myCBSEguide
- Business Studies
- CBSE Sample Papers Class...

CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Business Studies 2023-24
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Sample Question Paper for class 11 Business Studies – in PDF
CBSE Sample Papers 2024 of class 11 Business Studies have some changes this year. CBSE has updated the new marking scheme and blueprint for Class 11 Business Studies for the session 2023-24. We are also providing Business Studies sample papers for Class 11 CBSE exams on myCBSEguide app and website in PDF format. Although the business studies question paper has no numerical yet you will find lots of case study-based questions. So, knowledge of practical aspects is equally important in class 11th Business Studies.
Download Business Studies Sample Papers as PDF
CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Business Studies 2024
Our mobile app myCBSEguide provides CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers of Business Studies for the academic session 2023-24 with solutions in PDF format for free download. As we know, the examination pattern is updated this year. CBSE will ask not only objective questions but there will be subjective questions as well. So, Students have to put some extra effort into their studies. Especially Business Studies is a very dynamic subject. It needs special attention to solve real-life situation-based questions.
Marking Scheme for the Class 11 exam
If you have gone through the new format of the examination, you may have noticed that the class 11 marking scheme has also changed. CBSE has added a good amount of objective questions to the examination. Especially, CBSE has introduced competency-based questions this year. Such questions have both objective and subjective types of questions. We recommend students download class 11 Business Studied model question papers from the myCBSEguide app or from the CBSE official website and practice them.
Class 11 – Business Studies Sample Paper (2023-24)
Maximum Marks: 80 Time Allowed: : 3 hours
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 34 questions.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Answers should be brief and to the point.
- Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 4 marks may be about 150 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 6 marks may be about 200 words.
- Attempt all parts of the questions together.
- When two or more firms come together to create a new business entity that is legally separate and distinct from its parents it is known as ________. It brings in people with different cultures to work together. It also gives access to better resources like specialized staff and technology. a) contract manufacturing b) franchising c) joint ventures d) licensing
- Expand KVIC a) King of Village Investment Culture b) Khadi and Village Industries Commission c) Khadi and Village Industries Core d) King of Village Industries Commission
- Funding for Departmental Undertakings comes from which of the following sources: a) Debentures b) Shares c) Government Treasury d) Loans from Financial Institutions
- Which of the following is the advantage of Mall? a) Attract a large number of customers b) All of these c) Wide choice d) Convenience in shopping
- Which of the following is part of Village and Small Industries Sector? a) Handlooms b) All of these c) Sericulture d) Handicrafts
- Which of the following is a limitation of e-business? a) Low personal touch b) Ethical fallouts c) Risk d) All of these
- The District Industries Centers Programme was launched on: a) September 1, 1978 b) July 1, 1978 c) May 1, 1978 d) 15 August 1978
- Interest paid on debentures is tax-deductible.
- Debentures do not carry voting rights.
- It preferred by investors who want fixed income at lesser risk.
- Issue of debentures dilutes the control of equity shareholders on management.
- Assertion (A): Sole proprietorship is the least regulated form of business. Reason (R): There are minimal legal formalities and it is easy to start and close the sole proprietorship business as per the wish of the owner. a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. c) A is true but R is false. d) A is false but R is true.
- To sell ready-made garments for children, men, women, etc. is the example of: a) General Store b) Single-line shop c) Departmental Store d) Single-product shop
- ________ are agents who merely bring the buyer and the seller into contact. a) Commission agent b) Broker c) Stockist d) Selling agent
- Preliminary Contracts are signed a) After incorporation but before commencement of business b) After incorporation but before capital subscription c) After commencement of business d) Before the incorporation
- Which of the following are small industries? a) More labour intensive and less capital intensive. b) Less labour intensive and less capital intensive. c) More labour intensive and more capital intensive. d) Less labour intensive and more capital intensive.
- Social interests and business interests are ________. a) Contradictory b) Complementary c) Counteractive d) Conflicting
Assertion (A): The contract of fire insurance is a contract of strict indemnity. Reason (R): A person should not be allowed to gain by insurance.
- The investment limit of SSI does not exceed a) ₹10 crore b) ₹3 crore c) Above ₹25 lakh and upto ₹5 crore d) ₹2 crore
- Which industries include activities concerned with the extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living organisms? a) Tertiary b) Primary c) Secondary d) None of these
- What do you mean by an entrepreneur ? a) Job-hunter b) Job-seeker c) Job creator d) Job-applicant
- Statutory corporations are ________. a) none of these b) sole proprietorship c) private enterprises d) public enterprises
- How does market information provided by wholesalers benefit the manufacturers?
- Identify the type of retail selling where goods are supplied to the customers without the help of middlemen and without customers undertaking journeys to the retailer.
- Enlist any three merits of such retail business.
- What are auxiliaries to trade?
- Identify the different auxiliaries to trade that are being used by Harshit in his business by quoting lines from the paragraph.
Karan is running a grocery shop in the nearby local market whereas his friend Priyanshu works as a finance manager in a reputed IT company. In the context of the above case:
- Identify the different types of economic activities both the friends are engaged in.
- Distinguish between the two different types of economic activities as identified in part (i) of the question (any two points).
- How is the mode of business that Esha intends to adopt different from the one that her father has been following over the years?
- Distinguish between the two different modes of business as identified in part (a) of the question by giving any four points.
- Name and state the type of enterprise referred to in the above para.
- State its three features.
- Business has to safeguard not only the interests of the parties but the interests of several other parties also. The other parties are the employees, consumers, supplies, competitors/rivals, government, community and the world. Today, only that business is regarded as good which along with the interests of the owner takes care of the interests of all these parties also. Which concept of business has been talked about in this statement? Identify that concept and state its meaning.
- Discuss the various characteristics or features of Entrepreneurship.
- Why is approval from SEBI considered necessary?
- Who are underwriters? Is their appointment necessary whenever a public company wishes to raise the required funds from the public by means of an issue of shares and debentures?
Jagat is running a grocery store under the name ‘Morning Needs’ in a local market. He takes all decisions about business himself, without any interference from others and also earns a direct reward for his risk-bearing. In the context of the above case:
- Identify and define the form of business organization in which Jagat has promoted his business.
- State any four features of this form of business organization.
- Describe in brief the features of equity shares.
- Identify the feature of services being discussed above.
- Explain briefly three other features of services.
Class 11 – Business Studies Sample Paper Solution
- (c) joint ventures Explanation: A joint venture is a commercial enterprise undertaken jointly by two or more parties which otherwise retain their distinct identities.
- (b) Khadi and Village Industries Commission Explanation: The various policies, programmes and schemes related to agro and rural industries are implemented by the ministry through the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), Handicrafts Board, Coir Board, Silk Board, etc.
- (c) Government Treasury Explanation: The funding of these enterprises come directly from the Government Treasury and are an annual appropriation from the budget of the government.
- (b) All of these Explanation: With the coming of Malls, the consumers get a wide variety to chose from. The customers get a variety of brands under one roof which makes it convenient for them to shop.
- (b) All of these Explanation: The village and small industries (VSI) sector consist broadly of traditional industries (viz. handlooms, khadi, and village industries, sericulture, handicrafts, and coir) and modern small scale industries including ‘tiny’ units and power loom. To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App . It provides complete study material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar papers with their own name and logo.
- Low personal touch
- Ethical fallouts
- (b) Government Explanation: Government
- (c) May 1, 1978 Explanation: The District Industries Centers Programme was launched on May 1, 1978, with a view to providing an integrated administrative framework at the district level.
- (c) Only D Explanation: Debenture holders are a debt of the company and are not allowed to take their own decisions in the company.
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Explanation: A sole proprietorship business has minimum legal restrictions and formalities. Its life depends upon the life and wish of the sole proprietor. Therefore it is the least regulated form of business.
- (b) Single-line shop Explanation: This is an example of Single-line shop.
- (b) Broker Explanation: Brokers are agents who merely bring the buyer and the seller into contact. They execute the orders as per the buyer without physically involving the buyer in the transaction.
- (d) Before the incorporation Explanation: Before the incorporation
- (a) More labour intensive and less capital intensive. Explanation: Small scale industries employed more labour and less capital .
- (b) Complementary Explanation: Complementary, because both are linked to each other.
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Explanation: The purpose behind strict indemnity in case of fire insurance is that a person should not be allowed to gain by insurance.
- (c) Above ₹25 lakh and upto ₹5 crore Explanation: Above ₹25 lakh and upto ₹5 crore
- (b) Primary Explanation: Primary industries are those industries that get raw material from nature.
- (c) Job creator Explanation: An entrepreneur is a Job creator and not a job seeker or hunter.
- (d) public enterprises Explanation: Statutory corporations are public enterprises brought into existence by a special act of the parliament.
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development ( UNCTAD ): UNCTAD that comes into being in 1964 is the international institution shaping international trade. The widening trade gap between developed and developing countries. The general dis-satisfaction of developing countries with the GATT and the need for international economic cooperation led to the setting up of UNCTAD. Few basic functions of UNCTAD are: (i) To promote international trade with a view to accelerating economic development. (ii) To formulate principles and policies on international trade and related problems of economic development.
- MIGA : The Multinational Investment Guarantee Agency was established in April 1988 to supplement the functions of the World Bank and International Finance Corporation. Few objectives of MIGA are : (i) To encourage the flow of direct foreign investment into the less developed member countries. (ii) To provide insurance cover to investors against political risks. (iii) To provide promotional and advisory services. (iv) To establish creditability.
- Production of goods and services
- Distribution of goods
- A wholesaler provides almost all the relevant information regarding the preferences and expectations of the customers to the manufacturer. He also collects information regarding the products of the competitor, price of his product, promotional schemes running by competitor for increasing the sale of his product etc. Wholesalers make suggestions about the type and quality of goods required by the consumers, and he also gives an rough idea regarding the future expected demand of the product. Such information helps the producer to regulate production according to the changing requirement of the consumer.
Equity shares are the main source of finance of a firm. It gives the right to the holders to claim dividend on the surplus profits of the company. The rate of dividend on the equity capital is determined by the management of the company. Features:
- Equity shares are transferable in nature. They can be transferred from one person to another with or without consideration.
- Equity shareholders are the actual owners of the company and they bear the highest risk.
- This is mail-order business which is also known as shopping by post.
- Elimination of middlemen which results in lots of savings for both buyers and sellers.
- It does not require heavy expenditure on building and other infrastructure. Therefore, it can be started with limited capital.
- Since the mail order business does not extend credit facilities to the customers, there is no risk of bad debts to them.
- There is no direct contact between parties so it is through advertisement which saves time.
Both the expectations of the people can be fulfilled only by a wholesale trader. Therefore, it is clear that Bindu and Rekha are doing wholesale trade. A wholesale trader can do both the desired services in the following manner:
- Control on Market Fluctuations: A wholesaler controls huge fluctuations in the market by stocking goods. Therefore, the prices remain under control. This directly benefits consumers.
- Easy Availability of Goods: The presence of the wholesaler makes it easy for a retailer to get the goods according to the taste of the consumers at any time. Consequently, all things are readily available to consumers. In the absence of the wholesaler, the retailers cannot perform this job easily.
- Auxiliaries to Trade – It implies activities required to facilitate the purchase and sale of goods i.e. are meant for assisting trade.
- Transport as he procures different kinds of products from all over the country through railways, roadways, and airways.
- Warehousing as he owns a godown to hold the stocks.
- Insurance as he has taken an insurance policy worth Rs. 10 crores for his business.
- Banking and Finance as he has taken a loan of Rs. 2,00,000 from ICICI Bank in order to meet short term financial needs of his business.
- Advertising as he has placed information about his store on the hoardings, billboards, etc. in order to popularize them.
- The different types of economic activities both the friends are engaged in are: Karan is doing Business whereas the occupation of Priyanshu is Employment.
- Esha intends to start e-business, whereas her father is following the traditional business.
- Public Private Partnership (PPP) Public-Private Partnership means an enterprise in which a project or service is financed and operated through a partnership of Government and Private enterprises.
- PPP is suitable for big projects whose gestation period is very long.
- The purpose of PPP is to combine the skills, resources, expertise and experience of both the public and private sectors to deliver a better quality of services.
- In PPP both government and private enterprises share the revenue in the agreed ratio.
- Responsibility towards the shareholders or owners
- Responsibility towards the workers
- Responsibility towards the consumers
- Responsibility towards the government and community
- Ability to take Risks: This is the first and foremost trait of entrepreneurship. Starting any business involves a considerable amount of risk of failure. Therefore, the courage and capacity to take the said risk are essential for an entrepreneur.
- Innovation: In a world, where almost everything has been done, innovation is a priceless gift to have. Innovation basically means generating a new idea with which you can start a business and achieve a substantial amount of profits. Innovation can be in the form of a product, i.e., launching a product that no one is selling in the market. It can also be in the form of a process, i.e., doing the same work in a more efficient and economical way.
- Visionary: Every entrepreneur needs to be a visionary. Without a vision for the future of his venture, he or she would just be working aimlessly without reaching any point of success.
- Leadership: An entrepreneur has a vision. However, it takes a lot of resources to turn that vision into reality. One of these resources is the people that the entrepreneur hires to perform various functions like production, supplying, accounting, etc.
- Trade Enquiry:- The first stage in an import transaction is to conduct enquiry and collect information about Canada which can export the required goods and then the exporter sends a reply in the form of a quotation called proforma invoice.
- Procurement of Import License:- We will consult the Export-Import (EXIM) policy in force to know whether the textile machinery imports are subject to import licensing. In case it can be imported only against the licence, we will procure an import licence.
- Obtaining Foreign Exchange:- As payment for imports will be made in Canadian dollars, our firm will have to make an application to a bank authorized by RBI to issue a foreign exchange.
- Placing Order:- After obtaining the import license, our firm will place an import order or indent with the exporter for the supply of the specified products. This order is known as indent.
- Obtaining a Letter of Credit:- If the payment terms agreed between us and the overseas supplier then our firm should obtain the letter of credit from its bank and forward it to the overseas supplier.
- Arranging for Finance:- Our firm would make arrangements in advance to pay to the exporter on arrival of goods at the port.
- Receipt of Shipment Advice:- After loading the ordered textile machinery on the vessel, the overseas supplier will dispatch the shipment advice to our firm which contains information about the shipment of goods.
- Retirement of Import Documents:- After shipping the machinery, the overseas supplier will prepare a set of necessary documents including bill of exchange, commercial invoice.
- Arrival of Goods:- The officer in charge at the dock will provide the document called import general manifest on the basis of which unloading of cargo will take place.
- Customs Clearance and Release of Goods:- Textile machinery imported into India will have to pass through customs clearance.
In order to promote foreign trade, the Government has set up the following institutions:
- Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT): Established in 1963 under the Societies Registration Act, the IIFT is an autonomous body responsible for the management of the country’s foreign trade. It is also a deemed university that provides training in international trade, conducts research in areas of international business.
- Export Inspection Council (EIC) : The EIC was established by the Government of India under Section 3 of the Export Quality Control and Inspection Act, 1963, with the objective of promoting exports through quality control and pre-shipment inspections.
- Indian Institute of Packaging (IIP) : The IIP is a training and research institute established in 1966 by the joint efforts of the Ministry of Commerce of the Government of lndia, Indian Packaging Industry and Allied Industries. The institute caters to the packaging needs of domestic manufacturers and exporters.
- Indian Trade Promotion Organisation(ITPO): The ITPO was formed on January 1, 1992, under the Companies Act, 1956. Its main objective is to maintain close interactions among traders, industry and the government.
- Department of Commerce : The Department of Commerce is the apex body in the Ministry of Commerce of the Government of India and is responsible for formulating policies related to foreign trade as well as evolving import and export policies for the country.
- State Trading Organisation: State Trading Organisation (STC) was established in May 1956. The main purpose of STC is to promote trade, primarily export trade among different trading partners of the globe.
- Export Promotion Councils (EPCs): Export Promotion Councils are non-profit institutions register under the Companies Act or the Societies Registration Act. The fundamental objective of the export promotion councils is to market and produce the nation’s exports of particular products falling under their jurisdiction.
- SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) is the regulatory authority in India and has issued guidelines for the disclosure of information and investor protection. Therefore, any company who wishes to invite funds from the general public must make adequate disclosure of all relevant information and must not conceal any material information from the potential investors.
- In case a company is not reasonably assured of a good public response to the issue, it may appoint underwriters to the issue. Underwriters undertake to buy the shares if these are not subscribed by the public. They receive a commission for underwriting the issue. Appointment of underwriters is not necessary whenever a public company wishes to raise the required funds from the public by means of the issue of shares and debentures.
- Jagat has promoted his business organization in the form of Sole proprietorship. A sole proprietorship form of business organisation which is owned, managed and controlled by an individual who is the recipient of all profits and bearer of all risks.
- Ease of formation and closure: A sole proprietorship form of business organisation is not covered by a separate law. As a result, it is easy to form or close down it with minimum formalities.
- Unlimited liability: The liability of a sole proprietor is unlimited because in the eyes of the law the owner and his business are one and the same. Therefore, the personal assets of the sole proprietor may be utilised to settle the claims of the creditors if the business assets are insufficient to meet the debts.
- Sole risk bearer and profit recipient: A sole proprietor is not expected to share the gains of his business with anyone and remains the sole recipient of it and also the risk of failure of a business is borne all alone by him.
- Lack of business continuity: Since a sole proprietorship business doesn’t have a separate legal entity the death, insolvency or insanity of the sole proprietor may adversely affect the business and lead to its closure.
- Voting Rights: They have voting rights and hence they are the owners of the business.
- Participation in Management: Using their voting rights, equity shareholders get a right to participate in the company’s management.
- Return: These shareholders do not get a fixed dividend. They get according to the earnings of the company. They receive what is left after all other claims on the company’s income and assets have been settled.
- Risk: They enjoy the reward and also bear the risk of ownership. Therefore, it is also called risk capital.
- Permanent Capital: Equity capital serves as permanent capital as it is to be repaid only at the time of liquidation of a company.
- No charge on assets of the company: Funds can be raised through equity issues without creating any charge on the assets of a company. The assets of a company are, therefore, free to be mortgaged for the purpose of borrowings, if the need be.
- More Costly: The cost of equity shares is generally more as compared to the cost of raising funds through other sources.
- The feature of services being discussed above is ‘Inconsistency’. It means unlike goods, services are not standardised. It may differ from individual to individual and is based on consumer demands and expectations. Moreover, the quality of services may also vary depending upon the approach of the service providers. The efficiency of a dedicated and committed service provider will be more.
- Intangibility: Like goodwill of a business, services are intangible in nature. They cannot be touched. Since they are purely experiential is nature the quality of services cannot be determined before consumption. Therefore, it is essential that the service providers work deliberately towards creating desired services in order to ensure that the consumer undergoes a favourable experience. For example, watching a movie should be a pleasant experience for the audience.
- Inseparability: The presence of the customer is required and his/her interaction with the process of providing services has to be managed. It is the simultaneous activity of production and consumption, thereby making both of them inseparable.
- Inventory: Unlike goods, services cannot be produced and stored beforehand. The services have to be performed as and when a consumer asks for it. Services are perishable therefore, the marketers may keep an inventory of the related goods but not the services itself. For example, a beauty salon may only keep a ready stock of accessories like a comb, water dispenser, hairdryer, scissors, etc. which are needed to provide a haircut service to a client, but the service itself cannot be stored.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 2023-24
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Computer Science
- Informatics Practices
- English Core
- Hindi Elective
- Political Science
- Physical Education
- Other Subjects
To download sample papers for class 11 Physics, Chemistry, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check the myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solutions, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Papers all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and the myCBSEguide website.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Hindi Core 2024
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Physical Education
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Political Science 2024
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 History 2023-24
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 English Core 2023-24
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Computer Science
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Economics 2024
- CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Accountancy 2024
1 thought on “CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 Business Studies 2023-24”
Leave a comment.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Commerce Important Questions
- Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies are outlined by the subject matter experts from the latest edition of CBSE books. It is recommended for the students to practise the given Class 11 Business Studies chapter wise important questions with the answers. Learning these would definitely help the students in scoring good marks in the board examinations.
Chapter wise Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for other Commerce Subjects:
- Important Questions for Class 11 Economics
- Important Questions for Class 11 Accountancy
- Important Questions for Class 11 Statistics
- Business Studies MCQs
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions, question papers, sample papers, syllabus and Commerce notifications.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is so nice study platform
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Nature and Purpose of Business: Case Based Type Questions | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below Saransh and Vishal have their pharmaceutical factory in Jaipur. Their main focus is providing quality products at reasonable prices. They procure the services of a renowned medicine specialist Mr. Andrews from Germany who gives them feedback about the quality of their products. Because of increasing competition with foreign
Pharmaceutical Companies, their market share is decreasing and they are suffering huge losses. To ensure their existence in the market, their management is concentrating on full usage of machines, and reducing wastage, and effective promotion of their products to increase the sales. Question 1: ”Mr. Andrews from Germany who gives them feedback about the quality of their ........”Identify the economic activity Mr. Andrews performs. (a) Business (b) Profession (c) Employment (d) Partnership
Correct Answer is Option (b) A profession is an occupation founded upon specialized educational training, the purpose of which is to supply disinterested objective counsel and service to others, for a direct and definite compensation, wholly apart from expectation of other business gain. A profession is not a trade and not an industry.
Question 2: “Because of increasing competition with foreign Pharmaceutical Companies, their market share is decreasing...” Name the type of risk related to the above-stated line. (a) Speculative risk (b) Foreign risk (c) Pure risk (d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a) Speculative risk is a category of risk that, when undertaken, results in an uncertain degree of gain or loss. In particular, speculative risk is the possibility that an investment will not appreciate in value. Speculative risks are made as conscious choices and are not just a result of uncontrollable circumstances.
Question 3: Pharmaceutical industry is an example of which of the following types of secondary industries? (a) Genetic (b) Analytical (c) Synthetic (d) Processing
Correct Answer is Option (d) Secondary: Industries which are essentially manufacturing or assembling industries. It receives raw materials from primary industries and processes them to commodities for the customers. Example: Food manufacturing, Textile manufacturing etc.
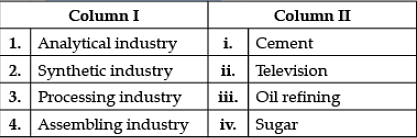
Correct Answer is Option (b) Analytical industry is the industry which analysis and separates different elements from the same materials. Synthetic industries are those industries that combine various ingredients and make a new product like Cement, fragrance and plastics. The process industries are those industries where the primary production processes are either continuous, or occur on a batch of materials that is indistinguishable. Assembling industry: These industries are engaged in bringing together various components or parts of bicycles, television, radio and these are some examples of assembling industries.
Question 5: ”To ensure their existence in the market, their management is concentrating...” Which economic objective is indicated in this statement? (a) Survival (b) Profit (c) Growth (d) Diversification
Correct Answer is Option (a) Business survival refers to keeping the business operating for a certain amount of time. Most businesses initially aim to survive their first year. Profit refers to any money left over after all costs have been taken away from any revenue made by a business.
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below. Oorza Limited is the manufacturer and trader of electrical goods. The company’s efficient management team, and effective marketing strategies have enabled it to carve a niche in the industry, allowing it to stand out. But, over the past few years, its profit margins and customer loyalty have been going down. After analysis of the reasons for lowering performance, the company executives suggested how CSR can improve profits. They understand that CSR can promote respect for their company in the marketplace which can result in higher sales, and enhance employee loyalty. Also, CSR activities focusing on sustainability issues may lower costs and improve efficiency as well. The company followed the CSR initiatives and is able to regain its market position and increase its goodwill.
Question 6: Which objective will be fulfilled by the company through CSR? (a) Economic (b) Social (c) Legal (d) Personal
Correct Answer is Option (b) Corporate Social Responsibility is a management concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and interactions with their stakeholders.
Question 7: Identify which of these is not a role of profit as stated above. (a) Survival of business (b) Enhancing goodwill (c) Increasing efficiency (d) Enhancing customer loyalty
Correct Answer is Option (d) Customer loyalty is an ongoing positive relationship between a customer and a business. It's what drives repeat purchases and prompts existing customers to choose your company over a competitor offering similar benefits.
Correct Answer is Option (c) Traders act as link between consumers and producers. Traders remove hindrance of persons by making goods available to consumer from producers.
Question 9: Identify the term which is related to uncertainties about the returns and chances of losses in the business. (a) Risk (b) Market trend (c) Natural calamities (d) Market standing
Correct Answer is Option (a) Business risk is the exposure a company or organization has to factor(s) that will lower its profits or lead it to fail. Anything that threatens a company's ability to achieve its financial goals is considered a business risk. There are many factors that can converge to create business risk.
Question 10: ”...may lower costs and improve efficiency as well.” If the company is able to achieve it, which business objectives are accomplished by the company? (a) Profit maximization (b) Social responsibility (c) Growth and expansion (d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a) Profit maximisation is a process business firms undergo to ensure the best output and price levels are achieved in order to maximise its returns. Influential factors such as sale price, production cost and output levels are adjusted by the firm as a way of realising its profit goals.
Top Courses for Commerce
Faqs on nature and purpose of business: case based type questions - business studies (bst) class 11 - commerce, mock tests for examination, nature and purpose of business: case based type questions | business studies (bst) class 11 - commerce, semester notes, previous year questions with solutions, viva questions, objective type questions, video lectures, shortcuts and tricks, study material, past year papers, extra questions, sample paper, important questions, practice quizzes.

Nature and Purpose of Business: Case Based Type Questions Free PDF Download
Importance of nature and purpose of business: case based type questions, nature and purpose of business: case based type questions notes, nature and purpose of business: case based type questions commerce, study nature and purpose of business: case based type questions on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Solution PDF
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Answers is an extremely useful revision tool. It is very beneficial for students who are aiming to make the most out of their exam preparation. Board exams examine the educational skills of the student. Practising CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question is a must. You can download here Business Studies Marks Wise Question with solutions at free of cost.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question

CBSE is one of the most preferred educational board in India. This renowned board was established in the year 1952. CBSE Board is known for its comprehensive syllabus and the quality of education and well-structured question paper. The board aims to give a good education to its students so that they can grow both mentally and physically.
CBSE Board conducts the exam for Class 11. The exams for Class 11 are usually conducted in the month of March every year and the results are announced in the month of May. The questions that are asked in the CBSE board examination are according to the pattern issued by the NCERT. Students who are preparing for their CBSE examination must know the benefits of solving the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question. The questions are designed by SelfStudys experts according to the CCE guidelines.

CBSE Business Studies Marks Wise Question for Class 11
One of the best way to prepare for the exam is by practising the Business Studies Marks Wise Question. Students will get an idea about the examination pattern and the marking scheme. It will also make students familiar with the question paper and the difficulty level of the questions asked in the examination. Some benefits of solving the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question are given below.
- Helps in brushing up the concepts completely
- Helps to overcome fear before the exam
- Improves time management skills
- Develops speed and accuracy
- Helps in correcting mistakes
If you are preparing for CBSE board exams, now is the time when you plan efficiently and work more smartly. One way of studying smarter is investing your efforts in the most important questions and make sure you are through with these questions. You must finish the chapters that have high weightage with maximum efficiency so that you can solve any question asked from them. In this page, we will provide you with the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question.
Ensure that you finish the complete CBSE syllabus of Class 11 based on the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question of each unit. The chapter with high weightage must be thoroughly completed. At the same time, you must have a basic understanding of all the chapters. Solve Business Studies Marks Wise Question of all types.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question PDF
Class 11 is considered to be the most important part for students aspiring to clear the NEET exam. In CBSE Class 11, several important chapters are presented to the students which are crucial to forming the basic skills required for a medical & engineer career.
CBSE Class 11 syllabus has various important topics, diagrams and definitions that the students require to be thorough with to be able to score well in the Class 11 board exam. To get good marks in Class 11, students require to prepare thoroughly and practice with CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question.
It is not easy to get high marks in CBSE, either. The curriculum of Class 11 has evolved over the years and become more complex. Students will require to put in the effort to remember the topic and work smartly to perform well in their board examinations. This means that it might not be sufficient to just attend the school and blindly mug up the CBSE syllabus. A lot of students go for tuition to be able to clear any doubts they have.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Solutions
To help the students to prepare for examination more effectively, we provide CBSE Business Studies Marks Wise Question for Class 11 are given here. It is suggested to check these Business Studies Marks Wise Question to be able to tackle any question in the examinations.
It is suggested to practice this CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question thoroughly before the exams. Apart from these Business Studies Marks Wise Question, students are also suggested to check the below-given links for sample and question papers and prepare more efficiently for the examinations.
As the importance of board examinations can never be understated, CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question can prove to be greatly beneficial for students. SelfStudys ensures that students can study better with our Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Answers. The carefully crafted questions and answers provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the chapters involved. A lot of these questions are likely to appear in the board examination, making this an ultimate guide for students before their examinations.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Answers
Why should students download cbse class 11 business studies marks wise question from selfstudys.
These CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question for exams are framed by our best teachers. They also give solutions to these questions that explain the concepts in a short yet easy to understand manner.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

Class 11th Business Studies - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Social responsibilities of business and business ethics case study questions with answer key.
11th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Business Studies
Maruti Suzuki strives to minimize the carbon footprint of its manufacturing facilities, products and supply chain operations. The Company believes that investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. Going beyond compliance, the Company works closely with its parent company, Suzuki Motor Corporation, to introduce the latest environment friendly technologiesin India, much ahead of statutory requirements. Maruti Suzuki became the first automobile company in India to register a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). In due course, the Company will earn tradable carbon credits. The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including nearmiss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council(CSLC)comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety. Source: https: / / www.marutisuzuki.com/social-performance.aspx Quoting lines from the above passage, mention social responsibilities that Maruti Suzuki is fulfilling.
Maruti Suzuki strives to minimize the carbon footprint of its manufacturing facilities, products and supply chain operations. The Company believes that investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. Going beyond compliance, the Company works closely with its parent company, Suzuki Motor Corporation, to introduce the latest environment-friendly technologies in India, much ahead of statutory requirements. Maruti Suzuki became the first automobile company in India to register a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). In due course, the Company will earn tradable carbon credits. The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including nearmiss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council(CSLC)comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety. Source: https: / / wwnw.marutisuzuki.com/social-performace.aspx Do you think it will affect earning capacity of the company adversely? Justify your answer.
Ten years ago only about a dozen Fortune 500 companies issued a CSR or sustainability report. Now the majority does. More than 8,000 businesses around the world have signed the UN Global Compact pledging to show good global citizenship in the areas of human rights, labor standards and environmental protection. The next generation of business leaders is even more likely to prioritize CSR. According to data released this month by Net Impact, the nonprofit that aims to help businesses promote sustainability, 65% of MBAs surveyed say they want to make a social or environmental difference through their jobs. Consumer Protection Act, 1986 and jago grahak jago campaigns have made consumers aware of their rights and businesses cannot afford to ignore their duties towards consumers. Today, amid a lingering recession that has dented corporate profits and intensified pressure from shareholders, companies are devising new CSR models. Rather than staffing a modest CSR department - and slapping it on the org chart as a small offshoot of the public relations (PR) or philanthropy division - many companies are instead trying to embed CSR into their operations because they have realized threat social interest and business interest are closely connected. Workers are no more illiterate. They are aware of their rights and in these situations, companies cannot afford to ignore their duties towards labour. Quoting lines from the above passage clarify reality of social responsibility.
*****************************************
Social responsibilities of business and business ethics case study questions with answer key answer keys.
(a) Concern for environment : That investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3 Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. (b) Optimum Utilization of national Resources: The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. (c) Safety of employees: The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including near-miss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council (CSLC) comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety.
No, it will not affect earning capacity of the company adversely. (a) No doubt, it involves cost but it will increase sales as people will prefer to buying fuel efficient cars. (b) Recycling and reuse will reduce cost. (c) Safety of employees will increase employees' morale and motivation. It will increase their productivity and employee turnover will decrease.
(a) Threat of Public Regulation: Ten years ago only about a dozen Fortune 500 companies issued a CSR or sustainability report. Now the majority does. More than 8,000 businesses around the world have signed the UN Global Compact pledging to show good global citizenship in the areas of human rights, labor standards and environmental protection. (b) Development of Professional Managerial class: According to data released this month by Net Impact, the nonprofit that aims to help businesses promote sustainability, 65% of MBAs surveyed say they want to make a social or environmental difference through their jobs. Consumer Protection Act, 1986and jago grahakjago campaigns have made consumers' aware oftheir rights and businesses cannot afford to ignore their duties towards consumers. (c) Relationship between social interest and public interest: Today, amid a lingering recession that has dented corporate profits and intensified pressure from shareholders, companies are devising new CSR models. Rather than staffing a modest CSR department - and slapping it on the org chart as a small offshoot of the public relations (PR) or philanthropy division - many companies are instead trying to embed CSR into their operations because they have realized threat social interest and business interest are closely connected. (d) Pressure of labour movement: Workers are no more illiterate. They are aware of their rights and in these situations, companies cannot afford to ignore their duties towards labour.
Related 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies Materials
11th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 11th physics motion in a straight line chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th physics units and measurements chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th chemistry structure of atom chapter case study question with answers, cbse 11th chemistry some basic concept of chemistry chapter case study questions with answers, 11th biology biological classification chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class 11th Applied Mathematics - Coordinate Geometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Class 11th applied mathematics - basics of financial mathematics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - descriptive statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - calculus case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - mathematical reasoning case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - algebra case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - numbers, quantification and numerical applications case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th biology - chemical coordination and integration case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

11th Standard CBSE Study Materials

11th Standard CBSE Subjects

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-2 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Class 11 students who are preparing for the business studies exams must try out these important questions of Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Forms of Business Organisations that our subject experts have framed by strictly following the CBSE syllabus and marking scheme. Students can prepare the chapter effectively for their exams by referring to the PDF files . These questions cover the crucial topics of the chapters. Students can refer to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions and Revision Note as well available on the main page of Vedantu. It will boost their preparation and help them fetch more marks during the exam. There is a high chance that some of these questions may be asked in the examination. Hence, downloading the psd to practice all the questions thoroughly is beneficial.
Topics Covered in Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2
Introduction to Forms of Business Organisation
Sole proprietorship
Joint Hindu Family Business
Partnership
Types of Companies
Choice of Forms of Business Organisation
Study Important Questions for class 11 Business studies Chapter— 2 Forms Of Business Organization
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Marks)
1. Who elects B.O.D of Joint Stock Company?
Ans : Shareholders elect the Board of Directors of a Joint Stock Company.
2. In which form of business profits are not shared?
Ans: In a sole proprietorship, the owner is solely responsible for all profits, losses, assets, and liabilities.
3. Where a business act as an artificial person what act as an official signature
Ans : As a substitute for the company's signature, the common seal with the company's name engraved on it is utilised.
4. Write the names of systems which govern membership in Joint Hindu Family business
Ans:
1. The Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) is governed by two schools of Hindu law: Mitakshara Law (Law of Mitakshara) Except for Bengal and Assam, the Mitakshara Law extends across India.
2. The Dayabhaga Law applies to Bengalis and Assamese who live in the states of Bengal and Assam, as well as other regions of the world.
5. Enumerate the two conditions necessary for formation of Joint Hindu Family business
1. At least two familial members
2. They will inherit ancestral property
6. What is the minimum no. of persons required to form a co-operative society?
Ans: A minimum of ten people are necessary to form a cooperative (10).
7. Explain the meaning of unlimited liability.
Ans : Unlimited responsibility refers to a firm's indefinite ability to fulfil its debts or commitments, which extends beyond the firm's owner(s), partners, or shareholders' investments to their personal assets. An unlimited liability company, such as a sole proprietorship or a general partnership, assumes this level of risk.
8. Identify a company which has no restriction of on transfer of shares
Ans : There are no restrictions on the transfer of shares in a public business.
9. Name two types of business in which sole proprietorship is very suitable
Ans: Tutorial classes and a small cell phone repair company are excellent examples of sole proprietorship businesses.
10. Write the name of form of business organisation found only in India
Ans: A joint Hindu family business is a type of business that can only be found in India.
11. Name the person who manages a Joint Hindu Family business
Ans: Karta is the person in charge of a Hindu joint family enterprise.
Short Answer Questions (2 OR 3 Marks)
12. Partners in affirm has different roles and liabilities, Identify and explain the type of partner in a firm from the given examples:
a) Rama is a partner in a business who has no actual interest in business trade or its profits but she is Paid fee by the firm for lending its name to firm.
Ans: Rama is a nominal partner in a firm who has no genuine interest in the firm's trade or earnings, but is paid a fee by the firm for providing its name to the firm.
b) In Ram Hari & co. Ltd, Ram & Hari declare Gopal as a partner with knowing that Gopal remain silent then Gopal will be liable to third parties for any loss.
Ans: Ram & Hari declare Gopal as a partner in Ram Hari & Co. Ltd, knowing that if Gopal remains silent, Gopal will be accountable to third parties for any losses.
c) What type of partner is Geeta if she only contribute capital, shar profit and loss if any?
Ans : Geeta is a sleeping partner if she merely contributes capital and shares profit and loss if any .
d) What type of patner is Giri in Ram Hari & co. Where he is an outsider but represent himself as a partner.
Ans: Giri in Ram Hari & co, Where he is an outsider but represent himself as a partner-Partner by Estoppel
13. Explain the forms: sole proprietorship, H.U.F & Joint stock company on the basis of following points: Liability, members & Continuity
Ans: The difference between sole proprietorship, H.U.F & Joint stock company is given below:
14. Explain the concept of mutual agency in partnership with suitable example.
Ans: The legal relationship between participants in a partnership in which each has authorisation powers and the authority to engage the partnership into business contracts is known as mutual agency. To put it another way, each partnership member has the capacity to make business decisions that commit or tie the partnership as a whole to a business deal with a third party or entity. Even though the partnership agreement expressly forbids it, a grocery store partner who purchases a delivery vehicle makes a legally binding contract in the name of the partnership. On the other hand, if a law firm partner bought a snowmobile for the firm, such behaviour would be illegal.
15. What is meant by partner by estoppel OR Mr. Singh is in ‘lighting’ business for the post 15 years. To help his friend, Mr Yadav, a beginner he projected himself as a partner before Mohd. Abdul, a whole sale dealer of fancy lights. Mohd. Abdul gave Mr. Yadav the stock without asking for payment and gave him credit limit of one month. Will Mr. Singh be liable to Md. Abdul if Mr. Yadav does not pay him on time ? Classify Mr. Singh’s role here along with an explanation
Ans: Partner by Estoppel is a legal term that refers to a legally binding partnership that can exist even though there is no formal partnership agreement in place. A person who advertises himself or herself as a partner in a firm through conduct or words, or enables himself or herself to be represented as such, is accountable for the credit or loans received by the firm on the basis of such representation. Also known as partnership presumption. The partner does not contribute to the capital or administration of the company, yet his responsibility is limitless.
16. What is secret partner
Ans : A secret partner is a person or partner who is not publicly known in a venture or business. He contributes money to the cause. He's a part of the management team, but only behind closed doors. He also shares in the profits and losses of the firm. His, and others', responsibilities are infinite.
17. Write a short note on producer co-operative society
Ans: Producers' Cooperative Societies were formed to safeguard the interests of small farmers. Producers interested in obtaining inputs for the creation of items to meet consumer demand are among the members. Profits are divided based on their contributions to the society's overall pool of products produced or sold.
18. Explain a co-operative organisation in democratic setup.
Ans: A cooperative society is a voluntary group of people who get together for the common good of its members. The cooperative society is governed by the premise of "one man, one vote." Each member has the same number of votes. As a result, democratic values govern cooperative society.
19. Shiv, Anandi & John were partners John died in a car accident Both Shiv & Anandi decided to admit his son Ryan who was 16 years old as partner. Can they do so? Justify.
Ans: Yes, they can admit Ryan as a partner to the partnership firm's advantages with the permission of the partners. A minor is a person who is under the age of eighteen. Because a minor is incapable of forming a legally binding contract. He is unable to become a partner in a firm. A minor can, however, be added to the advantages of an established partnership business with the agreement of all other partners. It's unrealistic to expect him to absorb the losses. His responsibility will be limited to the amount of money he has put into the business. He will be unable to engage fully in the running of the company.
20. Differentiate between private co. and public company
Ans: Difference between private company and public company are as following:
21. Akriti, Sonam & Supreeti were friends who started a partnership business. They did not get their firm registered as it was optional. Soon, Sonam & Supreeti started having conflicts. Sonam wanted to approach a lawyer. If you were a lawyer than how would you guide her ? OR Mangal, Sazia & Suqhbeer Singh wish to start a business in partnership. They want to make a partnership deed, Suggest what aspects of the deed should be included in it ?
Ans : The term "partnership" refers to a relationship between people who have agreed to split the profits from a firm that is run by all of them or by one of them acting on behalf of all of them. Although firm registration is optional, a partnership deed might be produced to avoid problems between partners. The partnership deed is a written agreement that contains the rules and conditions that govern the partnership.:
A partnership deed generally has the following elements:
• Firm name
• Nature of company and location of operation
• Duration of business
• Each partner's investment
• Profit and loss distribution
• The partners' responsibilities and obligations
• The partners' salaries and withdrawals
• The terms regulating a partner's admission, retirement, and expulsion
22. Explain limitations of Joint Stock Company
Ans: The following are the restrictions:
• When ownership as well as management are separated, there is a lack of effort and personal commitment on the part of the company's executives.
• A company's information is periodically given to the Registrar of Companies, and therefore information is available to the general public. This restricts a company's operational flexibility and wastes a significant amount of time, effort, and money.
• Communication and acceptance of various ideas to top, middle, and lower level management may cause delays in not just making choices but also carrying them out.
• The Board of Directors is made up of the company's owners, the shareholders.
23. Which form of business is suitable for following types of business and why ?
(a) Beauty Parlour
Ans: Sole Proprietorship for a Beauty Salon. Created and operated in a simple and cost-effective manner. On his or her personal tax return, the owner declares profit or loss.
(b) Coaching Centre for science students
Ans: Partnership with a science coaching centre. It's easy to make and run, and it's cheap. On their personal tax returns, partners record their share of profit or loss.
(c) Hotel
Ans: Joint Stock Companies in the Hotel Industry The limitation on their owners' personal liability for company debts and court judgements against the firm is the major aspect of LLCs and corporations that attracts small enterprises. Another issue to consider is income taxes: you can establish up an LLC or a corporation to take advantage of lower tax rates. Furthermore, an LLC or corporation may be able to offer a variety of fringe benefits to its employees (including the owners) and deduct the cost as a business expense.
(d) Shopping mall
Ans: JSCs (joint stock companies) are shopping malls. Owners' personal liability for commercial debts is limited .
(e) Restaurant
Ans : Sole proprietorship of a restaurant. Created and operated in a simple and cost-effective manner. On his or her personal tax return, the owner declares profit or loss.
(f) Small repair business
Ans: Sole Proprietorship for a small repair business. Created and operated in a simple and cost-effective manner. On his or her personal tax return, the owner declares profit or loss.
Long Answer Questions (5 OR 6 Marks)
24. In what type of business, individuals associate voluntarily for profit, having capital dividend into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership? Explain with features
Ans : A joint stock company is a voluntary group of people founded for the purpose of carrying out profit-making business activities. It has a different legal position from its members and a capital structure that is divided into transferable shares. A corporation is a legal entity that possesses its own legal identity, perpetual succession, and common seal. The shareholders are the company's owners, and the Board of Directors is the company's top management body, which is elected by the shareholders.
The company's capital is divided into smaller units called "shares," which can be freely transferred from one shareholder to another (except in a private company). The following are the characteristics of a joint stock company:
• A corporation is a fictitious person. It is a legal creation that exists independently of its members.
• A corporation acquires its own legal personality. The business and its owners are not considered one and the same by the law.
• Starting a business is a time-consuming, expensive, and difficult process. It is necessary for businesses to be incorporated.
• It will only be decommissioned after a specialised procedure known as winding up is finished. Members may come and leave, but the company remains in existence.
• A company's affairs are managed and controlled by the Board of Directors, which appoints top management for corporate operations.
• A company may or may not have a common seal.
• The risk of a company's losses is shared by all shareholders.
25. If registration is optional, why do partnership firms willingly go through this legal formality? Explain the reason with procedure to get them registered.
Ans: The registration of a partnership firm is optional. However, it is preferable to have a formal agreement to avoid problems between partners. The following are the implications of a firm's failure to register:
I. A partner in an unregistered firm cannot sue the firm or other partners;
Ii. The firm cannot sue third parties; and
iii. The firm cannot bring a case against the partners.
The partnership deed is a written agreement that contains the rules and conditions that govern the partnership.
The following elements are usually included in a partnership deed:
• Name of firm
• Nature of business and location of business
• Investment made by each partner
• Profit and loss distribution
• Partners' duties and obligations
• Salaries and withdrawals of partners
• Terms governing admission, retirement, and expulsion of a partner
• Interest on capital and interest on drawings
• Procedure for dissolution of a partnership
Firm registration procedure:
1. Submit an application to the Registrar of Firms in the specified form. The following information should be included in the application:
• The firm's name
• its location
• the names of other locations where the firm does business
• the date each partner joined the firm
• the partners' names and addresses
• the duration of the relationship All of the partners should sign this application.
2. Make a fee deposit with the Registrar of Firms.
3. Following approval, the Registrar will enter the firm into the register of firms and provide a certificate of registration.
26. Who have equal ownership right over the property of an ancestor? Highlight with its essential characteristics
Ans: A Joint Hindu Family is a type of organisation in which the members of the Hindu Undivided Family own and operate the business (HUF). Membership in the company is based on birth in a certain family, and three generations can be members. The eldest member of the family, known as karta, is in charge of the family's company. Co-parceners are members of a Joint Hindu Family Business who have equal ownership rights over an ancestor's property.
The following are the characteristics of a joint Hindu family business:
• There is no need for an agreement because membership is by birth.
• All members, excluding the karta, are only liable for their part of the business's co-parcenery property. The liability of the karta is limitless.
• The family business is controlled by Karta, and his decisions are binding on everybody.
• The business continues even after Karta's death, as the next eldest son becomes Karta.
26. Why cooperative forms of organisation are formed? Explain various types of cooperative societies
Ans: A cooperative society is a voluntary group of people who get together for the common good of its members. They are driven by a desire to protect their economic interests against potential abuse by middlemen who are just out to make more money. The procedure of forming a cooperative organisation is straightforward, and all that is required is the approval of at least ten adult individuals. The capital of a society is raised by issuing shares to its members. Following its registration, the society gains an unique legal identity .
Consumer Cooperative Societies are one type of cooperative society.
It was established to safeguard the interests of consumers.
The society aims to eliminate middlemen in order to achieve operational efficiencies. It buys goods in bulk directly from wholesalers and sells them to members.
Profits are distributed based on either capital contributions to the society or individual member purchases.
Producers' Cooperative Societies are a type of producer cooperative society.
It was created to protect the interests of small farmers.
Producers seeking inputs for the creation of commodities to meet consumer wants make up the members.
Profits are dispersed based on their contributions to the total pool of goods produced or sold by the society.
Marketing Cooperative Societies This organisation was founded to assist small producers in selling their goods.
The members are producers who want to get fair pricing for their goods.
It combines the production of individual members and engages in marketing operations such as shipping, storage, packaging, and so on in order to sell the items at the highest possible price. Profits are distributed according on how much each participant contributed.
Farmers' Cooperative Societies are founded to defend farmers' interests by offering superior inputs at a fair cost.
Members are farmers who want to take up farming activities together.
The goal is to reap the benefits of large-scale farming while increasing production. Improves yield and returns to farmers while also addressing the issues that come with farming on fragmented land holdings.
Cooperative Credit Societies: It was founded to provide members with quick credit on affordable terms.
The members are those who are looking for financial assistance in the form of loans.
The goal of such organisations is to safeguard members from being exploited by lenders who charge exorbitant interest rates on loans.
Cooperative Housing Societies are a type of cooperative housing organisation.
It was created to assist low-income people in building dwellings at an affordable cost.
People who want to get a cheaper place to live make up the members of these societies.
The goal is to solve the members' housing concerns by building houses and allowing them to pay in instalments.
27. Dhirubhai Chaurasiya operates a textile business. His family is joint and has a lot of ancestral property. All the 15 family members are a part of this business. He is the eldest male member in the family so he heads the business. He is liable to all the creditors of the business as he is the decision maker. Dhirubhai’s grandson has just born a few days ago and he is also the member of the business.
(a) Which form of business is being undertaken by Dhirubhai Chaurasiya ?
Ans : Dhirubhai Chaurasiya is involved in a joint Hindu family business.
(b) Identify the features of this form of business based on the information given.
Ans : The following are the features of a joint Hindu family company based on the previous information:
• As 15 family members are involved in the business and have a lot of ancestral property, there should be at least two individuals in the family and ancestral property to be inherited by them.
• Except for the karta, all members' responsibility is restricted to their share of co-parcenery property. The karta has unrestricted liability to all business creditors since he is the decision maker.
(c) Textile business is part of which type of industry according to you ?
Ans: Textile business is part of Agro based industries.
28. 'Reva Chemicals' is a partnership firm. Sona and Mona one two partners in this firm. It is recorded in the Partnership Deed that Sona's liability is unlimited, whereas Mona's is limited. Sona wants to set up the Anti-Pollution plant in his factory, but Mona does not let him do so. Almost all the transactions of this firm are done through the internet. The firm Sells its goods to other Business units only. The firm gets its Research and Development work done by another firm, who is a specialist of such work.
i. Describe the type of partnership.
Ans: It's a limited partnership in which at least one partner's liability is limitless, but the others may have limited liability. Limited partners have no management powers and are unaffected by the firm's or other partners' activities. A partnership of this nature must be registered.
ii. identify the two values being overlooked.
Ans: The following are the two ideals that are being overlooked:
• Government rules are being broken;
• The social responsibility clause is not being followed.
iii. Name the type-business being done by the firm
Ans : It is a B2B (Business to Business) transaction. Short for business-to-business electronic commerce, B2B e-commerce (sometimes written as e-Commerce, eCommerce, or similar variants) is the sale of items or services between businesses over the internet using an online sales portal. In general, it is utilised to help businesses become more efficient. Instead of manually processing orders over the phone or by e-mail, ecommerce allows orders to be processed digitally .
29. Ravi, Pradeep, Satyender and Dharmender are partners in a partnership firm. Ravi and Satyender take active part in the operation of business whereas Pradeep has contributed in Capital but do not take part in day to day activities of the business. Dharmender is a nominal partner. All four make partnership for a specified time period and also make written agreement to govern the partnership but they does not get the firm registered.
a. What is meant by nominal partner?
Ans: A nominal partner is one who permits a firm to use his or her name. He neither contributes to the capital nor participates in the administration of the company. He usually does not share profits or losses, and his liability is infinite.
b. Which type of partnership is there between the partners in above?
Ans: The partners have formed a general partnership. In a general partnership, the partners' responsibility is limitless and joint. The partners have the right to participate in the firm's management, and their actions are binding on both the partners and the firm.
c. What is written agreement between the partners called?
Ans: The partnership deed is a written agreement between the partners. The partnership deed is a written agreement that contains the rules and conditions that govern the partnership.
d. What type of partners Pradeep and Ravi are?
Ans : Ravi is a hands-on partner. Active partners are individuals who actively participate in the firm's business on behalf of their fellow partners. They invest money and participate in the operation of the company. He shares in the partnership's profit and loss. His legal responsibility is limitless.
Pradeep is my sleeping companion. Sleeping partners are those who do not participate in the day-to-day operations of the company. They invest capital but do not participate in the management of the company. He shares in the partnership's profit and loss. His legal responsibility is limitless.
e. Give two merits of getting firm registered.
Ans: The following are two advantages of registering a business:
• An unregistered firm's partner cannot sue the firm or other partners;
• The firm cannot sue third parties.
30. Explain different types of Partnership on the basis of duration and liability?
Ans: Types of Partnership are as follows:
On the basis of duration: It can endure as long as the partners want it to, and it will terminate when one of them gives written notice of his or her intention to leave the relationship. A partnership created for the aim of completing a specified project, such as the construction of a structure or the performance of a time-limited activity.
On the basis of Liability: Partners have unlimited and joint liability; they have the right to participate in the firm's management, and their acts bind them as well as the firm.
The limited partners have no authority over the firm or the other partners, and their acts have no legal consequences for the firm or the other partners. It is necessary to register such a partnership.
Importance of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions for Chapter 2
The questions cover all the necessary topics of the chapter so that students don’t miss out on any important concepts.
When it comes to the last-minute revision of the chapter, going through these important questions will be greatly beneficial.
It is considered the best reference study material for preparing the Business Studies chapter “Forms of Business Organisation” for exams
It highlights the important topics of the chapter that need to be studied well.
Extra Questions for Practice
List different forms of business organisation.
Write two merits and demerits of a business organisation.
What is a partnership?
Explain “Minor As A Partner”.
What is a partnership deed?
What is a cooperative society?
What is a Joint Stock Company?
Mention any 5 differences between a public company and a private company.
Explain the nature of business briefly.
Explain the process of setting up a cooperative society.
Why Vedantu Has Provided Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2?
The students studying this amazing subject sometimes find it problematic to deal with the question and answer pattern. The students study the chapters well enough, but when the question comes in the exam, they cannot give their best; this may happen for two reasons – they cannot frame the answers well or due to a shortage of time.
Also, this is quite common among students. After studying and understanding the whole concept of the chapter, students find themselves very reluctant to look for important questions and frame each answer for the same. Before the exam days, when students have limited hours to prepare for the exam, they find it very difficult to read the whole chapter with specific detail.
For all these problems, we at Vedantu have come up with a single solution to infuse these important questions into the study routine. We have prepared a series of important questions from chapter 2 of Business Studies. The students can now know the important questions from the chapter; they can prepare from the textbook while they can refer to our site for the guided important questions (Also, the students can check our site for full-fledged guidance of our master class in this subject of Business Studies). The students who ask for important questions and guidance at the last minute also benefit.
Chapterwise Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies
Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce
Chapter 3 - Private, Public and Global Enterprises
Chapter 4 - Business Services
Chapter 5 - Emerging Modes of Business
Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Chapter 7 - Formation of a Company
Chapter 8 - Sources of Business Finance
Chapter 9 - Small Business
Chapter 10 - Internal Trade
Chapter 11 - International Business
Summing up, these questions are designed solely with students’ interests. Hence, the students are highly requested to study the important questions from this chapter, as this is one of the important chapters concerning the exam view for their future study in the study of management or the study of business.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2
1. What is Chapter 2 of Class 11 Business Studies about?
Business Studies Chapter 2 of Class 11 elaborates on various forms of business organisation. Forms of organisations are businesses that differ from each other depending on their ownership and management and the nature of the enterprise. To provide a vivid insight into a business organisation, the Chapter explains properly using examples such as sole proprietorship, cooperative societies, partnership, a company, joint Hindu family, choice of organisation, etc.
2. According to Chapter 2 of Class 11 Business Studies, what is a sole proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a type of business in which a single person owns the entire enterprise, in which he/she is the only person who manages and owns the business. He/she will be the person enjoying all the profits or bearing all the losses of the enterprise. Most of these are small-scale businesses like small grocery stores or tea stalls.
3. What are the different types of business partners, according to Chapter 2 of Class 11 Business Studies?
There are six different types of business partners. They are classified as an active partner, sleeping partner, secret partner, nominal partner, partners by estoppel, and partners by holding out. Out of all these partners, an active partner contributes capital, manages the enterprise, and shares profits and losses. Sleeping partners only invest capital and share profit/loss but do not participate in management. Secret partners invest and share profit/loss and manage work secretly. Rest all the partners do not make any significant contribution.
4. According to Chapter 2 of Class 11 Business Studies, what is a cooperative society?
A cooperative society is a private organisation or a business set up by more than one person who comes together with the same motto of their welfare and members. The cooperative society act 1912 was imposed to protect the economic interest of the society, which would otherwise get exploited by middlemen. Hence the act urges all cooperative societies to get registered and should have at least 10 members in their society.
5. According to Chapter 2 of Class 11 Business Studies, what are the different types of cooperative societies?
The different types of cooperative societies based on their nature are listed below:
Consumer Cooperative Societies
Producers Cooperative Societies
Marketing Cooperative Societies
Farmers Cooperative Societies
Credit Cooperative Societies
Cooperative Housing Societies
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Studies Case Study 1. Read the hypothetical text given and answer the following questions: Manish, Rahul and Madhav live in the same locality. They used to meet and discuss their ideas. After discussing the recent fire breakout in their area, they decided to take fire insurance for their house or work area.
CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships ...
Class: XI Study Material Business Studies (2021-22 Term-1) Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan . 2 | P a g e TERM: I (2021-22) CHIEF PATRON: DR. JAIDEEP DAS ... Case Studies (source based questions) I Sankalp is a successful entrepreneur dealing in Automobile sector especially with Two
11th Cbse Bst Bull's Eye Case Study Final - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 11 class notes
To assess their preparation level, they can download and solve the Class 11 Business Studies term 2 Important Questions with Solutions developed by the subject experts of Vedantu. Find the solutions to these questions and take a step ahead in your preparation. CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-wise Important Questions 2024-25.
CBSE has updated the new marking scheme and blueprint for Class 11 Business Studies for the session 2023-24. We are also providing Business Studies sample papers for Class 11 CBSE exams on myCBSEguide app and website in PDF format. Although the business studies question paper has no numerical yet you will find lots of case study-based questions.
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies are outlined by the subject matter experts from the latest edition of CBSE books. It is recommended for the students to practise the given Class 11 Business Studies chapter wise important questions with the answers. Learning these would definitely help the students in scoring good marks in the board examinations.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Emerging Modes of Business, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Class 11 Business Studies NCERT Textbook Solutions - Free PDF download. Class 11 Business Studies is a compilation of 11 chapters that cater to the delivery of various fundamental concepts and topics related to business. These concepts and principles circle around major topics related to different types of businesses, modes of businesses and ...
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark) 1. Give an example of activity which is economic in one side and non-economic on other side. Ans: Profession requires specialized knowledge and it is economic on one side and non economic on the other side.
NCERT Class 11 Business Studies Books in English PDF Download. NCERT Class 11 Business Studies Books are provided in PDF form so that students can access it at any time anywhere. Class 11 NCERT Business Studies Books are created by the best professors who are experts in Business Studies and have good knowledge in the subject.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers 2020: Here we are providing CBSE Important Extra Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter Wise Pdf download of Part 1 Foundations of Business and Part 2 Corporate Organisation, Finance and Trade in Hindi and English Medium. Students can get Business Studies Class 11 NCERT Solutions, Business Studies Class 11 ...
Case Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Business studies case study for forms of business organisation.
Document Description: Nature and Purpose of Business: Case Based Type Questions for Commerce 2024 is part of Business Studies (BST) Class 11 preparation. The notes and questions for Nature and Purpose of Business: Case Based Type Questions have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Nature and Purpose of Business: Case Based Type Questions covers topics like ...
Long answer Questions (5 or 6 Marks) 18. Explain trade credit and Factoring as a source of finance for a business enterprise. Ans: Trade Credit. It refers to the extension and provision of credit by one one trader to another for the purchase of goods and services, or other supplies without on the spot payment..
Business Studies is an interesting and important subject for students to learn the fundamentals of marketing, accounting, and economics. All the concepts covered in the BST Textbooks are explained in the NCERT Solutions for class 11 Business Studies PDF.Kids must practice with this chapterwise class 11 BST NCERT Textbook Solutions PDF and start attempting question-answers of all concepts easily.
Class 11th Business Studies. Here are some important points to take note of. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies - You can use the NCERT Solutions or state board textbook solutions to answer all questions asked in 11th standard Business Studies textbook.; Class 11 Business Studies Book - First you should read the 11th standard Business Studies textbook to understand all topics.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question with Answers is an extremely useful revision tool. It is very beneficial for students who are aiming to make the most out of their exam preparation. Board exams examine the educational skills of the student. Practising CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Marks Wise Question is a must.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Ans: Tutorial classes and a small cell phone repair company are excellent examples of sole proprietorship businesses. 10. Write the name of form of business organisation found only in India. Ans: A joint Hindu family business is a type of business that can only be found in India. 11.