
Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.

MLA Style (9th Edition) Citation Guide: Books & Ebooks
- Introduction to MLA Style
- Journal Articles
- Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Books & Ebooks
- Government & Legal Documents
- Biblical Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Videos/DVDs/TV Shows
- How to Cite: Other
- 9th Edition Updates
- Additional Help
Table of Contents
Book in print, book with editor(s) but no author, translated book, chapters, short stories, essays, or articles from a book (anthology or collection), an introduction, preface, foreword, or afterword, article in a reference book (e.g. encyclopedias, dictionaries).
Note: For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
Authors/Editors
An author can be a person but can also be an organization, or company. These are called group or corporate authors.
If you are citing a chapter from a book that has an editor, the author of the chapter is listed first, and is the name listed in the in-text citation.
Capitalize the first letter of every important word in the title. You do not need to capitalize words such as: in, of, or an.
If there is a colon (:) in the title, include what comes after the colon (also known as the subtitle).
You have the option to use the shortened name of the publisher by abbreviating "University" and "Press" (e.g. Oxford UP, not Oxford University Press).
You also have the option to remove articles (A, An, The), business abbreviations (e.g. Co., Inc.) and descriptive words (e.g. Books, House, Press, Publishers).
The format of all dates is: Date Month (shortened) Year. e.g. 5 Sept. 2012.
Whether to give the year alone or include a month and day depends on your source: write the full date as you find it there.
If no date is listed, omit it unless you can find that information available in a reliable source. In that case the date is cited in square brackets. e.g. [2008]
Page Numbers
Page number on your Works Cited page (but not for in-text citations) are now proceeded by p. for a single page number and pp. for a range of page numbers. E.g. p. 156 or pp. 79-92.
Access Date
Date of access is optional in MLA 8th/9th edition; it is recommended for pages that may change frequently or that do not have a copyright/publication date.
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
Note : The city of publication should only be used if the book was published before 1900, if the publisher has offices in more than one country, or if the publisher is unknown in North America.
Works Cited List Example:
Kurlansky, Mark. Salt: A World History . Walker, 2002.
In-Text Citation Example:
(Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Kurlansky 10)
Two Authors
Last Name, First Name of First Author, and First Name Last Name of Second Author. Title of Book: Subtitle if Any. Edition if given and is not first edition, Publisher Name often shortened, Year of publication.
Note: Only the first author listed appears in "Last Name, First Name" format. Authors' names are separated by a comma. Before the last author to be listed, add the word "and."
Jacobson, Diane L., and Robert Kysar. A Beginner's Guide to the Books of the Bible, Augsburg, 1991.
(Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Jacobson and Kysar 25)
Three or More Authors
Last Name, First Name of First Author, et al. Title of Book: Subtitle if Any. Edition if given and is not first edition, Publisher Name often shortened, Year of publication.
Note: If you have three or more authors list only the first author's name followed by et al. instead of listing all authors names. For example Smith, John, et al. The first author is the first name listed on the work you are citing, not the first name alphabetically.
Nickels, William, et al. Understanding Business. 9th ed., McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2016.
(First Author's Last Name et al. Page Number)
Example: (Nickels et al. 5)
eBook from a Library Database
Last Name, First Name of First Author, et al. Title of Book: Subtitle if Any. Edition if given and is not first edition, Publisher Name often shortened, Year of publication. Name of eBook Database, doi:DOI number/URL/Permalink.
Calhoun, Craig. Sociology in America: A History . U of Chicago P, 2008. ProQuest Ebook Central , ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/up/detail.action?docID=408466&pq-origsite=primo.
(Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Calhoun 53)
eBook for Kindle or other eBook Reader
Note: The MLA uses the term "eBook" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an eBook reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application, which will not have URLs or DOIs. Citations will be very similar to physical book citations; just add the word "eBook" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
Silva, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing , eBook, American Psychological Association, 2007.
Example: (Silva 30)
Note : When no page numbers are listed on an eBook, cite the chapter number instead in your in-text citation. Example: (Smith ch. 2).
Last Name of editor, First Name, editor(s). Title of Book: Subtitle if Any. Edition if given and is not first edition, Publisher Name often shortened, Year of Publication.
Wolfteich, Claire E., editor. Invitation to Practical Theology: Catholic Voices and Visions . Paulist, 2014.
(Last name page number)
Example: (Wolfteich 103)
Electronic Materials
(More than one editor)
Kidwell, Jeremy, and Sean Doherty, editors. Theology and Economics: A Christian Vision of the Common Good. eBook, Palgrave Macmillan, 2015.
(Last name page number)
Example: (Kidwell and Doherty 103)
If you want to emphasize the work rather than the translator, cite as you would any other book. Add “translated by” and follow with the name(s) of the translator(s).
Boitani, Piero. The Bible and Its Rewritings . Translated by Anita Weston, Oxford UP, 1999.
Example: (Boitani 89)
Augustine. The Confessions of St. Augustine . Translated by Edward Bouverie Pusey, eBook, Floating Press, 1921.
Example: (Augustine 65)
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Short Story, Essay, or Article." Title of Book: Subtitle if Any, edited by Editor's First Name and Last Name, Edition if given and is not first, Publisher Name often shortened, Year of publication, Page numbers of the essay, article, or short story.
Boys, Mary C. “Learning in the Presence of the Other: Feminisms and the Interreligious Encounter.” Faith and Feminism: Ecumenical Essays , edited by Diane B. Lipsett, Westminster John Knox Press, 2014, pp. 103-114.
Note: The first author's name listed is the author of the chapter/essay/short story.
Note: If there is no editor given you may leave out that part of the citation.
Example: (Boys 110)
When citing an introduction, a preface, a foreword, or an afterword, write the name of the author(s) of the piece you are citing. Then give the name of the part being cited, which should not be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks; in italics, provide the name of the work and the name of the author of the introduction/preface/foreword/afterword. Finish the citation with the details of publication and page range.
Farrell, Thomas B. Introduction. Norms of Rhetorical Culture , by Farrell, Yale UP, 1993, pp. 1-13.
(Farrell 5)
If the writer of the piece is different from the author of the complete work, then write the full name of the principal work's author after the word "By." For example, if you were to cite Hugh Dalziel Duncan’s introduction of Kenneth Burke’s book Permanence and Change, you would write the entry as follows:
Duncan, Hugh Dalziel. Introduction. Permanence and Change: An Anatomy of Purpose, by Kenneth Burke, 1935, 3rd ed., U of California P, 1984, pp. xiii-xliv.
(Duncan xiv)
For entries in encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference works, cite the entry name as you would any other work in a collection but do not include the publisher information. Also, if the reference book is organized alphabetically, as most are, do not list the volume or the page number of the article or item.
"Ideology." The American Heritage Dictionary , 3rd ed., Dell, 1997, p. 369.
("Ideology" 369)
Online Reference book
Isaacson, Joel. "Monet, Claude." Grove Art Online , Oxford Art Online , www.oxfordartonline.com/subscriber/article/grove/art/T059077.
- << Previous: Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Next: Government & Legal Documents >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 3:07 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/mla
Works-Cited-List Entries
How to cite a book.
To create a basic works-cited-list entry for a book, list the author, the title, the publisher, and the publication date. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of book you are citing (e.g., an edited book, a translation) and how it is published (e.g., in print, as an e-book, online). Below are sample entries for books along with links to posts containing many other examples.
Book by One Author
Mantel, Hilary. Wolf Hall . Picador, 2010.
Book by an Unknown Author
Beowulf . Translated by Alan Sullivan and Timothy Murphy, edited by Sarah Anderson, Pearson, 2004.
An Edited Book
Sánchez Prado, Ignacio M., editor. Mexican Literature in Theory . Bloomsbury, 2018.
More Examples
Anthologies
Books Series
Edited Collections
Multivolume Works
Translations
- Next Example
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
MLA Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition): Books
- Understanding Core Elements
- Formatting Appendices and Works Cited List
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Academic Honesty and Citation
- In-Text Citation
- Charts, Graphs, Images, and Tables
- Class Notes and Presentations
- Encyclopedias and Dictionaries
- Generative AI
- In Digital Assignments
- Interviews and Emails
- Journal and Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Social Media
- Special Collections
- Videos and DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Citation Software
General Guideline
The general MLA 9 formatting for books is:
Work Cited List: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Date.
In-Text: (Author Last Name page number of quote or idea).
Book with One Author
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Date.
(Author Last Name page number).
Kirsh , Steven J. Children, Adolescents, and Media Violence: A Critical Look at the Research. Sage, 2006.
Book with More Than One Author
When a book has two authors , order the authors in the same way they are presented in the book.
Last Name, First Name of First Author, and First Name Last Name of Second Author. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Date.
(First Author Last Name page number).
Wykes , Maggie, and Barrie Gunter. The Media and Body Image: If Looks Could Kill. Sage, 2005.
If there are three or more authors , list only the first author followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for "and others") in place of the subsequent authors' names.
Last Name, First Name of First Author, et al. Title of Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
(First Author Last Name, et al. page number).
Nickels, William, et al. Understanding Canadian Business . McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2016.
(Nickel, et al)
Book with Editor(s) and No Author
Last Name of Editor, First Name, editor(s). Title of Book . Publisher, Publication Date.
Matuz, Roger, editor. Contemporary Canadian Artists . Gale Canada, 1997.
A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection
format.
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection, e dited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
(Last Name page number)
Example
Ross, Colin. "The Story of Grey Owl." Fiction/Non-Fiction: A Reader and Rhetoric, edited by Garry Engkent and Lucia Engkent , Thomson Nelson, 2006, pp. 327-333.
Note: The first author's name listed is the author of the chapter/essay/short story. If there is no editor given you may leave out that part of the citation.
Book by a Group or Corporate Author
Name of Corporate Author. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Date.
Calgary Educational Partnership Foundation. Employability Skills: Creating My Future, Nelson, 1996.
Note : When a work is published by an organization that is also its author, begin the entry with the title, skipping the author element. List the organization as publisher.
Self-Published
Last Name, First Name. Title. Date.
Hocking, Amanda. Fate. 2010.
(Hocking 10).
- << Previous: How Do I Cite?
- Next: Charts, Graphs, Images, and Tables >>
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite a Book Chapter in MLA
How to Cite a Book Chapter in MLA
This page is a how-to guide for using individual book chapters as sources and citing them correctly in your papers. This guide will help you determine when to cite a chapter separately and teach you how to cite a chapter both in the text of your paper and in the Works Cited page.
The information below follows the guidelines of the MLA Handbook , 9th Edition, but it is not associated with the Modern Language Association.
Table of Contents
Why you need to cite sources.
- When to Cite a Chapter
In-text citations
Works cited citations/references.
- Core elements of MLA citations
- Note on containers
Chapter/Article in an Edited Book
Chapter in an anthology/compilation/reference.
- Chapter in an Encyclopedia or Multi-volume set
Introduction/Preface/Foreword/Afterword
To write successful papers, you need to do research on your topic, and you include that research in your papers using citations. Citing a source in your paper means that you are using other people’s expertise to support your ideas. You “borrow” the credibility of these experts to increase your own credibility as a researcher. According to the Modern Language Association’s Handbook , “By giving credit to the precursors whose ideas they work with, scholars allow future researchers interested in the history of a conversation to trace the line of inquiry back to its beginning” (95).
In other words, when you cite sources properly, you are establishing and demonstrating your credibility as a researcher, and you ensure that you are not plagiarizing the material. This improves your writing and makes it more persuasive. The citations also allow readers to distinguish the information found in sources from your original thoughts on the topic.
When to Cite a Chapter
The main reason writers will cite a chapter of a book instead of the whole book is when the chapter is written by an author(s) different from the book’s editor(s). An editor compiles a selection of articles written by other experts in the field.
If the author of the book wrote all of the chapters, you do not need to cite the chapters separately even if the chapters have names, and can instead use the standard format for citing a book in MLA . You should, however, include page numbers.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Paper
You can use information from your research in three ways:
- Paraphrase – Take the information from a specific sentence, paragraph, or section of the chapter and rewrite it in your own words.
- Summarize – Take a larger view of the section or the chapter and rewrite it in your own words.
- Quote – Use the exact words written by the author and enclose the words in quotation marks.
With all the above methods of citing research in your paper, you need to follow that information with an in-text citation and create a corresponding reference for the source on the Works Cited page.
Creating correct in-text citations within your text are important. Each in-text citation
- Alerts your reader that you are using information from an outside source.
- Usually appears in parentheses at the end of a sentence.
- Is short and only has enough information to help the reader find the complete reference listed in the Works Cited page at the end of the paper.
An in-text citation in the Modern Language Association (MLA) style has two parts (227-228):
- Name of the author or authors
- While many online sources do not have a page number, academic journals almost always do, even when they are available online.
In most cases, the in-text citation is at the end of the sentence in parentheses. When you cite the author’s name in your text, you don’t have to repeat it in the parentheses at the end. Do not separate the author’s name and the page number with a comma. See below for examples.
In-text citations are helpful, but they do not give a lot of information on the source. That’s where your works cited citations come in handy. The works cited citations are designed to provide enough information so that your reader can find the original source, if needed. Every full citation follows the core elements outlined below.
Core Elements of MLA Citations
The outline for any MLA citation follows this format. Please note the punctuation at the end of each section.
Note on Containers
The 9th edition of the official Handbook uses a term for citing references that was first introduced in the 8th edition: c ontainers .
In books that have individual chapters written by different authors, the book is considered the container because it contains parts of a larger whole. The title of the first container, the book name, is printed in italics and follows the chapter name.
When accessing book chapters through a database, the database is considered the second container. This title is also printed in italics.
Below, let’s look at how to cite different types of chapters.
An edited book contains chapters that are written by authors different from the editor. When citing from a book that has been edited by someone other than the writer of the chapter, the chapter writer’s name is cited first, followed by the title of the chapter. The chapter is the source article, and the book is the first container. The editor’s name follows the name of the book.
Example citations for a chapter in an edited print book
Cite your source
Example citations for the same chapter accessed through an online source/database
Anthologies or compilations are collected works of literature such as poems or stories. An anthology can contain a selection of work from one author or from many authors. The editor of the book chooses the pieces to include and usually writes a foreword or introduction. When citing work from an anthology or compilation, the original creator of the work is listed first, followed by the title of the piece. The anthology is the first container and is listed in italics after the name of the individual piece. The editor’s name follows the name of the book.
Example of citations from a chapter in an anthology
Chapter in an Encyclopedia or Multivolume Set
Encyclopedias are reference works that provide summaries of information from all branches of knowledge or all branches of knowledge in a particular field. Entries in an encyclopedia often have a title, but no author listed. When citing a section of an encyclopedia, the section or chapter name is listed first. The name of the encyclopedia is the first container. The publisher of the encyclopedia follows its name.
Encyclopedia sections often do not have author names. If no author is listed, start the citation with the section name. Online sources will also not have page numbers, so omit them as well.
Examples of citations from an encyclopedia
Multivolume sets can have one title for the entire set and may have individual titles for each volume. When citing these sources, cite the title of the entire multi-volume set followed by the volume number.
Example of citations from a multivolume work
Books that are edited or are part of an anthology or compilation often have additional sections that are written by the book’s editor or another writer. These pieces can be an introduction, a preface, or a foreword, which is at the beginning of the book, or an afterword, which is at the end. When citing information from one of these sections, the writer of that section is listed first, followed by the name of the section (Introduction, Preface, etc.). This section name is not enclosed in quotation marks. The title of the book is the first container, and it is listed in italics after the section name. The editor’s name follows the name of the book.
Examples of Citations from an Introduction/Preface/Foreword/Afterword
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated June 19, 2021.
Written by Catherine Sigler . Catherine has a Ph.D. in English Education and has taught college-level writing for 15 years.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
It’s 100% free to create MLA citations. The EasyBib Citation Generator also supports 7,000+ other citation styles. These other styles—including APA, Chicago, and Harvard—are accessible for anyone with an EasyBib Plus subscription.
No matter what citation style you’re using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) the EasyBib Citation Generator can help you create the right bibliography quickly.
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Creating an account is not a requirement for generating MLA citations. However, registering for an EasyBib account is free and an account is how you can save all the citation you create. This can help make it easier to manage your citations and bibliographies.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
It supports MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and over 7,000 total citation styles.
To cite a book chapter in MLA style with an editor and/or a translator, you need to have basic information including the authors, chapter title, editors and/or translators, publication year, book title, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry of a book chapter (edited and translated) and examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname. In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Chris Rojek states that ….
Subsequent occurrences: Rojek confirms ….
Parenthetical:
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
Enclose the chapter title in double quotation marks and use title case. The title of the book is given in italics and title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited and translated by Name of the Editor(s)/Translator(s), Publisher, Publication Date, page range.
Rojek, Chris. “Indexing, Dragging and the Social Construction of Tourist Sights.” Touring Cultures: Transformations of Travel and Theory , edited and translated by Chris Rojek and John Urry, Routledge, 1997, pp. 52–74.
To cite a chapter in an edited book in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the authors, chapter title (unique title and/or generic label), editors, publication year, book title, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and works-cited-list entries for a chapter in an edited book written by a single author and some examples are given below:
First mention: Gayatri Gopinath ….
Subsequent occurrences: Gopinath ….
….(Gopinath).
Include the unique chapter title in title case and enclose it in double quotation marks. If the chapter does not have a unique title and instead uses a generic label, do not enclose it in quotation marks.
Include the book title in title case and in italics.
Surname, First Name. Generic Label. Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Date, page range.
Surname, First Name. “Unique Chapter Title.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Date, page range.
Surname, First Name. “Unique Chapter Title.” Generic Label. Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Date, page range.
Notice that the last template uses a chapter with both a unique chapter title and a generic label. In this case, use the unique chapter title first and enclose it in double quotation marks and follow it with the generic label (as shown in the third example below).
Gopinath, Gayatri. Introduction. Political Emotions , edited by Ann Cvetkovich et al., Routledge, 2010, pp. 167–92.
Gopinath, Gayatri. “Archive, Affect, and the Everyday: Queer Diasporic Re-Visions.” Political Emotions , edited by Ann Cvetkovich et al., Routledge, 2010, pp. 167–92.
Gopinath, Gayatri. “Archive, Affect, and the Everyday: Queer Diasporic Re-Visions.” Introduction. Political Emotions , edited by Ann Cvetkovich et al., Routledge, 2010, pp. 167–92.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

- Peterborough

MLA Style: Citing Sections of Books
- One part of a book by single author
- Article or chapter in edited book
- Article or entry in a reference book (print and online)
- Work in an anthology
- Introduction, preface, foreward, afterword
- Article, story, poem found in coursepack

One Part of a Book with a Single Author
In-text citation.
(Garrett-Petts 63)
Works Cited
Author's Last Name, Author’s First Name. "Article or Chapter Title." Title of Book, Publisher, Year of Publication, pp. Page Range.
Garrett-Petts, W.F. "Writing the Critical Essay: Form and the Critical Process." Writing about Literature: A Guide for the Student Critic, Broadview, 2000, pp. 57-86.
Article or Chapter in Edited Book in Which There Are Articles/Chapter by a Number of Writers
(Lacombe 126)
Author's Last Name, Author’s First Name. "Article or Chapter Title." Title of Book, edited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year of Publication, pp. Page Range.
Lacombe, Michele. "The Cybor Identities of Oryx and Crake." Margaret Atwood: The Open Eye, edited by John Moss and Tobi Kozakewich, U of Ottawa P, 2006, pp. 117-36.
Cross Referencing Articles Found in One Book
Sometimes, you may cite several articles by different authors from one edited book. MLA now indicates that you may “cross reference” within your Works Cited list, so you don’t have to write out the full publication information for every article you cite.
To cross reference, you would include in the Works Cited, an entry for the entire collection under the editor’s name, plus an entry for each article you are citing, under each author’s name, with abbreviated publication information. So, if you are citing two articles from one edited book, you would end up with three entries, one under the editor, plus two more, under each author:
Entire Collection:
Murphy, Christina, and Byron L. Stay, editors. The Writing Center Director’s Resource Book . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers, 2006.
Each Article:
Lerner, Neal. "Time Warp: Historical Representations of Writing Center Directors." Murphy and Stay, pp. 3-12.
Simpson, Jeanne. "Managing Encounters with Central Administration." Murphy and Stay, pp. 199-214.
- Each item appears in the Works Cited list in alphabetical order.
Entry in a Reference Book (including Encyclopedia) or Dictionary
Reference book/encyclopedia article - no author given.
"Reference/Article Title." Title of Reference Book. Year of edition, p. Page or pp. Page Range.
“Reference Book Article." Title Reference Book , Number of edition if given, Any Editor or Publisher Information provided, and Date Created if given, URL, permalink or doi.
"Chile." The Encyclopedia Americana. 2004, p. 146.
“Halloween." Encyclopaedia Britannica, 30 Oct. 2015, www.britannica.com/topic/Halloween.
Reference Book/Encyclopedia Article - Authored Entries
Works cited:.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Article title." Title of Reference Book, e dited by Editor's Name, Number of edition, Year of Publication, p. Page or pp. Page Range.
Author's Last Name, Author’s First Name. “Reference Book Article." Title Reference Book , Number of edition if given, URL, permalink or doi.
Popham, Elizabeth. "Arcadian Fiction." The Spenser Encyclopedia, edited by A.C. Hamilton, 2nd ed, 2006, pp. 51-2.
Pigliucci, Massimo. "Stoicism." Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, e dited by James Fiesser and Bradley Dawden, www.iep.utm.edu/stoicism/.
- When no author is given and you are using the article title in the in-text citation, you may shorten a longer title. When no author is given for the encyclopedia entry, the title of the entry begins the Works Cited list entry. Do not use Anonymous or Anon. Alphabetize the entry using the title.
Dictionary Entry
("Sickle") ("Sepulchre")
"Dictionary Entry." Title of Dictionary, e dited by Editor's Name, Year of Publication, p. Page or pp. Page Range.
"Dictionary Entry." Title of Dictionary, Any Editor, Publication, and Date Created Information Given, URL, permalink or DOI.
"Sickle, N." The Canadian Oxford Dictionary, e dited by Katherine Barber, 2nd ed., 2004, p. 1448.
"Sepulchre." OED Online, Oxford University Press, December 2016, www.oed.com/view/Entry/176261?rskey=zxKqzl&result=1#eid.
- If your source offers a stable URL or permalink, use that over a URL.
- When citing encyclopedias, dictionaries or other reference books, you do not need to give full publication information, as shown in the first example.
- Because the second example (from The Spenser Encyclopedia ) is not widely-used, but more specialized in topic, full publication information is given in the works cited list.
Work in an Anthology
Short work (eg. poem, short story, essay) in an anthology, in-text citation .
(Dickinson line 6)
Author's Name: Last Name First. "Short Work (Poem) Title." Title of Anthology, edited by Editor's Name, Publisher, Year of Publication, p. Page or pp. Page Range.
Dickinson, Emily. "You Cannot Make Remembrance Grow." The Poems of Emily Dickinson: Reading Edition, edited by R.W. Franklin, Belknapp P of Harvard U, 1999, p. 1536.
- Because the in-text citation is for a poem, 6 refers to a line instead of a page number; a page number is used for a short story or an article.
- As the works cited example shows, titles of short poems, short stories, essays or other works that have probably not been previously published on their own are enclosed in quotation marks.
Longer Work (eg. Play, Novel) in an Anthology
(Shakespeare 1.2.26-30)
Author's Name: Last Name First. Title of Short Work Previously Published on Its Own (Play). Title of Anthology, edited by Editor's Name, Publisher, Year of Publication, p. Page or pp. Page Range.
Shakespeare, William. Antony and Cleopatra. William Shakespeare: The Complete Works, edited by Alfred Harbage, Penguin, 1969, pp. 930-76.
- Because the in-text citation is for a play, 1.2.26-30 refers to act, scene and line numbers.
- In the works cited example, the work in the anthology is a play, which, like a novel or a long poem, has probably been previously published on its own. Therefore, the title of this work, as well as the title of the anthology, is put in italics. When in doubt, use quotation marks.
Introduction, Preface, Foreword, Afterword
(McGlinn viii)
Last Name of the Author (of the section/element), First Name. Description of section or "Title" (if unique title provided). Title of Book, by Author's Name, Publisher, Year of Publication, pp. Page Range.
McGlinn, Margeurite. Introduction. The Trivium: The Liberal Arts of Logic, Grammar, and Rhetoric, by Sister Miriam Joseph, Paul Dry Books, 2002, pp. vii-xi.
- If the part has a unique title, use it instead of a description such as Introduction, and place the title in quotation marks.
- Sometimes, the writer of the Introduction, Preface, Foreword, Afterword, etc is the same as the author of the complete work. In that case, write the author’s last name only after the word “by” in the entry.
- Sometimes, an Introduction is paginated in Roman Numerals. If so, use the Roman Numerals to indicate the page range of the Introduction, as is done here.
Article, Story, Poem etc. Found in a Course Pack
(Rossetti 55)
Author's Name: Last Name First. "Short Work (Poem) Title." Title of Course pack , compiled by Compiler's Name and/or Department, Publisher (if available), Year of Publication, p. Page or pp. Page Range. Location (institution name).
Rossetti, Christina. "Goblin Market." English 1000: Introduction to English Literature , compiled by Department of English Literature, Canadian Scholar's Press, 2009, pp. 52-57, Trent University.
- The author's name is followed by the title of the work in the course pack, in this example, a poem, followed by the title of the course pack.
- If the title is for a longer work, use italics not quotation marks.
- The editor and the department of the course pack follows the title. If no person is given, simply put the department, in this case, the English literature department at Trent University.
- Course pack publisher and date are followed by the page range. Some course packs are paginated continuously, some are not but include page numbers found on the work. Use what you have. If you have both, we suggest you use the continuous pagination of the whole course pack.
- Citing a source found on Blackboard.

ENGL 1101 Rose Spring 2024: MLA Citation Help
- Let's Begin
- Annotated Bibliography Basics
- Library Catalog
- MLA Citation Help
- Tutoring at Decatur
MLA In-Text Citation Basics
The basic in-text citation form for MLA style is the author's name and a page number within parentheses, like this: (Lessig 36) or (Asimov and Lazar 55). If the author's name is mentioned in your text, you can omit it from the citation: "Lessig has argued this point (36)."
The bibliography should appear on a new page at the end of the paper, entitled "Works Cited." Alphabetize the works cited list by author's last name, or by title if a work's author is unknown or not given.
Further Citation Resources
- GSU MLA Citation LibGuide
- MLA Style Center Citation Guide
- Purdue OWL (Online Writing Lab )
Citing Articles
Article citations consist of the basic form:
Author's last name, first name. "Title of the article." Publication information.
Publication information usually consists of the journal title in italics, the volume and issue number, the year of publication, the page numbers, and a period. If the article is retrieved online, the 8th edition of the MLA Style Manual dictates including the location from which the article was retrieved, followed by a period. For example:
Monk, Craig. "The Political F. Scott Fitzgerald: Liberal Illusion and Disillusion in This Side of Paradise and The Beautiful and Damned ." American Studies International , vol. 33, no. 2, 1995, pp. 60-70. EBSCOhost , https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=mzh&AN=1997060111&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=gsu1.

Citing Books
Book citations consist of the basic form:
Author's last name, first name. Title of the book . Publication information.
The publication information typically includes the publisher name, and the year of publication. If the work is an e-book, the 8th edition of the MLA Style Manual dictates including the database from which the book was retrieved, followed by a period. For example:
Zauditu-Selassie, K. African Spiritual Traditions in the Novels of Toni Morrison . UP of Florida, 2009.
EBSCOHost, https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=e000xna&AN=380225&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=gsu1.
Cite book chapters and essays in books as follows:
Careri, Elisabetta."Home, Streets, Nature: Esperanza's Itineraries in Sandra
Cisneros' The House on Mango Street." Landscapes of Writing in Chicano Literature , edited by Imelda Martín-Junquera, Palgrave Macmillan, 2013, pp. 13-22.
Citing Web Pages
Note: The examples here do not apply to articles retrieved from online library databases, such as JSTOR and MLA International Bibliography.
To cite an entire web site, include:
Author or compiler name (if available). Name of site . Name of institution or organization affiliated with the site
(sponsor or publisher), date of site creation (if available), URL, DOI, or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
For example:
Victorian Women Writers Project. Indiana University, https://webapp1.dlib.indiana.edu/ vwwp/welcome.do;jsessionid
=EF6E5C7368B07CAAAF93A4509B363499. Accessed 23 October 2020.
To cite a page on a web site, include:
Author (if available). "Name of page." Name of site , Date of page creation (if available), URL. Date of access
(if applicable).
"Mahogany L. Browne." Poets.org , https://poets.org/poet/mahogany-l-browne. Accessed 26 October 2020.
- << Previous: Databases
- Next: Tutoring at Decatur >>
- Last Updated: Mar 19, 2024 2:06 PM
- URL: https://research.library.gsu.edu/ENGL1101RoseSpring2024
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
The Cowardice of Guernica
The literary magazine Guernica ’s decision to retract an essay about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict reveals much about how the war is hardening human sentiment.

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
In the days after October 7, the writer and translator Joanna Chen spoke with a neighbor in Israel whose children were frightened by the constant sound of warplanes. “I tell them these are good booms,” the neighbor said to Chen with a grimace. “I understood the subtext,” Chen wrote later in an essay published in Guernica magazine on March 4, titled “From the Edges of a Broken World.” The booms were, of course, the Israeli army bombing Gaza, part of a campaign that has left at least 30,000 civilians and combatants dead so far.
The moment is just one observation in a much longer meditative piece of writing in which Chen weighs her principles—for years she has volunteered at a charity providing transportation for Palestinian children needing medical care, and works on Arabic and Hebrew translations to bridge cultural divides—against the more turbulent feelings of fear, inadequacy, and split allegiances that have cropped up for her after October 7, when 1,200 people were killed and 250 taken hostage in Hamas’s assault on Israel. But the conversation with the neighbor is a sharp, novelistic, and telling moment. The mother, aware of the perversity of recasting bombs killing children mere miles away as “good booms,” does so anyway because she is a mother, and her children are frightened. The act, at once callous and caring, will stay with me.
Not with the readers of Guernica , though. The magazine , once a prominent publication for fiction, poetry, and literary nonfiction, with a focus on global art and politics, quickly found itself imploding as its all-volunteer staff revolted over the essay. One of the magazine’s nonfiction editors posted on social media that she was leaving over Chen’s publication. “Parts of the essay felt particularly harmful and disorienting to read, such as the line where a person is quoted saying ‘I tell them these are good booms.’” Soon a poetry editor resigned as well, calling Chen’s essay a “horrific settler normalization essay”— settler here seeming to refer to all Israelis, because Chen does not live in the occupied territories. More staff members followed, including the senior nonfiction editor and one of the co-publishers (who criticized the essay as “a hand-wringing apologia for Zionism”). Amid this flurry of cascading outrage, on March 10 Guernica pulled the essay from its website, with the note: “ Guernica regrets having published this piece, and has retracted it. A more fulsome explanation will follow.” As of today, this explanation is still pending, and my request for comment from the editor in chief, Jina Moore Ngarambe, has gone unanswered.
Read: Beware the language that erases reality
Blowups at literary journals are not the most pressing news of the day, but the incident at Guernica reveals the extent to which elite American literary outlets may now be beholden to the narrowest polemical and moralistic approaches to literature. After the publication of Chen’s essay, a parade of mutual incomprehension occurred across social media, with pro-Palestine writers announcing what they declared to be the self-evident awfulness of the essay (publishing the essay made Guernica “a pillar of eugenicist white colonialism masquerading as goodness,” wrote one of the now-former editors), while reader after reader who came to it because of the controversy—an archived version can still be accessed—commented that they didn’t understand what was objectionable. One reader seemed to have mistakenly assumed that Guernica had pulled the essay in response to pressure from pro-Israel critics. “Oh buddy you can’t have your civilian population empathizing with the people you’re ethnically cleansing,” he wrote, with obvious sarcasm. When another reader pointed out that he had it backwards, he responded, “This chain of events is bizarre.”
Some people saw anti-Semitism in the decision. James Palmer, a deputy editor of Foreign Policy , noted how absurd it was to suggest that the author approved of the “good bombs” sentiment, and wrote that the outcry was “one step toward trying to exclude Jews from discourse altogether.” And it is hard not to see some anti-Semitism at play. One of the resigning editors claimed that the essay “includes random untrue fantasies about Hamas and centers the suffering of oppressors” (Chen briefly mentions the well-documented atrocities of October 7; caring for an Israeli family that lost a daughter, son-in-law, and nephew; and her worries about the fate of Palestinians she knows who have links to Israel).
Madhuri Sastry, one of the co-publishers, notes in her resignation post that she’d earlier successfully insisted on barring a previous essay of Chen’s from the magazine’s Voices on Palestine compilation. In that same compilation, Guernica chose to include an interview with Alice Walker, the author of a poem that asks “Are Goyim (us) meant to be slaves of Jews,” and who once recommended to readers of The New York Times a book that claims that “a small Jewish clique” helped plan the Russian Revolution, World Wars I and II, and “coldly calculated” the Holocaust. No one at Guernica publicly resigned over the magazine’s association with Walker.
However, to merely dismiss all of the critics out of hand as insane or intolerant or anti-Semitic would ironically run counter to the spirit of Chen’s essay itself. She writes of her desire to reach out to those on the other side of the conflict, people she’s worked with or known and who would be angered or horrified by some of the other experiences she relates in the essay, such as the conversation about the “good booms.” Given the realities of the conflict, she knows this attempt to connect is just a first step, and an often-frustrating one. Writing to a Palestinian she’d once worked with as a reporter, she laments her failure to come up with something meaningful to say: “I also felt stupid—this was war, and whether I liked it or not, Nuha and I were standing at opposite ends of the very bridge I hoped to cross. I had been naive … I was inadequate.” In another scene, she notes how even before October 7, when groups of Palestinians and Israelis joined together to share their stories, their goodwill failed “to straddle the chasm that divided us.”
Read: Why activism leads to so much bad writing
After the publication of Chen’s essay, one writer after another pulled their work from the magazine. One wrote, “I will not allow my work to be curated alongside settler angst,” while another, the Texas-based Palestinian American poet Fady Joudah, wrote that Chen’s essay “is humiliating to Palestinians in any time let alone during a genocide. An essay as if a dispatch from a colonial century ago. Oh how good you are to the natives.” I find it hard to read the essay that way, but it would be a mistake, as Chen herself suggests, to ignore such sentiments. For those who more naturally sympathize with the Israeli mother than the Gazan hiding from the bombs, these responses exist across that chasm Chen describes, one that empathy alone is incapable of bridging.
That doesn’t mean empathy isn’t a start, though. Which is why the retraction of the article is more than an act of cowardice and a betrayal of a writer whose work the magazine shepherded to publication. It’s a betrayal of the task of literature, which cannot end wars but can help us see why people wage them, oppose them, or become complicit in them.
Empathy here does not justify or condemn. Empathy is just a tool. The writer needs it to accurately depict their subject; the peacemaker needs it to be able to trace the possibilities for negotiation; even the soldier needs it to understand his adversary. Before we act, we must see war’s human terrain in all its complexity, no matter how disorienting and painful that might be. Which means seeing Israelis as well as Palestinians—and not simply the mother comforting her children as the bombs fall and the essayist reaching out across the divide, but far harsher and more unsettling perspectives. Peace is not made between angels and demons but between human beings, and the real hell of life, as Jean Renoir once noted, is that everybody has their reasons. If your journal can’t publish work that deals with such messy realities, then your editors might as well resign, because you’ve turned your back on literature.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Periodicals include magazines, newspapers, and scholarly journals. Works cited entries for periodical sources include three main elements—the author of the article, the title of the article, and information about the magazine, newspaper, or journal. MLA uses the generic term “container” to refer to any print or digital venue (a website or print journal, for example) in which an essay or article may be included.
Below is the generic citation for periodicals using the MLA style. Use this as guidance if you are trying to cite a type of source not described on this page, omitting any information that does not apply:
Author. Title. Title of container (self contained if book), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publisher Date, Location (pp.). 2nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Pub date, Location (pp.).
Article in a Magazine
Cite by listing the article's author, putting the title of the article in quotations marks, and italicizing the periodical title. Follow with the date of publication. Remember to abbreviate the month. The basic format is as follows:
Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Periodical , Day Month Year, pages.
Poniewozik, James. "TV Makes a Too-Close Call." Time, 20 Nov. 2000, pp. 70-71.
Buchman, Dana. "A Special Education." Good Housekeeping, Mar. 2006, pp. 143-48.
Article in a Newspaper
Cite a newspaper article as you would a magazine article, but note the different pagination in most newspapers. If there is more than one edition available for that date (as in an early and late edition of a newspaper), identify the edition after the newspaper title.
Brubaker, Bill. "New Health Center Targets County's Uninsured Patients." Washington Post, 24 May 2007, p. LZ01.
Krugman, Andrew. "Fear of Eating." New York Times, late ed., 21 May 2007, p. A1.
If the newspaper is a less well-known or local publication, include the city name in brackets after the title of the newspaper.
Behre, Robert. "Presidential Hopefuls Get Final Crack at Core of S.C. Democrats." Post and Courier [Charleston, SC],29 Apr. 2007, p. A11.
Trembacki, Paul. "Brees Hopes to Win Heisman for Team." Purdue Exponent [West Lafayette, IN], 5 Dec. 2000, p. 20.
To cite a review, include the title of the review (if available), then the phrase, “Review of” and provide the title of the work (in italics for books, plays, and films; in quotation marks for articles, poems, and short stories). Finally, provide performance and/or publication information.
Review Author. "Title of Review (if there is one)." Review of Performance Title, by Author/Director/Artist. Title of Periodical, Day Month Year, page.
Seitz, Matt Zoller. "Life in the Sprawling Suburbs, If You Can Really Call It Living." Review of Radiant City , directed by Gary Burns and Jim Brown. New York Times, 30 May 2007, p. E1.
Weiller, K. H. Review of Sport, Rhetoric, and Gender: Historical Perspectives and Media Representations , edited by Linda K. Fuller. Choice, Apr. 2007, p. 1377.
An Editorial & Letter to the Editor
Cite as you would any article in a periodical, but include the designators "Editorial" or "Letter" to identify the type of work it is.
"Of Mines and Men." Editorial. Wall Street Journal, eastern edition, 24 Oct. 2003, p. A14.
Hamer, John. Letter. American Journalism Review, Dec. 2006/Jan. 2007, p. 7.
Anonymous Articles
Cite the article’s title first, then finish the citation as you would any other for that kind of periodical.
"Business: Global Warming's Boom Town; Tourism in Greenland." The Economist , 26 May 2007, p. 82.
"Aging; Women Expect to Care for Aging Parents but Seldom Prepare." Women's Health Weekly, 10 May 2007, p. 18.
An Article in a Scholarly Journal
A scholarly journal can be thought of as a container, as are collections of short stories or poems, a television series, or even a website. A container can be thought of as anything that contains other pieces of work. In this case, cite the author and title of article as you normally would. Then, put the title of the journal in italics. Include the volume number (“vol.”) and issue number (“no.”) when possible, separated by commas. Finally, add the year and page numbers.
Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Journal , Volume, Issue, Year, pages.
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu ." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature, vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly , vol. 50, no. 3, 1994, pp. 127-53.
An Article in a Special Issue of a Scholarly Journal
When an article appears in a special issue of a journal, cite the name of the special issue in the entry’s title space, in italics. Add the descriptor “special issue of” and include the name of the journal, also in italics, followed by the rest of the information required for a standard scholarly journal citation.
Web entries should follow a similar format, and should include a DOI (if available), otherwise include a URL or permalink.
Burgess, Anthony. "Politics in the Novels of Graham Greene." Literature and Society, special issue of Journal of Contemporary History, vol. 2, no. 2, 1967, pp. 93-99.
Case, Sue-Ellen. “Eve's Apple, or Women's Narrative Bytes.” Technocriticism and Hypernarrative, special issue of Modern Fiction Studies, vol. 43, no. 3, 1997, pp. 631-50. Project Muse , doi:10.1353/mfs.1997.0056.
Scribbr MLA Citation Generator
Accurate MLA citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
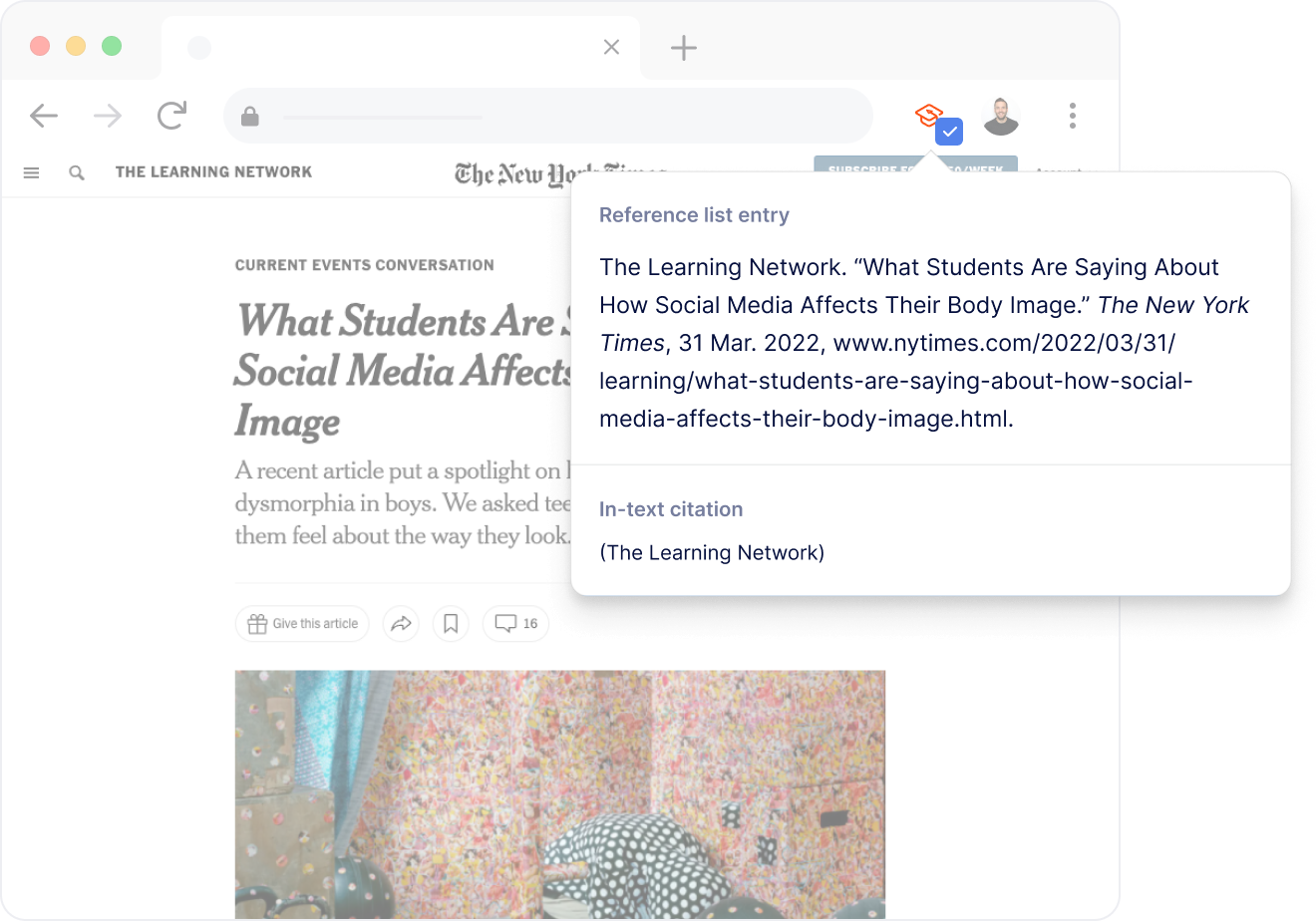
Scribbr's MLA Citation Generator for Chrome
Effortlessly cite any page or article directly from your browser with just one click. Our extension simplifies the citation process by automatically retrieving essential details such as the title, author(s), and publication date , ensuring accurate MLA citations in seconds.

Trust in expert-verified MLA citations
Avoid the risk of losing points due to incorrect citations. Our MLA citation experts have meticulously refined our algorithms, ensuring precision and reliability. This dedication has earned us recognition and recommendations from educators worldwide.
Experience distraction-free citation
Focus on your work without interruptions. Our citation generator provides a clean interface, free from distracting video pop-ups and flashing ads. Best of all, it's completely free for everyone.
Features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
MLA 8th & 9th edition
Scribbr's Citation Generator supports both MLA 8 and MLA 9 (as well as APA and Harvard ). No matter what edition you're using, we’ve got you covered!
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr's citation generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Create perfectly formatted MLA Style annotated bibliographies with just a few clicks.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Citation guides
Getting to grips with citation is simple with the help of our highly rated MLA citation guides and videos .
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Missing information
- No page numbers
- Scroll to top
How to cite in MLA format

MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook . You can also use Scribbr’s free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.
An MLA citation has two components:
- In-text citation : Every time you quote or paraphrase a source, you cite the author and the page number in parentheses.
- Works Cited : At the end of your paper, you give a full reference for every source you cited, alphabetized by the author’s last name.
MLA Works Cited list
The list of Works Cited (also known as the bibliography or reference page) gives full details of every source you cited in your text. Each entry is built from nine core elements:
Following this format, you can create a citation for any type of source—for example, a book , journal article , website , or movie . You only include information that’s relevant to the type of source you’re citing.
Missing information in MLA citations
Regardless of the source type, the most important elements of any MLA citation are the author , the source title , and the publication date. If any of these are missing from the source, the Works Cited entry will look slightly different.
MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate MLA citations in seconds
Get started
MLA in-text citations
MLA in-text citations are brief references that direct your reader to the full source entry. You include them every time you quote , block quote , paraphrase or summarize a source.
The in-text citation must match the first word of the Works Cited entry—usually the author’s last name . It also includes a page number or range to help the reader locate the relevant passage.
If you already named the author in your sentence, include only the page number in parentheses:
Sources with no page numbers
If the source has no page numbers, you either use an alternative locator, or leave the page number out of the citation:
Tools and resources
Besides the MLA Citation Generator, Scribbr provides many more helpful tools and resources;
- Citation generator : Generate flawless APA , MLA , and Harvard citations in seconds
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect and correct plagiarism with the most accurate plagiarism checker for students
- AI Proofreader : Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Hire a professional editor to improve your writing
- Citation checker : Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Guides and videos : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Read Your Way Through the San Francisco Bay Area
The Bay Area has had many lives. The Oakland novelist Leila Mottley shares books that paint a picture of the city that lives and breathes today.

By Leila Mottley
Read Your Way Around the World is a series exploring the globe through books.
The San Francisco Bay Area is anything but a monoculture. Go to San Francisco, hop across the Bay Bridge into Oakland, then head up into Richmond or down to Hayward, and the landscape around you — the people, the food, the particular cadence of walk and talk — will morph. To read the Bay Area is to traverse the spectrum of a place that has had many lives, simultaneously a landing spot for people seeking sanctuary and a place that has repelled the very people who have shaped it and loved it most.
The Bay Area is known for starting shit. We are the genesis for movements, trends, renaissances, from political uprisings to the artists who resonate from the stereos in our cars. The Bay Area is unafraid to be first. We are the creators of legacies — and also often overlooked.
I could tell you about Jack London’s early 1900s Oakland or John Steinbeck’s Salinas Valley, but that would tell you very little about the Bay Area that lives and breathes today — the people you will stumble into and love like your own, the dips in our roads and the weaving roots of our trees. It’s important to acknowledge the literary canon, but its gaps are deep, particularly when it comes to painting a full picture of one of the most racially and ethnically diverse regions in the country.
I’m here to give you a more complete vision of my home by sharing stories that see us as we see ourselves: stories of rebellion, of breath, of found family. Stories of creation.
What are your favorite books about Oakland?
Arguably the most foundational Oakland book from the past decade is “ There There ,” by Tommy Orange . Orange writes vignettes from the perspectives of different Native characters across the U.S. who gather for the Big Powwow at the Oakland Coliseum. Somehow, Orange’s sophomore novel, “ Wandering Stars, ” gives us even more Oakland, expanding through time and neighborhoods in his unforgettable voice. Yes, this is the Oakland we love: vibrant, scrappy and complex. And what a relief it is to finally see it woven in the glorious thread of language.
Young adult novels get a bad rap, maybe because, even when we were teenagers, we wanted more from the stories we were given and assume the same lack from the Y.A. that exists today. But Carolina Ixta’s debut Y.A. novel, “Shut Up, This Is Serious,” proves that it is possible — and vital — to give young people a story that is rooted and complicated, crafted by an author who believes these readers are competent enough to handle an honest depiction of Mexican American girlhood in East Oakland. Ixta tells a compelling and beautifully written coming-of-age story, and even if you’re not a young person, you will find this is one of the most nuanced contemporary novels set in Oakland.
What should I read to learn about the Black Panthers?
You cannot read the Bay Area without understanding the impact of the Black Panthers. In particular, Oakland’s history of resistance has an important place in the archives of the Black Power movement and its continuation in Black Lives Matter and beyond. “Seize the Time: The Story of the Black Panther Party and Huey P. Newton,” by Bobby Seale, and “Revolutionary Suicide,” Huey P. Newton’s autobiography, are important, but Elaine Brown’s memoir “A Taste of Power” deserves more attention as the firsthand account of the only chairwoman of the Black Panther Party in the organization’s history and a critical examination of misogyny within the movement.
You can find these books, and more by and about Black activists, at Marcus Books , one of the oldest Black-owned independent bookstores in the United States, which stocks classics as well as work from local authors and independent presses.
Where should I go to read at U.C. Berkeley?
Visit the Morrison Library , a beautiful, electronics-free reading room, and read cult classics by Berkeley alumni — like Theresa Hak Kyung Cha’s mesmerizing “Dictee,” which grapples with language in unexpected ways. You can also explore books by writers who taught at the university and left their mark on the literature of the Bay Area, such as “The Color Purple,” by Alice Walker , and “Naming Our Destiny: New and Selected Poems,” by June Jordan.
Then, visit Berkeley’s Poetry Walk on Addison Street between Shattuck Avenue and Milvia Street, where you’ll find cast-iron plaques inlaid in the sidewalk with selected poetry by local authors and internationally renowned writers.
What should I read to young people?
When I was a child, one of my favorite picture books was Patricia Polacco’s “In Our Mothers’ House,” about two lesbian moms and their adopted children, which honors queer families in the East Bay. In another remarkable picture book, “Last Stop on Market Street,” by Matt de la Peña, a Black boy travels by bus with his grandmother through the streets of San Francisco, asking questions about class from a child’s perspective. Like many Bay Area kids, I spent much of my childhood on the bus or on BART trains, and this book is a sweet ode to the view from those little windows.
For teenage (and adult) readers, Malinda Lo’s “Last Night at the Telegraph Club” portrays a Chinese American teenager coming of age and discovering her sexuality in 1954 San Francisco’s Chinatown. Gene Luen Yang’s graphic novel “ American Born Chinese ” explores race, home and identity through the story of a Chinese American boy growing up in a predominantly white San Jose suburb. Yang was born in the East Bay before his family moved to a suburb of San Jose, and his childhood spent across the Bay can be felt in this novel, which was recently adapted as a television show on Disney+.
What if I just want to have a good time?
If you’re looking to have a warm heart and a happy mind, try Rita Williams-Garcia’s “ One Crazy Summer ,” a novel for young people that tells the story of three sisters going to visit their mother in Oakland in 1968. It’s a refreshing book that reflects the activism and community work of the Black Panthers through a child’s eyes.
For romance fans, Jasmine Guillory should be at the top of your list. Guillory’s “The Wedding Date” spans the range of California, and is full of references to the Bay Area.
Danyel Smith’s “Shine Bright: A Very Personal History of Black Women in Pop” is a dissection of the history of pop music and Black women’s contributions to it. Smith is a music reporter from Oakland and this book is a testament to her abundant knowledge .
What can I read about other parts of the Bay Area?
Elaine Castillo’s “ America Is Not the Heart ” is a poignant portrayal of Filipino immigrant communities in Milpitas and the surrounding South Bay in the 1990s. The San Francisco Bay Area has the second largest Filipino population in the United States, and Castillo examines the divisions between different Filipino ethnic groups, the radical legacy of the New People’s Army and how a career might not follow you to a new country.
If you’d like to explore the area north of San Francisco, “Solito,” by Javier Zamora, is one of the most beautiful and devastating memoirs I have ever read. The book follows Zamora’s migration at 9 years old from El Salvador and through Mexico in an attempt to join his parents in San Rafael, California. While the book isn’t set in the Bay, it is the eventual landing point for Zamora. “Solito” captures the experience of having multiple homes and what it means to leave one home and seek belonging in another, an experience that’s common among immigrant communities in the Bay Area (and beyond).
For those looking for fiction that delves into untold histories, Margaret Wilkerson Sexton’s “ On the Rooftop ” explores the gentrification of San Francisco in the 1950s as it follows three sisters in a singing group in the Fillmore. It will transport you to a San Francisco that is rarely written of — except maybe in Maya Angelou’s “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings,” which is required reading for everyone, everywhere.
What poets should I read?
The Bay Area has a robust poetic legacy. In the 1950s, drawing from jazz improvisation, the Beat poets created a culture of free-verse poetry. Allen Ginsberg and Lawrence Ferlinghetti often get the most glory, but it would be remiss to forget Bob Kaufman, a Black poet known for reciting poems on the street. A comprehensive selection of his work, “ Collected Poems of Bob Kaufman ,” was published by San Francisco’s iconic and longstanding (Ferlinghetti-founded) City Lights Bookstore .
The Bay Area has produced some incredible contemporary poets like Chinaka Hodge (read her collection “Dated Emcees” — it’s brilliant) and Tongo Eisen-Martin, the most recent San Francisco poet laureate. Eisen-Martin’s collection “ Heaven Is All Goodbyes ” is one of my favorites, wielding words to deconstruct the language of capitalism and displacement. Pick this up if you want to read a poem and sit stunned, returning to it again and again.
A poet is also a performer, and some will take your breath away if you have the honor of witnessing them recite. Among them are Mahogany L. Browne , the author of the long-form book/poem/masterpiece “I Remember Death by Its Proximity to What I Love” and the recent collection “Chrome Valley,” and Darius Simpson , the author of “Never Catch Me.” A special shout-out to the spectacular Danez Smith poem “ Tonight, in Oakland ,” from his collection “Don’t Call Us Dead,” which brings me down to my bones every time:
Let wherever two people stand be a reunion of ancient lights. Let’s waste the moon’s marble glow shouting our names to the stars until we are the stars. O, precious God! O, sweet black town! I am drunk & I thirst.
Leila Mottley’s San Francisco Bay Area Reading List
“There There” and “Wandering Stars,” Tommy Orange
“Shut Up, This Is Serious,” Carolina Ixta
“Seize the Time: The Story of the Black Panther Party and Huey P. Newton,” Bobby Seale
“Revolutionary Suicide,” Huey P. Newton
“A Taste of Power,” Elaine Brown
“Dictee,” Theresa Hak Kyung Cha
“The Color Purple,” Alice Walker
“Naming Our Destiny: New and Selected Poems,” June Jordan
“In Our Mothers’ House,” Patricia Polacco
“Last Stop on Market Street,” Matt de la Peña
“Last Night at the Telegraph Club,” Malinda Lo
“American Born Chinese,” Gene Luen Yang
“One Crazy Summer,” Rita Williams-Garcia
“The Wedding Date,” Jasmine Guillory
“Shine Bright: A Very Personal History of Black Women in Pop,” Danyel Smith
“America Is Not the Heart,” Elaine Castillo
“Solito,” Javier Zamora
“On the Rooftop,” Margaret Wilkerson Sexton
“I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings,” Maya Angelou
“Collected Poems of Bob Kaufman,” Bob Kaufman
“Dated Emcees,” Chinaka Hodge
“Heaven Is All Goodbyes,” Tongo Eisen-Martin
“I Remember Death by Its Proximity to What I Love” and “Chrome Valley,” Mahogany L. Browne
“Never Catch Me,” Darius Simpson
“Don’t Call Us Dead,” Danez Smith
Leila Mottley ’s debut novel, “Nightcrawling,” published when she was 19 years old, was longlisted for the Booker Prize . It was also a New York Times best seller and an Oprah’s Book Club pick. Her poetry collection “woke up no light” will be published in April 2024. She was born and raised — and continues to live — in Oakland.
Let Books Take You to Your Next Destination
We asked renowned writers from around the world to compile literary guides to the places close to their hearts..
San Francisco: The Oakland novelist Leila Mottley shares books that paint a picture of a city that has had many lives, and still lives and breathes today .
Madrid: Elena Medel, a poet, forged her identity in the Spanish capital. She recommends books about the city that “refuses to be reduced to an ideal.”
Seoul: Han Kang, who grew up in the capital of South Korea, recommends reading that draws from the various eras that have defined her hometown.
Utah: The U.S. state is a place of paradoxes. The writer Terry Tempest Williams recommends books to help you explore its many facets .
Salvador: The writer Itamar Vieira Junior says that to feel the intensity of life on the streets of the Brazilian city, a reader must start with Jorge Amado .
Kerala : The author Abraham Verghese offers a guide to the literature of this strip of coastal territory at India’s southern tip.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author's name (s), chapter title, book title, editor (s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below: In-text citation template ...
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows: Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection, edited by Editor's Name (s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry. Some examples: Harris, Muriel.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Citing a book chapter. Use this format if the book's chapters are written by different authors, or if the book is a collection of self-contained works (such as stories, essays, poems or plays).A similar format can be used to cite images from books or dictionary entries.If you cite several chapters from the same book, include a separate Works Cited entry for each one.
Faith and Feminism: Ecumenical Essays, edited by Diane B. Lipsett, Westminster John Knox Press, 2014, pp. 103-114. Note: The first author's name listed is the author of the chapter/essay/short story. Note: If there is no editor given you may leave out that part of the citation. In-Text Citation Example: (Author's Last Name Page Number)
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
How to Cite a Book. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for a book, list the author, the title, the publisher, and the publication date. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of book you are citing (e.g., an edited book, a translation) and how it is published (e.g., in print, as an e-book, online).
Cite your book. *Keep "https:" at the beginning of the URL only when citing a DOI. Digital sources with no page numbers means that no page numbers should be included in the in-text citation. In-text Citation. Structure. (Last Names) OR Last Names. Example. (Austen and Grahame-Smith) OR Austen and Grahame-Smith.
Ross, Colin. "The Story of Grey Owl." Fiction/Non-Fiction: A Reader and Rhetoric, edited by Garry Engkent and Lucia Engkent , Thomson Nelson, 2006, pp. 327-333. (Ross 328) Note: The first author's name listed is the author of the chapter/essay/short story. If there is no editor given you may leave out that part of the citation.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Paper. You can use information from your research in three ways: Paraphrase - Take the information from a specific sentence, paragraph, or section of the chapter and rewrite it in your own words. Summarize - Take a larger view of the section or the chapter and rewrite it in your own words.
MLA Style: Citing Sections of Books. One part of a book by single author. Article or chapter in edited book. Article or entry in a reference book (print and online) Work in an anthology. Introduction, preface, foreward, afterword. Article, story, poem found in coursepack.
Cite book chapters and essays in books as follows: Careri, Elisabetta."Home, Streets, Nature: Esperanza's Itineraries in Sandra. Cisneros' The House on Mango Street." Landscapes of Writing in Chicano Literature, edited by Imelda Martín-Junquera, Palgrave Macmillan, 2013, pp. 13-22.
Highlight the whole list and click on Format > Align and indent > Indentation options. Under Special indent, choose Hanging from the dropdown menu. Set the indent to 0.5 inches or 1.27cm. You can also use our free template to create your Works Cited page in Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review's podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here. In her elegant essay collection, "Lessons for Survival ...
General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats. Basic Format Basic guidelines for formatting the works cited page at the end of an MLA style paper Books
The original book tells the story of the orphaned Alden siblings (Henry, Jessie, Violet and Benny), who strike out on their own and find refuge in an abandoned boxcar, which they gussy up with ...
It goes on for so long that the reader has time to love it, hate it, become exasperated with it, resign herself to it and, finally, admire its diabolical commitment. Now Oyler has returned with ...
To cite a book chapter, first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter. The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage. Author last name, First name.
00:00. 09:10. Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration. In the days after October 7, the writer and translator Joanna Chen spoke with a neighbor in Israel whose children ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Times New Roman 12. 1″ page margins. Double line spacing. ½" indent for new paragraphs. Title case capitalization for headings. For accurate citations, you can use our free MLA Citation Generator.
When I sat down to read, I almost immediately cringed. On the first page of the introduction, Cameron invokes "The Great Creator," a.k.a. capital "G" God. That immediately set off my ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review's podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here. Crafting the arguments in "You Get What You Pay For," her ...
By Leila Mottley. March 13, 2024. Read Your Way Around the World is a series exploring the globe through books. The San Francisco Bay Area is anything but a monoculture. Go to San Francisco, hop ...