Free printable resources to help you write better Chinese

Chinese character practice paper containing a grid that resembles the character for rice, 米.
A4 Paper: PDF | PNG US Paper: PDF | PNG

Chinese character practice paper containing a grid that resembles the character for field, 田.

Remove the stabilizers and go freestyle in the empty grid.
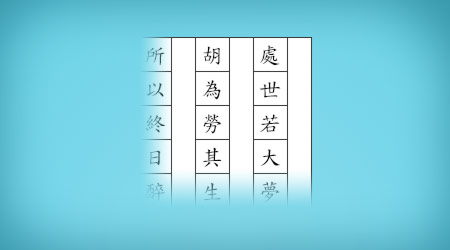

Essay Paper
The standard 20x20, 400 character essay writing paper for knuckling down and writing your Chinese homework.
Another Mandarin Poster Resource
Tag: Essays
Essay: 《不死鸟》the immortal bird by sanmao.
- Post author By Kendra
- Post date March 25, 2023
- 4 Comments on Essay: 《不死鸟》The Immortal Bird by Sanmao
In this tear-jerker essay, famous Taiwanese authoress Sanmao ponders on the value of her own life. It was written as she grieved the drowning of her beloved Spanish husband in 1979, and is all the more tragic in light of her suicide 12 years later.
- Tags Essays
Essay:《爱》Love by Zhang Ailing (Eileen Chang)
- Post date June 12, 2020
- 5 Comments on Essay:《爱》Love by Zhang Ailing (Eileen Chang)
A tragic, dreamlike little essay from writer Zhang Ailing (张爱玲, English name Eileen Chang) about love and destiny. This is one of her more well-known works of micro-prose, written in 1944. HSK 5-6.
Essay:《打人》Hitting Someone by Zhang Ailing (Eileen Chang)
- Post date June 10, 2020
- 1 Comment on Essay:《打人》Hitting Someone by Zhang Ailing (Eileen Chang)
An essay from Chinese lit diva Zhang Ailing about a scene of police brutality she witnessed in Shanghai in the 1940s. HSK 6 and up.
Essay: 《感谢困难》Thanking Life’s Challenges by Lin Qingxuan
- Post date May 19, 2020
- 5 Comments on Essay: 《感谢困难》Thanking Life’s Challenges by Lin Qingxuan
You can skip your Instagram yoga gratitude break today, here’s another one from Taiwanese Buddhist essayist Lin Qingxuan (林清玄). HSK 4-5.
Essay: 《蝴蝶的种子》Seed of a Butterfly by Lin Qingxuan
- Post date May 7, 2020
- 2 Comments on Essay: 《蝴蝶的种子》Seed of a Butterfly by Lin Qingxuan
Taiwanese Buddhist essayist Lin Qingxuan marvels at the wonders of nature, time, space, and reincarnation. This piece is all about awe of the natural world, and you’ll learn some Discovery Channel vocab, like “pupa”, “mate”, “breed”, “spawn”, and lots of animal names.
- Tags Essays , Science
Letter: Ba Jin’s Correspondence with “Young Friends Searching for Ideals” – Part II
- Post date May 5, 2020
- 3 Comments on Letter: Ba Jin’s Correspondence with “Young Friends Searching for Ideals” – Part II
In Part II of this two-part series, we’ll read acclaimed author Ba Jin’s reply to the 10 elementary school students who wrote him a letter asking him for moral guidance in 1987. I’m not a super weepy person, but I legit cried reading this. This is a noble, elevating piece of writing, and reading it, I’m reminded that in all societies, there are those who struggle with the materialism that engulfs us.
Essay:《帮忙》 Helping Out
- Post date May 4, 2020
- 3 Comments on Essay:《帮忙》 Helping Out
In this one-paragraph read (HSK 2-3), Little Brother wants to help dad get ready to leave the house, but his contribution falls flat.
Essay: 《丑石》The Ugly Rock by Jia Pingwa
- Post date April 29, 2020
- No Comments on Essay: 《丑石》The Ugly Rock by Jia Pingwa
Jia Pingwa (贾平凹) is one of China’s modern literary greats, and in this short story, it shows. I don’t know how this guy crammed so many insights on the human condition into a few paragraphs about a rock, but he undeniably did.
Letter: Ba Jin’s Correspondence with “Young Friends Searching for Ideals” – Part I
- Post date April 27, 2020
- No Comments on Letter: Ba Jin’s Correspondence with “Young Friends Searching for Ideals” – Part I
In the first of a two-part post, we’ll look at a letter sent in 1987 from a group of elementary school students to the anarchist writer Ba Jin (most famous for his 1931 novel The Family) as they struggle to cope with China’s changing social values. In Part II, I’ll translate Ba Jin’s reply.
Essay: Desk-chairs of the Future
- Post date May 28, 2014
- 15 Comments on Essay: Desk-chairs of the Future
This kid was asked to imagine the perfect desk-chair of the future – what it would look like, and what it would do – and boy, does he ever. The chair turns into all kinds of utopian machinery. It flies, it helps you sleep, and it carries your books to school. Sentence structure is pretty […]
Essay: Catching Frogs
- Post date May 7, 2014
- 52 Comments on Essay: Catching Frogs
Though this post is beginner-level, it’s also very condensed. I’d say you’ll have to stop and remind yourself what something means every few words or so.
Essay: My First Telephone Call
- Post date June 11, 2013
- 24 Comments on Essay: My First Telephone Call
Though the conclusion of this essay might fall a bit flat for all of us who are very used to having a telephone, this is an interesting glimpse into what a monumental rite of passage it is for children in rural areas to have one or use one for the first time.
Essay: Papa, Please Don’t Smoke!
- Post date June 3, 2013
- 17 Comments on Essay: Papa, Please Don’t Smoke!
In this essay, a child desperately (and very angrily) pleads their father not to smoke. Though this is classified as “Intermediate”, beginners should definitely try this read, leaning heavily on the hover word-list. The difficult parts are the mid-level turns of phrase, which are all explained below.
Guest Post: The exam of life
- Post date May 6, 2013
- 26 Comments on Guest Post: The exam of life
Well well well, lookie here. A guest post! Today we’ll be reading Rebecca Chua’s (Chinese name: 蔡幸彤) translation of an essay from her textbook. The post is about the rewards of honesty. I remember my own textbook being full of these types of essays, so thank you, Rebecca, for the traditional read.
My Gluttonous Elder Brother
- Post date January 8, 2013
- 10 Comments on My Gluttonous Elder Brother
I set out to do a beginner post since I haven’t done one in a while, but no joy, I think I have to classify this as intermediate. Beginners are welcome to try this out, as most of the words are simple and the subject matter is a bit immature (so of course it totally […]
News: Snowstorm has caused 15 deaths and 2000 flight delays or cancellations
- Post date January 2, 2013
- 8 Comments on News: Snowstorm has caused 15 deaths and 2000 flight delays or cancellations
In the spirit of the holiday season, which is winding to a blissfully overweight close, I give you an article about something you may or may not have just struggled through if you flew home for the holidays (which I did).
Our Family’s Jump Rope Contest
- Post date October 2, 2012
- 17 Comments on Our Family’s Jump Rope Contest
A single-paragraph essay about the results of a family jump rope competition.
After I Got My New Years’ Money
- Post date September 10, 2012
- 20 Comments on After I Got My New Years’ Money
For those of you new to Chinese culture, one thing a Chinese child most looks forward to all year is the time during Spring Festival (Chinese New Year) when they get to go ask their neighbors and other adults for red envelopes containing some money – it’s a bit like trick-or-treating for cash. This essay […]
Essay: A Foolish Affair from my Childhood
- Post date August 29, 2012
- 20 Comments on Essay: A Foolish Affair from my Childhood
This essay is about a kid who takes his father’s advice a little too literally (with amusing results).
Dear Diary: Mama Please Believe Me
- Post date May 3, 2012
- 18 Comments on Dear Diary: Mama Please Believe Me
And now a break from all the intermediate and advanced exercises I’ve been posting lately. This one is a straightforward beginner Chinese diary-style essay about a student whose mother is displeased with his (or her, it’s never clarified) homework.

How to Write a Chinese Essay
Dec 16, 2020 | Guest Blogs & Media
The more essays you write, the better you get at communicating with Chinese. To write a good essay, you first have to reach a high language mastery level.
Do you admire the students who write seamless Chinese essay? If you do, then you should know that you too can achieve this level of proficiency. In the meantime, don’t be afraid to pay for your essay if you cannot write it on your own. Online academic writers are a resource each student should take advantage of.
Here are tips to help you get better at writing essays in Chinese.

Learn New Chinese Words
The key to communicating in a new language is learning as many words as you can. Take it upon yourself to learn at least one Chinese word a day. Chinese words are to essay writing what bricks are to a building. The more words you have, the better you get at constructing meaningful sentences.
Case in point, if you’re going to write a Chinese sentence that constitutes ten words, but you don’t know the right way to spell three of those words, your sentence might end up not making sense.
During your Chinese learning experience, words are your arsenal and don’t forget to master the meaning of each word you learn.
Read Chinese Literature
Reading is the most effective way of learning a new language. Remember not to read for the sake of it; find out the meaning of each new word you encounter. When you are an avid reader of Chinese literature, nothing can stop you from writing fluent Chinese.
In the beginning, it might seem like you’re not making any progress, but after a while, you will notice how drastically your writing will change. Receiving information in Chinese helps your brain get accustomed to the language’s sentence patterns, and you can translate this to your essays.
Be extensive in your reading to ensure you get as much as possible out of each article. Remember that it’s not about how fast you finish an article, but rather, how much you gain from the exercise.
Translate Articles from your Native Language to Chinese
Have you ever thought about translating your favorite read to Chinese? This exercise might be tedious, but you will learn a lot from it. The art of translation allows you to seamlessly shift from one language’s sentence pattern into the other. The more you do this, the easier it will be for your brain to convert English sentences into Chinese phrases that people can comprehend.
You can always show your Chinese professor your translations for positive criticism. The more you get corrected, the better you will get at translation. Who knows, you might actually like being a translator once you graduate.
Final Thoughts

by Adrian Lomezzo
Adrian Lomezzo is a freelance writer. Firstly, he has been developing as a content manager and working with different websites, and the main goal of his was to develop the content making it in the first place. Secondly, Adrian had a big desire to help students and adults in self-development in this field and teach them to improve their skills. As a lover of traveling, he did not want to be in one place, and became a writer who could be closer to everyone, and share precious information from the corners of the world.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Other posts you might like

Congratulations That’s Mandarin Winter 2022 Graduates
Mar 31, 2022 | Beijing , News
We’re so excited and proud to see our students achieve goals and improve their Chinese skills at That’s Mandarin. We know how hardworking and diligent you are and we are happy to go through this incredible and at times difficult process of learning Chinese together...

News: NihaoKids Website Is Live!
Mar 3, 2022 | News , Online
A modern place for your children to learn Mandarin Chinese.

Mahjong Night Recap (Feb 23)
Feb 24, 2022 | Beijing , News , Shanghai
The best moments of Mahjong Night!
Get 2-week FREE Chinese Classes
Original Price: ¥ 600


Grammar , Vocabulary
Useful Chinese Essay Phrases
July 8, 2020
By Ellen

Nowadays, many international students have decided to study abroad, and China has become a highly popular destination. In universities, essay writing is a basic skill and the “Academic Writing” lectures are always attracting many students to attend.
Here we have summarized some “all-purpose” phrases and sentences which hopefully you would find useful.
Chinese Essay Phrases Used in Abstracts
The abstract should explain the purpose, method, results, and conclusion of your research, also highlighting the new ideas that you proposed; and do remember to keep your language concise while writing. The purpose of the abstract is to conclude and summarize the main contents of your essay so that the reader could have a brief understanding without having to read the entire paper. Chinese abstracts are usually around 200 characters.
Research Background, Significance, and Current Situation
Extremely useful/badly needed/affecting people’s lives (1-2 sentences)
Proposing the Object of Study
Played a very important role (1-2 sentences)
Purpose of the Study or Study Aim
The role of A in B, perhaps remains to be seen (1 sentence)
Research Methods and Results
Through what means/technique/experiment we achieved what result (several sentences)
Research Results
The phenomenon of A in B, shows what the function of B is, theoretical and applied value (1-2 sentences)

via Pixabay
Chinese Essay Phrases: Main Body
The main body includes the introduction and the main text. The introduction section could use similar phrases that we have just listed, focusing on research objects and purposes. The main text should include research methods, research results, and discussion. Writers should keep their sentences to the point and avoid rambling, also avoid using too much subjective perspective discourses, which shouldn’t be used as arguments as well.
Theoretical Basis, Approaches, and Methods
To express opinions, to emphasis, transitional expressions, chinese essay phrases: conclusion.
At the ending section of the paper, the writer should provide an objective summary, list out the future research objectives and directions, and perhaps look into the future. Keep optimistic even if your experiment results were negative.
Research Impact and Value
There you go. We hope this article helps you write amazing essays. Best of luck!
Ellen is a language specialist from China. She grew up in the US and received a master’s degree from the St Andrews University of UK. The multicultural experiences attributes to her understanding of the differences and similarities between the English and Chinese language. She currently works as an editor specialized in Language learning books.
related posts:
Must-Try Authentic Chinese Dishes
15 must-watch chinese movies for language learners, best chinese music playlists on spotify, get in touch.
Free printable Chinese character writing grids
Download these FREE Chinese character writing grids in three different sizes and three different styles.
Sign up to receive the latest updates, collections and worksheets sent directly to your inbox.
Chinese Radicals provide helpful hints to the meaning and sound of many characters. Learning the most common Chinese Radicals will help you memorize and recall Chinese characters faster! Don't wait! Learn these radicals now to start learning Chinese faster!

Large Writing Grids
These large Chinese Character writing grids are great for learners who are just getting started writing simplified and traditional Chinese characters.

Medium Writing Grids
These medium Chinese Character writing grids are great for transitioning from the large grids to the smaller grids for practicing your simplified and traditional Chinese characters.

Small Writing Grids
These small Chinese Character writing grids are great for more experienced writers practicing small versions of your simplified and traditional Chinese characters.

- Collections
- The Fine Print
© 2021 WriteMandarin • All rights reserved.

Improve Chinese Essay Writing- A Complete How to Guide
- Last updated: June 6, 2019
- Learn Chinese
Writing can reflect a writer’s power of thought and language organization skills. It is critical to master Chinese writing if you want to take your Chinese to the next level. How to write good Chinese essays? The following six steps will improve Chinese essay writing:
Before You Learn to Improve Chinese Essay Writing
Before you can write a good essay in Chinese, you must first be accustomed with Chinese characters. Unlike English letters, Chinese characters are hieroglyphs, and the individual strokes are different from each other. It is important to be comfortable with writing Chinese characters in order to write essays well in Chinese. Make sure to use Chinese essay writing format properly. After that, you will be ready to improve Chinese essay writing.

Increase Your Chinese Words Vocabulary
With approximately 100,000 words in the Chinese language, you will need to learn several thousand words just to know the most common words used. It is essential to learn as many Chinese words as possible if you wish to be a good writer. How can you enlarge your vocabulary? Try to accumulate words by reading daily and monthly. Memory is also very necessary for expanding vocabulary. We should form a good habit of exercising and reciting as more as we can so that to enlarge vocabulary. Remember to use what you have learned when you write in Chinese so that you will continually be progressing in your language-learning efforts.
Acquire Grammar,Sentence Patterns and Function Words
In order to hone your Chinese writing skills , you must learn the grammar and sentence patterns. Grammar involves words, phrases, and the structure of the sentences you form. There are two different categories of Chinese words: functional and lexical. Chinese phrases can be categorized as subject-predicate phrases (SP), verb-object phrases (VO), and co-ordinate phrases (CO). Regarding sentence structure, each Chinese sentence includes predicate, object, subject, and adverbial attributes. In addition, function words play an important role in Chinese semantic understanding, so try to master the Chinese conjunction, such as conjunction、Adverbs、Preposition as much as you can. If you wish to become proficient at writing in Chinese, you must study all of the aspects of grammar mentioned in this section.
Keep a Diary Regularly to Note Down Chinese Words,Chinese Letters
Another thing that will aid you in becoming a better writer is keeping a journal in Chinese. Even if you are not interested in expanding your writing skills, you will find that it is beneficial for many day-to-day tasks, such as completing work reports or composing an email. Journaling on a regular basis will help you form the habit of writing, which will make it feel less like a chore. You may enjoy expressing yourself in various ways by writing; for instance, you might write poetry in your journal. On a more practical side of things, you might prefer to simply use your journal as a way to purposely build your vocabulary .
Persistence in Reading Everyday
In addition to expanding your view of the world and yourself, reading can help you improve your writing. Reading allows you to learn by example; if you read Chinese daily, you will find that it is easier to write in Chinese because you have a greater scope of what you can do with the vocabulary that you’ve learned. Choose one favorite Chinese reading , Read it for an hour or 2,000 words or so in length each day.
Whenever you come across words or phrases in your reading that you don’t understand, take the time to check them in your dictionary and solidify your understanding of them. In your notebook, write the new word or phrase and create an example sentence using that new addition to your vocabulary. If you are unsure how to use it in a sentence, you can simply copy the sample sentence in your dictionary.
Reviewing the new vocabulary word is a good way to improve your memory of it; do this often to become familiar with these new words. The content of reading can be very broad. It can be from novels, or newspapers, and it can be about subjects like economics or psychology. Remember you should read about things you are interested in. After a certain period of accumulation by reading, you will greatly improve your Chinese writing.
Do Essay Writing Exercise on a Variety of Subjects
As the saying goes, “practice makes perfect.” In order to improve your China Essay Writing , you should engage in a variety of writing exercises. For beginners, you should start with basic topics such as your favorite hobby, future plans, favorite vacation spot, or any other topic that you can write about without difficulty.
For example :《我的一天》( Wǒ de yì tiān, my whole day’s life ),《我喜欢的食物》( Wǒ xǐhuan de shíwù, my favorite food ),《一次难忘的旅行》( yí cì nánwàng de lǚxíng, an unforgettable trip ) etc.
Generally the writing topics can be classified into these categories: a recount of an incident,a description of something/someone, a letter, formulate your own opinion on an issue based on some quote or picture etc.
Takeaway to Improve Chinese Essay Writing
Keep an excel spreadsheet of 口语(Kǒuyǔ, spoken Chinese) –书面语(Shūmiànyǔ, written Chinese) pairs and quotes of sentences that you like. You should also be marking up books and articles that you read looking for new ways of expressing ideas. Using Chinese-Chinese dictionaries is really good for learning how to describe things in Chinese.

Online Chinese Tutors
- 1:1 online tutoring
- 100% native professional tutors
- For all levels
- Flexible schedule
- More effective

Qin Chen focuses on teaching Chinese and language acquisition. She is willing to introduce more about Chinese learning ways and skills. Now, she is working as Mandarin teacher at All Mandarin .
You May Also Like

This Post Has 3 Comments
When I used the service of pro essay reviews, I was expecting to have the work which is completely error free and have best quality. I asked them to show me the working samples they have and also their term and condition. They provided me the best samples and i was ready to hire them for my work then.
This is fascinating article, thank you!
Thank you so much for sharing this type of content. That’s really useful for people who want to start learning chinese language. I hope that you will continue sharing your experience.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Guide to Writing Your First Mandarin Essay
When you want to be able to make writing your first Mandarin essay nice and easy, it pays to put plenty of thought and effort into the preparation. As the old saying goes ‘fail to prepare, prepare to fail.’ To give you plenty of food for thought we’ve put together everything you need to know to get things moving. All you need to do is work through the following steps, and you’ll be submitting your essay in no time at all.
Check you understand the basics
There are so many things you have to think about when writing an essay, particularly when it’s not in your native language. But as with any cognitively demanding task, the process for getting started is always the same. Check you understand the following basics and you’ll be heading in the right direction:
- Do you know what the question means?
- Have you made a note of the final submission date?
- Make sure you read some past examples to get a feel for what’s expected of you
- Do you understand the question that has been set?
- Do you know who you can talk to if you need advice along the way?
- Are there any restrictions on the dialect you should be aware of?
Once you can write the answers to the above down on a single side of the paper, you are ready to tackle the main part of the problem: putting pen to paper.
Set aside time to write
The chances are that you’re not going to be able to pen the entire essay in a single sitting, and that’s okay. It’s nothing to be ashamed of or to worry about, and it’s natural that you need to work across multiple days when writing your first essay.
If you want to be able to make great progress, the most important thing is sticking to a routine. You need to have consistency in your application, and you need to be able to know when you are at your most productive. It’s no good staying up late one night and then carrying on early the next morning. You’d be far better off writing for the same amount of time but on two successive afternoons. Think about how your studies fit in with the rest of your daily life, and then choose the time that seems most appropriate. If you box it off and decide it’s only for writing, you’ll be in a great routine before you even know it.
Clear space so you can focus
As well as having time to write each day, you need a place to write too. The world is full of distractions (most of them are digital and social) so that means you’re going to want to keep yourself to yourself, and your phone in a different room. It might seem a little boring or uncomfortable at first, but you need to practice the habit of deep work. It’s what will allow you to create the most in the shortest time — ideal if you want to have plenty of time leftover to spend doing the other things that matter to you.
Have a daily word count in mind
Telling yourself that you want to write an essay today is one thing, but if you’re really going to push yourself to stick to your goal then you need to get quantitative. If you have a word count in mind that you need to hit, then it will prevent you from giving up and throwing in the towel the minute you start having to think and concentrate more than feels normal. Just like working out in the gym, it’s the temporary moments of extra effort that really drive the big differences. It’s when you’ll see the biggest improvement in your writing ability, and the lessons you teach yourself will stay with you for years to come. Ideal if you want to become a fluent Mandarin writer, as well as an engaging face-to-face speaker.
Read widely to provide context
When you’re immersed in an essay it can be all too easy to become blinkered and fail to pay attention to everything else that’s going on around you. Of course, you want to be focused on the task at hand, but you don’t want to be single-minded to the point of ignoring other great learning resources that are just a click away.
Reading widely is one of the best ways to improve your essay writing because it exposes you to techniques and approaches used by the best of the best. You’re not expected to be able to instantly write like a native speaker after an hour of reading. But what you will be able to do with consistent application is build up confidence and familiarity with written Mandarin. Over time this will reflect on the quality and depth of your writing as you gradually improve and take onboard lessons you’ve learned.
Take a break before you proofread
Last but not least, you need to remember that essay writing is a marathon, not a sprint. It’s all about taking the time to get things written before you hand them in, not racing through to try and finish on time. If you want to get the most out of your writing you need to take a day off between finishing your draft and proofing it. That way your brain will have had plenty of time to reflect on the work you’ve produced, and you’ll be able to spot many more little mistakes and places for improvement than you would if you proofed right away.
Final Thoughts
Writing Mandarin is a challenging task that will test your language skills and make you think hard about how to apply what you’ve learned so far. It might be slow going to begin with, but that’s great as it means you’re pushing your limits and building on your existing skills. If you want to be able to master Mandarin, you need to persevere and stay the course. Once you do, you’ll start to improve a lot faster than you expect.
By Diana Adjadj | A Super Chineasian
You may also like

Dance into Language: 10 Essential Chinese Dance Words

Explore Earth: 10 Must-Know Chinese Words

Exploring 10 Food Words: Chinese Mandarin vs. Taiwanese Mandarin
Tell your chineasy stories.

Subscribe to our Newsletter
Copyright © 2024 Chineasy. All rights reserved.
- Be a Member
- English French Chinese
- General Chinese learning tips
How to Write a Good Chinese Essay
Posted by Lilian Li 17816
For any kind of language, the essay is the most difficult thing to do in the exam. Generally speaking, writing articles is just to tell a story, after you make the story clear, the article also is finished. But it also different with speaking. A good article is like a art, is worth for people to appreciate, to taste. But how to accomplish such a good art? I think the most important thing is the three points: attitude, subject matter, emotional.
A good beginning is half done. For writing, material selection and design are not the start. The most important thing still is to adjust their mentality as well. When you decided to write, then dedicated yourself to write, not half-hearted, and your thinking nature won't be upset. Once the train of thought was interrupted, your speed will be slow and the point will be word count. So how can you write down a interesting article with a good quality? All in all, attitude is can decide the success or failure of the articles.
Subject is the biggest problem in our writing. It is from life, but not all people can observe life, experience life. The only point is to write the true things, maybe not so tortuous plots, but can write a really life. Moreover, when you get the subject, there are some tips for students to pay attention:
1. Make the topic request clear: The article should around the topic, pay attention to the demand of genre and number of words, some restrictive conditions and avoid distracting, digression.
2. Determine the center, choose the right material. To conform to the fact that a typical, novel, so it’s easy to attract the attention of people.
3. Make a good outline, determine the general, write enough words.
4. Sentence writing smooth, there is no wrong character, no wrong grammar in article.
Emotion, it is very important. If we compared an article to be a human. So emotion is his soul. Man is not vegetation, when they meet something, there must be personal thoughts and feelings. Sometimes it also tend to have their own original ideas. If you can put your own thoughts, feelings and insights into the article, then this article will be very individual.
Chinese essay is not just meaning some simple Chinese characters and make a simple sentences, it needs the Chinese grammar and sentence structure, if you don't familiar with Chinese grammar, you can learn our Chinese grammar course .
At last, adhere to write diary at ordinary times, it can practicing writing. Try to read some good articles, good words and good paragraphs with a good beginning and end. Learn to accumulate and draw lessons from them.
If you are interested in our Chinese grammar course, you can try our one online free trial , you will enjoy it.
About The Author
Related articles.
Free Trial

Self-test

Concat Us

Chat online
Share Us
Want to receive regular Chinese language tips & trivia?

Chinese Literature: Essays, Articles, Reviews (CLEAR) is published annually.
CLEAR journal is a leading resource for Chinese Literature academic discussion worldwide and has been published for over 30 years.
Click below for two most recent CLEAR journal Table of Contents.
CLEAR History
CLEAR was created based on discussions between eight scholars‒Eugene Eoyang, Joseph S. M. Lau, Leo Ou-fan Lee, Wu-chi Liu, Irving Lo, Ronald Miao, William H. Nienhauser, Jr., and William Schultz‒from the universities of Arizona, Indiana and Wisconsin spread over the early months of 1977. The journal was formally launched at a meeting on 18 March 1977 in Irving Lo’s living room in Bloomington, IN. Over the next year the founding editors, Eoyang and Nienhauser, received grants from the American Council of Learned Societies, the Association for Asian Studies, and the three affiliated universities as well as from members of the original editorial board (especially Elling Eide and Irving Lo) and individuals (especially Nancy C. Ing), allowing the production of the first two issues in 1979. Over the years CLEAR has published symposia, essays, articles, reviews and occasional forums on all aspects of traditional and modern Chinese literature. It is still the only western-language periodical devoted to Chinese literature. Having gained a worldwide reputation and audience, CLEAR now appears annually in December under the direction of editors Haun Saussy, Michelle Yeh and Rania Huntington.

Characters on the website were written by Chow Tse-tsung (1916-2007). Copyright © 2012-2024 by CLEAR | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) #0161-9705
Hacking Chinese
A better way of learning mandarin, 36 samples of chinese handwriting from students and native speakers.
Unlike most other languages, handwriting in Chinese can be regarded as a separate skill. Learning to write by hand is not easy; learning to write well is even harder. In an earlier article, I discussed handwriting in details, including how to improve it as a student.
How to improve your handwriting in Chinese
I have collected more than thirty examples of handwriting in Chinese, most of them from students of different ages from various countries across the world. I also gather some examples from native speakers to show as a reference.
The examples below are presented roughly in the order of time spent learning the language, with beginners at the start and native speakers at the very end. Counting study time in years can be very misleading , but since there is no better way of sorting the samples, I chose to do that anyway.
The purpose of this article is not to make a systematic study of student handwriting, although that would be interesting. Apart from time spent learning, another important factor is what the student’s writing looks like in her native language. I have seen enough student handwriting to feel confident when I say that there’s a lot of positive transfer going on, so someone who writes neatly in their native language are likely to write neatly in Chinese too. Beginners of this kind might write neatly but with incorrect strokes and so on, but penmanship still carries over to learning Chinese.
Speaking of penmanship, it should be mentioned that there is probably a strong selection bias at work here. While not all who submitted their handwriting write well, I think it’s safe to assume that people who like handwriting are more likely to have submitted photos of their handwriting when I asked for it. In other words, the average student probably writes worse than the below photos show.
Chinese handwriting from 36 people, using exactly the same tex

Escape: A text adventure game for Chinese learners
Simplified Chinese:
你被关在一个小房间里。你并不记得发生了什么,也不知道为什么被关在这里。你以前从房门的窗口那儿得到食物,但是你用力敲门或者大叫都没有用。你决定一定要逃跑,要不然情况可能会变更不好。
Traditional Chinese:
你被關在一個小房間裡。你並不記得發生了什麼,也不知道為什麼被關在這裡。你以前從房門的窗口那兒得到食物,但是你用力敲門或者大叫都沒有用。你決定一定要逃跑,要不然情況可能會變更不好。
A big thank you to everyone who contributed!
Chinese handwriting after a year of studying (or less)
The first submission comes from the US, and also include some information about the student. I collected some submissions years ago, so “since the beginning of 2016” actually means less than a year of studying!

August from Suriname submitted the below sample. He’s 71 and has studied Chinese for one year.

Thomas Walker on Twitter writes: “Here is my effort. Been studying Chinese for about 8 months. Your site has been a massive help, keep up the good work!”

Chinese handwriting after studying between one and five years
A student from the US sent in the below photo of his handwriting, saying that he’s 51 years old and has been learning Chinese for a little more than one year.

This is from a 22-year-old Belgian student. She has been studying Chinese for little more than a year:

The next submission is from a 27-year-old Bulgarian student who has studied Chinese for three semesters in Wuhan:

From @fenma on Twtitter : “two years, self, no class, no visit, HSK3”:

A student from France submitted the following sample, saying “I’m around HSK3, with two years living in China where I self practiced writing despite everybody telling me it’s useless (it’s not; it was super useful every single day, whether teaching my Chinese pupils or writing some unknown OCR resistant character in the street in Pleco). I would practice every day with a cheap calligraphy marker (to force myself to write slowly and purposefully; the difference with using a pen/pencil is like night and day, for learning purposes) in a 10RMB kids hanzi practice book bought in Carrefour and I could totally feel the difference very quickly. I used a pen and wrote as fast as I could to give you something a bit more realistic.”
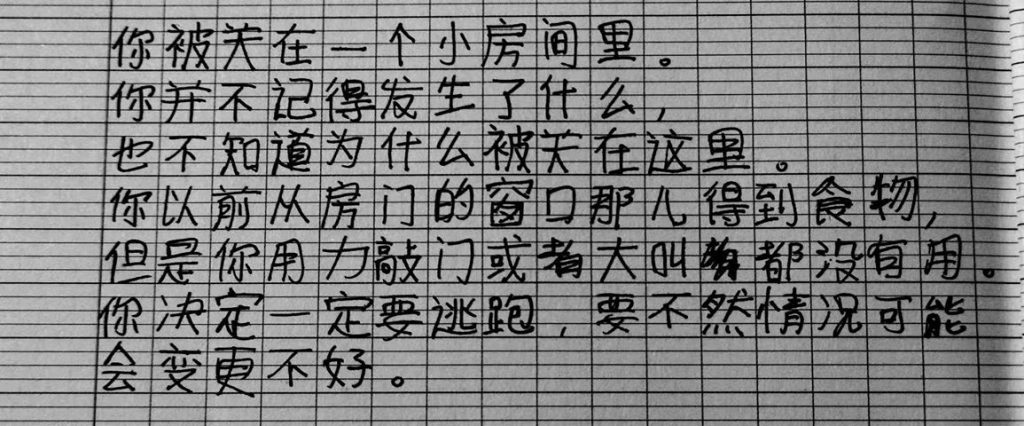
Next is a sample from a Peruvian student. She’s 24 and has studied Chinese for roughly three years:

The last sample in this category comes from 35-year-old Norwegian, who has studied four years of Chinese, mostly self-studying:

Chinese handwriting after having studied for five to ten years
Dr. Chuck on Twitter writes: “I haven’t tried learning how to speak it yet, but I’ve studied the traditional writing for fun in my spare time over the past 5 years. My closet is a graveyard of graph paper!”

Joey on Twitter writes: “I’ve been studying for a little over 5 years now. Hope this helps!”

MissFitti on Twitter writes: “I have been learning Mandarin for my BA and MA in Italy and I am now teaching it at Secondary in England. 5 years at uni in total, and lived in china for 1 year and 6 months :)”

A student from Scotland sent me the below sample of his handwriting. He says he’s been working in China for over five years, and have studied Chinese, but had very little teaching on how to write characters. Just like the rest of us, he mainly uses phones and computer for writing Chinese:

A student from the US submitted the below photo with this comment: “I have been studying, and I use the word studying loosely, Chinese for about 5-6 years. […] My reading skills far outweigh my listing, speaking, and as you can see from my attached text, writing skills. […] Thanks for all you do. I truly appreciate you.”

Brandon Rivington on Twitter writes: “I tried to make it as natural as possible. I’ve been studying Chinese for about 7 years. I look forward to reading the article!”

The next sample comes from a 36-year-old student from Spain, who has learnt Chinese for about nine years:

And another submission from Spain, from someone who is two years younger, but has also studied for about nine years:

A Polish student submitted the below photo of his handwriting and said: “I’m 24 years old and I’ve been learning Chinese for about 9 years. 3 years ago I passed HSK5 and I’m planning to pass HSK6 the next year.”

Chinese handwriting after studying for ten years or more
Anna K. on Twitter writes: “Studied Chinese 10+ years, taught it one year. Thanks for your excellent blog and work!”

Here’s a submission from Melbourne, Australia (information included). She has been learning for 12 years.

TranslationRaven writes on Twitter: “Studied Chinese for 12 years in school, didn’t read or write for 8 years after that. Returned to Asia and got my teaching diploma in Chinese after those 8 years. Not sure how I’d categorize myself, haha”

Miriam from Germany submitted the below sample:

David Hull 胡大衛 on Twitter writes: “Always been very self-conscious about my sloppy handwriting. Picked up Chinese late- in my mid 20s. Studied in PRC and US. I haven’t been writing by hand for years (except on the blackboard). I’m an asst Prof of Chinese now. Started in the army program at the Defense Language Institute in ’96 (we didn’t do much writing at all). I didn’t have a chance to formally study again until ’01, and by then it was almost all typed.”

The last sample in this category comes from the US. She has 26 years of formal and informal studying behind her:

Chinese handwriting from native speakers
Now, let’s move on to native speakers. For people who find some of these difficult to read, please check this article for some advice on how to proceed: Learning to read handwritten Chinese
Learning to read handwritten Chinese
A student, who grew up speaking Chinese with her mother and took a few years of Chinese in school, but then forgot most about it, sent in the following sample. She also writes that “this may be the most I’ve ever written by hand, I do everything digitally now, I practice my writing skills by writing to my mother on my cellphone.”

Vicky Lee on Twitter writes: “I am a little bit shamed to write the Chinese like this? It is only recognizable but far from being beautiful.”

Female native speaker, 30 years old:

This is from a 22-year-old native speaker (male):

A native speaker from China, submitted this through Facebook Age ~50. “You are very appreciated to promote Chinese culture.”

A native speaker who grew up in Malaysia, now in her fifties:

And another native speaker from Beijing (male, around 50):

Here’s another native speaker who teaches English near Shanghai (age unknown):

Native speaker, female, age around 50:

Native speaker, age unknown:

And an extra submission, provided after the article was published, so actually number 37: “Age 28, live in China mainland, written by Lamy Safari”, originally posted here .

Conclusion: Chinese handwriting in the 21st century
I’m not sure if any conclusion can be drawn from the samples shown above; that wasn’t really the intention. If you have some thoughts you want to share after checking them out, please leave a comment!
How good your handwriting is depends on many things, including how good your penmanship is in your native language. Time spent practising and how much you care are two other important factors. If you don’t think your handwriting is very good because you haven’t practised enough, that’s nothing to be ashamed of. In this electronic era, writing neatly by hand is not an essential skill for most students.
For those of you who want to improve your handwriting, I conclude here by linking to the previous article :
https://www.hackingchinese.com/how-to-improve-your-chinese-handwriting/

16 comments
The actor 黄轩 posts poems handwritten by his fans on 微博 the blog is called 瞬间MomentX, I find handwritten notes or artistic shop signs very difficult to read
This is fascinating! Thank you so much for this compilation. There’s something very touching about seeing hand-written notes, it’s hard to explain.
Most of the learners’ notes are easy to read, but on the other hand some of the natives’ notes are hard to decipher for the non-native eye. It can’t only be a question of speed, surely…
Thomas Walker is by far the best, in my opinion.
I totally agree. I would be interested to learn his methods. Pen thickness seems to be a major factor. Depending on the day, I can write well with a 0.4mm pen, other days, I need a 0.7mm one.
Thomas Walker’s is awesome – but the Australian teacher lady is really impressive, too (and she’s not working on handwriting grid paper.) Her English handwriting looks exactly like a teacher – she’s obviously used to being very tidy in her writing.
Maybe their chinese handwriting is correlated to their english handwriting. They seem to have similar style.
Yes, that’s a good point. I realised too late that I should have asked people to write the same passage in English as well.
Native here. Yes, our Chinese handwriting and English handwriting (that is, for those of us who can write English) pretty much correlates to each other in style
Age 28, live in China mainland, written by Lamy Safari:
https://igonejack.blogspot.com/2020/01/sample-of-chinese-handwriting.html
Thank you for your submission! I added your writing to the article and I will also mention it on social media, including a link to your page.
Hi, I’m studying in the UK and I have a few people I know from China. I’ve seen what they write a couple of times … it’s some kind of horror. I mean that it is very difficult, I do not envy them. Recently, I read an essay about stereotypes, and still, I will say that they are so true. People who have studied Chinese, tell me how long you have been learning this beautiful language, how long you have been learning to write in Chinese because as far as I understand, one wrong dash and you are writing about something completely different. This is tin, the most difficult language.
Learning to read and write Chinese characters certainly takes a long time, probably longer than learning any other written language. However, we don’t have to exaggerate the difficulty. A misplaced stroke will almost never influence the comprehensibility of what you write. There are specific cases where certain characters differ only in one stroke (position, length, relationship to other strokes), but these aren’t very common, and in context, it’s practically never an issue. That doesn’t make the writing system easy to learn, but it’s not impossible!
As a native Chinese/Cantonese speaker, I can conclude that people who learn Chinese writes better than natives haha
The range of handwriting among the two groups certainly overlaps! I think this is because penmanship is a completely different skill from other aspects of writing (such as composition). I have had beginner student of Chinese who write very good-looking characters from day one, although of course they still struggle with things that require knowledge of characters, such as how long certain strokes should be, which strokes should touch or cross certain other strokes and so on.
These all say the exact same thing, and it doesn’t make sense, or seems like a crazy person wrote it. If you’re going to scam people, put more effort into it.
I’m afraid I don’t understand your comment. They’re all the same because I asked people to write a specific passage; the first subheading even says “Chinese handwriting from 36 people, using exactly the same tex”, so what did you expect? The whole point is to use the same text so people can compare how different people write the same thing. Also, what scam?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
Chinese Writing Paper Proudly maintained by Dofufa Labs .

Printable Paper Templates
Sometimes it can be hard to get the simple things that you need like graph paper or even basic rule paper. For whatever the reasons are, we have you covered. Sino-Exchange offers a number of printable paper templates that you can download, print, and use in your class on a moment’s notice.

Chinese Paper Templates
Chinese writing paper templates for essays, calligraphy, or writing practice.
Chinese Essay Template
Chinese Character Writing Practice (for elementary school students)
Chinese Character Writing Practice (for middle school students)
Chinese Character Writing Practice (for high school students)

Design Templates
These design templates are great for architectural design, engineering, or a wide variety of classes where you need students to complete isometric or orthographic drawings.
A4 Dot Grid Template (Horizontal)
A4 Dot Grid Template (Vertical)
A4 Isometric Grid Template (Horizontal)
A4 Isometric Grid Template (Vertical)
A3 Dot Grid Template (Horizontal)
A3 Isometric Grid Tempalte (Horizontal)

Graph Paper
Select from a variety of graph paper templates that use either metric or imperial measurements for use in your class. These templates are great for math and science classes.
A4 Imperial 4 Index Graph Paper Template
A4 Imperial 8 Index Graph Paper Template
A4 Metric 2mm Grid Graph Paper Template
A4 Metric 2mm Dot Graph Paper Template
A4 Metric 5mm Grid Graph Paper Template
A4 Metric 5mm Dot Graph Paper Template
A4 Metric 5mm Isometric Graph Paper Template

Math Templates
Select your choice of metric or imperial graph paper to use in your class. These templates are great for math and science classes.
Domain & Range (9up)
Graphing Activity (4 up)
Graphing Activity (1 up)

Ruled Note Paper
A4 Ruled Paper (high school) Blank
A4 Ruled Paper (high school) With Project Leader
A4 Ruled Paper (middle school) Blank
A4 Ruled Paper (middle school) With Project Leader

Project Resources
Project Folder
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)

Chinese Americans
- Citing Chinese-language Resources
- Books & Articles
- Online Archives
- Communities and Organizations
- Chinatowns around the world
General Guidelines
Citing Chinese-language materials follows all the same principles as citing English-language resources . Differences arise from the fact that Chinese is written in a non-Roman script. See below for instructions and resources pertaining to the three most commonly used citation styles.
APA (American Psychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources within the social and behavioral sciences. For non-Roman scripts, you must:
- Provide a transliteration of the script into the English alphabet. APA does not specify the Romanization style, but pinyin is recommended.
- Provide an English translation of the title in brackets.
Title: 中國佛教的社會主義改造
Citation: Xue, Y. (2015). Zhongguo fojiao de shehuizhuyi gaizao [The socialist transformation of Chinese Buddhism]. Hong Kong: Xianggang Zhongwen daxue chubanshe.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. For citations in non-Roman scripts, MLA recommends you include:
- The title in the original script
- An English translation of the title in brackets and
- A transliteration of the Chinese characters in works geared to non-specialists (optional)
These three elements should be included in this order: original characters, then transliteration (if included), then translation.
Citation: Xue, Yu. 中國佛教的社會主義改造 Zhongguo fojiao de shehuizhuyi gaizao [The socialist transformation of Chinese Buddhism]. Hong Kong: Xianggang Zhongwen daxue chubanshe, 2015.
For more information on MLA Citation and how to order entries in non-Roman scripts, see this FAQ entry from the MLA Style Center.
Chicago Style
Chicago-style citation is most commonly used in history papers. There are two main types of citation in Chicago Style: notes and bibliography (preferred in the humanities) and author-date (preferred in the social sciences and sciences) style. Similar to APA and MLA, Chicago asks for:
- A transliteration of Chinese characters (required, using these pinyin transliteration practices from the Library of Congress )
- An English translation in brackets (recommended depending on the audience).
- The original Chinese characters (optional)
Author: 華林甫
Article Title: 清代以來三峽地區水旱災害的初步硏究
Journal Title: 中國社會科學
Citation: Hua Linfu 華林甫. “Qingdai yilai Sanxia diqu shuihan zaihai de chubu yanjiu” 清代以來三峽地區水旱災害的初步硏究 [A preliminary study of floods and droughts in the Three Gorges region since the Qing dynasty]. Zhongguo shehui kexue 中國社會科學 1 (1999): 168–79.
The online version of the Chicago Manual of Style includes Sections 11.102-11.110 on Chinese and Japanese languages.
Chinese-language Citation
There is no standard way to cite sources in Chinese papers. The University of Taipei has published this Chinese-language guide to APA Style.
Further Resources
- How to Cite Asian-Language Sources from the University of British Columbia's wiki.
- Quick Guide on Citation Style for Chinese, Japanese and Korean Sources from the Yale University Libraries (this guide is rich in examples for different formats in APA, MLA and Chicago styles)
- Citing Sources (APA, MLA, ...): In Chinese Papers (中文引證格式) from Hong Kong Baptist University (provides a few examples of style guides to reference)
- << Previous: Chinatowns around the world
- Last Updated: Dec 2, 2022 3:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/ChineseAmericans

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
The Chinese Essay
Edited and translated by David E. Pollard
Reviewed by Charles A. Laughlin MCLC Resource Center Publication (Copyright January 2004)

David E. Pollard, editor and translator. The Chinese Essay . New York: Columbia University Press, 2000. 372 pp. US $65.00, ISBN: 0-231-12118-0 (cloth); US $24.50, ISBN: 0-231-12119-9.
The Chinese Essay is the first anthology to provide a comprehensive introduction to Chinese literary non-fiction prose from earliest times to the present. Comparable collections in print, such as Richard Strassberg’s Inscribed Landscapes: Travel Writing from Imperial China and Sang Ye’s Vignettes from the Late Ming, are restricted to the premodern period, and until now modern essay translations (often Pollard’s) have only appeared scattered in journals like Renditions and Chinese Literature and in more general anthologies like The Literature of the Hundred Flowers , The Columbia Anthology of Modern Chinese Literature , and monographs devoted to individual authors such as Zhou Zuoren and Yu Pingbo. The selections in The Chinese Essay represent most of the best-known Chinese essayists, through some of their most anthologized and well-known works. Never have premodern and modern essays been placed next to each other, and never has the considerable tradition of the modern Chinese essay been presented so richly. Pollard’s effort is commendable, and should be interesting not only to the general reader but a great boon as well to instructors of courses devoted to Chinese literature or to the essay across cultures.
Pollard has translated all of the essays himself. As a much-published translator, and author of A Chinese Look at Literature: The Literary Values of Chou Tso-jen (Zhou Zuoren, the pioneer of the modern Chinese literary essay), there could hardly be a better choice for this task. Not only are the translations faithful to the semantic meaning of the original texts (as far as I can tell), but Pollard’s clipped, dry, and often humorous style is also often perfectly suited to the spirit of the essays presented here. The anthology also includes portraits or photographs of many of the authors as well as their calligraphy or handwriting. Though not numerous, these illustrations very effectively convey the love of writing and the emphasis on personal style that tie together the many phases of the Chinese literary essay’s long tradition.
Because of the infancy of the study of the Chinese essay in English, an anthology like this and its introduction are potentially seminal statements, situating this genre in the field of Chinese cultural studies in general, justifying our interest in it, and pointing the way to avenues of further inquiry. But if The Chinese Essay answers the question, Why publish or read such an anthology?, it does so only meekly. Pollard observes that there has not been a general anthology of Chinese essays published since Herbert Giles’ 1884 Gems of Chinese Literature , so his argument begins from a gap or lack in the representation of a genre. Rather than engage with this lack critically, Pollard goes on to assert two reasons for it, almost as if to justify it, namely, the inherent difficulty of representing and discussing linguistic style in a foreign language (but why should this not have been a hindrance to the translation and circulation of other Chinese literary genres?), and the decline in prestige of the essay in the English-speaking world. Thus, in effect, rather than answering the question of why he is offering this anthology now, Pollard is simply providing convincing reasons why it had not been done before. What is missing from this explanation is why the prestige of the essay in modern and contemporary China, unlike the English speaking world, has not declined. If this book could bring the English reader around to understand the power and agency of the essay in contemporary China, despite all that has been said in our field about the overwhelming importance of fiction, it would create more than enough motivation and capacity to appreciate the importance of the contents of this anthology on its own terms, even for a general reader.
The general reader, moreover, seems to be the main target of this anthology. Yet this general-audience orientation is belied by the inclusion of Chinese characters for authors’ names and titles to works. Indeed those who would benefit from the Chinese characters (most of the likely audience of this collection) will generally want more bibliographical information, as well as some engagement with scholarship in the field such as Yu-shih Chen’s Images and Ideas in Chinese Classical Prose: Studies of Four Masters , Chih-p’ing Chou’s Yuan Hung-tao and the Kung-an School . In addition to a more in-depth and informative introduction, I think the book as a whole could have included more scholarly apparatus, including a less sketchy, multi-lingual bibliography, without harming its appeal to a general audience.
If Pollard assumes anything about his audience, it is that they are familiar with the European prose essay, which I think leaves some room for doubt especially with respect to the younger generations. The European essay was of course an important context for the modern Chinese essay, but Pollard is probably putting unnecessary emphasis on features peculiar to the European tradition (“absence of dignity,” “refining and directing sensibilities to create a polity that was new and particular,” “entertainment value,” [p. xii-xiii] “independence of thought,” [p. 7] etc.) in the effort to define the Chinese essay for the general English reader. It might have been more effective and engaging to discuss what prose essays in China are like and what they are used for, rather than comparing them (often unfavorably) to the European tradition that the reader may not be very familiar with anyway.
After detailing in the Preface negative aspects of traditional Chinese culture and literary conventions that explain why premodern Chinese essays do not resemble those of Montaigne and Bacon, Pollard does go on to list what he feels are some of the positive aspects of the Chinese essay in general: “The qualities are on the one hand common to mankind, on the other particular to Chinese literary arts. The first kind includes the expression of character in the writer, either impressively strong or appealingly weak; the expression of sentiment, usually to commemorate friends and relatives; nostalgia for past times; appeals for justice and compassion; pleasure in diversions. The second kind concerns the musicality of the language, a prime and often, regrettably, the prime requirement for approval.” Then he goes on to explain why musicality cannot be translated. Thus, all of the positive aspects of the premodern Chinese essay that are particular to Chinese literary arts are here lost in translation, and what is left is a variety of expressions of ideas and sentiments. I am not certain, but a general English readership (which has already proven itself lukewarm to Chinese fiction and poetry in translation) may not be inclined to delve into this anthology thus described. Why not say more about the extraordinary personalities and intellectual genius evinced in included works by Tao Qian, Han Yu and Su Shi, Lu Xun, Zhou Zuoren, Feng Zikai and Zhang Ailing? Why not talk about some of the larger cultural themes for which the Chinese essay served as the principal vessel, and which through the essay traditional and modern writing are linked—the cultivation of the art of living, the struggle between transcendent and worldly values, or the contrarian resistance to “political correctness” of every imaginable kind?
In an anthology with such broad coverage but short length, the editor is obliged to explain his principles for selection, and Pollard very honestly acknowledges that it would have been impossible to adhere to a single principle. I applaud his insistence that personal taste—an important theme in ancient and modern essays—was his principal guide. This accounts for his enthusiastic inclusion of essays by Gui Youguang (1506-1571) despite their criticism by the modern essayist Lin Yutang, his exclusion of Lin Yutang’s own essays, and no doubt as well the inclusion of contemporary writer Yu Qiuyu, well-known for his popular, fictionalized imaginings of significant historical moments, over those with strong links to the Republican period essay tradition like Wang Zengqi, Zhang Zhongxing and Ji Xianlin. On the other hand, in his note on sources Pollard states that “the classical prose section consists almost entirely of anthology pieces; they had to be so in order to represent the classical heritage” (369). He also states that he felt he had to include certain perennial classics (both traditional and modern) that may not have been among his favorites, even when they were available in other collections. In saying this Pollard makes it clear that he intends this collection to represent the Chinese essay with some authority and self-sufficiency, which seems out of step with his claim of using personal taste as his guide. Nevertheless, I think the resulting balance between personal taste and the need to reflect the received canon makes for a selection that both makes good reading and a good textbook.
Though Pollard alludes to wide reading in anthologies, the only one he cites is a 1987 publication, implying that anthologies tend to select the same works for each author. I am currently in the midst of a survey of anthologies of premodern essays that so far suggests to me that selections vary significantly across eras (Qing, Republican, Taiwan, Early PRC, recent PRC) for various different reasons. For example, premodern anthologies such as the seventeenth-century Guwen guanzhi generally favor formal essays of serious import that cleave to Confucian values, while more modern collections increasingly favor heterodox views, and include more “individualistic” essays on small, private matters. This is in part due to the gradual acceptance in the late imperial period that informal or casual writing possesses its own aesthetic value that can be appreciated by posterity. Moreover certain Republican period publications such as Shen Qiwu’s 1932 Jindai sanwen chao (A selection of early modern essays), Zhang Dai’s Tao’an mengyi (Dreamlike remembrance) edited with prefaces by Yu Pingbo and Zhou Zuoren, and Shi Zhecun’s 1935 Wanming ershi jia xiaopin (The Late Ming xiaopin: twenty masters) exerted an influence on the modern Chinese essay, and these could at least have been mentioned. The reader who wants to explore the Chinese essay in more detail would have benefited greatly from some guidance as to which anthologies are best, and which exerted the greatest influence.
It is interesting that The Chinese Essay , covering both premodern and modern periods, devotes the lion’s share of its space to the modern period. There are about forty pages devoted to ancient-medieval times (through the Song Dynasty), forty to late imperial times (Ming and Qing dynasties), about 170 to the first half of the twentieth century, when the modern essay came into its own, and ninety to the post-war period; thus over seventy percent of this collection is from the past 100 years. The slant in favor of modern essay has the effect of showing the reader the pre-modern essay through modern eyes, which I applaud, but the editor could have been more forthcoming about this in the introduction. If, for example, the reader took The Chinese Essay to be a general survey of the Chinese essay from antiquity to the present, it would give the impression that the essays of the twentieth century are much more important than those in the more than two millennia before. Modern Chinese essays can often be understood better through their relationships (sometimes conspicuous) with premodern literary or philosophical trends, and these relationships do not in themselves lessen the modern texts’ “modernity,” but help constitute it. In this respect, if it was in fact Pollard’s intention to present premodern essays primarily as precursors to modern ones, he could have done more in the introduction, commentary and translator’s notes to emphasize which kinds of premodern texts have particularly exerted agency in modern times, which modern texts manifest their influence, and how.
Turning to the modern period, the cavalier dismissal of prose literature under leftism and socialism is unfortunate; the development of the genre of reportage is misrepresented in the introduction as originating as anti-Japanese propaganda in the War Against Japan and developing in Communist China only to extol the Party (p. 20), and no mention is made at all of prominent lyrical essayists within the socialist camp like Qin Mu, Yang Shuo and Liu Baiyu, leading to the mistaken impression that all socialist prose is reportage. The exclusion of all of this material detracts from the anthology’s authority as a survey of the genre. As I have argued elsewhere, reportage may be looked upon as the leftist answer to the essay, but it originates as a form of revolutionary social critique in the 1930s, and its use in the War Against Japan is much broader than just propaganda. Moreover, though it would not be appropriate to include examples in the anthology, it should have been pointed out in the introduction that reportage made an important revival in the 1980s and beyond in the hands of Liu Binyan, Su Xiaokang and others; the concern for the environment that Pollard so admiringly observes in the contemporary Taiwanese essay has been one of the major themes of mainland Chinese reportage literature for at least ten years.
Another ramification of the editor’s inattention to the condition of modernity is Pollard’s explanation of the Chinese term sanwen . Pollard presents the Chinese concept as stable and unchanging, and explains its meaning entirely in terms of contrasts with European concepts. But the term sanwen was not used to denote a literary genre until modern times and even now critics and literary historians struggle with the equivocal nature of the term (“literary genre” vs. “all kinds of writing not in verse form”). It would have been helpful to put more emphasis on the particular modes or genres that the premodern works belong to (memorials to the emperor, philosophical treatises, formal and informal correspondence, prefaces and colophons, travelogues, epitaphs, biographies, etc.). This is not to say that this variety of forms ought not to be placed in a more general category under the term “sanwen,” but it is regrettable that the modern cultural process by which this was achieved receives no emphasis or attention.
Pollard’s concern here with limiting the scope of the collection to a describable form (“a free-standing, self-contained, relatively short composition” that “surfaced in the stable empire of the Han dynasty”) is, I think, unnecessarily limiting, and in fact might hamper the uninformed reader’s understanding of the broader context of the Chinese essay’s evolution. On page 2 of the introduction, Pollard makes a convincing, if somewhat defensive, argument for excluding the writings of the ancient Daoist philosopher Zhuang Zi. However, informed readers reading through the selections throughout both premodern and modern periods will easily discern the pervasiveness of Zhuang Zi’s influence in this genre. Indeed, Zhuang Zi’s playful spirit and philosophical critique of Confucianism may be described as one of the principal characteristics that distinguish the Chinese informal essay, which was the principal model for the modern literary essay, from formal prose. Similarly, though he devotes a page or so to the tremendous significance of Sima Qian’s Records of the Grand Historian as a model for the spirit and the letter of prose writing, Pollard excludes it because, “[being] a work of objective history, however, or at least attempting to be such, the author’s own comments are minimal” (4), implying that self-expression is working as a criterion for selection (see also his comments on page 5 about Cao Pi’s use of the term qi to denote “the physical underpinning of the distinctive character, or personal stamp, that an author’s writing is imprinted with”), but that self-expression can only be manifested in the form of direct “comments.” How many readers of even a few biographies from the Shi ji , though, come away from it without feeling that Sima Qian has very forcefully expressed his own views through them? A similar example is the exclusion of the Six Dynasties collection of anecdotes, Shishuo xinyu (New account of tales of the world), of which a translation by Richard Mather was published a generation ago. Like Zhuang Zi and the wealth of apocryphal writings of the Daoist tradition, Liu Yiqing’s New Account , which describes remarkable events, actions and utterances of the medieval aristocracy, though perhaps not fitting. Pollard’s criterion, was an important and frequently imitated foundation of the Chinese essay tradition.
The introductions to the sections on each author, though at times impressionistic, often include insightful analytical meditations or epigrammatic summaries of the author’s style that strike me as most apt and useful. However, I am not sure it is necessary for Pollard to separately include “commentary” and “translator’s notes” (sometimes both) before or after certain works in addition to the introductory sections on each author. Often the translator’s note will emphasize interpretation in a cross-cultural context, as in the case of Zhu Ziqing’s “View from the Rear” (Bei ying), but I feet that such considerations would have been much more effectively delivered in a critical essay that treats a variety of issues of style or interpretation, or this could have been integrated with the historical overview given in the introduction. The second of the three paragraphs of commentary on Zhuge Liang, for example, is almost identical in content to the last page of Zhuge Liang’s own text; the first paragraph of the “Translator’s Note” to Han Yu’s “Address to the Crocodiles of Chaozhou” simply reiterates the corresponding section of the biography of Han Yu given in the “Commentary” two pages before. Together with the functional overlap of the preface and introduction, the commentary and translators notes make The Chinese Essay overly complex in its multilayered contextualization of the translations and thus unnecessarily confusing.
Apart from stealing thunder from the essays themselves, the volume of notes and commentary raises an important question that plagues the translation of Chinese literature into English in general: can these texts not speak for themselves? If this collection really is intended for a general readership, I think it is safe to assume that such readers would be more interested in texts that speak directly to them without a great deal of explanation from the translator. And it is not only a question of “how much” explanation would be needed to supplement a “raw” translation; the act of translation itself imparts meaning. If scholarly semantic fidelity were relaxed to the degree that items were made easier for the general reader to relate to with a reduced amount of explanation, the potential impact of this book would be greatly enhanced.
The Chinese Essay does nevertheless fill a crucial gap in materials for courses on Chinese literature in translation. While most scholars in the field of Chinese literature are probably not going to set up a course exclusively devoted to the essay even with a comprehensive anthology available, the selections in this book would mix well with other genres and materials in a more general course. I could see using it this way in either premodern or modern Chinese literary courses, but more likely for the modern period because of the greater concentration of material there.
Charles A. Laughlin Associate Professor, Chinese Literature Department of East Asian Languages and Literatures Yale University
Anna’s Archive

- - Option #1: Fast Partner Server #1 (no browser verification required)
- - Option #2: Fast Partner Server #2
- - Option #3: Fast Partner Server #3
- - Option #4: Fast Partner Server #4
- - Refer a friend, and both you and your friend get 50% bonus fast downloads! Learn more…
- - Option #1: Slow Partner Server #1 (might require browser verification — unlimited downloads!)
- - Option #2: Slow Partner Server #2
- - Convert: use online tools to convert between formats. For example, to convert between epub and pdf, use CloudConvert .
- - Kindle: download the file (pdf or epub are supported), then send it to Kindle using web, app, or email.
- - Support authors: If you like this and can afford it, consider buying the original, or supporting the authors directly.
- - Support libraries: If this is available at your local library, consider borrowing it for free there.
- - Option #1: Borrow from the Internet Archive (print disabled patrons only)
- - Option #2: Bulk torrent downloads (experts only) file
📂 File quality
Help out the community by reporting the quality of this file! 🙌
What is wrong with this file?
Please use the DMCA / Copyright claim form .
Please report metadata errors at the source library. If there are multiple source libraries, know that we pull metadata from top to bottom, so the first one might be sufficient.
Describe the issue (required)
MD5 of a better version of this file (if applicable). Fill this in if there is another file that closely matches this file (same edition, same file extension if you can find one), which people should use instead of this file. If you know of a better version of this file outside of Anna’s Archive, then please upload it .
You can get the md5 from the URL, e.g. https://annas-archive.org/md5/ 0b93ab93d7ae806550a54e025530829d
If this file has great quality, you can discuss anything about it here! If not, please use the “Report file issue” button.
Total downloads:
A "file MD5" is a hash that gets computed from the file contents, and is reasonably unique based on that content. All shadow libraries that we have indexed on here primarily use MD5s to identify files.
A file might appear in multiple shadow libraries. For information about the various datasets that we have compiled, see the Datasets page .
For information about this particular file, check out its JSON file .
Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics
- Announcements
- AUTHOR'S GUIDELINES
The Analysis of Customs Services Practice in the Conditions of the Eurasian Economic Union: Problems and Directions of Improvement
- Yuliya Evgenievna GUPANOVA Russian Customs Academy, Lyubertsy, Moscow Region, Russian Federation
- Gulzida Iksanovna NEMIROVA Russian Customs Academy, Lyubertsy, Moscow Region, Russian Federation
- Alexander Evgenievich SUGLOBOV Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russian Federation
One of the most important directions of customs authorities development at the present time is improvement of the customs services sphere that will allow to influence on trade expenses decreasing for business, ensuring economic security, increasing of the country attractiveness in the investment side. The matters gain the special importance in the conditions of integration development within the Eurasian Economic Union as they demand coordination of legislative, methodological, methodical and a number of practical aspects of providing customs services in the united customs territory.
The purpose of article is researching of customs services providing practice in conditions of the Eurasian Economic Union existence, identification of problems in this sphere and searching ways of their decision.
Methods of the comparative, retrospective and system analysis, analogy, generalization and grouping were applied during article creating that has allowed to reveal key discrepancies in customs services providing in the countries of EEU and to designate the possible directions of their improvement.
The results received in article cover the specified conceptual framework in the explored sphere, the designated methodological approaches to improvement of customs procedures. These approaches take into account interests of the main consumers of customs services – participants of foreign economic activity.

- EndNote - EndNote format (Macintosh & Windows)
- ProCite - RIS format (Macintosh & Windows)
- Reference Manager - RIS format (Windows only)
The Copyright Transfer Form to ASERS Publishing (The Publisher) This form refers to the manuscript, which an author(s) was accepted for publication and was signed by all the authors. The undersigned Author(s) of the above-mentioned Paper here transfer any and all copyright-rights in and to The Paper to The Publisher. The Author(s) warrants that The Paper is based on their original work and that the undersigned has the power and authority to make and execute this assignment. It is the author's responsibility to obtain written permission to quote material that has been previously published in any form. The Publisher recognizes the retained rights noted below and grants to the above authors and employers for whom the work performed royalty-free permission to reuse their materials below. Authors may reuse all or portions of the above Paper in other works, excepting the publication of the paper in the same form. Authors may reproduce or authorize others to reproduce the above Paper for the Author's personal use or for internal company use, provided that the source and The Publisher copyright notice are mentioned, that the copies are not used in any way that implies The Publisher endorsement of a product or service of an employer, and that the copies are not offered for sale as such. Authors are permitted to grant third party requests for reprinting, republishing or other types of reuse. The Authors may make limited distribution of all or portions of the above Paper prior to publication if they inform The Publisher of the nature and extent of such limited distribution prior there to. Authors retain all proprietary rights in any process, procedure, or article of manufacture described in The Paper. This agreement becomes null and void if and only if the above paper is not accepted and published by The Publisher, or is with drawn by the author(s) before acceptance by the Publisher.
- Come and join our team! become an author
- Soon, we launch the books app stay tune!
- Online support 24/7 +4077 033 6758
- Tell Friends and get $5 a small gift for you
- Privacy Policy
- Customer Service
- Refunds Politics
Mail to: [email protected]
Phone: +40754 027 417

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Chinese character practice paper containing a grid that resembles the character for field, 田. A4 Paper: PDF | PNG US Paper: PDF | PNG. Empty Grid. Remove the stabilizers and go freestyle in the empty grid. A4 Paper: PDF | PNG US Paper: PDF | PNG. Essay Paper. The standard 20x20, 400 character essay writing paper for knuckling down and writing ...
In the first of a two-part post, we'll look at a letter sent in 1987 from a group of elementary school students to the anarchist writer Ba Jin (most famous for his 1931 novel The Family) as they struggle to cope with China's changing social values. In Part II, I'll translate Ba Jin's reply. Essays.
Receiving information in Chinese helps your brain get accustomed to the language's sentence patterns, and you can translate this to your essays. Be extensive in your reading to ensure you get as much as possible out of each article. Remember that it's not about how fast you finish an article, but rather, how much you gain from the exercise.
Chinese Essay Phrases: Conclusion. At the ending section of the paper, the writer should provide an objective summary, list out the future research objectives and directions, and perhaps look into the future. Keep optimistic even if your experiment results were negative.
These large Chinese Character writing grids are great for learners who are just getting started writing simplified and traditional Chinese characters. Compact. 130 boxes. Regular. 100 boxes. Separate. 80 boxes.
It is important to be comfortable with writing Chinese characters in order to write essays well in Chinese. Make sure to use Chinese essay writing format properly. After that, you will be ready to improve Chinese essay writing. Increase Your Chinese Words Vocabulary. With approximately 100,000 words in the Chinese language, you will need to ...
When you want to be able to make writing your first Mandarin essay nice and easy, it pays to put plenty of thought and effort into the preparation. ... Once you can write the answers to the above down on a single side of the paper, you are ready to tackle the main part of the problem: putting pen to paper. ... 10 Essential Chinese Dance Words ...
Chinese"inanappendix "orinafootnote .Pinyinisnotnecessaryhere. Quotescan"eitherbe inline"orset"offasblockquotes.Generallys hortercitations"should"bequote d inlineusing" ] ] } v u l ^ o ] l Z ] X _ 1"(Afootnotenumber) "
Essays. Translations. Write Me. Short stories and essays by a contemporary Chinese writer, Yafei Hu.
2. Determine the center, choose the right material. To conform to the fact that a typical, novel, so it's easy to attract the attention of people. 3. Make a good outline, determine the general, write enough words. 4. Sentence writing smooth, there is no wrong character, no wrong grammar in article. Emotion, it is very important.
WELCOME Chinese Literature: Essays, Articles, Reviews (CLEAR) is published annually. CLEAR journal is a leading resource for Chinese Literature academic discussion worldwide and has been published for over 30 years. Click below for two most recent CLEAR journal covers CLEAR vol 32 (2021).pdf CLEAR vol 38 (2016).pdf CLEAR HISTORY CLEAR was created based on discussions…
36 samples of Chinese handwriting from students and native speakers. Unlike most other languages, handwriting in Chinese can be regarded as a separate skill. Learning to write by hand is not easy; learning to write well is even harder. In an earlier article, I discussed handwriting in details, including how to improve it as a student.
Article. The widespread use of paper and printing were features of ancient China which distinguished it from other ancient cultures. Traditionally, paper was invented in the early 2nd century CE, but there is evidence it was much earlier. As a cheaper and more convenient material than bamboo, wood, or silk, paper helped spread literature and ...
Print free paper, write better Chinese. 214 kangxi radicals chart. tian zi ge paper. square tile paper. mi zi ge paper. jiu gong ge paper. hui gong ge paper. essay paper. genko yoshi paper.
These templates are great for math and science classes. Sometimes it can be hard to get the simple things that you need like graph paper or even basic rule paper. For whatever the reasons are, we have you covered. Sino-Exchange offers a number of printable paper templates that you can download, print, and use in your class on a moment's notice.
— Chinese Hanzi Paper (x5 styles) — Various styles of gridded paper to neatly practice individual characters. • Tian Zi Ge standard grid and non-gridded • Mi Zi Ge star grid • Jiu Gong Ge 9 section • Hui Gong Ge inner box — Chinese Kong Ge Mansuscript Paper (x1 style) — Horizontal squares with appropriate row spacing for essay ...
Cambridge International A Level Chinese builds on the language skills gained at Cambridge IGCSE, Cambridge O Level or Cambridge International AS Level, and is the ideal foundation for university-level study, or to improve career prospects. ... Cambridge International A Level Chinese (9715) Past papers, examiner reports and specimen papers ...
Quick Guide on Citation Style for Chinese, Japanese and Korean Sources from the Yale University Libraries (this guide is rich in examples for different formats in APA, MLA and Chicago styles) Citing Sources (APA, MLA, ...): In Chinese Papers (中文引證格式) from Hong Kong Baptist University (provides a few examples of style guides to ...
The Chinese Essay is the first anthology to provide a comprehensive introduction to Chinese literary non-fiction prose from earliest times to the present. Comparable collections in print, such as Richard Strassberg's Inscribed Landscapes: Travel Writing from Imperial China and Sang Ye's Vignettes from the Late Ming, are restricted to the premodern period, and until now modern essay ...
📚 The largest truly open library in human history. ⭐️ We mirror Sci-Hub and LibGen. We scrape and open-source Z-Lib, Internet Archive Lending Library, DuXiu, and more. 📈 31,655,466 books, 99,901,370 papers — preserved forever. Learn more…
Sources. Губернатор Московской области. Постановление №123-ПГ от 28 сентября 2010 г. «Об учётных данных административно-территориальных и территориальных единиц Московской области», в ред.
See all articles by Jyh-An Lee Jyh-An Lee. The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) - Faculty of Law. Peng Zhou. The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), Faculty of Law, Students
The Author(s) warrants that The Paper is based on their original work and that the undersigned has the power and authority to make and execute this assignment. It is the author's responsibility to obtain written permission to quote material that has been previously published in any form. The Publisher recognizes the retained rights noted below ...
The results of this work indicate the need for prompt identification of patients who had previously undergone AMI upon their admission to the vascular center, as well as the development of more active prevention tactics for such patients. Aim. To study the features of the course of primary and recurrent myocardial infarction and compare their prognosis in the acute stage of the disease within ...