

Livestock Farming Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Livestock Farming Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their livestock farming companies. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a livestock farming business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Livestock Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your livestock farming business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Livestock Farm
If you’re looking to start a livestock farming business or grow your existing livestock farming company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your livestock farming business to improve your chances of success. Your livestock farming business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Livestock Farming Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a livestock farming business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan (hand it to them in person or email to them as a PDF file) and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for livestock farming companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a livestock farming business.
If you want to start a livestock farming business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide and sample below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your livestock farming business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of livestock farming business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a livestock farming business that you would like to grow, or are you operating several family-owned livestock farming businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overv iew of the livestock farming industry.
- Discuss the type of livestock farming business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of livestock farming business you are operating.
For example, you m ight specialize in one of the following types of livestock farming businesses:
- Cattle Ranching : In order to effectively raise cattle until market-ready, ranchers must have enough land for cattle to roam and eat grass. The rancher must also provide supplemental food, medicines and a number of procedures to ensure cattle sent to market are healthy and at an optimum weight.
- Sheep Farming: Sheep farming is a process of maintaining order in the herd and corralling sheep when necessary. Farmers must feed and medicate sheep efficiently and they use sheep dogs to assist in many daily efforts. Sheep are prized for their wool and may be sent to slaughter as lambs if they are young. Sheep are often used on vacant fields to graze with an environmentally-friendly outcome.
- Chicken Farming: Chicken farmers need to provide water, food and medications to raise chickens until market-ready. Chickens may be free-range or kept in sheds during growth cycles. While hens produce eggs, roosters provide barnyard protection and enjoyment.
- Hog Farming: Hogs are notoriously expensive to raise, primarily due to food costs and medications; however, they demand high prices at sale and produce generous profits when sent to market. Hogs are grown in pens to control weight gain and are carefully assessed for market-readiness.
In addition to explaining the type of livestock farming business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of cattle sold each season, the number of sheep successfully shorn each year, reaching X number of ranches owned, etc.
- What is your legal business structure? Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the livestock farming industry. While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the livestock farming industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your livestock farming business plan:
- How big is the livestock farming industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your livestock farming business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your livestock farming business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: corporate buyers, stockyard owners, and individual buyers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of livestock farming business you operate. Clearly, individuals would respond to different marketing promotions than stockyard owners, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers. Ideally you can speak with a sample of your target customers before writing your plan to better understand their needs.
Finish Your Livestock Farming Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are othe r livestock farming businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes specialty types of beef cattle, such as organic or grass-fed, imported lamb or beef, or eggs that are infused with additional supplements. You need to mention direct competition, as well.
For each direct competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of livestock farming business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide lower rates for stockyards despite fluctuating higher market prices?
- Will you offer beef cuts that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a livestock farming business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type o f livestock farming company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide uncured, smoked ham and bacon, pasteurized eggs, or free-range chicken?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of yo ur plan, yo u are presenting the livestock you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your livestock farming company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, does your cattle ranch contain grassy acreage, allowing cattle to eat naturally? Is your chicken ranch situated in a weather-friendly environment? Does your hog farm contain heated and cooled hog pens for the well-being of the hogs?
Promotions : The final part of your livestock farming marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to regional stockyards
- Distribute farmer newsletters to stockyards
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your livestock farming business; including caring for livestock, securing and maintaining food supplies and medications, planning transport to market, invoicing customers and paying bills.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to ship-to-market, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your livestock farming business to a new ranch or farm.
Management Team
To demonstrate your livestock farming business’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing livestock farming businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a livestock farming business or successfully running a livestock stockyard.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance s heet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you ship 500,000 head of cattle this season, or will you expand your farm by several hundred acres? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your livestock farming business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a livestock farming business:
- Cost of breeder chickens, lambs, farrow pigs or calves
- Cost of farming equipment and vehicles
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your ranch deed of ownership or a list of buyers you partner with in buying and selling operations.
Writing a business plan for your livestock farming business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the livestock farming industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful livestock farming business.
Livestock Farming Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my livestock farming business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your livestock farming business plan.
How Do You Start a Livestock Farming Business?
Starting a livestock farming business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Create Your Livestock Farming Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Livestock Farming Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Livestock Farming Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Livestock Farming Business Equipment
- Develop Your Livestock Farming Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Livestock Farming Business
- Open for Business
Where Can I Download a Free Business Plan Template PDF?
Click here to download the pdf version of our basic business plan template.
Our free business plan template pdf allows you to see the key sections to complete in your plan and the key questions that each must answer. The business plan pdf will definitely get you started in the right direction.
We do offer a premium version of our business plan template. Click here to learn more about it. The premium version includes numerous features allowing you to quickly and easily create a professional business plan. Its most touted feature is its financial projections template which allows you to simply enter your estimated sales and growth rates, and it automatically calculates your complete five-year financial projections including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Here’s the link to our Ultimate Business Plan Template.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Livestock Farming business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to learn about Growthink’s business plan writing services .
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Starting Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan (PDF)

Starting a beef cattle farming business presents a unique and lucrative opportunity for aspiring entrepreneurs. The demand for quality beef continues to rise globally, making this an opportune time to enter the market. With a growing population and a steady increase in the consumption of protein-rich diets, the beef industry is poised for sustained growth. This demand creates a fertile environment for new entrants, offering a chance to tap into a thriving market. Beef cattle farming involves breeding cows to get calves, which are then raised and sold for beef. Beef cattle production is a very profitable business, and many farmers are making money all over the world by starting cow-calf operations businesses. However, to build a profitable, sustainable beef cattle ranching business, you require sufficient knowledge of how to efficiently keep the beef cattle, good business management skills, and a good beef cattle farming business plan. This article will outline how to start the cattle production business, and the beef cattle farming business plan – PDF, Word and Excel.
Beef cattle farming is a lucrative business project that is providing income for a lot of livestock farmers. There are some important things you need to consider before you setup a beef cattle production business. You need to gather the correct resources, decide on the size of your cattle farming project this includes the number of cattle; location of the beef cattle production business, as well as your target market. These decisions will be affected by the amount of capital you have, and the size of your target market. If you do not have a lot of capital, you can always start small and grow your beef cattle breeding project overtime. You also need to carry out market research (Who are you going to sell the cattle to? At what price?) and write a cow-calf operations business plan before you start the project.
Market Research
Market research is a pivotal step when embarking on a beef cattle farming venture. It serves as the compass guiding your business decisions and can ultimately determine your success in this industry. Assessing the local demand is essential; understanding the existing market, who your potential customers are, and their preferences can help you tailor your cattle farming approach to meet these needs effectively. It’s imperative to delve into the pricing dynamics of various grades of beef within your target market. This involves a comprehensive examination of not only the prevailing prices but also the factors that influence them. Identifying potential customers and understanding their preferences and price sensitivity is equally vital, as it enables you to tailor your pricing strategy to match their expectations. Additionally, recognizing the seasonality of cattle and beef prices is key, as these fluctuations can significantly impact your revenue and profit margins. A competitive analysis will help you understand the landscape of existing cattle farms, their strategies, and what sets your venture apart. Identifying your competitive advantages and crafting a unique selling proposition can be key to carving out your niche in the market.
As a crucial component of market research in the context of starting a beef cattle farming business, the selection of the appropriate cattle breed plays a pivotal role. This decision encompasses a comprehensive assessment of various factors, including the availability of breeds in your region, their feed conversion efficiency, the cost associated with acquiring them, and the specific demands of the market. Each breed possesses distinct characteristics that impact their suitability for your business, such as their growth rate, meat quality, and adaptability to local conditions. Additionally, you should delve into supply chain considerations, establishing efficient logistics and partnerships to transport and distribute your products effectively.
Land for Beef Cattle Farming
Land is an important factor when you are starting a cattle ranching business. When selecting land for your cattle farm, some important considerations include: availability of good grass and pasture for grazing, availability of good, quality water supply, land size in relation to size of your cattle herd and soil type as it affects forage production potential. Other factors include availability of already made infrastructure like pens, sheds, buildings, as constructing new working facilities and buildings on a cattle farm is expensive.
A beef cattle farming venture requires huge tracts of land. This is because you will need spaces for grazing and other dedicated farm structures. You must consider the terrain; flat land that gently slopes is ideal. The soil characteristics are important as well – loam soil is the best. That soil type is best suited for consistent pasture and forage development. The availability of adequate pastures is yet another land consideration. You must ensure there are enough pastures. This connects to considering the quality of forage available. Ideally, you need pastures and forage mainly constituted of grasses and legumes. If the legumes composition is at least a third of the total, that would be great. Water availability is also a huge consideration. The best is to have a clean, fresh, and reliable water source. Preferably it should be within a 1 mile radius. This will be convenient for the cattle so that they do not have to go far to find water. It is advisable to check the quality of the water; especially if it is a natural water source. High salt and sulphur levels are detrimental to your cattle. Proximity of strategic road networks is of utmost importance for accessibility and mobility. Bear in mind that within the beef cattle farm, gravel roads are the best.
Housing for Beef Cattle Production Business
To be successful in the beef cattle ranching business, you need to provide proper shelter and housing for your cattle. Beef cattle can be negatively affected by mud, harsh winds, and extreme low temperatures. The design and type of beef cattle facilities should take into consideration the need to provide the required space, feed, shelter, water, waste management and livestock handling features. Beef cattle housing can broadly be in the form of cubicles, sheds, pens, corrals, barns, or open yards. However, it is important to ensure that there is enough shade for the cattle. That is why protection from the weather elements is a huge consideration in beef cattle housing. Protection from predators is also closely tied to that. Overall, the housing must be clean with good ventilation. Plus the beef cattle housing must generally be easy to clean. Ensure that there is dry surface, floor, or bedding. It is best to use dry straw on them; adding sand also helps in that regard.
The cattle housing must be big enough to allow free movement of the cattle. The housing must not be homogenous; there should be separate segments for different specific uses. For example, you need separate segments for calves, sick cattle, or newly arrived cattle. It is recommended that beef cattle housing must be set up on an elevated spot. This streamlines cleaning activities, drainage, and runoff. Take into account the prevailing wind direction in your chosen location – the beef cattle housing should be erected standing perpendicular to that. Other cattle handling structures include crowding pens, sorting corrals, working chutes & gates, squeeze gates and sick pens. However the necessity of the structures depends on the scale of the cattle farming business. The cattle ranch farm also requires good fencing. Pasture fencing for cow-calf operations business is a necessity, so as to contain the cattle and manage their grazing. This can be done by barbed wire, high tensile smooth wire or electric fencing. The costs of constructing the housing should be include in the beef cattle production business plan.
Equipment For Beef Cattle Farming Business
Beef cattle farming equipment mainly comprises of feed and water equipment. For example, you need feeding bunks and, feeding bins (or troughs) or portable hay feeders. Water equipment can be in the form of or involve drinkers, tanks, canals, pumps, pipes, and the like. Other handy equipment is for handling the beef cattle. For instance, chutes are central to this. Chutes are narrow mechanisms or passages used to control and guide the beef cattle in certain spaces. There are several different types of chutes e.g. holding chutes, working chutes, and loading chutes. Headgates are also central to the use of chutes. Cattle guards or grids are important in controlling the movement of the beef cattle. Then there are general equipment such as protective clothing, wheelbarrows, buckets & pails, livestock trailer, manure spreader, tractors, and the like. Specialized equipment for operations such as dehorning and castrating are needed too. Your cattle farming business plan should take into account the cost of purchasing or renting the land, structures and buying the equipment.
Breeding Stock for Beef Cattle Production Business
To start a beef cattle production business, you require the breeding stock. The breeding stock consists of male cattle which are known as bulls, and female cattle/cows. Alternatively, instead of using bulls, you can use artificial insemination for breeding the cattle. The selection of cattle breeding stock is basically two-tier. The first aspect involves choosing the cattle breed you want. Then the second aspect is choosing the individual cattle. You can choose to start with calves and rear them to maturity. You could also start with cows or heifers at various stages of development. Another approach can be to start with fully grown cattle. Always remember that choosing purebreds is the best way to go. Your overall choice should be informed by personal beef cattle farming goals. That should also go hand in hand with climatic considerations of your chosen location. Availability of cattle breeding stock is also another huge consideration.
There are a number of specific attributes to note when choosing your beef cattle breeding stock. You should consider the age; young livestock is usually the best to pick. Consider fertility or reproductive rate, and mothering or maternal ability. In beef cattle farming, feed efficiency and quality of meat are important factors. What is cattle’s performance and health status? What are their behavioural profiles? For instance, aggression in cattle is not a good trait. All of these specifics must be ascertained with the backing of comprehensive records. You must also be diligent enough to make physical inspections of the cattle. The idea is to note defects or desirable characteristics. The cattle breeds you choose will affect the beef production potential of your cattle farming business. Some breeds are better than others at producing cattle with good beef quality. Other characteristics which vary among breeds include calving ease, milking ability, feed conversion, diseases resistance, longevity and average birth weight. The most popular breeds used in the the beef cattle farming business include Angus, Brahman, Limousin, Hereford, Simmental, Shorthorn, Texas Longhorn, Nguni, Gelbvieh, Charolais, Africander, Highlands among others. The beef cattle farming business plan should include the costs of purchasing the breeding stock.
Feed And Nutrition
Success in the beef cow-calf production business is also greatly affected by the feeding program. The feeding program of the beef production business should ensure that adequate nutrition is provided to both the cows and calves at all growth stages and during all seasons. This should be done while keeping an eye on the feed costs, as they greatly affect profitability of the beef cattle farming business. Failure to provide adequate feeding for the beef cattle results in low reproductive performance, poor growth of the calves and poor disease resistance. These factors all lead to reduced revenues for the beef cattle production business, thus lower profits. In beef cattle farming business, weight and grade of meat are the major goals which informs the feeding regiment. Feeding generally depends on the size of the cattle. The bigger the frame, the higher the grain content should be. Cattle f eeding programs of beef farming are usually based on pasture grazing, in combination with supplementary feed. The supplementary feed for cow-calf operations include hay, salts & minerals, concentrates, silage, commercial beef feed, fodder, corn and grains. The most important dynamic is feed conversion or efficiency. Do not make the mistake of thinking overfeeding is a good thing. It usually leads to the build-up of excess fat thus lowering the beef quality. That is why it is important to seek guidance from experts on feeding using the right rations. The feed costs should be included in the beef cattle production business plan.

Health & Disease Management in Beef Cattle Farming
Ensuring the health and well-being of your beef cattle is of paramount importance in the successful operation of your farming business. A comprehensive approach to health and disease management is not only ethical but also integral to maintaining the quality and productivity of your cattle herd. To achieve this, preventative health measures are vital. This includes implementing a vaccination program tailored to your region’s prevalent diseases, providing access to clean water and nutritious feed, and maintaining a hygienic living environment. Regular monitoring and control of external parasites like ticks and flies are also crucial aspects of preventative care.
Disease monitoring and surveillance form another critical component. Regular health checks and veterinary consultations enable the early detection of potential health issues, while meticulous record-keeping helps track your cattle’s overall well-being. Staying informed about disease outbreaks in your area and having the ability to implement quarantine measures if needed is essential. Collaboration with a veterinarian ensures that sick cattle receive proper treatment and medication, administered according to recommended guidelines. Biosecurity measures should be in place to prevent disease introduction and spread, and continuous education and training ensure that both you and your farm staff are well-prepared to manage cattle health effectively. Prioritizing health and disease management not only benefits your cattle’s well-being but also contributes to the sustainability and profitability of your beef cattle farming business.
Beef Cattle Farming Business Model
The beef cattle farming business model involves a well-defined and cyclical process that begins with the acquisition of breeding bulls and cows. These animals form the foundation of your operation, as they play a crucial role in producing calves, which will eventually become your marketable cattle. The mating of bulls and cows leads to the birth of calves, and from that point onward, the focus shifts to feeding and raising these young cattle until they reach the desired market age, and you then sell them. This careful management ensures that the cattle are healthy, well-nourished, and ready for sale, optimizing their value in the market.
The central financial aspect of this business model lies in managing the costs associated with feeding the cattle, which constitutes the major expense. However, the revenue generated from selling the cattle at market age significantly surpasses these feeding costs and other operational expenses. This robust revenue-to-cost ratio results in a healthy profit margin for the business. The key to sustained success in this model is its repeatability throughout the year, which ensures a consistent and steady stream of income. By following this cycle of breeding, raising, and selling, you can create a reliable and profitable business model in the beef cattle farming industry.
Capital for Cattle Ranching Business
The amount of capital required for the beef cattle breeding business depends on the scale of the project. When starting a cow-calf operations business, most of the capital goes to acquiring the land, building infrastructure, and buying the breeding stock. You can get a loan from the bank, or funding from investors, to use as capital to start your beef cattle farming business. If you plan to raise capital from investors and a loan from the bank, you need a good cattle ranching business plan. If you don’t have access to investors and bank loan, you can use your personal savings and start small, and grow your business overtime. Beef cattle farming is profitable, so if you reinvest the profits you get, you can grow over time. Even if you are not planning to get a loan, you should still get a beef cattle farming project plan to guide you in starting and operating the business. It is essential for you to have a beef cattle farming business plan before you venture into the cattle ranching business, so that you know all the costs involved and you make an informed decision.
Market for Beef
The market for beef cattle is very huge and is ever increasing, annual beef global demand exceeds 75 million tonnes. You can sell live cattle or slaughter and sell as beef. The market for cattle/beef includes supplying to butcher shops, abattoirs, auctions, schools, companies, individual households, farmers, restaurants, organisations, supermarkets, events etc. It’s important for the beef cattle farming business plan to include a proper marketing plan to use in your beef farming business.
The export market for beef is also very huge! As you grow your cattle farming business you will be able to export the beef to other countries. The largest importers of beef are Russia, United States of America, Japan, China, South Korea, European Union, Hong Kong, Egypt, Canada, Chile and Malaysia. Currently, the top producers of beef are United States of America, Brazil, European Union, China, India, Argentina, Australia, Mexico, Pakistan, Turkey and Russia.
Keys To Profitability in Beef Cattle Farming
Profitability is the ultimate goal for those venturing into the world of beef cattle farming, and achieving it involves a multifaceted approach. Efficient resource management stands as a cornerstone, demanding a meticulous allocation of resources like land, water, and feed. Implementing rotational grazing systems can maintain pasture health and maximize forage production, thereby reducing the need for costly supplemental feed. Breeding and genetics play a pivotal role in profitability as well. Selecting cattle breeds that align with market preferences and local environmental conditions is crucial. Furthermore, a focus on breeding programs to enhance genetic traits such as growth rate, meat quality, and disease resistance can significantly impact the bottom line.
Health and disease management cannot be overlooked, as cattle health directly correlates with profitability. Prioritizing preventative measures and proactive disease management not only ensures the well-being of your herd but also reduces costs associated with medical interventions and promotes higher growth rates. Market timing and pricing strategies are equally vital, demanding a vigilant eye on market trends and pricing fluctuations. Utilizing market data to determine optimal pricing strategies ensures that you maximize your returns when selling cattle.
Cost control and budgeting, combined with strategic marketing and branding, enable efficient financial management. Keeping a detailed budget that tracks all expenses and revenue sources is imperative, allowing you to control costs effectively. Building a strong brand identity for your beef products and fostering relationships with local buyers, restaurants, and markets secures consistent sales channels. Finally, a commitment to continuous learning and improvement ensures your profitability endures. Staying updated on industry best practices, emerging technologies, and research in beef cattle farming equips you to adapt to industry changes, enhance productivity, and reduce waste, ultimately driving the success and profitability of your beef cattle farming business.
Why You Need a Cattle Farming Business Plan
Establishing and managing a thriving cattle farming business requires meticulous planning and strategic foresight. A well-structured cattle farming business plan is not merely a formality; it serves as an indispensable tool that can profoundly influence the trajectory of your venture. Financial planning and management is a vital aspect of a comprehensive business plan. It entails detailed financial projections, helping you estimate initial startup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential revenue streams. With insights into your cash flow, you can effectively manage your finances, make informed decisions regarding resource allocation (such as purchasing cattle, feed, and equipment), and maintain financial stability. Furthermore, if you require external financing or investment to initiate or expand your cattle farming business, a well-structured business plan is essential. Lenders and investors will scrutinize your plan to assess the viability and profitability of your venture, making a comprehensive and well-researched plan instrumental in instilling confidence in potential stakeholders.
A well-structured business plan for a beef cattle farming enterprise serves as a vital tool in comprehending the profitability of the business and identifying the key factors that influence it. It provides a detailed financial outlook, allowing you to assess the projected income, expenses, and potential returns on investment. By meticulously examining these financial projections, you gain a deep understanding of the financial health of your cattle farming venture. Additionally, the business plan facilitates an exploration of the factors that impact profitability, including feed costs, market pricing, and operational efficiency. With this insight, you can make informed decisions to optimize profitability, mitigate risks, and ensure the long-term success of your beef cattle farming business.
Pre-Written Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel): Comprehensive Version, Short Funding/Bank Loan Version and Automated Financial Statements
For an in-depth analysis of the beef cattle farming business, we encourage you to purchase our well-researched and comprehensive cattle farming business plan. We introduced the business plans after discovering that many were venturing into the beef cattle production business without enough knowledge and understanding of how to run the cattle ranching business, how to keep the calves, lack of understanding of the financial side of the business, lack of understanding of : the industry, the risks involved , costs and profitability of the business; which often leads to disastrous losses.
The StartupBiz Global cow-calf operations business plan will make it easier for you to launch and run your beef cattle farming business successfully, fully knowing what you are going into, and what’s needed to succeed in the business. It will be easier to plan and budget as you will be aware of all the costs involved in setting up and running the cattle ranching business.
Uses of the Beef Cattle Ranching Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The beef cattle farming business plan can be used for many purposes including:
- Raising capital from investors/friends/relatives
- Applying for a bank loan
- Start-up guide to launch your beef cattle farming business
- As a beef cattle farming business proposal
- Assessing profitability of the beef cattle production business
- Finding a business partner
- Assessing the initial start-up costs so that you know how much to save
- Manual for current business owners to help in business and strategy formulation
Contents of the Beef Cattle Production Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The beef cattle farming business plan include, but not limited to:
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial Statements (monthly cash flow projections, income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, break even analysis, payback period analysis, start-up costs, financial graphs, revenue and expenses, Bank Loan Amortization)
- Risk Analysis
- Industry Analysis
- Market Analysis
- SWOT & PEST Analysis
- Operational Requirements (Including technical aspects of how to keep the cattle, feed requirements etc)
- Operational Strategy
- Why some people in beef cattle farming business fail, so that you can avoid their mistakes
- Ways to raise capital to start your cattle farm business
The Pre-written beef cattle farm business plan package consists of 4 files
- Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan – PDF file (Comprehensive Version – 121 Pages)
- Cattle Farming Business Plan – Editable Word File (Comprehensive Version – 121 Pages)
- Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan Funding/Bank Loan Version- Editable Word File (Short version for applying for a loan/funding – 51 pages)
- Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan Automated Financial Statements – (Editable Excel File)
The business plan can be used in any country and can be easily edited. The financial statements are automated. This implies that you can change eg the number of cattle, selling price of the cattle etc, and all the other financial statements will automatically adjust to reflect the change.
Click below to download the Contents Page of the Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan (PDF)
Testimonial 4
The business plan which I purchased from your website saved me TIME and MONEY! The layout of the business plan was excellent. The financial statements were detailed and easy for me to edit. I will come back to purchase another business plan soon.
Testimonial 3
I was extremely lucky to come across StartupBiz Global. Their business plan exceeded my expectations, and most importantly I was able to secure a loan from my bank. Thank you guys, now my dreams are coming true!
Testimonial 8
Just wanted to say I am very happy with the business plan and I will gladly recommend your products, thank you very much and have a great day.
Testimonial 5
I was able to understand the business side of farming because of your business plan. You did extensive research; the business plan was well prepared and fully detailed. It made everything clear, and I have somewhere to start now. I am confident that I am going to succeed in my business because of the guidance from your business plan.
Testimonial 6
I purchased a business plan from you, and I’m glad to inform you that I was able to get my loan, and I’m starting my poultry farming business on the 1 st of July. This was made possible because of your business plan. Thank you very much, you made my dream come true.
Testimonial 7
I found Startupbiz Global online when I was in desperate need of a business plan. I was overwhelmed by the quality of the business plan, it’s comprehensive and well researched! I did not have to wait to get the business plan, I got it instantly after payment. I highly recommend Startupbiz Global, and would happily use them again in the future.
Testimonial 2
Many thanks for your incredibly efficient service and thorough business plan. I am very impressed with the business plan. Before I bought the business plan, I tried to do my own business plan – it was such a nightmare and it turned out badly, also not to mention the stress it caused me. I wish I knew about your website earlier!
Testimonial 1
StartupBiz Global provided a very professional and comprehensive business plan which I used for my business. The business plan was easy to edit, and I was able to get the funding which I wanted. I highly recommend their business plans.
Get the Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
Click Buy Now below to purchase using Paypal, Credit Card, or Debit Card. After you have purchased, you will immediately see the download link for the business plan package on the screen. You will also immediately get an email with the business plan download link. The Pre-written business plan package (PDF, Word, and Excel) costs $30 only!

If you want to purchase multiple business plans at once then click here: Business Plans Store.
The business plan package is a zipped compressed file containing the PDF, Word and Excel documents. To open the package after downloading it, just right click, and select Extract All. If you have any problems in downloading and opening the files, email us on [email protected] and we will assist you.
We wish you the best in your beef cattle farming business! Check out our collection of business plans , and more business ideas .
Related Posts

Starting A Guest House Business Plan (PDF)

Top 10 Food Business Ideas

How To Write A Small Farm Business Plan

Starting Catering Services Business Plan (PDF)

Join our mailing list to receive the latest posts and updates from our website.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Cattle Farming Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Cattle Farming Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Cattle Farming business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their cattle farms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Cattle Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm, located in Des Moines, Iowa, is a registered and licensed cattle farming company. The company operates a 500 acre farm that is home to over 300 cows, all of which are raised in an all-natural environment (no antibiotics, hormones, steroids, etc) and all animals are grass-fed. Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is also fully equipped with the latest technology and equipment used in the cattle farming industry.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is founded and run by Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Product Offering
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be involved in the commercial breeding of cows to provide the following products:
- Ground Beef
Customer Focus
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will target all residents living in Des Moines, Iowa and the surrounding areas. We will also target supermarkets, restaurants, and other retailers who are interested in selling our products to the public.
Management Team
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s most valuable asset is the expertise and experience of its founder, Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Success Factors
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: The company’s management team has years of business and marketing experience that allows them to market and serve customers in an improved and sophisticated manner than the competitors.
- Relationships: Having lived in the community for 20 years, Matthew Jones knows all of the local leaders, media, and other influencers. As such, it will be relatively easy for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm to build brand awareness and an initial customer base.
- Quality products at affordable pricing: The company will provide quality products at affordable pricing, as it has high-quality equipment and uses the latest techniques.
- Good packaging: Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will utilize product-oriented packaging materials that can reduce the damage in the products at the time of supply.
Financial Highlights
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is currently seeking $750,000 to start the company. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the farm land and purchasing the necessary equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff and marketing costs for the farm. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Land and Equipment: $250,000
- Cattle Care Supplies: $100,000
- Overhead Costs: $100,000
- Three Months of Overhead Expenses (Payroll, Rent, Utilities): $150,000
- Marketing Costs: $50,000
- Working Capital: $100,000
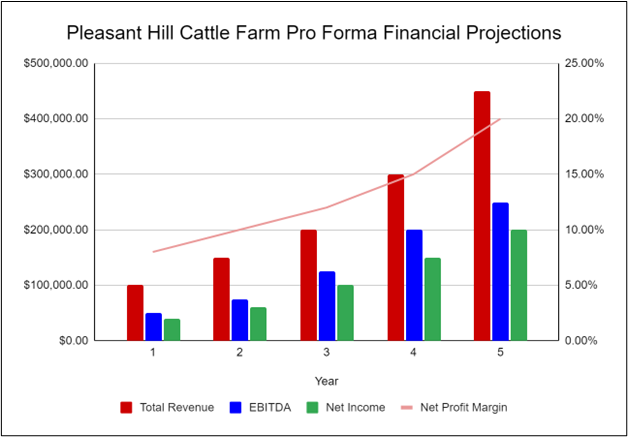
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm.
Company Overview
Who is pleasant hill cattle farm.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is founded and run by Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm History
Matthew Jones is an entrepreneur who seeks to contribute to the growing US economy through cattle farming. Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will become a recognized cattle farming company in Des Moines, Iowa, ensuring a continuous supply of cattle, milk, meat, and other dairy products.
Matthew has selected an initial location and is currently undergoing due diligence on it and the local market to assess if it is a suitable location for a commercial cattle farm.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found a farm location
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined supply requirements
- Began recruiting key employees
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm Services
Industry analysis.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm competes against large-scale cattle farmers in the U.S. With the largest fed-cattle industry in the world, the United States is also the world’s largest producer of beef, primarily high-quality, grain-fed beef for domestic and export use. According to the USDA, beef cattle production in the US is one of the largest agricultural industries, making up 17% of the agricultural sector. Though the industry has declined slightly in the past few years, the market size of the Beef Cattle Production industry is expected to increase by 4.5% over the next five years.
Improving the living standards of the people in the country has resulted in a shift in meat preferences, with most choosing beef-based products rather than products derived from pork and chicken. This trend has helped increase revenues and allowed the industry to grow. However, the beef cattle production industry faces many challenges including droughts, the price of feed, and the increasing popularity of plant-based diets.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will primarily serve local residents and retailers of cattle dairy products and meat within a 30-mile radius of the farm. These businesses typically gross from $5 million to $10 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from within a 30-mile radius of their facilities.
The precise demographics for Des Moines, Iowa are:
Customer Segmentation
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery Stores
- Local Residents
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Shayla Farms
Shayla Farms is one of the large-scale cattle farms in the US, owning an 8,000 ha area. It has well-established relationships with local retailers. It has been in business for 32 years. Shayla Farms offers good quality dairy products and meat. It also has automated equipment and machines, which helps in improving its operations. Moreover, it is also known for delivering large orders at the right time without delay.
Crimson Cattle Farm
Crimson Cattle Farm has been operating since 1995 and is a well-known company that provides good quality beef with affordable pricing as it has effective and efficient cattle rearing machines. It majorly targets local companies and retailers and has a large distribution network that can serve customers up to a 500-mile radius. Crimson Cattle Farm also has a very effective distribution and supply chain network. However, Crimson Cattle Farm’s offerings are only limited to beef.
Cattle USA has been in business for the past 50 years and enjoys great success. It is one of the largest beef producers in the 200-mile area. It easily caters to local residents primarily due to its prime location. It provides beef and a variety of dairy products including: cheese, yogurt, meat and milk.
Competitive Advantage
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Efficient and effective delivery network
- Good packaging
- Quality products at affordable pricing
- Providing excellent customer service and customer experiences
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is as follows:
Social Media Marketing
Social media is one of the most cost-effective and practical marketing methods for improving brand visibility. The company will use social media to develop engaging content, such as sharing pictures of the cows and creating educational content about the cattle farm industry.
Website/SEO
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will develop a professional website that showcases pictures of the farm and the cows. It will also invest in SEO so that the company’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Word of Mouth/Referrals
Matthew Jones has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by living and working in the midwestern farming industry. Since a number of local cattle farms have ceased operations, they have committed to Matthew that Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be their cattle supplier. They trust his work ethic and commitment to the local community.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will highlight our location, cows, and products on a major billboard facing the busiest highway in town. The billboard will provide the location of Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm and the website URL.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s pricing will be moderate, so customers feel they receive great value when availing of the products. Pricing will be about 50% lower than retail prices to allow wholesalers and retailers to earn their margins.
Operations Plan
Operation Functions: The following will be the operations plan for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm.
- Matthew Jones will be the Owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Matthew has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Sue Smith – will oversee all administrative aspects of running the cattle farm. This will include bookkeeping, tax payments, and payroll of the staff.
- George Baird– Head Farmhand who will oversee the farming staff and day to day operations.
- Ben Brown– Assistant Farmhand who will assist George.
- Frank White– Distribution Manager who will oversee the packaging and distribution of all products.
Milestones:
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 6/202X – Finalize purchase of farm land
- 7/202X – Purchase farm equipment, supplies and materials
- 8/202X – Finalize contracts for grocery store, chain, and restaurant clients
- 9/202X – Purchase initial set of cows
- 10/202X – Hire and train farm staff
- 11/202X – Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm begins farm operations
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s revenues will come from the sales of cattle meat and dairy products to its customers. The major costs for the company will be the cost of land and equipment. The staff will earn competitive salaries allowing Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm to hire experienced workers. In the initial years, the company’s marketing spend will be high, as it establishes itself in the market.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Cows: 300
- Average Revenue per Animal: $500
- Number of Products Sold Per Year: 100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, cattle farming business plan faqs, what is a cattle farming business plan.
A cattle farming business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your cattle farming business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Cattle Farming business plan using our Cattle Farming Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Cattle Farming Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of cattle farming businesses , some examples include: Cow-calf, Backgrounding, Finishing, and Specific Breed.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Cattle Farming Business Plan?
Cattle Farming businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Cattle Farming Business?
Starting a cattle farming business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Cattle Farming Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed cattle farming business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your cattle farming business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your cattle farming business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Cattle Farming Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your cattle farming business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your cattle farming business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Cattle Farming Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your cattle farming business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your cattle farming business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful cattle farming business:
- How to Start a Cattle Farm Business
The Farming Insider
Breeding livestock: basics for farm success.
Last Updated on November 27, 2023
Introduction
Attention grabber.
Breeding livestock is a vital aspect of farm success, ensuring high-quality animals and profitable results.
Background information on breeding livestock
Breeding livestock involves selectively mating animals to improve desirable traits and genetics.
Thesis statement introducing the importance of breeding for farm success
Effective breeding practices are crucial for farm success as they lead to improved productivity, profitability, and sustainability.
Understanding the Breeding Process
Definition of breeding.
Breeding refers to the purposeful mating of animals to produce offspring with desired traits.
Different methods of breeding
- Natural breeding: Natural breeding involves allowing animals to mate naturally without human intervention.
- Artificial insemination: In artificial insemination, semen from a male animal is collected and manually inserted into a female’s reproductive tract.
Explanation of the role of genetics in breeding
Genetics plays a crucial role in breeding as it determines the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring.
Importance of selecting high-quality breeding stock
Selecting high-quality breeding stock is essential for producing healthy and productive offspring.
Good breeding stock ensures the transmission of desirable traits, such as disease resistance and high productivity.
Breeding livestock is a fundamental aspect of successful farming.
It involves carefully selecting animals with desirable traits and using specific methods to ensure the production of high-quality offspring.
Understanding the breeding process is crucial for farmers who want to achieve desired outcomes and improve their livestock’s genetics.
Breeding is the deliberate mating of animals to produce offspring with desired characteristics.
It is a purposeful and controlled process that allows farmers to shape the future characteristics of their livestock.
By selecting animals with specific traits, farmers can enhance productivity, adaptability, and other desirable qualities within their herds.
- Natural breeding: Natural breeding occurs when animals mate without any human intervention. In this method, the male and female livestock are allowed to interact and mate naturally. Natural breeding is suitable for farmers looking to maintain the natural genetic diversity of their herds.
- Artificial insemination: Artificial insemination (AI) is a more controlled breeding method. It involves collecting semen from a male animal and manually introducing it into the reproductive tract of a female. AI offers several advantages, including the ability to utilize superior genetics from a distance and reduce the risk of transmitting diseases through natural mating.
Genetics plays a pivotal role in the breeding process. It determines the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring.
By selectively breeding animals with desired traits, farmers can enhance the overall quality of their herd.
Traits such as productivity, fertility, disease resistance, and conformation can be improved through careful breeding decisions.
Understanding the principles of genetics helps farmers make informed choices and achieve their breeding goals effectively.
Selecting high-quality breeding stock is crucial for long-term farming success. Quality breeding stock ensures the transmission of desirable traits to future generations.
Farmers should prioritize animals with superior genetics, as they are more likely to produce offspring with similar advantageous traits.
High-quality breeding stock also contributes to the overall health and productivity of the herd.
Regular evaluation, such as assessing physical traits, performance records, and genetic testing, helps in selecting the best animals for breeding purposes.
In short, understanding the breeding process is essential for farmers aiming to enhance their livestock’s genetics.
By defining breeding, exploring different breeding methods, considering the role of genetics, and prioritizing high-quality breeding stock, farmers can ensure optimal results.
Breeding livestock with purpose and knowledge leads to the production of healthier and more productive offspring, ultimately contributing to the success and sustainability of the farm.
Read: Optimizing Feed for Livestock: Expert Advice
Preparing for Breeding
Assessing the health and fertility of breeding animals.
- Schedule a thorough veterinary examination to assess the overall health of the breeding animals.
- Conduct fertility tests to ensure that the animals have the ability to reproduce successfully.
- Check for any genetic disorders or abnormalities that may affect the breeding process.
- Assess the animals’ temperament and behavior to ensure that they are suitable for breeding.
Implementing proper nutrition and care
- Provide a well-balanced diet that meets the specific nutritional needs of breeding animals.
- Incorporate supplements if necessary to enhance reproductive health and fertility.
- Ensure access to clean and fresh water at all times.
- Maintain appropriate body condition scores to optimize breeding potential.
- Regularly groom and provide necessary vaccinations and deworming to prevent diseases.
Ensuring a suitable environment for breeding
- Design and maintain comfortable and spacious housing facilities for breeding animals.
- Provide adequate ventilation to minimize the risk of respiratory infections.
- Control temperature and humidity levels to create an optimal breeding environment.
- Implement effective manure management practices to prevent the spread of diseases.
Developing a breeding plan based on farm goals and market demands
- Define the breeding objectives, such as improving specific traits or increasing flock/herd size.
- Consider market demands and consumer preferences when selecting breeding animals.
- Determine the appropriate breeding methods, such as natural mating or artificial insemination.
- Establish a breeding schedule that aligns with the reproductive cycles of the animals.
- Monitor and evaluate the progress of the breeding plan regularly to make necessary adjustments.
Preparing for breeding is crucial for farm success:
- Regular veterinary examinations assess overall health.
- Fertility tests confirm reproductive capability.
- Proper nutrition and care maximize breeding potential.
Ensure a suitable environment:
- Comfortable housing facilities for natural mating behaviors.
- Adequate ventilation to minimize respiratory infections.
- Controlled temperature and humidity for optimal reproduction.
- Effective manure management practices for a healthy breeding environment.
Develop a breeding plan:
- Define breeding objectives based on farm goals and market demands.
- Choose suitable breeding animals.
- Select appropriate breeding methods (natural mating or artificial insemination).
- Establish a breeding schedule aligned with reproductive cycles.
- Monitor and evaluate the plan for continuous improvement.
By prioritizing health, fertility, nutrition, care, environment, and a well-defined breeding plan, farmers increase breeding success.

Managing the Breeding Process
A successful breeding process is crucial for farm success. Here are some key steps to effectively manage the breeding process:
Tracking estrus cycles in females
- Observe behavioral changes: Pay attention to signs of heat in female livestock, such as mounting behavior and increased vocalization.
- Physical indicators: Look for physical signs like a swollen vulva, clear or bloody discharge, and increased activity.
- Keep records: Maintain accurate records of breeding dates, estrus symptoms, and any other relevant observations to track cycles.
- Use technology: Explore advanced tools like estrus detection patches or pedometers to help monitor estrus cycles more efficiently.
Timing mating or artificial insemination
- Understand the estrus period: Know the duration of the estrus cycle in your particular livestock breed.
- Identify the optimal time: Determine the best time for mating or artificial insemination based on the female’s estrus cycle.
- Consult professionals: Seek advice from veterinarians or experienced breeders to ensure accurate timing for successful breeding.
- Use synchronization protocols: Consider using hormonal treatments to synchronize estrus cycles and improve breeding efficiency.
Monitoring and optimizing conception rates
- Regular pregnancy checks: Conduct pregnancy tests to identify successful conceptions and confirm pregnancies.
- Address reproductive health issues: Treat any reproductive health problems in females to increase conception rates.
- Evaluate nutrition: Ensure a balanced and appropriate diet for females to improve their chances of successful conception.
- Optimal breeding age: Determine the ideal age at which females are most fertile to maximize conception rates.
Addressing potential breeding challenges or complications
- Infertility investigations: Conduct thorough examinations to identify potential infertility issues in both males and females.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with veterinarians or reproductive specialists to address specific breeding challenges.
- Manage breeding environment: Provide a clean and suitable breeding environment to minimize the risk of complications.
- Prepare for emergencies: Have a plan in place for handling any unforeseen breeding complications or emergencies.
By actively managing the breeding process, farmers can increase the success rate of their livestock breeding program.
Tracking estrus cycles, timing mating or artificial insemination accurately, optimizing conception rates, and addressing potential challenges are all fundamental elements of effective breeding management.
Read: Winter Care for Livestock: A Complete Guide
Caring for Pregnant Livestock
Providing appropriate nutrition for pregnant animals.
- Feed pregnant livestock a balanced diet that meets their increased nutritional needs.
- Consult with a veterinarian to develop a feeding plan tailored to the specific needs of each animal.
- Ensure pregnant animals have access to clean water and a constant supply of high-quality forage.
- Monitor their body condition closely and adjust their diet accordingly to prevent undernutrition or obesity .
Ensuring proper prenatal care and veterinary attention
- Schedule regular check-ups with a veterinarian to monitor the health of pregnant livestock.
- Vaccinate and deworm animals according to a recommended schedule to prevent diseases.
- Provide appropriate prenatal supplements to ensure the well-being of both the animal and the developing fetus.
- Detect any signs of illness or complications early and seek immediate veterinary assistance.
Managing the health and well-being of pregnant livestock
- Provide a clean and comfortable environment for pregnant animals to reduce stress and prevent diseases.
- Implement biosecurity measures to protect them from contagious diseases that could harm the unborn calves/foals.
- Prevent overcrowding to minimize the risk of injuries and the spread of infections.
- Monitor behavioral changes and promptly address any abnormalities to ensure the animals’ emotional well-being.
Preparing for birthing and postpartum care
- Set up a designated area or barn for the birthing process, ensuring it is clean, well-ventilated, and easily accessible.
- Prepare a birthing kit containing essential supplies such as clean towels, gloves, and disinfectants.
- Educate yourself about the signs of impending labor and be prepared to assist if necessary.
- Monitor the birthing process closely, ensuring the newborns are healthy and receive immediate postpartum care.
In essence, caring for pregnant livestock is crucial for farm success.
By providing appropriate nutrition and veterinary attention, managing their health, and preparing for birthing, farmers can ensure the well-being of both the pregnant animals and their newborns.
Read: Sustainable Grazing: Balancing Land & Livestock
Raising and Evaluating Offspring
Colostrum management for newborns.
- Colostrum is crucial for the health and survival of newborn livestock.
- Ensure newborns receive colostrum within the first few hours of life.
- Adequate colostrum intake helps boost the immune system of the offspring.
- Regularly monitor the quality of colostrum to ensure maximum effectiveness.
- Proper storage and handling of colostrum is essential to prevent contamination.
Monitoring the growth and development of offspring
- Regularly measure the weight and size of the offspring to track their growth.
- Document the growth patterns to identify any anomalies or potential health issues.
- Monitor the overall health and appearance of the offspring for signs of disease or distress.
- Keep thorough records of the offspring’s development for future reference and analysis.
- Adjust feeding and management practices based on the growth and development of the offspring.
Evaluating offspring for desired traits and genetic improvements
- Identify the desired traits that you want to improve in future generations.
- Observe and analyze the offspring’s physical characteristics, behavior, and performance.
- Assess the offspring’s genetic potential through pedigree analysis and parent evaluation.
- Use selection criteria to determine which offspring possess the desired traits.
- Maintain detailed records of each offspring’s traits and genetic background for informed breeding decisions.
Deciding on future breeding selections based on offspring performance
- Analyze the performance data collected from the offspring to make informed decisions.
- Consider the offspring’s growth rate, health, temperament, and overall performance.
- Assess the offspring’s ability to meet breeding goals and objectives.
- Prioritize offspring that consistently exhibit the desired traits and genetic improvements.
- Continually reassess and adjust breeding selections based on ongoing evaluation and results.
Raising and evaluating offspring is a crucial aspect of breeding livestock to achieve farm success.
Proper colostrum management for newborns is essential as it provides vital nutrients and boosts the immune system.
Regular monitoring of growth and development helps identify any anomalies or potential health issues.
To evaluate offspring for desired traits and genetic improvements, it is important to identify the specific traits that need improvement.
Physical characteristics, behavior, and performance should be observed and analyzed.
Pedigree analysis and parent evaluation can also provide insights into an offspring’s genetic potential.
Decisions regarding future breeding selections should be based on the performance data collected from the offspring.
Growth rate, health, temperament, and overall performance should all be taken into account.
Offspring that consistently exhibit the desired traits and genetic improvements should be prioritized.
It is crucial to continually reassess and adjust breeding selections based on ongoing evaluation and results.
Keeping detailed records of each offspring’s traits and genetic background is essential for making informed breeding decisions.
By implementing these practices in the breeding process, farmers can improve the quality of their livestock and attain long-term success in their farming endeavors.
Read: Livestock Disease Prevention: Must-Know Tips
Recap of the importance of breeding for farm success
Breeding livestock is a crucial aspect of achieving farm success. It ensures the production of high-quality animals that meet market demands.
Final thoughts and encouragements for farmers
As farmers, it is essential to prioritize breeding practices to enhance the overall health, productivity, and profitability of your livestock.
By doing so, you can stay ahead in the competitive agricultural industry.
Call to action for readers to implement best breeding practices on their farms
I encourage all readers to actively implement the best breeding practices on their farms.
This includes careful selection of breeding stock, genetic testing, proper nutrition, and regular monitoring of animal well-being.
Breeding livestock should not be taken lightly. It requires dedication, knowledge, and ongoing education to continually improve the quality of your animals.
Through comprehensive breeding programs, you can achieve optimal results and contribute to the long-term sustainability of your farm.
In conclusion, breeding livestock plays a vital role in farm success. It directly impacts the quality of your livestock and the overall profitability of your farm.
By understanding the importance of breeding and implementing the best practices, you can ensure the success and sustainability of your farm for generations to come.
So, take action today, implement the best breeding practices, and pave the way for a prosperous future in the agricultural industry.
Your farm and the quality of your livestock will thank you.
- Optimizing Feed for Livestock: Expert Advice
- Tech in Farming: Innovations in Livestock Care
You May Also Like

Organic Poultry Farming: A Comprehensive Guide

Duck Health Management & Disease Control

Optimal Nutrition for Chickens & Turkeys
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to write a business plan for a cattle farm?

Are you an aspiring cattle farmer looking to start up a business, or an existing one looking to expand and become more profitable? If so, then writing a business plan for your cattle farm is essential.
A well-crafted business plan can help you identify potential opportunities and risks associated with running a cattle farm, as well as guide you on how best to manage the operations of the farm.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore why it’s important to write a business plan for your cattle farm, what information is required to create one, what should be included in the document itself, and which tools are available that can make the process easier.
Let’s get started!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a cattle farm?
- Information needed to create a business plan for a cattle farm
- What goes into your cattle farm financial forecast?
- The written part of a cattle farm business plan
- What tool should I use to write my cattle farm business plan?
To draw up a roadmap
A business plan for a cattle farm helps you define your objectives and set goals for the next 3-5 years, which can be incredibly useful for achieving success in the long run.
The writing process of a business plan requires careful consideration of all aspects of running your cattle farm, from financial management to sales & marketing strategies and operational procedures.
Having these clear objectives laid out ahead of time will help ensure that your cattle farming venture runs smoothly and achieves its desired outcomes.
To compare financials and track progress
One of the main benefits of writing a business plan for a cattle farm is to be able to regularly compare your actual financial performance against what you planned in your forecast, and make adjustments where needed.
This enables you to maintain visibility on your future cash flows and make informed decisions about investments to grow your farm.
To secure funding
If you want to receive capital from investors or banks, you must have a comprehensive cattle farm business plan.
Financiers will be looking closely at your venture's growth prospects, profitability, and cash flow to estimate the possible returns on their investment.
Now that you know why it’s important to write a business plan for a cattle farm, let's look at the information needed to create one.
Create your cattle farm business plan online!
Think your cattle farm could be profitable? Find out how with a business plan!


What information is needed to create a business plan for a cattle farm?
Carrying out market research for a cattle farm.
Conducting market research is an essential step before creating a business plan for a cattle farm. Market research can help you to estimate revenues and provide insights into potential areas of growth or decline.
When you embark on market research of your cattle business, you seek to answer the following questions:
- Is the cattle industry growing?
- What segments (processed milk products, beef processing and packaging, breeding services, and cowhide sale) of the market are most attractive?
- Who is the competition?
- How long does it take from calving to sales?
- What is the best time for breeding?
- What are sales and profit margins like?
- What are the major trends in the cattle industry? For example, consumers are more interested in organic-bred cattle than those bred using hormones, steroids, and antibiotics.
This information will help you create and communicate in your business plan the strategies that will give your farm the best chance for success.
Developing the marketing plan for a cattle farm
Creating a sales & marketing plan for your cattle farm is the next step.
Having a concrete action plan in place will be necessary to create an accurate budget for sales and marketing expenses in your business plan, and to ensure that you have sufficient resources to deliver your sales forecast.
The staffing and equipment needs of a cattle farm
Before starting a cattle farm business plan, it is also key to take into consideration the investments and recruitment plan.
This will ensure that all necessary costs are accounted for and that sufficient capital is available to launch or grow the venture.
Some of the costs you must be aware of includes:
- Land purchase
- Fencing the land
- Land preparation
- Water source or supplies
- Tools and equipment costs
- Cattle shelter
- Cattle purchases
- Licenses and permits
Once you have gathered all the necessary information to create the business plan for your cattle farm, it is time to start building the financial forecast.
What goes in the financial forecast for a cattle farm?
The financial forecast of a cattle farm’s business plan will include important information like the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and sources and uses table.
Let’s have a look at each table in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement of a cattle farm business plan shows how much revenues it is expected to generate, how sales will evolve and how profitable it can be in the future.
The projected balance sheet of your cattle farm
The balance sheet of a cattle farm is an essential financial statement that provides a snapshot of the farm’s financial position at any given time.
It records the assets, liabilities, and equity of the farm and serves as a valuable tool for owners, investors, and lenders to understand the overall financial health of the venture.
Assets are what a business owns and uses to make money. Examples of assets for a cattle farm include:
- Machinery and equipment
Liabilities on the other hand are what the business owes, they include things like:
- Accounts payable (money owed to suppliers)
- Tax payables
When total liabilities are deducted from total assets, what is left is the owner’s equity which represents the net worth of the business for the owners.
The projected cash flow statement
A projected cash flow statement for a cattle farm is a financial document that shows how much cash the farm will generate and spend in the future.
All transactions that involve the inflow and outflow of cash from a business are recorded in the cash flow statement.
This statement makes it easy for financiers to understand how much money your business produces (or will produce) and how much cash it will need for smooth operations.

The initial financing plan
An initial financing plan is important when writing a cattle farm business plan. It is also called sources and uses table.
This table helps you figure out how much money you will need to start your farm, where it will come from, and what it will be used for.
Having this information all in one place makes it easier to plan your finances and prepare for the future of your business.
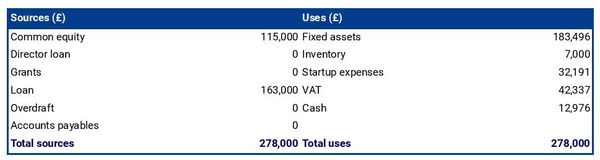
A solid financial forecast is the foundation for any successful cattle farm business plan. But to understand how relevant this financial data is, it's essential to provide context within the written part of the plan.
What goes in the written part of a cattle farm business plan?
The written part of a cattle farm business plan consists of 7 main sections:
The executive summary
The presentation of the company, the products and services section, the market analysis, the strategy section, the operations section, the financial plan.
The executive summary section of your cattle farm’s business plan should be a one-page (two-page maximum) summary presented in such a way that will convince investors and banks to read the rest of the plan.
The executive summary of your cattle farm business plan should begin with an overview of the farm itself, including key points such as the purpose of the business, its legal structure, its management team, and any pertinent information about the geographic area in which it operates.
After this should come a quick market overview highlighting who the farm sells to and who it competes with.
Then you should include key financials such as forecasted sales, growth, and profit, as well as expected cash flow projections and capital requirements.
This section of your business plan should include details about the ownership and legal structure of your cattle farm, your farm’s location, and information about the management team.
When writing about the legal structure, you should include information about the legal entity that owns the farm, such as whether it is a sole proprietorship, limited liability company, partnership, or other type of legal ownership.
You should also list the shareholders (people with a stake in the business) and the percentage of ownership each one holds.
The location section should provide an overview of the geographical area where the farm is located, with information about nearby cities and towns, access to major roads and highways, availability of water sources, climate considerations, and any other factors that could influence the success of the farm.
Then you should continue with the presentation of the management team which provides an in-depth look at who is running the farm’s day-to-day operations, including information about each individual's experience, education, and qualifications for their specific roles on the farm.
When writing the products and services section of your business plan for a cattle farm, it is important to clearly describe what breed of cattle (lisrace lumberjack, bos taurus, Angus cattle, etc.) you will raise and any other related services or products that you may offer.
This should include information about the size and quality of the herd, as well as any specialized breeds or special care practices used in raising them.
It is also important to outline any additional sources of income such as selling hay, feed, or providing agricultural consulting services.
Additionally, outlining plans for expansion into new markets could help convince investors that this is an enterprise with growth potential.

When presenting the conclusion of your market analysis in your cattle farm business plan, you should touch on demographic and segmentation information, your target market and competitors, and details about any barriers to entry and relevant regulations that you must comply with.
The demographic and segmentation section should include information about the different customer segments on the market and their purchasing habits for each of the main categories of products and services.
The target market section then zooms in on the segments you intend to serve and why your products and services match what customers are looking for.
Then you should explain who your main competitors are, and how your products and services compare to theirs.
You should also consider any potential barriers that can impede entry into the market (such as a limited availability of farm land for example) and relevant regulations that must be adhered to for compliance purposes.
In the strategy section of your cattle farm's business plan, you should explain your competitive advantage, price strategy, marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
To demonstrate the financial viability of your farm, you must be able to clearly explain what your competitive advantage is - i.e. how you intend to compete in an already crowded marketplace.
In addition, you should include details of your pricing strategy and show that it is profitable for you and attractive for customers.
Then comes your sales and marketing plan which outlines how you will reach your target markets, followed by any important and realistic milestones which are achievable within specified time frames.
Finally, you must detail any potential risks associated with your farm and possible solutions or mitigations for these risks.
The operations section of your cattle business plan should provide an overview of the functions and activities of your cattle farm.
It should cover information such as the staffing team, roles of staff members, recruitment plan, operating hours, key assets, and intellectual property needed to operate the farm.
A cattle farm may have the following type of staff on its payroll:
- Farm manager
- Slaughterer
- Veterinarian
For example, if you plan on hiring a veterinary technician or farm manager, explain their experience requirements and how they will contribute to the operation of your business.
You should also include your schedule and operating hours to give investors an idea of what a typical business day for your farm looks like, as well as information on the main assets and intellectual property that the business requires to operate.
These assets include any resources such as land, buildings, equipment or technology essential for running the farm. If you plan on leasing or buying any of these assets, provide details about the timelines and costs involved.
Lastly, the operations section should include information about the suppliers that you plan to work with. Be sure to provide details such as the cost of goods, delivery times and any other relevant commercial terms.
This will give investors a better understanding of how you plan on running your farming operation.
The financial plan section of the cattle farm business plan will include the financial forecast (balance sheet, P&L and cash flow statements, and the sources and uses table) that we talked about earlier.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the content of your cattle farm business plan, it's time to look at the tools available for creating one.
What tool should I use to write my cattle farm's business plan?
In this section, we will look at three options for writing a detailed business plan for your cattle farm: writing it yourself with Word and Excel, hiring a consultant to do it, and using online business plan software.
Create your cattle farm's business plan using Word or Excel
Creating a cattle farm business plan with Word or Excel is a possible option but usually not the best one.
On the plus side, both programs are relatively inexpensive. However, there are some significant drawbacks to using these programs to create a business plan.
Excel isn’t an easy tool to use, especially when it comes to creating financial forecasts without making mistakes.
As a result, it will be hard for financiers to trust the accuracy and validity of your numbers, and, therefore, using Excel isn’t recommended unless you are well versed into the art of accounting and finance.
Drafting the written part with Word also suffers from severe flaws. You start from scratch with no instructions to aid you, forcing you to think long and hard before filling up the pages. It is also time-consuming and tedious to format your business plan with Word.
Hire a business plan writer to draft your cattle farm's business plan
Outsourcing the business plan for a cattle farm to a consultant can be a viable solution as they are used to writing such plans. But this solution also comes with certain disadvantages.
Business plan writers may lack the livestock industry expertise needed to anticipate sales and cost accurately, forcing them to rely on your assumptions.
Hiring consultants to write a business plan is also expensive (budget a minimum of $2,000 or £1,500), with additional fees if the business plan needs to be updated after the initial version has been produced.
Finally, hiring a consultant gives you less control over the result than writing it yourself and your vision for the farm's future may not be adequately presented in the business plan.
Use an online business plan software for your cattle farm's business plan
Another alternative is to use online business plan software .
There are several advantages to using specialised software to write a cattle farm’s business plan:
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you, without error
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank
- You can easily update your financial forecast and track it against actual financial performance to see where the farm stands
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here .
We hope that this article has helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for a cattle farm. Do not hesitate to contact us if you still have questions.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a business plan for a poultry farm
- How to write a business plan for a fish farm
Know someone in the farming industry? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a livestock farming business requires careful planning and strategic thinking. To secure financing and attract investors, you need a comprehensive business plan that outlines your goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers comes in!
This template is specifically designed for livestock farmers and entrepreneurs in the agriculture industry, providing you with a step-by-step guide to creating a detailed and professional business plan. With ClickUp's template, you can:
- Outline your business goals and objectives for long-term success
- Develop strategies to effectively manage and grow your livestock farming business
- Create financial projections to attract investors and secure financing
- Streamline your planning process and save time with a ready-made template
Don't let the complexities of starting a livestock farming business overwhelm you. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll have all the tools you need to create a solid foundation for your venture. Start planning for success today!
Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers Benefits
Livestock farmers who use the Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers can enjoy the following benefits:
- Streamlined planning process to effectively outline goals, strategies, and operational details
- Increased chances of securing financing and attracting investors with a comprehensive business plan
- Clear financial projections to guide budgeting and financial decision-making
- Improved organizational and management skills with a structured business plan
- Enhanced ability to adapt to market changes and make informed business decisions
- Increased credibility and professionalism in the eyes of stakeholders and partners.
Main Elements of Livestock Farmers Business Plan Template
Are you a livestock farmer looking to create a comprehensive business plan? Look no further than ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers!
This template includes all the essential elements you need to develop a successful business plan for your livestock farming venture:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add specific information to your business plan with custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section, allowing you to keep all relevant details organized and easily accessible.
- Custom Views: Access different views to effectively manage your business plan, such as the Topics view to focus on specific areas, the Status view to track progress, the Timeline view to set deadlines, the Business Plan view to see the complete picture, and the Getting Started Guide view to help you navigate through the template.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers, you can confidently create a professional and comprehensive business plan to take your livestock farming business to new heights.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
If you're a livestock farmer and want to create a comprehensive business plan, follow these steps using the Business Plan template in ClickUp:
1. Define your vision and mission
Start by clarifying your vision and mission for your livestock farming business. What do you want to achieve? What values and principles guide your operations? Clearly defining your vision and mission will serve as a foundation for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline and articulate your vision and mission statements.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand the demand for your livestock products, identify your target audience, and analyze your competitors. Gathering this information will help you make informed decisions about your marketing strategies, pricing, and product development.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Develop a detailed financial plan
Creating a comprehensive financial plan is crucial for the success of your livestock farming business. Estimate your startup costs, projected revenue, and expenses. Consider factors such as feed costs, veterinary services, equipment, and labor. This will help you determine your breakeven point and financial viability.
Create custom fields in ClickUp to track your financial projections, budgets, and expenses.
4. Outline your operational plan
Your operational plan should outline how you will manage the day-to-day activities of your livestock farm. Consider aspects such as animal care, breeding and genetics, feed management, waste management, and equipment maintenance. Define standard operating procedures to ensure efficiency and productivity.
Use tasks in ClickUp to break down your operational plan into actionable steps and assign responsibilities to team members.
5. Develop a marketing strategy
To attract customers and promote your livestock products, you need a solid marketing strategy. Identify your unique selling points, determine your pricing strategy, and decide how you will reach your target audience. Consider online marketing, farmers markets, and partnerships with local businesses.
Use the Board view in ClickUp to visualize and track your marketing strategies and initiatives.
6. Monitor progress and adapt
Once your business plan is in motion, it's important to regularly monitor your progress and adapt as needed. Track key performance indicators such as sales volume, customer satisfaction, and profitability. Evaluate your plan's effectiveness and make adjustments to stay on track towards your goals.
Set up Automations in ClickUp to receive progress updates, schedule regular reviews, and ensure accountability.
By following these steps and utilizing the Business Plan template in ClickUp, you'll have a comprehensive roadmap for your livestock farming business. Good luck!
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
Livestock farmers and entrepreneurs in the agriculture industry can use the Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers in ClickUp to efficiently plan and manage their livestock farming businesses.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your business plan into different sections such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Financial Projections, and Operational Details
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, including statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and milestones for each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View will provide you with a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate between sections
- Create a Getting Started Guide View to outline the steps and resources needed to execute your business plan effectively
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional context and information
- Update statuses, custom fields, and collaborate with team members to ensure your business plan is comprehensive and accurate
- Business Plan Template for Facebook
- Business Plan Template for Grassroots Organizers
- Business Plan Template for Electricians
- Business Plan Template for Verizon
- Business Plan Template for Grocers
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Occupations
- Farm Animals and Livestock
How to Write a Business Plan for Farming and Raising Livestock
Last Updated: May 4, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Karin Lindquist . Karin Lindquist earned a BSc in Agriculture as an Animal Science major from the University of Alberta, Canada. She has over 20 years of experience working with cattle and crops. She's worked for a mixed-practice veterinarian, as a sales representative in a farm supply store, and as a research assistant doing rangeland, soil, and crop research. She currently works as a forage and beef agriculture extension specialist, advising farmers on a variety of issues relating to their cattle and the forages they grow and harvest. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 17 testimonials and 93% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 382,252 times.
A business plan is essential to have in place before you seek to start up a farm business, no matter what else you've done by way of preparation. In today's world, animal agriculture is more complex and more variable than it was 100 years ago. There are changing markets, high costs, low profit margins, different ways to raise cattle, and niche markets. The type of business plan you make is up to you, but the following step-by-step process of making a proper business plan will help you in the long run.

- You should be mainly brainstorming about your goals and objectives. [1] X Research source It's much more effective to run any business when you have a goal in mind to reach rather than having vague ideas of "wanting to do something with animals". That's simply not enough, and is certainly not going to get you anywhere fast!
- As you consider your goals, remember that strategy is not the same as marketing. The strategy for your business is how you plan to deliver value to your customers (your "value proposition"), how you intend to you convince potential customers to obtain that value from you by communicating your distinctiveness as a producer (or, what makes you different from other farms or ranches), and why you can deliver that value better than other producers (your performance anatomy). Your marketing plan should explain how you intend to communicate your strategy to your existing and potential customers. [2] X Research source

- Such an analysis is very simple and flexible to use, since you can use it to analyze your personal self, your business, or the industry you are wishing to start a career in.
- Internal forces that you have control over such as what breeds you choose, whether you want to run an intensive or extensive operation, how you feed your animals, etc.
- External forces that you have no control over such as the weather, the topography and soil-type of the land you are farming/ranching on, local, national and international industry issues, market prices, product demand and consumer preferences.
- Also analyze your farm, the land your farm sits on and your family. Ask similar questions as mentioned above, only with your family you will need to ask about times you should have to spend with them, what will happen if you put your farming operation before your family, what you can do to encourage and teach your kids to be involved in your operation, etc.
- The more research about what you're getting into that you do at this stage, the more aware you will be of what to expect when surprises do come. When you finally get started on your business plan, you'll be far more aware of the pitfalls, challenges , needs and requirements it takes to be involved and compete in the kind of livestock/farming operation you want to have.

- Where am I at now? Include a SWOT analysis (see earlier step), for these areas: customers, operations, human resources, and finance . If you don't have a business, a SWOT analysis as mentioned in the previous step is totally fine.
- Personal goals include things like working fewer hours, furthering your education in areas like different commodity markets or accounting and production programs, etc.
- Business goals are focused mainly on the farm unit as a business entity; examples include maximum debt load to carry, possibly owning or controlling x number acres, etc.
- How do I get there? This is the most important part of your business plan, because this is the area where you put on paper how you want to get the things you want for a better you, family and business. Brainstorming is great tool to use in this section, as you can always have a Plan B, C, D, etc., in addition to your Plan A.
- How do I know I have arrived? If you visualize your business plan as a journey, it is not difficult to understand that you will need to measure your progress along the way and determine if you are moving towards your goals, spinning your wheels or rolling backwards. This is done by defining, collecting and reviewing metrics, measurements and Key Performance Indicators on a regular basis in order to validate your plan and decisions, direct your future activities, justify any modifications to the plan and intervene when things are not happening according to the plan. All your goals should be measurable. Metrics and measurements will give you the answer to this important question.

- Vision Statement: A statement of what you or your farm will look like in the next 5 to 10 years.
- Mission: This determines or defines the purpose the organization attempts to perform in society. This statement should concisely explain what the company does, for whom and why.
- Values: These are general standards or guidelines that are important to your farm and farm family.
- Situational Analysis: This is the process of identifying and understanding how your business is positioned within the environment you operate, both internal and external. Step 3 is what this part of the strategic plan is all about.
- Goals: What are the major achievements you would like to accomplish in the next 3 to 5 years?
- Objectives: How do you plan on achieving your goals?
- Critical Success Factors: Areas of performance critical to long-term successes of an organization, and its development, growth and achievement. For each CSF you should define one or more Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which are metrics you will use to determine if you are achieving your CSFs. CSFs are expressed as general statements of goals ("Maintain customer satisfaction.") while KPIs are more specific ("Decrease in number of product packaging complaints.")
- In a nutshell, you don't have to go through the headache of answering all of the questions posted above. Instead, use the three simple questions above in Step 4 as a means to answer all 8 of these standard business-plan questions.
- Production resources are also important to mention: Land base, Equipment base, and Buildings and Structures.
- Marketing Plan: Where and how will you sell your commodities? Remember, selling is just getting rid of what you have. When you market, you have to plan to sell commodities at a good price.
- Financial Plan: This includes budget analysis, revenues and expenses, debt, unpaid labour, opportunity costs, benchmark analysis of yourself from other operations, statements of cash flow , depreciation of machinery, animals, buildings, etc., wages, family living costs, etc.
- Human Resources plan: Most farms rely on one worker (i.e., the owner) to run the operation. But, nonetheless, human resource plans should highlight hiring issues facing the business and how to address them. It should further describe the kind of people that are required to operate the business (general responsibilities, title, skills, availability and any training programs needed.)
- Plan: Establish the objectives for whatever it is you intend to do, the processes necessary achieve those objectives and the metrics and measurements required to control the processes and prove that the objectives are being achieved.
- Do: Execute the plan and collect metrics and measurements along the way as defined in the previous phase.
- Check: Review the results, metrics and measurements and determine if any improvements can and should be made to the plan.
- Act: Implement the improvements so the next time the process is executed the results will be better.
- Succession Planning . This can be the hardest part of a business plan, as one has to plan what should happen if the main operator is injured or worse, dies. Succession planning includes developing a continuity plan for your business and determining the process of transitioning a business to new owners. This transition may be an outside sale (equipment and land auction sale), or an inheritance sale (passing the business down to the next generation). [7] X Research source

- Proprietorship : This is the simplest form of business organization. It primarily involves one person running the whole she-bang. Debts and negligent acts committed by employees are the responsibility of the proprietor. But, all the legal complications and expenses and negotiations for agreements are not required, nor is a business name required.
- General Partnership : This means two or three people running an operation. With more than one person running a farm, this means that the business must have a registered name, and each partner is responsible for all debts, obligations and liabilities of the operation. This partnership automatically dissolves with a death, bankruptcy, or insolvency.
- Limited Partnership : This is basically one person is responsible for everything in the firm, whereas the other is only there to supply capital, nothing more or less. A limited partner has no active part in the goings-on of an operation, but he may inspect the books of the firm and advise management.
- Co-ownership : This is where two or more persons own property jointly.
- Joint Venture : This is commonly used in farming, where there is a joint partnership between parties, and is created in order to conduct a specific or limited commercial venture without creating a partnership. This is commonly a temporary arrangement between two parties.
- Corporations : These are legal entities where shareholders own the corporation through the ownership of shares. It is a separate legal entity, distinct from its shareholders. The individual shareholder's liability is limited to that person's investments in the corporation, unless the shareholder has personally guaranteed the obligations of the corporation. A corporation can provide very flexible framework in terms of succession to the next generation. The owner may also give employees shares in the growth and profit of the operation without giving up management rights of a partner.
- Trust: This is a relationship where legal ownership of the property is separated from beneficial ownership of the property.

Community Q&A
- Ask for help when writing a business plan. Get a professional business analyst or someone similar with lots of experience analyzing and writing up such plans so they can help you if and when you are stuck on a particular section. Thanks Helpful 33 Not Helpful 5
- A business plan is good to have when signing on for a loan at the bank. They will be more interested in the financial portion of your business plan, because they need to see how it will affect them in terms of what they can get out of it in terms of money. Thanks Helpful 30 Not Helpful 9
- Put everything in writing. Nothing's worse than not writing something down and suddenly forgetting it. Also, have a separate file folder for thus business plan so you know where it is and where you can access it in the future. If you have it on the computer, save it on a hard drive or a data stick so if your computer crashes on you and you can't get your work back up, you have it saved on a separate disk. Thanks Helpful 29 Not Helpful 10

- Don't go in over your head and attempt to write out a business plan in one sitting. It may take a week or more before you get it all done, so take your time. Indeed, many established businesses started by spending six months or more preparing business plans; rushing will simply harm your business in the long run. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 2
- Don't think that you won't have to look at your business plan ever again for the rest of the time you are running your operation. You should always try to analyze what yourself and your business at least once a year to know where you are struggling and where you are doing great. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 2
Things You'll Need
- Computer text program or paper/notepad and pens
- Printer if you want hard copies of computer documents
- Research tools such as the internet, local library, libraries of agricultural bodies, etc.
- Phone numbers of people in the industry that you're interested in so that you can ask any important questions
- Books or websites on making business plans (but don't over-complicate things)
- Books on information about certain livestock interested in raising
- Newspapers and magazines of industry news and events in your area or the area you are interested in pursuing your farming career
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://grasshopper.com/academy/developing-a-business-plan/brainstorming-tips/
- ↑ https://www.forbes.com/sites/michaelskok/2013/06/14/4-steps-to-building-a-compelling-value-proposition/
- ↑ https://www.business.qld.gov.au/starting-business/planning/market-customer-research/swot-analysis/conducting
- ↑ https://www.agriculture.com/farm-management/business-planning/do-a-swot-analysis-on-your-farm
- ↑ https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-strategic-planning-and-operational-planning.html
- ↑ https://fitsmallbusiness.com/business-succession-planning/
About This Article
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Michael Howe
May 11, 2016
Did this article help you?

Nwaokenye Nduka Philip
Oct 8, 2017
Feb 8, 2017
Jamiu Adewole
Aug 30, 2016
Nadia Niyonizeye
Mar 20, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

[Pdf Sample] Livestock Farming Business Plan Docx
In the world of agriculture, livestock farming is a prominent and profitable venture. It involves the rearing and management of animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs, and poultry for various purposes.
If you’re an aspiring livestock farmer and the proud owner of Agrolearners.com, this article will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive livestock farming business plan. By following this plan, you can establish a successful and sustainable livestock farming operation.
Livestock Farming Business Plan Proposal Docx
To write a business plan , here is a breakdown of how it should be structured and what should be in each category. After this instruction, I will provide you with a sample of one I wrote for my farm also subsequently as we go, so, let us go:
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides an overview of your livestock farming business plan. It highlights the key elements of your plan, including your objectives, strategies, and financial projections. The executive summary should be concise yet compelling, capturing the reader’s attention and providing a glimpse into the potential of your venture.
Company Overview
In this section, you will introduce Agrolearners.com and provide a brief background of your livestock farming business . Describe the mission and vision of your company, along with its core values. Explain the goals and objectives you aim to achieve through your livestock farming operations.
Market Analysis
Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the demand and potential for livestock products in your target market. Identify your target customers and their preferences. Analyze the competition and determine your unique selling points. Explore market trends and opportunities that can give your business a competitive edge.
Livestock Selection
Choose the livestock species and breeds that align with your business goals and market demand. Consider factors such as adaptability to local conditions, market value, and potential for growth and profitability. Outline the specific breeds you plan to raise and justify your choices based on market research.
Infrastructure and Facilities
Feed and nutrition.
Detail the feed and nutrition requirements for your livestock. Outline the types of feed and forage you will provide, including any additional supplements or concentrates. Highlight your approach to feed formulation , sourcing, and quality control. Emphasize the importance of a balanced diet for optimal growth and productivity .
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Palm Oil Farming & Production Business Plan Docx
Breeding and Genetics
Explain your breeding program and genetic selection strategy. Discuss the criteria you will use to select breeding stock and how you plan to improve the genetics of your livestock over time. Address the importance of maintaining genetic diversity and avoiding inbreeding. Describe any partnerships or collaborations you have established with reputable breeders or genetic companies.
Health and Disease Management
Livestock health is crucial for the success of your farming business . Outline your health management practices, including vaccination schedules , deworming protocols, and disease surveillance. Emphasize the importance of biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases. Establish a working relationship with a veterinarian to ensure regular health check-ups and prompt treatment when needed.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Present your marketing and sales strategy for promoting your livestock products. Identify your target market segments and outline your pricing strategy. Describe your distribution channels, including direct sales to consumers, partnerships with retailers, or participation in farmers’ markets. Highlight any unique selling points or certifications that differentiate your products from competitors.
Financial Projections
Provide a detailed financial analysis and projections for your livestock farming business . Include an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. Project your revenue streams, expenses, and profitability over a specific period. Consider factors such as initial investment, operational costs, pricing, and market demand. Use realistic assumptions and provide a sensitivity analysis to assess the financial viability of your business.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Cattle Farming In South Africa Docx
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Here is the Download Link to a sample of the Business Plan For Livestock Farming prepared By Agrolearner.com
How do I write a business plan for Animal Farm?
Discuss your farm’s infrastructure, facilities, feed and nutrition plans, health and disease management protocols, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections. Finally, evaluate risks, create an implementation plan, and conclude by summarizing key points and expressing confidence in the success of your animal farm .
How do I write a business plan for a cattle farm?
To write a business plan for a cattle farm , follow the general structure mentioned above. Begin with an executive summary highlighting your objectives and financial projections. Provide a company overview, including the legal structure and ownership details.
Conduct a market analysis to identify target market segments, assess competition, and analyze market size and growth trends. Describe your chosen cattle breeds and their market demand. Detail your farm’s infrastructure, housing, equipment, and waste management practices.
Discuss feed and nutrition plans, health and disease management protocols, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections. Evaluate risks, create an implementation plan, and conclude by summarizing key points.
What is the best livestock business?
Cattle Farming: Cattle can provide a steady income through beef and dairy production. There is consistent demand for beef products, and dairy farming can be lucrative with the right management.
Poultry Farming: The demand for chicken and eggs is consistently high, making poultry farming a profitable venture. It requires relatively less land and can yield quick returns.
Pig Farming: Pig farming can be profitable due to the high demand for pork products. However, it requires careful management and attention to disease prevention.
Ultimately, the best livestock business will depend on your knowledge, resources, market conditions, and personal interests. Thorough market research and analysis of local demand will help you determine the most suitable livestock business for your specific circumstances.
Through diligent execution, collaboration with industry experts, and continuous improvement, Agrolearners.com aims to contribute to the agricultural community while achieving long-term profitability and success.
Share this:
Author: adewebs, you may also like:, [pdf sample] business plan for pig farming docx, starting a poultry farm with limited resources in ghana: a comprehensive guide for new farmers, how to register agribusiness company in kenya (see full guide), starting a poultry farm with limited resources in nigeria: guide for new farmers, one reply to “[pdf sample] livestock farming business plan docx”, leave a reply cancel reply.

How To Create The Perfect Cattle Business Plan For Beginners
Creating a well-thought-out cattle business plan can make all the difference between success for the beginner farmer who makes one, and failure for the one that fails to write it.
This guide will help you create the perfect plan when starting your farm, even with little to no money .
Table of Contents
Reasons To Have A Business Plan
Having a workable business plan is important for the following reasons:
- It helps you raise capital from angel investors, relatives, friends, partners, and financial institutions like banks
- It acts as a living guide for the starting, implementation, operation, and ending of your cattle farm
- It helps keep all the involved persons in organic sync with the farm’s goals and objectives
- It boosts your chances of success with efficient management and acts as the stepping stone for a systematic record-keeping culture
- It helps you to theoretically analyze your business idea to measure its feasibility (practicality) and viability (success potential), and theoretically determine your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats ( SWOT analysis )
- It helps you plan for growth and expansion along the same operational procedures or branching into directly and indirectly related lines of action, such as value addition to your products
How To Write The Perfect Cattle Farm Business Plan
Writing the perfect business plan for a cattle farm doesn’t have to be challenging, whether yours is set to be a small-scale farm or a complex one.
To write an operational business plan, you must include:
- Organizational plan
- Management plan
- Financial plan
- Operations plan
- Marketing plan
- Exit strategy
Let’s take a closer look at each of these aspects.
Organizational Plan
The organizational plan provides a detailed description of the business concerning the reason for its existence, goals, and objectives.
The mission and vision statements usually appear in the executive summary of formal business plans.
If yours is an internal-use-only plan, you could place the two items in the organizational plan or leave them out altogether. However, this second option runs the risk of losing sight of what your vision is for the farm.
The organizational plan basically answers the question, “What business am I in?”. You can answer this question by listing your intended products, services, location, market, and what makes your business unique.
You could raise animals for milk, value-added dairy products, beef production, and high-quality semen. You can also make money selling live animals as calves, lactating cows, pet cows , and bred heifers.
Cattle services aren’t so popular, but you could look into cow tourism/cattle farm agri-tours, cow cuddling/hugging therapy, and educating aspiring and practicing cattle entrepreneurs.
Your organizational plan should also list your short-term and long-term goals and objectives for the farm. These could be guided by your reasons for the establishment of the farm.
Management Plan
The management of most small farms is easy. The farm owner doubles up as the farm manager and field worker, eliminating the need for an elaborate management plan.
Sometimes, family farm owners may receive free or paid assistance from family members or friends, making it necessary to expand the plan.
The management plan must also be detailed if the farm will involve other key players such as investment partners and specialized workers like the driver, farm manager, accountant, sales and marketing officer, and lawyer.
Your plan should provide details such as:
- All stakeholders enlisted by their experience in cattle farming or technical know-how of the business
- Names of staff and partners, together with their respective positions
- General responsibilities of each stakeholder
- The hierarchy of command from the management team down to the lowest employee on the farm
Financial Plan
Your financial plan can make or break your business. It comprises four key aspects:
- Your financial status and funds required: How much money do you have in savings or partner-raised capital? How much start-up capital do you need? And how much is required in operational expenses? Do you have an emergency or risk management fund? If you need outside money, what type of funding are you seeking? This could be credit card debt, grants, and loans from private lenders or commercial banks.
- Use of funds: What will your capital be used for? Typical uses include working capital, licensing, salaries/wages, infrastructure, pasture establishment/development, and daily operational costs. Other uses include cattle purchasing , raw materials for feeds, land, farm machinery and equipment, and unforeseen expenditure.
- Revenue model: How will your farm make money?
- Financial statements: You can’t improve what you haven’t measured. There’s every need to prepare financial reports like balance sheets, profit and loss statements, income statements, tax statements, and break-even analysis . You’ll also need to consider monthly cash flow projections, payback period , and repayment of loans and investor money with interest.
Operations Plan
The operations plan details the technical aspects of your day-to-day cattle-keeping business. It’s a detailed overview of how your business will run and how products will be manufactured.
It includes aspects such as:
- Feeding program: This details what you’ll feed your cattle to achieve the required nutritional levels and desired weights, production levels, and body condition. It shows the types of feeds and how they will be mixed and offered to cows.
- Quality assurance for products or services
- Health program: This details cattle treatment, vaccination procedures, disease prevention mechanisms, breeding protocols, vet and animal nutrition services, post-mortem procedures, and dead cow disposal measures.
- Operational strategy: Will yours be a cow-calf operation, feedlot finishing operation, backgrounding, zero-grazing, or open-range ranching?
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan provides details such as:
- Your target market
- Customer knowledge based on customer analysis of demographics, likes, dislikes, estimated disposable incomes, expectations, consumption behavior for the products you produce, and their location.
- Market analysis to learn cattle industry projections and prevailing market trends
- Pricing strategy for your services or products based on prevailing market prices or private calculations informed by your cost of production
- Competition analysis and how you’ll deal with business competition (both nearby farms and those out of state)
- Marketing strategy, promotion, and distribution of products or services
Exit Strategy
The exit strategy is useful when you want to leave the business permanently or temporarily. It shows when, how, and why you might exit the business. The most common reasons are prohibitive feed costs and ever-increasing operating expenses.
The exit plan details options such as:
- Selling your business to a larger farm (acquisition)
- Selling parts of the business or all of it to other smallholders, for example, through an auction
- Diluting or selling your ownership in a partnership farm
- Succession with a continuity plan for handing over to the next generation if you become incapacitated or your corporeal existence comes to an end.
When To Amend Your Business Plan
You might need to review and amend your cattle farming business plan along the way for the following reasons:
- Desire to change from one product line to another. You could shift from beef cattle like Hereford and Angus to dairy cattle like Friesians and Guernseys .
- Realization of objectives. You might realize the objectives you set out to achieve, making it necessary to change tactics if there’s nothing more to achieve.
- The departure of partners leading to a lower number of partners or a total shift to a sole proprietorship model
- Addition of new partners
- Substantive market changes or disruptions that warrant a change in standardized operation procedures
- The need to retreat to regroup if things haven’t been going according to plan and you wish to overhaul the business
- Changes in cattle, such as a shift from light-feeding cattle breeds to heavy feeders like Holsteins
- Changes in cattle feed crops. You might want to shift from grass-based farming to rearing cows using field forage crops like corn for silage.
Alex grew up in a rural area with chickens, cows, goats, and rabbits. He has always enjoyed waking up at 6 am to tend to his flock and vegetable garden. He bought his first cow at 25 and named her "104". In 2021, he set up an aquarium and now spends his lazy time watching his fish. He is happiest watching small animals and plants grow big, not to mention writing to share his farm-life experiences.
Recent Posts
RBGH: What Is It And Why Is It Given To Cows?
Recombinant bovine growth hormone (rBGH) is a manufactured or synthetic hormone that dairy farmers use to increase milk production in cows. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved rBGH in...
Beef Cuts On A Cow: A Guide For Home Butchering
There are many beef cuts on a cow that can be confusing for a beginner. It's best to start with having a trusted butcher prepare the first one or two animals you slaughter before you take over. Sit...
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Business Management
Raising beef cattle for profit requires land, money, and good business management skills. In this section, you will find information and advice on pricing meat cuts, conditioning cattle for market, and understanding beef carcass yields and losses during processing. Tips on applying RFID tags and performing beef quality audits are available as well.
Starting a Small Beef Cattle Farm
To start a beef farm, you will need to select the type of operation and develop a business plan that includes all startup and ongoing expenses. Consider necessary costs such as the purchase of land, animals, feed, and equipment. Other significant expenses include animal care, pasture management, labor, and building handling facilities.
In addition to the cattle farming business plan, you will need a solid management plan. This document should address beef cattle management practices regarding feed, health and nutrition, fencing, housing, and waste.
Note: The costs of beef enterprises are often specific for each operation. In order to better understand the financial aspect of beef production, producers need to consider direct expenses , direct income, and hidden costs.
Learn more about evaluating the potential financial impact of a decision (such as buying new equipment) with Penn State Extension’s Partial Budgeting online course .
Raising Beef Cattle for Profit
Beef farms generate income mainly from calf production . It is therefore recommended that cattle farmers select and maintain productive cows who produce a calf every year. The animals should be able to sustain their body condition and raise calves with a weaning weight that meets the end goals.
The retail beef price depends largely on the cost of production and the cost of getting the animal to slaughter weight. The production expenses vary based on the animals’ breed and production method (i.e. grain-fed or grass-fed cattle ).
The price of beef per pound can further be affected by factors such as fat percentage and type of cut. Obtaining a beef quality grade or an organic beef certification can help increase profits, as well.
Direct Income for Cattle Operations
Apart from the sale of cattle, beef producers can generate direct income from a number of other services. Depending on the enterprise, revenue can be generated from consulting, breeding cattle, hauling, and mowing pastures. Income may also be increased by selling embryos and bull sperm.
Selling hay and feed raised on the farm is another valuable option for cattle farmers. Estimating the expenses of home-raised feed, however, can be challenging.
One way for producers to calculate the actual feed costs is by using Penn State’s CropCents app . Once the data for all on-farm grown crops – including operating expenses – is entered, users can see the yield in tons/acre and the cost/ton.
Beef Cattle Market Trends
With a huge market for beef, raising cattle in the US is one of the most common and profitable farming businesses.
The way cows are raised and fed has a big effect on the retail price. Beef is very nutritious, but different feeds deliver different products and tastes. Currently, there is an increased interest in pasture-raised beef, as well as organic and/or locally grown meat products.
Educational Resources for Cattle Farmers
Raising beef cattle for profit is a huge undertaking. Find comprehensive information on beef cattle management with Penn State Extension’s articles, webinars, online courses, and workshops.
Items 1 - 25 of 33
- Product Name
- Date Posted

Northern Tier Beef Producer Meeting: Should She Stay or Should She Go?

Butcher Apprenticeship Program

Earn While You Learn - Animal Science Apprentice Program

Feeding Beef Cattle

What You Should Know About Buying Livestock

Crop Cents Mobile App

Survey of Pennsylvania Beef Producers

Navigating Pathways to Success: The 2016 National Beef Quality Audit

Grass-fed Beef Production

Advantages of Marketing Your Beef Directly

2017 Calf-fed Holstein Demonstration Results

2016 Calf-fed Holstein Demonstration Results

Calculating the Cost of Beef Production

Replacement Heifers: Management Options Benefit Bottom Line

Benefits of Weighing Beef Cattle

Building an Emergency Response Plan for Livestock Producers

Integrating Grazing into Cropping Systems: Infrastructure

Beef Cow-calf Operation

How Much Should You Charge? Pricing Your Meat Cuts

Beef Production

Understanding Beef Carcass Yields and Losses During Processing

Custom Feeding Cattle

Does the Growing Beef x Dairy Trend Work for the Feeders

The Most Valuable Investment in the Beef Herd - The Bull

Starting a Freezer Beef Business
You may also be interested in....

Personalize your experience with Penn State Extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture.

- Media releases

- Media centre
- Animals & livestock
- Beef cattle
- Breeding, selection and genetics
Developing an effective breeding plan for your beef business
This Primefact provides an overview of the important steps in designing and implementing an effective breeding program for your beef herd. It discusses the importance of establishing well defined breeding goals, a clear understanding of the requirements of the market(s) being targeted, and a good knowledge of the available differences in economically important traits both between and within breeds.
It will show that the key elements to success in any breeding program are careful long-term planning, the use of good information to help in decision-making, and, above all, consistency and patience in the pursuit of breeding goals.
Primefact 620
Published: 01 Apr 2007

Sample Livestock Farming Business Plan
Livestock farming business plan sample.
Do you want a business plan for farming and raising livestock? Here is what you need to know as you kick start your livestock farm.
Business plans are what lies between one’s business resources and business revenues. An excellent plan transforms a business idea into possible results using an actionable roadmap.
In simple words, a business plan acts as a guide to lead your business into the goals you want to achieve. Don’t get absorbed into thinking that a good plan must be officially documented, or contain a complex strategy; you can keep it more straightforward and still get results.
Here are some business plans for starting a livestock farm.
- Cattle farming business plan
- Pig farming business plan
- Dairy farming business plan
- Goat farming business plan
- Rabbit farming business plan
- Horse breeding business plan
- Calf operations business plan
The most common challenge to livestock farmers is earning a high income from their farming business. This challenge is not only confounded to small-scale farmers with relatively low resources but also to large-scale farmers who have the needed funds even to hire professional business managers.
READ: HOW TO BECOME A LIVESTOCK FEED DISTRIBUTOR
In some cases, your business revenue can continuously decrease over some time that you might decide to quit your business as well. These are the times when a good plan can act as your turning point.
HOW TO WRITE A LIVESTOCK FARMING BUSINESS PLAN
Even though you can farm livestock for non-profit purposes, many business experts advocate livestock farming for business. Imagine tapping into lucrative areas like dairy farming, poultry farming, aquafarming, and rabbit farming to supplement your income.
Better still, other areas like snails farming to earn money. To large-scale farmers, it is by default that you are yearning to learn what a good plan comprises. If you are a starter, this article also covers you to ensure you reap profits from your business.
A typical business plan takes any of these forms:
- One-page Plan: This is a plan that is short, simple, and clear to the point. Meant for you alone.
- Internal Plan : Meant for your workforce/employees.
- An External Plan: This is intended for people outside your business, possibly, potential investors or financiers.
How Will a Business Plan for My Livestock Farming Help Me?
If you are still puzzled upon whether to use a business plan for your livestock farming, then below are the various ways you will benefit when using a business plan:
- It is difficult to accomplish goals using a virtual roadmap. You can document and keep your paper for tracing your goals every day
- Helps understand your business better by recording your workforce, services, market demand, and so on.
- Gives you the chance to set achievable milestones, rather than focusing on a general goal
- You have an opportunity to analyze your strategies and use what works
- Comparison between your plan and results to make a result-centered plan.
Components of an Excellent Livestock Farming Business Plan
If you have ever found yourself jotting down points relating to what you want for your business, then you did a business plan. But, a good plan does not only entail writing down your ideas. It involves aspects that are tailored to your business. Thus, it is essential to understand your business and your market before crafting your business plan.
The first component should be a summary of your mission , business resources , and vision statement. This introductory part is known as an executive summary , and it needs to be personalized for your business. For instance, use “we” or “I” but not “you”.
Talk about:
- Location of your business depending on the market.
- What your business entails. Is it dairy farming? Do you want to keep cattle for beef, and which breed?
- How do you want to run the business? Is it through hired experts? Do you have employees, and what is the role of your employee(s) in your company?
Your plan should have a target market and the market advantage you have over your competitors. As an example, state something like, “ Our business will be located in the Lower Desert Region. Because the regions demand fresh daily milk, our workforce will be provided with quality working conditions to discharge their tasks efficiently .”
How will you get revenue? Describe your projection for your business revenue source. For instance, do you intend to generate revenue from actual sales of your livestock, or by selling livestock products?
You should also describe the sales projection of your business from past revenues. You can state the amount earned in the three previous years to understand what can be earned from your business.
Your business plan for livestock farming should also have the marketing and advertising strategies you intend to use. This strategy enables you to budget well.
It is relevant noting that even though an excellent business plan is a roadmap to achieving your goals, the plan should be unique. This is critical when using an external business plan with the sole aim of getting some external funding or lure investors.
The last thing every investor wants is a boring pitch that is repeated over and over. So, use your livestock business plan to detail as much information as possible that best describe your services.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Creating a Breeding Plan

Introduction to breeding plans
While economic and health planning receives widespread attention, the creation of breeding plans can sometimes be overlooked.
Within this article we look at the options for commercial sheep and beef producers that are interesting in assessing and changing the genetic merit of their herds and flocks.
We explain how they can develop breeding strategies that capitalise on genetic differences between animals (using EBVs) and exploit hybrid vigour to lift the financial and physical performance of their enterprise.
Creating a Breeding Plan for Your Sheep or Beef Enterprise
The physical and financial performance of any livestock enterprise is influenced by the genetic merit of the animals that are kept and the environment in which they are reared.
While changes to the environment, such as an improvement in livestock health or enhanced feed provision, can bring about rapid improvements in performance – improving the genetic merit of your herd or flock can provide a permanent and thus highly cost effective lift to productivity.
While the principle of introducing genetic change is simple, the development of a breeding strategy can be quite challenging – particularly when both the characteristics of the breeding female and their offspring (destined for slaughter) require simultaneous consideration.
To help make the right, long term decisions it is worth investing time in the production of a simple breeding plan. Here are some of the steps in creating that plan.
- Assess your strengths and weaknesses
- Compare your performance to national benchmarks.
- Define the market you will be producing for in the future
- For breeding females
- Recognising the antagonisms that may exist between them
- What type of sheep and cattle do you have at the moment?
- In terms of labour, feed, land and buildings
- Within breed selection (EBVs)
- Using a different breed – Crossbreeding/Breed Substitution
- Selection/Culling within the herd or flock
- Grading up existing breeding stock
- Buying in/using AI to introduce new genetics
- Develop a strategy to monitor changes in performance and assess your success over time
Making a start
Think about your current system and assess its strengths and weaknesses. Assess the KPI’s for your enterprise and determine what you want to change and how you want to do this; either by changing the genetic merit of your animals or the environment in which they are reared. Consider which areas of performance are best enhanced through genetic improvement and which would be better served by improving health or nutrition.
Assess the current performance of your breeding females and consider the most cost effective way to change them, as well as considering how this might influence the health status of the enterprise? If your breeding females are relatively young and have a high health status, then it may advisable to “breed up” from these animals. If the cows/ewes in your enterprise already have a number of health challenges and a rapidly aging profile, it might easier and quicker to buy in new females.
Set a breeding objective – for the future
For most farms, breeding objectives will be largely economic; identifying those traits that make them the most money. This doesn’t simply mean the traits that will produce the most valuable animal, it means those traits which leave the greatest return once enterprise costs have been taken into account. Traits that reduce costs, can be as important as those that increase output. Increasingly, farmers are also starting to think about environmental objectives; selecting breeding lines with a lower environmental impact.
Breeding improvement is a long process so think about the animals that you will want to farm in the future and their future market. How will the enterprise change over time? Will land and buildings remain available? Will labour availability reduce as the workforce grows older? Will the future market be the sale of stores or finished animals? How important is the sale of breeding stock? What genetic attributes will your customers find more important in the years to come?
Are genetics the answer?
Livestock performance will always be influenced by both an animal’s genetics and the environment; the use of genetics can’t compensate for poor management and for low heritability traits in particular greater short term rewards will be achieved through improved management. However, in an optimal environment the upper limits of performance are set by an animal’s genetics and thus the importance of getting the best breeding stock for the enterprise.
The degree to which an attribute will be influenced by an animal’s genetics will vary from trait to trait. The easiest traits to enhance through selective breeding within a breed (using Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) for example) tend to be those that are most heritable, where large amounts of the variation between animals can be attributed to their genes as opposed to non-genetic environment influences.
In the UK EBVs are produced by a number of different service providers. The main ones are shown here:-
* From AHDB’s National Beef Evaluation
** From RamCompare Project
*** Current AHDB funded research work
Major genes
The expression of most traits of economic importance is influenced by hundreds, perhaps thousands of genes and in using EBVs you are selecting animals which tend to have a combination of the better genes for any given attribute – with each gene having a small effect.
There are a few examples of so called “Major genes”; genes that have a large impact on performance and in some cases completely control the trait. In some cases, the sellers of rams and bulls are able to test for these genes and inform the buyer about the gene carrier status of the animal, which may mean it carries one or two copies of a given gene. Traits commonly influenced by major genes include polling/horns (cattle), coat colour (cattle), prolificacy (sheep) and muscling (sheep and cattle). Gene tests are also available for deleterious attributes, such as recessive diseases and yellow carcase fat (sheep).
Structural soundness – A reminder when buying a new sire
It should go without saying, that your investment in a new sire will only be cost effective if he has a long working lifespan. An assessment of pre-sale management, structural soundness, fertility and health (via blood tests) will help to ensure a long working life and thus a high return on investment; as well protecting your enterprise biosecurity. Click on these links for more information on buying fit for purpose rams and bulls .
Purebreeding or crossbreeding
While high heritability traits are relatively easy to improve through within breed selection, low heritability traits can be greatly enhanced through crossbreeding and the exploitation of hybrid vigour. Many low heritability traits are extremely important in breeding females, hence the widespread use of crossbred females in the pig and poultry industries. So whether the enterprise is going to focus on purebreeding or crossbreeding will greatly influence your breeding decisions.
Advantages of breeding purebreds
- Simple system, where only one breed is required
- Potential marketing advantages from purebred sales
- Greater uniformity amongst breeding stock
Advantages of crossbreeding
- Exploitation of hybrid vigour
- Wide access to different genetics
- Faster potential rates of genetic change
What is hybrid vigour and how can it be exploited?
Hybrid vigour (or heterosis) is the amount by which a crossbred animal is better than the average performance of both parents. The more genetically different each parent, the greater the impact. It is a proven way to enhance traits that are often hard to enhance through within-breed selection.
Remember, progeny performance still depends on the genetic merit of each parent; outstanding progeny can’t solely be produced through crossbreeding if the parent breeds are genetically poor.
There are many different ways to exploit crossbreeding, the important issue to consider is whether you want the hybrid vigour to be exploited in the maternal or paternal breeding lines (to enhance traits like fertility and longevity) or their offspring (to enhance neonatal vigour and survival).
Some of the crossbreeding strategies relevant to the UK include.
1). A two breed cross.
The crossing of two different breeds, so all of the hybrid vigour is expressed in the progeny (unless the parents are also crossbreds).
2). A rotational cross
Two breeding lines are kept, with Breed A sires mated to Breed B daughters and visa versa. Hybrid vigour is expressed by both the breeding female and her progeny
3). A terminal sire cross
A crossbred female is mated to a terminal sire of a different breed. This provides the maximum amount of hybrid vigour in both the breeding female and her progeny – but it doesn’t allow for the retention of breeding females.
4). Composite breeding
The use of composite breeds, which are usually the result of several generations of crossbreeding will introduce hybrid vigour, depending on how far back the purebreds arise in the pedigree. If purebreds are no longer being put into the composite, levels of hybrid vigour will reduce over time.
5). Backcrossing
Introducing a new breed to bring in a desirable characteristic (eg polling) and then a sustained programme of grading back to the original breed.
Should I change a trait through within breed selection (using EBVs) or crossbreeding?
For most traits producers can use both strategies, though for rapid improvement in low heritability traits, the exploitation of hybrid vigour will have the biggest short term impact. Purebred populations clearly don’t have the option to exploit hybrid vigour, though the use of a distantly related strain – such as an NZ import, may introduce additional vigour into the breeding programme.
Exploiting breed complementarity
When producing animals for slaughter, the male and female breeding lines can have very different genetic attributes. The male (terminal sire) line should produce progeny that are born easily and grow fast, while the female line requires maternal genes to enhance milk production, maternal care, fertility and longevity. The mature size of the breeding female can markedly influence the efficiency of the enterprise, so consider exploiting breed differences by mating smaller framed maternal breeds to larger, faster growing terminal sires to generate animals for slaughter.
Decide whether to breed your own female replacements or buy them in
Several factors influence the decision whether to retain home-bred female replacements or buy them in.
Producers considering breeding their own replacements must develop a plan which:
- Assesses the financial implications of keeping home-bred females
- Establishes performance-based breeding goals
- Considers the selection of rams and bulls based on Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) to improve economically important traits
- Considers capitalising on hybrid vigour
- Establishes simple recording systems to identify animals to keep or cull.
Don’t practise ‘negative selection’ – keeping poor performing, less saleable females for breeding.
Keeping replacement females should not be a knee-jerk reaction to high breeding stock prices, it should be a planned approach to enhance performance by keeping females of known breeding potential and health status.
Selective breeding within the enterprise
Once new genetics have been introduced onto the enterprise, improvements in performance can continue to be made through
- The selection of youngstock to be retained
- The culling of inferior breeding stock
Record keeping need not be a chore. A simple paper based or electronic system can quickly identify stock to keep as replacements and those that should be culled.
Identifying potential replacements
Selecting home-bred replacements for future breeding has two phases.
- At birth, ear tag or notch offspring that are born easily, suck without assistance and whose mothers demonstrate high levels of maternal care. In many lowland sheep flocks only multiple born ewe lambs will be marked.
- As youngstock approach slaughter weight, select from the group those that are well grown and structurally sound.
Deciding what to sell
Whether buying-in or breeding home-grown replacements, breeding stock will be periodically culled. In self-replacing enterprises these decisions are more important to prevent problem traits reoccurring in future generations.
Ear notching sheep provides a simple way to identify problem animals and can be completed throughout the year, especially at lambing time and immediately pre-mating. In recent years the use of EID readers and on-farm software has greatly assisted in the computerisation of this task.
If the trait has a high heritability, fast rates of change can be achieved through rapid culling. However replacement costs will also rise, so in practice a balanced approach is required. Where younger ewes are removed from the breeding flock, rather than being sold immediately they can be mated to a terminal sire to produce slaughter lambs.
Making faster genetic progress
With the average generation interval for sheep and cattle being around 4 and 5 years respectively, the process of changing the genetics within an enterprise can be a slow one when breeding your own replacements. Two ways to speed up genetic gain are to reduce the interval between generations and to increase the selection pressure placed on the genetics brought onto the farm.
- To speed up rates of genetic gain consider breeding replacement females from the youngest breeding females, perhaps lambing ewe lambs and calving heifers at 2 years of age to reduce the generation interval. The use of young males, such as ram lambs should also be considered.
- Using EBVs as your guide, select the best genetics that you can afford. On some farms the use of AI may provide a cost effective way to introduce elite genetics, particularly when mating heifers in commercial beef farmers.
Carefully plan what proportion of the breeding herd or flock is required to breed replacements, as further improvements can be achieved if you are able to preselect the very best females to breed from, using the lower quality females to produce progeny for slaughter.
- When making a breeding plan, assess the enterprise resources that you have at the moment and consider which genetic attributes you wish to change.
- Consider if genetic change is best achieved through within breed selection (using EBVs), a crossbreeding programme, breed substitution or on-farm selection/culling.
- Think how you will implement and monitor your breeding strategy over time.
Cookie Policy
Cookie Notice
We use cookies to help us improve this website and your visits to it.
If you continue without changing your cookie settings, we will assume that you are happy to accept cookies but you can change your settings at any time.
By using this site you agree to our Terms of use and our privacy policies.
Accept Cookies
LIVESTOCK FARMING BUSINESS PLAN + FINANCIALS
Looking for a livestock farming business plan for your new or existing enterprise?
Download this livestock farming business plan, which you can download to present to NIRSAL, TEF BOI, BOA, and other investors.
LIVESTOCK (GOAT, CATTLE, SNAIL, POULTRY) FARMING BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE
1.0. Executive Summary
Joe Farms Ltd is a registered Ilorin-based livestock farming company. Our livestock breeding company will be the standard one that,s involved in the commercial breeding of goats and other livestock. We will be providing the following services boarding services, breeding services, dairy support services, livestock health services, farrier services, and shearing services et al.
We have done our comprehensive market research and probability studies. We were able to secure one hundred hectares of land to set up our livestock breeding business.
Within the first five years of officially operating Joe Farms Ltd, we hope to start our meat processing plant and start exporting our products to other parts of the world.
Aside from the fact that we’ve secured the required farming land for breeding goats at the commercial level, we have also hired some key employees who are currently undergoing training to fit into the ideal picture of the 21st-century livestock breeding workforce that we want to build.
Joe Farms Ltd is a private registered livestock farming company that is owned by Joe Papa. The company will be fully financed and managed by the owner – Joe Papa at least for a while.
Before setting up Joe Farms Ltd, Joe Papa has worked with some of the leading livestock farms in Nigeria. He has worked in the livestock farming industry for ten years before resigning to start his own goat farming business.
2.0. Our Products and Services
Joe Farms Ltd is a licensed livestock farming business that is committed to goat farming, meat processing and packaging for both the Nigerian market and the global market. We will also be in the production of related raw materials for industries in commercial quantities.
These are the areas we will concentrate on in our livestock farming business;
- Boarding service
- Breeding service
- Dairy support service
- Livestock health service
- Farrier service
- Sale and export of cotton wool and other dairy products
- Sale of Cattle and milk (Including goats, sheep, grass – cutters, pigs and rabbits et al)
- Sale of processed meat (beef) / can – beef (Processed Dairy foods, and can beef et al)
- Shearing services
- Livestock farming-related consultancy and advisory services
3.0. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading livestock farming brands not just in Ilorin-Kwara, and also in Nigeria.
- Our mission is to sell our product and produce (goats), byproducts, and processed meat in commercial quantities at all market levels (locally, nationally, and internationally).
- Also, We want to establish a livestock farming business that can conveniently compete with other leading livestock farming brands in Nigeria.
4.0. Our Business Structure
Joe Farms Ltd is a livestock farming company that intends to start small in Ilorin-Kwara state but hopefully grow big to compete favorably with leading livestock farms in the business both in Nigeria and on a global stage.
We are aware of the significance of building a solid business structure that can support the idea of the kind of world-class business we want to build. This is why we are dedicated to only hire the best hands in and around Ilorin.
At Joe Farms Ltd, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, dedicated, customer-centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers).
Given the above, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
Below is the business structure of Joe Farms Ltd;
- Chief Operating Officer
- General Farm Manager
- Administrator / Accountant
- Cattle Ranch Manager / Supervisor
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Field Employees
- Front Desk Officer
5.0. SWOT ANALYSIS
5.1. Strength
Our strength as a livestock farming business is the fact that we have strong connections with several major agriculture merchants(both suppliers and buyers) in the livestock farming industry within and outside Nigeria.
We own some of the latest livestock farming machines, tools and equipment that will help us breed goats and other livestock in commercial quantities with less stress. Aside from our connection (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we are equipped with the most experienced hands in the livestock farming industry.
5.2. Weakness
Our weakness could be that we are new livestock farms in our location. We are aware of this and from our projection will overcome this weakness with time and turn it into a major advantage for the business.
5.3. Opportunities
Some several homeowners and industries will source for goats, goat meat, and milk and also industries that will source for the raw materials from our livestock farms both in Nigeria and other parts of the world which makes the opportunities in this industry limitless.
5.4. Threat
Some of the threats and challenges that we are likely going to face when we start our livestock farm are global economic downturn that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), unfavorable government policies, and the arrival of a competitor (a commercial farm that rear same animals) as our livestock farms within the same location.
6.0. Our Target Market
Our target market is the end consumer of livestock farm produce and those who benefit from the business value chain of the agriculture industry.
Every household consumes livestock farms product be it goat meat, goat milk, and the skin (leather) used for bags, belts and shoe production et al. Also, a large number of manufacturing companies depends on livestock farms for some of their raw materials.
7.0. Our competitive advantage
It is easier to find entrepreneurs crowding towards an industry that is known to generate constant income which is why there are more commercial farmers in Nigeria and of course in most parts of the world.
Entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace commercial farming/livestock farming. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her food and also export foods to other countries of the world.
Joe Farms Ltd is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling livestock and it produces all over the world, which is why we decided to carry out comprehensive market research on how to take advantage of the available market in Nigeria and other parts of the world.
How To Download Livestock Farming Business Plan PDF and Doc (With financial analysis)
Pay the sum of N5000 ( Five thousand naira only) to the account detail below: Bank: GTBank Name: Oyewole Abidemi (I am putting my name and not our company account so you know I am real and you can trust me, and trace me) Ac/No: 0238933625 Type: Saving
P.S: We can also tailor the business plan to your name, business size, capital requirements, and more to fit your direct needs. Call or message +234 701 754 2853 for inquiries.
Thereafter, send us your email address through text message to +234 701 754 2853. The text must contain the title of the business plan you want and also your email address. Immediately after the confirmation of your payment, we will send the livestock farming Business Plan to your email address where you can easily download it.
Dr. Abi Demi is a skilled technical writer and author with specialties in the martech and fintech space. Featured on Tekedia, Coin Review, Business Insider, Fintechna, Cryptocoin.news, Date 360 and several other sterling online publications, Demi is an astute technical writer that specializes in finance, marketing and technology - with over 500 published pieces across the internet ecosystem. Contact Abi Demi - [email protected]
How to Get Loan Without Collateral in Nigeria
Download restaurant business plan with financials, you may also like, feasibility study sample for private school, private school business plan sample, feasibility study template for zobo production, business plan sample for zobo production, ict feasibility study sample, download ict business plan sample, download snailery feasibility study sample, download snailery business plan sample business, 8 farming & agriculture business ideas in nigeria, 5 investment apps for saving, growing your money..., leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Livestock Farming Business Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their livestock farming companies. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan. In this article, you will learn some background information on ...
The amount of capital required for the beef cattle breeding business depends on the scale of the project. When starting a cow-calf operations business, most of the capital goes to acquiring the land, building infrastructure, and buying the breeding stock. ... Pre-Written Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel): Comprehensive ...
Business Overview. Bear Creek Farms is a new livestock farm located just outside of Austin, Texas, near Bear Creek. The company operates a 1000-acre farm that is home to hundreds of pastured cattle, pigs, and sheep. The farm will produce milk, cheese, and meat to sell to grocery stores, restaurants, and individuals located in the Austin area.
Outline your production targets, revenue goals, and growth projections in your business plan. This will guide your decision-making processes and allow you to track your progress effectively. Consider the specific needs of the livestock you plan to raise, including their housing, nutrition, and healthcare requirements.
Develop A Cattle Farming Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed cattle farming business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
Raising and evaluating offspring is a crucial aspect of breeding livestock to achieve farm success. Proper colostrum management for newborns is essential as it provides vital nutrients and boosts the immune system. Regular monitoring of growth and development helps identify any anomalies or potential health issues.
To draw up a roadmap. A business plan for a cattle farm helps you define your objectives and set goals for the next 3-5 years, which can be incredibly useful for achieving success in the long run. The writing process of a business plan requires careful consideration of all aspects of running your cattle farm, from financial management to sales ...
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers, you can confidently create a professional and comprehensive business plan to take your livestock farming business to new heights. ... Consider aspects such as animal care, breeding and genetics, feed management, waste management, and equipment maintenance. Define standard operating ...
Steps. Download Article. 1. Find some paper, a pencil, or a computer with Microsoft Word, One-Note or a similar text program. This will enable you to write or type down everything that comes to your mind, including the goals and aspirations you have for starting up a livestock operation.
The executive summary provides an overview of your livestock farming business plan. It highlights the key elements of your plan, including your objectives, strategies, and financial projections. The executive summary should be concise yet compelling, capturing the reader's attention and providing a glimpse into the potential of your venture.
A well-designed cattle farm business plan serves as the backbone of your operation, guiding your decisions and ensuring long-term success. ... healthy livestock, and strategic timing of breeding ...
The budget for key insurance policies, permits and business license - $2,500. The amount needed to acquire/lease a farm land - $150,000. The amount required for preparing the farm land (for construction of cattle ranch and cages/fencing et al et al) - $100,000.
Realization of objectives. You might realize the objectives you set out to achieve, making it necessary to change tactics if there's nothing more to achieve. Changes in cattle feed crops. You might want to shift from grass-based farming to rearing cows using field forage crops like corn for silage.
Beef cattle do not require much maintenance, as just sheltering them is enough. 5. Decide the Purpose of Your Farm. Decide on the type of breed of cattle that you want to farm. The maintenance and budget differ for each breed, so plan accordingly. Most of the time, beginners start it with dairy products or beef.
In addition to the cattle farming business plan, you will need a solid management plan. This document should address beef cattle management practices regarding feed, health and nutrition, fencing, housing, and waste. ... revenue can be generated from consulting, breeding cattle, hauling, and mowing pastures. Income may also be increased by ...
Business Summary. Riverland is currently a small cow/ calf operation with an estimated 50 total calves and cows. The farm sells beef calves to individuals and at the cattle auction. The company is completely operated by the Doe family which entails checking, feeding, giving shots, weaning, tagging, banding, and paperwork.
Remember that the breeding for today is already done. your breeding goals should relate to your vision of the likely future production environment and future customer requirements in at least 3 to 5 years' time. That's when the results of your current breeding decisions will be realised. Clearly, it is impossible to be definite about future
Summary. This Primefact provides an overview of the important steps in designing and implementing an effective breeding program for your beef herd. It discusses the importance of establishing well defined breeding goals, a clear understanding of the requirements of the market (s) being targeted, and a good knowledge of the available differences ...
Pig farming business plan. Dairy farming business plan. Goat farming business plan. Rabbit farming business plan. Horse breeding business plan. Calf operations business plan. The most common challenge to livestock farmers is earning a high income from their farming business. This challenge is not only confounded to small-scale farmers with ...
Livestock performance will always be influenced by both an animal's genetics and the environment; the use of genetics can't compensate for poor management and for low heritability traits in particular greater short term rewards will be achieved through improved management. ... When making a breeding plan, assess the enterprise resources ...
LIVESTOCK (GOAT, CATTLE, SNAIL, POULTRY) FARMING BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE. 1.0. Executive Summary. Joe Farms Ltd is a registered Ilorin-based livestock farming company. Our livestock breeding company will be the standard one that,s involved in the commercial breeding of goats and other livestock.