluation of the evidence, results, and conclusions made in the content.
Consider the weaknesses and strengths of the ideas presented in the content to make informed decisions or suggest alternative solutions:
- What is the gap between the evidence and the conclusion?
- What is my position on the subject?
- What other approaches can I use?
When do you apply critical thinking and how can you improve these skills?
1. reading academic texts, articles, and research papers.
- analyze arguments
- assess the credibility and validity of evidence
- consider potential biases presented
- question the assumptions, methodologies, and the way they generate conclusions
2. Writing essays and theses
- demonstrate your understanding of the information, logic of evidence, and position on the topic
- include evidence or examples to support your ideas
- make your standing points clear by presenting information and providing reasons to support your arguments
- address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints
- explain why your perspective is more compelling than the opposing viewpoints
3. Attending lectures
- understand the content by previewing, active listening , and taking notes
- analyze your lecturer’s viewpoints by seeking whether sufficient data and resources are provided
- think about whether the ideas presented by the lecturer align with your values and beliefs
- talk about other perspectives with peers in discussions

Related blog posts
- A beginner's guide to successful labs
- A beginner's guide to note-taking
- 5 steps to get the most out of your next reading
- How do you create effective study questions?
- An epic approach to problem-based test questions
Recent blog posts
Blog topics.
- assignments (1)
- Graduate (2)
- Learning support (25)
- note-taking and reading (6)
- organizations (1)
- tests and exams (8)
- time management (3)
- Tips from students (6)
- undergraduate (27)
- university learning (10)
Blog posts by audience
- Current undergraduate students (27)
- Current graduate students (3)
- Future undergraduate students (9)
- Future graduate students (1)
Blog posts archive
- December (1)
- November (6)
- October (8)
- August (10)

Contact the Student Success Office
South Campus Hall, second floor University of Waterloo 519-888-4567 ext. 84410
Immigration Consulting
Book a same-day appointment on Portal or submit an online inquiry to receive immigration support.
Request an authorized leave from studies for immigration purposes.
Quick links
Current student resources
SSO staff links
Employment and volunteer opportunities
- Contact Waterloo
- Maps & Directions
- Accessibility
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations .

How to Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
Traditional tools and new technologies..
Posted September 29, 2023 | Reviewed by Lybi Ma

Technology provides access to vast information and makes daily life easier. Yet, too much reliance on technology potentially interferes with the acquisition and maintenance of critical thinking skills in several ways:
1. Information Overload : The constant influx of data can discourage deep critical thinking as we may come to rely on quick, surface-level information rather than delving deeply into a subject.
2. Shortened Attention Span: Frequent digital distractions can disrupt our ability for the sustained focus and concentration required for critical thinking.
3. Confirmatory Bias and Echo Chambers: Technology, including social media and personalized content algorithms, can reinforce confirmation bias . People are often exposed to information that aligns with their beliefs and opinions, making them less likely to encounter diverse perspectives and engage in critical thinking about opposing views.
4. Reduced Problem-Solving Opportunities: Technology often provides quick solutions to problems. While this benefits efficiency, it may discourage individuals from engaging in complex problem-solving, a fundamental aspect of critical thinking.
5. Loss of Research Skills: The ease of accessing information online can diminish traditional research skills, such as library research or in-depth reading. These skills are essential for critical thinking, as they involve evaluating sources, synthesizing information, and analyzing complex texts.
While technology can pose challenges to developing critical thinking skills, it's important to note that technology can also be a valuable tool for learning and skill development. It can provide access to educational resources, facilitate collaboration , and support critical thinking when used thoughtfully and intentionally. Balancing technology use with activities that encourage deep thinking and analysis is vital to lessening its potential adverse effects on critical thinking.
Writing is a traditional and powerful tool to exercise and improve your critical thinking skills. Consider these ways writing can help enhance critical thinking:
1. Clarity of Thought: Writing requires that you articulate your thoughts clearly and coherently. When you need to put your ideas on paper, you must organize them logically, which requires a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
2. Analysis and Evaluation: Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information. When you write, you often need to assess the validity and relevance of different sources, arguments, or pieces of evidence, which hone your critical thinking skills.
3. Problem-Solving: Writing can be a problem-solving exercise in itself. Whether crafting an argument, developing a thesis, or finding the right words to express your ideas, writing requires thinking critically about approaching these challenges effectively.
4. Research Skills: Good writing often involves research, and research requires critical thinking. You need to assess the credibility of sources, synthesize information, and draw conclusions based on the evidence you gather.
5. Argumentation: Constructing a persuasive argument in writing is a complex process requiring critical thinking. You must anticipate counterarguments, provide evidence to support your claims, and address potential weaknesses in your reasoning.
6. Revision and Editing: To be an influential writer, you must learn to read your work critically. Editing and revising requires evaluating your writing objectively, identifying areas that need improvement, and refining your ideas and arguments.
7. Problem Identification: In some cases, writing can help you identify problems or gaps in your thinking. As you write, you might realize that your arguments are not as strong as you initially thought or that you need more information to support your claims. This recognition of limitations is a crucial aspect of critical thinking.
Writing is a dynamic process that engages multiple facets of critical thinking. It has been a valuable tool used in education , business, and personal development for centuries.
Yet, this traditional approach of self-generated written thoughts is rapidly being supplanted by AI -generated writing tools like Chat GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer. With over 100 million users of Chat GPT alone, we cannot ignore its potential impact. How might the increasing reliance on AI-generated writing tools influence our critical thinking skills? The impact can vary depending on how the tools are used and the context in which they are employed.

Critical thinking involves evaluating information sources for credibility, relevance, and bias. If individuals consistently trust the information provided by chatbots without critically assessing its quality, it can hinder their development of critical thinking skills. This is especially true if they depend on the chatbot to provide answers without questioning or verifying the information. Relying solely on chatbots for answers may also reduce people's effort in problem-solving. Critical thinking often requires wrestling with complex problems, considering multiple perspectives, and generating creative solutions. If we default to chatbots for quick answers, we may miss opportunities to develop these skills.
However, it's essential to note that the impact of chatbots on critical thinking skills may not be entirely negative. These tools can also have positive effects:
1. Chatbots provide quick access to vast information, which can benefit research and problem-solving. When used as a supplement to critical thinking, they can enhance the efficiency of information retrieval.
2. Chatbots can sometimes assist in complex tasks by providing relevant data or suggestions. When individuals critically evaluate and integrate this information into their decision-making process, it can enhance their critical thinking.
3. Chatbots can be used as learning aids. They can provide explanations, examples, and guidance, which can support skill development and, when used effectively, encourage critical thinking.
In summary, the impact of chatbots on critical thinking skills depends on how we use them. The effect will be harmful if they become a crutch to avoid independent thought or analysis. However, they can be valuable resources when used as tools to facilitate and augment critical thinking and writing processes. Individuals must balance leveraging the convenience of chatbots and actively engaging in independent critical thinking and problem-solving to maintain and enhance their cognitive abilities. You can do that effectively through writing regularly.
Copyright 2023 Tara Well, PhD

Tara Well, Ph.D. , is a professor in the department of psychology at Barnard College of Columbia University.
- Find Counselling
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- Richmond - Tweed
- Newcastle - Maitland
- Canberra - ACT
- Sunshine Coast
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer

How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
Why Schools Need to Change Yes, We Can Define, Teach, and Assess Critical Thinking Skills

Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him) Director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute in Washington, DC
Today’s learners face an uncertain present and a rapidly changing future that demand far different skills and knowledge than were needed in the 20th century. We also know so much more about enabling deep, powerful learning than we ever did before. Our collective future depends on how well young people prepare for the challenges and opportunities of 21st-century life.
Critical thinking is a thing. We can define it; we can teach it; and we can assess it.
While the idea of teaching critical thinking has been bandied around in education circles since at least the time of John Dewey, it has taken greater prominence in the education debates with the advent of the term “21st century skills” and discussions of deeper learning. There is increasing agreement among education reformers that critical thinking is an essential ingredient for long-term success for all of our students.
However, there are still those in the education establishment and in the media who argue that critical thinking isn’t really a thing, or that these skills aren’t well defined and, even if they could be defined, they can’t be taught or assessed.
To those naysayers, I have to disagree. Critical thinking is a thing. We can define it; we can teach it; and we can assess it. In fact, as part of a multi-year Assessment for Learning Project , Two Rivers Public Charter School in Washington, D.C., has done just that.
Before I dive into what we have done, I want to acknowledge that some of the criticism has merit.
First, there are those that argue that critical thinking can only exist when students have a vast fund of knowledge. Meaning that a student cannot think critically if they don’t have something substantive about which to think. I agree. Students do need a robust foundation of core content knowledge to effectively think critically. Schools still have a responsibility for building students’ content knowledge.
However, I would argue that students don’t need to wait to think critically until after they have mastered some arbitrary amount of knowledge. They can start building critical thinking skills when they walk in the door. All students come to school with experience and knowledge which they can immediately think critically about. In fact, some of the thinking that they learn to do helps augment and solidify the discipline-specific academic knowledge that they are learning.
The second criticism is that critical thinking skills are always highly contextual. In this argument, the critics make the point that the types of thinking that students do in history is categorically different from the types of thinking students do in science or math. Thus, the idea of teaching broadly defined, content-neutral critical thinking skills is impossible. I agree that there are domain-specific thinking skills that students should learn in each discipline. However, I also believe that there are several generalizable skills that elementary school students can learn that have broad applicability to their academic and social lives. That is what we have done at Two Rivers.
Defining Critical Thinking Skills
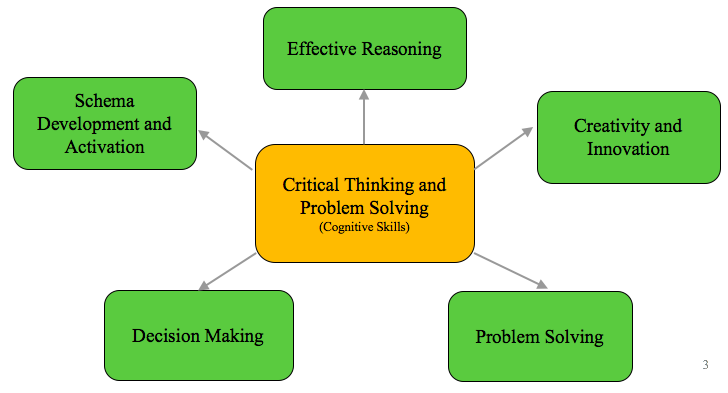
We began this work by first defining what we mean by critical thinking. After a review of the literature and looking at the practice at other schools, we identified five constructs that encompass a set of broadly applicable skills: schema development and activation; effective reasoning; creativity and innovation; problem solving; and decision making.
We then created rubrics to provide a concrete vision of what each of these constructs look like in practice. Working with the Stanford Center for Assessment, Learning and Equity (SCALE) , we refined these rubrics to capture clear and discrete skills.
For example, we defined effective reasoning as the skill of creating an evidence-based claim: students need to construct a claim, identify relevant support, link their support to their claim, and identify possible questions or counter claims. Rubrics provide an explicit vision of the skill of effective reasoning for students and teachers. By breaking the rubrics down for different grade bands, we have been able not only to describe what reasoning is but also to delineate how the skills develop in students from preschool through 8th grade.
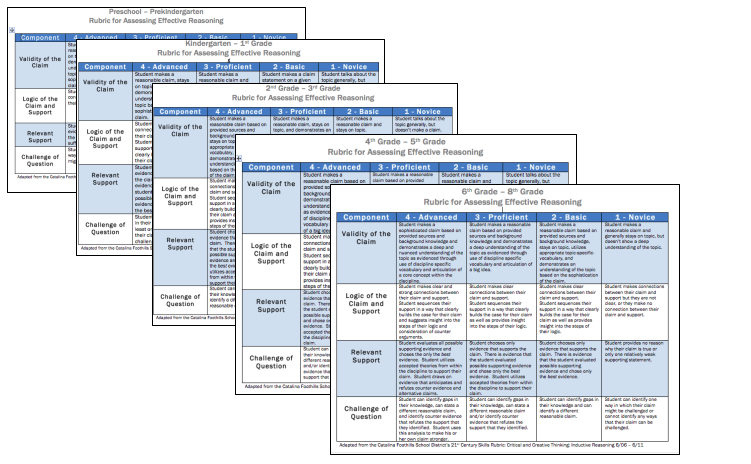
Before moving on, I want to freely acknowledge that in narrowly defining reasoning as the construction of evidence-based claims we have disregarded some elements of reasoning that students can and should learn. For example, the difference between constructing claims through deductive versus inductive means is not highlighted in our definition. However, by privileging a definition that has broad applicability across disciplines, we are able to gain traction in developing the roots of critical thinking. In this case, to formulate well-supported claims or arguments.
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills
The definitions of critical thinking constructs were only useful to us in as much as they translated into practical skills that teachers could teach and students could learn and use. Consequently, we have found that to teach a set of cognitive skills, we needed thinking routines that defined the regular application of these critical thinking and problem-solving skills across domains. Building on Harvard’s Project Zero Visible Thinking work, we have named routines aligned with each of our constructs.
For example, with the construct of effective reasoning, we aligned the Claim-Support-Question thinking routine to our rubric. Teachers then were able to teach students that whenever they were making an argument, the norm in the class was to use the routine in constructing their claim and support. The flexibility of the routine has allowed us to apply it from preschool through 8th grade and across disciplines from science to economics and from math to literacy.

Kathryn Mancino, a 5th grade teacher at Two Rivers, has deliberately taught three of our thinking routines to students using the anchor charts above. Her charts name the components of each routine and has a place for students to record when they’ve used it and what they have figured out about the routine. By using this structure with a chart that can be added to throughout the year, students see the routines as broadly applicable across disciplines and are able to refine their application over time.
Assessing Critical Thinking Skills
By defining specific constructs of critical thinking and building thinking routines that support their implementation in classrooms, we have operated under the assumption that students are developing skills that they will be able to transfer to other settings. However, we recognized both the importance and the challenge of gathering reliable data to confirm this.
With this in mind, we have developed a series of short performance tasks around novel discipline-neutral contexts in which students can apply the constructs of thinking. Through these tasks, we have been able to provide an opportunity for students to demonstrate their ability to transfer the types of thinking beyond the original classroom setting. Once again, we have worked with SCALE to define tasks where students easily access the content but where the cognitive lift requires them to demonstrate their thinking abilities.
These assessments demonstrate that it is possible to capture meaningful data on students’ critical thinking abilities. They are not intended to be high stakes accountability measures. Instead, they are designed to give students, teachers, and school leaders discrete formative data on hard to measure skills.
While it is clearly difficult, and we have not solved all of the challenges to scaling assessments of critical thinking, we can define, teach, and assess these skills . In fact, knowing how important they are for the economy of the future and our democracy, it is essential that we do.
Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him)
Director of the two rivers learning institute.
Jeff Heyck-Williams is the director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute and a founder of Two Rivers Public Charter School. He has led work around creating school-wide cultures of mathematics, developing assessments of critical thinking and problem-solving, and supporting project-based learning.
Read More About Why Schools Need to Change

Bring Your Vision for Student Success to Life with NGLC and Bravely
March 13, 2024

For Ethical AI, Listen to Teachers
Jason Wilmot
October 23, 2023

Turning School Libraries into Discipline Centers Is Not the Answer to Disruptive Classroom Behavior
Stephanie McGary
October 4, 2023

The Ultimate Guide To Developing Critical Thinking Skills For Success
Table Of Contents:
What is Critical Thinking?
What are critical thinking skills, and why are they important, tips to develop critical thinking skills, how to practice critical thinking skills at work, critical thinking example in real-life, applying critical thinking skills for success.
Critical thinking is a fundamental cognitive skill that involves the ability to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information in a systematic and rational manner. This section will delve into the core components of critical thinking, exploring its significance in fostering intellectual development and enhancing decision-making processes. Understanding the principles of critical thinking lays the groundwork for the subsequent sections that elaborate on its practical application in various aspects of life.

Critical thinking skills refer to the cognitive abilities that enable individuals to analyze, evaluate, and interpret information effectively. These skills encompass a range of intellectual processes, including logical reasoning, problem-solving, and the capacity to make well-informed decisions based on careful career assessment and understanding.
The importance of developing critical thinking skills lies in their transformative impact on both personal and professional realms. These skills empower individuals to navigate the complexities of the modern world with clarity and confidence, enabling them to:
- Foster Independent Thought: Critical thinking skills encourage individuals to question assumptions, challenge preconceived notions, and approach information with a discerning mindset. By fostering independent thought, these skills cultivate a deeper understanding of complex issues and promote intellectual autonomy.
- Enhance Problem-Solving Abilities: The ability to think critically equips individuals with the tools to identify and solve complex problems through logical analysis and innovative approaches. By honing critical thinking skills, individuals can devise effective strategies to address challenges, both within their personal lives and in professional contexts.
- Navigate Ambiguity and Uncertainty: In an ever-evolving and unpredictable world, critical thinking skills enable individuals to navigate ambiguity and uncertainty with confidence. These skills promote adaptability and resilience, allowing individuals to approach unfamiliar situations with a rational and analytical mindset.
- Make Informed Decisions: The cultivation of critical thinking skills empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions based on comprehensive analysis and thoughtful evaluation of available information. By developing the capacity to assess the validity and reliability of data, individuals can make sound judgments and choices that align with their goals and values.
- Promote Effective Communication: Critical thinking skills facilitate effective communication by enabling individuals to articulate their thoughts clearly, express ideas coherently, and engage in constructive discourse. These skills foster the ability to convey complex concepts and information in a manner that is accessible and engaging to diverse audiences.
- Encourage Lifelong Learning: By encouraging a mindset of curiosity and intellectual exploration, critical thinking skills promote a lifelong commitment to learning and personal development. Individuals who possess strong critical thinking skills are more inclined to seek out new knowledge, engage in continuous self-improvement, and adapt to the changing demands of the contemporary world.
Vati is a dynamic online career planning platform dedicated to fostering the development of critical thinking skills. With a comprehensive range of interactive courses, engaging resources, and personalized learning modules, VATI empowers learners to cultivate analytical acumen and navigate complex challenges with confidence and clarity.

Developing critical thinking skills is a dynamic process that involves fostering a combination of cognitive abilities and adopting a deliberate approach to intellectual growth. Here are some effective strategies to help you develop and enhance your critical thinking skills:
- Cultivate a questioning mindset: Encourage yourself to question assumptions, biases, and preconceived notions. Develop a habit of critically evaluating information and perspectives, fostering a more analytical and discerning approach to understanding complex issues.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Actively seek out opportunities to engage with diverse viewpoints and opinions. Embrace discussions and debates that challenge your perspectives, and strive to understand alternative viewpoints, fostering a more comprehensive and inclusive understanding of complex topics.
- Practice active listening: Hone your critical thinking skills by actively listening to others and seeking to understand their viewpoints without judgment. Pay attention to the underlying motivations and reasoning behind their arguments, enabling you to develop a more nuanced and empathetic understanding of different perspectives.
- Analyze and evaluate information: Practice analyzing and evaluating information from various sources, discerning credible and reliable information from misleading or biased sources. Develop the ability to identify logical fallacies, assess the validity of data, and differentiate between facts and opinions, fostering a more informed and evidence-based approach to critical thinking.
- Foster problem-solving skills: Engage in activities and challenges that require innovative problem-solving and logical reasoning. Practice approaching complex problems from multiple angles, exploring alternative solutions, and assessing the potential implications of each approach, thus fostering a more systematic and adaptive problem-solving approach.
- Embrace intellectual humility: Cultivate humility in your intellectual pursuits by acknowledging the limitations of your knowledge and expertise. Embrace the opportunity to learn from others and recognize that continuous learning and growth are essential aspects of developing robust critical thinking skills.
- Reflect on your thought processes: Allocate time for self-reflection and introspection to assess your cognitive processes and decision-making strategies. Reflective thinking enables you to gain insights into your reasoning patterns, identify areas for improvement, and refine your critical thinking skills through self-awareness and self-assessment.
- Apply critical thinking in real-life scenarios: Practice applying critical thinking skills to everyday situations, such as making decisions, evaluating information, and solving problems. Actively apply critical thinking methodologies to various aspects of your life, thereby honing your cognitive abilities and fostering a more analytical and discerning approach to navigating challenges and making informed decisions.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine and actively engaging in activities that promote critical thinking, you can cultivate a more analytical, adaptable, and insightful mindset, thus empowering yourself to navigate complex challenges and make well-informed decisions in both personal and professional contexts.

Practicing critical thinking skills at work is crucial for fostering a productive and innovative work environment. Here are some effective strategies to help you apply and enhance your critical thinking skills in the workplace:
- Analyze complex problems: Identify and analyze complex challenges or issues within your work environment. Break down the problem into manageable components, assess the underlying factors contributing to the issue, and develop a strategic plan to address it systematically and effectively.
- Evaluate information and data: Practice evaluating the credibility and reliability of information and data relevant to your work. Scrutinize reports, research findings, and market trends, and assess the validity of the information to make informed decisions and recommendations based on well-founded evidence.
- Engage in collaborative decision-making: Participate in collaborative decision-making processes by sharing your insights and perspectives with your colleagues. Encourage open discussions that involve diverse viewpoints and constructive debates, fostering a collaborative environment that values critical thinking and collective problem-solving.
- Anticipate potential challenges: Anticipate potential challenges or obstacles that may arise in your projects or tasks. Develop contingency plans and proactive strategies to mitigate risks and uncertainties, demonstrating your ability to think ahead and adapt to changing circumstances effectively.
- Seek feedback and constructive criticism: Welcome feedback and constructive criticism from your colleagues and supervisors. Actively solicit input on your ideas, proposals, and problem-solving approaches, and use the feedback as an opportunity to refine your critical thinking skills and enhance your decision-making capabilities.
- Implement innovative solutions: Identify opportunities to implement innovative solutions and approaches to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and foster growth within your organization. Encourage yourself to think creatively and propose novel ideas that address existing challenges or capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Foster a learning culture: Advocate for a learning culture within your workplace by encouraging continuous education and professional development. Engage in training programs, workshops, and seminars that promote critical thinking and encourage your colleagues to participate, fostering a culture of intellectual growth and innovation.
- Reflect on your decision-making processes: Allocate time for self-reflection and introspection to evaluate your decision-making processes and outcomes. Reflect on the effectiveness of your critical thinking approaches, identify areas for improvement, and implement strategies to refine your skills and enhance your contributions to the workplace.
By actively practicing these strategies, you can cultivate a workplace environment that values critical thinking, fosters innovation, and encourages proactive problem-solving, thereby contributing to the overall success and growth of your organization.

A compelling real-life example that illustrates the application of critical thinking is the decision-making process involved in a company’s expansion into a new market. Imagine a mid-sized technology firm considering the prospect of entering a foreign market to broaden its customer base and increase its global presence. The company’s leadership must apply critical thinking skills to assess the potential risks, benefits, and challenges associated with this strategic move.
In this scenario, the company’s executives engage in a comprehensive analysis of various factors, including market trends, consumer behavior, regulatory frameworks, and potential competitors within the target market. They critically evaluate the economic stability, cultural nuances, and political climate of the prospective region, aiming to understand the feasibility and sustainability of the expansion.
Through collaborative discussions and rigorous evaluation of market research data, the executives identify potential challenges, such as cultural barriers, regulatory complexities, and shifting consumer preferences. They critically analyze the implications of these challenges on the company’s resources, operations, and brand reputation, considering the long-term impact of their decisions on the company’s growth trajectory and financial stability.
Applying critical thinking skills, the company’s leadership devises a strategic plan that accounts for potential risks and challenges while leveraging the company’s strengths and competitive advantages. They develop contingency plans to mitigate potential risks, establish key performance indicators to monitor the progress of the expansion, and allocate resources effectively to support the successful entry into the new market.
By incorporating critical thinking into the decision-making process, the company’s leadership demonstrates their ability to assess complex information, evaluate potential outcomes, and make informed, strategic decisions that align with the company’s long-term goals and vision. This real-life example highlights the practical application of critical thinking in a business context, emphasizing the importance of thoughtful analysis, proactive problem-solving, and strategic planning in achieving successful and sustainable business expansion.
In the realms of education, career advancement, and personal growth, the application of critical thinking skills is pivotal for achieving success and reaching one’s full potential. By applying critical thinking methodologies to everyday decision-making, problem-solving, and strategic career planning process , individuals can position themselves to thrive in dynamic and competitive environments, fostering a culture of innovation and progress.
As the world continues to evolve and present new challenges, the development of critical thinking skills remains a cornerstone for personal and professional growth. By following the strategies outlined in this ultimate guide, individuals can harness the power of critical thinking to navigate complexities with clarity, make informed decisions, and contribute meaningfully to the advancement of their communities and organizations. Through a commitment to continuous learning , a questioning mindset, and a dedication to analytical evaluation, individuals can unlock their full potential and pave the way for a successful and fulfilling journey in both their personal and professional lives.
Previous Post Top Universities For Bachelors In Australia : Exploring the Finest
Next post how to apply for bachelor degree in australian universities: a step-by-step guide for international students, recommended for you.

12 Transferable Skills Employers Look For In 2024: Navigating The Evolving Job Landscape


Author Vati Team
Comments are closed.
- Vati AI Assist
- Vati Dashboard
- Partner with us
- Vati Community
- Request a Feature
- Help Center
© 2024 Vati | Career Assessment & Planning Platform | CAPP.
- google-plus
- Explore your Career Choices Choose how you prefer to work with your interest, profession, or degree, and get a list of possible career options to explore.
- Explore by Profession Discover the best profession for your skills and interests with in-depth profession overviews.
- Explore by Degree Discover what is best for you based on your degree choices, your skills, and interests.
- Explore by Interest Explore nearly 1000s of interest based careers, take a career assessment, and search the fastest growing careers.
- Career Assessment the Right Way Vati NEXT helps you choose, change or develop your career plan. You can use them as a starting point in your journey to get to know yourself better and explore the wide range of career opportunities available to you.
- Interest based Assessment Identify careers that are tailored to your interests, find out if you prefer directive, social, methodical, objective or innovative work.
- Activity based Assessment Understand how you work with data, people and things, find out how you see yourself working with these three components.
- Abilities based Assessment Find out which careers you’re most likely to succeed in, test your strength level in a variety of different areas, See what careers match your abilities
- Career Guide & Resources
- Parnter With Us
Come see us
422 Richards St Unit 170, Vancouver, BC V6B 2Z4
T: +1-415-481-3385 E: [email protected]
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Collaboration |
- How to build your critical thinking ski ...
How to build your critical thinking skills in 7 steps (with examples)

Critical thinking is, well, critical. By building these skills, you improve your ability to analyze information and come to the best decision possible. In this article, we cover the basics of critical thinking, as well as the seven steps you can use to implement the full critical thinking process.
Critical thinking comes from asking the right questions to come to the best conclusion possible. Strong critical thinkers analyze information from a variety of viewpoints in order to identify the best course of action.
Don’t worry if you don’t think you have strong critical thinking abilities. In this article, we’ll help you build a foundation for critical thinking so you can absorb, analyze, and make informed decisions.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to collect and analyze information to come to a conclusion. Being able to think critically is important in virtually every industry and applicable across a wide range of positions. That’s because critical thinking isn’t subject-specific—rather, it’s your ability to parse through information, data, statistics, and other details in order to identify a satisfactory solution.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

Top 8 critical thinking skills
Like most soft skills, critical thinking isn’t something you can take a class to learn. Rather, this skill consists of a variety of interpersonal and analytical skills. Developing critical thinking is more about learning to embrace open-mindedness and bringing analytical thinking to your problem framing process.
In no particular order, the eight most important critical thinking skills are:
Analytical thinking: Part of critical thinking is evaluating data from multiple sources in order to come to the best conclusions. Analytical thinking allows people to reject bias and strive to gather and consume information to come to the best conclusion.
Open-mindedness: This critical thinking skill helps you analyze and process information to come to an unbiased conclusion. Part of the critical thinking process is letting your personal biases go and coming to a conclusion based on all of the information.
Problem solving : Because critical thinking emphasizes coming to the best conclusion based on all of the available information, it’s a key part of problem solving. When used correctly, critical thinking helps you solve any problem—from a workplace challenge to difficulties in everyday life.
Self-regulation: Self-regulation refers to the ability to regulate your thoughts and set aside any personal biases to come to the best conclusion. In order to be an effective critical thinker, you need to question the information you have and the decisions you favor—only then can you come to the best conclusion.
Observation: Observation skills help critical thinkers look for things beyond face value. To be a critical thinker you need to embrace multiple points of view, and you can use observation skills to identify potential problems.
Interpretation: Not all data is made equal—and critical thinkers know this. In addition to gathering information, it’s important to evaluate which information is important and relevant to your situation. That way, you can draw the best conclusions from the data you’ve collected.
Evaluation: When you attempt to answer a hard question, there is rarely an obvious answer. Even though critical thinking emphasizes putting your biases aside, you need to be able to confidently make a decision based on the data you have available.
Communication: Once a decision has been made, you also need to share this decision with other stakeholders. Effective workplace communication includes presenting evidence and supporting your conclusion—especially if there are a variety of different possible solutions.
7 steps to critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that you can build by following these seven steps. The seven steps to critical thinking help you ensure you’re approaching a problem from the right angle, considering every alternative, and coming to an unbiased conclusion.
First things first: When to use the 7 step critical thinking process
There’s a lot that goes into the full critical thinking process, and not every decision needs to be this thought out. Sometimes, it’s enough to put aside bias and approach a process logically. In other, more complex cases, the best way to identify the ideal outcome is to go through the entire critical thinking process.
The seven-step critical thinking process is useful for complex decisions in areas you are less familiar with. Alternatively, the seven critical thinking steps can help you look at a problem you’re familiar with from a different angle, without any bias.
If you need to make a less complex decision, consider another problem solving strategy instead. Decision matrices are a great way to identify the best option between different choices. Check out our article on 7 steps to creating a decision matrix .
1. Identify the problem
Before you put those critical thinking skills to work, you first need to identify the problem you’re solving. This step includes taking a look at the problem from a few different perspectives and asking questions like:
What’s happening?
Why is this happening?
What assumptions am I making?
At first glance, how do I think we can solve this problem?
A big part of developing your critical thinking skills is learning how to come to unbiased conclusions. In order to do that, you first need to acknowledge the biases that you currently have. Does someone on your team think they know the answer? Are you making assumptions that aren’t necessarily true? Identifying these details helps you later on in the process.
2. Research
At this point, you likely have a general idea of the problem—but in order to come up with the best solution, you need to dig deeper.
During the research process, collect information relating to the problem, including data, statistics, historical project information, team input, and more. Make sure you gather information from a variety of sources, especially if those sources go against your personal ideas about what the problem is or how to solve it.
Gathering varied information is essential for your ability to apply the critical thinking process. If you don’t get enough information, your ability to make a final decision will be skewed. Remember that critical thinking is about helping you identify the objective best conclusion. You aren’t going with your gut—you’re doing research to find the best option
3. Determine data relevance
Just as it’s important to gather a variety of information, it is also important to determine how relevant the different information sources are. After all, just because there is data doesn’t mean it’s relevant.
Once you’ve gathered all of the information, sift through the noise and identify what information is relevant and what information isn’t. Synthesizing all of this information and establishing significance helps you weigh different data sources and come to the best conclusion later on in the critical thinking process.
To determine data relevance, ask yourself:
How reliable is this information?
How significant is this information?
Is this information outdated? Is it specialized in a specific field?
4. Ask questions
One of the most useful parts of the critical thinking process is coming to a decision without bias. In order to do so, you need to take a step back from the process and challenge the assumptions you’re making.
We all have bias—and that isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Unconscious biases (also known as cognitive biases) often serve as mental shortcuts to simplify problem solving and aid decision making. But even when biases aren’t inherently bad, you must be aware of your biases in order to put them aside when necessary.
Before coming to a solution, ask yourself:
Am I making any assumptions about this information?
Are there additional variables I haven’t considered?
Have I evaluated the information from every perspective?
Are there any viewpoints I missed?
5. Identify the best solution
Finally, you’re ready to come to a conclusion. To identify the best solution, draw connections between causes and effects. Use the facts you’ve gathered to evaluate the most objective conclusion.
Keep in mind that there may be more than one solution. Often, the problems you’re facing are complex and intricate. The critical thinking process doesn’t necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision.
6. Present your solution
Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers. It isn’t enough to think for yourself—you also need to share your conclusion with other project stakeholders. If there are multiple solutions, present them all. There may be a case where you implement one solution, then test to see if it works before implementing another solution.
7. Analyze your decision
The seven-step critical thinking process yields a result—and you then need to put that solution into place. After you’ve implemented your decision, evaluate whether or not it was effective. Did it solve the initial problem? What lessons—whether positive or negative—can you learn from this experience to improve your critical thinking for next time?
Depending on how your team shares information, consider documenting lessons learned in a central source of truth. That way, team members that are making similar or related decisions in the future can understand why you made the decision you made and what the outcome was.
Example of critical thinking in the workplace
Imagine you work in user experience design (UX). Your team is focused on pricing and packaging and ensuring customers have a clear understanding of the different services your company offers. Here’s how to apply the critical thinking process in the workplace in seven steps:
Start by identifying the problem
Your current pricing page isn’t performing as well as you want. You’ve heard from customers that your services aren’t clear, and that the page doesn’t answer the questions they have. This page is really important for your company, since it’s where your customers sign up for your service. You and your team have a few theories about why your current page isn’t performing well, but you decide to apply the critical thinking process to ensure you come to the best decision for the page.
Gather information about how the problem started
Part of identifying the problem includes understanding how the problem started. The pricing and packaging page is important—so when your team initially designed the page, they certainly put a lot of thought into it. Before you begin researching how to improve the page, ask yourself:
Why did you design the pricing page the way you did?
Which stakeholders need to be involved in the decision making process?
Where are users getting stuck on the page?
Are any features currently working?
Then, you research
In addition to understanding the history of the pricing and packaging page, it’s important to understand what works well. Part of this research means taking a look at what your competitor’s pricing pages look like.
Ask yourself:
How have our competitors set up their pricing pages?
Are there any pricing page best practices?
How does color, positioning, and animation impact navigation?
Are there any standard page layouts customers expect to see?
Organize and analyze information
You’ve gathered all of the information you need—now you need to organize and analyze it. What trends, if any, are you noticing? Is there any particularly relevant or important information that you have to consider?
Ask open-ended questions to reduce bias
In the case of critical thinking, it’s important to address and set bias aside as much as possible. Ask yourself:
Is there anything I’m missing?
Have I connected with the right stakeholders?
Are there any other viewpoints I should consider?
Determine the best solution for your team
You now have all of the information you need to design the best pricing page. Depending on the complexity of the design, you may want to design a few options to present to a small group of customers or A/B test on the live website.
Present your solution to stakeholders
Critical thinking can help you in every element of your life, but in the workplace, you must also involve key project stakeholders . Stakeholders help you determine next steps, like whether you’ll A/B test the page first. Depending on the complexity of the issue, consider hosting a meeting or sharing a status report to get everyone on the same page.
Analyze the results
No process is complete without evaluating the results. Once the new page has been live for some time, evaluate whether it did better than the previous page. What worked? What didn’t? This also helps you make better critical decisions later on.
Critically successful
Critical thinking takes time to build, but with effort and patience you can apply an unbiased, analytical mind to any situation. Critical thinking makes up one of many soft skills that makes you an effective team member, manager, and worker. If you’re looking to hone your skills further, read our article on the 25 project management skills you need to succeed .
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

Encyclopedia of Sustainability in Higher Education pp 1–6 Cite as
Critical Thinking and Sustainable Development
- Denise Minott 2 ,
- Therese Ferguson 3 &
- Garth Minott 4
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 07 February 2019
1098 Accesses
3 Citations
Critical thinking and sustainable development is an approach to meaningful dialogue for social, economic, political and environmental problem-solving and decision-making for current and future generations and the practice of engaging in analytical dialogue and problem-solving mechanisms, through active mental and emotional inquiry, for the transformation of individuals, communities and institutions.
Introduction
Critical thinking skills, acquired through a process of education, can equip learners with the ability to analyze and solve problems and to make decisions. Societal problems such as crime, poverty, and pollution are sometimes the result of the decisions made at a policy level in government and business which were not subject to critical thinking aided by research and due diligence in implementation. In such instances, for problems to be solved, adequate and relevant knowledge, an open disposition, and critical thinking skills are required. The decisions born out of...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Bailin S, Case R, Coombs JR, Daniels LB (2010) Common misconceptions of critical thinking. J Curric Stud 31(3):269–283
Article Google Scholar
Carroll J, Minkler M (2000) Freire's message for social workers: looking back, looking ahead. J Community Pract 8(1):21–36
Darder A (2017) Reinventing Paulo Freire: a pedagogy of love. Routledge Taylor and Francis Group, London/New York
Book Google Scholar
Duncan-Andrade JMR, Morrell E (2008) The art of critical pedagogy: possibilities for moving from theory to practice in urban schools. Peter Lang Publishing, Inc, New York
Emas R (2015) Brief for GSDR 2015. The concept of sustainable development: definition and defining principles . Retrieved from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5839GSDR%202015_SD_concept_definiton_rev.pdf
Ennis R (1991) Critical thinking: a streamlined conception. Teach Philos 14(1):5–24
Erskine NL (2008) Black theology and pedagogy. Palgrave/Macmillan, New York
Fien J, Tilbury D (2002) The global challenge of sustainability. Education and sustainability: responding to the global challenge. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/29452097_The_global_challenge_of_sustainability
Freire P (2001) Pedagogy of freedom: ethics, democracy and civic courage. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc., Lanham/Boulder/New York/Oxford
Google Scholar
Giroux HA (2011) On critical pedagogy. The Continuum International Publishing Group, New York
Holden E, Linnerud K, Banister D (2016) The imperatives of sustainable development. Sustain Dev 25(3):213–226
Luke C, Gore J (eds) (2014) Feminisms and critical pedagogy. Routledge Taylor and Francis Group, London/New York
Nixon-Ponder S (1995) Using problem-posing dialogue in adult literacy education. Teacher to teacher. Ohio Literacy Resource Center. Retrieved from https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/4112672
Parihar R (2017) Concept of education. Retrieved from https://rajnursing.blogspot.com/2017/09/concept-of-education.html
Paul R, Elder L (2008) The miniature guide to critical thinking concepts and tools. Foundation for Critical Thinking Press, Dillon Beach, CA
Rieckmann M (2011) Developing key competencies for sustainable development. Retrieved from https://www.leuphana.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Forschungseinrichtungen/infu/files/pdf/vortraege/Rieckmann_Competencies_and_Sustainability.pdf
Ruggiero VR (2012) The art of thinking: a guide to critical and creative thought, 10th edn. Longman, New York
Sachs J (2015) The age of sustainable development. Columbia University Press, New York
Siegel H (1988) Educating reason: Rationality, critical thinking and education. Routledge & Metheun, New York
Sunday BA (2012) Developing critical thinking skills in students: a mandate for higher education in Nigeria. Eur J Educ Res 1(2):155–161
Thomas I (2010) Critical thinking, transformative learning, sustainable education and problem – based learning in universities. J Transform Educ 7(3):245–264
United Nations (2016) Global sustainable development report 2016. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, New York. Retrieved from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/2328Global%20Sustainable%20development%20report%202016%20 (final).pdf
Wint E, Cooper C (eds) (2003) Bob Marley: the man and his music. Arawak Publications, Kingston
Wint E, Healy L (eds) (1998) Social work reality: illustrative case studies. Issue 2. Canoe Press/University of the West Indies, Kingston
World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) (1987) Our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Mico University College, Kingston, Jamaica
Denise Minott
School of Education, The University of the West Indies, Kingston, Jamaica
Therese Ferguson
United Theological College of the West Indies, Kingston, Jamaica
Garth Minott
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Denise Minott .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Life Sciences, Hamburg University of Applied Sciences Faculty of Life Sciences, Hamburg, Germany
Walter Leal Filho
Section Editor information
School of Architecture and Design,Program Manager, Master of Disaster Design and Development, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Judy Rogers
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Minott, D., Ferguson, T., Minott, G. (2019). Critical Thinking and Sustainable Development. In: Leal Filho, W. (eds) Encyclopedia of Sustainability in Higher Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63951-2_529-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63951-2_529-1
Received : 12 November 2018
Accepted : 21 January 2019
Published : 07 February 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-63951-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-63951-2
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PMC10300824

An Evaluative Review of Barriers to Critical Thinking in Educational and Real-World Settings
Associated data.
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Though a wide array of definitions and conceptualisations of critical thinking have been offered in the past, further elaboration on some concepts is required, particularly with respect to various factors that may impede an individual’s application of critical thinking, such as in the case of reflective judgment. These barriers include varying levels of epistemological engagement or understanding, issues pertaining to heuristic-based thinking and intuitive judgment, as well as emotional and biased thinking. The aim of this review is to discuss such barriers and evaluate their impact on critical thinking in light of perspectives from research in an effort to reinforce the ‘completeness’ of extant critical thinking frameworks and to enhance the potential benefits of implementation in real-world settings. Recommendations and implications for overcoming such barriers are also discussed and evaluated.
1. Introduction
Critical thinking (CT) is a metacognitive process—consisting of a number of skills and dispositions—that, through purposeful, self-regulatory reflective judgment, increases the chances of producing a logical solution to a problem or a valid conclusion to an argument ( Dwyer 2017 , 2020 ; Dwyer et al. 2012 , 2014 , 2015 , 2016 ; Dwyer and Walsh 2019 ; Quinn et al. 2020 ).
CT has long been identified as a desired outcome of education ( Bezanilla et al. 2019 ; Butler et al. 2012 ; Dwyer 2017 ; Ennis 2018 ), given that it facilitates a more complex understanding of information ( Dwyer et al. 2012 ; Halpern 2014 ), better judgment and decision-making ( Gambrill 2006 ) and less dependence on cognitive bias and heuristic thinking ( Facione and Facione 2001 ; McGuinness 2013 ). A vast body of research (e.g., Dwyer et al. 2012 ; Gadzella 1996 ; Hitchcock 2004 ; Reed and Kromrey 2001 ; Rimiene 2002 ; Solon 2007 ), including various meta-analyses (e.g., Abrami et al. 2008 , 2015 ; Niu et al. 2013 ; Ortiz 2007 ), indicates that CT can be enhanced through targeted, explicit instruction. Though CT can be taught in domain-specific areas, its domain-generality means that it can be taught across disciplines and in relation to real-world scenarios ( Dwyer 2011 , 2017 ; Dwyer and Eigenauer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 ; Gabennesch 2006 ; Halpern 2014 ). Indeed, the positive outcomes associated with CT transcend educational settings into real-world, everyday situations, which is important because CT is necessary for a variety of social and interpersonal contexts where good decision-making and problem-solving are needed on a daily basis ( Ku 2009 ). However, regardless of domain-specificity or domain-generality of instruction, the transferability of CT application has been an issue in CT research (e.g., see Dumitru 2012 ). This is an important consideration because issues with transferability—for example, in real-world settings—may imply something lacking in CT instruction.
In light of the large, aforementioned body of research focusing on enhancing CT through instruction, a growing body of research has also evaluated the manner in which CT instruction is delivered (e.g., Abrami et al. 2008 , 2015 ; Ahern et al. 2019 ; Cáceres et al. 2020 ; Byerly 2019 ; Dwyer and Eigenauer 2017 ), along with additional considerations for and the barriers to such education, faced by teachers and students alike (e.g., Aliakbari and Sadeghdaghighi 2013 ; Cáceres et al. 2020 ; Cornell et al. 2011 ; Lloyd and Bahr 2010 ; Ma and Liu 2022 ; Ma and Luo 2021 ; Rear 2019 ; Saleh 2019 ); for example, those regarding conceptualisation, beliefs about CT, having feasible time for CT application and CT’s aforementioned transferability. However, there is a significant lack of research investigating barriers to CT application by individuals in real-world settings, even by those who have enjoyed benefits from previous CT instruction. Thus, perhaps the previously conjectured ‘something lacking in CT instruction’ refers to, in conjunction with the teaching of what CT consists of, making clear to students what barriers to CT application we face.
Simply, CT instruction is designed in such a way as to enhance the likelihood of positive decision-making outcomes. However, there are a variety of barriers that can impede an individual’s application of CT, regardless of past instruction with respect to ‘how to conduct CT’. For example, an individual might be regarded as a ‘critical thinker’ because they apply it in a vast majority of appropriate scenarios, but that does not ensure that they apply CT in all such appropriate scenarios. What keeps them from applying CT in those scenarios might well be one of a number of barriers to CT that often go unaddressed in CT instruction, particularly if such instruction is exclusively focused on skills and dispositions. Perhaps too much focus is placed on what educators are teaching their students to do in their CT courses as opposed to what educators should be recommending their students to look out for or advising what they should not be doing. That is, perhaps just as important for understanding what CT is and how it is conducted (i.e., knowing what to do) is a genuine awareness of the various factors and processes that can impede CT; and so, for an individual to think critically, they must know what to look out for and be able to monitor for such barriers to CT application.
To clarify, thought has not changed regarding what CT is or the cognitive/metacognitive processes at its foundation (e.g., see Dwyer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2014 ; Ennis 1987 , 1996 , 1998 ; Facione 1990 ; Halpern 2014 ; Paul 1993 ; Paul and Elder 2008 ); rather, additional consideration of issues that have potential to negatively impact CT is required, such as those pertaining to epistemological engagement; intuitive judgment; as well as emotional and biased thinking. This notion has been made clear through what might be perceived of as a ‘loud shout’ for CT over at least the past 10–15 years in light of growing political, economic, social, and health-related concerns (e.g., ‘fake news’, gaps between political views in the general population, various social movements and the COVID-19 pandemic). Indeed, there is a dearth of research on barriers to CT ( Haynes et al. 2016 ; Lloyd and Bahr 2010 ; Mangena and Chabeli 2005 ; Rowe et al. 2015 ). As a result, this evaluative perspective review aims to provide an impetus for updating the manner in which CT education is approached and, perhaps most importantly, applied in real-world settings—through further identifying and elaborating on specific barriers of concern in order to reinforce the ‘completeness’ of extant CT frameworks and to enhance the potential benefits of their implementation 1 .
2. Barriers to Critical Thinking
2.1. inadequate skills and dispositions.
In order to better understand the various barriers to CT that will be discussed, the manner in which CT is conceptualised must first be revisited. Though debate over its definition and what components are necessary to think critically has existed over the 80-plus years since the term’s coining (i.e., Glaser 1941 ), it is generally accepted that CT consists of two main components: skills and dispositions ( Dwyer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2012 , 2014 ; Ennis 1996 , 1998 ; Facione 1990 ; Facione et al. 2002 ; Halpern 2014 ; Ku and Ho 2010a ; Perkins and Ritchhart 2004 ; Quinn et al. 2020 ). CT skills—analysis, evaluation, and inference—refer to the higher-order, cognitive, ‘task-based’ processes necessary to conduct CT (e.g., see Dwyer et al. 2014 ; Facione 1990 ). CT dispositions have been described as inclinations, tendencies, or willingness to perform a given thinking skill (e.g., see Dwyer et al. 2016 ; Siegel 1999 ; Valenzuela et al. 2011 ), which may relate to attitudinal and intellectual habits of thinking, as well as motivational processes ( Ennis 1996 ; Norris 1994 ; Paul and Elder 2008 ; Perkins et al. 1993 ; Valenzuela et al. 2011 ). The relationship between CT skills and dispositions has been argued to be mutually dependent. As a result, overemphasising or encouraging the development of one over the other is a barrier to CT as a whole. Though this may seem obvious, it remains the case that CT instruction often places added emphasis on skills simply because they can be taught (though that does not ensure that everyone has or will be taught such skills), whereas dispositions are ‘trickier’ (e.g., see Dwyer 2017 ; Ku and Ho 2010a ). That is, it is unlikely that simply ‘teaching’ students to be motivated towards CT or to value it over short-instructional periods will actually meaningfully enhance it. Moreover, debate exists over how best to train disposition or even measure it. With that, some individuals might be more ‘inherently’ disposed to CT in light of their truth-seeking, open-minded, or inquisitive natures ( Facione and Facione 1992 ; Quinn et al. 2020 ). The barrier, in this context, is how we can enhance the disposition of those who are not ‘inherently’ inclined. For example, though an individual may possess the requisite skills to conduct CT, it does not ensure the tendency or willingness to apply them; and conversely, having the disposition to apply CT does not mean that one has the ability to do so ( Valenzuela et al. 2011 ). Given the pertinence of CT skills and dispositions to the application of CT in a broader sense, inadequacies in either create a barrier to application.
2.2. Epistemological (Mis)Understanding
To reiterate, most extant conceptualisations of CT focus on the tandem working of skills and dispositions, though significantly fewer emphasise the reflective judgment aspect of CT that might govern various associated processes ( Dawson 2008 ; Dwyer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2014 , 2015 ; King and Kitchener 1994 , 2004 ; Stanovich and Stanovich 2010 ). Reflective judgment (RJ) refers to a self-regulatory process of decision-making, with respect to taking time to engage one’s understanding of the nature, limits, and certainty of knowing and how this can affect the defense of their reasoning ( Dwyer 2017 ; King and Kitchener 1994 ; Ku and Ho 2010b ). The ability to metacognitively ‘think about thinking’ ( Flavell 1976 ; Ku and Ho 2010b ) in the application of critical thinking skills implies a reflective sensibility consistent with epistemological understanding and the capacity for reflective judgement ( Dwyer et al. 2015 ; King and Kitchener 1994 ). Acknowledging levels of (un)certainty is important in CT because the information a person is presented with (along with that person’s pre-existing knowledge) often provides only a limited source of information from which to draw a conclusion. Thus, RJ is considered a component of CT ( Baril et al. 1998 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 ; Huffman et al. 1991 ) because it allows one to acknowledge that epistemological understanding is necessary for recognising and judging a situation in which CT may be required ( King and Kitchener 1994 ). For example, the interdependence between RJ and CT can be seen in the way that RJ influences the manner in which CT skills like analysis and evaluation are conducted or the balance and perspective within the subsequent inferences drawn ( Dwyer et al. 2015 ; King et al. 1990 ). Moreover, research suggests that RJ development is not a simple function of age or time but more so a function of the amount of active engagement an individual has working in problem spaces that require CT ( Brabeck 1981 ; Dawson 2008 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 ). The more developed one’s RJ, the better able one is to present “a more complex and effective form of justification, providing more inclusive and better integrated assumptions for evaluating and defending a point of view” ( King and Kitchener 1994, p. 13 ).
Despite a lesser focus on RJ, research indicates a positive relationship between it and CT ( Baril et al. 1998 ; Brabeck 1981 ; Dawson 2008 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 ; Huffman et al. 1991 ; King et al. 1990 )—the understanding of which is pertinent to better understanding the foundation to CT barriers. For example, when considering one’s proficiency in CT skills, there might come a time when the individual becomes so good at using them that their application becomes something akin to ‘second nature’ or even ‘automatic’. However, this creates a contradiction: automatic thinking is largely the antithesis of reflective judgment (even though judgment is never fully intuitive or reflective; see Cader et al. 2005 ; Dunwoody et al. 2000 ; Hamm 1988 ; Hammond 1981 , 1996 , 2000 )—those who think critically take their time and reflect on their decision-making; even if the solution/conclusion drawn from the automatic thinking is ‘correct’ or yields a positive outcome, it is not a critically thought out answer, per se. Thus, no matter how skilled one is at applying CT skills, once the application becomes primarily ‘automatic’, the thinking ceases to be critical ( Dwyer 2017 )—a perspective consistent with Dual Process Theory (e.g., Stanovich and West 2000 ). Indeed, RJ acts as System 2 thinking ( Stanovich and West 2000 ): it is slow, careful, conscious, and consistent ( Kahneman 2011 ; Hamm 1988 ); it is associated with high cognitive control, attention, awareness, concentration, and complex computation ( Cader et al. 2005 ; Kahneman 2011 ; Hamm 1988 ); and accounts for epistemological concerns—consistent not only with King and Kitchener’s ( 1994 ) conceptualisation but also Kuhn’s ( 1999 , 2000 ) perspective on metacognition and epistemological knowing . This is where RJ comes into play as an important component of CT—interdependent among the requisite skills and dispositions ( Baril et al. 1998 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 )—it allows one to acknowledge that epistemological understanding is vital to recognising and judging a situation in which CT is required ( King and Kitchener 1994 ). With respect to the importance of epistemological understanding, consider the following examples for elaboration.
The primary goal of CT is to enhance the likelihood of generating reasonable conclusions and/or solutions. Truth-seeking is a CT disposition fundamental to the attainment of this goal ( Dwyer et al. 2016 ; Facione 1990 ; Facione and Facione 1992 ) because if we just applied any old nonsense as justification for our arguments or solutions, they would fail in the application and yield undesirable consequences. Despite what may seem like truth-seeking’s obvious importance in this context, all thinkers succumb to unwarranted assumptions on occasion (i.e., beliefs presumed to be true without adequate justification). It may also seem obvious, in context, that it is important to be able to distinguish facts from beliefs. However, the concepts of ‘fact’ or ‘truth’, with respect to how much empirical support they have to validate them, also require consideration. For example, some might conceptualise truth as factual information or information that has been or can be ‘proven’ true. Likewise, ‘proof’ is often described as evidence establishing a fact or the truth of a statement—indicating a level of absolutism. However, the reality is that we cannot ‘prove’ things—as scientists and researchers well know—we can only disprove them, such as in experimental settings where we observe a significant difference between groups on some measure—we do not prove the hypothesis correct, rather, we disprove the null hypothesis. This is why, in large part, researchers and scientists use cautious language in reporting their results. We know the best our findings can do is reinforce a theory—another concept often misconstrued in the wider population as something like a hypothesis, as opposed to what it actually entails: a robust model for how and/or why a given phenomenon might occur (e.g., gravity). Thus, theories will hold ‘true’ until they are falsified—that is, disproven (e.g., Popper [1934] 1959 , 1999 ).
Unfortunately, ‘proof’, ‘prove’, and ‘proven’—words that ensure certainty to large populations—actually disservice the public in subtle ways that can hinder CT. For example, a company that produces toothpaste might claim its product to be ‘clinically proven’ to whiten teeth. Consumers purchasing that toothpaste are likely to expect to have whiter teeth after use. However, what happens—as often may be the case—if it does not whiten their teeth? The word ‘proven’ implies a false claim in context. Of course, those in research understand that the word’s use is a marketing ploy, given that ‘clinically proven’ sounds more reassuring to consumers than ‘there is evidence to suggest…’; but, by incorrectly using words like ‘proven’ in our daily language, we reinforce a misunderstanding of what it means to assess, measure and evaluate—particularly from a scientific standpoint (e.g., again, see Popper [1934] 1959 , 1999 ).
Though this example may seem like a semantic issue, it has great implications for CT in the population. For example, a vast majority of us grew up being taught the ‘factual’ information that there were nine planets in our solar system; then, in 2006, Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet—no longer being considered a ‘major’ planet of our solar system. As a result, we now have eight planets. This change might be perceived in two distinct ways: (1) ‘science is amazing because it’s always developing—we’ve now reached a stage where we know so much about the solar system that we can differentiate celestial bodies to the extent of distinguishing planets from dwarf planets’; and (2) ‘I don’t understand why these scientists even have jobs, they can’t even count planets’. The first perspective is consistent with that of an individual with epistemological understanding and engagement that previous understandings of models and theories can change, not necessarily because they were wrong, but rather because they have been advanced in light of gaining further credible evidence. The second perspective is consistent with that of someone who has failed to engage epistemological understanding, who does not necessarily see that the change might reflect progress, who might be resistant to change, and who might grow in distrust of science and research in light of these changes. The latter point is of great concern in the CT research community because the unwarranted cynicism and distrust of science and research, in context, may simply reflect a lack of epistemological understanding or engagement (e.g., to some extent consistent with the manner in which conspiracy theories are developed, rationalised and maintained (e.g., Swami and Furnham 2014 )). Notably, this should also be of great concern to education departments around the world, as well as society, more broadly speaking.
Upon considering epistemological engagement in more practical, day-to-day scenarios (or perhaps a lack thereof), we begin to see the need for CT in everyday 21st-century life—heightened by the ‘new knowledge economy’, which has resulted in exponential increases in the amount of information made available since the late 1990s (e.g., Darling-Hammond 2008 ; Dwyer 2017 ; Jukes and McCain 2002 ; Varian and Lyman 2003 ). Though increased amounts of and enhanced access to information are largely good things, what is alarming about this is how much of it is misinformation or disinformation ( Commission on Fake News and the Teaching of Critical Literacy in Schools 2018 ). Truth be told, the new knowledge economy is anything but ‘new’ anymore. Perhaps, over the past 10–15 years, there has been an increase in the need for CT above and beyond that seen in the ‘economy’s’ wake—or maybe ever before; for example, in light of the social media boom, political unrest, ‘fake news’, and issues regarding health literacy. The ‘new’ knowledge economy has made it so that knowledge acquisition, on its own, is no longer sufficient for learning—individuals must be able to work with and adapt information through CT in order to apply it appropriately ( Dwyer 2017 ).
Though extant research has addressed the importance of epistemological understanding for CT (e.g., Dwyer et al. 2014 ), it does not address how not engaging it can substantially hinder it—regardless of how skilled or disposed to think critically an individual may be. Notably, this is distinct from ‘inadequacies’ in, say, memory, comprehension, or other ‘lower-order’ cognitively-associated skills required for CT ( Dwyer et al. 2014 ; Halpern 2014 ; see, again, Note 1) in that reflective judgment is essentially a pole on a cognitive continuum (e.g., see Cader et al. 2005 ; Hamm 1988 ; Hammond 1981 , 1996 , 2000 ). Cognitive Continuum Theory postulates a continuum of cognitive processes anchored by reflective judgment and intuitive judgment, which represents how judgment situations or tasks relate to cognition, given that thinking is never purely reflective, nor is it completely intuitive; rather, it rests somewhere in between ( Cader et al. 2005 ; Dunwoody et al. 2000 ). It is also worth noting that, in Cognitive Continuum Theory, neither reflective nor intuitive judgment is assumed, a priori, to be superior ( Dunwoody et al. 2000 ), despite most contemporary research on judgment and decision-making focusing on the strengths of RJ and limitations associated with intuitive judgment ( Cabantous et al. 2010 ; Dhami and Thomson 2012 ; Gilovich et al. 2002 ). Though this point regarding superiority is acknowledged and respected (particularly in non-CT cases where it is advantageous to utilise intuitive judgment), in the context of CT, it is rejected in light of the example above regarding the automaticity of thinking skills.
2.3. Intuitive Judgment
The manner in which human beings think and the evolution of which, over millions of years, is a truly amazing thing. Such evolution has made it so that we can observe a particular event and make complex computations regarding predictions, interpretations, and reactions in less than a second (e.g., Teichert et al. 2014 ). Unfortunately, we have become so good at it that we often over-rely on ‘fast’ thinking and intuitive judgments that we have become ‘cognitively lazy’, given the speed at which we can make decisions with little energy ( Kahneman 2011 ; Simon 1957 ). In the context of CT, this ‘lazy’ thinking is an impediment (as in opposition to reflective judgment). For example, consider a time in which you have been presented numeric data on a topic, and you instantly aligned your perspective with what the ‘numbers indicate’. Of course, numbers do not lie… but people do—that is not to say that the person who initially interpreted and then presented you with those numbers is trying to disinform you; rather, the numbers presented might not tell the full story (i.e., the data are incomplete or inadequate, unbeknownst to the person reporting on them); and thus, there might be alternative interpretations to the data in question. With that, there most certainly are individuals who will wish to persuade you to align with their perspective, which only strengthens the impetus for being aware of intuitive judgment as a barrier. Consider another example: have you ever accidentally insulted someone at work, school, or in a social setting? Was it because the statement you made was based on some kind of assumption or stereotype? It may have been an honest mistake, but if a statement is made based on what one thinks they know, as opposed to what they actually know about the situation—without taking the time to recognise that all situations are unique and that reflection is likely warranted in light of such uncertainty—then it is likely that the schema-based ‘intuitive judgment’ is what is a fault here.
Our ability to construct schemas (i.e., mental frameworks for how we interpret the world) is evolutionarily adaptive in that these scripts allow us to: make quick decisions when necessary and without much effort, such as in moments of impending danger, answer questions in conversation; interpret social situations; or try to stave off cognitive load or decision fatigue ( Baumeister 2003 ; Sweller 2010 ; Vohs et al. 2014 ). To reiterate, research in the field of higher-order thinking often focuses on the failings of intuitive judgment ( Dwyer 2017 ; Hamm 1988 ) as being limited, misapplied, and, sometimes, yielding grossly incorrect responses—thus, leading to faulty reasoning and judgment as a result of systematic biases and errors ( Gilovich et al. 2002 ; Kahneman 2011 ; Kahneman et al. 1982 ; Slovic et al. 1977 ; Tversky and Kahneman 1974 ; in terms of schematic thinking ( Leventhal 1984 ), system 1 thinking ( Stanovich and West 2000 ; Kahneman 2011 ), miserly thinking ( Stanovich 2018 ) or even heuristics ( Kahneman and Frederick 2002 ; Tversky and Kahneman 1974 ). Nevertheless, it remains that such protocols are learned—not just through experience (as discussed below), but often through more ‘academic’ means. For example, consider again the anecdote above about learning to apply CT skills so well that it becomes like ‘second nature’. Such skills become a part of an individual’s ‘mindware’ ( Clark 2001 ; Stanovich 2018 ; Stanovich et al. 2016 ) and, in essence, become heuristics themselves. Though their application requires RJ for them to be CT, it does not mean that the responses yielded will be incorrect.
Moreover, despite the descriptions above, it would be incorrect, and a disservice to readers to imply that RJ is always right and intuitive judgment is always wrong, especially without consideration of the contextual issues—both intuitive and reflective judgments have the potential to be ‘correct’ or ‘incorrect’ with respect to validity, reasonableness or appropriateness. However, it must also be acknowledged that there is a cognitive ‘miserliness’ to depending on intuitive judgment, in which case, the ability to detect and override this dependence ( Stanovich 2018 )—consistent with RJ, is of utmost importance if we care about our decision-making. That is, if we care about our CT (see below for a more detailed discussion), we must ignore the implicit ‘noise’ associated with the intuitive judgment (regardless of whether or not it is ‘correct’) and, instead, apply the necessary RJ to ensure, as best we can, that the conclusion or solution is valid, reasonable or appropriate.
Although, such a recommendation is much easier said than done. One problem with relying on mental shortcuts afforded by intuition and heuristics is that they are largely experience-based protocols. Though that may sound like a positive thing, using ‘experience’ to draw a conclusion in a task that requires CT is erroneous because it essentially acts as ‘research’ based on a sample size of one; and so, ‘findings’ (i.e., one’s conclusion) cannot be generalised to the larger population—in this case, other contexts or problem-spaces ( Dwyer 2017 ). Despite this, we often over-emphasise the importance of experience in two related ways. First, people have a tendency to confuse experience for expertise (e.g., see the Dunning–KrugerEffect (i.e., the tendency for low-skilled individuals to overestimate their ability in tasks relevant to said skill and highly skilled individuals to underestimate their ability in tasks relevant to said skills); see also: ( Kruger and Dunning 1999 ; Mahmood 2016 ), wherein people may not necessarily be expert, rather they may just have a lot of experience completing a task imperfectly or wrong ( Dwyer and Walsh 2019 ; Hammond 1996 ; Kahneman 2011 ). Second, depending on the nature of the topic or problem, people often evaluate experience on par with research evidence (in terms of credibility), given its personalised nature, which is reinforced by self-serving bias(es).
When evaluating topics in domains wherein one lacks expertise, the need for intellectual integrity and humility ( Paul and Elder 2008 ) in their RJ is increased so that the individual may assess what knowledge is required to make a critically considered judgment. However, this is not necessarily a common response to a lack of relevant knowledge, given that when individuals are tasked with decision-making regarding a topic in which they do not possess relevant knowledge, these individuals will generally rely on emotional cues to inform their decision-making (e.g., Kahneman and Frederick 2002 ). Concerns here are not necessarily about the lack of domain-specific knowledge necessary to make an accurate decision, but rather the (1) belief of the individual that they have the knowledge necessary to make a critically thought-out judgment, even when this is not the case—again, akin to the Dunning–Kruger Effect ( Kruger and Dunning 1999 ); or (2) lack of willingness (i.e., disposition) to gain additional, relevant topic knowledge.
One final problem with relying on experience for important decisions, as alluded to above, is that when experience is engaged, it is not necessarily an objective recollection of the procedure. It can be accompanied by the individual’s beliefs, attitudes, and feelings—how that experience is recalled. The manner in which an individual draws on their personal experience, in light of these other factors, is inherently emotion-based and, likewise, biased (e.g., Croskerry et al. 2013 ; Loftus 2017 ; Paul 1993 ).
2.4. Bias and Emotion
Definitions of CT often reflect that it is to be applied to a topic, argument, or problem of importance that the individual cares about ( Dwyer 2017 ). The issue of ‘caring’ is important because it excludes judgment and decision-making in day-to-day scenarios that are not of great importance and do not warrant CT (e.g., ‘what colour pants best match my shirt’ and ‘what to eat for dinner’); again, for example, in an effort to conserve time and cognitive resources (e.g., Baumeister 2003 ; Sweller 2010 ). However, given that ‘importance’ is subjective, it essentially boils down to what one cares about (e.g., issues potentially impactful in one’s personal life; topics of personal importance to the individual; or even problems faced by an individual’s social group or work organisation (in which case, care might be more extrinsically-oriented). This is arguably one of the most difficult issues to resolve in CT application, given its contradictory nature—where it is generally recommended that CT should be conducted void of emotion and bias (as much as it can be possible), at the same time, it is also recommended that it should only be applied to things we care about. As a result, the manner in which care is conceptualised requires consideration. For example, in terms of CT, care can be conceptualised as ‘concern or interest; the attachment of importance to a person, place, object or concept; and serious attention or consideration applied to doing something correctly or to avoid damage or risk’; as opposed to some form of passion (e.g., intense, driving or over-powering feeling or conviction; emotions as distinguished from reason; a strong liking or desire for or devotion to some activity, object or concept). In this light, care could be argued as more of a dispositional or self-regulatory factor than emotional bias; thus, making it useful to CT. Though this distinction is important, the manner in which care is labeled does not lessen the potential for biased emotion to play a role in the thinking process. For example, it has been argued that if one cares about the decision they make or the conclusion they draw, then the individual will do their best to be objective as possible ( Dwyer 2017 ). However, it must also be acknowledged that this may not always be the case or even completely feasible (i.e., how can any decision be fully void of emotional input? )—though one may strive to be as objective as possible, such objectivity is not ensured given that implicit bias may infiltrate their decision-making (e.g., taking assumptions for granted as facts in filling gaps (unknowns) in a given problem-space). Consequently, such implicit biases may be difficult to amend, given that we may not be fully aware of them at play.
With that, explicit biases are just as concerning, despite our awareness of them. For example, the more important an opinion or belief is to an individual, the greater the resistance to changing their mind about it ( Rowe et al. 2015 ), even in light of evidence indicating the contrary ( Tavris and Aronson 2007 ). In some cases, the provision of information that corrects the flawed concept may even ‘backfire’ and reinforce the flawed or debunked stance ( Cook and Lewandowsky 2011 ). This cognitive resistance is an important barrier to CT to consider for obvious reasons—as a process; it acts in direct opposition to RJ, the skill of evaluation, as well as a number of requisite dispositions towards CT, including truth-seeking and open-mindedness (e.g., Dwyer et al. 2014 , 2016 ; Facione 1990 ); and at the same time, yields important real-world impacts (e.g., see Nyhan et al. 2014 ).
The notion of emotion impacting rational thought is by no means a novel concept. A large body of research indicates a negative impact of emotion on decision-making (e.g., Kahneman and Frederick 2002 ; Slovic et al. 2002 ; Strack et al. 1988 ), higher-order cognition ( Anticevic et al. 2011 ; Chuah et al. 2010 ; Denkova et al. 2010 ; Dolcos and McCarthy 2006 ) and cognition, more generally ( Iordan et al. 2013 ; Johnson et al. 2005 ; Most et al. 2005 ; Shackman et al. 2006 ) 2 . However, less attention has specifically focused on emotion’s impact on the application of critical thought. This may be a result of assumptions that if a person is inclined to think critically, then what is yielded will typically be void of emotion—which is true to a certain extent. However, despite the domain generality of CT ( Dwyer 2011 , 2017 ; Dwyer and Eigenauer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2015 ; Gabennesch 2006 ; Halpern 2014 ), the likelihood of emotional control during the CT process remains heavily dependent on the topic of application. Consider again, for example; there is no guarantee that an individual who generally applies CT to important topics or situations will do so in all contexts. Indeed, depending on the nature of the topic or the problem faced, an individual’s mindware ( Clark 2001 ; Stanovich 2018 ; Stanovich et al. 2016 ; consistent with the metacognitive nature of CT) and the extent to which a context can evoke emotion in the thinker will influence what and how thinking is applied. As addressed above, if the topic is something to which the individual feels passionate, then it will more likely be a greater challenge for them to remain unbiased and develop a reasonably objective argument or solution.
Notably, self-regulation is an important aspect of both RJ and CT ( Dwyer 2017 ; Dwyer et al. 2014 ), and, in this context, it is difficult not to consider the role emotional intelligence might play in the relationship between affect and CT. For example, though there are a variety of conceptualisations of emotional intelligence (e.g., Bar-On 2006 ; Feyerherm and Rice 2002 ; Goleman 1995 ; Salovey and Mayer 1990 ; Schutte et al. 1998 ), the underlying thread among these is that, similar to the concept of self-regulation, emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to monitor (e.g., perceive, understand and regulate) one’s own feelings, as well as those of others, and to use this information to guide relevant thinking and behaviour. Indeed, extant research indicates that there is a positive association between EI and CT (e.g., Afshar and Rahimi 2014 ; Akbari-Lakeh et al. 2018 ; Ghanizadeh and Moafian 2011 ; Kaya et al. 2017 ; Stedman and Andenoro 2007 ; Yao et al. 2018 ). To shed light upon this relationship, Elder ( 1997 ) addressed the potential link between CT and EI through her description of the latter as a measure of the extent to which affective responses are rationally-based , in which reasonable desires and behaviours emerge from such rationally-based emotions. Though there is extant research on the links between CT and EI, it is recommended that future research further elaborate on this relationship, as well as with other self-regulatory processes, in an effort to further establish the potentially important role that EI might play within CT.
3. Discussion
3.1. interpretations.
Given difficulties in the past regarding the conceptualisation of CT ( Dwyer et al. 2014 ), efforts have been made to be as specific and comprehensive as possible when discussing CT in the literature to ensure clarity and accuracy. However, it has been argued that such efforts have actually added to the complexity of CT’s conceptualisation and had the opposite effect on clarity and, perhaps, more importantly, the accessibility and practical usefulness for educators (and students) not working in the research area. As a result, when asked what CT is, I generally follow up the ‘long definition’, in light of past research, with a much simpler description: CT is akin to ‘playing devil’s advocate’. That is, once a claim is made, one should second-guess it in as many conceivable ways as possible, in a process similar to the Socratic Method. Through asking ‘why’ and conjecturing alternatives, we ask the individual—be it another person or even ourselves—to justify the decision-making. It keeps the thinker ‘honest’, which is particularly useful if we’re questioning ourselves. If we do not have justifiable reason(s) for why we think or intend to act in a particular way (above and beyond considered objections), then it should become obvious that we either missed something or we are biased. It is perhaps this simplified description of CT that gives such impetus for the aim of this review.
Whereas extant frameworks often discuss the importance of CT skills, dispositions, and, to a lesser extent, RJ and other self-regulatory functions of CT, they do so with respect to components of CT or processes that facilitate CT (e.g., motivation, executive functions, and dispositions), without fully encapsulating cognitive processes and other factors that may hinder it (e.g., emotion, bias, intuitive judgment and a lack of epistemological understanding or engagement). With that, this review is neither a criticism of existing CT frameworks nor is it to imply that CT has so many barriers that it cannot be taught well, nor does it claim to be a complete list of processes that can impede CT (see again Note 1). To reiterate, education in CT can yield beneficial effects ( Abrami et al. 2008 , 2015 ; Dwyer 2017 ; Dwyer and Eigenauer 2017 ); however, such efficacy may be further enhanced by presenting students and individuals interested in CT the barriers they are likely to face in its application; explaining how these barriers manifest and operate; and offer potential strategies for overcoming them.
3.2. Further Implications and Future Research
Though the barriers addressed here are by no means new to the arena of research in higher-order cognition, there is a novelty in their collated discussion as impactful barriers in the context of CT, particularly with respect to extant CT research typically focusing on introducing strategies and skills for enhancing CT, rather than identifying ‘preventative measures’ for barriers that can negatively impact CT. Nevertheless, future research is necessary to address how such barriers can be overcome in the context of CT. As addressed above, it is recommended that CT education include discussion of these barriers and encourage self-regulation against them; and, given the vast body of CT research focusing on enhancement through training and education, it seems obvious to make such a recommendation in this context. However, it is also recognised that simply identifying these barriers and encouraging people to engage in RJ and self-regulation to combat them may not suffice. For example, educators might very well succeed in teaching students how to apply CT skills , but just as these educators may not be able to motivate students to use them as often as they might be needed or even to value such skills (such as in attempting to elicit a positive disposition towards CT), it might be the case that without knowing about the impact of the discussed barriers to CT (e.g., emotion and/or intuitive judgment), students may be just as susceptible to biases in their attempts to think critically as others without CT skills. Thus, what such individuals might be applying is not CT at all; rather, just a series of higher-order cognitive skills from a biased or emotion-driven perspective. As a result, a genuine understanding of these barriers is necessary for individuals to appropriately self-regulate their thinking.
Moreover, though the issues of epistemological beliefs, bias, emotion, and intuitive processes are distinct in the manner in which they can impact CT, these do not have set boundaries; thus, an important implication is that they can overlap. For example, epistemological understanding can influence how individuals make decisions in real-world scenarios, such as through intuiting a judgment in social situations (i.e., without considering the nature of the knowledge behind the decision, the manner in which such knowledge interacts [e.g., correlation v. causation], the level of uncertainty regarding both the decision-maker’s personal stance and the available evidence), when a situation might actually require further consideration or even the honest response of ‘I don’t know’. The latter concept—that of simply responding ‘I don’t know’ is interesting to consider because though it seems, on the surface, to be inconsistent with CT and its outcomes, it is commensurate with many of its associated components (e.g., intellectual honesty and humility; see Paul and Elder 2008 ). In the context this example is used, ‘I don’t know’ refers to epistemological understanding. With that, it may also be impacted by bias and emotion. For example, depending on the topic, an individual may be likely to respond ‘I don’t know’ when they do not have the relevant knowledge or evidence to provide a sufficient answer. However, in the event that the topic is something the individual is emotionally invested in or feels passionate about, an opinion or belief may be shared instead of ‘I don’t know’ (e.g., Kahneman and Frederick 2002 ), despite a lack of requisite evidence-based knowledge (e.g., Kruger and Dunning 1999 ). An emotional response based on belief may be motivated in the sense that the individual knows that they do not know for sure and simply uses a belief to support their reasoning as a persuasive tool. On the other hand, the emotional response based on belief might be used simply because the individual may not know that the use of a belief is an insufficient means of supporting their perspective– instead, they might think that their intuitive, belief-based judgment is as good as a piece of empirical evidence; thus, suggesting a lack of empirical understanding. With that, it is fair to say that though epistemological understanding, intuitive judgment, emotion, and bias are distinct concepts, they can influence each other in real-world CT and decision-making. Though there are many more examples of how this might occur, the one presented may further support the recommendation that education can be used to overcome some of the negative effects associated with the barriers presented.
For example, in Ireland, students are not generally taught about academic referencing until they reach third-level education. Anecdotally, I was taught about referencing at age 12 and had to use it all the way through high school when I was growing up in New York. In the context of these referencing lessons, we were taught about the credibility of sources, as well as how analyse and evaluate arguments and subsequently infer conclusions in light of these sources (i.e., CT skills). We were motivated by our teacher to find the ‘truth’ as best we could (i.e., a fundament of CT disposition). Now, I recognise that this experience cannot be generalised to larger populations, given that I am a sample size of one, but I do look upon such education, perhaps, as a kind of transformative learning experience ( Casey 2018 ; King 2009 ; Mezirow 1978 , 1990 ) in the sense that such education might have provided a basis for both CT and epistemological understanding. For CT, we use research to support our positions, hence the importance of referencing. When a ‘reference’ is not available, one must ask if there is actual evidence available to support the proposition. If there is not, one must question the basis for why they think or believe that their stance is correct—that is, where there is logic to the reasoning or if the proposition is simply an emotion- or bias-based intuitive judgment. So, in addition to referencing, the teaching of some form of epistemology—perhaps early in children’s secondary school careers, might benefit students in future efforts to overcome some barriers to CT. Likewise, presenting examples of the observable impact that bias, emotions, and intuitive thought can have on their thinking might also facilitate overcoming these barriers.
As addressed above, it is acknowledged that we may not be able to ‘teach’ people not to be biased or emotionally driven in their thinking because it occurs naturally ( Kahneman 2011 )—regardless of how ‘skilled’ one might be in CT. For example, though research suggests that components of CT, such as disposition, can improve over relatively short periods of time (e.g., over the duration of a semester-long course; Rimiene 2002 ), less is known about how such components have been enhanced (given the difficulty often associated with trying to teach something like disposition ( Dwyer 2017 ); i.e., to reiterate, it is unlikely that simply ‘teaching’ (or telling) students to be motivated towards CT or to value it (or its associated concepts) will actually enhance it over short periods of time (e.g., semester-long training). Nevertheless, it is reasonable to suggest that, in light of such research, educators can encourage dispositional growth and provide opportunities to develop it. Likewise, it is recommended that educators encourage students to be aware of the cognitive barriers discussed and provide chances to engage in CT scenarios where such barriers are likely to play a role, thus, giving students opportunities to acknowledge the barriers and practice overcoming them. Moreover, making students aware of such barriers at younger ages—in a simplified manner, may promote the development of personal perspectives and approaches that are better able to overcome the discussed barriers to CT. This perspective is consistent with research on RJ ( Dwyer et al. 2015 ), in which it was recommended that such enhancement requires not only time to develop (be it over the course of a semester or longer) but is also a function of having increased opportunities to engage CT. In the possibilities described, individuals may learn both to overcome barriers to CT and from the positive outcomes of applying CT; and, perhaps, engage in some form of transformative learning ( Casey 2018 ; King 2009 ; Mezirow 1978 , 1990 ) that facilitates an enhanced ‘valuing’ of and motivation towards CT. For example, through growing an understanding of the nature of epistemology, intuitive-based thinking, emotion, bias, and the manner in which people often succumb to faulty reasoning in light of these, individuals may come to better understand the limits of knowledge, barriers to CT and how both understandings can be applied; thus, growing further appreciation of the process as it is needed.
To reiterate, research suggests that there may be a developmental trajectory above and beyond the parameters of a semester-long training course that is necessary to develop the RJ necessary to think critically and, likewise, engage an adequate epistemological stance and self-regulate against impeding cognitive processes ( Dwyer et al. 2015 ). Though such research suggests that such development may not be an issue of time, but rather the amount of opportunities to engage RJ and CT, there is a dearth of recommendations offered with respect to how this could be performed in practice. Moreover, the how and what regarding ‘opportunities for engagement’ requires further investigation as well. For example, does this require additional academic work outside the classroom in a formal manner, or does it require informal ‘exploration’ of the world of information on one’s own? If the latter, the case of motivational and dispositional levels once again comes into question; thus, even further consideration is needed. One way or another, future research efforts are necessary to identify how best to make individuals aware of barriers to CT, encourage them to self-regulate against them, and identify means of increasing opportunities to engage RJ and CT.
4. Conclusions
Taking heed that it is unnecessary to reinvent the CT wheel ( Eigenauer 2017 ), the aim of this review was to further elaborate on the processes associated with CT and make a valuable contribution to its literature with respect to conceptualisation—not just in light of making people explicitly aware of what it is, but also what it is not and how it can be impeded (e.g., through inadequate CT skills and dispositions; epistemological misunderstanding; intuitive judgment; as well as bias and emotion)—a perspective consistent with that of ‘constructive feedback’ wherein students need to know both what they are doing right and what they are doing wrong. This review further contributes to the CT education literature by identifying the importance of (1) engaging understanding of the nature, limits, and certainty of knowing as individuals traverse the landscape of evidence-bases in their research and ‘truth-seeking’; (2) understanding how emotions and biases can affect CT, regardless of the topic; (3) managing gut-level intuition until RJ has been appropriately engaged; and (4) the manner in which language is used to convey meaning to important and/or abstract concepts (e.g., ‘caring’, ‘proof’, causation/correlation, etc.). Consistent with the perspectives on research advancement presented in this review, it is acknowledged that the issues addressed here may not be complete and may themselves be advanced upon and updated in time; thus, future research is recommended and welcomed to improve and further establish our working conceptualisation of critical thinking, particularly in a real-world application.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge, with great thanks and appreciation, John Eigenauer (Taft College) for his consult, review and advice regarding earlier versions of this manuscript.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
1 Notably, though inadequacies in cognitive resources (apart from those explicitly set within the conceptualisations of CT discussed; e.g., see Section 2.1 ) are acknowledged as impediments to one’s ability to apply CT (e.g., a lack of relevant background knowledge, as well as broader cognitive abilities and resources ( Dwyer 2017 ; Halpern 2014 ; Stanovich and Stanovich 2010 )), these will not be discussed as focus is largely restricted to issues of cognitive processes that ‘naturally’ act as barriers in their functioning. Moreover, such inadequacies may more so be issues of individual differences than ongoing issues that everyone , regardless of ability, would face in CT (e.g., the impact of emotion and bias). Nevertheless, it is recommended that future research further investigates the influence of such inadequacies in cognitive resources on CT.
2 There is also some research that suggests that emotion may mediate enhanced cognition ( Dolcos et al. 2011 , 2012 ). However, this discrepancy in findings may result from the types of emotion studied—such as task-relevant emotion and task-irrelevant emotion. The distinction between the two is important to consider in terms of, for example, the distinction between one’s general mood and feelings specific unto the topic under consideration. Though mood may play a role in the manner in which CT is conducted (e.g., making judgments about a topic one is passionate about may elicit positive or negative emotions that affect the thinker’s mood in some way), notably, this discussion focuses on task-relevant emotion and associated biases that negatively impact the CT process. This is also an important distinction because an individual may generally think critically about ‘important’ topics, but may fail to do so when faced with a cognitive task that requires CT with which the individual has a strong, emotional perspective (e.g., in terms of passion , as described above).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
- Abrami Philip C., Bernard Robert M., Borokhovski Eugene, Waddington David I., Wade C. Anne, Persson Tonje. Strategies for teaching students to think critically: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research. 2015; 85 :275–314. doi: 10.3102/0034654314551063. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abrami Philip C., Bernard Robert M., Borokhovski Evgueni, Wade Anne, Surkes Michael A., Tamim Rana, Zhang Dai. Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: A stage 1 meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research. 2008; 78 :1102–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- Afshar Hassan Soodmand, Rahimi Masoud. The relationship among critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and speaking abilities of Iranian EFL learners. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2014; 136 :75–79. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.05.291. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahern Aoife, Dominguez Caroline, McNally Ciaran, O’Sullivan John J., Pedrosa Daniela. A literature review of critical thinking in engineering education. Studies in Higher Education. 2019; 44 :816–28. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2019.1586325. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akbari-Lakeh M., Naderi A., Arbabisarjou A. Critical thinking and emotional intelligence skills and relationship with students’ academic achievement. Prensa Médica Argentina. 2018; 104 :2. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aliakbari Mohammad, Sadeghdaghighi Akram. Teachers’ perception of the barriers to critical thinking. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2013; 70 :1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.031. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anticevic Alan, Repovs Grega, Corlett Philip R., Barch Deanna M. Negative and nonemotional interference with visual working memory in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry. 2011; 70 :1159–68. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.07.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baril Charles P., Cunningham Billie M., Fordham David R., Gardner Robert L., Wolcott Susan K. Critical thinking in the public accounting profession: Aptitudes and attitudes. Journal of Accounting Education. 1998; 16 :381–406. doi: 10.1016/S0748-5751(98)00023-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bar-On Reuven. The Bar-On model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI) Psicothema. 2006; 18 :13–25. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baumeister Roy. The psychology of irrationality: Why people make foolish, self-defeating choices. The Psychology of Economic Decisions. 2003; 1 :3–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bezanilla María José, Fernández-Nogueira Donna, Poblete Manuel, Galindo-Domínguez Hector. Methodologies for teaching-learning critical thinking in higher education: The teacher’s view. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2019; 33 :100584. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2019.100584. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brabeck Mary Margaret. The relationship between critical thinking skills and development of reflective judgment among adolescent and adult women; Paper presented at the 89th annual convention of the American Psychological Association; Los Angeles, CA, USA. August 24–26; 1981. [ Google Scholar ]
- Butler Heather A., Dwyer Christopher P., Hogan Michael J., Franco Amanda, Rivas Silvia F., Saiz Carlos, Almeida Leandro S. The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment and real-world outcomes: Cross-national applications. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2012; 7 :112–21. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2012.04.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Byerly T. Ryan. Teaching for intellectual virtue in logic and critical thinking classes: Why and how. Teaching Philosophy. 2019; 42 :1. doi: 10.5840/teachphil201911599. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cabantous Laure, Gond Jean-Pascal, Johnson-Cramer Michael. Decision theory as practice: Crafting rationality in organizations. Organization Studies. 2010; 31 :1531–66. doi: 10.1177/0170840610380804. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cáceres Martín, Nussbaum Miguel, Ortiz Jorge. Integrating critical thinking into the classroom: A teacher’s perspective. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2020; 37 :100674. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cader Raffik, Campbell Steve, Watson Don. Cognitive continuum theory in nursing decision-making. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2005; 49 :397–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03303.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Casey Helen. Doctoral dissertation. National University of Ireland; Galway, Ireland: 2018. Transformative Learning: An Exploration of the BA in Community and Family Studies Graduates’ Experiences. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chuah Lisa YM, Dolcos Florin, Chen Annette K., Zheng Hui, Parimal Sarayu, Chee Michael WL. Sleep deprivation and interference by emotional distracters. SLEEP. 2010; 33 :1305–13. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.10.1305. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark Andy. Mindware: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Cognitive Science. Oxford University Press; New York: 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Commission on Fake News and the Teaching of Critical Literacy in Schools . Fake News and Critical Literacy: Final Report. National Literacy Trust; London: 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook John, Lewandowsky Stephan. The Debunking Handbook. University of Queensland; St. Lucia: 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cornell Paul, Riordan Monica, Townsend-Gervis Mary, Mobley Robin. Barriers to critical thinking: Workflow interruptions and task switching among nurses. JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration. 2011; 41 :407–14. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0b013e31822edd42. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Croskerry Pat, Singhal Geeta, Mamede Sílvia. Cognitive debiasing 2: Impediments to and strategies for change. BMJ Quality and Safety. 2013; 22 :ii65–ii72. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001713. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Darling-Hammond Linda. How can we teach for meaningful learning? In: Darling-Hammond L., editor. Powerful Learning. Wiley; New York: 2008. pp. 1–10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dawson Theo L. Prepared in Response to Tasking from ODNI/CHCO/IC Leadership Development Office. Developmental Testing Service, LLC; Northampton: 2008. Metacognition and learning in adulthood. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denkova Ekaterina, Wong Gloria, Dolcos Sanda, Sung Keen, Wang Lihong, Coupland Nicholas, Dolcos Florin. The impact of anxiety-inducing distraction on cognitive performance: A combined brain imaging and personality investigation. PLoS ONE. 2010; 5 :e14150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014150. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dhami Mandeep K., Thomson Mary E. On the relevance of cognitive continuum theory and quasirationality for understanding management judgment and decision making. European Management Journal. 2012; 30 :316–26. doi: 10.1016/j.emj.2012.02.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dolcos Florin, Iordan Alexandru D., Dolcos Sanda. Neural correlates of emotion–cognition interactions: A review of evidence from brain imaging investigations. Journal of Cognitive Psychology. 2011; 23 :669–94. doi: 10.1080/20445911.2011.594433. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dolcos Florin, McCarthy Gregory. Brain systems mediating cognitive interference by emotional distraction. Journal of Neuroscience. 2006; 26 :2072–79. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5042-05.2006. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dolcos Florin, Denkova Ekaterina, Dolcos Sanda. Neural correlates of emotional memories: A review of evidence from brain imaging studies. Psychologia. 2012; 55 :80–111. doi: 10.2117/psysoc.2012.80. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dumitru Daniela. Critical thinking and integrated programs. The problem of transferability. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 33 :143–47. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.01.100. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dunwoody Philip T., Haarbauer Eric, Mahan Robert P., Marino Christopher, Tang Chu-Chun. Cognitive adaptation and its consequences: A test of cognitive continuum theory. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making. 2000; 13 :35–54. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0771(200001/03)13:1<35::AID-BDM339>3.0.CO;2-U. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P. Doctoral thesis. National University of Ireland; Galway, Ireland: 2011. The Evaluation of Argument Mapping as a Learning Tool. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P. Critical Thinking: Conceptual Perspectives and Practical Guidelines. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P. Teaching critical thinking. The SAGE Encyclopedia of Higher Education. 2020; 4 :1510–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P., Walsh Anne. A case study of the effects of critical thinking instruction through adult distance learning on critical thinking performance: Implications for critical thinking development. Educational Technology and Research. 2019; 68 :17–35. doi: 10.1007/s11423-019-09659-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P., Eigenauer John D. To Teach or not to Teach Critical Thinking: A Reply to Huber and Kuncel. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2017; 26 :92–95. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2017.08.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P., Hogan Michael J., Stewart Ian. An evaluation of argument mapping as a method of enhancing critical thinking performance in e-learning environments. Metacognition and Learning. 2012; 7 :219–44. doi: 10.1007/s11409-012-9092-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P., Hogan Michael J., Stewart Ian. An integrated critical thinking framework for the 21st century. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2014; 12 :43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2013.12.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher P., Hogan Michael J., Stewart Ian. The evaluation of argument mapping-infused critical thinking instruction as a method of enhancing reflective judgment performance. Thinking Skills & Creativity. 2015; 16 :11–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Christopher. P., Hogan Michael J., Harney Owen M., Kavanagh Caroline. Facilitating a Student-Educator Conceptual Model of Dispositions towards Critical Thinking through Interactive Management. Educational Technology & Research. 2016; 65 :47–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eigenauer John D. Don’t reinvent the critical thinking wheel: What scholarly literature says about critical thinking instruction. NISOD Innovation Abstracts. 2017; 39 :2. [ Google Scholar ]
- Elder Linda. Critical thinking: The key to emotional intelligence. Journal of Developmental Education. 1997; 21 :40. doi: 10.5840/inquiryctnews199616211. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ennis Robert H. A taxonomoy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. In: Baron J. B., Sternberg R. J., editors. Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice. W.H. Freeman; New York: 1987. pp. 9–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ennis Robert H. Critical Thinking. Prentice-Hall; Upper Saddle River: 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ennis Robert H. Is critical thinking culturally biased? Teaching Philosophy. 1998; 21 :15–33. doi: 10.5840/teachphil19982113. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ennis Robert. H. Critical thinking across the curriculum: A vision. Topoi. 2018; 37 :165–84. doi: 10.1007/s11245-016-9401-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Facione Noreen C., Facione Peter A. Analyzing explanations for seemingly irrational choices: Linking argument analysis and cognitive science. International Journal of Applied Philosophy. 2001; 15 :267–68. [ Google Scholar ]
- Facione Peter A. The Delphi Report: Committee on Pre-College Philosophy. California Academic Press; Millbrae: 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Facione Peter A., Facione Noreen C. CCTDI: A Disposition Inventory. California Academic Press; Millbrae: 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Facione Peter A., Facione Noreen C., Blohm Stephen W., Giancarlo Carol Ann F. The California Critical Thinking Skills Test: CCTST. California Academic Press; San Jose: 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feyerherm Ann E., Rice Cheryl L. Emotional intelligence and team performance: The good, the bad and the ugly. International Journal of Organizational Analysis. 2002; 10 :343–63. doi: 10.1108/eb028957. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flavell John H. Metacognitive aspects of problem solving. The Nature of Intelligence. 1976:231–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabennesch Howard. Critical thinking… what is it good for? (In fact, what is it?) Skeptical Inquirer. 2006; 30 :36–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gadzella Bernadette M. Teaching and Learning Critical Thinking Skills. 1996.
- Gambrill Eileen. Evidence-based practice and policy: Choices ahead. Research on Social Work Practice. 2006; 16 :338–57. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghanizadeh Afsaneh, Moafian Fatemeh. Critical thinking and emotional intelligence: Investigating the relationship among EFL learners and the contribution of age and gender. Iranian Journal of Applied Linguistics. 2011; 14 :23–48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilovich Thomas, Griffin Dale, Kahneman Daniel., editors. Heuristics and Biases: The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser Edward. M. An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking. Teachers College of Columbia University, Bureau of Publications; New York: 1941. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goleman Daniel. Emotional Intelligence. Bantam; New York: 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Halpern Diane F. Thought & Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking. 5th ed. Psychology Press; London: 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamm Robert M. Clinical intuition and clinical analysis: Expertise and the cognitive continuum. In: Dowie J., Elstein A. S., editors. Professional Judgment: A Reader in Clinical Decision Making. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1988. pp. 78–105. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammond Kenneth R. Principles of Organization in Intuitive and Analytical Cognition. Center for Research on Judgment and Policy, University of Colorado; Boulder: 1981. Report No. 231. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammond Kenneth R. Upon reflection. Thinking and Reasoning. 1996; 2 :239–48. doi: 10.1080/135467896394537. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammond Kenneth R. Judgments Under Stress. Oxford University Press on Demand; New York: 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haynes Ada, Lisic Elizabeth, Goltz Michele, Stein Barry, Harris Kevin. Moving beyond assessment to improving students’ critical thinking skills: A model for implementing change. Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 2016; 16 :44–61. doi: 10.14434/josotl.v16i4.19407. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hitchcock David. The effectiveness of computer-assisted instruction in critical thinking. Informal Logic. 2004; 24 :183–218. doi: 10.22329/il.v24i3.2145. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huffman Karen, Vernoy Mark W., William Barbara F. Studying Psychology in Action: A Study Guide to Accompany Psychology in Action. Wiley; Hoboken: 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Iordan Alexandru D., Dolcos Sanda, Dolcos Florin. Neural signatures of the response to emotional distraction: A review of evidence from brain imaging investigations. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2013; 7 :200. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00200. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson Marcia K., Raye Carol L., Mitchell Karen J., Greene Erich J., Cunningham William A., Sanislow Charles A. Using fMRI to investigate a component process of reflection: Prefrontal correlates of refreshing a just-activated representation. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. 2005; 5 :339–61. doi: 10.3758/CABN.5.3.339. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jukes I., McCain T. Minds in Play: Computer Game Design as a Context of Children’s Learning. Erlbaum; Hillsdale: 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahneman Daniel. Thinking Fast and Slow. Penguin; Great Britain: 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahneman Daniel, Frederick Shane. Representativeness revisited: Attribute substitution in 240 intuitive judgment. In: Gilovich T., Griffin D., Kahneman D., editors. Heuristics and Biases: The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment. Cambridge University Press; New York: 2002. pp. 49–81. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahneman Daniel, Slovic Paul, Tversky Amos., editors. Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1982. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaya Hülya, Şenyuva Emine, Bodur Gönül. Developing critical thinking disposition and emotional intelligence of nursing students: A longitudinal research. Nurse Education Today. 2017; 48 :72–77. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.09.011. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King Kathleen P. Adult Education Special Topics: Theory, Research, and Practice in Lifelong Learning. Information Age Publishing; Charlotte: 2009. The Handbook of the Evolving Research of Transformative Learning Based on the Learning Activities Survey. [ Google Scholar ]
- King Patricia M., Kitchener Karen S. Reflective judgment: Theory and research on the development of epistemic assumptions through adulthood. Educational Psychologist. 2004; 39 :5–18. doi: 10.1207/s15326985ep3901_2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King Patricia M., Wood Phillip K., Mines Robert A. Critical thinking among college and graduate students. The Review of Higher Education. 1990; 13 :167–86. doi: 10.1353/rhe.1990.0026. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King Patricia. M., Kitchener Karen. Developing Reflective Judgment: Understanding and Promoting Intellectual Growth and Critical Thinking in Adolescents and Adults. Jossey Bass; San Francisco: 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruger Justin, Dunning David. Unskilled and unaware of it: How difficulties in recognizing one’s own incompetence lead to inflated self-Assessments. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1999; 77 :1121–34. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.77.6.1121. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ku Kelly Y. L. Assessing students’ critical thinking performance: Urging for measurements using multi-response format. Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2009; 4 :70–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2009.02.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ku Kelly Y. L., Ho Irene T. Dispositional factors predicting Chinese students’ critical thinking performance. Personality and Individual Differences. 2010a; 48 :54–58. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2009.08.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ku Kelly Y. L., Ho Irene T. Metacognitive strategies that enhance critical thinking. Metacognition and Learning. 2010b; 5 :251–67. doi: 10.1007/s11409-010-9060-6. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn Deanna. A developmental model of critical thinking. Educational Researcher. 1999; 28 :16–25. doi: 10.3102/0013189X028002016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn Deanna. Metacognitive development. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2000; 9 :178–81. doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.00088. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leventhal Howard. A perceptual-motor theory of emotion. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology. 1984; 17 :117–82. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lloyd Margaret, Bahr Nan. Thinking critically about critical thinking in higher education. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 2010; 4 :1–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- Loftus Elizabeth. F. Eavesdropping on memory. Annual Review of Psychology. 2017; 68 :1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010416-044138. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma Lihong, Luo Haifeng. Chinese pre-service teachers’ cognitions about cultivating critical thinking in teaching English as a foreign language. Asia Pacific Journal of Education. 2021; 41 :543–57. doi: 10.1080/02188791.2020.1793733. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma Lihong, Liu Ning. Teacher belief about integrating critical thinking in English teaching in China. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2022; 49 :137–52. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2022.2044267. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahmood Khalid. Do people overestimate their information literacy skills? A systematic review of empirical evidence on the Dunning-Kruger effect. Communications in Information Literacy. 2016; 10 :199–213. doi: 10.15760/comminfolit.2016.10.2.24. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mangena Agnes, Chabeli Mary M. Strategies to overcome obstacles in the facilitation of critical thinking in nursing education. Nurse Education Today. 2005; 25 :291–98. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2005.01.012. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McGuinness Carol. Teaching thinking: Learning how to think; Presented at the Psychological Society of Ireland and British Psychological Association’sPublic Lecture Series; Galway, Ireland. March 6; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mezirow Jack. Perspective Transformation. Adult Education. 1978; 28 :100–10. doi: 10.1177/074171367802800202. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mezirow Jack. How Critical Reflection Triggers Transformative Learning. In: Mezirow J., editor. Fostering Critical Reflection in Adulthood. Jossey Bass; San Francisco: 1990. pp. 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Most Steven B., Chun Marvin M., Widders David M., Zald David H. Attentional rubbernecking: Cognitive control and personality in emotioninduced blindness. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review. 2005; 12 :654–61. doi: 10.3758/BF03196754. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niu Lian, Behar-Horenstein Linda S., Garvan Cyndi W. Do instructional interventions influence college students’ critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review. 2013; 9 :114–28. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Norris Stephen P. Critical Thinking: Current Research, Theory, and Practice. Kluwer; Dordrecht: 1994. The meaning of critical thinking test performance: The effects of abilities and dispositions on scores; pp. 315–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nyhan Brendan, Reifler Jason, Richey Sean, Freed Gary L. Effective messages in vaccine promotion: A randomized trial. Pediatrics. 2014; 133 :E835–E842. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-2365. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz Claudia Maria Alvarez. Master’s thesis. University of Melbourne; Melbourne, VIC, Australia: 2007. Does Philosophy Improve Critical Thinking Skills? [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul Richard W. Critical Thinking: What Every Person Needs to Survive in a Rapidly Changing World. Foundation for Critical Thinking; Santa Barbara: 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul Richard, Elder Linda. Critical. The Foundation for Critical Thinking; Dillon Beach: 2008. Thinking. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perkins David N., Jay Eileen, Tishman Shari. Beyond abilities: A dispositional theory of thinking. Merrill Palmer Quarterly. 1993; 39 :1. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perkins David, Ritchhart Ron. Motivation, Emotion, and Cognition. Routledge; London: 2004. When is good thinking? pp. 365–98. [ Google Scholar ]
- Popper Karl R. The Logic of Scientific Discovery. Routledge; London: 1959. First published 1934. [ Google Scholar ]
- Popper Karl R. All Life Is Problem Solving. Psychology Press; London: 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Quinn Sarah, Hogan Michael, Dwyer Christopher, Finn Patrick, Fogarty Emer. Development and Validation of the Student-Educator Negotiated Critical Thinking Dispositions Scale (SENCTDS) Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2020; 38 :100710. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100710. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rear David. One size fits all? The limitations of standardised assessment in critical thinking. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 2019; 44 :664–75. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reed Jennifer H., Kromrey Jeffrey D. Teaching critical thinking in a community college history course: Empirical evidence from infusing Paul’s model. College Student Journal. 2001; 35 :201–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rimiene Vaiva. Assessing and developing students’ critical thinking. Psychology Learning & Teaching. 2002; 2 :17–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rowe Matthew P., Gillespie B. Marcus, Harris Kevin R., Koether Steven D., Shannon Li-Jen Y., Rose Lori A. Redesigning a general education science course to promote critical thinking. CBE—Life Sciences Education. 2015; 14 :ar30. doi: 10.1187/cbe.15-02-0032. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saleh Salamah Embark. Critical thinking as a 21st century skill: Conceptions, implementation and challenges in the EFL classroom. European Journal of Foreign Language Teaching. 2019; 4 :1. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.2542838. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salovey Peter, Mayer John D. Emotional intelligence. Imagination, Cognition and Personality. 1990; 9 :185–211. doi: 10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schutte Nicola S., Malouff John M., Hall Lena E., Haggerty Donald J., Cooper Joan T., Golden Charles J., Dornheim Liane. Development and validation of a measure of emotional intelligence. Personality and Individual Differences. 1998; 25 :167–77. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(98)00001-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shackman Alexander J., Sarinopoulos Issidoros, Maxwell Jeffrey S., Pizzagalli Diego A., Lavric Aureliu, Davidson Richard J. Anxiety selectively disrupts visuospatial working memory. Emotion. 2006; 6 :40–61. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.6.1.40. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Siegel Harvey. What (good) are thinking dispositions? Educational Theory. 1999; 49 :207–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-5446.1999.00207.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simon Herbert A. Models of Man. Wiley; New York: 1957. [ Google Scholar ]
- Slovic Paul, Fischhoff Baruch, Lichtenstein Sarah. Behavioral decision theory. Annual Review of Psychology. 1977; 28 :1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.28.020177.000245. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slovic Paul, Finucane Melissa, Peters Ellen, MacGregor Donald G. Rational actors or rational fools: Implications of the affect heuristic for behavioral economics. The Journal of SocioEconomics. 2002; 31 :329–42. doi: 10.1016/S1053-5357(02)00174-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Solon Tom. Generic critical thinking infusion and course content learning in Introductory Psychology. Journal of Instructional Psychology. 2007; 34 :95–109. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich Keith E. Miserliness in human cognition: The interaction of detection, override and mindware. Thinking & Reasoning. 2018; 24 :423–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich Keith E., Stanovich Paula J. A framework for critical thinking, rational thinking, and intelligence. In: Preiss D. D., Sternberg R. J., editors. Innovations in Educational Psychology: Perspectives on Learning, Teaching, and Human Development. Springer Publishing Company; Berlin/Heidelberg: 2010. pp. 195–237. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich Keith E., West Richard F. Individual differences in reasoning: Implications for the rationality debate? Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 2000; 23 :645–65. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X00003435. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich Keith E., West Richard F., Toplak Maggie E. The Rationality Quotient: Toward a Test of Rational Thinking. MIT Press; Cambridge: 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stedman Nicole LP, Andenoro Anthony C. Identification of relationships between emotional intelligence skill and critical thinking disposition in undergraduate leadership students. Journal of Leadership Education. 2007; 6 :190–208. doi: 10.12806/V6/I1/RF10. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strack Fritz, Martin Leonard L., Schwarz Norbert. Priming and communication: Social determinants of information use in judgments of life satisfaction. European Journal of Social Psychology. 1988; 18 :429–42. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.2420180505. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swami Viren, Furnham Adrian. Political paranoia and conspiracy theories. In: van Prooijen J. W., van Lange P. A. M., editors. Power, Politics, and Paranoia: Why People Are Suspicious of Their Leaders. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2014. pp. 218–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sweller John. Cognitive load theory: Recent theoretical advances. In: Plass J. L., Moreno R., Brünken R., editors. Cognitive Load Theory. Cambridge University Press; New York: 2010. pp. 29–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tavris Carol, Aronson Elliot. Mistakes Were Made (But Not by Me) Harcourt; Orlando: 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Teichert Tobias, Ferrera Vincent P., Grinband Jack. Humans optimize decision-making by delaying decision onset. PLoS ONE. 2014; 9 :e89638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089638. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tversky Amos, Kahneman Daniel. Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science. 1974; 185 :1124–31. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4157.1124. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valenzuela Jorge, Nieto Ana, Saiz Carlos. Critical Thinking Motivational Scale: A 253 contribution to the study of relationship between critical thinking and motivation. Journal of Research in Educational Psychology. 2011; 9 :823–48. doi: 10.25115/ejrep.v9i24.1475. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Varian Hal, Lyman Peter. How Much Information? School of Information Management and Systems, UC Berkeley; Berkeley: 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Vohs Kathleen D., Baumeister Roy F., Schmeichel Brandon J., Twenge Jean M., Nelson Noelle M., Tice Dianne M. Making choices impairs subsequent self-control: A limited-resource account of decision making, self-regulation, and active initiative. Personality Processes and Individual Differences. 2014; 94 :883–98. doi: 10.1037/2333-8113.1.S.19. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yao Xiaonan, Yuan Shuge, Yang Wenjing, Chen Qunlin, Wei Dongtao, Hou Yuling, Zhang Lijie, Qiu Jiang, Yang Dong. Emotional intelligence moderates the relationship between regional gray matter volume in the bilateral temporal pole and critical thinking disposition. Brain Imaging and Behavior. 2018; 12 :488–98. doi: 10.1007/s11682-017-9701-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Self Development

Critical Thinking Skills in the Workplace: Navigating Challenges for Enhanced Decision-Making and Innovation

Introduction:
Critical thinking skills are increasingly recognized as essential components of success in the modern workplace. In a rapidly evolving global landscape, businesses and organizations face complex challenges that demand thoughtful analysis, strategic decision-making, and innovative solutions. This article explores the significance of critical thinking skills in the workplace, delving into their definition, key attributes, and practical applications for individuals and organizations alike.
Critical thinking skills are indispensable in the modern workplace, serving as the foundation for effective problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. In a rapidly evolving business landscape, where challenges are diverse and unpredictable, individuals equipped with strong critical thinking abilities stand out as invaluable assets to their organizations. This article will delve into the significance of critical thinking skills in the workplace, exploring how they contribute to individual and organizational success.
Defining Critical Thinking:
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing and evaluating information, arguments, or situations to make informed decisions. It goes beyond the acquisition of knowledge, emphasizing the ability to think objectively, consider multiple perspectives, and apply sound reasoning. In the workplace, critical thinking is a dynamic skill set that enables employees to navigate uncertainties, solve problems, and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Understanding Critical Thinking:
Critical thinking involves the analysis, interpretation, and evaluation of information and ideas to form well-reasoned judgments. It goes beyond simply accepting information at face value; instead, it encourages individuals to question assumptions, consider multiple perspectives, and assess the evidence before making decisions. In the workplace, critical thinking is not confined to any specific industry or role; it is a universal skill that empowers individuals across various domains.
Problem-Solving in the Workplace:
One of the primary applications of critical thinking in the workplace is problem-solving. In any professional setting, challenges and obstacles are inevitable. Critical thinkers approach problems methodically, breaking them down into manageable components, analyzing the root causes, and devising effective solutions. This skill is particularly crucial in complex business environments where multifaceted issues demand careful consideration and creative problem-solving approaches.
Decision-Making:
Critical thinking is inseparable from effective decision-making. Decision-makers often face situations where they must weigh competing options, anticipate potential outcomes, and make choices that align with organizational goals. Critical thinkers bring a systematic and logical approach to decision-making, minimizing the influence of biases and emotions. This not only leads to better decisions but also fosters a culture of accountability within the organization.
Innovation and Creativity:
Innovation is the lifeblood of progress in the business world. Critical thinking fuels creativity by encouraging individuals to think outside the box, challenge conventional wisdom, and explore novel ideas. In an era of constant change, organizations that foster a culture of innovation through critical thinking are better positioned to adapt to new trends, capitalize on opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition.
Effective Communication:
Communication is a cornerstone of collaboration and success in the workplace. Critical thinking skills enhance communication by enabling individuals to express their ideas clearly, listen actively to others, and engage in constructive dialogue. When team members approach discussions with a critical mindset, they are more likely to understand diverse perspectives, resolve conflicts, and arrive at well-informed decisions collectively.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning:
The modern workplace is dynamic, requiring individuals to adapt to changes swiftly and continuously acquire new skills. Critical thinkers embrace a mindset of lifelong learning, recognizing that staying relevant in their roles necessitates ongoing education and adaptation. This adaptability is particularly crucial in industries influenced by technological advancements and shifting market trends.
Challenges and Obstacles to Critical Thinking:
While critical thinking is highly beneficial, certain challenges may impede its development and application in the workplace. Common obstacles include time constraints, resistance to change, and a lack of awareness about the importance of critical thinking. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort from both individuals and organizations to prioritize and cultivate a culture that values critical thinking as a core competency.
Promoting Critical Thinking in the Workplace:
To harness the full potential of critical thinking in the workplace, organizations can implement strategies to promote and develop this skill among their employees. Training programs, workshops, and mentorship opportunities can provide individuals with the tools and techniques
Key Attributes of Critical Thinking:
1. **analysis and interpretation:**.
Critical thinkers excel in breaking down complex information into manageable parts, allowing for a deeper understanding of the nuances within a problem or situation. They can interpret data, trends, and patterns to extract meaningful insights.
2. **Objective Evaluation:**
A critical thinker remains impartial and objective when evaluating information. They consider evidence, assess the credibility of sources, and avoid being swayed by personal biases, ensuring a more accurate and well-rounded assessment.
3. **Effective Problem-Solving:**
Critical thinking is at the core of effective problem-solving. Individuals with strong critical thinking skills can identify challenges, analyze root causes, and develop innovative solutions that address the underlying issues.
4. **Decision-Making:**
In decision-making, critical thinkers weigh the pros and cons, anticipate potential consequences, and make informed choices. They are adept at managing risks and uncertainties, contributing to more robust and strategic decision-making processes.
5. **Creativity and Innovation:**
Critical thinking and creativity go hand in hand. The ability to think critically allows individuals to approach problems from unique perspectives, fostering creativity and promoting innovative solutions that can give organizations a competitive edge.
Practical Applications in the Workplace:
1. **strategic planning:**.
Critical thinking is fundamental to strategic planning. Organizations need leaders and employees who can analyze market trends, assess competitive landscapes, and make informed decisions to position the company for success in the future.
2. **Problem Identification and Resolution:**
One of the primary applications of critical thinking is in identifying and resolving workplace challenges. Whether it's a technical issue, interpersonal conflict, or a strategic roadblock, critical thinkers can assess the situation, identify the root cause, and implement effective solutions.
3. **Project Management:**
Successful project management requires a systematic approach to planning, execution, and problem-solving. Critical thinkers excel in project management by anticipating potential roadblocks, adapting to changes, and ensuring project success through well-informed decisions.
4. **Innovation and Continuous Improvement:**
Organizations that foster a culture of critical thinking encourage employees to question existing processes and seek better, more efficient ways of doing things. This leads to continuous improvement and a commitment to innovation.
5. **Team Collaboration:**
Critical thinking is not solely an individual skill; it's also crucial for effective team collaboration. Teams benefit when members can collectively analyze information, discuss ideas objectively, and make decisions that align with the organization's goals.
Challenges to Critical Thinking in the Workplace:
1. **confirmation bias:**.
Individuals may be prone to seeking or interpreting information in a way that confirms their pre-existing beliefs. Overcoming confirmation bias is crucial for maintaining objectivity in critical thinking.
2. **Time Constraints:**
In a fast-paced work environment, there is often pressure to make quick decisions. This can challenge the application of thorough critical thinking processes, making it essential for individuals to balance speed with thoughtful analysis.
3. **Lack of Information:**
Critical thinking relies on having access to relevant and accurate information. In situations where data is incomplete or unreliable, individuals may face challenges in making well-informed decisions.
4. **Resistance to Change:**
Employees or organizations resistant to change may struggle to adopt critical thinking approaches, hindering innovation and adaptability in the face of evolving challenges.
5. **Communication Barriers:**
Effective critical thinking often involves collaboration and open communication. When communication channels break down or are hindered, it can impede the exchange of ideas and hinder the collective critical thinking process within a team or organization.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, critical thinking skills are indispensable in the contemporary workplace. As organizations navigate an ever-changing landscape, the ability to think critically becomes a catalyst for innovation, strategic decision-making, and overall success. Recognizing the importance of cultivating and applying critical thinking skills is not only beneficial for individuals but is also a strategic imperative for organizations striving to thrive in today's complex and dynamic business environment. By fostering a culture that values critical thinking, businesses can empower their workforce to tackle challenges with agility, make informed decisions, and contribute to a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
- December 2023 1
Report Abuse
Search this blog, contact form, latest news.

Menu Footer Widget
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

10 Most In-Demand Soft Skills to Put on Your Resume
L ong gone are the days when listing hard skills was the best (and oftentimes only) way to get your foot in the door at a prestigious company. While technical knowledge and training will always be important, soft skills (or essentially personality traits) are becoming increasingly important to highlight on your resume. And it makes sense, as more companies prioritize work culture and, therefore, the personalities of those they’re hiring.
But which soft skills are the ones that standout the most on a resume? Using data from Indeed.com, CashNetUSA scoured job ads for 46 predetermined soft skills to find the ones that appeared the most on high-paid jobs that surpassed the 75th percentile of wages in America’s most populated cities as well as each state. These are the soft skills that came out on top.
10. Resilience
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 34.29%
Resilience is a soft skill that highlights your ability to handle stress and challenges that come up at work.
A good example of how to add this to your resume could be, “Showed resilience when leading a team after budget cuts by still delivering work on time and within scope.”
* Data comes from a January 2024 report released by CashNetUSA .
9. Financial Management
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 38.24%
If you’ve ever been in charge of a budget of any size, you can say that you have financial management skills.
For instance, something like “oversaw the financial management of the freelance budget” could work if you hired contractors for a specific project.
8. Innovation
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 39.24%
Sure, this one makes our eyes roll a bit, too, but in today’s fast-paced world, innovation is key. No one wants an employee that stays stagnant or, worse, digs their heels in at the slight mention of change.
You know who’s not stagnant? Someone who “excelled at brainstorming and ideation in the innovation process for [fill in project name].” You get it.
7. Emotional Intelligence
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 43.11%
We’re actually pleasantly surprised with this one. After all, we didn’t think corporations necessarily had it in them to care about this.
Jokes aside, having emotional intelligence is something that makes a good team member and an even better manager. After all, it’s hard to resolve team conflicts without it. The more a company emphasizes a “harmonious work environment,” the more this soft skill will matter.
6. Mentoring
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 47.89%
Here’s another managerial skill that job ads like to use to weed out the haves from the have-nots when it comes to managers. Do you actually enjoy mentoring people or have you just fallen up the corporate ladder into a management position?
True leaders will make mentoring a priority and want to highlight it on their resume.
5. Critical Thinking
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 47.94%
“Critical thinking” or “problem solving” can be put in the same bucket as resilience. How did you handle a challenging situation at work? It’s even better if you have data to back up your claim.
Well, maybe you “demonstrated strong critical-thinking skills when analyzing financial reports and making forecasts for the following quarter.”
4. Presentation Skills
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 56%
Presentation skills are the nature of the beast when it comes to today's Corporate America. That's because lots of today’s high-paying jobs require working with cross-functional teams and being able to explain your work in easy, digestible terms.
Think someone on a data science team explaining their findings to a marketing team. Along with "presentation skills," you could also add the specific presentation tools or software you use for your presentations on your resume.
3. Persuasion
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 57.41%
Persuasion sounds rather seductive, but it's crucial when trying to get specific projects across the finish line.
It's also a term that's used a lot in marketing when talking about "persuasive marketing skills" required to communicate well with a customer audience.
2. Negotiation
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 58.26%
This skill goes back to business basics. Proper negotiation skills come in handy in any aspect of life, whether you're negotiating a $1 billion merger or whether or not your toddler can have dessert for breakfast.
That said, it's a skill that takes time to hone — which is why it's considered all the more valuable.
1. Strategic Thinking
Percentage of highly paid jobs requiring the skill: 64.77%
Strategic thinking is essentially a combination of innovation and critical thinking, but the best way to incorporate this keyword on your resume is by using the CAR (challenge, action, result) technique.
You could say something like, "Used strategic thinking skills by analyzing user engagement data and running an A/B test that resulted in increased engagement of 20 percent."
For more resume advice, check out "How to Make Your Resume Shine."

- Entertainment
- KSAT Insider
- Newsletters
WEATHER ALERT
2 warnings and 2 advisories in effect for 14 regions in the area
Northside isd students participate in outdoor challenge testing teamwork, critical thinking skills, event taking place at eisenhower park march 19-20, april 2-4.
Tiffany Huertas , Reporter
Azian Bermea , Photojournalist
SAN ANTONIO – This week over 2,600 Northside ISD students in the gifted and talented program are competing in an outdoor challenge that will test them in many ways.
Third, fourth and fifth grade students from across the district must work together in the “Challenge Survivor GT”.
The event is taking place at Eisenhower Park March 19-21 and again April 2-4.
“We really just wanted to create an equitable experience for our students,” said Katie Hitchman, GT instructional support teacher at Northside ISD.
Students go through 17 different stations, testing their teamwork and critical thinking skills.
“Some of the different activities they will participate in today include puzzles. There is a human system where they actually have to use their bodies to create a pathway,” Hitchman said.
Just like the television show “Survivor”, students will also collect items along the way to build a shelter at the end.
Survivor GT aims to encourage students to explore, discover and deepen their connection to the complexities within the environment.
Copyright 2024 by KSAT - All rights reserved.
About the Authors:
Tiffany huertas.
Tiffany Huertas is a reporter for KSAT 12 known for her in-depth storytelling and her involvement with the community.
Azian Bermea
Azian Bermea is a photojournalist at KSAT.
INSIDE THE RING: Adrian Neaves ready for his pro debut
Scholar athlete of the week: jackson kahanek, central catholic high school, brahmas one week away from first home game, safc wins first match of 2024, ksat 12 nightbeat sunday : mar 24, 2024.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Scroll down to see all of the courses included, plus other bulk pricing options. Soft skills training materials to teach staff development training.
Whether at a networking event with new people or a meeting with close colleagues, try to engage with people who challenge or help you develop your ideas. Having conversations that force you to support your position encourages you to refine your argument and think critically. 11. Stay humble.
Instead, instructors ought to prioritize the development of critical thinking skills to support students along their respective transformative journeys. Nevertheless, it is perfectly consistent for a student to retain their viewpoint after engaging effectively with a perspective-taking exercise. ... Once again, we are faced with the challenge ...
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well. Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly ...
Developing critical thinking skills can help you to overcome groupthink and make more informed and effective decisions. By being aware of the challenges of group dynamics and actively seeking out diverse perspectives, you can cultivate a more independent and objective approach to critical thinking, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a ...
It's important to develop critical thinking skills for more than just academic reasons. Substantial critical thinking capacity serves us well in all aspects of our lives. It encompasses problem-solving, decision-making, personal responsibility, and managing relationships of every kind effectively, just to name a few things.
Sometimes your university classes might feel like a maze of information. Consider critical thinking skills like a map that can lead the way. Why do we need critical thinking? Critical thinking is a type of thinking that requires continuous questioning, exploring answers, and making judgments. Critical thinking can help you:
It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice. According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills.
Consider these ways writing can help enhance critical thinking: 1. Clarity of Thought: Writing requires that you articulate your thoughts clearly and coherently. When you need to put your ideas on ...
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
It's a challenge, but it's well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems. 7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper. Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you'll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions).
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills. The definitions of critical thinking constructs were only useful to us in as much as they translated into practical skills that teachers could teach and students could learn and use. Consequently, we have found that to teach a set of cognitive skills, we needed thinking routines that defined the regular ...
A sixth challenge of teaching critical thinking skills is to support your learners' ongoing development of critical thinking. Critical thinking is not a fixed or finite skill that can be mastered ...
room/instructional and out-of-class experiences both make positive, statistically sig- nificant, and unique contributions to gains in critical thinking above and beyond students' precollege characteristics and level of critical thinking. Theoreticians have long speculated that students' academic and nonacademic experiences jointly influ- ence ...
Vati is a dynamic online career planning platform dedicated to fostering the development of critical thinking skills. With a comprehensive range of interactive courses, engaging resources, and personalized learning modules, VATI empowers learners to cultivate analytical acumen and navigate complex challenges with confidence and clarity ...
The critical thinking process doesn't necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision. 6. Present your solution. Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers.
Sunday posits that critical thinking is a tool with which education can equip learners.Education is defined as a process "which brings about the development of the individual to the fullest extent and also the maximum development of society in such a way that both enjoy maximum happiness and prosperity" (Parihar 2017).Education can be regarded as one of the most effective means of ...
The 21st-century skillset is generally understood to encompass a range of competencies, including critical thinking, problem solving, creativity, meta-cognition, communication, digital and technological literacy, civic responsibility, and global awareness (for a review of frameworks, see Dede, 2010).And nowhere is the development of such competencies more important than in developing country ...
The development of critical thinking (CT) abilities, recognized as the foremost obligation ... (EFL) writing education, such as Barnawi (2011), there are still challenges to incorporating CT into writing classes for several underlying reasons, such as unclear ... Critical thinking skills rubric adapted from Facione: interpretation, analysis ...
1 Introduction and background. Critical thinking has been considered a key twenty-first century competence by different frameworks (Voogt and Roblin Citation 2012) and by STEM educators (Jang Citation 2016).An education contributing to the development of twenty-first century competences requires, among other things, a reconsideration of instructional processes and a shift from teaching to know ...
1. Introduction. Critical thinking (CT) is a metacognitive process—consisting of a number of skills and dispositions—that, through purposeful, self-regulatory reflective judgment, increases the chances of producing a logical solution to a problem or a valid conclusion to an argument (Dwyer 2017, 2020; Dwyer et al. 2012, 2014, 2015, 2016; Dwyer and Walsh 2019; Quinn et al. 2020).
Top 5 critical thinking skills. Here are five common and impactful critical thinking skills you might consider highlighting on your resume or in an interview: 1. Observation. Observational skills are the starting point for critical thinking. People who are observant can quickly sense and identify a new problem.
Critical thinking skills are indispensable in the modern workplace, serving as the foundation for effective problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. In a rapidly evolving business landscape, where challenges are diverse and unpredictable, individuals equipped with strong critical thinking abilities stand out as invaluable assets to ...
The purpose of the current study is to investigate post-basic English teachers` practice of critical thinking skills and the challenges they face while teaching skills in EFL classrooms.
Strategic thinking is essentially a combination of innovation and critical thinking, but the best way to incorporate this keyword on your resume is by using the CAR (challenge, action, result ...
Students go through 17 different stations, testing their teamwork and critical thinking skills. "Some of the different activities they will participate in today include puzzles.