Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Patient Case Presentation

Figure 1. Blue and silver stethoscope (Pixabay, N.D.)
Ms. S.W. is a 48-year-old white female who presented to an outpatient community mental health agency for evaluation of depressive symptoms. Over the past eight weeks she has experienced sad mood every day, which she describes as a feeling of hopelessness and emptiness. She also noticed other changes about herself, including decreased appetite, insomnia, fatigue, and poor ability to concentrate. The things that used to bring Ms. S.W. joy, such as gardening and listening to podcasts, are no longer bringing her the same happiness they used to. She became especially concerned as within the past two weeks she also started experiencing feelings of worthlessness, the perception that she is a burden to others, and fleeting thoughts of death/suicide.
Ms. S.W. acknowledges that she has numerous stressors in her life. She reports that her daughter’s grades have been steadily declining over the past two semesters and she is unsure if her daughter will be attending college anymore. Her relationship with her son is somewhat strained as she and his father are not on good terms and her son feels Ms. S.W. is at fault for this. She feels her career has been unfulfilling and though she’d like to go back to school, this isn’t possible given the family’s tight finances/the patient raising a family on a single income.
Ms. S.W. has experienced symptoms of depression previously, but she does not think the symptoms have ever been as severe as they are currently. She has taken antidepressants in the past and was generally adherent to them, but she believes that therapy was more helpful than the medications. She denies ever having history of manic or hypomanic episodes. She has been unable to connect to a mental health agency in several years due to lack of time and feeling that she could manage the symptoms on her own. She now feels that this is her last option and is looking for ongoing outpatient mental health treatment.
Past Medical History
- Hypertension, diagnosed at age 41
Past Surgical History
- Wisdom teeth extraction, age 22
Pertinent Family History
- Mother with history of Major Depressive Disorder, treated with antidepressants
- Maternal grandmother with history of Major Depressive Disorder, Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Brother with history of suicide attempt and subsequent inpatient psychiatric hospitalization,
- Brother with history of Alcohol Use Disorder
- Father died from lung cancer (2012)
Pertinent Social History
- Works full-time as an enrollment specialist for Columbus City Schools since 2006
- Has two children, a daughter age 17 and a son age 14
- Divorced in 2015, currently single
- History of some emotional abuse and neglect from mother during childhood, otherwise denies history of trauma, including physical and sexual abuse
- Smoking 1/2 PPD of cigarettes
- Occasional alcohol use (approximately 1-2 glasses of wine 1-2 times weekly; patient had not had any alcohol consumption for the past year until two weeks ago)

Mental Health Case Study: Understanding Depression through a Real-life Example
Imagine feeling an unrelenting heaviness weighing down on your chest. Every breath becomes a struggle as a cloud of sadness engulfs your every thought. Your energy levels plummet, leaving you physically and emotionally drained. This is the reality for millions of people worldwide who suffer from depression, a complex and debilitating mental health condition.
Understanding depression is crucial in order to provide effective support and treatment for those affected. While textbooks and research papers provide valuable insights, sometimes the best way to truly comprehend the depths of this condition is through real-life case studies. These stories bring depression to life, shedding light on its impact on individuals and society as a whole.
In this article, we will delve into the world of mental health case studies, using a real-life example to explore the intricacies of depression. We will examine the symptoms, prevalence, and consequences of this all-encompassing condition. Furthermore, we will discuss the significance of case studies in mental health research, including their ability to provide detailed information about individual experiences and contribute to the development of treatment strategies.
Through an in-depth analysis of a selected case study, we will gain insight into the journey of an individual facing depression. We will explore their background, symptoms, and initial diagnosis. Additionally, we will examine the various treatment options available and assess the effectiveness of the chosen approach.
By delving into this real-life example, we will not only gain a better understanding of depression as a mental health condition, but we will also uncover valuable lessons that can aid in the treatment and support of those who are affected. So, let us embark on this enlightening journey, using the power of case studies to bring understanding and empathy to those who need it most.
Understanding Depression
Depression is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. To comprehend the impact of depression, it is essential to explore its defining characteristics, prevalence, and consequences on individuals and society as a whole.
Defining depression and its symptoms
Depression is more than just feeling sad or experiencing a low mood. It is a serious mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. Individuals with depression often experience a range of symptoms that can significantly impact their daily lives. These symptoms include:
1. Persistent feelings of sadness or emptiness. 2. Fatigue and decreased energy levels. 3. Significant changes in appetite and weight. 4. Difficulty concentrating or making decisions. 5. Insomnia or excessive sleep. 6. feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or hopelessness. 7. Loss of interest or pleasure in activities.
Exploring the prevalence of depression worldwide
Depression knows no boundaries and affects individuals from all walks of life. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 264 million people globally suffer from depression. This makes depression one of the most common mental health conditions worldwide. Additionally, the WHO highlights that depression is more prevalent among females than males.
The impact of depression is not limited to individuals alone. It also has significant social and economic consequences. Depression can lead to impaired productivity, increased healthcare costs, and strain on relationships, contributing to a significant burden on families, communities, and society at large.
The impact of depression on individuals and society
Depression can have a profound and debilitating impact on individuals’ lives, affecting their physical, emotional, and social well-being. The persistent sadness and loss of interest can lead to difficulties in maintaining relationships, pursuing education or careers, and engaging in daily activities. Furthermore, depression increases the risk of developing other mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders or substance abuse.
On a societal level, depression poses numerous challenges. The economic burden of depression is significant, with costs associated with treatment, reduced productivity, and premature death. Moreover, the social stigma surrounding mental health can impede individuals from seeking help and accessing appropriate support systems.
Understanding the prevalence and consequences of depression is crucial for policymakers, healthcare professionals, and individuals alike. By recognizing the significant impact depression has on individuals and society, appropriate resources and interventions can be developed to mitigate its effects and improve the overall well-being of those affected.
The Significance of Case Studies in Mental Health Research
Case studies play a vital role in mental health research, providing valuable insights into individual experiences and contributing to the development of effective treatment strategies. Let us explore why case studies are considered invaluable in understanding and addressing mental health conditions.
Why case studies are valuable in mental health research
Case studies offer a unique opportunity to examine mental health conditions within the real-life context of individuals. Unlike large-scale studies that focus on statistical data, case studies provide a detailed examination of specific cases, allowing researchers to delve into the complexities of a particular condition or treatment approach. This micro-level analysis helps researchers gain a deeper understanding of the nuances and intricacies involved.
The role of case studies in providing detailed information about individual experiences
Through case studies, researchers can capture rich narratives and delve into the lived experiences of individuals facing mental health challenges. These stories help to humanize the condition and provide valuable insights that go beyond a list of symptoms or diagnostic criteria. By understanding the unique experiences, thoughts, and emotions of individuals, researchers can develop a more comprehensive understanding of mental health conditions and tailor interventions accordingly.
How case studies contribute to the development of treatment strategies
Case studies form a vital foundation for the development of effective treatment strategies. By examining a specific case in detail, researchers can identify patterns, factors influencing treatment outcomes, and areas where intervention may be particularly effective. Moreover, case studies foster an iterative approach to treatment development—an ongoing cycle of using data and experience to refine and improve interventions.
By examining multiple case studies, researchers can identify common themes and trends, leading to the development of evidence-based guidelines and best practices. This allows healthcare professionals to provide more targeted and personalized support to individuals facing mental health conditions.
Furthermore, case studies can shed light on potential limitations or challenges in existing treatment approaches. By thoroughly analyzing different cases, researchers can identify gaps in current treatments and focus on areas that require further exploration and innovation.
In summary, case studies are a vital component of mental health research, offering detailed insights into the lived experiences of individuals with mental health conditions. They provide a rich understanding of the complexities of these conditions and contribute to the development of effective treatment strategies. By leveraging the power of case studies, researchers can move closer to improving the lives of individuals facing mental health challenges.
Examining a Real-life Case Study of Depression
In order to gain a deeper understanding of depression, let us now turn our attention to a real-life case study. By exploring the journey of an individual navigating through depression, we can gain valuable insights into the complexities and challenges associated with this mental health condition.
Introduction to the selected case study
In this case study, we will focus on Jane, a 32-year-old woman who has been struggling with depression for the past two years. Jane’s case offers a compelling narrative that highlights the various aspects of depression, including its onset, symptoms, and the treatment journey.
Background information on the individual facing depression
Before the onset of depression, Jane led a fulfilling and successful life. She had a promising career, a supportive network of friends and family, and engaged in hobbies that brought her joy. However, a series of life stressors, including a demanding job, a breakup, and the loss of a loved one, began to take a toll on her mental well-being.
Jane’s background highlights a common phenomenon – depression can affect individuals from all walks of life, irrespective of their socio-economic status, age, or external circumstances. It serves as a reminder that no one is immune to mental health challenges.
Presentation of symptoms and initial diagnosis
Jane began noticing a shift in her mood, characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and a lack of interest in activities she once enjoyed. She experienced disruptions in her sleep patterns, appetite changes, and a general sense of hopelessness. Recognizing the severity of her symptoms, Jane sought help from a mental health professional who diagnosed her with major depressive disorder.
Jane’s case exemplifies the varied and complex symptoms associated with depression. While individuals may exhibit overlapping symptoms, the intensity and manifestation of those symptoms can vary greatly, underscoring the importance of personalized and tailored treatment approaches.
By examining this real-life case study of depression, we can gain an empathetic understanding of the challenges faced by individuals experiencing this mental health condition. Through Jane’s journey, we will uncover the treatment options available for depression and analyze the effectiveness of the chosen approach. The case study will allow us to explore the nuances of depression and provide valuable insights into the treatment landscape for this prevalent mental health condition.
The Treatment Journey
When it comes to treating depression, there are various options available, ranging from therapy to medication. In this section, we will provide an overview of the treatment options for depression and analyze the treatment plan implemented in the real-life case study.
Overview of the treatment options available for depression
Treatment for depression typically involves a combination of approaches tailored to the individual’s needs. The two primary treatment modalities for depression are psychotherapy (talk therapy) and medication. Psychotherapy aims to help individuals explore their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, while medication can help alleviate symptoms by restoring chemical imbalances in the brain.
Common forms of psychotherapy used in the treatment of depression include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy. These therapeutic approaches focus on addressing negative thought patterns, improving relationship dynamics, and gaining insight into underlying psychological factors contributing to depression.
In cases where medication is utilized, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed. These medications help rebalance serotonin levels in the brain, which are often disrupted in individuals with depression. Other classes of antidepressant medications, such as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), may be considered in specific cases.
Exploring the treatment plan implemented in the case study
In Jane’s case, a comprehensive treatment plan was developed with the intention of addressing her specific needs and symptoms. Recognizing the severity of her depression, Jane’s healthcare team recommended a combination of talk therapy and medication.
Jane began attending weekly sessions of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with a licensed therapist. This form of therapy aimed to help Jane identify and challenge negative thought patterns, develop coping strategies, and cultivate more adaptive behaviors. The therapeutic relationship provided Jane with a safe space to explore and process her emotions, ultimately helping her regain a sense of control over her life.
In conjunction with therapy, Jane’s healthcare provider prescribed an SSRI medication to assist in managing her symptoms. The medication was carefully selected based on Jane’s specific symptoms and medical history, and regular follow-up appointments were scheduled to monitor her response to the medication and adjust the dosage if necessary.
Analyzing the effectiveness of the treatment approach
The effectiveness of treatment for depression varies from person to person, and it often requires a period of trial and adjustment to find the most suitable intervention. In Jane’s case, the combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and medication proved to be beneficial. Over time, she reported a reduction in her depressive symptoms, an improvement in her overall mood, and increased ability to engage in activities she once enjoyed.
It is important to note that the treatment journey for depression is not always linear, and setbacks and challenges may occur along the way. Each individual responds differently to treatment, and adjustments might be necessary to optimize outcomes. Continuous communication between the individual and their healthcare team is crucial to addressing any concerns, monitoring progress, and adapting the treatment plan as needed.
By analyzing the treatment approach in the real-life case study, we gain insights into the various treatment options available for depression and how they can be tailored to meet individual needs. The combination of psychotherapy and medication offers a holistic approach, addressing both psychological and biological aspects of depression.
The Outcome and Lessons Learned
After undergoing treatment for depression, it is essential to assess the outcome and draw valuable lessons from the case study. In this section, we will discuss the progress made by the individual in the case study, examine the challenges faced during the treatment process, and identify key lessons learned.
Discussing the progress made by the individual in the case study
Throughout the treatment process, Jane experienced significant progress in managing her depression. She reported a reduction in depressive symptoms, improved mood, and a renewed sense of hope and purpose in her life. Jane’s active participation in therapy, combined with the appropriate use of medication, played a crucial role in her progress.
Furthermore, Jane’s support network of family and friends played a significant role in her recovery. Their understanding, empathy, and support provided a solid foundation for her journey towards improved mental well-being. This highlights the importance of social support in the treatment and management of depression.
Examining the challenges faced during the treatment process
Despite the progress made, Jane faced several challenges during her treatment journey. Adhering to the treatment plan consistently proved to be difficult at times, as she encountered setbacks and moments of self-doubt. Additionally, managing the side effects of the medication required careful monitoring and adjustments to find the right balance.
Moreover, the stigma associated with mental health continued to be a challenge for Jane. Overcoming societal misconceptions and seeking help required courage and resilience. The case study underscores the need for increased awareness, education, and advocacy to address the stigma surrounding mental health conditions.
Identifying the key lessons learned from the case study
The case study offers valuable lessons that can inform the treatment and support of individuals with depression:
1. Holistic Approach: The combination of psychotherapy and medication proved to be effective in addressing the psychological and biological aspects of depression. This highlights the need for a holistic and personalized treatment approach.
2. Importance of Support: Having a strong support system can significantly impact an individual’s ability to navigate through depression. Family, friends, and healthcare professionals play a vital role in providing empathy, understanding, and encouragement.
3. Individualized Treatment: Depression manifests differently in each individual, emphasizing the importance of tailoring treatment plans to meet individual needs. Personalized interventions are more likely to lead to positive outcomes.
4. Overcoming Stigma: Addressing the stigma associated with mental health conditions is crucial for individuals to seek timely help and access the support they need. Educating society about mental health is essential to create a more supportive and inclusive environment.
By drawing lessons from this real-life case study, we gain insights that can improve the understanding and treatment of depression. Recognizing the progress made, understanding the challenges faced, and implementing the lessons learned can contribute to more effective interventions and support systems for individuals facing depression.In conclusion, this article has explored the significance of mental health case studies in understanding and addressing depression, focusing on a real-life example. By delving into case studies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of depression and the profound impact it has on individuals and society.
Through our examination of the selected case study, we have learned valuable lessons about the nature of depression and its treatment. We have seen how the combination of psychotherapy and medication can provide a holistic approach, addressing both psychological and biological factors. Furthermore, the importance of social support and the role of a strong network in an individual’s recovery journey cannot be overstated.
Additionally, we have identified challenges faced during the treatment process, such as adherence to the treatment plan and managing medication side effects. These challenges highlight the need for ongoing monitoring, adjustments, and open communication between individuals and their healthcare providers.
The case study has also emphasized the impact of stigma on individuals seeking help for depression. Addressing societal misconceptions and promoting mental health awareness is essential to create a more supportive environment for those affected by depression and other mental health conditions.
Overall, this article reinforces the significance of case studies in advancing our understanding of mental health conditions and developing effective treatment strategies. Through real-life examples, we gain a more comprehensive and empathetic perspective on depression, enabling us to provide better support and care for individuals facing this mental health challenge.
As we conclude, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of continued research and exploration of mental health case studies. The more we learn from individual experiences, the better equipped we become to address the diverse needs of those affected by mental health conditions. By fostering a culture of understanding, support, and advocacy, we can strive towards a future where individuals with depression receive the care and compassion they deserve.
Similar Posts

Can You Have Bipolar and BPD? Understanding the Dual Diagnosis
Imagine living with two conflicting worlds inside your mind, constantly battling for control. One moment, you’re riding the waves of euphoria, feeling on top of the world; the next, you’re plummeting into the depths of despair,…

Natural Treatment for Postpartum Depression: Effective Remedies for New Moms
Imagine the joy and excitement of bringing new life into the world, only to find yourself overwhelmed with feelings of sadness, anxiety, and despair. This is the harsh reality for many new mothers experiencing postpartum depression….

Understanding How Anxiety Disorders Develop: Possible Causes and Triggers
Imagine feeling an intense sense of fear and unease, even when there is no real danger. Your heart races, your palms sweat, and your mind becomes consumed with worry. This is the experience of someone living…

Understanding Bipolar Denial: Causes, Signs, and Overcoming It
Imagine living in a world where your emotions swing like a pendulum, from the highest of highs to the lowest of lows. Where the very essence of who you are seems to fluctuate uncontrollably. This is…

Understanding the Symptoms of Childhood Anxiety Disorders
Childhood anxiety disorders are more prevalent than ever before, robbing our children of their potential to lead healthy, happy lives. Imagine a child waking up every morning, paralyzed by fear and worry, unable to fully participate…

How Long Does It Take for Vraylar to Take Effect?
Imagine living with a condition that constantly shifts your emotions, making you feel like you’re riding a rollercoaster of highs and lows. One moment, you’re on top of the world, full of energy and ideas. The…
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

4 Treatment of Depression
- Published: February 2013
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Chapter 4 covers the treatment of depression, and discusses popular myths regarding depression, its frequency, characteristics and diagnosis, and includes case studies, assessment, case conceptualization, intervention development and course of treatment, problems that may arise in therapy, ethical considerations, common mistakes in the course of treatment, relapse prevention, and cultural factors.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.

Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 05 April 2024
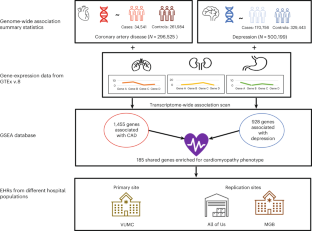
Genes associated with depression and coronary artery disease are enriched for cardiomyopathy and inflammatory phenotypes
- Kritika Singh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9872-7942 1 , 2 ,
- Hyunjoon Lee 3 , 4 , 5 na1 ,
- Julia M. Sealock 4 , 5 , 6 na1 ,
- Tyne Miller-Fleming 1 , 2 ,
- Peter Straub 1 , 2 ,
- Nancy J. Cox 1 , 2 ,
- Quinn S. Wells 7 ,
- Jordan W. Smoller 3 , 4 , 5 ,
- Emily C. Hodges 2 , 8 &
- Lea K. Davis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5143-2282 1 , 2 , 9 , 10 , 11
Nature Mental Health ( 2024 ) Cite this article
60 Accesses
103 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Gene regulation
Depression and coronary artery disease (CAD) are highly comorbid conditions. Approximately 40% of individuals who have one diagnosis will also develop the other within their lifetime. Despite the high prevalence of the comorbidity, the specific genes and pathways remain unknown. Here, by mapping known variants to genes, we identified genes, followed by pathways, that are associated with both depression and CAD. Next, we investigated the phenotypic consequences of the shared pathways in an electronic health record (EHR)-based setting. We identified 185 genes that were significantly associated with both depression and CAD and were enriched for inflammatory and cardiomyopathy phenotypes. We observed an increased rate of prevalent cardiomyopathy cases in individuals with comorbid depression–CAD compared with those with CAD alone in three large EHR datasets. The results of our study implicate genetically regulated inflammatory mechanisms in depression–CAD. Our results also raise the hypothesis that depression-associated CAD may be enriched for cardiomyopathy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
55,14 € per year
only 4,60 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
The effects of genetic and modifiable risk factors on brain regions vulnerable to ageing and disease
Jordi Manuello, Joosung Min, … Gwenaëlle Douaud

Genome-wide association studies
Emil Uffelmann, Qin Qin Huang, … Danielle Posthuma

The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence
Joanna Moncrieff, Ruth E. Cooper, … Mark A. Horowitz
Data availability
Data are available from Vanderbilt University Medical Center with institutional restrictions that apply to the acquisition, use and dissemination of data. To request reasonable access to data for work conducted in a non-profit academic setting, please contact the Vanderbilt Institute for Clinical and Translational Research ([email protected]) and request an application to the Integrated Data Access and Services Core.
Code availability
The code for the analysis is available at https://bitbucket.org/davislabteam/depression-cad/src/master/ .
Kendler, K. S., Gardner, C. O., Fiske, A. & Gatz, M. Major depression and coronary artery disease in the Swedish twin registry: phenotypic, genetic, and environmental sources of comorbidity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 66 , 857–863 (2009).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glassman, A. H. Depression and cardiovascular comorbidity. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 9 , 9–17 (2007).
Sullivan, M. et al. Depression in coronary heart disease. What is the appropriate diagnostic threshold? Psychosomatics 40 , 286–292 (1999).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
O’Neil, A. et al. Depression is a risk factor for incident coronary heart disease in women: an 18-year longitudinal study. J. Affect. Disord. 196 , 117–124 (2016).
Weeke, A., Juel, K. & Vaeth, M. Cardiovascular death and manic-depressive psychosis. J. Affect. Disord. 13 , 287–292 (1987).
Dennis, J. et al. Genetic risk for major depressive disorder and loneliness in sex-specific associations with coronary artery disease. Mol. Psychiatry 26 , 4254–4264 (2021).
Mazereeuw, G. et al. Platelet activating factors in depression and coronary artery disease: a potential biomarker related to inflammatory mechanisms and neurodegeneration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 37 , 1611–1621 (2013).
McCaffery, J. M. et al. Common genetic vulnerability to depressive symptoms and coronary artery disease: a review and development of candidate genes related to inflammation and serotonin. Psychosom. Med. 68 , 187–200 (2006).
Upadhyay, R. K. Emerging risk biomarkers in cardiovascular diseases and disorders. J. Lipids 2015 , 971453 (2015).
Shimokawa, H., Aarhus, L. L. & Vanhoutte, P. M. Porcine coronary arteries with regenerated endothelium have a reduced endothelium-dependent responsiveness to aggregating platelets and serotonin. Circ. Res. 61 , 256–270 (1987).
Brydon, L., Magid, K. & Steptoe, A. Platelets, coronary heart disease, and stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 20 , 113–119 (2006).
Huang, M. et al. Longitudinal association of inflammation with depressive symptoms: a 7-year cross-lagged twin difference study. Brain Behav. Immun. 75 , 200–207 (2019).
Beydoun, M. A. et al. White blood cell inflammatory markers are associated with depressive symptoms in a longitudinal study of urban adults. Transl. Psychiatry 6 , e895 (2016).
Kim, J.-M. et al. Changes in pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and late-life depression: a two year population based longitudinal study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 90 , 85–91 (2018).
Bränn, E. et al. Inflammatory markers in late pregnancy in association with postpartum depression—a nested case-control study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 79 , 146–159 (2017).
Bremmer, M. A. et al. Inflammatory markers in late-life depression: results from a population-based study. J. Affect. Disord. 106 , 249–255 (2008).
Martínez-Cengotitabengoa, M. et al. Peripheral inflammatory parameters in late-life depression: a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 , E2022 (2016).
Article Google Scholar
Gheysarzadeh, A. et al. Serum-based microRNA biomarkers for major depression: miR-16, miR-135a, and miR-1202. J. Res. Med. Sci. 23 , 69 (2018).
Schmidt, H. D., Shelton, R. C. & Duman, R. S. Functional biomarkers of depression: diagnosis, treatment, and pathophysiology. Neuropsychopharmacology 36 , 2375–2394 (2011).
Nurden, A. T. The biology of the platelet with special reference to inflammation, wound healing and immunity. Front. Biosci. 23 , 726–751 (2018).
Tsao, C.-W., Lin, Y.-S., Chen, C.-C., Bai, C.-H. & Wu, S.-R. Cytokines and serotonin transporter in patients with major depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 30 , 899–905 (2006).
Pandey, G. N. et al. Hyperactive phosphoinositide signaling pathway in platelets of depressed patients: effect of desipramine treatment. Psychiatry Res. 105 , 23–32 (2001).
van der Harst, P. & Verweij, N. Identification of 64 novel genetic loci provides an expanded view on the genetic architecture of coronary artery disease. Circ. Res. 122 , 433–443 (2018).
Howard, D. M. et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 22 , 343–352 (2019).
Barbeira, A. N. et al. Integrating predicted transcriptome from multiple tissues improves association detection. PLoS Genet. 15 , e1007889 (2019).
Sealock, J. M. et al. Use of the PsycheMERGE network to investigate the association between depression polygenic scores and white blood cell count. JAMA Psychiatry 78 , 1365 (2021).
Gidron, Y., Kupper, N., Kwaijtaal, M., Winter, J. & Denollet, J. Vagus–brain communication in atherosclerosis-related inflammation: a neuroimmunomodulation perspective of CAD. Atherosclerosis 195 , e1–e9 (2007).
Chan, K. L., Cathomas, F. & Russo, S. J. Central and peripheral inflammation link metabolic syndrome and major depressive disorder. Physiology 34 , 123–133 (2019).
Kempuraj, D. et al. Brain and peripheral atypical inflammatory mediators potentiate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11 , 216 (2017).
Sun, Y., Koyama, Y. & Shimada, S. Inflammation from peripheral organs to the brain: how does systemic inflammation cause neuroinflammation? Front Aging Neurosci 14 , 903455 (2022).
Twig, G. et al. White blood cell count and the risk for coronary artery disease in young adults. PLoS ONE 7 , e47183 (2012).
Zebrack, J. S., Muhlestein, J. B., Horne, B. D. & Anderson, J. L. C-reactive protein and angiographic coronary artery disease: independent and additive predictors of risk in subjects with angina. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 39 , 632–637 (2002).
Lu, Q. et al. Intranuclear cardiac troponin I plays a functional role in regulating Atp2a2 expression in cardiomyocytes. Genes Dis. 15 , 1689–1700 (2021).
Google Scholar
Alimadadi, A., Munroe, P. B., Joe, B. & Cheng, X. Meta-analysis of dilated cardiomyopathy using cardiac RNA-seq transcriptomic datasets. Genes 11 , 60 (2020).
Nakajima, K. et al. Brain-specific heterozygous loss-of-function of ATP2A2, endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ pump responsible for Darier’s disease, causes behavioral abnormalities and a hyper-dopaminergic state. Hum. Mol. Genet. 30 , 1762–1772 (2021).
Coste de Bagneaux, P. et al. A homozygous missense variant in CACNB4 encoding the auxiliary calcium channel beta4 subunit causes a severe neurodevelopmental disorder and impairs channel and non-channel functions. PLoS Genet. 16 , e1008625 (2020).
Andrade, A. et al. Genetic associations between voltage-gated calcium channels and psychiatric disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 , 3537 (2019).
Kanehisa, M. et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36 , D480–D484 (2007).
Xu, H. et al. A genome-wide association study of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy in African Americans. J. Pers. Med. 8 , 11 (2018).
Good, J.-M. et al. ACTN2 variant associated with a cardiac phenotype suggestive of left-dominant arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 6 , 15–19 (2020).
Haywood, N. J. et al. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations in the calponin-homology domain of ACTN2 affect actin binding and cardiomyocyte Z-disc incorporation. Biochem. J. 473 , 2485–2493 (2016).
Tiso, N. Identification of mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene in families affected with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy type 2 (ARVD2). Hum. Mol. Genet. 10 , 189–194 (2001).
Patel, R. et al. Variants of trophic factors and expression of cardiac hypertrophy in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 32 , 2369–2377 (2000).
Yadav, M. L., Bhasker, A. N., Kumar, A. & Mohapatra, B. Identification and characterization of genetic variants of TGFB1 in patients with congenital heart disease. Meta Gene 31 , 100987 (2022).
Bauer, R., MacGowan, G. A., Blain, A., Bushby, K. & Straub, V. Steroid treatment causes deterioration of myocardial function in the δ-sarcoglycan-deficient mouse model for dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 79 , 652–661 (2008).
Rutschow, D. et al. S151A δ-sarcoglycan mutation causes a mild phenotype of cardiomyopathy in mice. Eur J Hum Genet 22 , 119–125 (2014).
Coughlin, S. S. Post-traumatic stress disorder and cardiovascular disease. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 5 , 164–170 (2011).
Polimanti, R. et al. Understanding the comorbidity between posttraumatic stress severity and coronary artery disease using genome-wide information and electronic health records. Mol. Psychiatry 27 , 3961–3969 (2022).
Stein, M. B. et al. Genome-wide association analyses of post-traumatic stress disorder and its symptom subdomains in the Million Veteran Program. Nat. Genet. 53 , 174–184 (2021).
Pathak, G. A. et al. Genetically regulated multi-omics study for symptom clusters of posttraumatic stress disorder highlights pleiotropy with hematologic and cardio-metabolic traits. Mol. Psychiatry 27 , 1394–1404 (2022).
Pathak, G. A. et al. Genetic liability to posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms and its association with cardiometabolic and respiratory outcomes. JAMA Psychiatry 81 , 34–44 (2024).
Lynall, M.-E. et al. Peripheral blood cell-stratified subgroups of inflamed depression. Biol. Psychiatry 88 , 185–196 (2020).
McNally, L., Bhagwagar, Z. & Hannestad, J. Inflammation, glutamate, and glia in depression: a literature review. CNS Spectr. 13 , 501–510 (2008).
Troubat, R. et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: a review. Eur J Neurosci 53 , 151–171 (2021).
Eitel, I. et al. Inflammation in takotsubo cardiomyopathy: insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 20 , 422–431 (2010).
Adamo, L., Rocha-Resende, C., Prabhu, S. D. & Mann, D. L. Reappraising the role of inflammation in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 17 , 269–285 (2020).
Maisch, B., Ristic, A. D. & Pankuweit, S. Inflammatory cardiomyopathy and myocarditis. Herz 42 , 425–438 (2017).
Krejci, J., Mlejnek, D., Sochorova, D. & Nemec, P. Inflammatory cardiomyopathy: a current view on the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2016 , 4087632 (2016).
Tschöpe, C. et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 18 , 169–193 (2021).
Eitel, I. et al. Clinical characteristics and cardiovascular magnetic resonance findings in stress (takotsubo) cardiomyopathy. JAMA 306 , 277–286 (2011).
PubMed Google Scholar
Scally, C. et al. Myocardial and systemic inflammation in acute stress-induced (takotsubo) cardiomyopathy. Circulation 139 , 1581–1592 (2019).
Rroku, A., Grahl, S., Landmesser, U. & Heidecker, B. A case report of myocardial inflammation in takotsubo syndrome. A chicken-or-the-egg phenomenon. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 39 , 100958 (2022).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lonsdale, J. et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 45 , 580–585 (2013).
Bowton, E. et al. Biobanks and electronic medical records: enabling cost-effective research. Sci. Transl. Med. 6 , 234cm3 (2014).
The All of Us Research Program Investigators. The ‘All of Us’ Research Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 , 668–676 (2019).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the American Heart Association Fellowship AHA827137 (K.S.), National Institute of Mental Health R56MH120736 (L.K.D.), National Institute of Mental Health R01 H118233 (L.K.D. and J.W.S.), National Institutes of Health 1F31MH124306-01A1 (J.M.S.), and National Institutes of Health 1R01HL140074 (Q.S.W.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the paper. The de-identified EHR used at VUMC was supported by the National Center for Research Resources, Grant UL1 RR024975-01, and is now at the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Grant 2 UL1 TR000445-06. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. The dataset(s) used for the analyses described were obtained from Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s BioVU, which is supported by numerous sources: institutional funding, private agencies and federal grants. These include the NIH-funded Shared Instrumentation Grant S10RR025141, and CTSA grants UL1TR002243, UL1TR000445 and UL1RR024975. Genomic data are also supported by investigator-led projects that include U01HG004798, R01NS032830, RC2GM092618, P50GM115305, U01HG006378, U19HL065962 and R01HD074711, and additional funding sources listed at https://victr.vumc.org/biovu-funding/ . The All of Us Research Program is supported by grants through the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549, 1 OT2 OD026554, 1 OT2 OD026557, 1 OT2 OD026556, 1 OT2 OD026550, 1 OT2 OD026552, 1 OT2 OD026553, 1 OT2 OD026548, 1 OT2 OD026551 and 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA#: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205 and 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277, 3 OT2 OD025315, 1 OT2 OD025337 and 1 OT2 OD025276. In addition to the funded partners, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the contributions made by its participants.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Hyunjoon Lee, Julia M. Sealock.
Authors and Affiliations
Division of Genetic Medicine, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Kritika Singh, Tyne Miller-Fleming, Peter Straub, Nancy J. Cox & Lea K. Davis
Vanderbilt Genetics Institute, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Kritika Singh, Tyne Miller-Fleming, Peter Straub, Nancy J. Cox, Emily C. Hodges & Lea K. Davis
Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Genetics Unit, Center for Genomic Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
Hyunjoon Lee & Jordan W. Smoller
Center for Precision Psychiatry, Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
Hyunjoon Lee, Julia M. Sealock & Jordan W. Smoller
Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research, Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA
Analytical and Translational Genetics Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
Julia M. Sealock
Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Quinn S. Wells
Department of Biochemistry, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN, USA
Emily C. Hodges
Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Lea K. Davis
Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
Department of Medicine and Biomedical Informatics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
K.S. and L.K.D. conceptualized and designed the work. K.S., J.M.S., T.M.-F., P.S. and H.L. implemented the computational procedures and performed data analysis. N.J.C., J.W.S., Q.S.W. and E.C.H. provided important clinical and intellectual insights. All authors read, edited and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lea K. Davis .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
J.W.S. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Sensorium Therapeutics (with equity) and has received an honorarium for an internal seminar Tempus Labs. He is a principal investigator of a collaborative study of the genetics of depression and bipolar disorder sponsored by 23andMe for which 23andMe provides analysis time as in-kind support but no payments. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Mental Health thanks Janitza Montalvo-Ortiz and the other, anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary methods and results.
Reporting Summary
Supplementary tables.
Supplementary Tables 1–10.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Singh, K., Lee, H., Sealock, J.M. et al. Genes associated with depression and coronary artery disease are enriched for cardiomyopathy and inflammatory phenotypes. Nat. Mental Health (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-024-00219-z
Download citation
Received : 14 January 2023
Accepted : 22 February 2024
Published : 05 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-024-00219-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
The right amygdala and migraine: Analyzing volume reduction and its relationship with symptom severity
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Physiology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 2 Department of Neurology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3 Department of Radiology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 4 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital, Yokohama, Japan.
- PMID: 38557587
- PMCID: PMC10984416
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301543
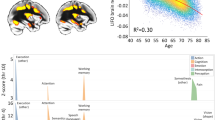
This study aimed to explore the relationship between gray matter volume changes and various clinical parameters in patients with migraine, focusing on symptom severity, quality of life, and states of depression and anxiety. Using a case-control design, we examined 33 patients with migraine, with or without aura, and 27 age-matched healthy subjects. We used magnetic resonance imaging to assess the volumes of 140 bilateral brain regions. Clinical evaluations included the Migraine Disability Assessment, the Migraine Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire, the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression scale, Spielberger's State and Trait Anxiety scales, and the Japanese version of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment. We compared the scores of these measures between migraine patients and healthy controls to examine the interplay between brain structure and clinical symptoms. Significant volumetric differences were observed in the pallidum and amygdala between migraine patients and healthy individuals. The reduction in the right amygdala volume correlated significantly with migraine severity as measured by the Migraine Disability Assessment. Path analysis revealed a model where Migraine Disability Assessment scores were influenced by Migraine Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire outcomes, which were further affected by depression, anxiety, and a low right pallidum volume. Our findings suggest that the chronicity and severity of migraine headaches specifically affect the right amygdala. Our path model suggests a complex relationship whereby migraine disability is strongly influenced by quality of life, which is, in turn, affected by psychological states, such as anxiety and depression.
Copyright: © 2024 Kosuge et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Migraine Disorders* / diagnosis
- Migraine with Aura*
- Quality of Life
Grants and funding
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(3); 2023 Mar
- PMC10097604

A Case Study of Depression in High Achieving Students Associated With Moral Incongruence, Spiritual Distress, and Feelings of Guilt
Bahjat najeeb.
1 Institute of Psychiatry, Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, PAK
Muhammad Faisal Amir Malik
Asad t nizami, sadia yasir.
Psychosocial and cultural factors play an important, but often neglected, role in depression in young individuals. In this article, we present two cases of young, educated males with major depressive disorder and prominent themes of guilt and spiritual distress. We explore the relationship between moral incongruence, spiritual distress, and feelings of guilt with major depressive episodes by presenting two cases of depression in young individuals who were high-achieving students. Both cases presented with low mood, psychomotor slowing, and selective mutism. Upon detailed history, spiritual distress and feelings of guilt due to internet pornographic use (IPU) and the resulting self-perceived addiction and moral incongruence were linked to the initiation and progression of major depressive episodes. The severity of the depressive episode was measured using the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D). Themes of guilt and shame were measured using the State of Guilt and Shame Scale (SSGS). High expectations from the family were also a source of stress. Hence, it is important to keep these factors in mind while managing mental health problems in young individuals. Late adolescence and early adulthood are periods of high stress and vulnerabe to mental illness. Psychosocial determinants of depression in this age group generally go unexplored and unaddressed leading to suboptimal treatment, particularly in developing countries. Further research is needed to assess the importance of these factors and to determine ways to mitigate them.
Introduction
More attention needs to be paid to the psychological and societal factors which precipitate, prolong, and cause a relapse of depression in high-achieving young individuals. A young, bright individual has to contend with the pressures of -- often quite strenuous -- moral and financial expectations from the family, moral incongruence, spiritual distress, and feelings of guilt.
Moral incongruence is the distress that develops when a person continues to behave in a manner that is at odds with their beliefs. It may be associated with self-perceptions of addictions, including, for example, to pornographic viewing, social networking, and online gaming [ 1 ]. Perceived addiction to pornographic use rather than use is related to the high incidence of feelings of guilt and shame and predicts religious and spiritual struggle [ 2 - 3 ]. Guilt is a negative emotional and cognitive experience that occurs when a person believes that they have negated a standard of conduct or morals. It is a part of the diagnostic criteria for depression and various rating scales for depressive disorders [ 4 ]. Generalized guilt has a direct relationship with major depressive episodes. Guilt can be a possible target for preventive as well as therapeutic interventions in patients who experience major depressive episodes [ 5 ].
We explored the relationship between moral incongruence, spiritual distress, and feelings of guilt with major depressive episodes in high-achieving students. Both patients presented with symptoms of low mood, extreme psychomotor slowing, decreased oral intake, decreased sleep, and mutism. The medical evaluation and lab results were unremarkable. The severity of depressive episodes was measured using the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D). Themes of guilt and shame were measured by using the State of Guilt and Shame Scale (SSGS). This case study was presented as a poster abstract at the ‘RCPsych Faculty of General Adult Psychiatry Annual Conference 2021.’
Case presentation
A 25-year-old Sunni Muslim, Punjabi male educated till Bachelors presented with a one-month history of fearfulness, weeping spells during prolonged prostration, social withdrawal, complaints of progressively decreasing verbal communication to the extent of giving nods and one-word answers, and decreased oral intake. His family believed that the patient's symptoms were the result of ‘Djinn’ possession. This was the patient’s second episode. The first episode was a year ago with similar symptoms of lesser severity that resolved on its own. Before being brought to us, he had been taken to multiple faith healers. No history of substance use was reported. Psychosexual history could not be explored at the time of admission. His pre-morbid personality was significant for anxious and avoidant traits.
On mental state examination (MSE), the patient had psychomotor retardation. He responded non-verbally, and that too slowly. Once, he wept excessively and said that he feels guilt over some grave sin. He refused to explain further, saying only that ‘I am afraid of myself.’ All baseline investigations returned normal. His score on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) was 28 (Very Severe). A diagnosis of major depressive disorder was made. The patient was started on tab sertraline 50 mg per day and tab olanzapine 5 mg per day. After the second electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), his psychomotor retardation improved and he began to open up about his stressors. His HAM-D score at this time was 17 (moderate). He revealed distress due to feelings of excessive guilt and shame due to moral incongruence secondary to internet pornography use (IPU). The frequency and duration of IPU increased during the last six months preceding current illness. That, according to him, led him to withdraw socially and be fearful. He felt the burden of the high financial and moral expectations of the family. He complained that his parents were overbearing and overinvolved in his life. His family lacked insight into the cause of his illness and had difficulty accepting his current state. All these factors, particularly spiritual distress, were important in precipitating his illness. He scored high on both the shame and guilt domains (14/25, and 20/25, respectively) of the State of Shame and Guilt Scale (SSGS).
He was discharged after three weeks following a cycle of four ECTs, psychotherapy, and psychoeducation of the patient and family. At the time of discharge, his HAM-D score was 10 (mild) and he reported no distress due to guilt or feeling of shame. He has been doing well for the past 5 months on outpatient follow-up.
A 21-year-old Sunni Muslim, Punjabi male, high-achieving student of high school presented with low mood, low energy, anhedonia, weeping spells, decreased oral intake, decreased talk, and impaired biological functions. His illness was insidious in onset and progressively worsened over the last 4 months. This was his first episode. He was brought to a psychiatric facility after being taken to multiple faith healers. Positive findings on the MSE included psychomotor slowing, and while he followed commands, he remained mute throughout the interview. Neurological examination and laboratory findings were normal. His score on HAM-D was 24 (very severe). He was diagnosed with major depressive disorder and started on tab lorazepam 1 mg twice daily with tab mirtazapine 15 mg which was built up to 30 mg once daily. He steadily improved, and two weeks later his score on HAM-D was 17 (moderate). His scores on SSGS signified excessive shame and guilt (16/25, and 21/25; respectively). He communicated his stressors which pertained to the psychosexual domain: he started masturbating at the age of 15, and he felt guilt following that but continued to do so putting him in a state of moral incongruence. He perceived his IPU as ‘an addiction’ and considered it a ‘gunahe kabira’ (major sin) and reported increased IPU in the months leading to the current depressive episode leading to him feeling guilt and anguish. Initially, during his illness, he was taken to multiple faith healers as the family struggled to recognize the true nature of the disease. Their understanding of the illness was of him being under the influence of ‘Kala Jadu’ (black magic). His parents had high expectations of him due to him being their only male child. After 3 weeks of treatment and psychotherapy, his condition improved and his HAM-D score came out to be 08 (mild). He was discharged on 30 mg mirtazapine HS and seen on fortnightly visits. His guilt and shame resolved with time after the resolution of depressive symptoms and counseling. We lost the follow-up after 6 months.
Late adolescence and young adulthood can be considered a unique and distinct period in the development of an individual [ 6 ]. It is a period of transition marked by new opportunities for development, growth, and evolution, as well as bringing new freedom and responsibilities. At the same time, this period brings interpersonal conflicts and an increased vulnerability to mental health disorders such as depression and suicidality. Biological, social, and psychological factors should all be explored in the etiology of mental health problems presenting at this age [ 6 ].
Socio-cultural factors played a significant role in the development and course of disease in our patients, and these included the authoritarian parenting style, initial lack of awareness about psychiatric illnesses causing a delay in seeking treatment, high expressed emotions in the family, and the burden of expectations from the family and the peer group. The strict and often quite unreasonable societal and family expectations in terms of what to achieve and how to behave and the resultant onus on a high-scoring, bright young individual make for a highly stressful mental state.
We used the ICD-10 criteria to diagnose depression clinically in our patients and the HAMD-17 to measure the severity of symptoms [ 7 ]. Both our patients had scores signifying severe depression initially. Psychomotor retardation was a prominent and shared clinical feature. Psychomotor retardation is the slowing of cognitive and motor functioning, as seen in slowed speech, thought processes, and motor movements [ 8 - 9 ]. The prevalence of psychomotor retardation in major depressive disorder ranges from 60% to 70% [ 10 ]. While psychomotor retardation often responds poorly to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI), both tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants (NaSSA) produce a better response [ 9 , 11 ]. In addition, ECT shows a high treatment response in cases with significant psychomotor retardation [ 11 - 12 ].
A growing body of evidence shows that shame and guilt are features of numerous mental health problems. Guilt is the negative emotional and cognitive experience that follows the perception of negating or repudiating a set of deeply held morals [ 4 ]. Guilt can be generalized as well as contextual and is distinct from shame [ 13 ]. The distinction between guilt and shame allows for an independent assessment of the association of both guilt and shame with depressive disorder. As an example, a meta-analysis of 108 studies including 22,411 individuals measuring the association of shame and guilt in patients with depressive disorder found both shame and guilt to have a positive association with depressive symptoms. This association was stronger for shame (r=0.43) than for guilt (r=0.28) [ 14 ]. In our study, we used the State of Shame and Guilt Scale (SSGS), to measure the feelings of guilt and shame [ 15 ]. The SSGS is a self-reported measure and consists of 5 items each for subsets of guilt and shame. SSGS scores showed high levels of guilt and shame in both of our patients.
During the course of treatment, we paid special attention to the psychological, cultural, and social factors that likely contributed to the genesis of the illness, delayed presentation to seek professional help, and could explain the recurrence of the depressive episodes. In particular, we observe the importance, particularly in this age group, of family and societal pressure, spiritual distress, moral incongruence, and feelings of guilt and shame. Moral incongruence is when a person feels that his behavior and his values or judgments about that behavior are not aligned. It can cause a person to more negatively perceive a behavior. As an example, the presence of moral congruence in an individual is a stronger contributor to perceiving internet pornographic use (IPU) as addictive than the actual use itself [ 16 ]. Therefore, moral congruence has a significant association with increased distress about IPU, enhanced psychological distress in general, and a greater incidence of perceived addiction to IPU [ 16 ].
Self-perceived addiction is an individual’s self-judgment that he or she belongs to the group of addicts. The pornography problems due to moral incongruence (PPMI) model is one framework that predicts the factors linking problematic pornographic use with self-perceived addiction. This model associates moral incongruence with self-perceived addiction to problematic pornographic use [ 17 ]. A recent study on the US adult population also showed a high association of guilt and shame with moral incongruence regarding IPU [ 18 ]. Another factor of importance in our patients was spiritual distress, which is the internal strain, tension, and conflict with what people hold sacred [ 19 ]. Spiritual distress can be intrapersonal, interpersonal, or supernatural [ 20 ]. Research indicates that IPU causes people to develop spiritual distress that can ultimately lead to depression [ 16 - 17 ].
Conclusions
In both our cases the initial presentation was that of psychomotor slowing, selective mutism, and affective symptoms of low mood, therefore, a diagnosis of depressive illness was made. One week into treatment, improvement was noted both clinically as well as on the psychometric scales. Upon engaging the patients to give an elaborate psychosexual history, moral incongruence, spiritual distress, and feelings of guilt, linked particularly to self-perceived addiction to IPU were found. Sensitivity to the expectations of the parents, the cognizance of failing them because of illness, and their own and family’s lack of understanding of the situation were additional sources of stress. Hence, it is imperative to note how these factors play an important role in the initiation, progression, and relapse of mental health problems in young individuals.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the participants of this study for their cooperation.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Human Ethics
Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sara, a 35-year-old married female. Sara was referred to treatment after having a stillbirth. Sara showed symptoms of grief, or complicated bereavement, and was diagnosed with major depression, recurrent. The clinician recommended interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a duration of 12 weeks. Bleiberg, K.L., & Markowitz, J.C. (2008).
When a patient with depression is feeling sleepy, be aware of sleep apnoea. A 67-year-old man was referred to an outpatient clinic of geriatric psychiatry because of persistent symptoms of depression and anxiety, accompanied by sleepiness. The latter had been evaluated multiple times in the general practice over several years; each time it was ...
Diagnosis of depression can be made using the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) or the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Disease and Related Health Problems (ICD-10). 5 (Refer to Appendix 3 and 4, pages 73-76 in CPG.) 6,7
the case study had a therapist who was a doctoral level graduate student in clinical psychology trained in CBT who received weekly supervision from a licensed clinical psychologist with a Ph.D. Qualitative data for this case study were analyzed by reviewing progress notes and video recordings of therapy sessions. SESSIONS 1-4
Dr. SooJeong Youn: This case highlights the importance of attending to the intricate, multilevel, systemic factors that affect the mental health experience and clinical presentation of patients ...
Key Clinical Message. We present an evolutionary-driven cognitive-behavioral intervention for a moderately depressed patient. Standard cognitive and behavioral therapy techniques focused on the patient's perfectionistic and self-downing beliefs, while novel, evolutionary-informed techniques were used to guide behavioral activation and conceptualize secondary emotional problems related to anger.
This clinical case is part of a feasibility study assessing the acceptability of Be a Mom Coping with Depression, and to our knowledge, this is the first blended CBT intervention developed for the treatment of PPD. In this case study, the intervention was effective in reducing anxiety and depressive symptoms.
Abstract. Depression is a common mental disorder affecting more than 264 million people worldwide. The first-line treatment for most cases of depression are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors ...
Interpersonal Therapy versus Medication: In a study of 239 outpatients diagnosed with major depressive disorder in a NIMH 16-week multi-center clinical trial, participants were assigned to interpersonal therapy, CBT, imipramine with clinical management, or placebo with clinical management.
Background: There is ample evidence of the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for depression in adolescents, including Puerto Rican adolescents. However, there is still a high percentage of adolescents who do not respond to a standard "dose" of 12 sessions of CBT. This clinical case study explores the characteristics associated with treatment response in a Puerto Rican ...
Patient Case Presentation. Figure 1. Blue and silver stethoscope (Pixabay, N.D.) Ms. S.W. is a 48-year-old white female who presented to an outpatient community mental health agency for evaluation of depressive symptoms. Over the past eight weeks she has experienced sad mood every day, which she describes as a feeling of hopelessness and emptiness.
current issue. current issue; browse recently published; browse full issue index; learning/cme
depression (e.g., avoidance, difficulty concentrating and making decisions, and fatigue) as additional signs of incompetence. Once he became depressed, he interpreted many of his experiences through the lens of his core belief of incompetence or failure. Three of these situations are noted at the bottom of the Case Conceptualization Diagram.
Interpersonal therapy emphasizes improving relationships. The therapy is brief and focuses on the problems that precipitated the current depressive episode. It helps the adolescent to reduce and cope with stress. Two studies 23, 24 have shown its effectiveness in reducing depression.
Clinician diagnosis means that depression levels were determined by a clinician based on interview transcripts or online posts. Among the 99 studies using language cues, only two identified ...
The case study underscores the need for increased awareness, education, and advocacy to address the stigma surrounding mental health conditions. Identifying the key lessons learned from the case study. The case study offers valuable lessons that can inform the treatment and support of individuals with depression: 1.
In this case situation a good cooperation between the clinical psychologist, psychotherapist and psy chiatrist wa s crucial to increase the patient compliance to the medical and psychotherapeutic ...
Chapter 4 covers the treatment of depression, and discusses popular myths regarding depression, its frequency, characteristics and diagnosis, and includes case studies, assessment, case conceptualization, intervention development and course of treatment, problems that may arise in therapy, ethical considerations, common mistakes in the course ...
Depression is a highly prevalent and severely disabling disease. The treatment effects, intensity and onset time of antidepressants have been highlighted in many studies. Recent studies on the rapid-onset of antidepressant response focused on the effect of a single low dose of intravenous ketamine.
A case study of person with depression: a cognitive behavioural case work approach Priyanka Saikia1, Nilesh Maruti Gujar2 ... Clinical social workers using CBT can possibly tackle interpersonal and social problems while treating individuals with mood disorders. The empirical evidence identifies the implication of CBT for clinical social workers ...
Clinical depression, also known as major depressive disorder (MDD), is a mental health condition that causes a persistently low or depressed mood and a loss of interest in activities that once brought joy. ... Studies show that the combination of these treatments is more effective than either of them alone. Psychotherapy involves talking with a ...
The clinical co-occurrence of depression and cardiomyopathy, taken together with findings from the TWAS implicating immune genes, raises the hypothesis that chronic low-grade inflammation may ...
In a study, part of the findings showed that low levels of education have been shown to be linked to post-stroke depression (but not severe or clinical depression outcomes) . A study within a systematic review indicated that having only primary education was associated with a higher risk of depression compared to having secondary or higher ...
This study aimed to explore the relationship between gray matter volume changes and various clinical parameters in patients with migraine, focusing on symptom severity, quality of life, and states of depression and anxiety. Using a case-control design, we examined 33 patients with migraine, with or without aura, and 27 age-matched healthy subjects.
The severity of depressive episodes was measured using the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D). Themes of guilt and shame were measured by using the State of Guilt and Shame Scale (SSGS). This case study was presented as a poster abstract at the 'RCPsych Faculty of General Adult Psychiatry Annual Conference 2021.'