London Case Study of Urban Area
What’s life like.

London is located in South East England, in the continent of Europe.
Located on the Thames River, the land is flat as it is on the flood plain. Located on the Thames as this was a ‘bridging point’ during Roman times. Economically this meant that businesses started in the area and trade soon started.
London is a very well connected city. It is situated in the south east of England, in Western Europe. The M25 runs around London. A number of other motorways lead to London. These include the M1, M11 and M23 meaning quick access to other cities across UK. There are 5 airports meaning tourists and trade are easily attracted- London can be considered a global hub for air travel. Ferries and Eurotunnel allow for further increase in trade which helps to boost FDI.

Some cities are better connected than others because of their physical geography. For example, a city with easy access to the sea will be better connected because of shipping and trade.
London’s structure is more complex than both the Burgess model and the Hoyt model. It’s main economic function has shifted to the Docklands and now includes world famous building like Canary Wharf. In some ways you could say London has 2 CBDs, many businesses and tourists are attracted to Central London
As with the Burgess model the city because more suburban in its function as you get further out. Housing age decreases and in many areas we are seeing new development in residential areas. With the internet and transport businesses are starting to move out of town for cheaper rent, they are ‘footloose’.
Environmental quality improves as you get further out, there is less traffic and pollution and population density decreases.
Pull factors (jobs, culture, infrastructure, education, health play a huge role in attracting migrants (both national and international to London).
Clusters of migrant populations occur as culture develops. New immigrants can be supported by friends and family with settling and language barriers.
Brick Lane is an example of immigration playing a role in changing culture, restaurants, shops selling saris and a mosque are all evidence of this.
The Index of multiple deprivation (IMD) measures inequalities across cities. In London inequality is highest is East London. Traditionally the London docks were in this area, transport links were poor to reduce potential for robbery as a result few businesses were located here. The means a negative multiplier effect where people don’t have jobs, there is less tax paid, councils have less to invest in education and services so people get worse jobs.
- Geographical skills and enquiry
- Human geography
- Physical geography
- Careers Spotlights
- Skills Boosts


Quizzes //
Urban case study - london.
Test your knowledge of London and urbanisation with this 15-question GCSE quiz.
If you haven't already done it, work through the urban case study of London on the PowerPoint (especially the graph on page 11). Or look at it again to help fill any gaps in what you know!
Open Resource
HIGH SCORES
Quizzes // urban case study - london, q1. which of these is not a borough of london.
Kingston upon Thames
City of London
Q2. The average UK house price was £272,000 in 2020. What was the average in London?
£272,000
£514,000
£356,000
£790,000
Q3. In the UK, the average salary was £22,044 in 2020. What was the average salary in London?
£22,044
£17,100
£34,473
£50,000
Q4. What causes counter urbanisation in London?
The movement of people out of London due to reasons such as house prices, traffic, crime and pollution
The movement of people into London after the redevelopment of East London for the Olympic Games in 2012
The movement of people from the countryside into the city of London
The movement of people from the centre of London to the suburban boroughs, such as Kingston Upon Thames
Q5. Which of these motorways circles London?
Q6. according to the mayor of london’s office, how many new homes are needed in london each year, q7. social deprivation is where people lack basic services such as housing or employment. approximately how many of london’s population are socially deprived, q8. what is the difference between site and situation.
Situation is the physical characteristics of the location you are studying, whereas site is the location of the place in relation to its physical and human surroundings
Site is the ability to see the physical characteristics of the location whereas situation is a position you may find yourself in
Site relates to the physical characteristics of the location you are studying, whereas situation is the location of the place in relation to its physical and human surroundings
Site refers to the factors that lead to the growth of a town or city, and situation is about the processes involved
Q9. Which of these describes a greenfield site for new housing development in London?
Land that has been used, usually for industry, but is now abandoned and awaiting redevelopment
A ring of protected land around a major town or city preventing further urban sprawl
An area of land that is undeveloped, usually at the edge of a town or city
Any area of the town or countryside which is grassed over, including gardens and parks
Q10. Which of these describes a brownfield site for new housing development in London?
A ring of protected land around a major city preventing further urban sprawl
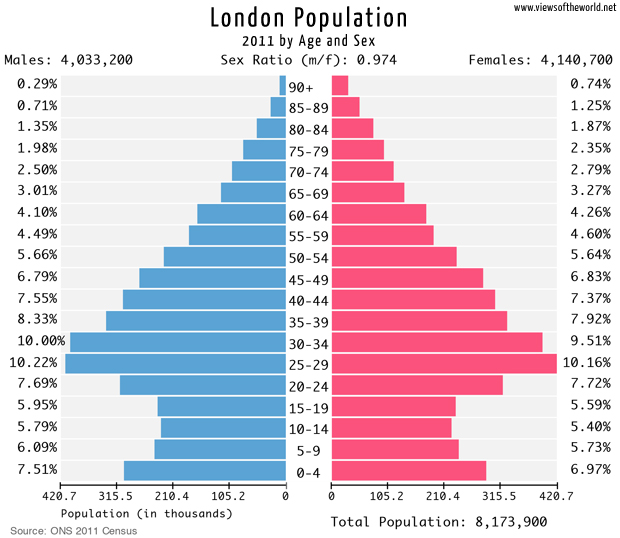
Q11. Study the population pyramid for London on page 11 of the PowerPoint. Which of the following statements is true?
The most populous age category in London is 25–29
The most populous age category in London is 10–14
The most populous age category in London is 65–69
The most populous age category in London is 30–34
Q12. Study the population pyramid again. Which of the following statements is true?
There are more men aged 65–69 than women
There are more women aged 65–69 than men
There are the same percentages of men and women aged 65–69
There are twice as many men aged 65–69 as women
Q13. Study the population pyramid again. Which of these statements is true?
There are the same number of men and women in London
There are 106,700 more women than men in London
There are 107,500 more men in London than women
There are 107,500 more women in London than men
Q14. When answering a GCSE style question what should you always include?
Place names from a case study or named example
Data such as facts, figures and dates
Ensure you answer the actual question set (for example describe, explain, evaluate)
All of the above
Q15. Parts of East London were redeveloped after the London 2012 Olympics. Which of these was not part of the plan?
New school: Chobham Academy
New housing estate: East Village
International Quarter Business development
Widening of the M25 motorway
You scored this time. The more correct answers you give, and the fewer incorrect answers you guess, the better your score.
Back to Quizzes
View our wide range of webinars
Search webinars

Get in Touch
The Geographical Association 160 Solly Street, Sheffield, S1 4BF
0114 296 0088 [email protected]
Stay Social
Cookies Privacy Terms Sitemap
© 2020 The Geographical Association. Charity no. 1135148. Company no. 07139068. Website by QWeb Ltd
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

AQA GCSE Geography - Urban London Case Study - Lessons
Subject: Geography
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
16 November 2023
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

GCSE AQA Geography - Urban - London lessons.
- Full set of lessons covering Urban London.
- Lots of resources to choose from.
- Easily adapted.
- Fully resourced.
- Modelled exam questions.
- Everything you need for teaching this unit.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.

Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Biophysical Interactions
- Senior Geography Project
- Population Geography
- Kosciuszko Alpine Ecosystem
- Great Barrier Reef
- People and Economic Activity
- Urban Places
- Changing Populations
- Global climate
- Oceans and their coastal margins
- Extreme environments
- Leisure, sport and tourism
- Food and health
- The variety or urban environments
- Changing Urban Systems
- Urban Environmental Stresses
- Sustainable Urban Systems
- Power, places and networks
- Human development and diversity
- Geo Researching Skills
- HSC Geo Skills
- SGP/Internal Assessment Projects
- National Geo Comp
- GTA NSW/ACT Fieldwork Awards
- Latitude Geography authors
London - A case study of the results of the urban dynamics in a large city selected from the developed world
Social structure and spatial patterns of advantage and disadvantage, wealth and poverty, ethnicity.
- Income and poverty
- Education levels, and
- Poverty in London is largely relative poverty, defined by the UK government as being below 60 per cent of median income.
- High levels of disadvantage in London coexist with some of the greatest concentrations of wealth in Britain.
- Inner London is by far the most deeply divided part of the country, with the highest proportions of both rich and poor people anywhere.
- Over a third of children in Greater London are living in households with incomes below the government’s poverty threshold.
- Income poverty affects one in four of London’s population.
- London now has one of the highest unemployment rates in England, reversing the position which obtained in the 1970s and 1980s when the unemployment rate in London tended to be among the lowest for any region.
- Homelessness is much higher in London than elsewhere in the UK.
- The ethnic dimension of poverty is far more pronounced in London than in other regions.
- The cost of housing, transport and childcare :
- T he pattern of demand for labour : London’s labour market has changed dramatically over the last twenty years,
- The openness of London’s economy :
- The distribution of earnings :

- London has the lowest proportion of people born in the UK (72.9 per cent)
- London has the highest proportion of people from minority ethnic groups apart from more who identified themselves as of Pakistani origin, of whom there is a higher proportion in Yorkshire and the Humber (2.9 per cent) and the West Midlands (2.9 per cent).
- In 2001 six out of ten Londoners were White British (nearly 4.3 million people) and four out of ten were from ethnic minority groups (nearly 2.9 million people).
- There were slightly more people who were Asian or Asian British (12 per cent of London’s population) than Black or Black British (11 per cent of London’s population).
- The largest ethnic minority group in London was the Other White group. (These were White people who were not White British or White Irish, and therefore the group includes many other European people). Following the Other White group in size were the Indian, Black African, Black Caribbean and White Irish groups. The Bangladeshi, Pakistani and Other Asian ethnic groups were next.
- Seven of the London boroughs with the highest proportions of ethnic minorities were in Inner London and three in Outer London, whereas nine of the ten boroughs with the lowest proportions of ethnic minorities were in Outer London.
- The borough with the largest proportion of ethnic minorities was Brent where 71 per cent of the population were from ethnic minority groups (including White minorities), followed by Newham, Tower Hamlets, Hackney and Ealing.
- There were nine boroughs in London which had ethnic minority populations which were more than half the borough’s population.
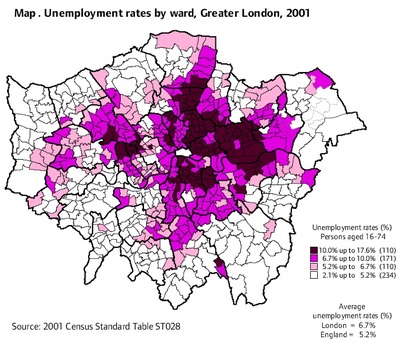
- In April 2001, the unemployment rate in Greater London was 6.7 per cent – one of the highest rates across England and Wales, second only to that of the North East.
- London’s regional position is largely driven by high unemployment levels across Inner London boroughs where unemployment rates average 8.9 per cent. Across Outer London, unemployment levels (5.4 per cent) are nearer the national average (5.2 per cent).
- Across London, borough rates vary from 3.6 per cent in Sutton up to 12.3 per cent in Newham. Rates are also very high in Hackney and Tower Hamlets (both 11.8 per cent).
- While Outer London has low unemployment relative to Inner London, it still has pockets of high unemployment – four per cent of wards in Outer London had rates of 10 per cent and over. 45 per cent of Outer London wards had rates above the national average.
- Unemployment rates are high for young Londoners. Rates among 16-24 year olds are 12.3 per cent – twice as high as rates for those aged 25 and over. Unemployment levels are higher still for those aged 16-19 (22.3 per cent).
- Unemployment rates for BME ( Black and minority ethnic groups) groups across Greater London average 11.3 per cent – more than twice as high as rates for White groups (5.3 per cent). Unemployment levels are highest for Bangladeshi (20.5 per cent) and Black groups (who have an average rate of 14.3 per cent).
- Women have lower unemployment rates than men across most ethnic groups except for Pakistani women who had higher rates (13.3 per cent) than those of Pakistani men (11.6 per cent). Bangladeshi and Indian women also had rates very close to those of men.
- Those in poor health are more than twice as likely to be unemployed as those in good health (14.1 per cent compared with 5.7 per cent). Unemployment rates for those with poor health are highest in the boroughs of Tower Hamlets (23.3 per cent) and Hackney (21.8 per cent).
- People with no qualifications are almost three times more likely to be unemployed than those with higher level qualifications (11.1 per cent compared with 4.2 per cent). Rates for those with no qualifications are very high across Inner London (17.1 per cent).
- In terms of their former jobs, unemployed people tended to be over-represented in lower paid occupations and sectors (eg hotels and catering sector, sales and customer service occupations), compared with workers generally.
Changing economic character, nature and location of residential land, commercial and industrial development
- London was a major city prior to the industrial revolution
- Early function as a seaport and commercial centre formed a building block for current financial developments
- Trade generated population growth and profits but also the need for financial service industries, such as insurance and accounting.
- The deregulation of the UK finnance sector is refered to as "the big bang" which allowed massive growth.
- Today London continues to be important as one of the three top world cities, exerting economic authority and control
- Since the 1960-70s manufacturing as been in decline in London. However, highly skilled manufacturing remains in demand.
- The service sector now dominates London’s economy. Over a third of jobs in London are in the business and finance industry. Other key services are, public sector, law, marketing and advertising, tourism and hospitality, creative and cultural industries.
- Manufacturing does still continue in the London economy
Culture of place

- Accents from around the world, and in particular the Cockney (east end) accent. (Multi coloured… no longer a white persons city)
- Frequent overcast weather and atmospheric dust (grey)
- Diesel engines (red buses and black cabs)
- Speaker’s corner in Hyde Park (expansive green spaces)
- Brit pop, club scene and Punk movements
- London is a quite patriotic city with the Union Jack (the combined flags of England, Scotland and Wales) frequently displayed (red white and blue)

- Monday to Friday is about work, while Friday and Saturday are about going out. Sundays include football, newspaper and roast lunch.
- 11 o’clock closing of pubs gives rise to binge drinking culture and late dinners at “curry restaurants”.
- London is an exhilarating, busy and fast paced city, but also a very expensive one.
- To buy an average home in London requires an average salary of £55,000 (AUS$136,800), however in reality the average salary is only £34,777 (AUS$86,500).
- Key workers are particularly hit as the average school teacher in London earns £26,360, a staff nurse makes £21,950 and a postal worker earns only £21,180. (note: in mid 2006, 1 UK£ = AUS$ 2.49).
- The overall average rent for two-bedroom accommodation for all boroughs is £214. The corresponding average rent for all central boroughs is £321, and for other boroughs £201.
- Only those earning over £60,000 would be considered affluent.
- Most Londoners have a strong pub culture and spend considerable time at the local pub or bar.
- The pull of people towards London means it contains much creative energy.
- London’s constant state of flux makes it a very vibrant and vigorous place in which to live and visit.
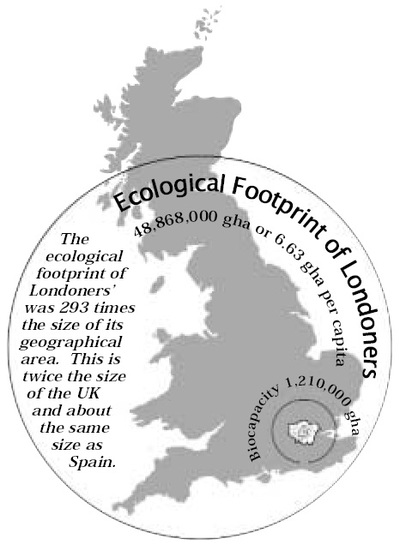
Growth, development, future trends and ecological sustainability
- Has a huge demand for natural resources
- Obliterates the natural hydrological system within its area
- Produces waste products, including solid and liquid waste, air pollutants, heat and noise, which alters the environment around it
- Reduces biomass and alters the species of plants and animals in and around it
- Creates new land through reclamation and landfill
- Encouraging households and industry to reduce the amount of resources they consume, such as encouraging energy efficient water heating, and increasing the price of water to discourage its wasteful use.
- Encouraging a reduction in the amount of waste created, such as reducing packaging, using more energy efficient equipment, re-using and recycling materials, educating citizens in more efficient ways of reducing resource use and waste production.
- London is also aiming to reduce transport pressures and hence fuel usage by promoting regional hubs of employment.
Further Reading
GCSE - Urban Issues and Challenges
UIC - Global Patterns of urban change UIC - Factors affecting urbanisation and megacities
YOU ONLY need to study one LIC/NEE case study
Urbanisation in the UK
UIC - UK overview of urban areas
YOU ONLY need to study one UK case study
SUSTAINABILITY IN URBAN AREAS
UIC - Sustainability in Urban areas UIC - Urban Transport Strategies
©2015 Cool Geography
- Copyright Policy
- Privacy & Cookies
- Testimonials
- Feedback & support

- 0 Shopping Cart

Shoreditch London Case Study
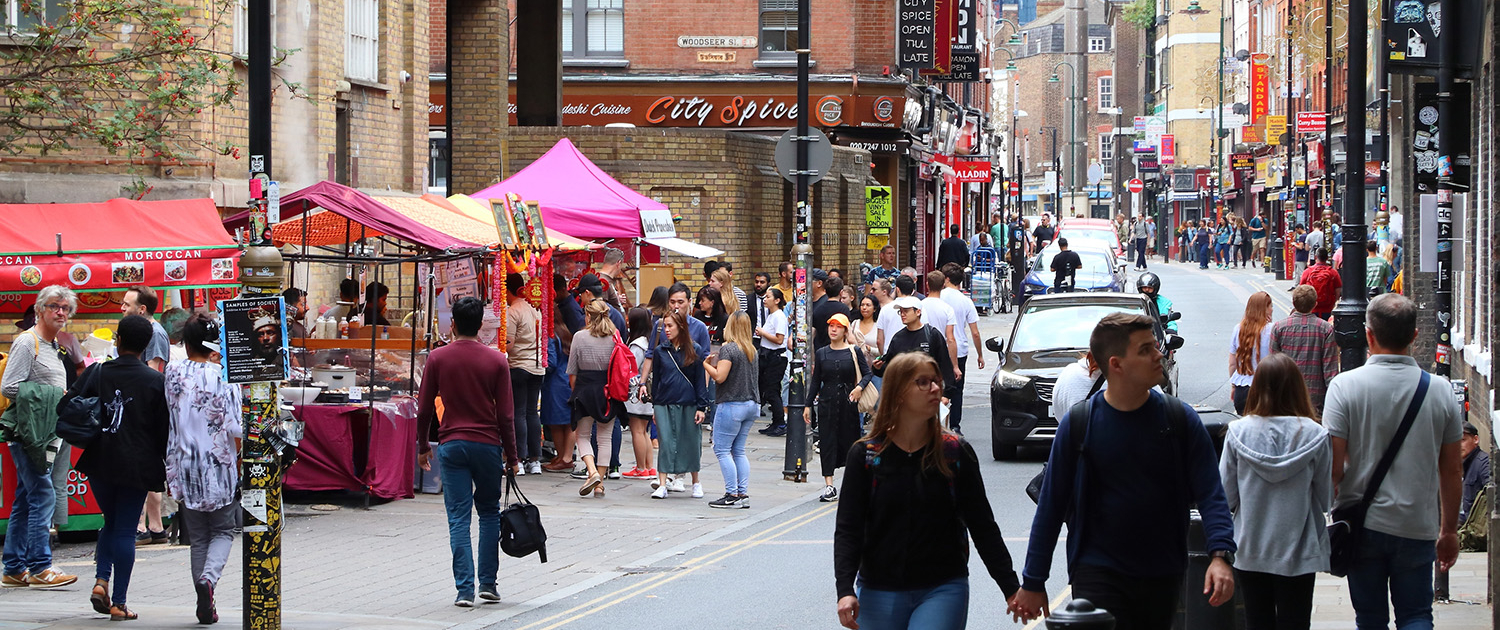

Shoreditch is an example of how urban change has created a cultural mix, recreation, and entertainment opportunities. This is one of a collection of four case studies covering social, economic and environmental opportunities resulting from urban change in London .
Case Study – Shoreditch, London
Shoreditch is a district in the East End of London, close to the city centre. It is typical of the sort of changes that have happened around London and other UK cities.
Shoreditch was once a run-down inner-city area, with ageing factories and warehouses that had ceased operations, prompting people to leave the vicinity. In their place, many Bangladeshi immigrants moved in, particularly around Brick Lane.
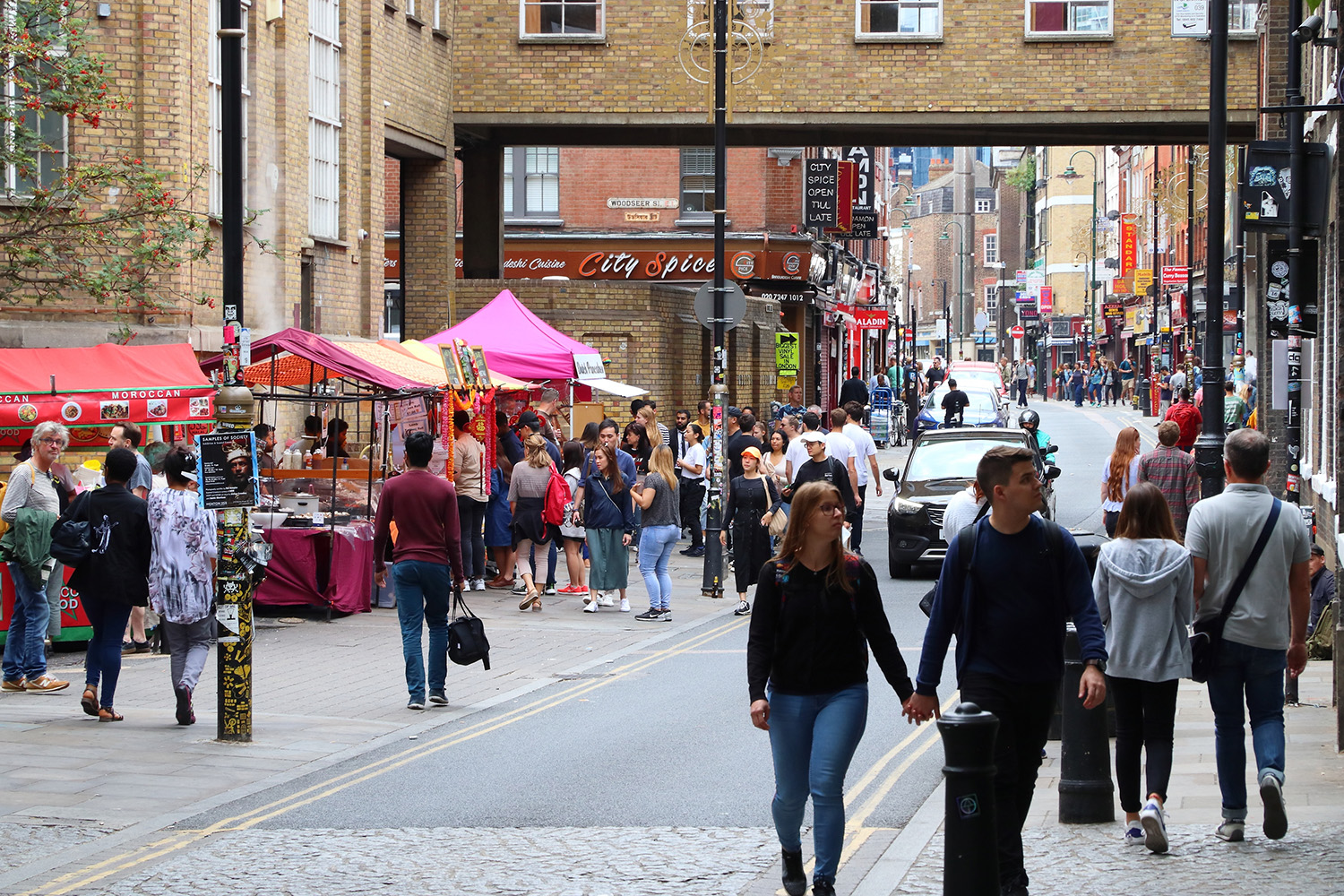

Brick Lane in Shoreditch, London
Today, the area has a diverse ethnic population.
What is the cultural mix found in Shoreditch?
Shoreditch boasts a diverse cultural blend and is almost unrecognisable from three decades ago. The old industrial structures have transformed into residential flats and office spaces. Additionally, pubs and bars have been revamped and repurposed into restaurants and art galleries. New job opportunities have emerged in creative industries, such as web design, filmmaking, and art, with a concentration around the Old Street roundabout. The rapid influx of hi-tech companies has earned the area the moniker “Silicon Roundabout,” reminiscent of Silicon Valley, California’s tech industry hub where numerous tech giants blossomed. Facebook, Google, and Microsoft have all channelled investments into the Silicon Roundabout region.
New, hi-tech companies around Old Street roundabout, nicknamed ‘Silicon Roundabout’
What are the opportunities for recreation and entertainment in Shoreditch?
Gentrification has caused a shift in the population of Shoreditch, with older residents and Bangladeshi families leaving due to increasing rents and property prices. In their place, young professionals in industries such as finance and the arts have moved in, changing the neighbourhood’s demographics.
This transformation has brought about a surge in new recreational and entertainment options, making Shoreditch one of London’s liveliest areas. During the day, the bustling cafes cater to the younger crowd, while at night, the clubs and bars enliven the streets. The walls are adorned with graffiti and artwork, which attracts many visitors.
In the mid-2000s, the Spitalfields market site was redeveloped. The new development , known as Spitalfields, is open every day of the week. The popular shopping area hosts various retail brands, street-food stalls, bars and restaurants, and independent traders showcasing handcrafted goods, artwork, fashion, and jewellery. It also hosts public art and events programmes.

Spitalfields Market, Shoreditch

Recreation and Entertainment in Shoreditch

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
How has urban change created opportunities in London?
Topic home, london docklands case study, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Urban case study - London. In this unit you'll investigate the growth of London and the processes and challenges leading to change in the city. Try the quiz to see how much you know about London and the processes of urbanisation. BACK TO GCSE MENU. Open PowerPoint.
Learn about and revise the challenges that London faces, including regeneration and urban sustainability, with GCSE Bitesize Geography (Edexcel).
A case study of a sparsely populated area - Himalayan Mountains; ... London Case Study. Main Menu. Use the images below to explore the London case study. ... AQA GCSE Geography Pre-release Resources 2024 24 March 2024 - 10:27 pm. GCSE Geography Mind Maps 14 March 2024 - 2:02 pm.
Revision notes on 4.2.1 Functions & Structure of London for the Edexcel GCSE Geography syllabus, written by the Geography experts at Save My Exams. Home. GCSE. Maths. GCSE Maths. Edexcel (Foundation) ... 4.2 Case Study of a UK City: London. 4.2.1 Functions & Structure of London; 4.2.2 Migration, Employment & Services in London;
Case study - urban regeneration in Stratford, London After the closure of many of London's docks in the 1960s, thousands of people lost their jobs. People left the area to look for jobs elsewhere.
Revision notes on 4.2.5 Sustainable Urban Living in London for the Edexcel GCSE Geography syllabus, written by the Geography experts at Save My Exams. ... 4.2 Case Study of a UK City: London. 4.2.1 Functions & Structure of London; 4.2.2 Migration, Employment & Services in London;
The means a negative multiplier effect where people don't have jobs, there is less tax paid, councils have less to invest in education and services so people get worse jobs. Everything you need to know about London Case Study of Urban Area for the GCSE Geography B Edexcel exam, totally free, with assessment questions, text & videos.
AQA GCSE Geography Urban Issues and Challenges Urbanisation in the UK: London Case Study. London is the capital city of the United Kingdom and stands as one of the world's dominant economic hubs. Since the late 18th century, it has experienced rapid growth in size and population, driven by increasing rates of urbanisation.
#gcsegeography #aqageography #sundaymorningcoffee Timestamps:00:48 London Facts01:27 Influential Sectors01:54 London PopulationSeries of 4 London case study ...
Regeneration - reuse of venues, new homes, and improved transportation. The key for this unit is Legacy point 4 - urban regeneration. Urban Regeneration is the whole sale improvement of the buildings and infrastructure of an area. The Olympic athletes village was converted to a new housing area in London.
Urban case study - London. Test your knowledge of London and urbanisation with this 15-question GCSE quiz. If you haven't already done it, work through the urban case study of London on the PowerPoint (especially the graph on page 11). Or look at it again to help fill any gaps in what you know!
GCSE AQA Geography - Urban - London lessons. Full set of lessons covering Urban London. Lots of resources to choose from. Easily adapted. Fully resourced. Modelled e ... AQA GCSE Geography - Urban London Case Study - Lessons. Subject: Geography. Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Unit of work. GeoReso High Quality Geography Resources. 5.00 4 reviews.
The London waste management strategy is aiming to; 1. To achieve zero municipal waste direct to landfill by 2025. 2. To reduce the amount of household waste produced from 970kg per household in 2009/10 to 790kg per household by 2031. This is equivalent to a 20 per cent reduction per household.
The graph shows that the economy of London is different to that of the rest of the UK. It is dominated by financial and insurance activities, mainly located in the City of London. Overall; • Productivity in London is 40% higher than the UK average • London accounts for 27.4% of the Gross Value added of the UK in 2018 at £425 billion!
3) WW2 caused a decrease in population until the end of the war in 1945. 4) During the 1900s other countries saw their cities experience huge population surges and London was overtaken. 5) London reached a record high population of 8.6 million in 2015. 6) The city is predicted to keep growing and to exceed a population of 10 million, becoming a ...
8.3 million. Location of London: - South-East of the UK. - In the county of Greater London. - The River Thames passes through it which is one of the largest major rivers in the UK. - It is situated on low-lying flat land. National importance: - 13% of the UK's population lives here. - London generates 22% of UK's GDP.
Location and population • London's population is 12.5% of the UK's on just 0.6% of the land • It is 36.5 miles west to east and 30 miles North to south • Peak population in 1939 • It is predicted to go beyond that level soon and is currently 8.98 million (2019) • 117,500 babies were born in London in 2019 • The wider London area ...
Geography Case Studies - A wide selection of geography case studies to support you with GCSE Geography revision, homework and research. X; Facebook; Youtube; 0 Shopping Cart ... Case Study - Inner City Redevelopment - London's Docklands; Volcanoes. What is a volcano? Where are volcanoes located?
London's regional position is largely driven by high unemployment levels across Inner London boroughs where unemployment rates average 8.9 per cent. Across Outer London, unemployment levels (5.4 per cent) are nearer the national average (5.2 per cent). Across London, borough rates vary from 3.6 per cent in Sutton up to 12.3 per cent in Newham.
Case Study - Docklands, London ... AQA GCSE Geography Pre-release Resources 2024 24 March 2024 - 10:27 pm. GCSE Geography Mind Maps 14 March 2024 - 2:02 pm. Statistical Techniques in Geography Poster 26 February 2024 - 2:11 pm. How do I revise GCSE Geography? 19 February 2024 - 12:33 pm.
Crossrail Case Study - Transport in London. London has a comprehensive, integrated travel system. ... AQA GCSE Geography Pre-release Resources 2024 24 March 2024 - 10:27 pm. GCSE Geography Mind Maps 14 March 2024 - 2:02 pm. Statistical Techniques in Geography Poster 26 February 2024 - 2:11 pm.
GCSE - Urban Issues and Challenges. UIC - Global Patterns of urban change UIC - Factors affecting urbanisation and megacities. YOU ONLY need to study one LIC/NEE case study. LIC or NEE case study 1 - MUMBAI CASE STUDY. LIC or NEE case study 2 - Lagos case study. UIC - Mumbai, location & Importance UIC - Mumbai, causes of growth UIC - Mumbai ...
Shoreditch London Case Study - Shoreditch is an example of how urban change has created cultural, recreation, and entertainment opportunities. X; Facebook; Youtube; 0 Shopping Cart +Plus. ... AQA GCSE Geography Pre-release Resources 2024 24 March 2024 - 10:27 pm. GCSE Geography Mind Maps 14 March 2024 - 2:02 pm.