202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples
Poverty is one of the most pressing global issues affecting millions of individuals. We want to share some intriguing poverty essay topics and research questions for you to choose the titles of your paper correctly. With the help of this collection, you can explore the intricate dimensions of poverty, its causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Have a look at our poverty topics to get a deeper understanding of poverty and its implications.

💸 TOP 10 Poverty Essay Topics
🏆 best poverty essay examples, 👍 catchy poverty research topics, 🧐 thought-provoking poverty topics, 🎓 interesting poverty essay topics, ❓ research questions about poverty.
- Poverty: Causes and Solutions to Problem
- Poverty as a Social Problem
- Homelessness and Poverty in Developed and Developing Countries
- The Eliminating Poverty Strategies
- Poverty Effects on an Individual
- How Access to Clean Water Influences the Problem of Poverty
- Correlation Between Poverty and Juvenile Delinquency
- Urbanization and Poverty in “Slumdog Millionaire” Film Boyle’s movie, “Slumdog Millionaire,” is one of many successful attempts to depict the conditions in which people who are below the poverty level live.
- Poverty Effects on Mental Health This paper examines the link between poverty and mental health, the literature findings on the topic, and proposes a potential solution.
- Poverty and Theories of Its Causes Poverty in schools is a significant barrier to education that needs to be overcome to improve teaching and learning.
- Global Poverty and Nursing Intervention It is evident that poor health and poverty are closely linked. Community nurses who are conversant with the dynamics of the health of the poor can run successful health promotion initiatives.
- Relationship Between Poverty and Crime The paper makes the case and discusses inequality rather than poverty being the prime reason for people committing crimes.
- Degrading Consequences of Poverty in “The Pearl” by John Steinbeck Poverty is identity in John Steinbeck’s The Pearl, and the main character Kino, a poor fisherman, manifests a transformation in his identity,
- Vicious Circle of Poverty In this essay, the author describes the problem of poverty, its causes and ways of optimizing the economy and increasing production efficiency.
- Effects of Poverty on Education in the USA Colleges It is clear that poverty affects not only the living standards and lifestyle of people but also the college education in the United States of America.
- The Orthodox and Alternative Poverty Explanations Comparison Poverty has over the years become a worldwide subject of concern for economies. This essay will explore two theories- the orthodox and the alternative theories to poverty.
- How Does Poverty Affect Crime Rates? On the basis of this research question, the study could be organized and conducted to prove the following hypothesis – when poverty increases, crime rates increase as well.
- Poverty from Functionalist and Rational Choice Perspectives Poverty is a persistent social phenomenon, which can be examined from both the functionalist and rational choice perspectives.
- “What Is Poverty” by Dalrymple The purpose of this paper is to present Dalrymple point of view and analyze it by applying philosophical concepts.
- Poverty from Christian Perspective Christians perceive poverty differently than people without faith, noting the necessity for integrated support to help those in need.
- The Poverty as an Ethical Issue Looking at poverty as an ethical issue, we have to consider the fact that there are people who control resource distribution, which then leads to wealth or poverty in a community.
- Empowerment and Poverty Reduction The objective of this essay will be to highlight the health issues caused by poverty and the strategies needed to change the situation of poor people through empowerment.
- Poverty in “Serving in Florida” and “Dumpster Diving” “Serving in Florida” by Barbara Ehrenreich describes the harsh reality of living in poverty while concentrating on the pragmatic dimension of the issue
- Bullying in Poverty and Child Development Context The aim of the present paper is to investigate how Bullying, as a factor associated with poverty, affects child development.
- Poverty and Homelessness in Jackson, Mississippi This paper will review the statistics and information about poverty and homelessness in Jackson, MS. The community of Black Americans is suffering from poverty and homelessness.
- Poverty in Young and Middle Adulthood According to functionalism, poverty is a dysfunctional aspect of interrelated components, which is the result of improper structuring.
- Poverty in “On Dumpster Diving” by Lars Eighner Essay “On Dumpster Diving” by Lars Eighner evokes compassion and prompts individuals to think about social problems existing nowadays.
- Effects of Divorce and Poverty in Families In the event of a divorce children are tremendously affected and in most cases attention is not given to them the way it should.
- Diana George’s Changing the Face of Poverty Book Diana George’s book, Changing the Face of Poverty, begins with a summary of several Thanksgiving commercials and catalogs.
- Poverty: Behavioral, Structural, Political Factors The research paper will primarily argue that poverty is a problem caused by a combination of behavioral, structural, and political systems.
- The Analysis of Henry George’s “Crime of Poverty” Reviewing Henry George’s Crime of Poverty, which was written in 1885, in its historical context can shed light on socio-political developments within the country.
- Poverty in the “LaLee’s Kin” Documentary In this paper, the author will analyse poverty as a social problem in the Mississippi Delta. The issue will be analysed from the perspective of the documentary “LaLee’s Kin”.
- Racial Discrimination and Poverty Racial discrimination and poverty have resulted in health disparities and low living standards among African Americans in the United States.
- Lessons Learned From the Poverty Simulation The main lesson learned from the poverty simulation is that poverty is far more serious than depicted in the media, which carelessly documents the numbers of poor people.
- The Problem of Poverty in Art of Different Periods Artists have always been at the forefront of addressing social issues, by depicting them in their works and attempting to draw the attention of the public to sensitive topics.
- Poverty in Ghana: Reasons and Solution Strategy The analysis provided in the paper revealed some internal and external factors that deter better economic and human development in Ghana.
- Love and Poverty in My Papa’s Waltz by Theodore Roethke The present paper includes a brief analysis of the poem ‘My Papa’s Waltz’ with a focus on imagery and figurative language.
- Child’s Development and Education: Negative Effects of Poverty Some adverse effects of poverty on a child’s development and education are poor performance academically, stagnant physical development, and behavioral issues.
- Poverty and Inequality: Income and Wealth Inequality The Stanford Center of Poverty and Inequality does an in-depth job of finding causes and capturing statistics on poverty and inequality.
- How Poverty Impacts on Life Chances, Experiences and Opportunities for Young People The paper specifically dwells on the social exclusion, class, and labeling theories to place youth poverty in its social context.
- Can Marriage End Poverty? Marriages to some degree alleviate poverty, but not all marriages can do so. Only marriages build on sound principles can achieve such a feat.
- Poverty and Its Negative Impact on Society Poverty affects many people globally, experiencing poor living conditions, limited access to education, unemployment, poor infrastructure, malnutrition, and child labor.
- The Concept of Poverty This work is aimed at identifying the key aspects associated with poverty and its impact on the lives of people in different contexts.
- The Ideal Society: Social Stratification and Poverty The paper argues social classes exist because of the variations in socioeconomic capacities in the world; however, an ideal society can eliminate them.
- Global Poverty and Education Economic theories like liberalization, deregulation, and privatization were developed to address global poverty.
- Global Issues of World Poverty: Reasons and Solutions The term ‘world poverty’ refers to poverty around the world and is not only limited to developing and under-developed nations.
- Poverty, Faith, and Justice: ”Liberating God of Life” by Elizabeth Johnson “Liberating God of Life Context: Wretched Poverty” by Johnson constructs that the main goal of human beings is to combat structural violence toward the poor.
- Poverty Relation With Immigrants Poverty-related immigration is usually caused by population pressures; as the natural land becomes less productive due to the increased technology and industrial production.
- Poverty and Homelessness in Canada Poverty and homelessness figure prominently in government policies and the aims of many social service organizations even in a country like Canada.
- Poverty: “$2.00 a Day” Book by Edin and Schaefer In their book “$2.00 a Day: Living on Almost Nothing in America,” Edin and Schaefer investigate problems that people who live in poverty face every day.
- How Poverty Affects Early Education? A number of people live in poor conditions. According to the researchers of the Department of Education in the United States, poverty influences academic performance in an adverse way.
- The Issue of Poverty in Savannah, Georgia The paper addresses a serious issue that still affects Savannah, Georgia, and it is poverty. This problem influences both individuals and society.
- Human Trafficking and Poverty Issues in Modern Society The problem of human trafficking affects people all over the world, which defines the need for a comprehensive approach to this issue from the criminology perspective.
- Poverty: Resilience and Intersectionality Theories This paper assesses the impact of poverty on adult life, looking at risk and protective factors and the impact of power and oppression on the experience of poverty.
- Carl Hart’s Talk on Racism, Poverty, and Drugs In his TED Talk, Carl Hart, a professor of neuroscience at Columbia University who studies drug addiction, exposes a relationship between racism, poverty, and drugs.
- Global Poverty and Human Development Poverty rates across the globe continue to be a major issue that could impair the progress of humanity as a whole.
- Donald Trump’s Policies of Poverty and Human Rights One of the events related to an acute social issue of poverty in the United States involves the U.N. report on extreme U.S. poverty and human rights in the context of Donald Trump’s policies.
- Immigrant Children and Poverty Immigrant child poverty poses considerable social predicaments, because it is related to several long lasting school and development linked difficulties.
- Poverty in 1930s Europe and in the 21st Century US The true face of poverty may be found in rural portions of the United States’ South and Southwest regions, where living standards have plummeted, and industries have yet to begin.
- Rutger Bregman’s Statement of Poverty The paper states that Bregman’s approach to poverty and the proposal of guaranteed regular income is more suitable for developing countries.
- The Impact of Poverty on Children and Minority Groups The problem of poverty, not only among children but also among adults, has plagued this planet for a long time.
- Habitat for the Homeless: Poverty The paper states that Habitat for the Homeless comes to fulfill American values by ensuring that Americans can afford houses at a low price.
- Wealth, Poverty, and Systems of Economic Class By examining wealth, poverty, and economic classes from the perspective of social justice, the socioeconomic inequalities persistent in society will become clear.
- Poverty: Causes and Reduction Measures Poverty is a global disaster and that a large percentage of the population has insufficient income or material possessions to satisfy their basic needs.
- The U.S. Education: Effect of Poverty Poverty effects on education would stretch to other aspects of life and this justifies that, poverty in United States not only affects social lifestyles but also college education.
- Global Poverty, Inequality, and Mass Migration Such global issues as poverty and inequality and mass migration are significant today since many people are involved in them.
- Household Energy Use and Poverty In many developing countries, as well as among disadvantaged populations of the industrial states, the lack or absence of energy for household use is an everyday reality.
- Utilitarianism: Poverty Reduction Through Charity This paper shows that poverty levels can be reduced if wealthy individuals donate a part of their earnings, using the main principles of the utilitarian theory.
- School System: Poverty and Education This short assessment presents at least three examples of differences between the schools that lead to disadvantages in the education system and finally provides a suggestion to help bridge the gap.
- Human Trafficking and Poverty Discussion This paper synthesize information on human trafficking and poverty by providing an annotated bibliography of relevant sources.
- Evaluating the “Expertness” of the Southern Law Poverty Center The Southern Law Poverty Center has garnered controversy for its list of so-called “hate groups” and how it spends its half-billion-dollar budget.
- Chronic Poverty and Disability in the UK The country exhibits absolute poverty and many other social issues associated with under-developed states. The issue is resolvable through policy changes.
- Should People Be Ashamed of Poverty? People on welfare should not feel ashamed because the definition of poverty does not necessarily place them in the category of the poor.
- Wealth and Poverty Sources in America This paper explains the causes and consequences of poverty in the United States, programs and systems to combat it, and government benefits to support families in distress.
- Poverty and Mental Health Correlation The analysis of the articles provides a comprehensive understanding of the poverty and mental health correlation scale and its current state.
- Attitudes to Poverty: Singer’s Arguments Singer argues against the observation by the rich than helping one poor person can repeat over and over again until the rich eventually becomes poor.
- Poverty: The Negative Effects on Children Poor children often do not have access to quality healthcare, so they are sicker and more likely to miss school. Poor children are less likely to have weather-appropriate clothes.
- The Issue of the Poverty in the USA The most sustainable technique for poverty elimination in the United States is ensuring equitable resource distribution, education, and healthcare access.
- Poverty and How This Problem Can Be Solved Poverty is one of the global social problems of our time, existing even in the countries of the first world despite the generally high standard of living of people.
- Poverty: An Interplay of Social and Economic Psychology The paper demonstrates an interplay of social and economic psychology to scrutinize the poverty that has given rise to a paycheck-to-paycheck nation.
- Refugees: Poverty, Hunger, Climate Change, and Violence Individuals struggling with poverty, hunger, climate change, and gender-based violence and persecution may consider fleeing to the United States.
- The Extent of Poverty in the United States The paper states that the issue of poverty in the USA is induced by a butterfly effect, starting with widespread discrimination and lack of support.
- Poverty in Puerto Rico and Eradication Measures Studying Puerto Rican poverty as a social problem is essential because it helps identify the causes, effects, and eradication measures in Puerto Rico and other nations.
- The City of Atlanta, Georgia: Poverty and Homelessness This project goal is to address several issues in the community of the City of Atlanta. Georgia. The primary concern is the high rate of poverty and homelessness in the city.
- Poverty and Homelessness Among African Americans Even though the U.S. is wealthy and prosperous by global measures, poverty has persisted in the area, with Blacks accounting for a larger share.
- Economic Inequality and Its Relationship to Poverty This research paper will discuss the problem of economic inequality and show how this concept relates to poverty.
- Discussion of Poverty and Social Trends The advances and consequent demands on society grounded on social class and trends profoundly influence poverty levels.
- Life of Humanity: Inequality, Poverty, and Tolerance The paper concerns the times in which humanity, and especially the American people, live, not forgetting about inequality, poverty, and tolerance.
- Poverty, Its Social Context, and Solutions Understanding past and present poverty statistics is essential for developing effective policies to reduce the rate of poverty at the national level.
- Poverty in the US: “Down and Out in Paris and London” by Orwell The essay compares the era of George Orwell to the United States today based on the book “Down and Out in Paris and London” in terms of poverty.
- Is It Possible to Reduce Poverty in the United States? Reducing poverty in the United States is possible if such areas as education, employment, and health care are properly examined and improved for the public’s good.
- Poverty Among Seniors Age 65 and Above The social problem is the high poverty rate among older people aged 65 and above. Currently, there are millions of elderly who are living below the poverty line.
- Social Issue of Poverty in America The paper states that poverty is not an individual’s fault but rather a direct result of social, economic, and political circumstances.
- Poverty, Housing, and Community Benefits The community will benefit from affordable housing and business places, creating job opportunities for the residents and mentoring and apprenticeship.
- The Uniqueness of the Extent of the Poverty Rate in America The United States ranked near the top regarding poverty and inequality, and compared to other developed countries, income and wealth disparity in the United States is high.
- Globalization and Poverty: Trade Openness and Poverty Reduction in Nigeria Globalization can be defined as the process of interdependence on the global culture, economy, and population. It is brought about by cross-border trade.
- Inequality and Poverty in the United States One of the most common myths is that the United States (US) is a meritocracy, where anyone can succeed if they maintain industriousness.
- Poverty, Politics, and Profit as US Policy Issue Poverty remains one of the most intractable problems to deal with, both in the international community and in the United States.
- Christian Perspective on Poverty Several Christian interpretations have different ideas about poverty and wealth. This paper aims to discuss the Christian perspective on poverty.
- Poverty and Problematic Housing in California The question is what are the most vulnerable aspects of the administrative system that lead to an aggravation of the situation of homelessness.
- Race, Poverty, and Incarceration in the United States The American justice system, in its current form, promotes disproportionally high incarceration rates among blacks and, to a lesser degree, Latinos from poor urban neighborhoods.
- Global Poverty and Factors of Influence This paper introduces a complex perspective on the issue of global poverty, namely, incorporating economic, social, cultural, and environmental factors into the analysis.
- Poverty Causes and Solutions in Latin America This paper aims to understand the importance of the interference of Europe in Latin American affairs and its referring to the general principles of poverty.
- Christ’s Relationships with Wealth and Poverty This paper attempts to examine Christ’s relationships with wealth, money and poverty and provide an analysis of these relationships.
- Gary Haugen’s Speech on Violence and Poverty In his speech, Gary Haugen discusses the causes of poverty and concludes that violence is a hidden problem that should be addressed and eliminated.
- The Child Poverty Problem in Alabama Alabama has a very high rate of child poverty, where a quarter or 24% of all children can be categorized as poor.
- Poverty Among Blacks in America
- Hard Questions About Living in Poverty or Slavery
- Relationship Between Poverty and Health People in 2020
- Solving the Problem of Poverty in Mendocino County
- “Promises and Poverty”: Starbucks Conceals Poverty and Deterioration of the Environment
- Poverty and Social Causation Hypothesis
- Global Poverty and Economic Globalization Relations
- Poverty Prevalence and Causes in the United States
- Policy Development to Overcome Child Poverty in the U.S.
- Global Poverty: Tendencies, Causes and Impacts
- The Problem of Poverty Among Children
- Poverty and Poor Health: Access to Healthcare Services
- African American Families in Poverty
- Effects of Poverty on Health Care in the US and Afghanistan
- Poverty Among Children from Immigrant Workers
- “8 Million Have Slipped Into Poverty Since May as Federal Aid Has Dried Up” by Jason DeParle
- Teenage Pregnancy After Exposure to Poverty: Causation and Communication
- Poverty and Covid-19 in Developing Countries
- Poverty in America: Socio-Economic Inequality
- Poverty and Its Effects Upon Special Populations
- Global Poverty and Education Correlation
- American Dream and Poverty in the United States
- Changing the Face of Poverty
- The Link Between Poverty and Criminal Behavior
- The Cost of Saving: The Problem of Poverty
- Sociological Issues About Social Class and Poverty, Race and Ethnicity, Gender
- Speech on Mother Teresa: Poverty and Interiority in Mother Teresa
- Federal Poverty, Welfare, and Unemployment Policies
- Aid Agency Discussing Different Solutions to Poverty in Urban Areas
- Poverty Elimination in Perspective
- Marriage and Divorce: Poverty Among Divorced Women
- Is Debt Cancellation the Answer to World Poverty?
- Reduction of Poverty in the Rural Areas Through ICT
🌶️ Hot Poverty Ideas to Write about
- Trade Effect on Environmentalism and Poverty
- Gay and Poverty Marriage
- “Combating Poverty in Latin America” by Robyn Eversole
- Are MNCs Responsible for Poverty and Violence in Developing Nations?
- “Globalization, Poverty and Inequality” by Kaplinsky
- Poverty in America: Issue Analysis
- Economic Development in LDCs and Eradication Absolute Poverty
- Economic Development in LDCs and Sufficient Conditions to Eradicate Absolute Poverty
- Social Policy and Welfare – Poverty and Deprivation
- Poverty in New York City and Media Representation
- India’s Policies to Tackle Poverty and Inequality
- Poverty and Inequality Reducing Policies in China
- Poverty and Homelessness: Dimensions and Constructions
- Henry George’s “Progress and Poverty” Book
- World Poverty as a Global Social Problem
- Poverty from a Sociological Standpoint
- Poverty Among the USA Citizens and Reduction Efforts
- Standards of the Ethical Code: Children and Poverty
- Grameen Banking System Alleviating Poverty
- Brazil’ Poverty and Inequality
- Child Poverty Assessment in Canada
- National Conversation about Poverty
- Poverty and Welfare Policies in the United States
- Poverty in “The Bottom Billion” by Paul Collier
- Modern Slavery, Human Trafficking and Poverty
- Poverty and Violence During the Mexican Revolution
- Affordable Housing Programs in “Poverty in America”
- The Government of Bangladesh: Corruption and Poverty
- Poverty in “I Beat the Odds” by Oher and Yaegar
- Inequality in Australia: Poverty Rates and Globalism
- The Issue of World Poverty and Ways to Alleviate the Poverty in the World
- Problem of World Poverty
- Drug’s, Poverty’s and Beauty’s Effects on Health
- Can Authorization Reduce Poverty Among Undocumented Immigrants?
- Can Higher Employment Levels Bring Lower Poverty in the EU?
- Are Private Transfers Poverty and Inequality Reducing?
- Can Group-Based Credit Uphold Smallholder Farmers Productivity and Reduce Poverty in Africa?
- Can Anti-Poverty Programs Improve Family Functioning and Enhance Children’s Well-Being?
- Can Laziness Explain Poverty in America?
- Are Social Exclusion and Poverty Measures Interrelated?
- Can Increasing Smallholder Farm Size Broadly Reduce Rural Poverty in Zambia?
- Can Crop Purchase Programs Reduce Poverty and Improve Welfare in Rural Communities?
- Does Aid Availability Affect Effectiveness in Reducing Poverty?
- Can Employer Credit Checks Create Poverty Traps?
- Are the Poverty Effects of Trade Policies Invisible?
- Can Foreign Aid Reduce Poverty?
- Are Education Systems Modern as Well as Practical Enough to Eliminate Unemployment, and Thus Poverty?
- Can High-Inequality Developing Countries Escape Absolute Poverty?
- Are Inequality and Trade Liberalization Influences on Growth and Poverty?
- Can Globalisation Realistically Solve World Poverty?
- Are Urban Poverty and Undernutrition Growing?
- Can Big Push Interventions Take Small-Scale Farmers Out of Poverty?
- Can Civilian Disability Pensions Overcome the Poverty Issue?
- Are Poverty Rates Underestimated in China?
- Does Agriculture Help Poverty and Inequality Reduction?
- Can Agricultural Households Farm Their Way Out of Poverty?
- Are Income Poverty and Perceptions of Financial Difficulties Dynamically Interrelated?
- Are Bangladesh’s Recent Gains in Poverty Reduction Different From the Past?
- Can Cash Transfers Help Households Escape an Intergenerational Poverty Trap?
- Are Remittances Helping Lower Poverty and Inequality Levels in Latin America?
- Can Foreign Aid Reduce Income Inequality and Poverty?
- Can Child-Care Subsidies Reduce Poverty?
- Can Income Inequality Reduction Be Used as an Instrument for Poverty Reduction?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/poverty-essay-topics/
"202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/poverty-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/poverty-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/poverty-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/poverty-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Poverty were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .
Poverty and Social Exclusion
Defining, measuring and tackling poverty, latest articles, home page featured articles, buenos aires 2017.

A recent report form the city of Buenos Aires measuring multi-dimensional poverty, using the consensual method, has found that in 2019, 15.3% of households were multi-dimensionally poor, rising to 25.7% for households with children under 18 years of age. The method established will be used to measure nu,ti-dimensional poverty on an ongoing basis.
6th Townsend poverty conference ad

We are now delighted to offer you the presentation slides and video recordings of sessions across the three days, featuring formal presentations, interactive Q&As, networking opportunities and much more.
Child deprivation in EU member states, 2018
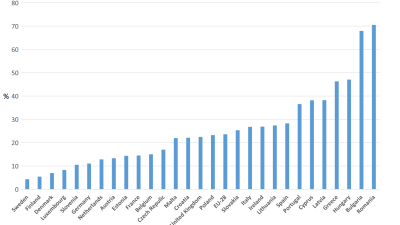
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) Steering Group on Measuring Poverty and Inequality has been tasked with producing a guide on Measuring Social Exclusion which references a lot of our PSE work.
100 questions about poverty
Progress in reducing or preventing poverty in the UK could be helped by the answers to 100 important research questions, according to a new report. The questions have been identified by the Joseph Rowntree Foundation and the Centre for Science and Policy at the University of Cambridge, based on an exercise involving 45 participants from government, non-governmental organisations, academia and research. They cover a range of themes, and indicate areas of particular research interest.
Key questions include:
- Attitudes towards poverty – To what extent does stigma contribute to the experience of living in poverty in the UK, and what can be done to address this?
- Education and family – To what extent do families (including extended families) provide the first line of defence against individual poverty, and what are the limits and geographical variations of this support?
- Employment – What explains variation in wages as a share of GDP internationally? What can countries do to combat low pay without causing unemployment in sectors that cannot move abroad?
- Health, well-being and inclusion – What is the nature and extent of poverty among those who do not, or cannot, access the safety net when they need it? What are the health risks associated with poor-quality work (low paid, insecure, poorly regulated etc) for individuals or households in poverty?
- Markets, service and the cost of living – What transport measures and interventions have the greatest negative/positive impact on poverty? What is the impact of up-front charging in public services on people in poverty?
- Place and housing – What is the effect of housing-related welfare changes on people and places in poverty?
- Tax, benefits and inequality – What would the impacts on poverty be of different models of more contributory benefit schemes? How can the effect on poverty of issues of diversity, such as ethnicity, disability, age, gender, sexual orientation or religion, be better understood and addressed? What relevance does inequality in the top half of the income distribution have for the reduction of poverty?
- Policy, power and agency – What forms of institutional structures, processes and reforms enable people living in poverty to hold state and non-state actors to account?
- The bigger picture – What are the most cost-effective interventions to prevent poverty over the life course? What differentiates the effects of poverty on men and women in terms of the impact on both their own quality of life and that of their families? Considering how much money has been spent on poverty alleviation, why has it not had more effect?
Source : William Sutherland et al., 100 Questions: Identifying Research Priorities for Poverty Prevention and Reduction , Joseph Rowntree Foundation Links : Report | JRF blog post
Tweet this page


- Policy Briefs
- Executive Committee
- Emeriti Faculty
- UC Network on Child Health, Poverty, and Public Policy
- Visting Graduate Scholars
- Media Mentions
- Center Updates
Contact the Center
- for Research Affiliates
- for Graduate Students
- Visiting Faculty Scholars
- External Opportunities
- The Non-traditional Safety Net: Health & Education
- Labor Markets & Poverty
- Children & Intergenerational Transmission of Poverty
- Immigration & Poverty
- Other Activities
- Past Events
- Policy Briefs Short summaries of our research
- Poverty Facts
- Employment, Earnings and Inequality
- Increasing College Access and Success for Low Income Students
- American Poverty Research
- Profiles in Poverty Research
- Government Agencies
- Other Poverty Centers
Primary Research Areas
Research on the non-traditional safety net: health & education.

Ten Important Questions About Child Poverty and Family Economic Hardship
- Publication Type Report
- Post date December 1, 2009
Download PDF
What is the Nature of Poverty and Economic Hardship in the United States?
- What does it mean to experience poverty?
- How is poverty measured in the United States?
- Are Americans who experience poverty now better off than a generation ago?
- How accurate are commonly held stereotypes about poverty and economic hardship?
How Serious is the Problem of Economic Hardship for American Families?
- How many children in the U.S. live in families with low incomes?
- Are some children and families at greater risk for economic hardship than others?
- What are the effects of economic hardship on children?
Is it Possible to Reduce Economic Hardship among American Families?
- Why is there so much economic hardship in a country as wealthy as the U.S.?
- Why should Americans care about family economic hardship?
- What can be done to increase economic security for America’s children and families?
1. What does it mean to experience poverty?
Families and their children experience poverty when they are unable to achieve a minimum, decent standard of living that allows them to participate fully in mainstream society. One component of poverty is material hardship. Although we are all taught that the essentials are food, clothing, and shelter, the reality is that the definition of basic material necessities varies by time and place. In the United States, we all agree that having access to running water, electricity, indoor plumbing, and telephone service are essential to 21st century living even though that would not have been true 50 or 100 years ago.
To achieve a minimum but decent standard of living, families need more than material resources; they also need “human and social capital.” Human and social capital include education, basic life skills, and employment experience, as well as less tangible resources such as social networks and access to civic institutions. These non-material resources provide families with the means to get by, and ultimately, to get ahead. Human and social capital help families improve their earnings potential and accumulate assets, gain access to safe neighborhoods and high-quality services (such as medical care, schooling), and expand their networks and social connections.
The experiences of children and families who face economic hardship are far from uniform. Some families experience hard times for brief spells while a small minority experience chronic poverty. For some, the greatest challenge is inadequate financial resources, whether insufficient income to meet daily expenses or the necessary assets (savings, a home) to get ahead. For others, economic hardship is compounded by social isolation. These differences in the severity and depth of poverty matter, especially when it comes to the effects on children.
2. How is poverty measured in the United States?
The U.S. government measures poverty by a narrow income standard — this measure does not include material hardship (such as living in substandard housing) or debt, nor does it consider financial assets (such as savings or property). Developed more than 40 years ago, the official poverty measure is a specific dollar amount that varies by family size but is the same across the continental U.S..

According to the federal poverty guidelines, the poverty level is $22,050 for a family of four and $18,310 for a family of three (see table). (The poverty guidelines are used to determine eligibility for public programs. A similar but more complicated measure is used for calculating poverty rates.)
The current poverty measure was established in the 1960s and is now widely acknowledged to be outdated. It was based on research indicating that families spent about one-third of their incomes on food — the official poverty level was set by multiplying food costs by three. Since then, the same figures have been updated annually for inflation but have otherwise remained unchanged.
Yet food now comprises only one-seventh of an average family’s expenses, while the costs of housing, child care, health care, and transportation have grown disproportionately. Most analysts agree that today’s poverty thresholds are too low. And although there is no consensus about what constitutes a minimum but decent standard of living in the U.S., research consistently shows that, on average, families need an income of about twice the federal poverty level to meet their most basic needs.
Failure to update the federal poverty level for changes in the cost of living means that people who are considered poor today by the official standard are worse off relative to everyone else than people considered poor when the poverty measure was established. The current federal poverty measure equals about 31 percent of median household income, whereas in the 1960s, the poverty level was nearly 50 percent of the median.
The European Union and most advanced industrialized countries measure poverty quite differently from the U.S. Rather than setting minimum income thresholds below which individuals and families are considered to be poor, other countries measure economic disadvantage relative to the citizenry as a whole, for example, having income below 50 percent of median.
3. Are Americans who experience poverty now better off than a generation ago?
Material deprivation is not as widespread in the United States as it was 30 or 40 years ago. For example, few Americans experience severe or chronic hunger, due in large part to public food and nutrition programs, such as food stamps, school breakfast and lunch programs, and WIC (the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children). Over time, Social Security greatly reduced poverty and economic insecurity among the elderly. Increased wealth and technological advances have made it possible for ordinary families to have larger houses, computers, televisions, multiple cars, stereo equipment, air conditioning, and cell phones.
Some people question whether a family that has air conditioning or a DVD player should be considered poor. But in a wealthy nation such as the US, cars, computers, TVs, and other technologies are considered by most to be a normal part of mainstream American life rather than luxuries. Most workers need a car to get to work. TVs and other forms of entertainment link people to mainstream culture. And having a computer with access to the internet is crucial for children to keep up with their peers in school. Even air conditioning does more than provide comfort — in hot weather, it increases children’s concentration in school and improves the health of children, the elderly, and the chronically ill.
Consider as well the devastating effects of Hurricane Katrina. Prior to the hurricane, New Orleans had one of the highest child poverty rates in the country — 38 percent (and this figure would be much higher if it included families with incomes up to twice the official poverty level). One in five households in New Orleans lacked a car, and eight percent had no phone service. The pervasive social and economic isolation increased the loss of life from the hurricane and exacerbated the devastating effects on displaced families and children.
Focusing solely on the material possessions a family has ignores the other types of resources they need to provide a decent life for their children — a home in a safe neighborhood; access to good schools, good jobs and basic services; and less tangible resources such as basic life skills and support networks.
4. How accurate are commonly held stereotypes about poverty?
The most commonly held stereotypes about poverty are false. Family poverty in the U.S. is typically depicted as a static, entrenched condition, characterized by large numbers of children, chronic unemployment, drugs, violence, and family turmoil. But the realities of poverty and economic hardship are very different.
Americans often talk about “poor people” as if they are a distinct group with uniform characteristics and somehow unlike the rest of “us.” In fact, there is great diversity among children and families who experience economic hardship. Research shows that many stereotypes just aren’t accurate: a study of children born between 1970 and 1990 showed that 35 percent experienced poverty at some point during their childhood; only a small minority experienced persistent and chronic poverty. And more than 90 percent of low-income single mothers have only one, two, or three children.
Although most portrayals of poverty in the media and elsewhere reflect the experience of only a few, a significant portion of families in America have experienced economic hardship, even if it is not life-long. Americans need new ways of thinking about poverty that allow us to understand the full range of economic hardship and insecurity in our country. In addition to the millions of families who struggle to make ends meet, millions of others are merely one crisis — a job loss, health emergency, or divorce — away from financial devastation, particularly in this fragile economy. A recent study showed that the majority of American families with children have very little savings to rely on during times of crisis. Recently, more and more families have become vulnerable to economic hardship.
5. How many children in the US live in families with low incomes?
Given that official poverty statistics are deeply flawed, the National Center for Children in Poverty uses “low income” as one measure of economic hardship. Low income is defined as having income below twice the federal poverty level — the amount of income that research suggests is needed on average for families to meet their basic needs. About 41 percent of the nation’s children — nearly 30 million in 2008 — live in families with low incomes, that is, incomes below twice the official poverty level (for 2009, about $44,000 for a family of four).
Although families with incomes between 100 and 200 percent of the poverty level are not officially classified as poor, many face material hardships and financial pressures similar to families with incomes below the poverty level. Missed rent payments, utility shut offs, inadequate access to health care, unstable child care arrangements, and running out of food are not uncommon for such families.

Low-income rates for young children are higher than those for older children — 44 percent of children under age six live in low-income families, compared to 39 percent of children over age six. Parents of younger children tend to be younger and to have less education and work experience than parents of older children, so their earnings are typically lower.
6. Are some children and families at greater risk for economic hardship than others?
Low levels of parental education are a primary risk factor for being low income. Eighty-three percent of children whose parents have less than a high school diploma live in low-income families, and over half of children whose parents have only a high school degree are low income as well. Workers with only a high school degree have seen their wages stagnate or decline in recent decades while the income gap between those who have a college degree and those who do not has doubled. Yet only 27 percent of workers in the U.S. have a college degree.
Single-parent families are at greater risk of economic hardship than two-parent families, largely because the latter have twice the earnings potential. But research indicates that marriage does not guarantee protection from economic insecurity. More than one in four children with married parents lives in a low-income family. In rural and suburban areas, the majority of low-income children have married parents. And among Latinos, more than half of children with married parents are low income. Moreover, most individuals who experience poverty as adults grew up in married-parent households.

Although low-income rates for minority children are considerably higher than those for white children, this is due largely to a higher prevalence of other risk factors, for example, higher rates of single parenthood and lower levels of parental education and earnings. About 61 percent of black, 62 percent of Latino children and 57 percent of American Indian children live in low-income families, compared to about 27 percent of white children and 31 percent of Asian children. At the same time, however, whites comprise the largest group of low-income children: 11 million white children live in families with incomes below twice the federal poverty line.
Having immigrant parents also increases a child’s chances of living in a low-income family. More than 20 percent of this country’s children — about 16 million — have at least one foreign-born parent. Sixty percent of children whose parents are immigrants are low-income, compared to 37 percent of children whose parents were born in the U.S.
7. What are the effects of economic hardship on children?
Economic hardship and other types of deprivation can have profound effects on children’s development and their prospects for the future — and therefore on the nation as a whole. Low family income can impede children’s cognitive development and their ability to learn. It can contribute to behavioral, social, and emotional problems. And it can cause and exacerbate poor child health as well. The children at greatest risk are those who experience economic hardship when they are young and children who experience severe and chronic hardship.
It is not simply the amount of income that matters for children. The instability and unpredictability of low-wage work can lead to fluctuating family incomes. Children whose families are in volatile or deteriorating financial circumstances are more likely to experience negative effects than children whose families are in stable economic situations.
The negative effects on young children living in low income families are troubling in their own right. These effects are also cause for concern because they are associated with difficulties later in life — dropping out of school, poor adolescent and adult health, poor employment outcomes and experiencing poverty as adults. Stable, nurturing, and enriching environments in the early years help create a sturdy foundation for later school achievement, economic productivity, and responsible citizenship.
Parents need financial resources as well as human and social capital (basic life skills, education, social networks) to provide the experiences, resources, and services that are essential for children to thrive and to grow into healthy, productive adults — high-quality health care, adequate housing, stimulating early learning programs, good schools, money for books, and other enriching activities. Parents who face chronic economic hardship are much more likely than their more affluent peers to experience severe stress and depression — both of which are linked to poor social and emotional outcomes for children.
Is it Possible to Reduce Economic Hardship for American Families?
8. why is there so much economic hardship in a country as wealthy as the u.s..
Given its wealth, the U.S. had unusually high rates of child poverty and income inequality, even prior to the current economic downturn. These conditions are not inevitable — they are a function both of the economy and government policy. In the late 1990s, for example, there was a dramatic decline in low-income rates, especially among the least well off families. The economy was strong and federal policy supports for low-wage workers with children — the Earned Income Tax Credit, public health insurance for children, and child care subsidies — were greatly expanded. In the current economic downturn, it is expected that the number of poor children will increase by millions.
Other industrialized nations have lower poverty rates because they seek to prevent hardship by providing assistance to all families. These supports include “child allowances” (typically cash supplements), child care assistance, health coverage, paid family leave, and other supports that help offset the cost of raising children.
But the U.S. takes a different policy approach. Our nation does little to assist low-income working families unless they hit rock bottom. And then, such families are eligible only for means-tested benefits that tend to be highly stigmatized; most families who need help receive little or none. (One notable exception is the federal Earned Income Tax Credit.)
At the same time, middle- and especially upper-income families receive numerous government benefits that help them maintain and improve their standard of living — benefits that are largely unavailable to lower-income families. These include tax-subsidized benefits provided by employers (such as health insurance and retirement accounts), tax breaks for home owners (such as deductions for mortgage interest and tax exclusions for profits from home sales), and other tax preferences that privilege assets over income. Although most people don’t think of these tax breaks as government “benefits,” they cost the federal treasury nearly three times as much as benefits that go to low- to moderate-income families. In addition, middle- and upper-income families reap the majority of benefits from the child tax credit and the child care and dependent tax credit because neither is fully refundable.
In short, high rates of child poverty and income inequality in the U.S. can be reduced, but effective, widespread, and long-lasting change will require shifts in both national policy and the economy.
9. Why should Americans care about family economic hardship?
In addition to the harmful consequences for children, high rates of economic hardship exact a serious toll on the U.S. economy. Economists estimate that child poverty costs the U.S. $500 billion a year in lost productivity in the labor force and spending on health care and the criminal justice system. Each year, child poverty reduces productivity and economic output by about 1.3 percent of GDP.
The experience of severe or chronic economic hardship limits children’s potential and hinders our nation’s ability to compete in the global economy. American students, on average, rank behind students in other industrialized nations, particularly in their understanding of math and science. Analysts warn that America’s ability to compete globally will be severely hindered if many of our children are not as academically prepared as their peers in other nations.
Long-term economic trends are also troubling as they reflect the gradual but steady growth of economic insecurity among middle-income and working families over the last 30 years. Incomes have increased very modestly for all but the highest earners. Stagnant incomes combined with the high cost of basic necessities have made it difficult for families to save, and many middle- and low-income families alike have taken on crippling amounts of debt just to get by.
Research also indicates that economic inequality in America has been on the rise since the 1970s. Income inequality has reached historic levels — the income share of the top one percent of earners is at its highest level since 1929. Between 1979 and 2006, real after-tax incomes rose by 256 percent for the top one percent of households, compared to 21 percent and 11 percent for households in the middle and bottom fifth (respectively).
Economic mobility—the likelihood of moving from one income group to another—is on the decline in the U.S. Although Americans like to believe that opportunity is equally available to all, some groups find it harder to get ahead than others. Striving African American families have found upward mobility especially difficult to achieve and are far more vulnerable than whites to downward mobility. The wealth gap between blacks and whites — black families have been found to have one-tenth the net worth of white families — is largely responsible.
What all of these trends reveal is that the American Dream is increasingly out of reach for many families. The promise that hard work and determination will be rewarded has become an increasingly empty promise in 21st century America. It is in the best interest of our nation to see that the American Dream, an ideal so fundamental to our collective identity, be restored.
10. What can be done to increase economic security for America’s children and families?
A considerable amount of research has been devoted to this question. We know what families need to succeed economically, what parents need to care for and nurture their children, and what children need to develop into healthy, productive adults. The challenge is to translate this research knowledge into workable policy solutions that are appropriate for the US.
For families to succeed economically, we need an economy that works for all — one that provides workers with sufficient earnings to provide for a family. Specific policy strategies include strengthening the bargaining power of workers, expanding the Earned Income Tax Credit, and increasing the minimum wage and indexing it to inflation. We also need to help workers get the training and education they need to succeed in a changing workforce. Dealing with low wages is necessary but not sufficient. Low- and middle-income families alike need relief from the high costs of health insurance and housing. Further programs that promote asset building among low-income families with children are also important.
As a nation, we also need to make it possible for adults to be both good workers and good parents, which requires greater workplace flexibility and paid time off. Workers need paid sick time, and parents need time off to tend to a sick child or talk to a child’s teacher. Currently, three in four low-wage workers have no paid sick days.
Despite the fact that a child’s earliest years have a profound effect on his or her life trajectory and ultimate ability to succeed, the U.S. remains one of the only industrialized countries that does not provide paid family leave for parents with a new baby. Likewise, child care is largely private in the U.S. — individual parents are left to find individual solutions to a problem faced by all working parents. Low- and middle-income families need more help paying for child care and more assistance in identifying reliable, nurturing care for their children, especially infants and toddlers.
These are only some of the policies needed to reduce economic hardship, strengthen families, and provide a brighter future for today’s — and tomorrow’s — children. With the right leadership, a strong national commitment, and good policy, it’s all possible.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

100 Questions: identifying research priorities for poverty prevention and reduction

Reducing poverty is important for those affected, for society and the economy. Poverty remains entrenched in the UK, despite considerable research efforts to understand its causes and possible solutions. The Joseph Rowntree Foundation, with the Centre for Science and Policy at the University of Cambridge, ran a democratic, transparent, consensual exercise involving 45 participants from government, non-governmental organisations, academia and research to identify 100 important research questions that, if answered, would help to reduce or prevent poverty. The list includes questions across a number of important themes, including attitudes, education, family, employment, heath, wellbeing, inclusion, markets, housing, taxes, inequality and power.
Related Papers
Policy & Politics
Justin Keen
Richard J White
This article explores the ways in which young people's decisions about post-compulsory education, training and employment are shaped by place, drawing on case study evidence from three deprived neighbourhoods in England. It discusses the way in which place-based social networks and attachment to place influence individuals' outlooks and how they interpret and act on the opportunities they see. While such networks and place attachment can be a source of strength in facilitating access to opportunities, they can also be a source of weakness in acting to constrain individuals to familiar choices and locations. In this way, 'subjective' geographies of opportunity may be much more limited than 'objective' geographies of opportunity. Hence it is important for policy to recognise the importance of 'bounded horizons'.
Michael Hirst , Anne Corden
Lisa Scullion
J. Poverty Soc. Justice
Toity Deave
Journal of Poverty and Social Justice
Kirsten Besemer
Stephen Sinclair , John McKendrick
Social Policy and Society
Line Nyhagen
John Hills , David Piachaud
The Joseph Rowntree Foundation has supported this project as part of its programme of research and innovative development projects, which it hopes will be of value to policy makers, practitioners and service users. The facts presented and views expressed in this report are, however, ...
CASE Papers
Ruth Lister
RELATED PAPERS
Jonathan Bradshaw
Ronald McQuaid
Colin Lindsay
Journal of Policy Analysis and Management
Liam Foster
Alison Garnham
Mark Tomlinson
Cambridge Journal of Economics
Kevin Albertson , Paul Stepney
Serena Romano
Mansel Aylward
Surya Monro
Alex Nunn , Ronald McQuaid , Tim Bickerstaffe
… by National Association of Welfare Rights …
Colin Talbot
GA Williams , Mark Tomlinson
Hilary Stevens
Chris Pittman
Ian Cummins
Information, communication & …
Abigail Davis
… , communication & society
Bryony Beresford
Martin Taulbut
research.dwp.gov.uk
Peter Allmark
Richard Riddell
Glen Bramley
Judy Corlyon
Ronald McQuaid , Vanesa Fuertes
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
Shoshana Pollack
alan france
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection


Politics of Poverty Governance: an Introduction
Zhongyuan wang.
Fudan Institute for Advanced Study in Social Sciences, Shanghai, China
Poverty alleviation and politics are interrelated in complex ways. Poverty governance is essentially a multi-faceted process of using political power, exercising political authority, mobilizing political resources, running political institutions, and gaining political legitimacy. However, the approach of economics has long dominated current discussions in the literature on poverty reduction, resulting in a relative lack of political science research on poverty reduction interventions. This special issue has gathered together carefully selected articles to examine the politics of poverty governance in non-electoral settings, with a specific area focus on China. Despite focusing on China, this special issue adopts a comparative analytical lens and extends beyond China studies by striving to position China’s poverty governance in relation to general theories of political science. This introductory article seeks to expound the motives highlighted in the special issue, identify the literature gap that the special issue aims to fill, summarize the key findings and contributions, and finally suggest some promising new areas of future research.
Introduction
The reason why the editors of the Journal of Chinese Political Science have chosen to devote an entire issue to the “politics of poverty governance” is because poverty remains one of the most enduring and unresolved problems that the world faces today. It appears in various forms, posing ongoing harm to many citizens in low-income countries, and even to many in affluent countries. Narrowly defined, poverty typically refers to a state in which the income level of a household or an individual is so low that essential human needs and a minimum standard of living cannot be met. The term “poverty” often brings to mind images in which impoverished people experience a lack of food, proper housing, clean water and sanitation. Broadly defined, poverty represents “pronounced deprivation in well-being” ([ 24 ], p1), which reflects a revised and increasing understanding that poverty is not simply defined as a low level of income. Instead, it describes a “deprivation of capabilities” that limits people’s freedoms to function fully in society and achieve their potential [ 2 , 47 ]. Regardless of whether one adopts the “thin” perspective of poverty as lacking the essentials for survival, or the “thick” perspective of poverty as the accumulation of multiple disadvantages, modern states are expected to commit and conduct due diligence in the battle against poverty.
Eradicating poverty in its all forms and promoting shared prosperity cannot be achieved without state intervention. Nowadays, many countries around the world attach great importance to solving the problem of acute poverty, adopting a variety of measures to help the poorest and most vulnerable groups within their territories escape the poverty trap. Meanwhile, the international community has also prioritized the eradication of poverty as one of the most urgent global goals, incorporating it into the 2030 UN Agenda for Sustainable Development. Thus, poverty reduction has gained much prominence at both the national and international levels. For nearly 25 years, global extreme poverty was steadily declining, with the share of the extreme poor plunging from 36% in 1990 to less than 10% in 2018. 1 Yet one of the greatest challenges facing many countries is the pursuit of continuous progress in poverty eradication [ 20 , 21 ]. In particular, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and its associated economic crisis, which disproportionally impact the world’s poor, are reversing hard-won gains in poverty eradication efforts and exacerbating income inequality [ 10 , 30 , 54 ]. It is the first time in a quarter century that we witness more new poor than the number of people lifted out of poverty, with an estimated 150 million people worldwide being pushed into extreme poverty in recent years. 2 Without a concerted and committed country-level response, growing poverty will potentially precipitate various negative social and political effects. Therefore, there is watershed opportunity present today to reexamine poverty dynamics and investigate the political logic of poverty governance.
The articles in this special issue are generally interested in the political logic of poverty governance in non-electoral settings with an analytic focus on China. Although a majority of the selected works relate to China, this special issue is not a collection of articles purely devoted to China studies. Instead, these articles extend beyond China, with the aim of better positioning China’s poverty governance in relation to general theories of political science, and analyzing it through the comparative lens of cross-case studies. All the contributors were asked to reflect on the politics of poverty governance by respectively uncovering the political motivations, policy processes, and political implications of the Party-led poverty alleviation in China, thus contributing novel insights to institutional and political explanations for poverty alleviation. Ultimately, the overarching goal of the special issue is to bring analytical frameworks of political science into the field of anti-poverty research.
Related literature
Poverty research largely concentrates on four fundamental questions. What is poverty? Why are some people poor? What are the repercussions of poverty? What can be done to reduce poverty? No doubt there is a rich tradition of social science research on poverty which has provided a wide range of answers to these key questions from a myriad of perspectives. However, poverty studies across different academic disciplines have long been very uneven and highly fragmented [ 9 ]. The current literature on poverty is mainly dominated by an economics-centric approach because poverty is of inherent interest to economists who are concerned with how to empirically measure poverty and evaluate its severity. This entails examining the nature and causes of poverty, investigating economic performance, which in turn shapes poverty, comparing macroeconomic and microeconomic tools that can be used to combat poverty, and identifying causal influences of various pro-poor economic experiments [ 5 , 28 , 42 , 44 ]. Economic explanations have already enhanced the theoretical and empirical knowledge on the meaning, origins, and consequences of poverty. Nevertheless, as defined by a more expanded conception of poverty, poverty not only refers to monetary scarcity, but also more broadly refers to marginalization and exclusion in political domains as an outcome of power relations. Therefore, the prevailing economic approach has proven limited in explaining poverty alleviation efforts from non-monetary angles. In addition, poverty and poverty governance are two related but significantly different research themes. The former focuses attention on the problem of poverty itself, while the latter centers on the broader processes of addressing poverty. Analyses of the meaning, drivers and impacts of poverty need to be distinguished from research on the motivations, processes and results of poverty governance. The economics approach might be more effective and fruitful for answering the questions pertaining to poverty, but it is rather limited to offer deeper insights into the more complex set of motivations, dynamic processes and far-reaching effects of poverty governance. For instance, economic investment, skills training, infrastructure construction, and agricultural development certainly play a pivotal role in tackling poverty, but these things do not emerge organically. State policies and political interventions can often be decisive in shaping the origin, process and outcome of poverty alleviation programs. To cite another example, the central government can devise a comprehensive set of policies, transfers, programs, and assistance aimed at reducing poverty and boosting development, but the bureaucracies located at the lower ends of the political hierarchy often vary in their competence in implementing top-level designed policies. This makes it difficult to reduce poverty effectively and consistently, or results in the elite capture of public interests even under democratic conditions.
In this regard, there is a need to borrow from the perspectives of other social science disciplines, especially that of political science, to study poverty governance [ 1 , 56 ]. This is because poverty governance is a multi-faceted process of using political power, exercising political authority, mobilizing political resources, running political institutions, and gaining political legitimacy. Poverty alleviation and politics are interrelated in complex ways. For instance, there are deep-seated political and institutional sources of protracted anti-poverty challenges. Initiatives to end poverty could be politically motivated, and the formulation of poverty reduction programs, as well as the performance of pro-poor policy implementation are greatly influenced by multiple political factors. The evolution of poverty reduction strategies depends largely on the political conditions that structure the policy process. In turn, the results of poverty governance will also generate profound political implications. As an independent variable, politics plays a central role in combating poverty. Good governance requires the state to be capable, responsive and accountable, and in the context of poverty governance, it means making the government work for the poor. As a dependent variable, the effectiveness and flaws of various poverty reduction strategies could also transform politics and affect political behavior, government legitimacy and regime survival. Furthermore, poverty-reduction interventions also encompass various political subjects ranging from state building, institutional adaption, party politics, state-society relations, and central-local government relations, as well as citizen participation, political attitudes and civil society. As the political scientist Harold Lasswell famously highlighted, politics is all about “who gets what, when, how” [ 33 ]. Thus, poverty alleviation which can be considered as a form of distributive politics lies at the heart of politics since it involves the allocation of governmental goods and services. Examining the underlying forces, processes, and political outcomes of poverty alleviation efforts helps to shed light on many critical political science questions. To date, with some notable exceptions ([ 14 , 17 ], relatively few in-depth studies on poverty governance have been conducted from a political science perspective. “Compared to the other social sciences, political scientists simply do not study poverty as much” ([ 9 ], p.2). It is with this gap in mind that this special issue aims to contribute with articles covering different political perspectives of poverty governance.
Traditionally, studies of poverty reduction neglected politics. As political and institutional explanations grow in prominence, the burgeoning literature linking politics, institutions and poverty alleviation can be generally classified into three groups. The first group adopts the approach of new institutionalism to examine the powerful role played by political regimes, bureaucratic systems and sub-national institutions in shaping the processes and outcomes of anti-poverty welfare programs [ 8 ]. Related studies delve into institution-specific variables including electoral systems, political parties, courts, administrative agencies, subnational power structures and social movements, that could largely determine the scale and scope of pro-poor policies [ 3 , 11 , 27 ]. This scholarship has therefore built on the traditional institutional arguments and further explored the salient impacts of left-wing parties, labor unions, and democratic institutions on poverty reduction programs.
The second set of studies concerns distributive politics of poverty-reducing interventions under competitive electoral systems. The scholarship identifies that as part of distributive policy, poverty alleviation is often instrumentalized by political parties and politicians as an electoral tool for staying in office and consolidating power. These studies usually focus on political favoritism and clientelist linkage in allocating anti-poverty resources, and investigate whether and how incumbents strategically allocate poverty-relief goods disproportionately to targeted groups of constituents (e.g. voters versus nonvoters, core voters versus swing voters, voters in electorally critical districts, culturally, regionally and ethnically identifiable subgroups) as well as choosing the timing of the anti-poverty goods delivery (e.g. during the electoral cycle) [ 6 , 18 , 34 ]. Scholars also seek to examine the success of these allocation activities, evaluating the electoral and political returns to government anti-poverty efforts [ 13 , 32 , 39 ]. These studies find that the allocation of poverty-relief resources under electoral democracies is not to fairly catered to the needs of the poor, but has been largely shaped by political calculations such as electoral interests, partisan favoritism and political survival [ 31 ]. This growing body of literature also reveals that such a pattern of anti-poverty resource distribution prevails not only in advanced Western democracies, but also in competitive authoritarian regimes [ 7 , 37 , 50 ]. Autocrats often allocate welfare resources to a targeted population as a means to improve their electoral prospects and prolong their political survival. Overall, these studies again exemplify Lasswell’s definition of politics, that is, politics is concerned with “who gets what, when, how”.
The third set of research highlights the importance of institutional reforms and good governance in improving the outcomes of poverty alleviation. Since the 1990s, international donors and academic researchers have both devoted increasing attention to identifying various political constraints and obstacles for carrying out anti-poverty programs in aid-recipient countries. This area of research discerns how poverty reduction can be most effectively achieved by expanding citizen participation and enhancing government accountability, transparency and responsiveness in under-developed countries [ 15 , 41 , 45 ]. By the same token, the notion of “good governance” has gradually gained widespread currency, underscoring the need to reform political systems and cultivate civil society for the sake of poverty elimination. Consequently, this constitutes a necessary condition for donors to disburse aid to impoverished countries [ 12 , 19 , 29 ]. This scholarship strongly reflects the normative power underlying research that attempts to improve the performance of poverty alleviation in developing countries by transforming their political systems and restructuring governmental institutions through neoliberal pathways, although the actual effects are largely arguable [ 43 ].
Poverty is a topic of lively debate in nearly all regime types. However, as demonstrated above, current scholarship on “the politics of poverty alleviation” focuses on discussing the allocation of public resources under electoral systems. This entails examining either the electoral motives and distributive favoritism underpinning poverty alleviation efforts, or the international community’s anti-poverty assistance to under-developed countries and its political stabilization effects. In short, current political studies on poverty governance maintain a typical neoliberal ideological stance, while paying scant attention to poverty governance models and their political logic, especially in non-liberal countries with weak electoral accountability such as China. Little is known about the political motivations, mechanisms, and effects of poverty governance under authoritarian systems. 3 In addition, both developing and developed countries today are experiencing poverty in different forms and of varying degrees. Much of the research on poverty in developed countries tends to predominantly focus on urban poverty and relative poverty [ 16 ], while studies on poverty in developing countries are mostly restricted to rural poverty and absolute poverty [ 40 ]. These two strands of research hardly intersect and in fact rarely engage with each other.
State actions in the fight against poverty have never been as prominent as today. China is a country that has made major strides in poverty reduction. By prioritizing poverty alleviation in the political agenda of the ruling party, China has become the first developing country in the world to attain the poverty reduction target set by the United Nations ten years ahead of schedule. At the end of 2020, the Chinese government officially declared victory in eradicating extreme poverty, claiming 93.48 million rural people and 832 poverty-stricken counties have been lifted out of poverty. Politics must take center stage if poverty is to be substantially reduced. In this regard, China has made a strong case for using its state capacity and political will, which have had transformative effects on poverty governance. What has driven China’s latest effort in targeted poverty alleviation in a system without electoral accountability? How are poverty identification policies and poverty assistance models crafted by the Chinese government? How can they be implemented locally? Why do local governments vary in their competence to transform their bureaucracy into an effective poverty governance institution? Who are the main bodies involved in China’s anti-poverty scheme, and how do they work together? What brings the unintended political consequences of poverty-reducing interventions? What does poverty alleviation mean for China’s political development and regime consolidation? After addressing extreme poverty, what political risks will growing income inequality generate? The above is a plethora of questions that political scientists are concerned with and need to answer. China is a typical single-party country, where the political logic and process of poverty governance are distinctive from those of electoral democracies. Therefore, we invite papers that consider these topics to contribute to the special issue, which tries to understand the politics of poverty governance in China from a comparative perspective with updated empirical evidence. Of course, the articles included in the special issue cannot fully answer all the above questions, but they represent a fruitful early attempt and effort in this direction, establishing a foundation for a comprehensive political science of poverty governance.
Contributions of the Special Issue
Collectively, the articles in this special issue hope to contribute by filling the scholarly gaps identified in the preceding section, and advancing research on the politics of poverty governance in the following three main areas.
First, the authors introduce various analytical frameworks of political science to advance scholarship on poverty governance. They delve into intricate political elements of poverty alleviation by using the concepts, theories and methods of political research. These efforts not only generate novel institutional and political explanations for the performance and outcomes of poverty eradication, but also unpack the complex linkage between politics and poverty alleviation. The special issue also enriches the existing scholarship on poverty research by expanding its regime focus beyond electoral democracies, and at the same time addresses the uneven development and segregation of poverty research across disciplines. It also enables a better understanding of how statecraft and politics matter to poverty alleviation and inspires further thinking on possible political pathways toward better poverty governance.
Second, the articles investigate China’s poverty alleviation efforts with evidence-based disciplinary analysis and meticulous rigorous cross-case comparisons. The current interpretations of China’s recent anti-poverty achievements lean toward polarization. On the one hand, the Chinese authorities utilize these data as propaganda on government performance and use their achievements to extol the success of the China model. On the other hand, foreign governments and international media tend to ignore, downplay and even question those achievements, assuming that countries without liberal-electoral systems cannot genuinely end poverty. With some notable exceptions [ 4 , 58 ], there has long been a palpable lack of in-depth social science scholarly analysis of China’s anti-poverty efforts, and especially few contributions by political scientists. This special issue represents a conscious attempt to move away from Chinese official propaganda and Western neoliberalism toward examining the politics of poverty alleviation in a non-electoral context through theory-driven and evidence-based empirical studies. As a result, several new promising areas of research can be uncovered.
Third, the articles in this special issue are thematically and methodologically diverse. They encompass topics ranging from policy design for poverty identification, to central-local government relations in poverty relief, state-business relations in poverty alleviation and formal-informal institutions in poverty governance, to outcome and political effects of poverty alleviation in China and beyond, thus speaking to the broader literature [ 23 , 49 , 51 ]. These studies also vary in research methods from case studies, within-case comparative analysis, and cross-case comparative analysis to quantitative regression analysis based on survey data and cutting-edge causal identification based on propensity score matching. The authors emphasize the complexity of relations between politics and poverty, and provide novel insights into the comprehensive picture of poverty governance through engaging with a variety of political science theories and using multiple methods.
Organization and Introduction of the Articles
One salient theme in this issue touches on the critical institutional foundation of poverty alleviation programs, poverty identification. The performance of Targeted Poverty Alleviation (TPA) heavily relies on the ability of grassroots cadres and the methods they use to accurately identify beneficiaries on the ground. Given the inherent difficulties of measuring poverty, the key to determining the success of poverty reduction rests on whether the method of poverty identification is scientific, whether the identification process is standardized, and whether the identification result is accurate. As an essential first step (“the first button” in the narratives of the Chinese government) in poverty alleviation programs, poverty targeting will also affect the overall public evaluation and the long-run political effects of the TPA project. In Who Are Identified as Poor in Rural China’s Targeted Poverty Alleviation Strategy? Li et al. [ 36 ] investigate how poverty identification had been carried out in rural China and show that a multidimensional poverty measure was employed to identify and register poor households in the TPA project. More specifically, the authors argue that instead of focusing only on the monetary dimension (as per previous poverty-reducing programs), those who suffered deprivations in education, health, employment, and living conditions had greater odds of being registered as poor in the new anti-poverty scheme, which resonated more with the capability approach advocated by Amartya Sen. Such an identification strategy compounded with the various forms of targeted assistance helps enhance the effectiveness of the TPA program by targeting and meeting the multidimensional needs of the poor. Based on a recent nationally representative survey dataset, the empirical analysis further reveals that registered households received significantly more government assistance than the non-registered (especially those in well-developed regions). These gaps raise concerns that although the multidimensional approach greatly improved the overall targeting performance, sizable targeting errors (e.g. inclusion errors and exclusion errors) still remain, which necessitates expanded support and more nuanced targeting strategies for both the poor and near-poor households around the country in the post-TPA era [ 53 ]. The findings will have policy implications not only for China’s future poverty monitoring and alleviation strategies, but also for related issue areas encountered by other developing countries and even the developed world.
A second theme highlights the essentially dynamic nature of policy implementation of the TPA program in China with a broader comparative perspective. It covers several key topics such as central-local government relations in poverty relief, state-society relations in poverty alleviation, and formal-informal institutions in poverty governance. First, countries with poverty reduction goals always face a dilemma of choosing decentralized versus centralized approaches to combating poverty. Neo-liberal norms such as representation, inclusiveness, empowerment, and decentralization have long been espoused by international organizations and western media to promote the interests of the poor, given their theoretically assumed advantages in achieving better poverty relief performance. Can this be supported by empirical evidence in the real world? In Integrating Devolution with Centralization, Zuo [ 57 ] rejects the prevailing traditional wisdom and argues that some specific forms of political centralization are of crucial and equal importance to the effective delivery of locally managed welfare distribution, because without strong top-down accountability and close monitoring mechanisms, decentralized institutions will often lead to elite capture and the misconduct of local officials. By adopting a “most-different-similar-outcome” research design, Zuo provides a nuanced comparison of three successful poverty alleviation programs carried out in India (West Bengal), Mexico, and China. The cross-case analysis illustrates that despite large differences in poverty rate, the level of wealth, and the economic and political settings, the three cases share striking common institutional features in their poverty alleviation initiatives. These are the ruling party’s credible commitment to reduce poverty and a set of well-designed institutions that monitor the program implementation and shape the incentives of local politicians. Albeit with varying levels of mixes, organizational arrangements that are both centralized and decentralized contribute to the efficiency of successful welfare programs in all three cases. Therefore, the article makes the argument that to generate pro-poor outcomes, decentralization should be integrated with top-down interventions with specific institutional designs in anti-poverty schemes, signifying a break with traditional ways of explaining anti-poverty success. Given the very fact that many under-developed countries suffer serious institutional deficits in carrying out decentralization, Zuo’s findings throw up more in-depth theoretical reflections on the devolution of decision-making powers and highlight the empirical necessity of developing more pragmatic central-local models in tackling poverty.
Second, governments at various levels are usually posited as the dominant player in implementing poverty alleviation programs, but they never act alone. What roles have non-governmental actors played in state-led poverty relief campaigns? What adaptive strategies were employed by the state and social forces respectively to reconcile their conflicting interests? In addition to central-local relations, we need also to look at the evolving government-business relations (state-society relations) in China’s recent war against poverty. In To Get Rich is Glorious, Huang and Xin [ 26 ] discuss entrepreneurs’ philanthropic participation in the TPA program. Focusing on the Guangcai Program in Shandong, the article first classifies local entrepreneurs into four types depending on the differences in their aim of participation and level of activeness: altruist, speculator, involuntarist and temporizer. These different types of China’s new rich reveal varying patterns in the strategies utilized to interact with the government in the TPA program, which are largely determined by the entrepreneurs’ business size, family backgrounds, and political linkages, and of course generate diverse returns. Accordingly, the Chinese state is also found to be very proactive in adapting its tactics which comprise a combination of carrots and sticks. This allows it to deftly engage with entrepreneurs of different kinds and mobilize their resources to attain the radical goal of poverty eradication. Huang and Xin’s work uses a fresh angle to explain China’s success in eradicating poverty by considering the strategic mutual infiltration of state-society relations, uncovering dynamic patterns of non-governmental participation in state-initiated poverty-reducing projects in China’s context. More generally, targeted poverty alleviation provides an apt case to observe the evolving relationship between government and business under the new leadership, a topic that extends broadly in Chinese political research.
Third, an array of formal institutions has been established by international organizations and national bureaucracies to facilitate poverty reduction endeavors in various parts of the world. The existing literature on China’s TPA program has also focused on state-designed formal institutions and their operations at subnational levels. These include but are not confined to managed campaigns, sent-down work teams, first party secretaries, and paired support networks. However, the swift success of China’s poverty alleviation cannot be adequately explained by rational institutional design and formal institutional arrangements, given the equally important role that informal institutions in multiple forms also play. In Formation of Relational Poverty Governance and Its Impacts, Xu, Xu & Chen [ 55 ] examine how the Chinese government has employed personalized approaches and soft measures, which is identified by the authors as “relational poverty governance”, to implement anti-poverty policies. Unlike networks built on traditional clientelistic ties (which usually lead to distortions of policy implementation), relational governance establishes a new web of “quasi-relative relations” in China’s anti-poverty projects. It is characterized by artificial informal modes like “building parent-like relations by superior cadres”, “signing kinship contracts” with local cadres, and “using pan-kinship relations by village cadres”. As highlighted by the authors, apart from campaign-style bureaucratic mobilization, the Chinese authorities often use combined strategies of emotion, ethics and moral obligations as the “soft weapon of the strong” to incentivize cadres at various levels to realize the goal of poverty reduction. As a result, by embedding personalized linkages into anti-poverty assistance and creating relational interactions, the state can exercise its power more precisely throughout the TPA process and therefore strengthens its authority to penetrate into rural regions. Articulating such a conceptual framework of “relational poverty governance” broadens our understanding of China’s anti-poverty battle in particular, and poverty governance through informal institutions in general.
A third theme pertains to the outcome and political effects of poverty alleviation in China and beyond. Pertinent issues such as the underlying conditions that contribute to the performance of poverty governance, whether and how poverty relief leads to unintended consequences such as corruption, and what will happen if poverty and inequality prevail in modern society, are examined. First, China’s recent campaign against poverty was mainly designed and promoted by the ruling party and the central leadership in Beijing. Top-level design ( dingceng sheji ) has been considered as one of the defining features of the party regime under Xi Jinping [ 46 , 48 ]. Under the unitary system, the Chinese government at various levels and in different localities are held accountable with the common task disseminated from top down. However, it does not mean that all the local governments performed equally well and met the targets at the same pace. How can the variance in the performance of local bureaucracies in accomplishing state anti-poverty tasks be explained? In Power and Poverty in China , Li and Wu [ 35 ] try to explain why some Chinese counties perform better in poverty alleviation (measured by the earlier year of counties being delisted from the poverty list). As such, this work sheds light on the micro-political setting of subnational power structures, which departs from the existing literature that mainly considers the historical, economic or macro-political accounts, by taking the county party secretaries holding a concurrent higher-ranking post as a core explanatory variable. A discrete-time event history analysis drawing on a unique county-level dataset of 832 nationally designated poor counties in China provides empirical evidence for the correlation of leadership concurrency and prominent performance in accomplishing the central task. Related plausible causal mechanisms, as argued by the authors, include the increased bargaining power and privileged political connections engendered by the concurrent upper-level posts, which allow the counties to obtain more assistance and support that are critical to better poverty governance performance. “Power is essential to alleviate poverty”, the authors stress. The findings not only affirm the underlying political logic of regional variance in anti-poverty performance in China, but also chime with the comparative politics literature on how powerful actors create and maintain favoritism in state welfare distribution [ 7 , 25 ], a phenomenon prevailing in different regime types.
Second, poverty relief has often been a political instrument strategically wielded by incumbent administrations to enhance regime legitimacy and consolidate ruling power [ 58 ]. In practice, however, it also results in unintended consequences that could undermine the desirable political effects and even change the course of regime development. One of the undesirable consequences that accompany poverty aid is the increased propensity for corruption [ 17 ], especially under circumstances where transparency and accountability are limited. How, then, can the magnitude and extent of corruption in poverty governance programs be estimated? What are the causal mechanisms that link poverty and corruption? In Does Poverty Relief Breed Corruption, Wang [ 52 ] evaluates the impact of earlier waves of China’s poverty reduction programs on corruption at the subnational level. Leveraging on a unique dataset on 881 low-income counties, Wang’s research uses propensity score weighted regression to address the confounding bias and identifies statistically significant findings on more corruption cases and more convicted officials in counties registered in the national poverty list. In other words, China’s pre-TPA anti-poverty programs (which mainly target counties), while greatly benefitting the poverty-stricken population and local economy, have actually caused more corruption in poor counties. This causal relation remains robust when using different model specifications. It seems that, as documented in many developing countries, China was stuck in the hard-to-escape poverty-corruption trap under the old anti-poverty schemes. Moreover, corrupt misconduct became a major impediment to further poverty reduction efforts in these places. The new targeted poverty alleviation program, which was initiated and enforced after 2014 and primarily focuses on precise poverty identification [ 36 ] and close monitoring [ 57 ], emerged against the backdrop of such a poverty-corruption dilemma in the early 2010s. Wang’s work highlights the risk of unintended political consequences and the importance of anti-corruption institutional design in welfare redistribution process. The lessons of how China, with weak electoral accountability but strong top-down accountability, escaped the poverty-corruption trap can benefit scholarship.
Third, poverty is one of the most acute problems in nearly all countries around the world. Although the aim of this special issue is to examine governance relating to extreme poverty in China and beyond, we take a step further by looking into the political impact of entrenched relative poverty in a global context. Although dramatic progress has been made in global poverty reduction since 2000, the disparity in the distribution of wealth continues to increase. As the Chinese saying goes, “scarcity poses no worry, but uneven distribution does”( bu huangua er huanbujun ). Higher levels of economic inequality could result in various political challenges that assail contemporary society. In Income Inequality and Global Political Polarization, Gu and Wang [ 22 ] investigate whether and how the proliferation of income inequality and rising political polarization in many parts of the world are related to each other. A plausible posited positive linkage between the two variables does not seem counter-intuitive, but there is a relative lack of strong empirical evidence on this interrelation across the globe. Using repeated cross-national data from six waves of the World Values Survey from 1990 up to 2020, this study identifies the potential polarizing effect of income inequality. As the authors illustrated, such a positive and statistically significant association remains very robust to different model specifications. Although not necessarily causal, the results can be viewed as suggestive evidence to the adverse political repercussions of income inequality, which can be further supported by multiple causal mechanisms identified in related qualitative literature. This inquiry attests to the complexity and long-term nature of poverty governance, which should not solely focus on lifting people out of absolute poverty (as China’s targeted poverty alleviation does), but should instead address the more salient problems of relative poverty and distribution inequity. Delays in finding an effective solution to economic inequality are likely to fuel social conflicts and trigger political instability. The political repercussions of income inequality pose a common challenge to regimes of various types all over the world. This also helps us to understand why China has been committed to promoting the goal of “common prosperity” through a grander development plan after its official declaration that extreme poverty had been eradicated by the end of 2020.
Looking Forward
Poverty is essentially a political phenomenon. To enhance poverty governance requires active government interventions and the effective pre-settlement of various political problems. With the prevalence of income inequality, political polarization, armed conflicts, and fragile states, particularly at a time when millions of vulnerable people are considered newly impoverished as a result of the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic, the prominence of politics, institutions and governance in shaping the performance of poverty alleviation cannot be overstated. It is with this goal in mind that the special issue attempts to reformulate the research agenda of poverty governance, bringing the analytical concepts, perspectives and methods of political science into poverty alleviation research, and drawing a clearer connection between politics and poverty governance. The articles in this special issue deepen our understanding of poverty alleviation as a multi-faceted process of using political power, exercising political authority, mobilizing political resources, running political institutions, and gaining political legitimacy. They also collectively highlight the importance and urgency for durable political reforms to be promulgated, both nationally and locally. As political scientists, it is our duty to meaningfully engage in conversation, analysis and reflection on poverty governance. With this special issue, we feel privileged to contribute to this endeavor.
The authors push the intellectual boundaries of the poverty literature forward in at least three ways. First, the disciplinary lens of political science is introduced to enrich the poverty governance literature, placing the focal point on politics and institutions to better understand poverty governance. Second, moving beyond China’s propagandistic discourse and Western neoliberal discourse, the special issue promotes evidence-based empirical research on poverty alleviation in China, and advances political science research of poverty governance in non-electoral regimes with evidence from the Chinese experience. Third, it thematically and methodologically expands the political study of poverty alleviation. We hope that this special issue points readers toward where this scholarship is headed and inspire growing scholarly interest in related topics. Nevertheless, despite the contributions to the literature, this special issue admittedly also grapples with several dilemmas and challenges. Some challenges are theoretical and methodological, while others are related to the research scope, which also pave the way for many more exciting and promising new areas of research in the future.
There are many themes worthy of scholarly attention for future research, including but not limited to: cross-national quantitative research on the politics of poverty governance, comparative research on poverty governance and welfare policies in authoritarian regimes, comparison of international promotion of distinctive anti-poverty models, political attitudes and political agency of the poor, the impact of shock events on poverty governance (e.g. a pandemic, international conflicts), the political influence of poverty governance on specific subgroups (e.g. women, ethnic minorities, the working class), and political strategies to provide universal welfare in the post-poverty era. Methodologically, in addition to descriptive explanations and regression analysis, more causal approaches can be carried out to test theoretical hypotheses by utilizing innovative research designs and cutting-edge estimation strategies. To conclude, this special issue aspires to open up a dialogue with the myriad of issues presented here to stimulate future research on the political science of poverty governance.
1 It is based on the estimate by the World Bank, see https://data.worldbank.org/topic/poverty (accessed November 27, 2021).
2 See https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2020/10/07/covid-19-to-add-as-many-as-150-million-extreme-poor-by-2021 (accessed November 27, 2021).
3 For some notable exceptions, see [ 4 , 38 , 58 ].
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
- 📑 Aspects to Cover in a Poverty Essay
Students who learn economics, politics, and social sciences are often required to write a poverty essay as part of their course. While everyone understands the importance of this topic, it can be hard to decide what to write about. Read this post to find out the aspects that you should cover in your essay on poverty.
🏆 Best Poverty Topics & Free Essay Examples
👍 powerful topics on poverty and inequality, 🎓 simple & easy topics related to poverty, 📌 interesting poverty essay examples, ⭐ strong poverty-related topics, 🥇 unique poverty topics for argumentative essay, ❓ research questions about poverty.
Topics related to poverty and inequality might seem too broad. There are so many facts, factors, and aspects you should take into consideration. However, we all know that narrowing down a topic is one of the crucial steps when working on an outline and thesis statement. You should be specific enough to select the right arguments for your argumentative essay or dissertation. Below, you will find some aspects to include in your poverty essay.
Poverty Statistics
First of all, it would be beneficial to include some background information on the issue. Statistics on poverty in your country or state can help you to paint a picture of the problem. Look for official reports on poverty and socioeconomic welfare, which can be found on government websites. While you are writing this section, consider the following:
- What is the overall level of poverty in your country or state?
- Has the prevalence of poverty changed over time? If yes, how and why?
- Are there any groups or communities where poverty is more prevalent than in the general population? What are they?
Causes of Poverty
If you look at poverty essay titles, the causes of poverty are a popular theme among students. While some people may think that poverty occurs because people are lazy and don’t want to work hard, the problem is much more important than that. Research books and scholarly journal articles on the subject with these questions in mind:
- Why do some groups of people experience poverty more often than others?
- What are the historical causes of poverty in your country?
- How is poverty related to other social issues, such as discrimination, immigration, and crime?
- How do businesses promote or reduce poverty in the community?
Consequences of Poverty
Many poverty essay examples also consider the consequences of poverty for individuals and communities. This theme is particularly important if you study social sciences or politics. Here are some questions that may give you ideas for this section:
- How is the psychological well-being of individuals affected by poverty?
- How is poverty connected to crime and substance abuse?
- How does poverty affect individuals’ access to high-quality medical care and education?
- What is the relationship between poverty and world hunger?
Government Policies
Governments of most countries have policies in place to reduce poverty and help those in need. In your essay, you may address the policies used in your state or country or compare several different governments in terms of their approaches to poverty. Here is what you should think about:
- What are some examples of legislation aimed at reducing poverty?
- Do laws on minimum wage help to prevent and decrease poverty? Why or why not?
- How do governments help people who are poor to achieve higher levels of social welfare?
- Should governments provide financial assistance to those in need? Why or why not?
Solutions to Poverty
Solutions to poverty are among the most popular poverty essay topics, and you will surely find many sample papers and articles on this subject. This is because poverty is a global issue that must be solved to facilitate social development. Considering these questions in your poverty essay conclusion or main body will help you in getting an A:
- What programs or policies proved to be effective in reducing poverty locally?
- Is there a global solution to poverty that would be equally effective in all countries?
- How can society facilitate the reduction of poverty?
- What solutions would you recommend to decrease and prevent poverty?
Covering a few of these aspects in your essay will help you demonstrate the in-depth understanding and analysis required to earn a high mark. Before you start writing, have a look around our website for more essay titles, tips, and interesting topics!
- Poverty Research Proposal To justify this, the recent and most current statistics from the Census Bureau shows that the level and rate of poverty in USA is increasing, with minority ethnic groups being the most disadvantaged.
- Poverty: A Sociological Imagination Perspective I was raised in a nuclear family, where my mum was a housewife, and my father worked in a local hog farm as the overall manager.
- “The Singer Solution to World Poverty” by Peter Singer The article “The Singer Solution to World Poverty” by author Peter Singer attempts to provide a workable solution to the world poverty problem.
- Poverty in the World In this paper, we will be looking at the situation of poverty in the world, its causes and the efforts of the international organizations to manage the same.
- Poverty in Africa These pictures have been published online to show the world the gravity of the poverty situation in the African continent. The pictures represent the suffering of majority of the African people as a result of […]
- The End of Poverty Philippe Diaz’s documentary, The End of Poverty, is a piece that attempts to dissect the causes of the huge economic inequalities that exist between countries in the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
- Poverty Areas and Effects on Juvenile Delinquency The desire to live a better life contributes to the youths engaging in crimes, thus the increase in cases of juvenile delinquencies amid low-income families. The studies indicate that the fear of poverty is the […]
- Poverty and the Environment The human population affects the environment negatively due to poverty resulting to environmental degradation and a cycle of poverty. Poverty and the environment are interlinked as poverty leads to degradation of the environment.
- The Philippines’ Unemployment, Inequality, Poverty However, despite the strong emphasis of the government on income equality and poverty reduction along with the growth of GDP, both poverty and economic and social inequality remain persistent in the Philippines.
- Max Weber’s Thoughts on Poverty Weber has contributed to the exploration of the origins of poverty and the impact of religions on the attitude to it.
- Is Poverty a Choice or a Generational Curse? The assumption that poverty is a choice persists in public attitudes and allows policy-makers to absolve themselves of any responsibility for ensuring the well-being of the lower socioeconomic stratum of society.
- Children Living in Poverty and Education The presence of real subjects like children is a benefit for the future of the nation and a free education option for poor families to learn something new and even use it if their children […]
- Analysis of Theodore Dalrymple’s “What Is Poverty?” With ethical arguments from Burnor, it can be argued that Dalrymple’s statements are shallow and based on his values and not the experience of those he is judging.
- What Causes Poverty in the World One of the major factors that have contributed to poverty in given areas of the world is overpopulation. Environmental degradation in many parts of the world has led to the increase of poverty in the […]
- Relationship Between Crime Rates and Poverty This shows that the strength of the relationship between the crime index and people living below the line of poverty is.427.
- Poverty Effects on Child Development and Schooling To help children from low-income families cope with poverty, interventions touching in the child’s development and educational outcomes are essential. Those programs campaign against the effects of poverty among children by providing basic nutritional, academic, […]
- Community Work: Helping People in Poverty The first project would be water project since you find that in most villages water is a problem, hence $100 would go to establishing this project and it’s out of these water then the women […]
- The Problem of Poverty in Bob Marley’s “No Woman, No Cry” To see the situation from the perspective of its social significance, it is necessary to refer to Mills’ concept of sociological imagination and to the division of problems and issues into personal and social ones.
- Poverty Alleviation and Sustainable Development The research focuses on the causes of poverty and the benefits of poverty alleviation in achieving sustainable development. One of the causes of poverty is discrimination and social inequality.
- The Singer Solution to World Poverty: Arguments Against The article compares the lives of people in the developed world represented by America and that of developing world represented by Brazil; It is about a school teacher who sells a young boy for adoption […]
- Cause and Effect of Poverty For example, the disparities in income and wealth are considered as a sign of poverty since the state is related to issues of scarcity and allocation of resources and influence.
- Poverty Simulation Reflection and Its Influence on Life Something that stood out to me during the process is probably the tremendous emotional and psychological impact of poverty on a person’s wellbeing.
- Social Issues of Families in Poverty With the tightened budget, parents of the families living in poverty struggle to make ends meet, and in the course of their struggles, they experience many stresses and depressions.
- The Myth of the Culture of Poverty Unfortunately, rather all of the stereotypes regarding poor people are widespread in many societies and this has served to further increase the problem of generational poverty. Poor people are regarded to be in the state […]
- Poverty Through a Sociological Lens Poverty-stricken areas, such as slums, rural villages, and places hit by disasters, lack the required economic activities to improve the employment and wealth status of the people.
- The Connection Between Poverty and Mental Health Problems The daily struggle to earn a daily bread takes a toll on an individual mental health and contributes to mental health problem.
- Social Issues; Crime and Poverty in Camden This has threatened the social security and peaceful coexistence of the people in the community. The larger the differences between the poor and the rich, the high are the chances of crime.
- Environmental Degradation and Poverty It is however important to understand the causes of the environmental degradation and the ways to reduce them, which will promote the improvement of the environmental quality.
- Poverty, Government and Unequal Distribution of Wealth in Philippines The author of the book Poverty And The Critical Security Agenda, Eadie, added: Quantitative analyses of poverty have become more sophisticated over the years to be sure, yet remain problematic and in certain ways rooted […]
- Health, Poverty, and Social Equity: The Global Response to the Ebola Outbreak Canada and Australia, as well as several countries in the Middle East and Africa, were the most active proponents of this ban, halting the movements for both people and goods from states affected by the […]
- Poverty in Bambara’s The Lesson and Danticat’s A Wall of Fire Rising It is important to note the fact that culture-based poverty due to discrimination of the past or political ineffectiveness of the nation can have a profound ramification in the lives of its victims.
- Wordsworth’s Vision of Childhood in His Poems “We Are Seven” and “Alice Fell or Poverty” Specifically, the joint publication he released in 1798 known as “Lyrical Ballads” are considered the most important publications in the rise of the Romantic literature in the UK and Europe.
- Poverty in India and China India’s slow rate of poverty reduction compared to China is due to the differences in their approach to the economy. Improving the living conditions and general well being of the people is not only the […]
- Consumerism: Affecting Families Living in Poverty in the United States Hence, leading to the arising of consumerism protection acts and policies designed to protect consumers from dishonest sellers and producers, which indicates the high degree of consumer’s ignorance, and hence failure to make decisions of […]
- Poverty in Rural and Urban Areas My main focus is on articles explaining the sources of poverty in rural and urban areas and the key difference between the two.
- Reflective Analysis of Poverty It can be further classified into absolute poverty where the affected do not have the capability to make ends meet, and relative poverty which refer to the circumstances under which the afflicted do not have […]
- Global Poverty: The Ethical Dilemma Unfortunately, a significant obstacle to such global reforms is that many economic systems are based on the concept of inequality and exploitation.
- Is Globalization Reducing Poverty and Inequality? & How to Judge Globalism The article Is Globalization Reducing Poverty and Inequality by Robert Hunter Wade explores the phenomenon of globalization and its influence on the poverty and inequality ratios all over the world.
- Analysis of a Social Problem: Poverty Furthermore, the World Bank predicts that both the number of people and the percentage of the population living in extreme poverty will increase in 2020 and 2021 due to the coronavirus outbreak.
- Poverty and Diseases A usual line of reasoning would be that low income is the main cause of health-related problems among vulnerable individuals. Such results that the relationship between mental health and poverty is, in fact, straightforward.
- Marginalization and Poverty of Rural Women The women are left to take care of the economic welfare of the households. I will also attempt to propose a raft of recommendations to alleviate poverty and reduce marginalization of women in the rural […]
- Poverty and Global Food Crisis: Food and Agriculture Model Her innovative approach to the issue was to measure food shortages in calories as opposed to the traditional method of measuring in pounds and stones.
- Poverty in Orwell’s “Down and Out in Paris and London” The fact that the structure of society is discussed is especially interesting, and it is suggested that opinions of people that live in poverty are not acknowledged most of the time.
- Poverty in the Bronx: Negative Effects of Poverty South Bronx is strictly the southwestern part of the borough of Bronx and Bronx is the only borough in New York city in the mainland.
- Poverty in Urban Areas The main reason for escalation of the problem of poverty is urban areas is because the intricate problems of urban poverty are considered too small to attract big policies.
- Poverty and Homelessness as a Global Social Problem What makes the task of defining poverty particularly difficult is the discrepancy in the distribution of social capital and, therefore, the resulting differences in the understanding of what constitutes poverty, particularly, where the line should […]
- “The Hidden Reason for Poverty…” by Haugen It is also noteworthy that some groups of people are specifically vulnerable and join the arrays of those living in poverty.
- Dependency Theory and “The End of Poverty?” It is also reflected in the film “The End of Poverty?” narrating the circumstances of poor countries and their precondition. It started at the end of the fifteenth century and marked the beginning of the […]
- Tourism Contribution to Poverty Reduction Managers usually make targeting errors such as poor delivery of tourism benefits to the poor and accruing tourism benefit to the rich in the society.
- “Life on a Shoestring – American Kids Living in Poverty” by Claycomb Life on a Shoestring – American Kids Living in Poverty highlights the widening disparity between the poor and the wealthy in America and how the economic systems are set up to benefit the rich and […]
- Poverty: $2.00 a Day in America When conversations about the poor occur in the city of Washington, they usually discuss the struggles of the working poor, forgetting about the issues that the non-working poor face day by day.
- “Facing Poverty With a Rich Girl’s Habits” by Suki Kim Finally, revealing the problems of adapting to a new social status, the story turns remarkably complex, which also lends it a certain charm.
- Concept of Poverty The main difference between this definition and other definitions of poverty highlighted in this paper is the broad understanding of the concept.
- Poverty as Capability Deprivation In this paper, the importance of social justice manifests through the understanding of social deprivation, as opposed to the understanding of income levels in the achievement of social justice.
- Poverty in Brazil The primary aim of the exploration was to relate and construe the experimental findings arising from the application of the FGT poverty standards reformulation to Brazilian domestic examination data.
- How Poverty Contributes to Poor Heath The results show that poverty is the main cause of poor health. The study was purposed to assess the effect of poverty in determining the health status of households.
- Global Poverty Project: A Beacon of Hope in the Fight Against Extreme Poverty The organization works with partners worldwide to increase awareness and understanding of global poverty and inspire people to take action to end it.
- The Causes of an Increase in Poverty in Atlanta, Georgia The key causes of the high poverty rise in the city include housing policies and instabilities, the lack of transit services and public transportation infrastructure in suburban areas, and childhood poverty.
- Thistle Farms: Help for Women Who Are Affected by Poverty As I said in the beginning, millions of women need help and assistance from the community to overcome poverty and heal emotional wounds caused by abuse. You can purchase a variety of its home and […]
- Median Household Incomes and Poverty Levels The patterns of poverty in the Denver urban area show that rates are higher in the inner suburb and the core city and lower in the outer suburb.
- Poverty: The American Challenge One of the main problems in the world is the problem of poverty, which means the inability to provide the simplest and most affordable living conditions for most people in a given country.
- The Poverty Issue From a Sociological Perspective The core of the perspective is the idea that poverty is a system in which multiple elements are intertwined and create outcomes linked to financial deficits.
- Saving the Planet by Solving Poverty The data is there to make the necessary links, which are needed when it comes to the economic variations and inadequate environmental impacts of climate change can be distinguished on a worldwide scale.
- Anti-Poverty Programs From the Federal Government The programs provide financial assistance to low-income individuals and families to cover basic needs like housing and food. The anti-poverty programs that have been most effective in reducing poverty rates in the United States are […]
- Rural Development, Economic Inequality and Poverty The percentage of the rural population is lower for developed countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom. Thus, the objective of the proposal is to determine how the inhabitants of the country in […]
- Global Poverty: Ways of Combating For example, one of such initiatives is social assistance and social protection programs, which ensure the safety and creation of various labor programs that will help increase the number of the working population.
- Poverty: Aspects of Needs Assessment The target neighborhood and population for the following analysis are women of reproductive age, defined as 15 to 49 years, in Elmhurst and Corona, Queens. 2, and the percentage of births to women aged over […]
- What Is Poverty in the United States? Estimates of the amount of income required to meet necessities serve as the foundation for both the official and supplemental poverty measurements.
- The Caribbean Culture: Energy Security and Poverty Issues Globally, Latin American and the Caribbean also has the most expensive energy products and services because of fuel deprivation in the Caribbean and the Pacific regions.
- Poverty: The Main Causes and Factors Because of the constant process of societal development, the concept of poverty changes rapidly, adapting to the new standards of modern human life.
- How to Overcome Poverty and Discrimination As such, to give a chance to the “defeated” children and save their lives, as Alexie puts it, society itself must change the rules so that everyone can have access to this ticket to success. […]
- Poverty and Homelessness in American Society It is connected with social segregation, stigmatization, and the inability of the person to improve their conditions of life. The problem of affordable housing and poverty among older adults is another problem that leads to […]
- Private Sector’s Role in Poverty Alleviation in Asia The ambition of Asia to become the fastest-growing economic region worldwide has led to a rapid rise of enterprises in the private sector.
- Connection of Poverty and Education The economy of the United States has been improving due to the efforts that have been made to ensure that poverty will not prevent individuals and families from having access to decent education.
- The Opportunity for All Program: Poverty Reduction The limiting factors of the program may be the actions of the population itself, which will not participate in the employment program because of the realized benefits.
- Early Childhood Financial Support and Poverty The mentioned problem is a direct example of such a correlation: the general poverty level and the well-being of adults are connected with the early children’s material support.
- Discussion: Poverty and Healthcare One of the research questions necessary to evaluate this issue is “How do ethical theories apply to the issue?” Another critical research question worth exploring is “Which cultural values and norms influence the problem?” These […]
- Explosive Growth of Poverty in America The three richest Americans now own 250 billion USD, approximately the same amount of combined wealth as the bottom 50 percent of the country. Wealth inequality is a disturbing issue that needs to be at […]
- Global Poverty: Famine, Affluence, and Morality In the article Famine, Affluence, and Morality, Michael Slote contends that rich people have a moral obligation to contribute more to charities.
- The Poverty and Education Quality Relationship Although the number of people living under the poverty threshold has decreased in the last 30 years, more than 800,000,000 people still have to live with insufficient money and a lack of food, water, and […]
- The Problems of Poverty and Hunger Subsequently, the cause in this case serves as a path to a solution – more social programs are needed, and wealthy citizens should be encouraged to become beneficiaries for the hungry.
- Decreasing Poverty With College Enrollment Program In order to achieve that, it is necessary, first and foremost, to increase the high school students’ awareness of the financial aid programs, possibilities of dual enrollment, and the overall reality of higher education.
- Reducing Poverty in the North Miami Beach Community The proposed intervention program will focus on the students in the last semester of the 9th and 10th grades and the first semester of the 11th and 12th grades attending the client schools.
- Food Banks Board Members and Cycle of Poverty What this suggests is that a large portion of the leadership within these collectives aim to provide assistance and food but not to challenge the current system that fosters the related issues of poverty, unemployment, […]
- Poverty as a Social Problem in Burundi The rationale for studying poverty as a social problem in Burundi is that it will help to combat poverty through the advocacy plan at the end of this paper.
- Poverty: Subsidizing Programs Subsidizing programs are considered welfare and net initiatives that the government takes to aid low-income families and individuals affected by poverty.
- The Problem of Poverty in Chad Thus, the study of the causes of poverty in the Republic of Chad will help to form a complete understanding of the problem under study and find the most effective ways to solve it.
- “Poverty, Toxic Stress, and Education…” Study by Kelly & Li Kelly and Li are concerned with the lack of research about poverty and toxic stress affecting the neurodevelopment of preterm children.
- Poverty in “A Modest Proposal” by Swift The high number of children born to poor families presents significant problems for a country.”A Modest Proposal” is a satirical essay by Jonathan Swift that proposes a solution to the challenge facing the kingdom.
- Life Below the Poverty Line in the US The major problem with poverty in the US is that the number of people living below the poverty threshold is gradually increasing despite the economic growth of the country. SNAP is not considered to be […]
- The Relationship Between Single-Parent Households and Poverty The given literature review will primarily focus on the theoretical and empirical aspects of the relationship between single-parent households and poverty, as well as the implications of the latter on mental health issues, such as […]
- Aspects of Social Work and Poverty In terms of work principle, both the poor working and the welfare poor have it to varying degrees, but it does not help them much because the only employment available is low paying and leads […]
- Poverty and Its Effect on Adult Health Poverty in the UK is currently above the world average, as more than 18% of the population lives in poverty. In 2020, 7% of the UK population lived in extreme poverty and 11% lived in […]
- Child Poverty in the United States The causes of child poverty in the United States cannot be separated from the grounds of adult poverty. Thus, it is essential to take care of the well-being of children living in poverty.
- Poverty in New York City, and Its Reasons The poverty rate for seniors in New York is twice the poverty rate in the United States. New York City’s blacks and Hispanics have a much higher poverty rate than whites and Asians in the […]
- Juvenile Violent Crime and Children Below Poverty The effect of this trend is that the number of children below poverty will continue to be subjected to the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
- Poverty and Homelessness as Social Problem The qualifications will include a recommendation from the community to ensure that the person is open to help and willing to be involved in the neighborhood of Non-Return.
- Discussion of the Problem of the Poverty To help prevent homelessness for the woman in question and her children, I think it would be essential to provide mental support for her not to turn to alcohol and drugs as a coping mechanism.
- Poverty Effects and How They Are Handled Quality jobs will provide income to the younger people and women in the community. The focus on developing and facilitating small and medium-sized enterprises is a great strategy but more needs to be done in […]
- Feminization of Poverty and Governments’ Role in Solving the Problem However, women form the greatest percentage of the poor, and the problem continues to spread. Furthermore, the public supports available are inaccessible and inadequate to cater for women’s needs.
- Free-Trade Policies and Poverty Level in Bangladesh The purpose of this paper is to examine the way in which the end of the quota system and introduction of a free-trade system for the garment industry in Bangladesh has impacted on poverty in […]
- Poverty and Risks Associated With Poverty Adolescents that are at risk of being malnourished can be consulted about the existing programs that provide free food and meals to families in poverty.
- Poverty and Inequality Reduction Strategies Thus, comprehending the causes of poverty and inequalities, understanding the role of globalization, and learning various theoretical arguments can lead to the establishment of appropriate policy recommendations.
- International Aid – Poverty Inc This film, the research on the impact of aid on the states receiving it, and the economic outcomes of such actions suggest that aid is a part of the problem and not a solution to […]
- Poverty Effects on American Children and Adolescents The extent to which poor financial status influences the wellbeing of the young children and adolescents is alarming and needs immediate response from the community.
- Progress and Poverty Book by Henry George George wrote the book following his recognition that poverty is the central puzzle of the 20th century. Thus, George’s allegation is inconsistent with nature because the number of living organisms can increase to the extent […]
- Vicious Circle of Poverty in Brazil The vicious circle of poverty is “a circular constellation of forces that tend to act and react on each other in such a way that the country in poverty maintains its poor state”.
- Global Education as the Key Tool for Addressing the Third World Poverty Issue Global education leads to improvements in the state economy and finances. Global education helps resolve the unemployment problem.
- Poverty, Partner Abuse, and Women’s Mental Health In general, the study aimed at investigating the interaction between poverty and the severity of abuse in women. The research question being studied in this article is how income intersects with partner violence and impacts […]
- America’s Shame: How Can Education Eradicate Poverty The primary focus of the article was global poverty, the flaws in the educational system, as well as the U.S.government’s role in resolving the problem.
- Global Poverty and Ways to Overcome It These are some of the strategies, the subsequent application of which would significantly reduce the level of poverty around the world.
- Social Work at Acacia Network: Poverty and Inequality Around the 1980s, the number of older adults was significantly increasing in society; the local government of New York established a home for the aged and was named Acacia Network. The supporting staff may bond […]
- Poverty and Sex Trafficking: Qualitative Systematic Review The proposed research question is to learn how the phenomenon of poverty is connected to sex trafficking. To investigate the relationship between the phenomenon of poverty and sex trafficking.
- Political Economy: Relationship Between Poverty, Inequality, and Nationalism The prevalence of nationalism leads to changes in the education system, as the government tries to justify the superiority of the country by altering the curriculum.
- End of Extreme Poverty Importantly, the ability to remain the owners of a substantial amount of accumulated wealth is the primary motivation for such individuals.
- Poverty and Inequality in the US Despite the progress of civilization and the establishment of democratic values, in the modern United States, such problems as poverty and inequality persist, which is a significant social gap.
- The Problem of Poverty in the United States The problem of increasing poverty is one of the major political issues in the United States, which became especially agile after the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic due to the difficult economic situation all over […]
- Poverty and Unemployment Due to Increased Taxation The government on its side defended the move while trying to justify the new measures’ benefits, a move that would still not benefit the country.
- Poverty as a Global Social Problem For example, the research shows that Kibera is the largest slum in the country, and this is where many people move to settle after losing hope of getting employed in towns.
- Researching the Problem of Poverty However, the rich people and the rich countries reduce poverty to some extent by providing jobs and markets to the poor, but the help is too little compared to the benefits they get thus accelerating […]
- Poverty, Social Class, and Intersectionality I prefer the structural approach to the issue as I believe the created structures are responsible for the existence of diverse types of oppression.
- Wealth and Poverty: The Christian Teaching on Wealth and Poverty To illustrate the gap between the world’s richest and the world’s poorest, a recent UN publication reported that the wealth of the three richest persons in the world is greater than the combined wealth of […]
- Guns Do Not Kill, Poverty Does It is widely accepted that stricter gun control policies are instrumental in alleviating the problem, as they are supposed to reduce the rate of firearm-related deaths, limiting gun access to individuals at-risk of participating in […]
- Poverty’s Effects on Delinquency The economic status of people determines their social class and the manner in which they get their basic needs. Seeing these things and the kind of life rich people lead motivates the poor to commit […]
- The Criminalization of Poverty in Canada In this regard, with a special focus on Canada, the objective of this essay is to investigate how public policy has transformed alongside the public perception of social welfare reform.
- The Issue of Vicious Circle of Poverty in Brazil The persistence of poverty, regardless of the many shocks that every state receives in the normal course of its survival, raises the feeling that underdevelopment is a condition of equilibrium and that there are pressures […]
- Community Health Needs: Poverty Generally, the higher the level of poverty, the worse the diet, and hence the higher the chances of developing diabetes. Consequently, a considerable disparity in the prevalence of diabetes occurs between communities with high levels […]
- “Poverty, Race, and the Contexts of Achievement” by Maryah Stella Fram et al. The article “Poverty, race, and the contexts of achievement: examining the educational experience of children in the U.S. Multilevel models were then applied in the analyses of how children varied in their reading scores depending […]
- Couple Aims to Fight Poverty, One Village at a Time People are not afraid to risk their own financial savings, their investments, and even life’s safety to help the chosen community and improve the conditions this community has to live under.
- Microeconomic Perspective on Poverty Evolution in Pakistan The periodic spike in poverty levels, notwithstanding economic growth, implies incongruous policy functionality in relation to drivers of poverty and the subsequent failure to improve the indicators.
- The Impact of Poverty on Children Under the Age of 11 The strengths of the Marxist views on poverty are in the structural approach to the problem. Overall, the Marxist theory offers a radical solution to the problem of child poverty.
- Poverty Policy Recommendations Different leaders have considered several policies and initiatives in the past to tackle the problem of poverty and empower more people to lead better lives.
- Poverty Reduction and Natural Assets Therefore, the most efficient way to increase the efficiency of agriculture and reduce its environmental impacts is ensuring the overall economic growth in the relevant region.
- Corporate Social Responsibility & Poverty Alleviation Researchers state that “preventing and managing the negative impacts of the core business on the poor” are essential indicators of the social responsibility of the company.
- Children in Poverty in Kampong Ayer, Brunei Part of the reason is likely malnutrition that results from the eating or consumption patterns of the families and also dependency on the children to help out with the family or house chores.
- Health, Poverty, and Social Equity: Indigenous Peoples of Canada Another problem that much of northern Canada’s Indigenous Peoples face is the availability of healthcare services and people’s inability to access medical help.
- The Problem of Childhood Poverty Unequal income distribution, adult poverty, government policies that exclude children and premature pregnancy are some of the items from the long list of childhood poverty causes. Before discussing the causes and effects of childhood poverty, […]
- Individualistic Concepts and Structural Views on Poverty in American Society The concepts presented in the book Poverty and power help to better understand the content of the article and the reasons for such a different attitude of people to the same problem.
- Poor Kids: The Impact of Poverty on Youth Nevertheless, the environment of constant limitations shapes the minds of children, their dreams and the paths they pursue in life, and, most importantly, what they make of themselves.
- Poverty: Causes and Effects on the Population and Country Thesis: There are a great number of factors and issues that lead a certain part of the population to live in poverty and the input that such great numbers of people could provide, would be […]
- The Internet and Poverty in Society The information that can be found on the web is a very useful resource but at the same time it is important to consider several things with the treatment and examination of the presented information.
- Poverty in Africa: Impact of the Economy Growth Rate Thus, a conclusion can be made that economic growth in Africa will result in the social stability of the local population.
- Poverty and Disrespect in “Coming of Age in Mississippi” by Anne Moody Life was not fair to a little Anne the chapters about her childhood are alike to a chain of unfortunate events that happened to her and her relatives.
- Vietnam’s Economic Growth and Poverty & Inequality A significant part of the population was active in employment, and this means that the numerous income-generating activities improved the economy of this country.
- Poverty and Disasters in the United States Focusing on the precaution measures and the drilling techniques that will help survive in case of a natural disaster is one of the most common tools for securing the population.
- Intro to Sociology: Poverty It is challenging to pinpoint the actual and not mythological reasons for the presence of poverty in America. The former can be summed up as a “culture of poverty”, which suggests that the poor see […]
- The Notion of “Poverty” Is a Key Word of a Modern Society As far as the countries of the Third World are deprived of these possibilities, their development is hampered and the problem of poverty has become a chronic disease of the society.
- The Problem of Poverty in Africa The major aim of the study is to identify the causes of poverty and propose best strategies that can help Africans come out of poverty.
- Poverty Sustainability in Sub-Saharan Countries: The Role of NGOs The position of research and statistics in undertaking social-counting work is not queried. It is after the research method is used in other tribulations of the charity that gaps emerge between management and research.
- “The End of Poverty” by Phillipe Diaz In the film End of Poverty, the filmmaker tries to unravel the mystery behind poverty in the world. The film is arranged in such a way that the author has persuasively argued his case that […]
- The Effects of Poverty Within Criminal Justice The approach used in this study is deductive since the reasoning in the study proceeds from the general principle regarding the fact that poverty has a role to play in the administering of fairness in […]
- The Poverty Rates in the USA Poverty in the U. Officially the rate of poverty was at14.3%.
- Poverty in America: A Paradox Many people especially the young people living in other countries and more so in developed countries wish to immigrate to America instead of working hard to achieve the dream of better opportunities.
- Values and Ethics: Poverty in Canada The case study1 has indicated for instance, that the number of people living in poverty in 2003 is at 4. A group of individuals would therefore be granted the mandate to lead the others in […]
- War and Poverty Connection in Developing Countries The scholars claim that conflict and war in most nations have been found to exacerbate the rate of poverty in the affected nations.
- Poverty in United States. Facts and Causes Schwartz carried out a research which showed that in the United States, about 13-17|% of the individuals live below the federal poverty line at any one single time and poverty is one of the main […]
- Cultures and Prejudice: Poverty Factors For instance, if the two cultures had in the past interacted in a negative way, the poor culture directs all the blame to the well up culture.
- Poverty and Criminal Behavoiur Relation The level of accuracy that the data collected holds cannot be 100%; there is a level of error that affects the reliability of the data collected.
- Urban Relationship Between Poverty and Crime The areas with high poverty level in the US urban areas have the highest cases of crime but this is inadequate to justify that poverty is the cause of crime.
- The End of Poverty Possibility He presents the difficulty as in inability of each poor country to get to the base rung of the ranking of economic progress if the rank is achieved; a country can drag itself up towards […]
- Poverty, Suburban Public School Violence and Solution
- Social and Economic Policy Program: Globalization, Growth, and Poverty
- Is Poverty From Developing Countries Imagined?
- How Gender and Race Structure Poverty and Inequality Connected?
- Poverty by Anarchism and Marxism Approaches
- Colonial Economy of America: Poverty, Slavery and Rich Plantations
- Poverty as a Great Social Problem and Its Causes
- Environmental Deterioration and Poverty in Kenya
- Management Issues: The Poverty Business
- Pockets of Poverty Mar the Great Promise of Canada
- Poverty. “How the Other Half Lives” by Jacob Riis
- The Underclass Poverty and Associated Social Problems
- Child Poverty in Toronto, Ontario
- Children’s Brain Function Affected by Poverty
- Poverty Issue in America Review
- Microeconomics. Poverty in America
- Poverty and Inequality in Modern World
- Poverty and Its Effects on Females
- Poverty and Its Effects on Women
- Poverty of America: Economic Assumptions
- Poverty as a General Problem
- Feminization of Poverty – A Grave Social Concern
- Global Poverty Dimensions and Alleviating Approaches
- Poverty Level in any Country
- Theories of Fertility. Economics Aspect and Poverty.
- The Cultural Construction of Poverty
- Poverty in the US: Causes and Measures
- Poverty Rates Issue in Alberta Analysis
- “Old Age Poverty” Study by Kwan & Walsh
- Phenomena of Poverty Review
- Development Economics: Poverty Traps in Africa
- Healthcare Development. Poverty in the 1800s
- Social Problem of Poverty in the United States
- Poverty and Hip-Hop: Notorious B.I.G.’s “Juicy”
- Globalization Issues and Impact on Poverty and Free Trade
- Anthropology: Culture of Poverty
- Poverty, Stratification and Gender Discrimination
- Teen Pregnancy Can Lead to Suicide and Poverty
- Poverty Around the World
- Poverty in Los Angeles
- “Rethinking the Sociological Measurement of Poverty” by Brady
- Poverty in the US: Essentials of Sociology
- Econometrics: Poverty, Unemployment, Household Income
- Religious Quotes on Poverty and Their Interpretations
- Poverty and Inequality in “Rich and Poor” by Peter Singer
- The Relation Between Poverty and Justice
- Canada and the Imposition of Poverty
- Poverty and Politics in “The Bottom Billion” by Collier
- The Impact of Poverty in African American Communities
- “Poverty and Joy: The Franciscan Tradition” by Short
- International Financial Institutions’ Poverty Reduction Strategy
- Social Study: Mamelodi Residents Living in Poverty
- Video Volunteers’ Interventions Against Poverty
- Poverty in American Single-Parent Families
- Single-Mother Poverty and Policies in the United States
- Poverty and Its Aspects in Historical Documents
- Economic Development: Prosperity and Poverty
- Poverty and Its Relative Definitions
- Poverty in America: An Ethical Dilemma
- Child Poverty and Academic Achievement Association
- Poverty as a Factor of Terrorist Recruitment
- Poverty Solution as a Political Issue in Australia
- Poverty: An Echo of Capitalism
- Poverty, Inequality and Social Policy Understanding
- Breastfeeding Impact on Canadian Poverty Gaps
- Urban and Suburban Poverty in the United States
- Inequality and Poverty Relationship
- Poverty and Child Health in the US and the UK
- Poverty Impact on Life Perception
- Energy Poverty Elimination in Developing Countries
- Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity and Poverty
- Vietnamese Poverty and Productivity Increase
- Global Health Governance and Poverty
- Poverty Rates Among Whites and Blacks Americans
- Culture of Poverty in the “Park Avenue” Documentary
- Poverty in the US
- Poor Economics and Global Poverty
- Poverty as a Cause of the Sudanese Civil War
- “Halving Global Poverty” by Besley and Burges
- Do Poverty Traps Exist? Assessing the Evidence
- Poverty Reasons in Ancient Times and Nowadays
- American War on Poverty Throughout US History
- Poverty and Challenges in Finding Solutions
- Children and Poverty in “Born into Brothels” Documentary
- Poverty and Social Welfare in the United States
- Poverty in “A Theology of Liberation” by Gutierrez
- Poverty Reduction Among American Single Mothers
- The Relationship Between Poverty and Education
- Divorce Outcomes: Poverty and Instability
- African Poverty at the Millennium: Causes and Challenges
- Poverty Effect on Children
- Poverty and Education: School Funding Reinforces Inequality
- Global Poverty and the Endeavors of Addressing It
- Global Poverty Reduction: Economic Policy Recommendation
- Global Conflict and Poverty Crisis
- Poverty in the Novel “Snow” by Orhan Pamuk
- The Rise of Poverty in the US
- Profit From Organizing Tours to Poverty Areas
- Detroit Poverty and “Focus Hope” Organization
- Poverty Controversy in the USA
- Poverty as the Deprivation of Capabilities
- Suburbanisation of Poverty in the USA
- The Solution to World Poverty by Peter Singer
- The Poverty Across the US Culture
- How Racial Segregation Contributes to Minority’s Poverty?
- Catholic Dealing With Poverty and Homelessness
- Human Capital and Poverty in Scottsdale
- Global Poverty Studies and Their Importance
- The World Bank and the Poverty of Reform
- Challenges of Social Integration: Poverty
- Globalization and the Issue of Poverty: Making the World a Better Place
- The Economic Effect of Issuing Food Stamps to Those in Poverty
- Business and Pollution Inequality in Poor States
- What Should You Do? Poverty Issue
- Causes of Poverty Traps in an Economy, Its Results and Ways of Avoiding Them
- Millennium Development Goals – Energy and Poverty Solutions
- Sociological Indicators of Energy Poverty
- Energy and Poverty Solutions – Non-Traditional Cookstoves
- Energy and Poverty Solutions – World Bank
- How do Migration and Urbanization Bring About Urban Poverty in Developing Countries?
- Poverty and Domestic Violence
- The Rise of Extremist Groups, Disparity and Poverty
- Measuring Poverty and Social Exclusion in Australia
- Does Poverty Lead to Terrorism?
- “Urban and Rural Estimates of Poverty: Recent Advances in Spatial Microsimulation in Australia” by Tanton, R, Harding, A, and McNamara, J
- Importance of Foreign Aid in Poverty Reducing
- Hispanic Childhood Poverty in the United States
- How Poverty Affects Children Development?
- Why Is Poverty Important in Contemporary Security Studies?
- Millennium Development Goals in Kenya, Ivory Coast, Haiti, and Chad
- Development Is No Longer the Solution to Poverty
- Issues Underlying Global Poverty and Provision of Aid
- Films Comparison: “The Fields” by Roland Joffe and “Hotel Rwanda” by Terry George
- Poverty Prevalence in the United States
- Terrorism, Poverty and Financial Instability
- Global Poverty and Education
- Critical Analyses of the Climate of Fear Report From Southern Poverty Law Center
- How World Vision International Contributes to Poverty Reduction
- Global Poverty, Social Poverty and Education
- Global Poverty, Social Policy, and Education
- Poverty Reduction in Africa, Central America and Asia
- Does Parental Involvement and Poverty Affect Children’s Education and Their Overall Performance?
- African Poverty: To Aid, or Not to Aid
- Poverty Fighting in Saudi Arabia and in USA
- Technological Development in Trade and Its Impacts on Poverty
- Poverty and Development Into the 21st Century
- Social Dynamics: The Southern Poverty Law Centre
- Property, Urban Poverty and Spatial Marginalization
- Rural Poverty in Indonesia
- Is Poverty of Poor Countries in Anyway Due to Wealth of the Rich?
- Poverty and Gender Violence in Congo
- Correlation Between Poverty and Obesity
- Fight Poverty, Fight Illiteracy in Mississippi Initiative
- Civil War and Poverty: “The Bottom Billion” by Paul Collier
- Analytical Research: Poverty in Thailand: Peculiarities and Perspectives
- Poverty Indicators in Developing Countries
- Poverty, Homelessness and Discrimination in Australia: The Case of the Aboriginal
- Social Business Scope in Alleviating Poverty
- Africa’s Poverty: The Influence of Western States
- Susceptibility of Women and Aboriginal People to Poverty in Canada
- MDG Poverty Goals May Be Achieved, but Child Mortality Is Not Improving
- We Can Stop Poverty in Ghana Today
- Third World Countries and the Barriers Stopping Them to Escape Poverty
- Microcredit: A Tool for Poverty Alleviation
- Impacts of Global Poverty Resistance
- Reducing Poverty: Unilever and Oxfam
- Poverty in the United States
- The Mothers Who Are Not Single: Striving to Avoid Poverty in Single-Parent Families
- Effect of Poverty on Children Cognitive and Learning Ability
- Sweatshops and Third World Poverty
- War on Poverty: Poverty Problem in US
- Freedom from Poverty as a Human Right and the UN Declaration of Human Rights
- War on Poverty in US
- The Causes of Poverty Concentration in the Modern World
- Poverty in Saudi Arabia
- Poverty as a Peculiarity of the Economical Development
- Capitalism and Poverty
- The Problems of Poverty in the Modern World
- Poverty Among Women and Aboriginals
- On (Not) Getting by in America: Economic Order and Poverty in the U.S.
- The Singer Solution to World Poverty
- Poverty and Inequality in Jacksonian America
- Poverty in America Rural and Urban Difference (Education)
- What Is the Relationship Between Race, Poverty and Prison?
- Poverty and Its Effects on Childhood Education
- Poverty in Russia During the Late Nineteenth Century
- Banker to the Poor: Micro-Lending and the Battle Against World Poverty: Advantages of Microcredit
- Social Welfare Policy That Facilitates Reduction of Poverty and Inequality in the US
- Immigrant Status and Poverty: How Are They Linked?
- Effects of Poverty on Immigrant Children
- The Problem of Immigrants Poverty in the US
- Why Poverty Rates are Higher Among Single Black Mothers
- Poverty and Its Impact on Global Health: Research Methodologies
- Poverty Concerns in Today’s Society
- Literature Study on the Modern Poverty Concerns
- Poverty and Wealth in “The Lesson” by Toni Cade Bambara
- Peter Singer on Resolving the World Poverty
- Aspects of Global Poverty
- Concepts of Prenatal Drug Exposure vs. Poverty on Infants
- UN Summit in New York: Ending Global Poverty
- Why Has Poverty Increased in Zimbabwe?
- Should Private Donations Help Eliminate Child Poverty?
- Why Was Poverty Re-Discovered in Britain in the Late 1950s and Early 1960?
- Why Does Child Labour Persist With Declining Poverty?
- Why Are Child Poverty Rates Higher in Britain Than in Germany?
- What Are the Principles and Practices for Measuring Child Poverty in Rich Countries?
- Why Did Poverty Drop for the Elderly?
- What Is the Relationship Between Income Distribution and Poverty Reduction in the UK?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Poverty in Latin America?
- Should Poverty Researchers Worry About Inequality?
- What Helps Households With Children in Leaving Poverty?
- What Is the Connection Between Poverty and Crime?
- Why Have Some Indian States Done Better Than Others at Reducing Rural Poverty?
- What Is the Relationship Between Lack of Education and Poverty?
- Why Are Child Poverty Rates So Persistently High in Spain?
- Trade Liberalisation and Poverty: What Are the Links?
- What Are Academic Programs Available for Youth in Poverty?
- What Are the Main Factors Contributing to the Rise in Poverty in Canada?
- Single-Mother Poverty: How Much Do Educational Differences in Single Motherhood Matter?
- What Are the Causes and Effects of Poverty in the United?
- Why Are Some Countries Poor?
- What Is the Link Between Globalization and Poverty?
- What Are the Factors That Influence Poverty Sociology?
- What Causes Poverty Within the United States Economy?
- What Is the Relationship Between Poverty and Obesity?
- Why Were Poverty Rates So High in the 1980s?
- With Exhaustible Resources, Can a Developing Country Escape From the Poverty Trap?
- Why Does Poverty Persist in Rural Ethiopia?
- Who Became Poor, Who Escaped Poverty, and Why?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/
"390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
- Social Problems Essay Ideas
- Economic Inequality Questions
- Minimum Wage Research Ideas
- Criminal Justice Essay Topics
- Social Democracy Essay Titles
- Corruption Ideas
- Criminal Behavior Essay Topics
- Social Norms Essay Ideas
- Drug Abuse Research Topics
- Juvenile Delinquency Essay Titles
- Segregation Research Topics
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Challenges Essay Topics
- Community Service Questions
- Discrimination Essay Titles
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Online Summarizer
- Rewording Tool
- Topic Generator
- Essay Title Page Maker
- Conclusion Writer
- Academic Paraphraser
- Essay Writing Help
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Guides
- Useful Information
230 Research Topics on Poverty: Argumentative, Solutions, Cause & Effect Topics about Poverty

Extreme poverty has been a hot-button issue for ages. Many of us expected the 21st century to become the era when the problem of drastic income inequality would be resolved. But the COVID-19 pandemic threw these initiatives back . Poverty has become as widespread as a hundred years before. Will we ever make the Earth a prosperous place for all?
This article features 230 poverty essay topics. They tackle every social, economic, psychological, and political aspect of this controversial issue. For your convenience, we grouped them according to the paper genre. Discrimination and limited access to education, malnutrition, health problems, mental disorders, and hunger are only some of the spheres you can debate.
🔝 Top 15 Poverty Essay Topics
- 📝 Topics & Issues to Cover in a Paper
🪙 Research Topics on Poverty
- 🗣️ Argumentative Essay Topics
- ➡️ Cause & Effect Essay Topics on Poverty
💡 Poverty Solutions Essay Topics
🧸 child poverty essay topics, 🌎 poverty in america essay topics, 🔗 references.
- Ending poverty in all its forms around the globe is our goal No.1.
- What does it mean to be poor?
- The pandemic can teach us a new lesson in fighting poverty worldwide.
- Child poverty essay: Lifelong ramifications.
- How does poverty measurement impact public opinion?
- Why does Africa remain to be the least developed country?
- Do we oversimplify when dividing people into wealthy and poor?
- Why should economics study the phenomenon of poverty?
- Poverty in America: An essay on its dynamics.
- How is deprivation linked to crime levels?
- Does overpopulation cause poverty?
- It is a myth that wealthy people are often obese.
- Fighting poverty is what all of us do throughout our lives.
- Can free education for all be a measure to eliminate poverty?
- Globalization will end poverty in developing countries.
📝 Topics & Issues to Cover in a Paper
Some poverty essay topics are too broad to prepare compelling argumentation. We have explored these directions to guide your research.
Defining Poverty
When the financial resources in a community are lacking, the basic needs of some people are not met. These circumstances do not allow poor people to enjoy an acceptable standard of life. They may not have a roof above their heads or may not be able to afford clothes and food. But the lack of income also causes many psychological and sociological consequences. Children of the poor have a higher probability of physical and mental health issues than their peers. They are also more likely to abuse substances and have problems with the law.
Measuring Poverty
The US Bureau of Census is responsible for calculating poverty rates in the US. They usually exclude anyone living in a mental health facility, prison, military quarters, and school dormitories. They do not count children under 15 years, either.
The World Bank established a new goal to eliminate extreme poverty in one generation starting in 2013. By 2030, They planned to decrease the number of the world’s population who live on $1.90 per day down to 3%. Measuring poverty shows which strategies work and which should be put aside. It also guides emerging countries in their development strategies to adapt to the rapidly changing world economy.
Poverty Facts & Statistics
- In 2018, four out of five individuals below the poverty line resided in rural areas.
- In 2020, extreme poverty rates rose for the first time over the last two decades. It happened due to the COVID-19 pandemic, military conflicts, and climate change.
- 97 million people crossed the poverty line because of the pandemic.
- Children make up 50% of the poor global population.
- 70% of the global poor above 15 have no or only primary school education.
- More than 40 % of the poor live in countries affected by conflict and violence. Over the next decade, the number is predicted to peak at 67%. Meanwhile, only 10% of the world’s population lives in such countries.
What Can Be Done About Poverty?
- At the moment, money is the best measure to reduce poverty . Investing in the markets of emerging countries could spur their economic growth. However, investors are often unwilling to do so, as these nations often struggle to sustain economic growth.
- The second way of problem-solving is education. It gives safety and support to children from low-income families (as they often suffer from domestic violence or sexual abuse). It also increases their future employment opportunities. But most importantly, it creates a culture of learning in families, and the next generations will benefit from it.
- The origin of poverty and the divergence of concepts depending on the context.
- Comparison of poverty concepts by UN, the World Bank and the EU.
- The difference between the definition of poverty in the EU and other world organizations.
- The difference between the UN definition of poverty and other world organizations.
- The World Bank’s definition of poverty differs from other world organizations.
- Aspects affecting the measurement of poverty.
- How Poverty Changes.
- When poverty is recognized as global?
- General level of development of the state affects the spread of poverty.
- Is poverty just an economic factor?
- When is a person recognized as poor determined?
- Poverty at the individual, local, national and global levels.
- Poverty hinders cognitive function.
- Poor people are often more susceptible to severe illness.
- Economic stability is paramount for a poor household.
- The rising cost of living makes poor people less able to afford things.
- Rising costs can push into poverty and others into poverty.
- Stress factors caused by poverty.
- Children living in poverty have lower cognitive thinking.
- Education in the US educational system is focused on students from more affluent families.
- Conditions in schools in poor areas prevent children from learning in a safe environment.
- High crime rate among children with low resources.
- Children from low-income families have higher rates of teenage pregnancy.
- Relationship of gender to poverty or location.
- In poorer countries, girls have lower completion rates.
- Most often, children end up in orphanages because of family poverty.
- Cultural factors can negatively affect productivity and perpetuate poverty in a state.
- Women are the group suffering from the highest levels of poverty after children.
- People living in poverty have an increased chance of getting a disability.
- Many women become victims of human trafficking.
- The most common form of survival is prostitution due to economic desperation.
- As poverty decreases, fewer incidents of violence will occur.
- Poverty Reduction Strategies.
- The improvement of cities and states can affect the reduction of the level of poverty of the population.
- Access to basic human needs is a way to fight poverty.
- Effect of deworming children on improving education among poor children.
- The fight against corruption is the same as the fight against poverty.
- Debt relief for countries can reduce countries poverty levels.
- Emigration from developing countries perpetuates poverty in them.
- Access to contraceptives directly impacts the poverty of the population and the country’s economy.
- Basic income is more effective in fighting poverty than the minimum wage and unemployment benefits.
- Reducing bureaucracy and increasing economic freedom would significantly reduce poverty.
- Greater access to markets brings more income to the poor.
- Road infrastructure directly affects poverty.
- Poverty causes environmental degradation.
- Climate change can hinder poverty reduction.
- Is spirituality the engine of poverty?
- Voluntary poverty.
- Climate change and poverty.
- Increased mortality due to poverty.
- The socio-economic gap between the poor and the rich.
- Is poverty linked to nationality?
- Religion and poverty.
- The influence of geographical location on the spread of poverty.
- Anti-poverty organizations and their strategies.
- Long-term consequences of poverty.
- Discrimination against the poor.
- Short-term and long-term strategies in the fight against poverty.
- Is it possible to get out of poverty, and what affects it?
- Your actions against poverty.
- Maintenance by the state of an adequate standard of living.
- The emergence of poverty as a social phenomenon.
- Is globalization exacerbating poverty?
- Social isolation of the population.
- Is poverty a choice?
- Health care for the poor.
- Human rights against poverty.
- Global poverty.
- Does moral poverty exist?
- Children’s perception of poverty.
- Poverty makes children grow up earlier.
- Digitalization help fight poverty.
- Does migration perpetuate poverty or fight it?
- Poor women are expected to marry early.
- Family planning prevents the spread of poverty.
- Development of poverty.
- Your understanding of poverty.
- Are there countries where there is no poverty?
- Political programs to combat poverty.
- What factors can exacerbate poverty problems?
- Poverty as a result of a natural disaster.
- Sustainable Development Goals: “No Poverty”.
- Dynamics of poverty levels.
- Are the poor themselves to blame for poverty?
- Ideological representations of poverty.
- Poverty is a result of discrimination.
- Do shelters for the poor help in the fight against poverty?
- Does a non-working family equal a poor family?
- Impact of the pandemic on the spread of poverty.
- Lack of medical care for the poor.
🗣️ Argumentative Essay Topics on Poverty
- Differences in prices between countries to adjust for purchasing power.
- What is extreme poverty?
- Measuring poverty: the monetary value of human consumption.
- The difficulty of measuring global poverty: difference between countries.
- International poverty line.
- Is poverty linked only to wealth?
- Industrialization and the fight against poverty: victory or even greater gap.
- Population growth leads to more poor people in the world.
- Growth of the global middle class and reduction of extreme poverty.
- Poverty forecast in 2030.
- Extreme poverty cannot be ended.
- The concentration of poverty in Africa.
- Countries that have reduced poverty: India, China, Ethiopia, Ghana.
- A growing global middle class and the stagnation of the world’s poorest people.
- Has modernity not reached the poor countries?
- The expansion of social protection policy helps to get rid of extreme poverty.
- Progress in the fight against all poverty lines.
- Importance of poverty reduction in developed countries.
- The demographic factor in the spread of poverty.
- Adjusting to Rising Costs of Living: Increasing or Reducing Poverty?
- Change in the international poverty line over time.
- Is it possible to eradicate extreme poverty?
- Multidimensional poverty: the diverse nature of poverty.
- Africa is the continent with the poorest people.
- Are there no poor people in rich countries?
➡️ Cause & Effect Essay Topics on Poverty
- The economic crisis in a country leads to an increase in poverty.
- Consequences of hunger for children and youth.
- The poverty of children is only the concern of parents.
- Most of the poor are from incomplete families.
- Historical barriers in the fight against poverty.
- Racial and ethnic gaps in poverty rates.
- Physical and mental well-being of poor children.
- Access to health care for poor families.
- Inadequate education exacerbates the vicious cycle of poverty.
- Children living in poverty are at greater risk for behavioral and emotional problems.
- Poverty breeds violent behavior in children.
- Poverty contributes to the spread of hard-to-treat diseases.
- Mortality of children in poor families.
- Protecting children from poor families.
- The prevalence of poverty among children in developed countries.
- Depression and poverty: children suffer from mental illnesses like adults.
- Family conflict as a cause of child homelessness.
- Homelessness harms children who are more prone to mental and physical illness.
- How does the labor market affect child poverty?
- Early pregnancy can lead to homelessness .
- Discrimination against LGBT people increases the level of homelessness among young people.
- Poverty contributes to the spread of STIs .
- Violent crime among the poor.
- Are violence and poverty inseparable?
- Substance abuse among children from poor families.
- What are the poverty solutions to stop hunger in the US?
- Reducing poverty through education – the US providing global solutions for emerging nations.
- How education helps break the cycle of poverty – evidence from the US communities.
- Providing water for communities overarched by bottled water producers – how does this help reduce poverty?
- Water resources and poverty among Native Americans – determining points of intersection.
- Clean water as a source of health and prosperity – how to preserve the national water resources of the United States?
- Basic health care – how free services affect global poverty.
- Why should basic medical care become a human right to overcome poverty?
- How do health insurance programs reduce poverty in the United States?
- Weaknesses in US health insurance programs: solutions for poverty alleviation.
- Empowering women to stop the poverty loops – solutions through micro-financing.
- Empowering women to reduce poverty – solutions for communities in the US.
- Global poverty and women’s power: three stories of entrepreneurship.
- How hunger and poverty affect the mental development of children – the need for immediate global solutions.
- Ensuring adequate nutrition for children and mothers to end poverty – lessons from Hawaii and Haiti.
- How can the American economy overcome poverty and hunger through macroeconomic solutions?
- The activities of international environmental organizations that led to poverty alleviation: the brightest victories.
- Fighting global warming to end poverty – how does planting trees improve living standards?
- Green energy and poverty alleviation – US macroeconomic solutions.
- Combating cycles of violence to overcome poverty – the US experience.
- Domestic violence as a factor in the growth of populations’ poverty.
- Violence against women – hotlines and other ways to help break cycles of poverty.
- Economic methods of overcoming poverty – international experience.
- Business and CSR practices as a means of influence in societies with low standards of living.
- Federal financing to reduce poverty – why is this a bad solution?
- Overcoming child homelessness as a way to end child poverty.
- Protecting orphans and securing their future through free education programs.
- Adoption programs as a way to combat child poverty among orphans.
- Work with refugees and assessment of child poverty in Europe and the US.
- Migrant children and stigmatization – how social institutions can avoid offensive meanings.
- Migration and the provision of education services – challenges related to overcoming child poverty.
- The health sector and overcoming child poverty: five important practices.
- Child nutrition in schools to overcome child poverty – stability and ways of implementing support programs.
- Child marriage and child poverty – how the mother’s age affects the well-being of children.
- Provision of education services for women as a way to overcome child poverty.
- Should free medicine for children become a right, not a privilege?
- How does the civilized world fight against child poverty that results from environmental disasters?
- Overcoming the consequences of global warming – programs of child poverty elimination.
- Overcoming child poverty with the involvement of parents – what programs exist in the US?
- Child support grants: three ways to overcome mistrust.
- Why does child poverty reduce the civilizational development of society?
- What are the five main consequences of child poverty?
- How does child poverty affect the economic development of countries?
- What is child poverty: studying the main determinants.
- Child poverty among the better-off sections of the US society – how do misleading concepts lead to social problems?
- Education of civilizational, moral, and cultural values to overcome child poverty – three ways of development.
- The ethical side of the issue of child poverty – why is society obliged to help?
- How preservation of cultural values leads to child poverty – lessons from national minorities.
- Why state control over culture and consciousness can lead to child poverty – the examples of the People’s Republic of China and North Korea.
- Propaganda as a way to reduce child poverty – the effectiveness of the approach.
- Poverty and national minorities – statistics and future trends.
- Overcoming poverty through healthcare services: interaction with vulnerable groups.
- Poverty and homelessness as consequences of unsuccessful political vectors – the American experience.
- Unemployment and poverty among non-citizens – ways to overcome the crisis.
- How has the pandemic deepened the crisis of poverty and unemployment in the US?
- Poverty and professions with the least demand on the labor market in the US: gaps and new opportunities.
- Democrats and Republicans – differences in approaches to overcoming poverty.
- Five successful democratic (republican) initiatives to overcome poverty.
- Conservatives in power and overcoming poverty – successes and failures.
- The top three policies of Donald Trump that led to the deepening of the poverty crisis in the US.
- Overcoming poverty in the US – the story of three presidencies (to choose from).
- Geographical prerequisites of regional poverty in the US – historical experience.
- Poverty crisis in the post-lockdown period – new ways of social development.
- Regional poverty in the US – solutions for selected regions.
- Is there a link between defense capability and poverty in the US?
- How science can help overcome poverty – the experience of American farmers in the mid-20th century.
- How big business harms the economy – the top 3 negative consequences of the work of unconscious producers that deepen the poverty crisis.
- How unconscious consumption of Chinese goods harms the US economy and deepens the poverty crisis.
- How can the United States overcome the unemployment crisis by stimulating small and medium-sized businesses?
- What inhumane manufacturing practices of the mid-to-late 19th century continue to exacerbate the poverty crisis in the United States?
- How are new technologies deepening the crisis of poverty and unemployment in the US?
- Why does the consumer society accelerate the decline of the economy and lead to poverty in the US?
- How can social science education programs help address the poverty crisis in the US?
- Three bright health care initiatives that help fight poverty in the US.
- Social determinants of poverty – how does the individual’s environment add to the creation of the poverty loop?
- Poverty Overview | The World Bank
- Poverty in the United States: 2021 | US Census Bureau
- Rural Poverty & Well-Being | US Department of Agriculture
- Child Poverty | UNICEF
- How Is Poverty Measured? | Institute for Research on Poverty
- What Is “Deep Poverty”? | Center for Poverty & Inequality Research
- Poverty Facts | University of Michigan
- LGBT Poverty in the United States | The Williams Institute

9 Questions You Have Asked About Poverty
Dec 13, 2016
Poverty across the USA is a systematic problem that touches all walks of life, including people in your own community. Consider your thoughts each time you see a homeless person. Have you ever wondered if they are on drugs or why don’t they just get a job?
Poverty is most commonly defined as lacking financial resources. The Federal Poverty Guidelines is how most public assistance is determined. For a family of four, earning less than $24,000 per year, they are considered 100% below the poverty line. The problem with this definition is that is doesn’t account for things such as lack of reliable transportation, mental and physical health, social capital, and emotional stress.

Here are nine important questions you may have asked about poverty and some insights to get you thinking.
Question #1: Why Does Poverty Still Exist? Unfortunately, the cycle of poverty is nearly impossible to climb out of, especially for those born into it. There are several factors that contribute to why poverty still exists. The economy, cost of living, education, wages, health insurance, housing, transportation, and mental health all play a role. One of the biggest barriers for self sufficiency is what’s known as The Cliff Effect. This is where they lose their assistance faster than they can make up the difference. Check out this great video.
Question #2: Isn’t Poverty a Choice? Living in poverty is often not a choice for many people. The majority of those in poverty are working very hard to get out, especially here in Utah County. Some are born into it (intergenerational poverty) and end up sacrifice schooling and other opportunities to just help their family survive. Others fall into it after an unexpected medical emergency or other unforeseen circumstance (situational poverty). They work hard at often stressful, low paying jobs that barely pay the rent. People with disabilities, single parents, international students, veterans and even maybe your next door neighbor all have their own insurmountable barriers whether visible or not. That’s why everything we do at Community Action is centered around providing the education, resources and support to achieve self-reliance.
Question #3: Is Poverty an Issue In Utah County? Yes, the fact is 14% of Utah County lives in Poverty. This means that there are over 70,000 of our own neighbors and friends struggling to make ends meet, including 22,000 children. We see the faces of young families, single moms, and seniors enter our doors every day. This not only impacts them, but our community as a whole. It impacts our schools, jobs, housing market, healthcare and future generations.
Question #4: Aren’t Most Homeless People Drug Addicts? Granted, the high toll drugs take on people’s lives can often lead to chronic homelessness, not everyone who is homeless has problems with drug abuse. Homelessness in Utah County looks very different that you might imagine. Most of Utah residents struggling with homelessness are what are referred to a vicariously housed. This means they are not necessarily living on the street but 14 days away from being evicted or are doubled up in a home somewhere. They might be facing eviction, living with a friend for a limited amount of time, paying for a motel until they can find affordable housing. While chronic homelessness is an issue in Utah County, precariously housed is the bigger issue. We recommend checking out this study for further understanding.
Question #5: Doesn’t The LDS Church Take Care of Everything? The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints does their part to help people in need and they do a really good job. Despite their incredible efforts, there are people who have needs not met by the LDS Church Welfare system. They recognize this and partner with many organization that have similar missions. The LDS Church also refers people to local organization like Community Action Services and Food Bank. It’s a personal decision when it comes to how and when you give. Do your research about the causes you care about and see if you have something to offer.
Question #6: Aren’t People On Welfare Just Lazy? No, in fact they are often some of the hardest working. They are master problem solvers, creative, and can survive in circumstance that many of us could barely function. They are often forced to make difficult decisions such as having heat in the winter or paying rent. It might surprise you to know that an estimated 73 percent of welfare recipients are actually working families that are struggling to make ends.
Question #7: Why Aren’t My Tax Dollars Doing More? The fact of the matter is that it’s complicated. The federal tax that people pay is supposed to fund public services. According to the Center On Budget and Policy Priorities, it’s split between public programs like Social Security, Medicare, defense of our country, international assistance, and other safety net programs that provide assistance to families. It may seem like an endless amount of money, but it’s spread thin between many places. A way that you can take change of the situation is to donate directly to organizations that you feel make a difference.
Question #8: What Does Generational Poverty Mean? Generational poverty is defined as a family living in poverty for two or more generations. The state report on inter-generational poverty shows that nearly 290,000 kids are at risk of a life on welfare if nothing is done. Lieutenant Governor Spencer Cox weighs in on how important this issue is in this article. The sad fact is that for many families getting out of poverty is a full time job. Hopefully with more assistance programs aimed at improving the education of our youth, with more opportunities to go to college, eventually this type of poverty will be eliminated. That’s the goal to end generational poverty. Utah specifically has a five and ten year plan to get rid of inter-generational poverty which you can read in their 20 page plan for a stronger future.
Question #9: How Can I Help? This is probably the absolute best question you can ask! The best thing you can do is do your research and act. Educate yourself on the needs in your own community and find an organization that matches your passion. Go to city council meetings, be informed about the regulations in question, talk to your neighbors, schools, and find out the issues on the minds of those with low-income. At Community Action Services and Food Bank we are always looking for passionate people willing to give through time, in-kind donations or monetary donations. You can visit the site to find out how you can do more to help those in great need.

Poverty Environment Network
- Go to CIFOR-ICRAF.org
- CIFOR-ICRAF’s website cifor-icraf.org features
- About CIFOR
- Research staff
- Research associates
- Procurement
- Annual reports
- Financial Statements
- Work with us
About CIFOR-ICRAF
- ABOUT CIFOR-ICRAF
- Common Board of Trustees
- Our Strategy
- Merger FAQs
Column-3 Ourwork
- ANONYMOUS REPORTING HOTLINE
- RESEARCH TEAMS
- Climate change, energy and low-carbon development
- Equal opportunities, gender, justice and tenure
- Sustainable landscapes and livelihoods
- Value chains, finance and investment
- PROJECT WEBSITES
- GLOBAL LANDSCAPES FORUM
- FORESTS, TREES AND AGROFORESTRY (FTA)
- OTHER CGIAR RESEARCH PROGRAMS
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- Publications
- Forests News
- Presentations
- Projects database
- Upcoming events
- Past events
Featured events
- Landscape News
- Social media
- Corporate news
- Press releases
- Media coverage
- News update
- Media inquiries
Latest news
- Global Landscapes Forum
- GCS: Global Comparative Study on REDD+
- The Sustainable Wetlands Adaptation and Mitigation Program (SWAMP)
- Community-Based Fire Prevention and Peatland Restoration
- Governing Multifunctional Landscapes
- Yangambi Engagement Landscape
- Water towers
- View all project
- CIFOR – ICRAF merger FAQ
- Board of Trustees
- Management group
- Contact our experts
- About our research
- West and Central Africa

- Justification
Key Research Questions
The overall research question for PEN is: What is the current role of forests in poverty alleviation, and how can that role be enhanced through better policy formulation and implementation? This question needs to be made more specific to become researchable. PEN will do this by looking at several dimensions of the forest-poverty link:
- the role in rural livelihoods (regular consumption, insurance, or poverty reduction):
- the role for different groups (degrees of poverty, but also other indicators, e.g. age, household headship, migrants);
- the role in different forest environments (forest abundance, condition, type, management etc.);
- the role in different institutional contexts (e.g., tenure regime and local management);
- the role in different market contexts (market access integration, competitiveness in forest products markets, etc.).
By carefully investigating how these dimensions determine the forest-poverty relationship, PEN can answer several more specific research questions, for example:
- What is the relationship between forest use/dependency and household income/assets in different forest environments (similarities and differences)?
- What are the common characteristics of high forest income across the different environments? Are the poor universally more forests dependent than the better-off households?
- Has local forest ownership and management increased the local forest benefits (and for which groups)?
- How does forest dependency shift (e.g., from products to services) with economic development and market integration?
- Is forest dependency just a temporary phenomenon that disappears when other opportunities arise?
- How do forest products markets shape the people-forest relationship (investments, management, degradation)?
- Is there something special (market and policy failures) about forests that prevent utilizing the full potential in poverty alleviation, and if so what is that?
Funding Partners

Stay connected
Diam habitant integer ultricies nonummy ducimus voluptatum parturient nec molestiae distinctio nascetur montes vitae! Torquent, cubilia.
Persistent Gender Disparities Hinder Women's Safety and Productivity in Zimbabwe

Gender-based violence is a significant concern in Zimbabwe, with a substantial number of women experiencing physical and sexual violence. Photo: Adobe Stock
In Zimbabwe, gender-based violence (GBV) is a significant concern, with a substantial number of women experiencing physical and sexual violence. Approximately 39.4% of women have been subjected to physical violence, and an estimated 11.6% have faced sexual violence. Although there has been a decline in child marriage rates, 16.2% of women were married before the age of 18 as of 2022.
While Zimbabwe has taken several legislative steps against GBV by adopting various international and domestic laws, the Zimbabwe Gender-Based Violence Assessment underscores the necessity for more effective enforcement of GBV legislation and the establishment of legal frameworks that categorically criminalize GBV acts. Zimbabwe is a party to several global and regional legal instruments that promote gender equality and combat GBV. Additionally, the 2013 National Constitution of Zimbabwe is forward-thinking, prohibiting gender discrimination and all forms of GBV.
The GBV Assessment commends the policymakers' commitment to eliminating violence against women and children in Zimbabwe, as espoused in the recently launched Zimbabwe National Strategy to Prevent and Address Gender-based Violence 2023–2030 . However, the assessment notes that more work must be done on the legislative front. "The 2007 Domestic Violence Act needs to be amended to tackle harmful cultural practices and extend coverage to GBV incidents outside the domestic sphere," said Eneida Fernandes, World Bank Country Manager for Zimbabwe.
The assessment urges prompt law harmonization and recommends strengthening coordination platforms to avoid duplication of efforts and overlapping mandates. All sub-platforms should report to the National Gender Forum. It also calls for strengthening the Anti-Domestic Violence Council, which has been inefficient recently.
Recommendations from the report , to prevent GBV, suggest designing, implementing, and evaluating targeted, systematic, evidence-based awareness campaigns to alter social and gender norms towards non-violence and respectful relationships, particularly in GBV hotspots. For GBV response, it is recommended that the justice delivery system be improved by addressing the bottlenecks that lead to delays in GBV case resolutions and establishing “Fast Track” GBV courts.
Accompanying the GBV assessment is the Zimbabwe Gender Assessment , which notes that despite advancements in gender equality, such as securing women's reproductive rights, achieving gender parity in primary education, and increasing female enrollment in higher education, significant gender inequalities remain. These include the underrepresentation of women in wage employment, their overconcentration in the informal labor market, high youth unemployment among women, and high rates of teenage pregnancies and child marriages.

The Gender Assessment reveals that women are less likely to be employed in wage work and more likely to earn less than men. The labor force participation rate for me is 53% compared to 34% for women, and men outnumber women in most sectors. In the agriculture, forestry, and fishing sectors, men account for 58% of the industry labor market, while women make up 42%. Only 22% of working women are employed in wage or salaried positions, compared to 41% for men. Waged women employees earn, on average, about two-thirds of their male counterparts. This is driven by women’s concentration in less renumerated fields, limited work experience and skills, and unequal family and household care responsibilities.
To address gender disparities, recommendations from the report include , among other things, supporting socio-economic skills training for women, which has been shown to increase business outcomes among women microentrepreneurs. It also recommends supporting childcare services, such as offering preferential tax regimes to childcare centers and ensuring that women can engage across all areas of the economy. Addressing the gender divide in land ownership and assets and ring-fencing low-cost finance for women to purchase and own titled land and agricultural implements would also contribute to closing the gender gap.
World Bank in Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe Gender-Based Violence Assessment
Zimbabwe Gender Assessment
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Methodology: 2023 focus groups of Asian Americans
Methodology: 2022-23 survey of asian americans, table of contents.
- About the focus groups
- Participant recruitment procedures
- Moderator and interpreter qualification
- Data analysis
- Sample design
- Data collection
- Weighting and variance estimation
- Analysis of Asians living in poverty
- Acknowledgments
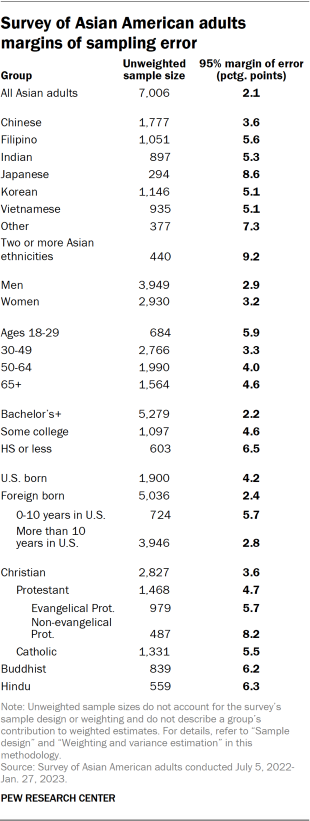
The survey analysis is drawn from a national cross-sectional survey conducted for Pew Research Center by Westat. The sampling design of the survey was an address-based sampling (ABS) approach, supplemented by list samples, to reach a nationally representative group of respondents. The survey was fielded July 5, 2022, through Jan. 27, 2023. Self-administered screening interviews were conducted with a total of 36,469 U.S. adults either online or by mail, resulting in 7,006 interviews with Asian American adults. It is these 7,006 Asian Americans who are the focus of this report. After accounting for the complex sample design and loss of precision due to weighting, the margin of sampling error for these respondents is plus or minus 2.1 percentage points at the 95% level of confidence.
The survey was administered in two stages. In the first stage, a short screening survey was administered to a national sample of U.S. adults to collect basic demographics and determine a respondent’s eligibility for the extended survey of Asian Americans. Screener respondents were considered eligible for the extended survey if they self-identified as Asian (alone or in combination with any other race or ethnicity). Note that all individuals who self-identified as Asian were asked to complete the extended survey.
To maintain consistency with the Census Bureau’s definition of “Asian,” individuals responding as Asian but who self-identified with origins that did not meet the bureau’s official standards prior to the 2020 decennial census were considered ineligible and were not asked to complete the extended survey or were removed from the final sample. Those excluded were people solely of Southwest Asian descent (e.g., Lebanese, Saudi), those with Central Asian origins (e.g., Afghan, Uzbek) as well as various other non-Asian origins. The impact of excluding these groups is small, as together they represent about 1%-2% of the national U.S. Asian population, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the 2021 American Community Survey.
Eligible survey respondents were asked in the extended survey how they identified ethnically (for example: Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean, Vietnamese, or some other ethnicity with a write-in option). Note that survey respondents were asked about their ethnicity rather than nationality. For example, those classified as Chinese in the survey are those self-identifying as of Chinese ethnicity, rather than necessarily being a citizen or former citizen of the People’s Republic of China. Since this is an ethnicity, classification of survey respondents as Chinese also includes those who are Taiwanese.
The research plan for this project was submitted to Westat’s institutional review board (IRB), which is an independent committee of experts that specializes in helping to protect the rights of research participants. Due to the minimal risks associated with this questionnaire content and the population of interest, this research underwent an expedited review and received approval (approval #FWA 00005551).
Throughout this methodology statement, the terms “extended survey” and “extended questionnaire” refer to the extended survey of Asian Americans that is the focus of this report, and “eligible adults” and “eligible respondents” refer to those individuals who met its eligibility criteria, unless otherwise noted.
The survey had a complex sample design constructed to maximize efficiency in reaching Asian American adults while also supporting reliable, national estimates for the population as a whole and for the five largest ethnic groups (Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean and Vietnamese). Asian American adults include those who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.
The main sample frame of the 2022-2023 Asian American Survey is an address-based sample (ABS). The ABS frame of addresses was derived from the USPS Computerized Delivery Sequence file. It is maintained by Marketing Systems Group (MSG) and is updated monthly. MSG geocodes their entire ABS frame, so block, block group, and census tract characteristics from the decennial census and the American Community Survey (ACS) could be appended to addresses and used for sampling and data collection.
All addresses on the ABS frame were geocoded to a census tract. Census tracts were then grouped into three strata based on the density of Asian American adults, defined as the proportion of Asian American adults among all adults in the tract. The three strata were defined as:
- High density: Tracts with an Asian American adult density of 10% or higher
- Medium density: Tracts with a density 3% to less than 10%
- Low density: Tracts with a density less than 3%
Mailing addresses in census tracts from the lowest density stratum, strata 3, were excluded from the sampling frame. As a result, the frame excluded 54.1% of the 2020 census tracts, 49.1% of the U.S. adult population, including 9.1% of adults who self-identified as Asian alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic ethnicity. For the largest five Asian ethnic subgroups, Filipinos had the largest percentage of excluded adults, with 6.8%, while Indians had the lowest with 4.2% of the adults. Addresses were then sampled from the two remaining strata. This stratification and the assignment of differential sampling rates to the strata were critical design components because of the rareness of the Asian American adult population.
Despite oversampling of the high- and medium-density Asian American strata in the ABS sample, the ABS sample was not expected to efficiently yield the required number of completed interviews for some ethnic subgroups. Therefore, the ABS sample was supplemented with samples from the specialized surname list frames maintained by the MSG. These list frames identify households using commercial databases linked to addresses and telephone numbers. The individuals’ surnames in these lists could be classified by likely ethnic origin. Westat requested MSG to produce five list frames: Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean and Vietnamese. The lists were subset to include only cases with a mailing address. Addresses sampled from the lists, unlike those sampled from the ABS frame, were not limited to high- and medium-density census tracts.
Once an address was sampled from either the ABS frame or the surname lists, an invitation was mailed to the address. The invitation requested that the adult in the household with the next birthday complete the survey.
To maximize response, the survey used a sequential mixed-mode protocol in which sampled households were first directed to respond online and later mailed a paper version of the questionnaire if they did not respond online.
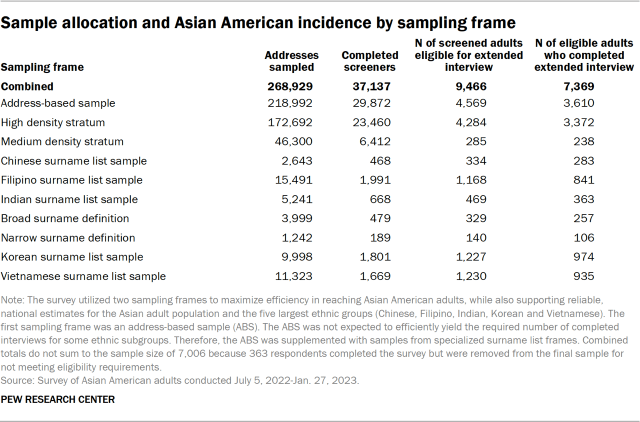
The first mailing was a letter introducing the survey and providing the information necessary (URL and unique PIN) for online response. A pre-incentive of $2 was included in the mailing. This and remaining screener recruitment letters focused on the screener survey, without mentioning the possibility of eligibility for a longer survey and associated promised incentive, since most people would only be asked to complete the short screening survey. It was important for all households to complete the screening survey, not just those who identify as Asian American. As such, the invitation did not mention that the extended survey would focus on topics surrounding the Asian American experience. The invitation was generic to minimize the risk of nonresponse bias due to topic salience bias.
After one week, Westat sent a postcard reminder to all sampled individuals, followed three weeks later by a reminder letter to nonrespondents. Approximately 8.5 weeks after the initial mailing, Westat sent nonrespondents a paper version screening survey, which was a four-page booklet (one folded 11×17 paper) and a postage-paid return envelope in addition to the cover letter. If no response was obtained from those four mailings, no further contact was made.
Eligible adults who completed the screening interview on the web were immediately asked to continue with the extended questionnaire. If an eligible adult completed the screener online but did not complete the extended interview, Westat sent them a reminder letter. This was performed on a rolling basis when it had been at least one week since the web breakoff. Names were not collected until the end of the web survey, so these letters were addressed to “Recent Participant.”
If an eligible respondent completed a paper screener, Westat mailed them the extended survey and a postage-paid return envelope. This was sent weekly as completed paper screeners arrived. Westat followed these paper mailings with a reminder postcard. Later, Westat sent a final paper version via FedEx to eligible adults who had not completed the extended interview online or by paper.
A pre-incentive of $2 (in the form of two $1 bills) was sent to all sampled addresses with the first letter, which provided information about how to complete the survey online. This and subsequent screener invitations only referred to the pre-incentive without reference to the possibility of later promised incentives.
Respondents who completed the screening survey and were found eligible were offered a promised incentive of $10 to go on and complete the extended survey. All participants who completed the extended web survey were offered their choice of a $10 Amazon.com gift code instantly or $10 cash mailed. All participants who completed the survey via paper were mailed a $10 cash incentive.
In December 2022 a mailing was added for eligible respondents who had completed a screener questionnaire, either by web or paper but who had not yet completed the extended survey. It was sent to those who had received their last mailing in the standard sequence at least four weeks earlier. It included a cover letter, a paper copy of the extended survey, and a business reply envelope, and was assembled in a 9×12 envelope with a $1 bill made visible through the envelope window.
In the last month of data collection, an additional mailing was added to boost the number of Vietnamese respondents. A random sample of 4,000 addresses from the Vietnamese surname list and 2,000 addresses from the ABS frame who were flagged as likely Vietnamese were sent another copy of the first invitation letter, which contained web login credentials but no paper copy of the screener. This was sent in a No. 10 envelope with a wide window and was assembled with a $1 bill visible through the envelope window.
The mail and web screening and extended surveys were developed in English and translated into Chinese (Simplified and Traditional), Hindi, Korean, Tagalog and Vietnamese. For web, the landing page was displayed in English initially but included banners at the top and bottom of the page that allowed respondents to change the displayed language. Once in the survey, a dropdown button at the top of each page was available to respondents to toggle between languages.
The paper surveys were also formatted into all six languages. Recipients thought to be more likely to use a specific language option, based on supplemental information in the sampling frame or their address location, were sent a paper screener in that language in addition to an English screener questionnaire. Those receiving a paper extended instrument were sent the extended survey in the language in which the screener was completed. For web, respondents continued in their selected language from the screener.
Household-level weighting
The first step in weighting was creating a base weight for each sampled mailing address to account for its probability of selection into the sample. The base weight for mailing address k is called BW k and is defined as the inverse of its probability of selection. The ABS sample addresses had a probability of selection based on the stratum from which they were sampled. The supplemental samples (i.e., Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean and Vietnamese surname lists) also had a probability of selection from the list frames. Because all of the addresses in the list frames are also included in the ABS frame, these addresses had multiple opportunities for these addresses to be selected, and the base weights include an adjustment to account for their higher probability of selection.
Each sampled mailing address was assigned to one of four categories according to its final screener disposition. The categories were 1) household with a completed screener interview, 2) household with an incomplete screener interview, 3) ineligible (i.e., not a household, which were primarily postmaster returns), and 4) addresses for which status was unknown (i.e., addresses that were not identified as undeliverable by the USPS but from which no survey response was received).
The second step in the weighting process was adjusting the base weight to account for occupied households among those with unknown eligibility (category 4). Previous ABS studies have found that about 13% of all addresses in the ABS frame were either vacant or not home to anyone in the civilian, non-institutionalized adult population. For this survey, it was assumed that 87% of all sampled addresses from the ABS frame were eligible households. However, this value was not appropriate for the addresses sampled from the list frames, which were expected to have a higher proportion of households as these were maintained lists. For the list samples, the occupied household rate was computed as the proportion of list cases in category 3 compared to all resolved list cases (i.e., the sum of categories 1 through 3). The base weights for the share of category 4 addresses (unknown eligibility) assumed to be eligible were then allocated to cases in categories 1 and 2 (known households) so that the sum of the combined category 1 and 2 base weights equaled the number of addresses assumed to be eligible in each frame. The category 3 ineligible addresses were given a weight of zero.
The next step was adjusting for nonresponse for households without a completed screener interview to create a final household weight. This adjustment allocated the weights of nonrespondents (category 2) to those of respondents (category 1) within classes defined by the cross-classification of sampling strata, census region, and sample type (e.g., ABS and list supplemental samples). Those classes with fewer than 50 sampled addresses or large adjustment factors were collapsed with nearby cells within the sample type. Given the large variance in the household weights among the medium density ABS stratum, final household weights for addresses within this stratum were capped at 300.
Weighting of extended survey respondents
The extended interview nonresponse adjustment began by assigning each case that completed the screener interview to one of three dispositions: 1) eligible adult completed the extended interview; 2) eligible adult did not complete the extended interview; and 3) not eligible for the extended interview.
An initial adult base weight was calculated for the cases with a completed extended interview as the product of the truncated number of adults in the household (max value of 3) and the household weight. This adjustment accounted for selecting one adult in each household.
The final step in the adult weighting was calibrating the adult weights for those who completed the extended interview so that the calibrated weights (i.e., the estimated number of adults) aligned with benchmarks for non-institutionalized Asian adults from the 2016-2020 American Community Surveys Public Use Microdata Sample (PUMS). Specifically, raking was used to calibrate the weights on the following dimensions:
- Ethnic group (Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, other single Asian ethnicities, and multiple Asian ethnicities)
- Collapsed ethnic group (Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean, Vietnamese, all other single and multiple Asian ethnicities) by age group
- Collapsed ethnic group by sex
- Collapsed ethnic group by census region
- Collapsed ethnic group by education
- Collapsed ethnic group by housing tenure
- Collapsed ethnic group by nativity
- Income group by number of persons in the household
The control totals used in raking were based on the entire population of Asian American adults (including those who live in the excluded stratum) to correct for both extended interview nonresponse and undercoverage from excluding the low-density stratum in the ABS frame.
Variance estimation
Because the modeled estimates used in the weighting are themselves subject to sampling error, variance estimation and tests of statistical significance were performed using the grouped jackknife estimator ( JK 2). One hundred sets of replicates were created by deleting a group of cases within each stratum from each replicate and doubling the weights for a corresponding set of cases in the same stratum. The entire weighting and modeling process was performed on the full sample and then separately repeated for each replicate. The result is a total of 101 separate weights for each respondent that have incorporated the variability from the complex sample design. 1
Response rates
Westat assigned all sampled cases a result code for their participation in the screener, and then they assigned a result for the extended questionnaire for those who were eligible for the survey of Asian Americans. Two of the dispositions warrant some discussion. One is the category “4.313 No such address.” This category is for addresses that were returned by the U.S. Postal Service as not being deliverable. This status indicates the address, which was on the USPS Delivery Sequence File at the time of sampling, currently is not occupied or no longer exists. The second category is “4.90 Other.” This category contains 588 addresses that were never mailed because they had a drop count of greater than four. Drop points are addresses with multiple households that share the same address. The information available in the ABS frame on drop points is limited to the number of drop points at the address, without information on the type of households at the drop point, or how they should be labeled for mailing purposes. In this survey, all drop points were eligible for sampling, but only those with drop point counts of four or fewer were mailed. Westat treated drop point counts of five or more as out of scope, and no mailing was done for those addresses.
Westat used the disposition results to compute response rates consistent with AAPOR definitions. The response rates are weighted by the base weight to account for the differential sampling in this survey. The AAPOR RR3 response rate to the screening interview was 17.0%. 2 The RR1 response rate to the extended Asian American interview (77.9%) is the number of eligible adults completing the questionnaire over the total sampled for that extended questionnaire. The overall response rate is the product of the screener response rate and the conditional response rate for the extended questionnaire. The overall response rate for the Asian American sample in the Pew Research Center survey was 13.3% (17.0% x 77.9%).
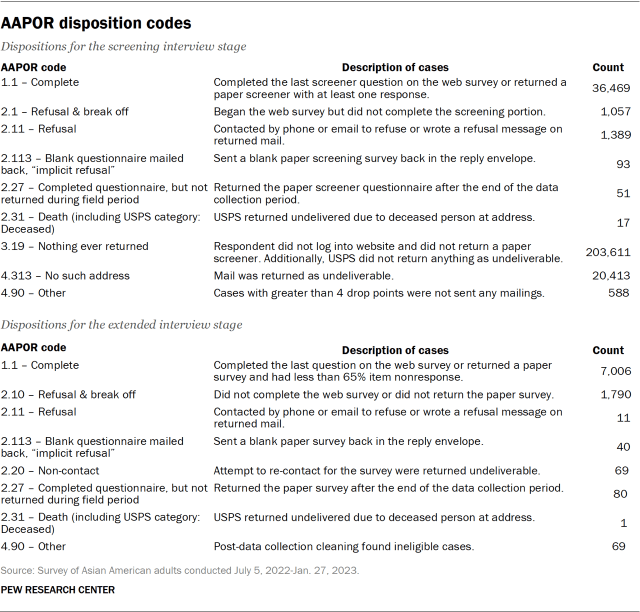
Survey analysis of Asian adults living in poverty is based on 561 respondents of the 2022-23 survey of Asian Americans whose approximate family income falls at or below the 2022 federal poverty line published by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
The survey asked respondents to choose their family income brackets in the 12 months prior to the survey. These income brackets were converted into dollars in the following ways:
- For those reporting a family income of less than $12,500, $12,499 was used as a proxy for their family income.
- For respondents reporting income brackets that are between $12,500 and $149,999, the midpoint of the selected income bracket was used as a proxy. For example, if they chose “$12,500 to $14,999,” $13,750 was used.
- For respondents reporting a family income of $150,000 or more, $150,000 was used.
The survey also asked respondents how many adults ages 18 or older live in their household including themselves, from one to 10 adults. Additionally, the survey asked how many children under 18 live in their household, from zero to 10 children. These responses were used to calculate their total family (household) size. Asian adults were categorized as “living near or below the poverty line” if their approximate family income, after being adjusted for family size, falls at or below 100% of the 2022 federal poverty line. Respondents with a household size of four were categorized as “living near or below the poverty line” if their approximate family income is $27,750 or less. 3 All Asian adults whose approximate family income is $12,499 were categorized as “living near or below” the poverty line regardless of family size, since those respondents have an income under the 2022 federal poverty line for a family of one. All Asian adults who meet the criteria above are used for the analysis of Asians in poverty, irrespective of their status as students or not.
A number of sensitivity checks were performed to test the robustness of the findings, and the main conclusions were consistently upheld. These sensitivity checks included using the poverty thresholds published by the Census Bureau instead of the poverty line published by HHS to define Asians in poverty, and excluding full-time students from the analysis even if their family income falls at or below the poverty line.
- For additional details on jackknife replication, refer to Rust, K.F., and J.N.K. Rao. 1996. “ Variance estimation for complex surveys using replication techniques .” Statistical Methods in Medical Research. ↩
- The weighted share of unscreened households assumed to be eligible for the screener interview (occupied “e”) was 87%. ↩
- The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has separate poverty guidelines for the 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia, Alaska and Hawaii. For all respondents in the 2022-23 survey of Asian Americans, poverty status was determined by applying the federal poverty line for the 48 contiguous states and D.C., regardless of respondents’ state of residence. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Asian Americans
- Homeownership & Renting
- Income & Wages
- Income, Wealth & Poverty
- Personal Finances
Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty
1 in 10: redefining the asian american dream (short film), the hardships and dreams of asian americans living in poverty, key facts about asian american eligible voters in 2024, striking findings from 2023, most popular, report materials.
- Moderator Guide
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Advancing social justice, promoting decent work ILO is a specialized agency of the United Nations

Main Figures on Forced Labour
27.6 million
people are in forced labour.
US$ 236 billion
generated in illegal profits every year.
3.9 million
of them are in State-imposed form of forced labour.
of them are women and girls (4.9 million in forced commercial sexual exploitation, and 6 million in other economic sectors).
of them are children (3.3 million). More than half of these children are in commercial sexual exploitation.
3 times more
risk of forced labour for migrant workers.
- Victims of forced labour include 17.3 million exploited in the private sector; 6.3 million in forced commercial sexual exploitation, and 3.9 million in forced labour imposed by State.
- The Asia and the Pacific region has the highest number of people in forced labour (15.1 million) and the Arab States the highest prevalence (5.3 per thousand people).
- Addressing decent work deficits in the informal economy, as part of broader efforts towards economic formalization, is a priority for progress against forced labour.
Source: 2022 Global Estimates
Forced Labour Observatory
The Forced Labour Observatory (FLO) is a database that provides comprehensive global and country information on forced labour, including on international and national legal and institutional frameworks; enforcement, prevention and protection measures, as well as information related to access to justice; remedies, and cooperation.
Global Reports

2021 Global Estimates of Modern Slavery: Forced Labour and Forced Marriage
The latest estimates show that forced labour and forced marriage have increased significantly in the last five years, according to the International Labour Organization, Walk Free and the International Organisation for Migration.
- Full Report
- Executive Summary
- Press Release
- Third estimates: Modern Slavery (2017)
- Second estimates: Forced Labour (2012)
- First estimates: Forced Labour (2005)

Profits and Poverty: The Economics of Forced Labour (2024)
The study investigates the underlying factors that drive forced labour, of which a major one is illegal profits.
- Press release
- First edition of the report and second estimates (2014)
- First estimates of illegal profits from forced labour (2005)
Main Statistical Tools on Forced Labour
- Hard to See, Harder to Count: Guidelines for Forced Labour Surveys
- Ethical Guidelines for Research on Forced Labour
- Evidence Gap Map on Forced Labour
- Global Research Agenda (child labour, forced labour and human trafficking)
ICLS and forced labour

The International Conference of Labour Statisticians (ICLS) is the authoritative body to set global standards in labour statistics. During its 20th meeting, in October 2018, the ICLS adopted the "Guidelines concerning the measurement of forced labour". The intent of the guidelines is to facilitate the process of testing the measurement of forced labour in different national circumstances and/or measurement objectives.
- Guidelines concerning the measurement of forced labour (ICLS 2018)
- Measurement of forced labour: stocktaking and way forward (ICLS 2023 Room document 22)
- All ICLS documents

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
202 Poverty Essay Topics & Examples. Poverty is one of the most pressing global issues affecting millions of individuals. We want to share some intriguing poverty essay topics and research questions for you to choose the titles of your paper correctly. With the help of this collection, you can explore the intricate dimensions of poverty, its ...
The official poverty rate is 11.6 percent, based on the U.S. Census Bureau's estimates for 2021. That year, an estimated 37.9 million Americans lived in poverty according to the official measure. Neither the rate nor the number differed significantly from 2020. According to the supplemental poverty measure, the poverty rate was 7.8 percent.
Such a direct link between lack of well-being and poverty can ultimately lead to family instability. In this paper, we will review select research findings of the past decade published in the Journal of Family and Economic Issues from 2010 to 2019 that have increased our understanding of low-income families living in poverty.
government, non-governmental org anisations, academia and research to identify 100 important. research questions that, if answered, would help to r educe or prevent poverty. The list includes ...
Progress in reducing or preventing poverty in the UK could be helped by the answers to 100 important research questions, according to a new report. The questions have been identified by the Joseph Rowntree Foundation and the Centre for Science and Policy at the University of Cambridge, based on an exercise involving 45 participants from ...
The Hardships and Dreams of Asian Americans Living in Poverty. About one-in-ten Asian Americans live in poverty. Pew Research Center conducted 18 focus groups in 12 languages to explore their stories and experiences. reportDec 4, 2023.
The World Development Report of 2013 measures, perhaps for the first time, inequality of opportunity to labor market outcomes in a discrete setting. It focuses on Europe and Central Asia. Latest research from the World Bank on Poverty, including reports, studies, publications, working papers and articles.
Overview. Around 700 million people live on less than $2.15 per day, the extreme poverty line. Extreme poverty remains concentrated in parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, fragile and conflict-affected areas, and rural areas. After decades of progress, the pace of global poverty reduction began to slow by 2015, in tandem with subdued economic growth.
Unfortunately, American poverty research has not traditionally aimed to explain the question of the systemically high poverty in the United States. Rather, the prevailing approaches have focused on the individual poor. This partly reflects America's uniquely strong individualistic ideology (1, 4, 10, 39). This section critically reviews three ...
The Center's focus on immigration and poverty is motivated by the important role immigrants play in the U.S. economy, and by the Center's location in the Central Valley of California. Each of our other research areas: Labor Markets and Poverty, the Intergenerational Transmission of Poverty, and the Non-cash Safety Net hold questions that ...
We decided to review both quantitative and qualitative evidence to generate a more comprehensive account of the research questions, and to gain a contextual understanding of how poverty stigma is experienced by individuals (Hong et al., 2020). The review was conducted by a multidisciplinary team of researchers with experience of working in ...
About 41 percent of the nation's children — nearly 30 million in 2008 — live in families with low incomes, that is, incomes below twice the official poverty level (for 2009, about $44,000 for a family of four). Although families with incomes between 100 and 200 percent of the poverty level are not officially classified as poor, many face ...
1. Introduction. Poverty "is one of the defining challenges of the 21st Century facing the world" (Gweshengwe et al., Citation 2020, p. 1).In 2019, about 1.3 billion people in 101 countries were living in poverty (United Nations Development Programme and Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative, Citation 2019).For this reason, the 2030 Global Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals ...
In 2019, when data collection for the Childhood and Family Experiences Study began, ap proximately 10.5 million children—about one out of every seven children— in the United States lived in families that were experiencing poverty. Considerable research evidence links childhood experiences of poverty to harmful effects on physical and mental ...
The impact of poverty on young children is significant and long lasting. Poverty is associated with substandard housing, hunger, homelessness, inadequate childcare, unsafe neighborhoods, and under-resourced schools. In addition, low-income children are at greater risk than higher-income children for a range of cognitive, emotional, and health ...
Reducing poverty is important for those affected, for society and the economy. Poverty remains entrenched in the UK, despite considerable research efforts to understand its causes and possible solutions. The Joseph Rowntree Foundation, with the
Pater Saunders holds a Research Chair in Social Policy in the social Policy Research Centre at UNSW, where he served as Director from February 1978 to July 2007. He served as Director of the Social Policy Research Centre at UNSW from February 1987 until July 2007. He is an authority on poverty, income distribution and household needs and living standards.
No doubt there is a rich tradition of social science research on poverty which has provided a wide range of answers to these key questions from a myriad of perspectives. However, poverty studies across different academic disciplines have long been very uneven and highly fragmented [ 9 ].
Poverty in "A Modest Proposal" by Swift. The high number of children born to poor families presents significant problems for a country."A Modest Proposal" is a satirical essay by Jonathan Swift that proposes a solution to the challenge facing the kingdom. Life Below the Poverty Line in the US.
This article features 230 poverty essay topics. They tackle every social, economic, psychological, and political aspect of this controversial issue. For your convenience, we grouped them according to the paper genre. Discrimination and limited access to education, malnutrition, health problems, mental disorders, and hunger are only some of the ...
Question #3: Is Poverty an Issue In Utah County? Yes, the fact is 14% of Utah County lives in Poverty. This means that there are over 70,000 of our own neighbors and friends struggling to make ends meet, including 22,000 children. We see the faces of young families, single moms, and seniors enter our doors every day.
Key Research Questions. The overall research question for PEN is: What is the current role of forests in poverty alleviation, and how can that role be enhanced through better policy formulation and implementation? This question needs to be made more specific to become researchable. PEN will do this by looking at several dimensions of the forest ...
With 189 member countries, staff from more than 170 countries, and offices in over 130 locations, the World Bank Group is a unique global partnership: five institutions working for sustainable solutions that reduce poverty and build shared prosperity in developing countries.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
This study aims to contribute to the empirical research on social and economic conditions of people with disabilities in developing countries. Using comparable data and methods across countries, this study presents a snapshot of economic and poverty situation of working-age persons with disabilities and their households in 15 developing countries.
Analysis of Asians living in poverty. Survey analysis of Asian adults living in poverty is based on 561 respondents of the 2022-23 survey of Asian Americans whose approximate family income falls at or below the 2022 federal poverty line published by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Topics; Forced Labour, Modern Slavery and Human Trafficking; ... Profits and Poverty: The Economics of Forced Labour (2024) 3.9 million. of them are in State-imposed form of forced labour. 2022 Global Estimates. ... Global Research Agenda (child labour, forced labour and human trafficking)