- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

Benjamin Franklin
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 28, 2023 | Original: November 9, 2009

One of the leading figures of early American history, Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) was a statesman, author, publisher, scientist, inventor and diplomat. Born into a Boston family of modest means, Franklin had little formal education. He went on to start a successful printing business in Philadelphia and grew wealthy. Franklin was deeply active in public affairs in his adopted city, where he helped launch a lending library, hospital and college and garnered acclaim for his experiments with electricity, among other projects. During the American Revolution , he served in the Second Continental Congress and helped draft the Declaration of Independence in 1776. He also negotiated the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the Revolutionary War (1775-83). In 1787, in his final significant act of public service, he was a delegate to the convention that produced the U.S. Constitution .
Benjamin Franklin’s Early Years
Benjamin Franklin was born on January 17, 1706, in colonial Boston. His father, Josiah Franklin (1657-1745), a native of England, was a candle and soap maker who married twice and had 17 children. Franklin’s mother was Abiah Folger (1667-1752) of Nantucket, Massachusetts , Josiah’s second wife. Franklin was the eighth of Abiah and Josiah’s 10 offspring.
Did you know? Benjamin Franklin is the only Founding Father to have signed all four of the key documents establishing the U.S.: the Declaration of Independence (1776), the Treaty of Alliance with France (1778), the Treaty of Paris establishing peace with Great Britain (1783) and the U.S. Constitution (1787).
Franklin’s formal education was limited and ended when he was 10; however, he was an avid reader and taught himself to become a skilled writer. In 1718, at age 12, he was apprenticed to his older brother James, a Boston printer. By age 16, Franklin was contributing essays (under the pseudonym Silence Dogood) to a newspaper published by his brother. At age 17, Franklin ran away from his apprenticeship to Philadelphia, where he found work as a printer. In late 1724, he traveled to London, England, and again found employment in the printing business.
Benjamin Franklin: Printer and Publisher
Benjamin Franklin returned to Philadelphia in 1726, and two years later opened a printing shop. The business became highly successful producing a range of materials, including government pamphlets, books and currency. In 1729, Franklin became the owner and publisher of a colonial newspaper, the Pennsylvania Gazette , which proved popular—and to which he contributed much of the content, often using pseudonyms. Franklin achieved fame and further financial success with “Poor Richard’s Almanack,” which he published every year from 1733 to 1758. The almanac became known for its witty sayings, which often had to do with the importance of diligence and frugality, such as “Early to bed and early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise.”
In 1730, Franklin began living with Deborah Read (c. 1705-74), the daughter of his former Philadelphia landlady, as his common-law wife. Read’s first husband had abandoned her; however, due to bigamy laws, she and Franklin could not have an official wedding ceremony. Franklin and Read had a son, Francis Folger Franklin (1732-36), who died of smallpox at age 4, and a daughter, Sarah Franklin Bache (1743-1808). Franklin had another son, William Franklin (c. 1730-1813), who was born out of wedlock. William Franklin served as the last colonial governor of New Jersey , from 1763 to 1776, and remained loyal to the British during the American Revolution . He died in exile in England.
Benjamin Franklin and Philadelphia
As Franklin’s printing business prospered, he became increasingly involved in civic affairs. Starting in the 1730s, he helped establish a number of community organizations in Philadelphia, including a lending library (it was founded in 1731, a time when books weren’t widely available in the colonies, and remained the largest U.S. public library until the 1850s), the city’s first fire company , a police patrol and the American Philosophical Society , a group devoted to the sciences and other scholarly pursuits.
Franklin also organized the Pennsylvania militia, raised funds to build a city hospital and spearheaded a program to pave and light city streets. Additionally, Franklin was instrumental in the creation of the Academy of Philadelphia, a college which opened in 1751 and became known as the University of Pennsylvania in 1791.
Franklin also was a key figure in the colonial postal system. In 1737, the British appointed him postmaster of Philadelphia, and he went on to become, in 1753, joint postmaster general for all the American colonies. In this role he instituted various measures to improve mail service; however, the British dismissed him from the job in 1774 because he was deemed too sympathetic to colonial interests. In July 1775, the Continental Congress appointed Franklin the first postmaster general of the United States, giving him authority over all post offices from Massachusetts to Georgia . He held this position until November 1776, when he was succeeded by his son-in-law. (The first U.S. postage stamps, issued on July 1, 1847, featured images of Benjamin Franklin and George Washington .)
Benjamin Franklin's Inventions
In 1748, Franklin, then 42 years old, had expanded his printing business throughout the colonies and become successful enough to stop working. Retirement allowed him to concentrate on public service and also pursue more fully his longtime interest in science. In the 1740s, he conducted experiments that contributed to the understanding of electricity, and invented the lightning rod, which protected buildings from fires caused by lightning. In 1752, he conducted his famous kite experiment and demonstrated that lightning is electricity. Franklin also coined a number of electricity-related terms, including battery, charge and conductor.
In addition to electricity, Franklin studied a number of other topics, including ocean currents, meteorology, causes of the common cold and refrigeration. He developed the Franklin stove, which provided more heat while using less fuel than other stoves, and bifocal eyeglasses, which allow for distance and reading use. In the early 1760s, Franklin invented a musical instrument called the glass armonica. Composers such as Ludwig Beethoven (1770-1827) and Wolfgang Mozart (1756-91) wrote music for Franklin’s armonica; however, by the early part of the 19th century, the once-popular instrument had largely fallen out of use.
READ MORE: 11 Surprising Facts About Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin and the American Revolution
In 1754, at a meeting of colonial representatives in Albany, New York , Franklin proposed a plan for uniting the colonies under a national congress. Although his Albany Plan was rejected, it helped lay the groundwork for the Articles of Confederation , which became the first constitution of the United States when ratified in 1781.
In 1757, Franklin traveled to London as a representative of the Pennsylvania Assembly, to which he was elected in 1751. Over several years, he worked to settle a tax dispute and other issues involving descendants of William Penn (1644-1718), the owners of the colony of Pennsylvania. After a brief period back in the U.S., Franklin lived primarily in London until 1775. While he was abroad, the British government began, in the mid-1760s, to impose a series of regulatory measures to assert greater control over its American colonies. In 1766, Franklin testified in the British Parliament against the Stamp Act of 1765, which required that all legal documents, newspapers, books, playing cards and other printed materials in the American colonies carry a tax stamp. Although the Stamp Act was repealed in 1766, additional regulatory measures followed, leading to ever-increasing anti-British sentiment and eventual armed uprising in the American colonies .
Franklin returned to Philadelphia in May 1775, shortly after the Revolutionary War (1775-83) had begun, and was selected to serve as a delegate to the Second Continental Congress, America’s governing body at the time. In 1776, he was part of the five-member committee that helped draft the Declaration of Independence , in which the 13 American colonies declared their freedom from British rule. That same year, Congress sent Franklin to France to enlist that nation’s help with the Revolutionary War. In February 1778, the French signed a military alliance with America and went on to provide soldiers, supplies and money that proved critical to America’s victory in the war.
As minister to France starting in 1778, Franklin helped negotiate and draft the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the Revolutionary War.
Benjamin Franklin’s Later Years
In 1785, Franklin left France and returned once again to Philadelphia. In 1787, he was a Pennsylvania delegate to the Constitutional Convention. (The 81-year-old Franklin was the convention’s oldest delegate.) At the end of the convention, in September 1787, he urged his fellow delegates to support the heavily debated new document. The U.S. Constitution was ratified by the required nine states in June 1788, and George Washington (1732-99) was inaugurated as America’s first president in April 1789.
Franklin died a year later, at age 84, on April 17, 1790, in Philadelphia. Following a funeral that was attended by an estimated 20,000 people, he was buried in Philadelphia’s Christ Church cemetery. In his will, he left money to Boston and Philadelphia, which was later used to establish a trade school and a science museum and fund scholarships and other community projects.
More than 200 years after his death, Franklin remains one of the most celebrated figures in U.S. history. His image appears on the $100 bill, and towns, schools and businesses across America are named for him.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Benjamin Franklin
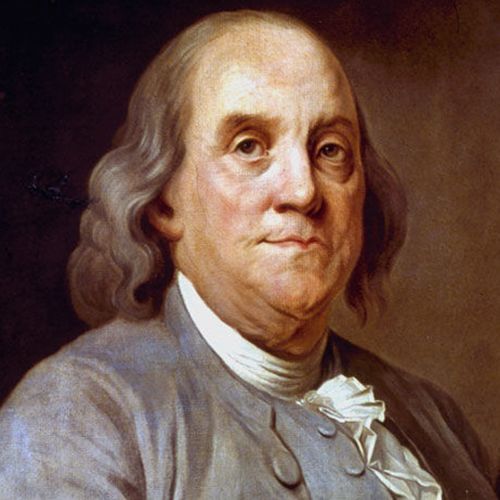

(1706-1790)
Who Was Benjamin Franklin?
His scientific pursuits included investigations into electricity, mathematics and mapmaking. A writer known for his wit and wisdom, Franklin also published Poor Richard’s Almanack , invented bifocal glasses and organized the first successful American lending library.
Franklin was born on January 17, 1706, in Boston, in what was then known as the Massachusetts Bay Colony.
Franklin’s father, English-born soap and candlemaker Josiah Franklin, had seven children with first wife, Anne Child, and 10 more with second wife, Abiah Folger. Franklin was his 15th child and youngest son.
Franklin learned to read at an early age, and despite his success at the Boston Latin School, he stopped his formal schooling at 10 to work full-time in his cash-strapped father’s candle and soap shop. Dipping wax and cutting wicks didn’t fire the young boy’s imagination, however.
Perhaps to dissuade him from going to sea as one of his other sons had done, Josiah apprenticed 12-year-old Franklin at the print shop run by his older brother James.
Although James mistreated and frequently beat his younger brother, Franklin learned a great deal about newspaper publishing and adopted a similar brand of subversive politics under the printer’s tutelage.
Silence Dogood
When James refused to publish any of his brother’s writing, 16-year-old Franklin adopted the pseudonym Mrs. Silence Dogood, and “her” 14 imaginative and witty letters delighted readers of his brother’s newspaper, The New England Courant . James grew angry, however, when he learned that his apprentice had penned the letters.
Tired of his brother’s “harsh and tyrannical” behavior, Franklin fled Boston in 1723 although he had three years remaining on a legally binding contract with his master.
He escaped to New York before settling in Philadelphia and began working with another printer. Philadelphia became his home base for the rest of his life.
Living in London
Encouraged by Pennsylvania Governor William Keith to set up his own print shop, Franklin left for London in 1724 to purchase supplies from stationers, booksellers and printers. When the teenager arrived in England, however, he felt duped when Keith’s letters of introduction never arrived as promised.
Although forced to find work at London’s print shops, Franklin took full advantage of the city’s pleasures—attending theater performances, mingling with the locals in coffee houses and continuing his lifelong passion for reading.
A self-taught swimmer who crafted his own wooden flippers, Franklin performed long-distance swims on the Thames River. (In 1968, he was inducted as an honorary member of the International Swimming Hall of Fame .)
In 1725 Franklin published his first pamphlet, "A Dissertation upon Liberty and Necessity, Pleasure and Pain," which argued that humans lack free will and, thus, are not morally responsible for their actions. (Franklin later repudiated this thought and burned all but one copy of the pamphlet still in his possession.)
Wife and Children
In 1723, after Franklin moved from Boston to Philadelphia, he lodged at the home of John Read, where he met and courted his landlord’s daughter Deborah.
After Franklin returned to Philadelphia in 1726, he discovered that Deborah had married in the interim, only to be abandoned by her husband just months after the wedding.
The future Founding Father rekindled his romance with Deborah Read and he took her as his common-law wife in 1730. Around that time, Franklin fathered a son, William, out of wedlock who was taken in by the couple. The pair’s first son, Francis, was born in 1732, but he died four years later of smallpox. The couple’s only daughter, Sarah, was born in 1743.
The two times Franklin moved to London, in 1757 and again in 1764, it was without Deborah, who refused to leave Philadelphia. His second stay was the last time the couple saw each other. Franklin would not return home before Deborah passed away in 1774 from a stroke at the age of 66.
In 1762, Franklin’s son William took office as New Jersey’s royal governor, a position his father arranged through his political connections in the British government. Franklin’s later support for the patriot cause put him at odds with his loyalist son. When the New Jersey militia stripped William Franklin of his post as royal governor and imprisoned him in 1776, his father chose not to intercede on his behalf.
Life in Philadelphia
After his return to Philadelphia in 1726, Franklin held varied jobs including bookkeeper, shopkeeper and currency cutter. In 1728 he returned to a familiar trade - printing paper currency - in New Jersey before partnering with a friend to open his own print shop in Philadelphia that published government pamphlets and books.
In 1730 Franklin was named the official printer of Pennsylvania. By that time, he had formed the “Junto,” a social and self-improvement study group for young men that met every Friday to debate morality, philosophy and politics.
When Junto members sought to expand their reading choices, Franklin helped to incorporate America’s first subscription library, the Library Company of Philadelphia, in 1731.
In 1729 Franklin published another pamphlet, "A Modest Enquiry into The Nature and Necessity of a Paper Currency," which advocated for an increase in the money supply to stimulate the economy.
With the cash Franklin earned from his money-related treatise, he was able to purchase The Pennsylvania Gazette newspaper from a former boss. Under his ownership, the struggling newspaper was transformed into the most widely-read paper in the colonies and became one of the first to turn a profit.
He had less luck in 1732 when he launched the first German-language newspaper in the colonies, the short-lived Philadelphische Zeitung . Nonetheless, Franklin’s prominence and success grew during the 1730s.
Franklin amassed real estate and businesses and organized the volunteer Union Fire Company to counteract dangerous fire hazards in Philadelphia. He joined the Freemasons in 1731 and was eventually elected grand master of the Masons of Pennsylvania.
Poor Richard's Almanack
At the end of 1732, Franklin published the first edition of Poor Richard’s Almanack .
In addition to weather forecasts, astronomical information and poetry, the almanac—which Franklin published for 25 consecutive years—included proverbs and Franklin’s witty maxims such as “Early to bed and early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise” and “He that lies down with dogs, shall rise up with fleas.”
Scientist and Inventor
In the 1740s, Franklin expanded into science and entrepreneurship. His 1743 pamphlet "A Proposal for Promoting Useful Knowledge" underscored his interests and served as the founding document of the American Philosophical Society , the first scientific society in the colonies.
By 1748, the 42-year-old Franklin had become one of the richest men in Pennsylvania, and he became a soldier in the Pennsylvania militia. He turned his printing business over to a partner to give himself more time to conduct scientific experiments. He moved into a new house in 1748.
Franklin was a prolific inventor and scientist who was responsible for the following inventions:
- Franklin stove : Franklin’s first invention, created around 1740, provided more heat with less fuel.
- Bifocals : Anyone tired of switching between two pairs of glasses understands why Franklin developed bifocals that could be used for both distance and reading.
- Armonica : Franklin’s inventions took on a musical bent when, in 1761, he commenced development on the armonica, a musical instrument composed of spinning glass bowls on a shaft. Both Ludwig van Beethoven and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart composed music for the strange instrument.
- Rocking chair
- Flexible catheter
- American penny
Franklin also discovered the Gulf Stream after his return trip across the Atlantic Ocean from London in 1775. He began to speculate about why the westbound trip always took longer, and his measurements of ocean temperatures led to his discovery of the existence of the Gulf Stream. This knowledge served to cut two weeks off the previous sailing time from Europe to North America.
Franklin even devised a new “scheme” for the alphabet that proposed to eliminate the letters C, J, Q, W, X and Y as redundant.
Franklin’s self-education earned him honorary degrees from Harvard , Yale , England’s University of Oxford and the University of St. Andrews in Scotland.
In 1749, Franklin wrote a pamphlet concerning the education of youth in Pennsylvania that resulted in the establishment of the Academy of Philadelphia, now the University of Pennsylvania .
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S BENJAMIN FRANKLIN FACT CARD

Electricity
In 1752, Franklin conducted the famous kite-and-key experiment to demonstrate that lightning was electricity and soon after invented the lightning rod.
His investigations into electrical phenomena were compiled into “Experiments and Observations on Electricity,” published in England in 1751. He coined new electricity-related terms that are still part of the lexicon, such as battery, charge, conductor and electrify.
In 1748, Franklin acquired the first of several enslaved people to work in his new home and in the print shop. Franklin’s views on slavery evolved over the following decades to the point that he considered the institution inherently evil, and thus, he freed his enslaved people in the 1760s.
Later in life, he became more vociferous in his opposition to slavery. Franklin served as president of the Pennsylvania Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery and wrote many tracts urging the abolition of slavery . In 1790 he petitioned the U.S. Congress to end slavery and the trade.
Election to the Government
Franklin became a member of Philadelphia’s city council in 1748 and a justice of the peace the following year. In 1751, he was elected a Philadelphia alderman and a representative to the Pennsylvania Assembly, a position to which he was re-elected annually until 1764. Two years later, he accepted a royal appointment as deputy postmaster general of North America.
When the French and Indian War began in 1754, Franklin called on the colonies to band together for their common defense, which he dramatized in The Pennsylvania Gazette with a cartoon of a snake cut into sections with the caption “Join or Die.”
He represented Pennsylvania at the Albany Congress, which adopted his proposal to create a unified government for the 13 colonies. Franklin’s “Plan of Union,” however, failed to be ratified by the colonies.
In 1757 Franklin was appointed by the Pennsylvania Assembly to serve as the colony’s agent in England. Franklin sailed to London to negotiate a long-standing dispute with the proprietors of the colony, the Penn family, taking William and his two enslaved people but leaving behind Deborah and Sarah.
He spent much of the next two decades in London, where he was drawn to the high society and intellectual salons of the cosmopolitan city.
After Franklin returned to Philadelphia in 1762, he toured the colonies to inspect its post offices.
Stamp Act and Declaration of Independence
After Franklin lost his seat in the Pennsylvania Assembly in 1764, he returned to London as the colony’s agent. Franklin returned at a tense time in Great Britain’s relations with the American colonies.
The British Parliament ’s passage of the Stamp Act in March 1765 imposed a highly unpopular tax on all printed materials for commercial and legal use in the American colonies. Since Franklin purchased stamps for his printing business and nominated a friend as the Pennsylvania stamp distributor, some colonists thought Franklin implicitly supported the new tax, and rioters in Philadelphia even threatened his house.
Franklin’s passionate denunciation of the tax in testimony before Parliament, however, contributed to the Stamp Act’s repeal in 1766.
Two years later he penned a pamphlet, “Causes of the American Discontents before 1768,” and he soon became an agent for Massachusetts, Georgia and New Jersey as well. Franklin fanned the flames of revolution by sending the private letters of Massachusetts Governor Thomas Hutchinson to America.
The letters called for the restriction of the rights of colonists, which caused a firestorm after their publication by Boston newspapers. In the wake of the scandal, Franklin was removed as deputy postmaster general, and he returned to North America in 1775 as a devotee of the patriot cause.
In 1775, Franklin was elected to the Second Continental Congress and appointed the first postmaster general for the colonies. In 1776, he was appointed commissioner to Canada and was one of five men to draft the Declaration of Independence.
Life in Paris
After voting for independence in 1776, Franklin was elected commissioner to France, making him essentially the first U.S. ambassador to France. He set sail to negotiate a treaty for the country’s military and financial support.
Much has been made of Franklin’s years in Paris, chiefly his rich romantic life in his nine years abroad after Deborah’s death. At the age of 74, he even proposed marriage to a widow named Madame Helvetius, but she rejected him.
Franklin was embraced in France as much, if not more, for his wit and intellectual standing in the scientific community as for his status as a political appointee from a fledgling country.
His reputation facilitated respect and entrees into closed communities, including the court of King Louis XVI . And it was his adept diplomacy that led to the Treaty of Paris in 1783, which ended the Revolutionary War. After almost a decade in France, Franklin returned to the United States in 1785.
Drafting the U.S. Constitution
Franklin was elected in 1787 to represent Pennsylvania at the Constitutional Convention , which drafted and ratified the new U.S. Constitution.
The oldest delegate at the age of 81, Franklin initially supported proportional representation in Congress, but he fashioned the Great Compromise that resulted in proportional representation in the House of Representatives and equal representation by state in the Senate . In 1787, he helped found the Society for Political Inquiries, dedicated to improving knowledge of government.
Franklin was never elected president of the United States. However, he played an important role as one of eight Founding Fathers, helping draft the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution.
He also served several roles in the government: He was elected to the Pennsylvania Assembly and appointed as the first postmaster general for the colonies as well as diplomat to France. He was a true polymath and entrepreneur, which is no doubt why he is often called the "First American."
Franklin died on April 17, 1790, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, at the home of his daughter, Sarah Bache. He was 84, suffered from gout and had complained of ailments for some time, completing the final codicil to his will a little more than a year and a half prior to his death.
He bequeathed most of his estate to Sarah and very little to his son William, whose opposition to the patriot cause still stung him. He also donated money that funded scholarships, schools and museums in Boston and Philadelphia.
Franklin had actually written his epitaph when he was 22: “The body of B. Franklin, Printer (Like the Cover of an Old Book Its Contents torn Out And Stript of its Lettering and Gilding) Lies Here, Food for Worms. But the Work shall not be Lost; For it will (as he Believ'd) Appear once More In a New and More Elegant Edition Revised and Corrected By the Author.”
In the end, however, the stone on the grave he shared with his wife in the cemetery of Philadelphia’s Christ Church reads simply, “Benjamin and Deborah Franklin 1790.”
Accomplishments
The image of Franklin that has come down through history, along with his likeness on the $100 bill, is something of a caricature—a bald man in a frock coat holding a kite string with a key attached. But the scope of things he applied himself to was so broad it seems a shame.
Founding universities and libraries, the post office, shaping the foreign policy of the fledgling United States, helping to draft the Declaration of Independence, publishing newspapers, warming us with the Franklin stove, pioneering advances in science, letting us see with bifocals and lighting our way with electricity—all from a man who never finished school but shaped his life through abundant reading and experience, a strong moral compass and an unflagging commitment to civic duty. Franklin illuminated corners of American life that still have the lingering glow of his attention.
Watch "Benjamin Franklin: Citizen of the World" on HISTORY Vault

QUICK FACTS
- Name: Benjamin Franklin
- Birth Year: 1706
- Birth date: January 17, 1706
- Birth State: Massachusetts
- Birth City: Boston
- Birth Country: United States
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Benjamin Franklin is best known as one of the Founding Fathers who never served as president but was a respected inventor, publisher, scientist and diplomat.
- U.S. Politics
- Writing and Publishing
- Business and Industry
- Science and Medicine
- Astrological Sign: Capricorn
- Boston Latin School
- Interesting Facts
- Benjamin Franklin helped draft the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution.
- Franklin was famous for his investigations into electricity and for writing 'Poor Richard's Almanack.'
- Death Year: 1790
- Death date: April 17, 1790
- Death State: Pennsylvania
- Death City: Philadelphia
- Death Country: United States
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Benjamin Franklin Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/scholar/benjamin-franklin
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E; Television Networks
- Last Updated: December 10, 2020
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- A house is not a home unless it contains food and fire for the mind as well as the body.
- Do not fear mistakes. You will know failure. Continue to reach out.
- From a child I was fond of reading, and all the little money that came into my hands was ever laid out in books.
- So convenient a thing it is to be a reasonable creature, since it enables one to find or make a reason for everything one has a mind to do.
- In reality, there is, perhaps, no one of our natural passions so hard to subdue as pride. Disguise it, struggle with it, beat it down, stifle it, mortify it as much as one pleases, it is still alive, and will every now and then peep out and show itself; you will see it, perhaps, often in this history; for, even if I could conceive that I had compleatly overcome it, I should probably be proud of my humility.
- Human felicity is produced not so much by great pieces of good fortune that seldom happen, as by little advantages that occur every day.
- There never was a good war or a bad peace.
- In this world nothing is certain but death and taxes.
- Freedom of speech is a principal pillar of a free government; when this support is taken away, the constitution of a free society is dissolved, and tyranny is erected on its ruins.
- He does not possess wealth, it possesses him.
- Experience keeps a dear school, yet fools will learn in no other.
American Revolutionaries

Cesare Beccaria

Samuel Adams

Andrew Jackson

George Rogers Clark

Roger Sherman

James Monroe

Martha Washington
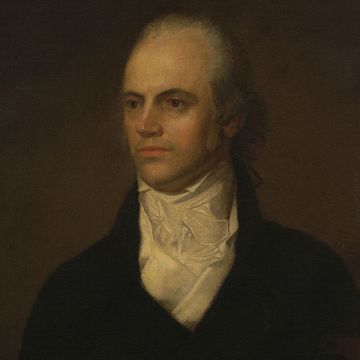
Biography Online

Benjamin Franklin Biography
Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) was a scientist, ambassador, philosopher, statesmen, writer, businessman and celebrated free thinker and wit. Franklin is often referred to as ‘America’s Renaissance Man’ and he played a pivotal role in forging a united American identity during the American Revolution.
Early life Benjamin Franklin

At an early age, he also started writing articles which were published in the ‘New England Courant’ under a pseudonym; Franklin wrote under pseudonyms throughout his life. After several had been published, he admitted to his father that he had written them. Rather than being pleased, his father beat him for his impudence. Therefore, aged 17, the young Benjamin left the family business and travelled to Philadelphia.
“The Constitution only guarantees the American people the right to pursue happiness. You have to catch it yourself.”
- Benjamin Franklin
In Philadelphia, Benjamin’s reputation as an acerbic man of letters grew. His writings were both humorous and satirical, and his capacity to take down powerful men came to the attention of Pennsylvania governor, William Keith. William Keith was fearful of Benjamin’s satire so offered him a job in England with all expenses paid. Benjamin took the offer, but once in England, the governor deserted Franklin, leaving him with no funds.
Benjamin Franklin frequently found himself in awkward situations, but his natural resourcefulness and determination always overcame difficult odds. Benjamin found a job at a printer in London. Here he was known as the “Water American” – as he preferred to drink water rather than the usual six pints of beer daily. Franklin remarked there was ‘more nourishment in a pennyworth of bread than in a quart of beer.’
In 1726, a Quaker Merchant, Mr Denham offered him a position in Philadelphia. Franklin accepted and sailed back to the US.
On his journey home, Benjamin wrote a list of 13 virtues he thought important for his future life. Amongst these were temperance, frugality, sincerity, justice and tranquillity. He originally had 12, but, since a friend remarked he had great pride, he added a 13th – humility (Imitate Jesus and Socrates.)
Virtues of Benjamin Franklin
1. “TEMPERANCE. Eat not to dullness; drink not to elevation.”
2. “SILENCE. Speak not but what may benefit others or yourself; avoid trifling conversation.”
3. “ORDER. Let all your things have their places; let each part of your business have its time.”
4. “RESOLUTION. Resolve to perform what you ought; perform without fail what you resolve.”
5. “FRUGALITY. Make no expense but to do good to others or yourself; i.e., waste nothing.”
6. “INDUSTRY. Lose no time; be always employed in something useful; cut off all unnecessary actions.”
7. “SINCERITY. Use no hurtful deceit; think innocently and justly, and, if you speak, speak accordingly.”
8. “JUSTICE. Wrong none by doing injuries, or omitting the benefits that are your duty.”
9. “MODERATION. Avoid extremes; forbear resenting injuries so much as you think they deserve.”
10. “CLEANLINESS. Tolerate no uncleanliness in body, cloaths, or habitation.”
11. “TRANQUILLITY. Be not disturbed at trifles, or at accidents common or unavoidable.”
12. “CHASTITY. Rarely use venery but for health or offspring, never to dullness, weakness, or the injury of your own or another’s peace or reputation.”
13. “HUMILITY. Imitate Jesus and Socrates.”
Franklin sought to cultivate these virtues throughout the remainder of life. His approach to self-improvement lasted throughout his life.
Back in America, Franklin had many successful endeavours in business, journalism, science and statesmanship.
Scientific Achievements of Benjamin Franklin
Science experiments were a hobby of Franklin. This led to the:
- Franklin stove – a mechanism for distributing heat throughout a room.
- The famous kite and key in the thunderstorm. This proved that lightning and electricity were one and the same thing.
- He was the first person to give electricity positive and negative charges
- The first flexible urinary catheter
- Glass harmonica (also known as the glass armonica)
- Bifocal glasses.
Franklin never patented his inventions, preferring to offer them freely for the benefit of society. As he wrote:
“… as we enjoy great advantages from the inventions of others, we should be glad of an opportunity to serve others by any invention of ours; and this we should do freely and generously.”
Benjamin Franklin as Ambassador
Franklin was chosen as an ambassador to England in the dispute over taxes. For five years he held conferences with political leaders as well as continuing his scientific experiments and musical studies.
Later on, Franklin played a key role in warning the British government over the dangers of taxing the American colonies. In a contest of wills, Franklin was instrumental in encouraging the British Parliament to revoke the hated Stamp Act. However, this reversal was to be short-lived. And when further taxes were issued, Franklin declared himself a supporter of the new American independence movement.
In 1775, he returned to an America in conflict. He was one of the five representatives chosen to draw up the American Declaration of Independence with Thomas Jefferson as the author.
Franklin was chosen to be America’s ambassador to France, where he worked hard to gain the support of the French in America’s war effort. During his time in French society, Franklin was widely admired, and his portrait was hung in many houses.
At the age of 75, the newly formed US government beseeched Franklin to be America’s representative in signing a peace treaty with Great Britain which was signed in 1783.
He was finally replaced as French ambassador by Thomas Jefferson, who paid tribute to his enormous capacity Jefferson remarked; “I succeed him; no one can replace him.”
Religious Beliefs of Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin believed in God throughout his life. In his early life, he professed a belief in Deism. However, he never gave too much importance to organised religion. He was well known for his religious tolerance, and it was remarked how people from different religions could think of him as one of them. As John Adams noted:
“The Catholics thought him almost a Catholic. The Church of England claimed him as one of them. The Presbyterian’s thought him half a Presbyterian, and the Friends believed him a wet Quaker.”
Franklin embodied the spirit of the enlightenment and spirituality over organised religion.
Franklin was a keen debater, but his style was to avoid confrontation and condemnation. He would prefer to argue topics through the asking of awkward questions, not dissimilar to the Greek philosopher Socrates .
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “Biography of Benjamin Franklin ”, Oxford, UK. www.biographyonline.net , 5th Feb 2010. Last updated 5 March 2019.
Benjamin Franklin: An American Life

Benjamin Franklin: An American Life at Amazon
The Autobiography Of Benjamin Franklin

The Autobiography Of Benjamin Franklin at Amazon
Related pages

Famous Americans – Great Americans from the Founding Fathers to modern civil rights activists. Including presidents, authors, musicians, entrepreneurs and businessmen.

- US politicians
- People who built America
- Quotes by Benjamin Franklin
- Ben Franklin at PBS

Benjamin Franklin

- Occupation: Statesman and Inventor
- Born: January 17, 1706 in Boston, Massachusetts
- Died: April 17, 1790 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- Best known for: Founding father of the United States

- Ben was his dad's 15th child of 17 total children!
- Ben Franklin was the first Postmaster General of the United States.
- Later in life, Ben set his slaves free and became a fighter for the freedom of slaves.
- He didn't patent any of his many inventions, letting people use his ideas for free.
- Franklin became fairly wealthy from the publishing of Poor Richard's Almanack .
- He loved playing chess and was inducted into the U.S. Chess Hall of Fame in 1999.
- As a teenager, Franklin had several letters published in his brother's newspaper under the fake name "Silence Dogood." His brother was not happy when he found out.
- During his life, Franklin's views on slavery changed dramatically. In 1748, he purchased his first slave, but by 1760 he had freed all of his slaves. He became a staunch abolitionist and spent much of his later life campaigning for an end to slavery.
- Listen to a recorded reading of this page:

- Grades K-1 Articles
- Grade 2 Articles
- Grades 3-4 Articles
- Grades 5-6 Articles
- Earth Science
- Engineering
- Environment
- Food and Nutrition
- Movies and Television
- Music and Theater
- Service Stars
- The Human Body
- Transportation
- Young Game Changers
- Grade 4 Edition
- Grade 5-6 Edition
- For Grown-ups
- Also from TIME for Kids:

- user_age: none
The page you are about to enter is for grown-ups. Enter your birth date to continue.
TFK Library
Benjamin franklin, june 14, 2018.
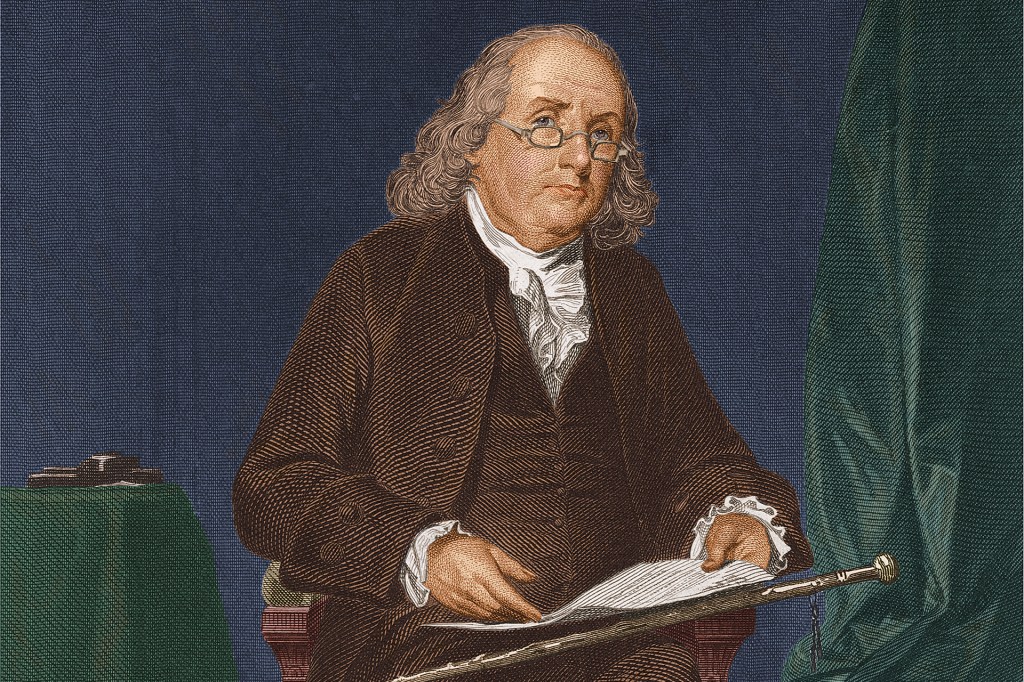

Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706—April 17, 1790) was a scientist, an inventor, a writer, and a statesman. He helped draft the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution.
Benjamin Franklin was born in Boston on January 17, 1706. He learned to read at an early age. But his father, Josiah Franklin, pulled him out of school when he was 10 years old. He sent Ben to work in the family candle and soap shop. Ben grew restless with the work. When he turned 12, his father sent him to work in a printer’s shop. It was owned by Ben’s older brother, James.
Ben learned all about the newspaper business. At the time, printing was done by hand. The printer laid out the page letter by letter on a printing press. Ben learned how to build sentences with care. He also learned to write. He wrote political essays. He did not sign his name to the essays. Instead, he signed them Silence Dogood. This was so readers would think they were written by an ordinary person in the town. But his brother James did not want Ben to write. He often beat him. So at 16, Ben fled to Philadelphia. He would call the city home for the rest of his life.
Ambition and Invention
Franklin became known in Philadelphia as a hardworking young man. In 1728, he and a friend opened a print shop. Then in 1729, he bought the Pennsylvania Gazette. He turned it into the most widely read newspaper in the American colonies. At the time, newspapers were the best way to spread ideas. Newspapers spread the ideas that would eventually bring about the American Revolution.
Over the years, Franklin became even more well-known. In 1732, he began publishing the yearly Poor Richard’s Almanack. He wrote in the voice of a farmer named Poor Richard. The almanac contained weather forecasts, information about astronomy, poetry, and other amusements. It became famous for its folksy proverbs. Two of the most famous proverbs are “No pains without gains” and “Early to bed, early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise.”

GRAPHICAARTIS/GETTY IMAGES
Franklin became one of the richest men in Pennsylvania. In 1748, he retired from the print business. He wanted to devote his time to science. His famous kite-and-key experiment in 1752 demonstrated that lighting was electricity. He invented the lightning rod. Some of the terms he coined are still used today, such as battery, charge, and electrify. He also invented bifocal eyeglasses and maybe even the first rocking chair.
Founding Father
In 1751, Franklin was elected as a representative to the Pennsylvania Assembly. He was reelected every year until 1764.
In March 1765, the British government passed the Stamp Act. This made the North American colonists angry. The act required that the colonists pay a tax on printed materials. The colonists used a lot of printed material. They used print documents for business and legal matters. At the time, Franklin was living in London. He was Pennsylvania’s agent in Britain. He went before the British Parliament to condemn the tax. The bill was repealed in 1766.
Franklin was elected to the Second Continental Congress in 1775. He believed the American colonies should separate from English rule. In 1776, he joined a committee to draft the Declaration of Independence. He then traveled to France. There, he negotiated a treaty. France agreed to lend the colonies money and soldiers to fight the war against Britain. After the war, Franklin went to Britain with John Adams and John Jay. They negotiated terms of peace with Britain. This led to the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
In 1787, Franklin represented the state of Pennsylvania at the Constitutional Convention. The purpose of the convention was to draft the U.S. Constitution. At 81, he was the oldest delegate. He went on to serve as president of the Pennsylvania Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery. Franklin once owned a slave. But in 1790, he urged Congress to abolish slavery in the U.S.
Franklin died on April 17, 1790, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. His memoirs were published the following year. They are known today as The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin.
Paired Text
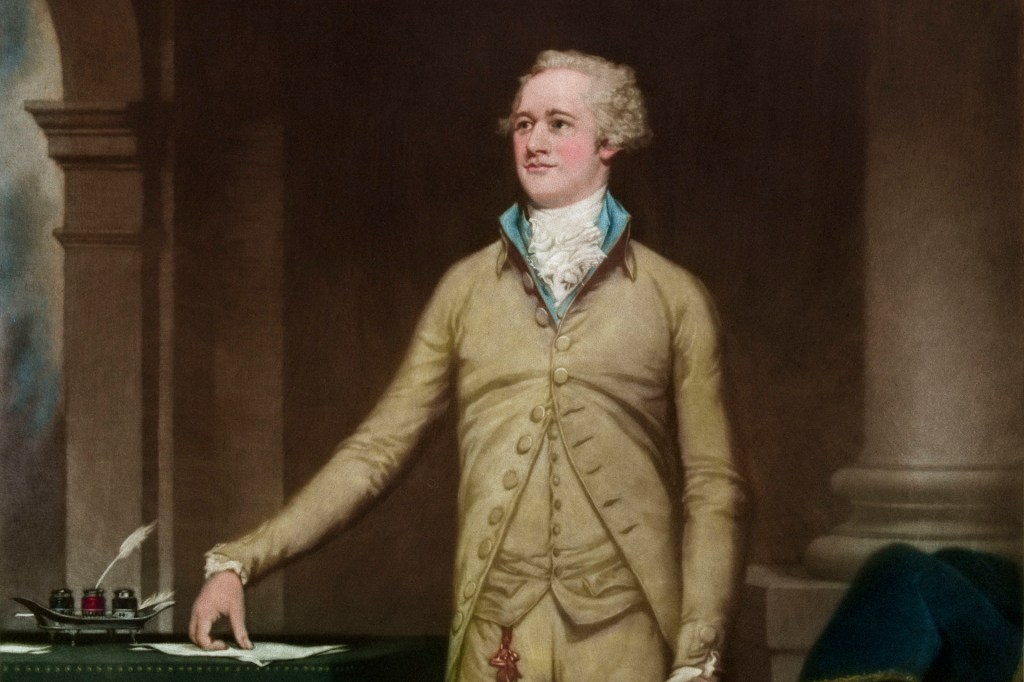

Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757—July 12, 1804) is one of America’s most influential Founding Fathers. In his short life, he served as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention, was the first U.S. secretary of the treasury, and established…

Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743–July 4, 1826) was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. He drafted the Declaration of Independence. He served as the country’s first secretary of state. He was elected the third U.S. president. As…
More from TFK Library
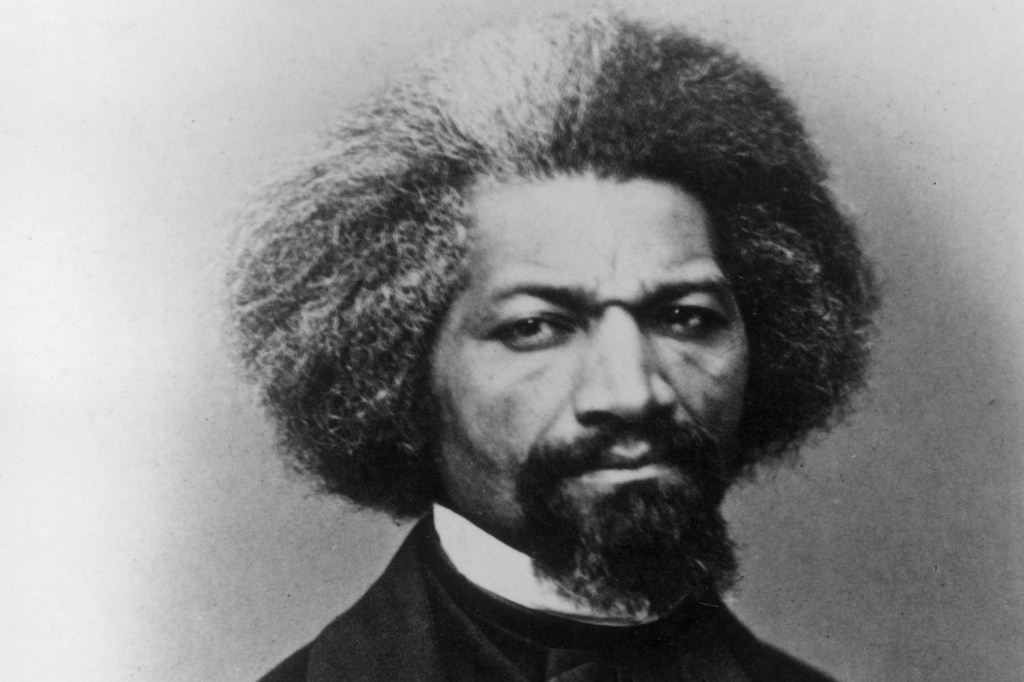

Frederick Douglass
In the years leading up to the Civil War, Frederick Douglass (February 1818—February 20, 1895) was the most powerful speaker and writer of the abolitionist movement. Frederick Douglass was born into slavery in Talbot County, Maryland. He was raised by…
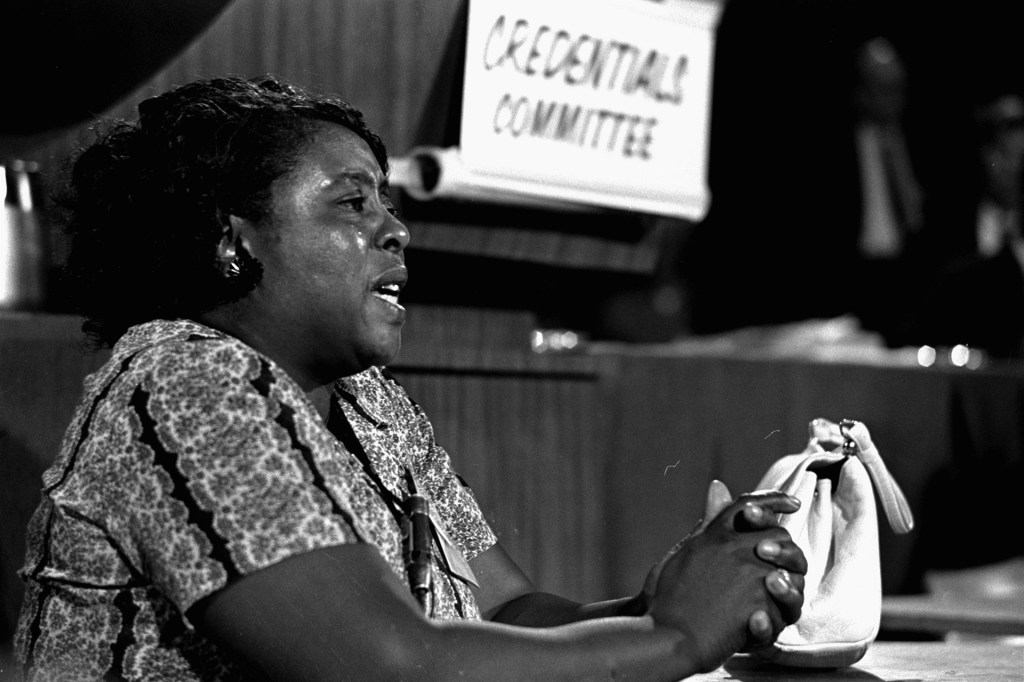

Fannie Lou Hamer
Fannie Lou Hamer (October 6, 1917—March 14, 1977) was a civil rights activist. She fought to expand voting rights for African Americans. Fannie Lou Hamer was born in Montgomery County, Mississippi, during a time of segregation. African Americans in the…
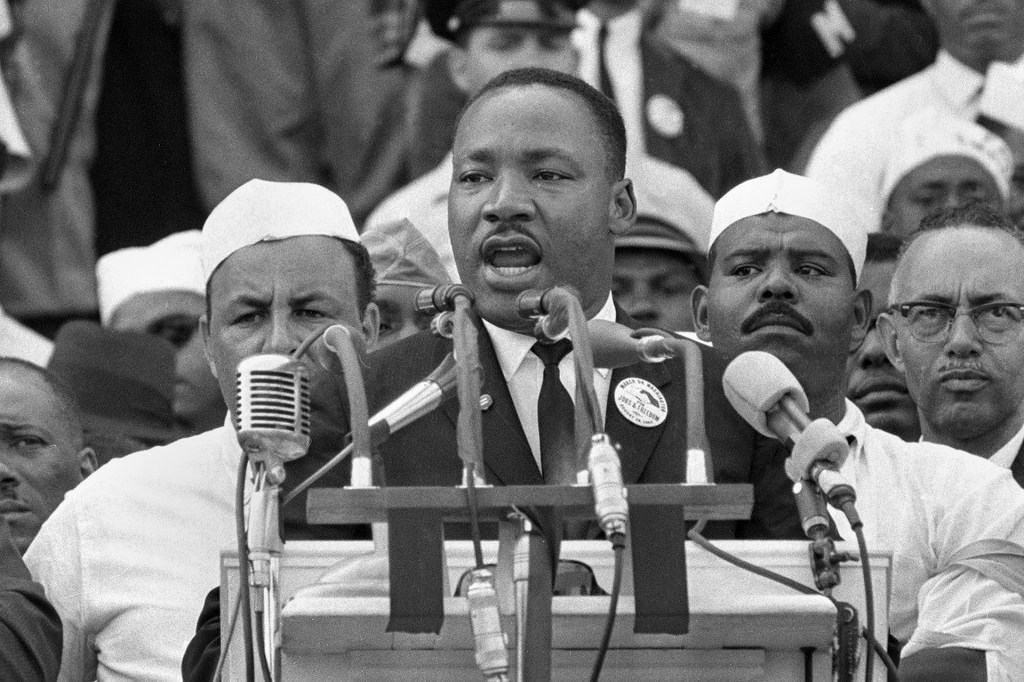

Martin Luther King, Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. is considered one of history’s greatest activists. His leadership helped end segregation during the civil rights movement. When Martin Luther King Jr. was born, his parents, Michael and Alberta, gave him a different name from the…
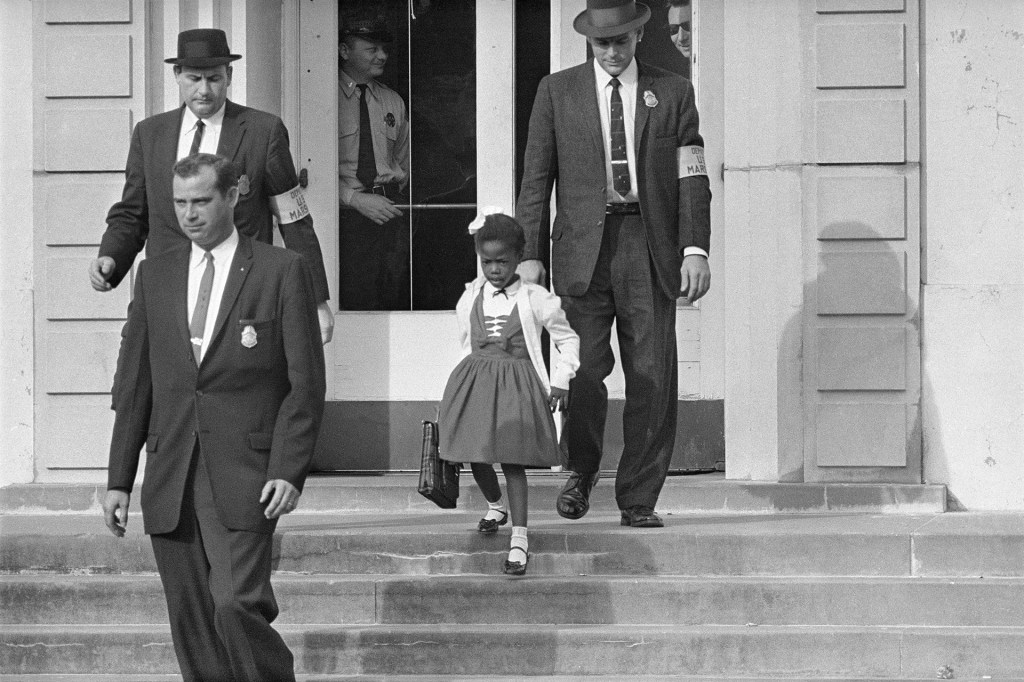

Ruby Bridges
In 1960, Ruby Bridges (September 8, 1954—) walked through the doors of William Frantz Elementary School, in New Orleans, Louisiana. By doing so, she became the first African-American student to attend an all-white elementary school in the Southern United States.…
Share a Link
- Click the icon above to copy the url link to your clipboard.

Google Classroom
- Click on the icon above to share the article with a class in your Google Classroom.
- Choose an action. Options might include creating an assignment or asking a question.

Benjamin Franklin
Short stories.

Benjamin Franklin, born in 1706 (adjusted from Old Style date 1705), died in 1790, is perhaps the most eccentric and broadly accomplished of all the nation's founding fathers, who is the only one to have signed all four major documents for a new nation: The Declaration of Independence (1776), the Treaty of Alliance with France (1778), the Treaty of Paris establishing peace with Great Britain (1783) and the U.S. Constitution (1787). He left his footprint on almost all aspects of forming the new nation: science, religion, education, government, finance, and international relations (ooh, lah, lah-- don't forget the French ladies!). The motivation for his curiosities, discoveries, and political philosophies told from his perspective rather than that of an impersonal third party account, makes his autobiography particularly interesting reading. Franklin sprinkles a healthy dose of humility and wit throughout his prose. He started composing what became The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin in 1771; it was published posthumously in 1793. Enjoy reading the introductory notes before diving in to his writings-- it offers fascinating details to better understand such an iconic American figure. Also enjoy his homely sayings that offer such rich meaning, published in the most popular almanac every published, Poor Richard's Almanack . Young readers will enjoy James Baldwin 's chapter book, The Story of Benjamin Franklin , and Nathaniel Hawthorne 's short story Benjamin Franklin , in which he steals a pile of rocks as a boy.

You may also enjoy reading D.H. Lawrence 's chapter about Franklin in his book, Studies in Classic American Literature .
A fitting end to this brief bio is his epitaph, humble and witty till the very end: "The body of Benjamin Franklin, printer; Like the cover of an old book— Its contents torn out, and script of its lettering and gilding: Lies here food for worms."


- Biographies & Memoirs
- Leaders & Notable People

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Buy new: $9.95
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

Benjamin Franklin - A Short Biography (30 Minute Book Series) Paperback – August 21, 2015
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Part of series 30 Minute Book Series
- Print length 62 pages
- Language English
- Publication date August 21, 2015
- Dimensions 5 x 0.14 x 8 inches
- ISBN-10 1517004780
- ISBN-13 978-1517004781
- See all details

Popular titles by this author

Product details
- Publisher : CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (August 21, 2015)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 62 pages
- ISBN-10 : 1517004780
- ISBN-13 : 978-1517004781
- Item Weight : 2.57 ounces
- Dimensions : 5 x 0.14 x 8 inches
- #3,809 in Scientist Biographies
- #4,806 in Presidents & Heads of State Biographies
- #9,334 in Political Leader Biographies
About the author
Doug West is a retired engineer, small business owner, and an experienced non-fiction writer of the 30 Minute Book Series. His writing interests are general, with expertise in science, biographies, and history. Doug has a B.S. in Physics from the Missouri School of Science and Technology and a Ph.D. in General Engineering from Oklahoma State University. He has also completed additional graduate studies in Astrophysics at Wichita State University. He lives with his wife and spoiled dog “Millie” near Kansas City, Missouri.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top review from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Start Selling with Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
- Short Biography
- Who was Ben Franklin?
- Why is Benjamin Franklin on the $100 bill?
- Google Plus
Category - Biography
Who was benjamin franklin.
Benjamin Franklin was America’s inventor, , and . He is best known as the only Founding Father who...
Birthplace and Parents Benjamin Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in Boston in what was known...
Benjamin Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in Boston in what was known as the Massachusetts Bay...
Acquiring skills in London
Since Franklin’swhen he worked in Boston as an apprentice in his brother James’...
Marriage and Children
A bachelor in his twenties was frowned upon and Franklin at age 24 was set to find a wife. Deborah...
In the fall of 1727 Benjamin Franklin and a group of friends founded the Junto Club also known as...
Benjamin Franklin, the Printer
The New England Courant Benjamin Franklin was introduced to the art of printing and journalism by...
Franchise and Retirement from Printing
Franchise By the early 1730’s Franklin’s business was thriving. was the most popular...
Postmaster General
Franklin’s postal career began in 1737 when he was appointed postmaster of Philadelphia. Franklin...
Declaration of Independence
Second Continental Congress After the English authorities accused Benjamin Franklin of treason. He...

COMMENTS
Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) was a statesman, author, publisher, scientist, inventor, diplomat, a Founding Father and a leading figure of early American history.
Armonica: Franklin's inventions took on a musical bent when, in 1761, he commenced development on the armonica, a musical instrument composed of spinning glass bowls on a shaft. Both Ludwig van ...
Benjamin Franklin FRS FRSA FRSE (January 17, 1706 [O.S. January 6, 1705] - April 17, 1790) was an American polymath, a leading writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Among the most influential intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States; a drafter and signer of the Declaration of ...
A Quick Biography of. Benjamin Franklin. Francis Folger Franklin, Ben's son. (Posthumous painting. Artist and date unknown) Benjamin Franklin was born in Boston on January 17, 1706. He was the tenth son of soap maker, Josiah Franklin. Benjamin's mother was Abiah Folger, the second wife of Josiah. In all, Josiah would father 17 children.
Dr. Franklin is appointed Agent for Georgia. — Causes the "Farmer's Letters" to be republished in London. — His Opinion of them. — Chosen President of the American Philosopical Society. — Promotes the of Culture of Silk in Pennsylvania. — Encourages his Countrymen to adhere to their Non-importation Agreements. — Journey to France.
Benjamin Franklin Biography. Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) was a scientist, ambassador, philosopher, statesmen, writer, businessman and celebrated free thinker and wit. ... However, this reversal was to be short-lived. And when further taxes were issued, Franklin declared himself a supporter of the new American independence movement.
Benjamin Franklin by David Martin (1737-1797). Oil on canvas, 1767. Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, Philadelphia. Benjamin Franklin was America's scientist, inventor, politician, philanthropist and business man. He is best known as the only Founding Father who signed all three documents that freed America from Britain.
Benjamin Franklin, (born Jan. 17, 1706, Boston, Mass.—died April 17, 1790, Philadelphia, Pa., U.S.), American printer and publisher, author, scientist and inventor, and diplomat.He was apprenticed at age 12 to his brother, a local printer. He taught himself to write effectively, and in 1723 he moved to Philadelphia, where he founded the Pennsylvania Gazette (1729-48) and wrote Poor Richard ...
Several biographies of Benjamin Franklin, including a short timeline, a brief biography, his autobiography and the biography by noted biographer Jared Sparks.
Brief Overview. Next. Benjamin Franklin was born in Boston on January 6, 1706. He was the eleventh child of Josiah Franklin, a candle maker; his mother was named Abiah. Franklin's father put him in grammar school to become a minister, but soon took him out again because he could not afford it. Franklin spent a year at a different school and ...
Benjamin Franklin. by Joseph Duplessis. Occupation: Statesman and Inventor. Born: January 17, 1706 in Boston, Massachusetts. Died: April 17, 1790 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Best known for: Founding father of the United States. Biography: Benjamin Franklin was one of the most important and influential Founding Fathers of the United States of ...
Legacy of Benjamin Franklin. Franklin was not only the most famous American in the 18th century but also one of the most famous figures in the Western world of the 18th century; indeed, he is one of the most celebrated and influential Americans who has ever lived. Although one is apt to think of Franklin exclusively as an inventor, as an early ...
Benjamin Franklin won fame as a writer, a publisher, a scientist, and an inventor. He is best remembered, however, for his leadership in the American colonies and the early United States.
June 14, 2018. Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706—April 17, 1790) was a scientist, an inventor, a writer, and a statesman. He helped draft the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution. Benjamin Franklin was born in Boston on January 17, 1706. He learned to read at an early age.
Benjamin Franklin His Autobiography 1706-1757 A Short Biography Franklin was born in 1706 at Boston. He was the tenth son of a soap and candlemaker. He received some formal education but was principally self-taught. After serving an apprenticeship to his father between the ages of 10 and 12, he went to work for his half-brother James, a printer.
Short Biography; Facts; Who was Ben Franklin? Why is Benjamin Franklin on the $100 bill? About us; Timeline; Short Biography; Facts; Who was Ben Franklin? Why is Benjamin Franklin on the $100 bill? About us; Biography. Early Life. Birthplace and Parents Benjamin Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in Boston in what was known...
And the reader seeking a thoughtful and well-written short biography of Franklin would do well to take up Edmund Morgan's 2002 book that is titled simply Benjamin Franklin. Historian Edmund Morgan, of Yale University, is one of the pre-eminent scholars of colonial, Revolutionary, and early-national American history.
Education. Boston Latin School is the oldest school in America. It was founded April 23, 1635. At 8 years old young Benjamin Franklin started attending South Grammar School (Boston Latin) showing early talent moving from the middle of the class to the top of it within a year. The following year he attended George Brownell's English School, a ...
Benjamin Franklin, born in 1706 (adjusted from Old Style date 1705), died in 1790, is perhaps the most eccentric and broadly accomplished of all the nation's founding fathers, who is the only one to have signed all four major documents for a new nation: The Declaration of Independence (1776), the Treaty of Alliance with France (1778), the Treaty of Paris establishing peace with Great Britain ...
Buy the book "Benjamin Franklin - A Short Biography" and find out! 30 Minute Book Series Welcome to the first book in the 30 Minute Book Series. Each book in the series is fast paced, well written, accurate, and covers the story in as much detail as a short book allows. In less than an hour, you can read or listen to the book; it is a ...
Short Biography; Facts; Who was Ben Franklin? Why is Benjamin Franklin on the $100 bill? About us; Timeline; Short Biography; Facts; Who was Ben Franklin? ... Benjamin Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in Boston in what was known as the Massachusetts Bay... Acquiring skills in London.