Page last updated : March 1, 2024

Introduction to Web3
Centralization has helped onboard billions of people to the World Wide Web and created the stable, robust infrastructure on which it lives. At the same time, a handful of centralized entities have a stronghold on large swathes of the World Wide Web, unilaterally deciding what should and should not be allowed.
Web3 is the answer to this dilemma. Instead of a Web monopolized by large technology companies, Web3 embraces decentralization and is being built, operated, and owned by its users. Web3 puts power in the hands of individuals rather than corporations. Before we talk about Web3, let's explore how we got here.
.css-1qbzvaj{transition-property:var(--eth-transition-property-common);transition-duration:var(--eth-transition-duration-fast);transition-timing-function:var(--eth-transition-easing-ease-out);cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;outline:2px solid transparent;outline-offset:2px;color:var(--eth-colors-primary-base);text-underline-offset:3px;position:absolute;right:100%;opacity:0;-webkit-transition:opacity 0.1s ease-in-out;transition:opacity 0.1s ease-in-out;}.css-1qbzvaj:hover,.css-1qbzvaj[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:var(--eth-colors-primary-hover);}.css-1qbzvaj:focus-visible,.css-1qbzvaj[data-focus-visible]{box-shadow:var(--eth-shadows-none);outline:2px solid;outline-color:var(--eth-colors-primary-hover);outline-offset:2px;border-radius:var(--eth-radii-sm);}.css-1qbzvaj[data-inline-link]:visited{color:var(--eth-colors-primary-visited);}[role=group]:hover .css-1qbzvaj,[role=group][data-hover] .css-1qbzvaj,[data-group]:hover .css-1qbzvaj,[data-group][data-hover] .css-1qbzvaj,.group:hover .css-1qbzvaj,.group[data-hover] .css-1qbzvaj{opacity:1;}.css-1qbzvaj:focus,.css-1qbzvaj[data-focus]{opacity:1;} .css-1ff30mc{width:1em;height:1em;display:inline-block;line-height:1em;-webkit-flex-shrink:0;-ms-flex-negative:0;flex-shrink:0;color:currentColor;font-size:var(--eth-fontSizes-xl);-webkit-margin-end:var(--eth-space-1);margin-inline-end:var(--eth-space-1);} The early Web
Most people think of the Web as a continuous pillar of modern life—it was invented and has just existed since. However, the Web most of us know today is quite different from originally imagined. To understand this better, it's helpful to break the Web's short history into loose periods—Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
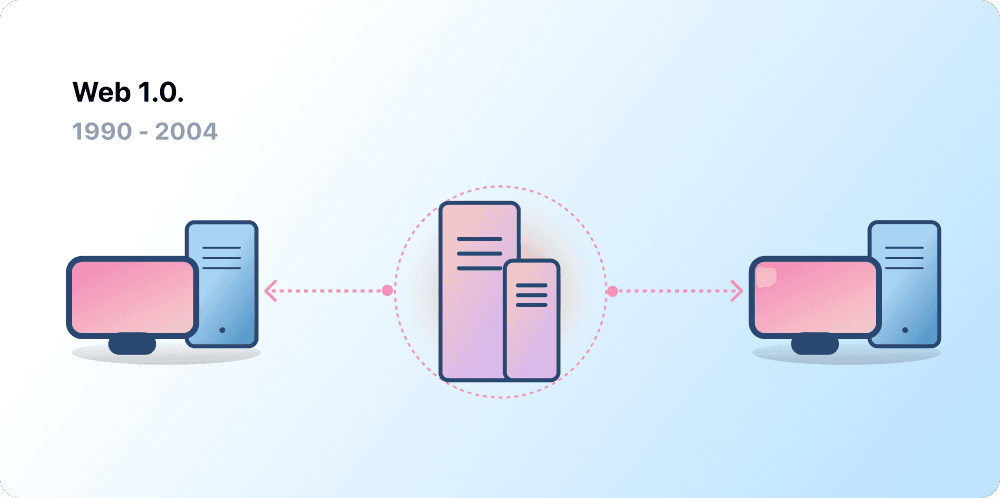
Web 1.0: Read-Only (1990-2004)
In 1989, at CERN, Geneva, Tim Berners-Lee was busy developing the protocols that would become the World Wide Web. His idea? To create open, decentralized protocols that allowed information-sharing from anywhere on Earth.
The first inception of Berners-Lee's creation, now known as 'Web 1.0', occurred roughly between 1990 to 2004. Web 1.0 was mainly static websites owned by companies, and there was close to zero interaction between users - individuals seldom produced content - leading to it being known as the read-only web.
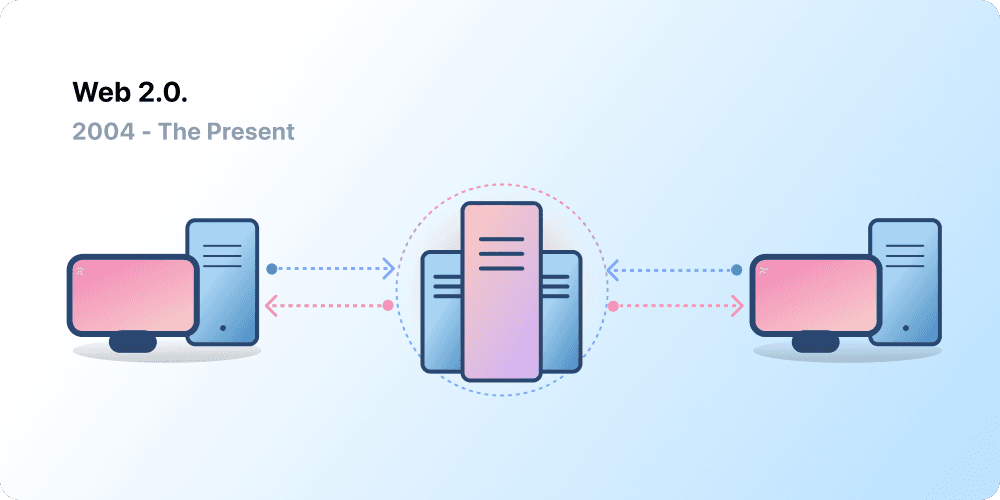
Web 2.0: Read-Write (2004-now)
The Web 2.0 period began in 2004 with the emergence of social media platforms. Instead of a read-only, the web evolved to be read-write. Instead of companies providing content to users, they also began to provide platforms to share user-generated content and engage in user-to-user interactions. As more people came online, a handful of top companies began to control a disproportionate amount of the traffic and value generated on the web. Web 2.0 also birthed the advertising-driven revenue model. While users could create content, they didn't own it or benefit from its monetization.
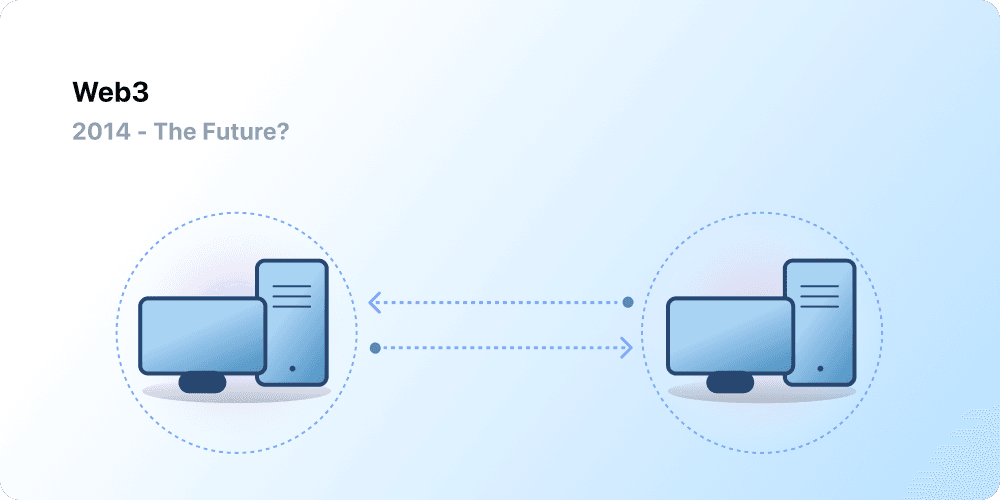
Web 3.0: Read-Write-Own
The premise of 'Web 3.0' was coined by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood shortly after Ethereum launched in 2014. Gavin put into words a solution for a problem that many early crypto adopters felt: the Web required too much trust. That is, most of the Web that people know and use today relies on trusting a handful of private companies to act in the public's best interests.
What is Web3?
Core ideas of web3.
Although it's challenging to provide a rigid definition of what Web3 is, a few core principles guide its creation.
- Web3 is decentralized: instead of large swathes of the internet controlled and owned by centralized entities, ownership gets distributed amongst its builders and users.
- Web3 is permissionless: everyone has equal access to participate in Web3, and no one gets excluded.
- Web3 has native payments: it uses cryptocurrency for spending and sending money online instead of relying on the outdated infrastructure of banks and payment processors.
- Web3 is trustless: it operates using incentives and economic mechanisms instead of relying on trusted third-parties.
Why is Web3 important?
Although Web3's killer features aren't isolated and don't fit into neat categories, for simplicity we've tried to separate them to make them easier to understand.
Web3 gives you ownership of your digital assets in an unprecedented way. For example, say you're playing a web2 game. If you purchase an in-game item, it is tied directly to your account. If the game creators delete your account, you will lose these items. Or, if you stop playing the game, you lose the value you invested into your in-game items.
Non-fungible token (NFT)
Censorship resistance.
The power dynamic between platforms and content creators is massively imbalanced.
OnlyFans is a user-generated adult content site with over 1-million content creators, many of which use the platform as their primary source of income. In August 2021, OnlyFans announced plans to ban sexually explicit content. The announcement sparked outrage amongst creators on the platform, who felt they were getting robbed of an income on a platform they helped create. After the backlash, the decision got quickly reversed. Despite the creators winning this battle, it highlights a problem for Web 2.0 creators: you lose the reputation and following you accrued if you leave a platform.
On Web3, your data lives on the blockchain. When you decide to leave a platform, you can take your reputation with you, plugging it into another interface that more clearly aligns with your values.
Web 2.0 requires content creators to trust platforms not to change the rules, but censorship resistance is a native feature of a Web3 platform.
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)
As well as owning your data in Web3, you can own the platform as a collective, using tokens that act like shares in a company. DAOs let you coordinate decentralized ownership of a platform and make decisions about its future.
Smart contract
However, people define many Web3 communities as DAOs. These communities all have different levels of decentralization and automation by code. Currently, we are exploring what DAOs are and how they might evolve in the future.
Traditionally, you would create an account for every platform you use. For example, you might have a Twitter account, a YouTube account, and a Reddit account. Want to change your display name or profile picture? You have to do it across every account. You can use social sign-ins in some cases, but this presents a familiar problem—censorship. In a single click, these platforms can lock you out of your entire online life. Even worse, many platforms require you to trust them with personally identifiable information to create an account.
Ethereum Name Service (ENS)
Native payments, web3 limitations.
Despite the numerous benefits of Web3 in its current form, there are still many limitations that the ecosystem must address for it to flourish.
Accessibility
User experience.
The technical barrier to entry to using Web3 is currently too high. Users must comprehend security concerns, understand complex technical documentation, and navigate unintuitive user interfaces. Wallet providers , in particular, are working to solve this, but more progress is needed before Web3 gets adopted en masse.
Web3 introduces new paradigms that require learning different mental models than the ones used in Web2.0. A similar education drive happened as Web1.0 was gaining popularity in the late 1990s; proponents of the world wide web used a slew of educational techniques to educate the public from simple metaphors (the information highway, browsers, surfing the web) to television broadcasts (opens in a new tab) . Web3 isn't difficult, but it is different. Educational initiatives informing Web2 users of these Web3 paradigms are vital for its success.
Ethereum.org contributes to Web3 education through our Translation Program , aiming to translate important Ethereum content to as many languages as possible.
Centralized infrastructure
The Web3 ecosystem is young and quickly evolving. As a result, it currently depends mainly on centralized infrastructure (GitHub, Twitter, Discord, etc.). Many Web3 companies are rushing to fill these gaps, but building high-quality, reliable infrastructure takes time.
A decentralized future
Web3 is a young and evolving ecosystem. Gavin Wood coined the term in 2014, but many of these ideas have only recently become a reality. In the last year alone, there has been a considerable surge in the interest in cryptocurrency, improvements to layer 2 scaling solutions, massive experiments with new forms of governance, and revolutions in digital identity.
We are only at the beginning of creating a better Web with Web3, but as we continue to improve the infrastructure that will support it, the future of the Web looks bright.
How can I get involved
- Get a wallet
- Find a community
- Explore Web3 applications
- Build on Web3
Further reading
Web3 isn’t rigidly defined. Various community participants have different perspectives on it. Here are a few of them:
- What is Web3? The Decentralized Internet of the Future Explained (opens in a new tab) – Nader Dabit
- Making Sense of Web 3 (opens in a new tab) – Josh Stark
- Why Web3 Matters (opens in a new tab) — Chris Dixon
- Why Decentralization Matters (opens in a new tab) - Chris Dixon
- The Web3 Landscape (opens in a new tab) – a16z
- The Web3 Debate (opens in a new tab) – Packy McCormick
Test your Ethereum knowledge
Was this article helpful.

The next phase of the internet is coming: Here’s what you need to know about Web3
Assistant Professor, Journalism, Toronto Metropolitan University
Disclosure statement
Adrian Ma does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Toronto Metropolitan University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation CA.
Toronto Metropolitan University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
View all partners
The rapid growth of cryptocurrencies and virtual non-fungible tokens have dominated news headlines in recent years. But not many may see how these modish applications connect together in a wider idea being touted by some as the next iteration of the internet — Web3.
There are many misconceptions surrounding this buzzy (and, frankly, fuzzy) term, including the conflation of Web3 with Web 3.0. Here’s what you need to know about these terms.
What is Web3?
Since Web3 is still a developing movement, there’s no universal agreement among experts about its definition. Simply put, Web3 is envisioned to be a “ decentralized web ecosystem ,” empowering users to bypass internet gatekeepers and retain ownership of their data.
This would be done through blockchain ; rather than relying on single servers and centralized databases, Web3 would run off of public ledgers where data is stored on computer networks that are chained together.
A decentralized Web3 would fundamentally change how the internet operates — financial institutions and tech companies would no longer need to be intermediaries of our online experiences.
As one business reporter put it :
“In a Web3 world, people control their own data and bounce around from social media to email to shopping using a single personalized account, creating a public record on the blockchain of all of that activity.”
Web3’s blockchain-based infrastructure would open up intriguing possibilities by ushering in the era of the “ token economy .” The token economy would allow users to monetize their data by providing them with tokens for their online interactions. These tokens could offer users perks or benefits, including ownership stakes in content platforms or voting rights in online communities.
To better understand Web3, it helps to step back and see how the internet developed into what it is now.
Web 1.0: The ‘read-only’ web
Computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee is credited with inventing the world wide web in 1989, which allowed people to hyperlink static pages of information on websites accessible through internet browsers.
Berners-Lee was exploring more efficient ways for researchers at different institutions to share information. In 1991, he launched the world’s first website , which provided instructions on using the internet.
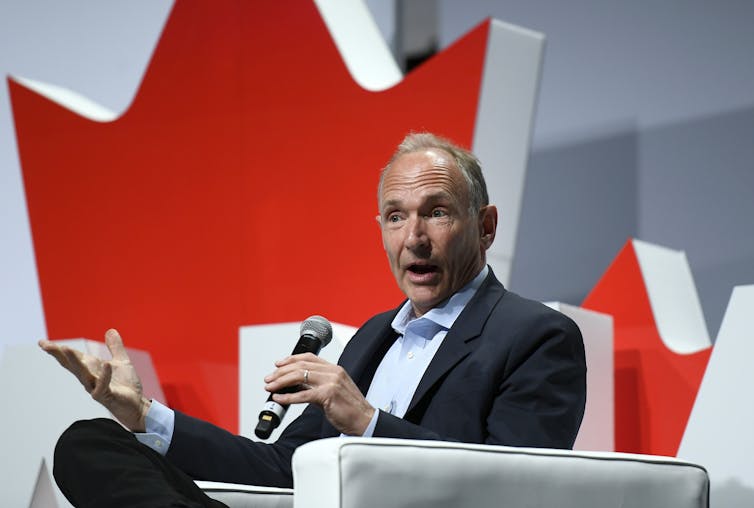

These basic “read-only” websites were managed by webmasters who were responsible for updating users and managing the information. In 1992, there were 10 websites . By 1994, after the web entered the public domain, there were 3,000.
When Google arrived in 1996 there were two million. Last year, there were approximately 1.2 billion websites , although it is estimated only 17 per cent are still active.
Web 2.0: The social web
The next major shift for the internet saw it develop from a “read-only web” to where we are currently — a “read-write web.” Websites became more dynamic and interactive. People became mass participants in generating content through hosted services like Wikipedia, Blogger, Flickr and Tumblr.
The idea of “Web 2.0” gained traction after technology publisher Tim O’Reilly popularized the term in 2004 .
Later on, social media platforms like Facebook, YouTube, Twitter and Instagram and the growth of mobile apps led to unparalleled connectivity, albeit through distinct platforms. These platforms are known as walled gardens because their parent companies heavily regulate what users are able to do and there is no information exchange between competing services.
Tech companies like Amazon, Google and Apple are deeply embedded into every facet of our lives, from how we store and pay for our content to the personal data we offer ( sometimes without our knowledge ) to use their wares.
Web3 vs. Web 3.0
This brings us to the next phase of the internet, in which many wish to wrest back control from the entities that have come to hegemonize it .
The terms Web3 and Web 3.0 are often used interchangeably, but they are different concepts.
Web3 is the move towards a decentralized internet built on blockchain. Web 3.0, on the other hand, traces back to Berners-Lee’s original vision for the internet as a collection of websites linking everything together at the data level .
Our current internet can be thought of as a gigantic document depot. Computers are capable of retrieving information for us when we ask them to, but they aren’t capable of understanding the deeper meaning behind our requests.

Information is also siloed into separate servers. Advances in programming, natural language processing, machine learning and artificial intelligence would allow computers to discern and process information in a more “human” way, leading to more efficient and effective content discovery, data sharing and analysis. This is known as the “semantic web” or the “read-write-execute” web.
In Berners-Lee’s Web 3.0 world, information would be stored in databases called Solid Pods , which would be owned by individual users. While this is a more centralized approach than Web3’s use of blockchain, it would allow data to be changed more quickly because it wouldn’t be distributed over multiple places.
It would allow, for example, a user’s social media profiles to be linked so that updating the personal information on one would automatically update the rest.
The next era of the internet
Web3 and Web 3.0 are often mixed up because the next era of the internet will likely feature elements of both movements — semantic web applications, linked data and a blockchain economy. It’s not hard to see why there is significant investment happening in this space.
But we’re just seeing the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the logistical issues and legal implications. Governments need to develop new regulations for everything from digital asset sales taxation to consumer protections to the complex privacy and piracy concerns of linked data .
There are also critics who argue that Web3, in particular, is merely a contradictory rebranding of cryptocurrency that will not democratize the internet. While it’s clear we’ve arrived at the doorstep of a new internet era, it’s really anyone’s guess as to what happens when we walk through that door.
- Social media
- Cryptocurrency
- Internet regulation
- Decentralised web

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Senior Disability Services Advisor

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

GRAINS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION CHAIRPERSON
What is Web3?

Third time’s the charm? You know that the internet is always growing and changing. But it’s not just websites and platforms that are falling in and out of favor; the very code on which the internet is built is constantly in flux. In the past few years, some tech futurists have started pointing to Web3, a term coined by computer scientist Gavin Wood , as a sign of things to come. Web3 is the idea of a new, decentralized internet built on blockchains , which are distributed ledgers controlled communally by participants. Because of the collective nature of blockchains, if and when Web3 fully arrives—elements of it are already in place—it will, in theory, signal a new era of the internet, one in which use and access are controlled by community-run networks rather than the current, centralized model in which a handful of corporations preside over Web2.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on Web3
Michael Chui is a partner with the McKinsey Global Institute and a partner in McKinsey’s Bay Area office, where Robert Byrne and Marie-Claude Nadeau are senior partners and Roger Roberts is a partner; Homayoun Hatami is the managing partner for global client capabilities and a senior partner in the Paris office, where Eric Hazan is also a senior partner.
Momentum around elements of Web3 has increased significantly since 2018, in areas like equity investment, online searches, patent filings, scientific publications, job vacancies, and press reports. The financial-services industry has been at the vanguard of emerging Web3 technologies and assets: at one point, the daily volume of transactions processed on so-called decentralized-finance exchanges exceeded $10 billion. As we’ll see, though, progress has come in fits and starts.
If you’re still not sure what Web3 is, you’re not alone. According to a 2022 Harvard Business Review poll, nearly 70 percent of the more than 50,000 people who responded admitted they don’t know what Web3 is. In this Explainer , you’ll learn more about Web3, its perils and possibilities, and when—or if—it will come to fruition.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Digital Practice .
What are Web1 and Web2?
First, if there’s going to be a Web3, you should understand what Web1 and Web2 are. Web1 was the first draft of the internet, the one that proliferated in the 1990s and early 2000s. Much of Web1 was built using “open protocols,” which are ways of exchanging information that can be used by anyone, rather than just one entity or organization. Back then, people mostly used the internet to read web pages and chat with friends or strangers. As Web1 progressed, individuals and companies began using the internet increasingly for e-commerce , as well as for academic and scientific research.
Web2 came about in the mid-2000s, when a new crop of internet companies—upstarts like Facebook, Twitter (now X), and Wikipedia—empowered users to create their own content. But there was a cost to these free-to-use “emergent social software platforms,” as MIT research scientist Andrew McAfee described them in a 2009 McKinsey Quarterly interview—a cost many users weren’t aware of. These companies monetized user activity and data by selling them to advertisers, while retaining control over proprietary decisions about functionality and governance.
What technologies support Web3?
Web3 describes what the internet could look like built on new types of technology. Here are the three main ones:
- Blockchain. A blockchain is a digitally distributed, decentralized ledger that exists across a computer network and facilitates recording of transactions. As new data are added to a network, a new block is created and appended permanently to the chain. All nodes on the blockchain are then updated to reflect the change. This means the system is not subject to a single point of control or failure.
- Smart contracts. Smart contracts are software programs that are automatically executed when specified conditions are met, like terms agreed on by a buyer and seller. Smart contracts are established in code on a blockchain that can’t be altered.
- Digital assets and tokens. These are items of value that exist only digitally. They can include cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and NFTs (nonfungible tokens). They can also include tokenized versions of assets, including real things like art or tickets to concerts or sporting events.
Later, we’ll see how each of these technologies is used in practice, with real-world examples of Web3-supported products.
How is Web3 different from Web2?
In the Web2 era, control—over transactions, content, and data—is centralized in tech corporations. In theory, that will change with the advent of Web3. Evangelists believe that in the Web3 era, users will have the power to control their own information without need for the intermediaries we see today. Web3 could change how information is managed, how the internet is monetized, and even, maybe, how web-based corporations function.
Another difference between the two is how they approach trust. In Web2, a transaction—whether it’s an exchange of money or information—relies on two parties (and usually a central facilitator as well) trusting each other with the information that’s being shared. By contrast, Web3 doesn’t ask users to trust one another. Instead, the technology is designed so that a transaction goes through only if certain criteria are met and data are verified.
Here’s a theoretical example to help illustrate how a Web3 transaction might work. Imagine that someone is looking to buy a concert ticket on the resale market. This person has been scammed before by someone selling a fake ticket; she trusted that the person was selling a real ticket and sent the person money, which the person then stole. This time, she decides to try a Web3-enabled, blockchain-based ticket exchange service. On these sites, every ticket is assigned a unique, immutable, and verifiable identity that is tied to a real person. Before the concertgoer purchases her ticket, the majority of the nodes on the network validate the seller’s credentials, ensuring that the ticket is in fact real. She buys her ticket and enjoys the concert.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
Crypto has faced some trouble. what does this mean for web3.
The cryptocurrency market is facing an uncertain future: in 2022, it lost more than 50 percent of its market capitalization, as several currencies lost value and multiple cryptocurrency exchanges closed. It’s true that cryptocurrencies and Web3 are both built on blockchains. But don’t throw the Web3 baby out with the cryptocurrency bathwater: other areas of Web3 experience continue to push forward. Check out these 2022 numbers :
- The sales count for NFTs increased 68 percent, despite a slowdown in the second half of the year. NFTs are digital representations of an asset stored on a blockchain. Because an NFT is, by definition, nonfungible, meaning it can’t be replicated, it serves as digital proof of ownership that can then be bought or sold.
- Core tool downloads for Ethereum increased by 87 percent. Ethereum is a smart-contract blockchain ; core tools are what developers need to work with it.
- On-chain stablecoin payment volume grew more than 50 percent. A stablecoin is a private, stabilized cryptocurrency pegged to another currency, commodity, or financial instrument.
- The number of active users of Web3 gaming increased 60 percent.
- The global tokenization market grew by about 23 percent. Tokenization is the process by which NFTs are created and has the potential to affect the structure of financial services and capital markets .
What are some examples of Web3 in the real world?
The number of Web3-supported transactions is still growing. Here are four examples that were noted in the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook for 2023:
- In November 2022, JPMorgan Chase made its first cross-border blockchain transaction, involving tokenized Singaporean dollar and Japanese yen deposits. The trade was part of Project Guardian, a partnership between JPMorgan Chase and DBS Bank.
- Securitize, a digital-asset securities firm, partnered with global investment firm KKR to launch a tokenized fund issued on the Avalanche blockchain. Tokenization opens up private equity to more individual investors by digitizing operations and lowering investment minimums.
- 100 Thieves, an esports and lifestyle brand, offered an NFT of a diamond necklace to fans if they created a digital wallet on the platform within 75 hours. More than 300,000 people redeemed the NFT.
- After acquiring the Web3 studio RTFKT in 2021, Nike launched its own Web3 platform in 2022 called .Swoosh and has since offered blockchain-based NFTs to customers. The .Swoosh platform is meant to serve as a hub for new product launches, as well as a space for customers to share virtual apparel designs.
Is Web3 the same as the metaverse?
Not quite. According to technologist Matthew Ball , Web3 refers to decentralized databases and systems architecture, whereas the metaverse is a new paradigm of computing and networking. They both may succeed what we experience as the internet today, but there’s a long way to go before that happens.
What are some concerns around Web3?
Web3 technologies are already being taken up by tech pioneers. But early Web3 adopters face several challenges, with more likely to crop up as Web3-enabled tools become more widespread. At present, challenges include the following:
- Evolving regulation. Authorities are developing their approaches to governing issues such as consumer and investor protection, legality and enforceability of blockchain-based contracts, and know-your-customer and anti-money-laundering standards.
- Value proposition and user experience. Compared with Web2 products, which have been fine-tuned over two decades of development, Web3 has relatively poor user experience standards. The utility of Web3 products, such as NFTs, also remains unclear to many consumers and enterprises.
- Consumer protection. Amid recent failures of several Web3 projects, consumer and investor protection is becoming a focal point for regulators and the general public.
Web3 isn’t a fix-all for the problems that plague Web2. In fact, we’ll likely have to work harder to address the same old problems in new ways necessitated by this new generation of the internet.
Learn more about the Financial Services , Risk & Resilience , Strategy & Corporate Finance , and Technology, Media & Telecommunications Practices, and check out Web3-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced:
- “ Rewriting the beauty code of the future ,” April 20, 2023, Hamza Khan
- “ Tokenizing nontraditional assets: A conversation with Ascent Bit’s Brian Clark ,” March 17, 2023, Andrew Roth and Dilip Mistry
- “ A CEO’s guide to the metaverse ,” January 24, 2023, Homayoun Hatami , Eric Hazan , Hamza Khan , and Kim Rants
- “ Web3 beyond the hype ,” September 26, 2022, Anutosh Banerjee , Robert Byrne , Ian De Bode , and Matt Higginson
- “ Forward Thinking on tech and the unpredictability of prediction with Benedict Evans ,” April 6, 2022, Janet Bush and Michael Chui
- “ The promise and peril of the metaverse ,” March 29, 2022, Mina Alaghband
- “ What is the metaverse—and what does it mean for business? ,” March 29, 2022, Mina Alaghband
- “ Blockchain’s Occam problem ,” January 4, 2019, Matt Higginson , Marie-Claude Nadeau , and Kausik Rajgopal
- “ Blockchain explained: What it is and isn’t, and why it matters ,” September 28, 2018, Brant Carson and Matt Higginson
- “ Blockchain beyond the hype: What is the strategic business value? ,” June 19, 2018, Brant Carson , Giulio Romanelli , Patricia Walsh, and Askhat Zhumaev
- “ How Web 2.0 is changing the way we work: An interview with MIT’s Andrew McAfee ,” McKinsey Quarterly , November 1, 2009, Roger Roberts

Want to know more about Web3?
Related articles.

McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2023

What’s the future of generative AI? An early view in 15 charts

Web3 beyond the hype
What is Web3?
Web3 is a new evolution of the Internet based around the principles of decentralization. Web3 combines the rich and interactive digital experiences that exist today with infrastructure that offers users ownership and cryptographic guarantees.
Web3 has recently burst into the mainstream consciousness, with industry leaders across the traditional tech sector and blockchain ecosystem weighing in with a wide range of perspectives on the past and future of the Internet. Before we dive in, a brief history of the term. The term “Web 3.0” was first used during the dotcom era by HTTP pioneer Tim Berners-Lee to describe an integrated communication framework in which Internet data is machine-readable across different applications and systems—a concept he also referred to as the Semantic Web. Later, in his 2014 blog post DApps: What Web 3.0 Looks Like , Ethereum Co-founder Gavin Wood repurposed Berners-Lee’s expression, using it to refer to the ability of blockchain technology to define a “fundamentally different model for the interactions between parties” based on “a zero-trust interaction system.” Wood’s writing focused not on cryptocurrencies but on protocols and technologies, such as consensus engines and cryptography, that could facilitate a stronger social contract across the web. He later described the aim of Web3 as “Less trust, more truth.” Now, the term is the subject of much debate, with both the tech giants of today and the vanguard of the blockchain industry continuing to reckon with Web3’s core propositions and protocols, and its implications for the trust models of the future. In this deep dive, we’ll define Web3 in relation to earlier iterations of the Internet, walk through the key technologies of the Web3 stack, and explore the current and future state of the Web3 landscape. A note on terminology: We’ll use the term “Web3” as distinct from “Web 3.0”, which is often associated with Berners-Lee’s vision of the Semantic Web.
The Evolution of the Internet: From Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 to Web3
To truly grasp the meaning of Web3, it’s important to understand the history of the Internet and how Web3 differs from the versions of the web that preceded it.
Web 1.0 (1994-2004)
Web 1.0 was the first iteration of the Internet we’re familiar with today, emerging in 1994 and ending around 2004 with the rise of social media giants like Twitter and Facebook. While the general public came to learn about the Web 1.0 Internet around 1994, Web 1.0 actually started as a U.S. government program called ARPANET, or Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, in 1968. ARPANET began as a small network of military contractors and university professors who exchanged data with one another.

The Web 1.0 Internet was mostly a collection of static HTML pages and afforded users limited ability to interact with each other. Although Internet gateways such as America Online (AOL) and discussion forums such as Usenet permitted private chat and discussion boards, for most the Internet remained a space where few interactions or financial transactions took place.

Where interactions and financial transactions did take place, they were limited in scope because there was a lack of secure infrastructure for transferring money. One of the most innovative Web 1.0 companies in this respect was Pizza Hut, which in 1995 created an order form for its customers that they could use to place an order and pay in cash once this order was delivered.

Despite America Online’s claim in a 1995 commercial that users could order flowers for their mom, buy tickets to a sports game, or write a research report on dinosaurs with AOL, exchanging money online required speaking with an operator since financial transactions were generally unsafe and had limited encryption.
Web 2.0 (2004-The Present)
The web evolved around 2004 as user demand for social interactions, music, video sharing, and financial transactions grew dramatically due to improved Internet speed, fiber optic infrastructure, and search engine improvements.

This demand for greater interactivity gave rise to many of today’s Internet institutions and companies. Social media platforms like Facebook, MySpace, and Twitter facilitated social interaction; data-sharing applications such as Napster met the demand for online music and video; Google provided an effective means for users to navigate the huge quantity of online information. Traditional institutions such as Bank of America met the demand for financial interactions and electronic fund transfers, enabled by new encryption standards such as 256-bit AES. This new, more interactive Internet improved users’ experiences of the web tremendously by adding new functionality. But it also presented a tradeoff that continues to define our online lives to this day: To benefit from these new functionalities and interactions, users have to delegate a large quantity of information and responsibility to siloed third-party platforms, granting these centralized entities a considerable amount of power and influence in terms of data and content ownership. This is, for the most part, how the Internet operates up until the present day. In the United States alone, Google, YouTube, Facebook, and Amazon combined received 23.56 billion visits in October 2021—roughly double the traffic of websites ranked 5-20.
Web3 (2008-The Future)
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper , which outlined the fundamentals of blockchain technology and a peer-to-peer digital currency, setting a course to change the Web 2.0 paradigm. Bitcoin transformed how we think about digital transactions and provided the first secure means of exchanging money over the Internet that didn’t require a trusted third party. “What is needed,” Satoshi wrote, “is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust.” It was not until the invention of smart contracts that a decentralized model of the Internet truly came into focus. If Bitcoin enabled secure peer-to-peer payments and smart contracts could expand this idea of programmable agreements to more advanced use cases—insurance, gaming, identity management, supply chains—how would the nature of web experience and digital interaction evolve? By enabling users to directly and securely transact with one another, smart contracts created a fresh vision for an Internet that is fair, transparent, and powered by cryptographic truth. Gavin Wood described this reimagined web—Web3—as a “Secure Social Operating System.” Put simply, Web3 is a decentralized vision of the Internet that aspires to create an entirely new system of contracts and change the way that individuals and institutions reach agreements. Web3 brings back the decentralized architecture of Web 1.0, the first version of the Internet, which was replete with user-hosted blogs and RSS feeds, and combines it with the rich, interactive experience of Web 2.0 web applications like social media platforms to provide a digital ecosystem where data is user-owned and transactions are backed by cryptographic guarantees. Rather than having to trust brand-based paper promises, users can rely on deterministic software logic to execute agreements exactly as programmed.
The Core Elements of Web3: Blockchains, Cryptocurrency, Smart Contracts, and Oracles
Powering the Web3 model is a growing stack of decentralized technologies, such as blockchains, smart contracts, oracles , crypto wallets, storage networks, and more. Below, we walk through some of the critical layers and componentry of the Web3 technology stack.
Blockchains
A blockchain is a highly secure and decentralized network that allows people to store data, exchange value, and record transaction activity in a shared ledger that is not controlled by any central authority. Blockchain networks serve as the backbone of Web3, providing secure execution environments that allow for the creation, distribution, and trading of cryptocurrencies, as well as the development of programmable smart contracts. Blockchains are the settlement layer of Web3.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are digital tokens that leverage the decentralized and tamper-proof environments of blockchain networks to facilitate highly secure transactions. They are the native currencies of Web3 decentralized applications (dApps) and can also be used to pay for Web3 services and participate in Web3 governance. Before blockchain technology, tokens were units of value that could be purchased and exchanged to pay for specific products and/or services, such as tokens for highway tolls or amusement park rides and games. In these earlier applications, tokens were useful to service providers because they allowed customers to pay upfront for services that they would consume in the future and because they facilitated transactions where exact change was required. Tokens in Web3 applications are also units of value issued to Web3 content creators, but these units of value are digital, programmable, and have functions beyond exchange. In Web3, a token might be held as an investment in a protocol, project, or blockchain. It might have utility for that project or protocol—for paying for a service or insuring a service, for example. It might also provide a gateway to participation in the governance of the protocol or project.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Smart contracts are tamper-proof programs on blockchains that facilitate automatic transactions by using conditional software logic such as, “ if x is true, then execute y .” Programmable smart contracts enable the creation of decentralized applications, or dApps, the cryptoeconomic protocols that bring Web3 to life and put it in the hands of users. dApps are different from the applications (apps) that we are familiar with in the Web 2.0 world and the static HTML pages from the Web 1.0 world because they are not maintained by any single individual or organization but rather powered by the decentralized infrastructure of blockchain networks. These seemingly simple, decentralized programs can be used to create complex, automated systems such as peer-to-peer financial services (DeFi) , data-driven insurance products , play-to-earn online games , and more.
To realize their full potential, smart contracts need to access and interact with data and systems outside of blockchain networks. Oracles are the entities that connect blockchains to real-world data and existing systems, and provide critical infrastructure for establishing a unified, interoperable Web3 ecosystem. Chainlink oracle networks not only feed financial market data on-chain to power DeFi applications, but they also provide a wide range of secure off-chain computations such as verifiable randomness and decentralized execution to enable dynamic NFTs and highly automated dApps. Moreover, with the development of the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) , oracle networks will help enable the fast-growing ecosystem of different blockchains and layer-2 scaling solutions to securely communicate with one another. Oracles have emerged as an expansive layer of the Web3 stack, providing off-chain data and services to facilitate smart contract innovation, and cross-chain interoperability to help ensure seamless connectivity between different on-chain environments. Chainlink’s oracle infrastructure is also the gateway to Web3 for Web 2.0 backends, serving as an abstraction layer for traditional systems to interact with any private or public blockchain. Ultimately, oracles are the infrastructure that extends the power of decentralized computation and cryptographic guarantees to existing systems, bridging Web 2.0 and Web3.

The renewed interest in NFTs has led to a Cambrian explosion of unique applications that leverage the property of non-fungibility in innovative ways, often with the goal of increasing efficiency in the transfer of asset ownership and reducing the need for intermediaries who siphon value away from creators and marketplaces. However, NFTs are still largely in their infancy, meaning there is a vast amount of opportunity for growth from innovative developers, creative artists, and traditional institutions wanting to bring distinct assets on-chain.
Web3 Applications
Web3 combines decentralization and interactivity to create a new model for the Internet where users can interact directly, without intermediaries. dApps allow users to access permissionless financial tools, trade cryptocurrencies in a peer-to-peer manner, receive parametric insurance payouts, buy and sell verifiably owned digital art through NFTs, play value-generating games, and a whole host of other activities—all without the intervention of a central arbiter. With this new structure, the proponents of Web3 hope to create a fairer, more open version of the Internet where parties can interact and transact directly. Currently, Web3 applications that leverage the three foundational technologies—blockchains, smart contracts, and decentralized oracle networks—are already unlocking use cases that are redefining sectors as diverse as real estate , education, finance , gaming, and healthcare, and are set to have a transformational impact well beyond these domains.
The technologies that comprise Web3 enable individuals to create and participate in financial protocols that offer unprecedented access, security, and transparency—a new economic landscape that is now widely known as decentralized finance (DeFi) . Unlike traditional financial services, DeFi protocols leverage the decentralized infrastructure of blockchains and the secure inputs of oracle networks to help users directly transact with one another in transparent and tamper-proof on-chain markets. Decentralized money markets such as Aave—which now secures over $12B in smart contract value using Chainlink oracles—operate in a non-custodial manner and enable users to lend and borrow funds peer-to-peer. Money markets are a key mechanism for supporting a healthy economy. By decentralizing control and leveraging predefined smart contract logic, on-chain money markets help increase economic access, reduce single points of failure, and mitigate system risk and fractional reserve practices. One great DeFi innovation is its composable architecture , which empowers developers to combine open-source protocols into more sophisticated financial instruments, such as no-loss savings games that use overcollateralized loan protocols, decentralized stablecoins, and interest-bearing tokens that put idle capital to work and unlock liquidity. While the novel financial applications offered by DeFi are currently one of the most prominent aspects of Web3, the Web3 model extends far beyond financial transactions, encompassing every area of the Internet, from entertainment and social media to browser software.
NFTs, Gaming, and the Metaverse
NFTs , blockchain gaming, and the metaverse are currently emerging as key pillars of the Web3 ecosystem. NFTs offer verifiable ownership of digital assets, allowing digital goods to have a functional level of uniqueness similar to that of items in the real world. With NFTs, one digital item can now be differentiated from another even if they present the same way, similar to how two copies of the same book can be differentiated through their unique markings and evidence of specific wear-and-tear. This has massive implications for digital art, metaverse applications, and video games. Currently, NFT projects such as Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) are popularizing NFTs and digital art, and blockchain games such as Axie Infinity are spearheading a paradigm shift in player economics in gaming. Underpinning this foundational transformation are blockchains, which operate as the underlying settlement layer, NFT smart contracts, which enable verifiable ownership of digital items, and decentralized oracles, which provide key services such as verifiable randomness , smart contract automation , off-chain data, and more.
Parametric Insurance
One exciting use case emerging within the blockchain industry is decentralized parametric insurance . Blockchain insurance projects such as Arbol and Etherisc are currently implementing novel implementations of frictionless and automated crop insurance, flight insurance, and more through a combination of smart contracts and off-chain data inputs facilitated by Chainlink Data Feeds. Let’s walk through a quick example. Imagine a farmer requires more than 20 inches of rain in a season for an adequate crop harvest. The farmer wants to hedge against the risk of a bad harvest through insurance. Normally, he would have to go through a lengthy process to receive funds and need to rely on a centralized insurance provider to verify the amount of rainfall. However, in Web3, anyone in the world can permissionlessly take on a policy with just an Internet connection. With the blockchain-based crop insurance provided by Arbol, the insurance cost and payout terms are automatically determined based on pre-defined parameters, and payment is automated through an insurance smart contract based on weather data provided Chainlink. The insurance process becomes quick and painless, with a simple binary that determines whether the farmer receives insurance funds. Did an IoT sensor record less than 20 inches of rain that season? If yes, pay the farmer immediately. If no, don’t pay the farmer. This model has the ability to be expanded to areas such as shipping and fire insurance, with blockchain-based parametric flight insurance already in operation.
What’s Next for Web3
In his recent Future of Chainlink presentation , Chainlink Co-founder Sergey Nazarov explained the emerging megatrends of the Web3 ecosystem that have recently pierced the mainstream: “What you really see with the implementation of cryptographic guarantees in the Web3 world is a very specific set of applications, and some of these applications are called DeFi, some of them are called NFTs, some of them are called tokenized ownership, but these are the very early examples of cryptographic guarantees making their way into people’s and industries’ daily operations.”

Web3—a term that has become shorthand for a reimagined Internet experience powered by decentralized technologies—is already transforming how we interact online, from how we invest and exchange to how we play and express ourselves artistically. More and more users and institutions across the globe are waking up to the power of zero-trust interactions and cryptographically-backed agreements. While Web3 is still in its early stages, it has the potential to realize the ideals of hardwired transparency, reliability, and expediency the Internet was built to fulfill. “At the end of the day,” Nazarov noted, “as Web3 approaches the speed, the efficiency, and the low cost of web systems, it has a guarantee that no Web 2.0 system can ever have, which is the trust minimization cryptographic guarantee.”
Start building with Chainlink today by visiting the developer documentation , joining the technical discussion on Discord , and/or reaching out to an expert .To learn more about Chainlink, visit the Chainlink website and follow the official Chainlink Twitter to keep up with the latest Chainlink news and announcements.
Related articles
Learn more about blockchain technology.

Asset Tokenization
Learn how tokenization could bring trillions in value to blockchains.

Blockchain Gaming
Learn how blockchain technology can enhance the gaming experience.

Cross-Chain
See how cross-chain solutions enable a new frontier of dApp functionality.

Take a deep dive into the burgeoning decentralized financial system.

Explore what’s possible in the metaverse and how you can visit it.

Discover how to create NFTs and make them dynamic using oracles.

Uncover why blockchains need oracles and how they power Web3.

Smart Contracts
Learn what smart contracts are and how you can build them.

Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
Explore how zero-knowledge proofs provide privacy guarantees.
Get the latest Chainlink content straight to your inbox.

- Get access now
Web 3.0 Presentation Template

Explore our range of free slides template for Web 3.0 presentations .Have you ever heard of Web 3.0? Yes, It’s an advanced version of the world wide web(www) based on blockchain technology. It includes the concepts of non-fungible tokens(NFTs) and cryptocurrencies. Spread the idea of web 3 using these web 3.0 presentation templates designed by our expert team. This template contains various slides that describe each and every concept related to web 3.0. You can use these templates to create awareness about web 3 and for any business-related presentations. Download these elegant web 3.0 presentation templates now, and create compelling presentations.
- All the slides are fully customizable with easy-to-edit features.
- Include slides with high-quality and engaging infographics.
- You can find a mix of dark blue and rose themes in all the slides.
- Contain a web 3 definition slide, a timeline slide, and many other slides describing web 3.
Additionally, explore our meet the teacher google slides and japan presentation template to find more captivating and versatile slide designs
Like this template?
Get access to this template
Try Our Google Slides Add-On and Get Access to 4500+ Slides
No. of slides, aspect ratio, related suggestions.

Daily & Monthly Planner Calendar Slide Template

Conference Slide Templates


Watercolor Presentation Template

Negotiation Slides Template
Company Profile Slide Template
Spring Presentation Template

Case Study Slide Deck Template

Cryptocurrency Slide Templates

Marketing Plan Template Slides

Jungle Theme Presentation Template

Free Jeopardy Game Theme Slides & Templates

Cloud Computing Presentation Template
Welcome back, please sign in to continue..
Please sign up to continue.

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Introduction To The Concept Of Web 3 0 Training Ppt
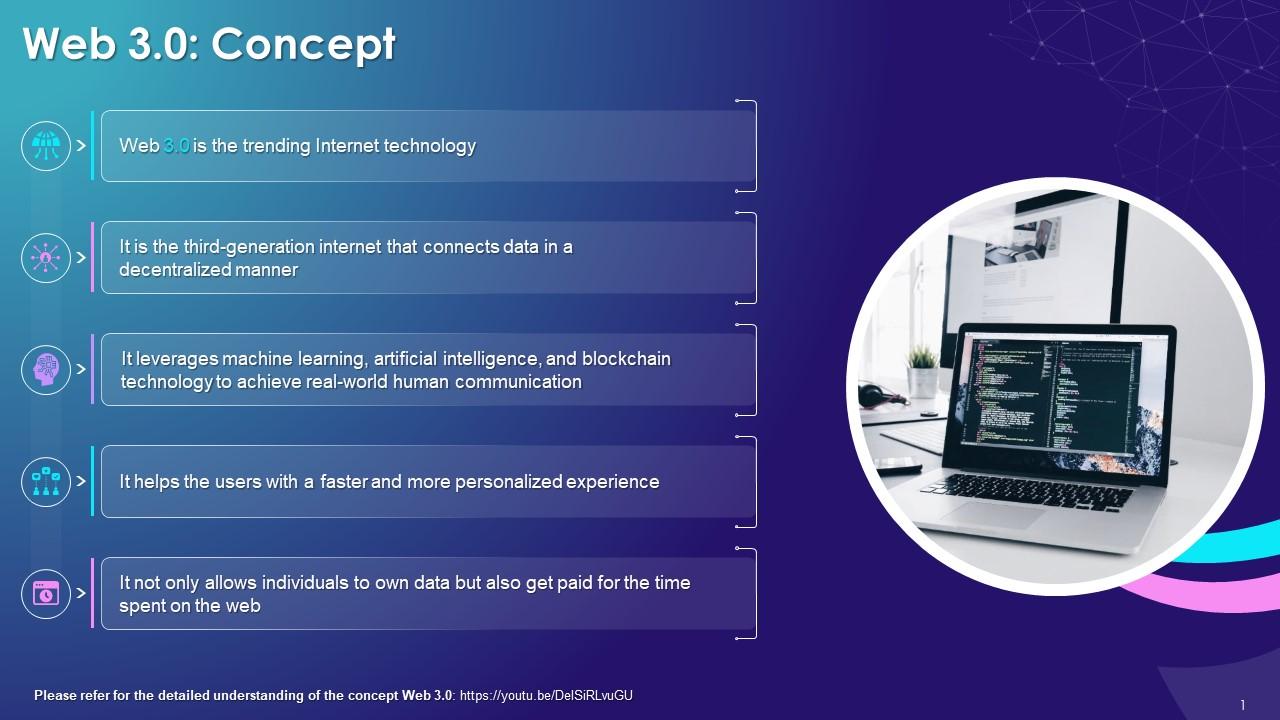
This slide explains the concept of web 3.0. It explains Web 3.0 uses technologies like Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to facilitate and achieve real-world human communication. Significantly, Web 3.0 not only allows individuals to own data but also get paid for their time spent on the web.
These PPT Slides are compatible with Google Slides
Compatible With Google Slides

- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
Get Presentation Slides in WideScreen
Get This In WideScreen
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
Do you want to remove this product from your favourites?
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Introduction to the Concept of Web 3.0. These slides are 100 Percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support is available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- IT , Blockchain
- Blockchain ,
- Blockchain Technology ,
- Cryptocurrency ,
Introduction To The Concept Of Web 3 0 Training Ppt with all 16 slides:
Use our Introduction To The Concept Of Web 3 0 Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Ratings and Reviews
by Damian Martin
October 26, 2022
by Courtney Griffin


MIT Connection Science
New “web 3.0” technologies….a combination of blockchain, and internet of things (iot), digital identity, distributed autonomous organization (daos), smart contracts, defi, non-fungible tokens and distributed artificial intelligence (ai)…are creating enormous new opportunities for virtually every digital domain. .
At the same time we are seeing emergence of Metaverse tech, which has already proven compelling for applications like training and collaborative design. Web 3.0 and Metaverse have great potential synergy, allowing people to bring their data and algortihms to different virtual and digital twin worlds, so that their digital self is synergistic with their physical self.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Imagination in Action Web 3.0 Summits
January 17, 2023 - Dome, Davos
Learn more and apply to attend
PAPERS AND PROJECTS
Synchronization between digital assets & real-world assets .
- Paper: Towards Blockchain-enabled Open Architectures for Scalable Digital Asset Platforms Denis Avrilionis (Compellio SA) & Thomas Hardjono (MIT)
- Presentation: Cross-Ledger Interoperability for Web3 Assets IETF113 Side Meeting Thomas Hardjono (MIT) & Martin Hargreaves (Quant Network)
- Paper: Do you Need a Digital Ledger Technology Interoperability Solution? TechRxiv by IEEE Rafael Belchior (Universidade de Lisboa & Quant Network), Luke Riley (Quant Network), Thomas Hardjono (MIT), André Vasconcelos (Universidade de Lisboa), Miguel Correia (Universidade de Lisboa)
Digital Privacy & Security
Paper: Privacy and Security Requirements for a Digital Data Hub TechRxiv by IEEE Martin Gfeller (Swisscom) & Thomas Hardjono (MIT)
Paper: A Digital Data Exchange for Australia TechRxiv by IEEE John Ruciak (Flinders University) & Thomas Hardjono (MIT)
Web 3.0 Landscape
- Paper: A Contract Service Provider Model for Virtual Assets Thomas Hardjono, Alexander Lipton, Alex Pentland (MIT)
- White Paper: Prevention of Digital Crime and Corruption in a Web3.0 World Alex Pentland (MIT)
Tutorial Playlist
Blockchain tutorial for beginners, what is blockchain technology how does it work, what is blockchain features and use cases, why is blockchain important and why does it matter, what is cryptocurrency: types, benefits, history and more, what is blockchain wallet and how does it work, what is ethereum understanding its features and applications, bitcoin vs ethereum: which one is better, understanding the fundamentals of ethereum mining, what is a smart contract in blockchain, what is dogecoin understanding the crypto-star, dogecoin vs. bitcoin : understanding the world of cryptocurrency, understanding the fundamentals of dogecoin mining, a look into the digital dogecoin wallet, 9 industries that blockchain will disrupt in future, emerging blockchain applications across industries, how to become a blockchain developer a step-by-step guide [updated], the ultimate guide to understand what is nft, the complete guide on solidity programming, the future of shiba inu coin and why invest in it, understanding the fundamentals of ethereum classic, understanding the fundamentals of merkle tree in blockchain, what is cardano: the complete guide of its concepts, what is matic network: exploring the concepts of matic, top 30 blockchain interview questions and answers for 2024, what is tether the ultimate guide, a comprehensive comparison of nft vs. crypto, what is web 3.0 everything you need to know about web 3.0, the complete guide for types of blockchain, what is defi: a new era of digital finance, the complete guide to understand ‘what is ripple’, the complete guide to understand the foundation of what binance is, what is dao: a brief introduction to a new era of technology, a complete guide to understand what stablecoin is, web 3.0 explained: a comprehensive guide.
Lesson 27 of 33 By Shyamli Jha

Table of Contents
Web 3.0 has the potential to be just as disruptive and to usher in a significant paradigm shift as Web 2.0 did. The fundamental ideas of decentralization, openness and increased consumer usefulness form the foundation of Web 3.0. Web 3.0, often known as Web 3, is the next step in the development of the internet.
Imagine a new kind of Internet that accurately translates what you type and understands what you say, whether through text, voice, or other media, and where all of the content you consume is more personalized than ever before. In the evolution of the Internet, you are about to enter a new era. It's been termed Web 3.0.
But, exactly what is Web 3.0 , how will it look, and how will it affect our lives? If you’re curious to know the above, you have reached the right place. In this tutorial, you will get all the answers to your questions related to Web 3.0.
Basics to Advanced - Learn It All!
What Is Web 3.0 Technology?
It is anticipated that Web 3.0 will be:-
- Open - Open-source software will be used to build content platforms.
- Trustless - Everyone will use Zero Trust, and network protection will reach the edge.
- Distributed - Interaction between devices, users, and services will be possible without a centralized authority's approval.
Blockchain technology will make it possible for users to communicate directly with one another throughout the next stage of the internet. Users will communicate by becoming a part of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), a group that is run and owned by its community.
Data belonging to the user will be protected via a network of openly available smart contracts. These contracts will be stored in a blockchain , which a decentralized network that nodes will control.
The following are further Web 3 forecasts:
- All transactions will be tracked on a distributed ledger that uses blockchain technology, and data transfers will be decentralized.
- Smart contracts that are open to everyone will relieve people of the need to rely on a centralized organization (like a bank) to maintain data integrity.
- The entertainment sector will significantly increase its revenue from the metaverse.
- Blockchain technology will make it possible for consumers to instantly produce digital goods and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which will protect intellectual property and personally identifiable information (PII).
- Users' data will be able to be profited from.
What Is Web 3.0?
Tim Berners-Lee, a developer who created the WWW or World Wide Web, originally referred to Web 3.0 as the Semantic Web and saw an intelligent, self-sufficient, and open Internet that employed AI and machine learning to function as a "global brain" and interpret content conceptually and contextually.
Due to technological constraints, such as how expensive and challenging it is to translate human language into machine understandable language, this idealized version didn't quite work out.
Following is a list of typical Web 3.0 traits:
- The semantic web is a development in online technology that enables people to produce, share, and connect material through search and analysis. Instead of using numbers and keywords, it is centered on word understanding.
- It uses machine learning and artificial intelligence. The final result is the formation of Web 3.0 to grow smarter and more receptive to user demands. If these ideas are paired with Natural Language Processing (NLP), the result is a computer that uses NLP.
- It illustrates how the Internet of Things connects various devices and applications ( IoT ). This procedure is made possible by semantic metadata, allowing for the efficient exploitation of all available data. In addition, anyone can access the internet from anywhere at any time without a computer or other smart device.
- It gives users a choice to interact in public or in private without exposing them to dangers through a third party, providing "trustless" data.
- 3-D graphics are used. In fact, this is already evident in e-commerce, virtual tours, and computer gaming.
- It makes participation easier without requiring consent from a ruling entity. It's without authorization.
- It is applicable to:
Metaverses: A limitless, virtual environment that is 3D-rendered
Blockchain video games adhere to the NFTs' ideals by enabling users to possess actual ownership of in-game resources.
- Digital infrastructure and privacy: Zero-knowledge proofs and more secure personal data are used in this application.
- Financial decentralization. Peer-to-peer digital financial transactions, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies are examples of this use.
- Autonomous decentralized organizations. Online communities are owned by the community.
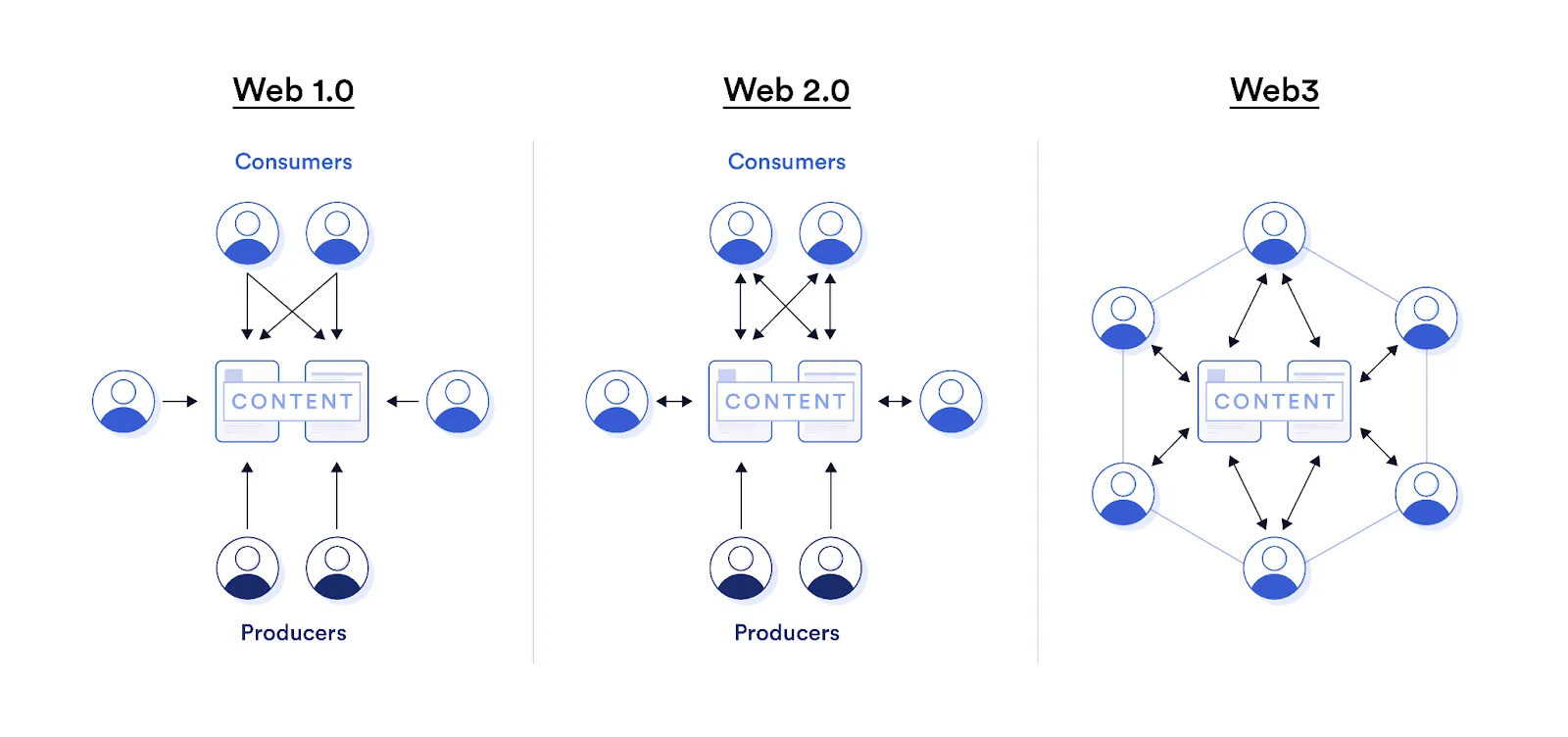
What Is Web 2.0?
If Web 1.0 consisted of a small group of individuals producing material for a bigger audience, Web 2.0 consists of many individuals producing even more content for an expanding audience. Web 2.0 places more emphasis on participation and contribution than Web 1.0 did on reading.
User-Generated Content (UGC), usability, interaction, and enhanced connectivity with other systems and devices are the main focuses of this Internet form. In Web 2.0, the experience of the user is everything. As a result, this Web form was in charge of establishing social media, collaborations, and communities. Web 2.0 is therefore regarded as the dominant method of web interaction for the majority of users in today's world.
Web 2.0 is described as "the participative social Web," whereas Web 1.0 was referred to as "the read-only Web." With the incorporation of web browser technologies like JavaScript frameworks, Web 2.0 is an improved and expanded version of its predecessor.
The typical traits of Web 2.0 are broken down as follows:
- It includes dynamic content that reacts to user input
- It uses developed application programming interfaces (API)
- It encourages self-use and allows forms of interaction like podcasting, social media, tagging, blogging, commenting, curating with RSS, social networking, and web content voting
- It offers free information sorting, allowing users to retrieve and classify data collectively
- It employs developed application programming interfaces (API)
- It uses developed information; it is used by society as a whole and is not just specific communities.
Here's How to Land a Top Software Developer Job
The Difference Between Web 1.0, Web 2.0, Web 3.0
Key features of web 3.0.
Although Web 3.0 has not yet been given a formal definition, it does have several distinguishing characteristics: -
- Decentralization: A fundamental principle of Web 3.0. In Web 2.0, computers search for data that is kept at a fixed location, typically on a single server, using HTTP in the form of distinct web addresses. Information might be stored simultaneously in numerous locations and become decentralized with Web 3.0 since it would be found based on its content rather than a single location. This would give individuals more power by dismantling the enormous databases that internet goliaths like Meta and Google presently maintain.
- With Web 3.0, users will be able to sell their own data through decentralized data networks, ensuring that they maintain ownership control. This data will be produced by various powerful computing resources, such as mobile phones, desktop computers, appliances, automobiles, and sensors.
- Decentralization and open source software-based Web 3.0 will also be trustless (i.e., participants will be able to interact directly without going via a trusted intermediary) and permissionless (meaning that each individual can access without any governing body's permission). This means that Web 3.0 applications—also known as dApps—will operate on blockchains, decentralized peer-to-peer networks, or a hybrid of the two —such decentralized apps are referred to as dApps.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning: With the help of the Semantic Web and natural language processing-based technologies, Web 3.0 will enable machines to comprehend information similarly to humans. Web 3.0 will also make use of machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that mimics human learning by using data and algorithms, gradually improving its accuracy. Instead of just targeted advertising, which makes up the majority of present efforts, these capabilities will result in faster and more relevant outcomes in a variety of fields like medical development and new materials.
- Connectivity and ubiquity: With Web 3.0, content and information are more accessible across applications and with a growing number of commonplace devices connected to the internet. The Internet of Things is one such example.
Layers of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is propelled by four new layers of technological innovation:
- Edge Computing - While web 2.0 changed currently commoditized personal computer technology in data centers, web 3.0 pushes the data center out to the edge (i.e. edge computing) and into our hands.
- Decentralized Data Network - Users will own their data on web 3.0 since data is decentralized. Different data generators can sell or share their data without losing ownership or relying on intermediaries using decentralized data networks.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning - Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have advanced to the level that they can now make useful and occasionally life-saving predictions and acts.
- Blockchain - Blockchain is a decentralized technology that uses smart contracts to execute transactions. These smart contracts define the semantics of a web 3.0 application. As a result, everyone who wants to develop a blockchain application must use the shared state machine.
How Does Web 3.0 Work?
Your information is stored on your cryptocurrency notecase in web3. On web3, you'll interact with apps and communities through your wallet, and when you log off, you'll take your data with you. Since you are the owner of the data, you may theoretically choose whether to monetize it.
With our guiding principles established, we can start looking at how certain web3 development features are meant to accomplish these objectives.
- Data ownership: When you use a platform like Facebook or YouTube, these businesses gather, own, and recoup your data. Your data is stored on your cryptocurrency wallet in web3. On web3, you'll interact with apps and communities through your wallet, and when you log off, you'll take your data with you. Since you are the owner of the data, you may theoretically choose whether to monetize it.
- Pseudonymity: Privacy is a feature of your wallet, just as data ownership. Your wallet serves as your identification on web3, which makes it difficult to connect it to your actual identity. Therefore, even if someone can observe the activity of a wallet, they won't be able to identify your wallet. "My personal information is hidden, but my behavior is visible." It was quoted by Neuroth.
There are services that help customers connect to their cryptocurrency wallets used for illegal behavior. However, your identity is concealed for daily use.
Although wallets increase the level of privacy for bitcoin transactions, privacy coins like Zcash and Monero give transactions total anonymity. Blockchains for privacy coins allow observers to track transactions, but they are unable to view the wallets involved.
Web3 will feature decentralized autonomous entities running apps (DAOs). As a result, decisions are no longer made by a centralized authority but rather by users who own governance tokens, which may be acquired by taking part in the maintenance of these decentralized programmes or by purchasing them.
In a typical corporation, the CEO is responsible for implementing changes approved by the shareholders. Token holders in a DAO can vote on modifications that, if approved, are immediately incorporated into the DAO's code via a smart contract. Everyone gets access to the source code of a DAO since they are democratized.
How Will Web 3.0 Change Our Lives?
Due to its decentralized nature, which is made possible by distributed ledger technology and smart contracts, Web 3.0 is intended to produce sustainable results. It also lowers costs by doing away with middlemen, manual mediation, and arbitration.
For everybody, Web 3.0 offers a much more individualized surfing experience. Websites will be able to automatically adjust to our device, location, and any accessibility needs we may have, and web apps will become far more receptive to our usage patterns.
We believe that the emergence of Web 3.0 will improve our lives for the following three reasons, which we believe are fairly appropriate:
1. A More Customized Browsing Process
There is no denying the ease of being able to quickly click through to a particular offer for something you actually need or desire and that you would have missed otherwise, regardless of how intrusive those advertisements may occasionally feel.
2. Improved search
As was already mentioned, using a search engine in natural language is highly effective. The benefits go far beyond the consumer as the learning curve virtually disappears, and businesses are increasingly able to optimize their websites for search engines in a more organic way as opposed to using complicated keyword techniques.
3. More Advanced App Interfaces
The multidimensional Web 3.0 will help more than just websites; it will also enable web apps to provide users with far richer experiences. Consider a mapping service like Google, which can now include route planning, lodging suggestions, and real-time traffic updates in addition to the fundamentals of location search. Simply put, in the Web 2.0 age, this was not feasible.
Key Applications of Web 3.0
With blockchain at its core, Web 3.0 makes it possible for an expanding range of new apps and services, such as the following:
- NFT: Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs) are tokens that are individually unique and are kept in a blockchain with a cryptographic hash.
- DeFi: Decentralized blockchain technology is being utilized as the foundation for decentralized finance (DeFi), a new use case for Web 3.0 that allows for the provision of financial services beyond the constraints of conventional centralized banking infrastructure.
- Cryptocurrency: A new universe of money that strives to be distinct from the traditional world of fiat cash is being created through Web 3.0 apps like cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
- dApp: Decentralized applications (dApps) are programmes that run programmatically and are logged in an immutable ledger. They are built on top of the blockchain and use smart contracts to facilitate service delivery.
- Chain-crossing bridges: In the Web 3.0 age, there are numerous blockchains, and cross-chain bridges provide some kind of connectivity between them.
- DAOs: DAOs are poised to potentially take on the role of Web 3.0's governing bodies, offering some structure and decentralized governance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Web 3.0
Advantages - .
- In terms of data security, end-users will benefit the most from data encryption.
- Due to decentralized data storage, users will be able to access data in any situation. Users will receive multiple backups that will aid them if the server crashes.
- Most blockchain systems are developed by non-profits, which provides an open-source blockchain platform that allows for collaborative design and development.
- The data will be provided from any location and on any device.
- Web 3.0 is useful for problem-solving and heavy knowledge-generation tasks.
Disadvantages -
- To make the technology accessible to more people worldwide, the devices' capabilities and qualities will need to be expanded.
- Any websites built on web 1.0 technology will become obsolete once web 3.0 is fully implemented on the Internet.
- Web 3.0 technology is more intelligent, efficient, and accessible than in previous generations. However, the technology isn't quite ready for general use.
- With easier access to a user's information and reduced privacy thanks to web 3.0, reputation management will be more important than ever.
The Future of the Internet
The world is on its way to an Internet where people have complete control over their data and privacy while also allowing companies to exploit it (or not). All of this will be made possible by blockchain technology.
As a result, web 3.0 will hasten the fair and transparent use of user data, ranging from personalized search results to cross-platform development tools and 3D graphics. The internet will become more immersive and engaging in the next years.
1. What are Web 3.0 tools?
AI, semantic web, and omnipresent qualities may all be taken into consideration when designing Web 3.0. The rationale for AI stems from the need to give users faster access to more accurate data. An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered website ought to be able to sort through the data and present the information it thinks a particular visitor will find useful. Given that the results are websites that users have chosen, social bookmarking as a search engine can yield superior outcomes to Google. However, humans are also capable of manipulating these outcomes. In order to provide outcomes comparable to social media and social bookmarking but without negative feedback, AI could be used to differentiate the true results from the fakes.
Virtual assistants, a component that is already becoming popular as an aspect integrated into a device or through third-party apps, will also be introduced by an artificially intelligent web.
The goal of the semantic web is to organize and store data in a way that can be used to teach a system what a given piece of information means. In order to create and distribute better content, a website should be able to comprehend the language in the same way humans comprehend. AI can process information into knowledge only if it comprehends the information.
2. Is Web 3.0 the future of the internet?
The Web 3.0 leverages AI, Machine Learning and blockchain technology. It is expected to achieve real-world communication. Individuals will own the data, and they will be compensated for the time they spend on the internet. This sounds futuristic, and the data and privacy of the users will increase with the blockchain technology. Thus if all goes well, Web 3.0 will be the future of the internet.
3. How do I create a Web 3.0 website?
First, you need to buy an NFT domain name. Next, you can make a website. The thing to remember is that the website needs to be made in one of the three ways: -
- Use existing templates on website builders.
- Host the website on an InterPlanetary File System Protocol or IPFS.
- Redirect to an existing Web 3.0 Website.
4. Why is Web 3.0 important?
The following are a few crucial aspects of Web 3.0 that help define what the third generation of the web is expected to be all about:
- Decentralized: Web 3.0 will be decentralized in contrast to the past two generations of the web, which had heavily centralized governance and applications. A distributed method without a centralized authority will enable applications and services.
- Blockchain-based: The development of decentralized applications and services is made possible by blockchain. In contrast to centralized database infrastructure, blockchain uses a distributed way to disseminate data and connections between services. In a decentralized environment, blockchain can also offer an immutable ledger of transactions and activities, assisting in the provision of verified authenticity.
- Cryptocurrency-enabled: The use of cryptocurrencies, which primarily replaces the use of fiat money, is a key component of Web 3.0 services.
- Artificially intelligent and autonomous: A key aspect of Web 3.0 is more automation overall, which will mostly be driven by AI.
Decipher the global craze surrounding Blockchain with the Blockchain Certification Training Course . Get trained today.
Web 3.0, sometimes known as Web 3, is the concept of the next generation of the web, in which most users will be connected via a decentralized network and have access to their own data. This article taught us about the technologies that are anticipated to advance and change in the upcoming years. Intelligent systems, semantic web, decentralization, metaverse, digital assets, and other emerging technologies will all be part of Web 3.0.
Whether Web 3.0 will be successful or not needs to be seen. But one thing most analysts agree is that the demand for data security will be of prime importance. It follows that there would be a great need for security specialists and security-related systems. Also the demand for blockchain developers will increase. If you want to understand more about blockchain and master the architectural principles and services of today’s top Blockchain solutions, you should check out Simplilearn’s Blockchain Bootcamp in collaboration with the University of Minnesota.
If you have any questions or doubts, feel free to post them in the comments section below. Our team of experts will review and get back to you at the earliest.
Do you have any questions for us? Leave them in the comments section of this tutorial and our experts will get back to you on it at the earliest.
Happy learning!
Find our Full Stack Java Developer Online Bootcamp in top cities:
About the author.
Shyamli is a Senior Research Analyst at Simplilearn. She is proficient in Blockchain and Cryptocurrency, Cloud Computing, Android Development and other coding languages like C, C++ and Java.
Recommended Resources
What is AWS: Introduction to Amazon Web Services
AWS Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
What Is Web 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 and How They Compare
Ascend to the Pinnacle of Cloud Excellence with AWS Cloud Architect Masters Program
AWS Fundamentals
AWS Introduction Guide
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

49 templates

18 templates

40 templates

american football
16 templates

41 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates
Web3 Architecture Thesis
Web3 architecture thesis presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
The world of internet is in constant evolution. Have you heard about "Web3"? It's like a new version of the World Wide Web based on blockchain, data "chained" together with cryptography. It's a concept that sounds too difficult to explain with just a couple of lines. So here's our idea: a futuristic-looking template for people who have written a thesis on Web3 architecture! You are the one who can explain this concept better, and this design, which focuses on neon-colored elements, will convey your points in a clear way.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 30 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

- Preferences

WHAT IS WEB 3.0 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

WHAT IS WEB 3.0
Web 3.0 is a more sophisticated beast. the ‘semantic web,' which analyses and uses user data and behaviour to create a more personalised web surfing experience, has emerged as a result of leveraging the power of big data and machine learning. this website is dedicated to providing knowledge on all things related to web 3. stay with us at dweb guide and grow with us - the future is here, and it's decentralised. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- The rise of internet use as we know it has been swift and fruitful. Upgrades are thought vital in many aspects of digital platforms in this day and age. Web 3.0 is the result of a decade-long search for a solution. In clear words, Web 3.0 is a read-write-execute web.'
- It is a solution in which data is shared rather than owned in what is known as the "Web 3.0." Web 3.0 allows systems to search for, generate, exchange, and connect material, and artificial intelligence enables web pages to grasp the meaning of words rather than just detecting relevant keywords.
- Web 3.0 encompasses a lot more. Web 3.0 is a new age technology that is very appealing due to the new and unique features that are calibrated within the existing Web 2.0 ecosystem. Web 3.0 has the potential to drastically change how people use the internet. With Web 3.0, automated routine chores, scheduled reminders, AI-based search, and other features will become increasingly ubiquitous.
- Users' digital experiences have been enhanced significantly by Web 3.0, which also provides security for web apps. The use of 3D graphics opens up a world of options for how content might be seen. Semantic metadata also facilitates information connectivity, allowing everyone on one common network to access all available information based on user behaviour. This goes beyond the concept of a simple website and builds its own website.
- At dWebGuide Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the Internet. As a result, by refusing to evolve with it, managers risk exposing their organisations to the risk of becoming outdated or irrelevant during breakthroughs, similar to the giants of the past such as Kodak, Nokia, and Altavista. However, many experts predict that Web 3.0 would enable a speedier, more intuitive web experience, allowing users to forsake command-line search keywords in favour of naturally speaking with Google. Show me all the movies playing at my local theatre tomorrow evening, is an excellent example of a search query that will get the desired results in the Web 3.0 era.
- Three reasons the rise of Web 3.0 will change our lives for the better
- 1. A more personalised browsing experience
- As distracting as those advertisements can be at times, there's no denying the convenience of being able to quickly click over to a unique offer for something you actually need or desire but might otherwise overlook. For all of us, Web 3.0 offers a considerably more personalised surfing experience. Websites will be able to adapt automatically to our device, location, and any accessibility needs we may have, and web apps will become significantly more aware of our usage patterns.
- 2. Better search
- As previously said, the capacity to converse with a search engine in natural language is quite powerful. Businesses will increasingly be able to take a more natural approach to search engine optimization on their websites, rather than resorting to difficult keyword techniques, and the benefits will extend far beyond the customer.
- 3. Richer app experiences
- The diverse Web 3.0 will help more than just websites web apps will begin to provide significantly richer experiences for consumers. Take, for example, Google Maps, which can now combine basic location search with route guidance, lodging recommendations, and real-time traffic updates. In the Web 2.0 era, this was just not achievable.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Jun 30, 2012
10.3k likes | 19.63k Views
Web 3.0. Supervisor : Professor A. Alsedik Presenters : Maram Bani Younes Marilu Cervantes Salgado. Outline . Generations of WWW. Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0 Experts Visions about Web 3.0: Semantic Web Video Web 3D Web Ubiquitous Web Where are we?
Share Presentation
- virtual web site applications
- ontology language
- eric schmidt
- spatial media fragments
- maram bani younes
- generations

Presentation Transcript
Web 3.0 Supervisor : Professor A. Alsedik Presenters : Maram Bani Younes Marilu Cervantes Salgado
Outline • Generations of WWW. • Web 1.0 • Web 2.0 • Web 3.0 • Experts Visions about Web 3.0: • Semantic Web • Video Web • 3D Web • Ubiquitous Web • Where are we? • Over Visions and Opinions about Web 3.0. • What does Web 3.0 need?
Before Now Future Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0
Web 1.0Info – Centric Web • The first generation of the World Wide Web (WWW), characterized by separate static websites. • It is one-way broadcasting. • It is invented 1989 by Tim Berners- Lee. • It was widely used between 1998 and 2001, and it is still used beside Web 2.0 in almost all web sites.
Web 2.0People Centric Web • Technologies and Trends • Social networking sites: • Facebook, MySpace, Hi5, … etc. • Tagging or Labeling Content: • Del.icio.us. • Wikis: • Wikipedia. • Community-generated content: • eBay. • Open Services: • Google. • P2P: • Bit Torrent. • New Web technologies: • XML, RSS, Ajax. • Open Source Software
Web 2.0People Centric Web • Web 2.0 has no single definition but can be explained through a series of Internet trends, one being the empowerment of the user . Deitel, Paul J; Deitel, Harvey M
Web 3.0Machine Centric Web • Different meanings are intended to describe the evolution of Web usage and interaction between the many possible evolutionary paths. • The third generation of Web technologies and services that emphasize a machine-facilitated understanding of information on the Web.
Web 3.0Evolution Paths • Semantic Web • Intelligent System Planning • Business and Network Applications • … etc. • Video Web • Web 3D • Ubiquitous and Pervasive Web
Web 3.0Semantic Web • It is a group of methods and technologies to allow machines to understand the meaning - or "semantics" - of information on the World Wide Web. • The semantic web is a vision of information that is understandable by computers, so computers can perform more of the tedious work involved in finding, combining, and acting upon information on the web.
Semantic WebThe Technology • It involves publishing in languages specifically designed for data: Resource Description Framework (RDF), Web Ontology Language (OWL), and Extensible Markup Language (XML): • HTML describes documents and the links between them. • RDF, OWL, and XML, by contrast, can describe arbitrary things such as people, meetings, or airplane parts.
Web 3.0Experts Statements' • Tim Berners-Lee • “…, you’ll Have access to an unbelievable data resource ”. • Nova Spivak • “…It's a set of standards that turns the Web into one big database,” . • “ …I call it the World Wide Database”.
Semantic WebIntelligent • The development of Web 3.0 focuses on adding metadata or information to describe the content of the web which: • Provide an intelligent level to the web site. • Enable the user to communicate completely with the machines. • Enable machines to communicate with each others.
Semantic WebIntelligent System Planning • Example: The Question: ”I’m looking for a warm place to vacation and I have a budget of $3000. and I have an 11-year-old child.” • Today’s System, such query can lead to hours of sifting (through lists of flights, hotel, car rentals) and the options are often at odds with one another. • Web 3.0 will call up a complete vacation package that was planned as meticulously as if it had been assembled by a human travel agent.
Semantic WebBusiness and Network Applications • Web 3.0 is the ability for customers to communicate with companies. • Directly, using blogs and other Web 2.0 applications, • Indirectly, as if we were holders of psychographic data analyzed by the semantic web and other marketing tools as Micro targeting / Silent Marketing.
Semantic WebSemantic Meaning • Having a semantic meaning on the web, evolution will lead to have more intelligent and specialized webs. • All next evolution paths in this paper depend on having information about the web components.
We can say that Semantic web is the main and starting point of Web 3.0 evolution.
Web 3.0Video Web Spatial Media Fragments Video Content • Reed Hasting, the founder and CEO of Netflix, described Web 3.0 as being the full-video Web that will be made possible by the increasing growth in bandwidth available to customers that will allow transmission of full movies over the Web.
Web 3.0Web 3D Web 3.0 will be 3D-Internet! • Web 3.0 will be nothing else than three-dimensional internet. • At list very moment thousands of users worldwide linger in 3D-worlds like second Life or 3D-Games such as Entropiauniverse and Active worlds. • Philip Rosedale, founder of Second Life, believes that one day 1500 million people will have a second existence. • The adding of the third dimension will shift the internet into a hyper-realistic parallel world . http://www.internet3d.org
Web 3.0Ubiquitous and pervasive web • “Our Vision of Web 3.0 is to link data and devices in new ways to achieve new insights, greater efficiencies, economic benefits and improved quality of life” Steve Bratt. • “The Web 3.0 will see applications that are pieced together, fast, customizable, run on any device, and most importantly, disseminate virally–through social networks” Eric Schmidt, CEO of Google
Web History and Future
Web 3.0Where are we? • After we illustrates Web 1.0, Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, we get that there are no boundaries of time for any of them. • So we should change our first idea about them into….
Now Before Future Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0
Our Expectations
Web 3.0Our Visions • Web 3.0 as we foresee it: having a Clever and On demand friend who is able to lead, advice, negotiate and support the user honestly. • This friend could be embedded in the smart devices, enabling the user to use his home, car or mobile remotely, safely and correctly.
That will affect our daily life and blue our real life with a virtual web site applications and services as Ubiquitous Web. • “If you find your TV on, you should expect one viruse.”
On the other hand, although Web 3D is considered as a huge evolution in the web history, we believe that human cannot satisfy in living as an avatar in a virtual life. • This could be used just for playing or entertaining.
Web 3.0Perspectives Two main paths: • Interchange of knowledge • Semantic Web • A ubiquitous Web • Video on the Web • Social Networks and Business Object • Social networking sites, 3DWeb • Video on Demand through Internet
Web 3.0Perspectives • Interchange of knowledge • Ubiquitous Web: I think is the Natural evolution of the Web. It has to be everywhere on everything by nature. And much of the work is going in that direction. All the science fiction about it is becoming reality. We want things easier
Web 3.0Perspectives • Interchange of knowledge • Video on the Web : On my point of view, there are two different sides of Video on the Web. • Consortiums are working in order to make Video description available and the one that wants to We will have a database of links and information in the background. That is useful in my opinion and an advance in the Video industry in which they can embed more than just the visual meaning • Video through the Web
Web 3.0Perspectives • Social Network and Business Object • Social networking sites, 3DWeb and Video on Demand through Internet: Things are not being done as before and some of them are the way people meet people and the way we get entertaining. For sure socializing within the Web has changed or is changing our behaviour. And the way we watch movies or series is not only in TV anymore. These two ways, some companies have converted the Web, cost us a lot of resources (bandwidth, money and time) and leave us with less physical and regular social activities
Web 3.0What does it need? • Advanced Technology; Software, Hardware and Protocols. • Larger Bandwidth and network capacity. • A good level of Privacy, Security and Controllability should be granted over Web 3.0 to encourage people to use it.
Questions???
- More by User

II. Web 3.0. explained with a stamp (English version) Part I: the basics Part II: techniques. A presentation from: Freek Bijl (Dutch) blog: Bijlbrand.nl. Web 3.0 - the semantic web - is about the meaning of data. This is a stamp. In 1980 you could buy this stamp for 1 cent.
1.11k views • 51 slides

Web 3.0. explained with a stamp (English version) Part I: the basics Part II: techniques. A presentation from: Freek Bijl (Dutch) blog: Bijlbrand.nl. When the web was in its early days, we didn’t know exactly what to show on a computer screen. A company card?. A call to action?.
2.14k views • 45 slides

Web 3.0. Casey Tyler. Web 2.0 vs. Web 3.0. Web 2.0 includes interaction between people Youtube Amazon Facebook Blogs Web 3.0 allows people to interact with information. …Continued. Web 2.0 searches return information that include keywords within the response
556 views • 6 slides

Web 3.0 update
eCircle SLC Emerging Entrepreneurs. Web 3.0 update. Topics. Google Panda Google Push into Social / +1 Keyword Targeted Domain Name Dropping Changes in Google Local Search Linked in Social - New Apps Facebook Experiments. Personalized Search .
519 views • 30 slides

Web 3.0 or The Semantic Web
Web 3.0 or The Semantic Web. By: Konrad Sit CCT355 November 21 st 2011. Web 1.0. Mostly flat information Some databases but content very functional Little engagement or interactivity. Web 1.0. Web 1.0 design elements Some typical design elements of a Web 1.0 site include:
517 views • 19 slides

Web 2.0 Web 3.0 and beyond
Web 2.0 Web 3.0 and beyond. Vocab. Web 2.0 Web 3.0 Collaborative online tools Wikis Blogs Micro-blogs RDF RSS. Mashups Forums Social bookmarking Online collaboartive application Podcasts Photocasts Vidcasts. Vocab (cont). Social networking sites Templatses Tagging
237 views • 6 slides

Web 3.0. Relative to 3D & Simulated Environments Specific to Healthcare. Education: “…finite opportunities within infinite possibilities…”. Supra Manohar Executive Vice President. Web 3.0: Exploration of 3D and Simulated environments.
554 views • 11 slides

EPIC Web 3.0 Demonstration
United States Department of Agriculture Office of the Chief Financial Officer National Finance Center. EPIC Web 3.0 Demonstration. January 16, 2008. Agenda. Introductions EPIC Application Document List Search Criteria New Document Type List Payroll Documents Personnel Documents
561 views • 31 slides

Web 3.0 emerges…
Web 3.0 emerges…. Jim Hendler Tetherless World Professor of Computer and Cognitive Science Assistant Dean of Information Technology and Web Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~hendler @jahendler (twitter). Semantic Web ca. 2010.
334 views • 14 slides

Ready for Web 3.0?
Ready for Web 3.0?. ALPSP Seminar July 2010 David R Worlock. The tower as an image of change …. The step as an image of progress…. The Logic of Change. Keyword searching in 1979 Thesaurus to taxonomy Algorithms and Inference Rules. Information Services and Solutions Value Model.
208 views • 11 slides

NRP Ver 3.0 WEB
System Overview Module 2 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Answer the ten module questions. The first two slides will have the questions and the next two slides will have the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly.
176 views • 6 slides

System Overview Module 4 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Answer as many of these questions as you can. The First slide will have the questions; the next slide will have the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly.
219 views • 6 slides

System Overview Module 6 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Answer as many of these questions as you can. The First slide will have the questions; the next slide will have the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly.
129 views • 4 slides

System Overview Module 3 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Answer as many of these questions as you can. The First slide will have the questions; the next slide will have the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly.
200 views • 4 slides

System Overview Module 1 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Match the term to its characteristic. The first slide is the activity. The next slide has the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB.
159 views • 4 slides

System Overview Module 5 Activity. NRP Ver 3.0 WEB. Activity Objective. Answer as many of these questions as you can. The First slide will have the questions; the next slide will have the answers. Return to your student guide and review any questions you answered incorrectly.
111 views • 4 slides

Web 2.0 + Web 3.0 = Web 5.0?
Web 2.0 + Web 3.0 = Web 5.0?. The HSFBCY + CIHR + Microsoft Research SADI and CardioSHARE Projects Mark Wilkinson & Bruce McManus Heart + Lung Institute iCAPTURE Centre, St. Paul’s Hospital, UBC. Non-logical reasoning and querying over distributed data that doesn’t exist.
449 views • 32 slides

What is web 3.0 and difference between web 2.0 and web 3.0
Web 3.0 can also be called third generation web.Web 3.0 is about the semantic web, dynamic applications, intelligent search, personalization and behavioral advertising, interactive services and machine to machine interaction. For more information - https://www.updateeverytime.com/what-is-web-3-0-and-difference-between-web-2-0-and-web-3-0/
287 views • 6 slides

Web 2.0 + Web 3.0 = Web 5.0?. The HSFBCY + CIHR + Microsoft Research SADI and CardioSHARE Projects Mark Wilkinson Heart + Lung Research Institute iCAPTURE Centre, St. Paul’s Hospital, UBC. “Non-logical” reasoning and SPARQL queries over distributed data that doesn’t exist.
583 views • 45 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Web 3.0, also known as web3, is the third generation of the internet that focuses on decentralized data interconnections. It aims to provide faster and more personalized user experiences through decentralization, user utility, and openness. Here, we will explain the fundamentals of web 3.0 and help you learn more about the use cases, features ...
Web 2.0 requires content creators to trust platforms not to change the rules, but censorship resistance is a native feature of a Web3 platform. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) As well as owning your data in Web3, you can own the platform as a collective, using tokens that act like shares in a company. DAOs let you coordinate ...
Disadvantages of web 3.0. Less advanced devices would be left out. With change in the cost model, some services may no longer be free. With internet providers under government control, the internet will still not be decentralized. decentralization will lead to difficulties in monitoring and regulating Web 3.
The next era of the internet. Web3 and Web 3.0 are often mixed up because the next era of the internet will likely feature elements of both movements — semantic web applications, linked data and ...
Web3 is the idea of a new, decentralized internet built on blockchains, which are distributed ledgers controlled communally by participants. Because of the collective nature of blockchains, if and when Web3 fully arrives—elements of it are already in place—it will, in theory, signal a new era of the internet, one in which use and access are ...
Web 1.0 was the first iteration of the Internet we're familiar with today, emerging in 1994 and ending around 2004 with the rise of social media giants like Twitter and Facebook. ... In his recent Future of Chainlink presentation, Chainlink Co-founder Sergey Nazarov explained the emerging megatrends of the Web3 ecosystem that have recently ...
The evolution of the internet — from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0. The web has come a long way in the past three decades. From the early days of 1.0, when the internet was primarily used for sharing text-based information, to today's 3.0 era, where we can share and interact with rich media content (such as audio, video, and images), the web has greatly evolved to meet user needs.
3 likes • 2,421 views. M. mcdowellmike. 1 of 21. Download Now. Download to read offline. Web 3.0 presentation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Download these elegant web 3.0 presentation templates now, and create compelling presentations. All the slides are fully customizable with easy-to-edit features. Include slides with high-quality and engaging infographics. You can find a mix of dark blue and rose themes in all the slides. Contain a web 3 definition slide, a timeline slide, and ...
The hype around rising levels of AR and VR gadget production is real. Web 3.0 aims to offer a three-dimensional digital world, which can allow users to access internet services. The immersive experiences in web3 applications through VR and AR platforms or metaverse projects could shape a three-dimensional internet.
Web 3.0 promises a decentralized internet built on the blockchain. Here's what that collection of buzzwords means for how you may access the web in the years to come. Even if you're not into ...
About Web 3.0. Web 3.0 is the inevitable change that will offer a more user-centric and personalized experience through the use of decentralization, Artificial Intelligence, extended reality technologies, etc. Web 3.0 presents an upgrade form the typical "read-write" methods used by Web 2.0. It not only offers a better protection of data ...
This slide explains the concept of web 3.0. It explains Web 3.0 uses technologies like Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to facilitate and achieve real-world human communication. Significantly, Web 3.0 not only allows individuals to own data but also get paid for their time spent on the web. «. ».
Web 3.0. New "web 3.0" technologies….a combination of blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT), digital identity, Distributed Autonomous Organization (DAOs), Smart Contracts, DeFi, Non-Fungible Tokens and distributed Artificial Intelligence (AI)…are creating enormous new opportunities for virtually every digital domain.
P. Pradeep Poosappan. Web 3.0 (Web3) is the third generation of the evolution of web technologies. Web 3.0 is a new platform that allows users to connect and share information more freely than ever before. It also offers new ways for businesses to connect with their customers, and makes it easier for people to find the information they need.
Cryptocurrency-enabled. Cryptocurrency is a key feature of Web 3.0 that is expected to largely replace the "fiat currency" issued by government central banks. Semantically organized. The idea behind the Semantic Web is to categorize and store information in a way that helps "teach" an AI-based system what data means.
Layers of Web 3.0. Web 3.0 is propelled by four new layers of technological innovation: Edge Computing - While web 2.0 changed currently commoditized personal computer technology in data centers, web 3.0 pushes the data center out to the edge (i.e. edge computing) and into our hands.; Decentralized Data Network - Users will own their data on web 3.0 since data is decentralized.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. The world of internet is in constant evolution. Have you heard about "Web3"? It's like a new version of the World Wide Web based on blockchain, data "chained" together with cryptography. It's a concept that sounds too difficult to explain with just a couple of lines. So here's our idea: a ...
In clear words, Web 3.0 is. a read-write-execute web.'. 2. It is a solution in which data is shared rather. than owned in what is known as the "Web 3.0." Web. 3.0 allows systems to search for, generate, exchange, and connect material, and artificial. intelligence enables web pages to grasp the.
Semantic WebBusiness and Network Applications • Web 3.0 is the ability for customers to communicate with companies. • Directly, using blogs and other Web 2.0 applications, • Indirectly, as if we were holders of psychographic data analyzed by the semantic web and other marketing tools as Micro targeting / Silent Marketing.
746 likes • 100,741 views. Jo Bhakdi for Pioneerradio. A comprehensive web 3.0 overview. User generated business. By John Bhakdi. More on Pioneerradio.us. Business Technology. 1 of 42. Download Now.
Introducing WEB 3.0 Powerpoint Presentation Template. This Presentation Template can be used for any variety of purposes, such as: Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Virtual Reality, Technology, Game, Creative, Company Profile, Corporate and Business, Project, Multipurpose,Startup, Industry, Minimal and also can be used for Personal Portfo. FEATURES.
Allan Cho. Technology Education. 1 of 14. Linking Mashups and Semantic Web Ideas - Download as a PDF or view online for free.