Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech

The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
Unlimited Academic AI-Proofreading
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- He is a good baseball player.
- He hits the ball well.

paper-free learning

- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun.
Why the Parts of Speech Are Important
Video Lesson

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
Five Quick Questions
This test is printable and sendable

Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences , such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes , these are the building blocks of grammar.
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , the label part of speech has generally been discarded in favor of the term word class or syntactic category . These terms make words easier to qualify objectively based on word construction rather than context. Within word classes, there is the lexical or open class and the function or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below and get started practicing identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence. They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Examples: softly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, softly, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spacial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet, with.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples: articles: a, an, the ; determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- The attributive noun [or converted adjective] work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a command to an understood "you".
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- Sentence Parts and Sentence Structures
- 100 Key Terms Used in the Study of Grammar
- Prepositional Phrases in English Grammar
- The Top 25 Grammatical Terms
- Foundations of Grammar in Italian
- Pronoun Definition and Examples
- What Is an Adverb in English Grammar?
- What Are the Parts of a Prepositional Phrase?
- Definition and Examples of Adjectives
- Definition and Examples of Function Words in English
- Lesson Plan: Label Sentences with Parts of Speech
- Sentence Patterns
- Nominal: Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Constituent: Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Adding Adjectives and Adverbs to the Basic Sentence Unit
- The Difference Between Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 8 parts of speech: definitions and examples.
General Education
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Your Guide to the 9 Parts of Speech
Grammarians categorize English words into groups, which we call Parts of Speech. Most guides will tell you that there are eight or nine parts of speech, depending on a few factors, like whether they include interjections. Each part of speech serves a particular function, which I will describe below.
The parts of speech we will cover are:
- noun,
- pronoun,
- verb,
- adjective,
- adverb,
- preposition,
- conjunction,
- determiner, and
- interjection.
I’ve also put together a table with all the parts of speech and examples of their use in sentences. Below the table, you’ll find a breakdown of each part of speech with further examples.
Are you responsible for editing, but find yourself with too much work? Consider EditorNinja’s professional editing services. With rates cheaper than working with freelancers directly and guaranteed turnaround times from professional editors, we can help you. Schedule a free Intro Call to learn more.
Parts of Speech Cheat Sheet
Nouns are things. Stuff. People. Places. Ideas. (Yeah, things, stuff, people, places, and ideas are all nouns.)
Common and Proper Nouns
Nouns can be common, like city, park, and building , or proper, like New York City, Central Park, and The Chrysler Building. Proper nouns are names. Michael and Mr. Blackwood , for example, are proper nouns.
Singular or Plural Nouns
Nouns can be singular or plural. A singular noun is when there’s only one. One man , one dog, one person . Plural nouns occur when there’s more than one. Two men , ten dogs , a million people .
Possessive Nouns
Nouns can also be possessive, which means a noun “owns,” belongs to, or is otherwise attached to another noun. In English, we use the apostrophe to denote possession. In the phrase “the man’s dog,” for example, man’s is possessive. Man owns (or belongs to) dog .
Pronouns substitute for nouns. Pronouns include he, she, they, you, it, and many more.
Plural, Possessive, and Plural–Possessive, Oh My
Pronouns can be possessive, like my, your, his, and her . Pronouns can also be plural like we and they. And pronouns can be plural and possessive, like our and their .
Words like that and which do double (or triple!) duty. That can be a determiner (see below), as in the phrase “ I ate that apple,” but can also become a pronoun, as in the phrase, “I ate that ” — where that substitutes for a noun, like apple.
To be or not to be, that is the…ultimate verb. Verbs show actions and states of being. This includes to be and its derivatives: is, are, were, will be, have been, etc. Verbs show all the things you can do . Crawl. Walk. Run. Sit, watch, enjoy, laugh, cry, and eat.
Verb Tense & Aspect
Verbs have a tense , which refers to when the thing is being done. There are three main tenses: Past, present, and future . In the past tense, I wrote. In the present tense, I write. In the future, I will write (which enlists the help of the “helping verb” will ) .
Furthermore, the tenses all have an aspect , which demonstrates further details, like whether an action is ongoing. The aspects are simple, perfect, continuous , and perfect continuous . So you can have any combination of aspects with tense; for example, simple past or perfect continuous future .
The subject of tenses and aspects is pretty complicated — it deserves its own article. But for now, here’s a simple chart that breaks down the tenses and aspects with examples.
Verb Tense and Aspect Chart
This information is pretty esoteric, so don’t get too distracted by it. The main thing to remember is that verbs show action and states of being.
Adjectives describe nouns.
When you’re telling someone about your favorite English language blog, you would use adjectives to describe it. Smart, witty, clever, helpful, accessible, and concise are all adjectives.
And were you to describe the writer of that blog you would continue to use adjectives. Smart, witty, clever, helpful, handsome, kind, approachable, and single are also adjectives.
Adverbs are like adjectives, except that they don’t describe nouns, they describe other parts of speech: verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs often end in -ly , but not always. They can come before verbs, as in, “she quickly ran,” or after, as in “she ran quickly. ”
Here are some examples of adverbs in a sentence:
Modifying a verb : He quietly tip-toed through the dark hallway.
( Quietly modifies the verb tip-toed. )
Modifying an adjective : He quietly tip-toed through the eerily dark hallway.
( Eerily modifies the adjective dark. )
Modifying another adverb : He totally quietly tip-toed through the eerily dark hallway.
( Totally modifies the other adverb quietly. )
Prepositions
Prepositions link nouns to other words, showing us the relationship between them. They show location or time. For example, “We will meet on the bridge during sunset.”
Prepositions can also be used to show purpose, as in, “I am walking for my heart.”
Prepositions include in, on, toward, with, through, at, upon, toward, via, and many more.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses together , so we can create complex sentences and express multiple ideas at once.
Conjunctions include and, but, or, yet, although, because, and others.
In this sentence, the conjunction joins two clauses: “I don’t like apples but I do like oranges.” And in this sentence, the conjunction joins just two words: “I like apples and oranges.”
One group of conjunctions (called correlative conjunctions) comes in pairs, like either/or, if/then, not only/but also . Here’s an example:
“ Either you will peel the oranges for me, or I won’t eat them.”
Determiners (Includes Articles)
Back in the day, your English teacher, like mine, may have taught you about articles: the , a , and an .
Grammarians more and more frequently include these in a group of words called determiners , words that limit or “determine” nouns, which, in addition to articles include that, this, these, those , and others — showing exactly which noun or nouns are being talked about. This includes possessive pronouns like my, your, their, her, and his.
Think of it this way: determiners often answer the questions What?, Which?, or Whose? For example, “Which article?” “ This article.” “Whose blog?” “ Our blog.”
Interjections (!)
Consult more than one English grammar guide, and you’re likely to see that there are eight or nine parts of speech. Why the difference? Well, some sources don’t include the interjection as its own part of speech. But some sources do, so you ought to know about it.
Interjections can be, um, tricky to define. They are spontaneous, sometimes emotional, and they come before or between complete thoughts . Sometimes they interrupt a sentence right in its tracks. They include exclamations like Wow!, Yikes!, and Oh! They also include curses ( damn! ), greetings (like hi ) , and filler words (like um ).
Some examples of interjections:
- Wow! Look at that sunset.
- Let’s go to the, um, store.
- I don’t understand why you would— oh! Now I get it.
Sometimes, other parts of speech can be interjections.
- Fantastic ! Let’s do it! (Here the adjective fantastic serves as an interjection.)
- I’m just going to open the blinds and— snow! It’s snowing now! (The noun snow serves as an interjection.)

The Parts of Speech in Sum
There you have it — the nine parts of speech. Noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, determiner, and interjection.
Got an exam coming up? Working on your writing? Consult this guide anytime you need a refresher.
Need Help with Parts of Speech and More?
EditorNinja is here to help! We’re a team of professional content editors, across line editing, copy editing, and proofreading. All EditorNinja editors are MFA trained and look forward to editing your written content!
Schedule a free Intro Call today to see how using EditorNinja can save you days of work each month, buy back hours that you can use to create more content or work on other things, and make on average a 3.5x ROI on your investment.
Michael Blackwood
" * " indicates required fields
Writer Recruiting
Once submitted, our team will review and be in contact directly. Our aim is to have a curated list of writers for you within 2-4 business days.

The 8 Parts of Speech Rules, Examples & Chart [Easy Tricks]
![part of speech word good Featured image for “The 8 Parts of Speech Rules, Examples & Chart [Easy Tricks]”](https://www.artisticenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/The-8-Parts-of-Speech-Rules-Exanples.jpg)
Parts of speech is one of the grammatical groups in which words are divided into 8 parts: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. If you are a student of school or college and want to build up your English grammatical base, parts of speech is the lesson, you should start with.
In English grammar parts of speech is considered as the pillar of English language. Without understanding the meaning, charecteristics, and function of each part of speech, you will not be able to form a sentence correctly or answer fill in the gaps questions in your academic exams.
This is why today we will discuss over the 8 parts of speech rules in detail with their examples and usages in a sentence. However, it’s recommended that you must have proper understanding of ‘ Classifications of Persons ‘ before starting this lesson as it will help you understand the current lesson.
What is Parts of Speech?
Parts of speech is a particular class of word in a sentence such as noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. It plays different functions in a sentence based on their position. There are 8 parts of speech in English language.
For Example: Mr. Sarowar likes hot coffee in breakfast.
At first notice this example and try to understand the parts of speeches and how you should classify them in sentences.
Classification of Parts of Speech
In English language, parts of speeche can be divided into 8 classes or parts based on their meaning, function, and usages such as:
Preposition
Conjunction, interjection.
You have to always remember the names, meanings, and rules of all parts of speech in order to recognize them in a sentence or use them to form a correct sentence.
Meaning of 8 Parts of Speech
Here are the meanings of all parts of speech in English grammar:
- Noun = name of any person, thing, or idea.
- Pronoun = the alternative name of noun.
- Adjective = the qualifier word of any person, thing, or idea.
- Verb = the word which indicates action or condition.
- Adverb = the qualifier of any action or the qualifier of the qualifier word of any person, thing, or idea.
- Preposition = the word which indicates the relationship between words.
- Conjunction = the word which connects several words.
- Interjection = the word which shows emotion such as wonder, sorrow, or joy.
Parts of Speech Rules
Rules of parts of speech indicate the function of 8 parts of speech in a sentence, the way they work, the meaning or quality they express all together. By learning parts of speech rules, you will be able to figure out the name of a part of speech whether it is a noun, pronoun, verb or adjective word.
However, it might be a little bit difficult for a student to remember all the characteristics of 8 parts of speech together.
As a solution, we have come with a simple word based logic which will help you understand and remember the rules and functions of all parts of speech and figure out the single part of speech among many words.
Have a look on the word theory given below:

This word theory is a shorter form of the Wh-question words such as who, what, why. These questions will help you figure out the exact name of a part of speech. If you ask the whole sentence or a word with these Wh-question words, you will find out names of the parts of speech based on answers.
Of course different Wh-question indicates different part of speech.
Now, see the questioning rules and examples below in this chart to understand the word theory ‘ WAH2ILI ‘ and how it works in this process.
So, here is the explanation for you on each element of this theory.
Parts of Speech Theory
Now notice the example sentence given below and apply the above theory to figure out each part of this sentence or speech.
Hurrah! we have won a prestigious prize for Soham and Robin finally.
Therefore, the final output is the example and answer given below:
Here are the list of the parts of speech and word examples which are used in English and you can easily figure out parts of speech by remembering these word sets.
Name of any person, thing, or idea: man, mountain, state, ocean, country, building, cat, airline love, wealth, happiness, pride, fear, religion, belief, history, communication milk, rice, snow, rain, water, food, music, bunch, audience, flock, team, group, family, band, village, etc.
For examples,
- Man is mortal.
- Everybody wants to get happiness.
- You should study History now.
The alternative name of noun: I, me, my, myself, mine, we, us, our, you, your, he, she, him, her, his, they, them, their, it, itself, ourselves, themselves, this, that, who, whom, which, both, none, somebody, something, nobody, nothing, all, any, etc.
For examples:
- I can help the boy now.
- They give him a nice gift.
- Will you help me?
The qualifier word of any person, thing, or idea: Bad, good, little, many, much, few, little, red, well, interesting, Able, Anxious, Beautiful , Certain, Continuous , Dangerous, Deep, Eager , Large, Equal, Fresh, Hard, Low, Joyful, Short, Mad , Married , Melodious, National , Natural , Necessary , Negative , Neutral
For instance,
- The boy has enough money.
- He is a good boy undoubtedly.
- Is this oil natural ?
The word which indicates action or condition: Am, is, are, was, were, being, been Have, has, had, having, Used to, Could, May, Must, Had better, Might, shall, will, Should, ought to, Come, Eat, Cry, Cut, Dance, Dare, Deal, Die, Dream, Feel
For Examples,
- I could buy the gift.
- He may think about it.
- My friend hates drinking now.
The qualifier of any action or the qualifier of the qualifier word of any person, thing, or idea: quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really, Ago Twice, Almost, Thrice, Daily, Again, Ever, Always , Hither, Early, Thither, Enough, Now, Fast, Then, Here, Once, There , Soon, More, Sometimes, Never, Yesterday, Only, Tomorrow, Quite
- He has just completed the work.
- He always helps the poor.
- I will go to Dhaka tomorrow .
The word which indicates the relationship between words: On, Over, Up, Upon, Beyond, Above, Under, Below, Down, Through, To, From, Towards, For, In, Into, Around, Out of, Of, About, At, By, With
- The student of this school is present.
- The letter has come from Dhaka.
- Put this cup on the table.
The word which connects several words or sentences: and, but, when, And, As , well as, Until, Or, Unless, But, Both ,Since, As, Lest , So, However , While, Still ,That, Why , So that, How ,If, When , Though, Although, Where, Because, Who, Before, Which, Than, Either …..or, As if, as though, Neither ….nor, After, Till
- Soham or Sajib will come here timely.
- He said that he was a regular student.
- I will help you unless you go there again.
The word which shows emotion such as wonder, sorrow, or joy: Hurrah!, Ha! Ha!, Alas!, Oh!, Bravo!, Shame!, Hush!, Hi!, Fie! How/what!, Hallo!
- Oh! What a nice place.
- Fie! You are a liar.
- Alas! His father has died.
Important Note:
Please note that there are 2 ways in English grammar through which we can analyze words/ parts of a sentence or speech. Firstly, for structural analysis, we use subject, verb, object, etc and you can read about them here: Structure of Sentences
On the other hand, for functional analysis, we use: noun, pronoun, adjective, verb, adverb, etc. and this is the lesson on the functional analysis of a sentence.
Parts of Speech Exercises
Please identify each part of these speeches or sentences given below:
- London is on the river of Thames.
- He tried to lift himself out of poverty.
- My father is reading a newspaper now.
- We answered our teacher respectfully.
- They are presiding over the meeting.
- Wow! It is a beautiful scene.
- You should work hard if you want to pass the exams.
- A student who is attentive is sure to excel.
- He gave me a bunch of grapes.
- Everyone wants to be successful.
In conclusion, This is all about parts of speech in English grammar and now you have understood the process and function, they work in a speech or sentence.
Last of all, please try to memorize the parts of speech words given above sothat you can recognize a part of speech easily in a sentence. Try to figure out all the parts of speech based on different sentences, you get here and there. It will definetly improve you skill of figuring out parts of speech or sentence.

Modal Verbs of Possibility | Impossibility | Expectation

Asking Questions about Something in Formal English

Right Forms of Verbs: 10 Rules, Examples & Exercises

5 Audio Lessons for English Listening Practice

Learn 5 Rules of Assertive to Imperative Sentence Transformation

Future Perfect Continuous Tense Formula with Examples

Future Perfect Tense Rules & Usages in English Grammar

Kinds of Sentences in English Grammar with Magical Theory

The Shortcut Method of Personal Application Writing in Board Exams

Most Confusing Words in English with Explanation & Usages
What part of speech is the word good?
Good can either be a noun as in: By saving the little puppy, Tim did good. It can also be used as an adjective i.e., This pie is good!
Add your answer:
What is the part of speech of the word Good At?
Good and At are two words. Good is an adjective, and at is a preposition.
What part of speech is the word healthy?
The word healthy is an adjective. It means to be in good health.
What part of speech is the word my-?
The part of speech that the word my is used as is an adjective.
What often changes a word's part of speech?
A suffix changes a word's part of speech. For example, the word 'happy' is an adjective. But when you add a suffix, which is an ending, it can change the part of speech. Happily is an adverb. Happiness is a noun.
What part of a speech is the word for?
Good what part of speech.
The word good is an adjective. It is another word for pleasant or enjoyable.
What part of speech is the word good in the sentence Clarice is an extremely good housekeeper?
Good is an adjective.
What part of speech is the word imaginative?
Imaginative mean you have a good imagination.
What part of speech is the word moments?
The part of speech for this particular word is a noun.
What part of speech is the word diplomacy?
The part of speech for the word diplomacy is a noun.
What is the part of speech for the word civilian?
The part of speech for the word civilian is English grammar.
What part of speech is H?
H is a letter, not a word. To be a part of speech, it needs to be a word.
What part of speech is speech?
The word speech is a noun.
What is the part of speech of healthy?
Top Categories

Understanding Parts of Speech (9 Types With Examples)

What are parts of speech? In the American English language, parts-of-speech is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. They exist under the verb , noun, pronoun, interjection , adjective , conjunction, adverb, and preposition forms.
Learn more about parts of the speech in this comprehensive worksheet…
What are parts of speech?
“Parts of speech” refers to the essential words used in sentence formation in the English language.
Every word used in a sentence structure plays an important role in defining the sentence’s meaning. These words use and placement give proper intentions in sentence structures.
Parts of speech are the basic grammar lessons taught during the primary phases of learning English.
Any word used in sentence formation falls into one of these categories for proper sentence structure.
Some of those words can be a part of one or more parts of speech. This topic further explores the essential parts of speech used in the English language.
Watch this as a video lesson
In total, there are nine categories of parts of speech
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns , Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs , Pronouns, Prepositions , Conjunctions, and Interjections.
Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e. , Articles, a subprogram of determiners.
To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to clearly understand the various parts of speech and select the right parts of speech form at the appropriate place in the sentence.
What are the 9 parts of speech with their functions?
Here are the nine parts of speech and how they impact the English language.
‘Verbs’ are the words used in a sentence to define the action/state of action being performed. Most of the sentences in sentence formation require the inclusion of verbs.
Some examples of verbs used in the English language are Love, Break, Fall , and Cry . These are the basic forms of verbs and are known as infinitives .
Most of the verbs used have two other major forms called participles . The use of these participles is for the formation of various verb-tense combinations.
These participles define the forms of verbs concerning the time of action/performance. These verb-tense combinations can be used in two types: Active voice and passive voice .
A ‘noun’ are words used in a sentence to give recognition or the name of an object, individual, or animal.
Nouns can be sub-classified into two major categories: Common nouns , which give generic descriptor names to things, and common items, such as a bat, a bicycle , etc. The other category of nouns is Proper nouns , which have specific descriptor names to refer to a specialized object, place, or individual, such as Charley, The Empire State Building, The Telegraph , etc.
Additionally, nouns can be classified as singular nouns and plural nouns based on the number of individuals/objects.
Singular Nouns
The definition of a Singular Noun is the same as that of a noun when used commonly. It carries the same definition as the noun: “A word referring towards an individual/object/event/material/place.”
Plural Nouns
The word plural relates to “more than one in certain languages or more than two in certain languages.”
Thus singular nouns can be converted to their plural noun format when there is an implication of more than one or two objects/individuals/places.
A general Singular/Common Noun can be turned into the appropriate form of a Plural Noun by adding a ‘s’/’es’/’ ies’/’ves.’ It is also initiated by changing ‘us’ to ‘i’, ‘is’ to ‘es’ , or ‘on’ to ‘a’ .
Some common nouns do not change when interchanged between their singular and plural noun forms. Some other common nouns do not fall under plural nouns and are called irregular nouns, which are made plural by changing the spelling or adding a suffix to the word.
‘Adjectives’ are words that give a description or modify the scope of nouns/pronouns by being specific. For example, adjectives used to define a noun can be red, small, hot, common, etc.
An adjective is usually placed before a noun or after the verb that it modifies. Three forms of adjectives are used to compare similar characteristics of different individuals/objects. These three degrees of comparison are:
- Positive/Absolute form
This comparison of adjectives defines the original form of the adjective as stated in English. For example, “this candy is tasty .” This degree of comparison states that no relative subject is available for comparison.
- Comparative form
This form of the adjective gives a relative comparison between two objects performing similar actions with identical characteristics. For example, “the candy we had today is tastier than the one we received yesterday.”
- Superlative form
This form of the adjective gives the superiority declaration of one object over similar objects possessing similar characteristics. For example, “this candy is the tastiest I have ever had in the last two years .”
Adjectives can be sub-classified based on their function in sentence formation. This sub-classification is:
- Possessive Adjectives
These adjectives show/represent the possessiveness of an object. For example, mine, my, his/her, their, its, etc.
- Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives modify the noun/pronoun by interrogation. Only a select few adjectives are available in this form. For example, whose, which, what, and where.
- Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives describe the current state/position of the noun/pronoun concerning space/time. For example, this, these, those, that.
- Compound Adjectives
These adjectives are a result of the combination of two or more adjectives. The resulting adjective modifies the subject in the sentence. For example, hand-dried, heavy-weighted, spike-haired, etc.
‘Determiners’ are the words placed before a noun/pronoun group terms to refer to a single/multiple things. Some commonly used determiners in English are ‘a’, ‘the’, ‘some’, ‘any’, and ‘this.’ Determiners are generally placed before descriptive adjectives . It tells the reader more about the description of the noun being referred to.
Determiners are classified into sub-categories, articles, and demonstratives.
An ‘Article’ can be either definite or indefinite. An article modifies a noun/pronoun without specifying any description of the object. In English, an example of a ‘definite article’ is the , whereas examples of two ‘indefinite articles’ are a and an .
Here, the refers to specific things or things that are identified beforehand. A or a refer to non-specific things that have not been identified beforehand.
Demonstratives
A ‘Demonstrative’ is defined as a demonstrative adjective/pronoun based on its usage in the sentence. Some examples of demonstratives are ‘this’, ‘that’, and ‘those’ .
A determiner has the same rules of use as in the case of adjectives in sentence formation. Thus, confusion takes place when carefully choosing the type of parts of speech to assign when given a choice of either a determiner or adjective.
An ‘Adverb’ defines essential information about the verb, similar to what an adjective is to a noun. It provides a descriptor for a verb used in a sentence and some cases, can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Some adverbs used in sentences with verbs are ‘slowly’, ‘hastily’, ‘unfortunately’, and ‘angrily’.
Adverbs are further sub-classified into various types based on their application in a sentence.
- Adverbs of Time (to inform about the occurrence of a verb), For example, ‘now’, ‘tomorrow’, and ‘soon’.
- Adverbs of Manner (to describe the action of a verb), For example, ‘hastily’, ‘slowly’, and ‘minutely’.
- Adverbs of Place (to indicate the place of action of the verb),
- Adverbs of Frequency (to describe the frequency of a verb action),
- Adverbs of Degree (to describe the intensity of an action),
- Conjunctive Adverbs (are used to link/act as a conjunction to two sentences).
A ‘Pronoun’ is a word used in specifically providing an alternate name for a non/noun phrase. They are alternate words for referring to an object/individual when the requirement of a noun is unnecessary, as the noun has been mentioned previously in some parts of the sentence.
Some examples of pronouns are ‘it’, ‘he/she’, and ‘himself/herself’.
Pronouns are sub-classified into different categories based on their use in the sentence.
Some of these sub-categories are:
- Relative Pronouns (to relate a part of a sentence with the other)
- Possessive Pronouns (to show possessiveness)
- Reflexive Pronouns (to refer back to the subject of discussion)
- Demonstrative Pronouns (to refer to specific objects/individuals)
- Interrogative Pronouns (to ask questions)
- Indefinite Pronouns (to avoid reference to any specific object/individual/place)
- Personal Pronouns (to use as substitutes for proper names)
- Subject Pronouns (to assign acting on an object)
- Object Pronouns (to assign receiving action towards an object)
- Reciprocal Pronouns (to express two-way/mutual relationship)
- Preposition
A ‘Preposition’ is a word used as a connective between a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun with another word.
Prepositions are used in sentence formations to convey these meanings:
- To show the direction towards/of something/someone
- To refer to the period of an action taking place
- To specify the location/position of an object
- To present the space and time relationship between objects
Based on their use and function, prepositions are classified into four subtypes:
- Prepositions of Time (to indicate the happening of an action/event)
- Preposition of Place (to indicate the location of an object)
- Preposition of Direction (to indicate the direction/orientation of an object)
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationship (to indicate an object moving away/towards a source)
- Conjunction
A ‘Conjunction’ is a word that combines two/more objects and behaves as connectives in a sentence. These can appear in the beginning/middle/end of the sentence following the location of the objects.
There are three types of conjunctions used in sentence formation:
- Coordinate conjunction (to combine two independent clauses )
- Subordinate conjunction (to combine an independent with a dependent clause)
- Correlation conjunction (to combine two phrases having equal weightage)
Interjection
An ‘Interjection’ is a word to convey the expression of a variety of emotions/feelings. As such, there is no specific rule for the use of interjection and where it is to be placed.
However, in most cases, it is placed at the beginning of the sentence. For example, some of the most commonly used interjections are ‘ouch’, ‘phew’, and ‘well’.
Parts of speech examples
Here are some examples of the parts of speech used in sentences. Note the placement and its relation with other parts of speech present in the sentence format.
- John is cutting a pipe.
- John intends to come to the office this Monday .
- Jogging regularly is good for health.
- Drinking and driving put other motorists in danger.
- Would you want to wear a suit?
- I love to sing in between classes.
See another example in the image below.
- Juno ran towards the classroom.
- The janitor requested the students to clear their lockers.
- The monkey was caged after being sedated.
- I gifted my brother a phone .
- Why did you purchase the book ?
- I misplaced the manuscript .
- Do you want to eat some ice cream ?
- Mum loved my new car .
- Daniel gifted his brother a Porsche.

- I purchased a blue suit for the reception.
- Mary purchased two oranges from the fruit seller.
- The curry is tasty .
- Juno’s brother is arrogant .
- The documentary that premiered on television was fascinating .
- Giovanni Giorgio is a great music composer.
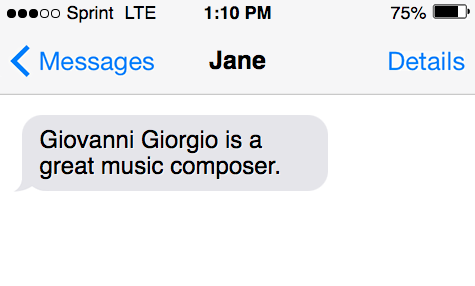
- My house is currently under lease.
- This novel is lengthy.
- I purchased some fruits and vegetables.
- She sent me an expensive watch.
- Velma loved the dress gifted by her parents.
- Joyce and Jill watched a movie together.
- Grandma gave us materials to prepare the dessert.

- Typically , we visit Mom on Mondays.
- Don’t you taste the coffee to be too bitter?
- Do not be nervous. You will eventually get the hang of it.
- The movie I watched was very scientific.
- It is scorching hot inside the workshop.
- Can I visit the office today ?
- His aunt will be staying at the apartment for a while .
- He is the man I was referring to.
- I found my missing luggage outside the airport.

- I won’t be coming to the office in the afternoon.
- He arranged the cutlery on the table.
- Bhaskar made the dog hide under its bed.
- I enjoy strolling by the lake in the mornings.
- James and I trekked to the hilltop today.
- I stayed back home because I felt uneasy.
- He did not enjoy the yogurt , yet he finished it.

- Interjection
- Hurray! We got the funding.
- Ouch! That wound looks severe.
- Wow! You look great in the wedding gown.
- Oh my God ! I hope he is safe.
See an example in the image below.
Words with more than one job
Many parts of speech can have more than one function/job in the sentence. This improves the versatility of the words being used and makes the use more situational in its placement and conveyance of meaning.
- Myers can shift for herself (Preposition)
- Give prayers to the Almighty; for He is the one above all (Conjunction)
- We require more women to have the same vigor. (Adjective)
- More of the women died in the operating room than in the cabin. (Pronoun)
- Agatha needs to shut the gossiping and work more (Adverb)
To see how all the objects work together, see the table below.
Here is a chart showing the parts of speech:
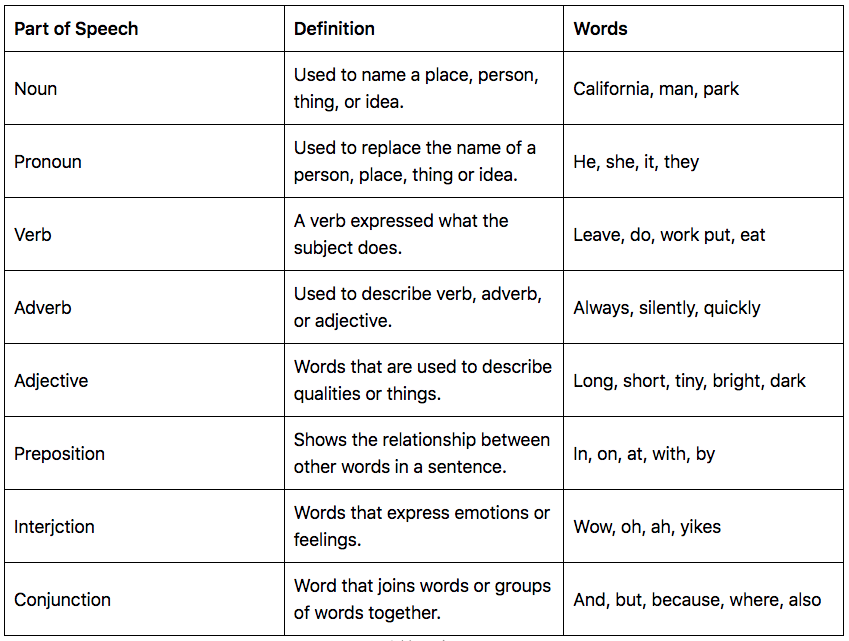
How to identify parts of speech
In sentence formation, it often becomes difficult to ascertain the parts of speech represented by each word. To help out and to make the process of identification easier, follow these steps:
- Identify any word which names an object/individual/place in a generalized form as a noun .
- To identify a specific noun, use pronouns .
- Any words which describe/identify actions/performance are verbs .
- Any word that modifies or gives a greater definition to nouns is an adjective.
- Any word that modifies or gives meaning to the actions of verbs, are adverbs.
- It is easy to pick out prepositions as they describe relationships between a noun/pronoun with other nouns/pronouns.
- Any joiner used to join two clauses is a conjunction .
- Exclamations generally follow any interjections in the text.

- Parts of speech
More parts of speech:
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Possessive nouns
- Irregular plural nouns
- Proper nouns
- Concrete nouns
- Collective nouns
- Possessive and plural nouns
- Verbs: The Definitive Guide
- Nouns | Explore Definition, Examples & Types with Examples
- What Are Pronouns? Definitions and Examples
- What Are Adverbs? (with Examples)
- Interjections – Explore Meaning, Definition, Usage and Examples
- What Is A Conjunction? Types & Examples
- The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- What Is a Determiner?
- The 8 Parts of Speech: Examples and Rules
- Adverbs – What is It? Explore the Meaning, Definition, Types, Usage and Examples
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

What is a Part of Speech?
A part of speech is one of the nine types of English words : VERB, NOUN, ADJECTIVE, ADVERB, PRONOUN, PREPOSITION, DETERMINER, CONJUNCTION, INTERJECTION
There are thousands of words but they don't all have the same job. For example:
- some words express action
- other words express things
- other words join one word to another word
And when we want to build a sentence, we use the different types of word .
Each type of word has its own job.
There are 9 basic types of word , and they are called " parts of speech ".
The most important parts of speech are the BIG FOUR, and the verb is the king of these. Here they are, each with an example and its basic "job":
- verb ( deliver - expresses action)
- noun ( computer - expresses a thing)
- adjective ( yellow - tells us more about a noun)
- adverb ( quickly - tells us more about a verb)
The other parts of speech are mostly small words:
- pronoun ( it - replaces a noun)
- preposition ( on - links a noun to another word)
- determiner ( the - limits a noun)
- conjunction ( and - joins words)
- interjection ( ouch ! - expresses feeling)

OASIS: Writing Center
Grammar: main parts of speech, definitions and examples.
The name of something, like a person, animal, place, thing, or concept. Nouns are typically used as subjects, objects, objects of prepositions, and modifiers of other nouns.
- I = subject
- the dissertation = object
- in Chapter 4 = object of a preposition
- research = modifier
This expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. In English, verbs follow the noun.
- It takes a good deal of dedication to complete a doctoral degree.
- She studied hard for the test.
- Writing a dissertation is difficult. (The "be" verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "writing a dissertation," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "hard.")
This describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives typically come before a noun or after a stative verb, like the verb "to be."
- Diligent describes the student and appears before the noun student .
- Difficult is placed after the to be verb and describes what it is like to balance time.
Remember that adjectives in English have no plural form. The same form of the adjective is used for both singular and plural nouns.
- A different idea
- Some different ideas
- INCORRECT: some differents ideas
This gives more information about the verb and about how the action was done. Adverbs tells how, where, when, why, etc. Depending on the context, the adverb can come before or after the verb or at the beginning or end of a sentence.
- Enthusiastically describes how he completed the course and answers the how question.
- Recently modifies the verb enroll and answers the when question.
- Then describes and modifies the entire sentence. See this link on transitions for more examples of conjunctive adverbs (adverbs that join one idea to another to improve the cohesion of the writing).
This word substitutes for a noun or a noun phrase (e.g. it, she, he, they, that, those,…).
- they = applicants
- He = Smith; that = ideas; those = those ideas
This word makes the reference of the noun more specific (e.g. his, her, my, their, the, a, an, this, these, … ).
- Jones published her book in 2015.
- The book was very popular.
Preposition
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,… ) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …).
- I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me.
- The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
- I stopped the recording in the middle of the interview due to a low battery.
Conjunction
A word that joins two clauses. These can be coordinating (an easy way to remember this is memorizing FANBOYS = for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) or subordinating (e.g., because, although, when, …).
- The results were not significant, so the alternative hypothesis was accepted.
- Although the results seem promising, more research must be conducted in this area.
Auxiliary Verbs
Helping verbs. They are used to build up complete verbs.
- Primary auxiliary verbs (be, have, do) show the progressive, passive, perfect, and negative verb tenses .
- Modal auxiliary verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) show a variety of meanings. They represent ability, permission, necessity, and degree of certainty. These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- Semimodal auxiliary verbs (e.g., be going to, ought to, have to, had better, used to, be able to,…). These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- primary: have investigated = present perfect tense; has not been determined = passive, perfect, negative form
- The modal could shows ability, and the verb conduct stays in its simple form; the modal may shows degree of certainty, and the verb lead stays in its simple form.
- These semimodals are followed by the simple form of the verb.
Common Endings
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs often have unique word endings, called suffixes . Looking at the suffix can help to distinguish the word from other parts of speech and help identify the function of the word in the sentence. It is important to use the correct word form in written sentences so that readers can clearly follow the intended meaning.
Here are some common endings for the basic parts of speech. If ever in doubt, consult the dictionary for the correct word form.
Common Noun Endings
Common verb endings, common adjective endings, common adverb endings, placement and position of adjectives and adverbs, order of adjectives.
If more than one adjective is used in a sentence, they tend to occur in a certain order. In English, two or three adjectives modifying a noun tend to be the limit. However, when writing in APA, not many adjectives should be used (since APA is objective, scientific writing). If adjectives are used, the framework below can be used as guidance in adjective placement.
- Determiner (e.g., this, that, these, those, my, mine, your, yours, him, his, hers they, their, some, our, several,…) or article (a, an, the)
- Opinion, quality, or observation adjective (e.g., lovely, useful, cute, difficult, comfortable)
- Physical description
- (a) size (big, little, tall, short)
- (b) shape (circular, irregular, triangular)
- (c) age (old, new, young, adolescent)
- (d) color (red, green, yellow)
- Origin (e.g., English, Mexican, Japanese)
- Material (e.g., cotton, metal, plastic)
- Qualifier (noun used as an adjective to modify the noun that follows; i.e., campus activities, rocking chair, business suit)
- Head noun that the adjectives are describing (e.g., activities, chair, suit)
For example:
- This (1) lovely (2) new (3) wooden (4) Italian (5) rocking (6) chair (7) is in my office.
- Your (1) beautiful (2) green (3) French (4) silk (5) business (6) suit (7) has a hole in it.
Commas With Multiple Adjectives
A comma is used between two adjectives only if the adjectives belong to the same category (for example, if there are two adjectives describing color or two adjectives describing material). To test this, ask these two questions:
- Does the sentence make sense if the adjectives are written in reverse order?
- Does the sentence make sense if the word “and” is written between them?
If the answer is yes to the above questions, the adjectives are separated with a comma. Also keep in mind a comma is never used before the noun that it modifies.
- This useful big round old green English leather rocking chair is comfortable . (Note that there are no commas here because there is only one adjective from each category.)
- A lovely large yellow, red, and green oil painting was hung on the wall. (Note the commas between yellow, red, and green since these are all in the same category of color.)
Position of Adverbs
Adverbs can appear in different positions in a sentence.
- At the beginning of a sentence: Generally , teachers work more than 40 hours a week.
- After the subject, before the verb: Teachers generally work more than 40 hours a week.
- At the end of a sentence: Teachers work more than 40 hours a week, generally .
- However, an adverb is not placed between a verb and a direct object. INCORRECT: Teachers work generally more than 40 hours a week.
More Detailed Rules for the Position of Adverbs
- Adverbs that modify the whole sentence can move to different positions, such as certainly, recently, fortunately, actually, and obviously.
- Recently , I started a new job.
- I recently started a new job.
- I started a new job recently .
- Many adverbs of frequency modify the entire sentence and not just the verb, such as frequently, usually, always, sometimes, often , and seldom . These adverbs appear in the middle of the sentence, after the subject.
- INCORRECT: Frequently she gets time to herself.
- INCORRECT: She gets time to herself frequently .
- She has frequently exercised during her lunch hour. (The adverb appears after the first auxiliary verb.)
- She is frequently hanging out with old friends. (The adverb appears after the to be verb.)
- Adverbial phrases work best at the end of a sentence.
- He greeted us in a very friendly way .
- I collected data for 2 months .
Main Parts of Speech Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Mastering the Mechanics: Nouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Verbs (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Articles (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Pronouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Modifiers (video transcript)
Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher Video
Note that this video was created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Main Parts of Speech
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Overview
- Next Page: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Introduction to grammar
Parts of Speech
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence.
There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections .
Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes. Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns etc.
It is important to know that a word can sometimes be in more than one part of speech. For example with the word increase .
Increase can be a verb e.g. Prices increased and increase can also be a noun e.g. There was an increase in the number of followers.
A list of parts of speech in English grammar include the following:
A verb is used to show an action or a state of being
go, write, exist, be
A noun is a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, substances, states, events, ideas and feelings. A noun functions as a subject or object of a verb and can be modified by an adjective.
John, lion, table, freedom, love ...
3. Adjective
Adjectives are used to describe or specify a noun or pronoun
good, beautiful, nice, my ...
An adverb is used to modify a verb, adjective and other adverbs.
completely, never, there ...
A pronoun is used in the place of a noun or phrase.
I, you, he, she, it ...
6. Preposition
Prepositions are used before nouns to form a phrase that shows where, when, how and why
in, above, to, for, at ...
7. Conjunction
Conjunctions join clauses or sentences or words
and, but, when ...
8. Interjection
Interjections are used to show surprise or emotion.
oh!, Good Lord
Examples of parts of speech
Here are some examples of parts of speech: My ( adjective ) friend ( noun ) speaks ( verb ) English ( noun ) fluently ( adverb ). Oh! ( interjection ) I ( pronoun ) went ( verb ) to ( preposition ) school ( noun ) and ( conjunction ) I ( pronoun ) met ( verb ) Fred ( noun ).
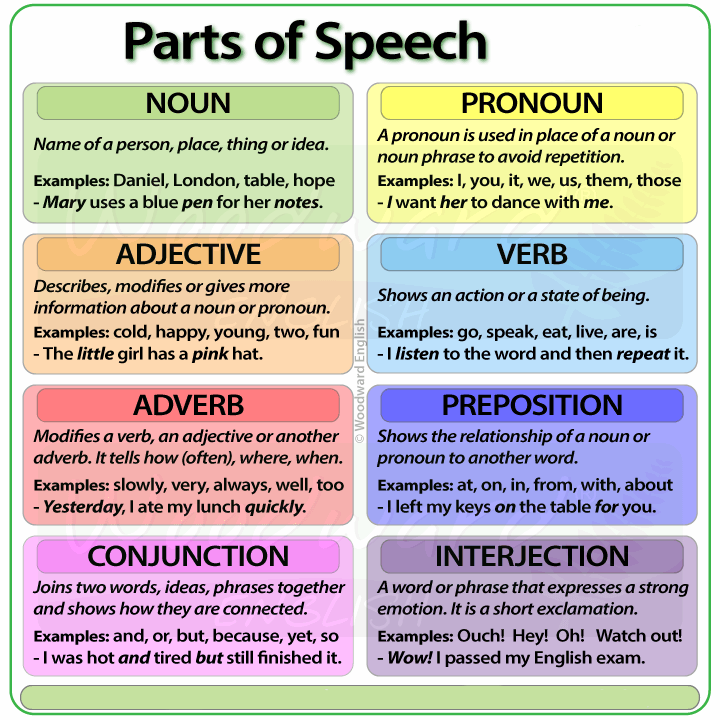
Course Curriculum
- Basic English Grammar Components 20 mins
- Auxiliary Verbs 30 mins
- Articles 20 mins
- Parts of Speech 20 mins

Image credit: Getty Images (Alessandro Biascioli)
World Happiness Report offers most comprehensive picture yet of happiness across generations
Fresh insights from the World Happiness Report 2024 paint the richest picture yet of happiness trends across different ages and generations.
The findings, announced today to mark the UN’s International Day of Happiness, are powered by data from the Gallup World Poll and analysed by some of the world’s leading wellbeing scientists.
Experts use responses from people in more than 140 nations to rank the world’s ‘happiest’ countries. Finland tops the overall list for the seventh successive year, though there is considerable movement elsewhere:
• Serbia (37th) and Bulgaria (81st) have had the biggest increases in average life evaluation scores since they were first measured by the Gallup World Poll in 2013, and this is reflected in climbs up the rankings between World Happiness Report 2013 and this 2024 edition of 69 places for Serbia and 63 places for Bulgaria. • The next two countries showing the largest increases in life evaluations are Latvia (46th) and Congo (Brazzaville) (89th), with rank increases of 44 and 40 places, respectively, between 2013 and 2024.
Significantly, the United States of America (23rd) has fallen out of the top 20 for the first time since the World Happiness Report was first published in 2012, driven by a large drop in the wellbeing of Americans under 30. Afghanistan remains bottom of the overall rankings as the world’s ‘unhappiest’ nation.
For the first time, the report gives separate rankings by age group, in many cases varying widely from the overall rankings. Lithuania tops the list for children and young people under 30, while Denmark is the world’s happiest nation for those 60 and older.
In comparing generations, those born before 1965 are, on average, happier than those born since 1980. Among Millennials, evaluation of one’s own life drops with each year of age, while among Boomers life satisfaction increases with age.
Rankings are based on a three-year average of each population’s average assessment of their quality of life1. Interdisciplinary experts from the fields of economics, psychology, sociology and beyond then attempt to explain the variations across countries and over time using factors such as GDP, life expectancy, having someone to count on, a sense of freedom, generosity and perceptions of corruption.
These factors help to explain the differences across nations, while the rankings themselves are based only on the answers people give when asked to rate their own lives.
The World Happiness Report is a partnership of Gallup, the Oxford Wellbeing Research Centre, the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network, and the WHR’s Editorial Board. The Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford is an interdisciplinary research group focussed on the empirical study of wellbeing. From 2024, the Wellbeing Research Centre is the publisher of the annual World Happiness Report, the world’s foremost publication on global happiness.
Professor Jan-Emmanuel De Neve , Director of Oxford’s Wellbeing Research Centre, Professor of Economics and Behavioural Science at the Saïd Business School, and an Editor of the World Happiness Report, said: 'Once again the World Happiness Report uncovers some special empirical insights at the cutting edge of the wellbeing research frontier. Piecing together the available data on the wellbeing of children and adolescents around the world, we documented disconcerting drops especially in North America and Western Europe. To think that, in some parts of the world, children are already experiencing the equivalent of a mid-life crisis demands immediate policy action.
'It is a great privilege and responsibility for our Centre at Oxford to become the next custodian of the World Happiness Report and we’re committed to continuing to give the world the best evidence on the state of global happiness in collaboration with our partners.'
Professor John F. Helliwell, Emeritus Professor of Economics at the Vancouver School of Economics, University of British Columbia, and a founding Editor of the World Happiness Report, said: 'The broad country coverage and annual surveys of the Gallup World Poll provide an unmatched source of data about the quality of lives all over the globe. There are now enough years of data, going back to 2006, to enable us this year to plausibly separate age and generational patterns for happiness.
'We found some pretty striking results. There is a great variety among countries in the relative happiness of the younger, older, and in-between populations. Hence the global happiness rankings are quite different for the young and the old, to an extent that has changed a lot over the last dozen years.'
Jon Clifton, CEO of Gallup, said: 'Effective policymaking relies on solid data, yet there remains a significant lack of it in various parts of the world. Today’s World Happiness Report attempts to bridge some of these gaps by offering insights into people’s perceptions of life on Earth. It offers more than just national rankings; it provides analytics and advice for evidence-based planning and policymaking. Our role in research on World Happiness is a natural fit with our longstanding mission: providing leaders with the right information about what people say makes life worthwhile.'
The World Happiness Report 2024 also features curated submissions on the theme of happiness across different age groups from experts at the forefront of wellbeing science.
Observing the state of happiness among the world’s children and adolescent population, researchers found that, globally, young people aged 15 to 24 report higher life satisfaction than older adults, but this gap is narrowing in Europe and recently reversed in North America.
Findings also suggest that the wellbeing of 15- to 24-year-olds has fallen in North America, Western Europe, the Middle East and North Africa, and South Asia since 2019 – but in the rest of world it has risen. Overall, though, there is a notable global scarcity of wellbeing data available for children below the age of 15.
Further work examines the relationship between wellbeing and dementia, identified as a significant area of research in a globally aging population.
Researchers highlight not only the impact of dementia on the wellbeing of individuals but also the reverse association: the demonstrable predictive power of higher wellbeing to reduce the risk of developing the disease in later life.
Finally, a team of researchers used a large survey of life satisfaction of older adults in what is now the world’s most populous nation: India. They found that within this older Indian population, increasing age is associated with higher life satisfaction, matching the findings of the global analyses.
These researchers also analysed the complex impact of India’s caste system on wellbeing among older adults, though satisfaction with living arrangements, perceived discrimination and self-rated health emerged as the top three predictors of life satisfaction in this study.
The report is produced under the editorial control of the WHR Editorial Board, formed of John F. Helliwell, Lord Richard Layard, Jeffrey D. Sachs, Jan-Emmanuel De Neve, Lara B. Aknin, and Shun Wang.
Read the report in full at worldhappiness.report .
DISCOVER MORE
- Support Oxford's research
- Partner with Oxford on research
- Study at Oxford
- Research jobs at Oxford
You can view all news or browse by category
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
Pornhub protest —
Pornhub blocks all of texas to protest state law—paxton says “good riddance”, pornhub went dark in texas and other states requiring age verification for porn..
Jon Brodkin - Mar 15, 2024 4:57 pm UTC

Pornhub has disabled its website in Texas following a court ruling that upheld a state law requiring age-verification systems on porn websites. Visitors to pornhub.com in Texas are now greeted with a message calling the Texas law "ineffective, haphazard, and dangerous."
"As you may know, your elected officials in Texas are requiring us to verify your age before allowing you access to our website. Not only does this impinge on the rights of adults to access protected speech, it fails strict scrutiny by employing the least effective and yet also most restrictive means of accomplishing Texas's stated purpose of allegedly protecting minors," Pornhub's message said.
Pornhub said it has "made the difficult decision to completely disable access to our website in Texas. In doing so, we are complying with the law, as we always do, but hope that governments around the world will implement laws that actually protect the safety and security of users."
The same message was posted on other sites owned by the same company, including RedTube, YouPorn, and Brazzers. Pornhub has also blocked its website in Arkansas, Mississippi, Montana, North Carolina, Utah, and Virginia in protest of similar laws . VPN services can be used to evade the blocks and to test out which states have been blocked by Pornhub.
Texas AG sued Pornhub, says “good riddance”
The US Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit upheld the Texas law in a 2–1 decision last week. The 5th Circuit appeals court had previously issued a temporary stay that allowed the law to take effect in September 2023.
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton last month sued Pornhub owner Aylo (formerly MindGeek) for violating the law. Paxton's complaint in Travis County District Court sought civil penalties of up to $10,000 for each day since the law took effect on September 19, 2023.
"Sites like Pornhub are on the run because Texas has a law that aims to prevent them from showing harmful, obscene material to children," Paxton wrote yesterday . "We recently secured a major victory against PornHub and other sites that sought to block this law from taking effect. In Texas, companies cannot get away with showing porn to children. If they don't want to comply, good riddance."
The 5th Circuit panel majority held that the Texas porn-site law should be reviewed on the "rational-basis" standard and not under strict scrutiny. In a dissent, Judge Patrick Higginbotham wrote that the law should face strict scrutiny because it "limits access to materials that may be denied to minors but remain constitutionally protected speech for adults."
"[T]he Supreme Court has unswervingly applied strict scrutiny to content-based regulations that limit adults' access to protected speech," Higginbotham wrote.
Pornhub wants device-based age verification instead
Pornhub's message to Texas users argued that "providing identification every time you want to visit an adult platform is not an effective solution for protecting users online, and in fact, will put minors and your privacy at risk." Pornhub said that in other states with age-verification laws, "such bills have failed to protect minors, by driving users from those few websites which comply, to the thousands of websites, with far fewer safety measures in place, which do not comply."
Pornhub's message advocated for a device-based approach to age verification in which "personal information that is used to verify the user's age is either shared in-person at an authorized retailer, inputted locally into the user's device, or stored on a network controlled by the device manufacturer or the supplier of the device's operating system."
Pornhub says this could be used to prevent underage users from accessing age-restricted content without requiring websites to verify ages themselves. "To come to fruition, such an approach requires the cooperation of manufacturers and operating-system providers," Pornhub wrote.
The age-verification question could eventually go to the Supreme Court. "This opinion will be appealed to the Supreme Court, alongside other cases over statutes imposing mandatory age authentication," Santa Clara University law professor Eric Goldman wrote .
The 5th Circuit panel majority's analysis relied on Ginsberg v. New York , a 1968 Supreme Court ruling about the sale of "girlie" magazines to a 16-year-old at a lunch counter. Goldman criticized the 5th Circuit for relying on Ginsburg "instead of the squarely on-point 1997 Reno v. ACLU and 2004 Ashcroft v. ACLU opinions, both of which dealt with the Internet." Goldman argued that decisions upholding laws like the Texas one could open the door to "rampant government censorship."
The Free Speech Coalition, an adult-industry lobby group that sued Texas over its law, said it "disagree[s] strenuously with the analysis of the Court majority. As the dissenting opinion by Judge Higginbotham makes clear, this ruling violates decades of precedent from the Supreme Court." The group is considering its "next steps in regard to both this lawsuit and others."
reader comments
Channel ars technica.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
Chuck Schumer on His Campaign to Oust Israel’s Leader
The senate majority leader, chuck schumer, explains why he decided to speak out against benjamin netanyahu, the israeli prime minister..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
From The New York Times, I’m Michael Barbaro. This is “The Daily.”
[MUSIC PLAYING]
Today, in a speech without precedent, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer called for Israelis to hold an election and vote out their current leader. Soon after, my colleague Annie Karni sat down with Schumer to understand why he did it. It’s Friday, March 13th.
Annie, this story begins with a speech. So let’s start there. Tell us about this speech.
I rise to speak today about what I believe can and should be the path forward to secure mutual peace and lasting prosperity for Israelis and Palestinians.
So last Thursday, without much warning, Chuck Schumer, the Senate Majority leader took to the Senate floor and started delivering what ended up being a really personal, really meaty speech about his Jewish identity and about Israel.
I speak for myself, but I also speak for so many mainstream Jewish-Americans, a silent majority whose nuanced views on the matter have never been well represented in this country’s discussions about the war in Gaza.
So he starts by describing himself and giving a sense of why he sees himself as a guardian of the people of Israel.
Of course, my first responsibility is to America and to New York. But as the first Jewish Majority Leader of the United States Senate, and the highest ranking Jewish elected official in America ever, I also feel very keenly my responsibility as a Shomer Yisrael, a guardian of the people of Israel.
But he quickly turns to the humanitarian catastrophe in Gaza and describes some of the suffering and displacement there.
Entire families wiped out, whole neighborhoods reduced to rubble, mass displacement, children suffering.
And he gets to his point very quickly that Israel has a moral obligation to do better.
Palestinian civilians do not deserve to suffer for the sins of Hamas. And Israel has a moral obligation to do better. The United States has an obligation to do better.
And that this is not in line with Israel’s values what’s happening in Gaza.
What horrifies so many Jews especially is our sense that Israel is falling short of upholding these distinctly Jewish values that we hold so dear. We must be better than our enemies, lest we become them.
That Israel’s approach to its war against Hamas in Gaza is not in sync with what he sees as the very meaning of being a Jew and what Israel is supposed to represent.
That’s right. And he also kind of frames it as this is not only hurting the Palestinians, but it’s hurting Israel.
Support for Israel has declined worldwide in the last few months. And this trend will only get worse if the Israeli government continues to follow its current path.
He thinks that when they’re prosecuting the war in this fashion, they are quickly losing global support, American support, their reputation on the world stage. And he thinks that Israel’s future is in jeopardy if it doesn’t have public support from the rest of the world.
The existence of Israel, he’s saying, is in jeopardy.
We cannot let anger or trauma determine our actions or cloud our judgment.
So Schumer in the speech carefully lays out that he thinks the only path out of this is a peace deal. He specifically says they need to work towards a two-state solution.
The only real and sustainable solution to this decades-old conflict is a negotiated two-state solution, a demilitarized Palestinian state, living side by side with Israel in equal measures of peace, security, prosperity, dignity, and mutual recognition.
And then he goes through four obstacles to such a peace deal.
Right now, there are four — four major obstacles standing in the way of two states. And until they are removed from the equation, there will never be peace in Israel and Gaza and the West Bank. The four major obstacles are — Hamas and the Palestinians who support and tolerate their evil ways; radical right wing Israelis in government and society.
The most shocking one that he lists —
Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas —
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
— Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel.
I will explain each in detail. The first major obstacle —
And what specifically does Schumer point to about Netanyahu?
Prime Minister Netanyahu has lost his way by allowing his political survival to take the precedence over the best interests of Israel.
He has filled his government with far right extremists that Schumer called out by name in the speech.
He has put himself in coalition with far right extremists like Minister Smotrich and Ben-Gvir. And as a result, he has been too willing to tolerate the civilian toll in Gaza which is pushing support for Israel worldwide to historic lows. Israel cannot survive if it becomes a pariah.
And Netanyahu has ruled out what Schumer is saying is the answer, which is a two-state solution.
And he has shown zero interest in doing the courageous and visionary work required to pave the way for peace even before this present conflict.
The way he’s carrying out this war, even the Biden administration has criticized him for not doing more to mitigate civilian deaths.
He won’t commit to a military operation in Rafah, that prioritizes protecting civilian life. He won’t engage responsibly in discussions about a day after plan for Gaza and a longer term pathway to peace.
In Schumer’s view —
The Netanyahu coalition no longer fits the needs of Israel after October 7th.
He is stuck in the past.
Nobody expects prime Minister Netanyahu to do the things that must be done to break the cycle of violence, to preserve Israel’s credibility on the world stage, and to work towards a two-state solution.
And can’t do the things necessary to move Israel into the future past this war.
Five months into this conflict, it is clear that Israelis need to take stock of the situation and ask, must we change course?
Then he gets to what becomes the real big headline of this speech and makes it kind of the bombshell moment in US-Israeli relations that it became.
I believe a new election is the only way to allow for a healthy and open decision-making process about the future of Israel.
He says that as the war winds down, Israel should have a new election. And he makes it clear that he thinks Netanyahu should be removed from power.
I also believe a majority of the Israeli public will recognize the need for change. And I believe that holding a new election, once the war starts to wind down, would give Israelis an opportunity to express their vision for the post-war future.
The reason he is saying this now is because Israel doesn’t have to hold an election until 2026.
Two years from now.
Yes. That’s a lot of time for Netanyahu to stay in power. And according to Schumer, watch Israel’s reputation abroad erode. So what Schumer is saying is, hold that election much sooner, as soon as this war is over, and get rid of Netanyahu so Israel can correct course.
I mean, everything about that is highly unconventional.
It’s unprecedented. And this is why Schumer is really careful with his language in this section of the speech.
Of course, the United States cannot dictate the outcome of an election, nor should we try. That is for the Israeli public to decide.
Making it clear that Israeli voters will decide. He’s not trying to decide for them.
If Prime Minister Netanyahu’s current coalition remains in power after the war begins to wind down —
But then later in the speech, he also makes it clear that if Netanyahu stays in power, the US will have no choice but to take additional measures to pushback on him.
Then the United States will have no choice but to play a more active role in shaping Israeli policy by using our leverage to change the present course.
And he is not specific about what those are, but makes clear that there will be more pushback from America if Netanyahu stays.
The United States’ bonds with Israel is unbreakable. But if extremists continue to unduly influence Israeli policy, then the administration should use the tools at its disposal to make sure our support for Israel is aligned with our broader goal of achieving long-term peace and stability in the region.
Right. And I was listening to this section of the speech. And he uses the word, “tools.” And it definitely felt to me, and I wonder how you heard it, that the word “tools” meant money, American aid to Israel.
Almost certainly. The US sends several billion of military aid to Israel every year that is underpinning this war in Gaza. Schumer’s critical to moving that aid through Congress. And this is him sort of saying that — not explicitly, he doesn’t say money, he says tools. But that they have a lot of leverage over Israel. And this is also what makes the speech so remarkable in the first place, because Schumer is calling for these new elections and then following it up by saying we have other tools if this continues in the direction it’s going right now.
From the ashes, may we light the candles that lead to a better future for all.
Right. And what did feel so historic about this speech I think to so many of us is that Schumer is saying so many quiet things out loud, the first being that the US sees Bibi Netanyahu as a problem that needs to be removed, big enough saying that. And on top of that, he says, we are willing and ready, if we need to, to essentially turn off the US financial spigot to Israel if the Netanyahu government doesn’t leave or significantly change. And both of those just cannot be overstated for their enormity and their unprecedentedness.
It was a huge, historic, risky speech that Chuck Schumer made. I mean, I think this was probably one of the riskiest moments of his career, that he is putting himself out there to make this call and ramp up this pressure on Netanyahu.
The people of Israel at home and in captivity deserve America’s support.
Immediately after Schumer leaves the floor, Mitch McConnell, the Minority Leader, takes to the podium and blasts the speech.
It is grotesque and hypocritical for Americans who hyperventilate about foreign interference in our own democracy to call for the removal of a democratically elected leader of Israel.
Republicans try immediately to say —
We need to be standing with Israel. And we need to give our friends and allies our full support.
Democrats aren’t being anti-Bibi, they’re being anti-Israel.
Chuck Schumer speech was an act of courage, an act of love for Israel.
Democratic response is mixed. Some said he did a great job. He did something brave. And others —
I’ve got full faith and confidence in the Israeli people to make the right determination about what their future should look like and —
Said he crossed a line, and this was inappropriate. President Biden was brief in responding, but he called it a good speech.
I’m not going to elaborate on his speech. He made a good speech. And I think he expressed a serious concern shared not only by him, but by many Americans.
Many people interpreted that as the administration thinking that Schumer speaking out was helpful to their aims. And then there’s Trump.
Because he was always pro-Israel. He’s very anti-Israel now.
— who called any Jew who votes for Democrats to be self-hating and hate Israel.
Any Jewish person that votes for Democrats hates their religion. They hate everything about Israel. And they should be ashamed of themselves.
And finally on Sunday, Netanyahu made the rounds on some of the Sunday shows here.
I think Schumer’s statements are wholly inappropriate. I think we’re not a banana republic. The people of Israel will choose when they’ll have elections who they elect. And it’s not something that will be foisted upon us.
And in fact, he continues to say we’re going to invade Rafah. We’re going to keep up the aggression in Gaza. So clearly, he doesn’t feel the need to react in terms of his policies to the speech in any way.
But we have to finish the job. We need total victory. There’s no substitute for total victory.
Netanyahu’s message to Schumer basically is, go fly a kite. I don’t care what you say to me. I am not changing a thing about my approach to this war.
That’s right. This is a watershed moment for Schumer and a turning point in the US relationship to Israel in the middle of this war. And in part, because the reaction to the speech was all over the place, I was left with a lot of questions about why Schumer decided to do this in the first place. And that’s how I ended up sitting with him in Brooklyn on Sunday afternoon to ask him, why did you give this speech? What were you hoping it would do? Who is it for? And how does it fit in with your long standing relationship with Israel and with your own Jewish faith?
We’ll be right back.
So Annie, tell us about this interview you end up having with Schumer in Brooklyn.
So we end up meeting at James Madison High School in Midwood, Brooklyn.
Nice to see you. Thank you. Want me to sign? Great. Thank you.
We walk in together. And he has to sign in at the front desk.
This is his alma mater a few blocks away from the house he grew up in the 1950s and ‘60s.
What a moment to come back here.
To where it all began.
Sort of. I guess that’s the golden nights.
It was a heavily Jewish neighborhood at the time.
OK. Now we can go — this is the library.
So as we’re walking around the school, he’s reminding me of what it was like to grow up in this neighborhood.
It was right after World War II. And America was advancing.
As a Jew in the shadow of the Holocaust.
Recent memory. There were ladies on my block who would show you the numbers on their arms from the camps. And I remember —
That was a very present reality for him.
And yet at the same time, for the Jewish people, for me, so much part of my existence, Israel was there. Well, out of the Holocaust came Israel. And we were so proud of Israel.
And he talked about how exciting and enamored he was with the creation of a Jewish state that came out of the Holocaust.
In the Holocaust, Jewish people, we didn’t fight back enough. And here is Israel fighting to create a homeland against overwhelming odds.
And in 1967, when Israel was fighting a war with Arab neighbors and was nearly wiped off the map, he was very invested.
When I walked around the halls of this high school, Madison High School, in 1967, I was walking with a transistor radio — it’s June, we’re ready to graduate — attached to my ear because I thought Israel would be pushed into the sea. That’s the connection. This is long before politics.
This was part of his identity in these formative high school years.
Right. The story he’s telling, which is familiar to many American Jews, is of growing up at a time when the Holocaust is still casting a very long shadow. And Israel is such a potent symbol of Jewish survival and strength. And for somebody like Schumer, the very idea of Israel, its very existence, tugs at their heart. They don’t live there, but it is a source of extraordinary inspiration.
That’s right. Absolutely. And by the time he gets into politics in the late ‘70s and early ‘80s, he’s also very aware of the fact that Israel is a bipartisan issue. Democrats and Republicans alike steadfastly support Israel. They’re committed to the close relationship and giving aid and military support to Israel. And he is really proud of the fact that he said, whenever I carried legislation for Israel, I always had a Republican. That was a credo. And that, he thinks, is key to Israel’s success, that it’s bipartisan.
So how do I know Bibi? I’ve known him for a long time. I didn’t know —
It’s around this time that he first crosses paths with Bibi Netanyahu. He had gone to Harvard with Bibi’s brother, who was an Israeli war hero who died in combat and became a huge national figure. They didn’t know each other personally, but he said that kind of helped foster a connection with Bibi.
And in the beginning, Bibi did a lot of good things for Israel. He was the economic minister and created almost an economic miracle. We were so proud that Israel was doing startups and tech and all these things. When he first became prime minister, he was fine. Look, he was to the right, but not far right.
And when Netanyahu becomes prime minister, he wanted to back him. His gut was to stay with him and back Netanyahu even as other Democrats thought he was moving too far to the right.
Right. And Bibi’s rightward drift becomes extremely pronounced, so much so that he opposes President Obama’s plan to make peace with Iran through a nuclear deal. And Netanyahu actually travels to the US Congress to give a speech asking Congress, asking someone like Schumer, to reject that nuclear deal.
Exactly. And Schumer at the time was the rare Democrat who broke with Obama over the Iran deal.
You sided with Netanyahu against Obama.
Yes. And I talked to Netanyahu quite a lot.
He must have been thrilled with that vote.
And said it was a matter of conscience to protect Israel. And he voted against that deal.
I mean, suffice it to say, for a very long time, Chuck Schumer is a supporter of Bibi Netanyahu, so much so that he is even willing to break with his own Democratic president because he agrees with Netanyahu that policies like the Iran nuclear deal are bad for Israel.
Yes. I’d say that maybe he had some criticisms, but Chuck Schumer was Netanyahu’s best hope in terms of Democratic leadership in the United States.
But somehow, Bibi drifted way to the right. And one of the turning points was when he just embraced Trump so completely.
For Schumer, his views on Bibi start to change when Donald Trump is elected here. And Netanyahu becomes extremely close with him and starts to pursue policies that Democrats see as not at all in keeping with their values. So Bibi, together with Trump, pursues diplomatic deals between Israel and its Arab neighbors that do not take into account the future of Palestinians. His government expands settlements with Trump’s support. And basically what this means is that Israel is taking the land that would be essential to creating a two-state peace deal in the future.
And all of this infuriates Democrats who think these policies are making a two-state solution impossible, and taking away the leverage that Palestinians might have had.
He has now become so interested in self-preservation that he does —
Bibi also faces corruption investigations, which force him to bring very right wing politicians into his government.
And Schumer told me that he thinks he never would have made these alliances 10 years ago. So really, what happens during the Trump years, in Schumer’s mind, is that Bibi just gives up on Democrats and what they want for Israel and the Palestinians, and just wants to be aligned with Trump.
— and I’ll tell you in a meeting I had. He comes in to see me. It’s about 2018/2019. And I said, Bibi, I agree with you. The greatest short-term threat to Israel is the rockets Iran gives Hezbollah, and they put them in Lebanon and shoot them at Israel. But the greatest middle and long-term danger is you lose America, particularly the half of America that’s more progressive and/or the half of America that’s young. And by your embracing Trump, you are making that happen.
So in his mind, Bibi chooses Republicans and walks away from this history of bipartisan support.
That’s right. And that becomes even more of a problem after October 7th.
Well, just explain that, Annie.
Well, after October 7th, there’s broad support for Israel, who was just the victim of a terrorist attack against defenseless citizens. But as the war continues and the Netanyahu regime starts to take these aggressive actions in Gaza, that support starts to dwindle.
— United States, because I look at the numbers, and they’re rapidly decreasing. When you ask people, do you support Israel or the Palestinians, it’s getting all too close.
And in his mind, his fear that Israel will lose the support of America seems to be playing out in a really acute way. He can see it in his party, who’s really divided over what’s happening in Gaza and the humanitarian crisis there.
I am worried, if Israel loses support from America, its future could well be over. I want —
And his fear, what he fears is that there could come a tipping point when the majority of this country does not support Israel, and it’s alone in a hostile goal Middle East without the necessary financial backing from the United States.
So as the highest elected Jewish official in America, and one of the leading Jewish — whatever you want, people in America, I felt an obligation to do this. This was not political.
And this is why he says he ultimately sat down to write this speech.
This is so part of my core, my soul, in Yiddish, my neshama —
In his mind, the goal here is to try to save Israel from Bibi’s actions, which he thinks imperil its future.
Once Schumer decides to write this speech, Annie, and to encourage Israelis to hold an election, and in that election vote out Netanyahu, I’m curious, how does Schumer tell you he thinks about the precedent that that sends, that the US will try to influence a foreign country’s decision about who should lead it?
I asked him about that. And he said he was aware that this section of the speech was the most delicate line he had to toe.
Did you consider — did you consider not personalizing it with Netanyahu and just calling for policy changes?
I didn’t think that would be enough. And he’s the fount of the problem. To just call for policy changes, I thought it wouldn’t pierce, it wouldn’t do anything.
It wouldn’t do anything. It would forgettable.
Yes. It’s so urgent and so important. I didn’t think it was appropriate to call for him to step down. But I thought the next step thing over, and say why I think he’s a bad leader.
And did you think —
So he was writing this speech with the notion of being careful about appearing to interfere front of mind. And he thought where he landed, going further than simply calling for policy changes, but stopping short of calling for her resignation and calling for new elections, he thinks he toed the line and didn’t cross it.
Got it. Now clearly, many people, including Netanyahu, disagree about whether Schumer crossed a line. But I’m curious if those people were his audience. I mean, who is Schumer really talking to with this speech? Does he think he’s speaking directly to Israelis and asking them to demand a new election and that they’re going to listen? Or actually, is he really talking to a more domestic audience, in particular his fellow Democrats, who are increasingly upset about this war, and potentially, it looks like willing to hold it against their party’s leaders?
He put this pretty simply when I asked him.
It’s intended for all people who love Israel and feel so conflicted by what’s going on there. The purpose of the speech is to say, you can still love Israel and feel strongly about Israel and totally disagree with Bibi Netanyahu and the policies of Israel.
He said that it was aimed, above all, at American Jews and non-Jews who love Israel. And what he wanted to do here was separate Netanyahu from Israel and make it crystal clear to people that you can be anti-Netanyahu, you can totally disagree with how he’s conducting the war in Gaza, and you can still be as pro-Israel as ever. He wanted to create this separation between Netanyahu and Israel and make Jews and non-Jews alike feel like it’s still OK to be pro-Israel.
This is kind of important, so I want to linger on it for a second, Annie. Schumer is telling you that what he’s really trying to do is give Americans a kind of new structure and vocabulary for thinking about Israel in this moment. And that structure and vocabulary is there is an Israel separate from Netanyahu. And so if you’re angry at Israel in this moment, you should really be angry at Netanyahu, not Israel.
That’s right. He’s asking them to blame Bibi, not Israel. That Israel is better than this, is better than Bibi, and to see it that way. It’s almost the same way that people who love America but hate Donald Trump would have felt during the Trump administration. That they still believe in this country, but they don’t believe in Trump.
That feels like a very complicated request that Schumer is making. Because the reality is that Israelis have repeatedly made Bibi Netanyahu their leader. So much so that if you’re an American, especially a younger American, and Schumer wants those younger Americans to separate Bibi from Israel, that would be pretty hard to accomplish. Because he’s been leader of Israel for as long as some of these young Americans have been alive. So how is Schumer thinking about whether what he’s asking for is really possible?
I mean, yes, it’s a little bit of wishful thinking. It’s true that a lot of Americans don’t really know the Israel of Schumer’s childhood that he’s able to remember. But they are not. He’s doing this in the middle of a six-month long war, where people are just horrified by the conditions in Gaza. And the Israeli government is the one that is carrying on this offensive.
But a lot of Jews, a lot of American Jews are really conflicted, because at the same time, they understand that Israel has a right to defend itself against Hamas. And I think that Schumer is trying to give voice to these conflicted, maybe middle-of-the-road politically American Jews who don’t know what to think about Israel right now, and do probably love Israel the way he does, but also feel awful about the images they’re seeing from Gaza.
So this call from Schumer for a new leader of Israel is kind of his way of resolving that internal conflict that people are feeling. But of course, it’s not clear if that election will be called. And even if it were called, it’s not clear whether Israelis would elect a new leader.
So I guess my question is, what then? Schumer’s speech does mention these other tools that the US has at its disposal. When would Schumer be willing to use those tools?
Yeah. I asked him about the question of, what then?
You don’t want a ceasefire, but is there like 30,000 more Palestinians dead —
Well, I wouldn’t I’d say — look, Israel — no, I have to, I just feel —
I said, what’s your red line? What is the civilian death toll that would have to be reached for you to say we’re pulling this funding?
You said in your speech, if something doesn’t change, then there’s the threat of American —
I didn’t say conditions and I didn’t say leverage. I just said America is going to look at it as a thing —
And you didn’t say exactly what —
No, because I didn’t want to.
You didn’t want to. But what would the scenario be where that would —
Well, you’d have to see. I couldn’t speculate on the future.
And he didn’t want to say.
Well, then why even give the speech if Schumer is not willing to talk about the real consequences for Israel, if there are no elections, and if Israelis don’t end up removing Netanyahu from office? If he can’t explain that, why give this speech?
I asked him that. And he kept coming back to the fact that, for him, this came from a deeply personal and emotional place, and a moral obligation that is central to him, to speak up for Jews and to stand up for the State of Israel. And he really dreads that Israel’s future, its very existence could be vulnerable, in the same way that it was when he was growing up, and in a way that he’s worked throughout his entire career to help fend off, and in a way, now Schumer at the pinnacle of his power as Senate Majority Leader, could be incapable of helping to fend off in the future.
No, I couldn’t look myself in the mirror if I didn’t do it. And then three, four months from now, the US has turned on Israel, and people, even my colleagues, are putting things, conditions and stuff, which will hurt Israel. I can’t do it. Couldn’t do it.
And I think that’s his deep terror about Israel’s future. And that’s why he felt called to do this speech now, he said, before it’s too late.
Well, Annie, thank you very much. We appreciate it.
Thank you, Michael.
On Thursday, Republican House Speaker Mike Johnson said that in the coming days, he plans to invite Netanyahu to address a joint session of Congress, an invitation that would first have to be approved by Senator Schumer.
Here’s what else you need to know today.
Apple has maintained monopoly power in the smartphone market, not simply by staying ahead of the competition on the merits, but by violating federal antitrust law.
On Thursday, the US government sued Apple for violating antitrust laws through practices that it says were designed to keep consumers reliant on Apple’s iPhone and unlikely to switch to a competing device.
We allege that Apple has employed a strategy that relies on exclusionary anticompetitive conduct that hurts both consumers and developers.
The lawsuit alleges that Apple has blocked rival software developers and mobile gaming companies from offering better options on the iPhone, resulting in higher prices for consumers. In response, Apple said it would vigorously defend itself in court and warned that if successful, the government’s lawsuit would hinder its ability to make the technology that customers want.
Today’s episode was produced by Will Reid and Michael Simon Johnson, with help from Eric Krupke. It was edited by Marc Georges and Paige Cowett, contains original music by Dan Powell and Marion Lozano, and was engineered by Alyssa Moxley. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Michael Barbaro. See you on Monday.

- March 26, 2024 • 29:13 The United States vs. the iPhone
- March 25, 2024 • 25:59 A Terrorist Attack in Russia
- March 24, 2024 • 21:39 The Sunday Read: ‘My Goldendoodle Spent a Week at Some Luxury Dog ‘Hotels.’ I Tagged Along.’
- March 22, 2024 • 35:30 Chuck Schumer on His Campaign to Oust Israel’s Leader
- March 21, 2024 • 27:18 The Caitlin Clark Phenomenon
- March 20, 2024 • 25:58 The Bombshell Case That Will Transform the Housing Market
- March 19, 2024 • 27:29 Trump’s Plan to Take Away Biden’s Biggest Advantage
- March 18, 2024 • 23:18 Your Car May Be Spying on You
- March 17, 2024 The Sunday Read: ‘Sure, It Won an Oscar. But Is It Criterion?’
- March 15, 2024 • 35:20 A Journey Through Putin’s Russia
- March 14, 2024 • 28:21 It Sucks to Be 33
- March 13, 2024 • 27:44 The Alarming Findings Inside a Mass Shooter’s Brain
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Annie Karni
Produced by Will Reid and Michael Simon Johnson
With Eric Krupke
Edited by Marc Georges and Paige Cowett
Original music by Dan Powell and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
In a pointed speech from the Senate floor this month, the majority leader, Chuck Schumer, called for Israel to hold a new election and for voters to oust the prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu.
Soon after, Annie Karni, a congressional correspondent for the Times, sat down with Mr. Schumer to understand why he did it.
On today’s episode

Annie Karni , a congressional correspondent for The New York Times.

Background reading
Mr. Schumer, America’s highest-ranking Jewish elected official, said he felt obligated to call for new leadership in Israel .
His speech was the latest reflection of the growing dissatisfaction among Democrats with Israel’s conduct of the war in Gaza.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Annie Karni is a congressional correspondent for The Times. She writes features and profiles, with a recent focus on House Republican leadership. More about Annie Karni
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
definition 1: having qualities that are desired, enjoyed, or beneficial; desirable. That was a really good movie, and I'd like to see it again. The cafeteria actually serves quite good food. She got a good score on her exam. synonyms: beneficial, desirable, positive. antonyms: bad, evil, ill.
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function In a sentence, every word or phrase can be classified as one of the nine parts of speech depending on its function in the sentence. ... So far so good. However, if you think it helps your reader, you can use a comma. The Bakerloo line runs between Elephant and Castle, and Harrow and ...
The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category. Take the word light as an example.
Dive deep into the multifaceted usage of the word good in English. Discover how it functions as an adverb, pronoun, noun, interjection, and adjective, complete with definitions and illustrative examples. ... Learn all the parts of speech for different words and understand how to use them in the English language. Noun. Definition:
Knowing the different parts of speech is essential for good grammar. Become an expert at knowing when and what parts of speech to use with these examples. ... A part of speech is a word with a specific purpose in a sentence. You can categorize every English word into these parts of speech, based on what they do. ...
Open and Closed Word Classes . The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much ...
Search for Parts of Speech. Parts of Speech for Good. Good is used as a Noun. Good is used as a Adverb.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here's a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. ... Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it's ...
The parts of speech we will cover are: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, determiner, and ; interjection. I've also put together a table with all the parts of speech and examples of their use in sentences. Below the table, you'll find a breakdown of each part of speech with further examples.
We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. ... Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word "but" has six jobs to do: verb, noun, adverb, pronoun ...
Parts of speech is a particular class of word in a sentence such as noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. It plays different functions in a sentence based on their position. There are 8 parts of speech in English language. For Example: Mr. Sarowar likes hot coffee in breakfast.
A suffix changes a word's part of speech. For example, the word 'happy' is an adjective. But when you add a suffix, which is an ending, it can change the part of speech.
The Verb (v.) A verb is one of the most important parts of speech and is a word that is used to describe an action. There are three main types of verbs which are detailed below. Examples: Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laugh, walk….
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs, Pronouns, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections. Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e., Articles, a subprogram of determiners. To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to ...
6. Conjunction. A conjunction is a word that binds words, clauses, and phrases. "And," "but," "because," and "consequently" are some examples of conjunctions. Conjunctions make it easy to construct more complex sentences because you can easily add new clauses. The category distinctions of this part of speech are: Coordinating ...
A part of speech is one of the nine types of English words: VERB, NOUN, ADJECTIVE, ADVERB, PRONOUN, PREPOSITION, DETERMINER, CONJUNCTION, INTERJECTION. There are thousands of words but they don't all have the same job. For example: some words express action. other words express things. other words join one word to another word.
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences ...
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,…) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …). I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me. The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples: 1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns. Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence. There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes.Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns ...
Piecing together the available data on the wellbeing of children and adolescents around the world, we documented disconcerting drops especially in North America and Western Europe. To think that, in some parts of the world, children are already experiencing the equivalent of a mid-life crisis demands immediate policy action.
Texas AG sued Pornhub, says "good riddance". The US Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit upheld the Texas law in a 2-1 decision last week. The 5th Circuit appeals court had previously issued ...
Trump made the comments at a rally in Ohio, where he spoke about auto manufacturing. The Biden campaign responded by criticizing the former president's "threats of political violence."
6 likes, 0 comments - englishessay_with_mureedjasra on March 8, 2024: " Word of the Day: Acumen Parts of speech: Noun Meaning: the ability to make good judgements and ...
Language constructors for the movies started with words Frank Herbert made up for his 1965 novel but went much further, creating an extensive vocabulary and specific grammar rules.
It's a terrible mistake on his part, for which he really ought to apologize but won't," Romney added. Sen. Rick Scott, R-Fla., meanwhile, appeared to echo Trump's position that Jewish voters ...
In a pointed speech from the Senate floor this month, the majority leader, Chuck Schumer, called for Israel to hold a new election and for voters to oust the prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu ...
And may the blessing of almighty God, the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit, come down on you and remain with you forever. Amen. Go in peace, glorifying the Lord, by your life. 12 noon Mass, Sun 24 Mar 2024, Palm Sunday of the Passion of the Lord Holy Week.