Librarians/Admins
- EBSCOhost Collection Manager
- EBSCO Experience Manager
- EBSCO Connect
- Start your research
- EBSCO Mobile App

Clinical Decisions Users
- DynaMed Decisions
- Dynamic Health
- Waiting Rooms
- NoveList Blog
EBSCO Open Dissertations
EBSCO Open Dissertations makes electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs) more accessible to researchers worldwide. The free portal is designed to benefit universities and their students and make ETDs more discoverable.
Increasing Discovery & Usage of ETD Research
EBSCO Open Dissertations is a collaboration between EBSCO and BiblioLabs to increase traffic and discoverability of ETD research. You can join the movement and add your theses and dissertations to the database, making them freely available to researchers everywhere while increasing traffic to your institutional repository.
EBSCO Open Dissertations extends the work started in 2014, when EBSCO and the H.W. Wilson Foundation created American Doctoral Dissertations which contained indexing from the H.W. Wilson print publication, Doctoral Dissertations Accepted by American Universities, 1933-1955. In 2015, the H.W. Wilson Foundation agreed to support the expansion of the scope of the American Doctoral Dissertations database to include records for dissertations and theses from 1955 to the present.
How Does EBSCO Open Dissertations Work?
Your ETD metadata is harvested via OAI and integrated into EBSCO’s platform, where pointers send traffic to your IR.
EBSCO integrates this data into their current subscriber environments and makes the data available on the open web via opendissertations.org .
You might also be interested in:

All virtual services are available and some libraries are open for in-person use, while others remain closed through January 23, 2022. Learn more .
- Ask a Librarian
How can I find theses and dissertations?
- COVID-19 Spring 2020
- FAS General
- Harvard Map Collection
- Houghton Library
- How to Do Research in...
- 2 African American Studies
- 1 Anthropology
- 1 Art in Harvard Libraries
- 2 Asian Studies
- 1 Audio Books
- 1 Biography
- 4 Borrow Direct
- 13 Borrowing
- 1 Calendars
- 6 Citation of Sources
- 1 Citation Tools
- 1 Computer Science
- 5 Computers
- 4 contemporary legends
- 1 Copyright
- 3 Crimson Cash
- 9 Databases
- 2 Digital Collections
- 2 Distance Learning
- 28 E-Resources
- 1 Economics
- 5 Electronic Books
- 1 Employment
- 1 Equipment
- 1 Extension School
- 1 Foreign Study
- 2 Genealogy
- 3 Government
- 2 Government Documents
- 1 Harvard Depository
- 3 Harvard Studies
- 3 Harvard University Archives
- 32 Harvardiana
- 5 HOLLIS help
- 5 Interlibrary Loan
- 1 Internet access
- 1 Language Resource Center
- 2 Languages
- 9 Libraries
- 3 Library History
- 1 Library science
- 3 Library services
- 1 Library student
- 1 Literature
- 2 Manuscripts
- 2 Microfilm
- 17 miscellaneous
- 17 Newspapers
- 4 Off-Campus
- 1 Permissions
- 1 Phillips Reading Room
- 3 Photographs
- 1 Plagiarism
- 4 Primary Sources
- 12 Privileges
- 1 Public Libraries
- 2 Purchase requests
- 4 Quotations
- 2 Rare Books
- 4 Reference
- 1 Reproduction Request
- 22 Research Assistance
- 1 Safari Books Online
- 1 Scan & Deliver
- 4 Special Borrowers
- 2 Special Collections
- 5 Statistics
- 1 Study Abroad
- 3 Study spaces
- 1 Summer School
- 2 technology
- 5 Theses, Dissertations & Prize Winners
- 3 Web of Science
For Harvard theses, dissertations, and prize winning essays, see our How can I find a Harvard thesis or dissertation ? FAQ entry.
Beyond Harvard, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses G lobal database (this link requires HarvardKey login) i s a good place to start:
- lists dissertations and theses from most North American graduate schools (including Harvard) and many from universities in Great Britain and Ireland, 1716-present
- You can get full text from Proquest Dissertations and Theses through your own institutional library or you can often purchase directly from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Express.
Other sources:
Databases beyond ProQuest Dissertations & Theses:
Some out of copyright works (pre-1924) are available via large digital libraries. Search online for the title.
Networked Digital Library of Electronic Theses and Dissertations ' Global Search scans participating international libraries
The Center for Research Libraries ' Dissertations database includes many non-US theses.
WorldCat describes many masters' & PhD theses. Use "Advanced Search" and limit to subtype "thesis/dissertation." No full text; it just tells you what libraries have reported having copies.
There are several excellent guides out there with international search recommendations like University College London's Institute of Education Theses and Dissertations LibGuide .
Institutions:
At the institution where the work originated or the national library of the country (if outside the US):
Online institutional repositories (like Harvard's DASH ): If the work was produced after the school's repository was established, it may well be found here in full text.
Libraries: Check the library catalog. There's often a reproductions service ($) for material that hasn't been digitized, but each school has its own policies. Most schools have some kind of "ask a librarian" service where you can ask what to do next.
At your own institution (where applicable) or public library: While many institutions will not lend theses and dissertations or send copies through Interlibrary loan, your Interlibrary Loan department may be able to help you acquire or pay for reproductions.
- Current Harvard faculty, staff and students: Once you identify a reproduction source you can place a request with Harvard Library ILL (in the notes field, ask for help with funding).
For Harvard theses and dissertations, see " How can I find a Harvard thesis or dissertation? "
If you're having trouble locating or acquiring a copy of/access to a dissertation, try " Why can't I find this thesis or dissertation?"
- Ask a Librarian, including chat and email, will be suspended from 5:00 pm on Thursday, December 22, through Monday, January 2, for the holiday break. Any questions received during this period will be answered beginning Tuesday, January 2, 2024 .
- If If you're experiencing an ongoing technical issue when you attempt to access library materials with your HarvardKey during these times, please report it to Library Technology Services.
Monday-Thursday 9am-9pm
Friday-Saturday 9am-5pm
Sunday 12noon-7pm
Chat is intended for brief inquiries from the Harvard community.
Reach out to librarians and other reference specialists by email using our online form . We usually respond within 24 hours Monday through Friday.
Talk to a librarian for advice on defining your topic, developing your research strategy, and locating and using sources. Make an appointment now .
These services are intended primarily for Harvard University faculty, staff and students. If you are not affiliated with Harvard, please use these services only to request information about the Library and its collections.
- Email Us: [email protected]
- Call Us: 617-495-2411
- All Library Hours
- Library Guides
- Staff Login
Harvard Library Virtual Reference Policy Statement
Our chat reference and Research Appointment Request services are intended for Harvard affiliates. All others are welcome to submit questions using the form on this page.
We are happy to answer questions from all Harvard affiliates and from non-affiliates inquiring about the library's collections.
Unfortunately, we're unable to answer questions from the general public which are not directly related to Harvard Library services and collections.
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
How to find resources by format
Why use a dissertation or a thesis.
A dissertation is the final large research paper, based on original research, for many disciplines to be able to complete a PhD degree. The thesis is the same idea but for a masters degree.
They are often considered scholarly sources since they are closely supervised by a committee, are directed at an academic audience, are extensively researched, follow research methodology, and are cited in other scholarly work. Often the research is newer or answering questions that are more recent, and can help push scholarship in new directions.
Search for dissertations and theses
Locating dissertations and theses.
The Proquest Dissertations and Theses Global database includes doctoral dissertations and selected masters theses from major universities worldwide.
- Searchable by subject, author, advisor, title, school, date, etc.
- More information about full text access and requesting through Interlibrary Loan
NDLTD – Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations provides free online access to a over a million theses and dissertations from all over the world.
WorldCat Dissertations and Theses searches library catalogs from across the U.S. and worldwide.
Locating University of Minnesota Dissertations and Theses
Use Libraries search and search by title or author and add the word "thesis" in the search box. Write down the library and call number and find it on the shelf. They can be checked out.
Check the University Digital Conservancy for online access to dissertations and theses from 2007 to present as well as historic, scanned theses from 1887-1923.
Other Sources for Dissertations and Theses
- Center for Research Libraries
- DART-Europe E-Thesis Portal
- Theses Canada
- Ethos (Great Britain)
- Australasian Digital Theses in Trove
- DiVA (Sweden)
- E-Thesis at the University of Helsinki
- DissOnline (Germany)
- List of libraries worldwide - to search for a thesis when you know the institution and cannot find in the larger collections
University of Minnesota Dissertations and Theses FAQs
What dissertations and theses are available.
With minor exceptions, all doctoral dissertations and all "Plan A" master's theses accepted by the University of Minnesota are available in the University Libraries system. In some cases (see below) only a non-circulating copy in University Archives exists, but for doctoral dissertations from 1940 to date, and for master's theses from 1925 to date, a circulating copy should almost always be available.
"Plan B" papers, accepted in the place of a thesis in many master's degree programs, are not received by the University Libraries and are generally not available. (The only real exceptions are a number of old library school Plan B papers on publishing history, which have been separately cataloged.) In a few cases individual departments may have maintained files of such papers.
In what libraries are U of M dissertations and theses located?
Circulating copies of doctoral dissertations:.
- Use Libraries Search to look for the author or title of the work desired to determine location and call number of a specific dissertation. Circulating copies of U of M doctoral dissertations can be in one of several locations in the library system, depending upon the date and the department for which the dissertation was done. The following are the general rules:
- Dissertations prior to 1940 Circulating copies of U of M dissertations prior to 1940 do not exist (with rare exceptions): for these, only the archival copy (see below) is available. Also, most dissertations prior to 1940 are not cataloged in MNCAT and can only be identified by the departmental listings described below.
- Dissertations from 1940-1979 Circulating copies of U of M dissertations from 1940 to 1979 will in most cases be held within the Elmer L. Andersen Library, with three major classes of exceptions: dissertations accepted by biological, medical, and related departments are housed in the Health Science Library; science/engineering dissertations from 1970 to date will be located in the Science and Engineering Library (in Walter); and dissertations accepted by agricultural and related departments are available at the Magrath Library or one of the other libraries on the St. Paul campus (the Magrath Library maintains records of locations for such dissertations).
- Dissertations from 1980-date Circulating copies of U of M dissertations from 1980 to date at present may be located either in Wilson Library (see below) or in storage; consult Libraries Search for location of specific items. Again, exceptions noted above apply here also; dissertations in their respective departments will instead be in Health Science Library or in one of the St. Paul campus libraries.
Circulating copies of master's theses:
- Theses prior to 1925 Circulating copies of U of M master's theses prior to 1925 do not exist (with rare exceptions); for these, only the archival copy (see below) is available.
- Theses from 1925-1996 Circulating copies of U of M master's theses from 1925 to 1996 may be held in storage; consult Libraries search in specific instances. Once again, there are exceptions and theses in their respective departments will be housed in the Health Science Library or in one of the St. Paul campus libraries.
- Theses from 1997-date Circulating copies of U of M master's theses from 1997 to date will be located in Wilson Library (see below), except for the same exceptions for Health Science and St. Paul theses. There is also an exception to the exception: MHA (Masters in Health Administration) theses through 1998 are in the Health Science Library, but those from 1999 on are in Wilson Library.
Archival copies (non-circulating)
Archival (non-circulating) copies of virtually all U of M doctoral dissertations from 1888-1952, and of U of M master's theses from all years up to the present, are maintained by University Archives (located in the Elmer L. Andersen Library). These copies must be consulted on the premises, and it is highly recommended for the present that users make an appointment in advance to ensure that the desired works can be retrieved for them from storage. For dissertations accepted prior to 1940 and for master's theses accepted prior to 1925, University Archives is generally the only option (e.g., there usually will be no circulating copy). Archival copies of U of M doctoral dissertations from 1953 to the present are maintained by Bell and Howell Corporation (formerly University Microfilms Inc.), which produces print or filmed copies from our originals upon request. (There are a very few post-1952 U of M dissertations not available from Bell and Howell; these include such things as music manuscripts and works with color illustrations or extremely large pages that will not photocopy well; in these few cases, our archival copy is retained in University Archives.)
Where is a specific dissertation of thesis located?
To locate a specific dissertation or thesis it is necessary to have its call number. Use Libraries Search for the author or title of the item, just as you would for any other book. Depending on date of acceptance and cataloging, a typical call number for such materials should look something like one of the following:
Dissertations: Plan"A" Theses MnU-D or 378.7M66 MnU-M or 378.7M66 78-342 ODR7617 83-67 OL6156 Libraries Search will also tell the library location (MLAC, Health Science Library, Magrath or another St. Paul campus library, Science and Engineering, Business Reference, Wilson Annex or Wilson Library). Those doctoral dissertations still in Wilson Library (which in all cases should be 1980 or later and will have "MnU-D" numbers) are located in the central section of the third floor. Those master's theses in Wilson (which in all cases will be 1997 or later and will have "MnU-M" numbers) are also located in the central section of the third floor. Both dissertations and theses circulate and can be checked out, like any other books, at the Wilson Circulation desk on the first floor.
How can dissertations and theses accepted by a specific department be located?
Wilson Library contains a series of bound and loose-leaf notebooks, arranged by department and within each department by date, listing dissertations and theses. Information given for each entry includes name of author, title, and date (but not call number, which must be looked up individually). These notebooks are no longer current, but they do cover listings by department from the nineteenth century up to approximately 1992. Many pre-1940 U of M dissertations and pre-1925 U of M master's theses are not cataloged (and exist only as archival copies). Such dissertations can be identified only with these volumes. The books and notebooks are shelved in the general collection under these call numbers: Wilson Ref LD3337 .A5 and Wilson Ref quarto LD3337 .U9x. Major departments of individual degree candidates are also listed under their names in the GRADUATE SCHOOL COMMENCEMENT programs of the U of M, available in University Archives and (for recent years) also in Wilson stacks (LD3361 .U55x).
- << Previous: Dictionaries and encyclopedias
- Next: E-books >>
- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Computer Science Library Research Guide
Find dissertations and theses.
- Get Started
- How to get the full-text
- What is Peer Review?
- Find Books in the SEC Library This link opens in a new window
- Find Conference Proceedings
- Find Patents This link opens in a new window
- Find Standards
- Find Technical Reports
- Find Videos
- Ask a Librarian This link opens in a new window
Engineering Librarian

How to search for Harvard dissertations
- DASH , Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard, is the university's central, open-access repository for the scholarly output of faculty and the broader research community at Harvard. Most Ph.D. dissertations submitted from March 2012 forward are available online in DASH.
- Check HOLLIS, the Library Catalog, and refine your results by using the Advanced Search and limiting Resource Type to Dissertations
- Search the database ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global Don't hesitate to Ask a Librarian for assistance.
How to search for Non-Harvard dissertations
Library Database:
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global
Free Resources:
- Many universities provide full-text access to their dissertations via a digital repository. If you know the title of a particular dissertation or thesis, try doing a Google search.
Related Sites
- Formatting Your Dissertation - GSAS
- Ph.D. Dissertation Submission - FAS
- Empowering Students Before you Sign that Contract! - Copyright at Harvard Library
Select Library Titles
- << Previous: Find Conference Proceedings
- Next: Find Patents >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/cs
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
EBSCO Open Dissertations
Search millions of electronic theses and dissertations (etds).
With EBSCO Open Dissertations, institutions and students are offered an innovative approach to driving additional traffic to ETDs in institutional repositories. Our goal is to help make their students’ theses and dissertations as widely visible and cited as possible.
This approach extends the work started in 2014, when EBSCO and the H.W. Wilson Foundation created American Doctoral Dissertations which contained indexing from the H.W. Wilson print publication, Doctoral Dissertations Accepted by American Universities, 1933-1955. In 2015, the H.W. Wilson Foundation agreed to support the expansion of the scope of the American Doctoral Dissertations database to include records for dissertations and theses from 1955 to the present.
Get involved in the EBSCO Open Dissertations project and make your electronic theses and dissertations freely available to researchers everywhere. Please contact Margaret Richter for more information.
Ask Yale Library
My Library Accounts
Find, Request, and Use
Help and Research Support
Visit and Study
Explore Collections
Resources to Find Dissertations: Home
Description.
This page provides links to databases and websites to find dissertations. This includes links to general databases to find dissertations, databases focused on the humanities, foreign dissertations, dissertations on religion, and dissertations hosted by other universities.
General Databases
Humanities dissertations, foreign dissertations, religion dissertations, dissertations of universities, yale divinity library.

Science Dissertations
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2023 5:35 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/dissertations
Site Navigation
P.O. BOX 208240 New Haven, CT 06250-8240 (203) 432-1775
Yale's Libraries
Bass Library
Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library
Classics Library
Cushing/Whitney Medical Library
Divinity Library
East Asia Library
Gilmore Music Library
Haas Family Arts Library
Lewis Walpole Library
Lillian Goldman Law Library
Marx Science and Social Science Library
Sterling Memorial Library
Yale Center for British Art
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
@YALELIBRARY

Yale Library Instagram
Accessibility Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Giving Privacy and Data Use Contact Our Web Team
© 2022 Yale University Library • All Rights Reserved

Dissertation Repositories, Open Access
How to find dissertations, open access repositories, selected university affiliated, open access repositories.
Use the websites listed below to find freely accessible (open access) dissertations from the United States and other countries. While all repositories listed here include doctoral dissertations, Master's theses may be available in some cases as well.
Regis College maintains print copies of Regis student theses and dissertations in the Regis Library. They are not digitized although individual students may have submitted their dissertation to a digital repository.
- American Doctoral Dissertations (EBSCO) A free resource, hosted by EBSCO, this database includes more than 172,000 theses and dissertations in total from 1902 to the present.
- British Library: EThOS, E-theses Online Service EThOS is the UK’s national thesis service. EThOS aims to hold a record for all doctoral theses awarded by all UK universities (institutions). Also available when using Regis Library discovery tool, PowerSearch.
- Digital Commons Network Free, full-text scholarly articles from hundreds of universities and colleges worldwide. Curated by university librarians and their supporting institutions, the Network includes a growing collection of peer-reviewed journal articles, book chapters, dissertations, working papers, conference proceedings, and other original scholarly work.
- Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD) The Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD) is an international organization dedicated to promoting the adoption, creation, use, dissemination, and preservation of electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs). We support electronic publishing and open access to scholarship in order to enhance the sharing of knowledge worldwide.
- Open Access Theses and Dissertations OATD.org aims to be the best possible resource for finding open access graduate theses and dissertations published around the world. Metadata (information about the theses) comes from over 1100 colleges, universities, and research institutions. OATD currently indexes 4,264,663 theses and dissertations.
- PQDT Open PQDT Open provides the full text of open access dissertations and theses free of charge. The authors of these dissertations and theses have opted to publish as open access.
- Theses Canada Theses Canada is a collaborative program between Library and Archives Canada (LAC) and nearly 70 universities accredited by Universities Canada. It strives to: acquire and preserve theses and dissertations from participating universities; provide free access to Canadian electronic theses and dissertations in the collection.
These digital repositories maintained by various universities enable public access to theses and dissertations. These are just a select sample; there are many other repositories associated with universities.
- Duke University: Duke Space, Theses and Dissertations
- Harvard University: Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH) Also available when using Regis Library discovery tool, PowerSearch.
- Johns Hopkins University: DSpace Repository
- Northeastern University: Digital Reposity Service: Theses and Dissertations
- University of Washington: ResearchWorks
- Walden University Dissertations and Doctoral Studies
- Last Updated: Jul 12, 2023 8:18 AM
- URL: https://libguides.regiscollege.edu/open_access_dissertations
- Boston University Libraries
Theses & Dissertations: Resources for Locating
Proquest dissertations & theses, ethos: electronic theses online service.
Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations
Theses Canada
Submitting a Thesis or Dissertation to the Library
Proquest Dissertations & Theses
The world’s most comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses. PQDT — Full Text includes millions of searchable citations to dissertation and theses from around the world from 1861 to the present day together with over a million full text dissertations that are available for download in PDF format. Over 2.1 million titles are available for purchase as printed copies. The database offers full text for most of the dissertations added since 1997 and strong retrospective full text coverage for older graduate works. All materials in full text are available to currently-registered students, faculty and staff for free.
More than 70,000 new full text dissertations and theses are added to the database each year through dissertations publishing partnerships with 700 leading academic institutions worldwide and collaborative retrospective digitization of dissertations through UMI’s Digital Archiving and Access Program.
Each dissertation published since July 1980 includes a 350-word abstract written by the author. Master’s theses published since 1988 include 150-word abstracts. Simple bibliographic citations are available for dissertations dating from 1637. Where available, PQDT — Full Text provides 24-page previews of dissertations and theses.
EThOS (Electronic Theses Online Service)
The aim of EThOS is to offer a ‘single point of access’ where researchers the world over can access ALL theses produced by UK Higher Education
Many UK institutions support Open Access to their theses, so download of their digital and digitized theses is free to the researcher. A small number of participating institutions may not be able to offer Open Access and in this case the researcher may have to pay for the digitization.
EThOS can only offer the theses of participating institutions. While we expect a large number of institutions to take part, we cannot supply from an institution which chooses not to. In this case, you should approach the institution’s library directly to gain access to a thesis. http://ethos.bl.uk/
The Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD) is an international organization that promotes the adoption, creation, use, dissemination and preservation of electronic theses and dissertations. The NDLTD Union Catalog contains more than one million records. http://www.ndltd.org/resources/find-etds
The mission of Theses Canada is to acquire and preserve a comprehensive collection of Canadian theses at Library and Archives Canada (LAC), to provide access to this valuable research within Canada and throughout the world. Its mission to preserve this portion of Canada’s bibliographic heritage is achieved through collaboration with the many Canadian universities who participate in the program. http://www.collectionscanada.gc.ca/thesescanada
Please consult the Research Guide: Guide for Writers of Theses & Dissertations for information about how to submit your thesis or dissertation to Boston University Libraries.

[email protected]
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2023 4:05 PM
- URL: https://library.bu.edu/dissertations

Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- Starting your Dissertation/Thesis
- Dissertation/Thesis Resources
- Books That May Help
- Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliography
- We Don't Have It? / Interlibrary Loan
- Online Learning Study Tips
- Search Strategy
- Advanced Search Techniques
- Kemp Library Video Tutorials
- Find Articles / Journals / Databases
- What are...
- Database Video Tutorials
- Peer Reviewed
- How to confirm and cite peer review
- Primary/Secondary Sources
- Other Types of Sources (i.e. Newspapers)
- Legal Research Resources
- Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
Google Scholar
- Website Evaluation
- Internet Searching
- Apps You Didn't Know You Needed
- Who is citing me?
- Questions After Hours
- ESU Thesis Submission
- ESU Dissertation Submission
- How to Integrate
- How to Use It
What is Google Scholar and Why Should You Care?
Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it's available for free.
Below are a few videos on how to use Google Scholar (you can skip the intros if you want) that will show you tips and tricks on how to best use Google Scholar.

Did you know that you can use Google Scholar in addition to Primo to help search Kemp library materials? You just have to add us to your Google Scholar and our results will show up in your searches showing you what you have access to as an ESU community member!
- Go to Google Scholar
- Make sure you're logged into your Google Account - you'll see your initials or your icon in the top right hand corner of the screen if you're logged in.
- Click on Settings (either from the top of the Scholar home page, or from the drop-down on the right hand side of the results page).
Choose Library Links .
Type ‘East Stroudsburg University’ into the search box.
Click the boxes next to “ESU” and "Kemp Library"
Click Save .
If you have other institutions you're affilitated with, or ResearchGate, you can add them too!
Getting to Google Scholar Settings:

The Library Link Screen: Search, Select and Save!

What your search results will look like:

Add / Reorder
Databases have more sophisticated search features than Google Scholar , but if you have a one or two word topic Google Scholar can be useful. You can also try using the Advanced Search in Google Scholar (see the first video below).
However, if you're having trouble finding something specific, i.e. a specific article, try Google Scholar. For example you want " Game of Thrones and Graffiti" and you don't see it in a database, search the title of the article in Google Scholar (here you'd search "Game of Thrones and Graffiti"). You may find it freely available OR discover it is available through the library, but in a database you didn't look at.
If we don't have it and you can't access it on Google Scholar, you can always request it via interlibrary loan .
"If Google Scholar isn’t turning up what you need, try an open Google search with the article title in quotes, and type the added filter “filetype:pdf”. This scours the open web for papers hosted somewhere, by someone, in PDF format. Google Books provides limited preview access to many copyrighted books. Other alternate services include SemanticScholar , Microsoft Academic , Dimensions , or GetTheResearch . Here too there are subject-specific portals like EconBiz or the Virtual Health Library , some of which offer multilingual search options." - Paragraph taken from A Wikipedia Librarian.
The other services like Microsoft Academic mentioned above are also useful when looking for freely available journal article and research! Don't forget to cite everything you use in your paper/project/presentation/etc.
Google Scholar Videos
- << Previous: Evidence Based Practice/Appraisal Resources
- Next: Website Evaluation >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 3:12 PM
- URL: https://esu.libguides.com/thesis

- What Is a PhD Thesis?
- Doing a PhD
This page will explain what a PhD thesis is and offer advice on how to write a good thesis, from outlining the typical structure to guiding you through the referencing. A summary of this page is as follows:
- A PhD thesis is a concentrated piece of original research which must be carried out by all PhD students in order to successfully earn their doctoral degree.
- The fundamental purpose of a thesis is to explain the conclusion that has been reached as a result of undertaking the research project.
- The typical PhD thesis structure will contain four chapters of original work sandwiched between a literature review chapter and a concluding chapter.
- There is no universal rule for the length of a thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 70,000 to 100,000 words .
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is the main output of a PhD as it explains your workflow in reaching the conclusions you have come to in undertaking the research project. As a result, much of the content of your thesis will be based around your chapters of original work.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available. As such, you can’t rely on other ideas or results to produce your thesis; it needs to be an original piece of text that belongs to you and you alone.
What Should a Thesis Include?
Although each thesis will be unique, they will all follow the same general format. To demonstrate this, we’ve put together an example structure of a PhD thesis and explained what you should include in each section below.
Acknowledgements
This is a personal section which you may or may not choose to include. The vast majority of students include it, giving both gratitude and recognition to their supervisor, university, sponsor/funder and anyone else who has supported them along the way.
1. Introduction
Provide a brief overview of your reason for carrying out your research project and what you hope to achieve by undertaking it. Following this, explain the structure of your thesis to give the reader context for what he or she is about to read.
2. Literature Review
Set the context of your research by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within your field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. You should conclude the literature review by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project.

3. Main Body
This section focuses on explaining all aspects of your original research and so will form the bulk of your thesis. Typically, this section will contain four chapters covering the below:
- your research/data collection methodologies,
- your results,
- a comprehensive analysis of your results,
- a detailed discussion of your findings.
Depending on your project, each of your chapters may independently contain the structure listed above or in some projects, each chapter could be focussed entirely on one aspect (e.g. a standalone results chapter). Ideally, each of these chapters should be formatted such that they could be translated into papers for submission to peer-reviewed journals. Therefore, following your PhD, you should be able to submit papers for peer-review by reusing content you have already produced.
4. Conclusion
The conclusion will be a summary of your key findings with emphasis placed on the new contributions you have made to your field.
When producing your conclusion, it’s imperative that you relate it back to your original research aims, objectives and hypotheses. Make sure you have answered your original question.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Many Words Is a PhD Thesis?
A common question we receive from students is – “how long should my thesis be?“.
Every university has different guidelines on this matter, therefore, consult with your university to get an understanding of their full requirements. Generally speaking, most supervisors will suggest somewhere between 70,000 and 100,000 words . This usually corresponds to somewhere between 250 – 350 pages .
We must stress that this is flexible, and it is important not to focus solely on the length of your thesis, but rather the quality.
How Do I Format My Thesis?
Although the exact formatting requirements will vary depending on the university, the typical formatting policies adopted by most universities are:
What Happens When I Finish My Thesis?
After you have submitted your thesis, you will attend a viva . A viva is an interview-style examination during which you are required to defend your thesis and answer questions on it. The aim of the viva is to convince your examiners that your work is of the level required for a doctoral degree. It is one of the last steps in the PhD process and arguably one of the most daunting!
For more information on the viva process and for tips on how to confidently pass it, please refer to our in-depth PhD Viva Guide .
How Do I Publish My Thesis?
Unfortunately, you can’t publish your thesis in its entirety in a journal. However, universities can make it available for others to read through their library system.
If you want to submit your work in a journal, you will need to develop it into one or more peer-reviewed papers. This will largely involve reformatting, condensing and tailoring it to meet the standards of the journal you are targeting.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you found this interesting and want advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the THE Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Finding theses and dissertations
Search online in library databases.
You can search the ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global Database to find theses and dissertations from institutions around the world. This database offers full text for most dissertations added since 1997 and strong retrospective full-text coverage for older graduate works. You can do a basic keyword search or search for a specific title, author, or institution.
Search for works for University of Nevada, Reno authors
There is no single search method that will find every thesis and dissertation by a University of Nevada, Reno author. These are your best options:
- Search ProQuest Dissertations & Theses @ University of Nevada, Reno to find online versions where available. You can limit by author, advisor, department, degree type, etc.
- Use the Advanced Library Search tool to narrow your search by the name of the department in which the degree is granted. In the “Any field” dropdown menu, select Author/Creator. In the “Enter a search term” field, type the University name and department granting the degree. For example, to find dissertations/theses from the Department of Computer Science & Engineering, type “University of Nevada, Reno Department of Computer Science and Engineering.”
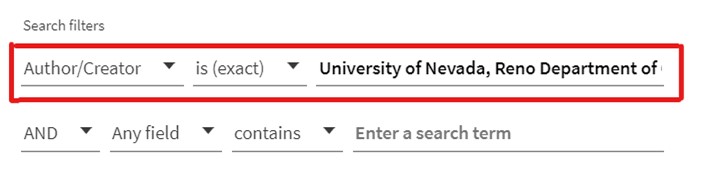
The “Author/Creator” and “is (exact)” fields are enclosed in a red rectangle to indicate these fields have been selected. “University of Nevada, Reno Department of” is written in the search box next to the selected fields.
Search more comprehensively
If you need a more comprehensive search, including materials other than theses and dissertations (articles, books, videos, etc.), or if you are looking for physical copies of theses and dissertations, use Library Search from the library homepage. Search for a keyword, author, date, and/or title. Use the filters on the left-hand side of the screen under “Resource Type” to narrow to “Dissertations” (although not indicated, the search will include theses).

The "Dissertations" filter is enclosed in a red rectangle to indicate its location on the Library Search results page.
If you use the filters to limit by Library Location and select libraries at University of Nevada, Reno (Knowledge Center, Special Collections & Archives, DeLaMare Library), you can limit to physical copies of dissertations or theses only . You can also use the “Held by library” filter under “Availability” to find physical copies.
Need more help?
Find more detailed information in the University Libraries' guide to Finding Dissertations & Theses .

- Queen's University Library
- Research Guides
Finding Theses and Dissertations
- International Theses
- Queen's University Theses
- Canadian Theses
- United States Theses
- Borrowing & Purchasing Copies of Theses
International Theses: Search Tools
Proquest dissertations and theses.
A comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses from around the world from 1861-present. Full text since 1997. Abstracts since 1980 for doctoral dissertations and 1988 for masters' theses. Citations since 1861.
Citations are indexed in Web of Science in the ProQuest ™ Dissertations & Theses Citation Index collection.
Center for Research Libraries
CRL holds more than 800,000 doctoral dissertations outside of the U.S. and Canada. Search dissertations in the dissertations section of the CRL catalogue. Digitized dissertations can be searched in the catalogue's e-resources section.
Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations
A collection of more than 800,000 international full text theses and dissertations.
Google Scholar
Try searching Google Scholar for theses posted on institutional digital repositories or on personal web pages.
ScienceDirect
A web search engine devoted to Science and Technology.
Search for dissertations, theses and published material based on theses catalogued in WorldCat by OCLC member libraries worldwide. In Advanced Search, you can search by author, title, subject, year, and keyword. Under Subtype Limits, select Theses/Dissertation from the Any Content menu
International Theses: By Country
Österreichische Dissertationsdatenbank
The Austrian dissertation database contains the bibliographical data of dissertations approved in Austria from 1990 on, and in most cases the relevant abstracts. (This website is hosted by the National Library of Austria).
National Library of Australia’s Trove Service
Search for full text digital theses from Australian universities. On the Advanced search screen under Format, select Thesis.
DART-Europe : Access to full text theses and dissertations from many countries in Europe.
Europeana : Additional electronic dissertations from other European libraries.
Système universitaire de documentation (Sudoc): Provides access to records and some electronic theses and dissertations published at French research institutions.
Fichier central des thèses
DissOnline provides information on the subject of electronic university publications. It can be used to find out directly all about online dissertations and post-doctoral theses. Sample documents can be downloaded to provide help in the creation of electronic university publications. For more information about the portal, please go to German National Library website (DNB) .
México
TESIUNAM: Tesis del Sistema Bibliotecario de la Unam
(Theses from the National University of Mexico / Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México). To search for electronic theses, click on “tesis electrónicas (REDUNAM).”
Middle East
The Center for Research Libraries and the British Library have made available online 400 UK doctoral theses focusing on the Middle East, Islamic studies, and related subjects. More information .
The Netherlands
Some Dutch e-theses are available through NARCIS.
South America
- Some electronic theses from Bolivia, Brasil, Chile and Peru can be found at Cybertesis.NET , a portal created by the University of Chile (Information Services & Library System) that provides an easily accessible tool to full text electronic theses published in different universities of the world.
For more university/national library catalogues, search for the word University/Universidad and the country (Argentina, Peru, etc.) in Google. Find the link to the library ( biblioteca ) and search the catalogue for theses ( tesis ). You may need to click on the advanced search function ( búsqueda guíada or búsqueda avanzada ) and select tesis as a format or type.
There are several portals/catalogues in Spain for theses and dissertations. Here are some examples listed on Spain’s National Library website:
Spain’s Ministry of Education thesis database (TESEO)
Biblioteca Virtual del Español (on the Biblioteca Virtual, Miguel de Cervantes website)
Universidad Complutense de Madrid’s catalogue
TDX (Tesis Doctorals en Xarxa)
This is a cooperative repository of digital theses from the University of Cataluña and other autonomous communities (such as Murcia, Cantabria, Barcelona, and Oviedo)
Switzerland
For print and electronic dissertations, please consult the Swiss National Library website.
- NDLTD: National Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations in Taiwan is an open full-text permanent archive of scholarly research in Taiwan.
EThOS : Access to doctoral dissertations (paper and electronic) from UK institutions of higher education.
- << Previous: United States Theses
- Next: Borrowing & Purchasing Copies of Theses >>
- Last Updated: Oct 18, 2023 3:58 PM
- Research Guides
- CUNY Graduate Center's Mina Rees Library
Dissertations and Theses
- Find Dissertations
- About the Dissertation Office
- Graduation Dates
- Deposit Procedure
- Format Requirements
- Survey of Earned Doctorates (SED)
- Master's Exit Survey
- Citation Styles
- Digital Dissertations
- Find CUNY Dissertations
Finding Dissertations
There is no single source for a comprehensive dissertation search. WorldCat and ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global include most American dissertations. Dissertations @ The Center for Research Libraries lends non-American dissertations to member borrowers. Library catalogs and specialized repositories contain other titles. Request any dissertation through Interlibrary Loan . Though not every title is available through ILL, it is worth a try.
Dissertation Databases & Repositories
- Graduate Center Dissertations in Academic Works, 2014-present As of 2014, all Graduate Center dissertations, theses, and capstone projects are posted to CUNY Academic Works. Some are immediately available to read and download, and some become available after an embargo period set by the author.
- U.S. and international legal and government resources
- ADT Australian Digital Theses Program
- Biblioteca Digital de Teses e Dissertações da USP Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations of the University of São Paulo
- Colección de Tesis Digitales Universidad de las Américas Puebla Tesis digitales Universidad de las Américas, Puebla, México
- Danish Royal Library
- DART Europe E-theses Europe except France
- Deutsche Nationalbibliothek Hochschulschriften in the German National Library
- Dissonline.de Full-text dissertations from the German and Swiss National Libraries
- E-theses University of Helsinki, Finland dissertations; all free full-text
- EThOS British Library Electronic Theses Online Searches 250,000+ theses, many available in full text with a free online account. Theses not available for immediate download take 30 days to digitize. Order via CUNY Graduate Center interlibrary loan to cover any digitization fees. Most UK universities participate except Oxford, Cambridge, and Univ of Southampton.
- JAIRO: Japanese Institutional Respositories Online Open access; full-text
- NARCIS Dissertations from all Dutch Universities
- National Library of Norway
- Nauka Polska Poland's dissertation repository
- Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations Global ETD Search NDLTD's Global ETD Search is a free service that allows researchers to find electronic theses and dissertations based on keyword, date, institution, language and subject.
- OAIster from open access digital archive world-wide
- Open Access Theses and Dissertations Metadata from over 1100 institutions, indexes over 2.5 million theses and dissertations.
- Osterreichischen Bibliothekenverbundes Austrian Hochschulschriften
- Russian State Library Digital Library Dissertations Over 650,000 free, full-text of dissertations from 1998
- Systeme Universitaire de Documentation French science theses from 1972; humanities, social sciences, law and health from 1983
- Tesi-online Italian university PhD theses; free full-text
- Theses.fr expanding index of French theses
- Theses Canada Canadian universities voluntarily submit approved theses and dissertation to Theses Canada
- Trove Australian university digital and print theses
Dissertation Indexes (Print & Microformat)
Use these to supplement searches in online databases. Historical information in print indexes is sometimes more complete (i.e. abstracts appear in print before 1980 in Dissertation Abstracts International, but are not currently online). Print indexes may contain earlier works not included in online databases.
- American Doctoral Dissertations 1933-1955 Digitized version of the print index, "Doctoral Dissertations Accepted by American Universities." Includes nearly 100,000 citations.
- Comprehensive Dissertation Index 1861 - 1972 37 volumes divided by subject with author index. Each subject has keyword index. Bibliographic citations include title, author, degree, year, institution. No abstracts. JFF 98-1512 in the NYPL Schwarzman Main Reading Room
- Deutsche Bibliographie: Hochschulschriften-Verzeichnis 1972 - 1990 German dissertations NYPL OFFSITE JFM 93-99
- Dissertation Abstracts 1938-1966 Index with abstracts to American doctoral dissertations. NYPL JFM 74-61 OFFSITE
- Dissertation Abstracts International, 1969 - These volumes succeed Dissertation Abstracts. Includes title, author, degree, institution, year, pages, and an abstract. Author and keyword indexes. Includes abstracts for pre-1980 works not abstracted in online version. Graduate Center 1970-1984 MIC-Per 164 NYPL Schwarzman Main Reading Room A: Humanities and Social Sciences JFM 74 - 62 B: Sciences and Engineering JFM 74 - 34 C: International/European 1977 - 2003 OFFSITE
- Dissertation Abstracts International 1966 - 1969 Ser A: Humanities and Social Sciences JFM 74 - 63 OFFSITE Ser B: Sciences and Engineering JFM 74 - 60 OFFSITE
- Dissertation Abstracts International Retrospective Index 1938 - 1969 Indexes Dissertation abstracts (v.1-26) and Dissertation Abstracts International (v.27-29); 1933 - 1969. NYPL: Offsite; request in avance.
- Dissertation Abstracts [Microfilm] 1952-1964 MIC-Per 164 at the Graduate Center Library
- Index to theses accepted for higher degrees by the universities of Great Britain and Ireland and the Council for National Academic Awards 1950 - 1985 NYPL OFFSITE JFM 88-379
- Jahresverzeichnis der Deutschen Hochschulschriften, 1936 - 1964 German dissertations NYPL OFFSITE L-10 9257
- Microfilm Abstracts 1938-1951 Graduate Center MIC-Per 164
CRL Dissertations
Based in Chicago, the Center for Research Libraries was founded in 1948 by a consortium of Midwestern universities seeking to pool lesser-used resources. The collection holds over 800,000 dissertations from 90+ universities in Germany (66%), Netherlands (2%), France (16%), Switzerland, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and the UK; also from Latin America, South America, and Africa. What CRL does not own, it will acquire for interlibrary loan to Graduate Center affiliates.
British Dissertations
The Center for Research Libraries reviews all Grad Center ILL requests for loan or demand purchase of UK dissertations. If CRL finds the title accessible through EThOS or that it can be digitized free of charge (in approx 30 days), CRL will notify the requesting institution of its availability via the EThOS online venue. CRL will also place orders via EThOS and alert requestors when a dissertation is available for download. If EThOS requires a fee for digitization, CRL will place the order on behalf of the requesting institution and pay for digitization.
- << Previous: Digital Dissertations
- Next: Find CUNY Dissertations >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gc.cuny.edu/dissertations

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
OATD is dealing with a number of misbehaved crawlers and robots, and is currently taking some steps to minimize their impact on the system. This may require you to click through some security screen. Our apologies for any inconvenience. Laboratoriotutkimuksiin tulevan potilaan ohjauksen kehittäminen. Alanko, Kaisa.
Over the last 80 years, ProQuest has built the world's most comprehensive and renowned dissertations program. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global (PQDT Global), continues to grow its repository of 5 million graduate works each year, thanks to the continued contribution from the world's universities, creating an ever-growing resource of emerging research to fuel innovation and new insights.
EBSCO Open Dissertations is a collaboration between EBSCO and BiblioLabs to increase traffic and discoverability of ETD research. You can join the movement and add your theses and dissertations to the database, making them freely available to researchers everywhere while increasing traffic to your institutional repository.
The Center for Research Libraries ' Dissertations database includes many non-US theses. WorldCat describes many masters' & PhD theses. Use "Advanced Search" and limit to subtype "thesis/dissertation." No full text; it just tells you what libraries have reported having copies. There are several excellent guides out there with international ...
A PhD thesis is a work of original research all students are requiured to submit in order to succesfully complete their PhD. The thesis details the research that you carried out during the course of your doctoral degree and highlights the outcomes and conclusions reached. The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral research degree ...
Use Libraries search and search by title or author and add the word "thesis" in the search box. Write down the library and call number and find it on the shelf. They can be checked out. Check the University Digital Conservancy for online access to dissertations and theses from 2007 to present as well as historic, scanned theses from 1887-1923.
How to search for Harvard dissertations. DASH, Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard, is the university's central, open-access repository for the scholarly output of faculty and the broader research community at Harvard.Most Ph.D. dissertations submitted from March 2012 forward are available online in DASH.; Check HOLLIS, the Library Catalog, and refine your results by using the Advanced ...
About. With EBSCO Open Dissertations, institutions and students are offered an innovative approach to driving additional traffic to ETDs in institutional repositories. Our goal is to help make their students' theses and dissertations as widely visible and cited as possible. This approach extends the work started in 2014, when EBSCO and the H ...
The ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global (PQDT) ™ database is the world's most comprehensive curated collection of multi-disciplinary dissertations and theses from around the world, offering over 5 million citations and 3 million full-text works from thousands of universities. Within dissertations and theses is a wealth of scholarship, yet ...
Dissertation Express Online version of Dissertation Abstracts from UMI Proquest. Good for US theses. The fastest way to identify and validate a dissertation is to enter the ProQuest publication number. If you don't have this, enter a word or phrase into the search terms field or the author's last name and the first four words of the dissertation title.
Open Access Repositories. A free resource, hosted by EBSCO, this database includes more than 172,000 theses and dissertations in total from 1902 to the present. EThOS is the UK's national thesis service. EThOS aims to hold a record for all doctoral theses awarded by all UK universities (institutions).
Each dissertation published since July 1980 includes a 350-word abstract written by the author. Master's theses published since 1988 include 150-word abstracts. Simple bibliographic citations are available for dissertations dating from 1637. Where available, PQDT — Full Text provides 24-page previews of dissertations and theses.
Google Scholar is a special division of Google that searches for academic content. It is not as robust as Google, and as such it can be harder to search. However, if you are looking for a specific article it is a fantastic resource for finding out if you can access it through your library or if it's available for free.
A PhD thesis is a concentrated piece of original research which must be carried out by all PhD students in order to successfully earn their doctoral degree. The fundamental purpose of a thesis is to explain the conclusion that has been reached as a result of undertaking the research project. The typical PhD thesis structure will contain four ...
A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time. In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master's) and a comprehensive exam (called a "field exam" or "dissertation qualifying exam") before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
Usually it's easier to find journal articles based on dissertations than the dissertation itself. So keep that in mind. I usually try to get both if the journal article is important as the dissertation often has extra details or tabulated data (compared against the plots in the journal article). Few Russian libraries are on WorldCat.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Spanning from the 'theses and quaestiones' of the 17th and 18th centuries to the current yearly output of student research, they include both the first Harvard Ph.D. dissertation (by William Byerly, Ph.D. 1873) and the dissertation of the first woman to earn a doctorate from Harvard (Lorna Myrtle Hodgkinson, Ed.D. 1922).. Other highlights include:
Use the Advanced Library Search tool to narrow your search by the name of the department in which the degree is granted. In the "Any field" dropdown menu, select Author/Creator. In the "Enter a search term" field, type the University name and department granting the degree. For example, to find dissertations/theses from the Department ...
ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. A comprehensive collection of dissertations and theses from around the world from 1861-present. Full text since 1997. Abstracts since 1980 for doctoral dissertations and 1988 for masters' theses. Citations since 1861.. Citations are indexed in Web of Science in the ProQuest ™ Dissertations & Theses Citation Index collection.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
The Center for Research Libraries reviews all Grad Center ILL requests for loan or demand purchase of UK dissertations. If CRL finds the title accessible through EThOS or that it can be digitized free of charge (in approx 30 days), CRL will notify the requesting institution of its availability via the EThOS online venue. CRL will also place orders via EThOS and alert requestors when a ...
While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length. Note. Sometimes, a research schedule or detailed budget may be necessary if you are pursuing funding for your work.